Page 1
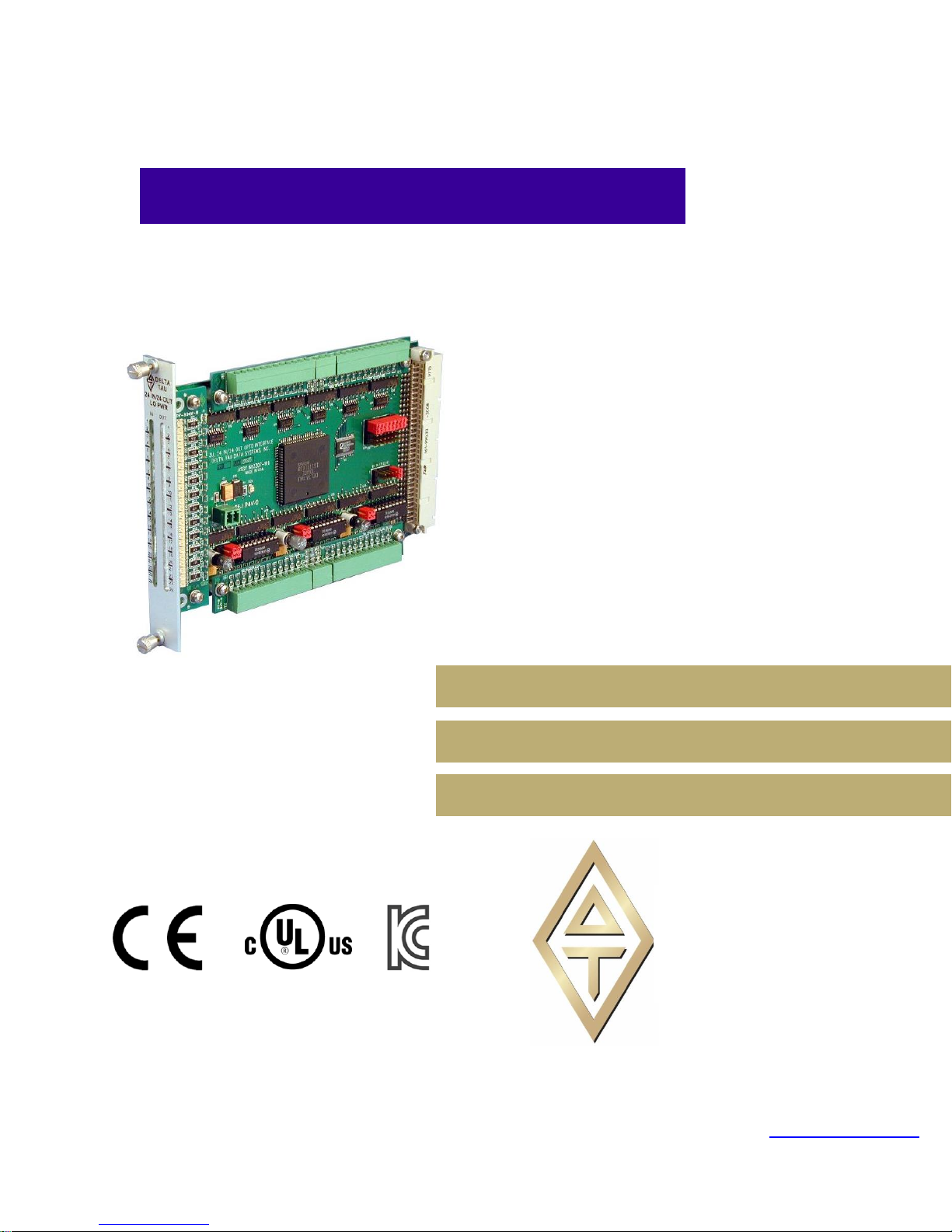
Single Source Machine Control Power // Flexibility // Ease of Use
21314 Lassen Street Chatsworth, CA 91311 // Tel. (818) 998-2095 Fax. (818) 998-7807 // www.deltatau.com
^1 USER MANUAL
^2 Accessory 11E
^3 24 Opto In/24 Opto Out
^4 3AX-603307-XUXX
^5 October 17, 2018
DELTA TAU
Data Systems, Inc.
NEW IDEAS IN MOTION …
Page 2
ACC-11E User Manual
Copyright Information
© 2018 Delta Tau Data Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
This document is furnished for the customers of Delta Tau Data Systems, Inc. Other uses are
unauthorized without written permission of Delta Tau Data Systems, Inc. Information contained in this
manual may be updated from time-to-time due to product improvements, etc., and may not conform in
every respect to former issues.
To report errors or inconsistencies, call or email:
Delta Tau Data Systems, Inc. Technical Support
Phone: (818) 717-5656
Fax: (818) 998-7807
Email: support@deltatau.com
Website: http://www.deltatau.com
Operating Conditions
All Delta Tau Data Systems, Inc. motion controller products, accessories, and amplifiers contain static
sensitive components that can be damaged by incorrect handling. When installing or handling Delta Tau
Data Systems, Inc. products, avoid contact with highly insulated materials. Only qualified personnel
should be allowed to handle this equipment.
In the case of industrial applications, we expect our products to be protected from hazardous or
conductive materials and/or environments that could cause harm to the controller by damaging
components or causing electrical shorts. When our products are used in an industrial environment, install
them into an industrial electrical cabinet or industrial PC to protect them from excessive or corrosive
moisture, abnormal ambient temperatures, and conductive materials. If Delta Tau Data Systems, Inc.
products are directly exposed to hazardous or conductive materials and/or environments, we cannot
guarantee their operation.
WARNING
A Warning identifies hazards that could result in personal injury
or death. It precedes the discussion of interest.
Caution
A Caution identifies hazards that could result in equipment damage. It
precedes the discussion of interest.
Note
A Note identifies information critical to the user’s understanding or
use of the equipment. It follows the discussion of interest.
Page 3
ACC-11E User Manual
MANUAL REVISION HISTORY
REV.
DESCRIPTION
DATE
CHG.
APPVD
1
ADDED CE DECLARATION
06/07/06
CP
SF
2
REVS. TO J1& J2, PINS 8 & 15, P. 31
05/11/07
CP
AO
3
REVS. TO ELEC. SPECS, P. 3
07/27/07
CP
BP
4
ADDED UL SEAL TO MANUAL COVER
UPDATED AGENCY APPROVAL/SAFETY SECTION
10/01/09
CP
SF
5
REFURBISHED ENTIRE MANUAL
12/17/12
GS
RN
6
ADDED KC CONFORMITY
10/17/18
SM
RN
Page 4

ACC-11E User Manual
Table of Contents 4
Table of Contents
INTRODUCTION......................................................................................................................... 6
SPECIFICATIONS....................................................................................................................... 7
Environmental Specifications ......................................................................................................... 7
Electrical Specifications.................................................................................................................. 7
Physical Specifications ................................................................................................................... 7
Agency Approval and Safety .......................................................................................................... 8
ADDRESSING ACC-11E ............................................................................................................. 9
Turbo/Power UMAC and MACRO Station Jumper Settings ......................................................... 9
Legacy MACRO Station Address Jumper Settings ........................................................................ 9
Sinking or Sourcing Output Select ............................................................................................... 10
I/O Gate Data Clock Select ........................................................................................................... 10
Hardware Address Limitations ..................................................................................................... 11
USING ACC-11E WITH TURBO UMAC ............................................................................... 13
Configuring the Control Word ...................................................................................................... 13
Accessing I/O data points (M-Variables) ..................................................................................... 14
USING ACC-11E WITH POWER UMAC SCRIPT PROGRAMING ................................. 16
Configuring the Control Word ...................................................................................................... 16
Accessing I/O Data Points (Pointers) ........................................................................................... 17
Suggested M-Variables ............................................................................................................ 17
USING ACC-11E WITH POWER UMAC C PROGRAMING ............................................. 18
Setting Up Digital I/O Access....................................................................................................... 18
Function for Setting the Control Word: ACC11E_SetControlWord() ..................................... 18
Function for Reading the State of Inputs: ACC11E_GetInputState() ...................................... 19
Function for Reading the State of Outputs: ACC11E_GetOutputState()................................. 19
Function for Writing to Outputs: ACC11E_SetOutputState() ................................................. 20
Header and Source File ........................................................................................................... 22
User Written Functions ............................................................................................................ 26
Setting Up the Control Word ........................................................................................................ 28
USING ACC-11E WITH UMAC MACRO STATION ........................................................... 30
Quick Review: Nodes and Addressing ......................................................................................... 30
Setting Up The Control Word ....................................................................................................... 33
Transferring Data Points over I/O Nodes ..................................................................................... 35
Preparing for I/O Data Transfer on the MACRO16 Station ................................................... 36
MS{anynode},MI71: 24-Bit Transfer ....................................................................................... 37
Page 5

ACC-11E User Manual
Table of Contents 5
MS{anynode},MI69 and MI70: 16-Bit Transfer ...................................................................... 42
MS{anynode}, MI171, MI172, and MI173: 24-Bit/16-Bit Transfer ........................................ 46
LAYOUTS & PINOUTS ............................................................................................................ 47
Board Layout Diagrams ................................................................................................................ 47
Wiring Considerations .................................................................................................................. 48
Terminal Block Option ................................................................................................................. 49
TB1 Top: Inputs 1 thru 12 ........................................................................................................ 49
TB2 Top: Inputs 13 thru 24 ...................................................................................................... 49
TB3 Top: Reference Voltages................................................................................................... 49
Wiring Input Terminal Blocks .................................................................................................. 50
TB1 Bottom: Outputs 1 thru 12 ................................................................................................ 51
TB2 Bottom: Outputs 13 thru 24 .............................................................................................. 51
TB3 Bottom: Reference Voltages ............................................................................................. 51
Wiring Output Terminal Blocks ............................................................................................... 52
D-Sub Option ................................................................................................................................ 53
J1 Top: Inputs 1 thru 12 ........................................................................................................... 53
J2 Top: Inputs 13 thru 24 ......................................................................................................... 53
Wiring Input DB15 Connectors ............................................................................................... 54
J1 Bottom: Outputs 1 thru 12 ................................................................................................... 55
J2 Bottom: Outputs 13 thru 24 ................................................................................................. 55
Wiring Output DB15 Connectors ............................................................................................. 56
SCHEMATICS ............................................................................................................................ 58
APPENDIX A: USING THE UMAC CONFIG PRO2 TOOL ............................................... 60
APPENDIX B: FULL TURBO UMAC M-VARIABLE MAPPINGS ................................... 66
APPENDIX C: FULL POWER UMAC M-VARIABLE MAPPINGS .................................. 78
APPENDIX D: THE CONTROL WORD ................................................................................ 90
Page 6

ACC-11E User Manual
Introduction 6
INTRODUCTION
The ACC-11E is a 24 In/24 Out general purpose I/O card. Built in the 3U euro card format, it can be used
in the following products:
- Turbo UMAC
- Power UMAC
- UMAC MACRO Station
All inputs and outputs are 12-24 VDC, optically isolated, and can be configured as sinking or sourcing.
Page 7
ACC-11E User Manual
Specifications 7
SPECIFICATIONS
Environmental Specifications
Description
Specification
Operating Temperature
0°C to 45°C,
Storage Temperature
-25°C to 70°C
Humidity
10% to 95 % non-condensing
Electrical Specifications
Description
Specification
Notes
Power Requirements
5V @ 0.05A (10%)
Output Current (individual)
100 mA
For UDN2981 and ULN2803
V1
12 – 24V
User-supplied voltage
Output Voltage
V1 – 1.1V
ULN2803 (See chip data sheet
for details)
V1 – 1.8V
UDN2981 (See chip data sheet
for details)
Fuse
125V @ 2.0A
Manufacturer: Little Fuse
Physical Specifications
Description
Specification
Notes
Dimensions
Length: 16.256 cm (6.4 in.)
Height: 10 cm (3.94 in.)
Width: 2.03 cm (0.8 in.)
Weight
180 g
Front Plate included
Terminal Block Connectors
FRONT-MC1,5/12-ST3,81
FRONT-MC1,5/5-ST3,81
FRONT-MC1,5/3-ST3,81
Terminal Blocks from Phoenix
Contact. UL-94V0
DB Option Connectors
DB15 Female
UL-94V0
The width is the width of the front plate. The length and height are the dimensions of the PCB.
Page 8
ACC-11E User Manual
Specifications 8
Agency Approval and Safety
Item
Description
CE Mark
EN61326-1
EMC
EN55011 Class A Group 1
EN61000-4-2
EN61000-4-3
EN61000-4-4
EN61000-4-5
EN61000-4-6
UL
UL 61010-1 File E314517
cUL
CAN/CSA C22.2 No. 1010.1-92 File E314517
Flammability Class
UL 94V-0
KC
EMI: KN 11
EMS: KN 61000-6-2
사 용 자 안 내 문
이 기기는 업무용 환경에서 사용할 목적으로 적합성평가를 받은 기기로서 가정
용 환경에서 사용하는 경우 전파간섭의 우려가 있습니다.
한국 EMC적용제품 준수사항
본 제품은 전파법(KC 규정)을 준수합니다. 제품을 사용하려면 다음 사항에 유
의하십시오. 이 기기는 업무용 환경에서 사용할 목적으로 적합성평가를 받은
기기로서 가정용 환경에서 사용하는 경우 전파간섭의 우려가 있습니다.
입력에 EMC 필터, 서지 보호기, 페라이트 코어 또는 1차측의 케이블에 노이즈
필터를 입력으로 사용하십시오.
Page 9
ACC-11E User Manual
Addressing and Jumper Settings 9
ADDRESSING ACC-11E
Several jumpers must be configured on the Accessory 11E in order for it to work properly with other I/O
cards in the UMAC rack. Jumpers E1-E4 select the starting base I/O address, and for within the base
address, jumpers E6A-E6H select whether the low, middle, or high byte will be used.
Turbo/Power UMAC and MACRO Station Jumper Settings
Chip
Select
TURBO
MACRO
POWER
Jumpers
Offset
Index
(n)
E1
E2
E3
E4
E6A-E6H
CS10
Y:$78C00,0,8
Y:$8800,0,8
$A00000.8.8
0
ON
OFF
OFF
OFF
1 to 2
CS10
Y:$78C00,8,8
Y:$8800,8,8
$A00000.16.8
0
ON
OFF
OFF
OFF
2 to 3
CS10
Y:$78C00,16,8
Y:$8800,16,8
$A00000.24.8
0
ON
OFF
OFF
OFF
4 to 5
CS12
Y:$78D00,0,8
Y:$8840,0,8
$B00000.8.8
1
OFF
ON
OFF
OFF
1 to 2
CS12
Y:$78D00,8,8
Y:$8840,8,8
$B00000.16.8
1
OFF
ON
OFF
OFF
2 to 3
CS12
Y:$78D00,16,8
Y:$8840,16,8
$B00000.24.8
1
OFF
ON
OFF
OFF
4 to 5
CS14
Y:$78E00,0,8
Y:$8880,0,8
$C00000.8.8
2
OFF
OFF
ON
OFF
1 to 2
CS14
Y:$78E00,8,8
Y:$8880,8,8
$C00000.16.8
2
OFF
OFF
ON
OFF
2 to 3
CS14
Y:$78E00,16,8
Y:$8880,16,8
$C00000.24.8
2
OFF
OFF
ON
OFF
4 to 5
CS16
Y:$78F00,0,8
Y:$88C0,0,8
$D00000.8.8
3
OFF
OFF
OFF
ON
1 to 2
CS16
Y:$78F00,8,8
Y:$88C0,8,8
$D00000.16.8
3
OFF
OFF
OFF
ON
2 to 3
CS16
Y:$78F00,16,8
Y:$88C0,16,8
$D00000.24.8
3
OFF
OFF
OFF
ON
4 to 5
E6A – E6H Layout Diagram
1
2
3
4
5
E6A
E6B
E6C
E6D
E6E
E6F
E6G
E6H
Legacy MACRO Station Address Jumper Settings
Chip Select
MACRO
Jumpers
E1
E2
E3
E4
CS10
$FFE0
ON
OFF
OFF
OFF
CS12
$FFE8
OFF
ON
OFF
OFF
CS14
$FFF0
OFF
OFF
ON
OFF
Page 10
ACC-11E User Manual
Addressing and Jumper Settings 10
Sinking or Sourcing Output Select
WARNING
Jumpers E16 thru E21 generally should be left at factory defaults.
They must not be changed without also changing their respective
buffer IC, ULN2803A for sinking or UDN2981A for sourcing.
Jumpers
Descriptions
E16 & E17
1-2 = Outputs 1 thru 8 Sinking
2-3 = Outputs 1 thru 8 Sourcing
E18 & E19
1-2 = Outputs 9 thru 16 Sinking
2-3 = Outputs 9 thru 16 Sourcing
E20 & E21
1-2 = Outputs 17 thru 24 Sinking
2-3 = Outputs 17 thru 24 Sourcing
I/O Gate Data Clock Select
Jumper
Function
E5
Servo Clock 2-3 Phase Clock (default)
Page 11

ACC-11E User Manual
Addressing and Jumper Settings 11
Hardware Address Limitations
The ACC-11E has a hardware address limitation relative to the newer type B series of UMAC high-speed
I/O cards. These new I/O cards have four base addresses per chip select (CS10, CS12, CS14, and CS16).
This enables these cards to have up to 16 different addresses. The type A cards have one base address per
chip select but also have the low-byte, middle-byte, and high-byte type of an addressing scheme and thus
allow for a maximum of twelve of these I/O cards.
Name
Type
Category
Possible Number
of Addresses
Maximum Number
of Cards in 1 Rack
ACC-9E
A
General I/O
4
12
ACC-10E
A
General I/O
4
ACC-11E
A
General I/O
4
ACC-12E
A
General I/O
4
ACC-14E
B
General I/O
16
16
ACC-28E
B
Analog I/O
16
ACC-36E
B
Analog I/O
16
ACC-53E
B
Feedback
16
ACC-57E
B
Feedback
16
ACC-58E
B
Feedback
16
ACC-59E
B
Analog I/O
12
12
ACC-65E
B
General I/O
16
16
ACC-66E
B
General I/O
16
ACC-67E
B
General I/O
16
ACC-68E
B
General I/O
16
ACC-84E
B
Feedback
12
12
Addressing Type A and Type B accessory cards requires attention to the following set of rules:
Populating Rack with Type A Cards Only (no conflicts)
In this mode, the card(s) can use any available Address.
Note
Type A cards can have up to 4 different base addresses. Because
each card can be setup to use the lower, middle, or high byte of a
specific base address, it is possible to populate a single rack with a
maximum of 12 Type A accessory cards.
Populating Rack with Type B Cards Only (no conflicts)
In this mode, the card(s) can potentially use any available Address.
Populating Rack with Type A & Type B Cards (possible conflicts)
Typically, Type A and Type B cards should not share the same Chip Select; however, if they do, the
following rules apply:
Type A and Type B Feedback Cards
Type A cards cannot share the same Chip Select as Type B Feedback cards.
Page 12

ACC-11E User Manual
Addressing and Jumper Settings 12
Type A and Type B General I/O Cards
Type A cards can share the same Chip Select as Type B general I/O cards; however, in this mode,
Type B cards naturally use the lower byte (default), and Type A cards must be set to the
middle/high byte of the selected base address.
Type A Cards and Type B Analog Cards
Type A cards can share the same Chip Select as Type B analog I/O cards; however, in this mode,
Type B cards naturally use the middle/high bytes (default), and Type A cards must be set to the
low byte of the selected base address.
Page 13

ACC-11E User Manual
Using ACC-11E with UMAC Turbo 13
USING ACC-11E WITH TURBO UMAC
The procedure for using the ACC-11E with Turbo UMAC has two steps:
1. Configure the Control Word
2. Accessing I/O data points (M-Variables)
Configuring the Control Word
Write a 7 to the control word which is located at {base address + 7}, n, 8 where:
n = 0 if using low byte addressing
n = 8 if using middle byte addressing
n = 16 if using high byte addressing
The control word must be configured every time the UMAC is powered or reset. This can be done in an
initialization (one that disables itself) PLC.
Example 1: Setting up Control Word at Startup for Card at Base Address $78C00, Low Byte Addressing
M3307->Y:$78C07,0,8 // I/O Card 1 control register from suggested M-Variables
Open PLC 1 Clear
M3307=$07
Disable PLC 1
Close
Example 2: Setting up Control Word at Startup for 3 Cards at Base Address $78C00; Low, Middle, and
High Byte Addressing
M3307->Y:$78C07,0,8 // I/O Card 1 control register using low byte
M3317->Y:$78C07,8,8 // I/O Card 2 control register using middle byte
M3327->Y:$78C07,16,8 // I/O Card 3 control register using high byte
Open PLC 1 Clear
M3307=$07
M3317=$07
M3327=$07
Disable PLC 1
Close
Note
See Appendix for control word details and explanations.
Page 14

ACC-11E User Manual
Using ACC-11E with UMAC Turbo 14
Accessing I/O data points (M-Variables)
Every ACC-11E has 48 bits of I/O data, which are comprised of one byte (8 bits) at the base address plus
five more bytes (8 x 6 = 48) at the next five consecutive addresses. Examples:
I/O data bits for card at base address
$78C00 using low bytes
I/O data bits for card at base address
$78C00 using high bytes
Y:$078C00,0,8
Y:$078C01,0,8
Y:$078C02,0,8
Inputs 1-8
Inputs 9-16
Inputs 17-24
Y:$078C00,16,8
Y:$078C01,16,8
Y:$078C02,16,8
Inputs 1-8
Inputs 9-16
Inputs 17-24
Y:$078C03,0,8
Y:$078C04,0,8
Y:$078C05,0,8
Outputs 1-8
Outputs 9-16
Outputs 17-24
Y:$078C03,16,8
Y:$078C04,16,8
Y:$078C05,16,8
Outputs 1-8
Outputs 9-16
Outputs 17-24
Example: Bitwise M-Variable mapping for ACC-11E at base address $78C00 using low bytes:
#define Input1 M7000 Input1->Y:$078C00,0,1
#define Input2 M7001 Input2->Y:$078C00,1,1
#define Input3 M7002 Input3->Y:$078C00,2,1
#define Input4 M7003 Input4->Y:$078C00,3,1
#define Input5 M7004 Input5->Y:$078C00,4,1
#define Input6 M7005 Input6->Y:$078C00,5,1
#define Input7 M7006 Input7->Y:$078C00,6,1
#define Input8 M7007 Input8->Y:$078C00,7,1
#define Input9 M7008 Input9->Y:$078C01,0,1
#define Input10 M7009 Input10->Y:$078C01,1,1
#define Input11 M7010 Input11->Y:$078C01,2,1
#define Input12 M7011 Input12->Y:$078C01,3,1
#define Input13 M7012 Input13->Y:$078C01,4,1
#define Input14 M7013 Input14->Y:$078C01,5,1
#define Input15 M7014 Input15->Y:$078C01,6,1
#define Input16 M7015 Input16->Y:$078C01,7,1
#define Input17 M7016 Input17->Y:$078C02,0,1
#define Input18 M7017 Input18->Y:$078C02,1,1
#define Input19 M7018 Input19->Y:$078C02,2,1
#define Input20 M7019 Input20->Y:$078C02,3,1
#define Input21 M7020 Input21->Y:$078C02,4,1
#define Input22 M7021 Input22->Y:$078C02,5,1
#define Input23 M7022 Input23->Y:$078C02,6,1
#define Input24 M7023 Input24->Y:$078C02,7,1
#define Output1 M7024 Output1->Y:$078C03,0,1
#define Output2 M7025 Output2->Y:$078C03,1,1
#define Output3 M7026 Output3->Y:$078C03,2,1
#define Output4 M7027 Output4->Y:$078C03,3,1
#define Output5 M7028 Output5->Y:$078C03,4,1
#define Output6 M7029 Output6->Y:$078C03,5,1
#define Output7 M7030 Output7->Y:$078C03,6,1
#define Output8 M7031 Output8->Y:$078C03,7,1
#define Output9 M7032 Output9->Y:$078C04,0,1
#define Output10 M7033 Output10->Y:$078C04,1,1
#define Output11 M7034 Output11->Y:$078C04,2,1
#define Output12 M7035 Output12->Y:$078C04,3,1
#define Output13 M7036 Output13->Y:$078C04,4,1
#define Output14 M7037 Output14->Y:$078C04,5,1
#define Output15 M7038 Output15->Y:$078C04,6,1
#define Output16 M7039 Output16->Y:$078C04,7,1
#define Output17 M7040 Output17->Y:$078C05,0,1
#define Output18 M7041 Output18->Y:$078C05,1,1
#define Output19 M7042 Output19->Y:$078C05,2,1
#define Output20 M7043 Output20->Y:$078C05,3,1
#define Output21 M7044 Output21->Y:$078C05,4,1
#define Output22 M7045 Output22->Y:$078C05,5,1
#define Output23 M7046 Output23->Y:$078C05,6,1
#define Output24 M7047 Output24->Y:$078C05,7,1
Page 15

ACC-11E User Manual
Using ACC-11E with UMAC Turbo 15
Note
See Appendix for suggested M-Variables for additional cards.
Note
Suggested M-Variable definitions are also available with the UMAC
Config. Pro2 tool (see Appendix).
Note
Most systems only use low byte addressing
Page 16
ACC-11E User Manual
Using ACC-11E with Power UMAC 16
USING ACC-11E WITH POWER UMAC SCRIPT PROGRAMING
The following section describes two software configuration procedures that are needed when using the
Power PMAC script programming language:
1. Configuring the Control Word
2. Accessing I/O data points (pointers)
Configuring the Control Word
Write a 7 to the control word which is located at {base address + 7}.n.8 where:
n = 8 if using low byte addressing
n = 16 if using middle byte addressing
n = 24 if using high byte addressing
The control word must be configured every time the POWER UMAC is powered or reset. This can be
done in an initialization (one that disables itself) PLC, usually PLC 1.
Example: Setting up Control Word at Startup for Card at $A00000, Low Byte Addressing
ptr IoCard0Reg7->u.io:$A0001C.8.8 // I/O Card 0 control register from suggested M-Variables
open plc 1
IoCard0Reg7=$7;
disable plc 1;
close
Example: Setting up Control Word at Startup for 3 Cards at Base Address $A00000; Low, Middle, and
High Byte Addressing
ptr IoCard0Reg7->u.io:$A0001C.8.8 // I/O Card 0 control register from suggested M-Variables
ptr IoCard1Reg7->u.io:$A0001C.16.8 // I/O Card 1 control register from suggested M-Variables
ptr IoCard2Reg7->u.io:$A0001C.24.8 // I/O Card 2 control register from suggested M-Variables
open plc 1
IoCard0Reg7=$7;
IoCard1Reg7=$7;
IoCard2Reg7=$7;
disable plc 1;
close
Note
See Appendix for control word details and explanations.
Page 17

ACC-11E User Manual
Using ACC-11E with Power UMAC 17
Accessing I/O Data Points (Pointers)
The simplest way to access I/O points on the ACC-11E is to define pointer variables (M-Variables) that
point to each bit on the I/O device.
Suggested M-Variables
Base offset $A00000, low byte addressing
// Single-bit variables used for accessing I/O points
ptr Input1->u.io:$A00000.8.1 // I/O Card 1 Input1
ptr Input2->u.io:$A00000.9.1 // I/O Card 1 Input2
ptr Input3->u.io:$A00000.10.1 // I/O Card 1 Input3
ptr Input4->u.io:$A00000.11.1 // I/O Card 1 Input4
ptr Input5->u.io:$A00000.12.1 // I/O Card 1 Input5
ptr Input6->u.io:$A00000.13.1 // I/O Card 1 Input6
ptr Input7->u.io:$A00000.14.1 // I/O Card 1 Input7
ptr Input8->u.io:$A00000.15.1 // I/O Card 1 Input8
ptr Input9->u.io:$A00004.8.1 // I/O Card 1 Input9
ptr Input10->u.io:$A00004.9.1 // I/O Card 1 Input10
ptr Input11->u.io:$A00004.10.1 // I/O Card 1 Input11
ptr Input12->u.io:$A00004.11.1 // I/O Card 1 Input12
ptr Input13->u.io:$A00004.12.1 // I/O Card 1 Input13
ptr Input14->u.io:$A00004.13.1 // I/O Card 1 Input14
ptr Input15->u.io:$A00004.14.1 // I/O Card 1 Input15
ptr Input16->u.io:$A00004.15.1 // I/O Card 1 Input16
ptr Input17->u.io:$A00008.8.1 // I/O Card 1 Input17
ptr Input18->u.io:$A00008.9.1 // I/O Card 1 Input18
ptr Input19->u.io:$A00008.10.1 // I/O Card 1 Input19
ptr Input20->u.io:$A00008.11.1 // I/O Card 1 Input20
ptr Input21->u.io:$A00008.12.1 // I/O Card 1 Input21
ptr Input22->u.io:$A00008.13.1 // I/O Card 1 Input22
ptr Input23->u.io:$A00008.14.1 // I/O Card 1 Input23
ptr Input24->u.io:$A00008.15.1 // I/O Card 1 Input24
ptr Output1->u.io:$A0000C.8.1 // I/O Card 1 Output1
ptr Output2->u.io:$A0000C.9.1 // I/O Card 1 Output2
ptr Output3->u.io:$A0000C.10.1 // I/O Card 1 Output3
ptr Output4->u.io:$A0000C.11.1 // I/O Card 1 Output4
ptr Output5->u.io:$A0000C.12.1 // I/O Card 1 Output5
ptr Output6->u.io:$A0000C.13.1 // I/O Card 1 Output6
ptr Output7->u.io:$A0000C.14.1 // I/O Card 1 Output7
ptr Output8->u.io:$A0000C.15.1 // I/O Card 1 Output8
ptr Output9->u.io:$A00010.8.1 // I/O Card 1 Output9
ptr Output10->u.io:$A00010.9.1 // I/O Card 1 Output10
ptr Output11->u.io:$A00010.10.1 // I/O Card 1 Output11
ptr Output12->u.io:$A00010.11.1 // I/O Card 1 Output12
ptr Output13->u.io:$A00010.12.1 // I/O Card 1 Output13
ptr Output14->u.io:$A00010.13.1 // I/O Card 1 Output14
ptr Output15->u.io:$A00010.14.1 // I/O Card 1 Output15
ptr Output16->u.io:$A00010.15.1 // I/O Card 1 Output16
ptr Output17->u.io:$A00014.8.1 // I/O Card 1 Output17
ptr Output18->u.io:$A00014.9.1 // I/O Card 1 Output18
ptr Output19->u.io:$A00014.10.1 // I/O Card 1 Output19
ptr Output20->u.io:$A00014.11.1 // I/O Card 1 Output20
ptr Output21->u.io:$A00014.12.1 // I/O Card 1 Output21
ptr Output22->u.io:$A00014.13.1 // I/O Card 1 Output22
ptr Output23->u.io:$A00014.14.1 // I/O Card 1 Output23
ptr Output24->u.io:$A00014.15.1 // I/O Card 1 Output24
// Byte-wide variables used for power-on configuration
ptr IoCard1Reg0->u.io:$A00000.8.8 // I/O Card 1 Inputs 1-8 as byte
ptr IoCard1Reg1->u.io:$A00004.8.8 // I/O Card 1 Inputs 9-16 as byte
ptr IoCard1Reg2->u.io:$A00008.8.8 // I/O Card 1 Inputs 17-24 as byte
ptr IoCard1Reg3->u.io:$A0000C.8.8 // I/O Card 1 Outputs 1-8 as byte
ptr IoCard1Reg4->u.io:$A00010.8.8 // I/O Card 1 Outputs 9-16 as byte
ptr IoCard1Reg5->u.io:$A00014.8.8 // I/O Card 1 Outputs 17-24 as byte
ptr IoCard1Reg6->u.io:$A00018.8.8 // I/O Card 1 latch inputs
ptr IoCard1Reg7->u.io:$A0001C.8.8 // I/O Card 1 control register
See Appendix for suggested M-Variables for additional cards.
Page 18

ACC-11E User Manual
Using ACC-11E with Power UMAC 18
USING ACC-11E WITH POWER UMAC C PROGRAMING
Setting Up Digital I/O Access
Delta Tau has developed the following functions which can be used to setup the ACC-11E using the C
Programming Language. The last entry in the list describes, as an alternative, how to create user written
functions.
Function for Setting the Control Word: ACC11E_SetControlWord()
Function for Reading the State of Inputs: ACC11E_GetInputState()
Function for Reading the State of Outputs: ACC11E_GetOutputState()
Function for Writing to Outputs: ACC11E_SetOutputState()
User Written Functions
Function for Setting the Control Word: ACC11E_SetControlWord()
Two parameters must be passed in the calling function:
BaseAddressOffset: One of the four base addresses (jumper selected) ACC-11E can take
=0xA00000
=0xB00000
=0xC00000
=0xD00000
ByteSelect: The byte used (jumper selected) for the I/O bits on this card
=1 for low byte
=2 for middle byte
=3 for high byte
The function is of type void, so it will not return any values.
void ACC11E_SetControlWord(unsigned int BaseAddressOffset, unsigned int ByteSelect)
/*
Input:
BaseAddressOffset: IO Card Base Address offset
ByteSelect: =1 for lowest 8 bits, =2 for middle 8 bits, =3 for high 8 bits
ControlWord: Control word value to which to set the card's Control Word
*/
{
volatile unsigned int *ioptr; // Create I/O pointer
ioptr = piom + BaseAddressOffset/4 + 7;// Initialize I/O pointer to Control Word register
*ioptr = 7 << (8*ByteSelect); // Write Control Word value to register
return;
}
Note
See Appendix for control word details and explanations.
Page 19
ACC-11E User Manual
Using ACC-11E with Power UMAC 19
Function for Reading the State of Inputs: ACC11E_GetInputState()
Three parameters must be passed in the calling function:
BaseAddressOffset: One of the four base addresses (jumper selected) ACC-11E can take
=0xA00000
=0xB00000
=0xC00000
=0xD00000
ByteSelect: The byte used (jumper selected) for the I/O bits on this card
=1 for low byte
=2 for middle byte
=3 for high byte
InputNumber: The number of the Input pin whose state one desires to read or modify.
Inputs are numbered 1–24 on ACC-11E
The function will return the state of the specified pin as an unsigned int:
=0, pin is low
=1, pin is high
unsigned int ACC11E_GetInputState(unsigned int BaseAddressOffset, unsigned int ByteSelect,
unsigned int InputNumber)
/*
Input:
------BaseAddressOffset: I/O Card Base Address Offset
InputNumber: Input Pin Number (1-24)
ByteSelect: =1 for lowest 8 bits, =2 for middle 8 bits, =3 for high 8 bits
Output:
------State of the I/O pin specified*/
{
volatile unsigned int *ioptr; // Create I/O pointer
// Compute location for high bit
unsigned int HighBitInCorrectLocation=0,ShiftValue;
InputNumber--;
ShiftValue = InputNumber%8 + 8*(ByteSelect-1);
HighBitInCorrectLocation = 1 << ShiftValue; // Shift bit to that location
ioptr = piom + BaseAddressOffset/4; // Initialize pointer
ioptr += InputNumber/8; // Increment to register containing the I/O bit
// Return state of I/O point
return ((*ioptr >> 8) & HighBitInCorrectLocation) >> ShiftValue;
}
Function for Reading the State of Outputs: ACC11E_GetOutputState()
Three parameters must be passed in the calling function:
BaseAddressOffset: One of the four base addresses (jumper selected) ACC-11E can take
=0xA00000
=0xB00000
=0xC00000
=0xD00000
Page 20
ACC-11E User Manual
Using ACC-11E with Power UMAC 20
ByteSelect: The byte used (jumper selected) for the I/O bits on this card
=1 for low byte
=2 for middle byte
=3 for high byte
OutputNumber: The number of the Onput pin whose state one desires to read or modify.
Outputs are numbered 1–24 on ACC-11E
The function will return the state of the specified pin as an unsigned int:
=0, pin is low
=1, pin is high
unsigned int ACC11E_GetOutputState(unsigned int BaseAddressOffset, unsigned int ByteSelect,
unsigned int OutputNumber)
/*
Input:
------BaseAddressOffset: I/O Card Base Address Offset
InputNumber: Input Pin Number (1-24)
ByteSelect: =1 for lowest 8 bits, =2 for middle 8 bits, =3 for high 8 bits
Output:
------State of the I/O pin specified*/
{
volatile unsigned int *ioptr; // Create I/O pointer
// Compute location for high bit
unsigned int HighBitInCorrectLocation=0,ShiftValue;
OutputNumber--;
ShiftValue=OutputNumber%8 + 8*(ByteSelect-1);
HighBitInCorrectLocation = 1 << ShiftValue; // Shift bit to that location
ioptr = piom + BaseAddressOffset/4; // Initialize pointer
ioptr += OutputNumber/8 + 3; // Increment to register containing the I/O bit
// Return state of I/O point
return ((*ioptr >> 8) & HighBitInCorrectLocation) >> ShiftValue;
}
Function for Writing to Outputs: ACC11E_SetOutputState()
Four parameters must be passed in the calling function:
BaseAddressOffset: One of the four base addresses (jumper selected) ACC-11E can take
=0xA00000
=0xB00000
=0xC00000
=0xD00000
ByteSelect: The byte used (jumper selected) for the I/O bits on this card
=1 for low byte
=2 for middle byte
=3 for high byte
OutputNumber: The number of the Output pin whose state one desires to read or modify.
Outputs are numbered 1–24 on ACC-11E
State: The state to which the desires to set the I/O pin.
=0, pin is OFF (low=false)
=1, pin is ON (high=true)
Page 21
ACC-11E User Manual
Using ACC-11E with Power UMAC 21
The function is of type void, so it will not return any values.
void ACC11E_SetOutputState(unsigned int BaseAddressOffset, unsigned int ByteSelect, unsigned int
OutputNumber, unsigned int State)
/*
Input:
BaseAddressOffset: I/O Card Base Address offset
ByteSelect: =1 for lowest 8 bits, =2 for middle 8 bits, =3 for high 8 bits
PinNumber: Output Pin Number (1-24)
State: Desired digital state of pin (0 = OFF, 1 = ON)
*/
{
volatile unsigned int *ioptr; // Create I/O pointer
// Compute location for high bit
unsigned int HighBitInCorrectLocation;
OutputNumber--;
HighBitInCorrectLocation = 1 << (OutputNumber%8 + 8*ByteSelect);
ioptr = piom + BaseAddressOffset/4; // Initialize pointer
ioptr += OutputNumber/8 + 3; // Increment to register containing the I/O bit
if(State==1) // If the user wants the pin to be ON (high true)
{// Logical OR with the bit the user desires to activate
*ioptr |= HighBitInCorrectLocation;
} else {
// Logical AND the register with a 0 in the desired location to bring the pin's state low
// right shift to push out garbage in lowest 8 bits, then shift back up 8 bits to have
// data in the proper location
*ioptr &= (((~0)^HighBitInCorrectLocation) >> 8) << 8;
}
return;
}
Page 22
ACC-11E User Manual
Using ACC-11E with Power UMAC 22
Header and Source File
The code for “acc11e.h” and “acc11e.c”, given below, contains the definitions for using the above
functions, prototypes, and the above listed functions. “acc11.h” should be included whenever using the
above ACC-11E C code. The files, acc11e.h and acc11e.c, must be put into the same folder as the C
program (BGCPLC, RTICPLC, or Background C Program.
#include "acc11e.h"
Below is the full code for both acc11e.h and acc11e.c.
acc11e.h
#include <gplib.h>
#include <RtGpShm.h> // Global Rt/Gp Shared memory pointers
//------------------------------------------------------------// The following is a projpp created file from the User defines
//-------------------------------------------------------------
#include "../../Include/pp_proj.h"
// Corresponds to E1 installed on ACC-11E, Turbo base address of $78C00
#define ACC11E_BaseAddressOffset_E1 0xA00000
// Corresponds to E2 installed on ACC-11E, Turbo base address of $78D00
#define ACC11E_BaseAddressOffset_E2 0xB00000
// Corresponds to E3 installed on ACC-11E, Turbo base address of $78E00
#define ACC11E_BaseAddressOffset_E3 0xC00000
// Corresponds to E4 installed on ACC-11E, Turbo base address of $78F00
#define ACC11E_BaseAddressOffset_E4 0xD00000
#define ON 1 // Assumes that (logic high)=true
#define OFF 0 // Assumes that (logic low)=false
#define ByteSelectLow 1
#define ByteSelectMiddle 2
#define ByteSelectHigh 3
void ACC11E_SetControlWord(unsigned int BaseAddressOffset, unsigned int ByteSelect);
unsigned int ACC11E_GetInputState(unsigned int BaseAddressOffset, unsigned int ByteSelect,
unsigned int InputNumber);
unsigned int ACC11E_GetOutputState(unsigned int BaseAddressOffset, unsigned int ByteSelect,
unsigned int OutputNumber);
void ACC11E_SetOutputState(unsigned int BaseAddressOffset, unsigned int ByteSelect, unsigned int
OutputNumber, unsigned int State);
Page 23
ACC-11E User Manual
Using ACC-11E with Power UMAC 23
acc11e.c
#include <gplib.h>
#include <RtGpShm.h> // Global Rt/Gp Shared memory pointers
//------------------------------------------------------------// The following is a projpp created file from the User defines
//-------------------------------------------------------------
#include "acc11e.h"
void ACC11E_SetControlWord(unsigned int BaseAddressOffset, unsigned int ByteSelect)
/*
Input:
BaseAddressOffset: IO Card Base Address offset
ByteSelect: =1 for lowest 8 bits, =2 for middle 8 bits, =3 for high 8 bits
ControlWord: Control word value to which to set the card's Control Word
*/
{
volatile unsigned int *ioptr; // Create I/O pointer
ioptr = piom + BaseAddressOffset/4 + 7;// Initialize I/O pointer to Control Word register
*ioptr = 7 << (8*ByteSelect); // Write Control Word value to register
return;
}
unsigned int ACC11E_GetInputState(unsigned int BaseAddressOffset, unsigned int ByteSelect,
unsigned int InputNumber)
/*
Input:
------BaseAddressOffset: I/O Card Base Address Offset
InputNumber: Input Pin Number (1-24)
ByteSelect: =1 for lowest 8 bits, =2 for middle 8 bits, =3 for high 8 bits
Output:
------State of the I/O pin specified*/
{
volatile unsigned int *ioptr; // Create I/O pointer
// Compute location for high bit
unsigned int HighBitInCorrectLocation=0,ShiftValue;
InputNumber--;
ShiftValue = InputNumber%8 + 8*(ByteSelect-1);
HighBitInCorrectLocation = 1 << ShiftValue; // Shift bit to that location
ioptr = piom + BaseAddressOffset/4; // Initialize pointer
ioptr += InputNumber/8; // Increment to register containing the I/O bit
// Return state of I/O point
return ((*ioptr >> 8) & HighBitInCorrectLocation) >> ShiftValue;
}
unsigned int ACC11E_GetOutputState(unsigned int BaseAddressOffset, unsigned int ByteSelect,
unsigned int OutputNumber)
/*
Input:
------BaseAddressOffset: I/O Card Base Address Offset
InputNumber: Input Pin Number (1-24)
ByteSelect: =1 for lowest 8 bits, =2 for middle 8 bits, =3 for high 8 bits
Output:
------State of the I/O pin specified*/
{
volatile unsigned int *ioptr; // Create I/O pointer
// Compute location for high bit
unsigned int HighBitInCorrectLocation=0,ShiftValue;
OutputNumber--;
ShiftValue=OutputNumber%8 + 8*(ByteSelect-1);
HighBitInCorrectLocation = 1 << ShiftValue; // Shift bit to that location
ioptr = piom + BaseAddressOffset/4; // Initialize pointer
ioptr += OutputNumber/8 + 3; // Increment to register containing the I/O bit
// Return state of I/O point
return ((*ioptr >> 8) & HighBitInCorrectLocation) >> ShiftValue;
Page 24

ACC-11E User Manual
Using ACC-11E with Power UMAC 24
}
void ACC11E_SetOutputState(unsigned int BaseAddressOffset, unsigned int ByteSelect, unsigned int
OutputNumber, unsigned int State)
/*
Input:
BaseAddressOffset: I/O Card Base Address offset
ByteSelect: =1 for lowest 8 bits, =2 for middle 8 bits, =3 for high 8 bits
PinNumber: Output Pin Number (1-24)
State: Desired digital state of pin (0 = OFF, 1 = ON)
*/
{
volatile unsigned int *ioptr; // Create I/O pointer
// Compute location for high bit
unsigned int HighBitInCorrectLocation;
OutputNumber--;
HighBitInCorrectLocation = 1 << (OutputNumber%8 + 8*ByteSelect);
ioptr = piom + BaseAddressOffset/4; // Initialize pointer
ioptr += OutputNumber/8 + 3; // Increment to register containing the I/O bit
if(State==1) // If the user wants the pin to be ON (high true)
{// Logical OR with the bit the user desires to activate
*ioptr |= HighBitInCorrectLocation;
} else {
// Logical AND the register with a 0 in the desired location to bring the pin's state low
// right shift to push out garbage in lowest 8 bits, then shift back up 8 bits to have
// data in the proper location
*ioptr &= (((~0)^HighBitInCorrectLocation) >> 8) << 8;
}
return;
}
Page 25
ACC-11E User Manual
Using ACC-11E with Power UMAC 25
Example: Reading from and Writing to I/O Points on One ACC-11E with CPLC0
This example is for an ACC-11E at base address offset $A00000 with low-byte addressing.
Every scan, the following Background CPLC (BGCPLC0) reads all inputs on the ACC-11E and places
them into P-Variables (P7000–P7023) for general purpose use. The BGCPLC will also read from
P-Variables (P8000–P8023) and write their values to the output pins of ACC-11E as follows:
P-Variable Number
Pin
Number
P-Variable Number
Pin
Number
P7000
Input 0 P8000
Output 0
P7001
Input 1 P8001
Output 1
P7002
Input 2 P8002
Output 2
P7003
Input 3 P8003
Output 3
P7004
Input 4 P8004
Output 4
P7005
Input 5 P8005
Output 5
P7006
Input 6 P8006
Output 6
P7007
Input 7 P8007
Output 7
P7008
Input 8 P8008
Output 8
P7009
Input 9 P8009
Output 9
P7010
Input 10 P8010
Output 10
P7011
Input 11 P8011
Output 11
P7012
Input 12 P8012
Output 12
P7013
Input 13 P8013
Output 13
P7014
Input 14 P8014
Output 14
P7015
Input 15 P8015
Output 15
P7016
Input 16 P8016
Output 16
P7017
Input 17 P8017
Output 17
P7018
Input 18 P8018
Output 18
P7019
Input 19 P8019
Output 19
P7020
Input 20 P8020
Output 20
P7021
Input 21 P8021
Output 21
P7022
Input 22 P8022
Output 22
P7023
Input 23 P8023
Output 23
Page 26

ACC-11E User Manual
Using ACC-11E with Power UMAC 26
Example Code: Using BGCPLC1 as an example.
This example assumes that “acc11e.h” and “acc11e.c” have already been placed into the same folder as
the BGCPLC under C LanguageCPLCsbgcplc00 in the Power PMAC IDE Solution Explorer.
#include <gplib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <dlfcn.h>
#include "../../Include/pp_proj.h"
#include "acc11e.h"
void user_plcc()
{
unsigned int ChannelNumber, ArrayIndex; // Allocate indices
for(ChannelNumber = 1; ChannelNumber < 25; ChannelNumber++)
{
ArrayIndex = ChannelNumber - 1;
/* Copy the state of each input into P7000-P7023 */
pshm->P[7000 + ArrayIndex] =
(double)ACC11E_GetInputState(ACC11E_BaseAddressOffset_E1, ByteSelectLow, ChannelNumber);
/* Copy the state of P8000-P8023 into outputs 1-24 */
ACC11E_SetOutputState(ACC11E_BaseAddressOffset_E1, ByteSelectLow, ChannelNumber,
(unsigned int)pshm->P[8000 + ArrayIndex]);
}
return;
}
User Written Functions
User written functions can be created as an alternative to the above described functions.
To do so:
Point a volatile unsigned int* pointer variable to the desired ACC-11E memory
location
Perform a whole 32-bit read of the memory location
To read I/O states, mask and shift to read the appropriate bit in the word; i.e., the state of
the I/O point
To write I/O states, perform a read-modify-write to change the appropriate bit in the
word (e.g., to enable or disable an output)
Table of ACC-11E I/O Registers in C
To access the I/O pins in ACC-11E, point a volatile unsigned int* pointer to the following registers:
Base Address
A00000
Base Address
B00000
Base Address
C00000
Base Address
D00000
Register
Description
piom+0xA00000/4+0
piom+0xB00000/4+0
piom+0xC00000/4+0
piom+0xD00000/4+0
Inputs 1–8
piom+0xA00000/4+1
piom+0xB00000/4+1
piom+0xC00000/4+1
piom+0xD00000/4+1
Inputs 9–16
piom+0xA00000/4+2
piom+0xB00000/4+2
piom+0xC00000/4+2
piom+0xD00000/4+2
Inputs 17–24
piom+0xA00000/4+3
piom+0xB00000/4+3
piom+0xC00000/4+3
piom+0xD00000/4+3
Outputs 1–8
piom+0xA00000/4+4
piom+0xB00000/4+4
piom+0xC00000/4+4
piom+0xD00000/4+4
Outputs 9–16
piom+0xA00000/4+5
piom+0xB00000/4+5
piom+0xC00000/4+5
piom+0xD00000/4+5
Outputs 17–24
piom+0xA00000/4+7
piom+0xB00000/4+7
piom+0xC00000/4+7
piom+0xD00000/4+7
Control Word
Page 27

ACC-11E User Manual
Using ACC-11E with Power UMAC 27
The useful data in each of these registers will be found in bits 8–32; the ACC-11E in Power PMAC does
not use bits 0–7 of any of its registers. The base addresses (left to right four columns) and bytes (right
end column) are selected with jumpers (see Addressing Setup and Jumper Settings section).
Only whole words at a time can be read in C; therefore, it is necessary to mask (using the bitwise “&”
operator) and shift (using the “<<” and “>>” operators) to obtain bit values.
A set of pointer variables can be predefined to each I/O register. Alternatively, a set of functions can be
created for reading and writing that will automatically point to, read from, and/or modify the appropriate
memory location, given the card’s base address, byte select, and pin number.
Page 28

ACC-11E User Manual
Using ACC-11E with Power UMAC 28
Setting Up the Control Word
The Control Word must be set equal to 7 every startup.
The function of each bit in the control word is as follows:
Control Word Bit Number
Value
I/O Bits
Modified
I/O Bits
Function
0
1
0–7
Inputs 1-8
1
1
8–15
Inputs 9-16
2
1
16–23
Inputs 17-24
3
0
24–31
Outputs 1-8
4
0
32–39
Outputs 9-16
5
0
40–47
Outputs 17-24
6
0
None
Register Select
7
0
None
Register Select
Example: Setting the Control Word in C in a Background C Program
This example Background C Program sets the Control Word equal to 7 for an ACC-11E at base address
offset $A00000 with low byte addressing using a Background C Program, and then returns.
#include <gplib.h> // Global Gp Shared memory pointer
#include "../../Include/pp_proj.h"
#include "acc11e.h"
int main(void)
{
InitLibrary();
ACC11E_SetControlWord(ACC11E_BaseAddressOffset_E1, ByteSelectLow);
CloseLibrary();
return 0;
}
In order for this program to run at startup, make sure to enable that option. For example, here a project
called “MultithreadedIO” has been created with the “acc11e_controlword” program created under C
LanguageBackground Programs. Then, from within the IDE Solution Explorer tree, go to
C LanguageBackground Programsacc11e_controlword, and then right-click on the
“acc11e_controlword” folder name and select Properties. Then, in the Properties tab, under “CPLC
Startup Option,” put a “1” (without the quotation marks) into the field next to the parameter “Run at
startup” (see the screenshot below).
Page 29

ACC-11E User Manual
Using ACC-11E with Power UMAC 29
Remember to put acc11e.c and acc11e.h from the previous section into the same folder as this BGCPLC
in order to run it properly.
Note
See Appendix for control word details and explanations.
Page 30

ACC-11E User Manual
Using ACC-11E with UMAC MACRO Station 30
USING ACC-11E WITH UMAC MACRO STATION
Setting up an ACC-11E on a MACRO station requires the following steps:
Establishing communication with the MACRO Station and enabling nodes
(Covered in alternate documentation i.e. MACRO16 CPU User Manual)
Setting up the control word
Transferring data over I/O Nodes
Quick Review: Nodes and Addressing
MACRO
CPU
ACC-11E
MACRO Station
Ring Controller
I/O Processing
User Access
$88XX$7 XXXX
I/O Data
Transfer
Automatic
Firmware Copy
Ultralite
Or
UMAC with ACC-5E
$C0XX
The above diagram represents three basic processes.
1. Starting on the right with I/O Processing, information is transferred to or from the ACC-11E I/O
Gate and the MACRO-Station CPU Gate 2B.
2. I/O is transferred between MACRO Station ($C0XX) and Ring Controller ($7XXXX) nodes.
ACC-11E input data is written to MACRO IC addresses ($7XXXX) on the Ring Controller, and
Ring Controller output data is written to MACRO Station IC addresses ($C0XX) on the MACRO
Station.
3. User Access: Ring Controller ($7XXXX) addresses are accessed thru M-Variables and used in
PLC and motion programs.
Note
The Ring Controller is sometimes referred to as the Master, but it is
the synchronizing Master. There can be more than one Master on a
MACRO ring, but there must be one, and only one, Ring Controller.
Note
Refer to the 16-Axis MACRO CPU manuals (SRM, USER, and
HRM) for more information on MACRO.
Page 31

ACC-11E User Manual
Using ACC-11E with UMAC MACRO Station 31
Each MACRO IC consists of 16 nodes: 2 auxiliary, 8 servo, and 6 I/O nodes.
Auxiliary nodes are for Ring Controller/Control registers and internal firmware use.
Servo nodes are used for motor control, carrying feedback, commands, and flag information.
I/O nodes are by default unoccupied and are user configurable for transferring various data.
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0Node
Auxiliary
Nodes
I/ O Nodes
Servo Nodes
Each I/O node consists of 4 registers; one 24-bit and three 16-bit registers for a total of 72 bits of data:
5 4 2 1 0
24-bit
1st 16-bit
2
nd
16-bit
3rd 16-bit
3
24-bit
1st 16-bit
2
nd
16-bit
3rd 16-bit
6
24-bit
1st 16-bit
2
nd
16-bit
3rd 16-bit
7
24-bit
1st 16-bit
2
nd
16-bit
3rd 16-bit
9 810
24-bit
1st 16-bit
2
nd
16-bit
3rd 16-bit
11
24-bit
1st 16-bit
2
nd
16-bit
3rd 16-bit
13 12
A given MACRO Station can be populated with either a MACRO8 or MACRO16 CPU:
MACRO8 supports 1 MACRO IC (IC#0).
MACRO16 supports 2 MACRO ICs (IC#0 and IC#1).
The I/O node addresses ($C0XX) on the MACRO Station ICs are:
MACRO Station IC #0 Node Registers
Node 2 3 6 7
10
11
24-bit
X:$C0A0
X:$C0A4
X:$C0A8
X:$C0AC
X:$C0B0
X:$C0B4
16-bit
X:$C0A1
X:$C0A5
X:$C0A9
X:$C0AD
X:$C0B1
X:$C0B5
16-bit
X:$C0A2
X:$C0A6
X:$C0AA
X:$C0AE
X:$C0B2
X:$C0B6
16-bit
X:$C0A3
X:$C0A7
X:$C0AB
X:$C0AF
X:$C0B3
X:$C0B7
MACRO Station IC #1 Node Registers
Node 2 3 6 7
10
11
24-bit
X:$C0E0
X:$C0E4
X:$C0E8
X:$C0EC
X:$C0F0
X:$C0F4
16-bit
X:$C0E1
X:$C0E5
X:$C0E9
X:$C0ED
X:$C0F1
X:$C0F5
16-bit
X:$C0E2
X:$C0E6
X:$C0EA
X:$C0EE
X:$C0F2
X:$C0F6
16-bit
X:$C0E3
X:$C0E7
X:$C0EB
X:$C0EF
X:$C0F3
X:$C0F7
Page 32

ACC-11E User Manual
Using ACC-11E with UMAC MACRO Station 32
A given Ring Controller (Turbo PMAC2 Ultralite or UMAC with
two ACC-5Es) can be populated with up to 4 MACRO ICs (IC#0,
IC#1, IC#2, and IC#3) which can be queried with global variable
I4902:
If I4902=
Populated
MACRO IC #s
$0
None
$1
0
$3
0, 1
$7
0, 1, 2
$F
0, 1, 2, 3
The I/O node addresses ($7XXXX) for each of the Ring Controller MACRO ICs are:
Ring Controller MACRO IC #0 Node Registers
Station I/O Node#
2 3 6 7 10
11
Ring Controller
I/O Node#
2 3 6 7 10
11
24-bit
X:$78420
X:$78424
X:$78428
X:$7842C
X:$78430
X:$78434
16-bit
X:$78421
X:$78425
X:$78429
X:$7842D
X:$78431
X:$78435
16-bit
X:$78422
X:$78426
X:$7842A
X:$7842E
X:$78432
X:$78436
16-bit
X:$78423
X:$78427
X:$7842B
X:$7842F
X:$78433
X:$78437
Ring Controller MACRO IC #1 Node Registers
Station I/O Node#
2 3 6 7 10
11
Ring Controller
I/O Node#
18
19
22
23
26
27
24-bit
X:$79420
X:$79424
X:$79428
X:$7942C
X:$79430
X:$79434
16-bit
X:$79421
X:$79425
X:$79429
X:$7942D
X:$79431
X:$79435
16-bit
X:$79422
X:$79426
X:$7942A
X:$7942E
X:$79432
X:$79436
16-bit
X:$79423
X:$79427
X:$7942B
X:$7942F
X:$79433
X:$79437
Ring Controller MACRO IC #2 Node Registers
Station I/O Node#
2 3 6 7 10
11
Ring Controller
I/O Node#
34
35
38
39
42
43
24-bit
X:$7A420
X:$7A424
X:$7A428
X:$7A42C
X:$7A430
X:$7A434
16-bit
X:$7A421
X:$7A425
X:$7A429
X:$7A42D
X:$7A431
X:$7A435
16-bit
X:$7A422
X:$7A426
X:$7A42A
X:$7A42E
X:$7A432
X:$7A436
16-bit
X:$7A423
X:$7A427
X:$7A42B
X:$7A42F
X:$7A433
X:$7A437
Ring Controller MACRO IC #3 Node Registers
Station I/O Node#
2 3 6 7 10
11
Ring Controller I/O
Node#
50
51
54
55
58
59
24-bit
X:$7B420
X:$7B424
X:$7B428
X:$7B42C
X:$7B430
X:$7B434
16-bit
X:$7B421
X:$7B425
X:$7B429
X:$7B42D
X:$7B431
X:$7B435
16-bit
X:$7B422
X:$7B426
X:$7B42A
X:$7B42E
X:$7B432
X:$7B436
16-bit
X:$7B423
X:$7B427
X:$7B42B
X:$7B42F
X:$7B433
X:$7B437
Page 33

ACC-11E User Manual
Using ACC-11E with UMAC MACRO Station 33
Setting Up The Control Word
The Control Word must be set equal to 7 once on power-up, usually in an initialization PLC. The advised
method to set up the control word with MACRO is using the direct read/write parameters:
MS{anynode}, MI198 Direct Read/Write Format and Address
MS{anynode}, MI199 Direct Read/Write variable
Note
The direct read/write parameters require MACRO16 CPU firmware
1.16 or later.
The MS{anynode}, MI198 setting is base address (and byte location) dependent:
Chip Select
Base Address
Byte Location
Control Word Location
MI198 Setting
CS10
Y:$8800
Low
Y:$8807,0,8
MI198=$408807
Middle
Y:$8807,8,8
MI198=$488807
High
Y:$8807,16,8
MI198=$508807
CS12
Y:$8840
Low
Y:$8847,0,8
MI198=$408847
Middle
Y:$8847,8,8
MI198=$488847
High
Y:$8847,16,8
MI198=$508847
CS14
Y:$8880
Low
Y:$8887,0,8
MI198=$408887
Middle
Y:$8887,8,8
MI198=$488887
High
Y:$8887,16,8
MI198=$508887
CS16
Y:$88C0
Low
Y:$88C7,0,8
MI198=$4088C7
Middle
Y:$88C7,8,8
MI198=$4888C7
High
Y:$88C7,16,8
MI198=$5088C7
Note
CS16 Cannot be used with legacy MACRO16 CPU’s (rev 100 –104)
Note
MI198 and MI199 can be written to directly from the Pewin32Pro2
terminal window. However, their values are not saved and should be
executed in a startup PLC.
Page 34

ACC-11E User Manual
Using ACC-11E with UMAC MACRO Station 34
Example: Writing control words for two ACC-11E cards set to base addresses $8800,0,8 and $8800,8,8
Open PLC 1 Clear
I5111=1000*8388608/I10 while(I5111>0) endw ; 1-sec delay
CMD"MS0,MI198=$408807" ; Set control word for first ACC-11E at $8800 low byte addresses
CMD"MS0,MI199=$07" ; Write $07 into Y:$8807,0,8 (control word)
I5111=50*8388608/I10 while(I5111>0) endw ; 50-msec delay
CMD"MS0,MI198=$488807" ; Set control word for second ACC-11E at $8800 mid byte addresses
CMD"MS0,MI199=$07" ; Write $07 into Y:$8807,8,8 (control word)
I5111=50*8388608/I10 while(I5111>0) endw ; 50-msec delay
Disable PLC 1
Close
Note
See appendix for further control word details.
Page 35

ACC-11E User Manual
Using ACC-11E with UMAC MACRO Station 35
Transferring Data Points over I/O Nodes
This section illustrates how I/O data is transferred from ACC-11E ($88XX) registers, thru I/O nodes
($C0XX), and finally to the ring controller ($7XXXX) for user access using M-Variable pointers.
Note
It is assumed that communication over the MACRO ring has already
been established, and that the user is familiar with node activation on
both the Ring Controller and MACRO Station. Thus, any node(s)
used in subsequent example(s) have to have been enabled
previously.
Generally, there are three basic transfer methods. The decision of which to use might depend on what
types of I/O cards, and how many, are being used. The MI71 method is the typical choice for handling up
to six ACC-11E cards in one rack.
MACRO Station IC#0
Transfer MI-Variable
Used For:
Transfer Type
MI71
Most Applications
24-bit
MI69, MI70
Special cases, if:
24-bit registers are already in use
More than six cards are needed
16-Bit
MI171, MI172,
MI173
Special cases, if:
It is desired to fit 3 cards into 2 I/O nodes
More than six cards needed
24-Bit / 16-Bit
MACRO Station IC#1
Transfer MI-Variable
Used For:
Transfer Type
MI1071
Most Applications
24-bit
MI1069, MI1070
Special cases, if:
24-bit registers are already in use
More than six cards are needed
16-Bit
MI1171, MI1172,
MI1173
Special cases, if:
It is desired to fit 3 cards into 2 I/O nodes
More than six cards needed
24-Bit / 16-Bit
Note
The MACRO16 CPU is populated with 2 MACRO ICs (IC #0 and
#1), each of which has its own I/O transfer variables.
Page 36

ACC-11E User Manual
Using ACC-11E with UMAC MACRO Station 36
Preparing for I/O Data Transfer on the MACRO16 Station
The following parameters should be configured properly for the I/O node transfer to work properly:
MS{anynode}, MI992 Max. Phase frequency control
Typically, set to equal to ring controller’s I6800
MS{anynode}, MI997 Phase clock frequency control
Typically, set to equal to ring controller’s I6801
MS{anynode}, MI995 MACRO Ring configuration/status
Typically, set to = $4080
MS{anynode}, MI996 MACRO IC#0 node activate control
MS{anynode}, MI975 MACRO IC#0 I/O Node enable
MI975 should match enabled I/O nodes in MI996
MS{anynode}, MI8 MACRO Ring check Period
Typically set to = 8 (with default clock settings)
MS{anynode}, MI9 MACRO Ring error shutdown count
Typically set to = 4 (with default clock settings)
MS{anynode}, MI10 MACRO Sync packet shutdown count
Typically set to = 4 (with default clock settings)
MS{anynode},MI19 I/O node data transfer rate
= 0, transfer disabled.
> 0, transfer period in Phase clock cycles (typically set =4).
MS{anynode}, MI1996 MACRO IC#1 node activate control (if IC#1 is used)
MS{anynode}, MI1975 MACRO IC#1 I/O Node enable (if IC#1 is used)
MI1975 should match enabled I/O nodes in MI1996
Note
The following I/O data transfer method examples assume that
MACRO communication, I/O nodes enabling, and other MACRO ring
parameters have been configured properly on both the ring Controller
and MACRO Station.
Page 37

ACC-11E User Manual
Using ACC-11E with UMAC MACRO Station 37
MS{anynode},MI71: 24-Bit Transfer
This method is typically used when six or less ACC-11E cards are present in the rack.
MS{anynode},MI71 processes 24-bit register transfers. It is a 48-bit variable represented as 12
hexadecimal digits which are set up as follows (digit #1 is leftmost when constructing the word):
No. of consecutive node pairs:
=1 for 2 IO nodes
=2 for 4 IO nodes
=3 for 6 IO nodes (max.)
Reserved, = 0
Starting I/O node register
($C0XX)
No. of 24-bit banks per board
Always = 2 for ACC-11E
1 2 3 - 6 7 8 9 - 12Digit #:
For ACC-11E, = 0
Starting ACC-11E base address
($88XX)
Example 1: Transferring I/O data of one ACC-11E card (total of 48 bits) at base address $8800 (using
low bytes) over MACRO using two consecutive 24-bit registers of I/O nodes 2 and 3 ($C0A0, and
$C0A4 respectively) yields:
MS0,MI71=$10C0A0208800
Inputs (24 bits) / Outputs(24 bits)
24 24
16
16
16
16
16
16
24 24
16
16
16
16
16
16
24 24
16
16
16
16
16
16
MACRO IC
I/O Node#: 2 3 6 7 10 11
$C0A0 $C0A4 $C0A8 $C0AC $C0B0 $C0B4
24-bit reg. Address:
ACC-11E ($8800)
Page 38

ACC-11E User Manual
Using ACC-11E with UMAC MACRO Station 38
Example 2: Transferring I/O data of two ACC-11E cards (total of 96 bits) at consecutive $8800 addresses
(using low and middle bytes) over MACRO using four consecutive 24-bit registers of I/O nodes 2, 3, 6,
and 7 ($C0A0, $C0A4, $C0A8, and $C0AC respectively) yields:
MS0,MI71=$20C0A0208800
Inputs (24 bits) / Outputs(24 bits)
24 24
16
16
16
16
16
16
24 24
16
16
16
16
16
16
24 24
16
16
16
16
16
16
MACRO IC
I/O Node#: 2 3 6 7 10 11
$C0A0 $C0A4 $C0A8 $C0AC $C0B0 $C0B4
24-bit reg. Address:
ACC-11E ($8800 low bytes)
Inputs (24 bits) / Outputs(24 bits)
ACC-11E ($8800 middle bytes)
Example 3: Transferring I/O data of three ACC-11E cards (total of 144 bits) at consecutive $8800
addresses (using low, middle, and high bytes) over MACRO using six consecutive 24-bit registers of I/O
nodes 2, 3, 6, 7, 10, and 11 ($C0A0, $C0A4, $C0A8, $C0AC, $C0B0, and $C0B4 respectively) yields:
MS0,MI71=$30C0A0208800
24 24
16
16
16
16
16
16
24 24
16
16
16
16
16
16
24 24
16
16
16
16
16
16
MACRO IC
I/O Node#: 2 3 6 7 10 11
$C0A0 $C0A4 $C0A8 $C0AC $C0B0 $C0B4
24-bit reg. Address:
Inputs (24 bits) / Outputs(24 bits)
ACC-11E ($8800 low bytes)
Inputs (24 bits) / Outputs(24 bits)
ACC-11E ($8800 middle bytes)
Inputs (24 bits) / Outputs(24 bits)
ACC-11E ($8800 high bytes)
Page 39

ACC-11E User Manual
Using ACC-11E with UMAC MACRO Station 39
Example 4: Transferring I/O data of the maximum of six ACC-11E cards (total of 288 bits) at
consecutive $8800 addresses (using low, middle, and high bytes) and consecutive $8840 addresses (using
low, middle, and high bytes) over MACRO using six consecutive 24-bit registers of IC#0 I/O nodes 2, 3,
6, 7, 10, and 11 ($C0A0, $C0A4, $C0A8, $C0AC, $C0B0, and $C0B4 respectively) and six consecutive
IC#1 I/O nodes 2, 3, 6, 7, 10, and 11 ($C0E0, $C0E4, $C0E8, $C0EC, $C0F0, and $C0F4 respectively)
yields:
MS0,MI71=$30C0A0208800
MS0,MI1071=$30 C0E0208840
Note
Transferring multiple ACC-11E cards using MS{anynode},
MI71 requires them to be at the same base address, starting with
the first card set for low byte addressing, the second card set for
middle byte addressing, and then a third card (if present) set for
high byte addressing.
The 24-bit node registers used with MS{anynode}, MI71 must
be at consecutive addresses.
Note
A save MSSAV{anynode}, followed by a reset MS$$${anynode) at
the MACRO station is necessary for MI71 transfers to take effect.
Once a transfer is enabled, the I/O data is copied automatically by the firmware into the ring controllers’
node registers ($7XXXX) where it is accessible to the user. However, the MACRO protocol limits
handling of these registers to full words (16- or 24-bit).
The inputs can be read directly in full word assignments. The outputs can be written to directly in full
word assignments, but cannot report their current state.
Note
Reading the state of inputs can be done directly from I/O node
registers ($7XXXX) using full word assignments.
Note
Writing to outputs can be done directly to I/O node registers
($7XXXX) using full word assignments; however, reading the state
of outputs is not possible.
Page 40

ACC-11E User Manual
Using ACC-11E with UMAC MACRO Station 40
Creating input and output image (mirrored) words in a PLC program allows bitwise assignments, full user
access, and state reporting. The following diagram illustrates the basic concept of mirroring:
$7XXXX
Inputs
Outputs
PLC program
If inputs state has changed:
Copy full word to unused memory location
If user outputs have changed:
Copy full word to unused memory location
User Access
Inputs
Outputs
Write
WriteRead
Read
Example: For “example 1” above, using MI71 24-bit transfer to process one ACC-11E over MACRO
using I/O nodes 2 and 3, the following assignments and PLC program demonstrate the mirroring
implementation:
#define Inputs M4000 ; M-Variable pointer to hold 24-bit inputs
#define Outputs M4001 ; M-Variable pointer to hold 24-bit outputs
Inputs->X:$78420,0,24,U ; I/O Node 2 24-bit register (inputs)
Outputs->X:$78424,0,24,U ; I/O Node 3 24-bit register (outputs)
#define InMirror M4002 ; M-Variable pointer to hold inputs mirror word
#define OutMirror M4003 ; M-Variable pointer to hold outputs mirror word
#define OutState M4004 ; M-Variable pointer to latch current outputs state
InMirror->X:$10F0,0,24,U ; Reserve unused memory register (to hold inputs)
OutMirror->Y:$10F0,0,24,U ; Reserve unused memory register (to hold outputs)
OutState->* ; Self referenced
OutState=0 ; Initialize =0 on download
Open plc 1 clear
If (InMirror!=Inputs) ; Inputs state changed?
InMirror=Inputs ; Update inputs mirror word to match current state
EndIf ;
If (OutState!=OutMirror) ; Outputs state changed?
OutState=OutMirror ; Update state of outputs mirror word
Outputs=OutMirror ; Update outputs
EndIf
Close
Note
With the ACC-11E (or any other 24In/24Out card), the inputs are
copied through the first of the two 24-bit registers, and the outputs
are copied through the second of the two 24-bit registers.
Note
Turbo PMAC unusued (open) memory registers can be either X or Y
located at X/Y:$10F0 - $10FF (total of 32).
Make sure that the registers chosen for mirroring are not used in
another process.
Page 41

ACC-11E User Manual
Using ACC-11E with UMAC MACRO Station 41
The I/O data is now available in the pre-defined open memory registers. Bitwise maping can be
implemented for direct and convenient user access:
// Inputs
#define Input1 M3300 Input1->X:$0010F0,0
#define Input2 M3301 Input2->X:$0010F0,1
#define Input3 M3302 Input3->X:$0010F0,2
#define Input4 M3303 Input4->X:$0010F0,3
#define Input5 M3304 Input5->X:$0010F0,4
#define Input6 M3305 Input6->X:$0010F0,5
#define Input7 M3306 Input7->X:$0010F0,6
#define Input8 M3307 Input8->X:$0010F0,7
#define Input9 M3308 Input9->X:$0010F0,8
#define Input10 M3309 Input10->X:$0010F0,9
#define Input11 M3310 Input11->X:$0010F0,10
#define Input12 M3311 Input12->X:$0010F0,11
#define Input13 M3312 Input13->X:$0010F0,12
#define Input14 M3313 Input14->X:$0010F0,13
#define Input15 M3314 Input15->X:$0010F0,14
#define Input16 M3315 Input16->X:$0010F0,15
#define Input17 M3316 Input17->X:$0010F0,16
#define Input18 M3317 Input18->X:$0010F0,17
#define Input19 M3318 Input19->X:$0010F0,18
#define Input20 M3319 Input20->X:$0010F0,19
#define Input21 M3320 Input21->X:$0010F0,20
#define Input22 M3321 Input22->X:$0010F0,21
#define Input23 M3322 Input23->X:$0010F0,22
#define Input24 M3323 Input24->X:$0010F0,23
// Outputs
#define Output1 M3325 Output1->Y:$0010F0,0
#define Output2 M3326 Output2->Y:$0010F0,1
#define Output3 M3327 Output3->Y:$0010F0,2
#define Output4 M3328 Output4->Y:$0010F0,3
#define Output5 M3329 Output5->Y:$0010F0,4
#define Output6 M3330 Output6->Y:$0010F0,5
#define Output7 M3331 Output7->Y:$0010F0,6
#define Output8 M3332 Output8->Y:$0010F0,7
#define Output9 M3333 Output9->Y:$0010F0,8
#define Output10 M3334 Output10->Y:$0010F0,9
#define Output11 M3335 Output11->Y:$0010F0,10
#define Output12 M3336 Output12->Y:$0010F0,11
#define Output13 M3337 Output13->Y:$0010F0,12
#define Output14 M3338 Output14->Y:$0010F0,13
#define Output15 M3339 Output15->Y:$0010F0,14
#define Output16 M3340 Output16->Y:$0010F0,15
#define Output17 M3341 Output17->Y:$0010F0,16
#define Output18 M3342 Output18->Y:$0010F0,17
#define Output19 M3343 Output19->Y:$0010F0,18
#define Output20 M3344 Output20->Y:$0010F0,19
#define Output21 M3345 Output21->Y:$0010F0,20
#define Output22 M3346 Output22->Y:$0010F0,21
#define Output23 M3347 Output23->Y:$0010F0,22
#define Output24 M3348 Output24->Y:$0010F0,23
Page 42

ACC-11E User Manual
Using ACC-11E with UMAC MACRO Station 42
MS{anynode},MI69 and MI70: 16-Bit Transfer
This method is generally only used in special cases in which the 24-bit transfer method cannot be used
because either the 24-bit registers are already being used or because more than six ACC-11E cards are
needed.
MS{anynode},MI69/70 processes 16-bit register transfers. It is a 48-bit variable represented as 12
hexadecimal digits which are set up as follows (digit #1 is leftmost when constructing the word):
No. of consecutive nodes:
=1 for 1 IO node
=2 for 2 IO nodes
=3 for 3 IO nodes (max.)
Reserved, = 0
Starting I/O node register
($C0XX)
No. of 16-bit banks per board
Always = 3 for ACC-11E
1 2 3 - 6 7 8 9 - 12Digit #:
For ACC-11E, = 0
Starting ACC-11E base address
($88XX)
Example: Transferring I/O data of one ACC-11E card (total of 48 bits) at base address $8800 over
MACRO using three consecutive 16-bit registers of I/O node 2 ($C0A1, $C0A2, and $C0A3,
respectively) yields:
MS0,MI69=$10C0A1308800
24
16
16
16
$C0A1
$C0A2
$C0A3
2
ACC-11E ($8800)
16 bits
Inputs
8 bits 8 bits
Outputs
16 bits
I/O Node#:
16-bit reg. Addresses:
Page 43

ACC-11E User Manual
Using ACC-11E with UMAC MACRO Station 43
Note
Transferring multiple ACC-11E cards using MS{anynode},
MI69 and MI70 requires them to be at the same base address,
starting with the first card set for low byte addressing, the second
card set for middle byte addressing, and then a third card (if
present) set for high byte addressing.
The 16-bit node registers used with MS{anynode}, MI69 and
MI70 must be at consecutive addresses.
Note
A save MSSAV{anynode}, followed by a reset MS$$${anynode) at
the MACRO station is necessary for MI69 and MI70 transfers to
take effect.
The I/O data is now copied automatically by the firmware into the ring controllers’ node registers
($7XXXX) where it is accessible by the user. However, the MACRO protocol limits handling of these
registers to full words (16- or 24-bit).
The inputs can be read directly in full word assignments. The outputs can be written to directly in full
word assignments, but cannot report their current state.
Note
Reading the state of inputs can be done directly from I/O node
registers ($7XXXX) using full word assignments.
Note
Writing to outputs can be done directly to I/O node registers
($7XXXX) using full word assignments; however, reading the state
of outputs is not possible.
Creating input and output image (mirrored) words in a PLC program allows bitwise assignments, full user
access, and state reporting. The following diagram illustrates the basic concept of mirroring:
$7XXXX
Inputs
Outputs
PLC program
If inputs state has changed:
Copy full word to unused memory location
If user outputs have changed:
Copy full word to unused memory location
User Access
Inputs
Outputs
Write
WriteRead
Read
Page 44

ACC-11E User Manual
Using ACC-11E with UMAC MACRO Station 44
Example: For the above example, using MI69 16-bit transfer to process one ACC-11E over MACRO
using I/O node 2, the following assignments and PLC program demonstrate the mirroring
implementation.
In 16-bit transfers, the middle 16-bit register is split into half inputs and half outputs. Because of this,
outputs must be masked when reading inputs, and inputs must be masked when writing outputs.
#define 16In M4015 ; M-Variable pointer to hold 16-bit inputs
#define 8In8Out M4016 ; M-Variable pointer to hold 8-bit inputs and 8-bit outputs
#define 16Out M4017 ; M-Variable pointer to hold 16-bit outputs
16In->X:$78421,8,16 ; I/O Node 2 1st 16-bit register (16 inputs)
8In8Out->X:$78422,8,16 ; I/O Node 2 2nd 16-bit register (8 inputs and 8 outputs)
16Out->X:$78423,8,16 ; I/O Node 2 3rd 16-bit register (16 outputs)
#define InMirror16 M4115 ; M-Variable pointer to hold 16-bit input mirror word
#define InMirror8 M4116 ; M-Variable pointer to hold 8 input mirror word
#define OutMirror8 M4117 ; M-Variable pointer to hold 8 output mirror word
#define OutMirror16 M4118 ; M-Variable pointer to hold 16-bit output mirror word
#define OutState8 M4119 ; M-Variable pointer to latch current state of 8 output bits
#define OutState16 M4120 ; M-Variable pointer to latch current state of 16 output bits
InMirror16->X:$10F8,8,16 ; Reserve unused memory register (to hold 16 inputs)
InMirror8->Y:$10F8,8,8 ; Reserve unused memory register (to hold 8 inputs)
OutMirror8->X:$10F9,8,16 ; Reserve unused memory register (to hold 8 outputs)
OutMirror16->Y:$10F9,8,16 ; Reserve unused memory register (to hold 16 outputs)
OutState8->* ; Self referenced
OutState16->* ; Self referenced
OutState8=0 ; Initialize =0 on download
OutState16=0 ; Initialize =0 on download
Open plc 1 clear
If (InMirror16!=16In) ; Inputs state changed?
Or (InMirror8!=8In8Out&$00FF)
InMirror16=16In ; Update inputs mirror word to match current state
InMirror8=8In8Out&$00FF ; Update inputs mirror byte to match current state
EndIf ;
If (OutState8!=OutMirror8&$FF00) ; Outputs state changed?
Or (OutState16!=OutMirror16)
OutState8=OutMirror8&$FF00 ; Update state of output mirrors
OutState16=OutMirror16
8In8Out=OutMirror8&$FF00 ; Update outputs
16Out=OutMirror16
EndIf
Close
Note
With the ACC-11E (or any other 24In/24Out card), the inputs are
copied through the entire first 16-bit register and the first byte of the
second 16-bit register. The outputs are copied through the second
byte of the second 16-bit register and the entire third 16-bit register.
Note
Turbo PMAC unusued (open) memory registers can be either X or Y
located at X/Y:$10F0 - $10FF (total of 32).
Make sure that the registers chosen for mirroring are not used in
another process.
Page 45

ACC-11E User Manual
Using ACC-11E with UMAC MACRO Station 45
The I/O data is now available in the pre-defined open memory registers. Bitwise mapping can be
implemented for direct and convenient user access:
//Inputs
//Inputs
#define Input1 M3600 Input1->X:$0010F8,8 ; 1st 16-bit register
#define Input2 M3601 Input2->X:$0010F8,9
#define Input3 M3602 Input3->X:$0010F8,10
#define Input4 M3603 Input4->X:$0010F8,11
#define Input5 M3604 Input5->X:$0010F8,12
#define Input6 M3605 Input6->X:$0010F8,13
#define Input7 M3606 Input7->X:$0010F8,14
#define Input8 M3607 Input8->X:$0010F8,15
#define Input9 M3608 Input9->X:$0010F8,16
#define Input10 M3609 Input10->X:$0010F8,17
#define Input11 M3610 Input11->X:$0010F8,18
#define Input12 M3611 Input12->X:$0010F8,19
#define Input13 M3612 Input13->X:$0010F8,20
#define Input14 M3613 Input14->X:$0010F8,21
#define Input15 M3614 Input15->X:$0010F8,22
#define Input16 M3615 Input16->X:$0010F8,23
#define Input17 M3616 Input17->Y:$0010F8,8 ; 2nd 16-bit register
#define Input18 M3617 Input18->Y:$0010F8,9
#define Input19 M3618 Input19->Y:$0010F8,10
#define Input20 M3619 Input20->Y:$0010F8,11
#define Input21 M3620 Input21->Y:$0010F8,12
#define Input22 M3621 Input22->Y:$0010F8,13
#define Input23 M3622 Input23->Y:$0010F8,14
#define Input24 M3623 Input24->Y:$0010F8,15
//Outputs
#define Output1 M3625 Output1->Y:$0010F8,16
#define Output2 M3626 Output2->Y:$0010F8,17
#define Output3 M3627 Output3->Y:$0010F8,18
#define Output4 M3628 Output4->Y:$0010F8,19
#define Output5 M3629 Output5->Y:$0010F8,20
#define Output6 M3630 Output6->Y:$0010F8,21
#define Output7 M3631 Output7->Y:$0010F8,22
#define Output8 M3632 Output8->Y:$0010F8,23
#define Output9 M3633 Output9->X:$0010F9,8 ; 3rd 16-bit register
#define Output10 M3634 Output10->X:$0010F9,9
#define Output11 M3635 Output11->X:$0010F9,10
#define Output12 M3636 Output12->X:$0010F9,11
#define Output13 M3637 Output13->X:$0010F9,12
#define Output14 M3638 Output14->X:$0010F9,13
#define Output15 M3639 Output15->X:$0010F9,14
#define Output16 M3640 Output16->X:$0010F9,15
#define Output17 M3641 Output17->X:$0010F9,16
#define Output18 M3642 Output18->X:$0010F9,17
#define Output19 M3643 Output19->X:$0010F9,18
#define Output20 M3644 Output20->X:$0010F9,19
#define Output21 M3645 Output21->X:$0010F9,20
#define Output22 M3646 Output22->X:$0010F9,21
#define Output23 M3647 Output23->X:$0010F9,22
#define Output24 M3648 Output24->X:$0010F9,23
Page 46

ACC-11E User Manual
Using ACC-11E with UMAC MACRO Station 46
MS{anynode}, MI171, MI172, and MI173: 24-Bit/16-Bit Transfer
This method of transfer is not commonly used with an ACC-11E and is therefore covered more briefly.
With this method, three ACC-11E cards make full use of only two I/O nodes. Note that if less than three
cards are used, nodes will be otherwise unusable.
MS{anynode},MI171/172/173 processes 24-bit and 16-bit register transfers. It is a 48-bit variable
represented as 12 hexadecimal digits which are set up as follows (digit #1 is leftmost when constructing
the word):
Reserved, = 0
Starting I/O node register
($C0XX)
1 2 3 - 6 7 8 9 - 12Digit #:
Starting ACC-11E base address
($88XX)
Reserved, = 0 Reserved, = 0
Reserved, = 0
Example: Transferring I/O data of three ACC-11E cards (total of 144 bits) at consecutive $88C0
addresses (using low, middle, and high bytes) over MACRO using six consecutive 16-bit registers
followed by two consecutive 24-bit registers of I/O nodes ($C0B1, $C0B2, $C0B3, $C0B5, $C0B6,
$C0B7, $C0B0, and $C0B4 respectively) yields:
MS0,MI171=$00C0B00088C0
16
16
24
MACRO IC
I/O Node#: 2
2 3
Inputs (16 bits) / Outputs (8 bits)
Inputs (8 bits) / Outputs (16 bits)
16
ACC-11E ($88C0 low bytes)
Inputs (16 bits) / Outputs (8 bits)
Inputs (8 bits) / Outputs (16 bits)
ACC-11E ($88C0 middle bytes)
Inputs (24 bits) / Outputs (24 bits)
ACC-11E ($88C0 high bytes)
16-bit
Registers:
$C0B1
$C0B2
$C0B3
16
16
3
16
$C0B5
$C0B6
$C0B7
24
$C0B4$C0B024-bit Registers:
I/O Node#:
Page 47

ACC-11E User Manual
Layouts and Pinouts 47
LAYOUTS & PINOUTS
Board Layout Diagrams
Terminal Block Option
Dimensions in Inches
D-Sub Option
D-Sub connectors on board are female.
Page 48

ACC-11E User Manual
Layouts and Pinouts 48
Wiring Considerations
The inputs have an activation range from 12 V to 24 V, and can be sinking or sourcing for each of three
8-bit groups, depending on the reference to the opto circuitry. The opto-isolator IC used is a PS27054NEC-ND quad photo-transistor output type. This IC allows the current to flow from return to flag
(sourcing) or from flag to return (sinking).
The output drivers are organized in a set of three 8-bit groups. Each group (or byte) may be ordered
either with current sourcing drivers (default) or with current sinking drivers. The default configuration of
this accessory board uses UDN2981 current sourcing drivers for the three 8-bit output groups. With this
configuration, the current drawn from each output line should be limited to 100 mA at voltage levels
between 12 V and 24 V. Custom configurations are available for current sinking applications. In current
sinking configurations, one ULN2803 driver is used per each 8-bit output group. Each open collector
output line can sink up to 100 mA when pulled up to a voltage level between 12 V and 24 V (external
pull-up resistors are not supplied).
Page 49

ACC-11E User Manual
Layouts and Pinouts 49
Terminal Block Option
TB1 Top: Inputs 1 thru 12
TB2 Top: Inputs 13 thru 24
TB3 Top: Reference
Voltages
Pin #
Function
Description
Pin #
Function
Description
Pin #
Function
Description
1
Input
Input #1
1 Input
Input #13
1 Reference
Inputs 1-8
2
Input
Input #2
2 Input
Input #14
2 Reference
Inputs 9-16
3
Input
Input #3
3 Input
Input #15
3 Reference
Inputs 17-24
4
Input
Input #4
4 Input
Input #16
5
Input
Input #5
5 Input
Input #17
6
Input
Input #6
6 Input
Input #18
7
Input
Input #7
7 Input
Input #19
8
Input
Input #8
8 Input
Input #20
9
Input
Input #9
9 Input
Input #21
10
Input
Input #10
10
Input
Input #22
11
Input
Input #11
11
Input
Input #23
12
Input
Input #12
12
Input
Input #24
Note
Can be wired for sinking or sourcing.
12-24V reference for sinking / 0V reference for sourcing.
Page 50

ACC-11E User Manual
Layouts and Pinouts 50
Wiring Input Terminal Blocks
Sourcing Inputs Sinking Inputs
12-24 VDC
Power Supply
INPUT1
INPUT2
INPUT3
INPUT4
INPUT5
INPUT6
INPUT7
INPUT8
INPUT9
INPUT10
INPUT11
INPUT12
1
TB1 TOP
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
+12VDC / +24VDC
INPUT13
INPUT22
INPUT23
INPUT24
1
TB2 TOP
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
TB1 TOP
INPUT19
INPUT20
INPUT21
INPUT16
INPUT17
INPUT18
INPUT14
INPUT15
1
2
3
TB3 TOP
COM
REFERENCE 1-8
REFERENCE 9-16
REFERENCE 17-24
12-24 VDC
Power Supply
INPUT1
INPUT2
INPUT3
INPUT4
INPUT5
INPUT6
INPUT7
INPUT8
INPUT9
INPUT10
INPUT11
INPUT12
1
TB1 TOP
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
+12VDC / +24VDC
INPUT13
INPUT22
INPUT23
INPUT24
1
TB2 TOP
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
TB1 TOP
INPUT19
INPUT20
INPUT21
INPUT16
INPUT17
INPUT18
INPUT14
INPUT15
1
2
3
TB3 TOP
COM
REFERENCE 1-8
REFERENCE 9-16
REFERENCE 17-24
Page 51

ACC-11E User Manual
Layouts and Pinouts 51
TB1 Bottom:
Outputs 1 thru 12
TB2 Bottom:
Outputs 13 thru 24
TB3 Bottom:
Reference Voltages
Pin #
Function
Description
Pin #
Function
Description
Pin #
Function
Description
1
Output
Output #1
1 Output
Output #13
1 Reference
0 V
2
Output
Output #2
2 Output
Output #14
2 Voltage
12-24 VDC
3
Output
Output #3
3 Output
Output #15
3 Reference
0 V
4
Output
Output #4
4 Output
Output #16
5
Output
Output #5
5 Output
Output #17
6
Output
Output #6
6 Output
Output #18
7
Output
Output #7
7 Output
Output #19
8
Output
Output #8
8 Output
Output #20
9
Output
Output #9
9 Output
Output #21
10
Output
Output #10
10
Output
Output #22
11
Output
Output #11
11
Output
Output #23
12
Output
Output #12
12
Output
Output #24
Note
Can be ordered Sinking or Sourcing.
See E16 thru E21 jumper settings in section titled Addressing and Jumper
Settings.
Page 52

ACC-11E User Manual
Layouts and Pinouts 52
Wiring Output Terminal Blocks
Sourcing Outputs Sinking Outputs
OUTPUT1
OUTPUT2
OUTPUT3
OUTPUT4
OUTPUT5
OUTPUT6
OUTPUT7
OUTPUT8
OUTPUT9
OUTPUT10
OUTPUT11
OUTPUT12
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
+12VDC / +24VDC
TB1 BOTTOM
1
2
3
TB3 BOTTOM
REFERENCE
12-24 VDC
REFERENCE
COM
OUTPUT13
OUTPUT14
OUTPUT15
OUTPUT16
OUTPUT17
OUTPUT18
OUTPUT19
OUTPUT20
OUTPUT21
OUTPUT22
OUTPUT23
OUTPUT24
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
TB2 BOTTOM
12-24 VDC
Power Supply
OUTPUT1
OUTPUT2
OUTPUT3
OUTPUT4
OUTPUT5
OUTPUT6
OUTPUT7
OUTPUT8
OUTPUT9
OUTPUT10
OUTPUT11
OUTPUT12
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
+12VDC / +24VDC
TB1 BOTTOM
1
2
3
REFERENCE
12-24 VDC
REFERENCE
COM
OUTPUT13
OUTPUT14
OUTPUT15
OUTPUT16
OUTPUT17
OUTPUT18
OUTPUT19
OUTPUT20
OUTPUT21
OUTPUT22
OUTPUT23
OUTPUT24
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
TB2 BOTTOM
12-24 VDC
Power Supply
TB3 BOTTOM
Page 53

ACC-11E User Manual
Layouts and Pinouts 53
D-Sub Option
J1 Top: Inputs 1 thru 12
2345
9101112
67
1314
8
15
1
Front View
Pin #
Function
Description
Notes
1
Input
Input #1
Sinking/Sourcing
2
Input
Input #3 3 Input
Input #5 4 Input
Input #7 5 Input
Input #9 6 Input
Input #11
7
Reference
Reference Voltage for Inputs 1-8
12-24V for sinking / 0V for sourcing
8
Reference
Reference Voltage for Inputs 17-24
9
Input
Input #2
Sinking/Sourcing
10
Input
Input #4
11
Input
Input #6
12
Input
Input #8
13
Input
Input #10
14
Input
Input #12
15
Reference
Reference Voltage for Inputs 9-16
12-24V for sinking / 0V for sourcing
J2 Top: Inputs 13 thru 24
2345
9101112
67
1314
8
15
1
Front View
Pin #
Function
Description
Notes
1
Input
Input #13
Sinking/Sourcing
2
Input
Input #15 3 Input
Input #17 4 Input
Input #19 5 Input
Input #21 6 Input
Input #23
7
Reference
Reference Voltage for Inputs 1-8
12-24V for sinking / 0V for sourcing
8
Reference
Reference Voltage for Inputs 17-24
9
Input
Input #14
Sinking/Sourcing
10
Input
Input #16
11
Input
Input #18
12
Input
Input #20
13
Input
Input #22
14
Input
Input #24
15
Reference
Reference Voltage for Inputs 9-16
12-24V for sinking / 0V for sourcing
Page 54

ACC-11E User Manual
Layouts and Pinouts 54
Wiring Input DB15 Connectors
Sourcing Inputs
Sinking Inputs
1234568
1112131415
7
INPUTS 1-8 REF
910
INPUT1
INPUT2
INPUT3
INPUT4
INPUT5
INPUT6
INPUT7
INPUT8
INPUT9
INPUT10
INPUT11
INPUT12
INPUTS 9-16 REF
INPUTS 17-24 REF
J1 TOP
INPUT13
INPUT14
INPUT15
INPUT16
INPUT17
INPUT18
INPUT19
INPUT20
INPUT21
INPUT22
INPUT23
INPUT24
J1 TOP
12-24 VDC
Power Supply
+12VDC / +24VDC
COM
12345678
1112131415
INPUTS 1-8 REF
910
INPUT1
INPUT2
INPUT3
INPUT4
INPUT5
INPUT6
INPUT7
INPUT8
INPUT9
INPUT10
INPUT11
INPUT12
INPUTS 9-16 REF
INPUTS 17-24 REF
12-24 VDC
Power Supply
+12VDC / +24VDC
COM
1234568
1112131415
7
INPUTS 1-8 REF
910
INPUTS 9-16 REF
INPUTS 17-24 REF
J2 TOP
J2 TOP
12-24 VDC
Power Supply
+12VDC / +24VDC
COM
12345678
1112131415
INPUTS 1-8 REF
910
INPUTS 9-16 REF
INPUTS 17-24 REF
12-24 VDC
Power Supply
+12VDC / +24VDC
COM
INPUT13
INPUT14
INPUT15
INPUT16
INPUT17
INPUT18
INPUT19
INPUT20
INPUT21
INPUT22
INPUT23
INPUT24
Page 55

ACC-11E User Manual
Layouts and Pinouts 55
J1 Bottom: Outputs 1 thru 12
2345
9101112
67
1314
8
15
1
Front View
Pin #
Function
Description
Notes
1
Output
Output #1
Can be Sinking or Sourcing.
See E16 thru E21 jumper settings in
section titled Addressing and Jumper
Settings.
2
Output
Output #3 3 Output
Output #5 4 Output
Output #7 5 Output
Output #9 6 Output
Output #11 7 Reference
Reference voltage
8
Reference
Reference voltage
9
Output
Output #2
10
Output
Output #4
11
Output
Output #6
12
Output
Output #8
13
Output
Output #10
14
Output
Output #12
15
Voltage
12-24V
J2 Bottom: Outputs 13 thru 24
2345
9101112
67
1314
8
15
1
Front View
Pin #
Function
Description
Notes
1
Output
Output #13
Can be Sinking or Sourcing.
See E16 thru E21 jumper settings in
section titled Addressing and Jumper
Settings.
2
Output
Output #15 3 Output
Output #17 4 Output
Output #19 5 Output
Output #21 6 Output
Output #23 7 Reference
Reference voltage
8
Reference
Reference voltage
9
Output
Output #14
10
Output
Output #16
11
Output
Output #18
12
Output
Output #20
13
Output
Output #22
14
Output
Output #24
15
Voltage
12-24V
Page 56

ACC-11E User Manual
Layouts and Pinouts 56
Wiring Output DB15 Connectors
Sourcing Outputs
12345678
1112131415 910
12-24 VDC
REFERENCE
OUTPUT1
OUTPUT2
OUTPUT3
OUTPUT4
OUTPUT5
OUTPUT6
OUTPUT7
OUTPUT8
OUTPUT9
OUTPUT10
OUTPUT11
OUTPUT12
J1 BOTTOM
12-24 VDC
Power Supply
+12VDC / +24VDC
COM
12345678
1112131415 910
12-24 VDC
REFERENCE
OUTPUT13
OUTPUT14
OUTPUT15
OUTPUT16
OUTPUT17
OUTPUT18
OUTPUT19
OUTPUT20
OUTPUT21
OUTPUT22
OUTPUT23
OUTPUT24
J2 BOTTOM
12-24 VDC
Power Supply
+12VDC / +24VDC
COM
Sinking Outputs
12345678
1112131415 910
12-24 VDC
REFERENCE
OUTPUT1
OUTPUT2
OUTPUT3
OUTPUT4
OUTPUT5
OUTPUT6
OUTPUT7
OUTPUT8
OUTPUT9
OUTPUT10
OUTPUT11
OUTPUT12
J1 BOTTOM
12-24 VDC
Power Supply
+12VDC / +24VDC
COM
12345678
1112131415 910
12-24 VDC
REFERENCE
OUTPUT13
OUTPUT14
OUTPUT15
OUTPUT16
OUTPUT17
OUTPUT18
OUTPUT19
OUTPUT20
OUTPUT21
OUTPUT22
OUTPUT23
OUTPUT24
J2 BOTTOM
12-24 VDC
Power Supply
+12VDC / +24VDC
COM
Page 57

ACC-11E User Manual
Layouts and Pinouts 57
UBUS Pinouts
P1 UBUS
(96-Pin Header)
Front View
Pin #
Row A
Row B
Row C
Notes
1
+5Vdc
+5Vdc
+5Vdc
2
GND
GND
GND
3
BD01
DAT0
BD00
4
BD03
SEL0
BD02
5
BD05
DAT1
BD04
6
BD07
SEL1
BD06
7
BD09
DAT2
BD08
8
BD11
SEL2
BD10
9
BD13
DAT3
BD12
10
BD15
SEL3
BD14
11
BD17
DAT4
BD16
12
BD19
SEL4
BD18
13
BD21
DAT5
BD20
14
BD23
SEL5
BD22
15
BS1
DAT6
BS0
16
BA01
SEL6
BA00
17
BA03
DAT7
BA02
18
BX/Y
SEL7
BA04
19
CS3-
BA06
CS2-
20
BA05
BA07
CS4-
21
CS12-
BA08
CS10-
22
CS16-
BA09
CS14-
23
BA13
BA10
BA12
24
BRD-
BA11
BWR-
25
BS3
MEMCS0-
BS2
26
WAIT-
MEMCS1-
RESET
27
PHASE+
IREQ1-
SERVO+
28
PHASE-
IREQ2-
SERVO-
29
ANALOG
GND IREQ3-
ANALOG GND
30
-15Vdc
PWRGND
+15Vdc
31
GND
GND
GND
32
+5Vdc
+5Vdc
+5Vdc
For more details about the JEXP, see the UBUS Specification Document.
Page 58

ACC-11E User Manual
Schematics 58
SCHEMATICS
R
G
D5
BRPG1204W
1 2
4 3
R
G
D11
BRPG1204W
1 2
4 3
R
G
D12
BRPG1204W
1 2
4 3
R
G
D10
BRPG1204W
1 2
4 3
R
G
D9
BRPG1204W
1 2
4 3
R
G
D3
BRPG1204W
1 2
4 3
R
G
D4
BRPG1204W
1 2
4 3
R
G
D2
BRPG1204W
1 2
4 3
R
G
D1
BRPG1204W
1 2
4 3
R
G
D17
BRPG1204W
1 2
4 3
R
G
D16
BRPG1204W
1 2
4 3
R
G
D15
BRPG1204W
1 2
4 3
R
G
D14
BRPG1204W
1 2
4 3
R
G
D13
BRPG1204W
1 2
4 3
R
G
D24
BRPG1204W
1 2
4 3
R
G
D23
BRPG1204W
1 2
4 3
R
G
D22
BRPG1204W
1 2
4 3
R
G
D21
BRPG1204W
1 2
4 3
R
G
D8
BRPG1204W
1 2
4 3
R
G
D7
BRPG1204W
1 2
4 3
R
G
D6
BRPG1204W
1 2
4 3
RP208 10K
12
34
56
78
RP207 10K
12
34
56
78
RP206 10K
12
34
56
78
RP205 10K
12
34
56
78
RP204 10K
12
34
56
78
RP203 10K
12
34
56
78
RP202 10K
12
34
56
78
RP201 10K
12
34
56
78
R
G
D20
BRPG1204W
1 2
4 3
R
G
D19
BRPG1204W
1 2
4 3
R
G
D18
BRPG1204W
1 2
4 3
RP212 10K
12
34
56
78
RP211 10K
12
34
56
78
RP210 10K
12
34
56
78
RP209 10K
12
34
56
78
IN01
IN00
IN02
IN03
I_RET_1
IN04
IN05
IN06
IN07
I_RET_1
IN08
IN10
IN09
IN11
IN12
I_RET_2
IN13
IN14
IN15
I_RET_2
IN16
IN17
IN19
IN18
I_RET_3
IN20
IN22
IN21
I_RET_3
IN23
Page 59

ACC-11E User Manual
Schematics 59
OO
O
SAME DIRECTION
MUST NUMBER IN THE
NOTE:
321
O
321
O O
JUMP 2-TO-3 FOR SOURCING OUTPUT
JUMP 1-TO-2 FOR SINKING OUTPUT
USE `UDN2981A' FOR SOURCING OUTPUTS
USE `ULN2803A' FOR SINKING OUTPUTS
NOTE:
321
O OO
321
O OO
SAME DIRECTION
MUST NUMBER IN THE
JUMP 1-TO-2 FOR SINKING OUTPUT
USE `UDN2981A' FOR SOURCING OUTPUTS
USE `ULN2803A' FOR SINKING OUTPUTS
1
O OO
JUMP 2-TO-3 FOR SOURCING OUTPUT
O OO
SAME DIRECTION
MUST NUMBER IN THE
NOTE:
32
321
E18
E16,E17
E17
E16
JUMP 2-TO-3 FOR SOURCING OUTPUT
JUMP 1-TO-2 FOR SINKING OUTPUT
USE `UDN2981A' FOR SOURCING OUTPUTS
USE `ULN2803A' FOR SINKING OUTPUTS
E20,E21
E21
E20
E18,E19
E19
OUT38
OUT37
OUT36
OUT46
OUT45
OUT44
OUT43
OUT42
OUT41
OUT40
OUT39
OUT42
OUT41
OUT40
OUT39
OUT38
OUT37
OUT36
OUT47
OUT47
OUT46
OUT45
OUT44
OUT43
Power Trace
O+V2
OGND2
OGND2
O+V2
OGND2
OGND2
U29
78L05
VIN
8
GND
2
VOUT
1
GND3GND6GND
7
OUT24
OUT32
OUT31
OUT30
OUT29
OUT28
OUT27
OUT26
OUT25
OUT28
OUT27
OUT26
OUT25
OUT24
OUT35
OUT34
OUT33
OUT35
OUT34
OUT33
OUT32
OUT31
OUT30
OUT29
+
C43
22UF
C42
0.1UF
+
C41
22UF
C40
0.1UF
D27
1SMC33AT3
F1
10A
D28
1SMC33AT3
U28
ULN2803A
(DIP18)
(IN-SOCKET)
OR
UDN2981A
IN1
1
IN2
2
IN3
3
IN4
4
IN5
5
IN6
6
IN7
7
IN8
8
GND9V+
10
OUT8/
11
OUT7/
12
OUT6/
13
OUT5/
14
OUT4/
15
OUT3/
16
OUT2/
17
OUT1/
18
U24
ULN2803A
(DIP18)
(IN-SOCKET)
OR
UDN2981A
IN1
1
IN2
2
IN3
3
IN4
4
IN5
5
IN6
6
IN7
7
IN8
8
GND9V+
10
OUT8/
11
OUT7/
12
OUT6/
13
OUT5/
14
OUT4/
15
OUT3/
16
OUT2/
17
OUT1/
18
+
C45
22UF
C44
0.1UF
RP72
3.3K
1
2345678
9
10
RP70
470
1
2345678
9
10
U32
ULN2803A
(DIP18)
(IN-SOCKET)
OR
UDN2981A
IN1
1
IN2
2
IN3
3
IN4
4
IN5
5
IN6
6
IN7
7
IN8
8
GND9V+
10
OUT8/
11
OUT7/
12
OUT6/
13
OUT5/
14
OUT4/
15
OUT3/
16
OUT2/
17
OUT1/
18
F3
10A
F2
10A
D29
1SMC33AT3
RP74
3.3K
1
2345678
9
10
RP73
470
1
2345678
9
10
RP71
3.3K
1
2345678
9
10
E20
2
3
1
E19
2
3
1
E18
2
3
1
E17
2
3
1
E16
2
3
1
RP78
3.3K
1
2345678
9
10
RP77
3.3K
1
2345678
9
10
RP76
470
1
2345678
9
10
RP75
3.3K
1
2345678
9
10
E21
2
3
1
UD27 PS2705-1NEC
ACIN1
1
ACIN22E1
3
C1
4
UA27 PS2705-1NEC
ACIN1
1
ACIN22E1
3
C1
4
UB27 PS2705-1NEC
ACIN1
1
ACIN22E1
3
C1
4
UC27 PS2705-1NEC
ACIN1
1
ACIN22E1
3
C1
4
+5V
+5V
+5V
I/O24-
I/O25-
I/O26-
OUT24
I/O27-
I/O28-
S+V4
I/O29-
I/O30-
I/O31-
J203
HEADER 2
1
2
J202
HEADER 2
1
2
J201
HEADER 2
1
2
J200
HEADER 2
1
2
J217
HEADER 2
1
2
J216
HEADER 2
1
2
J215
HEADER 2
1
2
J211
HEADER 2
1
2
J210
HEADER 2
1
2
J209
HEADER 2
1
2
J208
HEADER 2
1
2
J207
HEADER 2
1
2
J206
HEADER 2
1
2
J205
HEADER 2
1
2
J204
HEADER 2
1
2
J226
HEADER 2
1
2
J225
HEADER 2
1
2
J224
HEADER 2
1
2
J223
HEADER 2
1
2
J222
HEADER 2
1
2
J221
HEADER 2
1
2
J220
HEADER 2
1
2
J219
HEADER 2
1
2
J218
HEADER 2
1
2
I/O32-
I/O33-
I/O34-
I/O35-
OUT36
I/O36-
I/O37-
I/O38-
S+V5
I/O39-
U33
78L05
VIN
8
GND
2
VOUT
1
GND3GND6GND
7
I/O40-
I/O41-
I/O42-
I/O43-
I/O44-
I/O45-
UD22 PS2705-1NEC
ACIN1
1
ACIN22E1
3
C1
4
I/O46-
UA22 PS2705-1NEC
ACIN1
1
ACIN22E1
3
C1
4
UB22 PS2705-1NEC
ACIN1
1
ACIN22E1
3
C1
4
I/O47-
UC22 PS2705-1NEC
ACIN1
1
ACIN22E1
3
C1
4
UD31 PS2705-1NEC
ACIN1
1
ACIN22E1
3
C1
4
UA31 PS2705-1NEC
ACIN1
1
ACIN22E1
3
C1
4
UB31 PS2705-1NEC
ACIN1
1
ACIN22E1
3
C1
4
UC31 PS2705-1NEC
ACIN1
1
ACIN22E1
3
C1
4
O+V1
OGND1
OGND2
OGND2
O+V2
S+V6
UD30 PS2705-1NEC
ACIN1
1
ACIN22E1
3
C1
4
UA30 PS2705-1NEC
ACIN1
1
ACIN22E1
3
C1
4
UB30 PS2705-1NEC
ACIN1
1
ACIN22E1
3
C1
4
UC30 PS2705-1NEC
ACIN1
1
ACIN22E1
3
C1
4
J213
1
2
3
J214
1
2
3
O+V1
OGND1
OGND1
UD23 PS2705-1NEC
ACIN1
1
ACIN22E1
3
C1
4
UA23 PS2705-1NEC
ACIN1
1
ACIN22E1
3
C1
4
UB23 PS2705-1NEC
ACIN1
1
ACIN22E1
3
C1
4
UC23 PS2705-1NEC
ACIN1
1
ACIN22E1
3
C1
4
OUT37
OUT42
OUT40
OUT35
OUT30
OUT33
OUT25
OUT46
OUT38
OUT28
OUT39
OUT43
OUT44
OUT45
OUT29
OUT32
OUT31
OUT26
OUT27
OUT34
OUT47
OUT41
UD26 PS2705-1NEC
ACIN1
1
ACIN22E1
3
C1
4
UA26 PS2705-1NEC
ACIN1
1
ACIN22E1
3
C1
4
UB26 PS2705-1NEC
ACIN1
1
ACIN22E1
3
C1
4
UC26 PS2705-1NEC
ACIN1
1
ACIN22E1
3
C1
4
J212
1
2
3
U25
78L05
VIN
8
GND
2
VOUT
1
GND3GND6GND
7
Page 60

ACC-11E User Manual
Appendix A: Using the UMAC Config Pro2 Tool 60
APPENDIX A: USING THE UMAC CONFIG PRO2 TOOL
The UMAC Config Pro2 tool can be used to auto detect and display information on the CPU and
accessories present in the UMAC. It can be launched from the Executive:
Click on “Select”, and then select the correct UMAC communication connection.
Page 61

ACC-11E User Manual
Appendix A: Using the UMAC Config Pro2 Tool 61
The ACC-11E, like the other older Type A accessories, appears in the list as “Unknown”.
Left-click on the “Unknown” accessory.
Although the precise accessory number is not detected, the base address and address jumper settings are
detected and displayed.
Page 62

ACC-11E User Manual
Appendix A: Using the UMAC Config Pro2 Tool 62
Next, the correct accessory number can be entered and a list of suggested
M-Variable definitions can be accessed or downloaded. Right click on “Unknown” and select “Define
Accessory”.
Click on the “Next” button.
Page 63

ACC-11E User Manual
Appendix A: Using the UMAC Config Pro2 Tool 63
Select the accessory type and click “Next”.
Verify the jumper settings and click “Next”.
Page 64

ACC-11E User Manual
Appendix A: Using the UMAC Config Pro2 Tool 64
Click “Next”.
Click “Finish”.
Page 65

ACC-11E User Manual
Appendix A: Using the UMAC Config Pro2 Tool 65
Click on “M-Variables”. The list of M-Variable definitions that appears can be downloaded by clicking
the “Down” icon (yellow arrow pointing down). Click on the “File” icon to locate the text file.
Page 66

ACC-11E User Manual
Appendix B: Full Turbo UMAC M-Variable Mappings 66
APPENDIX B: FULL TURBO UMAC M-VARIABLE MAPPINGS
This appendix provides suggested M-Variables for all twelve possible ACC-11E address settings.
Base Address $78C00, Low Byte
// Single-bit variables used for accessing I/O points
M7000->Y:$078C00,0,1 ;Card 1, Input 1
M7001->Y:$078C00,1,1 ;Card 1, Input 2
M7002->Y:$078C00,2,1 ;Card 1, Input 3
M7003->Y:$078C00,3,1 ;Card 1, Input 4
M7004->Y:$078C00,4,1 ;Card 1, Input 5
M7005->Y:$078C00,5,1 ;Card 1, Input 6
M7006->Y:$078C00,6,1 ;Card 1, Input 7
M7007->Y:$078C00,7,1 ;Card 1, Input 8
M7008->Y:$078C01,0,1 ;Card 1, Input 9
M7009->Y:$078C01,1,1 ;Card 1, Input 10
M7010->Y:$078C01,2,1 ;Card 1, Input 11
M7011->Y:$078C01,3,1 ;Card 1, Input 12
M7012->Y:$078C01,4,1 ;Card 1, Input 13
M7013->Y:$078C01,5,1 ;Card 1, Input 14
M7014->Y:$078C01,6,1 ;Card 1, Input 15
M7015->Y:$078C01,7,1 ;Card 1, Input 16
M7016->Y:$078C02,0,1 ;Card 1, Input 17
M7017->Y:$078C02,1,1 ;Card 1, Input 18
M7018->Y:$078C02,2,1 ;Card 1, Input 19
M7019->Y:$078C02,3,1 ;Card 1, Input 20
M7020->Y:$078C02,4,1 ;Card 1, Input 21
M7021->Y:$078C02,5,1 ;Card 1, Input 22
M7022->Y:$078C02,6,1 ;Card 1, Input 23
M7023->Y:$078C02,7,1 ;Card 1, Input 24
M7024->Y:$078C03,0,1 ;Card 1, Output 1
M7025->Y:$078C03,1,1 ;Card 1, Output 2
M7026->Y:$078C03,2,1 ;Card 1, Output 3
M7027->Y:$078C03,3,1 ;Card 1, Output 4
M7028->Y:$078C03,4,1 ;Card 1, Output 5
M7029->Y:$078C03,5,1 ;Card 1, Output 6
M7030->Y:$078C03,6,1 ;Card 1, Output 7
M7031->Y:$078C03,7,1 ;Card 1, Output 8
M7032->Y:$078C04,0,1 ;Card 1, Output 9
M7033->Y:$078C04,1,1 ;Card 1, Output 10
M7034->Y:$078C04,2,1 ;Card 1, Output 11
M7035->Y:$078C04,3,1 ;Card 1, Output 12
M7036->Y:$078C04,4,1 ;Card 1, Output 13
M7037->Y:$078C04,5,1 ;Card 1, Output 14
M7038->Y:$078C04,6,1 ;Card 1, Output 15
M7039->Y:$078C04,7,1 ;Card 1, Output 16
M7040->Y:$078C05,0,1 ;Card 1, Output 17
M7041->Y:$078C05,1,1 ;Card 1, Output 18
M7042->Y:$078C05,2,1 ;Card 1, Output 19
M7043->Y:$078C05,3,1 ;Card 1, Output 20
M7044->Y:$078C05,4,1 ;Card 1, Output 21
M7045->Y:$078C05,5,1 ;Card 1, Output 22
M7046->Y:$078C05,6,1 ;Card 1, Output 23
M7047->Y:$078C05,7,1 ;Card 1, Output 24
// Byte-wide variables used for power-on configuration
M3300->Y:$78C00,0,8,U // I/O Card 1 Inputs 00-07 as byte
M3301->Y:$78C01,0,8,U // I/O Card 1 Inputs 08-15 as byte
M3302->Y:$78C02,0,8,U // I/O Card 1 Inputs 16-23 as byte
M3303->Y:$78C03,0,8,U // I/O Card 1 Outputs 00-07 as byte
M3304->Y:$78C04,0,8,U // I/O Card 1 Outputs 08-15 as byte
M3305->Y:$78C05,0,8,U // I/O Card 1 Outputs 16-23 as byte
M3306->Y:$78C06,0,8,U // I/O Card 1 latch inputs
M3307->Y:$78C07,0,8,U // I/O Card 1 control register
Page 67

ACC-11E User Manual
Appendix B: Full Turbo UMAC M-Variable Mappings 67
Base Address $78C00, Middle Byte
// Single-bit variables used for accessing I/O points
M7048->Y:$078C00,8,1 ;Card 2, Input 1
M7049->Y:$078C00,9,1 ;Card 2, Input 2
M7050->Y:$078C00,10,1 ;Card 2, Input 3
M7051->Y:$078C00,11,1 ;Card 2, Input 4
M7052->Y:$078C00,12,1 ;Card 2, Input 5
M7053->Y:$078C00,13,1 ;Card 2, Input 6
M7054->Y:$078C00,14,1 ;Card 2, Input 7
M7055->Y:$078C00,15,1 ;Card 2, Input 8
M7056->Y:$078C01,8,1 ;Card 2, Input 9
M7057->Y:$078C01,9,1 ;Card 2, Input 10
M7058->Y:$078C01,10,1 ;Card 2, Input 11
M7059->Y:$078C01,11,1 ;Card 2, Input 12
M7060->Y:$078C01,12,1 ;Card 2, Input 13
M7061->Y:$078C01,13,1 ;Card 2, Input 14
M7062->Y:$078C01,14,1 ;Card 2, Input 15
M7063->Y:$078C01,15,1 ;Card 2, Input 16
M7064->Y:$078C02,8,1 ;Card 2, Input 17
M7065->Y:$078C02,9,1 ;Card 2, Input 18
M7066->Y:$078C02,10,1 ;Card 2, Input 19
M7067->Y:$078C02,11,1 ;Card 2, Input 20
M7068->Y:$078C02,12,1 ;Card 2, Input 21
M7069->Y:$078C02,13,1 ;Card 2, Input 22
M7070->Y:$078C02,14,1 ;Card 2, Input 23
M7071->Y:$078C02,15,1 ;Card 2, Input 24
M7072->Y:$078C03,8,1 ;Card 2, Output 1
M7073->Y:$078C03,9,1 ;Card 2, Output 2
M7074->Y:$078C03,10,1 ;Card 2, Output 3
M7075->Y:$078C03,11,1 ;Card 2, Output 4
M7076->Y:$078C03,12,1 ;Card 2, Output 5
M7077->Y:$078C03,13,1 ;Card 2, Output 6
M7078->Y:$078C03,14,1 ;Card 2, Output 7
M7079->Y:$078C03,15,1 ;Card 2, Output 8
M7080->Y:$078C04,8,1 ;Card 2, Output 9
M7081->Y:$078C04,9,1 ;Card 2, Output 10
M7082->Y:$078C04,10,1 ;Card 2, Output 11
M7083->Y:$078C04,11,1 ;Card 2, Output 12
M7084->Y:$078C04,12,1 ;Card 2, Output 13
M7085->Y:$078C04,13,1 ;Card 2, Output 14
M7086->Y:$078C04,14,1 ;Card 2, Output 15
M7087->Y:$078C04,15,1 ;Card 2, Output 16
M7088->Y:$078C05,8,1 ;Card 2, Output 17
M7089->Y:$078C05,9,1 ;Card 2, Output 18
M7090->Y:$078C05,10,1 ;Card 2, Output 19
M7091->Y:$078C05,11,1 ;Card 2, Output 20
M7092->Y:$078C05,12,1 ;Card 2, Output 21
M7093->Y:$078C05,13,1 ;Card 2, Output 22
M7094->Y:$078C05,14,1 ;Card 2, Output 23
M7095->Y:$078C05,15,1 ;Card 2, Output 24
// Byte-wide variables used for power-on configuration
M3310->Y:$78C00,8,8,U // I/O Card 2 I/O00-07 as byte
M3311->Y:$78C01,8,8,U // I/O Card 2 I/O08-15 as byte
M3312->Y:$78C02,8,8,U // I/O Card 2 I/O16-23 as byte
M3313->Y:$78C03,8,8,U // I/O Card 2 I/O24-31 as byte
M3314->Y:$78C04,8,8,U // I/O Card 2 I/O32-39 as byte
M3315->Y:$78C05,8,8,U // I/O Card 2 I/O40-47 as byte
M3316->Y:$78C06,8,8,U // I/O Card 2 latch inputs
M3317->Y:$78C07,8,8,U // I/O Card 2 control register
Page 68

ACC-11E User Manual
Appendix B: Full Turbo UMAC M-Variable Mappings 68
Base Address $78C00, High Byte
// Single-bit variables used for accessing I/O points
M7096->Y:$078C00,16,1 ;Card 3, Input 1
M7097->Y:$078C00,17,1 ;Card 3, Input 2
M7098->Y:$078C00,18,1 ;Card 3, Input 3
M7099->Y:$078C00,19,1 ;Card 3, Input 4
M7100->Y:$078C00,20,1 ;Card 3, Input 5
M7101->Y:$078C00,21,1 ;Card 3, Input 6
M7102->Y:$078C00,22,1 ;Card 3, Input 7
M7103->Y:$078C00,23,1 ;Card 3, Input 8
M7104->Y:$078C01,16,1 ;Card 3, Input 9
M7105->Y:$078C01,17,1 ;Card 3, Input 10
M7106->Y:$078C01,18,1 ;Card 3, Input 11
M7107->Y:$078C01,19,1 ;Card 3, Input 12
M7108->Y:$078C01,20,1 ;Card 3, Input 13
M7109->Y:$078C01,21,1 ;Card 3, Input 14
M7110->Y:$078C01,22,1 ;Card 3, Input 15
M7111->Y:$078C01,23,1 ;Card 3, Input 16
M7112->Y:$078C02,16,1 ;Card 3, Input 17
M7113->Y:$078C02,17,1 ;Card 3, Input 18
M7114->Y:$078C02,18,1 ;Card 3, Input 19
M7115->Y:$078C02,19,1 ;Card 3, Input 20
M7116->Y:$078C02,20,1 ;Card 3, Input 21
M7117->Y:$078C02,21,1 ;Card 3, Input 22
M7118->Y:$078C02,22,1 ;Card 3, Input 23
M7119->Y:$078C02,23,1 ;Card 3, Input 24
M7120->Y:$078C03,16,1 ;Card 3, Output 1
M7121->Y:$078C03,17,1 ;Card 3, Output 2
M7122->Y:$078C03,18,1 ;Card 3, Output 3
M7123->Y:$078C03,19,1 ;Card 3, Output 4
M7124->Y:$078C03,20,1 ;Card 3, Output 5
M7125->Y:$078C03,21,1 ;Card 3, Output 6
M7126->Y:$078C03,22,1 ;Card 3, Output 7
M7127->Y:$078C03,23,1 ;Card 3, Output 8
M7128->Y:$078C04,16,1 ;Card 3, Output 9
M7129->Y:$078C04,17,1 ;Card 3, Output 10
M7130->Y:$078C04,18,1 ;Card 3, Output 11
M7131->Y:$078C04,19,1 ;Card 3, Output 12
M7132->Y:$078C04,20,1 ;Card 3, Output 13
M7133->Y:$078C04,21,1 ;Card 3, Output 14
M7134->Y:$078C04,22,1 ;Card 3, Output 15
M7135->Y:$078C04,23,1 ;Card 3, Output 16
M7136->Y:$078C05,16,1 ;Card 3, Output 17
M7137->Y:$078C05,17,1 ;Card 3, Output 18
M7138->Y:$078C05,18,1 ;Card 3, Output 19
M7139->Y:$078C05,19,1 ;Card 3, Output 20
M7140->Y:$078C05,20,1 ;Card 3, Output 21
M7141->Y:$078C05,21,1 ;Card 3, Output 22
M7142->Y:$078C05,22,1 ;Card 3, Output 23
M7143->Y:$078C05,23,1 ;Card 3, Output 24
// Byte-wide variables used for power-on configuration
M3320->Y:$78C00,16,8,U // I/O Card 3 I/O00-07 as byte
M3321->Y:$78C01,16,8,U // I/O Card 3 I/O08-15 as byte
M3322->Y:$78C02,16,8,U // I/O Card 3 I/O16-23 as byte
M3323->Y:$78C03,16,8,U // I/O Card 3 I/O24-31 as byte
M3324->Y:$78C04,16,8,U // I/O Card 3 I/O32-39 as byte
M3325->Y:$78C05,16,8,U // I/O Card 3 I/O40-47 as byte
M3326->Y:$78C06,16,8,U // I/O Card 3 latch inputs
M3327->Y:$78C07,16,8,U // I/O Card 3 control register
Page 69

ACC-11E User Manual
Appendix B: Full Turbo UMAC M-Variable Mappings 69
Base Address $78D00, Low Byte
// Single-bit variables used for accessing I/O points
M7144->Y:$078D00,0,1 ;Card 4, Input 1
M7145->Y:$078D00,1,1 ;Card 4, Input 2
M7146->Y:$078D00,2,1 ;Card 4, Input 3
M7147->Y:$078D00,3,1 ;Card 4, Input 4
M7148->Y:$078D00,4,1 ;Card 4, Input 5
M7149->Y:$078D00,5,1 ;Card 4, Input 6
M7150->Y:$078D00,6,1 ;Card 4, Input 7
M7151->Y:$078D00,7,1 ;Card 4, Input 8
M7152->Y:$078D01,0,1 ;Card 4, Input 9
M7153->Y:$078D01,1,1 ;Card 4, Input 10
M7154->Y:$078D01,2,1 ;Card 4, Input 11
M7155->Y:$078D01,3,1 ;Card 4, Input 12
M7156->Y:$078D01,4,1 ;Card 4, Input 13
M7157->Y:$078D01,5,1 ;Card 4, Input 14
M7158->Y:$078D01,6,1 ;Card 4, Input 15
M7159->Y:$078D01,7,1 ;Card 4, Input 16
M7160->Y:$078D02,0,1 ;Card 4, Input 17
M7161->Y:$078D02,1,1 ;Card 4, Input 18
M7162->Y:$078D02,2,1 ;Card 4, Input 19
M7163->Y:$078D02,3,1 ;Card 4, Input 20
M7164->Y:$078D02,4,1 ;Card 4, Input 21
M7165->Y:$078D02,5,1 ;Card 4, Input 22
M7166->Y:$078D02,6,1 ;Card 4, Input 23
M7167->Y:$078D02,7,1 ;Card 4, Input 24
M7168->Y:$078D03,0,1 ;Card 4, Output 1
M7169->Y:$078D03,1,1 ;Card 4, Output 2
M7170->Y:$078D03,2,1 ;Card 4, Output 3
M7171->Y:$078D03,3,1 ;Card 4, Output 4
M7172->Y:$078D03,4,1 ;Card 4, Output 5
M7173->Y:$078D03,5,1 ;Card 4, Output 6
M7174->Y:$078D03,6,1 ;Card 4, Output 7
M7175->Y:$078D03,7,1 ;Card 4, Output 8
M7176->Y:$078D04,0,1 ;Card 4, Output 9
M7177->Y:$078D04,1,1 ;Card 4, Output 10
M7178->Y:$078D04,2,1 ;Card 4, Output 11
M7179->Y:$078D04,3,1 ;Card 4, Output 12
M7180->Y:$078D04,4,1 ;Card 4, Output 13
M7181->Y:$078D04,5,1 ;Card 4, Output 14
M7182->Y:$078D04,6,1 ;Card 4, Output 15
M7183->Y:$078D04,7,1 ;Card 4, Output 16
M7184->Y:$078D05,0,1 ;Card 4, Output 17
M7185->Y:$078D05,1,1 ;Card 4, Output 18
M7186->Y:$078D05,2,1 ;Card 4, Output 19
M7187->Y:$078D05,3,1 ;Card 4, Output 20
M7188->Y:$078D05,4,1 ;Card 4, Output 21
M7189->Y:$078D05,5,1 ;Card 4, Output 22
M7190->Y:$078D05,6,1 ;Card 4, Output 23
M7191->Y:$078D05,7,1 ;Card 4, Output 24
// Byte-wide variables used for power-on configuration
M3330->Y:$78D00,0,8,U // I/O Card 4 I/O00-07 as byte
M3331->Y:$78D01,0,8,U // I/O Card 4 I/O08-15 as byte
M3332->Y:$78D02,0,8,U // I/O Card 4 I/O16-23 as byte
M3333->Y:$78D03,0,8,U // I/O Card 4 I/O24-31 as byte
M3334->Y:$78D04,0,8,U // I/O Card 4 I/O32-39 as byte
M3335->Y:$78D05,0,8,U // I/O Card 4 I/O40-47 as byte
M3336->Y:$78D06,0,8,U // I/O Card 4 latch inputs
M3337->Y:$78D07,0,8,U // I/O Card 4 control register
Page 70

ACC-11E User Manual
Appendix B: Full Turbo UMAC M-Variable Mappings 70
Base Address $78D00, Middle Byte
// Single-bit variables used for accessing I/O points
M7192->Y:$078D00,8,1 ;Card 5, Input 1
M7193->Y:$078D00,9,1 ;Card 5, Input 2
M7194->Y:$078D00,10,1 ;Card 5, Input 3
M7195->Y:$078D00,11,1 ;Card 5, Input 4
M7196->Y:$078D00,12,1 ;Card 5, Input 5
M7197->Y:$078D00,13,1 ;Card 5, Input 6
M7198->Y:$078D00,14,1 ;Card 5, Input 7
M7199->Y:$078D00,15,1 ;Card 5, Input 8
M7200->Y:$078D01,8,1 ;Card 5, Input 9
M7201->Y:$078D01,9,1 ;Card 5, Input 10
M7202->Y:$078D01,10,1 ;Card 5, Input 11
M7203->Y:$078D01,11,1 ;Card 5, Input 12
M7204->Y:$078D01,12,1 ;Card 5, Input 13
M7205->Y:$078D01,13,1 ;Card 5, Input 14
M7206->Y:$078D01,14,1 ;Card 5, Input 15
M7207->Y:$078D01,15,1 ;Card 5, Input 16
M7208->Y:$078D02,8,1 ;Card 5, Input 17
M7209->Y:$078D02,9,1 ;Card 5, Input 18
M7210->Y:$078D02,10,1 ;Card 5, Input 19
M7211->Y:$078D02,11,1 ;Card 5, Input 20
M7212->Y:$078D02,12,1 ;Card 5, Input 21
M7213->Y:$078D02,13,1 ;Card 5, Input 22
M7214->Y:$078D02,14,1 ;Card 5, Input 23
M7215->Y:$078D02,15,1 ;Card 5, Input 24
M7216->Y:$078D03,8,1 ;Card 5, Output 1
M7217->Y:$078D03,9,1 ;Card 5, Output 2
M7218->Y:$078D03,10,1 ;Card 5, Output 3
M7219->Y:$078D03,11,1 ;Card 5, Output 4
M7220->Y:$078D03,12,1 ;Card 5, Output 5
M7221->Y:$078D03,13,1 ;Card 5, Output 6
M7222->Y:$078D03,14,1 ;Card 5, Output 7
M7223->Y:$078D03,15,1 ;Card 5, Output 8
M7224->Y:$078D04,8,1 ;Card 5, Output 9
M7225->Y:$078D04,9,1 ;Card 5, Output 10
M7226->Y:$078D04,10,1 ;Card 5, Output 11
M7227->Y:$078D04,11,1 ;Card 5, Output 12
M7228->Y:$078D04,12,1 ;Card 5, Output 13
M7229->Y:$078D04,13,1 ;Card 5, Output 14
M7230->Y:$078D04,14,1 ;Card 5, Output 15
M7231->Y:$078D04,15,1 ;Card 5, Output 16
M7232->Y:$078D05,8,1 ;Card 5, Output 17
M7233->Y:$078D05,9,1 ;Card 5, Output 18
M7234->Y:$078D05,10,1 ;Card 5, Output 19
M7235->Y:$078D05,11,1 ;Card 5, Output 20
M7236->Y:$078D05,12,1 ;Card 5, Output 21
M7237->Y:$078D05,13,1 ;Card 5, Output 22
M7238->Y:$078D05,14,1 ;Card 5, Output 23
M7239->Y:$078D05,15,1 ;Card 5, Output 24
// Byte-wide variables used for power-on configuration
M3340->Y:$78D00,8,8,U // I/O Card 5 I/O00-07 as byte
M3341->Y:$78D01,8,8,U // I/O Card 5 I/O08-15 as byte
M3342->Y:$78D02,8,8,U // I/O Card 5 I/O16-23 as byte
M3343->Y:$78D03,8,8,U // I/O Card 5 I/O24-31 as byte
M3344->Y:$78D04,8,8,U // I/O Card 5 I/O32-39 as byte
M3345->Y:$78D05,8,8,U // I/O Card 5 I/O40-47 as byte
M3346->Y:$78D06,8,8,U // I/O Card 5 latch inputs
M3347->Y:$78D07,8,8,U // I/O Card 5 control register
Page 71

ACC-11E User Manual
Appendix B: Full Turbo UMAC M-Variable Mappings 71
Base Address $78D00, High Byte
// Single-bit variables used for accessing I/O points
M7240->Y:$078D00,16,1 ;Card 6, Input 1
M7241->Y:$078D00,17,1 ;Card 6, Input 2
M7242->Y:$078D00,18,1 ;Card 6, Input 3
M7243->Y:$078D00,19,1 ;Card 6, Input 4
M7244->Y:$078D00,20,1 ;Card 6, Input 5
M7245->Y:$078D00,21,1 ;Card 6, Input 6
M7246->Y:$078D00,22,1 ;Card 6, Input 7
M7247->Y:$078D00,23,1 ;Card 6, Input 8
M7248->Y:$078D01,16,1 ;Card 6, Input 9
M7249->Y:$078D01,17,1 ;Card 6, Input 10
M7250->Y:$078D01,18,1 ;Card 6, Input 11
M7251->Y:$078D01,19,1 ;Card 6, Input 12
M7252->Y:$078D01,20,1 ;Card 6, Input 13
M7253->Y:$078D01,21,1 ;Card 6, Input 14
M7254->Y:$078D01,22,1 ;Card 6, Input 15
M7255->Y:$078D01,23,1 ;Card 6, Input 16
M7256->Y:$078D02,16,1 ;Card 6, Input 17
M7257->Y:$078D02,17,1 ;Card 6, Input 18
M7258->Y:$078D02,18,1 ;Card 6, Input 19
M7259->Y:$078D02,19,1 ;Card 6, Input 20
M7260->Y:$078D02,20,1 ;Card 6, Input 21
M7261->Y:$078D02,21,1 ;Card 6, Input 22
M7262->Y:$078D02,22,1 ;Card 6, Input 23
M7263->Y:$078D02,23,1 ;Card 6, Input 24
M7264->Y:$078D03,16,1 ;Card 6, Output 1
M7265->Y:$078D03,17,1 ;Card 6, Output 2
M7266->Y:$078D03,18,1 ;Card 6, Output 3
M7267->Y:$078D03,19,1 ;Card 6, Output 4
M7268->Y:$078D03,20,1 ;Card 6, Output 5
M7269->Y:$078D03,21,1 ;Card 6, Output 6
M7270->Y:$078D03,22,1 ;Card 6, Output 7
M7271->Y:$078D03,23,1 ;Card 6, Output 8
M7272->Y:$078D04,16,1 ;Card 6, Output 9
M7273->Y:$078D04,17,1 ;Card 6, Output 10
M7274->Y:$078D04,18,1 ;Card 6, Output 11
M7275->Y:$078D04,19,1 ;Card 6, Output 12
M7276->Y:$078D04,20,1 ;Card 6, Output 13
M7277->Y:$078D04,21,1 ;Card 6, Output 14
M7278->Y:$078D04,22,1 ;Card 6, Output 15
M7279->Y:$078D04,23,1 ;Card 6, Output 16
M7280->Y:$078D05,16,1 ;Card 6, Output 17
M7281->Y:$078D05,17,1 ;Card 6, Output 18
M7282->Y:$078D05,18,1 ;Card 6, Output 19
M7283->Y:$078D05,19,1 ;Card 6, Output 20
M7284->Y:$078D05,20,1 ;Card 6, Output 21
M7285->Y:$078D05,21,1 ;Card 6, Output 22
M7286->Y:$078D05,22,1 ;Card 6, Output 23
M7287->Y:$078D05,23,1 ;Card 6, Output 24
// Byte-wide variables used for power-on configuration
M3350->Y:$78D00,16,8,U // I/O Card 6 I/O00-07 as byte
M3351->Y:$78D01,16,8,U // I/O Card 6 I/O08-15 as byte
M3352->Y:$78D02,16,8,U // I/O Card 6 I/O16-23 as byte
M3353->Y:$78D03,16,8,U // I/O Card 6 I/O24-31 as byte
M3354->Y:$78D04,16,8,U // I/O Card 6 I/O32-39 as byte
M3355->Y:$78D05,16,8,U // I/O Card 6 I/O40-47 as byte
M3356->Y:$78D06,16,8,U // I/O Card 6 latch inputs
M3357->Y:$78D07,16,8,U // I/O Card 6 control register
Page 72

ACC-11E User Manual
Appendix B: Full Turbo UMAC M-Variable Mappings 72
Base Address $78E00, Low Byte
// Single-bit variables used for accessing I/O points
M7288->Y:$078E00,0,1 ;Card 7, Input 1
M7289->Y:$078E00,1,1 ;Card 7, Input 2
M7290->Y:$078E00,2,1 ;Card 7, Input 3
M7291->Y:$078E00,3,1 ;Card 7, Input 4
M7292->Y:$078E00,4,1 ;Card 7, Input 5
M7293->Y:$078E00,5,1 ;Card 7, Input 6
M7294->Y:$078E00,6,1 ;Card 7, Input 7
M7295->Y:$078E00,7,1 ;Card 7, Input 8
M7296->Y:$078E01,0,1 ;Card 7, Input 9
M7297->Y:$078E01,1,1 ;Card 7, Input 10
M7298->Y:$078E01,2,1 ;Card 7, Input 11
M7299->Y:$078E01,3,1 ;Card 7, Input 12
M7300->Y:$078E01,4,1 ;Card 7, Input 13
M7301->Y:$078E01,5,1 ;Card 7, Input 14
M7302->Y:$078E01,6,1 ;Card 7, Input 15
M7303->Y:$078E01,7,1 ;Card 7, Input 16
M7304->Y:$078E02,0,1 ;Card 7, Input 17
M7305->Y:$078E02,1,1 ;Card 7, Input 18
M7306->Y:$078E02,2,1 ;Card 7, Input 19
M7307->Y:$078E02,3,1 ;Card 7, Input 20
M7308->Y:$078E02,4,1 ;Card 7, Input 21
M7309->Y:$078E02,5,1 ;Card 7, Input 22
M7310->Y:$078E02,6,1 ;Card 7, Input 23
M7311->Y:$078E02,7,1 ;Card 7, Input 24
M7312->Y:$078E03,0,1 ;Card 7, Output 1
M7313->Y:$078E03,1,1 ;Card 7, Output 2
M7314->Y:$078E03,2,1 ;Card 7, Output 3
M7315->Y:$078E03,3,1 ;Card 7, Output 4
M7316->Y:$078E03,4,1 ;Card 7, Output 5
M7317->Y:$078E03,5,1 ;Card 7, Output 6
M7318->Y:$078E03,6,1 ;Card 7, Output 7
M7319->Y:$078E03,7,1 ;Card 7, Output 8
M7320->Y:$078E04,0,1 ;Card 7, Output 9
M7321->Y:$078E04,1,1 ;Card 7, Output 10
M7322->Y:$078E04,2,1 ;Card 7, Output 11
M7323->Y:$078E04,3,1 ;Card 7, Output 12
M7324->Y:$078E04,4,1 ;Card 7, Output 13
M7325->Y:$078E04,5,1 ;Card 7, Output 14
M7326->Y:$078E04,6,1 ;Card 7, Output 15
M7327->Y:$078E04,7,1 ;Card 7, Output 16
M7328->Y:$078E05,0,1 ;Card 7, Output 17
M7329->Y:$078E05,1,1 ;Card 7, Output 18
M7330->Y:$078E05,2,1 ;Card 7, Output 19
M7331->Y:$078E05,3,1 ;Card 7, Output 20
M7332->Y:$078E05,4,1 ;Card 7, Output 21
M7333->Y:$078E05,5,1 ;Card 7, Output 22
M7334->Y:$078E05,6,1 ;Card 7, Output 23
M7335->Y:$078E05,7,1 ;Card 7, Output 24
// Byte-wide variables used for power-on configuration
M3360->Y:$78E00,0,8,U // I/O Card 7 I/O00-07 as byte
M3361->Y:$78E01,0,8,U // I/O Card 7 I/O08-15 as byte
M3362->Y:$78E02,0,8,U // I/O Card 7 I/O16-23 as byte
M3363->Y:$78E03,0,8,U // I/O Card 7 I/O24-31 as byte
M3364->Y:$78E04,0,8,U // I/O Card 7 I/O32-39 as byte
M3365->Y:$78E05,0,8,U // I/O Card 7 I/O40-47 as byte
M3366->Y:$78E06,0,8,U // I/O Card 7 latch inputs
M3367->Y:$78E07,0,8,U // I/O Card 7 control register
Page 73

ACC-11E User Manual
Appendix B: Full Turbo UMAC M-Variable Mappings 73
Base Address $78E00, Middle Byte
// Single-bit variables used for accessing I/O points
M7336->Y:$078E00,8,1 ;Card 8, Input 1
M7337->Y:$078E00,9,1 ;Card 8, Input 2
M7338->Y:$078E00,10,1 ;Card 8, Input 3
M7339->Y:$078E00,11,1 ;Card 8, Input 4
M7340->Y:$078E00,12,1 ;Card 8, Input 5
M7341->Y:$078E00,13,1 ;Card 8, Input 6
M7342->Y:$078E00,14,1 ;Card 8, Input 7
M7343->Y:$078E00,15,1 ;Card 8, Input 8
M7344->Y:$078E01,8,1 ;Card 8, Input 9
M7345->Y:$078E01,9,1 ;Card 8, Input 10
M7346->Y:$078E01,10,1 ;Card 8, Input 11
M7347->Y:$078E01,11,1 ;Card 8, Input 12
M7348->Y:$078E01,12,1 ;Card 8, Input 13
M7349->Y:$078E01,13,1 ;Card 8, Input 14
M7350->Y:$078E01,14,1 ;Card 8, Input 15
M7351->Y:$078E01,15,1 ;Card 8, Input 16
M7352->Y:$078E02,8,1 ;Card 8, Input 17
M7353->Y:$078E02,9,1 ;Card 8, Input 18
M7354->Y:$078E02,10,1 ;Card 8, Input 19
M7355->Y:$078E02,11,1 ;Card 8, Input 20
M7356->Y:$078E02,12,1 ;Card 8, Input 21
M7357->Y:$078E02,13,1 ;Card 8, Input 22
M7358->Y:$078E02,14,1 ;Card 8, Input 23
M7359->Y:$078E02,15,1 ;Card 8, Input 24
M7360->Y:$078E03,8,1 ;Card 8, Output 1
M7361->Y:$078E03,9,1 ;Card 8, Output 2
M7362->Y:$078E03,10,1 ;Card 8, Output 3
M7363->Y:$078E03,11,1 ;Card 8, Output 4
M7364->Y:$078E03,12,1 ;Card 8, Output 5
M7365->Y:$078E03,13,1 ;Card 8, Output 6
M7366->Y:$078E03,14,1 ;Card 8, Output 7
M7367->Y:$078E03,15,1 ;Card 8, Output 8
M7368->Y:$078E04,8,1 ;Card 8, Output 9
M7369->Y:$078E04,9,1 ;Card 8, Output 10
M7370->Y:$078E04,10,1 ;Card 8, Output 11
M7371->Y:$078E04,11,1 ;Card 8, Output 12
M7372->Y:$078E04,12,1 ;Card 8, Output 13
M7373->Y:$078E04,13,1 ;Card 8, Output 14
M7374->Y:$078E04,14,1 ;Card 8, Output 15
M7375->Y:$078E04,15,1 ;Card 8, Output 16
M7376->Y:$078E05,8,1 ;Card 8, Output 17
M7377->Y:$078E05,9,1 ;Card 8, Output 18
M7378->Y:$078E05,10,1 ;Card 8, Output 19
M7379->Y:$078E05,11,1 ;Card 8, Output 20
M7380->Y:$078E05,12,1 ;Card 8, Output 21
M7381->Y:$078E05,13,1 ;Card 8, Output 22
M7382->Y:$078E05,14,1 ;Card 8, Output 23
M7383->Y:$078E05,15,1 ;Card 8, Output 24
// Byte-wide variables used for power-on configuration
M3370->Y:$78E00,8,8,U // I/O Card 8 I/O00-07 as byte
M3371->Y:$78E01,8,8,U // I/O Card 8 I/O08-15 as byte
M3372->Y:$78E02,8,8,U // I/O Card 8 I/O16-23 as byte
M3373->Y:$78E03,8,8,U // I/O Card 8 I/O24-31 as byte
M3374->Y:$78E04,8,8,U // I/O Card 8 I/O32-39 as byte
M3375->Y:$78E05,8,8,U // I/O Card 8 I/O40-47 as byte
M3376->Y:$78E06,8,8,U // I/O Card 8 latch inputs
M3377->Y:$78E07,8,8,U // I/O Card 8 control register
Page 74

ACC-11E User Manual
Appendix B: Full Turbo UMAC M-Variable Mappings 74
Base Address $78E00, High Byte
// Single-bit variables used for accessing I/O points
M7384->Y:$078E00,16,1 ;Card 9, Input 1
M7385->Y:$078E00,17,1 ;Card 9, Input 2
M7386->Y:$078E00,18,1 ;Card 9, Input 3
M7387->Y:$078E00,19,1 ;Card 9, Input 4
M7388->Y:$078E00,20,1 ;Card 9, Input 5
M7389->Y:$078E00,21,1 ;Card 9, Input 6
M7390->Y:$078E00,22,1 ;Card 9, Input 7
M7391->Y:$078E00,23,1 ;Card 9, Input 8
M7392->Y:$078E01,16,1 ;Card 9, Input 9
M7393->Y:$078E01,17,1 ;Card 9, Input 10
M7394->Y:$078E01,18,1 ;Card 9, Input 11
M7395->Y:$078E01,19,1 ;Card 9, Input 12
M7396->Y:$078E01,20,1 ;Card 9, Input 13
M7397->Y:$078E01,21,1 ;Card 9, Input 14
M7398->Y:$078E01,22,1 ;Card 9, Input 15
M7399->Y:$078E01,23,1 ;Card 9, Input 16
M7400->Y:$078E02,16,1 ;Card 9, Input 17
M7401->Y:$078E02,17,1 ;Card 9, Input 18
M7402->Y:$078E02,18,1 ;Card 9, Input 19
M7403->Y:$078E02,19,1 ;Card 9, Input 20
M7404->Y:$078E02,20,1 ;Card 9, Input 21
M7405->Y:$078E02,21,1 ;Card 9, Input 22
M7406->Y:$078E02,22,1 ;Card 9, Input 23
M7407->Y:$078E02,23,1 ;Card 9, Input 24
M7408->Y:$078E03,16,1 ;Card 9, Output 1
M7409->Y:$078E03,17,1 ;Card 9, Output 2
M7410->Y:$078E03,18,1 ;Card 9, Output 3
M7411->Y:$078E03,19,1 ;Card 9, Output 4
M7412->Y:$078E03,20,1 ;Card 9, Output 5
M7413->Y:$078E03,21,1 ;Card 9, Output 6
M7414->Y:$078E03,22,1 ;Card 9, Output 7
M7415->Y:$078E03,23,1 ;Card 9, Output 8
M7416->Y:$078E04,16,1 ;Card 9, Output 9
M7417->Y:$078E04,17,1 ;Card 9, Output 10
M7418->Y:$078E04,18,1 ;Card 9, Output 11
M7419->Y:$078E04,19,1 ;Card 9, Output 12
M7420->Y:$078E04,20,1 ;Card 9, Output 13
M7421->Y:$078E04,21,1 ;Card 9, Output 14
M7422->Y:$078E04,22,1 ;Card 9, Output 15
M7423->Y:$078E04,23,1 ;Card 9, Output 16
M7424->Y:$078E05,16,1 ;Card 9, Output 17
M7425->Y:$078E05,17,1 ;Card 9, Output 18
M7426->Y:$078E05,18,1 ;Card 9, Output 19
M7427->Y:$078E05,19,1 ;Card 9, Output 20
M7428->Y:$078E05,20,1 ;Card 9, Output 21
M7429->Y:$078E05,21,1 ;Card 9, Output 22
M7430->Y:$078E05,22,1 ;Card 9, Output 23
M7431->Y:$078E05,23,1 ;Card 9, Output 24
// Byte-wide variables used for power-on configuration
M3380->Y:$78E00,16,8,U // I/O Card 9 I/O00-07 as byte
M3381->Y:$78E01,16,8,U // I/O Card 9 I/O08-15 as byte
M3382->Y:$78E02,16,8,U // I/O Card 9 I/O16-23 as byte
M3383->Y:$78E03,16,8,U // I/O Card 9 I/O24-31 as byte
M3384->Y:$78E04,16,8,U // I/O Card 9 I/O32-39 as byte
M3385->Y:$78E05,16,8,U // I/O Card 9 I/O40-47 as byte
M3386->Y:$78E06,16,8,U // I/O Card 9 latch inputs
M3387->Y:$78E07,16,8,U // I/O Card 9 control register
Page 75

ACC-11E User Manual
Appendix B: Full Turbo UMAC M-Variable Mappings 75
Base Address $78F00, Low Byte
// Single-bit variables used for accessing I/O points
M7432->Y:$078F00,0,1 ;Card 10, Input 1
M7433->Y:$078F00,1,1 ;Card 10, Input 2
M7434->Y:$078F00,2,1 ;Card 10, Input 3
M7435->Y:$078F00,3,1 ;Card 10, Input 4
M7436->Y:$078F00,4,1 ;Card 10, Input 5
M7437->Y:$078F00,5,1 ;Card 10, Input 6
M7438->Y:$078F00,6,1 ;Card 10, Input 7
M7439->Y:$078F00,7,1 ;Card 10, Input 8
M7440->Y:$078F01,0,1 ;Card 10, Input 9
M7441->Y:$078F01,1,1 ;Card 10, Input 10
M7442->Y:$078F01,2,1 ;Card 10, Input 11
M7443->Y:$078F01,3,1 ;Card 10, Input 12
M7444->Y:$078F01,4,1 ;Card 10, Input 13
M7445->Y:$078F01,5,1 ;Card 10, Input 14
M7446->Y:$078F01,6,1 ;Card 10, Input 15
M7447->Y:$078F01,7,1 ;Card 10, Input 16
M7448->Y:$078F02,0,1 ;Card 10, Input 17
M7449->Y:$078F02,1,1 ;Card 10, Input 18
M7450->Y:$078F02,2,1 ;Card 10, Input 19
M7451->Y:$078F02,3,1 ;Card 10, Input 20
M7452->Y:$078F02,4,1 ;Card 10, Input 21
M7453->Y:$078F02,5,1 ;Card 10, Input 22
M7454->Y:$078F02,6,1 ;Card 10, Input 23
M7455->Y:$078F02,7,1 ;Card 10, Input 24
M7456->Y:$078F03,0,1 ;Card 10, Output 1
M7457->Y:$078F03,1,1 ;Card 10, Output 2
M7458->Y:$078F03,2,1 ;Card 10, Output 3
M7459->Y:$078F03,3,1 ;Card 10, Output 4
M7460->Y:$078F03,4,1 ;Card 10, Output 5
M7461->Y:$078F03,5,1 ;Card 10, Output 6
M7462->Y:$078F03,6,1 ;Card 10, Output 7
M7463->Y:$078F03,7,1 ;Card 10, Output 8
M7464->Y:$078F04,0,1 ;Card 10, Output 9
M7465->Y:$078F04,1,1 ;Card 10, Output 10
M7466->Y:$078F04,2,1 ;Card 10, Output 11
M7467->Y:$078F04,3,1 ;Card 10, Output 12
M7468->Y:$078F04,4,1 ;Card 10, Output 13
M7469->Y:$078F04,5,1 ;Card 10, Output 14
M7470->Y:$078F04,6,1 ;Card 10, Output 15
M7471->Y:$078F04,7,1 ;Card 10, Output 16
M7472->Y:$078F05,0,1 ;Card 10, Output 17
M7473->Y:$078F05,1,1 ;Card 10, Output 18
M7474->Y:$078F05,2,1 ;Card 10, Output 19
M7475->Y:$078F05,3,1 ;Card 10, Output 20
M7476->Y:$078F05,4,1 ;Card 10, Output 21
M7477->Y:$078F05,5,1 ;Card 10, Output 22
M7478->Y:$078F05,6,1 ;Card 10, Output 23
M7479->Y:$078F05,7,1 ;Card 10, Output 24
// Byte-wide variables used for power-on configuration
M3390->Y:$78F00,0,8,U // I/O Card 10 I/O00-07 as byte
M3391->Y:$78F01,0,8,U // I/O Card 10 I/O08-15 as byte
M3392->Y:$78F02,0,8,U // I/O Card 10 I/O16-23 as byte
M3393->Y:$78F03,0,8,U // I/O Card 10 I/O24-31 as byte
M3394->Y:$78F04,0,8,U // I/O Card 10 I/O32-39 as byte
M3395->Y:$78F05,0,8,U // I/O Card 10 I/O40-47 as byte
M3396->Y:$78F06,0,8,U // I/O Card 10 latch inputs
M3397->Y:$78F07,0,8,U // I/O Card 10 control register
Page 76

ACC-11E User Manual
Appendix B: Full Turbo UMAC M-Variable Mappings 76
Base Address $78F00, Middle Byte
// Single-bit variables used for accessing I/O points
M7480->Y:$078F00,8,1 ;Card 11, Input 1
M7481->Y:$078F00,9,1 ;Card 11, Input 2
M7482->Y:$078F00,10,1 ;Card 11, Input 3
M7483->Y:$078F00,11,1 ;Card 11, Input 4
M7484->Y:$078F00,12,1 ;Card 11, Input 5
M7485->Y:$078F00,13,1 ;Card 11, Input 6
M7486->Y:$078F00,14,1 ;Card 11, Input 7
M7487->Y:$078F00,15,1 ;Card 11, Input 8
M7488->Y:$078F01,8,1 ;Card 11, Input 9
M7489->Y:$078F01,9,1 ;Card 11, Input 10
M7490->Y:$078F01,10,1 ;Card 11, Input 11
M7491->Y:$078F01,11,1 ;Card 11, Input 12
M7492->Y:$078F01,12,1 ;Card 11, Input 13
M7493->Y:$078F01,13,1 ;Card 11, Input 14
M7494->Y:$078F01,14,1 ;Card 11, Input 15
M7495->Y:$078F01,15,1 ;Card 11, Input 16
M7496->Y:$078F02,8,1 ;Card 11, Input 17
M7497->Y:$078F02,9,1 ;Card 11, Input 18
M7498->Y:$078F02,10,1 ;Card 11, Input 19
M7499->Y:$078F02,11,1 ;Card 11, Input 20
M7500->Y:$078F02,12,1 ;Card 11, Input 21
M7501->Y:$078F02,13,1 ;Card 11, Input 22
M7502->Y:$078F02,14,1 ;Card 11, Input 23
M7503->Y:$078F02,15,1 ;Card 11, Input 24
M7504->Y:$078F03,8,1 ;Card 11, Output 1
M7505->Y:$078F03,9,1 ;Card 11, Output 2
M7506->Y:$078F03,10,1 ;Card 11, Output 3
M7507->Y:$078F03,11,1 ;Card 11, Output 4
M7508->Y:$078F03,12,1 ;Card 11, Output 5
M7509->Y:$078F03,13,1 ;Card 11, Output 6
M7510->Y:$078F03,14,1 ;Card 11, Output 7
M7511->Y:$078F03,15,1 ;Card 11, Output 8
M7512->Y:$078F04,8,1 ;Card 11, Output 9
M7513->Y:$078F04,9,1 ;Card 11, Output 10
M7514->Y:$078F04,10,1 ;Card 11, Output 11
M7515->Y:$078F04,11,1 ;Card 11, Output 12
M7516->Y:$078F04,12,1 ;Card 11, Output 13
M7517->Y:$078F04,13,1 ;Card 11, Output 14
M7518->Y:$078F04,14,1 ;Card 11, Output 15
M7519->Y:$078F04,15,1 ;Card 11, Output 16
M7520->Y:$078F05,8,1 ;Card 11, Output 17
M7521->Y:$078F05,9,1 ;Card 11, Output 18
M7522->Y:$078F05,10,1 ;Card 11, Output 19
M7523->Y:$078F05,11,1 ;Card 11, Output 20
M7524->Y:$078F05,12,1 ;Card 11, Output 21
M7525->Y:$078F05,13,1 ;Card 11, Output 22
M7526->Y:$078F05,14,1 ;Card 11, Output 23
M7527->Y:$078F05,15,1 ;Card 11, Output 24
// Byte-wide variables used for power-on configuration
M3400->Y:$78F00,8,8,U // I/O Card 11 I/O00-07 as byte
M3401->Y:$78F01,8,8,U // I/O Card 11 I/O08-15 as byte
M3402->Y:$78F02,8,8,U // I/O Card 11 I/O16-23 as byte
M3403->Y:$78F03,8,8,U // I/O Card 11 I/O24-31 as byte
M3404->Y:$78F04,8,8,U // I/O Card 11 I/O32-39 as byte
M3405->Y:$78F05,8,8,U // I/O Card 11 I/O40-47 as byte
M3406->Y:$78F06,8,8,U // I/O Card 11 latch inputs
M3407->Y:$78F07,8,8,U // I/O Card 11 control register
Page 77

ACC-11E User Manual
Appendix B: Full Turbo UMAC M-Variable Mappings 77
Base Address $78F00, High Byte
// Single-bit variables used for accessing I/O points
M7528->Y:$078F00,16,1 ;Card 12, Input 1
M7529->Y:$078F00,17,1 ;Card 12, Input 2
M7530->Y:$078F00,18,1 ;Card 12, Input 3
M7531->Y:$078F00,19,1 ;Card 12, Input 4
M7532->Y:$078F00,20,1 ;Card 12, Input 5
M7533->Y:$078F00,21,1 ;Card 12, Input 6
M7534->Y:$078F00,22,1 ;Card 12, Input 7
M7535->Y:$078F00,23,1 ;Card 12, Input 8
M7536->Y:$078F01,16,1 ;Card 12, Input 9
M7537->Y:$078F01,17,1 ;Card 12, Input 10
M7538->Y:$078F01,18,1 ;Card 12, Input 11
M7539->Y:$078F01,19,1 ;Card 12, Input 12
M7540->Y:$078F01,20,1 ;Card 12, Input 13
M7541->Y:$078F01,21,1 ;Card 12, Input 14
M7542->Y:$078F01,22,1 ;Card 12, Input 15
M7543->Y:$078F01,23,1 ;Card 12, Input 16
M7544->Y:$078F02,16,1 ;Card 12, Input 17
M7545->Y:$078F02,17,1 ;Card 12, Input 18
M7546->Y:$078F02,18,1 ;Card 12, Input 19
M7547->Y:$078F02,19,1 ;Card 12, Input 20
M7548->Y:$078F02,20,1 ;Card 12, Input 21
M7549->Y:$078F02,21,1 ;Card 12, Input 22
M7550->Y:$078F02,22,1 ;Card 12, Input 23
M7551->Y:$078F02,23,1 ;Card 12, Input 24
M7552->Y:$078F00,16,1 ;Card 12, Output 1
M7553->Y:$078F00,17,1 ;Card 12, Output 2
M7554->Y:$078F00,18,1 ;Card 12, Output 3
M7555->Y:$078F00,19,1 ;Card 12, Output 4
M7556->Y:$078F00,20,1 ;Card 12, Output 5
M7557->Y:$078F00,21,1 ;Card 12, Output 6
M7558->Y:$078F00,22,1 ;Card 12, Output 7
M7559->Y:$078F00,23,1 ;Card 12, Output 8
M7560->Y:$078F01,16,1 ;Card 12, Output 9
M7561->Y:$078F01,17,1 ;Card 12, Output 10
M7562->Y:$078F01,18,1 ;Card 12, Output 11
M7563->Y:$078F01,19,1 ;Card 12, Output 12
M7564->Y:$078F01,20,1 ;Card 12, Output 13
M7565->Y:$078F01,21,1 ;Card 12, Output 14
M7566->Y:$078F01,22,1 ;Card 12, Output 15
M7567->Y:$078F01,23,1 ;Card 12, Output 16
M7568->Y:$078F02,16,1 ;Card 12, Output 17
M7569->Y:$078F02,17,1 ;Card 12, Output 18
M7570->Y:$078F02,18,1 ;Card 12, Output 19
M7571->Y:$078F02,19,1 ;Card 12, Output 20
M7572->Y:$078F02,20,1 ;Card 12, Output 21
M7573->Y:$078F02,21,1 ;Card 12, Output 22
M7574->Y:$078F02,22,1 ;Card 12, Output 23
M7575->Y:$078F02,23,1 ;Card 12, Output 24
// Byte-wide variables used for power-on configuration
M3410->Y:$78F00,16,8,U // I/O Card 12 I/O00-07 as byte
M3411->Y:$78F01,16,8,U // I/O Card 12 I/O08-15 as byte
M3412->Y:$78F02,16,8,U // I/O Card 12 I/O16-23 as byte
M3413->Y:$78F03,16,8,U // I/O Card 12 I/O24-31 as byte
M3414->Y:$78F04,16,8,U // I/O Card 12 I/O32-39 as byte
M3415->Y:$78F05,16,8,U // I/O Card 12 I/O40-47 as byte
M3416->Y:$78F06,16,8,U // I/O Card 12 latch inputs
M3417->Y:$78F07,16,8,U // I/O Card 12 control registe
Page 78

ACC-11E User Manual
Appendix C: Full Power UMAC M-Variable Mappings 78
APPENDIX C: FULL POWER UMAC M-VARIABLE MAPPINGS
This appendix provides suggested M-Variables for all twelve possible ACC-11E addressing settings.
Base Offset $A00000, Low Byte
// Single-bit variables used for accessing I/O points
ptr IoCard1Pt00->u.io:$A00000.8.1 // I/O Card 1 Input 00
ptr IoCard1Pt01->u.io:$A00000.9.1 // I/O Card 1 Input 01
ptr IoCard1Pt02->u.io:$A00000.10.1 // I/O Card 1 Input 02
ptr IoCard1Pt03->u.io:$A00000.11.1 // I/O Card 1 Input 03
ptr IoCard1Pt04->u.io:$A00000.12.1 // I/O Card 1 Input 04
ptr IoCard1Pt05->u.io:$A00000.13.1 // I/O Card 1 Input 05
ptr IoCard1Pt06->u.io:$A00000.14.1 // I/O Card 1 Input 06
ptr IoCard1Pt07->u.io:$A00000.15.1 // I/O Card 1 Input 07
ptr IoCard1Pt08->u.io:$A00004.8.1 // I/O Card 1 Input 08
ptr IoCard1Pt09->u.io:$A00004.9.1 // I/O Card 1 Input 09
ptr IoCard1Pt10->u.io:$A00004.10.1 // I/O Card 1 Input 10
ptr IoCard1Pt11->u.io:$A00004.11.1 // I/O Card 1 Input 11
ptr IoCard1Pt12->u.io:$A00004.12.1 // I/O Card 1 Input 12
ptr IoCard1Pt13->u.io:$A00004.13.1 // I/O Card 1 Input 13
ptr IoCard1Pt14->u.io:$A00004.14.1 // I/O Card 1 Input 14
ptr IoCard1Pt15->u.io:$A00004.15.1 // I/O Card 1 Input 15
ptr IoCard1Pt16->u.io:$A00008.8.1 // I/O Card 1 Input 16
ptr IoCard1Pt17->u.io:$A00008.9.1 // I/O Card 1 Input 17
ptr IoCard1Pt18->u.io:$A00008.10.1 // I/O Card 1 Input 18
ptr IoCard1Pt19->u.io:$A00008.11.1 // I/O Card 1 Input 19
ptr IoCard1Pt20->u.io:$A00008.12.1 // I/O Card 1 Input 20
ptr IoCard1Pt21->u.io:$A00008.13.1 // I/O Card 1 Input 21
ptr IoCard1Pt22->u.io:$A00008.14.1 // I/O Card 1 Input 22
ptr IoCard1Pt23->u.io:$A00008.15.1 // I/O Card 1 Input 23
ptr IoCard1Pt24->u.io:$A0000C.8.1 // I/O Card 1 Output 00
ptr IoCard1Pt25->u.io:$A0000C.9.1 // I/O Card 1 Output 01
ptr IoCard1Pt26->u.io:$A0000C.10.1 // I/O Card 1 Output 02
ptr IoCard1Pt27->u.io:$A0000C.11.1 // I/O Card 1 Output 03
ptr IoCard1Pt28->u.io:$A0000C.12.1 // I/O Card 1 Output 04
ptr IoCard1Pt29->u.io:$A0000C.13.1 // I/O Card 1 Output 05
ptr IoCard1Pt30->u.io:$A0000C.14.1 // I/O Card 1 Output 06
ptr IoCard1Pt31->u.io:$A0000C.15.1 // I/O Card 1 Output 07
ptr IoCard1Pt32->u.io:$A00010.8.1 // I/O Card 1 Output 08
ptr IoCard1Pt33->u.io:$A00010.9.1 // I/O Card 1 Output 09
ptr IoCard1Pt34->u.io:$A00010.10.1 // I/O Card 1 Output 10
ptr IoCard1Pt35->u.io:$A00010.11.1 // I/O Card 1 Output 11
ptr IoCard1Pt36->u.io:$A00010.12.1 // I/O Card 1 Output 12
ptr IoCard1Pt37->u.io:$A00010.13.1 // I/O Card 1 Output 13
ptr IoCard1Pt38->u.io:$A00010.14.1 // I/O Card 1 Output 14
ptr IoCard1Pt39->u.io:$A00010.15.1 // I/O Card 1 Output 15
ptr IoCard1Pt40->u.io:$A00014.8.1 // I/O Card 1 Output 16
ptr IoCard1Pt41->u.io:$A00014.9.1 // I/O Card 1 Output 17
ptr IoCard1Pt42->u.io:$A00014.10.1 // I/O Card 1 Output 18
ptr IoCard1Pt43->u.io:$A00014.11.1 // I/O Card 1 Output 19
ptr IoCard1Pt44->u.io:$A00014.12.1 // I/O Card 1 Output 20
ptr IoCard1Pt45->u.io:$A00014.13.1 // I/O Card 1 Output 21
ptr IoCard1Pt46->u.io:$A00014.14.1 // I/O Card 1 Output 22
ptr IoCard1Pt47->u.io:$A00014.15.1 // I/O Card 1 Output 23
// Byte-wide variables used for power-on configuration
ptr IoCard1Reg0->u.io:$A00000.8.8 // I/O Card 1 Inputs 00-07 as byte
ptr IoCard1Reg1->u.io:$A00004.8.8 // I/O Card 1 Inputs 08-15 as byte
ptr IoCard1Reg2->u.io:$A00008.8.8 // I/O Card 1 Inputs 16-23 as byte
ptr IoCard1Reg3->u.io:$A0000C.8.8 // I/O Card 1 Outputs 00-07 as byte
ptr IoCard1Reg4->u.io:$A00010.8.8 // I/O Card 1 Outputs 08-15 as byte
ptr IoCard1Reg5->u.io:$A00014.8.8 // I/O Card 1 Outputs 16-23 as byte
ptr IoCard1Reg6->u.io:$A00018.8.8 // I/O Card 1 latch inputs
ptr IoCard1Reg7->u.io:$A0001C.8.8 // I/O Card 1 control register
Page 79

ACC-11E User Manual
Appendix C: Full Power UMAC M-Variable Mappings 79
Base Offset $A00000, Middle Byte
// Single-bit variables used for accessing I/O points
ptr IoCard2Pt00->u.io:$A00000.16.1 // I/O Card 2 I/O00
ptr IoCard2Pt01->u.io:$A00000.17.1 // I/O Card 2 I/O01
ptr IoCard2Pt02->u.io:$A00000.18.1 // I/O Card 2 I/O02
ptr IoCard2Pt03->u.io:$A00000.19.1 // I/O Card 2 I/O03
ptr IoCard2Pt04->u.io:$A00000.20.1 // I/O Card 2 I/O04
ptr IoCard2Pt05->u.io:$A00000.21.1 // I/O Card 2 I/O05
ptr IoCard2Pt06->u.io:$A00000.22.1 // I/O Card 2 I/O06
ptr IoCard2Pt07->u.io:$A00000.23.1 // I/O Card 2 I/O07
ptr IoCard2Pt08->u.io:$A00004.16.1 // I/O Card 2 I/O08
ptr IoCard2Pt09->u.io:$A00004.17.1 // I/O Card 2 I/O09
ptr IoCard2Pt10->u.io:$A00004.18.1 // I/O Card 2 I/O10
ptr IoCard2Pt11->u.io:$A00004.19.1 // I/O Card 2 I/O11
ptr IoCard2Pt12->u.io:$A00004.20.1 // I/O Card 2 I/O12
ptr IoCard2Pt13->u.io:$A00004.21.1 // I/O Card 2 I/O13
ptr IoCard2Pt14->u.io:$A00004.22.1 // I/O Card 2 I/O14
ptr IoCard2Pt15->u.io:$A00004.23.1 // I/O Card 2 I/O15
ptr IoCard2Pt16->u.io:$A00008.16.1 // I/O Card 2 I/O16
ptr IoCard2Pt17->u.io:$A00008.17.1 // I/O Card 2 I/O17
ptr IoCard2Pt18->u.io:$A00008.18.1 // I/O Card 2 I/O18
ptr IoCard2Pt19->u.io:$A00008.19.1 // I/O Card 2 I/O19
ptr IoCard2Pt20->u.io:$A00008.20.1 // I/O Card 2 I/O20
ptr IoCard2Pt21->u.io:$A00008.21.1 // I/O Card 2 I/O21
ptr IoCard2Pt22->u.io:$A00008.22.1 // I/O Card 2 I/O22
ptr IoCard2Pt23->u.io:$A00008.23.1 // I/O Card 2 I/O23
ptr IoCard2Pt24->u.io:$A0000C.16.1 // I/O Card 2 I/O24
ptr IoCard2Pt25->u.io:$A0000C.17.1 // I/O Card 2 I/O25
ptr IoCard2Pt26->u.io:$A0000C.18.1 // I/O Card 2 I/O26
ptr IoCard2Pt27->u.io:$A0000C.19.1 // I/O Card 2 I/O27
ptr IoCard2Pt28->u.io:$A0000C.20.1 // I/O Card 2 I/O28
ptr IoCard2Pt29->u.io:$A0000C.21.1 // I/O Card 2 I/O29
ptr IoCard2Pt30->u.io:$A0000C.22.1 // I/O Card 2 I/O30
ptr IoCard2Pt31->u.io:$A0000C.23.1 // I/O Card 2 I/O31
ptr IoCard2Pt32->u.io:$A00010.16.1 // I/O Card 2 I/O32
ptr IoCard2Pt33->u.io:$A00010.17.1 // I/O Card 2 I/O33
ptr IoCard2Pt34->u.io:$A00010.18.1 // I/O Card 2 I/O34
ptr IoCard2Pt35->u.io:$A00010.19.1 // I/O Card 2 I/O35
ptr IoCard2Pt36->u.io:$A00010.20.1 // I/O Card 2 I/O36
ptr IoCard2Pt37->u.io:$A00010.21.1 // I/O Card 2 I/O37
ptr IoCard2Pt38->u.io:$A00010.22.1 // I/O Card 2 I/O38
ptr IoCard2Pt39->u.io:$A00010.23.1 // I/O Card 2 I/O39
ptr IoCard2Pt40->u.io:$A00014.16.1 // I/O Card 2 I/O40
ptr IoCard2Pt41->u.io:$A00014.17.1 // I/O Card 2 I/O41
ptr IoCard2Pt42->u.io:$A00014.18.1 // I/O Card 2 I/O42
ptr IoCard2Pt43->u.io:$A00014.19.1 // I/O Card 2 I/O43
ptr IoCard2Pt44->u.io:$A00014.20.1 // I/O Card 2 I/O44
ptr IoCard2Pt45->u.io:$A00014.21.1 // I/O Card 2 I/O45
ptr IoCard2Pt46->u.io:$A00014.22.1 // I/O Card 2 I/O46
ptr IoCard2Pt47->u.io:$A00014.23.1 // I/O Card 2 I/O47
// Byte-wide variables used for power-on configuration
ptr IoCard2Reg0->u.io:$A00000.16.8 // I/O Card 2 I/O00-07 as byte
ptr IoCard2Reg1->u.io:$A00004.16.8 // I/O Card 2 I/O08-15 as byte
ptr IoCard2Reg2->u.io:$A00008.16.8 // I/O Card 2 I/O16-23 as byte
ptr IoCard2Reg3->u.io:$A0000C.16.8 // I/O Card 2 I/O24-31 as byte
ptr IoCard2Reg4->u.io:$A00010.16.8 // I/O Card 2 I/O32-39 as byte
ptr IoCard2Reg5->u.io:$A00014.16.8 // I/O Card 2 I/O40-47 as byte
ptr IoCard2Reg6->u.io:$A00018.16.8 // I/O Card 2 latch inputs
ptr IoCard2Reg7->u.io:$A0001C.16.8 // I/O Card 2 control register
Page 80

ACC-11E User Manual
Appendix C: Full Power UMAC M-Variable Mappings 80
Base offset $A00000, High Byte
// Single-bit variables used for accessing I/O points
ptr IoCard3Pt00->u.io:$A00000.24.1 // I/O Card 3 I/O00
ptr IoCard3Pt01->u.io:$A00000.25.1 // I/O Card 3 I/O01
ptr IoCard3Pt02->u.io:$A00000.26.1 // I/O Card 3 I/O02
ptr IoCard3Pt03->u.io:$A00000.27.1 // I/O Card 3 I/O03
ptr IoCard3Pt04->u.io:$A00000.28.1 // I/O Card 3 I/O04
ptr IoCard3Pt05->u.io:$A00000.29.1 // I/O Card 3 I/O05
ptr IoCard3Pt06->u.io:$A00000.30.1 // I/O Card 3 I/O06
ptr IoCard3Pt07->u.io:$A00000.31.1 // I/O Card 3 I/O07
ptr IoCard3Pt08->u.io:$A00004.24.1 // I/O Card 3 I/O08
ptr IoCard3Pt09->u.io:$A00004.25.1 // I/O Card 3 I/O09
ptr IoCard3Pt10->u.io:$A00004.26.1 // I/O Card 3 I/O10
ptr IoCard3Pt11->u.io:$A00004.27.1 // I/O Card 3 I/O11
ptr IoCard3Pt12->u.io:$A00004.28.1 // I/O Card 3 I/O12
ptr IoCard3Pt13->u.io:$A00004.29.1 // I/O Card 3 I/O13
ptr IoCard3Pt14->u.io:$A00004.30.1 // I/O Card 3 I/O14
ptr IoCard3Pt15->u.io:$A00004.31.1 // I/O Card 3 I/O15
ptr IoCard3Pt16->u.io:$A00008.24.1 // I/O Card 3 I/O16
ptr IoCard3Pt17->u.io:$A00008.25.1 // I/O Card 3 I/O17
ptr IoCard3Pt18->u.io:$A00008.26.1 // I/O Card 3 I/O18
ptr IoCard3Pt19->u.io:$A00008.27.1 // I/O Card 3 I/O19
ptr IoCard3Pt20->u.io:$A00008.28.1 // I/O Card 3 I/O20
ptr IoCard3Pt21->u.io:$A00008.29.1 // I/O Card 3 I/O21
ptr IoCard3Pt22->u.io:$A00008.30.1 // I/O Card 3 I/O22
ptr IoCard3Pt23->u.io:$A00008.31.1 // I/O Card 3 I/O23
ptr IoCard3Pt24->u.io:$A0000C.24.1 // I/O Card 3 I/O24
ptr IoCard3Pt25->u.io:$A0000C.25.1 // I/O Card 3 I/O25
ptr IoCard3Pt26->u.io:$A0000C.26.1 // I/O Card 3 I/O26
ptr IoCard3Pt27->u.io:$A0000C.27.1 // I/O Card 3 I/O27
ptr IoCard3Pt28->u.io:$A0000C.28.1 // I/O Card 3 I/O28
ptr IoCard3Pt29->u.io:$A0000C.29.1 // I/O Card 3 I/O29
ptr IoCard3Pt30->u.io:$A0000C.30.1 // I/O Card 3 I/O30
ptr IoCard3Pt31->u.io:$A0000C.31.1 // I/O Card 3 I/O31
ptr IoCard3Pt32->u.io:$A00010.24.1 // I/O Card 3 I/O32
ptr IoCard3Pt33->u.io:$A00010.25.1 // I/O Card 3 I/O33
ptr IoCard3Pt34->u.io:$A00010.26.1 // I/O Card 3 I/O34
ptr IoCard3Pt35->u.io:$A00010.27.1 // I/O Card 3 I/O35
ptr IoCard3Pt36->u.io:$A00010.28.1 // I/O Card 3 I/O36
ptr IoCard3Pt37->u.io:$A00010.29.1 // I/O Card 3 I/O37
ptr IoCard3Pt38->u.io:$A00010.30.1 // I/O Card 3 I/O38
ptr IoCard3Pt39->u.io:$A00010.31.1 // I/O Card 3 I/O39
ptr IoCard3Pt40->u.io:$A00014.24.1 // I/O Card 3 I/O40
ptr IoCard3Pt41->u.io:$A00014.25.1 // I/O Card 3 I/O41
ptr IoCard3Pt42->u.io:$A00014.26.1 // I/O Card 3 I/O42
ptr IoCard3Pt43->u.io:$A00014.27.1 // I/O Card 3 I/O43
ptr IoCard3Pt44->u.io:$A00014.28.1 // I/O Card 3 I/O44
ptr IoCard3Pt45->u.io:$A00014.29.1 // I/O Card 3 I/O45
ptr IoCard3Pt46->u.io:$A00014.30.1 // I/O Card 3 I/O46
ptr IoCard3Pt47->u.io:$A00014.31.1 // I/O Card 3 I/O47
// Byte-wide variables used for power-on configuration
ptr IoCard3Reg0->u.io:$A00000.24.8 // I/O Card 3 I/O00-07 as byte
ptr IoCard3Reg1->u.io:$A00004.24.8 // I/O Card 3 I/O08-15 as byte
ptr IoCard3Reg2->u.io:$A00008.24.8 // I/O Card 3 I/O16-23 as byte
ptr IoCard3Reg3->u.io:$A0000C.24.8 // I/O Card 3 I/O24-31 as byte
ptr IoCard3Reg4->u.io:$A00010.24.8 // I/O Card 3 I/O32-39 as byte
ptr IoCard3Reg5->u.io:$A00014.24.8 // I/O Card 3 I/O40-47 as byte
ptr IoCard3Reg6->u.io:$A00018.24.8 // I/O Card 3 latch inputs
ptr IoCard3Reg7->u.io:$A0001C.24.8 // I/O Card 3 control register
Page 81

ACC-11E User Manual
Appendix C: Full Power UMAC M-Variable Mappings 81
Base Offset $B00000, Low Byte
// Single-bit variables used for accessing I/O points
ptr IoCard4Pt00->u.io:$B00000.8.1 // I/O Card 4 I/O00
ptr IoCard4Pt01->u.io:$B00000.9.1 // I/O Card 4 I/O01
ptr IoCard4Pt02->u.io:$B00000.10.1 // I/O Card 4 I/O02
ptr IoCard4Pt03->u.io:$B00000.11.1 // I/O Card 4 I/O03
ptr IoCard4Pt04->u.io:$B00000.12.1 // I/O Card 4 I/O04
ptr IoCard4Pt05->u.io:$B00000.13.1 // I/O Card 4 I/O05
ptr IoCard4Pt06->u.io:$B00000.14.1 // I/O Card 4 I/O06
ptr IoCard4Pt07->u.io:$B00000.15.1 // I/O Card 4 I/O07
ptr IoCard4Pt08->u.io:$B00004.8.1 // I/O Card 4 I/O08
ptr IoCard4Pt09->u.io:$B00004.9.1 // I/O Card 4 I/O09
ptr IoCard4Pt10->u.io:$B00004.10.1 // I/O Card 4 I/O10
ptr IoCard4Pt11->u.io:$B00004.11.1 // I/O Card 4 I/O11
ptr IoCard4Pt12->u.io:$B00004.12.1 // I/O Card 4 I/O12
ptr IoCard4Pt13->u.io:$B00004.13.1 // I/O Card 4 I/O13
ptr IoCard4Pt14->u.io:$B00004.14.1 // I/O Card 4 I/O14
ptr IoCard4Pt15->u.io:$B00004.15.1 // I/O Card 4 I/O15
ptr IoCard4Pt16->u.io:$B00008.8.1 // I/O Card 4 I/O16
ptr IoCard4Pt17->u.io:$B00008.9.1 // I/O Card 4 I/O17
ptr IoCard4Pt18->u.io:$B00008.10.1 // I/O Card 4 I/O18
ptr IoCard4Pt19->u.io:$B00008.11.1 // I/O Card 4 I/O19
ptr IoCard4Pt20->u.io:$B00008.12.1 // I/O Card 4 I/O20
ptr IoCard4Pt21->u.io:$B00008.13.1 // I/O Card 4 I/O21
ptr IoCard4Pt22->u.io:$B00008.14.1 // I/O Card 4 I/O22
ptr IoCard4Pt23->u.io:$B00008.15.1 // I/O Card 4 I/O23
ptr IoCard4Pt24->u.io:$B0000C.8.1 // I/O Card 4 I/O24
ptr IoCard4Pt25->u.io:$B0000C.9.1 // I/O Card 4 I/O25
ptr IoCard4Pt26->u.io:$B0000C.10.1 // I/O Card 4 I/O26
ptr IoCard4Pt27->u.io:$B0000C.11.1 // I/O Card 4 I/O27
ptr IoCard4Pt28->u.io:$B0000C.12.1 // I/O Card 4 I/O28
ptr IoCard4Pt29->u.io:$B0000C.13.1 // I/O Card 4 I/O29
ptr IoCard4Pt30->u.io:$B0000C.14.1 // I/O Card 4 I/O30
ptr IoCard4Pt31->u.io:$B0000C.15.1 // I/O Card 4 I/O31
ptr IoCard4Pt32->u.io:$B00010.8.1 // I/O Card 4 I/O32
ptr IoCard4Pt33->u.io:$B00010.9.1 // I/O Card 4 I/O33
ptr IoCard4Pt34->u.io:$B00010.10.1 // I/O Card 4 I/O34
ptr IoCard4Pt35->u.io:$B00010.11.1 // I/O Card 4 I/O35
ptr IoCard4Pt36->u.io:$B00010.12.1 // I/O Card 4 I/O36
ptr IoCard4Pt37->u.io:$B00010.13.1 // I/O Card 4 I/O37
ptr IoCard4Pt38->u.io:$B00010.14.1 // I/O Card 4 I/O38
ptr IoCard4Pt39->u.io:$B00010.15.1 // I/O Card 4 I/O39
ptr IoCard4Pt40->u.io:$B00014.8.1 // I/O Card 4 I/O40
ptr IoCard4Pt41->u.io:$B00014.9.1 // I/O Card 4 I/O41
ptr IoCard4Pt42->u.io:$B00014.10.1 // I/O Card 4 I/O42
ptr IoCard4Pt43->u.io:$B00014.11.1 // I/O Card 4 I/O43
ptr IoCard4Pt44->u.io:$B00014.12.1 // I/O Card 4 I/O44
ptr IoCard4Pt45->u.io:$B00014.13.1 // I/O Card 4 I/O45
ptr IoCard4Pt46->u.io:$B00014.14.1 // I/O Card 4 I/O46
ptr IoCard4Pt47->u.io:$B00014.15.1 // I/O Card 4 I/O47
// Byte-wide variables used for power-on configuration
ptr IoCard4Reg0->u.io:$B00000.8.8 // I/O Card 4 I/O00-07 as byte
ptr IoCard4Reg1->u.io:$B00004.8.8 // I/O Card 4 I/O08-15 as byte
ptr IoCard4Reg2->u.io:$B00008.8.8 // I/O Card 4 I/O16-23 as byte
ptr IoCard4Reg3->u.io:$B0000C.8.8 // I/O Card 4 I/O24-31 as byte
ptr IoCard4Reg4->u.io:$B00010.8.8 // I/O Card 4 I/O32-39 as byte
ptr IoCard4Reg5->u.io:$B00014.8.8 // I/O Card 4 I/O40-47 as byte
ptr IoCard4Reg6->u.io:$B00018.8.8 // I/O Card 4 latch inputs
ptr IoCard4Reg7->u.io:$B0001C.8.8 // I/O Card 4 control register
Page 82

ACC-11E User Manual
Appendix C: Full Power UMAC M-Variable Mappings 82
Base Offset $B00000, Middle Byte
// Single-bit variables used for accessing I/O points
ptr IoCard5Pt00->u.io:$B00000.16.1 // I/O Card 5 I/O00
ptr IoCard5Pt01->u.io:$B00000.17.1 // I/O Card 5 I/O01
ptr IoCard5Pt02->u.io:$B00000.18.1 // I/O Card 5 I/O02
ptr IoCard5Pt03->u.io:$B00000.19.1 // I/O Card 5 I/O03
ptr IoCard5Pt04->u.io:$B00000.20.1 // I/O Card 5 I/O04
ptr IoCard5Pt05->u.io:$B00000.21.1 // I/O Card 5 I/O05
ptr IoCard5Pt06->u.io:$B00000.22.1 // I/O Card 5 I/O06
ptr IoCard5Pt07->u.io:$B00000.23.1 // I/O Card 5 I/O07
ptr IoCard5Pt08->u.io:$B00004.16.1 // I/O Card 5 I/O08
ptr IoCard5Pt09->u.io:$B00004.17.1 // I/O Card 5 I/O09
ptr IoCard5Pt10->u.io:$B00004.18.1 // I/O Card 5 I/O10
ptr IoCard5Pt11->u.io:$B00004.19.1 // I/O Card 5 I/O11
ptr IoCard5Pt12->u.io:$B00004.20.1 // I/O Card 5 I/O12
ptr IoCard5Pt13->u.io:$B00004.21.1 // I/O Card 5 I/O13
ptr IoCard5Pt14->u.io:$B00004.22.1 // I/O Card 5 I/O14
ptr IoCard5Pt15->u.io:$B00004.23.1 // I/O Card 5 I/O15
ptr IoCard5Pt16->u.io:$B00008.16.1 // I/O Card 5 I/O16
ptr IoCard5Pt17->u.io:$B00008.17.1 // I/O Card 5 I/O17
ptr IoCard5Pt18->u.io:$B00008.18.1 // I/O Card 5 I/O18
ptr IoCard5Pt19->u.io:$B00008.19.1 // I/O Card 5 I/O19
ptr IoCard5Pt20->u.io:$B00008.20.1 // I/O Card 5 I/O20
ptr IoCard5Pt21->u.io:$B00008.21.1 // I/O Card 5 I/O21
ptr IoCard5Pt22->u.io:$B00008.22.1 // I/O Card 5 I/O22
ptr IoCard5Pt23->u.io:$B00008.23.1 // I/O Card 5 I/O23
ptr IoCard5Pt24->u.io:$B0000C.16.1 // I/O Card 5 I/O24
ptr IoCard5Pt25->u.io:$B0000C.17.1 // I/O Card 5 I/O25
ptr IoCard5Pt26->u.io:$B0000C.18.1 // I/O Card 5 I/O26
ptr IoCard5Pt27->u.io:$B0000C.19.1 // I/O Card 5 I/O27
ptr IoCard5Pt28->u.io:$B0000C.20.1 // I/O Card 5 I/O28
ptr IoCard5Pt29->u.io:$B0000C.21.1 // I/O Card 5 I/O29
ptr IoCard5Pt30->u.io:$B0000C.22.1 // I/O Card 5 I/O30
ptr IoCard5Pt31->u.io:$B0000C.23.1 // I/O Card 5 I/O31
ptr IoCard5Pt32->u.io:$B00010.16.1 // I/O Card 5 I/O32
ptr IoCard5Pt33->u.io:$B00010.17.1 // I/O Card 5 I/O33
ptr IoCard5Pt34->u.io:$B00010.18.1 // I/O Card 5 I/O34
ptr IoCard5Pt35->u.io:$B00010.19.1 // I/O Card 5 I/O35
ptr IoCard5Pt36->u.io:$B00010.20.1 // I/O Card 5 I/O36
ptr IoCard5Pt37->u.io:$B00010.21.1 // I/O Card 5 I/O37
ptr IoCard5Pt38->u.io:$B00010.22.1 // I/O Card 5 I/O38
ptr IoCard5Pt39->u.io:$B00010.23.1 // I/O Card 5 I/O39
ptr IoCard5Pt40->u.io:$B00014.16.1 // I/O Card 5 I/O40
ptr IoCard5Pt41->u.io:$B00014.17.1 // I/O Card 5 I/O41
ptr IoCard5Pt42->u.io:$B00014.18.1 // I/O Card 5 I/O42
ptr IoCard5Pt43->u.io:$B00014.19.1 // I/O Card 5 I/O43
ptr IoCard5Pt44->u.io:$B00014.20.1 // I/O Card 5 I/O44
ptr IoCard5Pt45->u.io:$B00014.21.1 // I/O Card 5 I/O45
ptr IoCard5Pt46->u.io:$B00014.22.1 // I/O Card 5 I/O46
ptr IoCard5Pt47->u.io:$B00014.23.1 // I/O Card 5 I/O47
// Byte-wide variables used for power-on configuration
ptr IoCard5Reg0->u.io:$B00000.16.8 // I/O Card 5 I/O00-07 as byte
ptr IoCard5Reg1->u.io:$B00004.16.8 // I/O Card 5 I/O08-15 as byte
ptr IoCard5Reg2->u.io:$B00008.16.8 // I/O Card 5 I/O16-23 as byte
ptr IoCard5Reg3->u.io:$B0000C.16.8 // I/O Card 5 I/O24-31 as byte
ptr IoCard5Reg4->u.io:$B00010.16.8 // I/O Card 5 I/O32-39 as byte
ptr IoCard5Reg5->u.io:$B00014.16.8 // I/O Card 5 I/O40-47 as byte
ptr IoCard5Reg6->u.io:$B00018.16.8 // I/O Card 5 latch inputs
ptr IoCard5Reg7->u.io:$B0001C.16.8 // I/O Card 5 control register
Page 83

ACC-11E User Manual
Appendix C: Full Power UMAC M-Variable Mappings 83
Base Offset $B00000, High Byte
// Single-bit variables used for accessing I/O points
ptr IoCard6Pt00->u.io:$B00000.24.1 // I/O Card 6 I/O00
ptr IoCard6Pt01->u.io:$B00000.25.1 // I/O Card 6 I/O01
ptr IoCard6Pt02->u.io:$B00000.26.1 // I/O Card 6 I/O02
ptr IoCard6Pt03->u.io:$B00000.27.1 // I/O Card 6 I/O03
ptr IoCard6Pt04->u.io:$B00000.28.1 // I/O Card 6 I/O04
ptr IoCard6Pt05->u.io:$B00000.29.1 // I/O Card 6 I/O05
ptr IoCard6Pt06->u.io:$B00000.30.1 // I/O Card 6 I/O06
ptr IoCard6Pt07->u.io:$B00000.31.1 // I/O Card 6 I/O07
ptr IoCard6Pt08->u.io:$B00004.24.1 // I/O Card 6 I/O08
ptr IoCard6Pt09->u.io:$B00004.25.1 // I/O Card 6 I/O09
ptr IoCard6Pt10->u.io:$B00004.26.1 // I/O Card 6 I/O10
ptr IoCard6Pt11->u.io:$B00004.27.1 // I/O Card 6 I/O11
ptr IoCard6Pt12->u.io:$B00004.28.1 // I/O Card 6 I/O12
ptr IoCard6Pt13->u.io:$B00004.29.1 // I/O Card 6 I/O13
ptr IoCard6Pt14->u.io:$B00004.30.1 // I/O Card 6 I/O14
ptr IoCard6Pt15->u.io:$B00004.31.1 // I/O Card 6 I/O15
ptr IoCard6Pt16->u.io:$B00008.24.1 // I/O Card 6 I/O16
ptr IoCard6Pt17->u.io:$B00008.25.1 // I/O Card 6 I/O17
ptr IoCard6Pt18->u.io:$B00008.26.1 // I/O Card 6 I/O18
ptr IoCard6Pt19->u.io:$B00008.27.1 // I/O Card 6 I/O19
ptr IoCard6Pt20->u.io:$B00008.28.1 // I/O Card 6 I/O20
ptr IoCard6Pt21->u.io:$B00008.29.1 // I/O Card 6 I/O21
ptr IoCard6Pt22->u.io:$B00008.30.1 // I/O Card 6 I/O22
ptr IoCard6Pt23->u.io:$B00008.31.1 // I/O Card 6 I/O23
ptr IoCard6Pt24->u.io:$B0000C.24.1 // I/O Card 6 I/O24
ptr IoCard6Pt25->u.io:$B0000C.25.1 // I/O Card 6 I/O25
ptr IoCard6Pt26->u.io:$B0000C.26.1 // I/O Card 6 I/O26
ptr IoCard6Pt27->u.io:$B0000C.27.1 // I/O Card 6 I/O27
ptr IoCard6Pt28->u.io:$B0000C.28.1 // I/O Card 6 I/O28
ptr IoCard6Pt29->u.io:$B0000C.29.1 // I/O Card 6 I/O29
ptr IoCard6Pt30->u.io:$B0000C.30.1 // I/O Card 6 I/O30
ptr IoCard6Pt31->u.io:$B0000C.31.1 // I/O Card 6 I/O31
ptr IoCard6Pt32->u.io:$B00010.24.1 // I/O Card 6 I/O32
ptr IoCard6Pt33->u.io:$B00010.25.1 // I/O Card 6 I/O33
ptr IoCard6Pt34->u.io:$B00010.26.1 // I/O Card 6 I/O34
ptr IoCard6Pt35->u.io:$B00010.27.1 // I/O Card 6 I/O35
ptr IoCard6Pt36->u.io:$B00010.28.1 // I/O Card 6 I/O36
ptr IoCard6Pt37->u.io:$B00010.29.1 // I/O Card 6 I/O37
ptr IoCard6Pt38->u.io:$B00010.30.1 // I/O Card 6 I/O38
ptr IoCard6Pt39->u.io:$B00010.31.1 // I/O Card 6 I/O39
ptr IoCard6Pt40->u.io:$B00014.24.1 // I/O Card 6 I/O40
ptr IoCard6Pt41->u.io:$B00014.25.1 // I/O Card 6 I/O41
ptr IoCard6Pt42->u.io:$B00014.26.1 // I/O Card 6 I/O42
ptr IoCard6Pt43->u.io:$B00014.27.1 // I/O Card 6 I/O43
ptr IoCard6Pt44->u.io:$B00014.28.1 // I/O Card 6 I/O44
ptr IoCard6Pt45->u.io:$B00014.29.1 // I/O Card 6 I/O45
ptr IoCard6Pt46->u.io:$B00014.30.1 // I/O Card 6 I/O46
ptr IoCard6Pt47->u.io:$B00014.31.1 // I/O Card 6 I/O47
// Byte-wide variables used for power-on configuration
ptr IoCard6Reg0->u.io:$B00000.24.8 // I/O Card 6 I/O00-07 as byte
ptr IoCard6Reg1->u.io:$B00004.24.8 // I/O Card 6 I/O08-15 as byte
ptr IoCard6Reg2->u.io:$B00008.24.8 // I/O Card 6 I/O16-23 as byte
ptr IoCard6Reg3->u.io:$B0000C.24.8 // I/O Card 6 I/O24-31 as byte
ptr IoCard6Reg4->u.io:$B00010.24.8 // I/O Card 6 I/O32-39 as byte
ptr IoCard6Reg5->u.io:$B00014.24.8 // I/O Card 6 I/O40-47 as byte
ptr IoCard6Reg6->u.io:$B00018.24.8 // I/O Card 6 latch inputs
ptr IoCard6Reg7->u.io:$B0001C.24.8 // I/O Card 6 control register
Page 84

ACC-11E User Manual
Appendix C: Full Power UMAC M-Variable Mappings 84
Base Offset $C00000, Low Byte
// Single-bit variables used for accessing I/O points
ptr IoCard7Pt00->u.io:$C00000.8.1 // I/O Card 7 I/O00
ptr IoCard7Pt01->u.io:$C00000.9.1 // I/O Card 7 I/O01
ptr IoCard7Pt02->u.io:$C00000.10.1 // I/O Card 7 I/O02
ptr IoCard7Pt03->u.io:$C00000.11.1 // I/O Card 7 I/O03
ptr IoCard7Pt04->u.io:$C00000.12.1 // I/O Card 7 I/O04
ptr IoCard7Pt05->u.io:$C00000.13.1 // I/O Card 7 I/O05
ptr IoCard7Pt06->u.io:$C00000.14.1 // I/O Card 7 I/O06
ptr IoCard7Pt07->u.io:$C00000.15.1 // I/O Card 7 I/O07
ptr IoCard7Pt08->u.io:$C00004.8.1 // I/O Card 7 I/O08
ptr IoCard7Pt09->u.io:$C00004.9.1 // I/O Card 7 I/O09
ptr IoCard7Pt10->u.io:$C00004.10.1 // I/O Card 7 I/O10
ptr IoCard7Pt11->u.io:$C00004.11.1 // I/O Card 7 I/O11
ptr IoCard7Pt12->u.io:$C00004.12.1 // I/O Card 7 I/O12
ptr IoCard7Pt13->u.io:$C00004.13.1 // I/O Card 7 I/O13
ptr IoCard7Pt14->u.io:$C00004.14.1 // I/O Card 7 I/O14
ptr IoCard7Pt15->u.io:$C00004.15.1 // I/O Card 7 I/O15
ptr IoCard7Pt16->u.io:$C00008.8.1 // I/O Card 7 I/O16
ptr IoCard7Pt17->u.io:$C00008.9.1 // I/O Card 7 I/O17
ptr IoCard7Pt18->u.io:$C00008.10.1 // I/O Card 7 I/O18
ptr IoCard7Pt19->u.io:$C00008.11.1 // I/O Card 7 I/O19
ptr IoCard7Pt20->u.io:$C00008.12.1 // I/O Card 7 I/O20
ptr IoCard7Pt21->u.io:$C00008.13.1 // I/O Card 7 I/O21
ptr IoCard7Pt22->u.io:$C00008.14.1 // I/O Card 7 I/O22
ptr IoCard7Pt23->u.io:$C00008.15.1 // I/O Card 7 I/O23
ptr IoCard7Pt24->u.io:$C0000C.8.1 // I/O Card 7 I/O24
ptr IoCard7Pt25->u.io:$C0000C.9.1 // I/O Card 7 I/O25
ptr IoCard7Pt26->u.io:$C0000C.10.1 // I/O Card 7 I/O26
ptr IoCard7Pt27->u.io:$C0000C.11.1 // I/O Card 7 I/O27
ptr IoCard7Pt28->u.io:$C0000C.12.1 // I/O Card 7 I/O28
ptr IoCard7Pt29->u.io:$C0000C.13.1 // I/O Card 7 I/O29
ptr IoCard7Pt30->u.io:$C0000C.14.1 // I/O Card 7 I/O30
ptr IoCard7Pt31->u.io:$C0000C.15.1 // I/O Card 7 I/O31
ptr IoCard7Pt32->u.io:$C00010.8.1 // I/O Card 7 I/O32
ptr IoCard7Pt33->u.io:$C00010.9.1 // I/O Card 7 I/O33
ptr IoCard7Pt34->u.io:$C00010.10.1 // I/O Card 7 I/O34
ptr IoCard7Pt35->u.io:$C00010.11.1 // I/O Card 7 I/O35
ptr IoCard7Pt36->u.io:$C00010.12.1 // I/O Card 7 I/O36
ptr IoCard7Pt37->u.io:$C00010.13.1 // I/O Card 7 I/O37
ptr IoCard7Pt38->u.io:$C00010.14.1 // I/O Card 7 I/O38
ptr IoCard7Pt39->u.io:$C00010.15.1 // I/O Card 7 I/O39
ptr IoCard7Pt40->u.io:$C00014.8.1 // I/O Card 7 I/O40
ptr IoCard7Pt41->u.io:$C00014.9.1 // I/O Card 7 I/O41
ptr IoCard7Pt42->u.io:$C00014.10.1 // I/O Card 7 I/O42
ptr IoCard7Pt43->u.io:$C00014.11.1 // I/O Card 7 I/O43
ptr IoCard7Pt44->u.io:$C00014.12.1 // I/O Card 7 I/O44
ptr IoCard7Pt45->u.io:$C00014.13.1 // I/O Card 7 I/O45
ptr IoCard7Pt46->u.io:$C00014.14.1 // I/O Card 7 I/O46
ptr IoCard7Pt47->u.io:$C00014.15.1 // I/O Card 7 I/O47
// Byte-wide variables used for power-on configuration
ptr IoCard7Reg0->u.io:$C00000.8.8 // I/O Card 7 I/O00-07 as byte
ptr IoCard7Reg1->u.io:$C00004.8.8 // I/O Card 7 I/O08-15 as byte
ptr IoCard7Reg2->u.io:$C00008.8.8 // I/O Card 7 I/O16-23 as byte
ptr IoCard7Reg3->u.io:$C0000C.8.8 // I/O Card 7 I/O24-31 as byte
ptr IoCard7Reg4->u.io:$C00010.8.8 // I/O Card 7 I/O32-39 as byte
ptr IoCard7Reg5->u.io:$C00014.8.8 // I/O Card 7 I/O40-47 as byte
ptr IoCard7Reg6->u.io:$C00018.8.8 // I/O Card 7 latch inputs
ptr IoCard7Reg7->u.io:$C0001C.8.8 // I/O Card 7 control register
Page 85

ACC-11E User Manual
Appendix C: Full Power UMAC M-Variable Mappings 85
Base Offset $C00000, Middle Byte
// Single-bit variables used for accessing I/O points
ptr IoCard8Pt00->u.io:$C00000.16.1 // I/O Card 8 I/O00
ptr IoCard8Pt01->u.io:$C00000.17.1 // I/O Card 8 I/O01
ptr IoCard8Pt02->u.io:$C00000.18.1 // I/O Card 8 I/O02
ptr IoCard8Pt03->u.io:$C00000.19.1 // I/O Card 8 I/O03
ptr IoCard8Pt04->u.io:$C00000.20.1 // I/O Card 8 I/O04
ptr IoCard8Pt05->u.io:$C00000.21.1 // I/O Card 8 I/O05
ptr IoCard8Pt06->u.io:$C00000.22.1 // I/O Card 8 I/O06
ptr IoCard8Pt07->u.io:$C00000.23.1 // I/O Card 8 I/O07
ptr IoCard8Pt08->u.io:$C00004.16.1 // I/O Card 8 I/O08
ptr IoCard8Pt09->u.io:$C00004.17.1 // I/O Card 8 I/O09
ptr IoCard8Pt10->u.io:$C00004.18.1 // I/O Card 8 I/O10
ptr IoCard8Pt11->u.io:$C00004.19.1 // I/O Card 8 I/O11
ptr IoCard8Pt12->u.io:$C00004.20.1 // I/O Card 8 I/O12
ptr IoCard8Pt13->u.io:$C00004.21.1 // I/O Card 8 I/O13
ptr IoCard8Pt14->u.io:$C00004.22.1 // I/O Card 8 I/O14
ptr IoCard8Pt15->u.io:$C00004.23.1 // I/O Card 8 I/O15
ptr IoCard8Pt16->u.io:$C00008.16.1 // I/O Card 8 I/O16
ptr IoCard8Pt17->u.io:$C00008.17.1 // I/O Card 8 I/O17
ptr IoCard8Pt18->u.io:$C00008.18.1 // I/O Card 8 I/O18
ptr IoCard8Pt19->u.io:$C00008.19.1 // I/O Card 8 I/O19
ptr IoCard8Pt20->u.io:$C00008.20.1 // I/O Card 8 I/O20
ptr IoCard8Pt21->u.io:$C00008.21.1 // I/O Card 8 I/O21
ptr IoCard8Pt22->u.io:$C00008.22.1 // I/O Card 8 I/O22
ptr IoCard8Pt23->u.io:$C00008.23.1 // I/O Card 8 I/O23
ptr IoCard8Pt24->u.io:$C0000C.16.1 // I/O Card 8 I/O24
ptr IoCard8Pt25->u.io:$C0000C.17.1 // I/O Card 8 I/O25
ptr IoCard8Pt26->u.io:$C0000C.18.1 // I/O Card 8 I/O26
ptr IoCard8Pt27->u.io:$C0000C.19.1 // I/O Card 8 I/O27
ptr IoCard8Pt28->u.io:$C0000C.20.1 // I/O Card 8 I/O28
ptr IoCard8Pt29->u.io:$C0000C.21.1 // I/O Card 8 I/O29
ptr IoCard8Pt30->u.io:$C0000C.22.1 // I/O Card 8 I/O30
ptr IoCard8Pt31->u.io:$C0000C.23.1 // I/O Card 8 I/O31
ptr IoCard8Pt32->u.io:$C00010.16.1 // I/O Card 8 I/O32
ptr IoCard8Pt33->u.io:$C00010.17.1 // I/O Card 8 I/O33
ptr IoCard8Pt34->u.io:$C00010.18.1 // I/O Card 8 I/O34
ptr IoCard8Pt35->u.io:$C00010.19.1 // I/O Card 8 I/O35
ptr IoCard8Pt36->u.io:$C00010.20.1 // I/O Card 8 I/O36
ptr IoCard8Pt37->u.io:$C00010.21.1 // I/O Card 8 I/O37
ptr IoCard8Pt38->u.io:$C00010.22.1 // I/O Card 8 I/O38
ptr IoCard8Pt39->u.io:$C00010.23.1 // I/O Card 8 I/O39
ptr IoCard8Pt40->u.io:$C00014.16.1 // I/O Card 8 I/O40
ptr IoCard8Pt41->u.io:$C00014.17.1 // I/O Card 8 I/O41
ptr IoCard8Pt42->u.io:$C00014.18.1 // I/O Card 8 I/O42
ptr IoCard8Pt43->u.io:$C00014.19.1 // I/O Card 8 I/O43
ptr IoCard8Pt44->u.io:$C00014.20.1 // I/O Card 8 I/O44
ptr IoCard8Pt45->u.io:$C00014.21.1 // I/O Card 8 I/O45
ptr IoCard8Pt46->u.io:$C00014.22.1 // I/O Card 8 I/O46
ptr IoCard8Pt47->u.io:$C00014.23.1 // I/O Card 8 I/O47
// Byte-wide variables used for power-on configuration
ptr IoCard8Reg0->u.io:$C00000.16.8 // I/O Card 8 I/O00-07 as byte
ptr IoCard8Reg1->u.io:$C00004.16.8 // I/O Card 8 I/O08-15 as byte
ptr IoCard8Reg2->u.io:$C00008.16.8 // I/O Card 8 I/O16-23 as byte
ptr IoCard8Reg3->u.io:$C0000C.16.8 // I/O Card 8 I/O24-31 as byte
ptr IoCard8Reg4->u.io:$C00010.16.8 // I/O Card 8 I/O32-39 as byte
ptr IoCard8Reg5->u.io:$C00014.16.8 // I/O Card 8 I/O40-47 as byte
ptr IoCard8Reg6->u.io:$C00018.16.8 // I/O Card 8 latch inputs
ptr IoCard8Reg7->u.io:$C0001C.16.8 // I/O Card 8 control register
Page 86

ACC-11E User Manual
Appendix C: Full Power UMAC M-Variable Mappings 86
Base Offset $C00000, High Byte
// Single-bit variables used for accessing I/O points
ptr IoCard9Pt00->u.io:$C00000.24.1 // I/O Card 9 I/O00
ptr IoCard9Pt01->u.io:$C00000.25.1 // I/O Card 9 I/O01
ptr IoCard9Pt02->u.io:$C00000.26.1 // I/O Card 9 I/O02
ptr IoCard9Pt03->u.io:$C00000.27.1 // I/O Card 9 I/O03
ptr IoCard9Pt04->u.io:$C00000.28.1 // I/O Card 9 I/O04
ptr IoCard9Pt05->u.io:$C00000.29.1 // I/O Card 9 I/O05
ptr IoCard9Pt06->u.io:$C00000.30.1 // I/O Card 9 I/O06
ptr IoCard9Pt07->u.io:$C00000.31.1 // I/O Card 9 I/O07
ptr IoCard9Pt08->u.io:$C00004.24.1 // I/O Card 9 I/O08
ptr IoCard9Pt09->u.io:$C00004.25.1 // I/O Card 9 I/O09
ptr IoCard9Pt10->u.io:$C00004.26.1 // I/O Card 9 I/O10
ptr IoCard9Pt11->u.io:$C00004.27.1 // I/O Card 9 I/O11
ptr IoCard9Pt12->u.io:$C00004.28.1 // I/O Card 9 I/O12
ptr IoCard9Pt13->u.io:$C00004.29.1 // I/O Card 9 I/O13
ptr IoCard9Pt14->u.io:$C00004.30.1 // I/O Card 9 I/O14
ptr IoCard9Pt15->u.io:$C00004.31.1 // I/O Card 9 I/O15
ptr IoCard9Pt16->u.io:$C00008.24.1 // I/O Card 9 I/O16
ptr IoCard9Pt17->u.io:$C00008.25.1 // I/O Card 9 I/O17
ptr IoCard9Pt18->u.io:$C00008.26.1 // I/O Card 9 I/O18
ptr IoCard9Pt19->u.io:$C00008.27.1 // I/O Card 9 I/O19
ptr IoCard9Pt20->u.io:$C00008.28.1 // I/O Card 9 I/O20
ptr IoCard9Pt21->u.io:$C00008.29.1 // I/O Card 9 I/O21
ptr IoCard9Pt22->u.io:$C00008.30.1 // I/O Card 9 I/O22
ptr IoCard9Pt23->u.io:$C00008.31.1 // I/O Card 9 I/O23
ptr IoCard9Pt24->u.io:$C0000C.24.1 // I/O Card 9 I/O24
ptr IoCard9Pt25->u.io:$C0000C.25.1 // I/O Card 9 I/O25
ptr IoCard9Pt26->u.io:$C0000C.26.1 // I/O Card 9 I/O26
ptr IoCard9Pt27->u.io:$C0000C.27.1 // I/O Card 9 I/O27
ptr IoCard9Pt28->u.io:$C0000C.28.1 // I/O Card 9 I/O28
ptr IoCard9Pt29->u.io:$C0000C.29.1 // I/O Card 9 I/O29
ptr IoCard9Pt30->u.io:$C0000C.30.1 // I/O Card 9 I/O30
ptr IoCard9Pt31->u.io:$C0000C.31.1 // I/O Card 9 I/O31
ptr IoCard9Pt32->u.io:$C00010.24.1 // I/O Card 9 I/O32
ptr IoCard9Pt33->u.io:$C00010.25.1 // I/O Card 9 I/O33
ptr IoCard9Pt34->u.io:$C00010.26.1 // I/O Card 9 I/O34
ptr IoCard9Pt35->u.io:$C00010.27.1 // I/O Card 9 I/O35
ptr IoCard9Pt36->u.io:$C00010.28.1 // I/O Card 9 I/O36
ptr IoCard9Pt37->u.io:$C00010.29.1 // I/O Card 9 I/O37
ptr IoCard9Pt38->u.io:$C00010.30.1 // I/O Card 9 I/O38
ptr IoCard9Pt39->u.io:$C00010.31.1 // I/O Card 9 I/O39
ptr IoCard9Pt40->u.io:$C00014.24.1 // I/O Card 9 I/O40
ptr IoCard9Pt41->u.io:$C00014.25.1 // I/O Card 9 I/O41
ptr IoCard9Pt42->u.io:$C00014.26.1 // I/O Card 9 I/O42
ptr IoCard9Pt43->u.io:$C00014.27.1 // I/O Card 9 I/O43
ptr IoCard9Pt44->u.io:$C00014.28.1 // I/O Card 9 I/O44
ptr IoCard9Pt45->u.io:$C00014.29.1 // I/O Card 9 I/O45
ptr IoCard9Pt46->u.io:$C00014.30.1 // I/O Card 9 I/O46
ptr IoCard9Pt47->u.io:$C00014.31.1 // I/O Card 9 I/O47
// Byte-wide variables used for power-on configuration
ptr IoCard9Reg0->u.io:$C00000.24.8 // I/O Card 9 I/O00-07 as byte
ptr IoCard9Reg1->u.io:$C00004.24.8 // I/O Card 9 I/O08-15 as byte
ptr IoCard9Reg2->u.io:$C00008.24.8 // I/O Card 9 I/O16-23 as byte
ptr IoCard9Reg3->u.io:$C0000C.24.8 // I/O Card 9 I/O24-31 as byte
ptr IoCard9Reg4->u.io:$C00010.24.8 // I/O Card 9 I/O32-39 as byte
ptr IoCard9Reg5->u.io:$C00014.24.8 // I/O Card 9 I/O40-47 as byte
ptr IoCard9Reg6->u.io:$C00018.24.8 // I/O Card 9 latch inputs
ptr IoCard9Reg7->u.io:$C0001C.24.8 // I/O Card 9 control register
Page 87

ACC-11E User Manual
Appendix C: Full Power UMAC M-Variable Mappings 87
Base offset $D00000, Low
// Single-bit variables used for accessing I/O points
ptr IoCard10Pt00->u.io:$D00000.8.1 // I/O Card 10 I/O00
ptr IoCard10Pt01->u.io:$D00000.9.1 // I/O Card 10 I/O01
ptr IoCard10Pt02->u.io:$D00000.10.1 // I/O Card 10 I/O02
ptr IoCard10Pt03->u.io:$D00000.11.1 // I/O Card 10 I/O03
ptr IoCard10Pt04->u.io:$D00000.12.1 // I/O Card 10 I/O04
ptr IoCard10Pt05->u.io:$D00000.13.1 // I/O Card 10 I/O05
ptr IoCard10Pt06->u.io:$D00000.14.1 // I/O Card 10 I/O06
ptr IoCard10Pt07->u.io:$D00000.15.1 // I/O Card 10 I/O07
ptr IoCard10Pt08->u.io:$D00004.8.1 // I/O Card 10 I/O08
ptr IoCard10Pt09->u.io:$D00004.9.1 // I/O Card 10 I/O09
ptr IoCard10Pt10->u.io:$D00004.10.1 // I/O Card 10 I/O10
ptr IoCard10Pt11->u.io:$D00004.11.1 // I/O Card 10 I/O11
ptr IoCard10Pt12->u.io:$D00004.12.1 // I/O Card 10 I/O12
ptr IoCard10Pt13->u.io:$D00004.13.1 // I/O Card 10 I/O13
ptr IoCard10Pt14->u.io:$D00004.14.1 // I/O Card 10 I/O14
ptr IoCard10Pt15->u.io:$D00004.15.1 // I/O Card 10 I/O15
ptr IoCard10Pt16->u.io:$D00008.8.1 // I/O Card 10 I/O16
ptr IoCard10Pt17->u.io:$D00008.9.1 // I/O Card 10 I/O17
ptr IoCard10Pt18->u.io:$D00008.10.1 // I/O Card 10 I/O18
ptr IoCard10Pt19->u.io:$D00008.11.1 // I/O Card 10 I/O19
ptr IoCard10Pt20->u.io:$D00008.12.1 // I/O Card 10 I/O20
ptr IoCard10Pt21->u.io:$D00008.13.1 // I/O Card 10 I/O21
ptr IoCard10Pt22->u.io:$D00008.14.1 // I/O Card 10 I/O22
ptr IoCard10Pt23->u.io:$D00008.15.1 // I/O Card 10 I/O23
ptr IoCard10Pt24->u.io:$D0000C.8.1 // I/O Card 10 I/O24
ptr IoCard10Pt25->u.io:$D0000C.9.1 // I/O Card 10 I/O25
ptr IoCard10Pt26->u.io:$D0000C.10.1 // I/O Card 10 I/O26
ptr IoCard10Pt27->u.io:$D0000C.11.1 // I/O Card 10 I/O27
ptr IoCard10Pt28->u.io:$D0000C.12.1 // I/O Card 10 I/O28
ptr IoCard10Pt29->u.io:$D0000C.13.1 // I/O Card 10 I/O29
ptr IoCard10Pt30->u.io:$D0000C.14.1 // I/O Card 10 I/O30
ptr IoCard10Pt31->u.io:$D0000C.15.1 // I/O Card 10 I/O31
ptr IoCard10Pt32->u.io:$D00010.8.1 // I/O Card 10 I/O32
ptr IoCard10Pt33->u.io:$D00010.9.1 // I/O Card 10 I/O33
ptr IoCard10Pt34->u.io:$D00010.10.1 // I/O Card 10 I/O34
ptr IoCard10Pt35->u.io:$D00010.11.1 // I/O Card 10 I/O35
ptr IoCard10Pt36->u.io:$D00010.12.1 // I/O Card 10 I/O36
ptr IoCard10Pt37->u.io:$D00010.13.1 // I/O Card 10 I/O37
ptr IoCard10Pt38->u.io:$D00010.14.1 // I/O Card 10 I/O38
ptr IoCard10Pt39->u.io:$D00010.15.1 // I/O Card 10 I/O39
ptr IoCard10Pt40->u.io:$D00014.8.1 // I/O Card 10 I/O40
ptr IoCard10Pt41->u.io:$D00014.9.1 // I/O Card 10 I/O41
ptr IoCard10Pt42->u.io:$D00014.10.1 // I/O Card 10 I/O42
ptr IoCard10Pt43->u.io:$D00014.11.1 // I/O Card 10 I/O43
ptr IoCard10Pt44->u.io:$D00014.12.1 // I/O Card 10 I/O44
ptr IoCard10Pt45->u.io:$D00014.13.1 // I/O Card 10 I/O45
ptr IoCard10Pt46->u.io:$D00014.14.1 // I/O Card 10 I/O46
ptr IoCard10Pt47->u.io:$D00014.15.1 // I/O Card 10 I/O47
// Byte-wide variables used for power-on configuration
ptr IoCard10Reg0->u.io:$D00000.8.8 // I/O Card 10 I/O00-07 as byte
ptr IoCard10Reg1->u.io:$D00004.8.8 // I/O Card 10 I/O08-15 as byte
ptr IoCard10Reg2->u.io:$D00008.8.8 // I/O Card 10 I/O16-23 as byte
ptr IoCard10Reg3->u.io:$D0000C.8.8 // I/O Card 10 I/O24-31 as byte
ptr IoCard10Reg4->u.io:$D00010.8.8 // I/O Card 10 I/O32-39 as byte
ptr IoCard10Reg5->u.io:$D00014.8.8 // I/O Card 10 I/O40-47 as byte
ptr IoCard10Reg6->u.io:$D00018.8.8 // I/O Card 10 latch inputs
ptr IoCard10Reg7->u.io:$D0001C.8.8 // I/O Card 10 control register
Page 88

ACC-11E User Manual
Appendix C: Full Power UMAC M-Variable Mappings 88
Base Offset $D00000, Middle Byte
// Single-bit variables used for accessing I/O points
ptr IoCard11Pt00->u.io:$D00000.16.1 // I/O Card 11 I/O00
ptr IoCard11Pt01->u.io:$D00000.17.1 // I/O Card 11 I/O01
ptr IoCard11Pt02->u.io:$D00000.18.1 // I/O Card 11 I/O02
ptr IoCard11Pt03->u.io:$D00000.19.1 // I/O Card 11 I/O03
ptr IoCard11Pt04->u.io:$D00000.20.1 // I/O Card 11 I/O04
ptr IoCard11Pt05->u.io:$D00000.21.1 // I/O Card 11 I/O05
ptr IoCard11Pt06->u.io:$D00000.22.1 // I/O Card 11 I/O06
ptr IoCard11Pt07->u.io:$D00000.23.1 // I/O Card 11 I/O07
ptr IoCard11Pt08->u.io:$D00004.16.1 // I/O Card 11 I/O08
ptr IoCard11Pt09->u.io:$D00004.17.1 // I/O Card 11 I/O09
ptr IoCard11Pt10->u.io:$D00004.18.1 // I/O Card 11 I/O10
ptr IoCard11Pt11->u.io:$D00004.19.1 // I/O Card 11 I/O11
ptr IoCard11Pt12->u.io:$D00004.20.1 // I/O Card 11 I/O12
ptr IoCard11Pt13->u.io:$D00004.21.1 // I/O Card 11 I/O13
ptr IoCard11Pt14->u.io:$D00004.22.1 // I/O Card 11 I/O14
ptr IoCard11Pt15->u.io:$D00004.23.1 // I/O Card 11 I/O15
ptr IoCard11Pt16->u.io:$D00008.16.1 // I/O Card 11 I/O16
ptr IoCard11Pt17->u.io:$D00008.17.1 // I/O Card 11 I/O17
ptr IoCard11Pt18->u.io:$D00008.18.1 // I/O Card 11 I/O18
ptr IoCard11Pt19->u.io:$D00008.19.1 // I/O Card 11 I/O19
ptr IoCard11Pt20->u.io:$D00008.20.1 // I/O Card 11 I/O20
ptr IoCard11Pt21->u.io:$D00008.21.1 // I/O Card 11 I/O21
ptr IoCard11Pt22->u.io:$D00008.22.1 // I/O Card 11 I/O22
ptr IoCard11Pt23->u.io:$D00008.23.1 // I/O Card 11 I/O23
ptr IoCard11Pt24->u.io:$D0000C.16.1 // I/O Card 11 I/O24
ptr IoCard11Pt25->u.io:$D0000C.17.1 // I/O Card 11 I/O25
ptr IoCard11Pt26->u.io:$D0000C.18.1 // I/O Card 11 I/O26
ptr IoCard11Pt27->u.io:$D0000C.19.1 // I/O Card 11 I/O27
ptr IoCard11Pt28->u.io:$D0000C.20.1 // I/O Card 11 I/O28
ptr IoCard11Pt29->u.io:$D0000C.21.1 // I/O Card 11 I/O29
ptr IoCard11Pt30->u.io:$D0000C.22.1 // I/O Card 11 I/O30
ptr IoCard11Pt31->u.io:$D0000C.23.1 // I/O Card 11 I/O31
ptr IoCard11Pt32->u.io:$D00010.16.1 // I/O Card 11 I/O32
ptr IoCard11Pt33->u.io:$D00010.17.1 // I/O Card 11 I/O33
ptr IoCard11Pt34->u.io:$D00010.18.1 // I/O Card 11 I/O34
ptr IoCard11Pt35->u.io:$D00010.19.1 // I/O Card 11 I/O35
ptr IoCard11Pt36->u.io:$D00010.20.1 // I/O Card 11 I/O36
ptr IoCard11Pt37->u.io:$D00010.21.1 // I/O Card 11 I/O37
ptr IoCard11Pt38->u.io:$D00010.22.1 // I/O Card 11 I/O38
ptr IoCard11Pt39->u.io:$D00010.23.1 // I/O Card 11 I/O39
ptr IoCard11Pt40->u.io:$D00014.16.1 // I/O Card 11 I/O40
ptr IoCard11Pt41->u.io:$D00014.17.1 // I/O Card 11 I/O41
ptr IoCard11Pt42->u.io:$D00014.18.1 // I/O Card 11 I/O42
ptr IoCard11Pt43->u.io:$D00014.19.1 // I/O Card 11 I/O43
ptr IoCard11Pt44->u.io:$D00014.20.1 // I/O Card 11 I/O44
ptr IoCard11Pt45->u.io:$D00014.21.1 // I/O Card 11 I/O45
ptr IoCard11Pt46->u.io:$D00014.22.1 // I/O Card 11 I/O46
ptr IoCard11Pt47->u.io:$D00014.23.1 // I/O Card 11 I/O47
// Byte-wide variables used for power-on configuration
ptr IoCard11Reg0->u.io:$D00000.16.8 // I/O Card 11 I/O00-07 as byte
ptr IoCard11Reg1->u.io:$D00004.16.8 // I/O Card 11 I/O08-15 as byte
ptr IoCard11Reg2->u.io:$D00008.16.8 // I/O Card 11 I/O16-23 as byte
ptr IoCard11Reg3->u.io:$D0000C.16.8 // I/O Card 11 I/O24-31 as byte
ptr IoCard11Reg4->u.io:$D00010.16.8 // I/O Card 11 I/O32-39 as byte
ptr IoCard11Reg5->u.io:$D00014.16.8 // I/O Card 11 I/O40-47 as byte
ptr IoCard11Reg6->u.io:$D00018.16.8 // I/O Card 11 latch inputs
ptr IoCard11Reg7->u.io:$D0001C.16.8 // I/O Card 11 control register
Page 89

ACC-11E User Manual
Appendix C: Full Power UMAC M-Variable Mappings 89
Base offset $D00000, High Byte
// Single-bit variables used for accessing I/O points
ptr IoCard12Pt00->u.io:$D00000.24.1 // I/O Card 12 I/O00
ptr IoCard12Pt01->u.io:$D00000.25.1 // I/O Card 12 I/O01
ptr IoCard12Pt02->u.io:$D00000.26.1 // I/O Card 12 I/O02
ptr IoCard12Pt03->u.io:$D00000.27.1 // I/O Card 12 I/O03
ptr IoCard12Pt04->u.io:$D00000.28.1 // I/O Card 12 I/O04
ptr IoCard12Pt05->u.io:$D00000.29.1 // I/O Card 12 I/O05
ptr IoCard12Pt06->u.io:$D00000.30.1 // I/O Card 12 I/O06
ptr IoCard12Pt07->u.io:$D00000.31.1 // I/O Card 12 I/O07
ptr IoCard12Pt08->u.io:$D00004.24.1 // I/O Card 12 I/O08
ptr IoCard12Pt09->u.io:$D00004.25.1 // I/O Card 12 I/O09
ptr IoCard12Pt10->u.io:$D00004.26.1 // I/O Card 12 I/O10
ptr IoCard12Pt11->u.io:$D00004.27.1 // I/O Card 12 I/O11
ptr IoCard12Pt12->u.io:$D00004.28.1 // I/O Card 12 I/O12
ptr IoCard12Pt13->u.io:$D00004.29.1 // I/O Card 12 I/O13
ptr IoCard12Pt14->u.io:$D00004.30.1 // I/O Card 12 I/O14
ptr IoCard12Pt15->u.io:$D00004.31.1 // I/O Card 12 I/O15
ptr IoCard12Pt16->u.io:$D00008.24.1 // I/O Card 12 I/O16
ptr IoCard12Pt17->u.io:$D00008.25.1 // I/O Card 12 I/O17
ptr IoCard12Pt18->u.io:$D00008.26.1 // I/O Card 12 I/O18
ptr IoCard12Pt19->u.io:$D00008.27.1 // I/O Card 12 I/O19
ptr IoCard12Pt20->u.io:$D00008.28.1 // I/O Card 12 I/O20
ptr IoCard12Pt21->u.io:$D00008.29.1 // I/O Card 12 I/O21
ptr IoCard12Pt22->u.io:$D00008.30.1 // I/O Card 12 I/O22
ptr IoCard12Pt23->u.io:$D00008.31.1 // I/O Card 12 I/O23
ptr IoCard12Pt24->u.io:$D0000C.24.1 // I/O Card 12 I/O24
ptr IoCard12Pt25->u.io:$D0000C.25.1 // I/O Card 12 I/O25
ptr IoCard12Pt26->u.io:$D0000C.26.1 // I/O Card 12 I/O26
ptr IoCard12Pt27->u.io:$D0000C.27.1 // I/O Card 12 I/O27
ptr IoCard12Pt28->u.io:$D0000C.28.1 // I/O Card 12 I/O28
ptr IoCard12Pt29->u.io:$D0000C.29.1 // I/O Card 12 I/O29
ptr IoCard12Pt30->u.io:$D0000C.30.1 // I/O Card 12 I/O30
ptr IoCard12Pt31->u.io:$D0000C.31.1 // I/O Card 12 I/O31
ptr IoCard12Pt32->u.io:$D00010.24.1 // I/O Card 12 I/O32
ptr IoCard12Pt33->u.io:$D00010.25.1 // I/O Card 12 I/O33
ptr IoCard12Pt34->u.io:$D00010.26.1 // I/O Card 12 I/O34
ptr IoCard12Pt35->u.io:$D00010.27.1 // I/O Card 12 I/O35
ptr IoCard12Pt36->u.io:$D00010.28.1 // I/O Card 12 I/O36
ptr IoCard12Pt37->u.io:$D00010.29.1 // I/O Card 12 I/O37
ptr IoCard12Pt38->u.io:$D00010.30.1 // I/O Card 12 I/O38
ptr IoCard12Pt39->u.io:$D00010.31.1 // I/O Card 12 I/O39
ptr IoCard12Pt40->u.io:$D00014.24.1 // I/O Card 12 I/O40
ptr IoCard12Pt41->u.io:$D00014.25.1 // I/O Card 12 I/O41
ptr IoCard12Pt42->u.io:$D00014.26.1 // I/O Card 12 I/O42
ptr IoCard12Pt43->u.io:$D00014.27.1 // I/O Card 12 I/O43
ptr IoCard12Pt44->u.io:$D00014.28.1 // I/O Card 12 I/O44
ptr IoCard12Pt45->u.io:$D00014.29.1 // I/O Card 12 I/O45
ptr IoCard12Pt46->u.io:$D00014.30.1 // I/O Card 12 I/O46
ptr IoCard12Pt47->u.io:$D00014.31.1 // I/O Card 12 I/O47
// Byte-wide variables used for power-on configuration
ptr IoCard12Reg0->u.io:$D00000.24.8 // I/O Card 12 I/O00-07 as byte
ptr IoCard12Reg1->u.io:$D00004.24.8 // I/O Card 12 I/O08-15 as byte
ptr IoCard12Reg2->u.io:$D00008.24.8 // I/O Card 12 I/O16-23 as byte
ptr IoCard12Reg3->u.io:$D0000C.24.8 // I/O Card 12 I/O24-31 as byte
ptr IoCard12Reg4->u.io:$D00010.24.8 // I/O Card 12 I/O32-39 as byte
ptr IoCard12Reg5->u.io:$D00014.24.8 // I/O Card 12 I/O40-47 as byte
ptr IoCard12Reg6->u.io:$D00018.24.8 // I/O Card 12 latch inputs
ptr IoCard12Reg7->u.io:$D0001C.24.8 // I/O Card 12 control register
Page 90

ACC-11E User Manual
Appendix D: The Control Word 90
APPENDIX D: THE CONTROL WORD
The Control Word must be set equal to 7 every startup, usually in PLC 1.
The function of each bit in the control word is as follows:
Control Word Bit Number
Value
I/O Bits
Modified
I/O Bits
Function
0
1
0–7
Inputs 1-8
1
1
8–15
Inputs 9-16
2
1
16–23
Inputs 17-24
3
0
24–31
Outputs 1-8
4
0
32–39
Outputs 9-16
5
0
40–47
Outputs 17-24
6
0
None
Register Select
7
0
None
Register Select
The ACC-11E will only operate with a control word value of 7 because it cannot be altered from its 24
input/24 output configuration. The value would only be different for an accessory with a different
configuration, for instance a 48-bit input card.
Register Select Control Bits
Note
The register select control bits are generally not applicable to the
ACC-11E and should therefore generally be left at the default value of
0.
Bits 6 and 7 of the control register together select which of four possible registers can be accessed at each
of the addresses {Base + 0} through {Base + 5}. They also select which of two possible registers can be
selected at {Base + 6}. The following table shows how these bits select registers:
Bit 7
Bit 6
Combined
Value
{Base + 0} to {Base + 5}
Register Selected
{Base + 6} Register
Selected
0 0 0
Data Register
Data Register
0 1 1
Setup Register 1
Setup Register
1 0 2
Setup Register 2
n. a.
1 1 3
Setup Register 3
n. a.
The setup registers can be used to configure the ACC-11E for gray code, logic inversion, or latching
inputs (see the ACC-14E manual for latching inputs).
Typically, bits 6 and 7 are left at zero. If not left at zero, typically non-zero combined values of bits 6 and
7 are only used for initial configuration of the IC. These values are used to access the setup registers at
the other addresses. After the configuration is finished, a zero is written to Bit 6 and 7 so that the data
registers can be accessed.
 Loading...
Loading...