Delta Tau GEO MACRO DRIVE User Manual

^1 USER MANUAL & REFERENCE
Geo MACRO Drive
^3 Direct PWM Amplifier over MACRO
^4 500-603701-xUxx
^5 April 27, 2010
Single Source Machine Control |
Power // Flexibility // Ease of Use |
21314 Lassen Street Chatsworth, CA 91311 // Tel. (818) 998-2095 Fax. (818) 998-7807 // www.deltatau.com

Copyright Information
© 2010 Delta Tau Data Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
This document is furnished for the customers of Delta Tau Data Systems, Inc. Other uses are unauthorized without written permission of Delta Tau Data Systems, Inc. Information contained in this manual may be updated from time-to-time due to product improvements, etc., and may not conform in every respect to former issues.
To report errors or inconsistencies, call or email:
Delta Tau Data Systems, Inc. Technical Support
Phone: (818) 717-5656
Fax: (818) 998-7807
Email: support@deltatau.com Website: http://www.deltatau.com
Operating Conditions
All Delta Tau Data Systems, Inc. motion controller products, accessories, and amplifiers contain static sensitive components that can be damaged by incorrect handling. When installing or handling Delta Tau Data Systems, Inc. products, avoid contact with highly insulated materials. Only qualified personnel should be allowed to handle this equipment.
In the case of industrial applications, we expect our products to be protected from hazardous or conductive materials and/or environments that could cause harm to the controller by damaging components or causing electrical shorts. When our products are used in an industrial environment, install them into an industrial electrical cabinet or industrial PC to protect them from excessive or corrosive moisture, abnormal ambient temperatures, and conductive materials. If Delta Tau Data Systems, Inc. products are directly exposed to hazardous or conductive materials and/or environments, we cannot guarantee their operation.
Safety Instructions
Qualified personnel must transport, assemble, install, and maintain this equipment. Properly qualified personnel are persons who are familiar with the transport, assembly, installation, and operation of equipment. The qualified personnel must know and observe the following standards and regulations:
IEC 364 resp. CENELEC HD 384 or DIN VDE 0100 IEC report 664 or DIN VDE 0110
National regulations for safety and accident prevention or VBG 4
Incorrect handling of products can result in injury and damage to persons and machinery. Strictly adhere to the installation instructions. Electrical safety is provided through a low-resistance earth connection. It is vital to ensure that all system components are connected to earth ground.
This product contains components that are sensitive to static electricity and can be damaged by incorrect handling. Avoid contact with high insulating materials (artificial fabrics, plastic film, etc.). Place the product on a conductive surface. Discharge any possible static electricity build-up by touching an unpainted, metal, grounded surface before touching the equipment.
Keep all covers and cabinet doors shut during operation. Be aware that during operation, the product has electrically charged components and hot surfaces. Control and power cables can carry a high voltage, even when the motor is not rotating. Never disconnect or connect the product while the power source is energized to avoid electric arcing.

After removing the power source from the equipment, wait at least 10 minutes before touching or disconnecting sections of the equipment that normally carry electrical charges (e.g., capacitors, contacts, screw connections). To be safe, measure the electrical contact points with a meter before touching the equipment.
The following text formats are used in this manual to indicate a potential for personal injury or equipment damage. Read the safety notices in this manual before attempting installation, operation, or maintenance to avoid serious bodily injury, damage to the equipment, or operational difficulty.
WARNING
A Warning identifies hazards that could result in personal injury or death. It precedes the discussion of interest.
Caution
A Caution identifies hazards that could result in equipment damage. It precedes the discussion of interest
Note
A Note identifies information critical to the user’s understanding or use of the equipment. It follows the discussion of interest.

REVISION HISTORY
REV. |
DESCRIPTION |
DATE |
CHG |
APPVD |
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
UPDATED ENDAT SETUP INFO, P. 82 |
07/18/06 |
CP |
P.SHANTZ |
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
UPDATED ERROR CODE EF GATE DRIVE INFO |
09/21/06 |
CP |
P.SHANTZ |
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
CORRECTED GP OUT INPUT FUNCTIONS, P. 39 |
06/11/08 |
CP |
K.ZHAO |
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
CORRECTED RESET COMMAND, P. 138 |
10/30/08 |
CP |
S. MILICI |
|
|
|
|
|
5 |
CORRECTED M-VARIABLE DEFINITIONS, P. 87 |
12/08/09 |
CP |
S. MILICI |
|
|
|
|
|
6 |
CORRECTED ERRORS PPS. 85-87 |
02/25/10 |
CP |
S. MILICI |
|
|
|
|
|
7 |
CORRECTED COVER PAGE FORMATTING |
03/01/10 |
CP |
C. PERRY |
|
|
|
|
|
8 |
ADDED SAFETY RELAY PN INFO, P. 108 |
04/27/10 |
CP |
S. MILICI |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

Geo MACRO Drive User and Reference Manual
|
Table of Contents |
Copyright Information................................................................................................................................................ |
i |
Operating Conditions ................................................................................................................................................. |
i |
Safety Instructions...................................................................................................................................................... |
i |
INTRODUCTION ....................................................................................................................................................... |
1 |
User Interface ............................................................................................................................................................ |
1 |
Geo MACRO Drives ............................................................................................................................................. |
1 |
Geo PMAC Drives ................................................................................................................................................ |
2 |
Geo Direct-PWM Drives....................................................................................................................................... |
2 |
MACRO Defined ...................................................................................................................................................... |
2 |
Feedback Devices...................................................................................................................................................... |
3 |
Compatible Motors.................................................................................................................................................... |
3 |
Maximum Speed.................................................................................................................................................... |
3 |
Torque................................................................................................................................................................... |
3 |
Motor Poles .......................................................................................................................................................... |
4 |
Motor Inductance.................................................................................................................................................. |
4 |
Motor Resistance .................................................................................................................................................. |
4 |
Motor Back EMF .................................................................................................................................................. |
4 |
Motor Torque Constant......................................................................................................................................... |
5 |
Motor Inertia ........................................................................................................................................................ |
5 |
Motor Cabling....................................................................................................................................................... |
5 |
SPECIFICATIONS ..................................................................................................................................................... |
7 |
Part Number .............................................................................................................................................................. |
7 |
Geo MACRO Feedback Options............................................................................................................................... |
8 |
Package Types........................................................................................................................................................... |
8 |
Electrical Specifications............................................................................................................................................ |
9 |
230VAC Input Drives........................................................................................................................................... |
9 |
480VAC Input Drives.......................................................................................................................................... |
11 |
Environmental Specifications.................................................................................................................................. |
13 |
Recommended Fusing and Wire Gauge .................................................................................................................. |
13 |
RECEIVING AND UNPACKING........................................................................................................................... |
15 |
Use of Equipment.................................................................................................................................................... |
15 |
MOUNTING .............................................................................................................................................................. |
17 |
Low Profile.............................................................................................................................................................. |
18 |
Single Width............................................................................................................................................................ |
19 |
Double Width .......................................................................................................................................................... |
20 |
CONNECTIONS ....................................................................................................................................................... |
21 |
System (Power) Wiring........................................................................................................................................... |
21 |
Wiring AC Input, J1 ............................................................................................................................................ |
23 |
Wiring Earth-Ground ......................................................................................................................................... |
23 |
Wiring 24 V Logic Control, J4............................................................................................................................ |
24 |
Wiring the Motors ................................................................................................................................................... |
24 |
J2: Motor 1 Output Connector Pinout............................................................................................................... |
24 |
J3: Motor 2 Output Connector Pinout............................................................................................................... |
24 |
Wiring the Motor Thermostats ................................................................................................................................ |
25 |
Wiring the Regen (Shunt) Resistor, J5 .................................................................................................................... |
25 |
J5: External Shunt Connector Pinout ................................................................................................................ |
26 |
Shunt Regulation................................................................................................................................................. |
27 |
Minimum Resistance Value................................................................................................................................. |
27 |
Maximum Resistance Value ................................................................................................................................ |
27 |
Energy Transfer Equations ................................................................................................................................. |
27 |
Bonding................................................................................................................................................................... |
29 |
Filtering................................................................................................................................................................... |
30 |
Table of Contents |
i |

|
Geo MACRO Drive User Manual |
CE Filtering ........................................................................................................................................................ |
30 |
Input Power Filtering ......................................................................................................................................... |
31 |
Motor Line Filtering ........................................................................................................................................... |
31 |
I/O Filtering........................................................................................................................................................ |
31 |
Connecting Main Feedback Sensors (X1 & X2) ..................................................................................................... |
32 |
Digital Quadrature Encoders ............................................................................................................................. |
32 |
Digital Hall Commutation Sensors..................................................................................................................... |
33 |
SSI Encoders....................................................................................................................................................... |
33 |
Sinusoidal Encoders ........................................................................................................................................... |
34 |
Hiperface® Interface .......................................................................................................................................... |
35 |
EnDat Interface................................................................................................................................................... |
36 |
Resolvers............................................................................................................................................................. |
37 |
Connecting Secondary Quad. Encoders (X8 & X9)................................................................................................ |
38 |
Connecting General Purpose I/O & Flags (X3)....................................................................................................... |
39 |
Sample wiring the I/O ......................................................................................................................................... |
39 |
Sample Wiring the Flags..................................................................................................................................... |
40 |
Connecting MACRO Ring ...................................................................................................................................... |
41 |
Fiber Optic MACRO connections (X5)............................................................................................................... |
41 |
RJ-45 Copper MACRO connections (X10 &X11)............................................................................................... |
41 |
Connecting optional Analog Inputs (X6 & X7) ...................................................................................................... |
42 |
SOFTWARE SETUP FOR GEO MACRO DRIVES............................................................................................. |
43 |
Introduction ............................................................................................................................................................. |
43 |
Establishing MACRO Communications with Turbo PMAC .................................................................................. |
43 |
MACRO Ring Frequency Control Variables ...................................................................................................... |
43 |
I7: Phase Cycle Extension .................................................................................................................................. |
43 |
I6840: MACRO IC 0 Master Configuration ....................................................................................................... |
44 |
I6890/I6940/I6990: MACRO IC 1/2/3 Master Configuration ............................................................................ |
44 |
I6841/I6891/I6941/I6991: MACRO IC 0/1/2/3 Node Activation Control........................................................... |
44 |
I70/I72/I74/I76: MACRO IC 0/1/2/3 Node Auxiliary Function Enable.............................................................. |
45 |
I71/I73/I75/I77: MACRO IC 0/1/2/3 Node Protocol Type Control .................................................................... |
46 |
I78: MACRO Master/Slave Auxiliary Communications Timeout ....................................................................... |
46 |
I79: MACRO Master/Master Auxiliary Communications Timeout..................................................................... |
46 |
I80, I81, I82: MACRO Ring Check Period and Limits ....................................................................................... |
46 |
MACRO Node Addresses .................................................................................................................................... |
47 |
Using the Turbo PMAC Setup Program ............................................................................................................. |
51 |
Using the PEWIN32PRO 2 MACRO Ring ASCII Feature.................................................................................. |
58 |
PEWIN32PRO Suite 2 MACRO Status window.................................................................................................. |
62 |
Ring Order Communications Method ................................................................................................................. |
63 |
MACRO ASCII Communications........................................................................................................................ |
64 |
How to Enable and Disable MACRO ASCII Communication Mode .................................................................. |
64 |
SETTING UP PRIMARY FEEDBACK.................................................................................................................. |
67 |
Device Selection Control......................................................................................................................................... |
67 |
Setting up Digital Quadrature Encoders................................................................................................................. |
67 |
Setting up SSI Encoders.......................................................................................................................................... |
67 |
Setting up Sinusoidal Encoders............................................................................................................................... |
69 |
Principle of PMAC Interpolation Operation ...................................................................................................... |
69 |
Setting up Endat ...................................................................................................................................................... |
72 |
Setting up Resolvers................................................................................................................................................ |
72 |
Setting up the Phase Shift (MI941) Manually ..................................................................................................... |
73 |
Setting up the Resolver for Power-On Absolute Position ................................................................................... |
73 |
Scaling the Feedback Units ................................................................................................................................ |
74 |
SETTING UP SECONDARY ENCODERS............................................................................................................ |
75 |
SETTING UP THE TURBO PMAC CONVERSION TABLE ............................................................................. |
77 |
ii |
Table of Contents |

Geo MACRO Drive User and Reference Manual
SETTING UP TURBO MOTOR OPERATION .................................................................................................... |
79 |
Turbo PMAC Basic Setup for Brushless Servo or Induction Motor ....................................................................... |
79 |
Turbo PMAC Basic Setup for DC Brush Motors ................................................................................................ |
80 |
Instructions for Direct-PWM Control of Brush Motors .......................................................................................... |
85 |
PWM/ADC Phase Match .................................................................................................................................... |
85 |
Synchronous Motor Stepper Action .................................................................................................................... |
85 |
Current Loop Polarity Check.............................................................................................................................. |
85 |
Troubleshooting.................................................................................................................................................. |
86 |
Testing PWM and Current Feedback Operation ..................................................................................................... |
86 |
Purpose............................................................................................................................................................... |
86 |
Preparation......................................................................................................................................................... |
87 |
Position Feedback and Polarity Test .................................................................................................................. |
87 |
Setting Up Hall Commutation Sensors.................................................................................................................... |
88 |
Signal Format ..................................................................................................................................................... |
88 |
Using Hall Effect Sensors for Phase Reference.................................................................................................. |
89 |
Determining the Commutation Phase Angle....................................................................................................... |
89 |
Finding the Hall Effect Transition Points........................................................................................................... |
89 |
Calculating the Hall Effect Zero Point (HEZ) .................................................................................................... |
90 |
Determining the Polarity of the Hall Effects – Standard or Reversed................................................................ |
92 |
Software Settings for Hall Effect Phasing........................................................................................................... |
92 |
Setting I2T Protection .............................................................................................................................................. |
96 |
Calculating Minimum PWM Frequency ................................................................................................................. |
97 |
SETTING UP DISCRETE INPUTS AND OUTPUTS........................................................................................... |
99 |
Inputs and Outputs .................................................................................................................................................. |
99 |
Ring Break Output indicator MS{node},MI13 ..................................................................................................... |
100 |
Setting up the Analog Inputs (X6 and X7)............................................................................................................ |
100 |
Limit and Flag Circuit Wiring............................................................................................................................... |
102 |
Connecting Limits/Flags to the Geo Drive ....................................................................................................... |
102 |
Setting up Position Compare (EQU) Outputs........................................................................................................ |
103 |
Setting up for a Single Pulse Output................................................................................................................. |
103 |
Setting up for Multiple Pulse Outputs............................................................................................................... |
104 |
CONNECTORS....................................................................................................................................................... |
105 |
Connector Pinouts ................................................................................................................................................. |
105 |
X1: Encoder Input 1......................................................................................................................................... |
105 |
X2: Encoder Input 2......................................................................................................................................... |
106 |
X3: General Purpose I/O.................................................................................................................................. |
107 |
X4: Safety Relay (Optional) ............................................................................................................................. |
108 |
X6: Analog IN 1 (Optional 3/4/5) .................................................................................................................... |
108 |
X7: Analog IN 2 (Optional 3/4/5) .................................................................................................................... |
108 |
X8: S. Encoder 1 .............................................................................................................................................. |
109 |
X9: S. Encoder 2 .............................................................................................................................................. |
109 |
X13: Discrete I/O............................................................................................................................................. |
109 |
J1: AC Input Connector Pinout ....................................................................................................................... |
110 |
J2: Motor 1 Output Connector Pinout............................................................................................................. |
110 |
J3: Motor 2 Output Connector Pinout (Optional) ........................................................................................... |
110 |
J4: 24VDC Input Logic Supply Connector ....................................................................................................... |
110 |
J5: External Shunt Connector Pinout .............................................................................................................. |
110 |
MACRO Link Connectors..................................................................................................................................... |
111 |
X5: MACRO I/O, MACRO Fiber Optic Transceiver (Optional)....................................................................... |
111 |
X10 and X11 MACRO RJ-45 Copper Connectors ............................................................................................ |
111 |
USB Connector ..................................................................................................................................................... |
111 |
X12: USB Universal Serial Bus Port ............................................................................................................... |
112 |
TROUBLESHOOTING.......................................................................................................................................... |
113 |
Error Codes ........................................................................................................................................................... |
113 |
Table of Contents |
iii |

|
|
|
Geo MACRO Drive User Manual |
D1: Geo MACRO Drive Status Display Codes................................................................................................. |
113 |
||
MACRO Network Errors |
................................................................................................................................... |
114 |
|
Status LEDs ...................................................................................................................................................... |
|
|
115 |
Geo MACRO Drive Ring Status Error Codes....................................................................................................... |
116 |
||
MS{node},MI4 |
Geo MACRO ...............................................................................Status Word (Read Only) |
116 |
|
MS{node},MI6 |
Status Word .............................................................................................................Control |
117 |
|
Status Word....................................................................................................................................................... |
|
|
117 |
TURBO PMAC2 RELATED ...............................................................................I-VARIABLE REFERENCE |
119 |
||
Ixx10: Motor xx Power-On ............................................................................................Servo Position Address |
119 |
||
Ixx25, Ixx24: Flag Address ..................................................................................................................and Mode |
121 |
||
Ixx70, Ixx71: Commutation ...............................................................................................................Cycle Size |
123 |
||
Ixx72: Commutation Phase .........................................................................................................................Angle |
123 |
||
Ixx75: Absolute Phase Position .................................................................................................................Offset |
123 |
||
Ixx81: Motor xx Power-On ...........................................................................Phase Position Address and Mode |
124 |
||
Ixx82: Current Loop Feedback ................................................................................................................Address |
125 |
||
Ixx83: Commutation Feedback ..............................................................................................................Address |
126 |
||
Ixx91: Motor xx Power-On .............................................................................................Phase Position Format |
126 |
||
Ixx95: Motor xx Power-On .............................................................................................Servo Position Format |
129 |
||
Ixx97 Motor xx Position Capture ...........................................................................................and Trigger Mode |
131 |
||
GEO MACRO DRIVE MI-VARIABLE ......................................................................................REFERENCE |
133 |
||
Global MI-Variables ............................................................................................................................................. |
|
133 |
|
MS{node},MI0 |
Geo MACRO ............................................................drive Firmware Version (Read Only) |
133 |
|
MS{node},MI1 |
Geo MACRO ................................................................drive Firmware Date (Read Only) |
133 |
|
MS{node},MI2 and MI3 ....................................................................................... |
(Reserved for future use) |
133 |
|
MS{node},MI4 |
Geo MACRO ......................................................................drive Status Word (Read Only) |
134 |
|
MS{node},MI5 |
Ring Error .............................................................................................................Counter |
134 |
|
MS{node},MI6 |
Status ............................................................................................................Word Control |
135 |
|
MS{node},MI7 |
Geo MACRO ...............................................................................................Error Counter |
135 |
|
MS{node},MI8 |
Geo MACRO ........................................................................................Ring Check Period |
135 |
|
MS{node},MI9 |
Geo MACRO ..........................................................................Ring Error Shutdown Count |
135 |
|
MS{node},MI10 |
Geo MACRO ......................................................................Sync Packet Shutdown Count |
136 |
|
MS{node},MI11 |
Station .......................................................................................................Order Number |
136 |
|
MS{node},MI12 |
Card ........................................................................................Identification (Read Only) |
137 |
|
MS{node},MI13 |
Ring .............................................................................................Break Output indicator |
137 |
|
MS{node},MI100 |
Motor .......................................................................................Activation Control word |
138 |
|
MS{node},MI101-102 ..................................................................................... |
Primary Feedback Selection |
138 |
|
MS{node},MI103 |
Sin Encoder/ ..........................................................................................Resolver #1 bias |
139 |
|
MS{node},MI104 |
Sin Encoder/ ..........................................................................................Resolver #2 bias |
139 |
|
MS{node},MI105 |
Cosine ....................................................................................Encoder/ Resolver #1 bias |
139 |
|
MS{node},MI106 |
Cosine ....................................................................................Encoder/ Resolver #2 bias |
139 |
|
MS{node},MI107 |
Motor ............................................................................................1 Encoder-Loss Mask |
140 |
|
MS{node},MI108 |
Motor ............................................................................................2 Encoder-Loss Mask |
140 |
|
Primary Channel Node-Specific ....................................................................................Gate Array MI-variables |
142 |
||
MS{node},MI910 |
Primary ......................................................................Encoder/Timer n Decode Control |
142 |
|
MS{node},MI911 |
Primary ..........................................................Enc. Position Compare n Channel Select |
143 |
|
MS{node},MI912 |
Primary ................................................................................Encoder n Capture Control |
143 |
|
MS{node},MI913 |
Primary .............................................................Encoder Capture n Flag Select Control |
144 |
|
MS{node},MI914 |
Primary ............................................................................Encoder n Gated Index Select |
144 |
|
MS{node},MI915 |
Primary .........................................................Encoder Index Gate State/Demux Control |
145 |
|
MS{node},MI910 |
Secondary ................................................................................Encoder Decode Control |
146 |
|
MS{node},MI911 |
Secondary .............................................................................Encoder counter Direction |
146 |
|
MS{node},MI912 |
Secondary ....................................................................Encoder Index Capture Control |
147 |
|
MS{node},MI913 |
Secondary ...........................................................Encoder Home Flag Capture Control |
147 |
|
MS{node},MI914 |
Secondary ...................................................................................Encoder Filter Control |
147 |
|
MS{node},MI915 |
Secondary ............................................................Encoder Capture Flag Select Control |
148 |
|
iv |
Table of Contents |

Geo MACRO Drive User and Reference Manual
MS{node},MI916 |
Output n Mode Select ....................................................................................................... |
148 |
|
MS{node},MI917 |
Output n Invert Control.................................................................................................... |
148 |
|
MS{node},MI918 |
Output n PFM Direction Signal Invert Control ............................................................... |
149 |
|
MS{node},MI919 |
Hardware 1/T ................................................................................................................... |
149 |
|
MS{node},MI921 |
Flag Capture Position (Read Only).................................................................................. |
150 |
|
MS{node},MI922 |
ADC A Input Value (Read Only) ...................................................................................... |
150 |
|
MS{node},MI923 |
Compare Auto-Increment Value....................................................................................... |
150 |
|
MS{node},MI924 |
ADC B Input Value (Read Only) ...................................................................................... |
150 |
|
MS{node},MI925 |
Compare A Position Value ............................................................................................... |
151 |
|
MS{node},MI926 |
Compare B Position Value ............................................................................................... |
151 |
|
MS{node},MI927 (Reserved for future use)...................................................................................................... |
151 |
||
MS{node},MI928 |
Compare-State Write Enable............................................................................................ |
151 |
|
MS{node},MI929 |
Compare-Output Initial State........................................................................................... |
151 |
|
General Hardware Setup MI-variables.................................................................................................................. |
152 |
||
MS{anynode}, MI930 SSI Channel 1 Control Word ..................................................................................... |
152 |
||
MS{anynode}, MI931 SSI Channel 2 Control Word .................................................................................... |
152 |
||
MS{anynode}, MI932 Resolver Excitation Frequency Divider.................................................................... |
153 |
||
MS{anynode}, MI933 SSI Clock Frequency Divider ................................................................................... |
153 |
||
MS{anynode},MI934-MI939 (Reserved for future use)................................................................................ |
153 |
||
MS{anynode}, MI940 |
Resolver Excitation Gain......................................................................................... |
153 |
|
MS{anynode}, MI941 |
Resolver Excitation Phase Offset............................................................................. |
154 |
|
MS{anynode},MI942 ADC Strobe Word Channel 1* & 2* .......................................................................... |
154 |
||
MS{node},MI943 |
Encoder Power control bit ............................................................................................... |
154 |
|
MS{node},MI944-MI949 |
(Reserved for future use) ..................................................................................... |
154 |
|
Global & 2-Axis Board I-Variables ...................................................................................................................... |
155 |
||
MS{node},MI992 |
MaxPhase Frequency Control.......................................................................................... |
155 |
|
MS{node},MI993 |
Hardware Clock Control Handwheel Channels............................................................... |
155 |
|
MS{node},MI994 |
PWM Deadtime ............................................................................................................... |
157 |
|
MS{node},MI995 |
MACRO Ring Configuration/Status ................................................................................. |
157 |
|
MS{node},MI996 |
MACRO Node Activate Control ....................................................................................... |
158 |
|
MS{node},MI997 |
Phase Clock Frequency Control ...................................................................................... |
160 |
|
MS{node},MI998 |
Servo Clock Frequency Control ....................................................................................... |
160 |
|
ABSOLUTE POWER ON ONLINE COMMANDS............................................................................................. |
161 |
||
$$*......................................................................................................................................................................... |
|
|
161 |
$*........................................................................................................................................................................... |
|
|
161 |
APPENDIX A........................................................................................................................................................... |
|
|
166 |
Fiber Optic Cable Ordering Information............................................................................................................... |
166 |
||
Mating Connector and Cable Kits ......................................................................................................................... |
166 |
||
Mating Connector and Cable Kits .................................................................................................................... |
166 |
||
Connector and pins Part numbers .................................................................................................................... |
168 |
||
Cable Drawings ................................................................................................................................................ |
|
|
170 |
Regenerative Resistor: GAR78/48 ....................................................................................................................... |
176 |
||
Type of Cable for Encoder Wiring........................................................................................................................ |
177 |
||
APPENDIX B........................................................................................................................................................... |
|
|
180 |
Schematics............................................................................................................................................................. |
|
|
180 |
X3: Discrete I/O............................................................................................................................................... |
|
|
180 |
X6 and X7: Analog Inputs................................................................................................................................ |
182 |
||
X8 and X9 Secondary Encoders (3 and 4) ........................................................................................................ |
183 |
||
APPENDIX C........................................................................................................................................................... |
|
|
184 |
Communication to the Geo MACRO via the USB Port ........................................................................................ |
184 |
||
APPENDIX D........................................................................................................................................................... |
|
|
186 |
MACRO Flag Transfer Location........................................................................................................................... |
186 |
||
Turbo PMAC2 Node Addresses............................................................................................................................ |
187 |
||
Table of Contents |
v |

|
Geo MACRO Drive User Manual |
ADC Register Table .............................................................................................................................................. |
189 |
Stepping through an Electrical Cycle .................................................................................................................... |
190 |
Manually Stepping through an Electrical Cycle at 30 degree increments........................................................ |
190 |
Example 1 of Hall Effect Values ....................................................................................................................... |
191 |
Example 2 of Hall Effect Values ....................................................................................................................... |
192 |
USEFUL NOTES..................................................................................................................................................... |
193 |
vi |
Table of Contents |

Geo MACRO Drive User and Reference Manual
INTRODUCTION
The Geo Drive family of “bookcase”-style servo amplifiers provides many new capabilities for users. This family of 1- and 2-axis 3-phase amplifiers, built around a common core of highly integrated IGBTbased power circuitry, supports a wide variety of motors, power ranges, and interfaces. The 2-axis configurations share common power input, bus, and shunt for a very economical implementation.
Three command interfaces are provided: direct-PWM, MACRO-ring, and integrated PMAC controller, each described in following sections. In all three cases, fully digital “direct PWM” control is used. Direct PWM control eliminates D-to-A and A-to-D conversion delays and noise, allowing higher gains for more robust and responsive tuning without sacrificing stability.
All configurations provide these power-stage features:
•Direct operation off AC power mains (100 – 240 or 300 – 480 VAC, 50/60 Hz) or optional DC power input (24 – 350 or 24 – 700 VDC)
•Integrated bus power supply including soft start and shunt regulator (external resistor required)
•Separate 24VDC input to power logic circuitry
•Complete protection: over voltage, under voltage, over temperature, PWM frequency limit, minimum dead time, motor over temperature, short circuit, over current, input line monitor
•Ability to drive brushed and brushless permanent-magnet servo motors, or AC induction motors
•Single-digit LED display and six discrete LEDs for status information
•Optional safety relay circuitry. Please contact factory for more details and pricing.
•Easy setup with Turbo PMAC and UMAC controllers.
User Interface
The Geo Drive family is available in different versions distinguished by their user interface styles.
Geo MACRO Drives
The Geo MACRO Drive interfaces to the controller through the 125 Mbit/sec MACRO ring, with either a fiber-optic or Ethernet electrical medium, accepting numerical command values for direct PWM voltages and returning numerical feedback values for phase current, motor position, and status. It accepts many types of position feedback to the master controller, as well as axis flags (limits, home, and user) and general-purpose analog and digital I/O. Typically, the Geo MACRO Drives are commanded by either a PMAC2 Ultralite bus-expansion board, or a UMAC rack-mounted controller with a MACRO-interface card. This provides a highly distributed hardware solution, greatly simplifying system wiring, while maintaining a highly centralized software solution, keeping system programming simple.
•Choices for main feedback for each axis: A/B quadrature encoder, sinusoidal encoder with EnDatTM or HiperfaceTM, SSI encoder, resolver
•Secondary A/B quadrature encoder for each axis
•General-purpose isolated digital I/O: 4 in, 4 out at 24VDC
•2 optional A/D converters, 12or 16-bit resolution
Note:
Geo MACRO is not using the regular 8-axis or 16-axis MACRO station CPU. A new MACRO CPU was developed for the Geo MACRO drive.
Introduction |
1 |

Geo MACRO Drive User Manual
Geo PMAC Drives
The Geo PMAC Drive is a standalone-capable integrated controller/amplifier with a built-in full PMAC2 controller having stored-program capability. It can be operated standalone, or commanded from a host computer through USB2.0 or 100 Mbps Ethernet ports. The controller has the full software capabilities of a PMAC (see descriptions), with an internal fully-digital connection to the advanced Geo power-stage , providing a convenient, compact, and cost-effective installation for one and two-axis systems, with easy synchronization to other drives and controls.
•Choices for main feedback for each axis: A/B quadrature encoder, sinusoidal encoder with EnDatTM or HiperfaceTM, SSI encoder, resolver
•Secondary A/B quadrature encoder for each axis
•General-purpose isolated digital I/O: 8 in, 6 out at 24VDC
•2 optional A/D converters 12or 16-bit resolution
Geo Direct-PWM Drives
The direct-PWM interface versions accept the actual power-transistor on/off signals from the PMAC2 controller, while providing digital phase-current feedback and drive status to the controller for closedloop operation. Interface to the direct-PWM amplifier is through a standard 36-pin Mini-D style cable. The drive performs no control functions but has protection features. Drive installation, maintenance, and replacement are simplified because there is less wiring (position feedback and I/O are not connected to the drive) and there are no variables to set or programs to install in the drive.
•Fully centralized control means that all gains and settings are made in the PMAC; no software setup of drive is required
•No position feedback or axis flags required at the drive
MACRO Defined
MACRO defined is a digital interface for connection of multi–axis motion controllers, amplifiers and other I/O devices on a fiber optic or twisted pair copper (RJ45 connector) ring.
MACRO operates in a ring topology. Data is transmitted serially. Each station on the ring has an in port for receiving data and an out port for transmitting data. Nodes, residing at a station can be amplifier axes, I/O banks, or communication interfaces to other devices. A station can have one or several nodes allowing for multi-axis amplifiers with a single in and single out port. Data packets, (groups of 96 bits of serial data) from the motion controller or master node are addressed to a specific amplifier or slave node. If the data packet is not for an amplifier, it is passed on unchanged. If it is for the node, it copies the contents of the data packet (typically commands), places feedback data into a packet, and transmits the data packet.
MACRO’s Advantages are:
•Single–plug connections between controls and amplifiers: A single fiber optic strand can provide a controller with: position feedback, flag status (limits, home flag), amplifier status and machine input status. This same strand can communicate to the amplifier and other devices on the MACRO network (Amplifier enable and amplifier command signals, machine outputs, commands to D/A converters; all can be implemented with a single plug connection).
•Noise Immunity: Fiber–optic cable transmits light, not electricity. Unlike electricity light is immune to electromagnetic noise, capacitive coupling, ground loops, and other wiring problems.
•Speed: MACRO’s operation is 125 Mbits/second. This is at least 25 times faster than other digital motion control interfaces.
2 |
Introduction |

Geo MACRO Drive User and Reference Manual
•One ring, multiple masters: In a ring network, several motion controllers (masters) can be on one ring. Each controller controls several axes (up to 32 ea.).
•Simplicity: Transmission within the MACRO ring requires no software intervention. The information sent to all nodes is written to a memory location and the MACRO hardware takes care of the rest.
Feedback Devices
Many motors incorporate a position feedback device. Devices are incremental encoders, resolvers, and sine encoder systems. The macro version of the Geo drive accepts feedback. In its standard form, it is set up to accept incremental encoder feedback. With the appropriate feedback option, it is possible to use either resolver or sinusoidal encoder feedback. Historically, the choice of a feedback device has been guided largely by cost and robustness. Today, feedbacks are relatively constant for the cost and picked by features such as size and feedback data. More feedback data or resolution provides the opportunity to have higher gains in a servo system.
Geo MACRO drives have standard secondary quadrature encoder feedback. One secondary encoder (X8) for one axis drive and two secondary encoders (X8 and X9) for dual axis drives (603542 rev-10A and above). Earlier versions of the Geo MACRO drive cannot use the secondary encoders.
Compatible Motors
The Geo drive product line is capable of interfacing to a wide variety of motors. The Geo drive can control almost any type of three-phase brushless motor, including DC brushless rotary, AC brushless rotary, induction, and brushless linear motors. Permanent magnet DC brush motors can also be controlled using two of the amplifiers three phases. Motor selection for an application is a science in itself and cannot be covered in this manual. However, some basic considerations and guidelines are offered. Motor manufacturers include a host of parameters to describe their motor.
Some basic equations can help guide an applications engineer to mate a proper drive with a motor. A typical application accelerates a load to a speed, running the speed for a while and then decelerating the load back into position.
Maximum Speed
The motor’s maximum rated speed is given. This speed may or may not be achievable in a given system. The speed could be achieved if enough voltage and enough current loop gain are available. Also consider the motor’s feedback adding limitations to achievable speeds. The load attached to the motor also limits the maximum achievable speed. In addition, some manufacturers will provide motor data with their drive controller, which is tweaked to extend the operation range that other controllers may be able to provide. In general, the maximum speed can be determined by input voltage line-to-line divided by Kb (the motor’s back EMF constant). It is wise to de-rate this a little for proper servo applications.
Torque
The torque required for the application can be viewed as both instantaneous and average. Typically, the instantaneous or peak torque is calculated as a sum of machining forces or frictional forces plus the forces required to accelerate the load inertia. The machining or frictional forces on a machine must be determined by the actual application. The energy required to accelerate the inertia follows the equation: T = JA, where T is the torque in Newton-meters or pound-feet required for the acceleration, J is the inertia in kilogram-meters-squared or pound-feet-second squared, and A is in radians per second per second. The required torque can be calculated if the desired acceleration rate and the load inertia reflected back to the motor are known. The T=JA equation requires that the motor’s inertia be considered as part of the inertia-requiring torque to accelerate.
Once the torque is determined, the motors specification sheet can be reviewed for its torque constant parameter (Kt). The torque required at the application divided by the Kt of the motor provides the peak current required by the amplifier. A little extra room should be given to this parameter to allow for good
Introduction |
3 |

Geo MACRO Drive User Manual
servo control.
Most applications have a duty cycle in which the acceleration profile occurs repetitively over time. Calculating the average value of this profile gives the continuous rating required by the amplifier. Applications also concern themselves with the ability to achieve a speed. The requirements can be reviewed by either defining what the input voltage is to the drive, or defining what the voltage requirements are at the motor. Typically, a system is designed at a 230 or 480V input line. The motor must be able to achieve the desired speed with this voltage limitation. This can be determined by using the voltage constant of the motor (Kb), usually specified in volts-per-thousand rpm. The application speed is divided by 1000 and multiplied by the motor's Kb. This is the required voltage to drive the motor to the desired velocity. Headroom of 20% is suggested to allow for good servo control.
Peak Torque
The peak torque rating of a motor is the maximum achievable output torque. It requires that the amplifier driving it be able to output enough current to achieve this. Many drive systems offer a 3:1 peak-to- continuous rating on the motor, while the amplifier has a 2:1 rating. To achieve the peak torque, the drive must be sized to be able to deliver the current to the motor. The required current is often stated on the datasheet as the peak current through the motor. In some sense, it can also be determined by dividing the peak amplifier's output rating by the motor's torque constant (Kt).
Continuous Torque
The continuous torque rating of the motor is defined by a thermal limit. If more torque is consumed from the motor than this on average, the motor overheats. Again, the continuous torque output of the motor is subject to the drive amplifier’s ability to deliver that current. The current is determined by the manufacturer’s datasheets stating the continuous RMS current rating of the motor and can also be determined by using the motor’s Kt parameter, usually specified in torque output per amp of input current.
Motor Poles
Usually, the number of poles in the motor is not a concern to the actual application. However, it should be noted that each pole-pair of the motor requires an electrical cycle. High-speed motors with high motor pole counts can require high fundamental drive frequencies that a drive amplifier may or may not be able to output. In general, drive manufacturers with PWM switching frequencies (16kHz or below) would like to see commutation frequencies less than 400 Hz. The commutation frequency is directly related to the number of poles in the motor.
Motor Inductance
PWM outputs require significant motor inductance to turn the on-off voltage signals into relatively smooth current flow with small ripple. Typically, motor inductance of servomotors is 1 to 15 mH. The Geo drive product series can drive this range easily. On lower-inductance motors (below 1mH), problems occur due to PWM switching where large ripple currents flow through the motor, causing excessive energy waste and heating. If an application requires a motor of less than 1mH, external inductors are recommended to increase that inductance. Motors with inductance in excess of 15mH can still be driven, but are slow to react and typically are out of the range of high performance servomotors.
Motor Resistance
Motor resistance is not really a factor in determining the drive performance, but rather, comes into play more with the achievable torque or output horsepower from the motor. The basic resistance shows up in the manufacturer's motor horsepower curve.
Motor Back EMF
The back EMF of the motor is the voltage that it generates as it rotates. This voltage subtracts from the bus voltage of the drive and reduces the ability to push current through the motor. Typical back EMF
4 |
Introduction |

Geo MACRO Drive User and Reference Manual
ratings for servomotors are in the area of 8 to 200 volts-per-thousand rpm. The Geo drive product series can drive any range of back EMF motor, but the back EMF is highly related to the other parameters of the motor such as the motor inductance and the motor Kt. It is the back EMF of the motor that limits the maximum achievable speed and the maximum horsepower capability of the motor.
Motor Torque Constant
Motor torque constant is referred to as Kt and usually it is specified in torque-per-amp. It is this number that is most important for motor sizing. When the load that the motor will see and knowing the motor’s torque constant is known, the drive amplifier requirements can be calculated to effectively size a drive amplifier for a given motor. Some motor designs allow Kt to be non-linear, in which Kt will actually produce less torque per unit of current at higher output speeds. It is wise to de-rate the systems torque producing capability by 20% to allow headroom for servo control.
Motor Inertia
Motor inertia comes into play with motor sizing because torque to accelerate the inertia of the motor is effectively wasted energy. Low inertia motors allow for quicker acceleration. However, consider the reflected inertia from the load back to the motor shaft when choosing the motor’s inertia. A high ratio of load-to-motor inertia can limit the achievable gains in an application if there is compliance in the transmission system such as belt-drive systems or rubber-based couplings to the systems. The closer the rotor inertia matches the load’s reflected inertia to the motor shaft, the higher the achievable gains will be for a given system. In general, the higher the motor inertia, the more stable the system will be inherently. Mechanical gearing is often placed between the load and the motor simply to reduce the reflected inertia back to the motor shaft.
Motor Cabling
Motor cables are an integral part of a motor drive system. Several factors should be considered when selecting motor cables. First, the PWM frequency of the drive emits electrical noise. Motor cables must have a good-quality shield around them. The motor frame must also have a separate conductor to bring back to the drive amplifier to help quench current flows from the motor due to the PWM switching noise. Both motor drain wire and the cable shield should be tied at both ends to the motor and to the drive amplifier.
Another consideration in selecting motor cables is the conductor-to-conductor capacitance rating of the cable. Small capacitance is desirable. Longer runs of motor cable can add motor capacitance loading to the drive amplifier causing undesired spikes of current. It can also cause couplings of the PWM noise into the earth grounds, causing excessive noise as well. Typical motor cable ratings would be 50 pf per foot maximum cable capacitance.
Another factor in picking motor cables is the actual conductor cross-sectional area. This refers to the conductors ability to carry the required current to and from the motor. When calculating the required cable dimensions, consider agency requirements, safety requirements, maximum temperature that the cable will be exposed to, the continuous current flow through the motor, and the peak current flow through the motor. Typically, it is not suggested that any motor cable be less than 14 AWG.
The motor cable’s length must be considered as part of the application. Motor cable length affects the system in two ways. First, additional length results in additional capacitive loading to the drive. The drive’s capacitive loading should be kept to no more than 1000pf. Additionally, the length sets up standing waves in the cable, which can cause excessive voltage at the motor terminals. Typical motor cable length runs of up to 60 meters (200 feet) for 230V systems and 15 meters (50 feet) for 480V systems are acceptable. Exceeding these lengths may put other system requirements in place for either a snubber at the motor end or a series inductor at the drive end. The series inductor at the drive end provides capacitance loading isolation from the drive and slows the rise time of the PWM signal into the cable, resulting in less voltage overshoot at the motor.
Introduction |
5 |

Geo MACRO Drive User Manual
6 |
Introduction |

Geo MACRO Drive User and Reference Manual
SPECIFICATIONS
Part Number
Geo MACRO Drive
Model Number Definition
G M L 03 1 R 0
Voltage Rating (Direct Mains)
L = 110 - 240 VAC
H = 300 - 480 VAC
Continuous/Peak Current Rating (Sinusoidal RMS)
01 = 1.5/4.5 Amp (one or 3φoperation ) 03 = 3/9 Amp (one or 3φoperation )
05 = 5/10 Amp (3φinput, for single φ need to derate 20%) 10 = 10/20 Amp (3φinput*)
15 = 15/30 Amp (3φinput*)
20 = 20/40 Amp (3φinput*)
30 = 30/60 Amp (3φinput*)
*For single phase input, need to derate 30%
Number of Axes
1 = Single Axis
2 = Dual Axis
Product Width According to Ratings |
|
|
Single-Width Units: |
Double-Width Units: |
|
1.5/4.5 Dual Axis |
10/20 Dual Axis (480VAC) |
|
3/9 |
Dual Axis |
15/30 Dual Axis |
5/10 |
Single and Dual Axis |
20/40 Single Axis |
10/20 |
Single Axis and Dual Axis (240VAC) |
30/60 Single Axis |
15/30 |
Single Axis |
|
Feedback Options
0 = No options, Default; Standard feedback per axis is quadrature differential encoder with hall effect inputs or SSI absolute encoder .
1 = Analog Feedback including :
•Option 0 Standard Feedback
•4096x Sin/Cos interpolator
•Resolver Interface
2 = Absolute Feedback including :
•Option 1 Analog Feedback
•Endat™
•Hiperface™
3, 4, 5 = Same as Options 0, 1 and 2 described above but with two 16-bit analog-to-digital converter inputs
Note: Any available method can be used for feedback but only one method can be used at any time . Feedback method is selected by wiring.
MACRO Link Options:
F = Fiber Optic
R = RJ/45 (Default)
|
|
GMx012xx |
GMx051xx |
GMx101xx |
GMx151xx |
GMx032xx |
GMx052xx |
GML102xx |
GMx201xx |
GMx301xx |
GMH102xx |
GMx152xx |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Axis |
Single axis |
|
√ |
√ |
√ |
|
|
|
√ |
√ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dual Axis |
√ |
|
|
|
√ |
√ |
√ |
|
|
√ |
√ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Size |
Single Width |
√* |
√ |
√ |
√ |
√ |
√ |
√ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Double width |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
√ |
√ |
√ |
√ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Low Profile Unit, No heatsink, no Fan
Specifications |
7 |

Geo MACRO Drive User Manual
Geo MACRO Feedback Options
Model |
Default Configuration: |
Analog (Sin/Cos) Encoders: |
Absolute Encoder |
Addition of two |
|
Quadrature Encoders |
x4096 Interpolator |
Interfaces: |
channels of 16-bit |
|
Or SSI Absolute Encoders |
Resolver to Digital |
EnDat |
A/D converters with |
|
And Hall Effect inputs |
Converters |
Hiperface |
each feedback option |
GMxxxxx0 |
√ |
|
|
|
GMxxxxx1 |
|
√ |
|
|
GMxxxxx2 |
|
|
√ |
|
GMxxxxx3 |
√ |
|
|
√ |
GMxxxxx4 |
|
√ |
|
√ |
GMxxxxx5 |
|
|
√ |
√ |
Package Types
Geo package types provide various power levels and one or two axis capability with three different package types.
The Geo Drive has a basic package size of 3.3"W x 11"H x 8.0"D(84mm W x 280mm H x 203mm D). This size includes the heat sink and fan. In this package size, Single Width, the Geo can handle one or two low-to-medium power axes or only a single axis for medium to high power.
The mechanical design of the Geo drive is such that it allows two heat sinks to be easily attached together to provide two high power axes in a double width configuration. This double package size is 6.5" W x 11" H x 8.0" D (165 mm W x 280 mm H x 203 mm D). It provides a highly efficient package size containing two axes of up to about 10kW each thus driving nearly 24kW of power, but using a single interface card. This results in a highly cost effective package.
There is also one more package type only for the low power (1.5A/4.5A) single width Geo drive, model Gxx012xx. This package substitutes the heatsink and the fan with a smaller plate which has the same mounting pattern as the regular single width drive, making the units depth 2.2inches (56mm) less than the single width drive, 5.8" D (148mm D).
•Low Profile: GMx012xx (only)
3.3" wide (84 mm) (no heatsink, no fan), Maximum Power Handling ~1200 watts Package Dimensions: 3.3" W x 11" H x 5.8" D (84 mm W x 280 mm H x 148 mm D) Weight: 4.3 lbs. (1.95kgs)
•Single Width: GMx051xx, GMx101xx, GMx151xx, GMH032xx, GMx052xx and GML102xx.
3.3" wide (84 mm)(with heatsink and fan), Maximum Power Handling ~12000 watts GML032xx Single Width, with heatsink, no Fan (Weight 5.4lbs/2.45kgs)
Package Dimensions: 3.3" W x 11" H x 8.0" D (84 mm W x 280 mm H x 203 mm D) Weight: 5.5 lbs. (2.50kgs)
•Double Width: GMx201xx, GMx301xx, GMH102xx and GMx152xx.
6.5” wide (164mm)(with heatsink and fan), Maximum Power Handling ~24,000 watts Package Dimensions: 6.5" W x 11" H x 8.0" D (164 mm W x 280 mm H x 203 mm D) Weight: 11.6lbs (5.3kgs)
8 |
Specifications |

Geo MACRO Drive User and Reference Manual
Electrical Specifications
230VAC Input Drives
|
|
GxL051 |
|
GxL101 |
GxL151 |
|
GxL201 |
|
GxL301 |
|
Nominal Input Voltage (VAC) |
|
|
|
230 |
|
|
|
|
|
Rated Input Voltage (VAC) |
|
|
|
97-265 |
|
|
|
|
|
Rated Continuous Input Current (A |
3.3 |
|
6.6 |
9.9 |
|
13.2 |
|
19.8 |
Main |
ACRMS) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Input |
Rated Input Power (Watts) |
1315 |
|
2629 |
3944 |
|
5259 |
|
7888 |
Power |
Frequency (Hz) |
|
|
|
50/60 |
|
|
|
|
|
Phase Requirements |
1Φ or 3Φ |
|
|
|
3Φ |
|
|
|
|
Charge Peak Inrush Current (A) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Main Bus Capacitance (µf) |
3380 |
5020 |
|
6800 |
||||
|
Rated Output Voltage (V) |
|
|
|
138 |
|
|
|
|
Output |
Rated Cont. Output Current per Axis |
5 |
|
10 |
15 |
|
20 |
|
30 |
Power |
Peak Output Current (A) for 2 seconds |
10 |
|
20 |
30 |
|
40 |
|
60 |
|
Rated Output Power per Axis (Watts) |
1195 |
|
2390 |
3585 |
|
4780 |
|
7171 |
Bus |
Nominal DC Bus |
|
|
|
325 |
|
|
|
|
Over-voltage Trip Level (VDC) |
|
|
|
410 |
|
|
|
|
|
Protection |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Under-voltage Lockout Level (VDC) |
|
|
|
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Shunt |
Turn-On Voltage (VDC) |
|
|
|
392 |
|
|
|
|
Turn-Off Voltage (VDC) |
|
|
|
372 |
|
|
|
|
|
Regulator |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Ratings |
Delta Tau Recommended Load Resistor |
GAR78 |
|
GAR48 |
|
GAR48-3 |
|||
(300 W Max.) |
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Control |
Input Voltage (VDC) |
|
|
|
20-27 |
|
|
|
|
Logic |
Input Current (A) |
|
|
|
2A |
|
|
|
|
Power |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Inrush Current (A) |
|
|
|
4A |
|
|
|
|
|
Current |
Resolution (bits) |
|
|
|
12 |
|
|
|
|
Feedback |
Full-scale Signed Reading (±A) |
16.26 |
|
32.53 |
48.79 |
|
65.05 |
|
97.58 |
|
Delta Tau Recommended PWM |
|
12 |
10 |
|
|
8 |
||
Transistor |
Frequency (kHz) @rated current |
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Control |
Minimum Dead Time (µs) |
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
Charge Pump Time (% of PWM period.) |
|
|
|
5 |
|
|
|
|
Note:
All values at ambient temperature of 0-45°C (113F) unless otherwise stated.
Specifications |
9 |

Geo MACRO Drive User Manual
|
|
|
GxL012 |
|
GxL032 |
GxL052 |
|
GxL102 |
GxL152 |
|
|
Output Circuits (axes) |
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
Nominal Input Voltage (VAC) |
|
|
|
230 |
|
|
|
|
|
Rated Input Voltage (VAC) |
|
|
|
97-265 |
|
|
|
|
|
Rated Continuous Input Current (A |
1.98 |
|
3.96 |
6.6 |
|
13.2 |
19.8 |
Main |
ACRMS) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Rated Input Power (Watts) |
789 |
|
1578 |
2629 |
|
5259 |
7888 |
||
Input |
|
|
|||||||
Frequency (Hz) |
|
|
|
50/60 |
|
|
|
||
Power |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Phase Requirements |
1Φ or 3Φ |
|
1Φ or 3Φ |
|
|
3Φ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Charge Peak Inrush Current (A) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Main Bus Capacitance (µf) |
|
|
3380 |
|
|
5020 |
|
|
|
Rated Output Voltage (V) |
|
|
|
138 |
|
|
|
Output |
Rated Cont. Output Current per Axis |
1.5 |
|
3 |
5 |
|
10 |
15 |
|
Power |
Peak Output Current (A) for 2 seconds |
4.5 |
|
9 |
10 |
|
20 |
30 |
|
|
|
Rated Output Power per Axis (Watts) |
359 |
|
717 |
1195 |
|
2390 |
3585 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Bus |
Nominal DC Bus |
|
|
|
325 |
|
|
|
|
Over-voltage Trip Level (VDC) |
|
|
|
410 |
|
|
|
||
Protection |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Under-voltage Lockout Level (VDC) |
|
|
|
10 |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Shunt |
Turn-On Voltage (VDC) |
|
|
|
392 |
|
|
|
|
Turn-Off Voltage (VDC) |
|
|
|
372 |
|
|
|
||
Regulator |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Ratings |
Delta Tau Recommended Load Resistor |
|
|
GAR78 |
|
|
GAR48 |
||
|
|
(300 W Max.) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Control |
Input Voltage (VDC) |
|
|
|
20-27 |
|
|
|
|
Logic |
Input Current (A) |
|
|
|
2A |
|
|
||
Power |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Inrush Current (A) |
|
|
|
4A |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Current |
Resolution (bits) |
|
|
|
12 |
|
|
|
|
Feedback |
Full-scale Signed Reading (±A) |
7.32 |
|
14.64 |
16.26 |
|
32.53 |
48.79 |
|
|
|
Delta Tau Recommended Maximum |
16 |
|
12 |
|
10 |
||
Transistor |
PWM Frequency (kHz) |
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Control |
Minimum Dead Time (µs) |
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Charge Pump Time (% of PWM period.) |
|
|
|
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Note:
All values at ambient temperature of 0-45°C (113F) unless otherwise stated.
10 |
Specifications |

Geo MACRO Drive User and Reference Manual
480VAC Input Drives
|
|
GxH051 |
GxH101 |
GxH151 |
|
GxH201 |
GxH301 |
|
Output Circuits (axes) |
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
Nominal Input Voltage (VAC) |
|
|
480 |
|
|
|
|
Rated Input Voltage (VAC) |
|
|
300-525 |
|
|
|
|
Rated Continuous Input Current (A |
3.3 |
6.6 |
9.9 |
|
13.2 |
19.8 |
Main |
ACRMS) |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Input |
Rated Input Power (Watts) |
2744 |
5487 |
8231 |
|
10974 |
16461 |
Power |
Frequency (Hz) |
|
|
50/60 |
|
|
|
|
Phase Requirements |
1Φ or 3Φ |
|
|
3Φ |
|
|
|
Charge Peak Inrush Current (A) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Main Bus Capacitance (µf) |
845 |
|
1255 |
|
1700 |
|
|
Rated Output Voltage (V) @ Rated |
|
|
288 |
|
|
|
|
Current |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Rated Cont. Output Current per Axis |
5 |
10 |
15 |
|
20 |
30 |
|
Peak Output Current (A) for 2 seconds |
10 |
20 |
30 |
|
40 |
60 |
|
Rated Output Power per Axis (Watts) |
2494 |
4988 |
7482 |
|
9977 |
14965 |
Bus |
Nominal DC Bus |
|
|
678 |
|
|
|
Over-voltage Trip Level (VDC) |
|
|
828 |
|
|
|
|
Protection |
|
|
|
|
|
||
Under-voltage Lockout Level (VDC) |
|
|
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Shunt |
Turn-On Voltage (VDC) |
|
|
784 |
|
|
|
Turn-Off Voltage (VDC) |
|
|
744 |
|
|
|
|
Regulator |
|
|
|
|
|
||
Ratings |
Delta Tau Recommended Load |
GAR78 |
GAR48 |
|
GAR48-3 |
||
Resistor (300 W Max.) |
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Control |
Input Voltage (VDC) |
|
|
20-27 |
|
|
|
Logic |
Input Current (A) |
|
|
2A |
|
|
|
Power |
Inrush Current (A) |
|
|
4A |
|
|
|
Current |
Resolution (bits) |
|
|
12 |
|
|
|
Feedback |
Full-scale Signed Reading (±Amperes) |
16.26 |
32.53 |
48.79 |
|
65.05 |
97.58 |
|
Delta Tau Recommended PWM |
12 |
10 |
|
8 |
|
|
|
Frequency (KHz) @ rated current |
|
|
||||
Transistor |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Minimum Dead Time (µs) |
|
|
1.6 |
|
|
|
|
Control |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Charge Pump Time (% of PWM |
|
|
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
period.) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Note:
All values at ambient temperature of 0-45°C (113F) unless otherwise stated.
Specifications |
11 |

Geo MACRO Drive User Manual
|
|
|
GxH012 |
|
GxH032 |
GxH052 |
GxH102 |
|
GxH152 |
|
|
|
Output Circuits (axes) |
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
Nominal Input Voltage (VAC) |
|
|
|
|
480 |
|
|
|
|
|
Rated Input Voltage (VAC) |
|
|
|
|
300-525 |
|
|
|
|
|
Rated Continuous Input Current (A |
1.98 |
|
3.96 |
|
6.6 |
13.2 |
|
19.8 |
Main |
ACRMS) |
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Input |
Rated Input Power (Watts) |
1646 |
|
3292 |
|
5487 |
10974 |
|
16461 |
|
Power |
Frequency (Hz) |
|
|
|
|
50/60 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Phase Requirements |
1Φ or 3Φ |
|
|
3Φ |
|
|
||
|
|
Charge Peak Inrush Current (A) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Main Bus Capacitance (µf) |
|
|
|
845 |
|
|
1255 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Rated Output Voltage (V) @ Rated |
|
|
|
|
288 |
|
|
|
|
|
Current |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Rated Cont. Output Current per Axis |
1.5 |
|
3 |
|
5 |
10 |
|
15 |
|
|
Peak Output Current (A) for 2 seconds |
4.5 |
|
9 |
|
10 |
20 |
|
30 |
|
|
Rated Output Power per Axis (Watts) |
748 |
|
1496 |
|
2494 |
4988 |
|
7482 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Bus |
Nominal DC Bus |
|
|
|
|
678 |
|
|
|
|
Over-voltage Trip Level (VDC) |
|
|
|
|
828 |
|
|
|
||
Protection |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Under-voltage Lockout Level (VDC) |
|
|
|
|
20 |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Shunt |
Turn-On Voltage (VDC) |
|
|
|
|
784 |
|
|
|
|
Turn-Off Voltage (VDC) |
|
|
|
|
744 |
|
|
|
||
Regulator |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Ratings |
Delta Tau Recommended Load Resistor |
|
|
GAR78 |
|
|
GAR48 |
|||
(300 W Max.) |
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Control |
Input Voltage (VDC) |
|
|
|
|
20-27 |
|
|
|
|
Logic |
Input Current (A) |
|
|
|
|
2A |
|
|
|
|
Power |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Inrush Current (A) |
|
|
|
|
4A |
|
|
|
||
Current |
Resolution (bits) |
|
|
|
|
12 |
|
|
|
|
Feedback |
Full-scale Signed Reading (±Amperes) |
7.32 |
|
14.64 |
|
16.26 |
32.53 |
|
48.79 |
|
|
|
Delta Tau Recommended PWM |
|
12 |
|
10 |
|
8 |
||
Transistor |
Frequency (KHz) @ rated current |
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Control |
Minimum Dead Time (µs) |
|
|
|
|
1.6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Charge Pump Time (% of PWM period.) |
|
|
|
|
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Note:
All values at ambient temperature of 0-45°C (113F) unless otherwise stated.
12 |
Specifications |

Geo MACRO Drive User and Reference Manual
Environmental Specifications
Description |
Unit |
Specifications |
Operating Temperature |
°C |
+0 to 45°C. Above 45°C, derate the continuous peak output current by |
|
|
2.5% per °C above 45°C. Maximum Ambient is 55°C |
Rated Storage Temperature |
°C |
-25 to +70 |
Humidity |
% |
10% to 90% non-condensing |
Shock |
|
Call Factory |
Vibration |
|
Call Factory |
Operating Altitude |
Feet |
To 3300 feet (1000meters). Derate the continuous and peak output |
|
(Meters) |
current by 1.1% for each 330 feet (100meters) above the 3300feet |
Air Flow Clearances |
in (mm) |
3" (76.2mm) above and below unit for air flow |
Recommended Fusing and Wire Gauge
Model |
Recommended Fuse (FRN/LPN) |
Recommended Wire Gauge* |
GxL012xx |
15 |
14 AWG |
GxL032xx |
20 |
12 AWG |
GxL051xx |
20 |
12 AWG |
GxL052xx |
20 |
12 AWG |
GxL101xx |
20 |
12 AWG |
GxL102xx |
20 |
12 AWG |
GxL151xx |
25 |
10 AWG |
GxL152xx |
25 |
10 AWG |
GxL201xx |
25 |
10 AWG |
GxL301xx |
30 |
8 AWG |
|
|
|
GxH012xx |
15 |
14 AWG |
GxH032xx |
20 |
12 AWG |
GxH051xx |
20 |
12 AWG |
GxH052xx |
20 |
12 AWG |
GxH101xx |
20 |
12 AWG |
GxH102xx |
20 |
12 AWG |
GxH151xx |
25 |
10 AWG |
GxH152xx |
25 |
10 AWG |
GxH201xx |
25 |
10 AWG |
GxH301xx |
30 |
8 AWG |
* See local and national code requirements
Wire Sizes
Geo Drive electronics create a DC bus by rectifying the incoming AC electricity. The current flow into the drive is not sinusoidal but rather a series of narrow, high-peak pulses. Keep the incoming impedance small so that these current pulses are not hindered. Conductor size, transformer size, and fuse size recommendations may seem larger than normally expected. All ground conductors should be 8AWG minimum using wires constructed of many strands of small gauge wire. This provides the lowest impedance to high-frequency noises.
Specifications |
13 |

Geo MACRO Drive User Manual
14 |
Specifications |

Geo MACRO Drive User and Reference Manual
RECEIVING AND UNPACKING
Delta Tau products are thoroughly tested at the factory and carefully packaged for shipment. When the Geo Drive is received, do the following immediately.
1.Observe the condition of the shipping container and report any damage immediately to the commercial carrier that delivered the drive.
2.Remove the drive from the shipping container and remove all packing materials. Check all shipping material for connector kits, documentation, diskettes, CD ROM, or other small pieces of equipment. Be aware that some connector kits and other equipment pieces may be quite small and can be discarded accidentally if care is not used when unpacking the equipment. The container and packing materials can be retained for future shipment.
3.Verify that the part number of the drive received is the same as the part number listed on the purchase order.
4.Inspect the control for external physical damage that may have been sustained during shipment and report any damage immediately to the commercial carrier that delivered the controller.
5.Electronic components in this amplifier are design-hardened to reduce static sensitivity. However, use proper procedures when handling the equipment.
6.If the Geo Drive is to be stored for several weeks before use, be sure that it is stored in a location that conforms to published storage humidity and temperature specifications stated in this manual.
Use of Equipment
The following guidelines describe the restrictions for proper use of the Geo Drive:
•The components built into electrical equipment or machines can be used only as integral components of such equipment.
•The Geo Drives are to be used only on grounded three-phase industrial mains supply networks (TNsystem, TT-system with grounded neutral point).
•The Geo Drives must not be operated on power supply networks without a ground or with an asymmetrical ground.
•If the Geo Drives are used in residential areas, or in business or commercial premises, implement additional filter measures.
•The Geo Drives may be operated only in a closed switchgear cabinet, taking into account the ambient conditions defined in the environmental specifications.
Delta Tau guarantees the conformance of the Geo Drives with the standards for industrial areas stated in this manual, only if Delta Tau components (cables, controllers, etc.) are used.
Receiving and Unpacking |
15 |

Geo MACRO Drive User Manual
16 |
Receiving and Unpacking |

Geo MACRO Drive User and Reference Manual
MOUNTING
The location of the controller is important. Installation should be in an area that is protected from direct sunlight, corrosives, harmful gases or liquids, dust, metallic particles, and other contaminants. Exposure to these can reduce the operating life and degrade the performance of the controller.
Several other factors should be evaluated carefully when selecting a location for installation:
•For effective cooling and maintenance, the controller should be mounted on a smooth, non-flammable vertical surface.
•At least 3 inches (76mm) top and bottom clearance must be provided for airflow. At least 0.4 inches (10mm) clearance is required between controls (each side).
•Temperature, humidity and vibration specifications should also be considered.
The Geo Drives can be mounted with a traditional 4-hole panel mount, two U shape/notches on the bottom and two pear shaped holes on top. This keeps the heat sink and fan (single width and double width drives), inside the mounting enclosure. On the low profile units (low power), the heat sink and fan are replaced with a flat plate and the mounting enclosure itself is used as a heat sink. This reduces the depth of the Geo amplifier by about 2.2 inches (~56 mm) to a slim 5.8 inch D (150 mm D). Mounting is also identical to the single and double width drives through the 4-hole panel mount.
If multiple Geo drives are used, they can be mounted side-by-side, leaving at least to of a 0.4 inch clearance between drives. This means a 3.7 inch center-to-center distance (94 mm) with the single width and low profile Geo drives. Double width Geo amplifiers can be mounted side by side at 6.9 inch center- to-center distance (175 mm).
It is extremely important that the airflow is not obstructed by the placement of conduit tracks or other devices in the enclosure.
The drive is mounted to a back panel. The back panel should be unpainted and electrically conductive to allow for reduced electrical noise interference. The back panel should be machined to accept the mounting bolt pattern of the drive. Make sure that all metal chips are cleaned up before the drive is mounted so there is no risk of getting metal chips inside the drive.
The drive is mounted to the back panel with four M4 screws and internal-tooth lock washers. It is important that the teeth break through any anodization on the drive’s mounting gears to provide a good electrically conductive path in as many places as possible. Mount the drive on the back panel so there is airflow at both the top and bottom areas of the drive (at least three inches).
Caution:
Units must be installed in an enclosure that meets the environmental IP rating of the end product (ventilation or cooling may be necessary to prevent enclosure ambient from exceeding 45° C [113° F]).
Note:
For more detail drawings (SolidWorks, eDrawings, DXF) visit our website under the product that you are looking for.
Mounting |
17 |
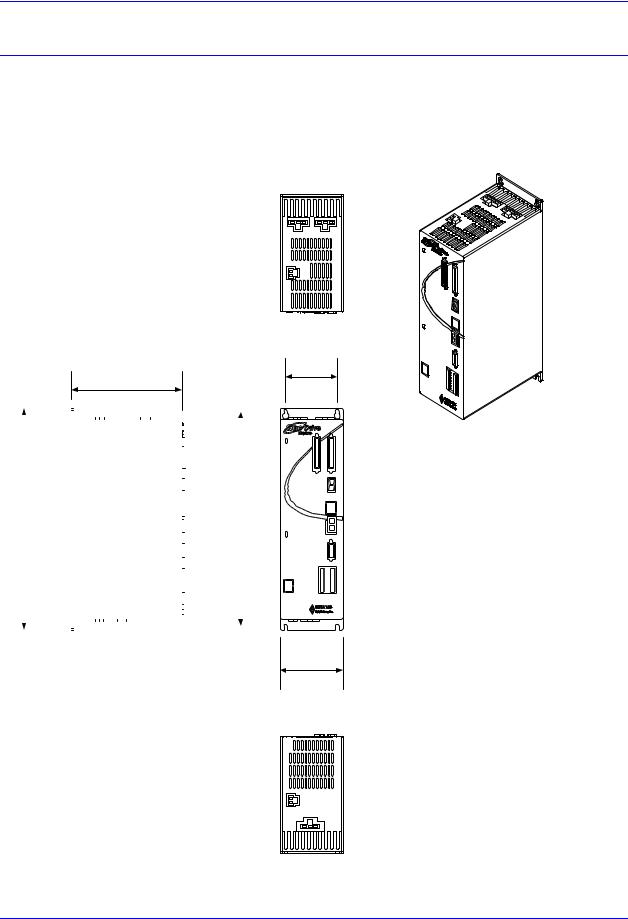
Geo MACRO Drive User Manual
Low Profile
Gxx012xx
|
Width |
Height |
Depth |
Weight |
Mounting dimensions |
3.30in./ 84mm |
11.00in./ 280mm |
5.79in./ 147.1mm |
4.3lbs/ 1.95kgs |
MACRO Version, No Heatsink, No Fan
(2.70)
(5.79)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(11.00) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(10.625) |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(3.30)
18 |
Mounting |
 Loading...
Loading...