Page 1

POWER SUPPLY KIT
MODEL XP-720K
Assembly Manual
Copyright © 2012, 1998 by ELENCO®All rights reserved. Revised 2012 REV-G 753269
No part of this book shall be reproduced by any means; electronic, photocopying, or otherwise without written permission from the publisher.
ELENCO
®
Page 2

PARTS LIST
If you are a student, and any parts are missing or damaged, please see instructor or bookstore.
If you purchased this kit from a distributor, catalog, etc., please contact Elenco®Electronics (address/phone/email is at the back of this manual) for additional assistance, if needed. DO NOT contact your place of purchase
as they will not be able to help you.
RESISTORS
Qty. Symbol Value Color Code Part #
r 1R5 .18Ω 5% 3W 101804
r 2 R3, R4 2.7Ω 5% 1/4W red-violet-gold-gold 112701
r 2 R1, R2 150Ω 5% 1/4W brown-green-brown-gold 131500
r 2 VR1, VR2 2kΩ Potentiometer 192422
CAPACITORS
Qty. Symbol Value Description Part #
r 5 C1 - C4, C8 10μF Electrolytic 271045
r 2 C5, C6 2200μF Electrolytic 292226
r 1 C7 4700μF Electrolytic 294744
SEMICONDUCTORS
Qty. Symbol Value Description Part #
r 4 D1 - D4 1N4001 Diode 314001
r 4 D5 - D8 1N5400 Diode 315400
r 1 Q1 A70 Transistor 320070
r 1 Q2 2N6124 Transistor 326124
r 1 IC1 LM-317 Integrated Circuit 330317
r 1 IC2 LM-337 Integrated Circuit 330337
r 1 IC3 LM-7805C Integrated Circuit 337805
MISCELLANEOUS
-1-
Qty. Description Part#
r 1 Transformer 440720
r 1 PC Board 512013
r 1 Fuse 1A 530100
r 1 Rocker Switch 541204
r 1 Cover 611120
r 1 Chassis 612012
r 1 Heat Sink 615010
r 2 Knob 622009
r 1 Strain Relief 624003
r 5 Insulator Washer 624007
r 4 PC Board Stand-off 625001
r 2 Black Binding Post 625031
r 7 Int. Lockwasher, Binding Post 625031LW
r 7 Nut, Binding Post 625031HN
r 2 Red Binding Post 625032
r 3 Yellow Binding Post 625034
r 5
Screw 6-32 x 3/8” Phillips, Pan, Machine
641640
r 2
Screw 8-32 x 3/8” Phillips, Pan, Machine
641840
r 4
Screw 6 x 3/8” black, AB, Phillips, Truss
642652
r 2 Screw 6 x 3/8” black, AB, Phillips, Pan 642660
Qty. Description Part#
r 2 Nut 7mm 644101
r 4 Nut 6-32 Small 644601
r 2 Nut 8-32 644800
r 1 Nut 6-32 644600
r 2 Flat Washer 8mm x 14mm 645101
r 2 Lockwasher 5/16” 646101
r 2 Lockwasher #8 646828
r 4 Rubber Feet 662003
r 1 Fuse Holder (Upper Body) 663005UB
r 1 Fuse Holder (Lower Body) 663005LB
r 1 Fuse Holder (Hex Nut) 663005N
r 1 Fuse Holder (Washer) 663005W
r 3 Mica Insulator 780002
r 1 Silicon Grease 790005
r 6” 20 Ga. Red Wire 813210
r 48” 22 Ga. Red Wire 814201
r 48” 22 Ga. Orange Wire 814310
r 48” 22 Ga. Blue Wire 814610
r 1 Line Cord 862105
r 2” Shrink Tubing 1/2” Dia. 891101-2
r 1.5” Shrink Tubing 3/4” Dia. 899110-2
r 1 Solder Lead-Free 9LF99
Screw Identification
6-32 x 3/8”
Phil., Pan, Machine
8-32 x 3/8”
Phil., Pan, Machine
6 x 3/8” Black
AB, Phillips, Pan
6 x 3/8” Black
AB, Phillips, Truss
Page 3
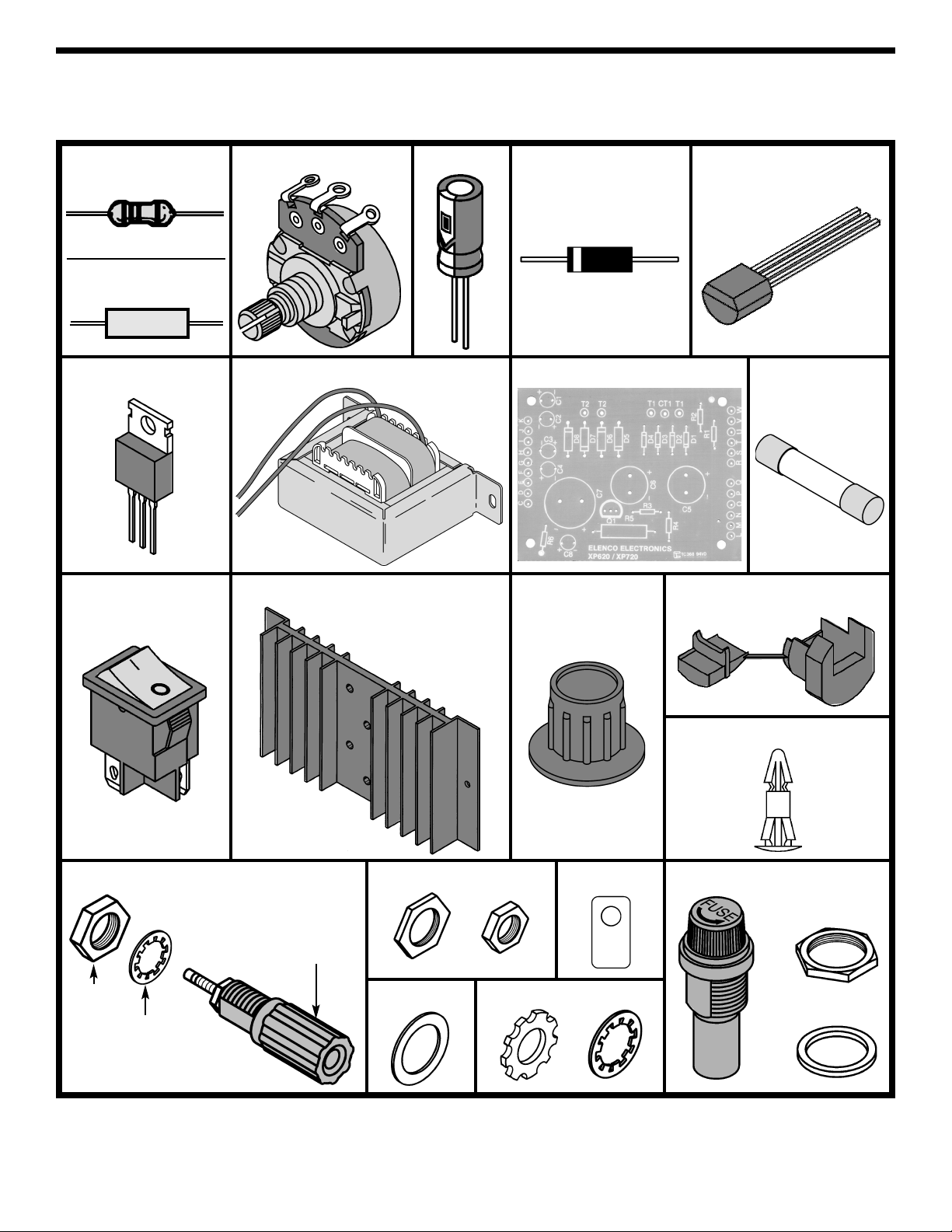
-2-
PARTS IDENTIFICATION
Resistor 2kΩ Potentiometer Capacitor Diode Transistor
Integrated Circuit Transformer PC Board Fuse
Heatsink
Switch
Knob
Strain Relief
PC Board Stand-off
Binding Post Assembly Fuse Assembly
Flat Washer Lockwashers
MicaNuts
7mm
6-32 / 8-32
#8 5/16”
Binding Post
Lockwasher
Nut
.18Ω 3W Resistor
Page 4
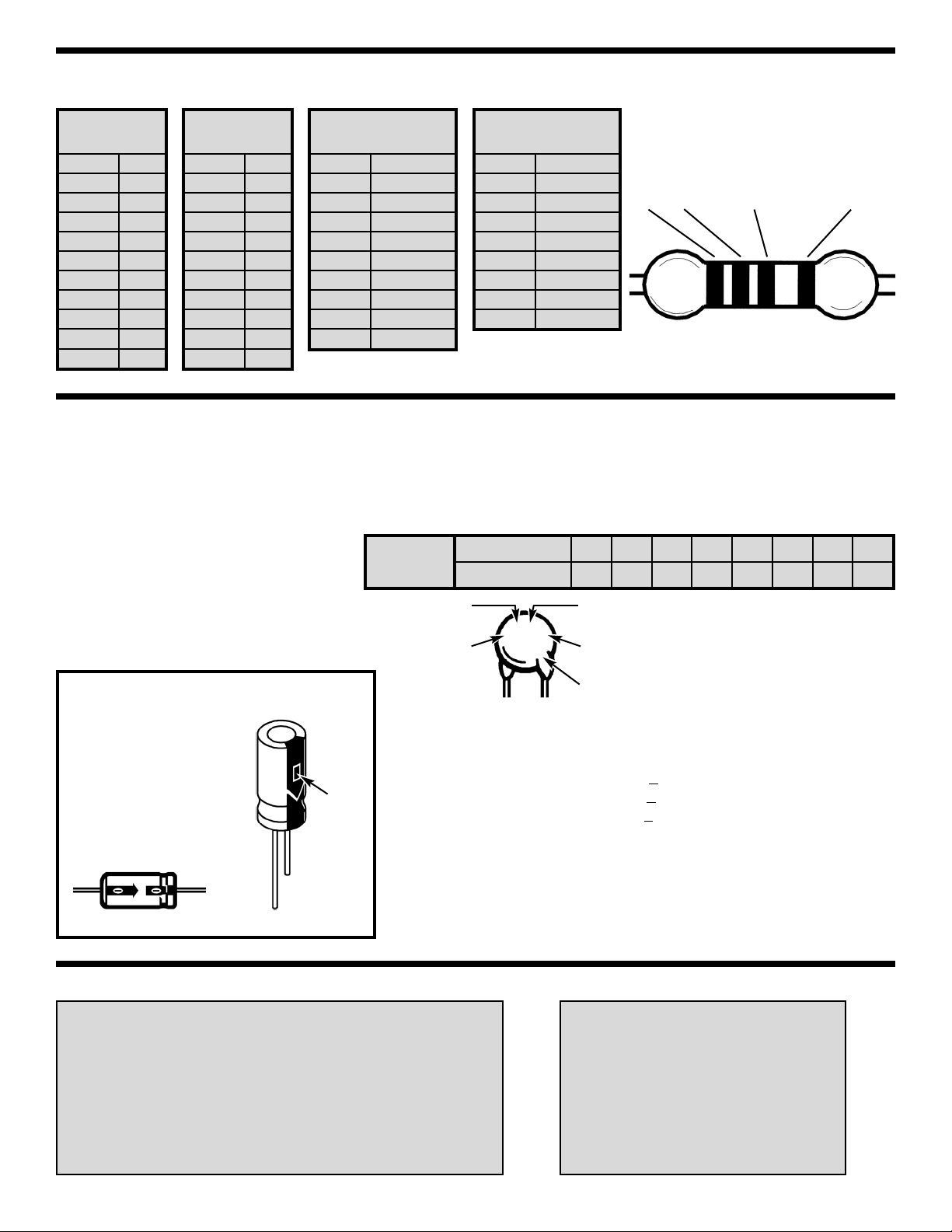
-3-
Warning:
If the capacitor is
connected with
incorrect polarity, it
may heat up and
either leak, or
cause the capacitor
to explode.
IDENTIFYING RESISTOR VALUES
Use the following information as a guide in properly identifying the value of resistors.
BANDS
METRIC UNITS AND CONVERSIONS
Abbreviation Means Multiply Unit By Or
p Pico .000000000001 10
-12
n nano .000000001 10
-9
μ micro .000001 10
-6
m milli .001 10
-3
– unit 1 10
0
k kilo 1,000 10
3
M mega 1,000,000 10
6
1. 1,000 pico units = 1 nano unit
2. 1,000 nano units = 1 micro unit
3. 1,000 micro units = 1 milli unit
4. 1,000 milli units = 1 unit
5. 1,000 units = 1 kilo unit
6. 1,000 kilo units = 1 mega unit
IDENTIFYING CAPACITOR VALUES
Capacitors will be identified by their capacitance value in pF (picofarads), nF (nanofarads), or μF (microfarads).
Most capacitors will have their actual value printed on them. Some capacitors may have their value printed in
the following manner. The maximum operating voltage may also be printed on the capacitor.
Second Digit
First Digit
Multiplier
Tolerance*
Note: The letter “R”
may be used at times
to signify a decimal
point; as in 3R3 = 3.3
103K
100V
The letter M indicates a tolerance of +20%
The letter K indicates a tolerance of +10%
The letter J indicates a tolerance of +5%
Maximum Working Voltage
The value is 10 x 1,000 =
10,000pF or .01μF 100V
*
Electrolytic capacitors have a positive
and a negative electrode. The
negative lead is indicated on the
packaging by a stripe with minus
signs and possibly arrowheads. Also,
the negative lead of a radial
electrolytic is shorter than the positive
one.
Polarity
marking
BAND 1
1st Digit
Color Digit
Black 0
Brown
1
Red 2
Orange 3
Yellow 4
Green 5
Blue 6
Violet 7
Gray 8
White 9
BAND 2
2nd Digit
Color Digit
Black 0
Brown 1
Red 2
Orange 3
Yellow 4
Green 5
Blue 6
Violet 7
Gray 8
White 9
Multiplier
Color Multiplier
Black 1
Brown 10
Red 100
Orange 1,000
Yellow 10,000
Green 100,000
Blue 1,000,000
Silver 0.01
Gold 0.1
Resistance
Tolerance
Color Tolerance
Silver ±10%
Gold ±5%
Brown ±1%
Red ±2%
Orange ±3%
Green ±0.5%
Blue ±0.25%
Violet ±0.1%
1
2 Multiplier Tolerance
Multiplier
For the No. 0 1 2 3 4 5 8 9
Multiply By 1 10 100 1k 10k 100k .01 0.1
(+)
(–)
(+)
(–)
Axial
Radial
Page 5
-4-
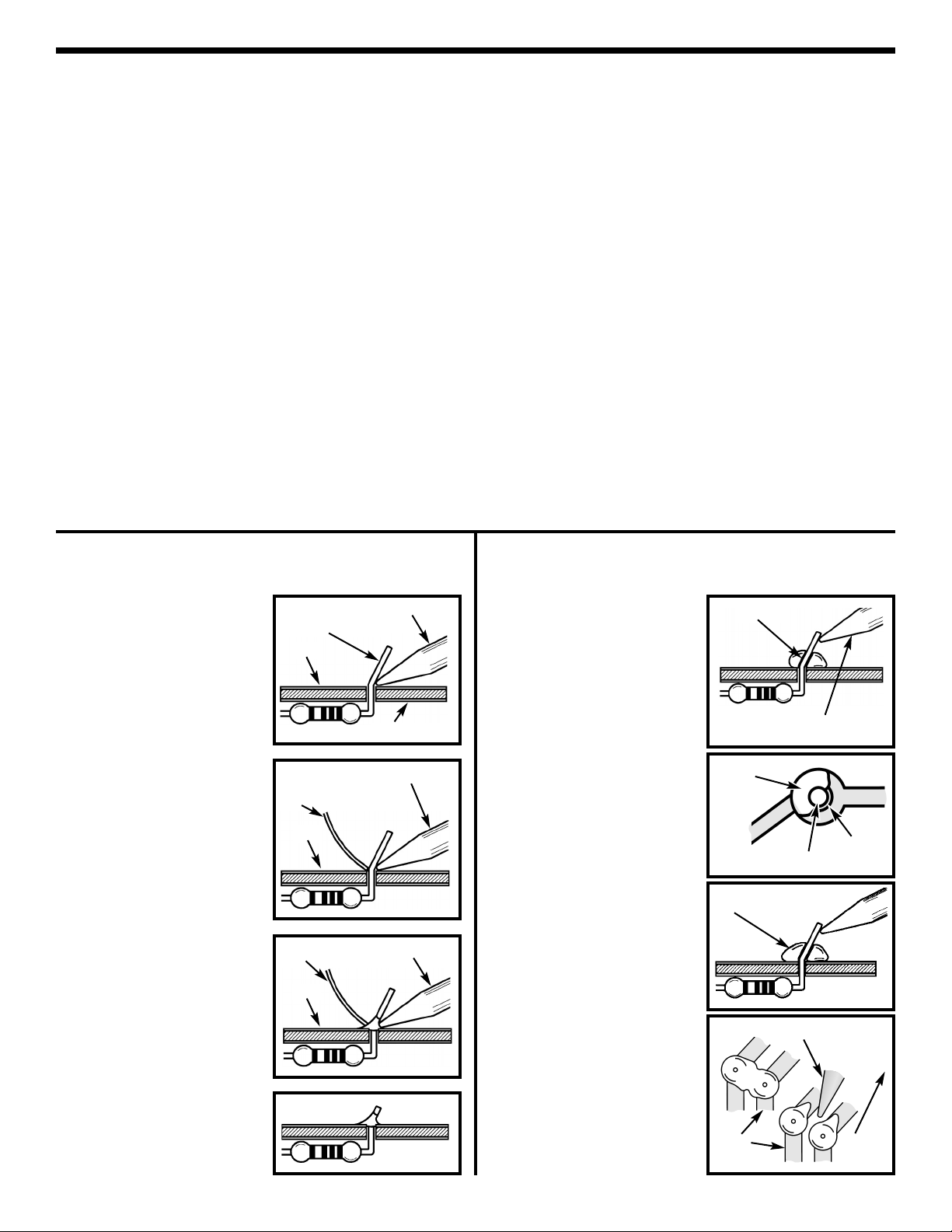
CONSTRUCTION
Solder
Soldering Iron
Foil
Solder
Soldering Iron
Foil
Component Lead
Soldering Iron
Circuit Board
Foil
Rosin
Soldering iron positioned
incorrectly.
Solder
Gap
Component Lead
Solder
Soldering Iron
Drag
Foil
1. Solder all components from the
copper foil side only. Push the
soldering iron tip against both the
lead and the circuit board foil.
2. Apply a small amount of solder to
the iron tip. This allows the heat to
leave the iron and onto the foil.
Immediately apply solder to the
opposite side of the connection,
away from the iron. Allow the
heated component and the circuit
foil to melt the solder.
1. Insufficient heat - the solder will
not flow onto the lead as shown.
3. Allow the solder to flow around
the connection. Then, remove
the solder and the iron and let the
connection cool. The solder
should have flowed smoothly and
not lump around the wire lead.
4.
Here is what a good solder
connection looks like.
2. Insufficient solder - let the
solder flow over the connection
until it is covered.
Use just enough solder to cover
the connection.
3. Excessive solder - could make
connections that you did not
intend to between adjacent foil
areas or terminals.
4. Solder bridges - occur when
solder runs between circuit paths
and creates a short circuit. This is
usually caused by using too much
solder.
To correct this, simply drag your
soldering iron across the solder
bridge as shown.
What Good Soldering Looks Like
A good solder connection should be bright, shiny, smooth, and uniformly
flowed over all surfaces.
Types of Poor Soldering Connections
Introduction
The most important factor in assembling your XP-720K Power Supply
Kit is good soldering techniques. Using the proper soldering iron is of
prime importance. A small pencil type soldering iron of 25 - 40 watts is
recommended. The tip of the iron must be kept clean at all times and
well tinned.
Solder
For many years leaded solder was the most common type of solder
used by the electronics industry, but it is now being replaced by leadfree solder for health reasons. This kit contains lead-free solder, which
contains 99.3% tin, 0.7% copper, and has a rosin-flux core.
Lead-free solder is different from lead solder: It has a higher melting
point than lead solder, so you need higher temperature for the solder to
flow properly. Recommended tip temperature is approximately 700
O
F;
higher temperatures improve solder flow but accelerate tip decay. An
increase in soldering time may be required to achieve good results.
Soldering iron tips wear out faster since lead-free solders are more
corrosive and the higher soldering temperatures accelerate corrosion,
so proper tip care is important. The solder joint finish will look slightly
duller with lead-free solders.
Use these procedures to increase the life of your soldering iron tip when
using lead-free solder:
• Keep the iron tinned at all times.
• Use the correct tip size for best heat transfer. The conical tip is the
most commonly used.
• Turn off iron when not in use or reduce temperature setting when
using a soldering station.
•
Tips should be cleaned frequently to remove oxidation before it becomes
impossible to remove. Use Dry Tip Cleaner (Elenco
®
#SH-1025) or Tip
Cleaner (Elenco®#TTC1). If you use a sponge to clean your tip, then use
distilled water (tap water has impurities that accelerate corrosion).
Safety Procedures
• Always wear safety glasses or safety goggles to
protect your eyes when working with tools or
soldering iron, and during all phases of testing.
• Be sure there is adequate ventilation when soldering.
•
Locate soldering iron in an area where you do not have to go around
it or reach over it. Keep it in a safe area away from the reach of
children.
• Do not hold solder in your mouth. Solder is a toxic substance.
Wash hands thoroughly after handling solder.
Assemble Components
In all of the following assembly steps, the components must be installed
on the top side of the PC board unless otherwise indicated. The top
legend shows where each component goes. The leads pass through the
corresponding holes in the board and are soldered on the foil side.
Use only rosin core solder.
DO NOT USE ACID CORE SOLDER!
'
Page 6
-5-
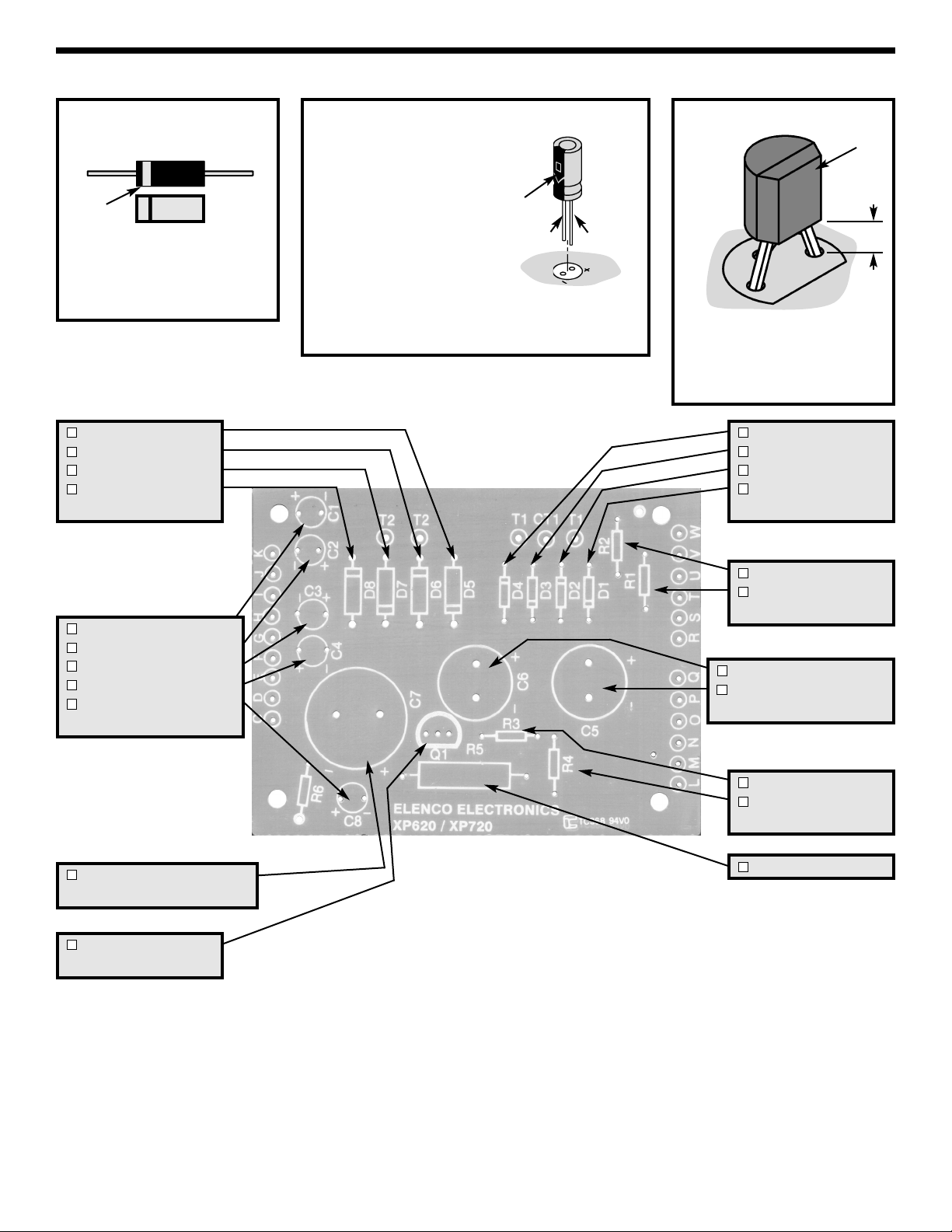
ASSEMBLE COMPONENTS TO PC BOARD
Figure A
Diodes have polarity. Be sure
that the band is in the correct
direction.
Figure B
Electrolytics have a
polarity marking
indicating the (–)
lead. The PC board
is marked to show
the lead position.
Warning: If the capacitor is connected with
incorrect polarity it may heat up and either leak
or cause the capacitor to explode.
Figure C
Mount the transistor with the
flat side as shown on the top
legend. Leave 1/4” between
the part and PC board.
Band
D5 - 1N5400 Diode
D6 - 1N5400 Diode
D7 - 1N5400 Diode
D8 - 1N5400 Diode
(see Figure A)
C1 - 10μF Electrolytic
C2 - 10μF Electrolytic
C3 - 10μF Electrolytic
C4 - 10μF Electrolytic
C8 - 10μF Electrolytic
(see Figure B)
C7 - 4700μF Electrolytic
(see Figure B)
Q1 - A70 Transistor
(see Figure C)
D4 - 1N4001 Diode
D3 - 1N4001 Diode
D2 - 1N4001 Diode
D1 - 1N4001 Diode
(see Figure A)
R2 - 150Ω Resistor
R1 - 150Ω Resistor
(brn-green-brn-gold)
C6 - 2200μF Electrolytic
C5 - 2200μF
Electrolytic
(see Figure B)
R3 - 2.7Ω Resistor
R4 - 2.7Ω Resistor
(red-violet-gold-gold)
R5 - .18Ω Resistor
Flat
1/4”
(–) (+)
Polarity
Mark
Page 7

-6-
PC BOARD WIRING
Cut the 22 gauge wires to the required length. Strip 1/4” of insulation off of both ends. Insert the lead into the
hole and solder it to the foil side.
0
1
2
3
Use this ruler to measure the wires when cutting them to their required lengths.
4
5
6
7
4” Red
Hole K
4” Orange
Hole J
3” Red
Hole I
4” Blue
Hole H
3” Orange
Hole G
4” Blue
Hole F
4” Red
Hole E
6” Blue
Hole D
4” Red
Hole C
3 1/2” Red
Hole W
3” Orange
Hole V
3 1/2” Blue
Hole U
3” Blue
Hole T
3 1/2” Orange
Hole S
3” Red
Hole R
4 1/2” Blue
Hole Q
5” Orange
Hole P
4 1/2” Red
Hole O
5” Blue
Hole N
4 1/2” Orange
Hole M
5” Red
Hole L
r Peel off the protective paper from the
bottom of the rubber feet and apply one
to each corner on the bottom of the
chassis, as shown.
Feet Feet
Page 8

-7-
r Install binding posts 1-7 with the colors in order, as shown in Figure D. Insert the post into the hole and fasten
it with the nut and lockwasher. Tighten down the nut with pliers.
r Cut off the tabs on the two potentiometers and install them with the lugs up, as shown in
Figure D. Secure in place with a 5/16” lockwasher, 8mm flat washer and 7mm nut.
r Turn both potentiometer shafts all the way counter-clockwise. Line up the line on the
knobs with the first line on the voltage scale. Press knobs onto the shaft of the
potentiometers.
r Note the lug configuration on the rocker switch. Push the switch into the hole in the
chassis with lug 1 on top as shown in Figure D.
PANEL ASSEMBLY
Figure D
Lug 1
Lockwasher
Nut
Black
Red
Black
Yellow
Rocker Switch
Rear View of Rocker Switch
7mm Nuts
8mm Washers
5/16” Lockwashers
Potentiometers
* Cut off tabs
Red
Yellow
Yellow
I
N
C
R
E
A
S
E
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
12
3
Page 9

Carefully bend the leads of IC1, IC2,
IC3 and Q2 on the heat sink at right
angles with pliers.
Install IC1, IC2 and Q2 in the positions
shown in Figure E. Fasten in place
using the parts shown in Figure F.
Spread the silicon grease on the back
of the transistor and ICs.
r IC1 - LM-317 IC
r IC2 - LM-337 IC
r Q2 - 2N6124 Transistor
Install IC3 as shown in Figure Fa.
r IC3 - LM-7805 IC
r Mount the fuse holder to the top hole in the back of the chassis,
with the side lug up, as shown in Figure G. Fasten in place with
the 3/8” nut. After the holder is secure, unscrew the top and insert
the fuse.
r
Separate the wires of the line cord 3” from the end. Strip the
insulation off the end of all two end wires to expose 1/4” of bare wire.
r
Insert 6” of the line cord into the bottom hole on the back of
the chassis, as shown in Figure G. Place the line cord into
the slot of the strain relief and squeeze the two sections
together with pliers. Then, insert the strain relief into the
hole.
r Install the transformer with the black wires side as shown
in Figure I. Use an 8-32 x 3/8” screw, #8 lockwasher and
an 8-32 nut on each side to fasten in place, as shown in
Figure H.
-8-
Figure E
Figure H
8-32 Nut
#8 Lockwasher
8-32 x 3/8” Screw
Figure F
Small 6-32 Nut
IC1, IC2,
Q2
Heat Sink
Insulator Washer
6-32 x 3/8”
Screw
LM7805
LM-337
LM-317
2N6124
Silicon GreaseMica
Figure Fa
Figure G
Side Lug
Pliers
Mica
Small 6-32 Nut
IC3
LM7805
Heat Sink
Insulator Washer
6-32 x 3/8” Screw
Insulator Washer
Ribbed
Smooth
1/4”
Heatsink
Page 10

-9-
r
Slip the 1/2” diameter shrink tubing over the 6” 20 ga. red wire and the smooth or round line cord wire. Solder
the line cord wire to the end lug on the fuse holder, as shown in Figure I. Solder the 6” 20 ga. red wire to the
side lug on the fuse holder. Slide the shrink tubing over the fuse holder, covering the two lugs
.
r Shrink the 1/2” and 3/4” tubings in place using a hair dryer, heat gun (at lowest setting or you will melt the
tubing), or the heat emitting from your soldering iron.
r Solder the two red transformer wires to the holes marked T2 on the PC board.
r Solder the black transformer wire to the hole marked CT1 on the PC board.
r Solder the two blue transformer wires to the holes marked T1 on the PC board.
r Solder the two yellow transformer wires to the yellow AC output binding posts.
r Cut a 6” blue wire and strip 1/4” of insulation off of both ends. Solder one end of the 6” blue wire and the blue
wire from point “D” to the black binding post.
r
Push the PC board stand-offs in the four holes in the bottom of the chassis (see Figure J). Push the PC board
down in place.
WIRING LINE CORD, FUSE, TRANSFORMER AND SWITCH
Figure I
r
Install the line cord ground lug to the chassis
using a 6-32 x 3/8” screw and a 6-32 large
nut in the location shown in Figure I.
r Strip the insulation off of both ends of the
6” red 20 ga. wire to expose 1/4” of bare
wire. Solder one end of the wire to lug 3 on
the rocker switch, as shown in Figure I.
r
Slip the other end of the 6” strip of red wire
(from lug 3), the (A) and (B) black
transformer wire, and the ribbed line cord
wire through the 3/4” diameter piece of
shrink tubing (as shown in Figure I).
r CAUTION: DO NOT touch any wires or
tubing with the iron.
r Solder the black transformer wire (B), as
shown in Figure I to lug 2 on the rocker
switch.
r Twist the black transformer wire (A) and
the ribbed or flat line cord wire together.
Solder the two wires to lug 1 on the rocker
switch, as shown in Figure I.
r Slide the 3/4” diameter shrink tubing over
the switch.
PC Board
Chassis
Figure J
Side Lug
End Lug
Smooth Line Cord
Flat or Ribbed Line Cord
1
2
3
(A) Black
Red
Red
1/2” Tubing
Yellow
Yellow
Yellow
Yellow
6” Blue
“D” Blue
AC Binding Posts
Ribbed
Line Cord
Blue
Black
Blue
(B) Black
J
K
T2
T2 T1
CT1
T1
W
VU
6-32
Large Nut
3/4” Shrink
Tubing
6” 20 Ga.
Red
6-32 x 3/8”
Screw
Page 11

-10-
WIRE BINDING POSTS AND 317, 337
Solder the wires from the board to the binding posts, as shown in Figure K.
r 3” Orange wire from (G) on the PC board; To the Yellow post (-1.25-15V).
r 4” Blue wire from (H) on the PC board and the 6” blue wire from the black AC binding post; To the Black post
(common).
r 3” Red wire from (I) on the PC board; To the Red post (+1.25-15V).
r 4” Red wire from (C) on the PC board; To the Red post (+5V 3A).
Place the heat sink with ICs and
transistor in the position, as shown in
Figure K. Insert the wires from the PC
board, through the rectangular hole in
the chassis, to the ICs and solder into
place.
Tin the leads. Form the end of the wires
into a tight loop, for easy, tight
connection to leads, before you apply
solder.
r 3 1/2” Red wire (W) from PC board; To
middle lead of LM-317.
r
3 1/2” Orange wire (S) from PC board;
To left lead of LM-317.
r 3 1/2” Blue wire (U) from PC board; To
right lead of LM-317.
r 3” Red wire (R) from PC board; To
middle lead of LM-337.
r 3” Blue wire (T) from PC board; To left
lead of LM-337.
r 3” Orange wire (V) from PC board; To
right lead of LM-337.
After wiring the ICs, be sure that none
of the leads touch each other and
cause a short.
Figure K
W
VU
TSR
3 1/2” Red
3” Orange
3 1/2” Blue
3” Blue
3 1/2” Orange
3” Red
I
H
G
D
C
Black
Post
Yellow
Post
6” Blue
6” Blue
3” Red
Red
Post
Black
Post
Yellow
Post
3” Orange
3” Blue
ELENCO ELECTRONICS INC.
XP-620
Yellow
Post
Red
Post
4” Red
LM-317
LM-337
Page 12

-11-
WIRE 2N6124, 7805 & POTENTIOMETERS
Insert the wires from the PC board through the
rectangular hole in the chassis to the 2N6124
and LM-7805, solder into place, as shown in
Figure L.
r 5” Red wire (L) from the PC board; To middle
lead 0f 2N6124.
r 5” Orange wire (P) from the PC board; To left
lead of 2N6124.
r 5” Blue wire (N) from the PC board; To right
lead of 2N6124.
r 4 1/2” Red wire (O) from PC board; To
middle lead of LM-7805.
r 4 1/2” Blue wire (Q) from PC board; To left
lead of LM-7805.
r 4 1/2” Orange Wire (M) from PC board; To
right lead of LM-7805.
After wiring, be sure that the leads do not touch
each other and cause a short.
Solder the wires from the PC board to the
potentiometers, as shown in Figure L.
r 4” Red wire (E) from PC board; To middle lug
of the positive voltage pot.
r 4” Blue wire (F) from PC board; To right lug
on the positive voltage pot.
r 4” Orange wire (J) from PC board; To middle
lug on the negative voltage pot.
r 4” Red wire (K) from PC board; To right lug
on negative voltage pot.
4 1/2” Blue
5” Orange
4 1/2” Red
5” Blue
4 1/2” Orange
5” Red
ELENCO ELECTRONICS INC.
XP-620
4” Blue
4” Red
EF
JK
4” Red
4” Orange
Negative VoltagePositive Voltage
Potentiometers
Figure L
Q
PO
NML
2N6124
7805
Page 13

-12-
FINAL ASSEMBLY
r Fasten the heat sink to the chassis with two 6 x 3/8” black pan head screws, as shown in Figure M.
r Fit the cover onto the chassis. Fasten in place with two 6 x 3/8” black truss head screws on each side, as
shown in Figure M.
Bottom View
Figure M
6 x 3/8” Pan
Head Screws
6 x 3/8” Truss
Head Screws
6 x 3/8” Truss
Head Screws
Page 14

-13-
TESTING THE XP-720 POWER SUPPLY
Testing the XP-720 Power Supply is very simple. Before applying power to the unit, be sure that all wiring and
soldering is firm. If so, obtain a digital voltmeter.
1. Apply power to the XP-720 and measure the output voltages.
Output Voltages:
Positive Variable DC 1.25 - 15V
Negative Variable DC –1.25 - –15V
+5VDC 4.75 - 5.25
12.6VAC 11 - 14
2. Short the output of each of the DC outputs to ground one at a time. ONLY SHORT THE DC OUTPUTS. They
should turn off and recover when the short is removed.
3. Load Test
In making these tests, the voltmeter leads should be clipped to the terminal directly and not the load, to prevent
errors in voltage drop due to contact resistance of the load.
You can use a lower wattage resistor, but only connect it for a few seconds.
Variable DC: Set the voltage to 10V. Connect a 10Ω, 10W resistor from the output to ground. The output
should not change more than 0.20V.
+5VDC: Connect a 2.5Ω, 12W resistor from the output to ground. The output should not change more
than 0.20V.
Should any of these tests fail, please refer to the troubleshooting guide.
TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE
No 1.25 - 15V Output Voltage
1) Check the AC voltage at anode of D1. It should read about 17VAC. If not, check the fuse, transformer, ON/OFF
switch or line cord.
2) Measure voltage at output of D1. It should read about 20VDC. If not, check D1, D3 and C5.
3) If 20V is OK, check IC1.
No Negative Voltage Output
1) Check the voltage at the output of D4. It should be –20VDC. Check D2, D4 and C6 and make sure that they are
not in backwards.
2) If DC is OK, then check IC2.
No 5V Output
1)
Check the voltage across the transformer winding. It should read about 12 volts. If not, check the diode bridge or C7.
2) Measure the DC voltage at the output of the diode bridge. It should read about 12 volts. If not, check the diode
bridge or C7.
3) If DC is OK, check IC3, Q1 and Q2.
Poor Regulation on any Supply
1)
Check DC voltage at the input of the regulator. It should be greater than 18 for 1.25 - 15V output and 8V for 5V output.
2) Check AC ripple at the input of the regulator. It should be less than 5V for the variable supply and the 5V supply.
3) If the ripple is greater, then check the diodes and its filter capacitor.
Fails to Shut Down on 5V Overload
1) Check transistor Q1 and resistors R3, R4 and R5.
Unable to Draw 3 Amps at 5 Volts
1) Check transistor Q2 and resistors R3 and R4.
No AC Output
1) Check the power switch and fuse.
2) Check the solder connections to the binding posts.
Page 15

-14-
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
Introduction
The Model XP-720 Power Supply features three solid-state DC power supplies and a 12.6VAC center tapped
output. The first two supplies consist of one positive and one negative 1.25 to 15 volts at 1 ampere. The third
has a fixed 5V at 3 amperes. All DC supplies are fully regulated. A special IC circuit keeps the output voltage
within .2V when going from no load to full load. The output is fully protected from short circuits. This supply is
ideal for use in school labs, service shops or anywhere a precise DC voltage is required. The AC section has
6.3VAC @ 1A and a 12.6 center tapped @ 1A.
The Positive 1.25-15V Power Supply
Figure 1 shows a simplified circuit diagram of the positive supply. It consists of a power transformer, a DC
rectifier stage and the regulator stage.
Transformer
The transformer T1 serves two purposes. First, it
reduces the 120VAC input to 17VAC to allow the
proper voltage to enter the rectifier stages. Second, it
isolates the power supply output from the 120VAC
line. This prevents the user from dangerous voltage
shock should the user be standing in a grounded area.
AC to DC Converter
The AC to DC converter consists of diodes D1 and D2
and capacitor C1. Transformer T1 has two secondary
windings which are 180 degrees out of phase. The AC
output at each winding is shown in Figure 2A and 2B.
Diodes are semiconductor devices that allow current
to flow in one direction. The arrow in Figure 3 points
to the direction that the current will flow. Only when
the transformer voltage is positive will current flow
through the diodes. Figure 3 shows the simplest
possible rectifier circuit. This circuit is known as a halfwave rectifier. Here the diode conducts only half of
the time when the AC wave is positive as shown in
Figure 2C. Use of this circuit is simple but inefficient. The big gap between cycles require much more filtering
to obtain a smooth DC voltage.
By addition of a second diode and transformer winding, we can fill in the gap between cycles as shown in
Figure 4. This circuit is called full-wave rectification. Each diode conducts when the voltage is positive. By
adding the two outputs, the voltage presented to capacitor C1 is more complete, thus easier to filter, as shown
in Figure 2E. When used in 60 cycles AC input power, the output of a full wave rectifier will be 120 cycles.
Capacitor C1 is used to store the current charges, thus smoothing the DC voltage. The larger the capacitor, the
more current is stored. In this design, 2200μF capacitors are used, which allows about 3 volts AC ripple when
one amp is drawn.
Figure 1
Simplified diagram of positive power supply
120VAC
Input
17VAC 20VDC
1.25 - 15V
Regulated
Output
Transformer
120V to 17V
AC to DC
Converter
Voltage
Regulator
Figure 2
Figure 3
Figure 4
Voltage Waveform for Supply
A) Transformer
Winding AB
B) Transformer
Winding BC
C) Output of
diode D1.
D) Output of
diode D2.
E) Total of diodes
D1 & D2.
20V
F) Output of capacitor C1
Ripple depends on load
current (expanded).
Half Wave Rectifier
Full Wave Rectifier
D1
D2
C1
C1
D1
Page 16

-15-
In practice, the current through the diodes is not as shown in Figure 2C. Because
capacitor C5 has a charge after the first cycle, the diode will not conduct until the
positive AC voltage exceeds the positive charge in the capacitor. Figure 5 shows
a better picture of what the current flow looks like, assuming no loss in the diode.
It takes a few cycles for the voltage to build up on the capacitor. This depends on
the resistance of the winding and diode. After the initial start-up, there will be a
charge and discharge on the capacitor depending on the current drawn by the
output load. Remember current only flows through the diode when the anode is
more positive than the cathode. Thus, current will flow in short bursts as shown
in Figure 5C.
The DC load current may be one ampere, but the peak diode current may be three times that. Therefore, the
diode rating must be sufficient to handle the peak current. The 1N4001 has peak current rating of 10 amps.
Regulator Circuit
The regulator circuit in the Model XP-720 power supply consists of a LM-317
integrated circuit. This IC is specially designed to perform the regulation
function. Figure 6 shows a simplified circuit of how the LM-317 IC works.
Transistors Q1 and Q2 form a circuit known as a differential amplifier.
Transistor Q1 base is connected to a stable 1.5V reference voltage. The base
of Q2 is connected to the regulator output circuit through a voltage divider
network. The collector of transistor Q2 is connected to a current source. This
basically is a PNP transistor biased to draw about 1mA of current. Transistor
Q2 sees the current source as a very high resistor of about 1 meg ohms. Thus,
the gain of transistor Q2 is extremely high.
Transistor Q5 is called the pass transistor. It controls the current reaching the output. Transistors Q3 and Q4
are emitter followers. Their function is to raise the impedance of the pass transistor. Note that transistors Q2,
Q3, Q4 and Q5 and resistor R1 form a close loop. Also, note that the feedback to the base of Q2 is negative,
that is, when the base of Q2 goes positive, the output at emitter Q5 goes negative. Now if the 1.25V output
voltage goes down because of current drain at the output, the base of Q2 will drop forcing the collector voltage
of Q2 to go higher. This will bring the output voltage back to 1.25V. This is the basis of all negative regulators.
Another feature of the LM-317 regulator is to protect the IC against overload and output shorts. If the IC is
overloaded, the junction of an overload transistor will overheat. A transistor will sense this overheating and shut
down transistor Q5.
Figure 5
A) Transformer
Winding
B) Voltage C1
C) Current
through diodes
20V
Peak
20V
Figure 6
1.25V
Output
R1
R2
Divider
Q1
Q2
1.5V
Q3
Q4
Q5
Current
Source
Equalized
to 1 Meg.
Page 17

-16-
The LM-317 IC is basically a 1.25V regulator. To be able to vary the output
1.25 - 15V, we stack the IC on a DC voltage as shown in Figure 6A. When
VR1 equals 0, the output voltage is 1.25V as determined by the LM-317 IC.
Note that the voltage across R1 is always 1.25V. When R1 equals VR1, the
voltage across VR1 will equal the two volts across R1, therefore, the output
voltage will be 2.5V. When VR1 is 5 times R1, the output voltage is 7.5V. As
you can see, varying resistor VR1 will vary the voltage from 1.25V to 15V.
The Negative Voltage Regulator
The theory of the negative voltage regulator is the same as the previously
discussed positive regulator. The basic differences is that diodes D2 and D4 are reversed, producing a negative
voltage across capacitor C6. The LM-337 IC is designed to operate from a negative supply.
The 5 Volt Power Supply
In the previous discussion of the variable voltage regulators, the ICs can handle about 1A of current. In the
design of the 5V supply, we need 3A of current. To meet this current requirement we must add an external pass
transistor capable of delivering 3A.
Figure 7 shows a simplified 5V regulator with an external PNP pass
transistor. In this circuit, transistor Q2 is a power transistor capable of
delivering over 3A. Transistor Q2 is biased off until the LM-7805 IC
draws about .2A. When .2A is drawn by the LM-7805 IC, the voltage
drop across the 3 ohm resistor is .6V, enough to turn on transistor Q2.
Transistor Q2 takes over and delivers the current to the output. Note that
if the output voltage goes down, the LM-7805 regulator will draw more
current, forcing the output voltage back to 5V. Thus, the LM-7805
regulator controls the output voltage and keeps it at 5V.
Unfortunately, this circuit has no control of the output maximum current. If the output is shorted to ground
transistor Q2 will be overloaded and eventually be damaged. The LM-7805 IC will only draw the .2A it was
designed to handle and never heat up to turn itself off. Another transistor Q1 is added to limit maximum current.
Resistor R5 is added to sense the current in transistor Q2. When approximately 3A is drawn in transistor Q2,
the voltage drop in resistor R5 will turn on transistor Q1. This will force more current in the LM-7805 IC.
Eventually the LM-7805 IC will overheat turning itself off and thus limiting the circuit at about 3.2A.
The first .2A of current is drawn by the LM-7805 IC. The next 3A are drawn by transistor Q2. Thereafter, the
current is drawn by the LM-7805 IC until it overheats and turns itself off. This is a very effective circuit capable
of regulating the output voltage at a constant 5 volts and yet delivering over 3A of current.
AC Power Supply
The section features a 12.6VAC center tapped output. Two secondary windings from the transformer are
connected directly to the yellow binding posts. Connecting from one of the outputs to the center black binding
post will give you 6.3VAC. The maximum output current for 12.6VAC and 6.3VAC is 1A.
This concludes the discussion on the operation of the XP-720 Power Supply.
Figure 6A
1.25 - 15V
R1
VR1
LM-317
Figure 7
Q2
8-12VDC
Page 18

-17-
1. AC voltage is supplied to the rectifier stages by the . . .
r A. step up transformer.
r B. step down transformer.
r C. 1 to 1 transformer.
r D. AC to DC transformer.
2. The secondary windings of the transformer are . . .
r A. 90
O
out of phase.
r B. 180
O
out of phase.
r C. 270
O
out of phase.
r D. 320
O
out of phase.
3. Diodes allow current to flow . . .
r A. when the anode is more negative than the cathode.
r B. when the cathode is more positive than the anode.
r C. in one direction.
r D. when a negative or positive voltage is on the anode.
4.
What circuit is more efficient for rectifying AC to DC?
r A. Hartley oscillator.
r B. Half-wave.
r C. Schmitt trigger.
r D. Full wave.
5. The DC voltage is smoothed by using a . . .
r A. half-wave rectification circuit.
r B. small value capacitor with a high voltage value.
r C. Large value capacitor.
r D. 90
O
out of phase rectification circuit.
6. An inefficient rectification circuit usually contains . . .
r A. large gaps between cycles.
r B. twice the AC voltage needed.
r C. more diodes.
r D. all of the above.
7. The maximum current that a diode can handle is determined by . . .
r A. the transformer’s current rating.
r B. the amount of AC ripple.
r C. three times the diode rating.
r D. peak current rating.
8. The LM-317 will shut down when . . .
r A. the output voltage is too high.
r B. no current is being drawn.
r C. the junction overheats.
r D. the output voltage drops to 1.25V.
9.
The LM-317 regulator contains . . .
r A. a pass transistor.
r B. a constant current source.
r C. a differential amplifier.
r D. all of the above.
10. The LM-317 is basically . . .
r A. a 1.25V regulator.
r B. a 6.25V regulator.
r C. a 2.5V regulator.
r D. a negative voltage regulator.
QUIZ
Answers: 1. B, 2. B, 3. C, 4. D, 5. C, 6. A, 7. D, 8. C, 9. D, 10. A
Page 19

SPECIFICATIONS ON XP-720 POWER SUPPLY
Input Voltage 110-130VAC
Current Protection 1A
Output Voltage 1) 1.25-15VDC @ 1A
(at 120V input) 2) –1.25 - –15VDC @ 1A
3) 5VDC @ 3A
4) 6.3, 12.6CTAC @ 1A
Output Regulation 200mV each supply
Line Regulation 100mV each supply
Ripple Max 5mV rms
Current Protection Thermal overload ±15VDC
Current limiting 5VDC
Fuse 6.3VAC
Short Protection Current limiting 5VDC, ±15VDC
Fuse 6.3VAC
Output Impedance .2Ω ±15VDC
.06Ω 5VDC
-18-
SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM
Maximum output individually rated.
Page 20

Elenco®Electronics, Inc.
150 Carpenter Avenue
Wheeling, IL 60090
(847) 541-3800
Website: www.elenco.com
e-mail: elenco@elenco.com
 Loading...
Loading...