Dell PowerConnect W-Series
ArubaOS 6.1
Command Line Interface
Reference Guide

Copyright
®
© 2011 Aruba Networks, Inc. Aruba Networks trademarks include , Aruba Networks
registered Aruba the Mobile Edge Company logo, and Aruba Mobility Management System
®
. Dell™, the DELL™ logo, and PowerConnect™ are
, Aruba Wireless Networks®, the
trademarks of Dell Inc.
All rights reserved. Specifications in this manual are subject to change without notice.
Originated in the USA. All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
Open Source Code
Certain Aruba products include Open Source software code developed by third parties, including software code subject to the GNU General
Public License (GPL), GNU Lesser General Public License (LGPL), or other Open Source Licenses. The Open Source code used can be found at
this site:
http://www.arubanetworks.com/open_source
Legal Notice
The use of Aruba Networks, Inc. switching platforms and software, by all individuals or corporations, to terminate other vendors’ VPN client
devices constitutes complete acceptance of liability by that individual or corporation for this action and indemnifies, in full, Aruba Networks, Inc.
from any and all legal actions that might be taken against it with respect to infringement of copyright on behalf of those vendors.
Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.1 CLI | Reference Guide 0510846-01 | July 2011

Introduction
The ArubaOS command line interface (CLI) allows you to configure and manage your controllers. The CLI is
accessible from a local console connected to the serial port on the controllers or through a Telnet or Secure Shell
(SSH) session from a remote management console or workstation.
NOTE: Telnet access is disabled by default. To enable Telnet access, enter the telnet cli command from a serial connection or an
SSH session, or in the WebUI navigate to the Configuration > Management > General page.
What’s New In ArubaOS 6.1
The following commands have been added in the ArubaOS 6.1 command line interface.
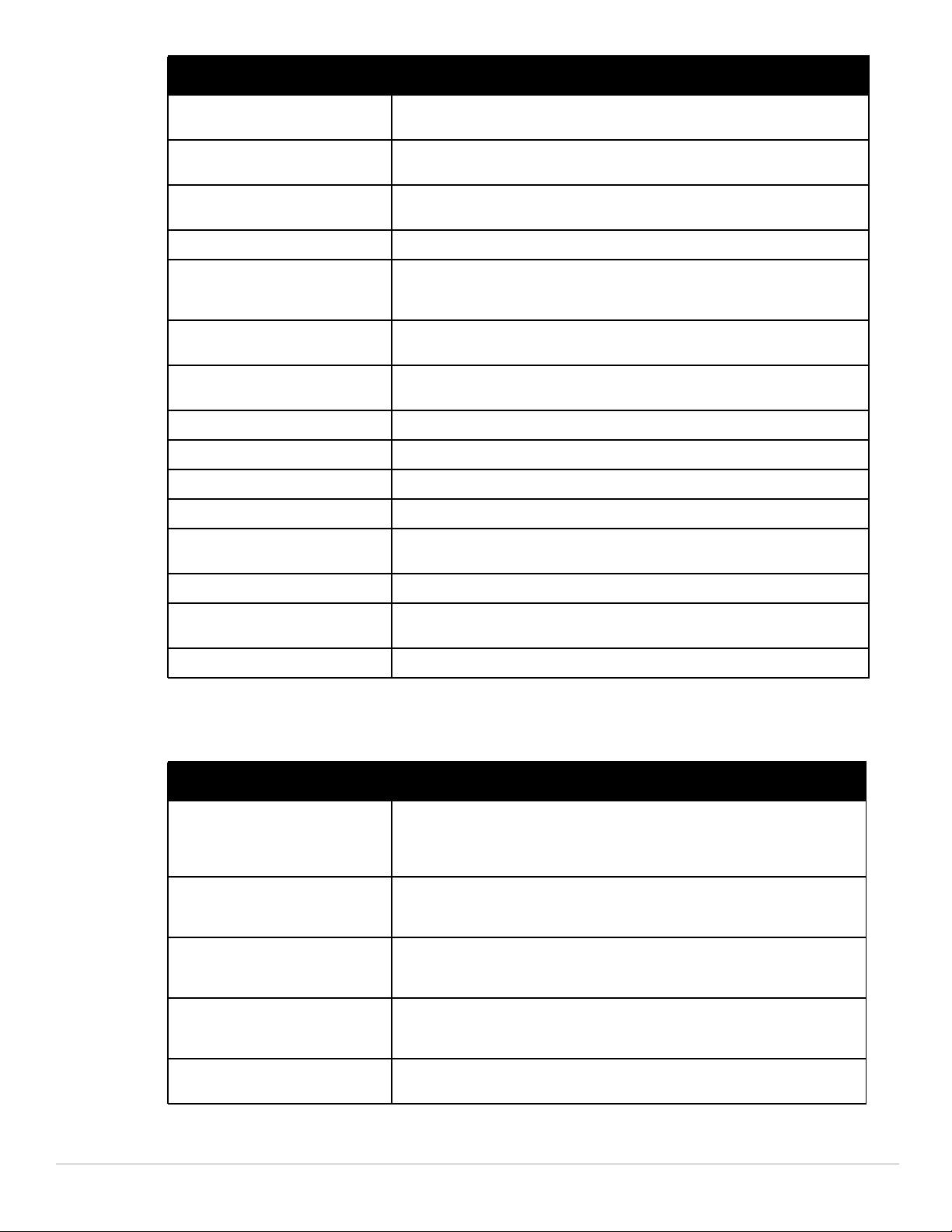
Command Description
clear wms wired-mac Clear learned and collected Wired MAC information.
cluster-member-customcert
cluster-member-factorycert
controller-ipv6 This command sets the default IPv6 address of the controller to the IPv6 loopback
crypto-local ipsec sacleanup
crypto-local isakmp
certificate-group
crypto-local isakmp sacleanup
crypto-local isakmp xauth This command assigns the server certificate used to authenticate the controller for
ip igmp Added parameters: max-members-per-group and quick-client-
interface vlan ipv6
address
ipv6 cp-redirect-address This command configures a redirect address for captive portal.
This command sets the controller as a control plane security cluster root, and
specifies a custom user-installed certificate for authenticating cluster members
This command sets the controller as a control plane security cluster root, and
specifies a custom user-installed certificate for authenticating cluster members.
interface address or a specific VLAN interface address.
Issue this command to clean IPsec security associations (SAs).
Issue this command to configure an IKE Certificate Group for VPN clients.
This command enables the cleanup of IKE SAs.
VPN clients using IKEv2.
conver
This command configures the link local address or the global unicast adress for this
interface.
ipv6 default-gateway This command configures an IPv6 default gateway.
ipv6 mld This command configures the IPv6 MLD(Multi-listener discovery) parameters.
ipv6 neighbor This command configures an IPv6 static neighbor on a VLAN interface.
ipv6 route This command configures static IPv6 routes on the controller.
local-custom-cert This command configures the user-installed certificate for secure communication
Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.1 CLI | Reference Guide Introduction | 3
between a local controller and a master controller.
Command Description
local-factory-cert This command configures the factory-installed certificate for secure
netdestination6 This command configures an alias for an IPv6 -only network host, subnetwork, or
netexthdr This command allows you to edit the packet filter options in the extension header
ntp authenticate This command enables or disables NTP authentication
ntp authentication-key This command configures a key identifier and secret key and adds them to the
ntp trusted-key This command configures an additional subset of trusted keys which can be used
remote-node-localfactory-cert
show controller-ipv6 This command displays the controller’s IPv6 address and VLAN interface ID.
show ipv6 interface This command displays IPv6-related information on all interfaces.
show ipv6 neighbors This command displays the IPv6 neighbors configured on a VLAN interface.
show ipv6 route This command displays the controller IPv6 routing table.
show local-cert-mac Display the IP, MAC address and certificate configuration of local controllers in a
communication between a local controller and a master controller.
range of addresses.
(EH).
.
database. NTP authentication works with a symmetric key configured by user. The
key is shared by the client (Dell controller) and an external NTP server.
for NTP authentication.
Configure factory certificates for secure traffic between Remote-Node-Masters
and Remote-Nodes.
master-local configuration.
show netexthdr This command displays the IPv6 extension header (EH) types that are denied.
show wms wired-mac Display a summary table of Wireless Management System (wms) wired MAC
tracepath Traces the path of an IPv6 host.
information.
Modified Commands
The following commands were modified in ArubaOS 6.1.
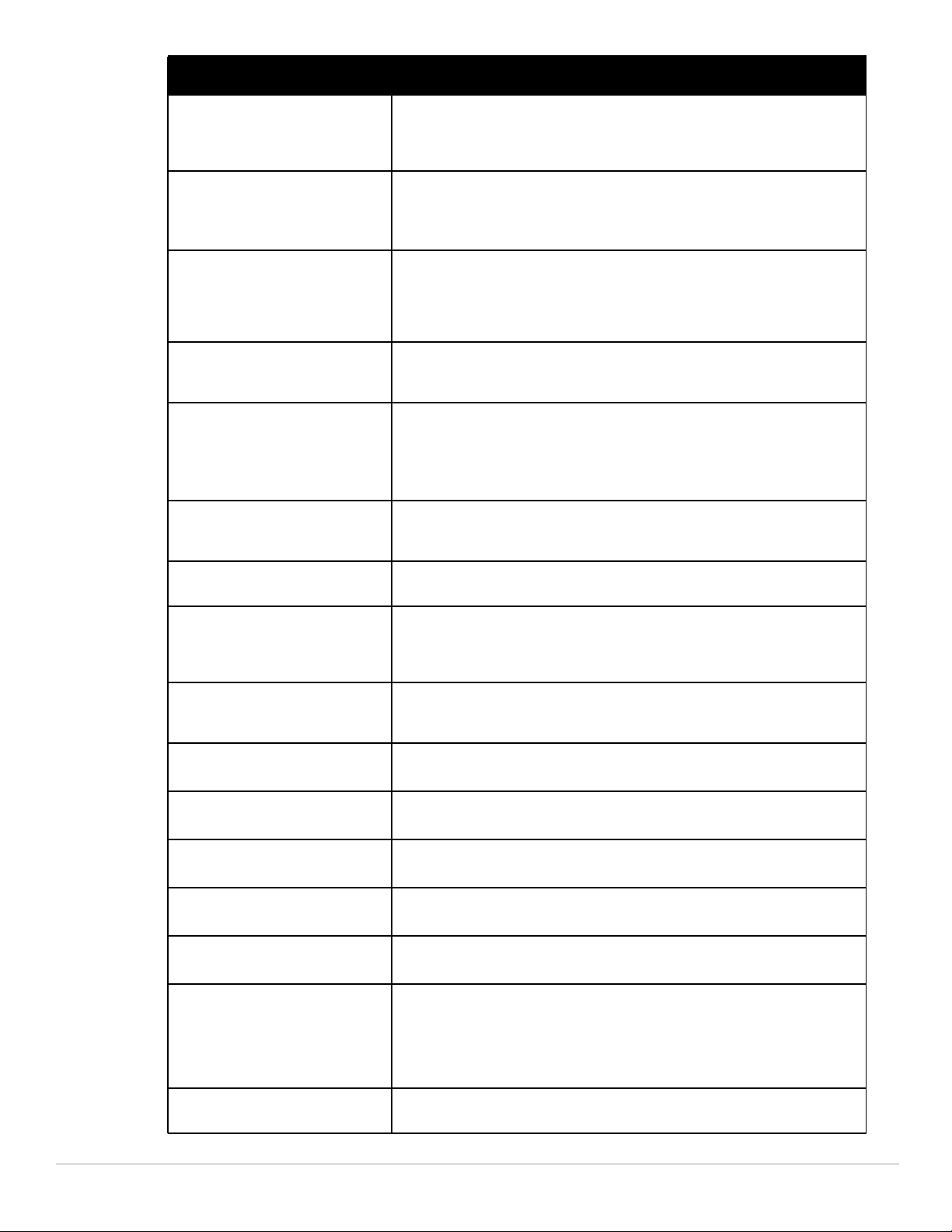
Command Parameter Description
aaa authentication
captive-portal black-list
<black-list> | white-list
<white-list>
aaa authentication-server
radius source-interface
<vlan>
aaa derivation-rules user
<name> set {role|vlan}
condition dhcp-option
aaa profile <profile>
devtype-clasification
Name of an existing black list or white list on an IPv4 or IPv6 network destination.
The black list contains websites (unauthenticated) that a guest cannot access. The
white list contains authenticated websites that a guest can access.
Associates a VLAN interface with the RADIUS server to allow the group-specific
source interface to override the global configuration.
Use DHCP signature matching to assign a role or VLAN to a specific device type.
When the devtype-classification parameter is enabled, the output of the show user
and show user-table commands shows each client’s device type, if that client
device can be identified
aaa profile <profile>
enforce-dhcp
4 | Introduction Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.1 CLI | Reference Guide
When you enable this option, clients must complete a DHCP exchange to obtain an
IP address.
Command Parameter Description
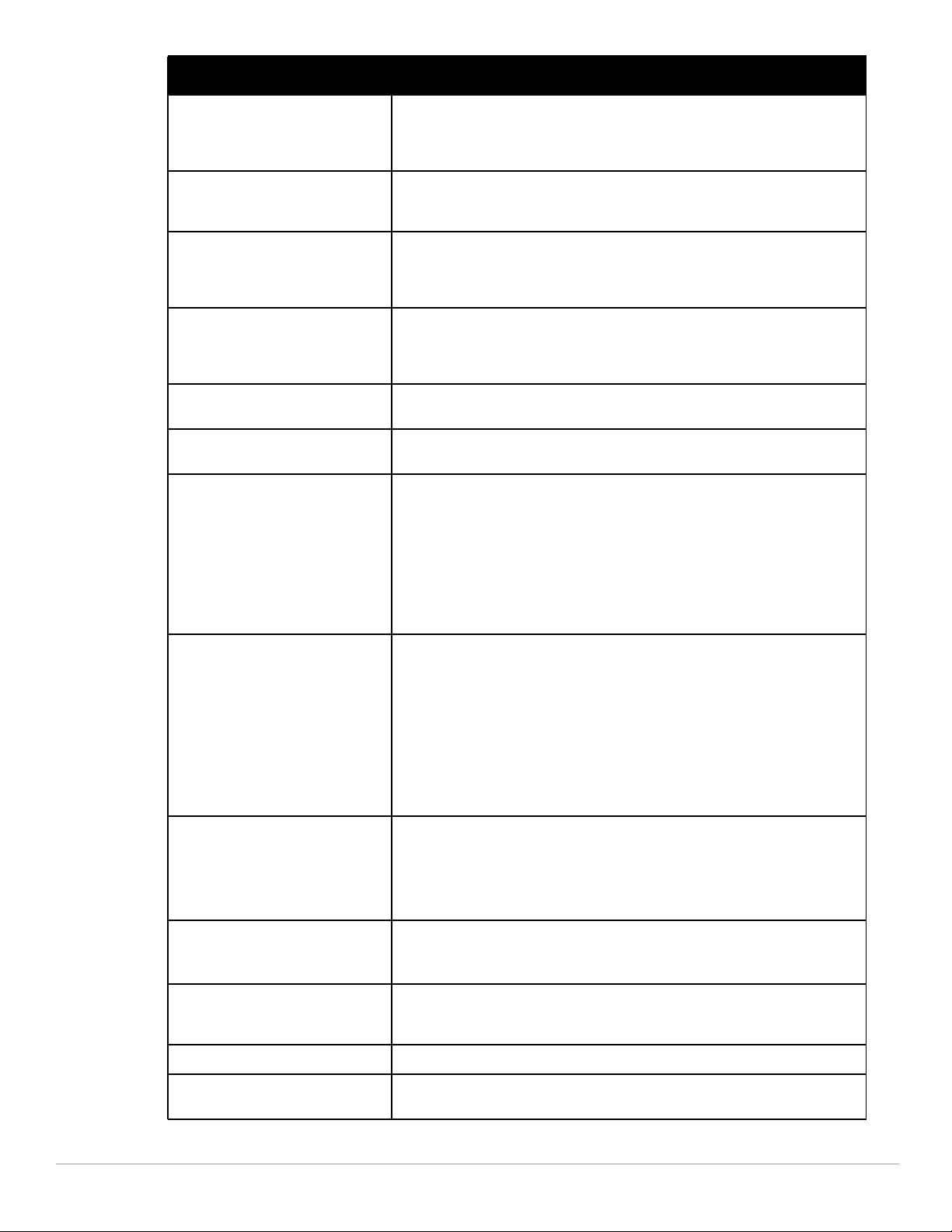
aaa profile <profile>
radius-interim-accounting
By default, the RADIUS accounting feature sends only start and stop messages to
the RADIUS accounting server. Issue the interim-radius-accounting command to
allow the controller to send Interim-Update messages with current user statistics
to the server at regular intervals.
aaa authentication via
connection-profile admin-
Use this option to specify scripts that must be executed after VIA connection is
established and terminated.
logoff-script |
admin-logon-script
aaa authentication via
Use this option to enable IKEv2 authentication mechanism.
connection-profile ikev2-
policy | ikev2-proto |
ikev2auth | ipsecv2cryptomap
aaa authentication via
Use this option to enable Suite B cryptography support.
connection-profile
suiteb-crypto
clear Clears all IPv6 session statistics, multicast listener discovery (MLD) group and
member information, MLD statistics, and counters. The following MLD parameters
are added to the ipv6 option:
mld group
mld stats-counters
cluster-root-ip
ipsec-factory-cert|
The ipsec-factory-cert and ipsec-custom-cert parameters were introduced to
allow certificate-based authentication of cluster members.
ipsec-custom-cert
crypto dynamic-map set
pfs group19|group20
crypto ipsec transform-
set <transform-set-mtu>
esp-aes128-gcm |espaes256-gcm
crypto isakmp eap-
passthrough eapmschapv2|eap-peap|eap-tls
crypto isakmp policy
authentication ecdsa-256
crypto isakmp policy
authentication ecdsa-384
crypto isakmp policy
hash sha1-96
crypto isakmp policy
hash sha2-256-128
crypto isakmp policy
hash sha2-384-192
crypto isakmp policy
prf
The pfs parameter was modified to support the group19 and group20 PFS group
values.
This command configures IPsec parameters.
Use ESP with 128-bit AES-GCM encryption.
Use ESP with 256-bit AES-GCM encryption.
Select one of the following authentication types for IKEv2 user authentication using
EAP.
Use ECDSA-256 signatures for IKE authentication.
Use ECDSA-384 signaturesfor IKE authentication.
Use SHA1-96 as the hash algorithm.
Use SHA2-256-128 as the hash algorithm.
Use SHA2-384-192 as the hash algorithm.
Set one of the following pseudo-random function (PRF) values for an IKEv2 policy:
PRF-HMAC-MD5 (default)
PRF-HMAC-SHA1
PRF-HMAC-SHA256
PRF-HMAC-SHA384
crypto pki ec curve-name
<key_val>
Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.1 CLI | Reference Guide Introduction | 5
The ec curve-name parameter was introduced to support certificate signing
requests using an elliptic-curve (EC) key
Command Parameter Description
crypto pki-import
{CRL|IntermediateCA|
CRL, IntermediateCA, OCSPResponderCert and OCSPSignerCert certificates can
now be imported.
OCSPResponderCert|
OCSPSignerCert} <name>
crypto-local ipsec-map
<map> <priority> peercert-dn <peer-dn>
crypto-local ipsec-map
<map> <priority> peer-
If you are using IKEv2 to establish a site-to-site VPN to a statically addressed
remote peer, identify the peer device by entering its certificate subject name in the
Peer Certificate Subject Name field
For site-to-site VPNs with dynamically addressed peers, specify a fully qualified
domain name (FQDN) for the controller.
fqdn any-fqdn|fqdn-id
<peer-id-fqdn>
crypto-local ipsec-map
<map> <priority> set pfs
{group1|group2|group19|gr
oup20}
crypto-local isakmp key
The set pfs command introduced the group19 and group20 parameters.
group19: 256-bit random Diffie Hellman ECP modulus group. (For IKEv2 only)
group20: 384-bit random Diffie Hellman ECP modulus group. (For IKEv2 only)
Configure the PSK for the specified FQDN.
fqdn <ike-id-fqdn>
crypto-local isakmp key
Configure the PSK for any FQDN.
fqdn-any
crypto-local pki The following parameters were added for the certificate revocation feature:
CRL
Intermediate CA
OCSPResponderCert
OCSPSignerCert
global-ocsp-signer-cert
rcp
service-ocsp-responder
firewall amsdu| clear-
sessions-role-update
The parameter amsdu, when enabled, causes Aggregated Medium Access Control
Service Data Units (AMSDU) packets to be dropped.
prohibit-ip-spoofing|
The parameter clear-sessions-role-update clears the datapath sessions when
roles are updated.
The funtionality of the prohibit-ip-spoofing feature was enhanced. In previous
versions of ArubaOS, this feature checked only the source IP and the source MAC
address in the frame. Starting with ArubaOS 6.1, this feature also checks the
destination IP and the destination MAC address in the frame.
ids dos-profile Added the following new parameters to detect Meiners DoS Power Save attack:
detect-power-save-dos-attack
power-save-dos-min-frames
power-save-dos-quiet-time
power-save-dos-threshold
ids unauthorized-deviceprofile
Added the following parameter to internally generate a list of valid SSIDs to use in
addition to the user configured list of Valid and Protected SSIDs
detect-valid-ssid-misuse
interface fastethernet |
gigabitethernet tunneled-
The parameter muxport has had a name change to tunneled-node-port. The
functionality has not changed.
node-port
interface loopback The parameter ipv6 address was added.
interface vlan option-82 Allows a DHCP relay agent to insert circuit specific information (about the AP and
SSID) into a request that is being forwarded to a DHCP server.
6 | Introduction Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.1 CLI | Reference Guide
Command Parameter Description
ipv6 firewall The enable parameter has been removed from this command. The ipv6 enable
command is the global command to enable/disable ipv6 processing on the
controller.
mgmt-server secondary-
The secondary-server parameter has been deprecated.
server <ip-addr>
masterip ipsec-custom-
cert| ipsec-factory-cert
master-redundancy peer-ip
ipsec-factory-cert|ipsec-
Use a custom-installed or factory-installed certificate on the master controller to
establish a master-local IPsec tunnel using IKEv2.
The ipsec-factory-cert and ipsec-custom-cert parameters were introduced to
allow certificate-based authentication of master and local controllers.
custom-cert
ntp server [key <key-id>] The key-id parameter authenticate sthe NTP server. This needs to match the key
identifier configured in the ntp authentication-key command.
netdestination This command configures an alias for an IPv4 -only network host, subnetwork, or
range of addresses.
ping Introduced ipv6 parameter to provide support for IPv6.
provision-ap The following new parameters were introduced for provisioning IPv6 APs:
dns-server-ip6
ip6addr
ip6prefix
gateway6
remote-node-masterip
ipsec-factory-cert
Secure communication between a Remote-Node and Remote-Node master by
identifying a factory-installed certificate on the Remote-Node Master.
remote-node-profile The following parameters were introduced for configuring a remote node profile:
ipv6
mgmt-server
mobility-manager
snmp-server
syscontact
syslocation
The controller-ip parameter has been deprecated.
rf dot11a-radio-profile
<profile> spectrummonitoring
Issue this command to turn an AP in ap-mode into a hybrid AP. An AP in hybrid AP
mode serves clients as an access point while it scans and analyzes spectrum
analysis data for a single radio channel. For further details on using hybrid APs and
spectrum monitors to examine the radio frequency (RF) environment in which the
Wi-Fi network is operating, refer to the Spectrum Analysis chapter of the Dell
PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.1 User Guide.
rf dot11g-radio-profile
<profile> spectrummonitoring
Issue this command to turn an AP in ap-mode into a hybrid AP. An AP in hybrid AP
mode serves clients as an access point while it scans and analyzes spectrum
analysis data for a single radio channel. For further details on using hybrid APs and
spectrum monitors to examine the radio frequency (RF) environment in which the
Wi-Fi network is operating, refer to the Spectrum Analysis chapter of the Dell
PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.1 User Guide.
show aaa state debug-
The Mobility Stats parameter was introduced.
statistics
show ap active The parameter ip6-addr was added to view data for an IPv6 AP.
show ap details The parameter ip6-addr was added to view data for an IPv6 AP.
Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.1 CLI | Reference Guide Introduction | 7
Command Parameter Description
show crypto-local pki The following new parameters now display output:
CRL
Intermediate CA
OCSPResponderCert
OCSPSignerCert
global-ocsp-signer-cert
rcp
service-ocsp-responder
show crypto-local isakmp The parameter certificate-group was introduced.
show datapath The crypto counters parameter now displays a number of TKIP/AESCCM/AESGCM
decriptions per priority level along with any counter errors per priority.
The ipv6 filter option is added to the following parameters in the command:
session
tunnel
user
route-cache
route
ip-reassembly
The parameter vlan-mcast has been added to view the datapath VLAN multicast
table entries.
show ip interface brief View IP-related information on all interfaces in summary format.
show ntp servers brief The key-id parameter output displays if configured for this ntp server.
show tunneled-node
[state|database]
This command name has changed from show mux to show tunneled node. A new
parameter, database, was added.
show tunneled-node config This command name has changed from show mux to show tunneled-node config.
The command functionality did not change..
show wms general Added the following display parameterss
adhoc-ap-ageout-interval
persistent-neighbor
event-correlation
event-correlation-quiet-time
Minutes Tick
tunnel-loop-prevention This command name has changed from mux-loop-prevention to
tunnel-loop-prevention. The command functionality did not change.
tunneled-node-address This command name has changed from mux-address to tunneled-node address.
The functionality command did not change.
vrrp The delay option is added to the preempt parameter.
user-role ipv6 session-acl parameter was removed. The session-acl parameter is common
for both IPv4 and IPv6 ACLs.
wlan ssid-profile
<profile>
The opmode options wpa2-aes-gcm-128 and wpa2-aes-gcm-256 were introduced.
The qbss-load-enable and local-probe-req-thresh options are included.
opmode wpa2-aes-gcm128|wpa2-aes-gcm-256
qbss-load-enable localprobe-req-thresh
wlan ht-ssid-profile The allow-weak-encrytion parameter was deprecated.
wms general learn-system-
Added parameter to enable or disable “learning” of wired MACs at the controller.
wired-macs
8 | Introduction Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.1 CLI | Reference Guide
Command Parameter Description
wms-local system max-
system-wm | system-wmupdate-interval
Added parameter to set the max number of system wired MAC table entries
learned at the controller and set the interval, in minutes, for repopulating the
system wired MAC table at the controller.
Deprecated Commands
The folowing commands were deprecated in ArubaOS 6.1:
Command Description
show ipv6 access-list
(deprecated)
show ipv6 datapath session
counters (deprecated)
show ipv6 datapath session
table (deprecated)
show ipv6 datapath user
counters (deprecated)
show ipv6 datapath user table
(deprecated)
Displays IPv6 access lists configured in the controller. This command has
been replaced by the show ip access-list command.
Displays datapath session table statistics. This command has been
replaced by the show datapath session ipv6 counters command.
Displays current IPv6 session on the controller. This command has been
replaced by the show datapath session ipv6 table command.
Displays datapath user table statistics. This command has been replaced
by the show datapath user ipv6 command.
Displays ipv6 datapath user table entries. This command has been
replaced by the show datapath user ipv6 command.
About this Guide
This guide describes the ArubaOS command syntax. The commands in this guide are listed alphabetically.
The following information is provided for each command:
Command Syntax—The complete syntax of the command.
Description—A brief description of the command.
Syntax—A description of the command parameters, including license requirements for specific parameters if
needed. The applicable ranges and default values, if any, are also included.
Usage Guidelines—Information to help you use the command, including: prerequisites, prohibitions, and
related commands.
Example—An example of how to use the command.
Command History—The version of ArubaOS in which the command was first introduced. Modifications and
changes to the command are also noted
Command Information—This table describes any licensing requirements, command modes and platforms for
which this command is applicable. For more information about available licenses, see the “Software Licenses”
chapter in the Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.1 User Guide.
Connecting to the Controller
This section describes how to connect to the controller to use the CLI.
Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.1 CLI | Reference Guide Introduction | 9
Serial Port Connection
The serial port is located on the front panel of the controller. Connect a terminal or PC/workstation running a
terminal emulation program to the serial port on the controller to use the CLI. Configure your terminal or
terminal emulation program to use the following communication settings.
Baud Rate Data Bits Parity Stop Bits Flow Control
9600 8 None 1 None
Telnet or SSH Connection
Telnet or SSH access requires that you configure an IP address and a default gateway on the controller and
connect the controller to your network. This is typically performed when you run the Initial Setup on the
controller, as described in the Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.1 Quick Start Guide. In certain
deployments, you can also configure a loopback address for the controller; see “The Basic User-Centric Network”
chapter in the Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.1 User Guide for more information.
Configuration changes on Master Controllers
Some commands can only be issued when connected to a master controller. If you make a configuration change
on a master controller, all connected local controllers subsequently update their configurations as well. You can
manually synchronize all of the controllers at any time by saving the configuration on the master controller.
CLI Access
When you connect to the controller using the CLI, the system displays its host name followed by the login
prompt. Log in using the admin user account and the password you entered during the Initial Setup on the
controller (the password displays as asterisks). For example:
(host)
User: admin
Password: *****
When you are logged in, the user mode CLI prompt displays. For example:
(host) >
User mode provides only limited access for basic operational testing such as running ping and traceroute.
Certain management functions are available in enable (also called “privileged”) mode. To move from user mode
to enable mode requires you to enter an additional password that you entered during the Initial Setup (the
password displays as asterisks). For example:
(host) > enable
Password: ******
When you are in enable mode, the > prompt changes to a pound sign (#):
(host) #
Configuration commands are available in config mode. Move from enable mode to config mode by entering
configure terminal at the # prompt:
(host) # configure terminal
Enter Configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z
When you are in basic config mode, (config) appears before the # prompt:
(host) (config) #
10 | Introduction Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.1 CLI | Reference Guide
NOTE: There are several other sub- command modes that allow users to configure individual interfaces, subinterfaces, loopback
addresses, GRE tunnels and cellular profiles. For details on the prompts and the available commands for each of these modes, see
“Appendix A: Command Modes” on page 1351
Command Help
You can use the question mark (?) to view various types of command help.
When typed at the beginning of a line, the question mark lists all the commands available in your current mode
or sub-mode. A brief explanation follows each command. For example:
(host) > ?
enable Turn on Privileged commands
logout Exit this session. Any unsaved changes are lost.
ping Send ICMP echo packets to a specified IP address.
traceroute Trace route to specified IP address.
When typed at the end of a possible command or abbreviation, the question mark lists the commands that match
(if any). For example:
(host) > c?
clear Clear configuration
clock Configure the system clock
configure Configuration Commands
copy Copy Files
If more than one item is shown, type more of the keyword characters to distinguish your choice. However, if only
one item is listed, the keyword or abbreviation is valid and you can press tab or the spacebar to advance to the
next keyword.
When typed in place of a parameter, the question mark lists the available options. For example:
(host) # write ?
erase Erase and start from scratch
file Write to a file in the file system
memory Write to memory
terminal Write to terminal
<cr>
The <cr> indicates that the command can be entered without additional parameters. Any other parameters are
optional.
Command Completion
To make command input easier, you can usually abbreviate each key word in the command. You need type only
enough of each keyword to distinguish it from similar commands. For example:
(host) # configure terminal
could also be entered as:
(host) # con t
Three characters (con) represent the shortest abbreviation allowed for configure. Typing only c or co would not
work because there are other commands (like copy) which also begin with those letters. The configure command
is the only one that begins with con.
As you type, you can press the spacebar or tab to move to the next keyword. The system then attempts to expand
the abbreviation for you. If there is only one command keyword that matches the abbreviation, it is filled in for
Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.1 CLI | Reference Guide Introduction | 11

you automatically. If the abbreviation is too vague (too few characters), the cursor does not advance and you must
type more characters or use the help feature to list the matching commands.
Deleting Configuration Settings
Use the no command to delete or negate previously-entered configurations or parameters.
To view a list of no commands, type no at the enable or config prompt followed by the question mark. For
example:
(host) (config) # no?
To delete a configuration, use the no form of a configuration command. For example, the following command
removes a configured user role:
(host) (config) # no user-role <name>
To negate a specific configured parameter, use the no parameter within the command. For example, the
following commands delete the DSCP priority map for a priority map configuration:
(host) (config) # priority-map <name>
(host) (config-priority-map) # no dscp priority high
Saving Configuration Changes
Each Dell controller contains two different types of configuration images.
The running config holds the current controller configuration, including all pending changes which have yet to
be saved. To view the running-config, use the following command:
(host) # show running-config
The startup config holds the configuration which is used the next time the controller is rebooted. It contains
all the options last saved using the write memory command. To view the startup-config, use the following
command:
(host) # show startup-config
When you make configuration changes via the CLI, those changes affect the current running configuration only.
If the changes are not saved, they are lost after the controller reboots. To save your configuration changes so they
are retained in the startup configuration after the controller reboots, use the following command in enable mode:
(host) # write memory
Saving Configuration...
Saved Configuration
Both the startup and running configurations can also be saved to a file or sent to a TFTP server for backup or
transfer to another system.
Commands That Reset the Controller or AP
If you use the CLI to modify a currently provisioned and running radio profile, those changes take place
immediately; you do not reboot the controller or the AP for the changes to affect the current running
configuration. Certain commands, however, automatically force the controller or AP to reboot. You may want to
consider current network loads and conditions before issuing these commands, as they may cause a momentary
disruption in service as the unit resets. Note also that changing the lms-ip parameter in an AP system profile
associated with an AP group causes all APs in that AP group to reboot.
12 | Introduction Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.1 CLI | Reference Guide

Commands that reset an AP
C
ommands that reset a controller
ap-regroup
ap-rename
apboot
apflash
provision-ap reprovision
ap wired-ap-profile <profile>
forward-mode {bridge|splittunnel|tunnel}
wlan virtual-ap <profile>
{aaa-profile
<profile>|forward-mode
{tunnel|bridge|splittunnel|decrypt-tunnel}|ssidprofile <profile>|vlan
<vlan>...}
ap system-profile <profile>
{bootstrap-threshold
<number>|lms-ip
<ipaddr>|master-ip <ipaddr>}
wlan ssid-profile <profile>
{battery-boost|deny-
bcast|essid|opmode|strictsvp|wepkey1 <key>|wepkey2
<key>|wepkey3 <key>|wepkey4
<key>|weptxkey
<index>|wmm|wmm-be-dscp <besteffort>|wmm-bk-dscp
<background>|wmm-ts-min-inactint <milliseconds>|wmm-vi-dscp
<video>|wmm-vo-dscp
<voice>|wpa-hexkey <psk>|wpapassphrase <string>}
wlan dotllk <profile> {bcn-
measurement-mode|dot11kenable|force-dissasoc}
reload
Command Line Editing
The system records your most recently entered commands. You can review the history of your actions, or reissue a
recent command easily, without having to retype it.
To view items in the command history, use the up arrow to move back through the list and the down arrow key to
forward. To reissue a specific command, press Enter when the command appears in the command history. You
can even use the command line editing feature to make changes to the command prior to entering it.
Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.1 CLI | Reference Guide Introduction | 13
The command line editing feature allows you to make corrections or changes to a command without retyping.
Table 1 lists the editing controls: To use key shortcuts, press and hold the Ctrl button while you press a letter key.
Table 1 Line Editing Keys
Key Effect Description
Ctrl A Home Move the cursor to the beginning of the line.
Ctrl B or the
left arrow
Ctrl D Delete Right Delete the character to the right of the cursor.
Ctrl E End Move the cursor to the end of the line.
Ctrl F or the
right arrow
Ctrl K Delete Right Delete all characters to the right of the cursor.
Ctrl N or the
down arrow
Ctrl P or
up arrow
Ctrl T Transpose Swap the character to the left of the cursor with the
Ctrl U Clear Clear the line.
Ctrl W Delete Word Delete the characters from the cursor up to and including
Back Move the cursor one character left.
Forward Move the cursor one character right.
Next Display the next command in the command history.
Previous Display the previous command in the command history.
character to the right of the cursor.
the first space encountered.
Ctrl X Delete Left Delete all characters to the left of the cursor.
Typographic Conventions
The following conventions are used throughout this manual to emphasize important concepts:
Table 2 Text Conventions
Type Style Description
Italics
Boldface
Commands This fixed-width font depicts command syntax and examples of commands
This style is used to emphasize important terms and to mark the titles of
books.
This style is used to emphasize command names and parameter options
when mentioned in the text.
and command output.
14 | Introduction Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.1 CLI | Reference Guide
Table 2 Text Conventions (Continued)
Type Style Description
<angle brackets> In the command syntax, text within angle brackets represents items that
[square brackets] In the command syntax, items enclosed in brackets are optional. Do not
{Item_A|Item_B} In the command examples, single items within curled braces and
{ap-name <ap-name>}|{ipaddr
<ip-addr>}
you should replace with information appropriate to your specific situation.
For example:
ping <ipaddr>
In this example, you would type “ping” at the system prompt exactly as
shown, followed by the IP address of the system to which ICMP echo
packets are to be sent. Do not type the angle brackets.
type the brackets.
separated by a vertical bar represent the available choices. Enter only one
choice. Do not type the braces or bars.
Two items within curled braces indicate that both parameters must be
entered together. If two or more sets of curled braces are separated by a
vertical bar, like in the example to the left, enter only one choice Do not
type the braces or bars.
Specifying Addresses and Identifiers in Commands
This section describes addresses and other identifiers that you can reference in CLI commands.
Table 3 Addresses and Identifiers
Address/Identifier Description
IP address For any command that requires entry of an IP address to specify a network entity, use IPv4
Netmask address For subnetwork addresses, specify a netmask in dotted decimal notation (for example,
Media Access Control
(MAC) address
Service Set Identifier
(SSID)
Basic Service Set
Identifier (BSSID)
Extended Service Set
Identifier (ESSID)
Fast Ethernet or Gigabit
Ethernet interface
network address format in the conventional dotted decimal notation (for example, 10.4.1.258).
For subnetwork addresses, specify a netmask in dotted decimal notation (for example,
255.255.255.0).
255.255.255.0).
For any command that requires entry of a device’s hardware address, use the hexadecimal
format (for example, 00:05:4e:50:14:aa).
A unique character string (sometimes referred to as a network name), consisting of no more
than 32 characters. The SSID is case-sensitive (for example, WLAN-01).
This entry is the unique hard-wireless MAC address of the AP. A unique BSSID applies to each
frequency— 802.11a and 802.11g—used from the AP. Use the same format as for a MAC
address.
Typically the unique logical name of a wireless network. If the ESSID includes spaces, you
must enclose the name in quotation marks.
Any command that references a Fast Ethernet or Gigabit Ethernet interface requires that you
specify the corresponding port on the controller in the format <slot>/<port>:
<slot> is always 1. except when referring to interfaces on the W-6000 controller (slots 0-3).
<port> refers to the network interfaces that are embedded in the front panel of the W-3000
Controller Series controller, or a W-6000M3 installed in the W-6000 controller. Port numbers
start at 0 from the left-most position.
Use the show port status command to obtain the interface information currently available
from a controller.
Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.1 CLI | Reference Guide Introduction | 15

16 | Introduction Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.1 CLI | Reference Guide
aaa authentication captive-portal
aaa authentication
aaa authentication captive-portal <profile>
black-list <black-list>
clone <source-profile>
default-guest-role <role>
default-role <role>
enable-welcome-page
guest-logon
ip-addr-in-redirection <ipaddr>
login-page <url>
logon-wait {cpu-threshold <percent>}|{maximum-delay <seconds>}|{minimum-delay <secs>
logout-popup-window
max-authentication-failures <number>
no ...
protocol-http
redirect-pause <secs>
server-group <group-name>
show-acceptable-use-policy
show-fqdn
single-session
controller-in-redirection-url <ipaddr>
use-chap
user-logon
user-vlan-in-redirection-url <vlan>
welcome-page <url>
white-list <white-list>
}
Description
This command configures a Captive Portal authentication profile.
Syntax
This command includes the following configuration parameters.
Parameter Description Range Default
<profile> Name that identifies an instance of the profile. The name
black-list
<black-list>
clone Name of an existing Captive Portal profile from which
default-guest-role Role assigned to guest. — guest
default-role
<role>
enable-welcomepage
must be 1-63 characters.
Name of an existing black list on an IPv4 or IPv6 network
destination. The black list contains websites
(unauthenticated) that a guest cannot access.
parameter values are copied.
Role assigned to the Captive Portal user upon login. When
both user and guest logon are enabled, the default role
applies to the user logon; users logging in using the guest
interface are assigned the guest role.
Displays the configured welcome page before the user is
redirected to their original URL. If this option is disabled,
redirection to the web URL happens immediately after the
user logs in.
— “default”
——
——
— guest
enabled/
disabled
enabled
guest-logon Enables Captive Portal logon without authentication. enabled/
disabled
Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.1 CLI | Reference Guide aaa authentication captive-portal | 17
disabled
Parameter Description Range Default
ip-addr-inredirection
<ipaddr>
login-page <url> URL of the page that appears for the user logon. This can be
logon-wait Configure parameters for the logon wait interval 1-100 60%
cpu-threshold
<percent>
maximum-delay
<seconds>
minimum-delay
<secs>
logout-popupwindow
maxauthenticationfailures <number>
Use this parameter to add one of the controller interfaces in
the redirection URL
set to any URL.
CPU utilization percentage above which the Logon wait
interval is applied when presenting the user with the logon
page.
Maximum time, in seconds, the user has to wait for the
logon page to pop up if the CPU load is high. This works in
conjunction with the Logon wait CPU utilization threshold
parameter.
Minimum time, in seconds, the user has to wait for the
logon page to pop up if the CPU load is high. This works in
conjunction with the Logon wait CPU utilization threshold
parameter.
Enables a pop-up window with the Logout link for the user
to logout after logon. If this is disabled, the user remains
logged in until the user timeout period has elapsed or the
station reloads.
Maximum number of authentication failures before the user
is blacklisted.
——
— /auth/index.
1-100 60%
1-10 10 seconds
1-10 5 seconds
enabled/
disabled
0-10 0
html
enabled
no Negates any configured parameter. — —
protocol-http Use HTTP protocol on redirection to the Captive Portal
redirect-pause
<secs>
server-group
<group-name>
show-fqdn Allows the user to see and select the fully-qualified domain
show-acceptableuse-policy
single-session Allows only one active user session at a time. — disabled
controller-inredirection-url
page. If you use this option, modify the captive portal policy
to allow HTTP traffic.
Time, in seconds, that the system remains in the initial
welcome page before redirecting the user to the final web
URL. If set to 0, the welcome page displays until the user
clicks on the indicated link.
Name of the group of servers used to authenticate Captive
Portal users. See “aaa server-group” on page 75.
name (FQDN) on the login page. The FQDNs shown are
specified when configuring individual servers for the server
group used with captive portal authentication.
Show the acceptable use policy page before the logon
page.
Sends the controller’s IP address in the redirection URL
when external captive portal servers are used. An external
captive portal server can determine the controller from
which a request originated by parsing the ‘switchip’
variable in the URL.
enabled/
disabled
1-60 10 seconds
——
enabled/
disabled
enabled/
disabled
enabled/
disabled
disabled
(HTTPS is used)
disabled
disabled
disabled
use-chap Use CHAP protocol. You should not use this option unless
instructed to do so by an Dell representative.
user-logon Enables Captive Portal with authentication of user
credentials.
18 | aaa authentication captive-portal Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.1 CLI | Reference Guide
enabled/
disabled
enabled/
disabled
disabled (PAP is
used)
enabled
Parameter Description Range Default
user-vlanredirection-url
welcome-page <url> URL of the page that appears after logon and before
white-list <whitelist>
Sends the user’s VLAN ID in the redirection URL when
external captive portal servers are used.
redirection to the web URL. This can be set to any URL.
Name of an existing white list on an IPv4 or IPv6 network
destination. The white list contains authenticated websites
that a guest can access.
——
— /auth/
welcome.html
——
Usage Guidelines
You can configure the Captive Portal authentication profile in the base operating system or with the Next
Generation Policy Enforcement Firewall (PEFNG) license installed. When you configure the profile in the base
operating system, the name of the profile must be entered for the initial role in the AAA profile. Also, when you
configure the profile in the base operating system, you cannot define the default-role.
Example
The following example configures a Captive Portal authentication profile that authenticates users against the
controller’s internal database. Users who are successfully authenticated are assigned the auth-guest role.
To create the auth-guest user role shown in this example, the PEFNG license must be installed in the controller.
aaa authentication captive-portal guestnet
default-role auth-guest
user-logon
no guest-logon
server-group internal
Command History
Version Description
ArubaOS 3.0 Command introduced.
ArubaOS 6.0 The max-authentication-failures parameter no longer requires a license.
ArubaOS 6.1 The sygate-on-demand, black-list and white-list parameters were added.
Command Information
Platforms Licensing Command Mode
All platforms Base operating system, except for
noted parameters
Config mode on master controllers
Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.1 CLI | Reference Guide aaa authentication captive-portal | 19

aaa authentication dot1x
aaa authentication dot1x {<profile>|countermeasures}
ca-cert <certificate>
cert-cn-lookup
clear
clone <profile>
eapol-logoff
enforce-suite-b-128
enforce-suite-b-192
framed-mtu <mtu>
heldstate-bypass-counter <number>
ignore-eap-id-match
ignore-eapolstart-afterauthentication
machine-authentication blacklist-on-failure|{cache-timeout <hours>}|enable|
{machine-default-role <role>}|{user-default-role <role>}
max-authentication-failures <number>
max-requests <number>
multicast-keyrotation
no ...
opp-key-caching
reauth-max <number>
reauthentication
server {server-retry <number>|server-retry-period <seconds>}
server-cert <certificate>
termination {eap-type <type>}|enable|enable-token-caching|{inner-eap-type (eap-
gtc|eap-mschapv2)}|{token-caching-period <hours>}
timer {idrequest_period <seconds>}|{mkey-rotation-period <seconds>}|{quiet-period
<seconds>}|{reauth-period <seconds>}|{ukey-rotation-period <seconds>}|{wpa groupkey-delay <seconds>}|{wpa-key-period <milliseconds>}|wpa2-key-delay
<milliseconds>
tls-guest-access
tls-guest-role <role>
unicast-keyrotation
use-session-key
use-static-key
validate-pmkid
voice-aware
wep-key-retries <number>
wep-key-size {40|128}
wpa-fast-handover
wpa-key-retries
xSec-mtu <mtu>
Description
This command configures the 802.1x authentication profile.
Syntax
This command includes the following configuration parameters.
Parameter Description Range Default
<profile> Name that identifies an instance of the profile. The name must be 1-63
characters.
clear Clear the Cached PMK, Role and VLAN entries. This command is
available in enable mode only.
20 | aaa authentication dot1x Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.1 CLI | Reference Guide
— “default”
——
Parameter Description Range Default
countermeasures Scans for message integrity code (MIC) failures in traffic received
ca-cert
<certificate>
cert-cn-lookup If you use client certificates for user authentication, enable this
eapol-logoff Enables handling of EAPOL-LOGOFF messages. — disabled
enforce-suite-b128
enforce-suite-b192
framed-mtu <MTU> Sets the framed MTU attribute sent to the authentication server. 500-1500 1100
heldstatebypass-counter
<number>
from clients. If there are more than 2 MIC failures within 60 seconds,
the AP is shut down for 60 seconds. This option is intended to slow
down an attacker who is making a large number of forgery attempts
in a short time.
CA certificate for client authentication. The CA certificate needs to be
loaded in the controller.
option to verify that the certificate's common name exists in the
server. This parameter is disabled by default.
Configure Suite-B 128 bit or more security level
authentication enforcement
Configure Suite-B 192 bit or more security level
authentication enforcement
(This parameter is applicable when 802.1x authentication is
terminated on the controller, also known as AAA FastConnect.)
Number of consecutive authentication failures which, when reached,
causes the controller to not respond to authentication requests from
a client while the controller is in a held state after the authentication
failure. Until this number is reached, the controller responds to
authentication requests from the client even while the controller is in
its held state.
— disabled
——
——
disabled
disabled
0-3 0
ignore-eap-idmatch
ignore-eapol
startafterauthenticat
ion
machineauthentication
blacklist-onfailure
cache-timeout
<hours>
enable Select this option to enforce machine authentication before user
machinedefault-role
<role>
user-defaultrole <role>
Ignore EAP ID during negotiation. — disabled
Ignores EAPOL-START messages after authentication. — disabled
(For Windows environments only) These parameters set machine
authentication:
NOTE: This parameter requires the PEFNG license.
Blacklists the client if machine authentication fails. — disabled
The timeout, in hours, for machine authentication. 1-1000 24 hours (1
authentication. If selected, either the machine-default-role or the
user-default-role is assigned to the user, depending on which
authentication is successful.
Default role assigned to the user after completing only machine
authentication.
Default role assigned to the user after 802.1x authentication. — guest
day)
— disabled
— guest
Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.1 CLI | Reference Guide aaa authentication dot1x | 21

Parameter Description Range Default
maxauthenticationfailures <number>
max-requests
<number>
multicast-key
rotation
no Negates any configured parameter. — —
opp-key-caching Enables a cached pairwise master key (PMK) derived with a client
reauth-max
<number>
reauthentication Select this option to force the client to do a 802.1x reauthentication
Number of times a user can try to login with wrong credentials after
which the user is blacklisted as a security threat. Set to 0 to disable
blacklisting, otherwise enter a non-zero integer to blacklist the user
after the specified number of failures.
NOTE: The RF Protect license must be installed.
Maximum number of times ID requests are sent to the client. 1-10 3
Enables multicast key rotation — disabled
and an associated AP to be used when the client roams to a new AP.
This allows clients faster roaming without a full 802.1x authentication.
NOTE: Make sure that the wireless client (the 802.1x supplicant)
supports this feature. If the client does not support this feature, the
client attempts to renegotiate the key whenever it roams to a new AP.
As a result, the key cached on the controller can be out of sync with
the key used by the client.
Maximum number of reauthentication attempts. 1-10 3
after the expiration of the default timer for reauthentication. (The
default value of the timer is 24 hours.) If the user fails to
reauthenticate with valid credentials, the state of the user is cleared.
If derivation rules are used to classify 802.1x-authenticated users,
then the reauthentication timer per role overrides this setting.
0-5 0 (disabled)
— enabled
— disabled
reload-cert Reload Certificate for 802.1X termination. This command is available
server Sets options for sending authentication requests to the
server-retry
<number>
server-retryperiod <seconds>
server-cert
<certificate>
termination Sets options for terminating 802.1x authentication on the controller.
eap-type
<type>
enable Enables 802.1x termination on the controller. — disabled
enable-token
-caching
in enable mode only.
authentication server group.
Maximum number of authentication requests that are sent to server
group.
Server group retry interval, in seconds. 5-65535 30 seconds
Server certificate used by the controller to authenticate itself to the
client.
The Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) method, either EAPPEAP or EAP-TLS.
If you select EAP-GTC as the inner EAP method, you can enable the
controller to cache the username and password of each
authenticated user. The controller continues to reauthenticate users
with the remote authentication server, however, if the authentication
server is not available, the controller inspects its cached credentials
to reauthenticate users.
——
0-3 2
——
eap-peap/
eap-tls
— disabled
eap-peap
22 | aaa authentication dot1x Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.1 CLI | Reference Guide
Parameter Description Range Default
inner-eap-type
eap-gtc|eapmschapv2
token-cachingperiod <hours>
timer Sets timer options for 802.1x authentication:
idrequestperiod
<seconds>
mkey-rotationperiod
<seconds>
quiet-period
<seconds>
reauth-period
<seconds>
When EAP-PEAP is the EAP method, one of the following inner EAP
types is used:
EAP-Generic Token Card (GTC): Described in RFC 2284, this EAP
method permits the transfer of unencrypted usernames and
passwords from client to server. The main uses for EAP-GTC are onetime token cards such as SecureID and the use of LDAP or RADIUS
as the user authentication server. You can also enable caching of
user credentials on the controller as a backup to an external
authentication server.
EAP-Microsoft Challenge Authentication Protocol version 2 (MSCHAPv2): Described in RFC 2759, this EAP method is widely supported
by Microsoft clients.
If you select EAP-GTC as the inner EAP method, you can specify the
timeout period, in hours, for the cached information.
Interval, in seconds, between identity request retries. 1-65535 30 seconds
Interval, in seconds, between multicast key rotation. 60-864000 1800 seconds
Interval, in seconds, following failed authentication. 1-65535 30 seconds
Interval, in seconds, between reauthentication attempts, or specify
server to use the server-provided reauthentication period.
eap-gtc/
eapmschapv2
(any) 24 hours
60-864000 86400
eap-mschap
v2
seconds
(1 day)
ukey-rotationperiod
<seconds>
wpa-groupkey
-delay
<milliseconds>
wpa-key-period
<milliseconds>
wpa2-key-delay
<milliseconds>
tls-guest-access Enables guest access for EAP-TLS users with valid certificates. — disabled
tls-guest-role
<role>
unicastkeyrotation
use-session-key Use RADIUS session key as the unicast WEP key. — disabled
use-static-key Use static key as the unicast/multicast WEP key. — disabled
validate-pmkid This parameter instructs the controller to check the pairwise master
Interval, in seconds, between unicast key rotation. 60-864000 900 seconds
Interval, in milliseconds, between unicast and multicast key
exchanges.
Interval, in milliseconds, between each WPA key exchange. 1000-5000 1000 ms
Set the delay between EAP-Success and unicast key exchange. 1-2000 0 ms
User role assigned to EAP-TLS guest.
NOTE: This parameter requires the PEFNG license.
Enables unicast key rotation. — disabled
key (PMK) ID sent by the client. When this option is enabled, the
client must send a PMKID in the associate or reassociate frame to
indicate that it supports OKC or PMK caching; otherwise, full 802.1x
authentication takes place. (This feature is optional, since most
clients that support OKC and PMK caching do not send the PMKID in
their association request.)
0-2000 0 ms
(no delay)
(no delay)
— guest
— disabled
Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.1 CLI | Reference Guide aaa authentication dot1x | 23
Parameter Description Range Default
voice-aware Enables rekey and reauthentication for VoWLAN clients.
NOTE: The Next Generation Policy Enforced Firewall license must be
installed.
wep-key-retries
<number>
wep-key-size Dynamic WEP key size, either 40 or 128 bits. 40 or 128 128 bits
wpa-fast-hand
over
wpa-key-retries Set the Number of times WPA/WPA2 Key Messages are retried — disabled
xSec-mtu <mtu> Sets the size of the MTU for xSec. 1024-1500 1300 bytes
Number of times WPA/WPA2 key messages are retried. 1-5 3
Enables WPA-fast-handover. This is only applicable for phones that
support WPA and fast handover.
— enabled
— disabled
Usage Guidelines
The 802.1x authentication profile allows you to enable and configure machine authentication and 802.1x
termination on the controller (also called “AAA FastConnect”).
In the AAA profile, you specify the 802.1x authentication profile, the default role for authenticated users, and the
server group for the authentication.
Examples
The following example enables authentication of the user’s client device before user authentication. If machine
authentication fails but user authentication succeeds, the user is assigned the restricted “guest” role:
aaa authentication dot1x dot1x
machine-authentication enable
machine-authentication machine-default-role computer
machine-authentication user-default-role guest
The following example configures an 802.1x profile that terminates authentication on the controller, where the
user authentication is performed with the controller’s internal database or to a “backend” non-802.1x server:
aaa authentication dot1x dot1x
termination enable
Command History
Version Description
ArubaOS 3.0 Command introduced.
ArubaOS 6.1 The cert-cn-lookup, enforce-suite-b-128 and enforce-suite-b-192 parameters were
introduced.
Command Information
Platforms Licensing Command Mode
All platforms Base operating system. The voice-
aware parameter requires the PEFNG
license
Config mode on master controllers
24 | aaa authentication dot1x Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.1 CLI | Reference Guide
aaa authentication mac
aaa authentication mac <profile>
case upper|lower
clone <profile>
delimiter {colon|dash|none}
max-authentication-failures <number>
no ...
Description
This command configures the MAC authentication profile.
Syntax
Parameter Description Range Default
<profile> Name that identifies an instance of the profile. The name must be
case The case (upper or lower) used in the MAC string sent in the
clone <profile> Name of an existing MAC profile from which parameter values
delimiter Delimiter (colon, dash, or none) used in the MAC string. colon|dash|
maxauthenticationfailures <number>
no Negates any configured parameter. — —
1-63 characters.
authentication request. If there is no delimiter configured, the
MAC address in lower case is sent in the format xxxxxxxxxxxx,
while the MAC address in upper case is sent in the format
XXXXXXXXXXXX.
are copied.
Number of times a client can fail to authenticate before it is
blacklisted. A value of 0 disables blacklisting.
— “default”
upper|lower lower
——
none
none
0-10 0 (disabled)
Usage Guidelines
MAC authentication profile configures authentication of devices based on their physical MAC address. MACbased authentication is often used to authenticate and allow network access through certain devices while
denying access to all other devices. Users may be required to authenticate themselves using other methods,
depending upon the network privileges.
Example
The following example configures a MAC authentication profile to blacklist client devices that fail to
authenticate.
aaa authentication mac mac-blacklist
max-authentication-failures 3
Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.1 CLI | Reference Guide aaa authentication mac | 25

Command History:
Release Modification
ArubaOS 3.0 Command introduced
ArubaOS 3.3.1.8 The max-authentication-failures parameter was allowed in the base operating system. In
earlier versions of ArubaOS, the max-authentication-failures parameter required the
Wireless Intrusion Protection license
Command Information
Platforms Licensing Command Mode
All platforms Base operating system Config mode on master controllers
26 | aaa authentication mac Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.1 CLI | Reference Guide
aaa authentication mgmt
aaa authentication mgmt
default-role {guest-provisioning|location-api-mgmt|network-operations|noaccess|read-only|root}
enable
no ...
server-group <group>
Description
This command configures authentication for administrative users.
Syntax
Parameter Description Range Default
default-role Select a predefined management role to assign to
default Default superuser role
guestprovisioning
location-apimgmt
networkoperations
no-access No commands are accessible for this role
read-only Read-only role
enable Enables authentication for administrative users. enabled|
no Negates any configured parameter. — —
server-group
<group>
authenticated administrative users:
Guest provisioning role
Location API role
Network operations role
Name of the group of servers used to authenticate
administrative users. See “aaa server-group” on page 75.
— default
disabled
disabled
— default
Usage Guidelines
If you enable authentication with this command, users configured with the mgmt-user command must be
authenticated using the specified server-group.
You can configure the management authentication profile in the base operating system or with the PEFNG
license installed.
Example
The following example configures a management authentication profile that authenticates users against the
controller’s internal database. Users who are successfully authenticated are assigned the read-only role.
aaa authentication mgmt
default-role read-only
server-group internal
Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.1 CLI | Reference Guide aaa authentication mgmt | 27

Command History:
Release Modification
ArubaOS 3.0 Command introduced
ArubaOS 3.2 The network-operations role was introduced.
ArubaOS 3.3 The location-api-mgmt role was introduced.
Command Information
Platforms Licensing Command Mode
All platforms Base operating system Config mode on master controllers
28 | aaa authentication mgmt Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.1 CLI | Reference Guide
aaa authentication stateful-dot1x
aaa authentication stateful-dot1x
default-role <role>
enable
no ...
server-group <group>
timeout <seconds>
Description
This command configures 802.1x authentication for clients on non-Dell APs.
Syntax
Parameter Description Range Default
default-role
<role>
enable Enables 802.1x authentication for clients on non-Dell APs.
no Negates any configured parameter. — —
server-group
<group>
timeout <seconds> Timeout period, in seconds. 1-20 10 seconds
Role assigned to the 802.1x user upon login.
NOTE: The PEFNG license must be installed.
Use no enable to disable this authentication.
Name of the group of RADIUS servers used to authenticate
the 802.1x users. See “aaa server-group” on page 75.
— guest
— enabled
——
Usage Guidelines
This command configures 802.1x authentication for clients on non-Dell APs. The controller maintains user
session state information for these clients.
Example
The following command assigns the employee user role to clients who successfully authenticate with the server
group corp-rad:
aaa authentication stateful-dot1x
default-role employee
server-group corp-rad
Command History
This command was introduced in ArubaOS 3.0.
Command Information
Platforms Licensing Command Mode
All platforms Base operating system Config mode on master controllers
Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.1 CLI | Reference Guide aaa authentication stateful-dot1x | 29

aaa authentication stateful-dot1x clear
aaa authentication stateful-dot1x clear
Description
This command clears automatically-created control path entries for 802.1x users on non-Dell APs.
Syntax
No parameters.
Usage Guidelines
Run this command after changing the configuration of a RADIUS server in the server group configured with the
aaa authentication stateful-dot1x command. This causes entries for the users to be created in the control path
with the updated configuration information.
Command History
This command was introduced in ArubaOS 3.0.
Command Information
Platforms Licensing Command Mode
All platforms Base operating system Enable mode on master controllers
30 | aaa authentication stateful-dot1x clear Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.1 CLI | Reference Guide
 Loading...
Loading...