Page 1

^1 USER MANUAL & REFERENCE
^2 Geo MACRO Drive
^3 Direct PWM Amplifier over MACRO
^4 500-603701-xUxx
^5 April 27, 2010
Single Source Machine Control Power // Flexibility // Ease of Use
21314 Lassen Street Chatsworth, CA 91311 // Tel. (818) 998-2095 Fax. (818) 998-7807 // www.deltatau.com
Page 2

Page 3

Copyright Information
© 2010 Delta Tau Data Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
This document is furnished for the customers of Delta Tau Data Systems, Inc. Other uses are
unauthorized without written permission of Delta Tau Data Systems, Inc. Information contained in this
manual may be updated from time-to-time due to product improvements, etc., and may not conform in
every respect to former issues.
To report errors or inconsistencies, call or email:
Delta Tau Data Systems, Inc. Technical Support
Phone: (818) 717-5656
Fax: (818) 998-7807
Email: support@deltatau.com
Website: http://www.deltatau.com
Operating Conditions
All Delta Tau Data Systems, Inc. motion controller products, accessories, and amplifiers contain static
sensitive components that can be damaged by incorrect handling. When installing or handling Delta Tau
Data Systems, Inc. products, avoid contact with highly insulated materials. Only qualified personnel
should be allowed to handle this equipment.
In the case of industrial applications, we expect our products to be protected from hazardous or
conductive materials and/or environments that could cause harm to the controller by damaging
components or causing electrical shorts. When our products are used in an industrial environment, install
them into an industrial electrical cabinet or industrial PC to protect them from excessive or corrosive
moisture, abnormal ambient temperatures, and conductive materials. If Delta Tau Data Systems, Inc.
products are directly exposed to hazardous or conductive materials and/or environments, we cannot
guarantee their operation.
Safety Instructions
Qualified personnel must transport, assemble, install, and maintain this equipment. Properly qualified
personnel are persons who are familiar with the transport, assembly, installation, and operation of
equipment. The qualified personnel must know and observe the following standards and regulations:
IEC 364 resp. CENELEC HD 384 or DIN VDE 0100
IEC report 664 or DIN VDE 0110
National regulations for safety and accident prevention or VBG 4
Incorrect handling of products can result in injury and damage to persons and machinery. Strictly adhere
to the installation instructions. Electrical safety is provided through a low-resistance earth connection. It is
vital to ensure that all system components are connected to earth ground.
This product contains components that are sensitive to static electricity and can be damaged by incorrect
handling. Avoid contact with high insulating materials (artificial fabrics, plastic film, etc.). Place the
product on a conductive surface. Discharge any possible static electricity build-up by touching an
unpainted, metal, grounded surface before touching the equipment.
Keep all covers and cabinet doors shut during operation. Be aware that during operation, the product has
electrically charged components and hot surfaces. Control and power cables can carry a high voltage,
even when the motor is not rotating. Never disconnect or connect the product while the power source is
energized to avoid electric arcing.
Page 4
After removing the power source from the equipment, wait at least 10 minutes before touching or
disconnecting sections of the equipment that normally carry electrical charges (e.g., capacitors, contacts,
screw connections). To be safe, measure the electrical contact points with a meter before touching the
equipment.
The following text formats are used in this manual to indicate a potential for personal injury or equipment
damage. Read the safety notices in this manual before attempting installation, operation, or maintenance
to avoid serious bodily injury, damage to the equipment, or operational difficulty.
WARNING
A Warning identifies hazards that could result in personal injury or death. It
precedes the discussion of interest.
Caution
A Caution identifies hazards that could result in equipment damage. It precedes
the discussion of interest
Note
A Note identifies information critical to the user’s understanding or use of the
equipment. It follows the discussion of interest.
Page 5
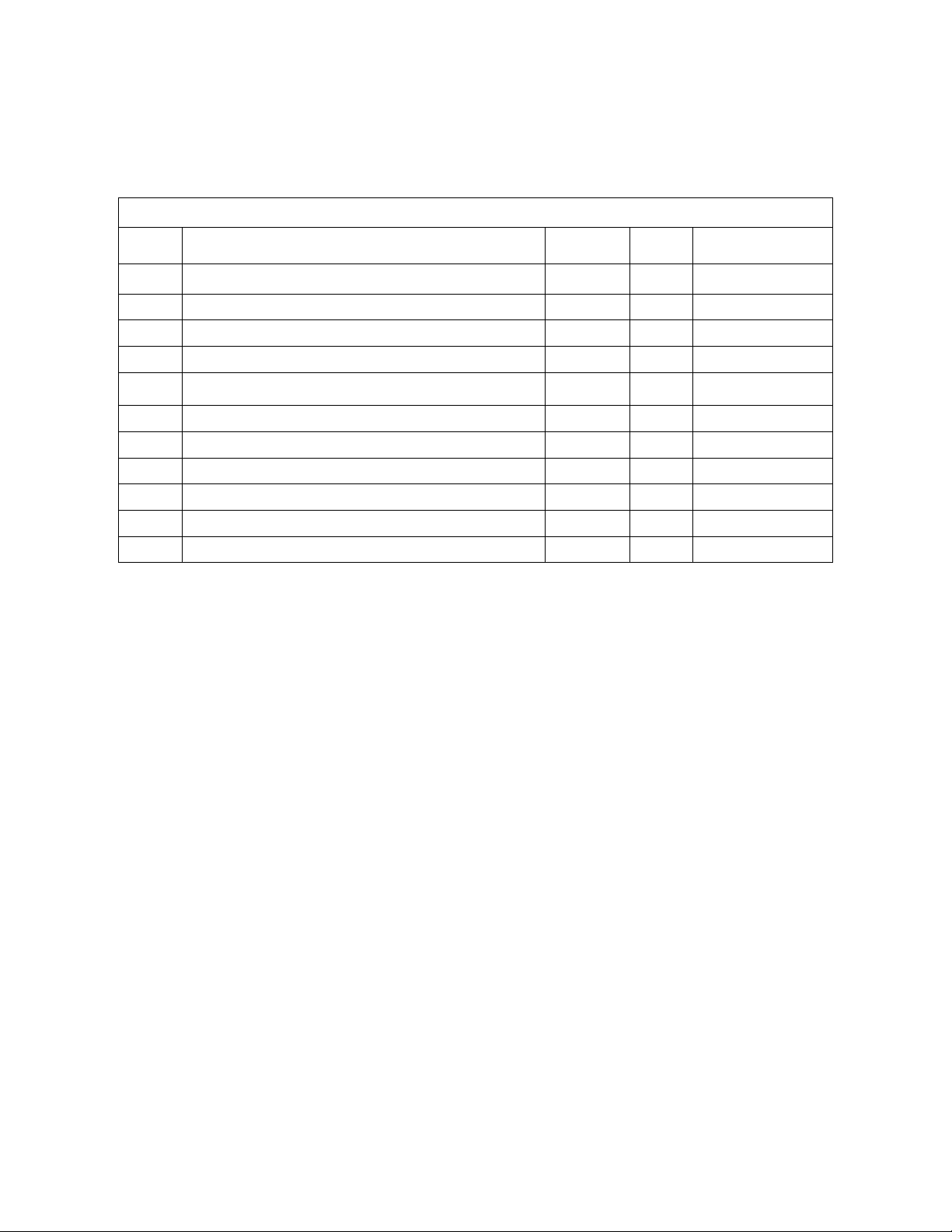
REVISION HISTORY
REV. DESCRIPTION DATE CHG APPVD
1 UPDATED ENDAT SETUP INFO, P. 82 07/18/06 CP P.SHANTZ
2 UPDATED ERROR CODE EF GATE DRIVE INFO 09/21/06 CP P.SHANTZ
3 CORRECTED GP OUT INPUT FUNCTIONS, P. 39 06/11/08 CP K.ZHAO
4 CORRECTED RESET COMMAND, P. 138 10/30/08 CP S. MILICI
5 CORRECTED M-VARIABLE DEFINITIONS, P. 87
6 CORRECTED ERRORS PPS. 85-87 02/25/10 CP S. MILICI
7 CORRECTED COVER PAGE FORMATTING 03/01/10 CP C. PERRY
8 ADDED SAFETY RELAY PN INFO, P. 108 04/27/10 CP S. MILICI
12/08/09 CP S. MILICI
Page 6

Page 7

Geo MACRO Drive User and Reference Manual
Table of Contents
Copyright Information................................................................................................................................................i
Operating Conditions .................................................................................................................................................i
Safety Instructions......................................................................................................................................................i
INTRODUCTION .......................................................................................................................................................1
User Interface ............................................................................................................................................................1
Geo MACRO Drives .............................................................................................................................................1
Geo PMAC Drives ................................................................................................................................................2
Geo Direct-PWM Drives.......................................................................................................................................2
MACRO Defined ......................................................................................................................................................2
Feedback Devices......................................................................................................................................................3
Compatible Motors....................................................................................................................................................3
Maximum Speed....................................................................................................................................................3
Torque...................................................................................................................................................................3
Motor Poles ..........................................................................................................................................................4
Motor Inductance..................................................................................................................................................4
Motor Resistance ..................................................................................................................................................4
Motor Back EMF ..................................................................................................................................................4
Motor Torque Constant.........................................................................................................................................5
Motor Inertia ........................................................................................................................................................5
Motor Cabling.......................................................................................................................................................5
SPECIFICATIONS .....................................................................................................................................................7
Part Number ..............................................................................................................................................................7
Geo MACRO Feedback Options...............................................................................................................................8
Package Types...........................................................................................................................................................8
Electrical Specifications............................................................................................................................................9
230VAC Input Drives...........................................................................................................................................9
480VAC Input Drives..........................................................................................................................................11
Environmental Specifications..................................................................................................................................13
Recommended Fusing and Wire Gauge..................................................................................................................13
RECEIVING AND UNPACKING...........................................................................................................................15
Use of Equipment....................................................................................................................................................15
MOUNTING ..............................................................................................................................................................17
Low Profile..............................................................................................................................................................18
Single Width............................................................................................................................................................19
Double Width ..........................................................................................................................................................20
CONNECTIONS .......................................................................................................................................................21
System (Power) Wiring...........................................................................................................................................21
Wiring AC Input, J1 ............................................................................................................................................23
Wiring Earth-Ground .........................................................................................................................................23
Wiring 24 V Logic Control, J4............................................................................................................................24
Wiring the Motors ...................................................................................................................................................24
J2: Motor 1 Output Connector Pinout...............................................................................................................24
J3: Motor 2 Output Connector Pinout...............................................................................................................24
Wiring the Motor Thermostats................................................................................................................................25
Wiring the Regen (Shunt) Resistor, J5....................................................................................................................25
J5: External Shunt Connector Pinout ................................................................................................................26
Shunt Regulation.................................................................................................................................................27
Minimum Resistance Value.................................................................................................................................27
Maximum Resistance Value................................................................................................................................27
Energy Transfer Equations.................................................................................................................................27
Bonding...................................................................................................................................................................29
Filtering...................................................................................................................................................................30
Table of Contents i
Page 8

Geo MACRO Drive User Manual
CE Filtering ........................................................................................................................................................30
Input Power Filtering .........................................................................................................................................31
Motor Line Filtering ...........................................................................................................................................31
I/O Filtering........................................................................................................................................................31
Connecting Main Feedback Sensors (X1 & X2).....................................................................................................32
Digital Quadrature Encoders .............................................................................................................................32
Digital Hall Commutation Sensors.....................................................................................................................33
SSI Encoders.......................................................................................................................................................33
Sinusoidal Encoders ...........................................................................................................................................34
Hiperface® Interface..........................................................................................................................................35
EnDat Interface...................................................................................................................................................36
Resolvers.............................................................................................................................................................37
Connecting Secondary Quad. Encoders (X8 & X9)................................................................................................38
Connecting General Purpose I/O & Flags (X3).......................................................................................................39
Sample wiring the I/O .........................................................................................................................................39
Sample Wiring the Flags.....................................................................................................................................40
Connecting MACRO Ring ......................................................................................................................................41
Fiber Optic MACRO connections (X5)...............................................................................................................41
RJ-45 Copper MACRO connections (X10 &X11)...............................................................................................41
Connecting optional Analog Inputs (X6 & X7) ......................................................................................................42
SOFTWARE SETUP FOR GEO MACRO DRIVES.............................................................................................43
Introduction .............................................................................................................................................................43
Establishing MACRO Communications with Turbo PMAC ..................................................................................43
MACRO Ring Frequency Control Variables ......................................................................................................43
I7: Phase Cycle Extension ..................................................................................................................................43
I6840: MACRO IC 0 Master Configuration .......................................................................................................44
I6890/I6940/I6990: MACRO IC 1/2/3 Master Configuration ............................................................................44
I6841/I6891/I6941/I6991: MACRO IC 0/1/2/3 Node Activation Control...........................................................44
I70/I72/I74/I76: MACRO IC 0/1/2/3 Node Auxiliary Function Enable..............................................................45
I71/I73/I75/I77: MACRO IC 0/1/2/3 Node Protocol Type Control ....................................................................46
I78: MACRO Master/Slave Auxiliary Communications Timeout .......................................................................46
I79: MACRO Master/Master Auxiliary Communications Timeout.....................................................................46
I80, I81, I82: MACRO Ring Check Period and Limits .......................................................................................46
MACRO Node Addresses ....................................................................................................................................47
Using the Turbo PMAC Setup Program .............................................................................................................51
Using the PEWIN32PRO 2 MACRO Ring ASCII Feature..................................................................................58
PEWIN32PRO Suite 2 MACRO Status window..................................................................................................62
Ring Order Communications Method.................................................................................................................63
MACRO ASCII Communications........................................................................................................................64
How to Enable and Disable MACRO ASCII Communication Mode ..................................................................64
SETTING UP PRIMARY FEEDBACK..................................................................................................................67
Device Selection Control.........................................................................................................................................67
Setting up Digital Quadrature Encoders.................................................................................................................67
Setting up SSI Encoders..........................................................................................................................................67
Setting up Sinusoidal Encoders...............................................................................................................................69
Principle of PMAC Interpolation Operation ......................................................................................................69
Setting up Endat ......................................................................................................................................................72
Setting up Resolvers................................................................................................................................................72
Setting up the Phase Shift (MI941) Manually.....................................................................................................73
Setting up the Resolver for Power-On Absolute Position ...................................................................................73
Scaling the Feedback Units ................................................................................................................................74
SETTING UP SECONDARY ENCODERS............................................................................................................75
SETTING UP THE TURBO PMAC CONVERSION TABLE .............................................................................77
ii Table of Contents
Page 9

Geo MACRO Drive User and Reference Manual
SETTING UP TURBO MOTOR OPERATION ....................................................................................................79
Turbo PMAC Basic Setup for Brushless Servo or Induction Motor .......................................................................79
Turbo PMAC Basic Setup for DC Brush Motors................................................................................................80
Instructions for Direct-PWM Control of Brush Motors ..........................................................................................85
PWM/ADC Phase Match ....................................................................................................................................85
Synchronous Motor Stepper Action ....................................................................................................................85
Current Loop Polarity Check..............................................................................................................................85
Troubleshooting..................................................................................................................................................86
Testing PWM and Current Feedback Operation .....................................................................................................86
Purpose...............................................................................................................................................................86
Preparation.........................................................................................................................................................87
Position Feedback and Polarity Test..................................................................................................................87
Setting Up Hall Commutation Sensors....................................................................................................................88
Signal Format .....................................................................................................................................................88
Using Hall Effect Sensors for Phase Reference..................................................................................................89
Determining the Commutation Phase Angle.......................................................................................................89
Finding the Hall Effect Transition Points...........................................................................................................89
Calculating the Hall Effect Zero Point (HEZ)....................................................................................................90
Determining the Polarity of the Hall Effects – Standard or Reversed................................................................92
Software Settings for Hall Effect Phasing...........................................................................................................92
Setting I2T Protection ..............................................................................................................................................96
Calculating Minimum PWM Frequency .................................................................................................................97
SETTING UP DISCRETE INPUTS AND OUTPUTS...........................................................................................99
Inputs and Outputs ..................................................................................................................................................99
Ring Break Output indicator MS{node},MI13 .....................................................................................................100
Setting up the Analog Inputs (X6 and X7)............................................................................................................100
Limit and Flag Circuit Wiring...............................................................................................................................102
Connecting Limits/Flags to the Geo Drive .......................................................................................................102
Setting up Position Compare (EQU) Outputs........................................................................................................103
Setting up for a Single Pulse Output.................................................................................................................103
Setting up for Multiple Pulse Outputs...............................................................................................................104
CONNECTORS.......................................................................................................................................................105
Connector Pinouts .................................................................................................................................................105
X1: Encoder Input 1.........................................................................................................................................105
X2: Encoder Input 2.........................................................................................................................................106
X3: General Purpose I/O..................................................................................................................................107
X4: Safety Relay (Optional).............................................................................................................................108
X6: Analog IN 1 (Optional 3/4/5) ....................................................................................................................108
X7: Analog IN 2 (Optional 3/4/5) ....................................................................................................................108
X8: S. Encoder 1 ..............................................................................................................................................109
X9: S. Encoder 2 ..............................................................................................................................................109
X13: Discrete I/O.............................................................................................................................................109
J1: AC Input Connector Pinout .......................................................................................................................110
J2: Motor 1 Output Connector Pinout.............................................................................................................110
J3: Motor 2 Output Connector Pinout (Optional) ...........................................................................................110
J4: 24VDC Input Logic Supply Connector .......................................................................................................110
J5: External Shunt Connector Pinout ..............................................................................................................110
MACRO Link Connectors.....................................................................................................................................111
X5: MACRO I/O, MACRO Fiber Optic Transceiver (Optional).......................................................................111
X10 and X11 MACRO RJ-45 Copper Connectors ............................................................................................111
USB Connector .....................................................................................................................................................111
X12: USB Universal Serial Bus Port...............................................................................................................112
TROUBLESHOOTING..........................................................................................................................................113
Error Codes ...........................................................................................................................................................113
Table of Contents iii
Page 10

Geo MACRO Drive User Manual
D1: Geo MACRO Drive Status Display Codes.................................................................................................113
MACRO Network Errors...................................................................................................................................114
Status LEDs ......................................................................................................................................................115
Geo MACRO Drive Ring Status Error Codes.......................................................................................................116
MS{node},MI4 Geo MACRO Status Word (Read Only) ...............................................................................116
MS{node},MI6 Status Word Control.............................................................................................................117
Status Word.......................................................................................................................................................117
TURBO PMAC2 RELATED I-VARIABLE REFERENCE ...............................................................................119
Ixx10: Motor xx Power-On Servo Position Address............................................................................................119
Ixx25, Ixx24: Flag Address and Mode..................................................................................................................121
Ixx70, Ixx71: Commutation Cycle Size ...............................................................................................................123
Ixx72: Commutation Phase Angle.........................................................................................................................123
Ixx75: Absolute Phase Position Offset.................................................................................................................123
Ixx81: Motor xx Power-On Phase Position Address and Mode...........................................................................124
Ixx82: Current Loop Feedback Address................................................................................................................125
Ixx83: Commutation Feedback Address ..............................................................................................................126
Ixx91: Motor xx Power-On Phase Position Format .............................................................................................126
Ixx95: Motor xx Power-On Servo Position Format .............................................................................................129
Ixx97 Motor xx Position Capture and Trigger Mode ...........................................................................................131
GEO MACRO DRIVE MI-VARIABLE REFERENCE......................................................................................133
Global MI-Variables .............................................................................................................................................133
MS{node},MI0 Geo MACRO drive Firmware Version (Read Only)............................................................133
MS{node},MI1 Geo MACRO drive Firmware Date (Read Only)................................................................133
MS{node},MI2 and MI3 (Reserved for future use).......................................................................................133
MS{node},MI4 Geo MACRO drive Status Word (Read Only) ......................................................................134
MS{node},MI5 Ring Error Counter .............................................................................................................134
MS{node},MI6 Status Word Control............................................................................................................135
MS{node},MI7 Geo MACRO Error Counter ...............................................................................................135
MS{node},MI8 Geo MACRO Ring Check Period ........................................................................................135
MS{node},MI9 Geo MACRO Ring Error Shutdown Count..........................................................................135
MS{node},MI10 Geo MACRO Sync Packet Shutdown Count......................................................................136
MS{node},MI11 Station Order Number.......................................................................................................136
MS{node},MI12 Card Identification (Read Only)........................................................................................137
MS{node},MI13 Ring Break Output indicator .............................................................................................137
MS{node},MI100 Motor Activation Control word.......................................................................................138
MS{node},MI101-102 Primary Feedback Selection .....................................................................................138
MS{node},MI103 Sin Encoder/ Resolver #1 bias..........................................................................................139
MS{node},MI104 Sin Encoder/ Resolver #2 bias..........................................................................................139
MS{node},MI105 Cosine Encoder/ Resolver #1 bias....................................................................................139
MS{node},MI106 Cosine Encoder/ Resolver #2 bias....................................................................................139
MS{node},MI107 Motor 1 Encoder-Loss Mask ............................................................................................140
MS{node},MI108 Motor 2 Encoder-Loss Mask ............................................................................................140
Primary Channel Node-Specific Gate Array MI-variables....................................................................................142
MS{node},MI910 Primary Encoder/Timer n Decode Control......................................................................142
MS{node},MI911 Primary Enc. Position Compare n Channel Select ..........................................................143
MS{node},MI912 Primary Encoder n Capture Control................................................................................143
MS{node},MI913 Primary Encoder Capture n Flag Select Control.............................................................144
MS{node},MI914 Primary Encoder n Gated Index Select ............................................................................144
MS{node},MI915 Primary Encoder Index Gate State/Demux Control.........................................................145
MS{node},MI910 Secondary Encoder Decode Control................................................................................146
MS{node},MI911 Secondary Encoder counter Direction .............................................................................146
MS{node},MI912 Secondary Encoder Index Capture Control ....................................................................147
MS{node},MI913 Secondary Encoder Home Flag Capture Control...........................................................147
MS{node},MI914 Secondary Encoder Filter Control ...................................................................................147
MS{node},MI915 Secondary Encoder Capture Flag Select Control ............................................................148
iv Table of Contents
Page 11

Geo MACRO Drive User and Reference Manual
MS{node},MI916 Output n Mode Select .......................................................................................................148
MS{node},MI917 Output n Invert Control....................................................................................................148
MS{node},MI918 Output n PFM Direction Signal Invert Control ...............................................................149
MS{node},MI919 Hardware 1/T ...................................................................................................................149
MS{node},MI921 Flag Capture Position (Read Only)..................................................................................150
MS{node},MI922 ADC A Input Value (Read Only) ......................................................................................150
MS{node},MI923 Compare Auto-Increment Value.......................................................................................150
MS{node},MI924 ADC B Input Value (Read Only) ......................................................................................150
MS{node},MI925 Compare A Position Value...............................................................................................151
MS{node},MI926 Compare B Position Value...............................................................................................151
MS{node},MI927 (Reserved for future use)......................................................................................................151
MS{node},MI928 Compare-State Write Enable............................................................................................151
MS{node},MI929 Compare-Output Initial State...........................................................................................151
General Hardware Setup MI-variables..................................................................................................................152
MS{anynode}, MI930 SSI Channel 1 Control Word .....................................................................................152
MS{anynode}, MI931 SSI Channel 2 Control Word ....................................................................................152
MS{anynode}, MI932 Resolver Excitation Frequency Divider....................................................................153
MS{anynode}, MI933 SSI Clock Frequency Divider ...................................................................................153
MS{anynode},MI934-MI939 (Reserved for future use)................................................................................153
MS{anynode}, MI940 Resolver Excitation Gain .........................................................................................153
MS{anynode}, MI941 Resolver Excitation Phase Offset.............................................................................154
MS{anynode},MI942 ADC Strobe Word Channel 1* & 2* ..........................................................................154
MS{node},MI943 Encoder Power control bit ...............................................................................................154
MS{node},MI944-MI949 (Reserved for future use) .....................................................................................154
Global & 2-Axis Board I-Variables ......................................................................................................................155
MS{node},MI992 MaxPhase Frequency Control..........................................................................................155
MS{node},MI993 Hardware Clock Control Handwheel Channels...............................................................155
MS{node},MI994 PWM Deadtime ...............................................................................................................157
MS{node},MI995 MACRO Ring Configuration/Status .................................................................................157
MS{node},MI996 MACRO Node Activate Control .......................................................................................158
MS{node},MI997 Phase Clock Frequency Control ......................................................................................160
MS{node},MI998 Servo Clock Frequency Control.......................................................................................160
ABSOLUTE POWER ON ONLINE COMMANDS.............................................................................................161
$$*.........................................................................................................................................................................161
$*...........................................................................................................................................................................161
APPENDIX A...........................................................................................................................................................166
Fiber Optic Cable Ordering Information...............................................................................................................166
Mating Connector and Cable Kits.........................................................................................................................166
Mating Connector and Cable Kits ....................................................................................................................166
Connector and pins Part numbers ....................................................................................................................168
Cable Drawings ................................................................................................................................................170
Regenerative Resistor: GAR78/48 .......................................................................................................................176
Type of Cable for Encoder Wiring........................................................................................................................177
APPENDIX B...........................................................................................................................................................180
Schematics.............................................................................................................................................................180
X3: Discrete I/O...............................................................................................................................................180
X6 and X7: Analog Inputs................................................................................................................................182
X8 and X9 Secondary Encoders (3 and 4)........................................................................................................183
APPENDIX C...........................................................................................................................................................184
Communication to the Geo MACRO via the USB Port........................................................................................184
APPENDIX D...........................................................................................................................................................186
MACRO Flag Transfer Location...........................................................................................................................186
Turbo PMAC2 Node Addresses............................................................................................................................187
Table of Contents v
Page 12

Geo MACRO Drive User Manual
ADC Register Table ..............................................................................................................................................189
Stepping through an Electrical Cycle....................................................................................................................190
Manually Stepping through an Electrical Cycle at 30 degree increments........................................................190
Example 1 of Hall Effect Values .......................................................................................................................191
Example 2 of Hall Effect Values .......................................................................................................................192
USEFUL NOTES.....................................................................................................................................................193
vi Table of Contents
Page 13

Geo MACRO Drive User and Reference Manual
INTRODUCTION
The Geo Drive family of “bookcase”-style servo amplifiers provides many new capabilities for users.
This family of 1- and 2-axis 3-phase amplifiers, built around a common core of highly integrated IGBTbased power circuitry, supports a wide variety of motors, power ranges, and interfaces. The 2-axis
configurations share common power input, bus, and shunt for a very economical implementation.
Three command interfaces are provided: direct-PWM, MACRO-ring, and integrated PMAC controller,
each described in following sections. In all three cases, fully digital “direct PWM” control is used. Direct
PWM control eliminates D-to-A and A-to-D conversion delays and noise, allowing higher gains for more
robust and responsive tuning without sacrificing stability.
All configurations provide these power-stage features:
• Direct operation off AC power mains (100 – 240 or 300 – 480 VAC, 50/60 Hz) or optional DC
power input (24 – 350 or 24 – 700 VDC)
• Integrated bus power supply including soft start and shunt regulator (external resistor required)
• Separate 24VDC input to power logic circuitry
• Complete protection: over voltage, under voltage, over temperature, PWM frequency limit,
minimum dead time, motor over temperature, short circuit, over current, input line monitor
• Ability to drive brushed and brushless permanent-magnet servo motors, or AC induction motors
• Single-digit LED display and six discrete LEDs for status information
• Optional safety relay circuitry. Please contact factory for more details and pricing.
• Easy setup with Turbo PMAC and UMAC controllers.
User Interface
The Geo Drive family is available in different versions distinguished by their user interface styles.
Geo MACRO Drives
The Geo MACRO Drive interfaces to the controller through the 125 Mbit/sec MACRO ring, with
either a fiber-optic or Ethernet electrical medium, accepting numerical command values for direct
PWM voltages and returning numerical feedback values for phase current, motor position, and status.
It accepts many types of position feedback to the master controller, as well as axis flags (limits, home,
and user) and general-purpose analog and digital I/O. Typically, the Geo MACRO Drives are
commanded by either a PMAC2 Ultralite bus-expansion board, or a UMAC rack-mounted controller
with a MACRO-interface card. This provides a highly distributed hardware solution, greatly
simplifying system wiring, while maintaining a highly centralized software solution, keeping system
programming simple.
• Choices for main feedback for each axis: A/B quadrature encoder, sinusoidal encoder with
• Secondary A/B quadrature encoder for each axis
• General-purpose isolated digital I/O: 4 in, 4 out at 24VDC
EnDat
TM
or HiperfaceTM, SSI encoder, resolver
• 2 optional A/D converters, 12- or 16-bit resolution
Note:
Geo MACRO is not using the regular 8-axis or 16-axis MACRO station CPU.
A new MACRO CPU was developed for the Geo MACRO drive.
Introduction 1
Page 14

Geo MACRO Drive User Manual
Geo PMAC Drives
The Geo PMAC Drive is a standalone-capable integrated controller/amplifier with a built-in full
PMAC2 controller having stored-program capability. It can be operated standalone, or commanded
from a host computer through USB2.0 or 100 Mbps Ethernet ports. The controller has the full
software capabilities of a PMAC (see descriptions), with an internal fully-digital connection to the
advanced Geo power-stage , providing a convenient, compact, and cost-effective installation for one
and two-axis systems, with easy synchronization to other drives and controls.
• Choices for main feedback for each axis: A/B quadrature encoder, sinusoidal encoder with
• Secondary A/B quadrature encoder for each axis
• General-purpose isolated digital I/O: 8 in, 6 out at 24VDC
• 2 optional A/D converters 12- or 16-bit resolution
EnDat
TM
or HiperfaceTM, SSI encoder, resolver
Geo Direct-PWM Drives
The direct-PWM interface versions accept the actual power-transistor on/off signals from the PMAC2
controller, while providing digital phase-current feedback and drive status to the controller for closedloop operation. Interface to the direct-PWM amplifier is through a standard 36-pin Mini-D style
cable. The drive performs no control functions but has protection features. Drive installation,
maintenance, and replacement are simplified because there is less wiring (position feedback and I/O
are not connected to the drive) and there are no variables to set or programs to install in the drive.
• Fully centralized control means that all gains and settings are made in the PMAC; no software
setup of drive is required
• No position feedback or axis flags required at the drive
MACRO Defined
MACRO defined is a digital interface for connection of multi–axis motion controllers, amplifiers and
other I/O devices on a fiber optic or twisted pair copper (RJ45 connector) ring.
MACRO operates in a ring topology. Data is transmitted serially. Each station on the ring has an in port
for receiving data and an out port for transmitting data. Nodes, residing at a station can be amplifier axes,
I/O banks, or communication interfaces to other devices. A station can have one or several nodes
allowing for multi-axis amplifiers with a single in and single out port. Data packets, (groups of 96 bits of
serial data) from the motion controller or master node are addressed to a specific amplifier or slave node.
If the data packet is not for an amplifier, it is passed on unchanged. If it is for the node, it copies the
contents of the data packet (typically commands), places feedback data into a packet, and transmits the
data packet.
MACRO’s Advantages are:
• Single–plug connections between controls and amplifiers: A single fiber optic strand can provide a
controller with: position feedback, flag status (limits, home flag), amplifier status and machine input
status. This same strand can communicate to the amplifier and other devices on the MACRO network
(Amplifier enable and amplifier command signals, machine outputs, commands to D/A converters; all
can be implemented with a single plug connection).
• Noise Immunity: Fiber–optic cable transmits light, not electricity. Unlike electricity light is immune
to electromagnetic noise, capacitive coupling, ground loops, and other wiring problems.
• Speed: MACRO’s operation is 125 Mbits/second. This is at least 25 times faster than other digital
motion control interfaces.
2 Introduction
Page 15
Geo MACRO Drive User and Reference Manual
• One ring, multiple masters: In a ring network, several motion controllers (masters) can be on one
ring. Each controller controls several axes (up to 32 ea.).
• Simplicity: Transmission within the MACRO ring requires no software intervention. The
information sent to all nodes is written to a memory location and the MACRO hardware takes care of
the rest.
Feedback Devices
Many motors incorporate a position feedback device. Devices are incremental encoders, resolvers, and
sine encoder systems. The macro version of the Geo drive accepts feedback. In its standard form, it is set
up to accept incremental encoder feedback. With the appropriate feedback option, it is possible to use
either resolver or sinusoidal encoder feedback. Historically, the choice of a feedback device has been
guided largely by cost and robustness. Today, feedbacks are relatively constant for the cost and picked by
features such as size and feedback data. More feedback data or resolution provides the opportunity to
have higher gains in a servo system.
Geo MACRO drives have standard secondary quadrature encoder feedback. One secondary encoder (X8)
for one axis drive and two secondary encoders (X8 and X9) for dual axis drives (603542 rev-10A and
above). Earlier versions of the Geo MACRO drive cannot use the secondary encoders.
Compatible Motors
The Geo drive product line is capable of interfacing to a wide variety of motors. The Geo drive can
control almost any type of three-phase brushless motor, including DC brushless rotary, AC brushless
rotary, induction, and brushless linear motors. Permanent magnet DC brush motors can also be controlled
using two of the amplifiers three phases. Motor selection for an application is a science in itself and
cannot be covered in this manual. However, some basic considerations and guidelines are offered. Motor
manufacturers include a host of parameters to describe their motor.
Some basic equations can help guide an applications engineer to mate a proper drive with a motor. A
typical application accelerates a load to a speed, running the speed for a while and then decelerating the
load back into position.
Maximum Speed
The motor’s maximum rated speed is given. This speed may or may not be achievable in a given system.
The speed could be achieved if enough voltage and enough current loop gain are available. Also consider
the motor’s feedback adding limitations to achievable speeds. The load attached to the motor also limits
the maximum achievable speed. In addition, some manufacturers will provide motor data with their drive
controller, which is tweaked to extend the operation range that other controllers may be able to provide.
In general, the maximum speed can be determined by input voltage line-to-line divided by Kb (the
motor’s back EMF constant). It is wise to de-rate this a little for proper servo applications.
Torque
The torque required for the application can be viewed as both instantaneous and average. Typically, the
instantaneous or peak torque is calculated as a sum of machining forces or frictional forces plus the forces
required to accelerate the load inertia. The machining or frictional forces on a machine must be
determined by the actual application. The energy required to accelerate the inertia follows the equation:
T = JA, where T is the torque in Newton-meters or pound-feet required for the acceleration, J is the inertia
in kilogram-meters-squared or pound-feet-second squared, and A is in radians per second per second.
The required torque can be calculated if the desired acceleration rate and the load inertia reflected back to
the motor are known. The T=JA equation requires that the motor’s inertia be considered as part of the
inertia-requiring torque to accelerate.
Once the torque is determined, the motors specification sheet can be reviewed for its torque constant
parameter (Kt). The torque required at the application divided by the Kt of the motor provides the peak
current required by the amplifier. A little extra room should be given to this parameter to allow for good
Introduction 3
Page 16

Geo MACRO Drive User Manual
servo control.
Most applications have a duty cycle in which the acceleration profile occurs repetitively over time.
Calculating the average value of this profile gives the continuous rating required by the amplifier.
Applications also concern themselves with the ability to achieve a speed. The requirements can be
reviewed by either defining what the input voltage is to the drive, or defining what the voltage
requirements are at the motor. Typically, a system is designed at a 230 or 480V input line. The motor
must be able to achieve the desired speed with this voltage limitation. This can be determined by using
the voltage constant of the motor (Kb), usually specified in volts-per-thousand rpm. The application
speed is divided by 1000 and multiplied by the motor's Kb. This is the required voltage to drive the motor
to the desired velocity. Headroom of 20% is suggested to allow for good servo control.
Peak Torque
The peak torque rating of a motor is the maximum achievable output torque. It requires that the amplifier
driving it be able to output enough current to achieve this. Many drive systems offer a 3:1 peak-tocontinuous rating on the motor, while the amplifier has a 2:1 rating. To achieve the peak torque, the drive
must be sized to be able to deliver the current to the motor. The required current is often stated on the
datasheet as the peak current through the motor. In some sense, it can also be determined by dividing the
peak amplifier's output rating by the motor's torque constant (Kt).
Continuous Torque
The continuous torque rating of the motor is defined by a thermal limit. If more torque is consumed from
the motor than this on average, the motor overheats. Again, the continuous torque output of the motor is
subject to the drive amplifier’s ability to deliver that current. The current is determined by the
manufacturer’s datasheets stating the continuous RMS current rating of the motor and can also be
determined by using the motor’s Kt parameter, usually specified in torque output per amp of input current.
Motor Poles
Usually, the number of poles in the motor is not a concern to the actual application. However, it should
be noted that each pole-pair of the motor requires an electrical cycle. High-speed motors with high motor
pole counts can require high fundamental drive frequencies that a drive amplifier may or may not be able
to output. In general, drive manufacturers with PWM switching frequencies (16kHz or below) would like
to see commutation frequencies less than 400 Hz. The commutation frequency is directly related to the
number of poles in the motor.
Motor Inductance
PWM outputs require significant motor inductance to turn the on-off voltage signals into relatively
smooth current flow with small ripple. Typically, motor inductance of servomotors is 1 to 15 mH. The
Geo drive product series can drive this range easily. On lower-inductance motors (below 1mH), problems
occur due to PWM switching where large ripple currents flow through the motor, causing excessive
energy waste and heating. If an application requires a motor of less than 1mH, external inductors are
recommended to increase that inductance. Motors with inductance in excess of 15mH can still be driven,
but are slow to react and typically are out of the range of high performance servomotors.
Motor Resistance
Motor resistance is not really a factor in determining the drive performance, but rather, comes into play
more with the achievable torque or output horsepower from the motor. The basic resistance shows up in
the manufacturer's motor horsepower curve.
Motor Back EMF
The back EMF of the motor is the voltage that it generates as it rotates. This voltage subtracts from the
bus voltage of the drive and reduces the ability to push current through the motor. Typical back EMF
4 Introduction
Page 17

Geo MACRO Drive User and Reference Manual
ratings for servomotors are in the area of 8 to 200 volts-per-thousand rpm. The Geo drive product series
can drive any range of back EMF motor, but the back EMF is highly related to the other parameters of the
motor such as the motor inductance and the motor Kt. It is the back EMF of the motor that limits the
maximum achievable speed and the maximum horsepower capability of the motor.
Motor Torque Constant
Motor torque constant is referred to as Kt and usually it is specified in torque-per-amp. It is this number
that is most important for motor sizing. When the load that the motor will see and knowing the motor’s
torque constant is known, the drive amplifier requirements can be calculated to effectively size a drive
amplifier for a given motor. Some motor designs allow Kt to be non-linear, in which Kt will actually
produce less torque per unit of current at higher output speeds. It is wise to de-rate the systems torque
producing capability by 20% to allow headroom for servo control.
Motor Inertia
Motor inertia comes into play with motor sizing because torque to accelerate the inertia of the motor is
effectively wasted energy. Low inertia motors allow for quicker acceleration. However, consider the
reflected inertia from the load back to the motor shaft when choosing the motor’s inertia. A high ratio of
load-to-motor inertia can limit the achievable gains in an application if there is compliance in the
transmission system such as belt-drive systems or rubber-based couplings to the systems. The closer the
rotor inertia matches the load’s reflected inertia to the motor shaft, the higher the achievable gains will be
for a given system. In general, the higher the motor inertia, the more stable the system will be inherently.
Mechanical gearing is often placed between the load and the motor simply to reduce the reflected inertia
back to the motor shaft.
Motor Cabling
Motor cables are an integral part of a motor drive system. Several factors should be considered when
selecting motor cables. First, the PWM frequency of the drive emits electrical noise. Motor cables must
have a good-quality shield around them. The motor frame must also have a separate conductor to bring
back to the drive amplifier to help quench current flows from the motor due to the PWM switching noise.
Both motor drain wire and the cable shield should be tied at both ends to the motor and to the drive
amplifier.
Another consideration in selecting motor cables is the conductor-to-conductor capacitance rating of the
cable. Small capacitance is desirable. Longer runs of motor cable can add motor capacitance loading to
the drive amplifier causing undesired spikes of current. It can also cause couplings of the PWM noise
into the earth grounds, causing excessive noise as well. Typical motor cable ratings would be 50 pf per
foot maximum cable capacitance.
Another factor in picking motor cables is the actual conductor cross-sectional area. This refers to the
conductors ability to carry the required current to and from the motor. When calculating the required
cable dimensions, consider agency requirements, safety requirements, maximum temperature that the
cable will be exposed to, the continuous current flow through the motor, and the peak current flow
through the motor. Typically, it is not suggested that any motor cable be less than 14 AWG.
The motor cable’s length must be considered as part of the application. Motor cable length affects the
system in two ways. First, additional length results in additional capacitive loading to the drive. The
drive’s capacitive loading should be kept to no more than 1000pf. Additionally, the length sets up
standing waves in the cable, which can cause excessive voltage at the motor terminals. Typical motor
cable length runs of up to 60 meters (200 feet) for 230V systems and 15 meters (50 feet) for 480V
systems are acceptable. Exceeding these lengths may put other system requirements in place for either a
snubber at the motor end or a series inductor at the drive end. The series inductor at the drive end
provides capacitance loading isolation from the drive and slows the rise time of the PWM signal into the
cable, resulting in less voltage overshoot at the motor.
Introduction 5
Page 18

Geo MACRO Drive User Manual
6 Introduction
Page 19
Geo MACRO Drive User and Reference Manual
SPECIFICATIONS
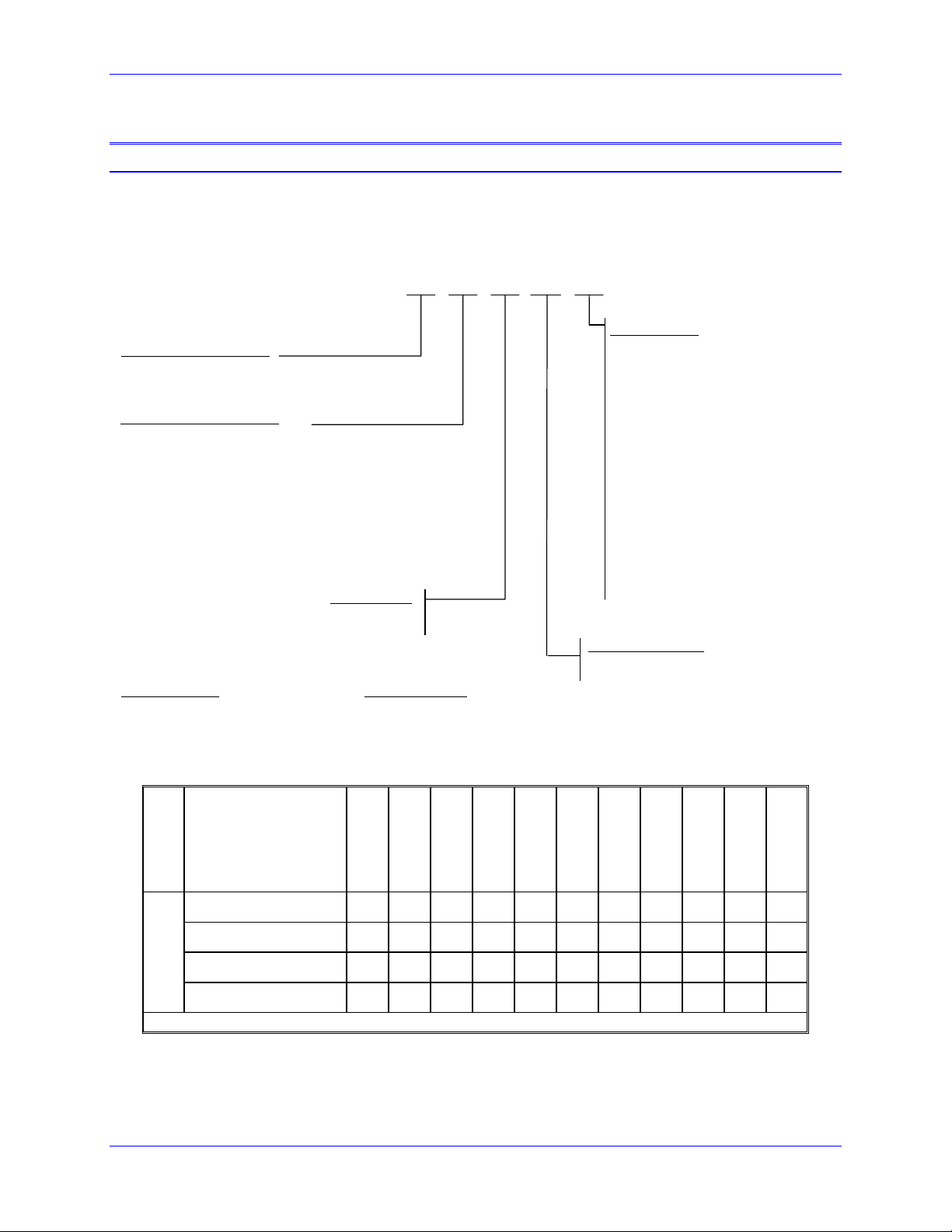
Part Number
Geo MACRO Drive
Model Number Definition
GL03 1 0
Voltage Rating (Direct M ains )
L = 110 - 240 VAC
H = 300 - 480 VAC
Continuous/Peak Current Rating
(Sinusoidal RMS)
φ
01 = 1.5/4.5 Amp (one or 3
03 = 3/9 Amp (one or 3
05 = 5/10 Amp (3
10 = 10/20 Amp (3
15 = 15/30 Amp (3
20 = 20/40 Amp (3
30 = 30/60 Amp (3
*For single phase input, need to derate 30%
Product Width According to Ratings
Single -Width U nits :
1.5/4.5 Dual Axis 10/20 Dual Axis (480VAC)
3/9 Dual Axis 15/30 Dual Axis
5/10 Single and Dual Axis 20/40 Single Axis
10/20 Single Axis and Dual Axis (240VAC) 30/60 Single Axis
15/30 Single Axis
φ
φ
φ
φ
φ
operation )
φ
operation )
input, for single φ need to derate 20%)
input*)
input*)
input*)
input*)
Number of Axes
1 = Single Axis
2 = Dual Axis
Double-Width Units:
RM
Feedback Options
0 = No options, Default; Standard feedback
per axis is quadrature differential
encoder with hall effect inputs or SSI
absolute encoder .
1 = Analog Feedback including:
• Option 0 Standard Feedback
• 4096x Sin/Cos interpolator
• Resolver Interface
2 = Absolute Feedback including :
• Option 1 Analog Feedback
• Endat™
• Hiperface™
3, 4, 5 = Same as Options 0, 1 and 2
described above but with two 16-bit
analog-to-digital converter inputs
Note: Any available method can be used for
feedback but only one method can be used at
any time . Feedback method is selected by
wiring.
MACRO Link Options:
F = Fiber Optic
R = RJ/45 (Default)
GMx012xx
GMx051xx
GMx101xx
GMx151xx
GMx032xx
GMx052xx
GML102xx
GMx201xx
GMx301xx
GMH102xx
GMx152xx
Single axis
Dual Axis
Single Width
Size Axis
Double width
√ √ √ √ √
√ √ √ √ √ √
√* √ √ √ √ √ √
√ √ √ √
* Low Profile Unit, No heatsink, no Fan
Specifications 7
Page 20
Geo MACRO Drive User Manual
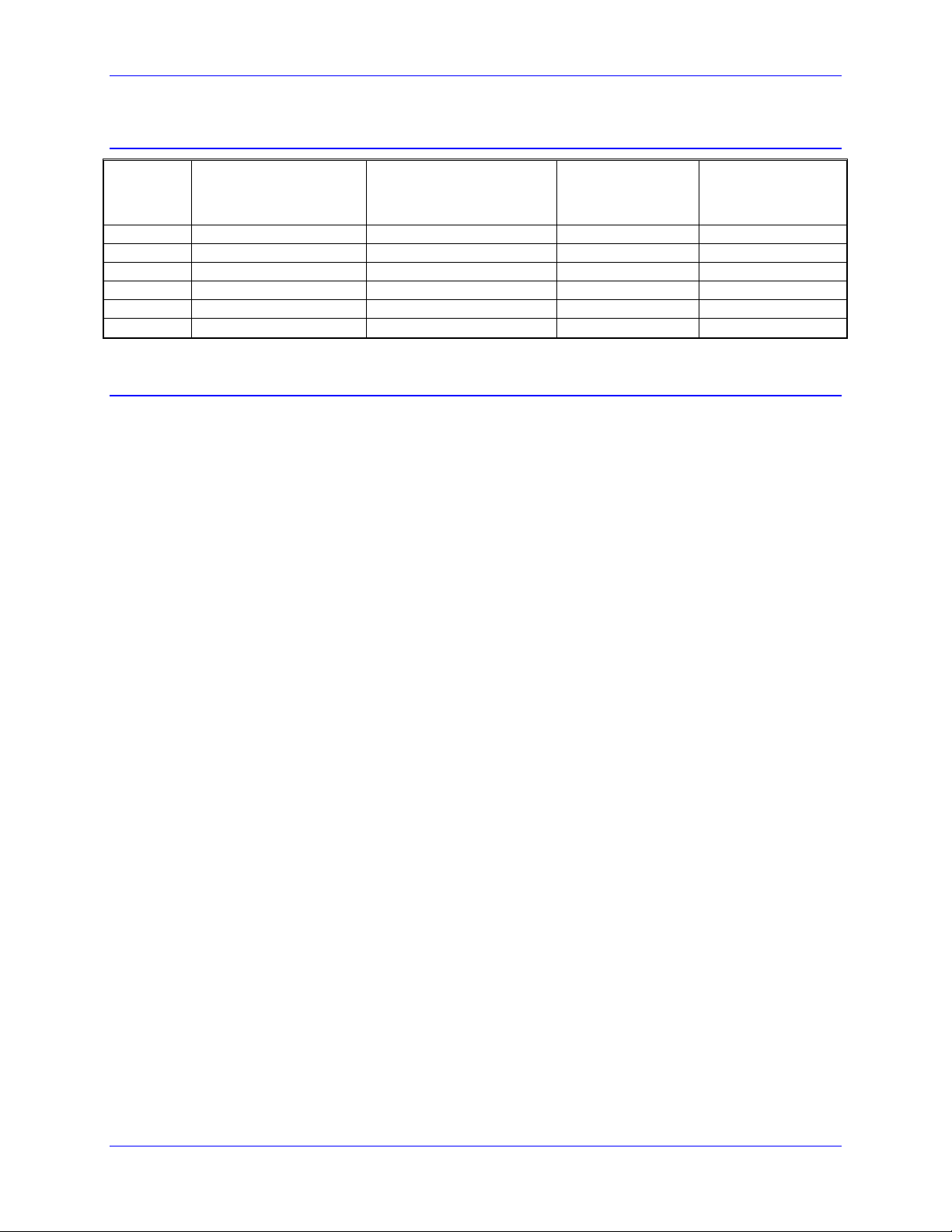
Geo MACRO Feedback Options
Model Default Configuration:
Quadrature Encoders
Or SSI Absolute Encoders
And Hall Effect inputs
GMxxxxx0
GMxxxxx1
GMxxxxx2
GMxxxxx3
GMxxxxx4
GMxxxxx5
√
√
√
√ √
√ √
√ √
Analog (Sin/Cos) Encoders:
x4096 Interpolator
Resolver to Digital
Converters
Absolute Encoder
Interfaces:
EnDat
Hiperface
Addition of two
channels of 16-bit
A/D converters with
each feedback option
Package Types
Geo package types provide various power levels and one or two axis capability with three different
package types.
The Geo Drive has a basic package size of 3.3"W x 11"H x 8.0"D(84mm W x 280mm H x 203mm D).
This size includes the heat sink and fan. In this package size, Single Width, the Geo can handle one or
two low-to-medium power axes or only a single axis for medium to high power.
The mechanical design of the Geo drive is such that it allows two heat sinks to be easily attached together
to provide two high power axes in a double width configuration. This double package size is 6.5" W x
11" H x 8.0" D (165 mm W x 280 mm H x 203 mm D). It provides a highly efficient package size
containing two axes of up to about 10kW each thus driving nearly 24kW of power, but using a single
interface card. This results in a highly cost effective package.
There is also one more package type only for the low power (1.5A/4.5A) single width Geo drive, model
Gxx012xx. This package substitutes the heatsink and the fan with a smaller plate which has the same
mounting pattern as the regular single width drive, making the units depth 2.2inches (56mm) less than the
single width drive, 5.8" D (148mm D).
• Low Profile: GMx012xx (only)
3.3" wide (84 mm) (no heatsink, no fan), Maximum Power Handling ~1200 watts
Package Dimensions: 3.3" W x 11" H x 5.8" D (84 mm W x 280 mm H x 148 mm D)
Weight: 4.3 lbs. (1.95kgs)
• Single Width: GMx051xx, GMx101xx, GMx151xx, GMH032xx, GMx052xx and GML102xx.
3.3" wide (84 mm)(with heatsink and fan), Maximum Power Handling ~12000 watts
GML032xx Single Width, with heatsink, no Fan (Weight 5.4lbs/2.45kgs)
Package Dimensions: 3.3" W x 11" H x 8.0" D (84 mm W x 280 mm H x 203 mm D)
Weight: 5.5 lbs. (2.50kgs)
• Double Width: GMx201xx, GMx301xx, GMH102xx and GMx152xx.
6.5” wide (164mm)(with heatsink and fan), Maximum Power Handling ~24,000 watts
Package Dimensions: 6.5" W x 11" H x 8.0" D (164 mm W x 280 mm H x 203 mm D)
Weight: 11.6lbs (5.3kgs)
8 Specifications
Page 21
Geo MACRO Drive User and Reference Manual
g
g
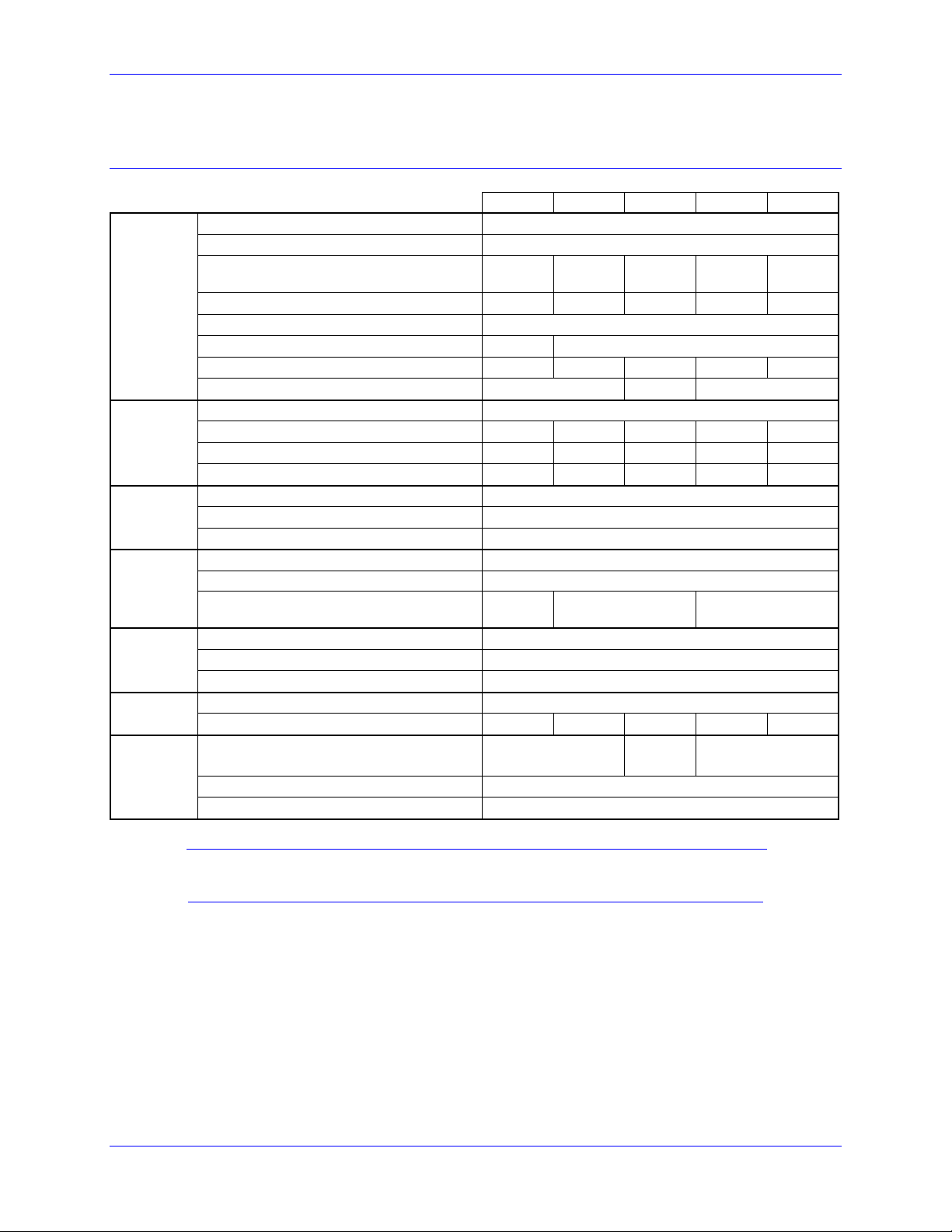
Electrical Specifications
230VAC Input Drives
Main
Input
Power
Output
Power
Bus
Protection
Shunt
Re
ulator
Ratings
Control
Lo
Power
Current
Feedback
Transistor
Control
GxL051 GxL101 GxL151 GxL201 GxL301
Nominal Input Voltage (VAC)
Rated Input Voltage (VAC)
Rated Continuous Input Current (A
AC
)
RMS
Rated Input Power (Watts)
Frequency (Hz)
Phase Requirements
Charge Peak Inrush Current (A)
Main Bus Capacitance (µf)
Rated Output Voltage (V)
Rated Cont. Output Current per Axis
Peak Output Current (A) for 2 seconds
Rated Output Power per Axis (Watts)
Nominal DC Bus
Over-voltage Trip Level (VDC)
Under-voltage Lockout Level (VDC)
Turn-On Voltage (VDC)
Turn-Off Voltage (VDC) 372
Delta Tau Recommended Load Resistor
(300 W Max.)
Input Voltage (VDC)
Input Current (A)
ic
Inrush Current (A)
Resolution (bits)
Full-scale Signed Reading (±A)
Delta Tau Recommended PWM
Frequency (kHz) @rated current
Minimum Dead Time (µs)
Charge Pump Time (% of PWM period.)
230
97-265
3.3 6.6 9.9 13.2 19.8
1315 2629 3944 5259 7888
50/60
1Φ or 3Φ 3Φ
3380 5020 6800
138
5 10 15 20 30
10 20 30 40 60
1195 2390 3585 4780 7171
325
410
10
392
GAR78 GAR48 GAR48-3
20-27
2A
4A
12
16.26 32.53
12 10 8
48.79 65.05 97.58
1
5
Note:
All values at ambient temperature of 0-45°C (113F) unless otherwise stated.
Specifications 9
Page 22
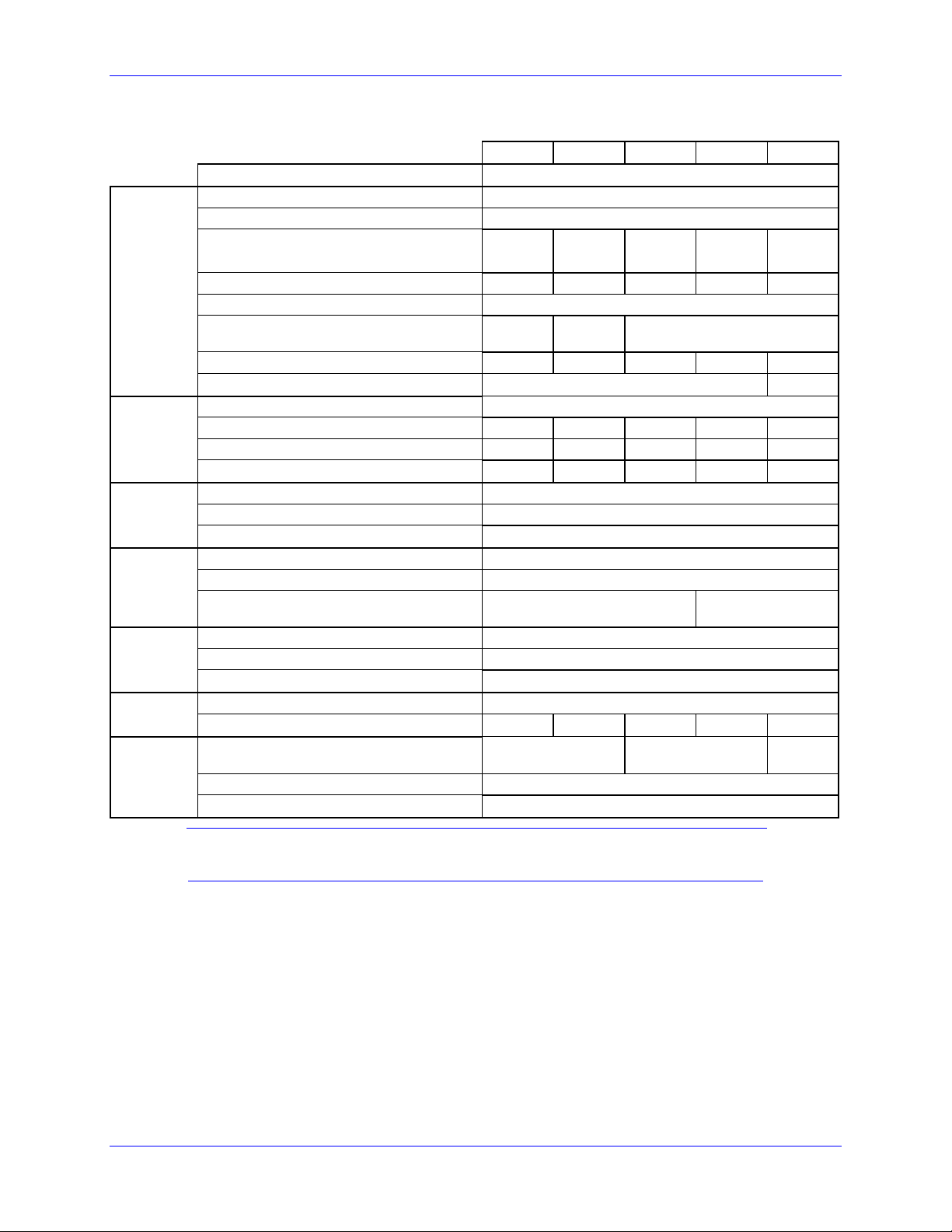
Geo MACRO Drive User Manual
g
g
Main
Input
Power
Output
Power
Bus
Protection
Shunt
Re
ulator
Ratings
Control
Lo
ic
Power
Current
Feedback
Transistor
Control
GxL012 GxL032 GxL052 GxL102 GxL152
Output Circuits (axes)
Nominal Input Voltage (VAC)
Rated Input Voltage (VAC)
Rated Continuous Input Current (A
AC
)
RMS
Rated Input Power (Watts)
Frequency (Hz)
Phase Requirements
Charge Peak Inrush Current (A)
Main Bus Capacitance (µf)
Rated Output Voltage (V)
Rated Cont. Output Current per Axis
Peak Output Current (A) for 2 seconds
Rated Output Power per Axis (Watts)
Nominal DC Bus
Over-voltage Trip Level (VDC)
Under-voltage Lockout Level (VDC)
Turn-On Voltage (VDC)
Turn-Off Voltage (VDC)
Delta Tau Recommended Load Resistor
(300 W Max.)
Input Voltage (VDC)
Input Current (A)
Inrush Current (A)
Resolution (bits)
Full-scale Signed Reading (±A)
Delta Tau Recommended Maximum
PWM Frequency (kHz)
Minimum Dead Time (µs)
Charge Pump Time (% of PWM period.)
1.98 3.96 6.6 13.2 19.8
789 1578 2629 5259 7888
1Φ or 3Φ 1Φ or 3Φ 3Φ
1.5 3 5 10 15
4.5 9 10 20 30
359 717 1195 2390 3585
GAR78 GAR48
7.32 14.64
16 12 10
2
230
97-265
50/60
3380 5020
138
325
410
10
392
372
20-27
2A
4A
12
16.26 32.53
1
5
48.79
Note:
All values at ambient temperature of 0-45°C (113F) unless otherwise stated.
10 Specifications
Page 23
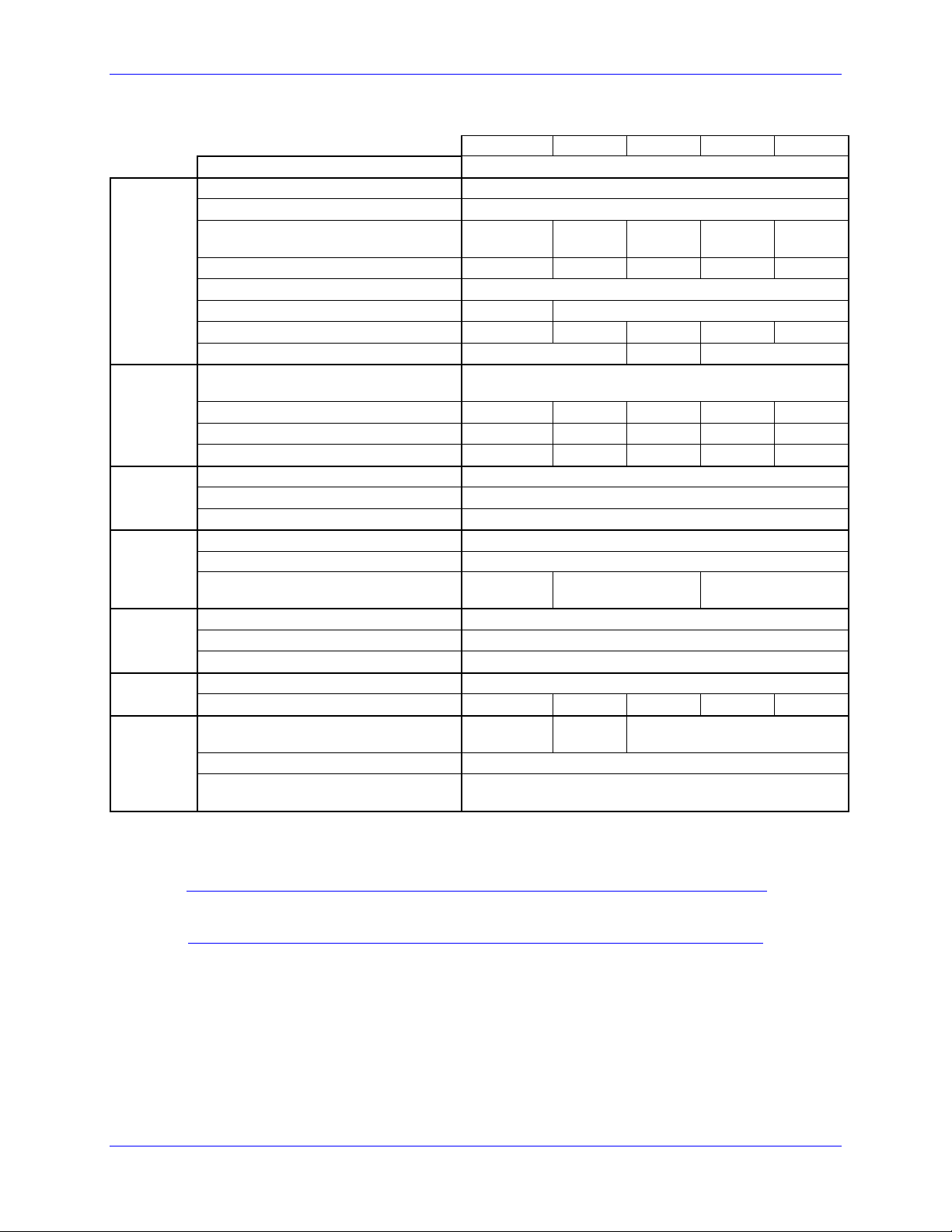
Geo MACRO Drive User and Reference Manual
g
g
480VAC Input Drives
Main
Input
Power
Bus
Protection
Shunt
Re
ulator
Ratings
Control
Lo
Power
Current
Feedback
Transistor
Control
GxH051 GxH101 GxH151 GxH201 GxH301
Output Circuits (axes)
Nominal Input Voltage (VAC)
Rated Input Voltage (VAC)
Rated Continuous Input Current (A
AC
)
RMS
Rated Input Power (Watts)
Frequency (Hz)
Phase Requirements
Charge Peak Inrush Current (A)
Main Bus Capacitance (µf)
Rated Output Voltage (V) @ Rated
Current
Rated Cont. Output Current per Axis
Peak Output Current (A) for 2 seconds
Rated Output Power per Axis (Watts)
Nominal DC Bus
Over-voltage Trip Level (VDC)
Under-voltage Lockout Level (VDC)
Turn-On Voltage (VDC)
Turn-Off Voltage (VDC) 744
Delta Tau Recommended Load
Resistor (300 W Max.)
Input Voltage (VDC)
Input Current (A)
ic
Inrush Current (A)
Resolution (bits)
Full-scale Signed Reading (±Amperes)
Delta Tau Recommended PWM
Frequency (KHz) @ rated current
Minimum Dead Time (µs)
Charge Pump Time (% of PWM
period.)
1
480
300-525
3.3 6.6 9.9 13.2 19.8
2744 5487 8231 10974 16461
50/60
1Φ or 3Φ 3Φ
845 1255 1700
288
5 10 15 20 30
10 20 30 40 60
2494 4988 7482 9977 14965
678
828
20
784
GAR78 GAR48 GAR48-3
20-27
2A
4A
12
16.26 32.53 48.79 65.05 97.58
12 10 8
1.6
5
Note:
All values at ambient temperature of 0-45°C (113F) unless otherwise stated.
Specifications 11
Page 24
Geo MACRO Drive User Manual
g
g
Main
Input
Power
Bus
Protection
Shunt
Re
ulator
Ratings
Control
Lo
ic
Power
Current
Feedback
Transistor
Control
GxH012 GxH032 GxH052 GxH102 GxH152
Output Circuits (axes)
Nominal Input Voltage (VAC)
Rated Input Voltage (VAC)
Rated Continuous Input Current (A
AC
)
RMS
Rated Input Power (Watts)
Frequency (Hz)
Phase Requirements
Charge Peak Inrush Current (A)
Main Bus Capacitance (µf)
Rated Output Voltage (V) @ Rated
Current
Rated Cont. Output Current per Axis
Peak Output Current (A) for 2 seconds
Rated Output Power per Axis (Watts)
Nominal DC Bus
Over-voltage Trip Level (VDC)
Under-voltage Lockout Level (VDC)
Turn-On Voltage (VDC)
1.98 3.96 6.6 13.2 19.8
1646 3292 5487 10974 16461
1Φ or 3Φ 3Φ
1.5 3 5 10 15
4.5 9 10 20 30
748 1496 2494 4988 7482
2
480
300-525
50/60
845 1255
288
678
828
20
784
Turn-Off Voltage (VDC) 744
Delta Tau Recommended Load Resistor
(300 W Max.)
Input Voltage (VDC)
Input Current (A)
Inrush Current (A)
Resolution (bits)
Full-scale Signed Reading (±Amperes)
Delta Tau Recommended PWM
Frequency (KHz) @ rated current
Minimum Dead Time (µs)
Charge Pump Time (% of PWM period.)
7.32 14.64 16.26 32.53 48.79
GAR78 GAR48
20-27
2A
4A
12
12 10 8
1.6
5
Note:
All values at ambient temperature of 0-45°C (113F) unless otherwise stated.
12 Specifications
Page 25
Geo MACRO Drive User and Reference Manual
Environmental Specifications
Description Unit Specifications
Operating Temperature °C +0 to 45°C. Above 45°C, derate the continuous peak output current by
2.5% per °C above 45°C. Maximum Ambient is 55°C
Rated Storage Temperature °C -25 to +70
Humidity % 10% to 90% non-condensing
Shock Call Factory
Vibration Call Factory
Operating Altitude Feet
(Meters)
Air Flow Clearances in (mm) 3" (76.2mm) above and below unit for air flow
To 3300 feet (1000meters). Derate the continuous and peak output
current by 1.1% for each 330 feet (100meters) above the 3300feet
Recommended Fusing and Wire Gauge
Model Recommended Fuse (FRN/LPN) Recommended Wire Gauge*
GxL012xx 15 14 AWG
GxL032xx 20 12 AWG
GxL051xx 20 12 AWG
GxL052xx 20 12 AWG
GxL101xx 20 12 AWG
GxL102xx 20 12 AWG
GxL151xx 25 10 AWG
GxL152xx 25 10 AWG
GxL201xx 25 10 AWG
GxL301xx 30 8 AWG
GxH012xx 15 14 AWG
GxH032xx 20 12 AWG
GxH051xx 20 12 AWG
GxH052xx 20 12 AWG
GxH101xx 20 12 AWG
GxH102xx 20 12 AWG
GxH151xx 25 10 AWG
GxH152xx 25 10 AWG
GxH201xx 25 10 AWG
GxH301xx 30 8 AWG
* See local and national code requirements
Wire Sizes
Geo Drive electronics create a DC bus by rectifying the incoming AC electricity. The current flow into
the drive is not sinusoidal but rather a series of narrow, high-peak pulses. Keep the incoming impedance
small so that these current pulses are not hindered. Conductor size, transformer size, and fuse size
recommendations may seem larger than normally expected. All ground conductors should be 8AWG
minimum using wires constructed of many strands of small gauge wire. This provides the lowest
impedance to high-frequency noises.
Specifications 13
Page 26

Geo MACRO Drive User Manual
14 Specifications
Page 27

Geo MACRO Drive User and Reference Manual
RECEIVING AND UNPACKING
Delta Tau products are thoroughly tested at the factory and carefully packaged for shipment. When the
Geo Drive is received, do the following immediately.
1. Observe the condition of the shipping container and report any damage immediately to the
commercial carrier that delivered the drive.
2. Remove the drive from the shipping container and remove all packing materials. Check all shipping
material for connector kits, documentation, diskettes, CD ROM, or other small pieces of equipment.
Be aware that some connector kits and other equipment pieces may be quite small and can be
discarded accidentally if care is not used when unpacking the equipment. The container and packing
materials can be retained for future shipment.
3. Verify that the part number of the drive received is the same as the part number listed on the purchase
order.
4. Inspect the control for external physical damage that may have been sustained during shipment and
report any damage immediately to the commercial carrier that delivered the controller.
5. Electronic components in this amplifier are design-hardened to reduce static sensitivity. However,
use proper procedures when handling the equipment.
6. If the Geo Drive is to be stored for several weeks before use, be sure that it is stored in a location that
conforms to published storage humidity and temperature specifications stated in this manual.
Use of Equipment
The following guidelines describe the restrictions for proper use of the Geo Drive:
• The components built into electrical equipment or machines can be used only as integral components
of such equipment.
• The Geo Drives are to be used only on grounded three-phase industrial mains supply networks (TN-
system, TT-system with grounded neutral point).
• The Geo Drives must not be operated on power supply networks without a ground or with an
asymmetrical ground.
• If the Geo Drives are used in residential areas, or in business or commercial premises, implement
additional filter measures.
• The Geo Drives may be operated only in a closed switchgear cabinet, taking into account the ambient
conditions defined in the environmental specifications.
Delta Tau guarantees the conformance of the Geo Drives with the standards for industrial areas stated in
this manual, only if Delta Tau components (cables, controllers, etc.) are used.
Receiving and Unpacking 15
Page 28

Geo MACRO Drive User Manual
16 Receiving and Unpacking
Page 29

Geo MACRO Drive User and Reference Manual
MOUNTING
The location of the controller is important. Installation should be in an area that is protected from direct
sunlight, corrosives, harmful gases or liquids, dust, metallic particles, and other contaminants. Exposure
to these can reduce the operating life and degrade the performance of the controller.
Several other factors should be evaluated carefully when selecting a location for installation:
• For effective cooling and maintenance, the controller should be mounted on a smooth, non-flammable
vertical surface.
• At least 3 inches (76mm) top and bottom clearance must be provided for airflow. At least 0.4 inches
(10mm) clearance is required between controls (each side).
• Temperature, humidity and vibration specifications should also be considered.
The Geo Drives can be mounted with a traditional 4-hole panel mount, two U shape/notches on the
bottom and two pear shaped holes on top. This keeps the heat sink and fan (single width and double
width drives), inside the mounting enclosure. On the low profile units (low power), the heat sink and fan
are replaced with a flat plate and the mounting enclosure itself is used as a heat sink. This reduces the
depth of the Geo amplifier by about 2.2 inches (~56 mm) to a slim 5.8 inch D (150 mm D). Mounting is
also identical to the single and double width drives through the 4-hole panel mount.
If multiple Geo drives are used, they can be mounted side-by-side, leaving at least to of a 0.4 inch
clearance between drives. This means a 3.7 inch center-to-center distance (94 mm) with the single width
and low profile Geo drives. Double width Geo amplifiers can be mounted side by side at 6.9 inch centerto-center distance (175 mm).
It is extremely important that the airflow is not obstructed by the placement of conduit tracks or other
devices in the enclosure.
The drive is mounted to a back panel. The back panel should be unpainted and electrically conductive to
allow for reduced electrical noise interference. The back panel should be machined to accept the
mounting bolt pattern of the drive. Make sure that all metal chips are cleaned up before the drive is
mounted so there is no risk of getting metal chips inside the drive.
The drive is mounted to the back panel with four M4 screws and internal-tooth lock washers. It is
important that the teeth break through any anodization on the drive’s mounting gears to provide a good
electrically conductive path in as many places as possible. Mount the drive on the back panel so there is
airflow at both the top and bottom areas of the drive (at least three inches).
Caution:
Units must be installed in an enclosure that meets the environmental IP rating of
the end product (ventilation or cooling may be necessary to prevent enclosure
ambient from exceeding 45° C [113° F]).
Note:
For more detail drawings (SolidWorks, eDrawings, DXF) visit our website under
the product that you are looking for.
Mounting 17
Page 30
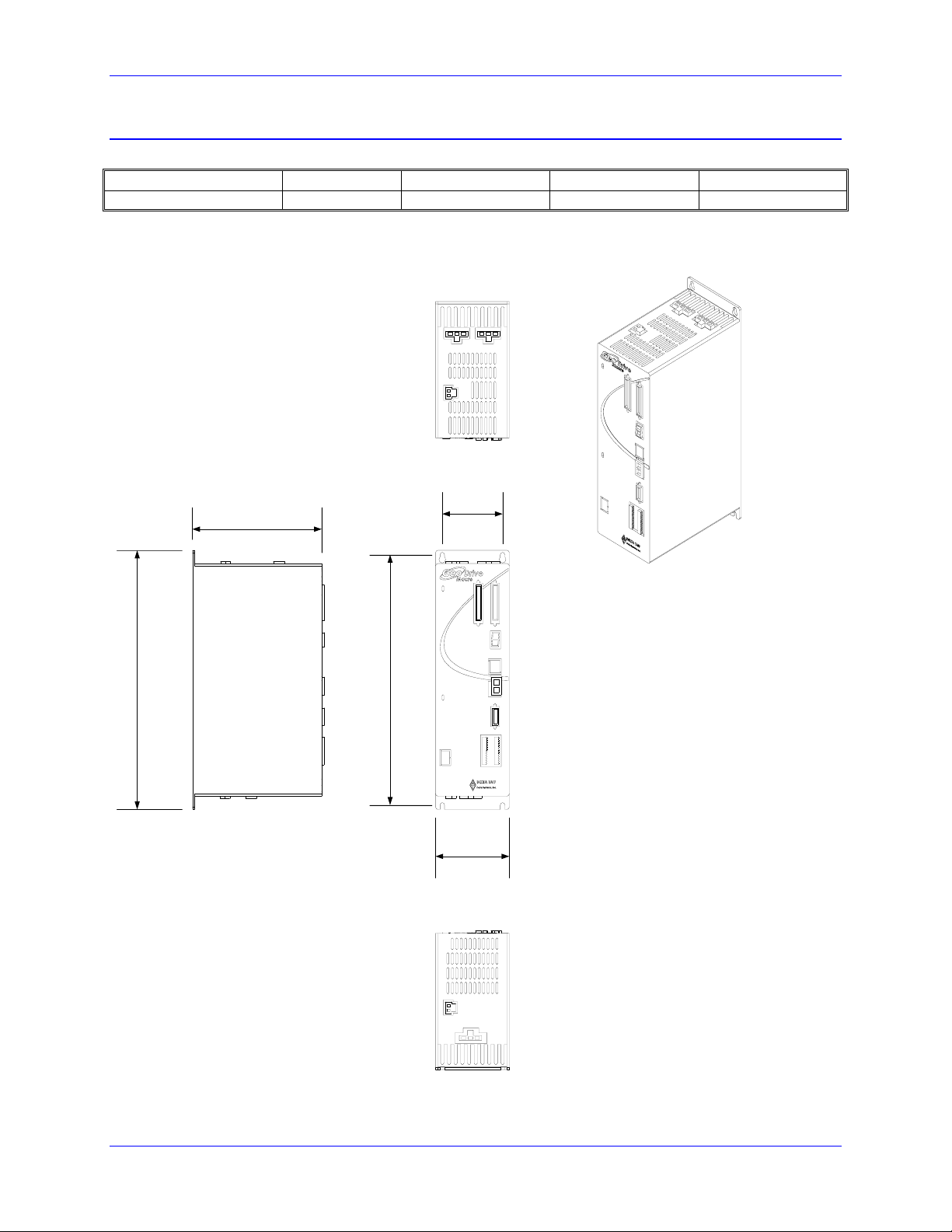
Geo MACRO Drive User Manual
Low Profile
Gxx012xx
Mounting dimensions 3.30in./ 84mm 11.00in./ 280mm 5.79in./ 147.1mm 4.3lbs/ 1.95kgs
Width Height Depth Weight
MACRO Version, No Heatsink, No Fan
(5.79)
(2.70)
(11.00)
(10.625)
(3.30)
18 Mounting
Page 31

Geo MACRO Drive User and Reference Manual
Single Width
Gxx051xx, Gxx101xx, Gxx151xx, Gxx032xx, Gxx052xx and GxL102xx
Mounting dimensions 3.30in./ 84mm 11.00in./ 280mm 8.00in./ 203mm 5.5lbs/ 2.5kgs
Width Height Depth Weight
Mounting 19
Page 32

Geo MACRO Drive User Manual
Double Width
Gxx201xx, Gxx301xx, GxH102xx and Gxx152xx
Mounting dimensions 6.50in./ 165mm 11.00in./ 280mm 8.00in./ 203mm Call the factory
Width Height Depth Weight
20 Mounting
Page 33

Geo MACRO Drive User and Reference Manual
CONNECTIONS
System (Power) Wiring
MAIN
POWER
GARxx
SHUNT
RESISTOR
24V
POWER
SUPPLY
EARTH
FRAME
+24 V
Red
Blk
24V RET
WHT
WHT
LOGIC
Twisted Wires
RE GEN -
J5
SHU NT
Geo
MACRO
J4
+24 VDC
24 VDC RET
BLK
RED
RE GEN +
GRN\Y EL
SC RE W HE AD
BLK
BLU
MOTOR 2
J3
WHT
MOTOR 1
J1
AC IN PUT
L2L
L
1
BLK
BLU
GRN\Y EL
WHT
WVUWVU
J2
SCREW HEAD
X1X2
SCREW HEAD
3
t
e
xt
t
e
xt
8AWG
to Main
Earth
Block
t
e
xt
t
e
xt
OPTI ONAL
EMI FILTER
EARTH
BLOCK
BLK
BLK
MCR
Fusing
WARNING:
Installation of electrical control equipment is subject to many regulations including
national, state, local, and industry guidelines and rules. General recommendations
can be stated but it is important that the installation be carried out in accordance
with all regulations pertaining to the installation.
Motor 2
Motor 1
Encoders
Fuse and Circuit Breaker Selection
In general, fusing must be designed to protect the weakest link from fire hazard. Each Geo drive is designed
to accept more than the recommended fuse ratings. External wiring to the drive may be the weakest link as
the routing is less controlled than the drive’s internal electronics. Therefore, external circuit protection, be it
fuses or circuit breakers, must be designed to protect the lesser of the drive or external wiring.
High peak currents and high inrush currents demand the use of slow blow type fuses and hamper the use
of circuit breakers with magnetic trip mechanisms. Generally, fuses are recommended to be larger than
what the rms current ratings require. Remember that some drives allow three times the continuous rated
current on up to two axis of motion. Time delay and overload rating of protection devices must consider
this operation.
Use of GFI Breakers
Ground Fault Interrupter circuit breakers are designed to break the power circuit in the event that
outgoing currents are not accompanied by equal and opposite returning currents. These breakers assume
that if outgoing currents are not returning then there is a ground path in the load. Most circuit breakers of
this type account for currents as low as 10mA PWM switching in servo drives coupled with parasitic
capacitance to ground in motor windings and long cables generate ground leakage current. Careful
Connections 21
Page 34

Geo MACRO Drive User Manual
installation practices must be followed. The use of inductor chokes in the output of the drive will help
keep these leakage currents below breaker threshold levels.
Transformer and Filter Sizing
Incoming power design considerations for use with Geo Drives require some over rating. In general, it is
recommended that all 3-phase systems using transformers and incoming filter chokes be allotted a 25%
over size to keep the impedances of these inserted devices from affecting stated system performance. In
general, it is recommended that all single-phase systems up to 1kW be designed for a 50% overload. All
single-phase systems over 1kW should be designed for a 200% overload capacity.
Noise Problems
When problems do occur often it points to electrical noise as the source of the problem. When this
occurs, turn to controlling high-frequency current paths. If following the grounding instructions does not
work, insert chokes in the motor phases. These chokes can be as simple as several wraps of the individual
motor leads through a ferrite ring core (such as Micrometals T400-26D). This adds high-frequency
impedance to the outgoing motor cable thereby making it harder for high-frequency noise to leave the
control cabinet area. Care should be taken to be certain that the core’s temperature is in a reasonable
range after installing such devices.
Operating Temperature
It is important that the ambient operating temperature of the Geo Drive be kept within specifications. The
Geo Drive is installed in an enclosure such as a NEMA cabinet. The internal temperature of the cabinet
must be kept under the Geo Drive Ambient Temperature specifications. It is sometimes desirable to
roughly calculate the heat generated by the devices in the cabinet to determine if some type of ventilation
or air conditioning is required. For these calculations the Geo Drive’s internal heat losses must be known.
Budget 100W per axis for 1.5A drives, 150W per axis for 3A drives, 200W per axis for 5A drives, 375W
per axis for 10A drives, 500W per axis for 15A drives, 650W per axis for 20A drives.
From 0°C to 45°C ambient no derating required. Above 45°C, derate the continuous and peak output
current by 2.5% per °C above 45°C. Maximum ambient is 55°C.
Single Phase Operation
Due to the nature of power transfer physics, it is not recommended that any system design attempt to
consume more than 2kW from any single-phase mains supply. Even this level requires careful
considerations. The simple bridge rectifier front end of the Geo Drive, as with all other drives of this
type, require high peak currents. Attempting to transfer power from a single-phase system getting one
charging pulse each 8.3 milliseconds causes excessively high peak currents that can be limited by power
mains impedances. The Geo Drive output voltage sags, the input rectifiers are stressed, and these current
pulses cause power quality problems in other equipment connected to the same line. While it is possible
to operate drives on single-phase power, the actual power delivered to the motor must be considered.
Never design expecting more than 1.5 HP total from any 115V single-phase system and never more than
2.5 HP from any 230V single-phase system.
22 Connections
Page 35

Geo MACRO Drive User and Reference Manual
Wiring AC Input, J1
The main bus voltage supply is brought to the Geo drive through connector J1. 1.5A continuous and 3A
continuous Geo drives can be run off single-phase power. It is acceptable to bring the single-phase power
into any two of the three input pins on connector J1. Higher-power drive amplifiers require three-phase
input power. It is extremely important to provide fuse protection or overload protection to the input
power to the Geo drive amplifier. Typically, this is provided with fuses designed to be slow acting, such
as FRN-type fuses. Due to the various regulations of local codes, NEC codes, UL and CE requirements,
it is very important to reference these requirements before making a determination of how the input power
is wired.
Additionally, many systems require that the power be able to be turned on and off in the cabinet. It is
typical that the AC power is run through some kind of main control contact within the cabinet, through
the fuses, and then fed to a Geo drive. If multiple Geo drives are used, it is important that each drive has
its own separate fuse block.
Whether single- or three-phase, it is important that the AC input wires be twisted together to eliminate
noise radiation as much as possible. Additionally, some applications may have further agency noise
reduction requirements that require that these lines be fed from an input filtering network.
The AC connections from the fuse block to the Geo drive are made via a cable that is either purchased as
an option from Delta Tau (CABKITxx) or made with the appropriate connector kit (CONKITxx).
(Appendix A)
J1: AC Input Connector Pinout
Pin # Symbol Function Description Notes
1 L3 Input Line Input Phase 3
2 L2 Input Line Input Phase 2
3 L1 Input Line Input Phase 1 (not used for single Phase Input)
On Gxx201xx and Gxx301xx, there is a fourth pin for Ground connection.
If DC bus is used, use L3 for DC+ and L2 for DC return.
Connector is located at the bottom side of the unit.
Wiring Earth-Ground
Panel wiring requires that a central earth-ground location be installed at one part of the panel. This
electrical ground connection allows for each device within the enclosure to have a separate wire brought
back to the central wire location. Usually, the ground connection is a copper plate directly bonded to the
back panel or a copper strip with multiple screw locations. The Geo drive is brought to the earth-ground
via a wire connected to the M4 stud (5mm thread) on the top of the location through a heavy gauge,
multi-strand conductor to the central earth-ground location. On some models, a fourth pin is provided on
the 3-phase AC input connector (J1) and on the motor output connectors to provide a ground connection.
Earth Grounding Paths
High-frequency noises from the PWM controlled power stage will find a path back to the drive. It is best
that the path for the high-frequency noises be controlled by careful installation practices. The major
failure in problematic installations is the failure to recognize that wire conductors have impedances at
high frequencies. What reads 0 ohms on a handheld meter may be hundreds of ohms at 30MHz.
Consider the following during installation planning:
1. Star point all ground connections. Each device wired to earth ground should have its own conductor
brought directly back to the central earth ground plate.
2. Use unpainted back panels. This allows a wide area of contact for all metallic surfaces reducing high
frequency impedances.
3. Conductors made up of many strands of fine conducts outperform solid or conductors with few
strands at high frequencies.
Connections 23
Page 36

Geo MACRO Drive User Manual
4. Motor cable shields should be bonded to the back panel using 360-degree clamps at the point they
enter or exit the panel.
5. Motor shields are best grounded at both ends of the cable. Again, connectors using 360-degree shield
clamps are superior to connector designs transporting the shield through a single pin. Always use
metal shells.
6. Running motor armature cables with any other cable in a tray or conduit should be avoided. These
cables can radiate high frequency noise and couple into other circuits.
Wiring 24 V Logic Control, J4
An external 24VDC power supply is required to power the logic portion of the Geo drive. This power can
remain on, regardless of the main AC input power, allowing the signal electronics to be active while the
main motor power control is inactive. The 24V is wired into connector J4. The polarity of this
connection is extremely important. Carefully follow the instructions in the wiring diagram. This
connection can be made using 16 AWG wire directly from a protected power supply. In situations where
the power supply is shared with other devices, it may be desirable to insert a filter in this connection.
The power supply providing this 24V must be capable of providing an instantaneous current of at least
1.5A to be able to start the DC-to-DC converter in the Geo drive. In the case where multiple drives are
driven from the same 24V supply, it is recommended that each drive be wired back to the power supply
terminals independently. It is also recommended that the power supply be sized to handle the
instantaneous inrush current required to start up the DC-to-DC converter in the Geo drive.
J4: 24VDC Input Logic Supply Connector
Pin # Symbol Function Description Notes
1
2 +24VDC Input Control power input 24V+/-10%, 2A
Connector is located at the bottom side of the unit.
24VDC RET Common Control power return
Wiring the Motors
The cable wiring must be shielded and have a separate conductor connecting the motor frame back to the
drive amplifier. The cables are available in cable kits (CABKITxx) from Delta Tau. (See Appendix A.)
Motor phases are conversed in one of three conventions. Motor manufacturers will call the motor phases
A, B, or C. Other motor manufacturers call them U, V, W. Induction motor manufacturers may call them
L1, L2, and L3. The drive’s inputs are called U, V, and W. Wire U, A, or L1 to the drive’s U terminal.
Wire V, B, or L2 to the drive’s V terminal. Wire W, C, or L3 to the drive’s W terminal.
The motor’s frame drain wire and the motor cable shield must be tied together at the mounting stud (5mm
thread) on top of the Geo drive product.
J2: Motor 1 Output Connector Pinout
Pin # Symbol Function Description Notes
1 U Output Axis 1 Phase1
2 V Output Axis 1 Phase2
3 W Output Axis 1 Phase3
On Gxx201xx and Gxx301xx, there is a fourth pin for Ground connection. Connector is located at the top
side of the unit.
J3: Motor 2 Output Connector Pinout
Pin # Symbol Function Description Notes
1 U Output Axis 2 Phase1 2- Axis drives only
2 V Output Axis 2 Phase2 2- Axis drives only
3 W Output Axis 2 Phase3 2- Axis drives only
Connector is located at the top side of the unit.
24 Connections
Page 37

Geo MACRO Drive User and Reference Manual
Wiring the Motor Thermostats
Some motor manufacturers provide the motors with integrated thermostat overload detection capability.
Typically, it is in one or two forms: a contact switch that is normally closed or a PTC. These sensors can
be wired into the Geo drive’s front panel at connector X1 and X2.
Motor 1 thermostat output is wired to pin 23 of X1,
In_Therm_Mot1, and referenced to the GND
pin13 or 25. In addition, if dual axis drive is
ordered, Motor 2 thermostat output is wired to pin
23 of X2, In_Therm_Mot2, and referenced to the
GND pin 13 or 25.
Function Pin #
In_Therm_Mtr 23
GND 13,25
Wiring the Motor Thermostats
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
X1/X2
In_Therm_Mot
GND
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
MS{node},MI100 has special functions for Geo MACRO drives ( firmware 1.006 and above) to enable
the motor over-temperature function of the drive, default this function is disabled (firmware 1.006 and
above). If someone wants to enable the motor #1 over-temperature input to his Geo then he needs to set
MS{node},MI100= $4. For motor #2 over-temperature input to be enabled MS{node},MI100=$8 and if
the user wants both motor over-temperature inputs enable then MS{node},MI100=$C.
For earlier drives (firmware 1.005 and before) If the motor over-temperature protection is not required,
In_Therm_Mot1/2 should be connected to GND, pin 13 or 25. Otherwise, the drive status display will
show a warning error code 5 for motor #1 over -temperature, or an A for motor 2 over -temperature. If
both pins are not shorted to GND, display will show 5 (the first error gets triggered)
Wiring the Regen (Shunt) Resistor, J5
The Geo Drive family offers compatible regen resistors as optional equipment. The regen resistor is used
as a shunt regulator to dump excess power during demanding deceleration profiles. The GAR48 and
GAR78 resistors are designed to dump the excess bus energy very quickly.
The regen circuit is also known as a shunt regulator. Its purpose is to dump power fed back into the drive
from a motor acting as a generator. Excessive energy can be dumped via an external load resistor. The
Geo product series is designed for operation with external shunt resistors of 48 Ω for the 10 and 15 amp
versions or 78 Ω for the 1.5, 3, and 5 amp versions. These are available directly from Delta Tau as
GAR48 and GAR78, respectively. These resistors are provided with pre-terminated cables that plug into
connector J5.
Each resistor is the lowest ohm rating for its compatible drive and is limited for use to 200 watts RMS.
There are times the regen design might be analyzed to determine if an external Regen resistor is required
or what its ratings can be. The following data is provided for such purpose.
Connections 25
Page 38

Geo MACRO Drive User Manual
Caution:
The black wires are for the thermostat and the white wires are for the regen resistor
on the external regen resistor (pictured below). These resistors can reach
temperatures of up to 200 degrees C. These resistors must be mounted away from
other devices and near the top of the cabinet. Additionally, precautions must be
made to ensure the resistors are enclosed and cannot be touched during operation
or anytime they are hot. Sufficient warning labels should be placed prominently
near these resistors.
The regen resistors incorporate a thermal overload protection thermostat that opens when the core
temperature of the resistor exceeds 225 degrees C. This thermostat is available through the two black
leads exiting the resistor. It is important that these two leads be wired in a safety circuit that stops the
system from operating should the thermostat open.
J5: External Shunt Connector Pinout
Pin # Symbol Function
1 Regen2 Regen+ Output
Connector is located at the top side of the unit
DT Connector part number #014-000F02-HSG and pins part number #014-043375-001
Molex Crimper tool p/n#63811-0400
For the high Current Drives, Gxx201xx and Gxx301xx , this connector is a 3 pin
Large Molex connector
1 CAP2 Regen- Output
3 Regen+ Output
Connector is located at the top side of the unit.
DT Connector part number #014-H00F03-049 and pins part number #014-042815-001.
Molex Crimper tool p/n#63811-1500
26 Connections
Output
Output
Page 39

Geo MACRO Drive User and Reference Manual
Shunt Regulation
When the motor is used to slow the moving load, this is called regenerative deceleration. Under this
operation, the motor is acting as a generator consuming energy from the load while passing the energy
into the DC Bus storage capacitors. Left unchecked, the DC Bus voltage can raise high enough to
damage the drive. For this reason there are protection mechanisms built into the Geo Drive product such
as shunt regulation and over-voltage protection.
The shunt regulator monitors the DC Bus voltage. If this voltage rises above a present threshold (Regen
Turn On Voltage), the Geo Drive will turn on a power device intended to place the externally mounted
regen resistor across the bus to dump the excessive energy. The power device keeps the regen resistor
connected across the bus until the bus voltage is sensed to be below the Regen Turn Off voltage at which
time the power device removes the resistor connection.
Minimum Resistance Value
The regen resistor selection requires that the resistance value of the selected resistor will not allow more
current to flow through the Geo Drive’s power device than specified.
Maximum Resistance Value
The maximum resistor value that will be acceptable in an application is one that will not let the bus
voltage reach the drive’s stated over voltage specification during the deceleration ramp time. The
following equations defining energy transfer can be used to determine the maximum resistance value.
Energy Transfer Equations
Regen, or shunt, regulation analysis requires study of the energy transferred during the deceleration
profile. The basic philosophy can be described as follows:
• The motor and load have stored kinetic energy while in motion.
• The drive removes this energy during deceleration by transferring to the DC bus.
• There are losses during this transfer, both mechanical and electrical, which can be significant in some
systems.
• The DC bus capacitors can store some energy.
• The remaining energy, if any, is transferred to the regen resistor.
Kinetic Energy
The first step is to ascertain the amount of kinetic energy in the moving system, both the motor rotor and
the load it is driving. In metric (SI) units, the kinetic energy of a rotating mass is:
1
2
E
where:
is the kinetic energy in joules, or watt-seconds (J, W-s)
E
K
J is the rotary moment of inertia in kilogram-meter
ω is the angular velocity of the inertia in radians per second (1/s)
If the values are not in these units, first convert them. For example, if the speed is in revolutions per
minute (rpm), multiply this value by 2π/60 to convert to radians per second.
When English mechanical units are used, there are additional conversion factors must be included to get
the energy result to come out in joules. For example, if the rotary moment of inertia J is expressed in lb-
2
, the following equation should be used:
ft-sec
E
K
If the rotary moment of inertia J is expressed in lb-in-sec
E
K
In standard metric (SI) units, the kinetic energy of a linearly moving mass is:
Connections 27
J
ω
=
K
2
2
(kg-m2)
J678.0
=
=
ω
2
, the following equation should be used:
J0565.0
ω
2
2
Page 40

Geo MACRO Drive User Manual
ω
=
=
1
2
E =
mv
K
2
where:
is the kinetic energy in joules (J)
E
K
m is the mass in kilograms (kg)
v is the linear velocity of the mass in meters/second (m/s)
Here also, to get energy in Joules from English mechanical units, additional conversion factors are
required. To calculate the kinetic energy of a mass having a weight of W pounds, the following equation
can be used:
E ==
K
W
2
v
678.0
g
2
Wv0211.0
where:
is the kinetic energy in joules (J)
E
K
W is the weight of the moving mass in pounds (lb)
g is the acceleration of gravity (32.2 ft/sec
2
)
v is the linear velocity of the mass in feet per second (ft/sec)
Energy Lost in Transformation
Some energy will be lost in the transformation from mechanical kinetic energy to electrical energy. The
losses will be both mechanical due to friction and electrical due to resistance. In most cases, these losses
will comprise a small percentage of the transformed energy and can be safely ignored especially because
ignoring losses leads to a conservative design. However, if the losses are significant and the system
should not be over-designed, calculate these losses.
In metric (SI) units, the mechanical energy lost due to Coulomb (dry) friction in a constant deceleration to
stop of a rotary system can be expressed as:
LM
1
=
ω
T
dtf
2
where:
E
is the lost energy in joules (J)
LM
T
is the resistive torque due to Coulomb friction in newton-meters (N-m)
f
E
ω is the starting angular velocity of the inertia in radians per second (1/s)
t
is the deceleration time in seconds (s)
d
If the frictional torque is expressed in the common English unit of pound-feet (lb-ft), the comparable
expression is:
E
LM
T678.0
d
f
t
In metric (SI) units, the mechanical energy lost due to Coulomb (dry) friction in a constant deceleration to
stop of a linear system can be expressed as:
LM
1
F
=
dvtf
2
where:
E
is the lost energy in joules (J)
LM
T
is the resistive force due to Coulomb friction in newtons (N)
f
E
v is the starting linear velocity in meters/second (m/s)
t
is the deceleration time in seconds (s)
d
If the frictional force is expressed in the English unit of pounds (lb) and the velocity in feet per second
(ft/sec), the comparable expression is:
E
LM
F678.0
dvtf
The electrical resistive losses in a 3-phase motor in a constant deceleration to stop can be calculated as:
where:
E
LE
3
2
i
=
rms
2
t
R
pp
d
28 Connections
Page 41

Geo MACRO Drive User and Reference Manual
−−−
=
(
ELE is the lost energy in joules (J)
i
is the current required for the deceleration in amperes (A), equal to the required deceleration torque
rms
divided by the motor’s (rms) torque constant K
R
is the phase-to-phase resistance of the motor, in ohms (Ω)
pp
t
is the deceleration time in seconds (s)
d
T
Capacitive Stored Energy in the Drive
The energy not lost during the transformation is initially stored as additional capacitive energy due to the
increased DC bus voltage. The energy storage capability of the drive can be expressed as:
where:
E
is the additional energy storage capacity in joules (J)
C
E −=
C
1
VC
regen
2
V
22
nom
)
C is the total bus capacitance in Farads
V
is the DC bus voltage at which the regeneration circuit would have to activate, in volts (V)
regen
V
is the normal DC bus voltage, in volts (V)
nom
Evaluating the Need for a Regen Resistor
Any starting kinetic energy that is not lost in the transformation and cannot be stored as bus capacitive
energy must be dumped by the regeneration circuitry in to the regen (shunt) resistor. The following
equation can be used to determine whether this will be required:
LE
E
C
If E
LM
E
E
E
excess
in this equation is greater than 0, a regen resistor will be required.
excess
E
K
Regen Resistor Power Capacity
A given regen resistor will have both a peak (instantaneous) and a continuous (average) power dissipation
limit. It is therefore necessary to compare the required peak and continuous regen power dissipation
requirements against the limits for the resistor.
The peak power dissipation that will occur in the regen resistor in the application will be:
=
peak
Note:
V
regen
% timeon
2
R
100
where:
P
is peak power dissipation in watts (W)
peak
V
is the DC bus voltage at which the regeneration circuit activates, in volts (V)
regen
P
peak
R is the resistance value of the regen resistor, in ohms (Ω)
However, this power dissipation will not be occurring all of the time, and in most applications, only for a
small percentage of the time. Usually, the regen will only be active during the final part of a lengthy
deceleration, after the DC bus has charged up to the point where it exceeds the regen activation voltage.
The average power dissipation value can be calculated as:
where:
P
is average power dissipation in watts (W)
avg
P−=
avg
P
%on-time is the percentage of time the regen circuit is active
The Turn-on voltage for the shunt circuitry for all Low power Geo drives is 392V
(high power is 784V). There is a Hysteresis of 20V, so if the regen turns on @
392V (784V) it will not turn off until it drops to 372V (744V).
Bonding
The proper bonding of shielded cables is imperative for minimizing noise emissions and increasing
immunity levels. The bonding effect is to reduce the impedance between the cable shield and the back
Connections 29
Page 42

Geo MACRO Drive User Manual
panel.
Power input wiring does not require shielding (screening) if the power is fed to the enclosure via metal
conduit. If metal conduit is not used in the system, shielded cable is required on the power input wires
along with proper bonding techniques.
Filtering
CE Filtering
Apply proper bonding and grounding techniques, described earlier in this section, when incorporating
EMC noise filtering components to meet this standard.
Noise currents often occur in two ways. The first is conducted emissions passed through ground loops.
The quality of the system-grounding scheme inversely determines the noise amplitudes in the lines.
These conducted emissions are of a common-mode nature from line-to-neutral (ground). The second is
radiated high-frequency emissions that usually are capacitively coupled from line-to-line and are
differential in nature.
When mounting the filters, make sure the enclosure has an unpainted metallic surface. This allows more
surface area to be in contact with the filter housing and provides a lower impedance path between the
housing and the back plane. The back panel should have a high frequency ground strap connection to the
enclosure frame and earth ground.
30 Connections
Page 43

Geo MACRO Drive User and Reference Manual
Input Power Filtering
Caution:
To avoid electric shock, do not touch filters for at least 10 seconds after removing
the power supply.
The Geo Drive electronic system components require EMI filtering in the input power leads to meet the
conducted emission requirements for the industrial environment. This filtering blocks conducted-type
emissions from exiting onto the power lines and provides a barrier for power line EMI.
Adequately size the system. The type of filter must be based on the voltage and current rating of the
system and whether the incoming line is single or three-phase. One input line filter may be used for
multi-axis control applications. These filters should be mounted as close to the incoming power as
possible so noise is not capacitively coupled into other signal leads and cables. Implement the EMI filter
according to the following guidelines:
• Mount the filter as close as possible to the incoming cabinet power.
• When mounting the filter to the panel, remove any paint or material covering. Use an unpainted
metallic back panel.
• Filters are provided with a ground connection. All ground connections should be tied to ground.
• Filters can produce high leakage currents; they must be grounded before connecting the supply.
• Do not touch filters for a period of ten seconds after removing the power supply.
Motor Line Filtering
Motor filtering may not be necessary for CE compliance of Geo Drives. However, this additional
filtering increases the reliability of the system. Poor non-metallic enclosure surfaces and lengthy,
unbonded (or unshielded) motor cables that couple noise line-to-line (differential) are some of the factors
that may lead to the necessity of motor lead filtering.
Motor lead noise is either common-mode or differential. The common-mode conducted currents occur
between each motor lead and ground (line-to-neutral). Differential radiated currents exist from one motor
lead to another (line-to-line). The filtering of the lines feeding the motor provides additional attenuation
of noise currents that may enter surrounding cables and equipment I/O ports in close proximity.
Differential mode currents commonly occur with lengthy motor cables. As the cable length increases, so
does its capacitance and ability to couple noise from line-to-line. While every final system is different
and every application of the product causes a slightly different emission profile, it may become necessary
to use differential mode chokes to provide additional noise attenuation to minimize the radiated
emissions. The use of a ferrite core placed at the Geo Drive end on each motor lead attenuates differential
mode noise and lowers frequency (30 to 60 MHz) broadband emissions to within specifications. Delta
Tau recommends a Fair-Rite P/N 263665702 (or equivalent) ferrite core.
Common mode currents occur from noise spikes created by the PWM switching frequency of the Geo
Drive. The use of a ferrite or iron-powder core toroid places common mode impedance in the line
between the motor and the Geo Drive. The use of a common mode choke on the motor leads may
increase signal integrity of encoder outputs and associated I/O signals.
I/O Filtering
I/O filtering may be desired, depending on system installation, application, and integration with other
equipment. It may be necessary to place ferrite cores on I/O lines to avoid unwanted signals entering and
disturbing the Geo.
Connections 31
Page 44

Geo MACRO Drive User Manual
Connecting Main Feedback Sensors (X1 & X2)
X1 is for motor #1 and X2 for motor #2.
Digital Quadrature Encoders
Quadrature encoders provide two digital signals that are a function of the position of the encoder, each
nominally with 50% duty cycle, and nominally one-quarter cycle apart. This format provides four distinct
states per cycle of the signal, or per line of the encoder. The phase difference of the two signals permits the
decoding electronics to discern the direction of travel, which would not be possible with a single signal.
Typically, these signals are at 5V TTL/CMOS levels, whether single-ended or differential. The input
circuits are powered by the main 5V supply for the controller, but they can accept up to +/-12V between
the signals of each differential pair, and +/-12V between a signal and the GND voltage reference.
Differential encoder signals can enhance noise immunity by providing common-mode noise rejection.
Modern design standards virtually mandate their use for industrial systems, especially in the presence of
PWM power amplifiers, which generate a great deal of electromagnetic interference.
Hardware Setup
The Geo Drive accepts inputs from two digital encoders and
provides encoder position data to the motion processor. X1 is
encoder 1 and X2 is encoder 2. The differential format
provides a means of using twisted pair wiring that allows for
better noise immunity when wired into machinery.
Geo Drives encoder interface circuitry employs differential
line receivers. The wiring diagram on the right shows an
example of how to connect the Geo drive to a quadrature
encoder.
Function Pin #
ChA+ 1
ChA- 14
ChB+ 2
ChB- 15
ChC+ 3
ChC- 16
X1/ X2
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
CHA+
14
CHA-
CHB+
15
CHB-
CHC+
16
CHC-
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
5V
Shield
GND
GND
Quadrature
Encoder
32 Connections
Page 45

Geo MACRO Drive User and Reference Manual
Digital Hall Commutation Sensors
Many motor manufactures now give the consumer the option of placing both Hall effect sensors and
quadrature encoders on the end shaft of brushless motors. This will allow the controller to estimate the
rotor magnetic field orientation and adjusts the command among the motor phases properly without
rotating the motor at power-up. If this is not done properly, the motor or amplifier could be damaged.
Note:
These digital hall-effect position sensors should not be confused with analog halleffect current sensors used in many amplifiers to provide current feedback data for
the current loop.
Hardware Setup
The Geo Drive accepts digital hall sensor inputs.
X1 is for motor #1 and X2 for motor #2.
The wiring diagram on the right shows an example
of how to connect the Geo drive to Digital Hall
sensors.
Function Pin #
U 8
V 21
W 9
T 22
5V 12/24
GND 13/25
X1/ X2
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
U
21
V
W
22
T
23
24
5V
25
GND
Shield
Hall Sensors
SSI Encoders
Geo Drive was designed to work with either Gray Code or Binary Style SSI Encoders. The Geo Drive
takes the gray/binary code information and converts it into a parallel binary word for absolute and
ongoing position data.
Hardware Setup
The differential format provides a means of using
twisted pair wiring that allows for better noise immunity
when wired into machinery.
The wiring diagram to the right shows an example of
how to connect the Geo Drive to an SSI encoder.
Function Pin#
CLK+ 6
DATA+ 7
CLK- 19
DATA- 20
ENCPWR/5V 12/24
GND 13/25
Note: We assume the SSI Encoder power requirements
are for 5V, else use of an external power supply for the SSI
encoder is required. Tie together the Geo Drive GND and
the power supply for noise immunity
X1/X2
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
CLK+
19
CLK-
DAT+
20
DAT-
21
22
23
24
25
Shield
SSI
encoder
+5V
GND
Connections 33
Page 46

Geo MACRO Drive User Manual
Sinusoidal Encoders
The Geo Drive with the Interpolator option accepts inputs from two sinusoidal or quasi-sinusoidal
encoders and provides encoder position data to the motion processor. This interpolator creates 4,096
steps per sine-wave cycle. User needs to order the option.
Be sure to use shielded, twisted pair cabling for sinusoidal encoder wiring. Double insulated is the best.
The sinusoidal signals are very small and must be kept as noise free as possible. Avoid cable routing near
noisy motor or driver wiring. Refer to the appendix for tips on encoder wiring.
It is possible to reduce noise in the encoder lines of a motor-based system by the use of inductors that are
placed between the motor and the amplifier. Improper grounding techniques may also contribute to noisy
encoder signals.
Note:
Voltage mode encoders are becoming the more popular choice for machine designs
due to their lower impedance outputs. Lower impedance outputs represent better
noise immunity, and therefore more reliable encoder interfaces.
The Geo Drive uses 1 Vp-p voltage mode encoders only.
Hardware Setup
The differential format provides a means of using
twisted pair wiring that allows for better noise
immunity when wired into machinery.
Sinusoidal encoders operate on the concept that
there are two analog signal outputs 90 degrees out
of phase.
Geo Drives can be used only with the voltage
mode encoder type, and the lines have to be
differential. The wiring diagram to the right
shows an example of how to connect the Geo drive
to a sinusoidal encoder.
Function Pin#
Sin+ 1
Cos+ 2
Cos- 15
Index+ 3
Index- 16
Sin- 14
X1/X2
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
Cos+
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
In_Therm_Mot
24
+5V
25
GND
Sin+
Index+
Sin-
Cos-
Index-
Sinusoidal
Encoder
1Vpp A
1Vpp B
index
Up Power
0V Supply
Shield
34 Connections
Page 47

Geo MACRO Drive User and Reference Manual
Hiperface® Interface
The Geo Drive will read the absolute data from the Hiperface® interface only if the appropriate option is
ordered. (Not yet released firmware).
Hardware Setup
The differential format provides a means of using
twisted pair wiring that allows for better noise
immunity when wired into machinery.
• Safe data transmission
• Absolute positioning
• Only 8 leads
The wiring diagram to the right shows an example
of how to connect the Geo Drive with Hiperface.
Function Pin#
Sin+/ ChA+ 1
Cos+/ChB+ 2
Sin-/ChA- 14
Cos-/ChB- 15
DATA+ 7
DATA- 20
ENCPWR/5V 12/24
GND 13/25
Note: We assume the Hiperface Interface power
requirements are for 5V, else use of an external
power supply for the Hiperface is required. Tie
together the Geo Drive GND and the power supply
GND for noise immunity.
X1/X2
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
Cos+
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
In_Ther m_Mot
24
+5V
25
GND
Hiperface® Interface
Sin+
Sin-
Cos-
DATA+
DATA-.
Shield
Hiperface Interface
1Vpp A
1Vpp B
Up Power
0V Supply
DATA
DATA
Connections 35
Page 48

Geo MACRO Drive User Manual
EnDat Interface
The Geo Drive will read the absolute data from the EnDat (Encoder Data) interface only if the
appropriate option is ordered. (Not yet released firmware)
Hardware Setup
The differential format provides a means of
using twisted pair wiring that allows for
better noise immunity when wired into
machinery.
The wiring diagram to the right shows an
example of how to connect the Geo Drive to
an EnDat interface.
Function Pin#
Sin+/ ChA+ 1
Cos+/ChB+ 2
Sin-/ChA- 14
Cos-/ChB- 15
CLK+ 6
DATA+ 7
CLK- 19
DATA- 20
ENCPWR/5V 12/24
GND 13/25
Note: We assume the EnDat
Interface power requirements are
for 5V, else use of an external
power supply for the EnDat is
required. Tie together the Geo
Drive GND and the power supply
GND for noise immunity.
X1/X2
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
Cos+
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
In_Therm_Mot
24
+5V
25
GND
EnDat Interface
Sin+
Sin-
Cos-
CLK+
CLK-
DATA+
DATA-.
Shield
1Vpp A
1Vpp B
Up Power
0V Supply
DATA
EnDat Interface
DATA
CLOCK
CLOCK
36 Connections
Page 49

Geo MACRO Drive User and Reference Manual
Resolvers
The Geo Drive can interface to most industry standard resolvers if the appropriate option is ordered.
Typical resolvers requiring 5 to 10 kHz excitation frequencies with voltages ranging from 5 to 10V peakto-peak are compatible with this drive.
Fundamentally, the Geo Drive connects three differential analog signal pairs to each resolver: a single
excitation signal pair, and two analog feedback signal pairs. The wiring diagram below shows an
example of how to connect the Geo drive to the Resolver
Hardware Setup
The differential format
provides a means of using
twisted pair wiring that
allows for better noise
immunity when wired into
machinery.
The wiring diagram to the
right shows an example of
how to connect the Geo
Drive to a Resolver.
Function Pin #
ResSin+ 4
ResSin- 17
ResCos+ 5
ResCos- 18
ResOut 11
GND 13,25
Geo Drive Resolver Wiring Diagram
Sin+
Sin-
Twisted pair Screened
Cable
Cos+
Cos-
ResOut
GND
Notes:
Terminate shields on pins 13 and 25
Shield
ResSin+
ResSinResCos+
ResCos-.
ResOut
GND
GND
X1 or X2
1
14
2
15
3
16
4
17
5
18
6
19
7
20
8
21
9
22
10
23
11
24
12
25
13
Connections 37
Page 50

Geo MACRO Drive User Manual
Connecting Secondary Quad. Encoders (X8 & X9)
Secondary encoders in the Geo MACRO Amplifier are standard since logic board revision -10A and
above, and are found on Db-connectors X8 and X9. They must be Quadrature TTL encoders.
Hardware Setup
The Geo Drive also accepts inputs from two
digital quadrature encoders and provides
encoder position data to the motion
processor. X8 is secondary encoder #1 and
X9 is secondary encoder #2. The
differential format provides a means of
using twisted pair wiring that allows for
better noise immunity when wired into
machinery.
Geo Drives encoder interface circuitry
employs differential line receivers. The
wiring diagram on the right shows an
example of how to connect the Geo drive to
a quadrature encoder.
Function Pin #
ChA+ 1
ChA- 6
ChB+ 2
ChB- 7
ChC+ 3
ChC- 8
ENCPWR 5V 4
GND 5
1
2
3
4
5
Secondary Encoders
Quadrature
X8 / X9
CHA+
CHA-
6
CHB+
CHB-
7
CHC+
CHC-
8
5V
9
GND
Shield
Fl oat
Shield
Encoder
38 Connections
Page 51

Geo MACRO Drive User and Reference Manual
Connecting General Purpose I/O & Flags (X3)
X3 provides the connector for general purpose I/O (12-24VDC) and the input flags for each axis (Positive
Limit, Negative Limit, Home Switch and USER flag input). The outputs are rated for 0.5A and have to be
set up all sinking or all sourcing, no mixing topologies. Same is true for the inputs, no mixing topologies,
all sinking or all sourcing.
24V
Flag Supply
12-24VDC
0V
Flag
Return
Sample wiring the I/O
Sourcing Inputs and Sourcing Outputs
Function Pin #
GP_OUT 1 EMT 2
GP_OUT 2 EMT 4
GP_OUT 3 EMT 6
GP_OUT 4 EMT 8
COM COL 9
GP IN 1 11
GP IN 2 12
GP IN 3 13
GP IN 4 14
I/O RTN 15
Sourcing
Separate
Supply
Flag Supply
12-24VDC
24V
Return
Flag
0V
Sinking
Separate
Supply
24
23
Geo MACRO
22
Sourcing Inputs
21
Sourcing Outputs
20
19
18
17
16
15
Input Return
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
Input4
Input3
Input2
Input1
Com_Col
Output4
Output3
Output2
Output1
24V Supply
0V 24V
Connections 39
Page 52

Geo MACRO Drive User Manual
Sinking Inputs and Sinking Outputs
Function Pin #
GP_OUT 1 COL 1
GP_OUT 2 COL 3
GP_OUT 3 COL 5
GP_OUT 4 COL 7
COM EMT 10
GP IN 1 11
GP IN 2 12
GP IN 3 13
GP IN 4 14
I/O RTN 15
Sample Wiring the Flags
Geo MACRO
Sourcing Flags
24V Supply
24V 0V
24
23
22
Geo MACRO
21
Sinking Inputs
20
Sinking Outputs
19
18
17
16
15
Input Return
14
Input4
13
Input3
12
Input2
11
Input1
10
Com_EMT
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
Geo MACRO
Sinking Flags
Output4
Output3
Output2
Output1
24V Supply
24V 0V
24V Supply
0V 24V
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
USER 2
Home 2
Neg.Limit 2
Pos .Lim it 2
USER 1
Home 1
Neg.Limit 1
Pos .Lim it 1
FLG_RTN
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
USER 2
Home 2
Neg.Limit 2
Pos .Lim it 2
USER 1
Home 1
Neg.Limit 1
Pos .Lim it 1
FLG_RTN
Function Pin #
FLG_RTN 16
PLIM1 17
NLIM1 18
HOME1 19
USER1 20
PLIM2 21
NLIM2 22
HOME2 23
USER2 24
40 Connections
Page 53

Geo MACRO Drive User and Reference Manual
Connecting MACRO Ring
Fiber Optic MACRO connections (X5)
Output
/
Previous
ACC-5E
Turbo Ultralite/
Input
/
Next
RJ-45 Copper MACRO connections (X10 &X11)
MACRO
(X5)
Geo MACRO
Input
I/O
Output
Geo MACRO
Output
ACC-5E
Turbo Ultralite/
Previous
Input
/
Next
/
Output
Input
RJ45
Out
(X11)
RJ45
In
(X12)
Connections 41
Page 54

Geo MACRO Drive User Manual
Connecting optional Analog Inputs (X6 & X7)
The MACRO Geo Drive can be ordered with two analog to digital converters (option 3/4/5). These A/D
converters are 16-bit devices that are ready to be used without any software setup. Delta Tau uses the
Burr Brown ADS8343 for this circuit.
The analog signals for analog input #1 are wired in to pins 5 (ADC1+) and 9 (ADC1-) of X6, and for
analog input #2 into pins 5 (ADC2+) and 9 (ADC2-) of X7.
Bipolar Analog Input
Function Pin #
GND 4
ANALOG+ 5
ANALOG- 9
Unipolar Analog Input
Function Pin #
GND 4
ANALOG+ 5
ANALOG- 9
1
2
3
4
5
1
2
3
4
5
X6/X7
6
7
8
9
X6/X7
6
7
8
9
-5VDC to
5VDC
Source
ANALOG- .
ANALOG+
-10VDC to
10VDC
Source
GND
ANALOG-.
ANALOG+
42 Connections
Page 55

Geo MACRO Drive User and Reference Manual
SOFTWARE SETUP FOR GEO MACRO DRIVES
Introduction
Turbo PMAC2 controllers can command axes and I/O over the MACRO ring. Most commonly, this is
done with an Ultralite board-level Turbo PMAC2 controller that is installed as an expansion card in the
host computer, communicating to MACRO Stations, MACRO-based drives, and/or MACRO peripheral
devices over the MACRO ring. However, it is also possible for a UMAC Turbo with the ACC-5E
MACRO interface, to command devices over the MACRO ring.
It is advisable to the user to use the Turbo Setup program to set up his Geo MACRO application(MACRO
communications, feedback setup, commutation, and motor setup), or to use the MACRO Ring ASCII
setup tool which comes with the PEWIN32PRO2 and sets up the MACRO communications, and displays
to the user some useful information about his system. Sample screens and procedures for these programs
are shown in the following section
Establishing MACRO Communications with Turbo PMAC
Several variables must be set up properly for proper ring operation. Usually, this is done automatically
through use of the Turbo Setup program or with the new application tool PEWIN32PRO2 MACRO Ring
ASCII on a PC. The following instructions permit direct manual setting of these variables.
MACRO Ring Frequency Control Variables
The MACRO ring update frequency is the phase clock frequency of the ring master controller. If there is
more than one Turbo PMAC2 controller on the ring, only one of them can be the ring master controller
(others are masters, but not ring masters). Of course, if there is only one Turbo PMAC2 controller on the
ring, it will be the ring master controller. Determining which Turbo PMAC2 (technically, which
MACRO IC on a Turbo PMAC2) is ring master is explained below.
While the ring master has the capability to force the clock generation of other devices on the ring into
synchronization, it is strongly recommended that all devices on the ring, both other Turbo PMAC2
controllers, and any slave devices, be set up for the same phase clock frequency. Determining which IC
sets the phase clock frequency and the actual setting the phase clock frequency for a Turbo PMAC2
controller is explained above.
For a Turbo PMAC2 driving a MACRO ring, MACRO IC 0 should generate the phase clock signal. This
means that I19 should be set to 6807 (which it will be by default on virtually any Turbo PMAC2 capable
of driving a MACRO ring), and that I6800 and I6801 set the phase clock frequency.
I7: Phase Cycle Extension
On the Turbo PMAC2 board, it is possible to skip hardware phase clock cycles between executions of the
phase update software. A Turbo PMAC2 board will execute the phase update software – commutation
and/or current-loop closure – every (I7+1) hardware phase clock cycles. The default value for I7 is 0, so
normally Turbo PMAC2 executes the phase update software every hardware phase clock cycle.
If the Turbo PMAC2 board is closing the current loop for direct PWM control over the MACRO ring, it is
desirable to have two hardware ring update cycles (which occur at the hardware phase clock frequency)
per software phase update. This eliminates one ring cycle of delay in the current loop, which permits
slightly higher gains and performance. To do this, I7 would be set to 1, so the phase update software
would execute every second hardware phase clock cycle, and ring update cycle.
Normally it is desirable to close the current loop at an update rate of about 9 kHz (the default rate). If two
ring updates were desired per current loop update, the ring update frequency would need to be set to 18
kHz. This is possible if there are no more than 40 total active nodes on the ring. To implement this,
I6800 would be set to one-half of the default value, and I6801 to the default value of 0.
Software Setup 43
Page 56

Geo MACRO Drive User Manual
Note:
When making this change, change the Turbo PMAC2’s I6800 variable first, then
the MACRO Station’s MI992. Changing the MACRO Station’s MI992 alone,
followed by an MSSAVE<node> command and an MS$$$<node>, could cause
the Station’s watchdog timer to trip.
I6840: MACRO IC 0 Master Configuration
Any MACRO IC on a Turbo PMAC2 talking to a MACRO Station must be configured as a master on the
ring. For purposes of the MACRO protocol, each MACRO IC is a separate logical master with its own
master number, even though there may be multiple MACRO ICs on a single physical Turbo PMAC2.
Each ring must have one and only one ring controller (synchronizing master). This should be the
MACRO IC 0 one and only one of the Turbo PMAC2 boards on the ring.
On a Turbo PMAC2, set I6840 to $30 to make the card’s MACRO IC 0 the ring controller. This sets bits
4 and 5 of the variable to 1. Setting bit 4 to 1 makes the IC a master on the ring; setting bit 5 to 1 makes
the IC the ring controller” starting each ring cycle by itself.
On a Turbo PMAC2 whose MACRO IC 0 will be a master but not ring controller, I6840 should be set to
$90. This sets bits 4 and 7 of the variable to 1. Setting bit 4 to 1 makes the IC a master on the ring;
setting bit 7 to 1 will cause this IC to be synchronized to the ring controller IC every time it receives a
ring packet specified by I6841.
I6890/I6940/I6990: MACRO IC 1/2/3 Master Configuration
A Turbo PMAC2 Ultralite may have additional MACRO ICs if Options 1U1, 1U2, and/or 1U3 are
ordered. A UMAC Turbo system may have additional MACRO ICs if Option 1 on an Acc-5E is ordered,
or if multiple Acc-5E boards are ordered. These additional ICs should be set to be masters but not ring
controllers by setting I6890, I6940, and I6990, respectively to $10. This sets bit 4 of the variable to 1,
making the IC a master on the ring. These ICs should never be synchronizing masters, and since they do
not control the clock signals on their own board, their internal clocks do not need to be synchronized to
the ring (only MACRO IC 0 needs to do this).
I6841/I6891/I6941/I6991: MACRO IC 0/1/2/3 Node Activation Control
I6841, I6891, I6941, and I6991 on Turbo PMAC2 control which of the 16 MACRO nodes for MACRO
ICs 0, 1, 2, and 3, respectively, on the card are activated. They also control the master station number for
their respective ICs, and the node number of the packet that creates a synchronization signal. The bits of
these I-variables are arranged as follows:
Bits 0-15: Activation of MACRO Nodes 0 to 15, respectively (1 = active, 0 = inactive). These 16 bits
(usually read as four hex digits) individually control the activation of the MACRO nodes in the MACRO
IC on a Turbo PMAC2. Each node that is active on the matching MACRO Station, whether for servo,
I/O, or auxiliary communications, should have its node activation bit set to 1.
When working with a Delta Tau MACRO Station, Node 15 of each MACRO IC on a Turbo PMAC2
must be activated to permit auxiliary communications, so bit 15 of this variable should always be set to 1
if the IC is used to communicate with a MACRO Station.
Bits 16-19: Packet Sync Node Slave Number. These four bits together (usually read as one hex digit)
form the slave number (0 to 15) of the packet whose receipt by the PMAC2 will set the Sync Packet
Received status bit in the MACRO IC. Usually, this digit is set to $F (15), because Node 15 is always
activated.
Turbo PMAC2 must see this bit set regularly; otherwise it will assume ring problems and shut down servo
and I/O outputs on the ring. Bit 7 of I6840 must be set to 1 on the MACRO IC 0 of all Turbo PMAC2s
that are not ring controllers to enable the synchronization of their phase clocks to that of the ring
controller based on receipt of the sync packet.
44 Software Setup
Page 57

Geo MACRO Drive User and Reference Manual
Bits 20-23: Master Number. These four bits together form the master number (0 to 15) of the MACRO
IC on the MACRO ring. Each MACRO IC acting as a master on the ring, whether on the same card or
different cards, must have its own master number, and acts as a separate master station for the purposes of
the ring protocol. This master number forms half of the address byte with each packet sent by the
PMAC2 over the MACRO ring.
The master number can be the same number as the MACRO IC number (e.g. MACRO IC 0 has master
number 0, MACRO IC 1 has master number 1, and so on), and if there is only one Turbo PMAC2 in the
ring, this probably will be the case. However, this is not required. The MACRO IC that is the ring
controller must have master number 0 if Type 1 master-to-master auxiliary communications are to be used.
Hex ($) 000
Bit
Slavenode Enables
000
Sync nodeAddress
MasterAddress (0-15)
(0-15)
The table shown in an above section and in the Hardware Reference Manual for the 3U MACRO
Station’s SW1 switch setting provides a starting point for the Turbo PMAC2’s I6841/I6891/I6941/I6991
value. Additional bits of these I-variables may be set to 1 if I/O nodes are enabled or if more than one 3U
MACRO station is commanded from a single MACRO IC.
I70/I72/I74/I76: MACRO IC 0/1/2/3 Node Auxiliary Function Enable
I70, I72, I74, and I76 are 16-bit I-variables (bits 0 - 15) in which each bit controls the enabling or
disabling of the auxiliary flag function for the MACRO node number matching the bit number for
MACRO ICs 0, 1, 2, and 3, respectively. A bit value of 1 enables the auxiliary flag function; a bit value
of 0 disables it. If the function is enabled, PMAC automatically copies information between the MACRO
interface flag register and RAM register $00344n, $00345n, $00346n, and $00347n (where n is the IC’s
node number 0 – 15) for MACRO ICs 0, 1, 2, and 3, respectively.
Note that Turbo PMAC MACRO node numbers (as opposed to individual MACRO IC node numbers) go
from 0 to 63, with board nodes 0 – 15 on MACRO IC 0, board nodes 16 – 31 on MACRO IC 1, board
nodes 32 – 47 on MACRO IC 2, and board nodes 48 – 63 on MACRO IC 3.
Each MACRO node n that is used for servo functions should have the corresponding bit n of I70, I72,
I74, or I76 set to 1. Ixx25 for the Motor x that uses Node n should then address $00344n, $00345n,
$00346n, or $00347n, not the address of the MACRO register itself (see below). If Register 3 of a
MACRO node n is used for other purposes, such as direct I/O, the corresponding bit n of I70, I72, I74, or
I76 should be set to 0, so this copying function does not overwrite these registers.
Typically, non-servo I/O functions with a MACRO Station do not involve auxiliary flag functions, so this
flag copy function should remain disabled for any node used to transmit I/O between the Turbo PMAC2
and the MACRO Station. If any auxiliary communications is done between the Turbo PMAC2 and the
MACRO Station on Nodes 14 and/or 15, bits 14 and 15 of these variables must be set to 0.
Examples:
I70=$3 ; Enabled for MACRO IC 0, Nodes 0 and 1
I72=$30 ; Enabled for MACRO IC 1, Nodes 4 and 5
I74=$3300 ; Enabled for MACRO IC 2, Nodes 8,9,12,13
Software Setup 45
Page 58

Geo MACRO Drive User Manual
I76=$3333 ; Enabled for MACRO IC 3, Nodes 0,1,4,5,8,9,12,13
I71/I73/I75/I77: MACRO IC 0/1/2/3 Node Protocol Type Control
I71, I73, I75, and I77 are 16-bit I-variables (bits 0 - 15) in which each bit controls whether PMAC uses
the uses MACRO Type 0 protocol or the MACRO Type 1 protocol for the node whose number matches
the bit number for the purposes of the auxiliary servo flag transfer for MACRO ICs 0, 1, 2, and 3,
respectively. A bit value of 0 sets a Type 0 protocol; a bit value of 1 sets a Type 1 protocol.
All 3U MACRO Station nodes use the Type 1 protocol, so each MACRO node n used for servo purposes
with a MACRO Station must have bit n of I1002 set to 1. Generally I71 = I70, I73 = I72, I75 = I74, and
I77 = I76 on a Turbo PMAC2 communicating with a MACRO Station.
Remember that if servo nodes for more than one MACRO Station are commanded from a single MACRO
IC, the protocol must be selected for all of the active servo nodes on each station.
I78: MACRO Master/Slave Auxiliary Communications Timeout
If I78 is set greater than 0, the MACRO Type 1 Master/Slave Auxiliary Communications protocol using
Node 15 is enabled. Turbo PMAC implements this communications protocol using the MACROSLAVE
(MS), MACROSLVREAD (MSR), and MACROSLVWRITE (MSW) commands.
If this function is enabled, I78 sets the timeout value in PMAC servo cycles. In this case, if PMAC does
not get a response to a Node 15 auxiliary communications command within I78 servo cycles, it will stop
waiting and register a MACRO auxiliary communications error, setting Bit 5 of global status register
X:$000006.
I78 must be set greater than 0 if any auxiliary communications is desired with a MACRO Station. This
reserves Node 15 for the Type 1 Auxiliary Communications. A value of 32 is suggested. If I78 is set
greater than 0, bit 15 of I70, I72, I74, and I76 must be set to 0, so Node 15 is not used for flag transfers also.
I79: MACRO Master/Master Auxiliary Communications Timeout
If I79 is set greater than 0, the MACRO Type 1 Master/Master Auxiliary Communications protocol using
Node 14 is enabled. Turbo PMAC implements this communications protocol using the MACROMASTER
(MM), MACROMSTREAD (MMR), and MACROMSTWRITE (MMW) commands. Only the Turbo PMAC that is
the “ring controller” can execute these commands; other Turbo PMACs that are masters on the ring can
respond to these commands from the ring controller.
If this function is enabled, I79 sets the “timeout” value in PMAC servo cycles. In this case, if the Turbo
PMAC does not get a response to a Node 14 master/master auxiliary communications command within
I79 servo cycles, it will stop waiting and register a “MACRO auxiliary communications error,” setting Bit
5 of global status register X:$000006.
I79 must be set greater than 0 if any auxiliary communications is desired with a MACRO Station. A
value of 32 is suggested. If a value of I79 greater than 0 has been saved into PMAC’s non-volatile
memory, then at subsequent power-up/resets, bit 14 of I70 is set to 0, the node-14 broadcast bit (bit 14 of
I6840) is set to 1, and activation bit for node 14 (bit 14 of I6841) is set to 1, regardless of the value saved
for these variables. This reserves Node 14 of MACRO IC 0 for the Type 1 Master/Master Auxiliary
Communications.
I80, I81, I82: MACRO Ring Check Period and Limits
If I80 is set to a value greater than zero, Turbo PMAC will monitor for MACRO ring breaks or repeated
MACRO communications errors automatically. A non-zero value sets the error detection cycle time in
Turbo PMAC servo cycles. Turbo PMAC checks to see that “sync node” packets (see I6840 and I6841)
are received regularly, and that there have not been regular communications errors.
The limits for these checks can be set with variables I81 and I82. If less than I82 sync node packets have
been received and detected during this time interval, or if I81 or more ring communications errors have
46 Software Setup
Page 59

Geo MACRO Drive User and Reference Manual
been detected in this interval, Turbo PMAC will assume a major ring problem, and all motors will be shut
down. Turbo PMAC will set the global status bit “Ring Error” (bit 4 of X:$000006) as an indication of
this error.
Turbo PMAC looks for receipt of sync node packets and ring communications errors once per real-time
interrupt – every (I8 + 1) servo cycles). The time interval set by I80 must be large enough that I82 realtime interrupts in PMAC can execute within the time interval, or false ring errors will be detected.
Remember that long motion program calculations can cause skips in the real-time interrupt. Typically
values of I80 setting a time interval of about 20 milliseconds are used. I80 can be set according to the
formula:
I80 = Desired cycle time (msec) * Servo update frequency (kHz)
For example, with the default servo update frequency of 2.26 kHz, to get a ring check cycle interval of 20
msec, I80 would be set to 20 * 2.26 ≅ 45.
MACRO Node Addresses
The MACRO ring operates by copying registers at high speed across the ring. Therefore, each Turbo
PMAC2 master controller on the ring communicates with its slave stations by reading from and writing to
registers in its own address space. MACRO hardware handles the data transfers across the ring automatically.
Starting in Turbo firmware version 1.936, the base addresses of the up to 4 MACRO ICs must be
specified in I20 – I23, for MACRO IC 0 – 3 respectively. Before this, the base addresses were fixed at
$078400, $079400, $07A400, and $07B400, respectively. Only UMAC Turbo systems can support any
other configuration, and only rarely will another configuration be used.
The following table gives the addresses of the MACRO ring registers for Turbo PMAC2 controllers.
Note:
It is possible, although unlikely, to have other addresses in a UMAC Turbo system.
In these systems, the fourth digit does not have to be 4; it can also take the values
5, 6, and 7.
Software Setup 47
Page 60

Geo MACRO Drive User Manual
Register Addresses for MACRO IC 0 with I20=$078400 (default)
Turbo PMAC2 Addresses: MACRO IC 0
Node # Reg. 0 Reg. 1 Reg. 2 Reg. 3
0 Y:$078420 Y:$078421 Y:$078422 Y:$078423
1 Y:$078424 Y:$078425 Y:$078426 Y:$078427
2 X:$078420 X:$078421 X:$078422 X:$078423
3 X:$078424 X:$078425 X:$078426 X:$078427
4 Y:$078428 Y:$078429 Y:$07842A Y:$07842B
5 Y:$07842C Y:$07842D Y:$07842E Y:$07842F
6 X:$078428 X:$078429 X:$07842A X:$07842B
7 X:$07842C X:$07842D X:$07842E X:$07842F
8 Y:$078430 Y:$078431 Y:$078432 Y:$078433
9 Y:$078434 Y:$078435 Y:$078436 Y:$078437
10 X:$078430 X:$078431 X:$078432 X:$078433
11 X:$078434 X:$078435 X:$078436 X:$078437
12 Y:$078438 Y:$078439 Y:$07843A Y:$07843B
13 Y:$07843C Y:$07843D Y:$07843E Y:$07843F
14 X:$078438 X:$078439 X:$07843A X:$07843B
15 X:$07843C X:$07843D X:$07843E X:$07843F
Register Addresses for MACRO IC 1 with I21=$079400 (default)
Turbo PMAC2 Addresses: MACRO IC 1
Node # Reg. 0 Reg. 1 Reg. 2 Reg. 3
0 Y:$079420 Y:$079421 Y:$079422 Y:$079423
1 Y:$079424 Y:$079425 Y:$079426 Y:$079427
2 X:$079420 X:$079421 X:$079422 X:$079423
3 X:$079424 X:$079425 X:$079426 X:$079427
4 Y:$079428 Y:$079429 Y:$07942A Y:$07942B
5 Y:$07942C Y:$07942D Y:$07942E Y:$07942F
6 X:$079428 X:$079429 X:$07942A X:$07942B
7 X:$07942C X:$07942D X:$07942E X:$07942F
8 Y:$079430 Y:$079431 Y:$079432 Y:$079433
9 Y:$079434 Y:$079435 Y:$079436 Y:$079437
10 X:$079430 X:$079431 X:$079432 X:$079433
11 X:$079434 X:$079435 X:$079436 X:$079437
12 Y:$079438 Y:$079439 Y:$07943A Y:$07943B
13 Y:$07943C Y:$07943D Y:$07943E Y:$07943F
14 X:$079438 X:$079439 X:$07943A X:$07943B
15 X:$07943C X:$07943D X:$07943E X:$07943F
48 Software Setup
Page 61

Geo MACRO Drive User and Reference Manual
Register Addresses for MACRO IC 2 with I22=$07A400 (default)
Turbo PMAC2 Addresses: MACRO IC 2
Node # Reg. 0 Reg. 1 Reg. 2 Reg. 3
0 Y:$07A420 Y:$07A421 Y:$07A422 Y:$07A423
1 Y:$07A424 Y:$07A425 Y:$07A426 Y:$07A427
2 X:$07A420 X:$07A421 X:$07A422 X:$07A423
3 X:$07A424 X:$07A425 X:$07A426 X:$07A427
4 Y:$07A428 Y:$07A429 Y:$07A42A Y:$07A42B
5 Y:$07A42C Y:$07A42D Y:$07A42E Y:$07A42F
6 X:$07A428 X:$07A429 X:$07A42A X:$07A42B
7 X:$07A42C X:$07A42D X:$07A42E X:$07A42F
8 Y:$07A430 Y:$07A431 Y:$07A432 Y:$07A433
9 Y:$07A434 Y:$07A435 Y:$07A436 Y:$07A437
10 X:$07A430 X:$07A431 X:$07A432 X:$07A433
11 X:$07A434 X:$07A435 X:$07A436 X:$07A437
12 Y:$07A438 Y:$07A439 Y:$07A43A Y:$07A43B
13 Y:$07A43C Y:$07A43D Y:$07A43E Y:$07A43F
14 X:$07A438 X:$07A439 X:$07A43A X:$07A43B
15 X:$07A43C X:$07A43D X:$07A43E X:$07A43F
Register Addresses for MACRO IC 3 with I23=$07B400 (default)
Turbo PMAC2 Addresses: MACRO IC 3
Node # Reg. 0 Reg. 1 Reg. 2 Reg. 3
0 Y:$07B420 Y:$07B421 Y:$07B422 Y:$07B423
1 Y:$07B424 Y:$07B425 Y:$07B426 Y:$07B427
2 X:$07B420 X:$07B421 X:$07B422 X:$07B423
3 X:$07B424 X:$07B425 X:$07B426 X:$07B427
4 Y:$07B428 Y:$07B429 Y:$07B42A Y:$07B42B
5 Y:$07B42C Y:$07B42D Y:$07B42E Y:$07B42F
6 X:$07B428 X:$07B429 X:$07B42A X:$07B42B
7 X:$07B42C X:$07B42D X:$07B42E X:$07B42F
8 Y:$07B430 Y:$07B431 Y:$07B432 Y:$07B433
9 Y:$07B434 Y:$07B435 Y:$07B436 Y:$07B437
10 X:$07B430 X:$07B431 X:$07B432 X:$07B433
11 X:$07B434 X:$07B435 X:$07B436 X:$07B437
12 Y:$07B438 Y:$07B439 Y:$07B43A Y:$07B43B
13 Y:$07B43C Y:$07B43D Y:$07B43E Y:$07B43F
14 X:$07B438 X:$07B439 X:$07B43A X:$07B43B
15 X:$07B43C X:$07B43D X:$07B43E X:$07B43F
Software Setup 49
Page 62

Geo MACRO Drive User Manual
Note:
With the MACRO station, only nodes that map into Turbo PMAC2 Y registers (0,
1, 4, 5, 8, 9, 12, and 13) can be used for servo control. These nodes are unshaded
in the above table. The nodes that map into X registers (2, 3, 6, 7, 10, 11, and 14)
can be used for I/O control. Node 15 is reserved for Type 1 auxiliary
communications. Node 14 is often reserved for broadcast communications.
50 Software Setup
Page 63

Geo MACRO Drive User and Reference Manual
Using the Turbo PMAC Setup Program
The following captured screens are taken from the Turbo Setup program.
First the user needs to start the Turbo Setup Application. From the Menu Bar move the mouse over the
“Tools” and select with double click the “Turbo/UMAC Setup Pro (2)”
Another way to start the Turbo Setup Application the user can double click the Turbo
Setup shortcut on the desktop.
So as to use the Geo MACRO drive: Turbo Ultralite, UMAC MACRO or QMAC with MACRO option
needs to be used, and if they do then at the first pop up window, user needs to click Yes. If your system
doesn’t use any of the above Controllers then Turbo Setup cannot be used, click No
Software Setup 51
Page 64

Geo MACRO Drive User Manual
Then the first step is to select the kind of communications you have established with your PMAC device
that would be used as your Controller.
• UMAC and QMAC controllers can communicate to the PC via Serial Port, USB and Ethernet
• Turbo PMAC2 Ultralite controllers have two versions: the older ISA Bus and the newer PCI bus
o The ISA boards
can communicate to the PC via Serial Port and ISA Bus (manual
registration).
o The PCI boards
can communicate to the PC via Serial Port and PCI Bus. (Plug and
Play)
If there are no Devices on the list, then the user needs to Insert new devices.
For more information and details about the Communication of the devices, please read the appropriate
manual:
• PEWIN32 PRO
http://www.deltatau.com/fmenu/PEWIN32%20PRO.PDF
• PEWIN32 PRO Suite 2
http://www.deltatau.com/fmenu/PEWIN%2032%20PRO%202%20SOFTWARE.PDF
After you select the communications scheme, double click on the Test button and if everything is set
correct then a pop-up window will show saying that “the PMAC was successfully founded”. Press ok and
the Turbo Setup Application starts.
52 Software Setup
Page 65

Geo MACRO Drive User and Reference Manual
The first setup screen is to set some information about your PMAC controller and the ACCessories that
are used. Currently there are only two options that can be used with Geo MACRO drives.
Turbo/UMAC MACRO or QMAC
On the same setup screen the user needs to select how many MACRO ICs the used Turbo Ultralite or
ACC-5E have installed, and how many MACRO Stations will be controlled. If UMAC MACRO is used
then the user needs to know if he has in his UMAC rack an ACC-24E or/and ACC-51E. After selecting
all the correct options (appropriate to your system) click the Next button.
A pop up window will show asking you if your Geo MACRO drive is a 16-axis MACRO station. Geo
MACRO drives are neither 16-axis nor 8-axis MACRO stations. Geo MACRO drives use special
MACRO CPU. So click on the N
o button.
Software Setup 53
Page 66

Geo MACRO Drive User Manual
The next window that will appear is to set up your PWM frequency.
After you select the dominant PWM frequency, click on Next.
A new setup screen will appear to Assign your MACRO Master number to the MACRO IC’s. For
most of the systems default values are good.
54 Software Setup
Page 67

Geo MACRO Drive User and Reference Manual
The following screen of the Setup program selects which method to use to bind the MACRO stations to
the MACRO controller.
Geo MACRO drives are using the Ring Order Method. After clicking the Next button the program will
use some time for its calculations.
The setup program will come back with any MACRO stations that were found with the Ring order
Method. MS<node>,MI996 needs to be set manually
on this screen to enable the nodes.
MI996 controls which of the MACRO nodes on the Geo MACRO Station are activated. It also controls
the master station number, and the node number of the packet that creates a synchronization signal.
Bits 0 to 15 are individual control bits for the matching node number 0 to 15. If the bit is set to 1, the
node is activated; if the bit is set to 0, the node is de-activated. Node 15 should always be activated to
support the Type 1 auxiliary communications.
Bits 16-19 specify the slave number of the packet which will generate the “sync pulse” on the Geo
MACRO Station. This is always set to 15 ($F) on the Geo MACRO Station.
Software Setup 55
Page 68

Geo MACRO Drive User Manual
Bits 20-23 specify the master number (0-15) for the Geo MACRO Station. At power-up/reset, these bits
get the value set by SW2. The number must be specified whether the card is a master station or a slave
station.
Hex ($) 000
Bit
Slave node Enables
Sync nodeAddress
MasterAddress (0-15)
000
(0-15)
After setting the correct value to the MI996, click the Next button to move on.
The Setup software will come up with a new pop-up window asking if it is a Geo MACRO drive. You
should reply by clicking the Yes button.
56 Software Setup
Page 69

Geo MACRO Drive User and Reference Manual
All the screens following are the Steps to setup your motors, so check the boxes and enter the correct data
to the questions, to setup, phase and tune your motors. There are 23 steps.
Note:
Geo Drives are using Digital Current Loop, with PWM outputs
User needs with the current version of Turbo Setup (before 9/1/05) to manually
edit at the terminal window MI101 and MI102 for the Encoders
Software Setup 57
Page 70

Geo MACRO Drive User Manual
Using the PEWIN32PRO 2 MACRO Ring ASCII Feature
With the new PEWIN32PRO Suite2 a new configuration application has been added to initiate the
MACRO Ring ASCII communication between the Ring Controller and other Slave stations and/or
secondary Masters/Slaves. This new application allows the user to setup the Ring Controller, detect or
reinitialize all other stations on the Ring, set up all communication parameters, save these parameters in a
backup file, and can start or stop MACRO Ring ASCII communication to any station on the Ring.
So as to start the application you need to start your PEWIN32 PRO Suite2 and with the mouse on the
Menu Bar select the Configure Menu and click on the MACRO Ring ASCII
The new application starts, make sure you have selected which PMAC device the PEWIN32PRO
communicates to, else with the right click on the application click on the Select PMAC.
Detect MACRO Ring
Detects all MACRO IC’s that are
connected to the Ring.
• Ring Controller
• MACRO Station #n
Setup Ring Controller
It will re-initialize the MACRO
controller (Turbo PMAC), and all
clocks and nodes will be reset. It gives
the option of a re-initialize and a reset.
Reinit. MACRO Ring
The program will reinitialize the
MACRO stations on the ring.
Ring Check
A small troubleshooting tool for the
MACRO ring communications
The first thing the user needs to do when he starts the program is to make sure that everything is
58 Software Setup
Page 71

Geo MACRO Drive User and Reference Manual
connected and powered up. Then if it is the first time he tries to setup his system, its advisable to click on
the Setup Ring Controller and Click Yes on the pop-up window to do a global re-initialization of the
Turbo PMAC controller.
If the user wants just to do some change of values, troubleshooting or setup some new MACRO Stations
then he should just press the No in the above window or not even press on the Setup Ring Controller and
press on Detect MACRO Ring button. If the user wants to reinitialize every I-variable on the Turbo
PMAC will be set back to factory default.
Note
If by accident or error the user pressed the Yes button on the reinitialize of the
controller, and he wants to reverse, then he needs issue a reset “$$$” or a couple of
seconds powercycle. This will load the last saved I-variables before the re
initialization.
Do NOT issue a save after the re-initialize if you want to reverse; if Save is issued
then there is no way to reverse unless the user restores with a backup file.
If the user chooses to Detect MACRO Ring, the program will automatically show how many Stations
were detected.
Software Setup 59
Page 72

Geo MACRO Drive User Manual
The user has to first setup his Ring Controller and save any changes and then Setup each of his MACRO
stations. So select at the Stations Detected window the Ring Controller. The Application automatically
gives the user a Description
online
commands that the Application send to the controller.
of his Motion Controller Card. The window below the description, are the
• User can select which MACRO
IC he would like to setup.
• Set the I-variables for the systems
frequencies. And mainly set I6841.
Then issue a Save Changes, I70 &
I71 will automatically be set
according to the I6841 value.
If the user clicks on his Right mouse button on
the Ring Controller Window, a new menu
window will show up on screen.
*All the I-variables on this screen are in
detail explained at the Appendix of this
manual
Reset All Stations to Default, sends the
command MS$$$**255 and re-initializes all
MACRO stations on the ring.
Reset all Stations to Last Saved, sends the
online command “MS$$$255” and does a
reset to the last saved by the user values. It is
the same with Power cycle at all the units.
Save All Station Variables, saves all the
MI-variables at the MACRO Stations.
Clear All Stations Faults, mainly sends the
command “CLRF255”
Backup MACRO Ring creates a backup file
with all the MACRO I-variables from all the
MACRO stations on the ring.
Restore MACRO Ring downloads the
backup file with all the MACRO I-variables
to all the MACRO stations on the ring.
After the Ring Controller is set up the user needs to setup his MACRO Stations.
60 Software Setup
Page 73

Geo MACRO Drive User and Reference Manual
First the user needs to select which MACRO
station to start with. Set the MI-variables
(MI : MACRO Station I-variables), and
enable the nodes with MI996.
Note
MI996 and I6841 need to comply
Then the user should click on the Save
Changes button.
If the user clicks on his Right mouse button on
the Station Window, a new menu window will
show up on screen.
Start MACRO ASCII, it starts MACRO
ASCII communications. Sends the online
command “MACSTA<node>”
Stop MACRO ASCII, it stops MACRO
ASCII communications. Sends the online
command “^T” (Ctrl+T)
Station Specific Commands
Reset Station to Default, sends the
command MS$$$**<node> and reinitializes the MACRO station #n on the ring.
Reset Station to Last Saved, sends the
online command “MS$$$<node>” and does
a reset to the last saved by the user values. It
is the same with Power cycle at all the units.
Save Station Variables, it saves all the MIvariables of the station that the application
currently is communicating to. The online
command is “MSSAVE<node>”
Clear Station Faults, it clears all the faults,
unless there is a hardware fault. The online
command is “CLRF<node>”
Software Setup 61
Page 74

Geo MACRO Drive User Manual
PEWIN32PRO Suite 2 MACRO Status window
One more new addition to the new PEWIN32PRO (Suite2) is the MACRO Status window.
So as to open it, the user needs to select the View Menu from the Menu Bar and click on the MACRO
Status.
A new window will open showing the Status at the Geo MACRO Station, which is the same with
MS<node>,MI4
62 Software Setup
Page 75

Geo MACRO Drive User and Reference Manual
Ring Order Communications Method
The Ring Order Method has been developed to allow MACRO Devices to be set up with software. Since
the Geo MACRO drive has no hardware switches (SW1 and SW2) to activate nodes and assign it to a
master, the ring order method is necessary. The Turbo Setup program can do this automatically for you;
thi section tells you how to do it manually.
Factory default state for the I-Variables to the Turbo Ultralite ($$$***) and that firmware version 1.939
or above are necessary. In addition, the Geo MACRO drive should have version 1.004 and above
firmware.
1. To initiate the Ring Order Method, start with the new hardware and then enable the MACRO ASCII
Communication Mode by typing MACSTA255 in the terminal window. At this point, the Software
Interface will seek the first device that has not been setup (i.e. MI11=0). Once communicating with
the device, activate the nodes with MI996 and set up any critical MI-variables that need to be set for
the application. Upon completion of these MI-variable settings, assign a Station Number to the
device with the STN=n command where n can be set from 1 to 254. As soon a station number is
assigned to the device, the system will look for the next device that has not been set up (MI11=0). If
assigning a MACRO device as Station Number 20, type STN=20 in the terminal window and MI11
will be set to 20.
• If a Macro I/O error is received, make sure I6840, I6841 and I79 are set correctly. Also, make
sure that the unit has not been already assigned a station number.
• If the Station has been assigned a Station number already, there are two options:
a) Find out the station number n by typing the STN command and enter MACSTA<n>, where n is
the station number, to initiate MACRO ASCII communication with the Station.
b) Reset the station number of all the stations by entering MACSTA0 and then STN=0. Exit
MACRO ASCII communications by typing <Control-T> (^T). Then enter MACSTA255
to access the first Station. Now assign it a Station number by entering STN=n where n is the
Station number. Enter (^T) to exit MACRO ASCII Communications. Enter MACSTA255
again to access the next station and repeat this process until a MACRO I/O error is received
stating that there are no further unassigned stations.
2. Enter MACSTA<n> where n is the Station number. Enter I996=$F4004. (Binds to Ring Controller
0 and Node2)
3. Enter ^T. (Control-T terminates MACRO ASCII Communications.)
4. Enter MSCLRF2. (Clears any faults at Node 2.)
5. Enter I6841= $0FC004. (Enable Node 2.)
Issue the SAVE and MSSAVE{node} commands to save the parameters in memory
Software Setup 63
Page 76

Geo MACRO Drive User Manual
MACRO ASCII Communications
MACRO ASCII Communication Mode allows direct access to the MACRO Device. This mode of
communication allows the Master controller to set up all MACRO devices in the ring one at a time using
the Ring Order Method. One other benefit to this method of communications is that it allows direct
communication to the MACRO device without having to issue MS commands as in the traditional
PEWIN Terminal window.
At a minimum, the following I-variables must be set to the Turbo PMAC to enable MACRO ASCII mode
communications.
I6840=$4030 ; to enable MACRO IC0 as sync-master and node 14 for auxiliary communications
I6841=$0FCxxx ; to enable node 15 and 14. If activating nodes 0,1,4,5 set I6841=$0FC033
I79=32 ; Timeout value for Node 14 Auxiliary communications
If using more than one MACRO IC, set up I6890, I6891, I6940, I6941, I6990, and I6991 appropriately.
Once the communication variables are modified, save them to the memory of the controller with the SAVE
command and then reset the controller with either a $$$ command or power cycle the controller.
Note:
The PMAC controller can communicate to the MACRO Device in MACRO ASCII
communication mode after the unit has been restarted with the changes saved to its
memory.
How to Enable and Disable MACRO ASCII Communication Mode
To start the MACRO ASCII Mode, issue the MACSTAn (n stands for the assigned station number for the
device) command to the device in the ring.
Note:
For MACRO ASCII communication via PEWIN 32 Pro, close all other windows
of the PEWIN other than the terminal window.
HyperTerminal also can be used for MACRO ASCII communication to the Geo
MACRO drive. PEWIN32 Pro must be totally closed.
In many cases, there will be only one device and a number may not be assigned to the device. In that case,
use the MACSTA255 or MACSTA0 commands. The actual number that is assigned to the device resides in
MI11 of the MACRO Device and the default value is 0. If there are multiple MACRO devices in the ring
and communication is in MACRO ASCII mode, set up the systems with the Ring Order Method and assign
station numbers to each device. If the assigned station number is not known, check MI11.
Once in MACRO ASCII Mode, communicate to the MACRO device is done directly. To change/monitor
an MI-variable, write directly to the Variable in the terminal window.
MI996=$0F803F ;To activate Nodes 0,1,2,3,4,5 at the MACRO Device
To exit or disable MACRO ASCII Communication mode, issue the <CTRL>T command.
Note:
The MACSTA255 command will look for the first MACRO device that does not
have a station number assigned to it (MI11=0). As soon as MI11 is changed to a
value greater than zero, then it will look immediately for the next device with
MI11 set to zero.
MACRO ASCII Communication global commands
1. VID Vendor ID (Delta Tau = 1, Range=1- 65535)
2. CID Vendor Card ID, Part Number, (Range=1- 4,294,967,295) 32 bit unsigned.
Delta Tau: Turbo PMAC2 VME = 602413 (MACRO Master)
64 Software Setup
Page 77

Geo MACRO Drive User and Reference Manual
Delta Tau: Turbo PMAC2 Ultralite = 603182 (MACRO Master)
Delta Tau: UMAC Turbo = 603382 (MACRO Master)
Delta Tau: UMAC MACRO 8 = 602804 (MACRO Slave)
Delta Tau: UMAC MACRO 16 = 603719 (MACRO Slave)
Delta Tau: Geo MACRO Drive = 603542 (MACRO Slave)
Delta Tau: ACC-65M = 603740 (MACRO Slave)
Delta Tau: ACC-68M = 603747 (MACRO Slave)
3. SID Serial ID (Range = 64 bit unsigned, 0=Serial ID not available)
4. $$$** - Station to reset to default parameter with no station number and ready for Ring location
identification.
Note
Do not use $$$***.
5. SAVE – Save station number and initialization parameters.
6. $$$ – Reset Station to saved station number and initialization parameters.
7. STN=n <n=0-254> – Assigns the MACRO station number. Normally, this would be its order in
the Ring. A STN=0 resets the station number and is reserved for the Ring Controller Master.
8. Commands with STN=0 is a broadcast to all stations in the ring.
9. Commands with STN=255 is a request for communication with the first station in the ring with its
STN=0.
10. Commands with STN=1-254 is a request for communication with the station in the ring with
STN=1-254.
11. STN – The addressed MACRO Station responds with its station number (n).
Software Setup 65
Page 78

Geo MACRO Drive User Manual
66 Software Setup
Page 79

Geo MACRO Drive User and Reference Manual
SETTING UP PRIMARY FEEDBACK
Device Selection Control
Geo Drives with the appropriate options can handle Quadrature Encoder Input (Shift / No Shift), Resolver
Feedback, Sinusoidal Encoder Input, SSI Absolute Encoders, ENDAT Interface (future release) and
Hiperface Interface (future release).
The main encoder input channels for the Geo PMAC Drive supports a variety of encoder feedback types.
5V supply to power the encoder is provided from each encoder connector.
Encoder #1 Encoder #2 Value Decode Function
MS{node},MI101 MS{node},MI102 0 Quadrature Encoder, Normal Shifting (1/T) (5-bits)
MS{node},MI101 MS{node},MI102 1 Quadrature Encoder, No shifting
MS{node},MI101 MS{node},MI102 2 SSI encoder, CW
MS{node},MI101 MS{node},MI102 3 SSI encoder, CCW
MS{node},MI101 MS{node},MI102 4 Resolver CW
MS{node},MI101 MS{node},MI102 5
MS{node},MI101 MS{node},MI102 6 Sinusoidal Encoder x4096
MS{node},MI101 MS{node},MI102 12 Write the arctangent value of the Sin and Cos to the
MS{node},MI101 MS{node},MI102 13 Write the arctangent value of the Sin and Cos to the
MS{node},MI101 MS{node},MI102 14 Write the Sin and Cos values to the MACRO IO node
Resolver CCW
MACRO IO node (Resolver CCW +8)
MACRO IO node (Resolver CW +8)
(Sin enc.) For troubleshooting
Setting up Digital Quadrature Encoders
Digital quadrature encoders are the most common position sensors used with Geo Drives. Interface
circuitry for these encoders comes standard on board-level Turbo PMAC controllers, UMAC axisinterface boards, Geo drives, and QMAC control boxes.
User needs to set up his MS<node>, MI101 equal to 0 for channel #1 of his Geo MACRO drive for
normal quadrature encoder with 5-bit shifting (1/T). If the user doesn’t want to use the 1/T shifting then
he needs to set MS<node>, MI101 equal to 1.
For the second channel use MS<node>, MI102 and the same with channel #1.
So as to change the direction of the encoder feedback the user can either swap the cable leads or an easier
way would be to set MS<node>, MI910 equal to 3, clockwise, or equal to 7 for counterclockwise. MI910
can be set to more values for different options, please look at the Software Reference Appendix.
Setting up SSI Encoders
The Geo Drive will take the data from the SSI encoder and process it as a binary parallel word (12 or 24
bits). This data can then be processed in the PMAC encoder conversion table for position and velocity
feedback. With proper setup, the information can also be used to commutate brushless and AC induction
motors.
Caution:
Geo Drive was designed to work with either Gray Code or Binary Style SSI
Encoders. The Geo Drive takes the gray/binary code information and converts it
into a parallel binary word for absolute and ongoing position data
User needs to set up his MS<node>, MI101 equal to 2 (CW) or 3 (CCW) and then set 2 I-variables per
channel.
Setting Up Primary Feedback 67
Page 80

Geo MACRO Drive User Manual
The user needs to set the control word MS<node>,MI930 (channel#1) and MS<node>,MI931
(channel#2) depending on the SSI encoder that the system uses, the control word specifies the mode that
the data are coming back to the PMAC (binary or gray code) and the length of the word.
• A 12-bit numeric binary encoder would mean the control word (MI930/MI931) need to be set equal
to $2, if the encoder is outputting gray code then the control word needs to be set equal to $3.
• A 16-bit numeric binary encoder would mean the control word (MI930/MI931) need to be set equal
to $6, if the encoder is outputting gray code then the control word needs to be set equal to $7.
• A 20-bit numeric binary encoder would mean the control word (MI930/MI931) need to be set equal
to $A, if the encoder is outputting gray code then the control word needs to be set equal to $B.
• A 24-bit numeric binary encoder would mean the control word (MI930/MI931) need to be set equal
to $E, if the encoder is outputting gray code then the control word needs to be set equal to $F.
And the second I-variable the user needs to set is the clock output (frequency) to the SSI- encoder
interface (MS<node>, MI933). A value of 0 sets the Clock output @ 153.6 KHz. If higher clock
frequency required then MI933 can be set equal to 1 which sets the clock output @ 307.2 KHz, while a
value of 2 sets the clock output @ 614.4 KHz to the SSI-encoder interface. And the highest value the
clock can be set would be when MI933=3 setting the clock output @1.23MHz. MI933 is setting the clock
output for both channels #1 and #2, so user can not have different excitation frequencies for his two SSIinterface encoders.
SSI encoders (especially multi-turn) generally provide absolute position information that eliminates the
need for a homing-search move to establish a position reference.
68 Setting Up Primary Feedback
Page 81

Geo MACRO Drive User and Reference Manual
Setting up Sinusoidal Encoders
The Geo Drive with the Interpolator option accepts inputs from two sinusoidal or quasi-sinusoidal
encoders and provide encoder position data to the motion processor. This interpolator creates 4,096 steps
per sine-wave cycle.
The Geo MACRO drive so as to read the sinusoidal encoders needs the device control variable
MS<node>, MI101 (for the first channel #1) or MS<node>, MI102 (for the second channel #2) equal to 6.
Also the user can reverse the direction of the sinusoidal encoder by setting the MS<node>, MI910 equal
to 3 (ClockWise) or 7 (CounterClockWise)
If the direction decode variable is changed, the user must save the setting, MSSAVE{node} and reset the
card MS$$${node} before the fractional direction sense matches.
Note
Home Capture with high resolution feedback requires bit 11 of Ixx24 on the Turbo
PMAC to be set to one (value $800 or 2,048). Bit 12 of Ixx24 enables the Sub-
count Capture while the Geo MACRO’s: MS<node>, MI7mn9 is set to one.
Principle of PMAC Interpolation Operation
Decoder /
Counter
A
A
Comparator
1 - Bit A/D
B
B
Analog
Photo
Current
Differential
Amplifier
Sin / Cos
Signals
Encoder
n-bit
A/D
n-bit
A/D
Controller
The sine and cosine signals from the encoder are processed in two ways in the Geo Drive board (see
above diagram). First, they are sent through comparators that square up the signals into digital quadrature
and sent into the quadrature decoding and counting circuit of the Servo IC on the Geo Drive. The units of
the hardware counter, which are called hardware counts, are thus ¼ of a line. For most users, this fact is
an intermediate value, an internal detail that does not concern them. However, this is important in two
cases. First, if the sinusoidal encoder is used for PMAC-based brushless-motor commutation, the
hardware counter, not the fully interpolated position value, will be used for the commutation position
feedback. Therefore, the units of Ixx71 will be hardware counts.
Second, if the hardware position-compare circuits in the Servo IC are used, the units of the compare
register are hardware counts. (The same is true of the hardware position-capture circuits, but often these
scaling issues are handled automatically through the move-until-trigger constructs).
The second, parallel, processing of the sine and cosine signals is through analog-to-digital converters,
which produce numbers proportional to the input voltages. These numbers are used to calculate
mathematically an arctangent value that represents the location within a single line. This is calculated to
Setting Up Primary Feedback 69
Page 82

Geo MACRO Drive User Manual
1/4096 of a line, so there are 4096 unique states per line, or 1024 states per hardware count.
For historical reasons, PMAC expects the position it reads for its servo feedback software to have units of
1/32 of a count. That is, it considers the least significant bit (LSB) of whatever it reads for position
feedback to have a magnitude of 1/32 of a count for the purposes of its software scaling calculations. We
call the resulting software units software counts and any software parameter that uses counts from the
servo feedback (e.g., jog speed in counts/msec, axis scale factor in counts/engineering-unit) is using these
software counts. In most cases, such as digital quadrature feedback, these software counts are equivalent
to hardware counts.
However, with the added resolution produced by the Geo Drive interpolator option, software counts and
hardware counts are no longer the same. The LSB produced by the interpolator (through the encoder
conversion table processing) is 1/1024 of a hardware count, but PMAC software considers it 1/32 of a
software count. Therefore, with the Geo drive, a software count is 1/32 the size of a hardware count.
The following equations express the relationships between the different units when using the Geo Drive:
1 line = 4 hardware counts = 128 software counts = 4096 states (LSBs)
¼-line = 1 hardware count = 32 software counts = 1024 states (LSBs)
1/128-line = 1/32-hardware count = 1 software count = 32 states (LSBs)
1/4096-line = 1/1024-hardware count = 1/32-software count = 1 state (LSB)
Note that these are all just naming conventions. Even the position data that is fractional in terms of
software counts is real. The servo loop can see it and react to it, and the trajectory generator can
command to it.
128 whole software counts and 3 bits
of fractional counts (1024) states per line)
One HW count
Four hardware counts per line
The Interpolator can accept a voltage-source (1Vp-p) signal from the encoder. The maximum sine-cycle
frequency input is approximately 8 MHz (1,400,000 SIN cycles/sec), which gives a maximum speed of
about 5.734 billion steps per second.
When used with a 1000 line sinusoidal rotary encoder, there will be 4,096,000 discrete states per
revolution (128,000 software counts). The maximum calculated electrical speed of this encoder would be
1,400 RPS or 84,000 RPM, which exceeds the maximum physical speed of most encoders.
Example 1:
A 4-pole rotary brushless motor has a sinusoidal encoder with 2000 lines. It directly drives a screw with a
5-mm pitch. The encoder is used for both commutation and servo feedback. The user first needs to set
MS<node>, MI101=6 and/or MS<node>, MI102=6 for sinusoidal encoder. If needed the direction decode
can also be reversed with MS<node>, MI910 equal to 3 (CW) or 7 (CCW)
70 Setting Up Primary Feedback
Page 83

Geo MACRO Drive User and Reference Manual
The commutation uses the hardware counter. There are 8000 hardware counts per revolution, and two
commutation cycles per revolution of the 4-pole motor. Therefore, Ixx70 will be set to 2, and Ixx71 will
be set to 8000. Ixx83 will contain the address of the hardware counter’s phase capture register.
For the servo, the interpolated results of the conversion table are used. There are 128 software counts per
line, or 256,000 software counts per revolution. With each revolution corresponding to 5 mm on the
screw, there are 51,200 software counts per millimeter. The measurement resolution, at 4096 states per
line, is 1/8,192,000 of a revolution, or 1/1,638,400 of a millimeter (~0.6 nanometers/state).
Example 2:
A linear brushless motor has a commutation cycle of 60.96 mm (2.4 inches). It has a linear scale with a
20-micron line pitch. The scale is used for both commutation and servo feedback. The user first needs to
set MS<node>,MI101=6 and/or MS<node>,MI102=6 for sinusoidal encoder. If needed the direction
decode can also be reversed with MS<node>,MI910 equal to 3 (CW) or 7 (CCW)
The commutation uses the hardware counter. There are 200 hardware counts per millimeter (5 microns
per count), so 12,192 hardware counts per commutation cycle. Ixx70 should be set to 1, and Ixx71 should
be set to 12,192.
The servo uses the interpolated results of the conversion table. With 128 software counts per line, and 50
lines per millimeter, there are 6400 software counts per millimeter (or 162,560 software counts per inch).
The measurement resolution, at 4096 states per line, is 204,800 states per mm (~5 nanometers/state).
Setting Up Primary Feedback 71
Page 84

Geo MACRO Drive User Manual
Setting up Endat
The Geo Drive can be ordered to accept Heidenhain Corporations proprietary Endat 2.1 absolute
feedback.
Requires firmware version 1.009 or higher on the Geo MACRO.
New variables:
1. MI111 and MI112 are the two new I variables that will be used on the Geo MACRO to setup the
Endat power on position and phasing. These variables read the absolute position into MI920 for
the respective node. The MI920 returns a 48 bit value. The MI111 and MI112 are set as follows:
Bits 0-4: First Shift Left to move the MSB of the data being read to the 47
Bits 8-12: Second Shift Right to scale the data properly with the ongoing position.
Bit 13: 0 for 1 error bit, 1 for 2 error bits.
Bit 14: Complement the data if the direction sense is reversed. This is set to 1 or 0 based on
the direction sense of the ongoing position encoder
Bit 15: Set to 0 for unsigned data. Set to 1 for Signed data.
th
bit.
Examples:
For a 25-bit Endat with 512 lines on the sinusoidal encoder:
Unsigned setup: MI111=$5417 (23 bits Shift Left, 20 bits Shift Right, complemented,
unsigned, 1 error bit).
Signed setup: MI111=$D417 (23 bits Shift Left, 20 bits Shift Right, complemented, signed, 1
error bit).
2. Ix10 and Ix95 will be setup for MACRO absolute position parallel read. E.g. for motor 1 on node
0: I110=$100 and I195=$740000.
3. Ix81 and Ix91 will be setup for MACRO absolute parallel power on phasing. E.g. for motor 1 on
node 0: I181=$100 and I195=$740000.
4. To set the value for Ix75:
Set Ix69=0. Next do a #xO0, then set Ix79=2000 (Safe current value). Do a #x$, set Ix75=Mx71. Now set Mx71=0 and Ix79=original offset value. Set #xk and Ix69 back to the original
value.
Setting up Resolvers
The Geo MACRO Drive has up to two channels of resolver inputs. The inputs may be used as feedback or
master reference signals for the PMAC servo loops. The basic configuration of the drive contains one 12-bit
resolution (x4096) tracking resolver-to-digital (R-to-D) converter, with an optional second resolver when a
dual axis driver is ordered. The Geo drive creates the AC excitation signal (ResOut) for up to two resolvers,
accepts the modulated sine and cosine signals back from these resolvers, demodulates the signals and
derives the position of the resolver from the resulting information, in an absolute sense if necessary.
The Geo MACRO drive so as to read the Resolver feedback needs the device control variable MS<node>,
MI101 (for the first channel #1) or MS<node>, MI102 (for the second channel #2) equal to 4
(ClockWise) or equal to 5 (CounterClockWise).
Then the user has to set three (3) MI-variables so as the Resolvers to function correctly.
The ResOut signal, Resolver excitation frequency, from the Geo MACRO Drive is derived from the
72 Setting Up Primary Feedback
Page 85

Geo MACRO Drive User and Reference Manual
Phase Clock frequency of the PMAC set by I7m00 and I7m01. The user has the ability to select the
excitation frequency to be equal with the Phase Clock frequency (default) by setting MS<node>,MI932
equal to 0. Or use lower frequencies by increasing the value of MI932.
• Excitation frequency could be set equal to a half (1/2) the Phase Clock Frequency if MI932=1
• Excitation frequency could be set equal to a quarter (1/4) the Phase Clock Frequency if MI932=2
• Excitation frequency could be set equal to a sixth (1/6) the Phase Clock Frequency if MI932=3,
this would be and the lowest available excitation frequency.
Also the user needs to set the Excitation output gain for the systems resolvers, by setting
MS<node>,MI940. Default MI940 is set to 0, which means a 2.5V gain peak-to-peak. If a gain of 5V
peak-to-peak is needed then the user needs to set MI940=1. With MI940=2 the output gain is 7.5V, and
the maximum gain would be 10V peak-to-peak when MI940=3.
Finally the resolver excitation phase time offset, MS<node>, MI941, needs to be set. The optimum
setting f MI941 depends on the L/R time constant of the resolver circuit. So MI941 should be set
interactively to maximize the magnitudes of the feedback ADC values. Turbo PMAC setup handles these
calculations, the section below shows how someone can set it up manually.
Setting up the Phase Shift (MI941) Manually
Set up the MS<node>, MI101 or MS<node>MI102 equal to 12 ($C) or 13 ($D) depending if it was $4 or
$5 respectively (basically add +8 to the value of MI101 or MI102). This decode value puts the ADC
values of the Sine and Cosine into the ADC registers of the corresponding IO node register.
For example, if using a resolver for motor #1 on Node 0:
MS0,MI101
5
MS0,MI101=13
This would enable the ADCs of the first resolver to come back on X:$78421 and X:$78422. (Check
Appendix D, ADC Registers Table.)
Now, setup two M-variables to point to these registers:
M905->X:$78421,8,16,s and M906->X:$78422,8,16,s were used in the example.
The values of these registers will toggle between a + and - value, sign does not matter; only the absolute
value is important. As the motor shaft is rotated, observe these values, if either of them is saturated to +/32767, the resolver gain is too high (MI940). Decrease its value.
Next, position the motor shaft so that one of the ADC values is close to the maximum value that can be
monitored. The other register will be close to 0.
MI941 default value is 0, start increasing its (MI941) value by increments of 25. The value of the large
ADC should slowly start increasing. If it decreases, start with MI941=255 and slowly start decreasing it
in increments of 25. The ADC value should increase up to a maximum point and then start to decrease
again. This point to the MI941 value that should be set to get the maximum ADC value possible.
Finally, if the maximum value of the large ADC is less than 16000, increase the gain of the resolver
(MI940).
Setting up the Resolver for Power-On Absolute Position
It is possible to get absolute position directly to the Geo drive. Most commonly, this is just the absolute
position within one motor revolution or even one commutation cycle to establish the commutation phase
reference position without any motion. This section summarizes the variable settings for this technique;
refer to the Appendix B or to the Software Reference Manual for details.
Setting Up Primary Feedback 73
Page 86

Geo MACRO Drive User Manual
WARNING:
An unreliable phasing reference method can lead to a runaway condition. Test the
phasing reference method carefully to make sure it works properly under all
conceivable conditions. Make sure the Ixx11 fatal following error limit is active
and as tight as possible so the motor will be killed quickly in the event of a serious
phasing search error.
Absolute Phase Power-On Position Address and Format: Ixx81, Ixx91, Ixx75
To read an R/D converter for absolute phase position, Ixx81 is set equal to the MACRO node’s position
feedback register, and Ixx91 is set to $180000.
Motor phase offset variable Ixx75 contains the difference between the absolute resolver position and the
resulting phase angle position (if any).
Absolute Servo Power-On Position Address and Format: Ixx10, Ixx95
Turbo PMAC will obtain the absolute servo power-on position through the MACRO ring. To read an
R/D converter for absolute power on position, Ixx10 specifies the address of the register containing the
position data from the Geo MACRO drive, which points to the ECT (See Appendix under Ixx95). And
Ixx95 is set to $5B0000, Parallel X-register, unsigned value, 19 bits, Motor xx will do parallel data read
of the Turbo PMAC memory at the address specified by Ixx10.
Motor offset variable Ixx26 contains the difference between the absolute resolver position and the
resulting motor position (if any).
Scaling the Feedback Units
The Geo Drive R/D converter is a 12-bit converter. It reports 4096 separate states per electrical cycle of
the resolver (per mechanical revolution for a typical 2-pole resolver, per half revolution for a 4-pole
resolver.
74 Setting Up Primary Feedback
Page 87

Geo MACRO Drive User and Reference Manual
SETTING UP SECONDARY ENCODERS
Geo Drives have also secondary encoder inputs that can be used for dual feedback. The input signals need
to be digital quadrature encoders. Single Axis drives have one secondary encoder and dual axis drives
have two secondary encoders.
Secondary encoders so as to be enabled require a motor node. So the user needs to “burn” a motor
channel/node so he can read the encoder feedback. The motors need to be activated Ixx00 equal to one,
and activate the MACRO motor nodes I6841/I6891/I6941/I6991, and set MS<node>, I996 enabled.
Note:
The Secondary Encoders of a Geo MACRO drive can not be assigned to nodes before the
primary nodes of that drive. For example if you have for your primary encoders node 4
(channel#1) and node 5 (channel#2), then the secondary encoders can be in any free motor
node after that 8/9/12/13 ( MACRO IC0) , 16/17/20/21/24/25/28/29 (MACRO IC1),
32/33/36/3/40/41/44/45 (MACRO IC2), 48/49/52/53/56/57/60/61 (MACRO IC3), and
cannot be assigned as node 1 or 2 or any occupied by another motor node.
For the Secondary encoders at the Geo MACRO drives the MI variables are a little different than the
primary encoder channels. By setting MI910 equal to 0 (default) the encoder decode is x4 (cts.) or it can
be set equal to 1 for an encoder decode x1 (cts.)
The user can only reverse the direction by setting the MS<node>,MI911 equal to 0 for Clockwise(CW) or
equal to 1 for CounterClockWise (CCW). Make sure when you change the direction decode that the
output sense direction also follows, else runaway can occur.
For capturing the user needs first to select which input to use, Home Flag or Index channel. MS<node>,
MI915 . If the user wants to capture on the Index channel (only) then MI915 has to be set equal to $C0. If
the user wants to capture on the Home Flag then MI915 needs to be set equal to $6000. For capturing to
both inputs, Home Flag and Index Input, MI915 needs to be set equal to $40C0. Depending on the input
that the user chose, MI912 or MI913 need to be set respectively. For Capturing at the Index input (C
channel) MS<node>,MI912 can be set equal to 0 for capturing at the rising edge, or equal to 1 for
capturing at the falling edge (edge trigger not level trigger). Default the value is equal to 0. The trigger
would be armed as soon as the position capture register is read.
If the user wants to capture at the Home Flag (HMFL) then MS<node>, MI913 has to be set equal to 0 for
capturing on the rising edge, or equal to 1 for capturing on the falling edge (edge trigger not level trigger).
Using the secondary encoder requires enabling an additional motor (not I/O) node, in both the Geo
MACRO drive and the Turbo PMAC to transfer the data back to the Turbo PMAC.
If the user wants to use only one primary encoder and one secondary encoder without “burning” extra
motor nodes, it is possible to disable the second primary encoder of the drive (check “MS<node>,MI100”
variable), and enable the appropriate motor nodes. For example, if the user wants to setup a single axis
Geo MACRO (Station=1) with one quadrature primary encoder and one secondary encoder, he would
have to enable two motor nodes. (no I/O nodes are being set for this example)
MS0,MI996=$FC003 ; Enable motor nodes 0 and 1
MS0,MI100=1 ; Disable second primary channel
MS0,MI101=0 or 1 ; Set up the primary encoder channel for quadrature feedback
MSSAVE0 ; All changes to take effect
MS$$$0 or power cycle
I100=1 ; Activates axis #1 position
I200=1 ; Activates axis #2 position
Setting Up Secondary Encoders 75
Page 88

Geo MACRO Drive User Manual
76 Setting Up Secondary Encoders
Page 89

Geo MACRO Drive User and Reference Manual
SETTING UP THE TURBO PMAC CONVERSION TABLE
The position feedback from the Geo MACRO drive must be processed in the Turbo PMAC’s encoder
conversion table (ECT) before it can be used for servo purposes, such as position or velocity loop
feedback. The position feedback, whether primary or secondary, appears in the 24-bit Register 0 for the
servo node used. This is mapped as a Y-register in the Turbo PMAC, and the servo tasks can only access
X-registers for their source data.
So the primary purpose of the Turbo PMAC ECT entries for processing feedback from the Geo MACRO
drive is to move the data from the Y-registers in the MACRO ICs to X-registers in RAM, where they can
quickly be accessed by servo tasks, without requiring other processing.
This task is accomplished by conversion method “$2”: parallel read of a Y-register, no filtering.
Typically, the data from the Geo MACRO drive has already been shifted the standard 5 bits, so the
standard shifting in the ECT can be disabled by setting bit 19 of the first setup word (first I-variable of the
entry) to 1. This makes the method word $280000 + {Node Register 0 address}.
The second and last line (I-variable) of the entry should be set to $018000. The “018” (hexadecimal)
specifies that all 24 bits of the source register be used; the “000” specifies that the bits used start at bit 0.
The following table shows an ECT in which the first eight entries are conversions of the first eight
MACRO servo nodes. Note have the combination of the bit 19 “shift disable bit and the “7” in the second
digit of the register address (e.g. $078420 for Node 0 Register 0) make the second hex digit of setup word
of each entry equal to “F”.
I-Var. Setting Meaning Turbo PMAC Address
I8000 $2F8420 MACRO Node 0 Reg. 0 Read $003501
I8001 $018000 24 bits, bit 0 LSB $003502
I8002 $2F8424 MACRO Node 1 Reg. 0 Read $003503
I8003 $018000 24 bits, bit 0 LSB $003504
I8004 $2F8428 MACRO Node 4 Reg. 0 Read $003505
I8005 $018000 24 bits, bit 0 LSB $003506
I8006 $2F842C MACRO Node 5 Reg. 0 Read $003507
I8007 $018000 24 bits, bit 0 LSB $003508
I8008 $2F8430 MACRO Node 8 Reg. 0 Read $003509
I8009 $018000 24 bits, bit 0 LSB $00350A
I8010 $2F8434 MACRO Node 9 Reg. 0 Read $00350B
I8011 $018000 24 bits, bit 0 LSB $00350C
I8012 $2F8438 MACRO Node 12 Reg. 0 Read $00350D
I8013 $018000 24 bits, bit 0 LSB $00350E
I8014 $2F843C MACRO Node 13 Reg. 0 Read $00350F
I8015 $018000 24 bits, bit 0 LSB $003510
The I-variables that use the results of the conversions (e.g. Ixx03 and Ixx04 for position and velocity-loop
feedback) will be set to the address of the last line of the entry. For example, if Motor 1 used the
processed data for Node 0 Register 0 from the above table for position-loop feedback, I103 would be set
to $3502. It is also possible to set these variables by specifying that you want to use the address of the last
I-variable in the entry. The command I103=@I8001 performs the same action as I103=$3502.
Setting Up Turbo PMAC Conversion Table 77
Page 90

Geo MACRO Drive User Manual
78 Setting Up Turbo PMAC Conversion Table
Page 91

Geo MACRO Drive User and Reference Manual
SETTING UP TURBO MOTOR OPERATION
Turbo PMAC Basic Setup for Brushless Servo or Induction Motor
1) Basic I-variable settings:
• Ixx00 = 1
• Ixx01=3 ;setting for commutation across MACRO
• Ixx02 = node address – base +0 – output address
I102 $078420 MACRO IC 0 Node 0 Reg. 0 I1702 $07A420 MACRO IC 2 Node 0 Reg. 0
I202 $078424 MACRO IC 0 Node 1 Reg. 0 I1802 $07A424 MACRO IC 2 Node 1 Reg. 0
I302 $078428 MACRO IC 0 Node 4 Reg. 0 I1902 $07A428 MACRO IC 2 Node 4 Reg. 0
I402 $07842C MACRO IC 0 Node 5 Reg. 0 I2002 $07A42C MACRO IC 2 Node 5 Reg. 0
I502 $078430 MACRO IC 0 Node 8 Reg. 0 I2102 $07A430 MACRO IC 2 Node 8 Reg. 0
I602 $078434 MACRO IC 0 Node 9 Reg. 0 I2202 $07A434 MACRO IC 2 Node 9 Reg. 0
I702 $078438 MACRO IC 0 Node 12 Reg. 0 I2302 $07A438 MACRO IC 2 Node 12 Reg. 0
I802 $07843C MACRO IC 0 Node 13 Reg. 0 I2402 $07A43C MACRO IC 2 Node 13 Reg. 0
I902 $079420 MACRO IC 1 Node 0 Reg. 0 I2502 $07B420 MACRO IC 3 Node 0 Reg. 0
I1002 $079424 MACRO IC 1 Node 1 Reg. 0 I2602 $07B424 MACRO IC 3 Node 1 Reg. 0
I1102 $079428 MACRO IC 1 Node 4 Reg. 0 I2702 $07B428 MACRO IC 3 Node 4 Reg. 0
I1202 $07942C MACRO IC 1 Node 5 Reg. 0 I2802 $07B42C MACRO IC 3 Node 5 Reg. 0
I1302 $079430 MACRO IC 1 Node 8 Reg. 0 I2902 $07B430 MACRO IC 3 Node 8 Reg. 0
I1402 $079434 MACRO IC 1 Node 9 Reg. 0 I3002 $07B434 MACRO IC 3 Node 9 Reg. 0
I1502 $079438 MACRO IC 1 Node 12 Reg. 0 I3102 $07B438 MACRO IC 3 Node 12 Reg. 0
I1602 $07943C MACRO IC 1 Node 13 Reg. 0 I3202 $07B43C MACRO IC 3 Node 13 Reg. 0
• Ixx03 = ECT address for position encoder - $35xy
• Ixx04 = ECT address for velocity encoder - $35xy
• Ixx24 = flag mode (limit switches)
• Ixx25 = node space for flags - $34xy
I125 $003440 MACRO Flag Register Set 0 I1725 $003460 MACRO Flag Register Set 32
I225 $003441 MACRO Flag Register Set 1 I1825 $003461 MACRO Flag Register Set 33
I325 $003444 MACRO Flag Register Set 4 I1925 $003464 MACRO Flag Register Set 36
I425 $003445 MACRO Flag Register Set 5 I2025 $003465 MACRO Flag Register Set 37
I525 $003448 MACRO Flag Register Set 8 I2125 $003468 MACRO Flag Register Set 40
I625 $003449 MACRO Flag Register Set 9 I2225 $003469 MACRO Flag Register Set 41
I725 $00344C MACRO Flag Register Set 12 I2325 $00346C MACRO Flag Register Set 44
I825 $00344D MACRO Flag Register Set 13 I2425 $00346D MACRO Flag Register Set 45
I925 $003450 MACRO Flag Register Set 16 I2525 $003470 MACRO Flag Register Set 48
I1025 $003451 MACRO Flag Register Set 17 I2625 $003471 MACRO Flag Register Set 49
I1125 $003454 MACRO Flag Register Set 20 I2725 $003474 MACRO Flag Register Set 52
I1225 $003455 MACRO Flag Register Set 21 I2825 $003475 MACRO Flag Register Set 53
I1325 $003458 MACRO Flag Register Set 24 I2925 $003478 MACRO Flag Register Set 56
I1425 $003459 MACRO Flag Register Set 25 I3025 $003479 MACRO Flag Register Set 57
I1525 $00345C MACRO Flag Register Set 28 I3125 $00347C MACRO Flag Register Set 60
I1625 $00345D MACRO Flag Register Set 29 I3225 $00347D MACRO Flag Register Set 61
Setting Up Turbo Motor Operation 79
Page 92

Geo MACRO Drive User Manual
• Ixx66 = 16384 ; Geo MACRO PWM scale factor
• Ixx82 = node address = base node address + 2 (ADC B) – commutation current feedback
I182 $078422 MACRO IC 0 Node 0 Reg. 2 I1782 $07A422 MACRO IC 2 Node 0 Reg. 2
I282 $078426 MACRO IC 0 Node 1 Reg. 2 I1882 $07A426 MACRO IC 2 Node 1 Reg. 2
I382 $07842A MACRO IC 0 Node 4 Reg. 2 I1982 $07A42A MACRO IC 2 Node 4 Reg. 2
I482 $07842E MACRO IC 0 Node 5 Reg. 2 I2082 $07A42E MACRO IC 2 Node 5 Reg. 2
I582 $078432 MACRO IC 0 Node 8 Reg. 2 I2182 $07A432 MACRO IC 2 Node 8 Reg. 2
I682 $078436 MACRO IC 0 Node 9 Reg. 2 I2282 $07A436 MACRO IC 2 Node 9 Reg. 2
I782 $07843A MACRO IC 0 Node 12 Reg. 2 I2382 $07A43A MACRO IC 2 Node 12 Reg. 2
I882 $07843E MACRO IC 0 Node 13 Reg. 2 I2482 $07A43E MACRO IC 2 Node 13 Reg. 2
I982 $079422 MACRO IC 1 Node 0 Reg. 2 I2582 $07B422 MACRO IC 3 Node 0 Reg. 2
I1082 $079426 MACRO IC 1 Node 1 Reg. 2 I2682 $07B426 MACRO IC 3 Node 1 Reg. 2
I1182 $07942A MACRO IC 1 Node 4 Reg. 2 I2782 $07B42A MACRO IC 3 Node 4 Reg. 2
I1282 $07942E MACRO IC 1 Node 5 Reg. 2 I2882 $07B42E MACRO IC 3 Node 5 Reg. 2
I1382 $079432 MACRO IC 1 Node 8 Reg. 2 I2982 $07B432 MACRO IC 3 Node 8 Reg. 2
I1482 $079436 MACRO IC 1 Node 9 Reg. 2 I3082 $07B436 MACRO IC 3 Node 9 Reg. 2
I1582 $07943A MACRO IC 1 Node 12 Reg. 2 I3182 $07B43A MACRO IC 3 Node 12 Reg. 2
I1682 $07943E MACRO IC 1 Node 13 Reg. 2 I3282 $07B43E MACRO IC 3 Node 13 Reg. 2
• Ixx83 = node address = base node address +0 – commutation position feedback address
I183 $078420 MACRO IC 0 Node 0 Reg. 0 I1783 $07A420 MACRO IC 2 Node 0 Reg. 0
I283 $078424 MACRO IC 0 Node 1 Reg. 0 I1883 $07A424 MACRO IC 2 Node 1 Reg. 0
I383 $078428 MACRO IC 0 Node 4 Reg. 0 I1983 $07A428 MACRO IC 2 Node 4 Reg. 0
I483 $07842C MACRO IC 0 Node 5 Reg. 0 I2083 $07A42C MACRO IC 2 Node 5 Reg. 0
I583 $078430 MACRO IC 0 Node 8 Reg. 0 I2183 $07A430 MACRO IC 2 Node 8 Reg. 0
I683 $078434 MACRO IC 0 Node 9 Reg. 0 I2283 $07A434 MACRO IC 2 Node 9 Reg. 0
I783 $078438 MACRO IC 0 Node 12 Reg. 0 I2383 $07A438 MACRO IC 2 Node 12 Reg. 0
I883 $07843C MACRO IC 0 Node 13 Reg. 0 I2483 $07A43C MACRO IC 2 Node 13 Reg. 0
I983 $079420 MACRO IC 1 Node 0 Reg. 0 I2583 $07B420 MACRO IC 3 Node 0 Reg. 0
I1083 $079424 MACRO IC 1 Node 1 Reg. 0 I2683 $07B424 MACRO IC 3 Node 1 Reg. 0
I1183 $079428 MACRO IC 1 Node 4 Reg. 0 I2783 $07B428 MACRO IC 3 Node 4 Reg. 0
I1283 $07942C MACRO IC 1 Node 5 Reg. 0 I2883 $07B42C MACRO IC 3 Node 5 Reg. 0
I1383 $079430 MACRO IC 1 Node 8 Reg. 0 I2983 $07B430 MACRO IC 3 Node 8 Reg. 0
I1483 $079434 MACRO IC 1 Node 9 Reg. 0 I3083 $07B434 MACRO IC 3 Node 9 Reg. 0
I1583 $079438 MACRO IC 1 Node 12 Reg. 0 I3183 $07B438 MACRO IC 3 Node 12 Reg. 0
I1683 $07943C MACRO IC 1 Node 13 Reg. 0 I3283 $07B43C MACRO IC 3 Node 13 Reg. 0
• Ixx84 = $fff000 - mask word
Turbo PMAC Basic Setup for DC Brush Motors
Special settings are needed to use the direct-PWM algorithms for DC brush motors. The basic idea is to
trick the commutation algorithm into thinking that the commutation angle is always stuck at 0 degrees, so
current into the A phase is always quadrature (torque-producing) current. These instructions assume:
• The brush motor’s rotor field comes from permanent magnets or a wound field excited by a separate
means; the field is not controlled by one of the phases of this channel.
80 Setting Up Turbo Motor Operation
Page 93

Geo MACRO Drive User and Reference Manual
• The two leads of the brush motor’s armature are connected to amplifier phases (half-bridges) that are
driven by the A and C-phase PWM commands from Turbo PMAC. The amplifier may have an
unused B-phase half-bridge, but this does not need to be present.
The following settings are the same as for permanent-magnet brushless servo motors with an absolute
phase reference:
• Ixx01=3 (commutation over the MACRO ring)
• Ixx02 should contain the address of the PWM A register for the output channel used or the MACRO
Node register 0 (these are the defaults), just as for brushless motors.
• Ixx29 and Ixx79 phase offset parameters should be set to minimize measurement offsets from the A
and B-phase current feedback circuits, respectively.
• Ixx61, Ixx62, and Ixx76 current loop gains are set just as for brushless motors.
• Ixx73 = 0, Ixx74 = 0: These default settings ensure that Turbo PMAC will not try to do a phasing
search move for the motor. A failed search could keep Turbo PMAC from enabling this motor.
• Ixx77 = 0 to command zero direct (field) current.
• Ixx78 = 0 for zero slip in the commutation calculations.
• Ixx82 should contain the address of ADC B register for the feedback channel used (just as for
brushless motors) when the ADC A register is used for the rotor (armature) current feedback. The B
register itself should always contain a zero or near-zero value.
• Ixx81 > 0: Any non-zero setting here makes Turbo PMAC do a phasing read instead of a search
move for the motor. This is a dummy read, because whatever is read is forced to zero degrees by the
settings of Ixx70 and Ixx71, but Turbo PMAC demands that some sort of phase reference be done.
(Ixx81=1 is fine.)
• Ixx84 is set just as for brushless motors, specifying which bits the current ADC feedback uses.
Usually, this is $FFF000 to specify the high 12 bits.
Special settings for brush motor direct PWM control:
• Ixx70 = 0: This causes all values for the commutation cycle to be multiplied by 0 to defeat the
rotation of the commutation vector.
o
• Ixx72 = 512 (90
the same. If the amplifier would use 683 (120
1365 (240
e) if voltage and current numerical polarities are opposite, 1536 (270oe) if they are
o
e) for a 3-phase motor, use 1536 here.
o
e) for a 3-phase motor, use 512 here; if it would use
• Ixx96 = 1: This causes Turbo PMAC to periodically clear the integrator for the (non-existent) direct
current loop, which could slowly charge up due to noise or numerical errors and eventually interfere
with the real quadrature current loop.
Settings that do not matter:
• Ixx71 (commutation cycle size) does not matter because Ixx70 setting of 0 defeats the commutation
cycle.
• Ixx75 (Offset in the power-on phase reference) does not matter because commutation cycle has been
defeated. Leaving this at the default of 0 is fine.
• Ixx83 (ongoing commutation position feedback address) doesn’t matter, since the commutation has
been defeated. Leaving this at the default value is fine.
Ixx91 (power-on phase position format) does not matter, because whatever is read for the poweron phase position is reduced to zero.
2) Set up all M-Var definitions. If using PEWIN32Pro and using a node space setup which equates
each motor number with the sequential node number (i.e. motor 1 is node 0, motor 2 is node 1, motor
Setting Up Turbo Motor Operation 81
Page 94

Geo MACRO Drive User Manual
3 is node 4, motor 4 is node 5, motor 6 is node 8, etc) then you can simply use the Configure M
Variables utility in PEWIN32Pro. Tell it to “Download Suggested M Variable Definitions” and click
on the “Use Suggested M Variable Definitions” checkbox. This is highly recommended. You may
wish to replace M-Var definitions for flag variables with those of the MACRO Flag address
definitions.
3) Set MACRO Ivariables:
• I70-I77 ;all motor node bits go high if used – i.e. $33 for nodes 0,1,4,5
• I80 = 5 ;ring check period
• I81=2 ;max ring errors in ring check period
• I82=2 ;minimum sync packets in ring check period
• I6840=$30 ;set MACRO IC 0 as synchronizing ring master
• I6890,I6940,I6990 = $90 ;set MACRO ICs 1,2,3 as ring masters if present
• I6841=$f8000 + $xyza where xyza are the high bits for each node used
• I6891=$1f8000 +$xyza if used
• I6941=$2f8000 +$xyza if used
• I6991=$3f8000 + $xyza if used
4) Issue a “SAVE” command and a “$$$” command from the terminal window in PEWIN32Pro
5) Set up Geo MACRO address, MI996, either by MACSTA command (recommended) or by USB.
This will be equal to bF0000 + xyza where xyza are high bits for each node used and b is the
MACRO IC Master number. At the same time set the station number (MI11) on each drive.
6) Issue a “mssav15mssav31mssav47mssav63” command from the terminal window in PEWIN32Pro,
or a “SAVE” command from Hyperterminal if using USB communications. Now issue a
“ms$$$15ms$$$31ms$$$47ms$$$63” to reset
You should be able to now query the drives from PEWINPro. To confirm that simply issue a
“MSn,MI996” command from the terminal window where n is an active node on the drive you want to
talk to. You should get the value of that MI variable back in the terminal window.
This assumes that you are using the default 2.2kHz servo and 4.5 kHz PWM rate. Note that the max
PWM rate for the Geo MACRO drive is 9 KHz. If you are using another PWM rate you will need to set
the I68xx variables which deal with that.
Issue a “SAVE” and then a Reset “$$$”. It is recommended to then create a backup file with the
PEWIN32PRO.
Now to set up PWM.
1) Check encoder direction – move the motor by hand in the positive direction and make sure that it is
counting up. If it is counting in a negative direction then reverse the value of MI910 – change a 7 to a
3 or a 3 to a 7. Now check again and it should have changed direction.
2) Write a PLC like so:
Open plc10 clear
Mx02=P2
Mx04 = P4
Mx07=P7
Close
Set I5=3 and issue a “SAVE” command from the terminal window. Be sure that there are no other PLCs
in memory as we want this to execute at a very high rate.
3) Check ADC connection. Set Ixx00 = 0 for the motor in question. Add Mx05, Mx06, Mx54 to the
watch window. Set Mx54=1 for that motor. You should now see the enable LED come on for that
82 Setting Up Turbo Motor Operation
Page 95

Geo MACRO Drive User and Reference Manual
motor on the drive, and Mx54 in the watch window should be 1. If not, be sure that Ix00=0 for that
motor and that there are no amp faults on the drive. If there is an amp fault then issue a “MS$$$n” for
that drive where n is an active node on that drive. Enable PLC10. Set P2=500 P4=-500 P7=0 from
the terminal window. You should now see some rather noisy values in Mx05 and Mx06 of the watch
window. If the sign of Mx05 is positive and the sign of Mx06 is negative then the phases match the
ADC inputs and Ixx72 will be greater than 1024. For a three phase motor it will be 1365. If not, then
Ixx72 will be less than 1024. For a three phase motor it will be 683. Set p2=0p4=0p7=0 and
Mx54=0.
4) Now it is time to check the PWM phasing.
• Set Ixx70= ½ the number of poles of your motor for a rotary motor, or 1 for a linear motor.
• Set Ixx71 = 32*counts in one revolution of a rotary motor or 32 * counts in one commutation
cycle for a linear motor.
• Set Ixx80 for your phasing method – it should always be disabled on startup or reset with a
MACRO drive – the MACRO station will always lose communications with the PMAC on reset
or startup and you will need to explicitly reset the MACRO drives after each PMAC reset
BEFORE attempting to phase. Usually Ixx80=0.
• Set Ixx73 for the amount of effort used in finding phase. Around 3000 is probably ok, but this
needs to be checked against the maximums for your system and the phasing type. If phasing to
Halls or an absolute encoder this number can be very small as there will be no actual motion. If
there is a large load, friction or other, this number may need to be fairly high. For very small
loads this number may be fairly small (~1500).
• Set Ixx74 for the phase finding time – probably around 10. For Halls or absolute encoder this can
be 1. For large load it may need to be higher to allow time to settle.
• Issue a “save” command, then a “$$$”, then “ms$$$15ms$$$31ms$$$47ms$$$63”
• Run the Tuning Pro package and tune the current loop for the motor. You should end up with a
good step move with minimal dithering, at least 200 Hz natural frequency, and around 2 ms
settling time. As a rule of thumb your integral should be about one tenth of your forward path
proportional.
• Check that your motor is free to move. Probably you will want to point an unused motor at the
encoder space for this motor and set Ix00 = 1 for that motor so that you can monitor movement
during this test. Set Ix00=0 for the motor being tested. Set Ixx29=0 and Ixx79=0 (no phase
offsets active). Set Mx54 = 1 (check enable LED on drive) and enable PLC 10. Now set P2, P4,
and P7 according to the chart below. Record the position of the motor at each step. You may
need to lower or raise the magnitude of the command value for your system. Your motor should
move through 1/6 of a commutation cycle for each step, and through an entire cycle for the test.
P2 P4 P7
0 2000 -2000 0
2000 0 -2000 60
2000 -2000 0 120
0 -2000 2000 180
-2000 0 2000 -120
-2000 2000 0 -60
0 2000 -2000 0
Electrical
Position
Setting Up Turbo Motor Operation 83
Page 96

Geo MACRO Drive User Manual
5. The motor is now at electrical 0, so set Mx71=0 in order to force the phase position to zero. If
you moved negative through the positions during this test them Ixx72 should be greater than
1024; otherwise it will be less than 1024. If Ixx72 and the direction of motion do not match then
you need to switch either the direction of the encoder or the direction of motion of the motor.
You can switch the encoder direction by changing MI910. You can change the motor direction
by swapping any two motor leads.
6. Now you should be able to run your motor open loop. Issue “Oxx” commands (open loop
commands, xx: stands for any value from 00 up to 100 (maximum output)) from the terminal
window, gradually stepping up from “O0” ( O zero) until you either get motion or fault. If you
do not get motion then you have an issue with your phasing. Check the values of all of the IVariables listed above. Check them again. Try again.
7. Finally tune the position loop using the Tuning Pro package, and you are ready to start
programming.
84 Setting Up Turbo Motor Operation
Page 97

Geo MACRO Drive User and Reference Manual
Instructions for Direct-PWM Control of Brush Motors
WARNING:
Make sure before applying any PWM commands to the drive and motor in this
fashion that the resulting current levels are within the continuous current rating of
both drive and motor.
First, enable the amp, then apply a very small positive command value to Phase A and a very small
negative command value to Phase B with the on-line commands:
M114=1 ; Enable amplifier
M102=I6800/50 M104=-I6800/50 M107=0 ; A pos, B neg, C zero
This provides a command at 2% of full voltage into the motor; this should be well within the continuous
current rating of both drive and motor. It is a good idea to make the sum of these commands equal to zero
so as not to put a net DC voltage on the motor; putting all three commands on one line causes the changes
to happen virtually instantaneously.
With power applied to the drive and the amplifier enabled (M114=1), current readings should be received
in the ADC registers as shown by the M-Variables M105 and M106 in the Watch window.
Since the M-Variables are defined as +/-32,768 for full current range, which should correspond
approximately to the instantaneous current limit. Make sure that the value read does not exceed the
continuous current limit, usually which is about 1/3 of the instantaneous limit. If well below the
continuous current limit, increase the voltage command to 5% to 10% of maximum. For example:
M102=I7000/10 M104=-I7000/10 M107=0 ; 10% of maximum
PWM/ADC Phase Match
Command values from Turbo PMAC’s Phase A PWM outputs should cause a roughly proportionate
response of one sign or the other on Turbo PMAC’s Phase A ADC input (whatever the phase is named in
the motor and drive). The same is true for Phase B.
If no response is received on either phase, re-check the entire setup, including:
• Is the drive properly wired to Turbo PMAC, either directly or through an interface board?
• Is the motor properly connected to the drive?
• Is the drive properly powered, both the power stage, and the input stage?
• Is the interface board properly powered?
• Is the amplifier enabled (M114=1 on Turbo PMAC and indicator ON at the drive)?
• Is the amplifier in fault condition? If so, why?
If only an ADC response is received on one phase, the phase outputs and inputs may not be matched
properly. For example, the Phase B ADC may be reading current from the phase commanded by the
Phase C PWM output. Confirm this by trying other combinations of commands and checking which
ADC responds to which phase command. If there is not a proper match, change the wiring between
Turbo PMAC and the drive. Changing the wiring between drive and motor will not help here.
Synchronous Motor Stepper Action
With a synchronous motor, this command should cause the motor to lock into a position, at least weakly,
like a stepper motor. This action may be received temporarily on an induction motor, due to temporary
eddy currents created in the rotor. However, an induction motor will not keep a holding torque
indefinitely at the new location.
Current Loop Polarity Check
Observe the signs of the ADC register values in M105 and M106. These two values should be of
approximately the same magnitude, and must be of the opposite sign from each other. (Again, remember
Setting Up Turbo Motor Operation 85
Page 98

Geo MACRO Drive User Manual
that these readings may appear noisy. Observe the base value underneath the noise.) If M105 is positive
and M106 is negative, the sign of the PWM commands matches the sign of the ADC feedback values. In
this case, the Turbo PMAC phase angle parameter I172 must be set to a value greater than 1024 (1365 for
a 3-phase motor).
If M105 is negative and M106 is positive, the sign of the PWM commands is opposite that of the ADC
feedback values. In this case, I172 must be set to a value less than 1024 (683 for a 3-phase motor).
Make sure your I172 value is set properly before attempting to close the digital current loops on Turbo
PMAC. Otherwise positive feedback will occur, creating unstable current loops which could damage the
amplifier and/or motor.
If M105 and M106 have the same sign, the polarities of the current sense circuitry for the two phases is
not properly matched. In this case, something has been mis-wired in the drive or between Turbo PMAC
and the drive to give the two phase-current readings opposite polarity. One of the phases will have to be
fixed.
Do not attempt to close the digital current loops on Turbo PMAC until the polarities of the current sense
circuitry for the two phases have been properly matched. This will involve a hardware change in the
current sense wiring, the ADC circuitry, or the connection between them. As an extra protection against
error, make sure that Ixx57 and Ixx58 are set properly for I
quickly if there is saturation due to improper feedback polarity.
2
T protection that will shut down the axis
Troubleshooting
If not getting the current readings that are expected, probe the motor phase currents on the motor cables
with a snap-on hall-effect current sensor. If the current is not seen when commanding voltages, check for
phase-to-phase continuity and proper resistance when the motor is disconnected.
Testing PWM and Current Feedback Operation
WARNING:
On many motor and drive systems, potentially deadly voltage and current levels
are present. Do not attempt to work directly with these high voltage and current
levels unless fully trained on all necessary safety procedures. Low-level signals on
Turbo PMAC and interface boards can be accessed much more safely.
Usually, in setting up a direct PWM interface there is no need to execute all of the steps listed in these
sections (or the Turbo Setup program will do them automatically). However, the first time this type of
interface is setup or there are problems, these steps will be of assistance.
For safety reasons, all of these tests should be done with the motor disconnected from any loads. All
settings made as a result of these tests are independent of load properties, so will still be valid when the
load is connected.
Before testing any of Turbo PMAC’s software features for digital current loop and direct PWM interface,
it is important to know whether the hardware interface is working properly. PMAC’s M-Variables are
used to access the input and output registers directly. The examples shown here use the suggested MVariable definitions for Motor 1.
Purpose
The purpose of these tests is to confirm the basic operation of the hardware circuits on PMAC, in the
drive, and in the motor, and to check the proper interrelationships. Specifically:
• Confirm operation of encoder inputs and decode
• Confirm operation of PWM outputs
• Confirm operation of ADC inputs
• Confirm correlation between PWM outputs and ADC inputs
86 Setting Up Turbo Motor Operation
Page 99

Geo MACRO Drive User and Reference Manual
• Determine proper current loop polarity
• Confirm commutation cycle size
• Determine proper commutation polarity
Preparation
First, define the M-Variables for the encoder counter; the three PWM output registers, the amplifierenable output bit, and the two ADC input registers. Using the MACRO suggested definitions for Motor
1, utilizing MACRO IC 0, Node 0:
M101->Y:$078420,0,24,S ; Channel 1 Encoder position register (read only)
M102->Y:$078420,8,16,S ; Channel 1 PWM Phase A command value (write only)
M104->Y:$078421,8,16,S ; Channel 1 PWM Phase B command value (write only)
M107->Y:$078422,8,16,S ; Channel 1 PWM Phase C command value (write only)
M105->Y:$078421,8,16,S ; Channel 1 Phase A ADC input value (read only)
M106->Y:$078422,8,16,S ; Channel 1 Phase B ADC input value (read only)
M114->X:$003440,14 ; Channel 1 Amp Enable command bit
Note:
The ADC values are declared as 16-bit variables even though typically, 12-bit
ADCs are used; this puts the scaling of the variable in the same units as Ixx69,
Ixx57, Ixx29, and Ixx79.
It is useful to monitor these values in the Watch window of the Executive program. Therefore, add the
variable names to the Watch window which causes the program to repeatedly query Turbo PMAC for the
values and display them. Then the hardware can be exercised with on-line commands issued through the
Terminal window.
To prepare Turbo PMAC for these tests:
1. Set I100 to 0 to deactivate the motor.
2. Set I101 to 0 to disable commutation. (This allows for manual use of these registers.)
3. Make sure that I6800, I6804, I6816, and I6817 are set up properly to provide the PWM signals desired.
4. If the Amplifier Enable bit is 1, set it to zero with the command M114=0.
5. Set Ixx00 and Ixx01 for all other motors to zero.
Position Feedback and Polarity Test
If the PWM command values observed in the Watch window are not zero, set them to zero with the
command:
M102=0 M104=0 M107=0
The motor can be turned (or pushed) freely by hand now. As the motor is turned, monitor the M101 value
in the Watch window. Look for the following:
• It should change as the motor is moved.
• It should count up in one direction, and count down in the other direction.
• It should provide the expected number of counts in one revolution or linear distance increment.
• As the motor is returned repeatedly to a reference position, it should report (approximately) the same
position value each time.
If these things do not happen, check the encoder/resolver operation, its connection to Turbo PMAC and
the Turbo PMAC decode variable I7mn0. Double-check that the sensor is powered. In addition, look at
the encoder waveforms with an oscilloscope.
If the direction of motion to be the positive direction is known, check this here. If the direction is
incorrect, invert it by changing I7mn0, usually from 7 to 3, or from 3 to 7. If the direction is not known,
change it later, but make another change at that time to maintain the proper commutation polarity match;
Setting Up Turbo Motor Operation 87
Page 100

Geo MACRO Drive User Manual
usually by exchanging two of the motor phase leads at the drive.
Note:
Because I100 has been set to 0, and I103 may not yet have been set properly, any
change of position will not be reflected in the motor position window.
Setting Up Hall Commutation Sensors
Many motor manufactures now give the consumer the option of placing both Hall effect sensors and
quadrature encoders on the end shaft of brushless motors. This will allow the controller to estimate the
rotor magnetic field orientation and adjusts the command among the motor phases properly without
rotating the motor at power-up. If this is not done properly, the motor or amplifier could be damaged.
Three-phase digital hall-effect position sensors (or their equivalent) are popular for commutation
feedback. They can also be used with Turbo PMAC as low-resolution position/velocity sensors. As
commutation position sensors, typically, they are just used by Turbo PMAC for approximate power-up
phase position; ongoing phase position is derived from the same high-resolution encoder that is used for
servo feedback. (Many controllers and amplifiers use these hall sensors as their only commutation
position feedback, starting and ongoing, but that is a lower-performance technique.)
Many optical encoders have hall tracks. These commutation tracks provide signal outputs equivalent to
those of magnetic hall commutation sensors, but use optical means to create the signals.
Note:
These digital hall-effect position sensors should not be confused with analog halleffect current sensors used in many amplifiers to provide current feedback data for
the current loop.
Signal Format
Digital hall sensors provide three digital signals that are a function of the position of the motor, each
nominally with 50% duty cycle, and nominally one-third cycle apart. (This format is often called 120
spacing. Turbo PMAC has no automatic hardware or software features to work with 60
o
spacing.) This
format provides six distinct states per cycle of the signal. Typically, one cycle of the signal set
corresponds to one electrical cycle, or pole pair, of the motor. These sensors, then, can provide absolute
(if low resolution) information about where the motor is in its commutation cycle, and eliminate the need
to do a power-on phasing search operation.
Note:
In the case of magnetic hall sensors, the feedback signals often come back to the
controller in the same cable as the motor power leads. In this case, the possibility
o
88 Setting Up Turbo Motor Operation
 Loading...
Loading...