Page 1

Page 2
5SX_
LANlink
Router Option
User Manual
WARNING - BEFORE INSTALLATION, PLEASE
REFER TO SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS IN
APPENDIX A, AND EMC INSTRUCTIONS IN
APPENDIX C
Certified Compliant in the EC, when fitted in accordance with the installation
instructions, against the following directives/standards:
Low Voltage Directive
EN60950 : 1992 (Safety)
Electromagnetic Compatibility
subsequent amendm ents to date):
EN55022 : 1994 (Emissions)
EN50082-1 : 1992 (Immunity)
Telecommunications Terminal Equipment
(91/263/EEC and amendment 93/68/EEC) where indicated in
approvals requirements section.
(73/23/EEC and am endment 93/68/EEC)
directive (89/336/EEC and
directive
Part Number: E A88001A
Echo LANli nk Router Option User Manual Issue 1.0 04 December 1997 Page 2 of 59
Page 3

CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION.................................................................... 6
1.1 Functional Overview............................................................................. 7
1.2 Typical Applications .............................................................................7
2 USE AND CONFIGURATION................................................ 9
2.1 Router Configuration............................................................................ 9
2.2 Supervisor Terminal Requirements...................................................... 9
2.3 Router Terminal Display....................................................................... 9
2.4 Router Management........................................................................... 11
2.4.1 General Keyboard Conventions.................................................. 11
2.4.2 Parameter Selection.................................................................... 11
2.5 Multiplexer Management....................................................................13
2.5.1 Allocating bandwidth to the Router ............................................. 13
2.5.2 Returning to the Main Menu Screen............................................ 14
2.5.3 Clearing the Configuration back to Factory Default .................... 14
2.6 System Status.....................................................................................14
2.6.1 MAIN LINK CARRIER LOSS.......................................................15
2.6.2 D/I CARRIER LOSS.................................................................... 15
2.6.3 REMOTE ALARM........................................................................ 15
2.6.4 Nx64 CHANNEL x CONTROL DISAFFIRMED............................ 15
2.6.5 Nx64 CHANNEL x CLOCK FAIL ................................................. 15
2.6.6 MAIN LINK HIGH BIT ERROR RATE.......................................... 15
2.6.7 LOCAL/REMOTE MAP MISMATCH............................................ 15
2.6.8 D/I REMOTE ALARM.................................................................. 15
2.6.9 ROUTER WAN LINK STATUS.................................................... 16
3 INSTALLATION................................................................... 17
3.1 Opening the Multiplexer ..................................................................... 17
3.2 Internal Link LK13 .............................................................................. 18
3.3 Installing the Router Option................................................................ 18
3.4 Testing................................................................................................ 19
3.5 Data Connections............................................................................... 19
3.6 Front Panel LEDs............................................................................... 19
3.7 Quick Configuration............................................................................ 20
3.7.1 Multiplexer Configuration ............................................................ 20
3.7.2 Router Configuration................................................................... 20
4 ROUTER MENU OPTIONS................................................. 23
4.1 UNIT STATUS.................................................................................... 23
4.2 TRAFFIC ANALYSIS.......................................................................... 24
4.2.1 IP: ROUTING TABLE.................................................................. 24
4.2.2 IP: ARP TABLE........................................................................... 25
4.2.3 IPX: RIP TABLE.......................................................................... 26
Echo LANli nk Router Option User Manual Issue 1.0 04 December 1997 Page 3 of 59
Page 4

4.2.4 IPX: SAP TABLE ......................................................................... 27
4.2.5 SHOW TRAFFIC DETAILS......................................................... 28
4.3 NETWORK LOADING........................................................................ 28
4.4 REMOTE MANAGEMENT.................................................................. 29
4.4.1 TELNET OUT.............................................................................. 29
4.4.2 NAME SERVER CONFIGURATION............................................ 29
4.4.3 SECURITY.................................................................................. 30
4.4.4 SNMP SETUP............................................................................. 31
4.5 UNIT CONFIGURATION.................................................................... 31
4.6 SERVICE SETUP............................................................................... 32
4.6.1 ETHERNET SERVICE SETUP.................................................... 32
4.6.2 WAN SERVICE SETUP .............................................................. 34
4.7 FILTER SETUP.................................................................................. 36
4.7.1 MAC FILTERS (WAN or Ethernet).............................................. 36
4.7.2 IP FILTER (WAN or Ethernet)..................................................... 37
4.7.3 IPX SAP FILTER MENU (WAN or Ethernet)............................... 38
4.7.4 IPX HEADER FILTERS............................................................... 40
4.7.5 NOVELL KEEP-ALIVES.............................................................. 41
4.8 EVENTS............................................................................................. 41
4.8.1 PPP EVENTS.............................................................................. 42
4.8.2 SYSTEM EVENTS....................................................................... 4 2
Appendix A WARNINGS............................................................. 44
Appendix B APPROVAL REQUIREMENTS .............................. 47
Appendix C EMC REQUIREMENTS .......................................... 48
Appendix D REAR PANEL LAYOUT ......................................... 49
Appendix E AUI PORT (15-WAY D-TYPE) PINOUT.................. 50
Appendix F 10BASE-T (RJ45) PORT PINOUT.......................... 51
Appendix G IP FILTER EXAMPLES........................................... 52
Appendix H IP SUBNETS........................................................... 55
Appendix I ROUTER MAINTENANCE MENU.......................... 56
Echo LANli nk Router Option User Manual Issue 1.0 04 December 1997 Page 4 of 59
Page 5

GLOSSARY
ADPCM Adaptive Differential Pulse-Code Modulation
ARP Address Resolution Protocol
ARPA Advanced Research Projects Agency
ASCII American Standard Code for Information Interchange
BER Bit Error Rate
BOOTP Bootstrap Protocol
bps bits per second
CHAP Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol
CRC Cyclic Redundancy Check
D&I Drop and Insert
DNS Domain Name Server
EEPROM Electrically Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory
FAS Frame Alignment Synchronisation
GND Ground
ICMP Internet Control Message Protocol
IP Internet Protocol
IPX Internetwork Packet Exchange
LAN Local Area Network
LED Light Emitting Diode
MAC Media Access Control
NCP NetWare Core Protocol
PABX Privat e Automatic Branch Exchange
PAP Password Authentication Protocol
PC Personal Computer
PCM Pulse Code Modulation
PPP Point to Point Protocol
RIP Routing Information Protocol
SAP Server Advertising Protocol
SELV Safety Extra Low Voltage
SKT Socket
SNMP Simple Network Management Protocol
TCP Transmission Control Protocol
TDM Time Division Multiplexer
TFTP Trivial File Transfer Protocol
UDP User Datagram Protocol
WAN Wide Area Network
Echo LANli nk Router Option User Manual Issue 1.0 04 December 1997 Page 5 of 59
Page 6
Echo LA Nlink
Router Option
User Manual
1 INTRODUCTION
This user manual describes installation, configuration and operation of the
Echo LANlink Multiplexer Router option, and must be referred to in
conjunction with the Echo LANlink Multiplexer User Manual.
The Echo LANlink is an E1 time division multiplexer (TDM) operating at
2Mbps compliant with both EUROPEAN and UK G.703 communications
standards. The Router Option card adds the capability of connecting two
Local Area Networks (LANs), via the E1 communication link, using some or
all of the link bandwidth.
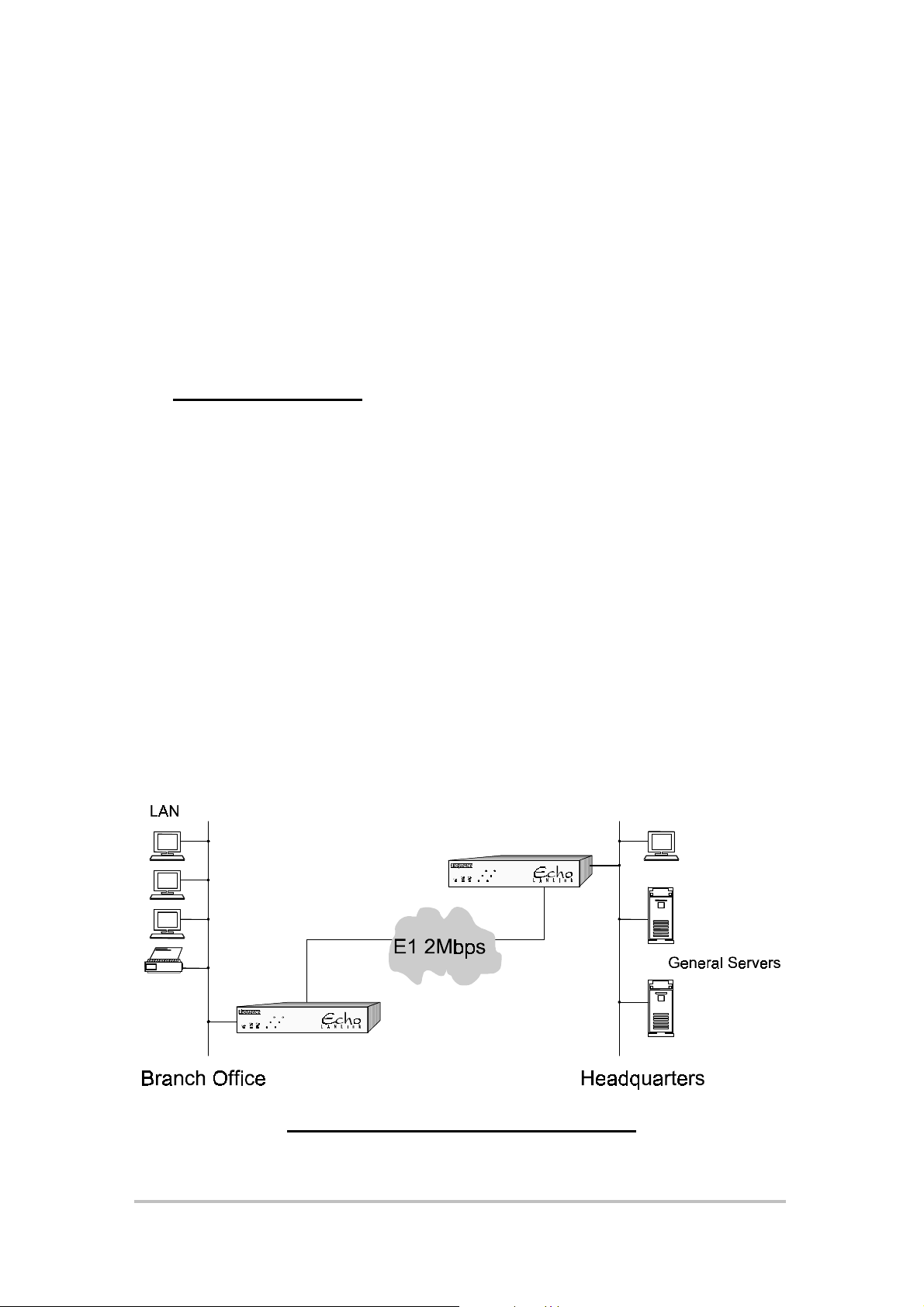
A Router Option card needs to be installed i nside the Echo LANlink at both
ends of the communications link. Each Router examines addressing
information on each LAN, and on recognition of an address on the distant
LAN, forwards the frame via the communication link, thereby linki ng the two
LANs together (see Figure 1).
Figure 1 Linking two LANs together
Echo LANli nk Router Option User Manual Issue 1.0 04 December 1997 Page 6 of 59
Page 7

The Router Option card is easily confi gured using the management terminal
connected to the Echo LANlink from either end of the link, or through Telnet
at a relevant workstation either LAN.
1.1 Functional Overview
The Router Option card supports both transceiver connection (AUI port) and
hub (10BASE-T por t) connection to a 10MHz Ethernet LAN. Ethernet frames
are transported to/from the remote LAN using some or all of the main
communications link bandwidth. The bandwidth is allocated in 64Kbps
timeslots amongst the various functions of the multiplexer as required by the
user. Up to 1984Kbps free bandwidth is available on an E1 link, 64Kbps is
permanently assigned for E1 frame synchronisation and signalling.
The router supports both the popular Internet Protocol (IP) and Internetwork
Packet Exchange (IPX) protocols. Many other protocols may be used
encapsulated by these as required: e.g. TCP, UDP, and NetWare.
The router maintains dynamic routing tables so that Ethernet frames are
routed to their correct destinati on. This capability is performed automatically
by the router as it “learns” routes and addresses available in the network. The
router will also broadcast its own routing information to other devices on the
network. Inoperative routes will time-out and be removed from the routing
tables so that alternative routes may be used in the event a communications
circuit failure.
A data compression algorithm is used when transporting Ethernet frames
through the communications link to increase the throughput of data.
Comprehensive filtering options are available so the router may act as a
sophisticated firewall to give added security for the LAN.
1.2 Typical Applications
The simplest application for the Router Option is to link two LANs as shown in
Figure 1. In this example, the Branch Office is linked to the Headquarters via
the Echo LANlinks and users at the Branch office will be able to access the
General Servers as if they were on the same network.
Further use of the router functionality can give sophisticated security for
network elements. Restrictive firewalls are easily built usi ng subnet masking.
Entire subnets can be isolated from the network by simply entering
appropriate configurations – see Fi gure 2. In this example the Salesperson i n
Echo LANli nk Router Option User Manual Issue 1.0 04 December 1997 Page 7 of 59
Page 8

the Branch Office could access the Headquarters General Server via the
Echo LANlink, but accesses to the Finance Server could be stopped using
subnet masking in the Echo LANlink.
Figure 2 Restrictive Firewall Example
In addition to the features of the router, all the existing functions of the Echo
LANlink are still available. This means that as well as connecting two remote
LANs, the Echo LANlink can also carry PABX voice tra ffic (using D&I option
card or ADPCM option card), and data traffic between the two sites, all
simultaneously multiplexed onto one E1 communication link.
Echo LANli nk Router Option User Manual Issue 1.0 04 December 1997 Page 8 of 59
Page 9
2 USE AND CONFIGURATION
This section covers connection and set-up of the Echo LANlink Router
Option, and must be used in conjunction with the Echo LANli nk User Manual.
If you are not familiar with the general configuration procedure for the Echo
LANlink, please refer to that manual before reading further and attempting to
configure the Router Option.
2.1 Router Configuration
The Router is initially configured using an asynchronous terminal, or PC
using a suitable terminal emulation package such as Wi ndows Terminal. The
terminal should be connected via its serial port to the SUPERVISOR port on
the rear of the Echo LANlink (see Echo LANlink User Manual).
2.2 Supervisor Terminal Requirements
The terminal should be configured as follows:
8 bit character, no parity, one stop bit, speed 9.6Kbps,
2.3 Router Terminal Display
After power up, the terminal will display the following message:
login:
Either type in the factory default login, mgr, or your login name if one has
previously been set and press <return>. The system will also prompt for a
password if one has been set - initially no password is required, but password
protection of the router configuration system is imperative to reduce the risk
of unauthorized changes. The set-up of a password is covered later.
The terminal will then display the following question.
Default terminal VT 100/220/320/420. OK (y or n)?
Echo LANli nk Router Option User Manual Issue 1.0 04 December 1997 Page 9 of 59
Page 10
If you are using a terminal from this list type
n <return>
to enter another type: supported terminal types are shown in
y <return>
, or alternatively press
Figure 3 - type one of them in to select a suitable terminal type and press
<return>
VT100
VT220
VT320
FALCO SUNVIEW
SUN
WYSE50 A210
TVI925
TVI910
VT420
Figure 3 Supported Terminal Types
Once a terminal type has been selected, the main menu screen shown in
Figure 4 will be displayed. Using the keyboard arrow keys you should be able
to move the highlighted cursor between the various menu items. If this is not
the case, or the display is corrupted, i t may be because the terminal type is
incorrect, or the terminal settings are wrong. In this case, pressi ng L followed
by
<return>
+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| UNIT: S1234 LOGOUT |
+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
ROUTER MANAGEMENT
MULTIPLEXER MANAGEMENT NONE
SYSTEM STATUS NO ALARMS
should lead you back to the login prompt.
Figure 4 Main Menu Screen
The Echo LANlink with Router Option is configured in two parts: Router
Management (for all the router functions) and Multiplexer Management (for all
the multiplexer functions).
Echo LANli nk Router Option User Manual Issue 1.0 04 December 1997 Page 10 of 59
Page 11
2.4 Router Management
Selecting ROUTER MANAGEMENT from the main menu allows the user to
configure the router. The router management screen is shown in Figure 5.
Refer to Section 4 for details on each menu option.
+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| ROUTER: S1234 EXIT |
+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
UNIT STATUS
TRAFFIC ANALYSIS
NETWORK LOADING
REMOTE MANAGEMENT
UNIT CONFIGURATION
SERVICE SETUP
FILTER SETUP
EVENTS
Figure 5 Router Management Screen
2.4.1 General Keyboard Conventions
The following keys are used to navigate the configuration screens for the
router management.
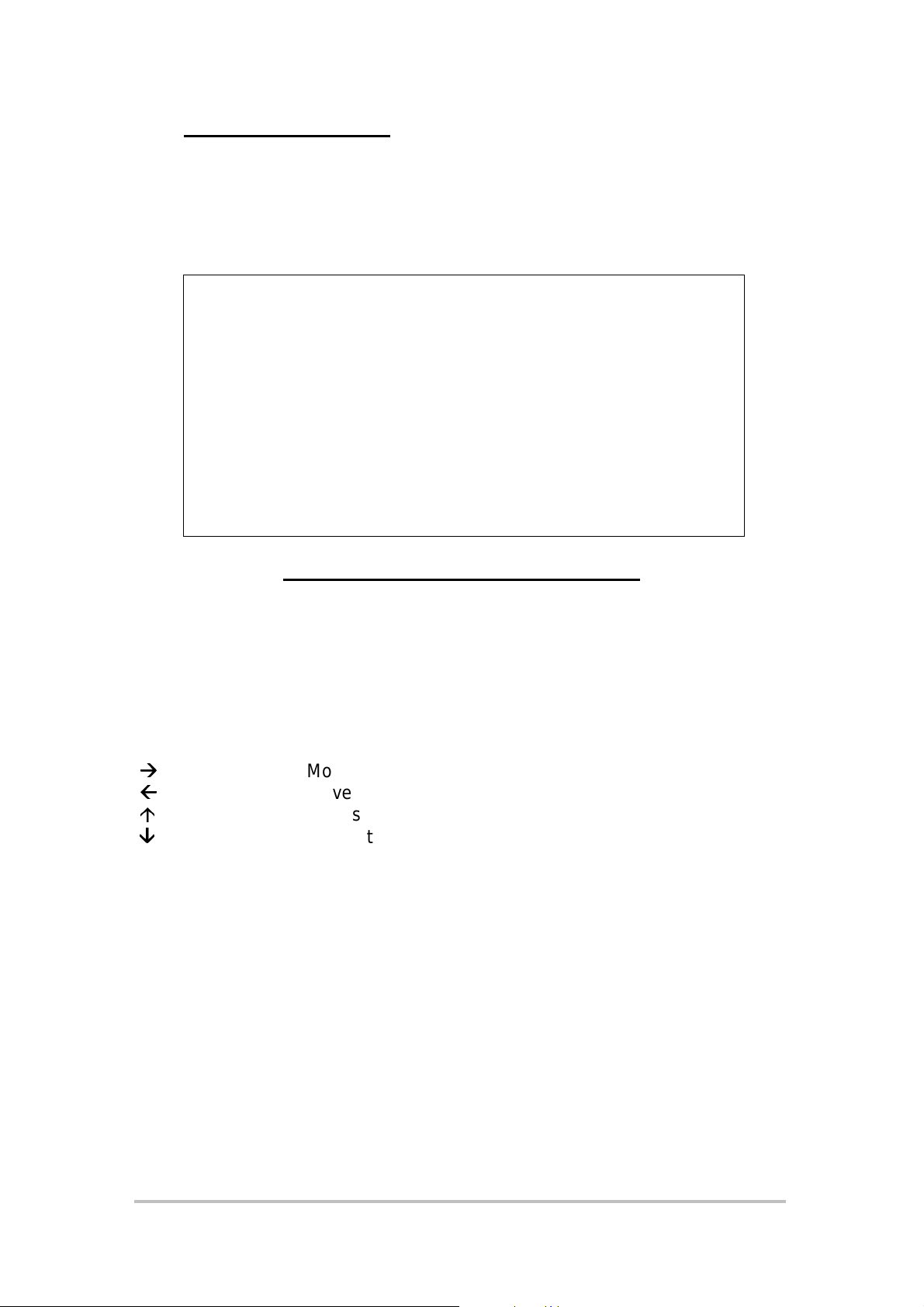
Æ
Æ
Å
Å
Ç
È
È
Moves the cursor block to the right
Moves the cursor block to the left
Moves the cursor block upwards
Moves the cursor block downwards
<return> selects/initiates the highlighted option
2.4.2 Parameter Selection
When a command is selected from the command line using the cursor,
pressing <return> will initiate action.
Some commands require the user to enter data. In Figure 6, a user has
selected to ADD a new W AN IP filter. A new line has appeared allowing the
user to enter the source IP address for the WAN filter. In this case, type in the
required value using the keyboard and press <return>. Press <esc> to
cancel any data entry operation
Echo LANli nk Router Option User Manual Issue 1.0 04 December 1997 Page 11 of 59
Page 12

+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| WAN IP FILTER 1 - WAN IP FILTER 1: S1234 EXIT |
| ADD EDIT DELETE CLEAR NAME |
+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
ENTER THE SOURCE I.P. ADDRESS (RETURN = ALL):
LINE SRC ADDR SRC MASK DEST ADD DEST MASK PROT S.PRT D.PRT RSLT
Figure 6 Entering a Parameter
Echo LANli nk Router Option User Manual Issue 1.0 04 December 1997 Page 12 of 59
Page 13
2.5 Multiplexer Management
Selecting
MULTIPLEXER MANAGEMENT
from the main menu allows the
user to configure the multiplexer functions. If another user is currently
accessing the multiplexer management page (e.g. via a Telnet session) this
will be indicated next to the menu item. Only one session is allowed access to
the multiplexer functions at any one time. If
NONE
is displayed the user is
free to enter multiplexer management. If an IP address is displayed, then this
is the address of the user currently accessing the multiplexer functions. If
CONSOLE
is displayed, then the multiplexer functions are being accessed
via the multiplexer supervisor port. You may choose to break their session if
absolutely necessary but this shoul d be used with caution.
Figure 7 shows the main multiplexer configuration page. Refer to the Echo
LANlink User manual for details on how to configure the multiplexer. New
options that are availabl e when the Router Option is fitted are detailed below.
2 MEGABIT E1 MULTIPLEXER V1.04
================================ 00:00 25/12/97 ===============================
Main Link (UK) : SYNCHRONISED Exit to Router:
Mode : NORMAL * Nx64 Channels : 2 + ROUTER
Framing : CRC4 D&I Channels : NOT FITTED
Idle Bandwidth : 1984K Alarms : None
Clock Reference : INTERNAL Statistics : Main Link
Configuration :>LOCAL Events : Log
Nx64 Channel : 1 2 ROUTER
Rate : OFF OFF OFF
Mode : NORMAL NORMAL
Tx Clock : INT INT
Rx Clock : INT INT
Indicate : ON ON
Control : ON ON
------------------------TIMESLOT MAP-------------------------- 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 3 3
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1
-------------------------------------------------------------- S - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Cursor keys to move, CTRL-U to save, ESC to abandon
===============================================================================
Use <SPACEBAR>/<+>/<-> to select
Figure 7 Main Multiplexer Configuration Page
2.5.1 Allocating bandwidth to the Router
The amount of bandwidth allocated to the router determines the throughput of
Ethernet data through the router. Bandwidth is allocated using the timeslot
map on the multipl exer
Nx64 Channels
page. Typing ‘R’ in the timeslot map
will assign that timeslot to the router. Any combination of timeslots may be
allocated to the router (except timeslot 0, which is always reserved) and each
timeslot assigned will cont r ibu t e 6 4Kbps of bandw idth. The
Rate
field for the
route r will automatically be updated to show the bandwidth assigned.
Echo LANli nk Router Option User Manual Issue 1.0 04 December 1997 Page 13 of 59
Page 14

Figure 8 shows an exam ple tim eslot set-up with 512Kbps allocated to channel 1,
320Kbps allocated to channel 2, and 1152Kbps allocated to the router.
2 MEGABIT E1 MULTIPLEXER V1.04
================================ 00:00 25/12/97 ===============================
Main Link (UK) : SYNCHRONISED Exit to Router:
Mode : NORMAL * Nx64 Channels : 2 + ROUTER
Framing : CRC4 D&I Channels : NOT FITTED
Idle Bandwidth : 0K Alarms : None
Clock Reference : INTERNAL Statistics : Main Link
Configuration :>LOCAL Events : Log
Nx64 Channel : 1 2 ROUTER
Rate : 512K 320K 1152K
Mode : NORMAL NORMAL
Tx Clock : INT INT
Rx Clock : INT INT
Indicate : ON ON
Control : ON ON
------------------------TIMESLOT MAP-------------------------- 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 3 3
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1
-------------------------------------------------------------- S R 1 R 1 R R 2 2 R R R R R R R R R R R 1 1 1 1 1 1 R R R 2 2 2
Cursor keys to move, CTRL-U to save, ESC to abandon
===============================================================================
Use <SPACEBAR>/<+>/<-> to select
Figure 8 Example Timeslot Set-up
2.5.2 Returning to the Main Menu Screen
Selecting the
Exit to Router
menu option will return the user back to the
main menu screen. If any unsaved changes have been left, a prompt will
appear to confirm the action, as any unsaved changes will be lost after
leaving the multiplexer management page.
2.5.3 Clearing the Configuration back to Factory Default
The multiplexer may be reset back to the factory default configuration by
pressing
CTRL-R
four times when the cursor is on the
Configuration
item. A
confirm message will be displayed before the configuration is reset. The
previous configuration will be lost.
2.6 System Status
The main menu
SYSTEM STATUS
overall system. Selecting this item gives the status of all the alarms in the
system as detailed below. Note the router monitors the alarm status of the
multiplexer and therefore the alarms have to be configured under multiplexer
management to be valid.
item displays the alarm status of the
Echo LANli nk Router Option User Manual Issue 1.0 04 December 1997 Page 14 of 59
Page 15

2.6.1 MAIN LINK CARRIER LOSS
The local Multiplexer cannot identify a valid synchronisation sequence (FAS,
CRC4 etc) from the remote multiplexer.
2.6.2 D/I CARRIER LOSS
The Multiplexer cannot identify a valid synchronisation sequence (FAS,
CRC4 etc) from the unit attached to the D&I port.
2.6.3 REMOTE ALARM
The unit attached to the D&I port is generating an
alarm
in the framing
information, that is, it is reporting that it has a problem.
2.6.4 Nx64 CHANNEL x CONTROL DISAFFIRMED
One of the channel ports (which is in use) is not providing the multiplexer with
a
CONTROL signal. This may mean that the signals have not been
true
connected at all. Note that unconnected CONTROL inputs will produce a
random
ON or OFF indication. Control inputs from ports that are not
allocated in the timeslot map are ignored.
2.6.5 Nx64 CHANNEL x CLOCK FAIL
One of the data channels cannot synchronise its clock to the global network
clock. This may occur if a channel is set to
external
clock, and either no
clock at all is connected, or the clock that is connected is the wrong rate.
2.6.6 MAIN LINK HIGH BIT ERROR RATE
Shows FAULT if the Bit Error Rate exceeds the threshold set. With an error
free link, this fault will eventually clear when the BER becomes less than the
threshold set.
2.6.7 LOCAL/REMOTE MAP MISMATCH
The configuration in the l ocal unit
does not match
that in the remote unit.
This would almost certainly lead to data errors on some channels.
2.6.8 D/I REMOT E ALARM
The unit attached to the D&I port is generating an
alarm
in the framing
information, that is, it is reporting that it has a problem.
Echo LANli nk Router Option User Manual Issue 1.0 04 December 1997 Page 15 of 59
Page 16

2.6.9 ROUTER WAN LINK STATUS
The status of the link between the two routers is displayed.
Echo LANli nk Router Option User Manual Issue 1.0 04 December 1997 Page 16 of 59
Page 17
3 INSTALLATION
WARNI N G – Refer to Appendix A for Safety Instruction s.
WARNING - The multiplexer must be disconnected from the power supply
and all peripher al con n ection s before open i ng.
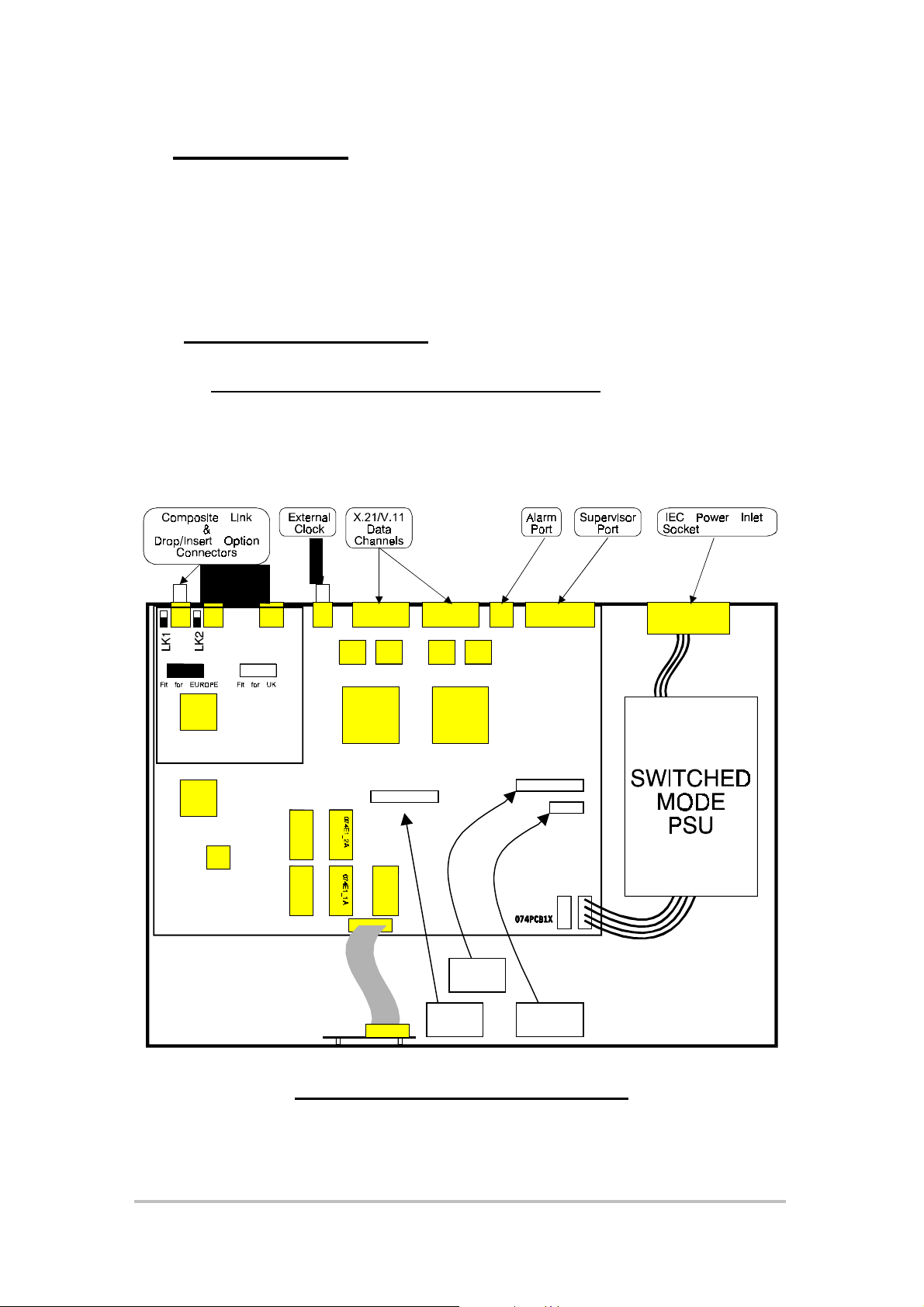
3.1 Opening the Multiplexer
With the power cord and all peripherals DISCONNECTED, the screws on the left,
right and top of the multiplexer are removed using a Pozidrive screwdriver to gain
access to the interior of the multiplexer. This allows installation of the option
cards
J15
J10 LK13
Figure 9 Echo LANlink Baseboard
Echo LANli nk Router Option User Manual Issue 1.0 04 December 1997 Page 17 of 59
Page 18
3.2 Internal Link LK13
Locate the internal connector LK13 on the motherboard (refer to Figure 9). This
will be fitted with shorting links if the Echo LANlink was supplied without the
Router Option. Remove the shorting links before fitting the Router Option. The
links may be repositioned on one pin for storage.
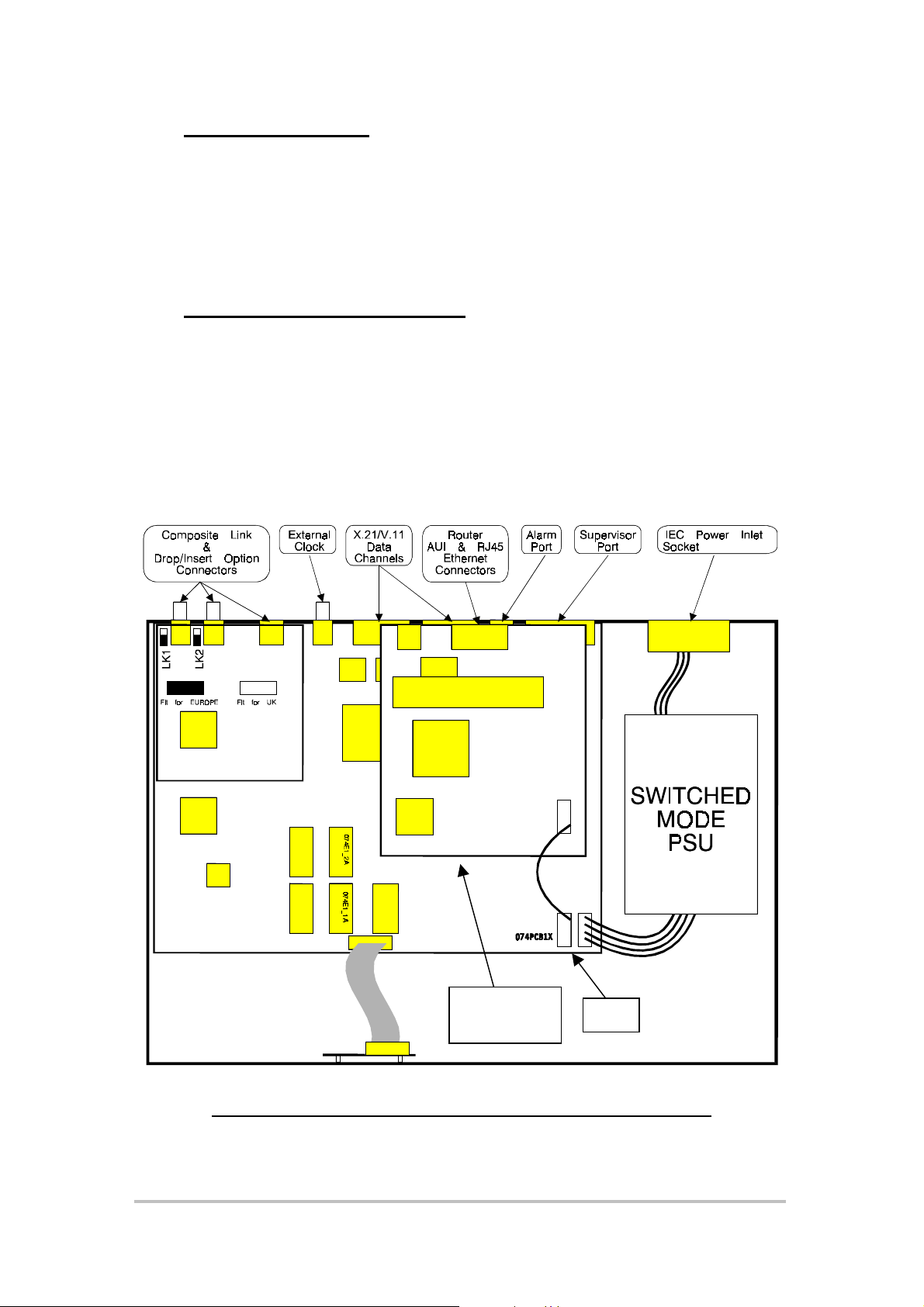
3.3 Installing the Router Option
Remove the option blanking plate above the CH 1 and CH2 connectors on the
rear panel of the multiplexer. The blanking plate may be discarded if not required.
The Router Option card should be carefully fi tted in the posi ti on shown i n Figure
10, connecting to J10 and J15 on the motherboard (refer to Figure 9). The Router
Option power connector (flying lead) should be connected to J12 (ensure correct
polarisation). Refit the rear panel screws to secure the option card
Router
Option
Figure 10 Echo LANlink showing Router Option Fitted
Echo LANli nk Router Option User Manual Issue 1.0 04 December 1997 Page 18 of 59
J12
Page 19
3.4 Testing
Replace the cover and screws before powering up the unit. Correct
installati on of the Router Option may be confirmed by the login prompt (see
section 2.3) appearing on the terminal screen. If the red error LED on the
front panel is on, this indicates hardware fault has occurred. In this case,
disconnect the power cable and check the instal lation of the Router Opti on is
correct.
3.5 Data Connections
The Ethernet connection is made using either the AUI (15-way D-type – see
Appendix E) or 10BASE-T (RJ45 see Appendix F) port at the rear of the unit
(refer to Appendix D).
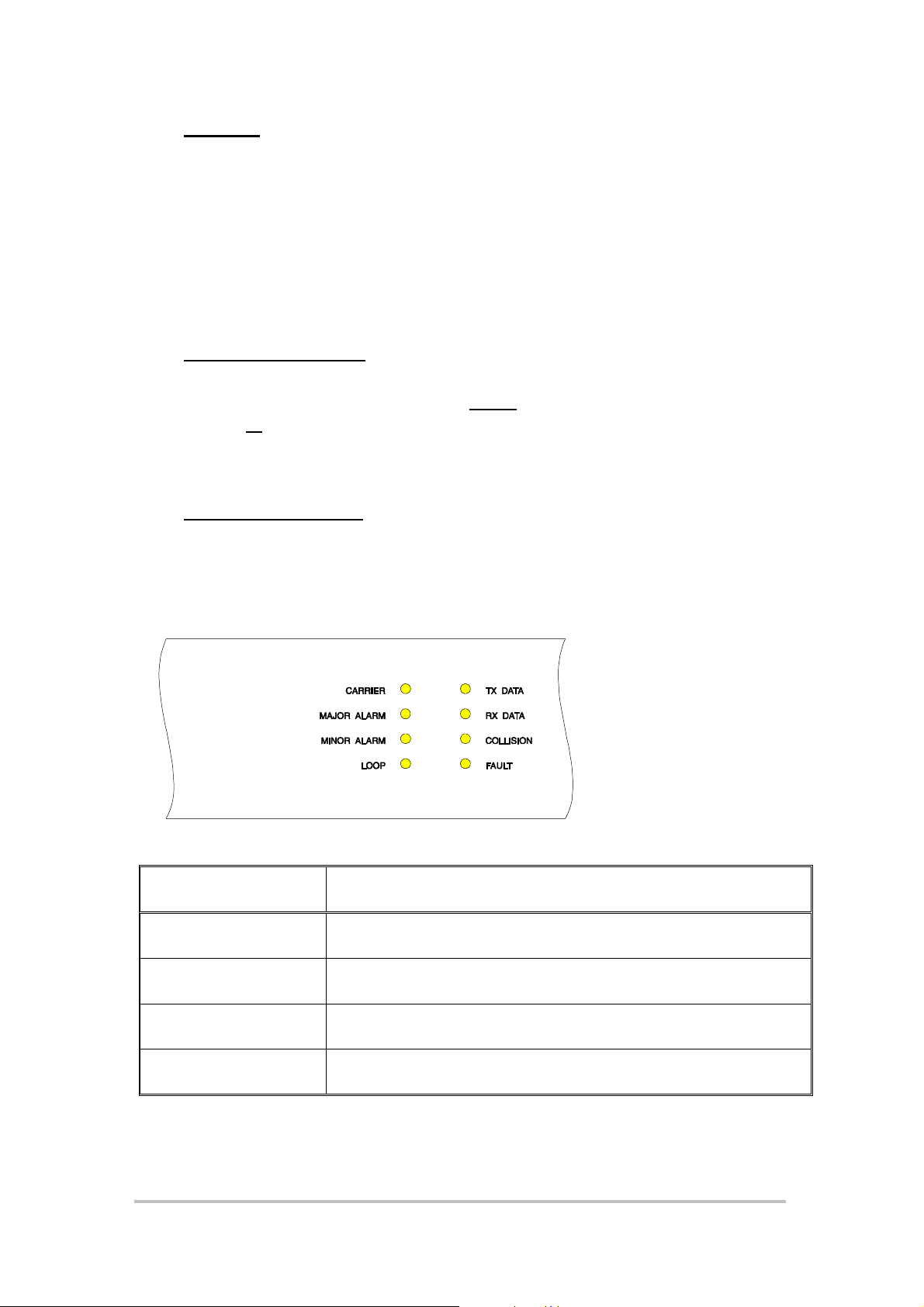
3.6 Front Panel LEDs
For information regarding CARRIER, MAJOR ALARM, MINOR ALARM and
LOOP, refer to the Echo LANlink User Manual.
LED Label Notes
TX DATA Flashes when unit i s transmitting Ethernet data
RX DATA Flashes when unit is receiving Ethernet data
COLLISION Flashes if an Ethernet collision is detected
FAULT RED if a power up hardware fault has occurred
Echo LANli nk Router Option User Manual Issue 1.0 04 December 1997 Page 19 of 59
Page 20

3.7 Quick Configuration
The first stage in configuration is to allocate some bandwidth of the
communication link to the router. The second stage is to configure the
SERVICE SETUP
3.7.1 Multiplexer Configuration
to allow communication between the two routers.
From the main menu enter
bandwidth to the router by entering ‘R’ in any free timeslot positions near the
bottom of the screen. Each timeslot allocated will contribute 64Kbps of
bandwidth to the router.
Save the multiplexer configuration using
Leave MULTIPLEXER MANAGEMENT by selecting
right of the screen.
3.7.2 Router Configuration
From the main menu enter
SETUP
be set. N.B. IP service must be configured even when IP is not bei ng used on
the local Ethernet network.
3.7.2.1 Service Name
A name to identify the local Ethernet Network, this is displayed i n the
IPX RIP
and enter
IPX SAP
and
ETHERNET SERVICE
MULTIPLEXER MANAGEMENT
CTRL-U
ROUTER MANAGEMENT
. The following parameters need to
tables and should ideally refer to network location.
.
Exit to Router
. Allocate
. Go into
at the top
SERVICE
IP RIP
,
3.7.2.2 IP Address
A unique address within the IP network connected to the local Ethernet port.
This is the IP Address of the Router and is used as the gateway address for
routing between the local Ethernet network and the WAN link.
3.7.2.3 IP Subnet Bits
The Subnet Bits should be set if subnetting is to be used on the local
network, otherwise the default 0 should be used.
Echo LANli nk Router Option User Manual Issue 1.0 04 December 1997 Page 20 of 59
Page 21

3.7.2.4 Receive IP RIP
To enable routes to destinations within the l ocal network to be added to the
routing table this field should be set to the appropriate protocol ; NONE, RIP1,
RIP2 or both RIP1 and RIP2. If the RIP version is unknown then set BOTH.
3.7.2.5 Transmit IP RIP
To allow the Router to propagate routes learnt from the WAN to the local
network, this field must be set to the correct value for the RIP protocol being
used or to NONE to disable RIP transmission. Available options include
NONE, RIP1, RIP1 compatible or RIP2.
3.7.2.6 IP Broadcast
This field enables the IP broadcast bits to be set to either all ones or all
zeroes depending on the requirements of the local Ethernet equipment.
Normally this would be set to All Ones.
3.7.2.7 IP Filter
The IP Filter is used to prevent specifi c IP packets bei ng transmitted over the
WAN li nk. The Filter Table is defined in the Static Routes and Fil ter Setup
Menu.
For initial confi gurati on this fi eld shoul d be l eft set to NO until the Fi l ter Table
entries are defined. Set to YES, the d ef au l t a ction of a n e mpty Filte r T ab l e is
to block all IP transmissions.
3.7.2.8 IPX Configuration
If IPX (Internetworking Protocol Exchange) is not being used then these fields
can be left at their default values to disable.
3.7.2.9 IPX Network Number
If there is no file server on the local Ethernet then the network number must
be specified. If a local file server is present the Network Number can be left
set to zero, and the Router will auto-sense the number when connected.
3.7.2.10 IPX Frame Types
The default frame type is Ethernet 802.3. If 802.2 is required this setting can
be changed.
Echo LANli nk Router Option User Manual Issue 1.0 04 December 1997 Page 21 of 59
Page 22

3.7.2.11 Receive IPX RIP
Set this field to YES to receive IPX RIP responses from other routers or
servers on the local network.
3.7.2.12 Transmit IPX RIP
Set thi s f i el d to YES to tr an smit r egul ar IPX RIP responses to other routers or
servers on the local network. If set to NO, IPX RIP responses will only be
sent as a result of receiving a RIP request.
3.7.2.13 Receive IPX SAP
Set this field to YES if you wish to receive IPX SAP responses from other
routers or servers on the local network. Requests are still received and
replied to.
3.7.2.14 Transmit IPX SAP
Set to YES to allow transmission of regular IPX SAP responses to other
router s or serve rs on the loc al n etwork. If set to NO, I PX SAP responses will
only be sent as a result of receiving a SAP request.
3.7.2.15 IPX SAP Filter
The IPX SAP F ilt er is u sed to r emove unwant ed serv er entr ies fr om the SAP
table and their propagation to the W AN link. If no filter table entries have
been created and this option is set to YES, the d efault a ction i s to ignore al l
SAP entries.
Once configuration is complete, move the cursor to the
press
<return>
.
position and
EXIT
Echo LANli nk Router Option User Manual Issue 1.0 04 December 1997 Page 22 of 59
Page 23

4 ROUTER ME NU OP TIONS
The menu options allow the user to configure the router to individual
requirements. The menu tree is shown in the diagram below, and each
option is discussed i n the following section.
Login Prompt
Unit Status
Router
Management
Traffic
Analysis
Network
Loading
Multiplexer
Management
Remote
Management
Unit
Configuration
Service
Setup
System
Status
Filter
Setup
Events
4.1 UNIT STATUS
This option displays statistics for the Ethernet and WAN links. At the top of
the screen the unit name and time since power on are displayed.
The user can use the CLEAR option to reset the data counts to begin new
analysis or EXIT option to leave the page.
The following table describes the parameters that are displayed:
PARAMETER DESCRIPTION OPTIONS
STATE
Ethernet segment nameNAME
WAN service name
Port status for the
Ethernet Interface
User defined
ACTIVE
FILTER
Service status for WAN
Interfaces
IP MODE Current WAN IP routing
status
LINK DOWN
COMPRESSED
ROUTE
BLOCK
BRIDGE
IPX MODE Current WAN IPX
routing status
ROUTE
BLOCK
BRIDGE
Echo LANli nk Router Option User Manual Issue 1.0 04 December 1997 Page 23 of 59
Page 24

PARAMETER DESCRIPTION OPTIONS
OTHER MODE Current OTHER
protocol routing status
Rx PACKET COUNT Number of packets seen
on the segment
connected to the port
displayed.
Rx PACKET ERROR Number of packets
received with CRC or
Frame errors.
Tx PACKET COUNT Number of packets
transmitted by Router.
Tx PACKET
OVERFLOW
LINE SPEED Indicates the amount of
Number of packets
discarded by Router
owing to queue time
exceeding the permitted
maximum delay.
bandwidth (in bps)
allocated to the router
by the multiplexer
BLOCK
BRIDGE
4.2 TRAFFIC ANALYSIS
Menu options available from the Traffic Analysis selection are detailed below.
4.2.1 IP: ROUTING TABLE
This table displays the current IP routes in the routing table. Information in
this table comes from four sources:
1. The IP address of the router determines which network is physically
connected to the Ethernet Port.
2. RIP Packets received from the Ethernet Port.
3. RIP Packets received from the WAN port.
4. Static (permanent) entries entered by the user.
The user can define up to 16 static routes in this table. The simplest means
to allow the router to 'learn' network routes is to use
configuration see the Ethernet Service Setup section. The user can then
highlight all routes to be made static using the cursor and press
The user will be prompted to either delete the entry or make it part of the
IP RIP Receive
. For
<return>
.
Echo LANli nk Router Option User Manual Issue 1.0 04 December 1997 Page 24 of 59
Page 25

routing table. Turning off IP RIP Receive as before will cause other learned
routes to age out after about four minutes.
PARAMETER DESCRIPTION
NETWORK The IP Network number to which this
RIP entry relates.
SUBNET BITS/MASK This shows the subnet mask detected
by the Router.
GATEWAY The IP Address of the next gateway
used in this route to send a packet to
the specified network.
SERVICE The required service that must be
used to reach a specified network.
TIMER This will display the time interval in
seconds, since this routing entry
was last updated. For the attached
Network this will be left blank. For
static IP Routes this will be STATIC.
METRIC This will indicate the number of
nodes passed in the route to the
Network. RIP packets pass on a
value that is incremented at each
node. The metric is used for
selecting the best route if a multiple
route network exists.
4.2.2 IP: ARP TABLE
This table gives the current ARP table for the router.
PARAMETER DESCRIPTION
IP ADDRESS The IP Network number to which this
entry relates.
MAC ADDRESS The MAC Address (Ethernet
Address) associated with an IP
address. If no MAC address is
available “NONE” will be displayed.
TIMER Displays the time interval in seconds
since a routing entry was last
updated. For the attached Network
this will be left blank.
Echo LANli nk Router Option User Manual Issue 1.0 04 December 1997 Page 25 of 59
Page 26

4.2.3 IPX: RIP TABLE
This table displ ays the current IPX routes in the IPX RIP table. Information in
this table comes from four sources:
1. The IPX network number determines which network is physically attached
to the Ethernet port.
2. IPX SAP Packets received from the Ethernet Port.
3. IPX SAP Packets received from the WAN port.
4. Static (permanent) entries entered by the user.
The user can define up to 16 static routes in this table. The simplest means
to allow the router to 'learn' available services is to use
IPX RIP Receive
. For
configuration see the Ethernet Service Setup section. The user can then
highlight all routes to be made static using the cursor and press
<return>
The user will be prompted to either delete the entry or make it part of the IPX
RIP table. Turning off IPX RIP Receive as before will cause other learned
services to age out after about four minutes.
PARAMETER DESCRIPTION
IPX NETWORK The IPX Network number to which
this entry relates.
SERVICE The service that must be used to
reach a specified Network.
NODE This is the Ethernet address of the
next node on the route to the
Network.
HOPS Thi s indicates the number of hops on
the preferred route to the Network.
TICKS This gives the delay in ticks (18
ticks/second) to be expected when
communicating with the Network.
TIMER This will display the time in seconds
since the routing entry was last
updated. For the attached Network
this will be left blank.
.
Echo LANli nk Router Option User Manual Issue 1.0 04 December 1997 Page 26 of 59
Page 27

4.2.4 IPX: SAP TABLE
This table disp lays th e IPX serv ices i n the I PX SAP tabl e. I nformati on i n th is
table comes from three sources:
1. IPX SAP Packets received from the Ethernet Port.
2. IPX SAP Packets received from the WAN port.
3. Static entries entered by the user.
The user can define up to 16 static routes in this table. The simplest means
to allow the router to 'learn' available services is to use
IPX SAP Receive
For configuration see the Ethernet Service Setup section. The user can then
highlight all services to be made static using the cursor and press
<return>
The user will be prompted to either delete the entry or make it part of the IPX
SAP table . Turni ng off IPX SAP Rece ive as bef ore will cause other learned
services to age out after about four minutes.
PARAMETER DESCRIPTION
TYPE Server identification number, defined
by IPX e.g. file server: 4, print server:
47.
NETWORK Server network number.
SERVICE The service that must be used to
reach a specified Network.
NODE Server node address.
SOCKET Node address socket number used to
access the server.
HOPS Number of hops in the preferred route
to this server.
TIMER Time interval in seconds, since this
routing entry was last updated. For
the attached Network, this will be left
blank.
NAME This will display the time in seconds
since the routing entry was last
updated. For the attached Network
this will be left blank.
.
.
Echo LANli nk Router Option User Manual Issue 1.0 04 December 1997 Page 27 of 59
Page 28

4.2.5 SHOW TRAFFIC DETAILS
Displays a li st of the current traffic received by the router.
PARAMETER DESCRIPTION
ADDRESS MAC address
AGE Time since packet last received
FLAGS L = local to the attached LAN
H = addressed to this unit
4.3 NETWORK LOADING
This option shows the load on the WAN and Ethernet ports over five second,
one minute and five minute periods.
PARAMETER DESCRIPTION
AVERAGE PACKETS The average number of packets seen
by the Router on a per second basis
over the displayed time period at that
port.
PEAK PACKETS The peak number of packets seen by
the Router on a per second basis
over the displayed time period.
AVERAGE BANDWIDTH The average percentage of available
bandwidth used by the segment or
serial link attached to that port on a
per second basis over the selected
time period.
PEAK BANDWIDTH The peak percentage of available
bandwidth used by the segment or
serial link attached to that port on a
per second basis over the selected
time period.
Echo LANli nk Router Option User Manual Issue 1.0 04 December 1997 Page 28 of 59
Page 29

4.4 REMOTE MANAGEME NT
Selecting the Remote Management menu presents the user with the follo wing
four options.
Unit Status
Telnet Out
Traffic
Analysis
Name Server
Configuration
View Name to
IP Cache
Network
Loading
Security
Remote
Management
SNMP
Security
Unit
Configuration
Service
Setup
Filter
Setup
Events
4.4.1 TELNET OUT
This option will enable tel net connection, by enteri ng the rel evant IP Address,
to a remote workstation.
4.4.2 NAME SERVER CONFIGURATION
This menu allows the user to configure the Router DNS Client features.
PARAMETER DESCRIPTION OPTIONS
TYPE The type of name server in use. NONE
DNS
SERVER IP
ADDRESS
IP TO NAME
MAPPING
The IP address of the name
server.
Type of mapping between
addresses and names. Some
User defined
REVERSE MAPPING
IN-ADDR.ARPA DOMAIN
servers allow address entry to get
names, in addition to entering
names to get addresses (reverse
mapping.)
NAME TO IP
CACHE
If an address is requested from
the DNS server the Router
Go to Name to IP Cache
Table
caches the map. This map can
therefore be viewed.
Echo LANli nk Router Option User Manual Issue 1.0 04 December 1997 Page 29 of 59
Page 30

4.4.2.1 NAME TO IP CACHE
PARAMETER DESCRIPTION
IP ADDRESS The name server IP address.
NAME The name associated to this IP address.
TIMER If a name request is made to the DNS it will allocate a
time period to retain the information. The ti mer shows
how much time re mains.
4.4.3 SECURITY
PARAMETER DESCRIPTION OPTIONS
CHANGE USER
PASSWORD
Allows user to change
password. Old
password must be
entered prior to
acceptance.
USER
PASSWORD
USER CHANGE
OWN PASSWORD
User password access
control.
User password change
access control
ENABLE
DISABLE
ENABLE
DISABLE
USER LOGIN User access control ENABLE
DISABLE
USER TELNET
LOGIN FROM
Telnet access control NONE
ANY
IP ADDRESS
IP NAME
CHANGE
MANAGER
Factory pre-set:
SYSTEM.
ENTER NEW
PASSWORD
MANAGER
PASSWORD
Manager password
access control
ENABLE
DISABLE
MANAGER
TELNET LOGIN
FROM
Restricts Telnet access
to the Router
management to the
following. Up to four IP
names/addresses can
NONE
ANY
IP ADDRESS
IP NAME
be used.
Echo LANli nk Router Option User Manual Issue 1.0 04 December 1997 Page 30 of 59
Page 31

PARAMETER DESCRIPTION OPTIONS
READ
CONFIGURATION
FROM
Access permission to
read configuration from
the Router from
external source.
NONE
ANY
IP ADDRESS
IP NAME
EXTERNAL UNIT
LOGIN
4.4.4 SNMP SETUP
PARAMETER DESCRIPTION
COMMUNITY SNMP Community: default PUBLIC
CONTACT NAME Responsible for equipment. Useful to
EQUIPMENT LOCATION Allows rapid location of equipment
SEND SNMP TRAPS TO IP addresses of four SNMP stations.
External unit access
control
give telephone number.
when required.
ENABLE
DISABLE
4.5 UNIT CONFIGURAT ION
PARAMETER DESCRIPTION
ROUTER NAME User defined identification.
ETHERNET ADDRESS Unique Ethernet address.
UNIT SERIAL NUMBER Fixed serial number for Router
option.
SOFTWARE REVISION Router software version/date.
DEFAULT TERMINAL Default terminal type for access.
Echo LANli nk Router Option User Manual Issue 1.0 04 December 1997 Page 31 of 59
Page 32

4.6 SERVICE SETUP
Unit Status
Traffic
Analysis
Network
Loading
Remote
Management
Unit
Configuration
Ethernet
Service
Service
Setup
Filter
Setup
WAN Service
PPP Setup
Events
PARAMETER DESCRIPTION
ETHERNET SERVICE Brief summary of the LAN service
available, including IP and IPX
addresses as appropriate.
WAN SERVICE Summary of traffic filters in use on
WAN link.
4.6.1 ETHERNET SERVICE SETUP
PARAMETER DESCRIPTION OPTIONS
SERVICE NAME User defined name for
the local Ethernet
network
IP ADDRESS IP Address of the
Router Ethernet Port.
IP SUBNET BITS The number of subnet
bits and subnet masks
corresponding to this IP
Address.
RECEIVE IP RIP Defines the type of RIP
Packets received on the
Ethernet Interface.
NONE
RIP 1 ONLY
RIP 2 ONLY
BOTH
TRANSMIT IP RIP Defines the type of RIP
Packets used to
transmit Routing
information
NONE
RIP 1 ONLY
RIP 1 COMP
RIP 2 ONLY
BOTH
Echo LANli nk Router Option User Manual Issue 1.0 04 December 1997 Page 32 of 59
Page 33

PARAMETER DESCRIPTION OPTIONS
IP BROADCAST IP Broadcast Packet
structure
IP FILTER Enable or disable the IP
Filter Table defined for
ONES
ZEROS
ON
OFF
the Ethernet port. N.B.
If the IP filter table has
no entries then all IP
packets are ignored if
enabled
MAC FILTER Enables or disables
MAC filtering
IPX NETWORK The Network number of
the attached IPX
network.
IPX FRAME IPX Packet Framing
type
RECEIVE IPX RIP This enables or disables
the reception of IPX RIP
ON
OFF
User defined,
Set to 0 if server
present to auto-sense.
ETHERNET 802.3
ETHERNET 802.2
ON
OFF
Packets over the
Ethernet
TRANSMIT IPX RIP This enables or disables
the transmission of IPX
ON
OFF
Routing information
over the Ethernet
RECEIVE IPX SAP This enables or disables
the reception of IPX
ON
OFF
SAP Packets over the
Ethernet.
TRANSMIT IPX SAP This enables or disables
the transmission of IPX
ON
OFF
SAP Packets over the
Ethernet.
IPX SAP FILTER Enables or disable the
SAP Filter Table
ON
OFF
defined for the Ethernet
Port. N.B. If the SAP
filter table has no
entries then all SAP
packets are ignored if
enabled.
Echo LANli nk Router Option User Manual Issue 1.0 04 December 1997 Page 33 of 59
Page 34

4.6.2 WAN SERVICE SETUP
PARAMETER DESCRIPTION OPTIONS
SERVICE NAME WAN service name. User defined.
COMPRESSION Router compression
facility
LINE PROTOCOL Multi-vendor
compatibility option.
ENABLED
DISABLED
Forward to PPP Setup
menu
MAC FILTER MAX filter capacity ENABLE
DISABLED
IP MODE Controls transmission of
received IP packets
IP RIP UPDATES Control s transmission of
IP Routing Information
ROUTE
BLOCK
YES
NO
on the WAN Link.
BOOTP PROCESSING Controls transmission of
BOOTP packets over
YES
NO
the WAN
IP HOPS Number of hops added
User defined
to a route to access this
Router.
IP FILTER IP filter table name for
received IP packets.
User defined
NONE
N.B.
IPX MODE Controls IPX routing of
packets received from
ROUTE
BLOCK
WAN.
IPX RIP UPDATES Control s transmission of
IPX routing information
NO
YES
over the WAN
IPX SAP UPDATES Controls transmission of
IPX SAP packets over
NONE
CHANGES
the WAN
PROPOGATE
NETBIOS
IPX HOPS Number of hops added
Controls NETBIOS
propagation
YES
NO
User defined
to a route to access this
Router.
IPX TICKS Time in ticks for IPX
packets to be
retransmitted over the
WAN (1 tick = 1/18
second.)
IPX SAP FILT ER Name of IPX filter table
used for received IPX
User defined
NONE
packets.
Echo LANli nk Router Option User Manual Issue 1.0 04 December 1997 Page 34 of 59
Page 35

PARAMETER DESCRIPTION OPTIONS
OTHER Controls bridging of
other protocols.
BRIDGE
BLOCK
4.6.2.1 PPP SETUP
Authentication is not normally used on leased lines.
PARAMETER DESCRIPTION OPTIONS
Required By Remote Router/Service
AUTHENTICATION TYPE Type of authentication
required by remote router
to accept connection.
N.B. CISCO equipment will
negotiate so PAP or
not
NONE
PAP
CHAP
PAP OR CHAP
CHAP is unacceptable.
PAP PASSWORD Password expected by
User defined
remote router
CHAP SECRET Password expected by
User defined
remote router
Required By Th is Service
AUTHENTICATION TYPE Type of authentication
required by this router to
accept connection.
NONE
PAP
CHAP
USERNAME Name of local Router User defined
PAP PASSWORD Password expected by
User defined
remote router
CHAP SECRET Password expected by
User defined
remote router
Echo LANli nk Router Option User Manual Issue 1.0 04 December 1997 Page 35 of 59
Page 36

4.7 FILTER SETUP
N.B. IP and IPX filter tables are created using these menus BUT
are activated using the SERVICE SETUP menu.
Unit Status
Traffic
Analysis
Ethernet MAC
Filter
Network
Loading
MAC Filter
WAN MAC
Management
Filter
Remote
Configuration
Ethernet IP
FIlter
Unit
IP Filter
WAN MAC
FIlter
Service
Setup
IPX SAP
Ethernet IPX
SAP Filter
Filter
Setup
Filter
WAN IPX
SAP Filter
Events
There are filter tables available for both the Ethernet connection and WAN
link. Whil st it is preferable to block packets prior to forwarding them to the
WAN link, it may arise that control of the remote site is not possible, and
therefore WAN filters must be used to protect from unwanted incoming traffic.
Filters are referenced for receive traffic only i.e. all IP packets from the
Ethernet will be referenced through the Ethernet IP filter before forwarding to
the internal routing tables. If the user configures both Ethernet and WAN
filters they should be a mirror image of one another, except for the swapped
IP source/destination Address and Port numbers.
4.7.1 MAC FILTERS (WAN or Ethernet)
MENU SELECTION DESCRIPTION
LIST Displays all addresses from which
packets are by the Router.
ADD MAC addresses can be added to list
from which the Router can forward
packets. Maximum number in list is
200. The addresses must be entered
in 2x6, 4x3 or 12x1 format.
DELETE Deletes MAC address from the list.
CLEAR Clears all list entries.
SAVE FILTER Filtering tables will run from RAM
however the configuration, must
be saved to operate after a reset.
When creati ng a large filter table
it is advised that the user save
progress regularly.
Echo LANli nk Router Option User Manual Issue 1.0 04 December 1997 Page 36 of 59
Page 37

4.7.2 IP FILT ER (WAN or Ethernet)
Both the Ethernet and WAN ports on the router can have an individual IP
filter table. If IP filtering is active then any packets received are checked
against the filter table before processing by the Router.
Each port IP filter table can have 64 entries. When the first entries are made
they will not become active until the table screen is exited. Any future input
will become active immediately.
The filter table is sequentially searched for each IP packet received until a
match is found. A filter table with multiple entries will impose significant
processor loading and a corresponding drop i n throughput.
The filter table is spl i t into three parts. The fi rst part is source and destinati on
IP address. The second part is protocol selection, and the thi rd port or socket
selection for TCP and UDP packets. Each section supports the use 'wild card'
entries to allow any value to be matched e.g. to pass only TCP packets the
user 'wild cards' the both source and destination IP address, and the port
numbers.
Each line in the filter table can be configured as a pass or fail. The normal
operation would be to put a number of entries in the filter table that would
pass if a match occurs. By default the last entry in the fil ter table must be a
failure, however it is possibl e to use the filter table in a reverse fashion and
define each line so that a match results in fail ure. The last entry would have
wild card entries for all three sections and results in a pass
.
MENU SELECTION DESCRIPTION
ADD A new entry may be added to the end
of the Table or after an entry
EDIT To edit an entry, selecting the
relevant line number entering
required amendments.
DELETE Enter the line number to delete.
CLEAR To delete the entire table.
NAME Define a name for this filter table
LIST PARAMETER DESCRIPTION
LINE Line number of Filter Table entry to
be amended/deleted
SRC ADDR The source address for IP packets to
be filtered. A network address,
individual IP address or ALL may be
specified.
Echo LANli nk Router Option User Manual Issue 1.0 04 December 1997 Page 37 of 59
Page 38

MENU SELECTION DESCRIPTION
SRC MASK The IP mask associated with the
Source Address in hexadecimal
format. Left blank if ALL source
addresses are forwarded.
DEST ADDR The destination address of IP packets
to be filtered. A network address,
individual IP address or ALL may be
specified.
DEST MASK The IP mask associated with the
Destination Address in hexadecimal
format. Left blank if ALL destination
addresses are specified.
PROT Indicated the protocol this entry will
filter on e.g. ANY, TCP ONLY, UDP
ONLY, ICMP ONLY
S.PRT The Source Port that this entry will
Filter on.
D.PRT The Destination Port that this entry
will filter on.
RSLT
4.7.3 IPX SAP FILTER MENU (WAN or Ethernet)
SAP (Service Advertising Protocol) is used on Novell™ networks to inform
workstations and file servers of what services the network can offer. The IPX
SAP filter only operates when the IPX mode is set to route.
The Router maintains an internal table of known services. It receives SAP
updates on either port and broadcasts the information to the other port. The
filter allows selected information to be ignored on receipt and hence not
stored in the SAP filter tabl e. If a SAP update is not in the table it will be
dropped and propagated to the other port.
A filter table is available for each port. Each table has 16 entries and is
searched sequentially unti l a match is found. Each li ne can be set to pass or
fail.
A SAP entry contai ns si x ele ments, b ut the fi lte r can onl y act on th e fol lo wing
three; Service
NAME
.
TYPE,
Socket Address (
FROM SKT, TO SKT
) and
SERVER
The following fields are ignored:
Network Address
Echo LANli nk Router Option User Manual Issue 1.0 04 December 1997 Page 38 of 59
(32 bits)
Page 39

This is the source IPX network number of the service. Services will not be
entere d into the in ternal SAP table if the RI P table has no e ntry for the rou te
to this address.
Node Address
(48 bits)
This is the Ethernet or Token Ring MAC address from where the SAP
originated.
Hops
(16 bits)
This is the number of Routers that must be traversed to reach this service.
Every time this SAP passes another Router this count is incremented to a
maximum of 16.
MENU SELECTION DESCRIPTION
ADD A new entry may be added to the end
of the Table or after an entry
EDIT To edit an entry, selecting the
relevant line number entering
required amendments.
DELETE Enter the line number to delete.
CLEAR To delete the entire table.
NAME Define a name for this filter table
LIST PARAMETER DESCRIPTION
LINE The Line Number of the Filter Table
entry used to specify an entry to be
changed or deleted.
TYPE The type of service advertised by a
SAP packet or ALL to include all
service types in the filter.
FROM SKT Initia l Socket Number for selecting a
range of socket numbers to be
filtered. To select all Sockets use
ALL.
TO SKT The final Socket Number for sel ecting
a range of socket numbers to be
filtered.
SERVER NAME The unique name of a Server to be
filtered or ALL to filter on all Server
Names.
RSLT The action to be taken as a result of
SAP packet s meeting f ilt er conditi ons
e.g. F AIL (dro p) or PASS (route.)
Echo LANli nk Router Option User Manual Issue 1.0 04 December 1997 Page 39 of 59
Page 40

4.7.4 IPX HEADER FILTERS
There is a single IPX header filter that can control the forwarding of packets
from each port. The user can select if this fil ter is applied to packets received
from either or both ports.
The filter can have up to 128 entries. If IPX filtering is active, then any
packets received are checked against the fil ter table before processi ng by the
Router. The operation of the IPX filter does not effect RIP and SAP packets
as they are processed directly by the Router.
It should be noted that the filter tabl e is sequentially searched for each IPX
packet received until a match is found. A filter table with multiple entri es will
impose a significant processor loading and a corresponding drop in
performance.
In most cases IPX conversations require packets to be passed in both
directions. Stopping packet flow i n one direction will stop any conversation
taking place. It may not be necessary to use filters in both directions.
The filter table is configured depending upon which networks, nodes and
sockets are expected to be found connected to each port. The actual
comparison of the packet source or destination address in the IPX Header to
the filter table changes depending upon which port the packet is received
from. If network 45 is set by the filter as connected to Port A then packets
received from Port A would have the IPX header source network number
compared to the entry for network 45. Packets received from Port B would
have the IPX header destination network number compared to 45.
Each of the seven fields can be set to pass ALL. The result of any entry can
be set to PASS or F AIL. If the se arch reach es the end of the table with no
match then the result is an automatic FAIL.
MENU SELECTION DESCRIPTION
ADD A new entry may be added to the end
of the Table or after an entry
EDIT To edit an entry, selecting the
relevant line number entering
required amendments.
DELETE Enter the line number to delete.
CLEAR To delete the entire table.
NAME Define a name for this filter table
LIST PARAMETER DESCRIPTION
LINE The Line Number of the Filter Table
entry used to specify an entry to be
changed or deleted.
Echo LANli nk Router Option User Manual Issue 1.0 04 December 1997 Page 40 of 59
Page 41
MENU SELECTION DESCRIPTION
NETWORK Source or destination IPX number
(eight digit hexadecimal.)
MAC NODE ADR Ethernet MAC address of the network
adapter card (twelve digit
hexadecimal. File servers are
usually designated 000000000001.
SOCKET Designates a conversation between
two addresses.
P.T An 8-bit field that specifi es the upper-
layer protocol to receive the packet's
information e.g. NCP or SPX.
RSLT The action to be taken as a result of
IPX packets meeting filter conditions
e.g. F AIL (dro p) or PASS (route.)
4.7.5 NOVELL KEEP-ALIVES
Novell Fil e Servers poll all workstations that are attached to the server i f they
have not seen any traffic from that station for a certain period. This is to
detect situations where the workstation has been turned off without being
logged out. If these Poll Inactive Station packets or the reply are filtered out,
then any workstation that is unused for approximately 15 minutes will lose the
network connection.
The request from the server is from source socket 4001 to destinati on socket
4004 with a Packet Type of zero. The reply from the workstation is from
source socket 4004 to destination socket 4001.
If you do not make provision for these packets i n the IPX header fil ter table
then any workstations unused for approximately 15 minutes will lose their
network connection.
4.8 EVENTS
Echo LANli nk Router Option User Manual Issue 1.0 04 December 1997 Page 41 of 59
Page 42

Unit Status
Traffic
Analysis
Network
Loading
Remote
Management
Unit
Configuration
Service
Setup
Filter
Setup
Events
PPP Events
System
Events
This menu option allows the user to display significant event activity for
the Router. These displa ys are intended for use as diagnosti c tools for
engineers or planning ai ds for the network manager.
4.8.1 PPP EVENTS
This display shows connection ‘conversations’ held between the l ocal
Router and remote equipment allowing quick and effective fault
diagnosis. The last 100 events in each of the PPP or system event
logs are held in the dynamic memory of the Router.
4.8.2 SYSTEM EVENTS
This display shows the 100 most recent system events, to assist in the
diagnosis of connectivity problems. The various events recorded are listed
below.
MAIN LINK CARRIER LOSS
MAIN LINK CARRIER RESTORED
D/I CARRIER LOSS
D/I CARRIER RESTORED
REMOTE ALARM
REMOTE ALARM CLEARED
Nx64 CHANNEL x CONTROL DISAFFIRMED
Nx64 CHANNEL x CONTROL AFFIRMED
Nx64 CHANNEL x CLOCK FAIL
Nx64 CHANNEL x CLOCK RESTORED
MAIN LINK HIGH BIT ERROR RATE
MAIN LINK HIGH BIT ERROR RATE CLEARED
LOCAL/REMOTE MAP MISMATCH
LOCAL/REMOTE MAP MISMATCH CLEARED
D/I REMOTE ALARM
D/I REMOTE ALARM CLEARED
Echo LANli nk Router Option User Manual Issue 1.0 04 December 1997 Page 42 of 59
Page 43

FLASH ERASE ERROR PARAMETER x
FLASH PROGRAMMING TIMEOUT
FLASH VERIFY ERROR
COMPRESSION ERROR HISTORY x STATUS y
COMPRESSION TIMEOUT HI STORY x STATUS y
DECOMPRESSION ERROR HISTORY x STATUS y
DECOMPRESSION TIMEOUT HI STORY x STATUS y
Echo LANli nk Router Option User Manual Issue 1.0 04 December 1997 Page 43 of 59
Page 44

APPENDIX A WARNINGS
WARNING: THIS EQUIPMENT MUST BE EARTHED/
GROUNDED
This equipment relies on the EARTH /
GROUND connection to ensure safe operation
such that the user and TELECOM Network are
adequately protected. It must not under any
circumstances be operated without an earth
connection, which could nullify its approval
for connect ion to a ne twork.
WAR N IN G: INS TALLATION OF EQUIPMENT
Installation of this equipment must only be
performed by suitably trained service
personnel.
WAR N IN G: CON N E C TION OF OTH ER E QU IPMEN T
This equipment allows connection only of
suitably approved equipment to its ports, the
safety status of which ar e de fine d be low.
SELV Ports:
i) Supervisor port
ii) MAIN port
iii) D&I port
iv) CH1 and CH2 (Channel ports)
v) EXT CLOCK
vi) ALARM port
vii) AUI port
viii) 10BASE-T port
The above named ports are classified as SELV (Safety
Extra Low Voltage) in accordance with in Clause 2.3 of
EN60950 (BS7002, IEC950 as applicable), and mus t only
be connected to equipment which similarly complies with
the SELV safety classification.
Echo LANli nk Router Option User Manual Issue 1.0 04 December 1997 Page 44 of 59
Page 45

Warnung: Dieses Gerät Muß an einem Anschluß mit
Schutzleiter be tr ie be n werden.
Zum sicheren Betrieb ist der Anschluß des Gerätes an
Spannungsversorgungen mit Schutzleiter notwendig.
Nur so kann ein optimaler Schutz für Bedienpersonal
und Übertragungseinrichtungen gewährleistet werden.
Unter keinen Umständen darf dieses Gerät ohne
Schutzleiter betrieben werden, da ansonsten die
Zulassung fü r den Anschluß an N etzen er lischt.
Warnung: Installation des Ge r ä te s
Die Installation des Gerätes darf nur von entsprechend
ausgebildetem und autorisiertem Personal
durchgeführt werden.
Warnung: Ansc hluß v on a nde r en Geräten
Angeschlossen werden dürfen nur Systeme mit
entsprechenden zugelassenen und geeigneten
Schnittstellen , sieh e auch n ach folgen de Tabelle:
SELV Ports
i)
ii)
iii)
iv)
v)
vi)
vii)
viii)
Die oben aufgeführten Ports sind klassifiziert als SELV
(Safety Extra Low Voltage) in Übereinsti mmung mit Absatz
2.3 der Verordnung EN60950 (BS7002, IEC950 soweit
anwendbar), und dürfen nur zusammen mit Geräten
verwendet werden, die dieser Bestim mung entsprechen.
Supervisor
port
MAIN
port
D&I
and
CH1
EXT CLOCK
ALARM
port
AUI
10BASE-T
CH2
port
port
(Channel ports)
port
Echo LANli nk Router Option User Manual Issue 1.0 04 December 1997 Page 45 of 59
Page 46

Mise en garde : Cet équipe m e nt doit ê tr e r e lié a la te r r e
Cet équipement doit posséder une prise de terre de
manière à ce que le réseau télécom et ses utilisateurs
soient équitablement protégés. Tout manquement à
cette obligation entraînerait l'annulation de
l'autorisation de con n exion a un r éseau .
Mise en garde : Installation de l' é quipm e nt
L'installation doit être assurée uniquement par des
personnels convenablement formés à ce type de
matériel.
Mise en garde : Connexion d' a utr e s é quipe m e nts
Des équipement complémentaires pourrant être
connectés aux ports de cet équipement à la seule
condition que ceux-ci soient agrées. Les conditions
optimales de sécurité pour toute connexion sont
définies ci-dessous:
Ports SELV.
i) port
ii) port
iii) port
iv) ports pour les canaux
v) port
vii) port
vii) port
viii) port
Les ports cités ci-dessous sont classés dans la catégorie
SELV (Safety Extra Low Voltage) conformément à la classe
2.3 de EN60950 (BS7002, IEC950 applicable) et doivent
être connectés à des équipements répondant à la norme de
sécurité SELV.
Supervisor
MAIN
D&I
EXT CLOCK
ALARM
AUI
10BASE-T
CH1
à
CH2
Echo LANli nk Router Option User Manual Issue 1.0 04 December 1997 Page 46 of 59
Page 47

APPENDIX B APPROVAL REQUIREMENTS
There are no specifi c approval requirements for the Router Option - refer to
Echo LANlink User Manual for general approval requirements.
Echo LANli nk Router Option User Manual Issue 1.0 04 December 1997 Page 47 of 59
Page 48

APPENDIX C EMC REQUIREMENTS
There are no specific EMC requirements for the Router Option - refer to Echo
LANlink User Manual for general EMC requirements.
Echo LANli nk Router Option User Manual Issue 1.0 04 December 1997 Page 48 of 59
Page 49

APP ENDIX D REAR PANEL LAYOUT
The layout of all ports on the rear panel of the Echo LANlink with Router
Option fitted is shown in the diagram below:
Echo LANli nk Router Option User Manual Issue 1.0 04 December 1997 Page 49 of 59
Page 50

APPENDIX E AUI PORT (15-WAY D-TYPE) PINOUT
The AUI port connector is a 15-pin, D-type socket.
Pin No Signal Type Description
SHELL SCREEN Chassis Earth
1GND 0V
2 ACX+ Input Collision Detect Input (positive)
3 ATX+ Output Transmit Data (positive)
4GND 0V
5 ARX+ Input Receive Data (positive)
6 GND Power supply 0V
7 Not connected
8GND 0V
9 ACX- Input Collision Detect Input (negative)
10 ATX- Output Transmit Data (negative)
11 GND 0V
12 ARX- Input Receive Data (negative)
13 +12V Output +12V power supply 0.5A max
14 GND 0V
15 Not connected
Echo LANli nk Router Option User Manual Issue 1.0 04 December 1997 Page 50 of 59
Page 51

APP E NDIX F 10BASE-T (RJ45) PORT PINOUT
The twisted-pair Ethernet port connector is a 8-pin, RJ45 socket, conforming
to the 10BASE-T standard and suitable for connection to an Ethernet hub.
Pin No Signal Type Description
SHELL Chassis Earth
1 TPTX+ Output Twisted-Pair Transmit Data (positive)
2 TPTX- Output Twisted-Pair Transmit Data (negative)
3 TPRX+ Input Twisted-Pair Receive Data (positive)
4 Not connected
5 Not connected
6 TPRX- Input Twisted-Pair Receive Data (negative)
7 Not connected
8 Not connected
Echo LANli nk Router Option User Manual Issue 1.0 04 December 1997 Page 51 of 59
Page 52

APPENDIX G IP FILTER EXAMPLES
If IP filtering is active then all packets recei ved are checked against the filter
table before processing by the Router. Packets are also compared to the IP
Filter Table when the IP Filter is set to Bridge.
The IP Filter can have 32 lines or entries. An entry does not initial ly become
active until the user exits the menu. Future amendments are acted upon
immediately after entry.
It should be noted that the filter table is sequentially searched for any IP
packet received until a match is found. A filter table with many entries can
impose significant processor loading and a leads to increased latency.
The filter table is made up of three elements:
1. Source and destination IP address.
2. Protocol selection
3. Port or socket selection for TCP and UDP packets.
Each section supports a ‘wildcard’ for a match e.g. to pass only TCP packets
you would wildcard the source and destination IP address and wildcard the
port numbers.
Each li ne in the fi l te r tab l e c an be con figure d t o PASS o r F AIL . By de fau l t t his
value is FAIL. Normal operation would put a number of entries in the filter
table that would pass packets if a match occurs. It is possible to use the
reverse and define each line so that a match results in failure. You could then
enter a last line with wildcards i n all three sections to pass.
G.1 Source and Destination IP Address
Each filter table entry consists of an IP address and a mask. The IP address
in the packet is combined with the mask and compared with the entry in the
table. If the result matches then processing continues along the li ne. If the
result fails then the same operation is performed against the next line entry.
Masks are displayed in hexadecimal format for ease of bit identification.
Values can be entered in the normal decimal dot notation or as a singl e hex
number e.g. 255.128.0.0 or FF800000. Any value or order of bits can be
entered as the mask. A mask of FFCF0040 is a valid mask.
Echo LANli nk Router Option User Manual Issue 1.0 04 December 1997 Page 52 of 59
Page 53

G.1.1 Examples
To pass any packet coming from the Class A 89.0.0.0 network you would
enter:
SRC ADDR SRC MASK
89.0.0.0 FF000000
The mask of FF00000 limits the comparison to the first 8 bi ts of the i ncoming
address.
If a Class B address of 130.140 has a subnet with 8 bits to provide the
network/subnet of 130.140.5, then to filter any packet from this subnet you
would enter:
SRC ADDR SRC MASK
130.140.5.0 FFFFFF00
If you wanted to filter a specific address on the Class B network/subnet with
an address of 130.140.5.10 then you would enter:
SRC ADDR SRC MASK
130.140.5.10 FFFFFFFF
For the equipment at address 130.140.5.10 to talk to any address on the
network/subnet of 130.140.6.0 then you would enter:
SRC ADDR SRC MASK DEST ADDR DEST MASK
130.140.5.10 FFFFFFFF 130.140.6.0 FFFFFF00
For the equipment at address 130.140.5.10 to talk to any network you would
enter:
SRC ADDR SRC MASK DEST ADDR DEST MASK
130.140.5.10 FFFFFFFF ALL
G.2 PROTOCOL SELECTION
Protocols can be defined as TCP, UDP, ICMP or ALL
G.2.1 Examples
To stop all UDP traffic you would enter.
SRC ADDR SRC MASK DEST ADDR DEST MASK PROT S.PRT D.PRT RSL
ALL ALL UDP ALL ALL FAIL
In this case you would need a second line to pass other traffic.
SRC ADDR SRC MASK DEST ADDR DEST MASK PROT S.PRT D.PRT RSL
ALL ALL UDP ALL ALL PAS
G.3 Source and Destination Ports
Echo LANli nk Router Option User Manual Issue 1.0 04 December 1997 Page 53 of 59
Page 54

Ports can be given a specific value or the user can use wildcards to pass all
values. Various services use a specific port number e.g. Telnet uses Port 23,
FTP uses port 21. RFC 1700 gives a list of standard port values.
G.3.1 Examples
If 130.140.5.10 wishes to be able to Telnet to 130.140.6.32, but does not
wish 130.140.6.32 to be able to Telnet back to him the following line should
be used:
SRC ADDR SRC MASK DEST ADDR DEST MASK PROT S.PRT D.PRT RSL
130.140.5.10 FFFFFFFF 130.140.6.32 FFFFFFFF TCP ALL 23 PAS
When 130.140.5.10 initi ates a connection his packet will include the following
information:
IP Destination 130.140.6.32
IP Source 130.140.5.10
Protocol TCP
Port Destination 23
Port Source 1024
The key to this is the source port that will be assigned by the system. These
numbers usually start at 1024 and are incremented each time a new TCP
connection is made.
If the other machine 130.140.6.32 initiates the connection then the reply
coming from 130.140.5.10 would have the following information.
IP Destination 130.140.6.32
IP Source 130.140.5.10
Protocol TCP
Port Destination 1024
Port Source 23
You should note that the source and destination ports are now swapped. The
first packet from 130.140.6.32 will get to the other machine. However his
reply will fail when checked with the filter because the destinati on port is not
23.
If you wanted only these two machines to be able to telnet to each other and
either machine to initiate the connecti on then you would need two lines i n the
filter table.
SRC ADDR SRC MASK DEST ADDR DEST MASK PROT S.PRT D.PRT RSL
130.140.5.10 FFFFFFFF 130.140.6.32 FFFFFFFF TCP ALL 23 PAS
130.140.5.10 FFFFFFFF 130.140.6.32 FFFFFFFF TCP 23 ALL PAS
Echo LANli nk Router Option User Manual Issue 1.0 04 December 1997 Page 54 of 59
Page 55

APP ENDIX H IP SUBNETS
An Internet Protocol (IP) address is 32 bits long and is split into two parts.
The first part is the network number and the second part is the unit number.
Combined they make a unique address.
An address with a different network number can only be reached via a
Router.
The way the IP address is split into these two parts varies on the upper bits of
the network number. This fi xed split is defined as three classes.
Class A Address
Network 8 bits Unit 24 bits
Class B Address
Network 16 bits Unit 16 bits
Class C Address
Network 24 bits Unit 8 bits
Any equipment can establish the network element of an address based on the
upper bits of its IP address. This information is then used to work out the
network mask. When a target IP address is entered this network mask is
used to see if the target is on the same network number. If they do not match
then the packet must be sent via a Router to reach the target.
Subnets allow the boundary to be moved to the right by a given number of
bits. So if we take a Class A address and add an eight bit subnet we make
the network element 16 bits and the unit element 16 bits.
Class A Address + 8 bits of Subnet
Network 8+8bits (16 bits) Unit 16 bits
The problem is that every machine on this new 16 bit network must know of
the ‘new’ network/unit spli t as they can no longer automatically establish the
split based on the upper bits of the IP address. All equi pment must now be
configured to use the correct number of subnet bits. Any equipment not
configured with the same number of subnet bits will not route correctly.
The number of subnet bits is variable between zero (use standard
network/unit split) to two less than the number of unit bits for this Class.
A router network can internally report the number of subnet bits by using
OSPF or RIP 2. RIP 1 cannot carry subnet information.
Echo LANli nk Router Option User Manual Issue 1.0 04 December 1997 Page 55 of 59
Page 56

APP ENDIX I ROUTER M AINTENANCE MENU
For security reasons the Multipl exer must be directl y connected to a terminal
to access the MAINTENANCE MENU.
Login to the unit as CMGR at the initial prompt. All access passwords will
apply as usual. On logi n a $$ prompt will appear. Type UPGRADE MENU
<return>. The prompt ARE YOU SURE? will appear. Type YES <return>
and the MAINTENANCE MENU will appear.
I.1 KERMIT
A new version of the Router firmware may be downloaded to flash memory
via the console port using Kermit.
If a suitable communications program is resident on the PC it may be used. If
there is no such program available the upgrade disk includes a shareware
version of ProComm.
Connect the PC via COM1 or COM2 to the SUPERVISOR port of the
Multiplexer. This port is configured DCE and therefore a straight cable (no
crossover) is required (see Echo LANlink User manual.) The
communications package shoul d be configured to 9.6Kbps, 8 bits, 1 stop bit
and no parity.
Start the PC communications program, or ProComm from the upgrade disc.
ProComm will default to COM1. Should the Multiplexer be connected to
COM2 press ALT P and select 22 for COM2.
If ProComm is being used press the <PgUp> key on the PC, then enter 2 for
Kermit.
Enter the Upgrade File Name e.g. A:\>LANLINK1.1.
ProComm will display the file size and how many bytes have been
transferred. The download should take approximately 15 minutes.
CTRL-A Abort Transfer
CTRL-B Cancel Ba tch
CTRL-F Cancel File
When the download has been completed the following messages will be
displayed:
Enter Ke y: 1
Start Remote Kermit…
Normal end 136904 bytes received
Echo LANli nk Router Option User Manual Issue 1.0 04 December 1997 Page 56 of 59
Page 57

Erasing Flash Memory
Programming Flash Memory
Verifying Flash Memory
Flash Memory OK
AN8100B Small Office Server Maintenance Menu Vx.x
1) Update Flash from Console port with Kermit
2) Update Flash from Ethernet with TCP Loader
3) Update Flash from Ethernet with TFTP Loader
4) Restore configuration from Ethernet via TFTP
6) Set new IP Address (xx.xx.xx.xx)
7) Set default Gatewa y (xx. xx.xx.xx)
8) Run Flash Program
9) Reset Password
B)Boot File using TCP Loader
C)Boot File using TFTP Loader
M)Run monitor
Enter Ke y:
Type in 8 to run the new revision of software.
I.2 Download New Firmware using TCP loader
This option is for factory use only.
I.3 Download New Firmware using TFTP
Selecting this option will allow the Manager to TFTP software upgrades to the
Router. The Router will act as a server, enabling the files to be downloaded
from the PC in Binary or Octet formats (not ASCII.)
I.4 Restore Configuration using TFTP
The configuration for Router is stored in the EEPROM. This configuration
may also be saved to a PC. This must be carried out while the Router is
operational (see the Security Section for set-up detail s.) Restoration must be
carried out in the Maintenance mode.
Selecting this option will allow the Manager to TFTP to the Router a stored
configuration. The Router will act as a server, enabling the files to be
downloaded from the PC in a Binary or Octet formats (not ASCII.)
Echo LANli nk Router Option User Manual Issue 1.0 04 December 1997 Page 57 of 59
Page 58

I.5 Set New IP Address
Selecting this option will allow the Manager to set a new IP address for the
Router if required to facilitate the file transfer. Note the burnt in MAC address
will be used in the Maintenance mode.
I.6 Set Default Gateway
Selecting this option will allow the Manager to set a default gateway (should
RIP not be transmitted) for the Router i f required to facilitate the file transfer.
I.7 Run Flash Program
This will reboot the Router.
I.8 Reset Password
In order to give the network manager the ability to reset the Password on the
Router the factory uses a unique system to reset the default password to
SYSTEM. Using the number gives t he user two minutes, and one attempt to
reset the password to SYSTEM.
Type 9 and press <RETURN>
This will display:
Enter Ke y: 9
Unit Serial: ****
Enter Magic Number:
Type in the unique Magic Number supplied with the Router option, or a copy
obtained from your distributor.
Press 8 <RETURN> to reboot the Router, and access the Security Menu to
reset the password.
I.9 Boot File Using TCP Loader
This is for factory use only
Echo LANli nk Router Option User Manual Issue 1.0 04 December 1997 Page 58 of 59
Page 59

I.10 Boot File Using TFTP Loader
This option will remotely upgrade the BOOT code. The program is loaded
into RAM and executed.
Selecting this option will allow the Manager to TFTP download the firmware
upgrade to the Router. The Router will act as a server, enabling the files to
be downloaded from the PC in a Binary or Octet formats (not ASCII.)
I.11 Run Monitor
This will enable the factory to monitor memory functions within the Router.
Echo LANli nk Router Option User Manual Issue 1.0 04 December 1997 Page 59 of 59
 Loading...
Loading...