
Street Atlas USA 2012 User Guide


Table of Contents
Getting Started .......................................................................................................... 1
Welcome to Street Atlas USA .................................................................................... 1
Frequently Asked Questions ...................................................................................... 2
Learning the Basics .................................................................................................. 8
Helpful Tips ............................................................................................................ 9
Activating Advanced/Simplified File Management ....................................................... 12
Glossary Term s ..................................................................................................... 13
Basic Functions ..................................................................................................... 18
Zooming In and Out .............................................................................................. 18
Panning/Centering the Map ..................................................................................... 19
Copying Your Map to the Clipboard .......................................................................... 20
Saving a Map as a Bitmap or JPEG Image ................................................................. 20
Measuring Distance and Area .................................................................................. 21
Chart of Supported Coordinate Formats.................................................................... 22
Searching Tips ...................................................................................................... 24
About the Interface................................................................................................ 24
Tab Area .............................................................................................................. 24
Control Panel ........................................................................................................ 25
Overview Map ....................................................................................................... 26
Toolbar ................................................................................................................ 26
Using the Help System ........................................................................................... 27
Help Overview....................................................................................................... 27
Using the Help System ........................................................................................... 28
Help Documentation Conventions ............................................................................ 29
Tutorials ................................................................................................................. 31
Tutorial: Use the E-Z Nav Route Wizard ................................................................... 31
Tutorial: Find Points of Interest on a Route ............................................................... 35
Tutorial: Plan a Long Distance Trip .......................................................................... 37
Tutorial: Share Maps .............................................................................................. 39
Tutorial: Route with XData Points ............................................................................ 43
Map Legend ............................................................................................................. 45
Map Legend .......................................................................................................... 45
Using the Toolbar ..................................................................................................... 49
Showing/Hiding Toolbar Options .............................................................................. 49
Reordering the Toolbar Options ............................................................................... 49
To Create a New Map File ....................................................................................... 49
To Open a Map File ................................................................................................ 50
To Save a Map File ................................................................................................ 50
To Share Maps ...................................................................................................... 50
To Create a Route ................................................................................................. 50
iii

Street Atlas USA 2012 User Guide
To Start/Stop Your GPS Connection ......................................................................... 51
To Use GPS NavMode ............................................................................................. 51
To Open the Map Library ........................................................................................ 52
To View Imagery ................................................................................................... 52
To Get Information About a Location ........................................................................ 53
To Choose Options ................................................................................................. 54
To Exchange Files with a GPS .................................................................................. 55
To Add Images to a GPS Location ............................................................................ 55
To Grab and Pan the Map ....................................................................................... 55
To Measure Distance .............................................................................................. 55
To Print ................................................................................................................ 56
To Print the Map Screen ......................................................................................... 56
Customizing the Map and Tab Display ......................................................................... 57
Display Options Overview ....................................................................................... 57
Customizing the Interface ....................................................................................... 57
Displaying Basic Map Features ................................................................................ 58
Customizing the Map Feature Preferences ................................................................. 59
Changing the Map Colors ........................................................................................ 60
Changing the Map Magnification Level ...................................................................... 61
Changing How POIs Display on the Map ................................................................... 61
Setting Units of Measure Preferences ....................................................................... 62
Resizing the Map and Tab Areas .............................................................................. 64
Showing or Hiding Tabs .......................................................................................... 66
Importing/Exporting Tab Manager Preferences .......................................................... 67
Reordering the Tabs .............................................................................................. 68
Using Keyboard Shortcuts ......................................................................................... 69
Selecting a Keyboard Shortcut Scheme .................................................................... 69
Creating a New Custom Scheme .............................................................................. 69
Assigning Keyboard Shortcuts in a Cust om Scheme ................................................... 70
Customizing a DeLorme Sch eme ............................................................................. 71
Renaming a Custom Scheme .................................................................................. 71
Deleting a Custom Scheme ..................................................................................... 72
Importing a Custom Scheme ................................................................................... 72
Exporting a Custom Scheme ................................................................................... 73
Searching For Commands ....................................................................................... 73
Viewing All of the Shortcut Keys for a Scheme .......................................................... 73
Viewing Map Data .................................................................................................... 75
Saving Data to Your Hard Drive ............................................................................... 75
Connecting Data .................................................................................................... 75
Viewing Imagery ................................................................................................... 76
Showing Roads in Raster Data ................................................................................ 76
iv

Table of Contents
Using Map Files ........................................................................................................ 77
Map Files Overview ................................................................................................ 77
Creating and Deleting Map Files .............................................................................. 78
Opening an Existing Map File .................................................................................. 78
Setting which Map File Opens with Stree t Atlas USA .................................................. 79
Saving a Map File .................................................................................................. 80
Editing a Map File .................................................................................................. 80
Creating Transfer Files ........................................................................................... 81
Creating Transfer Files with Hyperlinked Files ............................................................ 82
Importing Transfer Files ......................................................................................... 83
E-mailing a Transfer File ......................................................................................... 84
Printing ................................................................................................................... 87
Printing a Map ....................................................................................................... 87
Printing a Route and Directions ............................................................................... 88
Adding Text or Graphics to Your Map ....................................................................... 89
Aligning Text and Graphic Items on Your Map ........................................................... 91
Snapping Text and Graphic Items on Your Map ......................................................... 93
Layering Multiple Text and Graphic Items on a Printed Map ........................................ 93
Changing the Background Color of a Printed Map ....................................................... 94
Manually Assembling a Multi-page Map .................................................................... 95
Finding a Location on the Map.................................................................................... 99
Find Overview ....................................................................................................... 99
Find Options ......................................................................................................... 99
Performing a Basic Search .................................................................................... 100
Performing an Advanced Search ............................................................................ 101
Performing a POI Search ...................................................................................... 104
Finding Points Near Your Current Location .............................................................. 105
Finding a Symbol by its Name ............................................................................... 106
Tips on Viewing Search Results ............................................................................. 107
Keywords for Cat egory Searches ........................................................................... 108
MapTags: Converting, Moving, Hiding, and Deleting ................................................. 110
Using Address Book Contacts ................................................................................... 113
Searching for Address Book Contacts ..................................................................... 113
Importing Existing Address Book Information .......................................................... 113
Manually Entering Address Book Information .......................................................... 114
Centering the Map on an Address Book Contact ....................................................... 114
Editing a Contact In Your Address Book .................................................................. 115
Manually Moving a Contact on the Map ................................................................... 115
Relocating Address Book Contacts ......................................................................... 116
Deleting a Contact In Your Address Book ................................................................ 116
Showing/Hiding Address Book Contacts o n the Map ................................................. 117
Deleting Your Entire Address Book ......................................................................... 117
v

Street Atlas USA 2012 User Guide
Exporting Your Address Book ................................................................................ 118
Searching for Phone Book Listings ............................................................................ 119
Using Phone Data ................................................................................................ 119
Searching for a Pho n e Book Listing ........................................................................ 120
Finding Phone Book Listings for a Specific Ro a d ....................................................... 123
Using XData .......................................................................................................... 125
XData Overview .................................................................................................. 125
Importing Data ................................................................................................... 125
Managing Datasets .............................................................................................. 127
Viewing Dataset Records ...................................................................................... 128
Creating a Route with XData Records ..................................................................... 129
Geocoding or Moving a Record's Location ............................................................... 129
Exporting Data .................................................................................................... 130
Printing XData Dataset Records ............................................................................. 131
Using the Draw Tools .............................................................................................. 133
Draw Overview ................................................................................................... 133
Viewing Hidden Draw Tools ................................................................................... 136
Draw File Management ......................................................................................... 136
Creating a New Draw File ..................................................................................... 136
Saving a Draw File ............................................................................................... 137
Deleting a Draw File ............................................................................................. 138
Hiding Draw Files ................................................................................................ 139
Editing/Locking Draw Files .................................................................................... 139
Exporting Draw Files to Text Files .......................................................................... 140
Exporting Track or Waypoint Files to GPX Files ........................................................ 141
Importing Files to Draw Files................................................................................. 142
Formatting a Text File to Import as a Draw File ....................................................... 144
Copying a Map Line to a Draw File ......................................................................... 145
Saving a Track as a GPS Log ................................................................................. 146
Viewing the Contents of a Draw File ....................................................................... 146
Copying a Draw File ............................................................................................. 148
Changing Draw Object Types ................................................................................ 148
Renaming a Draw File .......................................................................................... 150
Copying a Draw Object From One Draw File to Another ............................................ 150
Moving a Draw Object to a Different Draw File ........................................................ 151
Using Draw Objects ............................................................................................. 152
Copying and Placing Draw Objects ......................................................................... 152
Moving Draw Objects ........................................................................................... 152
Renaming a Draw Object ...................................................................................... 154
Deleting Draw Objects ......................................................................................... 154
Snapping Draw Objects ........................................................................................ 155
Adding Points to Draw Objects .............................................................................. 156
vi

Table of Contents
Deleting Points and Line Segments from Draw Objects ............................................. 157
Labeling a Draw Object ........................................................................................ 157
Routable Roads, Tracks, Lines, Arcs, and S plines ..................................................... 158
Drawing Routable Roads on the Map ...................................................................... 158
Drawing a Line, Arc, or Spline on the Map .............................................................. 159
Drawing a Track on the Map ................................................................................. 160
Editing a Routable Road, Line, Arc, or Spline ........................................................... 161
Editing a Track .................................................................................................... 161
Placing a Routable Road, Line, Arc, or Spline at a Specific Location ............................ 162
Joining and Breaking Linear Objects ....................................................................... 163
Circles, Rectangles, and Polygons .......................................................................... 164
Drawing a Circle, Rectangle, or Polygon on the Map ................................................. 164
Editing a Circle, Rectangle, or Polygon ................................................................... 165
Placing a Circle, Rectangle, or Polygon on the Map .................................................. 166
Waypoints, Symbols, MapNotes, Text Labels, and Images ........................................ 166
Adding a Waypoint, Symbol, MapNote, Text Labe l, or Image to the Map ..................... 166
Editing a Waypoint, Symbol, MapNote, Text Label, or Image ..................................... 169
Placing a Waypoint, Symbol, Text Labe l, or Image at a Specific Loc ation .................... 169
Moving and Deleting Draw MapNotes ..................................................................... 170
Custom Symbols ................................................................................................. 171
Custom Symbols Overview ................................................................................... 171
Creating a New Symbol ........................................................................................ 172
GPS Device Custom Symbols ................................................................................ 173
Editing a Symbol ................................................................................................. 174
Finding a Custom Symbol ..................................................................................... 175
Importing a Bitmap ............................................................................................. 175
Copying and Pasting ............................................................................................ 176
Pasting a Bitmap into XSym .................................................................................. 177
Dragging a Bitmap into XSym ............................................................................... 178
Removing a Symbol ............................................................................................. 179
Draw Tool Box .................................................................................................... 179
Using the Transparency Option ............................................................................. 180
Anchor Positi on ................................................................................................... 180
Cursor Posi ti on .................................................................................................... 181
Creating a New Symbol Set .................................................................................. 181
Opening a Symbol Set ......................................................................................... 182
Routing ................................................................................................................. 183
Creating a Route ................................................................................................. 183
Adding and Inserting Stops and Vias ...................................................................... 184
Changing the Routing Method ............................................................................... 187
Changing the Properties of a Stop Along Your Route ................................................ 187
Viewing Route Directions ...................................................................................... 188
vii

Street Atlas USA 2012 User Guide
Avoiding a Specified Area When Routing ................................................................. 188
Saving Route Directions as Text ............................................................................ 189
Setting Your Routing Preferences .......................................................................... 189
Editing a Route ................................................................................................... 190
Editing Roads ...................................................................................................... 191
Labeling a Route Point with a MapNote ................................................................... 192
Moving Route MapNotes ....................................................................................... 193
Displaying and Centering Routes on the Map........................................................... 193
Saving a Route .................................................................................................... 194
Deleting a Route ................................................................................................. 194
Importing Routes ................................................................................................ 195
Setting Your End of Day and Fuel Break Preferences ................................................ 195
Estimating the Fuel Cost of Your Route................................................................... 196
Converting a Route to a GPS Log ........................................................................... 197
Using GPS ............................................................................................................. 199
GPS Overview ..................................................................................................... 199
GPS Options/Initializing GPS ................................................................................. 199
Using NavMode or GPS Tab View ........................................................................... 202
Tracking a Route with GPS.................................................................................... 203
Getting Back on Track When Off Course ................................................................. 205
Using the E-Z Nav Route Wizard ............................................................................ 205
Panning the Map Auto matically While GPS Tracking ................................................. 207
Playin g Back a Log File ......................................................................................... 207
Previewing a GPS Lo g File ..................................................................................... 209
Viewing File Details for a GPS Log .......................................................................... 209
Monitoring Your GPS S tatus .................................................................................. 209
Monitoring GPS Satellite Information...................................................................... 211
Viewing Sun and Moon Information........................................................................ 212
GPS Devices ....................................................................................................... 212
About GPS .......................................................................................................... 213
Using Small-screen Devices ..................................................................................... 215
Using Small-screen Devices .................................................................................. 215
Using Voice Navigation and Speech Recognition ......................................................... 217
Voice Overview ................................................................................................... 217
Voice Options ...................................................................................................... 217
Activating and Monitoring Speech Recognition ......................................................... 218
Training the Speech R ecognition Engine ................................................................. 219
Voice Commands ................................................................................................. 220
Speech Recognition Tips ....................................................................................... 223
Changing Voice Output ......................................................................................... 224
Voice Preferences ................................................................................................ 225
Voice Prompts ..................................................................................................... 225
viii

Table of Contents
Exchanging Information with a Third-party GPS Device ............................................... 227
Sending Route Information ................................................................................... 227
Sending Tracks ................................................................................................... 228
Sending Waypoints .............................................................................................. 228
Receiving a Route ................................................................................................ 229
Receiving a Track ................................................................................................ 230
Receiving Waypoints ............................................................................................ 230
Using NetLink ........................................................................................................ 233
NetLink .............................................................................................................. 233
Using GeoTagger .................................................................................................... 235
Getting Started with GeoTagger ............................................................................ 235
Tagging an Image ............................................................................................... 235
Calculate the Timestamp Offset ............................................................................. 236
Legal Information ................................................................................................... 237
Street Atlas USA® 2012 Plus Single-User License Agreement ................................... 237
Important Notices................................................................................................ 241
Apache License, Version 2.0 ................................................................................. 246
Index .................................................................................................................... 251
ix

Getting Started
Welcome to Street Atlas USA
Tip
Additio n al informatio n is av a i la ble online:
support.delorme.com
forum.delorme.com
Street Atlas USA Features
• GPS NavMode—a hands free full-screen view that you can view in 2-D or 3-D. GPS
Radar results display on the screen. Optimized for use on netbooks.
• Find a street address, city/town, ZIP/Postal Code, coordinate, point of interest, and
more. Use the advanced search function to locate the intersection of two streets, a
specific category of map items, such as landmarks along the current route, or an
area code and exchange.
• Connect your GPS device to the program and track your progre ss on a portable
computer as you travel. View your next turn as well as the turn after that—very
helpful when you need to make a turn directly af t er another turn. You can even use
automatic back-on-track feature to recalculate your route when detours v9er you
the
off course.
• Use MapShare to share your current map view and even route directions with
anyone.
• Use the NetLink tab to get free downloads of data and imagery from the Map Library
for your area of interest.
• Use Canadian data to create door-to-door routes in Canada.
• Import your personal address book information
map. You can even use them as a start, stop, or finish route point or search for them
using the Find tab.
• Create custom keyboard shortcuts to navigate the program more easily than ever.
• Combine digital photos with GPS locations using GeoTagger.
• Use the toolbar to creat e rou t e s, sh are maps, open/ cr ea t e/save map files, an d edi t
your preferences.
• Print high quality, detailed, single-page maps or mural maps as large as 3 x 3 pages.
• Print your route and/or route directions.
• Customize your map with routable roads, text, MapNotes, and more!
With the Phone tab in Str eet Atlas USA Plus, you can also:
• Search over 121 million residential and business phone listings
• Find phone numbers for a specific roa d .
and visualize your contacts on the
, including Canada.
1

Street Atlas USA 2012 User Guide
Frequently Asked Questions
These questions are asked most frequently by our customers.
• Where do I find the map and other options settings?
All options are located in the Options dialog box. To open it, click the Options button
on the toolbar. You can use it to modify GPS, voice, map feature,
display, and keyboard shortcut preferences. For more information, see the Toolbar
topic.
Notes
• Some tabs also have an Options button , which opens the same dialog
box.
• You can also click the arrow next to the Options toolbar button to open the
Options menu. Then, click Options to open the dialog box.
• How can I make the program open with my most recent map file instead of in Salt
Lake City?
Use the Welcome Screen to determine if you want to create a new map file project
each time you open Street Atlas USA or if you want to open a recent map file. When
you use the new map file option, the default location is Salt Lake City.
• Upgraders only: What happens to my map files when I upgrade?
Your map files, draw files, route files, and log files are stored in the DeLorme Docs
folder, usually found on the root of your computer's C: drive. They are not affected
by an install or removal of DeLorme software.
• Upgraders only: Why doesn't this version of Street Atlas USA overwrite the older
version?
This allows you to view both versions on the same computer.
• Upgraders only: Should I uninstall my pre vious version before installing this
version of Street Atlas USA?
Uninstalling is not necessary; however, you can uninstall the previous edition of the
software ei ther before or after installing this version of Street Atlas USA.
• Can I see my imagery and data from Topo USA, Topo North America, and XMap on
the map?
Yes, as long as the DeLorme Docs\Downloads is located in the same location for
Street Atlas USA as it was in Topo USA, Topo North America, or XMap.
Note You cannot view 7.5-minute USGS Quad maps, NOAA charts, or DigitalGlobe®
maps in Street Atlas USA.
• How do I create a route?
2
You can create a ro ute using the Route tab, right-click menu options, or the toolbar.
If you are using a GPS, you can use E-Z Nav to quickly create a route to a location.
See the following topics for more information about creating routes.

Getting Started
Creating a Route
Tutorial: Plan a Long Distance Trip
Tutorial: Use the E-Z Nav Route Wizard
• How do I import files from an earlier version of Street Atlas USA into this version?
You can import map files, routes, and draw files from many other DeLorme mapping
programs by using a drag-and-drop operation or by using the import function in
Street Atlas USA.
Note Information for Street Atlas USA 9.0 and earlier users.
The structure of map files has changed throughout the life of Street Atlas USA. Map
files in older products, such as Street Atlas USA 9.0 and earlier, are a single file that
contain route information, draw objects , and the current display settings. These map
files cannot be opened in this version of Street Atlas USA; however, you can view the
route and/or draw information that the map file c ontains using the import and dragand-drop functions within Street Atlas USA.
Map files do not contain the draw and route information but connect to separate
route and draw files. You can open these map files in Street Atlas USA to view their
contents. Or, you can import/drag-and-drop the draw/route information individually.
To Open A Map File
1. Click the Map Files tab.
2. Click File and then click Open.
3. Select the map file you want to view and then click Open.
Notes
Street Atlas USA can ope n only map files with an .saf extension.
Regular Street Atlas USA only: If you have simplified file management
activated and the map file you are opening contains more then one draw file
or route file, you will be prompted to select the file you want to open.
4. Click OK. The files are imported into one .saf file.
Note Once you save the map file in Street Atlas USA, you can no longer
open it in previous versions of Street Atlas USA. If you want to continue to
use the map file in a previous version, select Save As and rename the file.
To Import a Route
1. Using Windows® Explorer®, browse to the source folder of the route file. The
default directory is C:\DeLorme Docs\Navigation or C:\Program Files\Street
Atlas USA.
2. Locate the file you want to import.
3. While holding the left mouse button, drag the file to the Windows task bar
button for Street Atlas USA (Street Atlas USA opens) and then drag the file to
the map. Release the mouse button when finished.
4. Drag the file on top of the map and release the left mouse button. The file
imports and displays the route.
To Import a Draw File
1. Click the Draw tab, click File, and then click Import.
2. Browse to the path where your draw files are stored. The default directory is
C:\DeLorme Docs\Draw.
3

Street Atlas USA 2012 User Guide
3. Under Files of Type, select the file type from the list. If the type is not listed,
select All File s; for example, All Files (*.*).
4. Click the file to select it and then click Open. The imported draw layer
displays in Street Atlas USA. A copy of the draw layer is imported into the
current map file and the original file is not modified.
• What is the difference between NavMode a nd the GPS t a b view when using GPS?
The default GPS view is NavMode—a hands free full-screen view that you can display
in 2-D or 3-D. By default, the Control Panel is hidden and the tabs are minimized;
however, you can customize your interface
route wizard so you can quickly plan a trip.
The GPS tab view option allows you to use the GPS tab to control navigating and
tracking. By default, the tabs and Control Panel are visible, but
them. It is av ailable only in 2-D mode. For more information, see Using NavMode or
GPS Tab View.
To turn NavMode on or off, click the NavMode button on the toolbar. When the
. By default, NavMode uses the E-Z Nav
you can opt to hide
button appears indented,
Note The button is grayed out
playing back a GPS log file
You can also change your GPS view in the Options dialog box:
1. Click the Options button
You can also click the Options button
2. Clear the Use NavMode check box to turn it off, or select the check box to
turn it on.
3. Click OK.
• How do I find a specif ic location?
Street Atlas USA offers powerful search too ls t hat enable you to locate any place in
the United States or Canada.
In addition, you ca n search for places along your route, within a cert ain radius of the
current map center, or within a particular region.
To access the search features in Street Atlas USA, click the Find tab. For more
information on searching for specific locations, see Performing a Basic Search
Performing a POI Search, Performing an Advanced Search, and Finding POIs Near
Your Current Location.
• How can I find all of the nearby points of interest?
NavMode is on.
unless you have a GPS device plugged in or are
on the toolbar and click the GPS tab.
on the GPS tab.
,
4
Right-click your location on the map, click Find Travel POIs, and then click the
distance you want to search within (1 mile, 5 miles, or 10 miles). The points of
interest display in Find tab results area.
OR
If you are tracking with a GPS device, do a radar search
within a designated distance of your c urre nt GPS po sition.
to locate points of interest
Getting Started
• How do I perform an Along the Way search in the Find tab and print my results?
You can search for names or categories along your current route by doing an
advanced searc h in the Find tab. You can then pr int your search results using the
Along the Way print option. Use the following steps to search for a name/category
along your current route and print the results:
1. Click the Find tab and then click Advanced. The Advanced dialog area
displays.
2. Select Category from the From drop-down list.
3. Select Current Route from the Within drop-down list.
4. Type the appropriate keyword in the Keywords text box.
5. Type the distance w ithin w h ich you want to searc h in the Distance text box.
6. Click Search. The search results display in the dialog area.
7. Click the Print tab and then click Route. The Route dialog area displays.
8. Select the Along the Way check box.
9. Click Print. The search results print.
• How do I turn on voice navigation?
Voice is used in the following ways:
• Listen to your route directions
• Use the speech recognition feature to issue commands or ask questions about
map panning and zooming, navigation, or GPS functio ns.
while tracking alon g a route using GPS.
• Why can't I hear the vo i ce during voice navigation?
The voice navigation system depends on your computer's sound system for volume
levels.
To Set the Volume Level
If your system is no t playing the sound loud enough, use the following steps to verify
the Wave volume control is set to its highest levels.
1. From the Start menu, point to Programs, point to Accessories, point to
Multimedia (or Entertainment depending on your operating system) and
then click Volume Control.
OR
If available, click the audio control shortcut on your taskbar.
2. In the Wave column, move the Volume slider to the top.
3. Close the Volume Control dialog box.
If the voice commands are still not loud enough t o hear, contact your sound card
manufacturer to download and install the latest driver for your specific model sound
card. The new driver may be able to provide louder output.
There are a variety of external speaker output options for your laptop. Some of them
are simply larger external speakers; others allow you to send the voice to your car
stereo speakers.
• Why doesn't Street Atlas USA recognize my voice?
To troubleshoot why Street Atlas USA may not recognize your voice, verify the
following:
• Ensure Street Atlas USA is the active application.
5
Street Atlas USA 2012 User Guide
• Ensure you are wearing your microphone correctly. See your microphone's
user guide for more information.
• Train your speech engine in the environment in which you are using the Voice
tab of Street Atlas USA. It is important to speak as na t urally as you did during
the training.
Note You can also designate a phrase with which to prefix all of your comma nds
(similar to Simon Says) within the program or the Speech settings in your Windows
Control Panel to change your voice settings.
• How do I get data updates or fix the roads on my map?
The data in Street Atlas USA can be updated only by buying a more recent version of
the product when it is available.
However, if you find there is a local road that is missing, you can add it to the
current draw layer using the Routable Roads Draw tool. For more information, see
the topic Drawing Routable Roads on the Ma p
Note You can also report data corrections to DeLorme using the NetLink tab.
• What is a map file?
Street Atlas USA lets you save all of the wor k you have done in the mapping
application as a single workspace so you can open it later. These saved workspaces
are called map files.
A map file consists of the following items: coordinates of the map center, current
zoom level, current magnification, map display preferences, any added items: such
as draw layers, routes, and so forth. As you create new routes or draw layers,
change preferences or the map center, and so forth, they are added to the current
map file. Changes can be saved or discarded.
To learn how to create a map file in Street Atlas USA, see
Files.
.
Creating and Deleting Map
• What do the different colors and symbols on the map m ean?
The different colors on the map represent different areas of land use and land cover
(parks, population centers, water, forests, and so on). The Map Legend provides
examples and descriptions of the map features.
Click the Help button
to display the Map Legend
• What's the difference between a stop and a via?
When routing in Street Atlas USA, you have the o p tion of adding/inserting stops or
vias in the route. A st op is a location in the middle of a route where you want to stop
and then proceed from. A via is a road on the map that you want to specifically use
when routing.
• What's the difference between adding and inserting a stop or via?
The Insert Stop/Via function arranges stops/vias geographically in the route. The Ad d
Stop/Via function adds stops/vias in the order you add them to the route.
on the Street Atlas USA toolbar and click Map Legend
Help topic.
6

• Why does my route fail to calculate?
Your route will fail to calculate if you create a route:
• With a route start, stop, via, or finish point in an ar ea that you have
designated as a Route Avoid
• That includes route points outside the United S tates, Mexico, or Canada.
• On an island without roads. In this case, S tr eet Atlas USA will look for the
nearest road to that island to place the route point. If the nearest road is not
routable (for example, it is the only road on the island and/or the island does
not have ferry access), you will get an error message saying "Route failed to
calculate."
• Why do X marks display on the map when I calculate a route?
• When you place a ro ute point in a location that isn't on a street, Street Atlas
USA finds the closest street to that location, marks the space between the
point you clicked and the street with X marks, and starts the route at the
street.
• If you search for an address that is on a walkway and place a route point on
it, Street Atlas USA finds the closest street to that location, ma rks the space
between the point you clicked and the street w ith X marks, and starts the
route at the street.
.
Getting Started
• Why are the tab area and control panel so narrow?
Street Atlas USA was designed to accommodate resolutions of 800 x 600 or higher.
If you are using a very high resolution (such as 1920 x 1200), the tab area and
control panel in Street Atlas USA may appear to be very narrow.
Note Use the Windows Control Panel to adjust your display settings.
• Can I send maps to my GPS device?
You cannot export maps to a GPS device with Street Atlas USA. You can send routes,
draw files, waypoints, and tracks.
• Why can’t I see all the information abo ut my route on the Route tab?
If your have your scre en resolution set to 800 x 600, some information, such as the
route summary, may not display for a longer route. Increase your screen resolution
to view all details.
• Regular Street Atlas USA only: What's the difference between advanced and
simplified file ma nagement?
Simplified file management allows you to save one route or draw layer in a single
map file.
Advanced file management allows you to save multiple routes and draw layers in
a single map file.
During the product installation, you chose to use simplified or advanced file
management. Once the program is installed, you can verify the type of file
management you are us ing an d change it. Click the arrow next to the Options
button
on the toolbar to o pe n t he m enu, and then click Change File
7

Street Atlas USA 2012 User Guide
Management. Your current option displays in the dialog box. To cha nge the option,
click the button for the file management option you want to use. For more
information, see Activating Advanced/Simplified File Management
.
Learning the Basics
Below is a list of some of the basic tab functions. Click the question to open the related Help
topic.
Controlling the Map
How do I pan the map?
How do I zoom the map in and out?
How do I change the map view to show the left map view, right map view, or both?
Display Preferences
How do I change the map colors?
Draw Tools
How do I add a road to my map?
GPS
How do I start tracking with my GPS device?
How do I switch from NavMode to GPS tab view?
The default view for GPS navigating and track ing is NavMode. When NavMode is on, the
button appears indented
on the toolbar.
You can also change your GPS view in the Options dialog box:
1. Click the Options button
also click the Options button
2. Clear the Use NavMode check box to turn it off, or select the check box to turn it
on.
3. Click OK.
See also, Routing
. To switch to the GPS tab view, click the NavMode button
on the toolbar and click the GPS tab. You can
on the GPS tab.
Map Data
How do I view imagery?
How can I work without the data DVD?
Map Files
What is a map file?
Phone
How do I install the phone data or use it from the DVD without installing it?
8
Getting Started
Routing
How do I create a route?
How do I track a route with my GPS receiver?
How can I automatically recalculate my route when I'm off course?
How can I avoid a specific area when routing?
Printing
How do I print a map?
Helpful Tips
These tips may help you use the features in your DeLorme mapping program. The Did You
Know? pop-up tutorials provide hints while you are working in the application.
Tips
• To disable a specific pop-up tutorial, select the Don't Show Again check box before
you close it.
• To disable all pop-up tutorials, click the Help button
Shut Off All Pop-up Tutorials.
• To enable all pop-tutorials after you have shut off one or more, click the Help button
on the toolbar and click Reset All Pop-up Tutorials.
on the toolbar and click
Control Panel
If you want to... Use this tip...
Zoom the map out/in
quickly
Pan the map quickly Position your cursor on the edge of the map; it becomes a
Update the coordinate
format that displays in the
Control Panel
View the last map center Press the middle button in the Compass Rose in the
Drag the map cursor in a n up-left direction to zoom the
map out or drag it in a down-right direction to zoom the
map in.
white hand that you ca n use to drag the map to the new
location.
Update your measurement preferences at any time using
the Display tab in the Options dialog box.
Control Panel to center the map on the previous map view.
This button performs an undo function for the last pan or
zoom (up to 256 times).
9
Street Atlas USA 2012 User Guide
Draw
If you want to... Use this tip...
Create a route using a
road you have added to
the map with the Draw tab
When drawing a routable road, click each existing road it
crosses to ensure that you can route on the new ro ad. When
you open a track you've imported from your GPS device, join
the imp orted line with existing lines by right-clicking each
intersection and selecting Manage Draw/Join.
Find
If you want to... Use this tip...
Modify a Find search result Right-click a result item in the Find tab to add it as a
MapNote, insert it as a stop in your route, copy the
information to your clipboard, and so on.
Find a custom point of
interest (such as a Chinese
restaurant) when
performing a GPS radar
search in Find
You can use the Custom option to find other categories
besides those listed, or to find multiple categories at once.
GPS
If you want to... Use this tip...
View a GPS log on the map Use the Draw tab to import a GPS log fi le and view it as a line
object on the map.
Info
If you want to... Use this tip...
Quickly view information
for a location on the map.
Hover your cursor over objects on the map to see information
(such as road names, city/town, details about draw objects,
etc.) in the status line that appears at the bottom of the map,
just above the tab area.
Map Files
If you want to... Use this tip...
Determine which map file
opens when you open
Street Atlas USA.
Learn how to add route
and/or draw layers to your
map file
Use the Welcome Screen to set which map file opens with
Street Atlas USA.
Add existing route and/or draw files to your map file by
clicking the Add button and selecting the Draw File or Route
File option.
Note In Street Atlas USA, you must use Advanced File
Management to use this option. This does no t apply to Street
Atlas USA Plus.
10
Measurement Tool
If you want to... Use this tip...
Getting Started
Measure the
area/perimeter of a
location on the map
Use the measure tool to draw a polygon on the map and
determine its area and perimeter. Just click point-by-point
to draw the polygon on the map and then double-click to
close the polygon. The area and perimeter display in the
center of the polygon.
Phone
If you want to... Use this tip...
Get all of the phone
listings for a particular
road.
Note The Phone tab is available only in Street Atlas USA Plus.
You can right-click the map on a road to view phone
listings for that road.
If you want to... Use this tip...
Stop a page in a multipage map from printing
If you do not want to print all the pages in a multi-page
map, on the Layout graphic, click each page you do no t
want to print.
Route
If you want to... Use this tip...
Reorder inserted stops Reorder your inserted route stops using the Advanced
features in the Route tab.
Create a route quickly For quick route creation, right-click the map and select one
of the Create Route options or use the Route buttons on
the toolbar.
Reorder the columns in the
Route Directions list
Determine the difference
between adding and
inserting stops and vias
View information about
your second turn
Click the Directions list column headers to change the
column order.
Added stops/vias are placed in the order you add them to
the route. Inserted stops/vias are placed in the order you
would approach them between the Start and Finish points
of the route.
Click the Show Turns button when GPS tracking to view
information about the following turn.
Tab Area
If you want to... Use this tip...
Adjust the size of the tab
area
Adjust the size of the tab area by dragging the top or right
side of the tab area.
11
Street Atlas USA 2012 User Guide
Show, hide, or reorder
tabs
Import or export a tab
configuration file
Use the Tab Manager
or reorder tabs.
Use the Tab Manager option in the Help menu to import or
export a tab configuration file
Voice
If you want to... Use this tip...
Create new speech
reco gnition profiles
You can create a new speech recognition profile for each of
your working environments (noisy, quiet) and users (your
spouse or child) by clicking the Speech settings in the
Windows Control Panel.
Learn how to make the
microphone more sensitive
to your commands in noisy
environments
If there is background noise while you are speaking, it may be
helpful to precede all of your voice commands with a special
phrase (like Simon Says). See the Voice Settings tab of the
Options dialog box.
XData
If you want to... Use this tip...
Geoplace XData records
that do not have complete
address information or
were not correctly located
during the import process
You can drag a record from the Query list and place it at the
correct geo-location on the map.
option in the Help menu to show, hide,
Add a blank record to your
XData database
To add a blank record to an XData database, you mus t select
All Records as the Table Display type.
Note The XData tab is available only in Street Atlas Plus.
Activating Advanced/Simplified File Management
Note for regular Street Atlas USA only
Advanced file management allows you to save multiple routes and draw layers in
a single map file. With simplified file management, you can sa ve only one route
and/or draw layer in a single map file. I f you did not select to enable advanced
file management during the product installation , you can still change the settings
using the Change File Management option in the Options menu.
This note does not apply to Street Atlas USA Plus users.
When you installed Street Atlas USA, you were given the option to use simplified or
advanced file management. Simplified file management allows you to have one route or
draw layer saved in a map file. If you want to save multiple route and/or draw layers in a
map file, you must activate advance d file ma na gement.
12

To Activate Advanced/Simplified File Management
Use the following steps to change your file management preferences.
Getting Started
1. Click the arrow next to the Options button
2. Click Change File Management.
The Change File Management dialog box opens, indicating if the program is set to
use advanced or simplified file management.
3. To use advanced file management, click Advanced.
OR
To use simplified file management, click Simplified.
4. At the confirmation message, click OK.
5. You must restart Street Atlas USA to view the change in f ile m a na g ement.
Note Some of the Help topics related to the Map Files tab, Route tab, and Dr a w tab include
instructions for both simplified and advanc ed file management. Be sure to follow the
instructions for the file management system you have selected. A note appears at the end
of each related Help topic.
on the toolbar.
Glossary Terms
ADT
Alaska Daylight Time
Almanac
Data downloaded from satellites that contains t he identity codes, location, and time
informati on for each sa tellite.
Arctic Circle
Parallel, or line of latitude aro und the Earth, at approximately 66°30' N. Because of the
Earth's inclination of about 23 1/2° to the vertical, it marks the southern limit of the area
within which, for one day or more each year, the Sun does not set (about June 21) or rise
(about December 21).
AST
Alaska Standard Time
Average Grade
Average of the grade from the start to the current cursor position (o r finish).
Azimuth
The direction of travel or the direction between two points in reference to true or magnetic
north. When expressed in degrees, its value ranges from 0 to 360. A compass heading is an
azimuth. In most places, the word bearing has grown to mean the same thing as azimuth.
However, azimuth is always measured from true or magnetic north in a clockwise direction.
For example, due east is 90 and due west is 270. See also, Bearing.
13

Street Atlas USA 2012 User Guide
Bearing
Like an azimuth, a bearing is measured in reference to true or magnetic north, but its value
never goes over 90. A bearing is always measured from the cardinal directions of north or
south. A typical bearing would be N45 E, which is the same as an azimuth of 45. The
bearing S45 W is an azimuth of 225. The use of the word bearing has changed over the
years and now means the same as azimuth. When tracking, bearing displays the direction of
travel between your current position and your next waypoint, relative to true or magnetic
North.
Bread crumb trail
A set of dots that display on your computer screen to record your progress as you travel.
CDT
Central Daylight Time
Climbing Distance
The total distance where the terrain is uphill.
Climbing Elevation
The amount of ascending vertical distance .
Coordinates
A set of numbers (e.g., latitude and longitude) us ed to identify the specific location of a
point.
Course
The azimuth and length of a line, considered together.
CST
Central Standard Time
Current Elevation
The elevation above sea level at a specific point.
Descending Distance
The total distance where the terrain is downhil l.
Descending Elevation
The amount of descending vertical distance.
Differential GPS (DGPS)
A technique to improve GPS accuracy that uses pseudo -range errors recorded at a known
location to improve the measurements made by other GPS receivers within the same
general geographic area.
14

Getting Started
Dilution of Precision (DOP)
The total effect of all error so urces in locating a position.
Download
To transfer information from a remote unit, such as a GPS receiver, to a computer.
EDT
Eastern Daylight Time
Easting
The measure of a position relative to the x-axis (horizontal) of a grid system.
Elevation Gain
The difference in elevation from the start of the profile to the end of the profile.
Ephemeris
Data that indicates the position and status of satellites.
EST
Eastern Standard Time
GMT
Greenwich Mean Time; used as the standard of time throughout the world.
GPS
Global Positioning System; a "constellation" of orbiting satellites used to calculate a precise
position on or near the earth's surface.
Grade
Actually percent grade, rise over run (100 x (rise/run)). For example, 6 means that for
every 100 ft, you gain 6 ft in elevation.
HDOP
Horizontal Dilution of Position ; the measure of how much the geometry of the satellites
affects the horizontal position estimate.
Heading
Azimuth of the longitudinal axis of an aircraft or ship. Heading may differ from direction of
travel when flying or boating due to currents in the air or water.
Initialize
To set to a starting position, as in obtaining initial coordinates for a GPS receiver.
15

Street Atlas USA 2012 User Guide
Latitude
The measure of a position on the earth's surface north or south of the equator in degrees,
minutes, and seconds. Defined as the angle from the equator's horizontal plane
perpendicular to the polar axis. All lines of latitude are parallel and are often referred to as
parallels.
Log
A record of the speed, direction, and route of travel as obtained via GPS.
Logging
Recording the speed, direction, and route traveled using GPS.
Longitude
The measure of a position on the surface of the earth east or west of the Prime Meridian in
degrees, minutes, and seconds. Defined as the angle from the vertical plane running
through the polar axis and the prime meridian. All lines of longitude meet at the poles and
are often referred to as meridians.
Maximum Elevation
The elevation of t he h ighest point on a profi le .
Maximum Speed field
When GPS tracking, displays your maximum speed.
MDT
Mountain daylight time
Minimum Elevation
The elevation of the lowest point on a profile.
MST
Mountain standard time
NMEA
National Marine Electron ics Association
Northing
The measure of a position relative to the y-axis (vertical) of a grid system.
PDOP
The measure of how much the error in the position estimate produced from satellite range
measurements is amplified by a poor arrangement of satellites (with respect to the receiver
antenna).
16

Getting Started
Port
A hardware interface used by a computer to communicate with an external device.
PPS
Precise Positioning System; radio signals ava i lable to military and other authorized
personnel for GPS.
Real time
The actual time during which something takes place.
Receiver
Hardware device that receives data, such as from satellites.
Snapping
Attaching a point on one draw object to the exact coord inates of a point in another draw
object. You can snap the central shape point of an arc to another object or snap a routable
road to an existing road, enabling routing from the drawn road to the road system on the
map database.
Speed field
When GPS tracking, displays your speed as you travel.
Terrain Distance
The 3-D distance of the profile accounting for elevation rise and descent.
Third-party GPS device
A GPS receiver manufactured by a company other than DeLorme, such as GARMIN,
Magellan, Brunton, Lowrance, Trimble, and so forth.
Time field
When connected to a DeLorme GPS receiver, displays the Greenwich mean time.
Track
To observe or plot the moving path of an object.
Upload
To transfer information from a computer to a remote unit, such as a GPS receiver.
VDOP
The measure of how much the geometry of the satellites affects the vertical position
estimate.
17

Street Atlas USA 2012 User Guide
Waypoints
Marked positions with specific coordinates that can be downloaded or uploaded.
Zone
A named grid system of any of the UTM/UPS, MGRS, or State Plane coordinate systems and
used as a basis for coordinate display. For example, UTM zone 19 specifies the six-degree
swath between longitude 66W to 72W and running from 84S to 80N. Anothe r example is
zone ME-W in the State Plane coordinate system, which specifies an area that covers the
western half of Ma ine. When using one these coordinate systems, the current zone and
coordinates east and north (the eastings and northings) of the zone origin are displayed.
Basic Functions
Zooming In and Out
You can use the drag and zoom feature, zoom tools, or the data zoom level(Data zoom level
is the relationship between what you see i n a map vie w and ho w it exists in reality. It is the
amount of geographic data displayed on a computer monitor. The data zoom level is similar
to the traditional fractional relationship expressed on paper maps. For example, 1 :24,000,
1:100,000, 1:500,000, and so on.) to quickly change the zoom level of the map view.
Notes
• Increase the data zoom level number to show a smaller geographic area at greater
detail.
• Decrease the data zoom level number to show a larger geographic area at lesser
detail.
• If you view both the right (primary) and left (secondary) maps at different data
zoom levels, a box (or lines, depending on the current data zoom level) displays on
the map that is zoomed out the furthest. The box/lines indicate the area that is in
view on the other map.
• If you view the right and left maps at the same data zoom level but they are not
equally represented on the screen (50 /5 0), a box (or lines) displays on the map that
is covering the most screen area. The box/lines indicate the area that is in view on
the other map.
To Drag and Zoom In
Use the following steps to zoom in either the right or left map.
1. Click and hold down the left mouse button as you drag the mouse in a down-right
direction on the map to encompass the area you want to display. A view box displays
on the screen and ch anges dimension as you move the mouse. A label disp lays the
data zoom level at the current map center.
2. Once you reach the map area or data zoom level you want to display, release the
mouse button. The area you selected fills the map window, the map re-centers, and
the map view adjusts to show the appropriate level of detail.
Tip To move the view box to another location, press the SHIFT key at any time.
18
Getting Started
To Drag and Zoom Out
Use the following steps to zoom in either the right or left map.
1. Click and hold down the le ft mouse button as you drag the mouse in an up-left
direction on the map. A staircase with a small circle displays on the screen.
2. Continue dragging the mouse in an up-left direction. The small circle moves up the
steps, one step per data zoom level. A label displays the d a ta zoom level to the
bottom-right of the staircase.
3. Once you reach the data zoom level you want to display, r elease the mouse button.
The map view adjusts to display the appropriate level of detail. The map center is
retained on your screen.
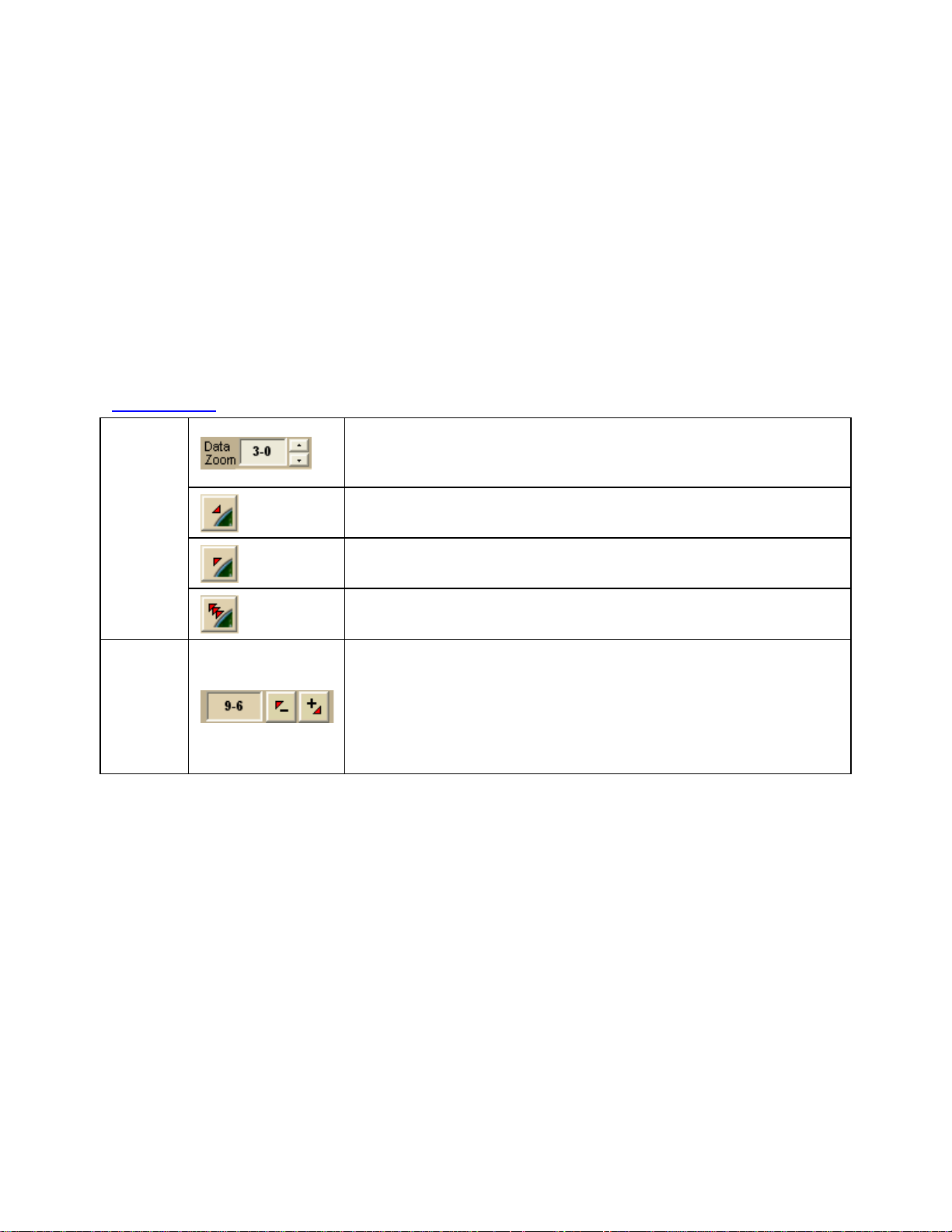
To Zoom In/Out Using the Zoom Tools
There are two sets of zoom tools. The zoom tools for the right map are located in the
Control Panel
. The zoom tools for the left map are located at the top of the left map view.
Click the up arrow to zoom out one minor data zoom level at
a time. Click the down arrow to zoom in one minor data
zoom level at a time.
Right
Map
Controls
Click the Zoom In 1 tool to increase the detail number to
the next full level.
Click the Zoom Out 1 tool to decrease the detail number to
the next full level.
Click the Zoom Out 3 tool to decrease the detail number by
three full levels.
Click the plus button to increase the detail number to the
next fu ll level.
Left
Map
Controls
Click the minus button to decrease the detail numb er to the
next fu ll level.
The data zoom level of the left map displays in the text area
to the left of the buttons.
Tips
• Press ALT+PAGE UP on your keyboard to zoom out to the next full data zoom level.
Press ALT+PAGE DOWN on your keyboard to zoom in to the next full data zoom
level.
• Use the mouse wheel to zoom the map in and out. Rotate the mouse wheel to zoom
in by individual data zoom level steps or hold the SHIFT key while rotating the
mouse wheel to zoom to the next full data zoom level.
Panning/Centering the Map
Use any of the following methods to pan (move) or center the map.
• Click anywhere on the map. The point you click becomes the new map center.
• When you point near the map edge, a white hand displays. D rag the hand to move
the map in that direction.
19

Street Atlas USA 2012 User Guide
• Click the Map Panning button
direction.
• Click anywhere on the overview map
center. This allows you to traverse greater distances with each mouse click than you
can within the main map.
• Point anywhere on t he black view box in the overview map window. When the
pointer becomes a
• Use the search features on the Find tab to center the map on a particular location.
• Assign shortcut keys
, drag the view box to the new location.
to pan the map up, down, left, or right in small increments.
on the toolbar to drag/pan the map in any
. The point you click becomes the new map
Copying Your Map to the Clipboard
Click the Copy to Clipboard button on the Print tab to copy your map to the clipboard.
You can then paste it into another program.
You can also right-click an ywhere on the map and click Copy Map to Clipboard.
Saving a Map as a Bitmap or JPEG Image
You can save the current map view as a bitmap (.bmp) or JPEG (.jpg) image in all page
layout formats: Single, 2 x 2, and 3 x 3. If you select a multi-page format, all the active
pages are saved as individual bitmaps or JPEGs. The file name is the specified file name
with an incremental page number at the end.
See Printing a Map
To Save a Map as a Bitmap or JPEG
Use the following steps to save a map as an image.
1. Locate the area on the map that you want to save as an image.
2. Click the Print tab and then click the Map subtab (if it is not already selected).
3. Under Print Layout, select Page(the map print area is based on the paper size
specified in the Setup options) or Screen(the map print area is based on the screen
size).
The print area for a Page map displays as a red box and the print area for a Screen
map displays as a blue box on the overview map.
4. If you selected Page in step 3, the following options are available.
• Under Print Layout, select a layout option (Single, 2 x 2, or 3 x 3). The
for information about printing a map without sav ing it as a file.
print area displays on both the Map and the Overv iew Map. In the example
below, 2 x 2 is selected. This means the print area encompasses four
20
 Loading...
Loading...