Page 1

Remote Booster Power
Supply Technical
Reference Manual
P/N 3100485-EN • REV 04 • ISS 28AUG12
Page 2
r
Y
Copyright © 2012 UTC Fire & Security. All rights reserved.
Trademarks and
patents
The Remote Booster Power Supply name and logo are trademarks
of UTC Fire & Security.
Other trade names used in this document may be trademarks or
registered trademarks of the manufacturers or vendors of the
respective products.
Manufacture
Edwards, A Division of UTC Fire & Security
Americas Corporation, Inc.
8985 Town Center Parkway, Bradenton, FL 34202, USA
Certification
FCC compliance Class A: This equipment has been tested and found to comply with
the limits for a Class A digital device, pursuant to part 15 of the FCC
Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection
against harmful interference when the equipment is operated in a
commercial environment. This equipment generates, uses, and can
radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in
accordance with the instruction manual, may cause harmful
interference to radio communications. Operation of this equipment in
a residential area is likely to cause harmful interference in which
case the user will be required to correct the interference at his own
expense.
FDN
NYC Fire Department Certificate of Approval: MEA 476-91-E XIII
European Union
directives
1999/5/EC (R&TTE directive): Hereby, UTC Fire & Security
declares that this device is in compliance with the essential
requirements and other relevant provisions of Directive 1999/5/EC.
2002/96/EC (WEEE directive): Products marked with this symbol
cannot be disposed of as unsorted municipal waste in the European
Union. For proper recycling, return this product to your local supplier
upon the purchase of equivalent new equipment, or dispose of it at
designated collection points. For more information see:
www.recyclethis.info.
2006/66/EC (battery directive): This product contains a battery that
cannot be disposed of as unsorted municipal waste in the European
Union. See the product documentation for specific battery
information. The battery is marked with this symbol, which may
include lettering to indicate cadmium (Cd), lead (Pb), or mercury
(Hg). For proper recycling, return the battery to your supplier or to a
designated collection point. For more information see:
www.recyclethis.info.
Contact information For contact information, see www.utcfireandsecurity.com.
Page 3

Content
Important information iii
Limitation of liability iii
Remote Booster Power Supply FCC compliance iv
Introduction 1
Models covered 1
Compatibility 1
Installation procedure checklist 2
Getting started 3
Description 3
Component descriptions 4
Specifications 5
LED indicators 6
Installing the enclosure 7
Installing option modules in the enclosure 8
Installing the circuit board in the enclosure 10
Setting the jumpers 12
NAC Class A or Class B (JP1 and JP2) 12
Ground fault enable (JP3) 12
Battery charging (JP4) 13
UL 864 programming requirements 14
Setting the DIP switches 15
Sense 1 and 2 operation (SW1-1 to 3) 15
Synchronization control (SW1-4) 16
NAC circuit operation (SW1-5 to 8 and SW2-1 to 4) 17
Genesis mode for continuous NACs (SW2-5) 19
AC power loss reporting (SW2-6) 19
Auxiliary control during AC power loss (SW2-7) 19
Class A or B NAC configuration (SW2-8) 20
Remote Booster Power Supply Technical Reference Manual i
Page 4

Wire routing 21
Connecting the field wiring 22
AC power wiring 22
Battery wiring 22
NAC Class B wiring 24
NAC Class A wiring 25
Sense circuit wiring 26
AUX power wiring 26
Common trouble relay wiring 27
NAC wiring using CC1(S) modules 29
Installing the 3-TAMP tamper switch 34
Battery calculation worksheet 35
Notification appliance circuit calculations 37
Introduction 37
What you’ll need 37
Worksheet method 39
Equation method 40
Understanding BPS synchronization 43
Connection of booster power supplies 43
Synchronization of visible outputs 44
Synchronization of visible and audible outputs 44
Applications 46
Key 46
Genesis circuit notification 47
Conventional visible and audible circuit notification 48
Conventional visible and audible circuit to Genesis notification 49
Conventional audible or visible circuit to Genesis notification 50
Genesis visible circuit and conventional audible circuit to Genesis
notification 51
Conventional split mode circuit with fault tolerance notification 52
Genesis split mode circuit with fault tolerance notification 53
CDR-3 Coder to Genesis notification 54
CDR-3 Coder to conventional notification 55
CDR-3 Coder to Genesis visibles and conventional audibles 56
Access control power supply 57
ii Remote Booster Power Supply Technical Reference Manual
Page 5
Important information
Limitation of liability
To the maximum extent permitted by applicable law, in no event will UTCFS be
liable for any lost profits or business opportunities, loss of use, business
interruption, loss of data, or any other indirect, special, incidental, or
consequential damages under any theory of liability, whether based in contract,
tort, negligence, product liability, or otherwise. Because some jurisdictions do not
allow the exclusion or limitation of liability for consequential or incidental
damages the preceding limitation may not apply to you. In any event the total
liability of UTCFS shall not exceed the purchase price of the product. The
foregoing limitation will apply to the maximum extent permitted by applicable law,
regardless of whether UTCFS has been advised of the possibility of such
damages and regardless of whether any remedy fails of its essential purpose.
Installation in accordance with this manual, applicable codes, and the instructions
of the authority having jurisdiction is mandatory.
While every precaution has been taken during the preparation of this manual to
ensure the accuracy of its contents, UTCFS assumes no responsibility for errors
or omissions.
Advisory messages
Advisory messages alert you to conditions or practices that can cause unwanted
results. The advisory messages used in this document are shown and described
below.
WARNING: Warning messages advise you of hazards that could result in injury
or loss of life. They tell you which actions to take or to avoid in order to prevent
the injury or loss of life.
Caution: Caution messages advise you of possible equipment damage. They tell
you which actions to take or to avoid in order to prevent the damage.
Note: Note messages advise you of the possible loss of time or effort. They
describe how to avoid the loss. Notes are also used to point out important
information that you should read.
Remote Booster Power Supply Technical Reference Manual iii
Page 6

Remote Booster Power Supply FCC compliance
This equipment can generate and radiate radio frequency energy. If the
equipment is not installed in accordance with this manual, it may cause
interference to radio communications. This equipment has been tested and found
to comply with the limits for Class A computing devices pursuant to Subpart B of
Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These rules are designed to provide reasonable
protection against such interference when this equipment is operated in a
commercial environment. Operation of this equipment is likely to cause
interference, in which case the user, at his own expense, will be required to take
whatever measures may be required to correct the interference.
iv Remote Booster Power Supply Technical Reference Manual
Page 7

Introduction
This installation manual is intended for use by installers and field technicians. It
provides the installation procedures, wiring diagrams, DIP switch settings, etc.
required to install and set up the Remote Booster Power Supply (BPS).
Models covered
The following table lists the booster power supply models that are covered in this
manual.
Catalog number Description
BPS6A 6.5 A booster power supply
BPS6A/230 6.5 A booster power supply
BPS6AC 6.5 A booster power supply
MIRBPS6A 6.5 A booster power supply
MIRBPS6A/230 6.5 A booster power supply
XLS-BPS6A 6.5 A booster power supply
XLS-BPS6A/230 6.5 A booster power supply
EBPS6A 6.5 A booster power supply
EBPS6A/230 6.5 A booster power supply
BPS10A 10 A booster power supply
BPS10A/230 10 A booster power supply
BPS10AC 10 A booster power supply
MIRBPS10A 10 A booster power supply
MIRBPS10A/230 10 A booster power supply
XLS-BPS10A 10 A booster power supply
XLS-BPS10A/230 10 A booster power supply
EBPS10A 10 A booster power supply
EBPS10A/230 10 A booster power supply
Compatibility
The input circuits of the booster power supply can be connected to 12 VDC or
24 VDC systems.
For details about device compatibility, refer to the Remote Booster Power Supply
Compatibility List (P/N 3100656).
Remote Booster Power Supply Technical Reference Manual 1
Page 8

Installation procedure checklist
Follow these steps to install and set up the booster power supply (BPS).
Verify that all power and field wiring are de-energized before proceeding.
Unpack the equipment.
Review the “Getting started” section.
Review the applications: Review the applications to determine how you want
to use the BPS. See the “Applications” section.
Prepare the site: Make sure the installation location is free from construction
dust and debris and extreme temperature ranges and humidity.
Install the enclosure: See “Installing the enclosure” for enclosure dimensions.
Install option modules if required: See “Installing option modules in the
enclosure.”
Install the 3-TAMP tamper switch (if one is used): See “Installing the 3-TAMP
tamper switch.”
Set the jumpers: See “Setting the jumpers.”
Set the DIP switch options: See “Setting the DIP switches.”
Review wire routing: See “Wire routing.”
Check field wiring for shorts, opens, and grounds.
Connect the field wiring: See “Connecting the field wiring.”
Turn on the AC mains power.
Connect the battery compliment.
Verify that no defaults are displayed.
Test the system for proper operation.
2 Remote Booster Power Supply Technical Reference Manual
Page 9

Getting started
Description
The 6.5 A and 10 A booster power supplies are designed to extend the power
capacity of an emergency communication, life safety, fire alarm, security, or
access control system. You can activate the BPS from options modules or from a
control circuit. It has four independent NAC/AUX circuits that are supervised,
when configured for NAC. It is also equipped with a fault relay that you can
configure for common trouble (with immediate AC failure indication), or as an AC
mains failure indication relay (with delayed output). The BPS’s sense input #1
also provides a common fault indicator by opening the output side of the sense
circuit.
Remote Booster Power Supply Technical Reference Manual 3
Page 10
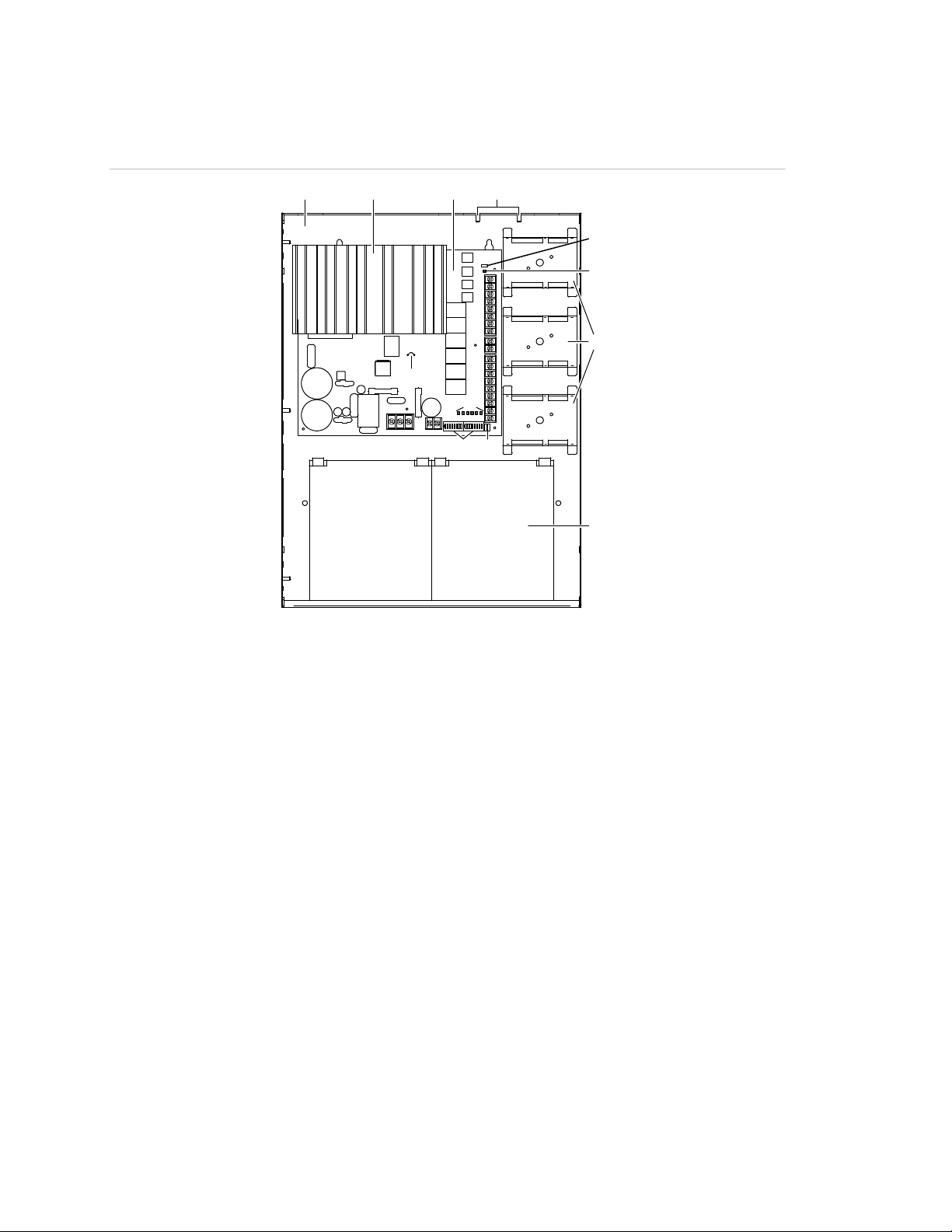
Component descriptions
Figure 1: Components
(1) (2)
(12)
(3)
(4)
(5)
(6)
(7)
(10)
(8)(9)
(11)
(1) Enclosure: Houses the electronics and two standby batteries
(2) Heat sink: Distributes heat away from the circuit board
(3) Circuit board: Provides connections for all circuits
(4) Tamper switch standoffs: 3-TAMP mounting standoffs
(5) Jumper JP3: Ground fault enable or disable option
(6) AC LED: AC power on
(7) Mounting brackets: Option module mounting brackets
(8) Jumpers JP1 and JP2: Class A or Class B NAC option
(9) DIP switches: Two eight-position DIP switches used for configuration
(10) Circuit LEDs: NAC, battery, and ground fault trouble LEDs
(11) Batteries: Up to two 10 Ah batteries fit in the enclosure. For larger batteries, use an external
battery cabinet (BC-1 or BC-2).
(12) Jumper JP4: Battery charging jumper
4 Remote Booster Power Supply Technical Reference Manual
Page 11

Specifications
The following specifications apply to all BPS models.
AC line voltage
6.5 A BPS
120 VAC / 230 VAC (50/60 Hz), 390 W
10 A BPS
Sense voltage (input) 6 to 45 VDC (FWR and unfiltered DC)
Sense current (input) 6 mA at 24 VDC, 3 mA at 12 VDC, 12 mA at 45 VDC
NAC output voltage
(special application circuit)
AUX output voltage
(special application circuit)
NAC/AUX output current 3.0 A max. per circuit with 0.35 power factor
NAC/AUX capacitive loading 10,000 F max. for continuous NAC circuits
NAC/AUX class Class A or Class B
Wire size 18 to 12 AWG (0.75 to 2.5 mm2)
NAC EOL UL: 15 k (P/N EOL-15)
120 VAC / 230 VAC (50/60 Hz), 580 W
19.1 to 26.40 VDC
Note: All NACs are supervised. Refer to the Remote Booster
Power Supply Compatibility List P/N 3100656 for the maximum
number of devices that can be used on a NAC circuit.
19.0 to 26.48 VDC
(6.5 A or 10 A max. total for all NACs)
(6 A or 8 A max. total for all AUXs)
2,200 F max. for coded rate NAC circuits
2,200 F max. for AUX circuits
ULC: Use P/N EOL-P1 and select the 15 k resistor
Auxiliary output (continuous) 1 dedicated unsupervised, unswitched 200 mA auxiliary output
Voltage range: 19.49 to 26.85 VDC
Common trouble relay Form C, 1 A, 30 VDC (resistive)
Battery capacities 6.5 to 24 Ah for ECS/MNS/LSS applications
6.5 to 24 Ah for Security/Access Control applications
10 Ah maximum in BPS enclosure applications
Battery charger current limit [1] 1.2 A when the battery jumper wire is cut
2.1 A when the battery jumper wire is not cut
Operating environment
Operating temperature
Relative humidity
Ground fault impedance 10 k
Intended installation
environment
[1] The battery charger is disabled automatically and will not charge the batteries when the unit is
activated via either of its sense inputs.
32 to 120°F (0 to 49°C)
0 to 93% noncondensing
Indoor-dry
Remote Booster Power Supply Technical Reference Manual 5
Page 12

LED indicators
The BPS has seven LED indicators. See “Component descriptions” for the
location of the LEDs.
Table 1: LED indicators
LED Color Description
AC Green AC power on.
NAC1 Yellow NAC1/AUX1 trouble [1].
NAC2 Yellow NAC2/AUX2 trouble [1].
NAC3 Yellow NAC3/AUX3 trouble [1].
NAC4 Yellow NAC4/AUX4 trouble [1].
BAT Yellow Battery trouble. Indicates that the battery level has fallen below
acceptable levels.
GND Yellow Ground fault. Indicates that a ground fault has been detected on
the field wiring.
[1] The NAC LEDs indicate a trouble with the load or external wiring on the NAC/AUX circuit. For
circuits configured as NACs, this could be an open circuit trouble, short circuit trouble, or an
overload trouble.
For short circuit troubles, the NAC does not activate until the short circuit condition is removed.
For overload troubles, an active NAC is shutdown. After shutdown, if there is no short circuit
condition, the NAC reactivates after 30 seconds and checks to see if the overload condition still
exists.
For AUX circuits, the trouble indicates an overload condition. The AUX circuit is shutdown for
30 seconds and then is reactivated to see if the overload condition still exists.
Trouble indicating and reporting
When the BPS trouble relay is not dedicated to AC power loss reporting (DIP
switch SW2-6 OFF), the trouble conditions listed in the table above are reported
through the trouble relay. Other internal troubles that do not have an associated
LED are also reported via the BPS trouble relay. Other internal troubles include:
DIP switch read trouble, RAM failure, code checksum failure, A to D failure, and
battery charger failure.
All troubles are also reported through both sense circuit trouble relays.
6 Remote Booster Power Supply Technical Reference Manual
Page 13
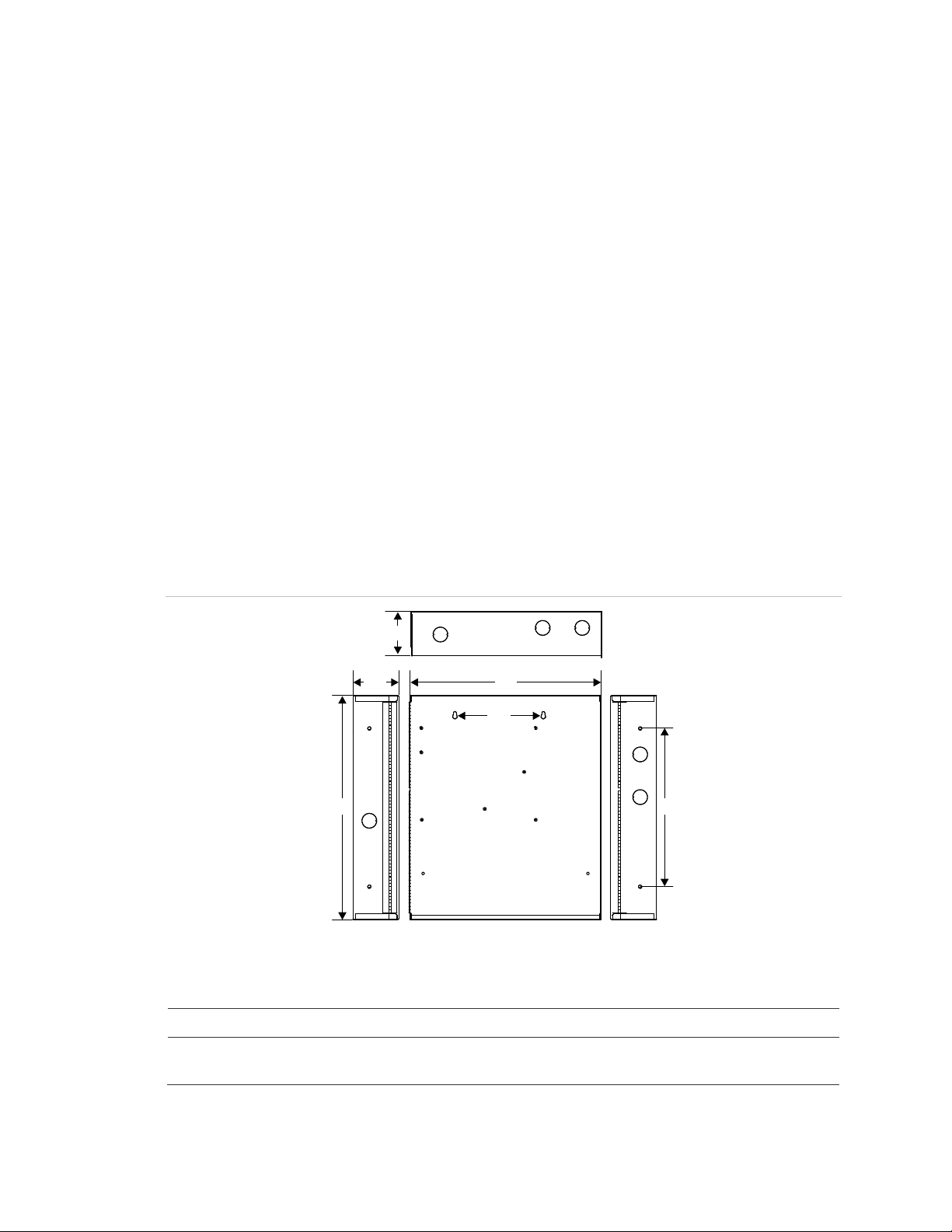
Installing the enclosure
When installing this system, be sure to follow all applicable national and local
codes and standards.
The enclosure can be surface mounted or semiflush mounted. See “Enclosure
dimensions” below for details.
To surface mount the enclosure:
1. Position the enclosure on the finished wall surface.
2. Fasten the enclosure to the wall surface where indicated.
3. Install all conduits and pull all wiring into the enclosure before proceeding.
To semiflush mount the enclosure:
1. Frame the interior wall as required so that it supports the full weight of the
enclosure and standby batteries.
2. Fasten the enclosure to the framing studs where indicated.
3. Install all conduits and pull all wiring into the enclosure before proceeding.
Figure 2: Enclosure dimensions
D5
D2
(3)
D1
(1) Top view
(2) Front view
D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 D6
(1)
D3
D4
(2)
D6
(3)
(4)
(3) Side view
(4) All knockouts are a combination
0.5 in. (1.27 cm) and 0.75 in. (1.9 cm)
17.0 in
(43.2 cm)
Remote Booster Power Supply Technical Reference Manual 7
3.5 in
(8.9 cm)
13.0 in
(33.0 cm)
6.5 in
(16.5 cm)
3.375 in
(8.6 cm)
12.0 in
(30.4 cm)
Page 14
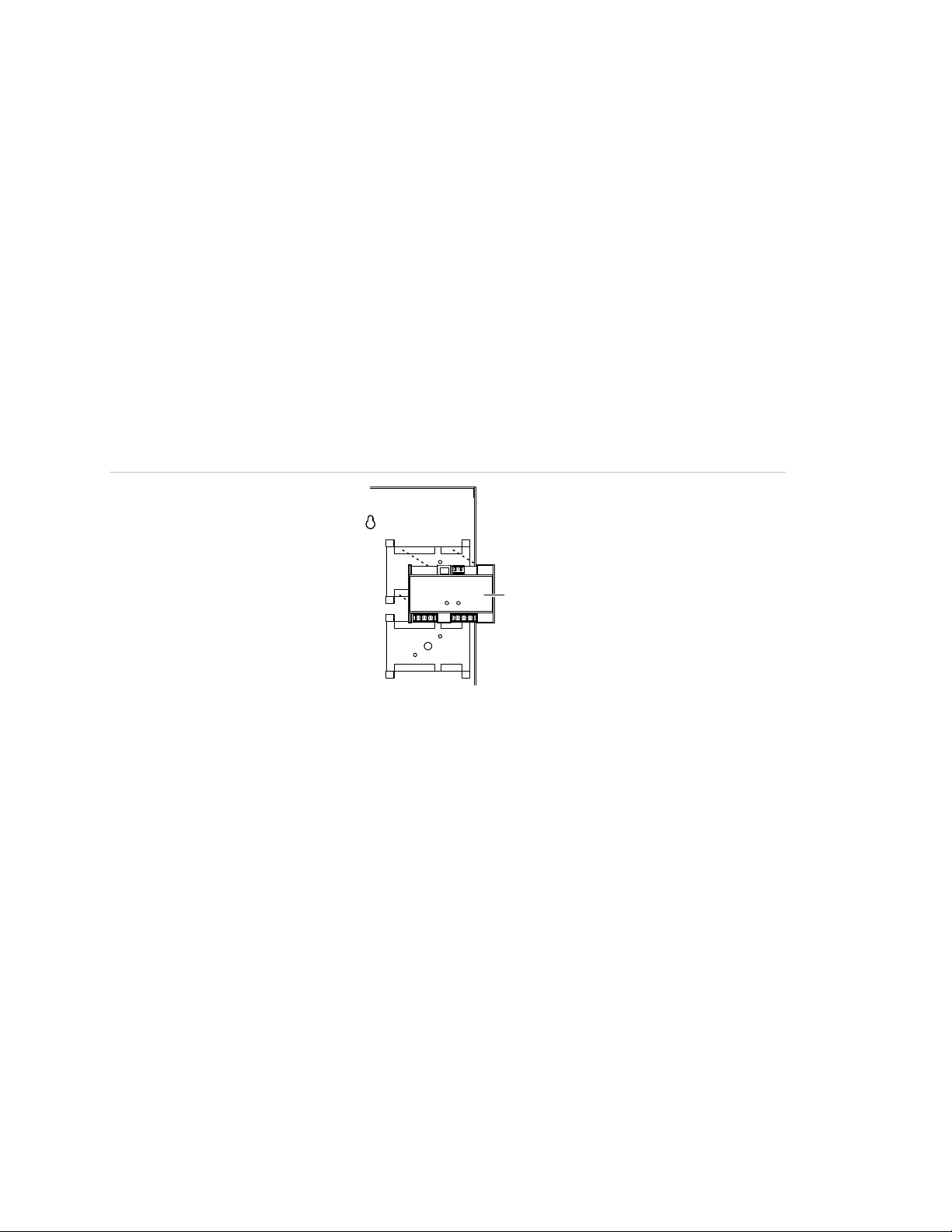
Installing option modules in the enclosure
Up to three option modules can be installed on the mounting brackets inside the
enclosure. Depending on the model, the device must be either screw-mounted or
snap-mounted to the bracket.
To snap-mount modules on a bracket:
1. Snap the module into a mounting bracket.
2. Connect all wiring. Refer to the module’s installation sheet for wiring
information or to the Signature Series Component Installation Manual
(P/N 270497).
Note: Route the wiring around the perimeter of the enclosure, not across the
circuit board.
Figure 3: Mounting brackets with an option module
(1)
(2)
(1) Mounting brackets
(2) Option module
To screw-mount Signature Series modules on a bracket:
1. Remove the module’s plastic cover.
2. Remove the circuit board from the plastic backing.
3. Screw the plastic backing to the mounting bracket using two #6, 1/4 flat head
sheet metal screws. See Figure 4 on page 9.
Note: For mounting MN-NETRLY4 modules, refer to the MN-NETRLY4
Network Relay Module Installation Sheet, P/N 310-1827-ML.
4. Insert the circuit board into the plastic backing.
5. Snap the module’s plastic cover into place.
6. Connect all wiring. Refer to the module’s installation sheet for wiring
information or to the Signature Series Component Installation Manual
(P/N 270497).
8 Remote Booster Power Supply Technical Reference Manual
Page 15
Note: Route the wiring around the perimeter of the enclosure, not across the
circuit board.
Figure 4: Inserting the circuit board
Remote Booster Power Supply Technical Reference Manual 9
Page 16
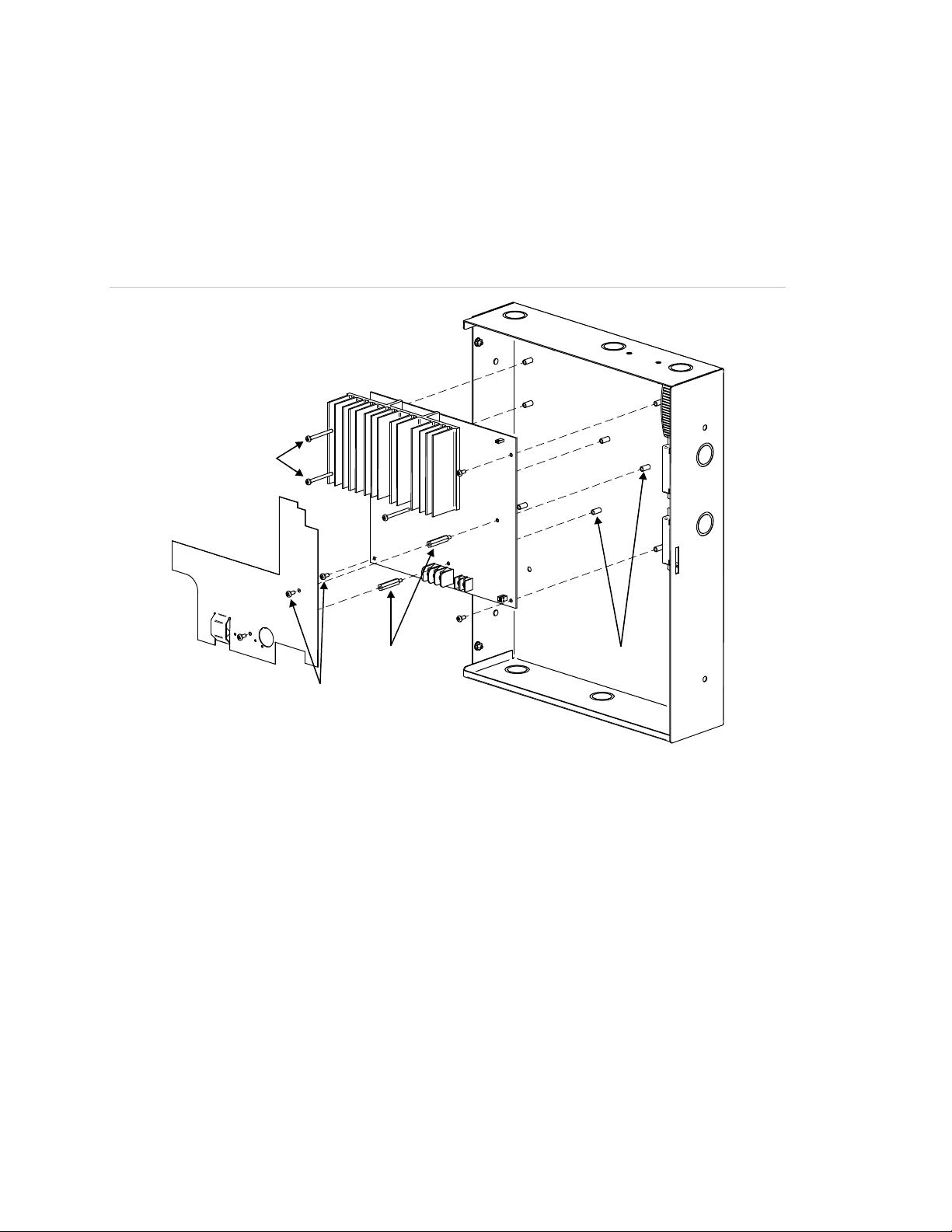
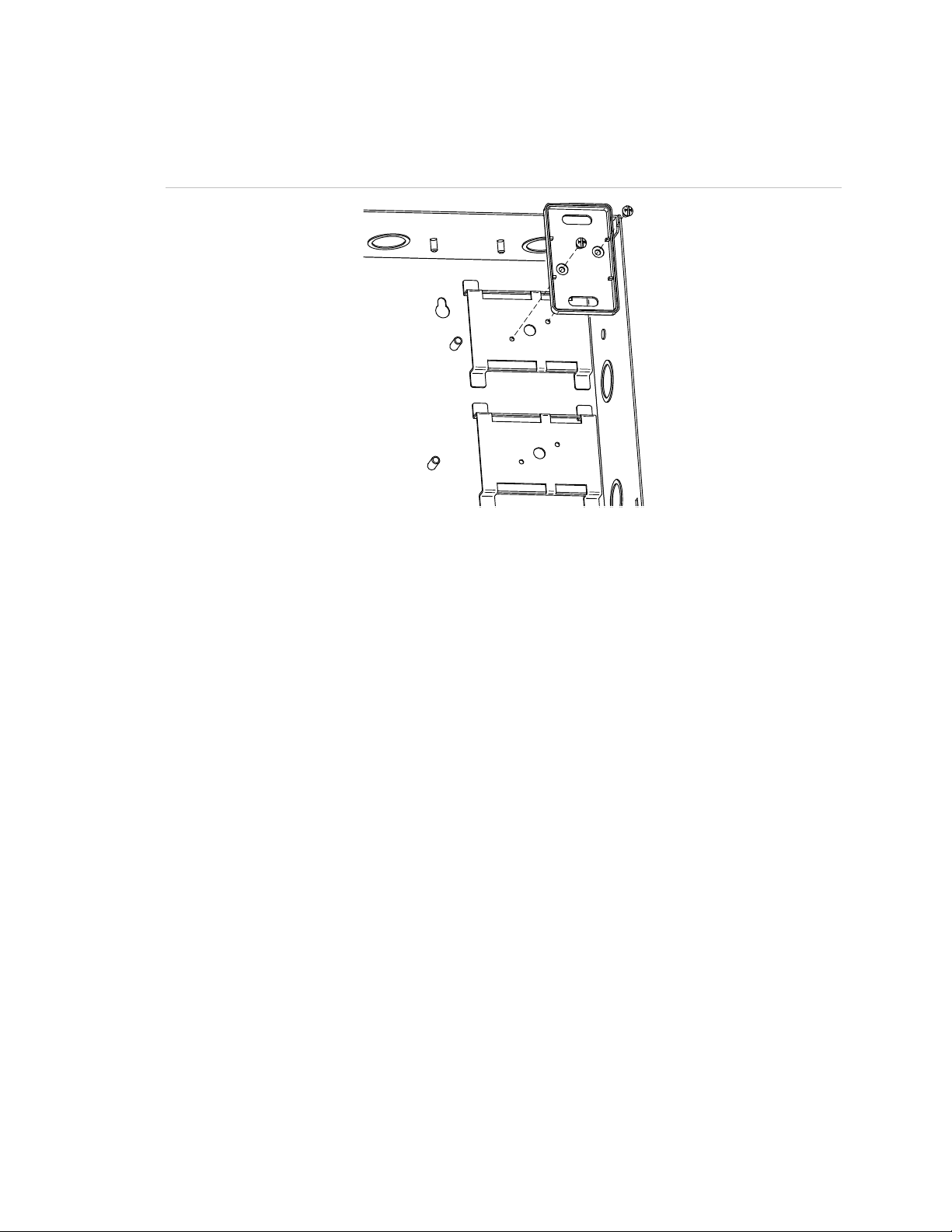
Installing the circuit board in the enclosure
You may have to remove the circuit board to install the enclosure. Reinstalling
the circuit board in the enclosure must be done with accuracy to avoid causing
ground faults or shorts. The screws and standoffs must be installed correctly and
in the right positions. Use the diagrams below to install the circuit board.
Figure 5: Complete circuit board installation
(4)
(3)
(2)
(1)
(6)
(7)
(1) Cover (“C” models, only)
(2) Long screws
(3) Circuit board
(4) Enclosure
(5) Enclosure standoffs
(6) Barrel spacers, see Figure 6 on page 11
(7) Short screws
(5)
10 Remote Booster Power Supply Technical Reference Manual
Page 17
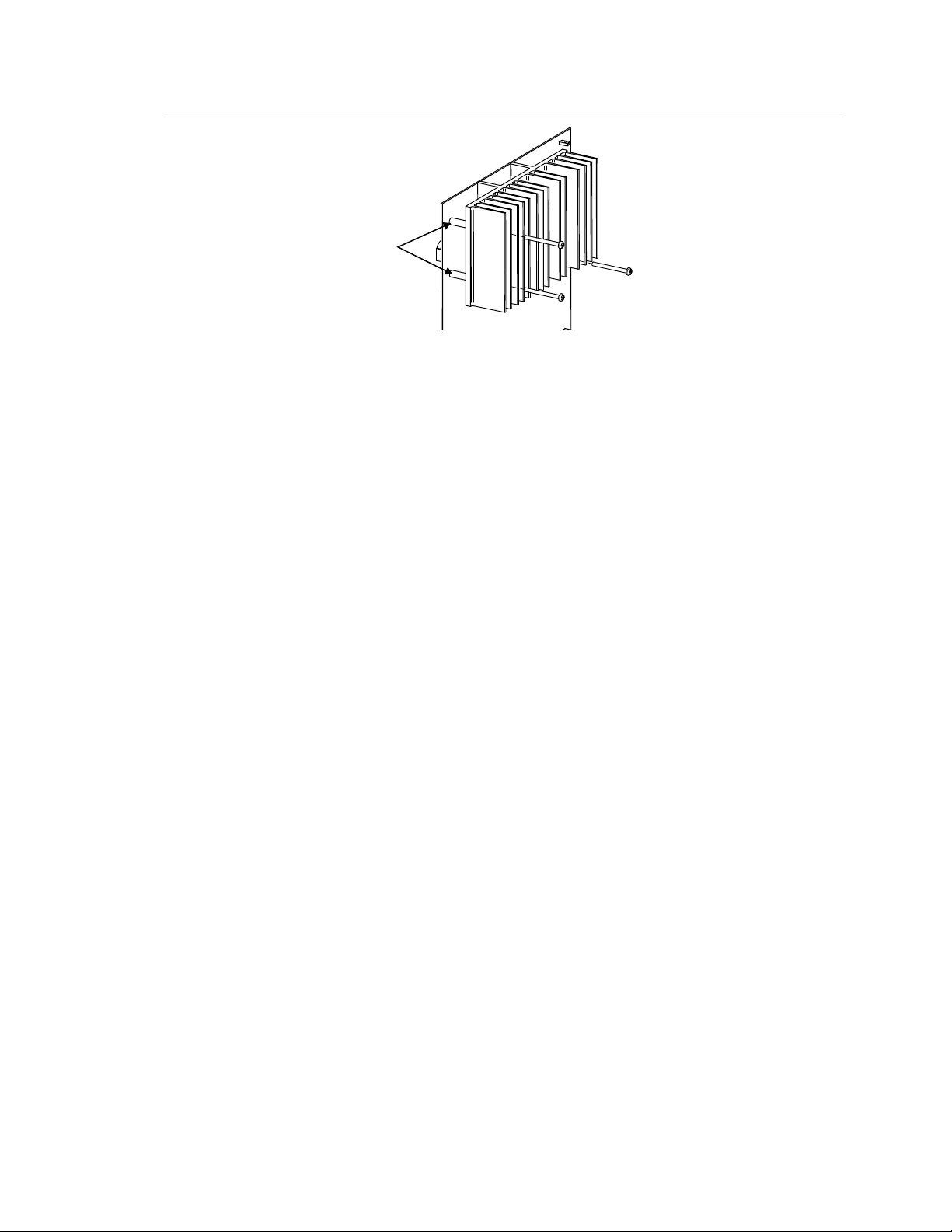
Figure 6: Barrel spacer installation
(1)
(2)
(1) Barrel spacers
(2) Long screws
Note: The barrel spacers must be positioned correctly so that the long screw can
pass through the spacer and into the enclosure standoff.
Remote Booster Power Supply Technical Reference Manual 11
Page 18
Setting the jumpers
There are four jumpers on the BPS. See Figure 1 on page 4 for the location of
the jumpers.
NAC Class A or Class B (JP1 and JP2)
JP1 and JP2 are used to select a Class A or Class B NAC wiring configuration
for all NACs. The default is Class B.
Note: JP1 and JP2 must be positioned to match the SW2-8 DIP switch selection
(Class A or Class B).
Figure 7: JP1 and JP2
11
22
33
JP1 JP2
(1) Class A
(2) Class B
(1) (1)
(2) (2)
Ground fault enable (JP3)
JP3 is used to set the NAC/AUX circuits for ground fault enabled or disabled
operation. The sense inputs are always isolated from local power.
Enabled: Allows the BPS to perform its own ground fault checking. This is the
default position.
Disabled: Disable the BPS's ground fault detection only when the controlling
panel is providing ground fault detection for the BPS output circuits. See
Figure 8 on page 13 for wiring information.
12 Remote Booster Power Supply Technical Reference Manual
Page 19
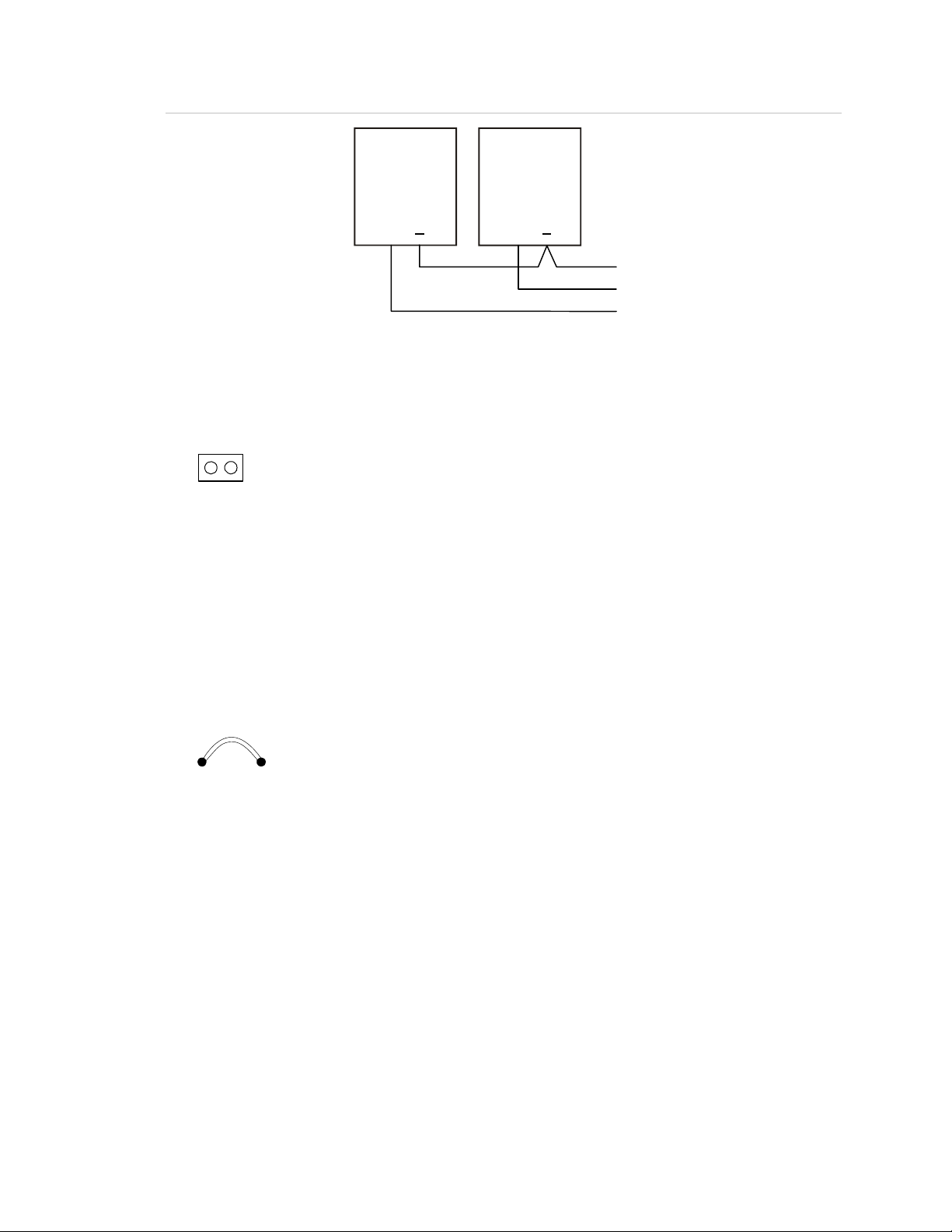
)
Figure 8: Ground fault enable
(1)
(2)
+ +
(3
(1) Control panel. The control panel is responsible for ground fault detection when the BPS is
wired in this fashion.
(2) BPS. Disable the BPS’s ground fault jumper (JP3).
(3) To next BPS that requires ground fault detection from the control panel.
JP3
1
2
GF disable: Do not install jumper
GF enable: Install jumper
Battery charging (JP4)
The battery charging jumper is a small wire that controls how the batteries are
charged. Battery size determines whether you must cut the jumper wire or leave
it intact.
JP4
Cut the jumper wire when using batteries under 10 Ah.
Do not cut the jumper wire when using batteries 10 Ah or over.
Remote Booster Power Supply Technical Reference Manual 13
Page 20

UL 864 programming requirements
NOTICE TO USERS, INSTALLERS, AUTHORITIES HAVING JURISDICTION, AND OTHER
INVOLVED PARTIES
This product incorporates field-programmable options. In order for the product to comply with the
requirements in the Standard for Control Units and Accessories for Fire Alarm Systems, UL 864,
certain programming features or options must be limited to specific values or not used at all as
indicated below. Some options were permitted under the previous versions of UL 864 and are
provided to allow for service replacements on those systems.
Programmable feature or
option
Four second NAC audible
synchronization delay [1]
AC power delay Y On (3 hour, no
[1] This option is controlled by switch SW1-4. See “Synchronization control (SW1-4)” on page 16.
Permitted in
UL 864? (Y/N)
N On (4 second delay)
Possible settings Settings permitted
Off (1 second delay)
dedicated AC failure
contact)
Off (no delay)
in UL 864
Off
On
14 Remote Booster Power Supply Technical Reference Manual
Page 21

Setting the DIP switches
Two eight-position DIP switches are used to configure the BPS. The following
sections show the DIP switch settings for the various input and output
configurations.
Note: As shipped from the factory, all switches are in the OFF position.
Figure 9: Switch settings
ON
12345678
SW1 SW2
12345678
Sense 1 and 2 operation (SW1-1 to 3)
The BPS has three operating modes, as shown in the following table. Switches
SW1-1, -2, and -3 determine which mode is used.
Table 2: Switch settings
Operating mode [1] SW1-1 SW1-2 SW1-3
Correlate mode OFF – –
Genesis Master mode ON OFF ON
Nondelayed mode ON ON –
[1] See the descriptions below for operation details
These switches also determine how Sense 1 and 2 correlate to the NAC circuits.
Details for each mode are described below.
Correlate mode
In correlate mode, switches SW1-2 and SW1-3 control which NACs activate
when the sense circuits activate. The correlations do not affect output circuits
that are operating as AUX circuits.
The following table details which NACs activate when the sense circuits activate.
Remote Booster Power Supply Technical Reference Manual 15
Page 22

Table 3: Sense circuit to NAC correlations
Switch settings Class B Class A
SW1-2 SW1-3 Sense 1 Sense 2 Sense 1 Sense 2
OFF OFF 1, 2, 3, 4 1, 2, 3, 4 1/2, 3/4 1/2, 3/4
OFF ON 1 2, 3, 4 1/2 3/4
ON OFF 1, 2 3, 4 – –
ON ON 1, 2, 3 4 – –
Genesis Master mode
In Genesis Master mode, Sense 1 is connected to a visible zone and Sense 2 is
connected to an audible zone. All NACs are activated when Sense 1 activates.
Continuous NACs generate Genesis audible on/off signals based on the Sense 2
input circuit.
Nondelayed mode
Nondelayed mode is intended to support coders. In this mode, there is no delay
between activation of the sense input and activation of the NAC.
In nondelayed mode, switch SW1-3 controls which NACs activate when the
sense circuits activate. The correlations do not affect output circuits that are
operating as AUX circuits.
The following table details which NACs activate when the sense circuits activate.
Table 4: Sense circuit to NAC correlations
SW1-3 setting Class B Class A
SW1-3 Sense 1 Sense 2 Sense 1 Sense 2
OFF 1, 2, 3, 4 1, 2, 3, 4 1/2, 3/4 1/2, 3/4
ON 1, 2 3, 4 1/2 3/4
In nondelayed mode, SW2-5 can be used to generate sync pulses for NACs
configured in continuous mode. This supports applications that include Genesis
strobes and conventional audibles. For this operation, the NACs for the audible
signals must be configured in sense follow mode. There is no delay for either the
visibles or the audibles.
Synchronization control (SW1-4)
Switch SW1-4 controls the synchronization of signals with either one- or foursecond delay times. See the topic “Understanding BPS synchronization” for more
information.
Note: When using nondelayed mode, this switch is inactive.
16 Remote Booster Power Supply Technical Reference Manual
Page 23

Table 5: Switch settings (SW1-4)
Switch setting Operation description
ON NACs turn on 4 seconds after the sense input is
activated (e.g. Genesis NACs sync with the second
round of the temporal signal)
OFF NACs turn on 1 second after the sense input is
activated (e.g. the Genesis NACs sync with the second
flash of the Genesis strobes)
NAC circuit operation (SW1-5 to 8 and SW2-1 to 4)
Switch SW1-5 to 8 and SW2-1 to 4 control NAC operation.
Table 6: Switch settings (SW1-5 to 8 and SW2-1 to 4)
Operating mode
Sense Follow [1] OFF OFF OFF OFF OFF OFF OFF OFF
Continuous [1] OFF ON OFF ON OFF ON OFF ON
Temporal [1] [2] ON OFF ON OFF ON OFF ON OFF
Auxiliary [1] ON ON ON ON ON ON ON ON
[1] See the descriptions below for operation details
[2] For externally coded or temporal operations, set the BPS to sense follow mode and use an
externally coded or temporal source to activate the BPS sense circuit to generate the coded or
temporal pattern.
NAC1
SW1-5 SW1-6
NAC2
SW1-7 SW1-8
NAC3
SW2-1 SW2-2
NAC4
SW2-3 SW2-4
Sense follow mode
In sense follow mode, NACs are activated following the sense circuits that are
defined to turn on the NACs. The NACs turn on with a one- or four-second delay
to allow Genesis strobes to synchronize on the NAC side and sense side. The
four-second delay does not comply with UL864 9th edition. In this mode, a
continuous input, 120 ppm, temporal, or coded input can be used.
Note: Sense follow must be used when the sense circuit is connected to a
SIGA-CC1S, Genesis G1M-RM, FireShield panel, or a BPS generating Genesis
sync pulses.
Remote Booster Power Supply Technical Reference Manual 17
Page 24

Continuous mode
In continuous mode, NACs are activated following the sense circuits in
continuous mode. They activate one or four seconds after the sense input
activates and restore seven seconds after the sense input restores.
Note: Activating the NACs four seconds after the sense input restores does not
comply with UL 864 9th edition.
Temporal mode
In temporal mode, NACs are activated following the sense circuits in temporal
mode. They activate one or four seconds after the sense input activates and
restore seven seconds after the sense input restores. NACs generate temporal
output as defined by NFPA.
Note: Activating the NACs four seconds following sense circuits in temporal
mode does not comply with UL 864 9th edition.
Auxiliary
In auxiliary mode, NACs turn on during power-up. Sync pulses are not
generated. Aux circuits can be configured to stay active during a power fail or
load shed on a power fail (after a 20 second delay). Aux circuits are load shed
when the system reaches low battery to prevent deep discharge of the batteries.
18 Remote Booster Power Supply Technical Reference Manual
Page 25

Genesis mode for continuous NACs (SW2-5)
Switch SW2-5 controls NAC operation for Genesis synchronization in continuous
mode.
Table 7: Switch settings (SW2-5)
Switch setting Operation description
ON Continuous NACs are Genesis strobe or horn/strobe
circuits. Continuous NACs generate a Genesis sync
pulse. In Genesis Master mode, continuous NACs
generate Genesis audible on/off signals based on the
Sense 2 input circuit.
OFF Continuous NACs do not generate Genesis signaling
pulses
AC power loss reporting (SW2-6)
Switch SW2-6 controls when a report is sent to the system for an AC power loss.
Table 8: Switch settings (SW2-6)
Switch setting Operation description
ON The BPS trouble relay is dedicated to AC power loss
reporting. The trouble relay switches within 20 seconds
when AC fails or restores.
The sense circuits immediately signal a fault condition
for any non-AC power loss faults. If AC power fails, the
sense circuits signal a fault condition after three hours
of power loss.
OFF The trouble relay operates for any trouble on the BPS.
The sense circuits signal a fault for any troubles.
Auxiliary control during AC power loss (SW2-7)
Switch SW2-7 controls auxiliary outputs during AC loss.
Note: The 200 mA continuous AUX circuit is not affected by AC power loss.
Table 9: Switch settings (SW2-7)
Switch setting Operation description
ON Auxiliary outputs turn off 20 seconds after power fail
OFF Auxiliary outputs stay on after AC power fail until the
battery is less than 18.4 VDC
Remote Booster Power Supply Technical Reference Manual 19
Page 26

Class A or B NAC configuration (SW2-8)
Switch SW2-8 controls NAC Class A or B operation for all NACs.
Note: Jumpers JP1 and JP2 must be set to match the operation of this switch.
Table 10: Switch settings (SW2-8)
Switch setting Operation description
ON Class A NACs
OFF Class B NACs
20 Remote Booster Power Supply Technical Reference Manual
Page 27

Wire routing
Separate power-limited from nonpower-limited wiring. Wiring within the enclosure
should be routed around the perimeter of the enclosure, not across the circuit
board.
Figure 10: Wire routing
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
Legend
(1) Power-limited wiring area
(2) Route AC supply through knockouts in nonpower-limited area
(3) Battery wiring
(4) Battery
Notes
• Maintain 0.25 in. (6 mm) spacing between power-limited and nonpower-limited wiring.
• NAC circuits are power-limited and supervised for opens, shorts, and overcurrents. When
configured as auxiliary power circuits, they are power-limited and supervised for shorts and
overcurrents.
• Source must be power-limited. Source determines supervision.
• Position the battery terminals towards the door.
(4)
Remote Booster Power Supply Technical Reference Manual 21
Page 28

Connecting the field wiring
Caution: Break the wire run at each terminal connection to provide proper
connection supervision. Do not loop wires under the terminals.
AC power wiring
Figure 11: AC power wiring
TB3
LNG
(1)
(1) 120 VAC connection shown. For 230 VAC connections, connect L1 to L and L2 to N. Do not
operate unit without a ground connection.
TB4
+
-
Battery wiring
Two backup batteries are required with the BPS. The largest batteries that fit in
the BPS enclosure are 10 Ah. Batteries larger than 10 Ah must be installed in a
BC-1 or BC-2 battery cabinet.
Caution: For proper battery charging, the battery charging jumper wire (JP4)
must be set according to the battery size you are using. Refer to “Setting the
jumpers” for details about jumper JP4 and Figure 1 for the location of JP4.
Notes
• Batteries should be replaced every five years, or as required by local codes.
• Refer to local and national codes for battery maintenance requirements.
22 Remote Booster Power Supply Technical Reference Manual
Page 29

Figure 12: Battery wiring
(1) Red
(2) Black
(3) Blue
(4) Top view
TB3
LNG
TB4
-
+
(3)
Remote Booster Power Supply Technical Reference Manual 23
Page 30

NAC Class B wiring
Connect a single NAC circuit to one NAC output. Terminate the circuit with a
15 k EOL resistor.
Figure 13: NAC class B wiring
(15)
(19)
(16)
(20)
(21)
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
(5)
(6)
(7)
(8)
(9)
(10)
(11)
(12)
(13)
(14)
TB1
+
+++
TB5
TB2
++
(18)
Legend
(1) NAC1
(2) NAC2
(3) NAC3
(4) NAC4
(5) 200 mA AUX Continuous
(6) Sense 1 IN
(7) Sense 1 COM
(8) Sense 1 OUT
(9) Sense 2 IN
(10) Sense 2 COM
(11) Sense 2 OUT
(12) Trouble NO
Notes
• A trouble on the booster power supply is sensed on the circuit that connects to the BPS
sense input. This removes the need to separately monitor the trouble contact except for AC
power failure.
• In an alarm condition, the booster power supply allows NAC current to move downstream to
devices connected to the existing control panel’s NAC circuit.
• Refer to the connected control module or control unit’s documentation for more details on
control circuit wiring.
• The AC power failure panel connection annunciates at the panel but does not report off
premises for a predetermined time in U.S. fire applications. See Table 8 on page 19.
(13) Trouble COM
(14) Trouble NC
(15) Notification appliance circuit (NAC),
typical of up to four NACs
(16) Input from signaling circuit. This is a
control circuit. NACs are not permitted.
(17) To next booster, or NAC end-of-line
resistor
(18) EOL
(19) EOL (UL listed 15 k for NAC)
(20) Control circuit source
(21) AC power fail monitoring
24 Remote Booster Power Supply Technical Reference Manual
Page 31

NAC Class A wiring
Connect one NAC circuit to one NAC output, either NAC1 or NAC3. Terminate
the circuit at the NAC2 or NAC4 terminal screw, respectively.
Figure 14: NAC class A wiring
TB1
+
(1)
(2)
+++
(15)
(3)
(4)
(5)
TB5
(6)
(7)
(8)
(9)
(10)
(11)
(12)
(13)
(14)
TB2
Legend
(1) NAC1/AUX1
(2) NAC2/AUX2 (return for NAC1)
(3) NAC3/AUX3
(4) NAC4/AUX4 (return for NAC3)
(5) 200 mA AUX Continuous
(6) Sense 1 IN
(7) Sense 1 COM
(8) Sense 1 OUT
(9) Sense 2 IN
(10) Sense 2 COM
(11) Sense 2 OUT
++
(19)
(16)
(17)
(20)
(21)
(12) Trouble NO
(13) Trouble COM
(14) Trouble NC
(15) Notification appliance circuit (NAC)
(16) Notification appliance circuit (NAC)
(17) Input from signaling circuit
(18) To next booster, or NAC returning to
existing control panel
(19) EOL for IDC circuit
(20) Control circuit source
(21) AC power fail monitoring
Note: The AC power failure panel connection annunciates at the panel but does not report off
premises for a predetermined time in US fire applications. See Table 8 on page 19.
Remote Booster Power Supply Technical Reference Manual 25
Page 32

Sense circuit wiring
The BPS has two Class B sense (activation) circuits (Sense 1 and Sense 2). See
Figure 13 and Figure 14.
Note: When NACs 1, 2, 3, and 4 are configured for AUX (Figure 16), sense
activation of NAC circuits reports a trouble condition to the control panel using
these circuits.
Any BPS trouble opens the sense circuit, which sends a trouble event message
to the control panel, indicating that a trouble exists on that circuit.
AUX power wiring
Figure 15: Dedicated AUX power
TB5
+
(1)
(1) AUX power 200 mA continuous
NAC configured as AUX power
Each NAC can be configured through a DIP switch for use as AUX power. A DIP
switch also controls AUX operation during AC power loss. See “Setting the DIP
switches” for details.
This auxiliary configuration is compatible with fire alarm, security, and access
control applications, which can be combined in a single system, if all of the
devices are listed.
Trouble relay wiring with four AUX circuits
When all four NAC/AUX circuits are configured as AUX circuits and DIP switch
SW2-6 is ON, a SIGA-CT2 module must be used to monitor the sense 1 trouble
contacts and the trouble relay.
26 Remote Booster Power Supply Technical Reference Manual
Page 33

Figure 16: Trouble relay wiring with four AUX circuits
TB1
++++
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
(5)
(6)
(7)
(8)
(9)
(10)
(11)
(12)
(13)
(14)
TB5
TB2
(15)
(15)
(15)
(15)
(16)
++
(18)
(17)
(19)
Legend
(1) NAC1/AUX1
(2) NAC2/AUX2
(3) NAC3/AUX3
(4) NAC4/AUX4
(5) 200 mA AUX Continuous
(6) Sense 1 IN (trouble contact)
(7) Sense 1 COM (trouble contact)
(8) Sense 1 OUT (trouble contact)
(9) Sense 2 IN
(10) Sense 2 COM
(11) Sense 2 OUT
(12) Trouble NO
(13) Trouble COM
(14) Trouble NC
(15) To auxiliary device.
(16) EOL 47 k
(17) CT2 module
(18) Data in from previous device or
Signature controller
(19) Data out to next device
Notes
• The NAC/AUX circuit must be configured for AUX operation using the DIP switches. See
“Setting the DIP switches” for details.
• CT2 modules must be wired and programmed on the Signature controller for proper
operation.
• AC power loss causes circuit 2 on the CT2 to report a trouble to the control panel (see panel
programming). All other BPS troubles cause circuit 1 (Sense 1) on the CT2 to report a trouble
to the panel.
Common trouble relay wiring
The BPS has a Form C common trouble relay that provides a normally open and
normally closed contact. The trouble relay switches under any trouble condition
when DIP switch SW2-6 is off. When the switch is on, the BPS trouble relay is
dedicated to AC power loss reporting. The trouble relay switches within
20 seconds when AC fails or restores. The sense circuits immediately signal a
fault condition for any non-AC power loss faults. When AC power fails, the sense
circuits signal a fault condition after three hours of power loss.
Remote Booster Power Supply Technical Reference Manual 27
Page 34

Figure 17: Common trouble relay wiring
CO
OUT
SEN
(1)
(1) To booster trouble monitoring device
TB2
COM NO
TROUBLE
NC
When using the sense circuit as common trouble relays, the BPS operates as
outlined in the following scenarios.
Scenario 1: Trouble on any non-AC power fault
Result:
• Sense 1 opens.
• An AC power failure closes the trouble contact at 20 seconds and activates
Sense 1 at three hours.
For a wiring example, see Figure 16 on page 27.
Scenario 2: Sense 1 activates all four NAC circuits
Result:
• Sense 1 opens.
• An AC power failure closes the trouble contact at 20 seconds and activates
Sense 1 at three hours.
For a wiring example, see Figure 19 on page 30.
Scenario 3: Sense 1 and Sense 2 are operating with multiple CC1 modules
Result:
• A fault on NAC 1 or NAC 2 causes Sense 1 to open.
• A fault on NAC 3 or NAC 4 causes Sense 2 to open.
• A panel-related fault other than an AC failure (e.g., ground fault or battery
fault) causes Sense 1 and Sense 2 to open.
• An AC power failure closes the trouble contact at 20 seconds and activates
Sense 1 at three hours
For a wiring example, see Figure 20 on page 32.
28 Remote Booster Power Supply Technical Reference Manual
Page 35

NAC wiring using CC1(S) modules
The following wiring diagrams show Signature Series CC1(S) module
connections. However, other Signature Series signal modules can be used.
Figure 18: Single CC1(S) using the BPS’s 200 mA AUX continuous circuit
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
(5)
(6)
(7)
(8)
(9)
(10)
(11)
(12)
(13)
(14)
TB1
+
+++
TB5
TB2
(20)
+
+
(17)
CT1
++
(15)
(16)
(15)
(16)
9
10
CC1(S)
48372
6
5
++++
(21)
(18)
1
(19)
Legend
(1) NAC1/AUX1
(2) NAC2/AUX2
(3) NAC3/AUX3
(4) NAC4/AUX4
(5) 200 mA AUX Continuous
(6) Sense 1 IN
(7) Sense 1 COM
(8) Sense 1 OUT
(9) Sense 2 IN
(10) Sense 2 COM
(11) Sense 2 OUT
(13) Trouble COM
(14) Trouble NC
(15) Notification appliance circuit (NAC)
(16) UL listed EOL 15 k
(17) EOL 47 k
(18) Data in from previous device or
Signature controller
(19) Data out to next device
(20) Data in from previous device or
Signature controller
(21) Data out to next device
(12) Trouble NO
Remote Booster Power Supply Technical Reference Manual 29
Page 36

Notes
• CC1(S) modules must be wired and programmed on the Signature controller for proper
operation.
• Any BPS trouble causes the CC1(S) supervision to report a trouble to the main control panel
when DIP switch SW2-6 is on. AC power failure is delayed for three hours.
• CC1(S) wiring must be within three feet of the BPS enclosure and in conduit or mounted
within the BPS’s enclosure. If CC1(S) wiring is more than three feet from a BPS enclosure,
then a separate listed EOL relay (PAM1, 6254A-003, or 73402A) or equivalent must be used
to supervise the 200 mA AUX circuit wiring.
• When configured for AC power loss reporting using the trouble relay (DIP switch SW2-6 ON),
the CT1 module supervises and reports the AC power loss to the control panel. When DIP
switch SW2-6 is OFF, the CT1 module is not required.
Figure 19: Multiple CC1(S) modules using the BPS’s sense inputs
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
(5)
(6)
(7)
(8)
(9)
(10)
(11)
(12)
(13)
(14)
TB1
+
+++
TB5
TB2
CT1
(15)
(16)
(15)
(16)
+
+
(17)
+
9
10
CC1(S)
48372
6
5
+
+ +
1
6
+
CC1(S)
5
10
48372
+
9
1
(19)
++
(18)
30 Remote Booster Power Supply Technical Reference Manual
Page 37

Legend
(1) NAC1/AUX1
(2) NAC2/AUX2
(3) NAC3/AUX3
(4) NAC4/AUX4
(5) 200 mA AUX Continuous
(6) Sense 1 IN
(7) Sense 1 COM
(8) Sense 1 OUT
(9) Sense 2 IN
(12) Trouble NO
(13) Trouble COM
(14) Trouble NC
(15) Notification appliance circuit (NAC)
(16) UL listed EOL 15 k
(17) EOL 47 k
(18) Data in from previous device or
Signature controller
(19) Data out to next device
(10) Sense 2 COM
(11) Sense 2 OUT
Notes
• CC1(S) modules must be wired and programmed on the Signature controller for proper
operation.
• Any BPS trouble causes the CC1(S) supervision to report a trouble to the main control panel
when DIP switch SW2-6 is on. AC power failure is delayed for three hours.
• If CC1(S) wiring is more than three feet from a BPS enclosure, then a separate listed EOL
relay (PAM1, 6254A-003, or 73402A) or equivalent must be used to supervise the 200 mA
AUX circuit wiring.
• When configured for AC power loss reporting using the trouble relay (DIP switch SW2-6 ON),
the CT1 module supervises and reports the AC power.
Remote Booster Power Supply Technical Reference Manual 31
Page 38

Figure 20: Multiple CC1(S) modules using one of the BPS’s NAC/AUX circuits
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
(5)
(6)
(7)
(8)
(9)
(10)
(11)
(12)
(13)
(14)
TB1
+
+++
TB5
TB2
(15)
(16)
(15)
(16)
(17)
+
(18)
+
(19)
(20)
10
9
CC1(S)
48372
6
5
++++
+
1
(21)
(22)
(27)
(22)
(26)
CT1
(25)
(21)
+
6
5
10
CC1(S)
48372
+++
(22)
(23)
(24)
9
1
(21)
65
RM1
(22)
(21)
32 Remote Booster Power Supply Technical Reference Manual
Page 39

Legend
(1) NAC1/AUX1
(2) NAC2/AUX2
(3) NAC3/AUX3
(4) NAC4/AUX4
(5) 200 mA AUX Continuous
(6) Sense 1 IN
(7) Sense 1 COM
(8) Sense 1OUT
(9) Sense 2 IN
(10) Sense 2 COM
(11) Sense 2 OUT
(12) Trouble NO
(13) Trouble COM
(14) Trouble NC
(16) UL listed EOL 15 k
(17) From existing fire alarm panel
notification circuit or CC1(S) module
(18) Out to EOL or next device
(19) NAC circuit
(20) UL listed EOL 15 k
(21) Data out to next device
(22) Data in from previous device or
Signature controller
(23) NAC circuit
(24) UL listed EOL 15 k
(25) EOL 15 k, when used as a NAC
(26) UL listed EOL relay
(27) EOL 47 k
(15) Notification appliance circuit (NAC)
Notes
• When a booster power supply output is programmed as an AUX output, a listed EOL relay
(PAM1, 6254A-003, or 73402A) or equivalent must be used to supervise the AUX output.
• When a booster power supply output is programmed as an NAC output, a 15 k EOL resistor
must be used for supervision.
Remote Booster Power Supply Technical Reference Manual 33
Page 40

(3)
Installing the 3-TAMP tamper switch
The 3-TAMP tamper switch is used to detect an open enclosure door for security
purposes.
Note: The 3-TAMP tamper switch must be used for security applications and
connected to a SIGA-SEC2 module mounted in the enclosure.
To install the tamper switch:
1. Install an EOL resistor on the 3-TAMP. Refer to the
3-TAMP Installation Sheet (P/N 387422) for more information.
2. Position the tamper switch over the mounting standoffs. See the diagram
below.
3. Use the two locking nuts provided to secure the tamper switch. See the
diagram below.
4. Connect all wiring to the tamper switch. Refer to the
3-TAMP Installation Sheet (P/N 387422) for details on wiring the tamper
switch.
Figure 21: Tamper switch installation
(1)
(1) 3-TAMP tamper switch
(2) Mounting standoffs
(3) Locking nuts
(2)
34 Remote Booster Power Supply Technical Reference Manual
Page 41

Battery calculation worksheet
Supervisory (AUX1, AUX2, AUX3, AUX4)
Note: Only add auxiliary current if SW2-7 is OFF. Auxiliary output stays on
after AC power failure.
Device type Quantity Current (mA) Total/device
Total AUX current (0 if switch SW2-7 is off, maximum 6.5 A
for BPS6A and 8 A for BPS10A):
Number of circuits set to
AUX
200 mA AUX
Device type Quantity Current (mA) Total/device
Alarm (NAC1, NAC2, NAC3, NAC4)
35 mA (per AUX
circuit)
Total 200 mA AUX current: mA (C)
Rated base BPS supervisory current: 70 mA (D)
Total supervisory current (A + B + C + D): mA (E)
Hours of supervisory: Hrs (F)
Supervisory mAh (E x F): mAh (G)
mA (B)
mA (A)
Device type Quantity DC current (mA,
RMS)
Total NAC current: mA (H)
Total/device
Rated base BPS alarm current: 270 mA (J)
Total alarm current (E + H + J): mA (K)
Minutes of alarm: Min (L)
Hours of alarm (L/60): Hr (M)
Remote Booster Power Supply Technical Reference Manual 35
Page 42

Alarm mAh required (K x M): mAh (N)
Total battery mAh (N + G): mAh (O)
Total battery Ah (O/1000): Ah (P)
Factor of safety 20% [1] (P x 1.20) Ah (Q)
Supervisory battery current (E/1000): A (R)
[1] Twenty percent safety margin per NFPA 72-2010 10.5.6.3.1 (1).
36 Remote Booster Power Supply Technical Reference Manual
Page 43

Notification appliance circuit calculations
Introduction
This topic shows you how to determine the maximum cable length of a
notification appliance circuit (NAC) for a given number of appliances.
Two methods are presented: worksheet and equation. The worksheet method is
simpler, but your installation must meet the criteria listed on the worksheet. If
your installation does not meet these criteria, you need to use the equation
method.
The methods given here determine cable lengths that work under all operating
conditions. The calculations ensure that the required operating voltage and
current will be supplied to all notification appliances. To do this, we assume these
two worst-case conditions:
• The voltage at the NAC terminals is the minimum provided by the power
supply
• The notification appliances are clustered at the end of the NAC circuit
Other, more detailed methods that distribute the appliance load along the NAC
cable may indicate that longer cable runs are possible.
What you’ll need
Appliance and cable values
Whether you use the worksheet method or the equation method, you’ll need to
know:
• The minimum operating voltage required for the appliances
• The maximum operating current drawn by each appliance
• The resistance per unit length of the wire used (/ft)
This information can be found on the appliance installation sheets and on the
cable specification sheet.
Power supply values
For either method, you’ll need some fixed or calculated operating values for your
specific power supply. The fixed values are:
• Maximum voltage = 26.3 V
• Source voltage = 19.1 V
• Load factor = 0.59 V/A
• Power type = DC (filtered/regulated)
Remote Booster Power Supply Technical Reference Manual 37
Page 44

The maximum voltage is the highest voltage measured at the NAC terminals.
This value is not used in the calculations, but is given so you can ensure
appliance compatibility.
The source voltage is the BPS is 19.1 VDC operating minimum for the power
supply, and is calculated as 85% of 24 volts minus the internal panel loss.
The load factor is a measure of how the power supply voltage reacts when a load
is applied. The load factor measures the voltage drop per ampere of current
drawn by the load.
The power type reflects the type of power supplied to the NAC terminals at
minimum voltage. The current draw of notification appliances can vary
substantially with the type of power supplied: full-wave rectified (VFWR) or direct
current (VDC). It is important to know the power type at minimum terminal
voltage.
You’ll need to calculate the following values relating to your power supply and to
the NAC circuit current. These are:
• Minimum voltage
• Voltage drop
The minimum vol tage is the lowest voltage measured at the NAC terminals when
the power supply is under the maximum load for that circuit (i.e. for the
appliances that constitute the NAC.)
The voltage drop is the difference between the minimum voltage and 16 V. This
value is for use with the worksheet only.
38 Remote Booster Power Supply Technical Reference Manual
Page 45

Worksheet method
Use this worksheet to determine the maximum cable length of a notification
appliance circuit for a given number of appliances.
Use this worksheet only if all the appliances are regulated. That is, they must
have a minimum operating voltage of 16 V. For other appliances, use the
“Equation method.”
Worksheet 1: NAC cable length
NAC1 NAC2 NAC3 NAC4
Total operating current [1]
Load factor × 0.59
Load voltage drop =
Source voltage
Load voltage drop
Minimum voltage =
Regulated appliance voltage
Voltage drop [2] =
Total operating current
Maximum resistance =
Wire resistance (/ft) [3]
19.1
16.0
0.59 0.59 0.59 V/A
19.1 19.1 19.1
16.0 16.0 16.0
A
V
V
V
V
V
V
A
Maximum wire length =
Maximum cable length =
[1] Total of the maximum operating currents for all appliances as specified for DC power. See
the appliance installation sheets for operating currents.
[2] This voltage drop is valid for regulated notification appliances only. For special application
appliances, see “Equation method,” later in this topic.
[3] Use the manufacturer’s published wire resistance expressed in ohms per foot. For typical
values, see Table 11 on page 40.
Remote Booster Power Supply Technical Reference Manual 39
2
2 2 2
ft
ft
Page 46

Equation method
Appliance operating voltage and current
Regulated notification appliances have an operating range from 16 V to 33 V.
Use 16 V as the minimum appliance voltage when using regulated notification
appliances.
When using special application appliances, refer to the installation sheets to
determine the minimum appliance voltage required.
What if there are different types of appliances in the NAC, and each type has a
different minimum operating voltage? In this case, use the highest minimum
voltage required by any appliance.
The total current requirement for the appliances will be the sum of the individual
maximum currents drawn by each appliance when using DC power. Use the
maximum current for the appliance over the 16 V to 33 V range.
If all appliances draw the same maximum current, the total current is the
maximum current multiplied by the number of appliances. If different appliance
types have different maximum currents, the total current is the sum of the
maximum current for each appliance type multiplied by the number of appliances
of that type.
Wire resistance
Typical wire resistances are shown in the following table.
Table 11: Typical wire resistances
Wire
gauge
(AWG)
per foot per meter per foot per meter
12 0.00193 0.00633 0.00198 0.00649
14 0.00307 0.01007 0.00314 0.01030
16 0.00489 0.01604 0.00499 0.01637
18 0.00777 0.02549 0.00795 0.02608
Resistance
Solid uncoated copper
Resistance
Stranded uncoated copper
Note: When performing these calculations, always refer to the actual cable
supplier documentation and use the actual /ft (or /m) at the appropriate
temperature for the cable being used.
40 Remote Booster Power Supply Technical Reference Manual
Page 47

Calculating cable length
To calculate the maximum NAC cable length:
1. Calculate the total current (Itot) as the sum of the maximum operating
currents for all the appliances.
Itot = Ia
Where:
Ia = appliance maximum current
See the appliance installation sheets for Ia. Remember to use the maximum
operating current specified for DC power.
2. Calculate the minimum voltage (Vm).
Vm = Vs (Itot × K)
Where:
Vs = source voltage
Itot = total current (from above)
K = load factor
For the power supply, Vs is 19.1 V and K is 0.59 V/A.
3. Calculate the allowable voltage drop (Vd) between the power supply and the
appliances.
Vd = Vm Va
Where:
Vm = minimum voltage (from above)
Va = appliance minimum voltage
For regulated notification appliances, Va is 16 V. For special application
appliances, Va is the lowest operating voltage specified on the appliance
installation sheet.
4. Calculate the maximum resistance (Rmax) for the wire.
Rmax = Vd / Itot
Where:
Vd = voltage drop
Itot = total current
5. Calculate the maximum length of the cable (Lc), based on the maximum
resistance allowed, the resistance of the wire, and the number of wires in the
cable (two).
Lc = (Rmax / Rw) / 2
Remote Booster Power Supply Technical Reference Manual 41
Page 48

Where:
Rmax = maximum resistance
Rw = wire resistance factor
Example: You’re using regulated notification appliances. Assume that the
maximum operating current for each appliance is 100 mA for DC power, and that
20 appliances will be placed on the NAC. The cable is 12 AWG wire, and the
manufacturer specifies a wire resistance factor of 0.002 /ft.
Itot = Ia
= 20 × 0.1 A
= 2 A
Vm = Vr (Itot × K)
= 19.1 V (2 A × 0.59 V/A)
= 19.1 V 0.76 V
= 18.94 V
Vd = Vm Va
= 18.94 V 16.0 V
= 2.94 V
Rmax = Vd / Itot
= 2.94 V / 2.0 A
= 1.47
Lc = (Rmax / Rw) / 2
= (1.47 / 0.002 /ft) / 2
= (367.5 ft) / 2
= 367.5 ft
So the maximum wire run for this NAC would be 367.5 ft (rounding down for
safety).
42 Remote Booster Power Supply Technical Reference Manual
Page 49

Understanding BPS synchronization
When using Genesis devices, the activation of the visible and audible output
circuits on the BPS are determined by how the BPSs are connected. No matter
how BPSs are connected, their outputs are “in sync” but there is an output
activation delay of either one or four seconds. This section details how BPS
outputs work based on how they are connected.
Connection of booster power supplies
Multiple BPSs can be connected in parallel. How you connect your BPSs affects
the synchronization of your system’s outputs.
BPSs can be connected in parallel using their sense circuits. When connected
via the sense circuits, all BPS outputs have either a one- or four-second delay
from the time the driver NAC turns on to the time the BPS NACs turn on. The
four-second delay does not comply with UL 864 9th edition. Delay time is
controlled by DIP switch SW1-4. See “Setting the DIP switches” for more
information.
Figure 22: BPSs connected in parallel with sense circuits
(1)
(2)
(5)
(3)
(5)
(4)
Legend
(1) NAC circuit
(2) BPS 1
(3) BPS 2
(4) BPS x
(5) Sense circuit
Notes
• To ensure all BPSs are synchronized in a Genesis application, the driving NAC must provide
the Genesis synchronization pulse. Therefore, the BPSs must not be set to Genesis mode.
• The quantity of BPSs that can be connected is limited by wire run length and available
current.
Remote Booster Power Supply Technical Reference Manual 43
Page 50

Synchronization of visible outputs
In the figure below, all visible output circuits on each BPS activate with a one
second delay. This requires that the BPSs be connected in parallel through their
sense circuits.
Figure 23: Synchronization with a one second output activation delay
12345678910111213
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
(5)
(1) On Sense Off
(2) Output booster 1
(3) Output booster 2
(4) Output booster 3
(5) Output booster n
Sync diagram key
Strobe flash
Audible tone
Synchronization of visible and audible outputs
One-second delay of outputs
In the figure below, all visible and audible circuits are synchronized with a one
second output activation delay when the BPSs are connected in parallel through
their sense circuits.
Note: Delay time is controlled by DIP switch SW1-4. See “Setting the DIP
switches” for more information.
44 Remote Booster Power Supply Technical Reference Manual
Page 51

Figure 24: BPSs connected in parallel with sense circuits
12345678910111213
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
(5)
(1) On Sense Off
(2) Output booster 1
(3) Output booster 2
Sync diagram key
Strobe flash
Audible tone
(4) Output booster 3
(5) Output booster n
(6) Visible
(7) Audible
Four-second delay of outputs (temporal setting)
(6)
(7)
(6)
(7)
(6)
(7)
(6)
(7)
(6)
(7)
Note: Four-second delay operation does not comply with UL 864 9th edition.
In Figure 25 all visible and audible circuits are synchronized with a four second
output activation delay when the BPSs are connected in parallel through their
sense circuits.
Note: Delay time is controlled by DIP switch SW1-4. See “Setting the DIP
switches” for more information.
Figure 25: BPSs connected in parallel with sense circuits
(1)
(2)
(3)
(1) On Sense Off
(2) Output booster 1
(3) Output booster 2
(4) Visible
(5) Audible
12345678910111213
Sync diagram key
Strobe flash
Audible tone
(4)
(5)
(4)
(5)
(4)
(5)
Remote Booster Power Supply Technical Reference Manual 45
Page 52

G
Applications
Disclaimer: The applications in this section are shown in general terms. It is the
responsibility of the installer and designer to adhere to the local and national
codes when applying and installing the BPS.
Key
The following symbols and notations are found on the application diagrams in
this section.
Device labels
Symbol Description
V
A
G
V
A
BPS modes (controlled by DIP switch)
Notation Description
COR Correlate mode
GM Genesis Master mode
ND Nondelayed mode
Visible device
Audible device
Genesis visible/audible device
Visible or audible device
Device generating the Genesis sync pulse
Note: When this symbol appears on a BPS, the
Genesis sync pulse is controlled by DIP switch
SW2-5.
NAC settings (controlled by DIP switch)
Notation Description
SF Sense follow
CONT Continuous
Temp/Cal Temporal/California
AUX Auxiliary
46 Remote Booster Power Supply Technical Reference Manual
Page 53

S
Genesis circuit notification
Figure 26: Genesis circuit notification
BP
(1)
G
(2)
(3)
(4)
BPS
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
(5)
(6)
(7)
(8)
(5)
(6)
(7)
(8)
G
G
GG
G G
GG
G
G
GG
G G
GG
(10)
(10)
(1) Sense 1
(2) Sense 2
(3) Mode: COR
(4) NACs: SF
(5) NAC 1
(9)
(6) NAC 2
(7) NAC 3
(8) NAC 4
(9) To BPS, or EOL resistor
(10) To next device or EOL resistor
Note: The maximum number of BPSs that can be connected on a single NAC from sense circuit
to sense circuit is limited by available current and wire run length.
DIP switch settings for this application
Each BPS DIP switch can be set this way for the application to work correctly. If
other BPS options are required, refer to “Setting the DIP switches” for more
information.
Figure 27: Switch settings
ON
12345678
SW1 SW2
12345678
Remote Booster Power Supply Technical Reference Manual 47
Page 54

)
Conventional visible and audible circuit notification
Figure 28: Conventional visible and audible circuit notification
BPS
V/A
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
(5)
(6)
BPS
(3)
(4)
(5)
(6)
(7)
(8)
(9)
(10)
(7)
(8)
(9)
(10)
V
V
VV
A A
AA
V
V
VV
AA
AA
(12
(12)
Legend
(1) NAC visible circuit
(2) NAC audible circuit
(3) Sense 1
(4) Sense 2
(5) Mode: COR
(6) NACs: SF
(11)
(7) NAC 1
(8) NAC 2
(9) NAC 3
(10) NAC 4
(11) To BPS, or EOL resistor
(12) To next device or EOL resistor
Note: The maximum number of BPSs that can be connected on a single NAC from sense circuit
to sense circuit is limited by available current and wire run length.
DIP switch settings for this application
Each BPS DIP switch can be set this way for the application to work correctly. If
other BPS options are required, refer to “Setting the DIP switches” for more
information.
Figure 29: Switch settings
ON
12345678
SW1 SW2
12345678
48 Remote Booster Power Supply Technical Reference Manual
Page 55

Conventional visible and audible circuit to Genesis
notification
Figure 30: Conventional visible and audible circuit to Genesis notification
BPS
(7)
G G
V/A
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
(5)
(6)
G
G
(8)
(9)
(10)
G G
GG
GG
GG
GG
GG
GG
(12)
(11)
(1) NAC visible circuit
(2) NAC audible circuit
(3) Sense 1
(4) Sense 2
(5) Mode: GM
(6) NACs CONT
Note: The maximum number of BPSs that can be connected on a single NAC from sense circuit
to sense circuit is limited by available current and wire run length.
(7) NAC 1
(8) NAC 2
(9) NAC 3
(10) NAC 4
(11) To next device or EOL resistor
(12) To BPS, or EOL resistor
DIP switch settings for this application
BPS DIP switches can be set this way for the application to work correctly. Refer
to “Setting the DIP switches” for other options.
Figure 31: Switch settings
ON
12345678
SW1 SW2
12345678
Remote Booster Power Supply Technical Reference Manual 49
Page 56

Conventional audible or visible circuit to Genesis
notification
Figure 32: Conventional audible or visible circuit to Genesis notification
BPS
(6)
V/A
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
(5)
G
G G
(7)
(8)
GG
(9)
GG
GG
(11)
(10)
(1) Visible or audible circuit
(2) Sense 1
(3) Sense 2
(4) Mode: COR
(5) NACs: CONT
(6) NAC 1
Note: The maximum number of BPSs that can be connected on a single NAC from sense circuit
to sense circuit is limited by available current and wire run length.
(7) NAC 2
(8) NAC 3
(9) NAC 4
(10) To BPS, or EOL resistor
(11) To next device or EOL resistor
DIP switch settings for this application
BPS DIP switches can be set this way for the application to work correctly. Refer
to “Setting the DIP switches” for other options.
Figure 33: Switch settings
ON
1234567812345678
SW1 SW2
50 Remote Booster Power Supply Technical Reference Manual
Page 57

Genesis visible circuit and conventional audible circuit
to Genesis notification
Figure 34: Genesis visible circuit and conventional audible circuit to Genesis notification
BPS
(7)
G
G
GG
G G
GG
G
G
GG
G G
GG
(12)
(12)
G
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
(5)
(6)
BPS
(3)
(4)
(5)
(6)
(8)
(9)
(10)
(7)
(8)
(9)
(10)
(1) NAC visible circuit
(2) NAC audible circuit
(3) Sense 1
(4) Sense 2
(5) Mode: GM
(6) NACs: SF
(11)
(7) NAC1
(8) NAC 2
(9) NAC 3
(10) NAC 4
(11) To next BPS, or EOL resistor
(12) To next device or EOL resistor
Note: The maximum number of BPSs that can be connected on a single NAC from sense circuit
to sense circuit is limited by available current and wire run length.
DIP switch settings for this application
BPS DIP switches can be set this way for the application to work correctly. Refer
to “Setting the DIP switches” for other options.
Figure 35: Switch settings
ON
12345678
SW1 SW2
12345678
Remote Booster Power Supply Technical Reference Manual 51
Page 58

)
S
S
Conventional split mode circuit with fault tolerance
notification
Figure 36: Conventional split mode circuit with fault tolerance notification
BP
V/A
(1)
(2)
BP
(5)
(5)
(6)
(6)
(7)
(7)
(8)
(8)
(9)
(9)
(10)
(10)
(11)
(11)
(12)
(12)
V
V
A
A
V
V
V
AVA
V
V
AVA
A
A
(13)
V/A
(3)
(4)
BPS
(5)
(6)
(7)
(8)
(9)
(10)
(11)
(12)
V
V
A
A
V
V
V
AVA
V
V
AVA
A
A
(13
Legend
(1) Primary visible or audible circuit,
(2) To next BPS, or EOL resistor
(3) To next BPS, or EOL resistor
(4) Secondary visible or audible circuit
(5) Sense 1
(6) Sense 2
(8) NACs: SF
(9) NAC1
(10) NAC 2
(11) NAC 3
(12) NAC 4
(13) To next device or EOL resistor
(7) Mode: COR
Notes
• The maximum number of BPSs that can be connected on a single NAC from sense circuit to
sense circuit is limited by available current and wire run length.
• Fault tolerance can be increased by using Class A wiring.
DIP switch settings for this application
BPS DIP switches can be set this way for the application to work correctly. Refer
to “Setting the DIP switches” for other options.
Figure 37: Switch settings
ON
12345678
SW1 SW2
52 Remote Booster Power Supply Technical Reference Manual
12345678
Page 59

Genesis split mode circuit with fault tolerance
notification
Figure 38: Genesis split mode circuit with fault tolerance notification
BPS
G
G
G
(1)
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
(5)
(6)
(7)
(8)
BPS
(5)
(6)
(7)
(8)
(9)
(11)
(12)
(9)
(11)
(12)
G
G
GG
G G
GG
G
G
GG
G G
GG
(13)
(13)
Legend
(1) Primary visible or audible circuit
(2) To next BPS, or EOL resistor
(3) To next BPS, or EOL resistor
(4) Secondary visible or audible circuit
(5) Sense 1
(6) Sense 2
(7) Mode: COR
Notes
• The maximum number of BPSs that can be connected on a single NAC from sense circuit to
sense circuit is limited by available current and wire run length.
• Fault tolerance can be increased by using Class A wiring.
(8) NACs: SF
(9) NAC1
(10) NAC 2
(11) NAC 3
(12) NAC 4
(13) To next device or EOL resistor
DIP switch settings for this application
BPS DIP switches can be set this way for the application to work correctly. Refer
to “Setting the DIP switches” for other options.
Figure 39: Switch settings
ON
12345678
SW1 SW2
Remote Booster Power Supply Technical Reference Manual 53
12345678
Page 60

CDR-3 Coder to Genesis notification
Figure 40: CDR-3 Coder to Genesis notification
BPS
(7)
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
(5)
(6)
G
(8)
(9)
(10)
G
GG
G
GG
GG
(12)
Legend
(1) NAC visible circuit
(2) NAC/CDR-3 audible circuit
(3) Sense 1
(4) Sense 2
(5) Mode: GM
(6) NACs: CONT
(11)
(7) NAC1
(8) NAC 2
(9) NAC 3
(10) NAC 4
(11) To next BPS, or EOL resistor
(12) To next device or EOL resistor
Notes
• In order for the audible appliances to follow the CDR-3 coder signals, you must modify each
Genesis audible-capable appliance that is connected to a coded NAC. For Genesis G1
Series appliances cut open Circle. For Genesis WG4 horns & horn/strobes, cut jumper
JP4. For Genesis GC(F)-HDVM(H) appliances, cut JP1.
• The maximum number of BPSs that can be connected on a single NAC from sense circuit to
sense circuit is limited by available current and wire run length.
DIP switch settings for this application
BPS DIP switches can be set this way for the application to work correctly. Refer
to “Setting the DIP switches” for other options.
Figure 41: Switch settings
ON
12345678
SW1 SW2
54 Remote Booster Power Supply Technical Reference Manual
12345678
Page 61

CDR-3 Coder to conventional notification
Figure 42: CDR-3 Coder to conventional notification
BPS
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
(5)
(6)
(7)
(8)
(9)
(10)
V/A
V
V
VV
AA
A
A
(12)
(1) NAC visible circuit
(2) NAC/CDR-3 audible circuit
(3) Sense 1
(4) Sense 2
(5) Mode: ND
(6) NACs: SF
(11)
(7) NAC1
(8) NAC 2
(9) NAC 3
(10) NAC 4
(11) To next BPS, or EOL resistor
(12) To next device or EOL resistor
Note: The maximum number of BPSs that can be connected on a single NAC from sense circuit
to sense circuit is limited by available current and wire run length.
DIP switch settings for this application
BPS DIP switches can be set this way for the application to work correctly. Refer
to “Setting the DIP switches” for other options.
Figure 43: Switch settings
ON
12345678
SW1 SW2
12345678
Remote Booster Power Supply Technical Reference Manual 55
Page 62

CDR-3 Coder to Genesis visibles and conventional
audibles
Figure 44: CDR-3 Coder to Genesis visibles and conventional audibles
BPS
(7)
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
(5)
(6)
G
(8)
(9)
(10)
G G
GG
AA
A
A
(12)
(1) NAC visible circuit
(2) NAC/CDR-3 audible circuit
(3) Sense 1
(4) Sense 2
(5) Mode: ND
(6) NACs: CONT, SF
(11)
(7) NAC1
(8) NAC 2
(9) NAC 3
(10) NAC 4
(11) To next BPS or EOL resistor
(12) To next device or EOL resistor
DIP switch settings for this application
BPS DIP switches can be set this way for the application to work correctly. Refer
to “Setting the DIP switches” for other options.
NAC1 and NAC2 are configured for continuous mode. NAC3 and NAC4 are
configured for sense follow mode. SW2-5 is set to generate a sync pulse on the
continuous circuits.
Figure 45: Switch settings
ON
12345678
SW1 SW2
12345678
Security
In this application, 24 VDC is converted to 12 VDC for use with security devices.
56 Remote Booster Power Supply Technical Reference Manual
Page 63

Figure 46: Security 24 VDC to 12 VDC
BPS
24 V
24DC12
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
TB1
++++
12 V
(5)
(6)
(7)
(1) NAC1/AUX1
(2) NAC2/AUX2
(3) NAC3/AUX3
(5) Security device
(6) Security device
(7) EOL monitoring device
(4) NAC4/AUX4
Note: NAC1 must be set for auxiliary. Any of the BPS NACs can be used in auxiliary mode for
12 V security applications.
DIP switch settings for this application
BPS DIP switches can be set this way for the application to work correctly. Refer
to “Setting the DIP switches” for other options.
Figure 47: Switch settings
ON
12345678
SW1 SW2
12345678
Access control power supply
Figure 48: Access control power supply
(1)
+ +
(1) Control panel
(2) Card reader controller
(2)
(2)
+ + +
(3) BPS, Disable the BPS’s ground fault
(3)
jumper (JP3)
(2)
(4)
(4) To next device or end
Remote Booster Power Supply Technical Reference Manual 57
Page 64

58 Remote Booster Power Supply Technical Reference Manual
 Loading...
Loading...