Page 1

Single Source Machine Control Power // Flexibility // Ease of Use
21314 Lassen Street Chatsworth, CA 91311 // Tel. (818) 998-2095 Fax. (818) 998-7807 // www.deltatau.com
^1 HARDWARE MANUAL
^2 PMAC Mini PCI
^3 Programmable Multi-Axis Controller
^4 5xx-603712-xHxx
^5 April 26, 2010
Page 2

Copyright Information
© 2010 Delta Tau Data Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
This document is furnished for the customers of Delta Tau Data Systems, Inc. Other uses are
unauthorized without written permission of Delta Tau Data Systems, Inc. Information contained in
this manual may be updated from time-to-time due to product improvements, etc., and may not
conform in every respect to former issues.
To report errors or inconsistencies, call or email:
Delta Tau Data Systems, Inc. Technical Support
Phone: (818) 717-5656
Fax: (818) 998-7807
Email: support@deltatau.com
Website: http://www.deltatau.com
Operating Conditions
All Delta Tau Data Systems, Inc. motion controller products, accessories, and amplifiers contain
static sensitive components that can be damaged by incorrect handling. When installing or handling
Delta Tau Data Systems, Inc. products, avoid contact with highly insulated materials. Only
qualified personnel should be allowed to handle this equipment.
In the case of industrial applications, we expect our products to be protected from hazardous or
conductive materials and/or environments that could cause harm to the controller by damaging
components or causing electrical shorts. When our products are used in an industrial environment,
install them into an industrial electrical cabinet or industrial PC to protect them from excessive or
corrosive moisture, abnormal ambient temperatures, and conductive materials. If Delta Tau Data
Systems, Inc. products are directly exposed to hazardous or conductive materials and/or
environments, we cannot guarantee their operation.
Page 3
REVISION HISTORY
REV. DESCRIPTION DATE CHG APPVD
1 REVISIONS TO FLEX CPU BAUD RATE, PPS. 6 &21 05/09/06 CP S. SATTARI
2 UPDATED ENCODER SETTING DESC., PPS. 6 & 20 01/30/09 CP S. MILICI
3 CORRECTED JUMPER LAYOUT E85-E87-E88, P. 25 04/26/10 CP S. MILICI
Page 4

Page 5

PMAC Mini PCI Hardware Reference Manual
Table of Contents
INTRODUCTION .....................................................................................................................................................1
Features ...................................................................................................................................................................1
Dimensions..............................................................................................................................................................2
HARDWARE SETUP ...............................................................................................................................................3
Board Configuration................................................................................................................................................3
Base Version .......................................................................................................................................................3
Option 2: Dual-Ported RAM .............................................................................................................................3
Option 5xF: CPU Speed Options .......................................................................................................................3
Option 6: Extended Servo Algorithm Firmware................................................................................................4
Option 6L: Special Lookahead Firmware .........................................................................................................4
Option 8A: High-Accuracy Clock Crystal.........................................................................................................4
Option 10: Firmware Version Specification.......................................................................................................4
Option 15: V-to-F Converter for Analog Input ..................................................................................................4
General Purpose Digital Inputs and Outputs (JOPTO Port) .............................................................................4
Power Supply Configuration Jumpers.....................................................................................................................5
Clock Configuration Jumpers..................................................................................................................................5
Encoder Configuration Jumpers..............................................................................................................................6
Single-Ended Encoders.......................................................................................................................................6
Differential Encoders..........................................................................................................................................6
Board Reset/Save Jumpers ......................................................................................................................................7
Communication Jumpers.........................................................................................................................................7
Reserved Configuration Jumpers ............................................................................................................................7
I/O Configuration Jumpers......................................................................................................................................7
Resistor Pack Configuration: Termination Resistors .............................................................................................8
The Optional Dual-Ported RAM .............................................................................................................................9
LED Indicators ........................................................................................................................................................9
Input and Output Mapping ......................................................................................................................................9
Y:$FFC0 J1 (JDISP) Outputs..........................................................................................................................9
Y:$FFC1 J3 (JTHW) Inputs.............................................................................................................................9
Y:$FFC2 J3 (JTHW) Outputs ........................................................................................................................10
Y:$FFC3 J5 (JOPTO) Inputs.........................................................................................................................10
Y:$FFC4 J5 (JOPTO) Outputs ......................................................................................................................10
Y:$FFC5 Dedicated Use................................................................................................................................10
Y:$FFC6 Dedicated Use................................................................................................................................10
OPTION 15 — VOLTAGE TO FREQUENCY CONVERTER .........................................................................12
Configuration as Analog Input with a 0-100 kHz Frequency Range ...............................................................12
Configuration as Analog Input with a 0-2 MHz Frequency Range..................................................................13
General Configuration for Step and Direction Outputs ...................................................................................13
0-100 kHz Frequency Range and Pseudo-Feedback (no External Encoder Connected).................................14
0-2 MHz Frequency Range and Pseudo-Feedback (no External Encoder Connected) ...................................14
0-100 kHz Frequency Range and Pseudo-Feedback (no External Encoder Connected).................................14
0-2 MHz Frequency Range and External Encoder Feedback Connected ........................................................14
SUGGESTED I/O M-VARIABLE DEFINITIONS .............................................................................................16
General Purpose Inputs and Outputs.....................................................................................................................16
Thumbwheel Port Bits (Can be Used as General Purpose I/O).............................................................................16
E-POINT JUMPER DESCRIPTIONS..................................................................................................................18
E0: Reserved for Future Use .................................................................................................................................18
E1 - E2: Machine Output Supply Voltage Configure ...........................................................................................18
E3 - E6: Servo Clock Frequency Control.............................................................................................................19
E7: Machine Input Sourcing/Sinking Control......................................................................................................19
Table of Contents i
Page 6

PMAC Mini PCI Hardware Reference Manual
E8 – E10: Synchronizing PMAC .........................................................................................................................20
E10A - E10C: Flash Firmware Bank Select.........................................................................................................20
E11-E14: Encoder Single Ended/Differential Select (Note: REV-103 and above).......................................................20
E17A - E17D: Amplifier-Enable/Direction Polarity Control...............................................................................21
E19: Watchdog Disable........................................................................................................................................21
E20 - E22: Flash Firmware Bank Select ..............................................................................................................21
E23: Firmware Load.............................................................................................................................................21
E29 - E33A: Phase Clock Frequency Control......................................................................................................22
E34A - E37: Encoder Sampling Clock Frequency Control..................................................................................22
E44 - E47: Communications Control...................................................................................................................23
E48: Reserved for future use.................................................................................................................................23
E49: Serial Communications Parity Control ........................................................................................................24
E50: EAROM Save Enable/Disable.....................................................................................................................24
E51: Normal/Re-Initializing Power-Up ...............................................................................................................24
E85, E87, E88: Analog Power Source Configuration...........................................................................................25
E89: Amplifier-Supplied Switch Pull-Up Enable ................................................................................................26
E90: Host-Supplied Switch Pull-Up Enable ........................................................................................................26
E98: DAC/ADC Clock Frequency Control..........................................................................................................26
E101 - E102: Amplifier Enable Output Configure ...............................................................................................27
E110 - E115: V/F Converter Configuration..........................................................................................................27
E116 - E119: V/F Converter Configuration..........................................................................................................28
MATING CONNECTORS .....................................................................................................................................30
J1 (JDISP)/Display Port...................................................................................................................................30
J2 (JEXP)/Expansion........................................................................................................................................30
J3 (JTHW)/Multiplexer Port.............................................................................................................................30
J4 (JRS232)/Serial Communications................................................................................................................30
J5 (JOPT)/OPTO I/O........................................................................................................................................30
J7 (JS1)/A-D Inputs 1-4....................................................................................................................................30
J8 (JAUX)/Auxiliary I/O ...................................................................................................................................30
J11 (JMACH)/Machine Connector...................................................................................................................30
TB1 (JPWR)......................................................................................................................................................30
CONNECTOR PINOUTS ......................................................................................................................................32
Headers..................................................................................................................................................................32
J1 JDISP (14-Pin Header)................................................................................................................................32
J3 JTHW (26-Pin Header)................................................................................................................................33
J4 JRS232 (10-Pin Header)..............................................................................................................................34
J5 JOPT (34-Pin Connector)............................................................................................................................34
J7 JS1 (16- Pin Header) ...................................................................................................................................35
J8 JAUX (14-Pin Header) ................................................................................................................................36
J11 JMACH (60-Pin Header)...........................................................................................................................37
Terminal Block......................................................................................................................................................39
TB1 (JPWR) (4-Pin Terminal Block)................................................................................................................39
JUMPERS AND CONNECTORS LAYOUT .......................................................................................................40
SCHEMATICS ........................................................................................................................................................42
ii Table of Contents
Page 7

PMAC-Mini PCI Hardware Reference Manual
INTRODUCTION
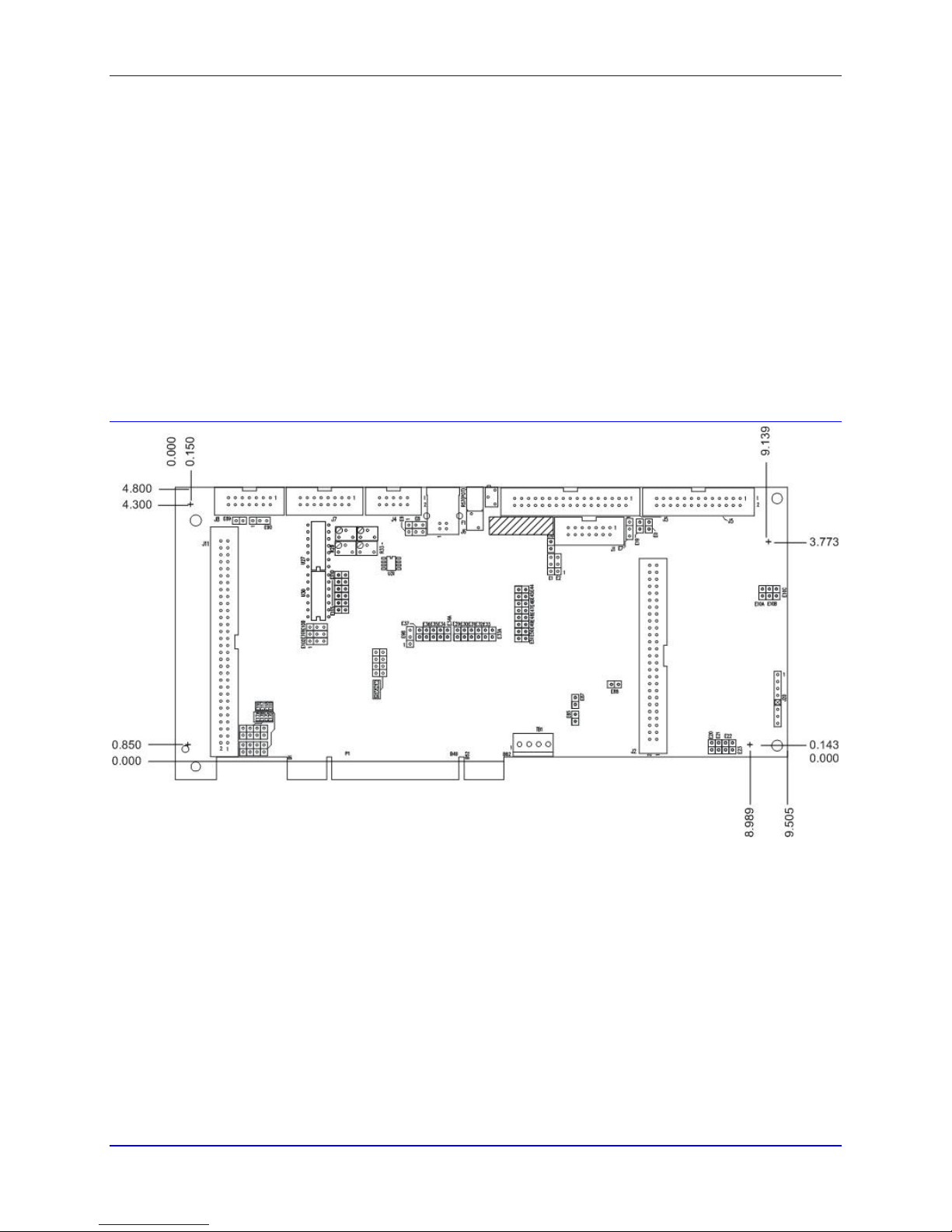
The PMAC Mini PCI is an inexpensive, compact 2-axis version of the PMAC family.
It can be used in a PC’s PCI slot as a half-sized board (230 mm, 9” long) or it can be used as a standalone
using serial communications for setup and/or application control.
Programs for the PMAC Mini PCI, both motion and PLC, are 100% compatible with other versions of
PMAC. However, there are several features unique to the PMAC Mini PCI:
1. There are only two output digital-to-analog converters: DAC1 and DAC2 (DAC3 and DAC4 do not
exist). Both have differential outputs. The two analog outputs on the PMAC Mini PCI can be used
as velocity or torque commands for separate axes, or as phase current commands for a single axis
commutated by the card. However, there are four incremental encoder interfaces that can be used for
feedback or master positions. Two of these may alternately be used to process analog voltages
through optional on-board V/F converters.
2. There is no JPAN control panel port. There are no digital inputs dedicated to the functions of this
port on other PMACs. To obtain equivalent functions, general-purpose inputs must be used along
with a PLC program reading these inputs. Handwheel encoders may be brought in through the
JMACH port. Wiper inputs may be brought in through the JAUX port if Option 15 is purchased.
3. The memory mapping of the general-purpose digital I/O is different from other versions of the
PMAC. Different M-Variable definitions are required for these I/Os on the PMAC Mini PCI (see
below).
4. The serial port is RS-232 only. There is no on-board or optional capability to use RS-422 format.
5. Dual-ported RAM (Option 2) is an on-board option that must be factory-installed. The PMAC Mini
PCI cannot use the separate Option 2 DPRAM board.
6. The JTHW multiplexer port outputs are not as powerful as on other PMACs. There should be no
more than one meter (three feet) of cable to any device on the port, instead of the three meters (ten
feet) on other PMACs. Anything longer should use the Acc-35A driver board.
7. There are no jumpers to control the open-circuit voltage of the complementary inputs. Instead, there
are removable socketed SIP resistor packs. At the factory, these are configured to tie the
complementary lines to 2.5V. Removed, they will tie the complementary lines to 5V.
8. There is no JXIO connector to provide clock signals to mating connectors on Acc-24P or Acc-8D
Option 8 boards. If either of these boards is used with the PMAC Mini PCI, a custom cable should be
made to connect the DCLK signal on the PMAC Mini PCI J7 port to both the DCLK and SCLK
inputs on the Acc-24P JXIO port, or the SCLK input on the Acc-8D Option 8 JXIO port.
9. The HMFLn, PLIMn, and MLIMn flag inputs on the PMAC Mini PCI can accept signals from both
sourcing and sinking drivers. If the A+15V on JMACH is used to supply the flag isolators through
E89 and E90, only sinking drivers can be used. But, if pin 13 on J8 (JAUX) is used to supply the
isolators, a +12V to +24V supply can be used for sinking drivers, or a 0V supply can be used for
sourcing drivers.
10. The PMAC Mini PCI has an interlock circuit that drops out the +/-15V supplies to the analog outputs
through a fail-safe relay if any supply on PMAC is lost.
11. If Option 15 is purchased, the PMAC Mini PCI has the capability for two on-board voltage-tofrequency (V/F) converters. These may be used for two Wiper analog inputs, or to convert the two
analog outputs to pulse trains for stepper-type drives. The V/F converters can each take an input of 010V referenced to AGND. The pulse trains can be tied into encoder channels 3 or 4 for counting. (It
is also possible, but more expensive, to use the first two channels of the off-board Acc-8D Option 2
board.)
Features
Introduction 1
Page 8
PMAC Mini PCI Hardware Reference Manual
• Motorola DSP 563xx Digital Signal Processor
• Two output digital-to-analog (DAC) converters
• Four full encoder channels
• 16 general purpose I/O, OPTO-22 compatible
• Multiplexer port for expanded I/O
• Overtravel limit, home, fault amplifier enable flags
• Display port for LCD and VFD displays
• Optional on-board dual-ported RAM
• Optional two on-board V to F converters
• Optional on-board stepper control
• PCI Bus and/or RS-232 control
Dimensions
• Stand-alone operation
• G-Code command processing for CNC
• Linear and circular interpolation
• 256 motion programs capacity
• Asynchronous PLC program capability
• Rotating buffer for large programs
• 36-bit position range (+/- 64 billion counts)
• 16-bit DAC output resolution
• S-curve acceleration and deceleration
• Cubic trajectory calculations, splines
• Electronic gearing
2 Introduction
Page 9
PMAC-Mini PCI Hardware Reference Manual
HARDWARE SETUP
The PMAC contains a number of jumpers (pairs of metal prongs) called E-points. These jumpers
customize the hardware features of the board for a given application and must be set up appropriately.
The following is an overview of the several PMAC jumpers grouped in appropriate categories. For a
complete description of the jumper setup configuration, refer to the E-Point Descriptions section of this
manual.
Board Configuration
Base Version
The base version of the PMAC Mini PCI provides a half sized board with:
• 40 MHz DSP563xx CPU
• 128k x 24 zero-wait-state flash-backed SRAM
• 512k x 8 flash memory for firmware and user backup
• Latest released firmware version
• RS232 serial interface, 33Mhz PCI bus interface
• Two channels axis interface circuitry, each including:
• 16-bit +/-10V analog output
• 3-channel (AB quad with index) differential/single-ended encoder input
• Four input flags, two output flags
• Interface to four external 16-bit serial ADC
• Display, muxed I/O, direct I/O interface ports
• Buffered expansion port
• Clock crystal with +/-100 ppm accuracy
• PID/notch/feedforward servo algorithms
• 1-year warranty from date of shipment
• One manuals CD per set of one to four PMACs in shipment (cables, mounting plates, mating
connectors not included)
Option 2: Dual-Ported RAM
Dual-ported RAM provides a high-speed communications path for bus communications with the host
computer through a bank of shared memory. DPRAM is advised if more than 100 data items per second
are to be passed between the controller and the host computer in either direction.
• Option 2 provides an 8k x 16 bank of on-board dual-ported RAM. The key component on the board
is U20 (located at the back of the board).
Part number: 302-603712-OPT
Option 5xF: CPU Speed Options
The base PMAC Mini PCI has a 40 MHz DSP563xx CPU. This is Option 5AF that is provided
automatically if no CPU speed option is specified.
• Option 5AF: 40 MHz DSP563xx CPU (80 MHz 56002 equivalent). This is the default CPU speed.
Part number: 5AF-603712-OPT
• Option 5CF: 80 MHz DSP563xx CPU (160 MHz 56002 equivalent)
Part number: 5CF-603712-OPT
• Option 5EF: 160 MHz DSP563xx CPU (320 MHz 56002 equivalent)
Part number: 5EF-603712-OPT
Hardware Setup 3
Page 10

PMAC Mini PCI Hardware Reference Manual
Option 6: Extended Servo Algorithm Firmware
• Option 6 provides an Extended (Pole-Placement) Servo Algorithm firmware instead of the regular
servo algorithm firmware. This is required only in difficult-to-control systems (resonances, backlash,
friction, disturbances, changing dynamics).
Part number: 306-00PMAC-OPT
Option 6L: Special Lookahead Firmware
• Option 6L provides a special lookahead firmware for sophisticated acceleration and cornering profile
execution. With the lookahead firmware, PMAC controls the speed along the path automatically (but
without changing the path) to ensure that axis limits are not violated.
Part number: 3L6-00PMAC-OPT
Option 8A: High-Accuracy Clock Crystal
The PMAC Mini PCI has a clock crystal of nominal frequency 19.6608 MHz (~20 MHz). The standard
crystal’s accuracy specification is +/-100 ppm.
• Option 8A provides a nominal 19.6608 MHz crystal with a +/-15 ppm accuracy specification.
Part number: 3A8-603712-OPT
Option 10: Firmware Version Specification
Normally the PMAC Mini PCI is provided with the newest released firmware version. A label on the
memory IC (U13) shows the firmware version loaded at the factory.
• Option 10 provides for a user-specified firmware version. (1.17 or newer)
Part number: 310-00PMAC-OPT
Option 15: V-to-F Converter for Analog Input
The Mini PMAC PCI has an optional analog input called Wiper (because it is often tied to a
potentiometer’s wiper pin). Mini PMAC PCI can digitize this signal by passing it through an optional
voltage-to-frequency converter. The key component on the board is U27 and U30.
• Option 15 provides a voltage-to-frequency converter that permits the use of the Wiper input on the
auxiliary port J8 (JAUX).
Part number: 315-603712-OPT
General Purpose Digital Inputs and Outputs (JOPTO Port)
PMAC Mini PCI’s J5 or JOPTO connector provides eight general-purpose digital inputs and eight
general-purpose digital outputs. Each input and each output has its own corresponding ground pin in the
opposite row. The 34-pin connector was designed for easy interface to OPTO-22 or equivalent optically
isolated I/O modules. Acc-21F is a six-foot cable for this purpose. Characteristics of the JOPTO port on
the PMAC:
• 16 I/O points. 100mA per channel, up to 24V
• Hardware selectable between sinking and sourcing in groups of eight; default is all sinking (inputs
can be changed simply by moving a jumper; sourcing outputs must be special-ordered or fieldconfigured)
• Eight inputs, eight outputs only; no changes. Parallel (fast) communications to PMAC CPU
• Not opto-isolated; easily connected to Opto-22 (PB16) or similar modules through Acc-21F cable
Jumper E7 controls the configuration of the eight inputs. If it connects pins 1 and 2 (the default setting),
the inputs are biased to +5V for the OFF state, and they must be pulled low for the ON state. If E7
connects pins 2 and 3, the inputs are biased to ground for the OFF state, and must be pulled high for the
ON state. In either case, a high voltage is interpreted as a 0 by the PMAC software, and a low voltage is
interpreted as a 1.
4 Hardware Setup
Page 11
PMAC-Mini PCI Hardware Reference Manual
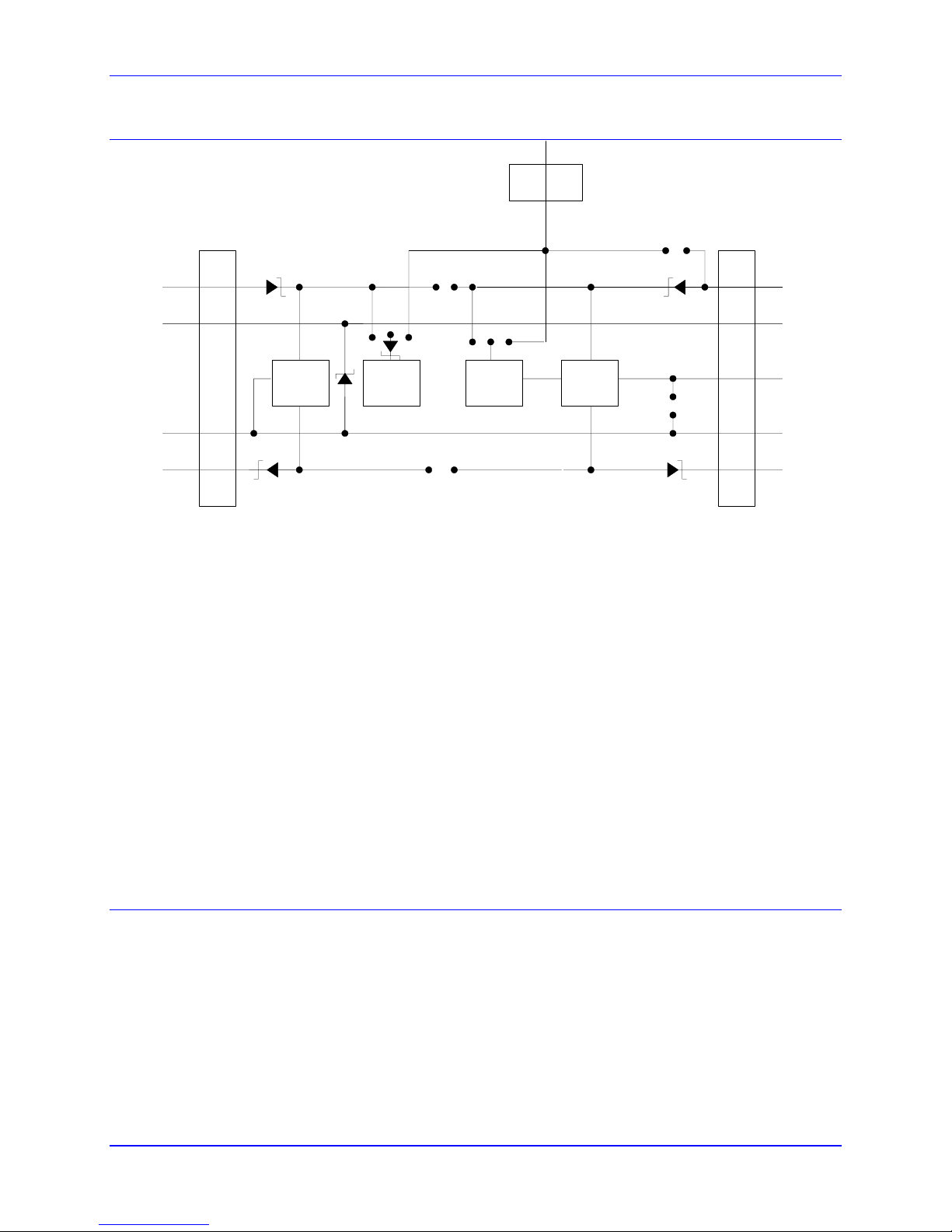
Power Supply Configuration Jumpers
(12-24V) A+V (pin 9)
J9 (JEQU)
E89
+12V
+5V
GND
-12V
P1 (Bus) / TB1
E90
3
V/F DACs
Input
Flags
E85
E100
1
1
E88
AENAs
(EQUs)
3
AGND
E87
JMACH1
A+15V
+5V
AGND
GND
A-15V
E85, E87, E88: Analog Circuit Isolation Control – These jumpers control whether the analog circuitry
on the PMAC is isolated from the digital circuitry, or electrically tied to it. In the default configuration,
these jumpers are off, keeping the circuits isolated from each other (provided separate isolated supplies
are used).
E89-E90: Input Flag Supply Control – If E90 connects pins 1 and 2 and E89 is on, the input flags
(+LIMn, -LIMn, HMFLn, and FAULTn) are supplied from the analog A+15V supply, which can be
isolated from the digital circuitry. If E90 connects pins 1 and 2 and E89 is off, the input flags are
supplied from a separate A+V supply brought in on pin 13 of the J8 JAUX connector. This supply can be
in the +12V to +24V range and can be kept isolated from the digital circuitry. If E90 connects pins 2 and
3, the input flags are supplied from the digital +12V supply and isolation from the digital circuitry is
defeated.
E100: AENA/EQU Supply Control – If E100 connects pins 1 and 2, the circuits related to the AENAn,
EQUn and FAULTn signals will be supplied from the analog A+15V supply which can be isolated from
the digital circuitry. If E100 connects pins 2 and 3, the circuits will be supplied from a separate A+V
supply brought in on pin 13 of the J8 JAUX connector. This supply can be in the +12V to +24V range
and can be kept isolated from the digital circuitry.
Clock Configuration Jumpers
E3-E6: Servo Clock Frequency Control – The jumpers E3 – E6 determine the servo-clock frequency
by controlling how many times it is divided down from the phase-frequency. The default setting of E3
and E4 off, E5 and E6 on divides the phase-clock frequency by 4, creating a 2.25 kHz servo-clock
frequency. This setting is seldom changed.
E29-E33A: Phase Clock Frequency Control – Only one of the jumpers E29 – E33A which select the
phase-clock frequency may be on in any configuration. The default setting of E31 on which selects a 9
kHz phase-clock frequency, is seldom changed.
Hardware Setup 5
Page 12

PMAC Mini PCI Hardware Reference Manual
E34A-E37: Encoder Sample Clock – Only one of the jumpers E34A – E37 which select the encoder
sample clock frequency, may be on in any configuration. The frequency must be high enough to accept
the maximum true count rate (no more than one count in any clock period), but a lower frequency can
filter out longer noise spikes. The anti-noise digital delay filter can eliminate noise spikes up to one
sample-clock cycle wide.
E98: DAC/ADC Clock Frequency Control – Leave E98 in its default setting of 1-2 which creates a
2.45 MHz DCLK signal, unless connecting an Acc-28 A/D-converter board. In this case, move the
jumper to connect pins 2 and 3 which creates a 1.22 MHz DCLK signal.
Encoder Configuration Jumpers
Encoder Complementary Line Control – PMAC has differential line receivers for each encoder
channel, but can accept either single-ended (one signal line per channel) or differential (two signal lines,
main and complementary, per channel).
REV 102 and below:
made through resistor packs configurations and not through jumper configurations: RP13, RP14, RP20
and RP21.
REV 103 and above:
made through jumper configurations: E11, E12, E13 and E14.
The selection of the type of encoder used, either single ended or differential, is
The selection of the type of encoder used, either single ended or differential, is
Single-Ended Encoders
With the jumper for an encoder set for single-ended, the differential input lines for that encoder are tied to
2.5V; the single signal line for each channel is then compared to this reference as it changes between 0
and 5V.
When using single-ended TTL-level digital encoders, the differential line input should be left open, not
grounded or tied high; this is required for The PMAC differential line receivers to work properly.
Differential Encoders
Differential encoder signals can enhance noise immunity by providing common-mode noise rejection.
Modern design standards virtually mandate their use for industrial systems, especially in the presence of
PWM power amplifiers, which generate a great deal of electromagnetic interference.
Connect pin 1 to 2 to tie differential line to +2.5V
• Tie to +2.5V when no connection
• Tie to +2.5V for single-ended encoders
Connect pin 2 to 3 to tie differential line to +5V
• Don’t care for differential line driver encoders
Tie to +5V for complementary open-collector encoders (obsolete)
E117, E118: Wiper to Encoder Input Enable – Putting these jumpers on ties the output of the Option
10 voltage-to-frequency converter that can process the Wiper analog input on the JAUX port to the
Channel 3 (E117) or 4 (E118) encoder circuitry. If the frequency signal is connected to one of these
channels, no encoder should be connected through the JMACH1 connector.
6 Hardware Setup
Page 13

PMAC-Mini PCI Hardware Reference Manual
Board Reset/Save Jumpers
E50: Flash-Save Enable/Disable Control – If E50 is on (default), the active software configuration of
the PMAC can be stored to non-volatile flash memory with the SAVE command. If the jumper on E50 is
removed, this SAVE function is disabled and the contents of the flash memory cannot be changed.
E51: Re-Initialization on Reset Control – If E51 is off (default), PMAC executes a normal reset,
loading active memory from the last saved configuration in non-volatile flash memory. If E51 is on,
PMAC re-initializes on reset, loading active memory with the factory default values.
Communication Jumpers
PCI Bus Base Address Control – The selection of the base address of the card in the I/O space of the
host PC’s expansion bus is assigned automatically by the operating system and it is not selected through a
jumper configuration.
E44-E47: Serial Baud Rate Selection – The serial baud rate is determined by a combination of the
setting of jumpers E44-E47 and the CPU frequency on a PMAC board. If the CPU’s operational
frequency has been determined by a non-zero setting of I46, the serial communications baud rate is
determined at power-up/reset by variable I54 alone. Currently, the Flex CPU’s serial baud rate is
determined at power-up/reset by variable I54 alone.
E49: Serial Communications Parity Control – Jump pin 1 to 2 for no serial parity. Remove jumper for
odd serial parity.
Reserved Configuration Jumpers
E0: Reserved for future use.
E48: Reserved for future use.
I/O Configuration Jumpers
Warning:
A wrong setting of these jumpers will damage the associated output IC.
E1-E2: Machine Output Supply Configure – With the default sinking output driver IC (ULN2803A or
equivalent) in U55 for the J5 JOPTO port outputs, these jumpers must connect pins 1 and 2 to supply the
IC correctly. If this IC is replaced with a sourcing output driver IC (UDN2981A or equivalent), these
jumpers must be changed to connect pins 2 and 3 to supply the new IC correctly.
E7: Machine Input Source/Sink Control – With this jumper connecting pins 1 and 2 (default), the
machine input lines on the J5 JOPTO port are pulled up to +5V or the externally provided supply voltage
for the port. This configuration is suitable for sinking drivers. If the jumper is changed to connect pins 2
and 3, these lines are pulled down to GND. This configuration is suitable for sourcing drivers.
E17A - E17D: Motors 1-4 Amplifier-Enable Polarity Control – Jumpers E17A through E17D control
the polarity of the amplifier enable signal for the corresponding motor 1 to 4. When the jumper is on
(default), the amplifier-enable line for the corresponding motor is low true so the enable state is lowvoltage output and sinking current and the disable state is not conducting current. With the default
ULN2803A sinking driver used by the PMAC on U44, this is the fail-safe option, allowing the circuit to
fail in the disable state. With this jumper off, the amplifier-enable line is high true so the enable state is
not conducting current and the disable state is low-voltage output and sinking current. This setting is not
recommended.
Hardware Setup 7
Warning:
Page 14
PMAC Mini PCI Hardware Reference Manual
A wrong setting of these jumpers will damage the associated output IC.
E101-E102: Motors 1-4 AENA/EQU Voltage Configure – The U37 driver IC controls the AENA and
EQU signals of motors 1-4. With the default sinking output driver IC (ULN2803A or equivalent) in U44,
these jumpers must connect pins 1 and 2 to supply the IC correctly. If this IC is replaced with a sourcing
output driver IC (UDN2981A or equivalent), these jumpers must be changed to connect pins 2 and 3 to
supply the new IC correctly.
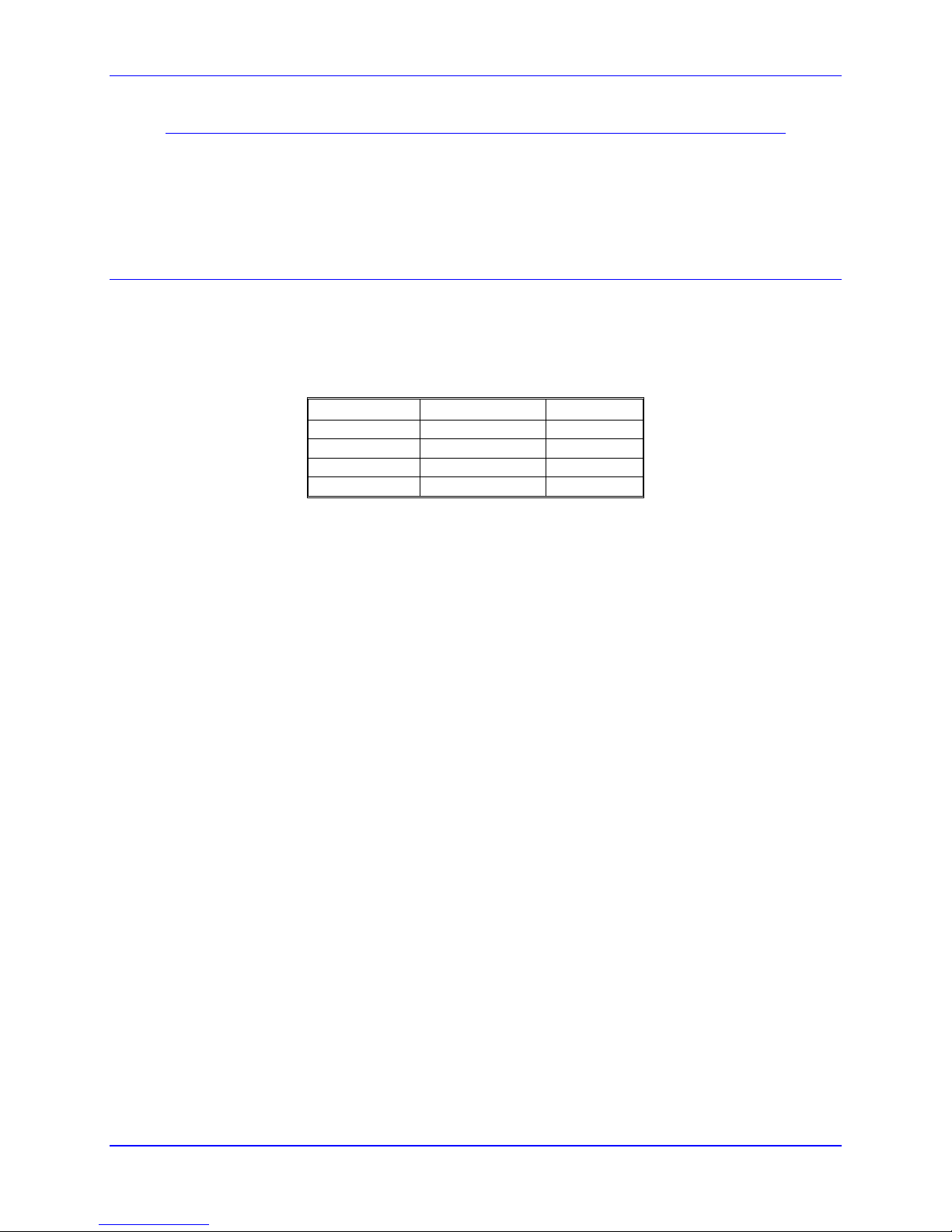
Resistor Pack Configuration: Termination Resistors
The PMAC provides sockets for termination resistors on differential input pairs coming into the board. If
these signals are brought long distances into the PMAC board and ringing at signal transitions is a
problem, SIP resistor packs may be mounted in these sockets to reduce or eliminate the ringing.
All termination resistor packs have independent resistors (no common connection) with each resistor
using two adjacent pins. The following table shows which packs are used to terminate each input device:
Device Resistor Pack Pack Size
Encoder 1 RP15 6-pin
Encoder 2 RP18 6-pin
Encoder 3 RP23 6-pin
Encoder 4 RP25 6-pin
8 Hardware Setup
Page 15

PMAC-Mini PCI Hardware Reference Manual
The Optional Dual-Ported RAM
When the PMAC Mini PCI Option 2 is ordered, U20 is installed on-board at the factory. The DPRAM is
located on the back of the board.
See the PMAC User Manual for more information.
LED Indicators
The PMAC Mini PCI has two sets (front side and back) of three LED indicators.
D9 and D9A
(green)
D10 and
D10A (red)
D19 and
D19A
(yellow)
When the green LED is lit, this indicates that power is applied to the +5V input and it is good.
When the red LED is lit, this indicates that the watchdog timer has tripped and shut down the
PMAC.
The PMAC Mini PCI has an interlock circuit that drops out the +/-15V supplies to the analog
outputs through a fail-safe relay if any supply on PMAC is lost. In this case, the LED will be
off.
Input and Output Mapping
Y:$FFC0 J1 (JDISP) Outputs
0 DB0 Display Data 0 (J1-8)
1 DB1 Display Data 1 (J1-7)
2 DB2 Display Data 2 (J1-10)
3 DB3 Display Data 3 (J1-9)
4 DB4 Display Data 4 (J1-12)
5 DB5 Display Data 5 (J1-11)
6 DB6 Display Data 6 (J1-14)
7 DB7 Display Data 7 (J1-13)
Y:$FFC1 J3 (JTHW) Inputs
0 DAT0 THW Data 0 (J3-3)
1 DAT1 THW Data 1 (J3-5)
2 DAT2 THW Data 2 (J3-7)
3 DAT3 THW Data 3 (J3-9)
4 DAT4 THW Data 4 (J3-11)
5 DAT5 THW Data 5 (J3-13)
6 DAT6 THW Data 6 (J3-15)
7 DAT7 THW Data 7 (J3-17)
Hardware Setup 9
Page 16

PMAC Mini PCI Hardware Reference Manual
Y:$FFC2 J3 (JTHW) Outputs
0 SEL0 THW Select 0 (J3-4)
1 SEL1 THW Select 1 (J3-6)
2 SEL2 THW Select 2 (J3-8)
3 SEL3 THW Select 3 (J3-10)
4 SEL4 THW Select 4 (J3-12)
5 SEL5 THW Select 5 (J3-14)
6 SEL6 THW Select 6 (J3 16)
7 SEL7 THW Select 7 (J3 18)
Y:$FFC3 J5 (JOPTO) Inputs
0 MI1 Machine Input 1 (J5-15)
1 MI2 Machine Input 2 (J5-13)
2 MI3 Machine Input 3 (J5-11)
3 MI4 Machine Input 4 (J5-9)
4 MI5 Machine Input 5 (J5-7)
5 MI6 Machine Input 6 (J5-5)
6 MI7 Machine Input 7 (J5-3)
7 MI8 Machine Input 8 (J5-1)
Y:$FFC4 J5 (JOPTO) Outputs
0 MO1 Machine Output 1 (J5-31)
1 MO2 Machine Output 2 (J5-29)
2 MO3 Machine Output 3 (J5-27)
3 MO4 Machine Output 4 (J5-25)
4 MO5 Machine Output 5 (J5-23)
5 MO6 Machine Output 6 (J5-21)
6 MO7 Machine Output 7 (J5-19)
7 MO8 Machine Output 8 (J5-17)
Y:$FFC5 Dedicated Use
0 ENA422 Serial Enable
1 RS Display Control
2 R/W Display Control
3 E Display Control
4 E44 Jumper E44
5 E45 Jumper E45
6 E46 Jumper E46
7 E47 Jumper E47
Y:$FFC6 Dedicated Use
0 E48 Jumper E48
1 E49 Jumper E49
2 E50 Jumper E50
3 E51 Jumper E51
4 PWR_GUD- Power Supply Detect
5 (Reserved for future use)
6 (Reserved for future use)
7 (Reserved for future use)
10 Hardware Setup
Page 17

PMAC-Mini PCI Hardware Reference Manual
Hardware Setup 11
Page 18

PMAC Mini PCI Hardware Reference Manual
OPTION 15 — VOLTAGE TO FREQUENCY CONVERTER
When the PMAC Mini PCI Option 15 is ordered, the following components are installed on-board at the
factory:
Configuration as Analog Input with a 0-100 kHz Frequency Range
Input 1 Input 2
E110 E111 E112 E116 E117 E113 E114 E115 E118 E119
OFF ON ON ON ON OFF ON ON ON ON
Software configuration to be typed in the terminal window:
WY$0724,$400722,1280 ;Timebase Encoder Conversion entry for Input #1
WY$0726,$400723,1280 ;Timebase Encoder Conversion entry for Input #2
I910=4 ;Encoder channel 3 for pulse-and-direction decode
I915=4 ;Encoder channel 4 for pulse-and-direction decode
M34->X:$0725,24 ;Result of the analog conversion. The range of
M35->X:$0727,24 ;Result of the analog conversion. The range of
12 Option 15 — Voltage to Frequency Converter
Jumpers Setting
;(Input #1)
;(Input #2)
;M34 is from 0 to the ;I10 value, proportional
;to the 0-10V range on the analog input #1.
;M35 is from 0 to the I10 value, proportional to
;the 0-10V range on the analog input #2.
Page 19

PMAC-Mini PCI Hardware Reference Manual
Configuration as Analog Input with a 0-2 MHz Frequency Range
Jumpers Setting
Input 1 Input 2
E110 E111 E112 E116 E117 E113 E114 E115 E118 E119
OFF OFF OFF ON ON OFF OFF OFF ON ON
E34 - E37: Encoder Sampling Clock Frequency Control
E34A E34 E35 E36 E37 SCLK Clock Frequency
ON OFF OFF OFF OFF 19.6608 MHz
Software configuration to be typed on the terminal window:
WY$0724,$40722,64 ;Timebase Encoder Conversion entry for Input #1
WY$0726,$40723,64 ;Timebase Encoder Conversion entry for Input #2
I911=1 ;Encoder 3 digital delay filter disabled (bypassed)
I916=1 ;Encoder 4 digital delay filter disabled (bypassed)
I910=4 ;Encoder channel 3 for pulse-and-direction decode
;(Input #1)
I915=4 ;Encoder channel 4 for pulse-and-direction decode
;(Input #2)
M34->X:$0725,24 ;Result of the analog conversion. The range of
;M34 is from 0 to the I10 value, proportional
;to the 0-10V range on the analog input #1.
M35->X:$0727,24 ;Result of the analog conversion. The range of
;M35 is from 0 to the I10 value, proportional to
;the 0-10V range on the analog input #2.
General Configuration for Step and Direction Outputs
• Set the appropriate jumpers as shown in the diagrams below.
• Wire the PULSEn and AENAn/DIRn open-collector outputs on the JAUX connector to the stepper
drive inputs with AGND as the reference.
• Tie the DACn output to the WIPERn input by putting the jumper on.
• Select the desired frequency range with the two jumpers for the channel.
• If true open-loop operation is desired, tie the PULSEn output to the CHAm input with the jumper and
tie the AENAn/DIRn output to the CHBm input; otherwise leave these jumpers off.
• If true open-loop operation is desired, set up the encoder channel for pulse-and-direction decode by
setting I910 or I915 to 4; otherwise, use as normal for real encoder feedback.
• If true open-loop operation is desired and the 0-2 MHz frequency range is selected, set I911=1 or
I916=1. This will disable the digital delay filter for Encoder 3 or Encoder 4, respectively.
• Put the PMAC output channel in magnitude-and-direction mode by setting bit 16 of Ix02 to 1 and bit
16 of Ix25 to 1
• Choose the appropriate simulated or real encoder for the motor’s feedback loop by setting Ix03 and
Ix04 to the address in the conversion table of the proper encoder channel. Assuming the default
conversion table, the value is $0720 for ENC1, $0721 for ENC2, $0722 for ENC3, and $0723 for
ENC4.
• If the simulated feedback is used, set Ix30 to 550,000 for 100 kHz max.; or Ix30 to 27,500 for 2 MHz
max. Set Ix31 to 0, Ix32 to 1000, Ix33 to 0, and Ix35 to 0. If real feedback is used, tune the motor
the same as for a velocity-mode amplifier.
Option 15 — Voltage to Frequency Converter 13
Page 20

PMAC Mini PCI Hardware Reference Manual
0-100 kHz Frequency Range and Pseudo-Feedback (no External Encoder
Connected)
Jumpers Setting
Input 1 Input 2
E110 E111 E112 E116 E117 E113 E114 E115 E118 E119
ON ON ON ON ON ON ON ON ON ON
0-2 MHz Frequency Range and Pseudo-Feedback (no External Encoder
Connected)
Jumpers Setting
Input 1 Input 2
E110 E111 E112 E116 E117 E113 E114 E115 E118 E119
ON OFF OFF ON ON ON OFF OFF ON ON
E34 - E37: Encoder Sampling Clock Frequency Control
E34A E34 E35 E36 E37 SCLK Clock Frequency
ON OFF OFF OFF OFF 19.6608 MHz
0-100 kHz Frequency Range and Pseudo-Feedback (no External Encoder
Connected)
Jumpers Setting
Input 1 Input 2
E110 E111 E112 E116 E117 E113 E114 E115 E118 E119
ON ON ON OFF OFF ON ON ON OFF OFF
0-2 MHz Frequency Range and External Encoder Feedback Connected
Jumpers Setting
Input 1 Input 2
E110 E111 E112 E116 E117 E113 E114 E115 E118 E119
ON OFF OFF OFF OFF ON OFF OFF OFF OFF
14 Option 15 — Voltage to Frequency Converter
Page 21

PMAC-Mini PCI Hardware Reference Manual
Option 15 — Voltage to Frequency Converter 15
Page 22

PMAC Mini PCI Hardware Reference Manual
SUGGESTED I/O M-VARIABLE DEFINITIONS
General Purpose Inputs and Outputs
M1->Y:$FFC4,0,1 ; Machine Output 1
M2->Y:$FFC4,1,1 ; Machine Output 2
M3->Y:$FFC4,2,1 ; Machine Output 3
M4->Y:$FFC4,3,1 ; Machine Output 4
M5->Y:$FFC4,4,1 ; Machine Output 5
M6->Y:$FFC4,5,1 ; Machine Output 6
M7->Y:$FFC4,6,1 ; Machine Output 7
M8->Y:$FFC4,7,1 ; Machine Output 8
M9->Y:$FFC4,0,8,U ; Machine Outputs 1-8 treated as byte
M11->Y:$FFC3,0,1 ; Machine Input 1
M12->Y:$FFC3,1,1 ; Machine Input 2
M13->Y:$FFC3,2,1 ; Machine Input 3
M14->Y:$FFC3,3,1 ; Machine Input 4
M15->Y:$FFC3,4,1 ; Machine Input 5
M16->Y:$FFC3,5,1 ; Machine Input 6
M17->Y:$FFC3,6,1 ; Machine Input 7
M18->Y:$FFC3,7,1 ; Machine Input 8
M19->Y:$FFC3,0,8,U ; Machine Inputs 1-8 treated as byte
Thumbwheel Port Bits (Can be Used as General Purpose I/O)
(These definitions are valid for PMAC Mini PCI only)
M40->Y:$FFC2,0,1 ; SEL0 Output
M41->Y:$FFC2,1,1 ; SEL1 Output
M42->Y:$FFC2,2,1 ; SEL2 Output
M43->Y:$FFC2,3,1 ; SEL3 Output
M44->Y:$FFC2,4,1 ; SEL4 Output
M45->Y:$FFC2,5,1 ; SEL5 Output
M46->Y:$FFC2,6,1 ; SEL6 Output
M47->Y:$FFC2,7,1 ; SEL7 Output
M48->Y:$FFC2,0,8,U ; SEL0-7 Outputs treated as a byte
M50->Y:$FFC1,0,1 ; DAT0 Input
M51->Y:$FFC1,1,1 ; DAT1 Input
M52->Y:$FFC1,2,1 ; DAT2 Input
M53->Y:$FFC1,3,1 ; DAT3 Input
M54->Y:$FFC1,4,1 ; DAT4 Input
M55->Y:$FFC1,5,1 ; DAT5 Input
M56->Y:$FFC1,6,1 ; DAT6 Input
M57->Y:$FFC1,7,1 ; DAT7 Input
M58->Y:$FFC1,0,8,U ; DAT0-7 Inputs treated as a byte
Suggested I/O M-Variable Definitions
16
Page 23

PMAC-Mini PCI Hardware Reference Manual
Suggested I/O M-Variable Definitions 17
Page 24

PMAC Mini PCI Hardware Reference Manual
E-POINT JUMPER DESCRIPTIONS
E0: Reserved for Future Use
E-Point and
Location Description Default
Physical Layout
E0
F1
Reserved for future use No jumper
Warning:
The jumper setting must match the type of driver IC, or damage to the IC will result.
E1 - E2: Machine Output Supply Voltage Configure
E-Point and
Physical Layout
E1
E2
Note: E1 and E2 must number in the same direction.
Location Description Default
E1
E1
Jump pin 1 to 2 to apply +V (+5V to 24V) to pin 10
of U55 (should be ULN2803A for sink output
configuration) JOPTO Machine outputs M01-M08.
Jump pin 2 to 3 to apply GND to pin 10 of U55
(should be UDN2981A for source output
configuration).
Also see E2.
Jump pin 1 to 2 to apply GND to pin 9 of U55 (should
be ULN2803A for sink output configuration).
Jump pin 2 to 3 to apply +V (+5V to 24V) to pin 9 of
"U55" (should be UDN2981A for source output
configuration).
Also see E1.
installed
1-2 Jumper
installed
1-2 Jumper
installed
18 E-Point Jumper Descriptions
Page 25

PMAC-Mini PCI Hardware Reference Manual
E3 - E6: Servo Clock Frequency Control
The servo clock (which determines how often the servo loop is closed) is derived from the phase clock
(see E29 - E33A and E98) through a divide-by-N counter. Jumpers E3 through E6 control this dividing
function.
E3 E4 E5 E6 Servo Clock Frequency
Default and Physical Layout
E3 E4 E5 E6
ON ON ON ON = Phase Clock Divided by 1
OFF ON ON ON = Phase Clock Divided by 2
ON OFF ON ON = Phase Clock Divided by 3
OFF OFF ON ON = Phase Clock Divided by 4 Only E5 and E6 On
ON OFF ON ON = Phase Clock Divided by 5
OFF ON OFF ON = Phase Clock Divided by 6
ON OFF OFF ON = Phase Clock Divided by 7
OFF OFF OFF ON = Phase Clock Divided by 8
ON ON ON OFF = Phase Clock Divided by 9
OFF ON ON OFF = Phase Clock Divided by 10
ON OFF ON OFF = Phase Clock Divided by 11
OFF OFF ON OFF = Phase Clock Divided by 12
ON ON OFF OFF = Phase Clock Divided by 13
OFF ON OFF OFF = Phase Clock Divided by 14
ON OFF OFF OFF = Phase Clock Divided by 15
OFF OFF OFF OFF = Phase Clock Divided by 16
The setting of I-Variable I10 should be adjusted to match the servo interrupt cycle time set by E98, E3–E6, E29–
E33 and the master clock frequency. I10 holds the length of a servo interrupt cycle, scaled so that 8,388,608
equals one millisecond. Since I10 has a maximum value of 8,388,607, the servo interrupt cycle time should
always be less than a millisecond (unless the basic unit of time on PMAC should be something other than a
millisecond. To have a servo sample time for a motor greater than one millisecond, the sampling may be slowed
in software for that motor with variable Ix60.
Approximate servo frequency may be measured by typing successive RX0 commands in a PMAC terminal
window to read the servo cycle counter with the carriage return characters for the two commands hit exactly ten
seconds apart. To obtain the servo frequency in kHz, take the difference of the two responses and divide by
10,000.
E7: Machine Input Sourcing/Sinking Control
E-Point and
Physical Layout
E7
E-Point Jumper Descriptions 19
Location Description Default
F1
Jump pin 1 to 2 to apply +5V to input
reference resistor sip pack. This will bias MI1
to MI8 inputs to +5V for off state; input must
then be grounded for on state.
Jump pin 2 to 3 to apply GND to input
reference resistor sip pack. This will bias MI1
to MI8 inputs to GND for off state; input must
then be pulled up for on state (+5V to +24V)
1-2 Jumper installed
Page 26

PMAC Mini PCI Hardware Reference Manual
E8 – E10: Synchronizing PMAC
E-Point and
Location Description Default
Physical Layout
E8
E9
E10
Note: Jumpers E8 and E9 must have the same settings.
C1
C1
E1
Jump pin 1-2 for NULL modem connection
(DTR connects to DSR).
Jump pin 2-3 for differential Phase signal
(PHASE/).
Jump pin 1-2 for NULL modem connection
(DTR connects to DSR).
Jump pin 2-3 for differential Servo signal
(SERVO/).
Jump pin 1-2 to select to receive external
clocks CARD0.
E10A - E10C: Flash Firmware Bank Select
E-Point and
Physical Layout
E10A
E10B
E10C
Location Description Default
G2
G2
G2
Flash firmware bank, select jumper 1. No jumper installed
Flash firmware bank, select jumper 2. No jumper installed
Flash firmware bank, select jumper 3. No jumper installed
No jumper installed
No jumper installed
No jumper installed
E11-E14: Encoder Single Ended/Differential Select (Note: REV-103 and above)
E Point and
Physical Layout
E11
E12
E13
E14
Location Description Default
Jump pin 2 to 3 to obtain differential
1-2 Jumper installed
encoder input mode. This will bias
encoder negative inputs to VCC = 5V
Jump pin 1 to 2 to obtain non-differential
encoder input mode. This will bias
encoder negative inputs to 1/2 VCC =
2.5V
20 E-Point Jumper Descriptions
Page 27

PMAC-Mini PCI Hardware Reference Manual
E17A - E17D: Amplifier-Enable/Direction Polarity Control
E-Point and
Location Description Default
Physical Layout
E17A
E17B
E17C
E17D
Low-true enable is the fail-safe option with the default sinking (open-collector) ULN2803A output driver IC in
U44. If U44 is replaced with a UDN2981A sourcing driver IC (and E101 and E102 are changed), high-true
enable is the fail-safe option.
A3
A3
A3
A3
Jump 1-2 for high TRUE AENA1.
Remove jumper for low TRUE AENA1.
Jump 1-2 for high TRUE AENA2.
Remove jumper for low TRUE AENA2.
Jump 1-2 for high TRUE AENA3.
Remove jumper for low TRUE AENA3.
Jump 1-2 for high TRUE AENA4.
Remove jumper for low TRUE AENA4.
No jumper installed
No jumper installed
No jumper installed
No jumper installed
E19: Watchdog Disable
E-Point and
Physical Layout
E19
Location Description Default
F1
Jump pin 1 to 2 to disable Watchdog timer (for
test purposes only).
Remove jumper to enable Watchdog timer.
No jumper installed
E20 - E22: Flash Firmware Bank Select
E-Point and
Physical Layout
E20
E21
E22
Other combinations are for factory use only; the board will not operate in any other configuration
Location Description Default
G3
G3
G3
Power Up/Reset Load Source Jumper 1. No jumper installed
Power Up/Reset Load Source Jumper 2.
Install to read flash IC on power-up/ reset.
Power Up/Reset Load Source Jumper 3.
Install to read flash IC on power-up/ reset.
Jumper installed
Jumper installed
E23: Firmware Load
E-Point and
Physical Layout
E23
Location Description Default
G3
Remove jumper for normal operation.
Jump pin 1 to 2 to reload firmware through
serial or bus port.
No jumper installed
E-Point Jumper Descriptions 21
Page 28

PMAC Mini PCI Hardware Reference Manual
E29 - E33A: Phase Clock Frequency Control
E29 E30 E31 E32 E33 E33A Phase
Clock
Freq.
E98@1-2
ON OFF OFF OFF OFF OFF 2.26 kHz 1.13 kHz
OFF ON OFF OFF OFF OFF 4.52 kHz 2.26 kHz
OFF OFF ON OFF OFF OFF 9.04 kHz 4.52 kHz E31 ON
OFF OFF OFF ON OFF OFF 18.07 kHz 9.04 kHz
OFF OFF OFF OFF ON OFF 36.14 kHz 18.07 kHz
OFF OFF OFF OFF OFF ON 72.28 kHz 36.14 kHz
Jumpers E29 through E33A control the speed of the phase clock, and, indirectly, the servo clock, which is
divided down from the phase clock (see E3 - E6). No more than one of these six jumpers may be on at a time.
Phase
Clock
Freq.
E98@2-3
Default and Physical Layout
E33A E33 E32 E31 E30 E29
E34A - E37: Encoder Sampling Clock Frequency Control
E34A E34 E35 E36 E37 SCLK Clock Frequency
19.6608 MHz Master
Clock
ON OFF OFF OFF OFF 19.6608 MHz
OFF ON OFF OFF OFF 9.8304 MHz E34 On
OFF OFF ON OFF OFF 4.9152 MHz
OFF OFF OFF ON OFF 2.4576 MHz
OFF OFF OFF OFF ON 1.2288 MHz
Jumpers E34 - E37 control the encoder-sampling clock (SCLK) used by the gate array ICs. No more than one of
these five jumpers may be on at a time.
Default and Physical Layout
E34A E34 E35 E36 E37
22 E-Point Jumper Descriptions
Page 29

PMAC-Mini PCI Hardware Reference Manual
E44 - E47: Communications Control
Baud Rate Control
E Points
E44 E45
E46 E47 Standard CPU,
Baud Rate
40 MHz Flash
CPU (Opt 5A)
60 MHz
Flash CPU
(Opt 5B)
Default and Physical
Layout
E44 E45 E46 E47
ON ON ON ON Disabled Disabled
OFF ON ON ON 600 900
ON OFF ON ON 800* 1200
OFF OFF ON ON 1200 1800
ON ON OFF ON 1600* 2400
OFF ON OFF ON 2400 3600
ON OFF OFF ON 3200* 4800
OFF OFF OFF ON 4800 7200
ON ON ON OFF 6400* 9600 Opt 5B
OFF ON ON OFF 9600 14400 Standard, Opt 5A
ON OFF ON OFF 12800* 19200
OFF OFF ON OFF 19200 28800
ON ON OFF OFF 25600* 38400
OFF ON OFF OFF 38400 57600
ON OFF OFF OFF 51200* 76800
OFF OFF OFF OFF 76800 115200
Jumpers E44 - E47 control what baud rate is used for serial communications. Any character received over the
bus causes PMAC to use the bus for its standard communications. The serial port is disabled if E-points E44E47 are all on.
These jumpers are read only at power-up/reset to set the baud rate at that time. Currently, Flex CPU’s
communication baud rate is determined at power-up/reset by variable I54.
* Non-standard baud rate
E48: Reserved for future use
E-Point and
Physical Layout
E48
E-Point Jumper Descriptions 23
Location Description Default
E2
Reserved for future use No jumper installed
Page 30

PMAC Mini PCI Hardware Reference Manual
E49: Serial Communications Parity Control
E-Point and
Location Description Default
Physical Layout
E49
E2
Jump pin 1 to 2 for no serial parity; remove jumper for
odd serial parity.
E50: EAROM Save Enable/Disable
E-Point and
Physical Layout
E50
Location Description Default
E2
Jump pin 1 to 2 to enable save to EAROM or flash
memory; remove jumper to disable save to EAROM or
flash memory.
E51: Normal/Re-Initializing Power-Up
E-Point and
Physical Layout
E51
Location Description Default
E2
Jump pin 1 to 2 to re-initialize on power-up/reset;
remove jumper for normal power-up/reset.
Jumper installed
Jumper installed
No jumper
installed
24 E-Point Jumper Descriptions
Page 31

PMAC-Mini PCI Hardware Reference Manual
E85, E87, E88: Analog Power Source Configuration
E-Point and
Physical Layout
E85
E88
E87
E85
E87
E88
E87
E85
E88
E88
E87
E85
Location Description Default
E3
E3
E3
Jump pin 1 to pin 2 to allow analog +V to come from
digital side -- P1 or TB1 -- ties amplifier and PMAC
Mini PCI power supply together, defeats opto-isolation.
Remove jumper to keep analog +V separate from
digital +12V.
Note: If E85 is changed, E88 and E87 must also be
changed
Also see E90.
Jump pin 1 to pin 2 to tie analog common AGND to
digital common GND -- defeats opto-isolation.
Remove jumper to keep AGND and GND separate.
Note: If E87 is changed, E85 and E88 must also be
changed
Also see E90.
Jump pin 1 to pin 2 to allow analog -V to come from
digital side -- P1or TB1 – ties amplifier and PMAC
Mini PCI power supply together, defeats opto-isolation.
Remove jumper to keep analog -V separate from digital
-12V.
Note: If E88 is changed, E85 and E87 must also be
changed
Also see E90.
No jumper
No jumper
No jumper
E-Point Jumper Descriptions 25
Page 32

PMAC Mini PCI Hardware Reference Manual
E89: Amplifier-Supplied Switch Pull-Up Enable
E-Point and
Location Description Default
Physical Layout
E89
A1
Jump pin 1 to 2 to allow A+V on J8 (JAUX) pin 13, to
tie to A+15V on J11 (JMACH1) pin 59.
Remove jumper to permit separate voltage supply from
A+V for input flags (+12V to +24V for sinking drivers,
0V for sourcing drivers).
This jumper must be installed to allow A+15V to power
the OPTO switch sensor inputs (including limits) from
the same OPTO-power supply that powers the amplifier
output stage.
Also see E90.
E90: Host-Supplied Switch Pull-Up Enable
E-Point and
Physical Layout
E90
Location Description Default
A1
Jump pin 1 to 2 to allow A+V/FRET on J8 pin 13 and/or
J11 pin 59 (also see E89), to power OPTO switch sensor
inputs (including limits).
Jump pin 2 to 3 to allow +12V from DC bus connector P1pin B09 to power "OPTO" switch sensor inputs (including
limits). Optical isolation is then lost.
Also see E85, E87, E88 and PMAC opto-isolation
diagram.
Jumper
installed
1-2 Jumper
installed
E98: DAC/ADC Clock Frequency Control
E-Point and
Physical Layout
E98
Location Description Default
C2
Jump 1-2 to provide a 2.45 MHz DCLK signal to DACs
and ADCs. Jump 2-3 to provide a 1.23 MHz DCLK signal
to DACs and ADCs. Important for high accuracy A/D
conversion on Acc-28A boards.
Note: This also divides the phase and servo clock freq. in
half.
See E29-E33, E3-E6
1-2 Jumper
installed
26 E-Point Jumper Descriptions
Page 33

PMAC-Mini PCI Hardware Reference Manual
E101 - E102: Amplifier Enable Output Configure
E-Point and
Location Description Default
Physical Layout
E100
E101
E102
Note: E100, E101 and E102 must number in the same direction
B2
B2
B2
Jump pin 1 to 2 to apply A+15V from J11 pin 59 to pin 1 of
E101, pin 3 of E102, and FAULT input flag return. This
makes U44 AENA/ EQU / PULSE / DIR / FEFCO driver IC
work from analog A+15V supply.
Jump pin 2 to 3 to apply A+V (12-24V) from J8 pin 13 to pin
1 of E101, pin 3 of E102, and FAULT input flag return. This
makes U44 AENA/EQU/PULSE/DIR/FEFCO driver IC work
from separate A+V (12-24V) supply. (This cannot be used
when A+V is brought from digital side through E85.)
Jump pin 1 to 2 to apply A+15V/A+V (as set by E100) to pin
11 of U44 AENAn and EQUn driver IC (should be
ULN2803A for sink output configuration).
Jump pin 2 to 3 to apply GND to pin 11 of U44 (should be
UDN2981A for source output configuration).
Jump pin 1 to 2 to apply GND to pin 11 of U44 AENAn and
EQUn (should be ULN2803A for sink output configuration).
Jump pin 2 to 3 to apply A+15V/A+V (as set by E100) to pin
11 of U44 (should be UDN2981A for source output
configuration).
E110 - E115: V/F Converter Configuration
(Voltage-to-Frequency Converter Option [OPT 15] Required)
1-2 Jumper
installed
1-2 Jumper
installed
1-2 Jumper
installed
E-Point and
Physical Layout
E110
E111
E112
E113
E114
E115
Location Description Default
B1
B1
B1
B2
B2
B2
Jump pin 1 to 2 to tie DAC1 output to WIPER1 input (stepper
drive).
Remove jumper to keep lines separate.
Jump pin 1 to 2 to set 10kHz/V gain (100kHz max) on 1st V/F
converter.
Remove jumper to set 200kHz/V gain (2MHz max) on 1st V/F
converter.
Jump pin 1 to 2 to set 10kHz/V gain (100kHz max) on 1st V/F
converter.
Remove jumper to set 200kHz/V gain (2MHz max) on 1st V/F
converter.
Jump pin 1 to 2 to tie DAC2 output to WIPER2 input (stepper
drive).
Remove jumper to keep lines separate.
Jump pin 1 to 2 to set 10kHz/V gain (100kHz max) on 2nd
V/F converter.
Remove jumper to set 200kHz/V gain (2MHz max) on 2nd
V/F converter.
Jump pin 1 to 2 to set 10kHz/V gain (100kHz max) on 2nd
V/F converter.
Remove jumper to set 200kHz/V gain (2MHz max) on 2nd
V/F converter.
No jumper
installed
No jumper
installed
No jumper
installed
No jumper
installed
No jumper
installed
No jumper
installed
E-Point Jumper Descriptions 27
Page 34

PMAC Mini PCI Hardware Reference Manual
E116 - E119: V/F Converter Configuration
(Voltage-to-Frequency Converter Option [OPT 15] Required)
E-Point and
Location Description Default
Physical Layout
E116
E117
E118
E119
Note: For stepper Feedback install E116 and E119
A3
A3
A3
A3
Jump pin 1 to 2 to tie AENA1/DIR1 output to CHB3
input.
Remove jumper to keep lines separate.
Jump pin 1 to 2 to tie PULSE1 output to CHA3 input.
Remove jumper to keep lines separate.
Jump pin 1 to 2 to tie PULSE2 output to CHA4 input.
Remove jumper to keep lines separate.
Jump pin 1 to 2 to tie AENA2/DIR2 output to CHB4
input.
Remove jumper to keep lines separate.
No jumper
installed
No jumper
installed
No jumper
installed
No jumper
installed
28 E-Point Jumper Descriptions
Page 35

PMAC-Mini PCI Hardware Reference Manual
E-Point Jumper Descriptions 29
Page 36

PMAC Mini PCI Hardware Reference Manual
MATING CONNECTORS
This section lists several options for each connector. Choose an appropriate one for your application.
J1 (JDISP)/Display Port
1. Two 14-pin female flat cable connector Delta Tau P/N 014-R00F14-0K0 T&B Ansley P/N 609-1441
2. 171-14 T&B Ansley standard flat cable stranded 14-wire
3. Phoenix varioface modules type FLKM14 (male pins) P/N 22 81 02 1
J2 (JEXP)/Expansion
1. Two 50-pin female flat cable connector Delta Tau P/N 014-R00F50-0K0 T&B Ansley P/N 609-5041
2. 171-50 T&B Ansley standard flat cable stranded 50-wire
3. Phoenix varioface module type FLKM 50 (male pins) P/N 22 81 08 9 used for daisy chaining acc-14
I/0, -23 A and D connectors -24 expansion
J3 (JTHW)/Multiplexer Port
1. Two 26-pin female flat cable connector Delta Tau P/N 014-R00F26-0K0 T&B Ansley P/N 609-2641
2. 171-26 T&B Ansley standard flat cable stranded 26-wire
3. Phoenix varioface module type FLKM 26 (male pins) P/N 22 81 05 0
J4 (JRS232)/Serial Communications
1. Two 10-pin female flat cable connector Delta Tau P/N 014-R00F10-0K0 T&B Ansley P/N 609-1041
2. 171-10 T&B Ansley standard flat cable stranded 26-wire
3. Phoenix varioface module type FLKM 34 (male pins) P/N 22 81 06 3
J5 (JOPT)/OPTO I/O
1. Two 34-pin female flat cable connector Delta Tau P/N 014-R00F34-0K0 T&B Ansley P/N 609-3441
2. 171-34 T&B Ansley standard flat cable stranded 34 wire
3. Phoenix varioface module type FLKM 34 (male pins) P/N 22 81 06 3
J7 (JS1)/A-D Inputs 1-4
1. Two 16-pin female flat cable connector Delta Tau P/N 014-R00F16-0K0 T&B Ansley P/N 609-1641-16
2. 171-16 T&B Ansley standard flat cable stranded 16 wire
3. Phoenix varioface module type FLKM 16 (male pins) P/N 22 81 03 4
J8 (JAUX)/Auxiliary I/O
1. Two 14-pin female flat cable connector Delta Tau P/N 014-R00F14-0K0 T&B Ansley P/N 609-1641-14
2. 171-14 T&B Ansley standard flat cable stranded 14 wire
3. Phoenix varioface module type FLKM 14(male pins)
J11 (JMACH)/Machine Connector
1. Two 60-pin female flat cable connector Delta Tau P/N 014-R00F60-0K0 T&B Ansley P/N 609-6041
available as ACC 8P or 8D
2. 171-60 T&B Ansley standard flat cable stranded 60 wire
3. Phoenix varioface module type FLKM 60 (male pins) P/N 22 81 09 2
Note:
Normally, J11 is used with Acc-8P or 8D with Option P which provides complete
terminal strip fan-out of all connections.
TB1 (JPWR)
1. 4-pin terminal block, Phoenix Connector, MKDS41-3.5
30 Mating Connectors
Page 37

PMAC-Mini PCI Hardware Reference Manual
Mating Connectors 31
Page 38

PMAC Mini PCI Hardware Reference Manual
CONNECTOR PINOUTS
Headers
J1 JDISP (14-Pin Header)
Front View
Pin # Symbol Function Description Notes
1 Vdd Output +5V Power Power Supply Out
2 Vss Common PMAC Common
3 Rs Output Read Strobe TTL Signal Out
4 Vee Output Contrast Adjust. VEE 0 to +5VDC *
5 E Output Display Enable High is Enable
6 R/W Output Read or Write TTL Signal Out
7 DB1 Output Display Data 1
8 DB0 Output Display Data 0
9 DB3 Output Display Data 3
10 DB2 Output Display Data 2
11 DB5 Output Display Data 5
12 DB4 Output Display Data 4
13 DB7 Output Display Data 7
14 DB6 Output Display Data 6
The JDISP connector is used to drive the 2-line x 24-character (Acc-12), 2 x 40 (Acc-12A) LCD, or the 2 x 40
vacuum fluorescent (ACC. 12C) display unit. The DISPLAY command may be used to send messages and
values to the display.
See Also:
Program Commands; DISPLAY
Accessories; Acc-12, ACC16D
Memory Map; Y:$0780 - $07D1
Note: There is no J2 (JPAN) control panel connector on PMAC Mini PCI.
* Controlled by potentiometer R57
32 Connector Pinouts
Page 39

PMAC-Mini PCI Hardware Reference Manual
J3 JTHW (26-Pin Header)
Front View
Pin # Symbol Function Description Notes
1 GND Common PMAC Common
2 GND Common PMAC Common
3 DAT0 Input Data-0 Input Data Input from Thumbwheel Switches
4 SEL0 Output Select-0 Output Scanner Output for reading TW Switches
5 DAT1 Input Data-1 Input Data Input from Thumbwheel Switches
6 SEL1 Output Select-1 Output Scanner Output for reading TW Switches
7 DAT2 Input Data-2 Input Data Input from Thumbwheel Switches
8 SEL2 Output Select-2 Output Scanner Output for reading TW Switches
9 DAT3 Input Data-3 Input Data Input from Thumbwheel Switches
10 SEL3 Output Select-3 Output Scanner Output for reading TW Switches
11 DAT4 Input Data-4 Input Data Input from Thumbwheel Switches
12 SEL4 Output Select-4 Output Scanner Output for reading TW Switches
13 DAT5 Input Data-5 Input Data Input from Thumbwheel Switches
14 SEL5 Output Select-5 Output Scanner Output for reading TW Switches
15 DAT6 Input Data-6 Input Data Input from Thumbwheel Switches
16 SEL6 Output Select-6 Output Scanner Output for reading TW Switches
17 DAT7 Input Data-7 Input Data Input from Thumbwheel Switches
18 SEL7 Output Select-7 Output Scanner Output for reading TW Switches
19 N.C. N.C. No Connection
20 GND Common PMAC Common
21 BFLD/ N.C. No Connection
22 GND Common PMAC Common
23 IPLD/ N.C. No Connection
24 GND Common PMAC Common
25 +5V Output +5VDC Supply Power Supply Out
26 INIT/ Input PMAC Reset Low is Reset
The JTHW multiplexer port provides eight inputs and eight outputs at TTL levels. While these I/O can be used
in un-multiplexed form for 16 discrete I/O points, most will utilize PMAC software and accessories to use this
port in multiplexed form to multiply the number of I/O that can be accessed on this port. In multiplexed form,
some of the SELn outputs are used to select which of the multiplexed I/O are to be accessed.
See also:
I/O and Memory Map Y:$FFC1, Y:$FFC2
Suggested M-variables M40 - M58
M-variable formats TWB, TWD, TWR, TWS
Acc-8D Opt 7, Acc-8D Opt 9, Acc-18, Acc-34x, NC Control Panel
Connector Pinouts 33
Page 40

PMAC Mini PCI Hardware Reference Manual
J4 JRS232 (10-Pin Header)
Front View
Pin # Symbol Function Description Notes
1 PHASE+ Bidirectional Receive/Transmit Phase Clock. Check Jumpers E10, E8 and E9
2 PHASE-
Bidirectional Data Term Ready Tied to DSR
or DTR
3 TXD/ Input Receive Data Host Transmit Data
4 CTS Input Clear to Send Host Ready Bit
5 RXD/ Output Send Data Host Receive Data
6 RTS Output Request to Send PMAC Ready Bit
7 SERVO-
Bidirectional Data set Ready Tied to DTR
or DSR
8 SERVO+ Bidirectional Receive/Transmit Servo Clock. Check Jumpers E10, E8 and E9
9 GND Common PMAC Common
10 +5V Output +5VDC Supply Power Supply Out
The JRS232 connector provides the PMAC Mini PCI with the ability to communicate serially with an RS232 port.
This connector can be used for daisychain interconnection of multiple PMACs. Check E10.
See Also: Serial Communications
J5 JOPT (34-Pin Connector)
Front View
Pin # Symbol Function Description Notes
1 MI8 Input Machine Input 8 Low is true
2 GND Common PMAC Common
3 MI7 Input Machine Input 7 Low is true
4 GND Common PMAC Common
5 MI6 Input Machine Input 6 Low is true
6 GND Common PMAC Common
7 MI5 Input Machine Input 5 Low is true
8 GND Common PMAC Common
9 MI4 Input Machine Input 4 Low is true
10 GND Common PMAC Common
11 MI3 Input Machine Input 3 Low is true
12 GND Common PMAC Common
13 MI2 Input Machine Input 2 Low is true
14 GND Common PMAC Common
15 MI1 Input Machine Input 1 Low is true
16 GND Common PMAC Common
17 MO8 Output Machine Output 8 If Sinking Out Low True; If Source Out High True
18 GND Common PMAC Common
19 MO7 Output Machine Output 7 If Sinking Out Low True; If Source Out High True
20 GND Common PMAC Common
21 MO6 Output Machine Output 6 If Sinking Out Low True; If Source Out High True
22 GND Common PMAC Common
23 MO5 Output Machine Output 5 If Sinking Out Low True; If Source Out High True
24 GND Common PMAC Common
25 MO4 Output Machine Output 4 If Sinking Out Low True; If Source Out High True
26 GND Common PMAC Common
34 Connector Pinouts
Page 41

PMAC-Mini PCI Hardware Reference Manual
J5 JOPT (34-Pin Connector)
Continued
Front View
Pin # Symbol Function Description Notes
27 MO3 Output Machine Output 3 If Sinking Out Low True; If Source Out High True
28 GND Common PMAC Common
29 MO2 Output Machine Output 2 If Sinking Out Low True; If Source Out High True
30 GND Common PMAC Common
31 MO1 Output Machine Output 1 If Sinking Out Low True; If Source Out High True
32 GND Common PMAC Common
33 +V I/O +V Power I/O +V = +5V TO +24V
+5V Out from PMAC, +5 to +24V in from
External Source, Diode Isolation from PMAC
34 GND Common PMAC Common
This connector provides means for eight general-purpose inputs and eight general-purpose outputs. Inputs and
outputs may be configured to accept or provide either +5V or +24V signals. Outputs can be made sourcing with
an IC (U55 to UDN2981) and jumper (E1 and E2) change. E7 controls whether the inputs are pulled up or down
internally. Outputs are rated to 100mA per line.
J7 JS1 (16- Pin Header)
Front View
Pin # Symbol Function Description Notes
1 DCLK Output D to A, A to D Clock DAC and ADC Clock for Chan. 1, 2, 3, 4
2 DATA+ Output D to A Data DAC Data for Chan. 1, 2, 3, 4
3 ASEL0/ Output Chan. Select Bit 0 Select for Chan. 1, 2, 3, 4
4 ASEL1/ Output Chan. Select Bit 1 Select for Chan. 1, 2, 3, 4
5 CNVRT Output A to D Convert ADC Convert Sig. Chan. 1, 2, 3, 4
6 ADCIN Input A to D Data ADC Data for Chan. 1, 2, 3, 4
7 OUT1/ Output Amp. Enable/Dir. Jumper-Set Polarity (E17A)
8 OUT2/ Output Amp. Enable/Dir. Jumper-Set Polarity (E17B)
9 OUT3/ Output Amp. Enable/Dir. Jumper-Set Polarity (E17C)
10 OUT4/ Output Amp. Enable/Dir. Jumper-Set Polarity (E17D)
11 AFLT1+ Input Amp. Fault Input Programmable Polarity (Ix25)
12 AFLT2+ Input Amp. Fault Input Programmable Polarity (Ix25)
13 AFLT3+ Input Amp. Fault Input Programmable Polarity (Ix25)
14 AFLT4+ Input Amp. Fault Input Programmable Polarity (Ix25)
15 +5V Output +5V Supply Power Supply Out
16 GND Common PMAC Common
This connector is used to communicate with an Acc-28 A/D converter board. It can be used also to build a digital
amplifier interface. All signals are referenced to the digital common GND.
Connector Pinouts 35
Page 42

PMAC Mini PCI Hardware Reference Manual
J8 JAUX (14-Pin Header)
Front View
Pin # Symbol Function Description Notes
1 WIPER1 Input 0-10V Analog Input 1, 2
2 WIPER2 Input 0-10V Analog Input 1, 2
3 AGND Common Analog/Flag Common
4 AGND Common Analog/Flag Common
5 EQU1/ Output Enc. 1 Position Compare 3
6 EQU2/ Output Enc. 2 Position Compare 3
7 AENA1/
DIR1
8 AENA2/
DIR2
9 PULSE1 Output Chan. 1 Pulse Command 1,3
10 PULSE2 Output Chan. 2 Pulse Command 1,3
11 FEFCO/ Output Watchdog Output 3
12 AGND Common Analog/Flag Common
13 A+V/FRET Input Flag Supply Volt 6
14 A-15V I/O Analog Minus Supply
This connector provides auxiliary signals for the PMAC Mini PCI, including analog inputs, position compare
outputs, pulse-and-direction outputs, and a flag supply/return voltage. All signals are referenced to AGND,
isolated from the 5V digital circuitry.
Notes:
1. Requires Option 15 V/F Converters be installed to use.
2. WIPER1 is tied to DAC1 if jumper E110 is installed; WIPER2 is tied to DAC2 if jumper E113 is installed.
3. Open-collector sinking output in standard configuration (ULN2803A in U44); Can be replaced with sourcing
driver (UDN2981A) in U44 socket; 100 mA per point sinking/sourcing capability.
4. Function of this signal determined by Ix02 and Ix25.
5. Can be tied to Encoder 3 or 4 feedback with jumpers (see E111, E112, E114, E115).
6. With jumper E89 ON, tied to A+15V from J11 pin 59; with E89 OFF and E90 at 1-2, can be separate +12V to
+24V for input flags (HMFLn, PLIMn, MLIMn) with sinking drivers, or 0V for input flags with sourcing
drivers.
Output Amp. 1 Enable/Direction 3,4,5
Output Amp. 2 Enable/Direction 3,4,5
36 Connector Pinouts
Page 43

PMAC-Mini PCI Hardware Reference Manual
J11 JMACH (60-Pin Header)
Pin # Symbol Function Description Notes
1 +5V Output +5V Power For Encoders, 1
2 +5V Output +5V Power For Encoders, 1
3 GND Common Digital Common
4 GND Common Digital Common
5 CHC3 Input Encoder C Ch. Pos. 2
6 CHC4 Input Encoder C Ch. Pos. 2
7 CHC3/ Input Encoder C Ch. Neg. 2,3
8 CHC4/ Input Encoder C Ch. Neg. 2,3
9 CHB3 Input Encoder B Ch. Pos. 2
10 CHB4 Input Encoder B Ch. Pos. 2
11 CHB3/ Input Encoder B Ch. Neg. 2,3
12 CHB4/ Input Encoder B Ch. Neg. 2,3
13 CHA3 Input Encoder A Ch. Pos. 2
14 CHA4 Input Encoder A Ch. Pos. 2
15 CHA3/ Input Encoder A Ch. Neg. 2,3
16 CHA4/ Input Encoder A Ch. Neg. 2,3
17 CHC1 Input Encoder C Ch. Pos. 2
18 CHC2 Input Encoder C Ch. Pos. 2
19 CHC1/ Input Encoder C Ch. Neg. 2,3
20 CHC2/ Input Encoder C Ch. Neg. 2,3
21 CHB1 Input Encoder B Ch. Pos. 2
22 CHB2 Input Encoder B Ch. Pos. 2
23 CHB1/ Input Encoder B Ch. Neg. 2,3
24 CHB2/ Input Encoder B Ch. Neg. 2,3
25 CHA1 Input Encoder A Ch. Pos. 2
26 CHA2 Input Encoder A Ch. Pos. 2
27 CHA1/ Input Encoder A Ch. Neg. 2,3
28 CHA2/ Input Encoder A Ch. Neg. 2,3
29 N.C. No Connect
30 N.C. No Connect
31 N.C. No Connect
32 N.C. No Connect
33 EQU1/ Output Position Compare 1 6
34 EQU2/ Output Position Compare 2 6
35 N.C. No Connect
36 N.C. No Connect
37 N.C. No Connect
38 N.C. No Connect
39 N.C. No Connect
40 N.C. No Connect
41 N.C. No Connect
42 N.C. No Connect
43 DAC1 Output Ana. Out Pos. 1 4,11
44 DAC2 Output Ana. Out Pos. 2 4,11
Connector Pinouts 37
Page 44

PMAC Mini PCI Hardware Reference Manual
J11 JMACH (60-Pin Header)
-Continued
Pin # Symbol Function Description Notes
45 DAC1/ Output Ana. Out Neg. 1 4,5
46 DAC2/ Output Ana. Out Neg. 2 4,5
47 AENA1/DIR1 Output Amp.-Ena/Dir. 1 6
48 AENA2/DIR2 Output Amp.-Ena/Dir. 2 6
49 FAULT1 Input Amp.-Fault 1 7
50 FAULT2 Input Amp.-Fault 2 7
51 MLIM1 Input Neg. End Limit 1 8,9
52 MLIM2 Input Neg. End Limit 2 8,9
53 PLIM1 Input Pos. End Limit 1 8,9
54 PLIM2 Input Pos. End Limit 2 8,9
55 HMFL1 Input Home-Flag 1 10
56 HMFL2 Input Home-Flag 2 10
57 FEFCO/ Output Watchdog Out Indicator/Driver
58 AGND Input Analog Common
59 A+15V/OPT+V Input Analog +15V Supply
60 A-15V Input Analog -15V Supply
The J11 connector is used to connect PMAC to the servo amps, flags, and encoders.
Notes:
1. In standalone applications, these lines can be used as +5V power supply inputs to power PMAC’s digital
circuitry. However, if a terminal block is available on the version of PMAC, bring the +5V power in
through the terminal block.
2. Referenced to digital common (GND). Maximum of + 12V permitted between this signal and its
complement.
3. If not used, leave this input floating (i.e. digital single-ended encoders).
4. + 10V, 10mA max, referenced to analog common (AGND).
5. Leave floating if not used; do not tie to AGND. In this case, AGND is the return line.
6. Functional polarity controlled by jumper E17. Sinking/sourcing nature of output control by IC type in U44
socket (default sinking) and E101/E102 configuration. Choice between AENA and DIR use controlled by
Ix02 and Ix25.
7. Functional polarity controlled by variable Ix25. Must be conducting to AGND (sinking driver) to produce a
0 in PMAC software. Pull-up is to A+15V or A+V (12-24V) as determined by E100. Automatic fault
function can be disabled with Ix25.
8. Pins marked PLIMn should be connected to switches at the positive end of travel. Pins marked MLIMn
should be connected to switches at the negative end of travel.
9. Must be conducting to 0V (usually AGND) for PMAC to consider itself not into this limit. Automatic limit
function can be disabled with Ix25.
10. Functional polarity for homing or other trigger use of HMFLn controlled by Encoder/Flag Variable 2 (I902,
I907, etc.) HMFLn selected for trigger by Encoder/Flag Variable 3 (I903, I908, etc.). Must be conducting to
0V (usually AGND) to produce a 0 in PMAC software.
11. If DAC calibration is needed, R37 is for offset DAC1, and R41 is for offset DAC2.
38 Connector Pinouts
Page 45

PMAC-Mini PCI Hardware Reference Manual
Terminal Block
TB1 (JPWR) (4-Pin Terminal Block)
Pin # Symbol Function Description Notes
1 GND Common Digital Ground
2 +5V Input +5V Supply Reference to digital ground
3 +12V Input +12V to +15V Supply Reference to digital ground
4 -12V Input -12V to -15V Supply Reference to digital ground
This terminal block may be used as an alternative power supply connector if PMAC Lite is not installed in a PCbus. The +5V powers the digital electronics. If jumpers E85, E87, and E88 are installed, the +12V and -12V
power the analog output stage (this defeats the optical isolation on PMAC).
To keep the optical isolation between the digital and analog circuits on PMAC, provide analog power (+/-12V to
+/-15V and AGND) through the JMACH connector, instead of the bus connector or this terminal block.
Connector Pinouts 39
Page 46

PMAC-Mini PCI Hardware Reference Manual
Jumpers and Connectors Layout
40
JUMPERS AND CONNECTORS LAYOUT
E1
D1
E7
D1
E30
E2
E35
D2
E46
C1
E66
E2
E85
F3
E92
E2
E104
A3
E114
E1
E2
D1
E17A
F2
E31
E2
E36
D2
E47
C1
E67
E2
E87
F3
E98
D2
E105
A3
E115
E1
E3
D3
E17B
F2
E32
E2
E37
D2
E48
C1
E68
E2
E88
G3
E100
G1
E110
F1
E116
G2
E4
D3
E17C
F2
E33
E2
E39
A3
E49
C1
E69
E2
E89
G1
E101
F1
E111
F1
E117
G2
E5
D3
E17D
F2
E33A
E2
E44
C1
E50
C1
E70
E2
E90
G1
E102
F1
E112
F1
E118
G2
E6
D3
E29
E2
E34A
D2
E45
C1
E51
C1
E71
E2
E91
E2
E103
A1
E113
E1
E119
G2
E34
D2
Page 47

PMAC-Mini PCI Hardware Reference
Jumpers and Connectors Layout
41
Page 48

Mini PMAC Hardware Reference Manual
42 Schematics
SCHEMATICS
BD13_A
I/O30
I/O09
MI7
BA07_A
BD06_A
I/O02
SEL5
I/O06
optionally stuff zero ohm resistors or 74aca16245
SEL4
BD06_A
CE2 0.1 mfd
DSR
I/O43
RP44
3.3KSIP10C
12
3456789 10
MO8
SER
DAT4
PA4
C136
0.1 mfd
DAT3
OF THE `RS232' I/O SECTION.
MO4
BA02_A
BA01_A
MI2
BRD_A-
BD17_A
I/O33
I/O19
MI2
MO7
SEL7
+
C133
4.7 mfd tant
RP45
3.3KSIP10C
12
3456789 10
DAT0
25mill ETCH
I/O07
SC01
R73 220
PHASE
BD07_A
RP48
1KSIP10C
12
3456789 10
BD10_A
I/O19
CS00-
MO1
E1
SEL1
I/O20
IOG_INT-
PA6
PA3
E45
GND
BD07_A
BD14_A
E6
I/O41
BD15_A
CE4 0.1 mfd
M2
SAME DIRECTION
+5V
MI2
MI1
I/O05
RP53
3.3KSIP10C
12
3456789 10
F1
2AMP_FUSE
TXD-
DB5
MI5
SHOULD BE
GND
+5V
I/O37
I/O04
BD12_A
E
+5V
ENA422
DAT6
BD05_A
RP55 0ohmSIP8I
12
34
56
78
(USB CONN)
I/O22
MI7
GND
TO PROVIDE `ESD' PROTECTION
MI3
I/O02
N.C.
+5V
BD03_A
BD16_A
E4
E46
DB1
DAT4
PHA
I/O38
I/O11
E2
SEL4
MI8
I/O41
DAT1
BA03_A
GND
I/O14
BD13_A
J1
I/O32
I/O12
3
GND
DAT5
BX/Y_A
CE5 0.1 mfd
(JDISP)
DAT5
CTS
I/O36
I/O27
MI4
BD09_A
SERVO
E2
MI8
25mill ETCH
I/O07
DAT0
RP57 0ohmSIP8I
12
34
56
78
J3
HEADER 26
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
RP56 0ohmSIP8I
12
34
56
78
RP52
10KSIP8I
1 2
3 4
5 6
7 8
U55
ULN2803A
OR
UDN2981A
(DIP18)
(IN SOCKET)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9 10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
IN1
IN2
IN3
IN4
IN5
IN6
IN7
IN8
GND V+
OUT8/
OUT7/
OUT6/
OUT5/
OUT4/
OUT3/
OUT2/
OUT1/
(JTHW)
I/O23
MO4
BD00_A
RP47
1KSIP10C
12
3456789 10
J4
+5V
E5
R72 220
E1
DAT2
I/O10
E49
E51
BD04_A
BD22_A
BD15_A
BD11_A
SEL3
GND
DAT7
PHASE
E48
THIS PART MUST BE `MAX202ECWE'
MO6
E2
RXD
MI6
I/O18
I/O17
MO1
O
SERVO
PWR_GUD-
BD04_A
Vss
BD00_A
BD20_A
E7
I/O20
BD03_A
U51
74ac16245DL
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
2425
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
1dir
1b1
1b2
gnd
1b3
1b4
vcc
1b5
1b6
gnd
1b7
1b8
2b1
2b2
gnd
2b3
2b4
vcc
2b5
2b6
gnd
2b7
2b8
2dir2oe-
2a8
2a7
gnd
2a6
2a5
vcc
2a4
2a3
gnd
2a2
2a1
1a8
1a7
gnd
1a6
1a5
vcc
1a4
1a3
gnd
1a2
1a1
ioe-
U53
74AC540
(SOL20)
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
1
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
A7
A8
G1
G2
Y1
Y2
Y3
Y4
Y5
Y6
Y7
Y8
E3
INIT-
2
O
SEL0
I/O03
MI1
MO7
C156
0.1 mfd
DAT1
I/O15
MO3
MO8
BD00_A
C41
.1UF
O
GND
+5V
INIT-
SEL7
BD20_A
E44
E47
DTR
I/O06
I/O13
E46
R/W
+5V
MO4
I/O29
BA02_A
RP51
10KSIP8I
1 2
3 4
5 6
7 8
DB0
BA05_A
TXD
I/O28
I/O05
CE1 0.1 mfd
DB4
GND
O
GND
E45
I/O17
MI3
I/O00
E2
2
3
1
MO5
25mill ETCH
I/O03
MO3
I/O46
BD21_A
MO5
I/O15
I/O44
C134
0.1 mfd
RESET
J1
HEADER 14
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
FOR CE CERTIFICATION ONLY
PA5
I/O42
SEL5
I/O34
MO2
DO NOT INSTALL
GND
MI7
C140
0.1 mfd
SEL0
GND
1
BD09_A
BD18_A
MO1
BWR_A-
BD22_A
C42
.1UF
`E-POINTS' SHOULD BE IN ORDER AS SHOWN
+V
RESET
MO7
BD14_A
E48
E1
2
3
1
CE3 0.1 mfd
I/O11
I/O08
E
+5V
E46
RP50
3.3KSIP10C
12
3456789 10
U61
LTC1384CS
(SOL18)
3
2
4
12
13
11
10
17
7
5
6
15
14
8
9
16
1 18
+V
C1+
C1-
TXD
RXD
RTS
CTS
VCC
V-
C2+
C2-
TXD
RXD
RTS
CTS
VSS
RXEN TXEN
R57
5K POT
CW
DAT6
MI1
BD06_A
I/O08
J4
HEADER 10
(BOX)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
Vee
NOTE:
DAT3
E1
SEL1
MO5
SEL2
GND
GND
I/O42
I/O16
I/O21
SEL3
I/O43
RP54
3.3KSIP10C
(SIP SOCKET)
1 2
3456789
10
MI4
+5V
BA10_A
BD12_A
CEL-
I/O16
PA0
PA1
+5V
RS
M5
E44
HEADER 34
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
MO2
+5V
BA11_A
BD21_A
E49
D24
MBRS140T3
I/O00
PWR_GUD-
E45
C147
0.1 mfd
SHOULD BE
BA09_A
DAT5
DAT0
BFLD-
I/O04
U49
74ac16245DL
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
2425
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
1dir
1b1
1b2
gnd
1b3
1b4
vcc
1b5
1b6
gnd
1b7
1b8
2b1
2b2
gnd
2b3
2b4
vcc
2b5
2b6
gnd
2b7
2b8
2dir2oe-
2a8
2a7
gnd
2a6
2a5
vcc
2a4
2a3
gnd
2a2
2a1
1a8
1a7
gnd
1a6
1a5
vcc
1a4
1a3
gnd
1a2
1a1
ioe-
3
I/O22
BD03_A
BD04_A
I/O13
SEL6
MI8
DB3
I/O24
MO8
MI6
C135
0.1 mfd
DB7
GND
RESET-
SEL6
MO6
DAT7
GND
SHOULD BE
GND
RTS
INIT-
MO6
RESET-
GND
PA2
M3
C142
0.1 mfd
CHGND
BA00_A
BA06_A
CTS-
I/O09
I/O47
E9
2 1
E50
BA08_A
CEL-
BD19_A
BD05_A
DAT4
BD19_A
RXD
MI2
E47
C143
0.1 mfd
Vdd
E7
OEL-
SEL6
J3
MI4
BD10_A
GND
BA00_A
BD17_A
C150
0.1 mfd
GND
I/O31
GND
SEL5
I/O12
E51
DAT7
SEL1
C40
.1UF
U50
IOGATE (PLCC84)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42 43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
VSS
IO36
IO37
IO38
IO39
E5
IO40
IO41
IO42
IO43
VSS
IO44
IO45
IO46
IO47
E6
E7
D0
D1
D2
VDD
VSS
D3
D4
D5
D6
D7
RD
CS
WR
A0
VSS
A1
A2
RESET
INT
E0
IO0
IO1
IO2
IO3
VDD VSS
IO4
IO5
IO6
IO7
E1
IO8
IO9
IO10
IO11
VSS
IO12
IO13
IO14
IO15
E2
IO16
IO17
IO18
IO19
TEST
VSS
IO20
IO21
IO22
IO23
E3
IO24
IO25
IO26
IO27
VSS
IO28
IO29
IO30
IO31
E4
IO32
IO33
IO34
IO35
VDD
E1 AND E2
I/O18
PA7
E0
O
SC01
M1
E7
2
3
1
GND
I/O26
I/O23
BD18_A
BD02_A
RS
IPLD-
OEL-
BD11_A
I/O25
I/O10
R/W
GND
(JOPT)
J5
BD01_A
BD01_A
I/O01
CTS-
RP49
1KSIP10C
12
3456789 10
E47
1
(JRS232)
BA04_A
DAT6
MO2
E44
C39
.1UF
RXD-
I/O40
MI6
BD07_A
SEL2
MI5
C153
0.1 mfd
O
BD08_A
BD23_A
MI5
U62
SN75240PW
1
2
3
4 5
6
7
8
GND
C
GND
D GND
B
GND
A
MI1
E8
2 1
U54
NC7SZ00M5
(SOT23-5)
1
2
4
53
DB2
BD02_A
BD23_A
DB6
GND
-
gate arrays and i/o
DELTA TAU DATA SYSTEMS, Inc.
C
46Wednesday, November 27, 2002
603712-320
Title
Size Document Number Rev
Date: Sheet
of
I/O21
BD02_A
BD05_A
BA01_A
E50
MO3
+5V
BD01_A
RP46
1KSIP10C
12
3456789 10
2
+5V
CS00-
SEL0
DAT3
BD16_A
SEL7
+5V
SEL4
C38
.1UF
I/O39
MI3
SEL3
I/O01
C141
0.1 mfd
BD08_A
DAT2
GND
SEL2
I/O45
DAT1
NOTE:
I/O35
DAT2
MUST NUMBER IN THE
I/O14
GND
Page 49

PMAC-Mini PCI Hardware Reference
Schematics 43
+5V
BD15_B
BD22_A
C48
0.1 mfd
+5V
D3
CS00-
D2
PA17
D20
BRD_B-
BD22_B
D22
BA13
BRD-
D3
BA04_B
A8
BD17_A
A9
D16
BD23_A
BA12_B
BD00_B
DATA SYSTEMS INC. AND IS LOANED SUBJECT TO RETURN UPON
BA04
BA08
BD05_B
+5V
D1
D19
BD00_A
BD07_A
BD17_A D17
BA04_B
E10A
-
mini - PMAC1 MEMORY,I/O
Delta Tau Data Systems, Inc.
C
26Tuesday, May 07, 2002
603712-320
Title
Size Document Number Rev
Date: Sheet
of
PA20
BA14
IOCS_A-
D13
BA12
D7
IOCS_A-
BD10_A
D0
RESET-
BD01_B
BD17_B
TRANSFERRED FOR ANY REASON. THIS DOCUMENT IS TO BE USED
+3P3V
BA15
A13
BA10
BD05_A
+5V
GND
A8
D4
D17
BA01
INVENTIONS ARE RESERVED BY DELTA TAU DATA SYSTEMS INC.
A4
D4
BD17_A
BA04
A16
BA03_B
A6
BD03_A
CS10-
BD10_A
BD13_A
BA00
BX/Y_B
POSSESSION OF THIS DOCUMENT INDICATES ACCEPTANCE OF THE
BD16_A
PA21
A15
BD18_A
D5
BD11_A
BA01_B
BA02_A
OF DELTA TAU DATA SYSTEMS INC. ALL RIGHTS TO DESIGNS AND
D0
D16
D13
CS3-
D5
WAIT2-
BA04_A
D12
D19
BD03_B
D8
D14
A7
A2
BD09_B
BA13_B
J2
HEADER 25X2
12
34
56
78
910
11 12
13 14
15 16
17 18
19 20
21 22
23 24
25 26
27 28
29 30
31 32
33 34
35 36
37 38
39 40
41 42
43 44
45 46
47 48
49 50
A5
BRD-
BD22_A
BD08_B
U13
E28F320J3A
(TSOP56)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28 29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
A22
CE1A21
A20
A19
A18
A17
A16
VCC
A15
A14
A13
A12
CE0
VPEN
RPA11
A10
A09
A08
GND
A07
A06
A05
A04
A03
A02
A01 CE2
A23
BYTE-
A00
DQ0
DQ8
DQ1
DQ9
VCC
DQ2
DQ10
DQ3
DQ11
GND
VCCQ
DQ4
DQ12
DQ5
DQ13
GND
DQ6
DQ14
DQ7
DQ15
STS
OE-
WE-
A24_WP
A14
D0
BD23_B
BA12_B
FLASHCS-
BD12_A BD13_A
C49
0.1 mfd
D23
BD03_A
BWR_B-
BD12_B
W1
SOLDER
JUMPER
2
3
1
BA09
BA01_A
D7
+3P3V/+5V
BA06
BD20_A
BA13_B
A16
BA15
BD02_A
BA00_A
SER_B
SER_B
CS14-
A4
D10
INVENTIONS ARE RESERVED BY DELTA TAU DATA SYSTEMS INC.
A5
BA08
ONLY PURSUANT TO WRITTEN LICENSE OR WRITTEN INSTRUCTIONS
BA03
LA13
BD06_A
D1
BD12_B
D20
BA03
THIS DOCUMENT IS THE CONFIDENTIAL PROPERTY OF DELTA TAU
CS14-
BWR-
D6
BD14_B
BA02
BD02_B
BD17_B
D23
+3p3V
RESET-
D8
BD06_A
D10
BD20_A
`W1'= 2 TO 3 FOR 28F320J5A
D13
BWR-
BD16_B
D12
BD21_A
BA03
BD03_B
BA00
D2
PA19
BD12_A
BA05
BD08_B
BD16_A
BD18_A
LA12
BD04_A
PA16
RESET_B
D7
BD19_A
A0
A14
D19
DPRCS-
PHA_B
ONLY PURSUANT TO WRITTEN LICENSE OR WRITTEN INSTRUCTIONS
+3P3V
D21
D1
D2
BD14_A
BD20_B
C46
0.1 mfd
C51
0.1 mfd
+3P3V
D2
D21
CS16-
A19X/YP
D5
BA13
BA10
BA02_B
BX/Y_B
C50
0.1 mfd
E10B
A1
BA07
BD18_B
D18
U16
IDT74FCT164245TPA
(TSSOP48)
2
3
5
6
8
9
11
12
46
44
43
41
40
38
37
36
1
4
7
10
47
48
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
2425
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
39
42
45
B0
B1
B2
B3
B4
B5
B6
B7
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
A7
A8
T/R1
GND
VCCB
GND
A0
OE1
B8
B9
GND
B10
B11
VCCB
B12
B13
GND
B14
B15
T/R2
OE2
A15
A14
GND
A13
A12
VCCA
A11
A10
GND
A9
GND
VCCA
GND
DATA SYSTEMS INC. AND IS LOANED SUBJECT TO RETURN UPON
FLASHCS-
CS2-
BD02_B
BA12
BRD-
BD15_A
BA00_B
C178
0.1 mfd
BD19_B
*NETLIST CHANGE*
+5V
D17
D9
BA05
BA11
D21
BPHA
BD04_B
A1
BPHA
BA04
BD09_A
D15
BA02
E10B
ABOVE AGREEMENT.
D18
D11
D4
D8
BD10_A
POSSESSION OF THIS DOCUMENT INDICATES ACCEPTANCE OF THE
D15
PA18
BD08_A
D8
C45
0.1 mfd
A11
BA03_A
BA04_A
BD04_A
BD16_A
LA13
BA10
BD00_A
D14 D14
CS06-
D19
U17
IDT74FCT164245TPA
(TSSOP48)
2
3
5
6
8
9
11
12
46
44
43
41
40
38
37
36
1
4
7
10
47
48
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
2425
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
39
42
45
B0
B1
B2
B3
B4
B5
B6
B7
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
A7
A8
T/R1
GND
VCCB
GND
A0
OE1
B8
B9
GND
B10
B11
VCCB
B12
B13
GND
B14
B15
T/R2
OE2
A15
A14
GND
A13
A12
VCCA
A11
A10
GND
A9
GND
VCCA
GND
PA21
+5V
D6
BA09
IOCS_B-
BA00_B
PHA_B
ABOVE AGREEMENT.
+3P3V
BA14
BA01
BA01
D7
D13
BD22_B
THIS DOCUMENT IS THE CONFIDENTIAL PROPERTY OF DELTA TAU
BA00_A
A17
BD05_A
D9
D11
CS2-
A12
D3
BD19_A
BD21_B
BA04
BA13
D9
BD11_A
A6
A7
PRDY
D10
BD09_A
D12
D23
BD06_B
+5V
D5
A3
BD07_A
D15
BA11
BD06_A D6
BA08
BSER
D0
D1
D18
BD11_B
BD01_B
BA11
PA17
D10
WAIT2-
BD16_B
BD13_A
BD07_A
BRD-
IOCS_B-
CS16-
BA03
BD05_A
CS12-
BSER
BD15_B
E10C
A13
A19X/YP
D3
BA01
BD05_B
BD08_A
BX/Y_A
BX/Y
D0
D5
BD12_A
BRD-
BD07_B
BD19_A
D23
A11
BD04_A
BRD-
DEMAND. TITLE TO THIS DOCUMENT IS NEVER SOLD OR
D21
BA02
D14
D15
BD09_B
R3
3.3K
+3P3V
BD00_A
CS0-
BA15
PA20
D22
BD14_B
"E10" FLASH BANK SELECT
BA07
BA02_A
BA12
BD00_B
D9
BX/Y
C43
0.1 mfd
BA07
BD11_B
BD19_B
BD10_B
U14
IDT74FCT164245TPA
(TSSOP48)
2
3
5
6
8
9
11
12
46
44
43
41
40
38
37
36
1
4
7
10
47
48
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
2425
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
39
42
45
B0
B1
B2
B3
B4
B5
B6
B7
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
A7
A8
T/R1
GND
VCCB
GND
A0
OE1
B8
B9
GND
B10
B11
VCCB
B12
B13
GND
B14
B15
T/R2
OE2
A15
A14
GND
A13
A12
VCCA
A11
A10
GND
A9
GND
VCCA
GND
D7
BA03_B
E10A
+5V
A9
BA00
BD23_B
DEMAND. TITLE TO THIS DOCUMENT IS NEVER SOLD OR
BD20_A
BA02
D12
BD13_B
BD20_B
PA19
BA00
BD02_A
+5V
D4
BA02
BD01_A
BD10_B
(JEXP)
CS04-
PA18
D2
VMECS-
BD21_B
CS04-
CS06-
CS00-
BA05
LA12
BD01_A
D1
BD01_A
CS12-
TRANSFERRED FOR ANY REASON. THIS DOCUMENT IS TO BE USED
BA14
BD14_A
BA01_B
R5
3.3K
A12
D3
BD02_A
BD06_B
BA00
R4
3.3K
A2
VMECS-
PRDY
D16
CS3-
D20
A15
D20
BA03
BA01
U15
IDT74FCT164245TPA
(TSSOP48)
2
3
5
6
8
9
11
12
46
44
43
41
40
38
37
36
1
4
7
10
47
48
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
2425
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
39
42
45
B0
B1
B2
B3
B4
B5
B6
B7
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
A7
A8
T/R1
GND
VCCB
GND
A0
OE1
B8
B9
GND
B10
B11
VCCB
B12
B13
GND
B14
B15
T/R2
OE2
A15
A14
GND
A13
A12
VCCA
A11
A10
GND
A9
GND
VCCA
GND
C44
0.1 mfd
D11
DPRCS-
+3P3V/+5V
BD11_A
BD21_A
`W1'= 1 TO 2 FOR 28F320J3A
D16
BRD-
BD07_B
CS0-
CS10-
BA02_B
W1
CS1-
BD23_A
D17
BD23_A
A10
BD03_A
BD21_A
BD18_A
BA01_A
BD22_A
BD14_A
C177
0.1 mfd
C47
0.1 mfd
OF DELTA TAU DATA SYSTEMS INC. ALL RIGHTS TO DESIGNS AND
D6
A17
BRD_B-
BA09
BA06
BD09_A
BX/Y
D11
D22
BA06
A0
RESET_B
CS1-
D22
BX/Y
PA16
BWR_B-
BD04_B
BA03_A
BX/Y_A
D18
BD15_A
BRD-
BA04
D4
A3
A10
D6
BD08_A
BD15_A
BD18_B
BD13_B
E10C
Page 50

Mini PMAC Hardware Reference Manual
44 Schematics
int_vccio
GND
HREQ-
CS02-
irdy#
C96
0.1 mfd
-12V
tck_pci
EQU_2
18.07Khz
9.8304Mhz
MI1
VCC
HDB06
int_vccio
ad11
ad19
4.53Khz
aselx2
s2
SA7
BA10_A
par
HDB03
serr#
R13
200.0
1%
irdy#
SA11
E5
BA01_A
ad15
int_ground
BD09_A
BD07_A
R/WL-
2.4576Mhz
+
C78
68 mfd
25V
-
mini - PMAC1, PCI AND DUAL PORT RAM
Delta Tau Data Systems, Inc.
D
36Tuesday, May 07, 2002
603712-320
Title
Size Document Number Rev
Date: Sheet
of
RESET
BRD_A-
PHASE
VMECS-
idsel
c/be#1
SD7
bus_+5V
9.8304Mhz
TP5
A-14V
+5V
A+14V
devsel#
trst#
tms_pci
ad6
ad31
+12V
+5V
BD01_A
BD13_A
data0
HDB15
(ON HEATSINK)
int_vccio
+5V
BD15_A
E33
GND
GND
HDB14
SA9
19.6608Mhz
RESET
clock/phaseb
E6
+5V
A+5V
ad23
bus_gnd
+
C82
10 mfd tant/ceramic
16V
(TANT)
EQU_3
ad30
BUSYL-
E31
GND
SA9
AGND
18.07Khz
E35
+
C85
22 mfd
35V
E4
E36
C67
0.22 mfd
+
C77
10 mfd tant/ceramic
35V
(TANT)
VR3LM1117MPX-ADJ
MC33269ST-ADJ
(SOT-223)
312
IN
GND
OUT
BD08_A
BWR_A-
HDB01
ad14
int_ground
HDB09
BD04_A
BD05_A
SA0
BD05_A
R28
1K
R70
10K
ad2
BD07_A
VMECS-
C91
1 mfd
50V
JOIN GND, INT_GROUND
RAISE RESISTOR OFF BOARD
int_vccio
BD00_A
par
HDB08
SERVO
WDTC
C59
0.22 mfd
+5V
int_vccio
HDB07
SERVO
OEL-
WDO
HDB02
+12V
BX/Y_A
INIT-
WDTC
BA02_A
tdi_pci
ad26
ad24
BD02_A
s0
BSA04
C68
0.22 mfd
nstatus
ad0
UBL-
BUSYR-
SD6
s1
CEL-
D5
1SMC18AT3
R12 10k
-11V
trdy#
ad6
SD5
L1
56uh
+5V
HDB05
BA02_A
HDB04
SD4
SA1
BD23_A
ad[0..31]
ad26
EQU_1
HDB02
BSA04
INT_GROUND FROM C13 PIN 2
ad23
PWR
BD03_A
19.6608Mhz
BD05_A
BSA11
D2
1SMC15.0AT3
GND
SRD-
ad8
ad30
BD00_A
SCLK
bus_-12V
C53
0.22 mfd
int_vccint
nce
HDB00
ad27
BSA00
ASEL0
R22
1k
int_vccio
BA08_A
+12V
+5V
GND
HDB09
ad1
BD11_A
GND
bus_gnd
tdo_pci
ad12
ad3
BD00_A
led_rst
C66
0.22 mfd
+5V
BD11_A
tck_pci
tdi_pci
ad29
ad17
BSA02
1.2288Mhz
R28A
1K
SD5
ad1
ad7
ad16
RP11
10KSIP10C
1 2
345678910
D9A
LED
GRN
SA0
EQU_1
frame#
c/be#2
BD08_A
PHASE
R7
100
TP4
AGND
SA6
c/be#[0..3]
BSA05
SD1
ad3
ad22
SA5
rst#
E88
-12V
AGND
BA11_A
aselx2
C60
0.22 mfd
OR
int_vccio
SD3
HEN-
c/be#0
led_rst
TP2
A+14V
D10
LED
RED
A-14V
GND
BSA00
BD01_A
-11V
+5V
SD7
BD07_A
c/be#3
ad20
BD03_A
BD18_A
s0
BSA03
C62
0.1 mfd
+5V
idsel
ad11
BSA09
E85
VR5
LM7805T
(TO-220)
123
IN
GND
OUT
ad18
s1
C73
0.22 mfd
E37
C95
0.1 mfd
E85
BA11_A
ad10
HDB03
ASEL1
R27A1KR27
1K
R6
47k
VR4LM1117MPX-ADJ
MC33269ST-ADJ
(SOT-223)
312
IN
GND
OUT
SA3
SA8
ad24
HDB11
BSA02
C72
0.1 mfd
int_vccio
GND
CLKOUTR
SD4
HDB07
tdo_pci
SA14
D6
1SMC5.0AT3
+
C94
22 mfd
25V
GND
OEL-
IRQB-
MI1
int_vccint
GND
GND
ad28
HDB14
OPT 2
GND
GND
BSA00
BD07_A
BD00_A
PHASE
U22
epc1
1
2
3
4 5
6
7
8
data
dclk
oe
ncs gnd
ncasc
vcc
vcc
C57
0.22 mfd
WITH COPPER PAD
GND
DCLK
PHASE
ad5
BD17_A
GND
BD18_A
BD10_A
ad19
clock/phaseb
R19
121.0
1%
+5V
HDB01
SA2
-12V
BSA10
BD06_A
ODCLK
odflt
4.7 mfd tant
C79
"AGND" PLANE
vcc
+12V
ad21
BD02_A
E30
C86
0.01 mfd
WAIT1-
DPRBSY-
clk
R/WL-
+
C90
22 mfd
25V
U21
10k30eqc240 / 10k50eqc240
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
616263646566676869707172737475777678798081828384858687888990919293949596979899
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
233
234
235
236
237
238
239
240
tck
conf_done
nceo
tdo
vccint
io
io
io
io
gndint
clkusr
io
io
io
io
vccio
io
io
io
io
io
gndint
rdynbsy
io
io
init_done
vccint
io
io
io
io
gndint
io
io
io
io
vccio
io
io
io
io
gndint
io
io
io
io
vccint
io
io
io
io
gndint
io
io
io
io
vccio
tms
trst
nstatus
ioioioioioioioiogndintioioioioioio
vccioioioioioioioioio
gndintioioiovccintinded. clkingndintioio
vccintioioioioioioiogndintioioioioioioiovccioioioioioioioioio
nconfig
vccint
msel1
msel0
gndint
io
io
io
io
vccint
io
io
io
io
gndint
io
io
io
io
vccio
io
io
io
io
gndint
io
io
io
io
vccint
io
io
io
io
gndint
io
io
io
io
vccio
io
io
io
io
gndint
io
io
io
io
vccint
io
io
io
io
io
gndint
tdi
nce
dclk
d0
d0/io
d1/io
d3/ioiod4/io
d5/ioiod6/io
vccio
d7/io
ioioioioio
io
gndint
ioioioioioioio
vccio
ioioio
dev_clrn
in
ded. clk
in
dev_oe
io
io
gndint
ioioioioioioio
vccio
ioioioioioioio
gndint
ioioio
nrs
io
nws
cs
ncs
BD15_A
rst#
BSA13
2.26Khz
int_ground
BD12_A
BD05_A
SD2
SA6
BD13_A
WD
SA1
ad7
9.035Khz
R25
1k
R8
1k
E98
JUMPER3
2
3
1
C71
0.1 mfd
0.2 mfd ceramic per each power
ground pair
SERVO
c/be#1
HDB00
BD02_A
BD21_A
1.2288Mhz
+5V
BD10_A
WDO
BA07_A
2.26Khz
BSA01
P1
pcibus_connector
a58
b58
a57
b56
a55
b55
a54
b53
b52
a49
b48
a47
b47
a46
b45
a44
a32
b32
a31
b30
a29
b29
a28
b27
a25
b24
a23
b23
a22
b21
a20
b20
a52
b44
b33
b26
a43
a34
a36
b35
a38
b37
a26
b39
b40
b42
b16
a15
a6
b7
a7
b8
b18
a17
b11
b9
b2
a4
b4
a3
a1
a40
a41
a60
b60
b1
a2
b5
a5
b6
a8
a10
a16
b19
b3
b12
a12
b13
a13
b15
b17
a18
b22
a24
a30
b28
b34
a35
a37
b38
a42
b46
b49
b57
a48
a56
a61
b61
a62
b62
ad0
ad1
ad2
ad3
ad4
ad5
ad6
ad7
ad8
ad9
ad10
ad11
ad12
ad13
ad14
ad15
ad16
ad17
ad18
ad19
ad20
ad21
ad22
ad23
ad24
ad25
ad26
ad27
ad28
ad29
ad30
ad31
c/be#0
c/be#1
c/be#2
c/be#3
par
frame#
trdy#
irdy#
stop
devsel#
idsel
lock#
perr#
serr#
clk
rst#
inta#
intb#
intc#
intd#
req#
gnt#
prsnt2#
prsnt1#
tck
tdi
tdo
tms
trst#
sdone
sbo#
req64#
ack64#
-12V
+12V
+5V
+5V
+5V
+5V
+5V
+5V
+5V
gnd
gnd
gnd
gnd
gnd
gnd
gnd
gnd
gnd
gnd
gnd
gnd
gnd
gnd
gnd
gnd
gnd
gnd
gnd
gnd
gnd
gnd
+5V
+5V
+5V
+5V
int_vccio
+5V
GND
A+15V
AGND
BSA02
ad21
C74
0.22 mfd
C65
0.22 mfd
+
C76
4.7 mfd tant
16V
(TANT)
"DGND" PLANE
SD2
SA15
BA00_A
inta#
ad31
ad20
HDB13
BD19_A
BD03_A
BSA06
+5V
SA13
R9
10k
R21
1k
(JPWR)
+5V
SCLK
c/be#2
ad4
ad28
HDB05
BSA01
19.6608Mhz
SHOULD JOIN "GND" NET AT
THIS POINT
int_vccint
+5V
+11V
ODCLK
BA01_A
SA10
SA15
D7
1SMC18AT3
E34A
GND
+5V
c/be#3
int_vccint
CEL-
GND
VCC
SA11
+5V
BD09_A
nconfig
HDB04
ad10
ASEL0
UBL-
E87
BA05_A
c/be#3
BA00_A
C52
1.0 mfd
+
C84
68 mfd
25V
needs to be inverted for use with the phase/servo generator
int_vccint
EQU_1
BD12_A
L3
56uh
BD14_A
BD23_A
ASEL0
int_vccio
BSA08
R71
10K
OR
bus_-12V
BD06_A
data0
devsel#
ad0
ad18
+5V
IPOS
trdy#
HDB10
SA8
BD20_A
R10
1k
U19
NC7SZ14M5
234
5
234
5
L2
56uh
BD19_A
WDO
BUSYL-
+
C81
4.7 mfd tant
16V
(TANT)
R17
121.0
1%
+11V
-12V
SD0
c/be#2
c/be#0
ad4
BSA13
D3
1SMC15.0AT3
JP1
SOLDER JUMPER
E29
SA5
BUSYR-
s3
C83
0.1 mfd
SD0
SA4
BD06_A
BD09_A
R18
1k
U18
NC7SZ14M5
234
5
234
5
+5V
BD04_A
c/be#1
ad15
+5V
HR/W-
BD17_A
BD20_A
EQU_2
nce
ad27
BD01_A
E3
AGND
HDB05
c/be#[0..3]
ad9
C56
0.22 mfd
R16
1k
C75
0.22 mfd
PWR
HOSTINT
BD02_A
tms_pci
DPRCS-
R11
1k
+
C93
22 mfd
35V
U20
CY7C025-TQFP
(TQFP100)
11
10
8
7
6
5
100
99
98
97
96
95
94
93
91
90
82
81
80
79
78
77
76
71
70
69
68
67
66
87
84
83
85
89
64
86
65
35
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
21
20
19
18
16
15
14
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
55
56
57
58
59
37
41
42
40
36
61
39
60
62
38
34
9
13
63
92
88
17
12
I/O-15L
I/O-14L
I/O-13L
I/O-12L
I/O-11L
I/O-10L
I/O-09L
I/O-08L
I/O-07L
I/O-06L
I/O-05L
I/O-04L
I/O-03L
I/O-02L
I/O-01L
I/O-00L
A12L
A11L
A10L
A09L
A08L
A07L
A06L
A05L
A04L
A03L
A02L
A01L
A00L
R/WL
UBL
LBL
CEL
OEL
BUSYL
SEML
INTL
I/O-15R
I/O-14R
I/O-13R
I/O-12R
I/O-11R
I/O-10R
I/O-09R
I/O-08R
I/O-07R
I/O-06R
I/O-05R
I/O-04R
I/O-03R
I/O-02R
I/O-01R
I/O-00R
A12R
A11R
A10R
A09R
A08R
A07R
A06R
A05R
A04R
A03R
A02R
A01R
A00R
R/WR
UBR
LBR
CER
OER
BUSYR
SEMR
INTR
M/S
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
VCC
VCC
VCC
+5V
SA4
HREQ-
ASEL1
conf_done
BD03_A
SA7
BD14_A
BD10_A
GND
BA04_A
perr#
ad12
SA2
SERVO
C61
0.001 mfd
int_vccio
GND
HDB00
semi1
odflt
HDB11
WAIT1-
BD04_A
9.035Khz
D10A
LED
RED
D4
MBRS140T3
ad2
72.28Khz
4.9152Mhz
BSA07
+
C89
22 mfd
25V
HDB04
ad17
HDB12
BSA11
BD13_A
BD04_A
D9
LED
GRN
19.6608Mhz
SA14
ad22
HDB07
+
C88
22 mfd
35V
R14 10k
VCC
EQU_2
int_ground
BSA10
+5V
HDB06
nconfig
RESET-
ad13
bus_+12V
HDB15
+5V
BD16_A
+
C92
22 mfd
35V
VCC
GND
RESET-
SD6
EQU_4
HDB13
HREQ-
+5V
+5V
bus_+5V
USBOE-
BA03_A
ad9
TP3
+A5V
+5V
trst#
ad13
HDB01
BD11_A
s2
s3
E34
+5V
+5V
BD22_A
CEL-
ad16
int_ground
BSA08
SA3
BD15_A
BD14_A
BD06_A
C63
0.1 mfd
E88
BD21_A
RESET-
U24
NC7SZ14M5
234
5
234
5
E87
R23
1k
GND
BSA01
SA12
ad25
msel1
C64
0.22 mfd
D8
MBRS140T3
stop#
HDB08
frame#
ad29
SA12
C55
0.22 mfd
SA10
BD01_A
HDB03
SA13
BA09_A
BA06_A
conf_done
ad[0..31]
ad5
OEL-
DCLK
C70
0.22 mfd
C54
0.22 mfd
R20
121.0
1%
C58
0.22 mfd
+12V
nstatus
BSA12
BSA03
BD08_A
E33A
semi0
BSA06
"AGND" PLANE
+5V
BSA09
BSA12
HDB06
SD1
BD16_A
BRD_A-
stop#
ad25
36.14Khz
AT THIS POINT
+5V
ad8
SD3
C80
0.1 mfd
C69
0.22 mfd
A-15V
R15
10k
E32
SWR-
HDB02
c/be#0
HDB12
msel0
BD22_A
BD12_A
4.53Khz
R24
1k
"DGND" PLANE
GND
BWR_A-
BFUL
inta#
GND
HDB10
perr#
C87
0.1 mfd
-12V
DPRCS-
serr#
clk
ad14
2.4576Mhz
WD
bus_+12V
EROR
F1ER
BSA07
4.9152Mhz
BSA05
R26
18 OHM
2.25W
TB1
1
2
3
4
U23
NC7SZ14M5
234
5
234
5
Page 51

PMAC-Mini PCI Hardware Reference
Schematics 45
A+15V
CHB2+
RP26
1KSIP8I
1 2
3 4
5 6
7 8
+5V
PLIM1+
pul_ena
PLIM2
CHA3+
DAC1-
OUT2/
RP39A
10K
1 2
J11
12
34
56
78
910
11 12
13 14
15 16
17 18
19 20
21 22
23 24
25 26
27 28
29 30
31 32
33 34
35 36
37 38
39 40
41 42
43 44
45 46
47 48
49 50
51 52
53 54
55 56
57 58
59 60
"AGND" PLANE
A-14V
MLIM3+
CHC3+
FAULT2
R33
50K
12 TURN
CW
"AGND" PLANE
A+14V
A+15V
HOME1+
CHB1+
CHB4+
MLIM3
RP40
10KSIP10C
12
3456789 10
PLIM3
OSEL0-
RP21
1KSIP10C
12
3456789 10
RP16
4.7KSIP8I
1 2
3 4
5 6
7 8
RP39B
10KSIP8I
3 4
C98
0.1 mfd
SA-14V
CHA1+
EQU2-
EQ4
RP9
47kSIP10C
12
3456789 10
E101
2
3
1
RP19
1KSIP8I
1 2
3 4
5 6
7 8
+5V
AFLT4+
PUL1
AENA1-
EQU2/
WDO
AENA_4
RP37A
10K
1 2
RP29
4.7KSIP8I
12
34
56
78
HOME3+
DAC1+
CHA3-
MLIM2+
EQU2-
HMFL1
RP35A
330SIP8I
1 2
RP41
470SIP10C
12
3456789 10
ENC_B1
CHA3+
ODATA
pul_ena
D19A
LED-GRN
"DGND" PLANE
O
CHA2+
CHA1-
C107
0.1 mfd
U31
HCPL-2630 (DIP8)
1
2
3
4 5
6
7
8
ANODE#1
CATHODE#1
CATHODE#2
ANODE#2 GND
VO2
VO1
VCC
EQ3
INTERFACE TO
"DGND" PLANE
PULSE2-
C113
0.1 mfd
IN SIP SOCKET
O
PLIM3+
CHC3-
ENC_C3
A+5V
E111
21
C97
4700pf
INSTALL FOR 0-TO-100Khz
A+V
AENA2/DIR2
EQU4-
RP31
4.7KSIP8I
1 2
3 4
5 6
7 8
MUST NUMBER IN THE
1
E100
A-15V
HMFL4
CNVRT-
R38
47K
-
+
U41C
LM139/SO
9
8
14
312
C127
10 mfd tant/ceramic
RP12
10KSIP10C
12
3456789 10
CNVRT
AFLT1+
NOTE:
A+15V
HOME4+
CHA4-
ASEL1+
CHC1-
MLIM1
E115
21
EQ1
D21
1n4001
O
AMP+V
CHB1-
OUTPUT
A+5V
AFLT2+
EQU_2
ENC_A3
R32
1K
ENC_B1
RP36A
1KSIP8I
1 2
RP39C
10KSIP8I
5 6
FAULT2
AENA2/DIR2
D19
LED-GRN
C132
0.1 mfd
O
O
ENC_C1
CHA3+
FAULT3
U35
MC34C87D (SO16)
1 2
16
5
13
10
8
3
6
14
7
4
11
9
15
12
IN-A OUT-A
VCC
OUT-C
OUT-B
OUT-D
GND
OUT-A
OUT-C
OUT-B
IN-C
EN-A,C
OUT-D
IN-D
IN-B
EN-B,D
PLIM1+
MLIM1
CHB3-
CHA4+
EQU1-
AFLT2+
A+5V
DCLK
J8
PLIM2
AFLT3+
OSEL0-
RP34
1KSIP8I
1 2
3 4
5 6
7 8
U44
ULN2803A
OR
UDN2981A
(DIP18)
(IN SOCKET)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9 10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
IN1
IN2
IN3
IN4
IN5
IN6
IN7
IN8
GND V+
OUT8/
OUT7/
OUT6/
OUT5/
OUT4/
OUT3/
OUT2/
OUT1/
ASEL1-
REMOVE FOR 0-TO-2Mhz
"AGND" PLANE
O
AGND
ENC_C1
AENA_4
MLIM1+
CHB3+
HMFL4
DAC1+
C103
0.1 mfd
C131
0.1 mfd
R37
5K POT
"DGND" PLANE
+5V
EQU_4
RP38D
220SIP8I
7 8
POT
ENC_C2
CHB4+
DAC2+
+
-
U38A
AD822AR
(SO8)
3
2
1
84
RP23
2.2KSIP6C
2
3
4
5
6
1
E117
21
R50
4.7k
INSTALL FOR STEPPER FEEDBACK
"AGND" PLANE
"DGND" PLANE
EQU1-
safety_relay
D13 bat54
E116
21
+
-
U39D
LF347M
(SO14)
12
13
14
AGND
CHC3+
C130
0.1 mfd
ON SOLDER SIDE
WIPER2
AFLT3+
CHC2-
A+5V
HOME1+
ODCLK
EQU2-
CHA4+
ASEL0-
MLIM2
R44
2670
C115
0.1 mfd
RP20
2.2KSIP10C
12
3456789 10
ENC_A1
CHB1+
CHB2-
DATA+
PULSE1-
RP35D
330SIP8I
7 8
"DGND" PLANE
2
AMP+V
A+5V
MLIM2
DCLK-
EQU1/
C110
0.1 mfd
C129
0.1 mfd
D12
MMBD301LT1
1 3
GND
AGND
RESET-
AENA1/DIR1
RP36D
1KSIP8I
7 8
(JAUX)
A+5V
CHB4+
+
-
U39C
LF347M
(SO14)
10
9
8
C104
4700pf
RP37B
10KSIP8I
3 4
-
+
U41B
LM139/SO
5
4
2
312
+5V
PLIM4+
+11V
CHC1+
CHB3-
U25
MC34C86D (SO16)
1
2
4
6
7
15
14
12
10
9
3
16
5
13
11
8
IN-A
IN-A
ENA-A,C
IN-C
IN-C
IN-B
IN-B
ENA-B,D
IN-D
IN-D
OUT-A
VCC
OUT-C
OUT-B
OUT-D
GND
AGND
R36
1K
OUT2/
3
HMFL3
MLIM4+
U47
6N137 (DIP8)
8
5
7
6
1
2
3
4
VCC
GND
VE
VOUT
N.C.
ANO
CAT
N.C.
R53 1k
RP24
4.7KSIP8I
12
34
56
78
R30
1M
ADCIN
OFFSET
AFLT2+
CHB2-
RP35C
330SIP8I
5 6
D22
1SMC33AT3
C101
56pf
RP32
4.7KSIP8I
12
34
56
78
PWR-GOOD-LED
A+5V
CHB3+
MLIM3+
DACOUT
C116
U42C
74ACT86
(SO14)
9
10
8
RP37D
10K
7 8
DAC3-
A+14V
ENC_B2
CHB3+
C126
C121
0.1 mfd
R31
34.0K
A+14V
AENA_3
CHA4+
CHC1-
FEFCO-
U46
PS2701-1NEC
1
2 3
4
A1
C1 E1
C1
R74A 2.2k
(812-4SH3.SCH)
DIP14 SOCKET
ENC_B3
EQU_4
U40
HCPL-2630 (DIP8)
1
2
3
4 5
6
7
8
ANODE#1
CATHODE#1
CATHODE#2
ANODE#2 GND
VO2
VO1
VCC
INSTALL FOR STEPPER DRIVE
"DGND" PLANE
CHC1-
DCLK+
ODCLK
(JS1)
REMOVE FOR 0-TO-2Mhz
+5V
ENC_A1
OUT2/
IN SIP SOCKET
3
AGND
MLIM2+
CHC2+
+
C119
4.7 mfd tant
1
AENA1/DIR1
OUT4/
D14
bat54
RP38C
220SIP8I
5 6
"AGND" PLANE
ENC_A4
CHC4-
DCLK+
CHA4-
DAC1+
R46
1.82k
SAME LOCATION AS (JMACH1) ON `602399-1'
ASEL0
EQU1-
CHC2-
OSEL0
D23
MBRS140T3
E90
2
3
1
A-14V
AFLT3+
DATA-
DAC1-
RP42
3.3KSIP10C
12
3456789 10
C123
0.1 mfd
+
C118
4.7 mfd tant
POT
O
SA+14V
AENA2/DIR2
OSEL0
RESET-
-
+
U41D
LM139/SO
11
10
13
312
C112
0.1 mfd
E90
1
DIP14 SOCKET
A+5V
DCLK
AFLT1+
AENA2-
REMOVE FOR 0-TO-2Mhz
"AGND" PLANE
E100,E101 AND E102
A+V
U28
MC34C86D (SO16)
1
2
4
6
7
15
14
12
10
9
3
16
5
13
11
8
IN-A
IN-A
ENA-A,C
IN-C
IN-C
IN-B
IN-B
ENA-B,D
IN-D
IN-D
OUT-A
VCC
OUT-C
OUT-B
OUT-D
GND
C128
0.1 mfd
C108
2200pf
E17A
21
MLIM1+
CHB2+
AENA1-
D11
MMBD301LT1
1 3
EQ2
RP27
10KSIP10C
12
3456789 10
INSTALL FOR 0-TO-100Khz
(JMACH1)
ON COMPONENT SIDE
AFLT1+
CHA2-
PLIM3+
ENC_C2
FEFCO-
EQU_3
WIPER1
CHB2+
PLIM3
E100
2
3
1
U37
AD1866R
(SOL16)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8 9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
VL
LL
DL
CK
DR
LR
DGND
VBR VS
VOR
NRR
AGND
NRL
VOL
VS
VBL
U34
PS2705-4NEC
1
215
16
3
4
5
6
78910
11
12
13
14
ACI1A
ACI1BE1
C1
ACI2A
ACI2B
ACI3A
ACI3B
ACI4A
ACI4BE4
C4
E3
C3
E2
C2
A+5V
RP15
2.2KSIP6C
2
3
4
5
6
1
D20
1n750
RP39D
10K
7 8
+5V
PWR_GUD-
HMFL2
ASEL0+
AENA1/DIR1
C105
0.1 mfd
E17D
21
+
-
U39B
LF347M
(SO14)
5
6
7
FA+5V
A-14V
PLIM1
CHA2+
"AGND" PLANE
SAME DIRECTION
CHC4+
CHC3-
R45
150k
E113
21
SOT23
Q2
2N7002
3
12
ADCIN
ENC_A2
FAULT1
OUT4/
PWR_GUD-
EQU_2
SMT & THRU-HOLE
DAC4+
A-15V
MLIM4+
CHA1-
ENC_B3
AFLT4+
ASEL1
R49
330
RP28
4.7KSIP8I
1 2
3 4
5 6
7 8
IN SIP SOCKET
2
2
odflt
CHC1+
ASEL1-
ASEL0-
AENA_2
D15
BAS70-04
J7
E102
CHB1-
CHC4+
ASEL1-
ODCLK
R43
1k
R34
1M
-
Mini-Pmac MACHINE INTERFACE SECTION
DELTA TAU DATA SYSTEMS, Inc.
D
56Tuesday, May 07, 2002
603712-320
Title
Size Document Number Rev
Date: Sheet
of
A+5V
ENC_A2
WDO-
U42A
74ACT86
(SO14)
1
2
3
AENA_2
+5V
CHA4-
C102
0.1 mfd
SOT23
Q3
2N7002
3
12
OUT3/
A+5V
ENC_C3
CHB4-
CHB4-
PUL1
R47
10k
RP37C
10KSIP8I
5 6
D17
MBRS140T3
AFLT2+
AGND
ENC_B2
DAC2+
RP35B
330SIP8I
3 4
-
+
U41A
LM139/SO
7
6
1
312
U42D
74ACT86
(SO14)
12
13
11
ACC28A,ACC28B
A-14V
MLIM3
R35
34.0K
INSTALL FOR 0-TO-100Khz
+5V
SA+14V
PLIM1
RP17
4.7KSIP8I
12
34
56
78
R48
4.7k
E118
21
HOME2+
ENC_C4
OUT1/
E119
21
R41
5K POT
DCLK
3
+5V
WIPER1
D18
MMBD301LT1
1 3
PLIM2+
CHB4-
PLIM4
MLIM4
RP13
2.2KSIP10C
12
3456789 10
C111
0.1 mfd
U36
HCPL-2630 (DIP8)
1
2
3
4 5
6
7
8
ANODE#1
CATHODE#1
CATHODE#2
ANODE#2 GND
VO2
VO1
VCC
C106
0.1 mfd
INSTALL FOR STEPPER DRIVE
+11V
ENC_A3
CHA3-
C120
O
+5V
CHA1-
CHB1-
DAC2-
EQU3-
R42
47K
RP38A
220SIP8I
1 2
A-14V
AGND
PLIM4
RP38B
220SIP8I
3 4
"DGND" PLANE
AFLT4+
CHC3+
C100
2200pf
RP18
2.2KSIP6C
2
3
4
5
6
1
C117
0.1 mfd
J8
HEADER 7X2
12
34
56
78
910
11 12
13 14
R40
10k
K1
FBR12ND05
4
3
5
9
10
8
1
12
E17B
21
"AGND" PLANE
AGND
WDO
EQU2-
E17C
21
E110
21
C124
DATA
HOME3+
CHA2-
REMOVE FOR 0-TO-2Mhz
CNVRT-
CHC4-
PUL2
EQU1-
AENA_1
RP14
1KSIP10C
12
3456789 10
FAULT3
AFLT4+EQU_1
RP25
2.2KSIP6C
2
3
4
5
6
1
R56 330
E89
HMFL1
PULSE2-
CHA4+
CHA1+
OUT1/
U27
VFC110
(DIP14)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7 8
9
10
11
12
13
14
IIN
VIN
+5VO
-VS
ENA
COS
DGND FOUT
N.C.
+VS
COMP
VOUT
AGND
INCOM
C122
0.1 mfd
R74 2.2k
OUT1/
SA-14V
ENC_C4
CHA3-
CHB3+
CHC2+
ODATA
EQU_3
RP33
470SIP10C
12
3456789 10
OFFSET
AGND
HOME4+
CHC4-
HMFL3
safety_relay
U26
PS2705-4NEC
1
215
16
3
4
5
6
78910
11
12
13
14
ACI1A
ACI1BE1
C1
ACI2A
ACI2B
ACI3A
ACI3B
ACI4A
ACI4BE4
C4
E3
C3
E2
C2
A+14V
ENC_B4
FAULT4
A+5V
E112
21
PLIM2+
AFLT1+
DAC2-
U43
PS2701-4NEC
1
2 15
16
3
4
5
6
7
8 9
10
11
12
13
14
A1
C1 E1
C1
A2
C2
A3
C3
A4
C4 E4
C4
E3
C3
E2
C2
C125
0.1 mfd
U32
PS2705-4NEC
1
215
16
3
4
5
6
78910
11
12
13
14
ACI1A
ACI1BE1
C1
ACI2A
ACI2B
ACI3A
ACI3B
ACI4A
ACI4BE4
C4
E3
C3
E2
C2
DAC4-
connect to analog power and ground.
DCLK-
pul_ena
AENA_1
CHC4+
U33
MC34C86D (SO16)
1
2
4
6
7
15
14
12
10
9
3
16
5
13
11
8
IN-A
IN-A
ENA-A,C
IN-C
IN-C
IN-B
IN-B
ENA-B,D
IN-D
IN-D
OUT-A
VCC
OUT-C
OUT-B
OUT-D
GND
CHC2+
CHB1+
OUT3/
R52
1K
R55
1k 1%
OUTPUT
A+5V
HMFL2
FEFCO-
CNVRT
RP36C
1KSIP8I
5 6
R29
50K
12 TURN
CW
ASEL0-
INSTALL FOR 0-TO-100Khz
DAC3+
INSTALL FOR STEPPER FEEDBACK
CHC2-
RP22
4.7KSIP8I
1 2
3 4
5 6
7 8
U42B
74ACT86
(SO14)
4
5
6
U30
VFC110
(DIP14)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7 8
9
10
11
12
13
14
IIN
VIN
+5VO
-VS
ENA
COS
DGND FOUT
N.C.
+VS
COMP
VOUT
AGND
INCOM
U29
PS2705-4NEC
1
215
16
3
4
5
6
78910
11
12
13
14
ACI1A
ACI1BE1
C1
ACI2A
ACI2B
ACI3A
ACI3B
ACI4A
ACI4BE4
C4
E3
C3
E2
C2
+5V
+5V
GND
CHB2-
OUT3/
ENC_A4
ENC_B4
E102
2
3
1
OUT4/
E101
DAC2+
SOT23
Q1
2N7002
3
12
C99
0.1 mfd
AFLT3+
optional - on the back
CHA1+
ADCIN
+
-
U39A
LF347M
(SO14)
3
2
1
411
E89
21
RP30
1KSIP8I
1 2
3 4
5 6
7 8
+5V
IN SIP SOCKET
+5V
CHC3-
FAULT4
C114
0.1 mfd
D16
MBRS140T3
PUL2
PLIM4+
U45
74ACT540
(SOL20)
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
19
1
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
20
10
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
A7
A8
G2
G1
Y1
Y2
Y3
Y4
Y5
Y6
Y7
Y8
VCC
GND
R54 5.1k 1%
+5V
ASEL1
CHA3+
CHA2-
CHB3-
RP36B
1KSIP8I
3 4
+5V
DACOUT
pul_ena
PULSE1-
AENA_3
R39 10k
STEPPER OPTION 15
"DGND" PLANE
A+14V
HOME2+
EQU_1
CHC1+
MLIM4
E114
21
FAULT1
J7
HEADER 16
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
LAYOUT FOR BOTH
RESET-
CHB4+
C109
56pf
J11
WIPER2
ASEL0
DATA+
O
+5V
A-14V
AGND
AENA2-
A-14V
CHA2+
CNVRT
R51
330
+
-
U38B
AD822AR
(SO8)
5
6
7
 Loading...
Loading...