Page 1

Dell Shared PowerEdge RAID Controller
(PERC) 8 For Dell PowerEdge VRTX Systems
User’s Guide
Regulatory Model: UCPM-800
Page 2

Notes, Cautions, and Warnings
NOTE: A NOTE indicates important information that helps you make better use of your computer.
CAUTION: A CAUTION indicates either potential damage to hardware or loss of data and tells you
how to avoid the problem.
WARNING: A WARNING indicates a potential for property damage, personal injury, or death.
Copyright © 2014 Dell Inc. All rights reserved. This product is protected by U.S. and international copyright and
intellectual property laws. Dell™ and the Dell logo are trademarks of Dell Inc. in the United States and/or other
jurisdictions. All other marks and names mentioned herein may be trademarks of their respective companies.
2014 - 11
Rev. A03
Page 3

Contents
1 About The Shared PERC 8 Card..........................................................................6
Configurations of the Shared PERC 8 card..........................................................................................6
Specifications of a Shared PERC 8 card............................................................................................... 7
Supported Operating Systems..............................................................................................................9
Best Practices For Shared PERC 8........................................................................................................ 9
Related Documentation........................................................................................................................9
Locating your system Service Tag......................................................................................................10
Contacting Dell....................................................................................................................................10
Documentation Feedback................................................................................................................... 11
2 Shared PERC 8 Card Features...........................................................................12
Physical Disk Power Management......................................................................................................12
Consistency Checks............................................................................................................................ 12
Virtual Disk Initialization...................................................................................................................... 12
Background Initialization Of Virtual Disks.....................................................................................13
Full Initialization Of Virtual Disks...................................................................................................13
Fast Initialization Of Virtual Disks.................................................................................................. 13
Physical Disk Roaming.........................................................................................................................13
Using Physical Disk Roaming........................................................................................................ 14
FastPath................................................................................................................................................14
Virtual Disk Migration.......................................................................................................................... 14
Migrating Virtual Disks If The Target System Is Turned Off......................................................... 15
Migrating Virtual Disks If The Target System Is Turned On..........................................................15
Virtual Disk Cache Policies..................................................................................................................15
Virtual Disk Write Cache Policies.................................................................................................. 16
Write-Back .................................................................................................................................... 16
Conditions Under Which Write-Back Is Employed...................................................................... 16
Conditions Under Which Forced Write-Back With No Battery Is Employed.............................. 16
Write-through................................................................................................................................16
Conditions under which write-through is employed...................................................................17
Virtual Disk Read Cache Policies...................................................................................................17
Physical Disk Write Cache Policy........................................................................................................ 17
Fault Tolerance.................................................................................................................................... 17
The SMART Feature....................................................................................................................... 18
Patrol Read.....................................................................................................................................18
Physical disk failure detection.......................................................................................................19
Physical Disk Hot Swapping.......................................................................................................... 19
Auto Replacement Of A Virtual Disk Member And Revertible Hot Spares.................................. 19
Page 4

Shared PERC 8 Card Cache Preservation.....................................................................................19
Battery Transparent Learn Cycle.................................................................................................. 20
The Controller Failover Feature....................................................................................................20
Multipath Support................................................................................................................................21
Configuring Multipath Support In Windows.................................................................................21
Configuring Multipath Support In VMWare.................................................................................. 21
Multipath support in Linux.............................................................................................................21
3 Deploying The Shared PERC 8 Card................................................................22
Installing A New Shared PERC 8 Card................................................................................................22
Replacing A Shared PERC 8 Card.......................................................................................................22
Prerequisites For Removing The Shared PERC 8 Card................................................................23
Removing The Shared PERC 8 Card.............................................................................................23
Installing The Shared PERC 8 Card...............................................................................................25
Post-Installation Tasks For Shared PERC 8 Card......................................................................... 25
Firmware installation or update..........................................................................................................26
Updating firmware.........................................................................................................................26
4 Driver Installation............................................................................................... 27
Downloading Drivers and Firmware For Shared PERC 8 From The Dell Support Website For
All Operating Systems......................................................................................................................... 27
Downloading Drivers From The Dell Systems Service And Diagnostic Tools Media For
Windows.............................................................................................................................................. 27
Installing Or Updating Windows Drivers For Shared PERC 8............................................................28
Installing Or Updating Linux Drivers For Shared PERC 8.................................................................. 29
Installing Or Updating The Driver Package On RHEL Using KMOD Support..............................29
Installing Or Updating The Driver Package On SLES Using KMP Support.................................. 29
Installing Or Updating VMware Drivers For Shared PERC 8..............................................................29
5 Management Applications For Shared PERC 8 Card................................... 30
6 Troubleshooting................................................................................................. 31
Performance variations between write-back and write-through cache modes..............................31
Shared PERC 8 Card Boots Into Safe Mode....................................................................................... 31
Degraded State Of Virtual Disks..........................................................................................................32
General Issues..................................................................................................................................... 32
Shared PERC 8 Card Has Yellow Exclamation Mark In Device Manager.................................... 32
Shared PERC 8 Card Not Seen In Device Manager..................................................................... 32
Critical Errors Or Disk Warning Messages Seen In The Windows Event Log..............................32
Shared PERC 8 Cards Fail To Function.........................................................................................33
Physical disk issues..............................................................................................................................33
Incorrect Number of Virtual Disks Displayed In Windows Disk Manager................................... 33
Page 5

Physical Disk In Failed State.......................................................................................................... 33
Unable to rebuild a fault tolerant virtual disk............................................................................... 33
Fatal Error Or Data Corruption Reported.....................................................................................34
Physical Disk Displayed As Blocked By Management Application.............................................. 34
Multiple Disks Become Inaccessible.............................................................................................34
Rebuilding A Failed Physical Disk..................................................................................................34
Virtual Disk Fails During Rebuild Using A Global Hot Spare........................................................ 35
Virtual Disk Fails During Rebuild Using A Dedicated Hot Spare.................................................. 35
Physical disk takes a long time to rebuild.....................................................................................35
Controller cache issues.................................................................................................................35
SMART Errors.......................................................................................................................................36
SMART Error Detected On A Physical Disk In A Redundant Virtual Disk.................................... 36
SMART Error Detected On A Physical Disk In A Non-Redundant Virtual Disk............................37
Auto Replacement Member Errors.....................................................................................................37
Source Disk Fails............................................................................................................................37
Target Disk Fails.............................................................................................................................37
General Disk Fails...........................................................................................................................37
Hard-Drive Indicator Patterns............................................................................................................ 38
7 Getting help.........................................................................................................39
Contacting Dell................................................................................................................................... 39
Locating your system Service Tag......................................................................................................39
Documentation feedback.............................................................................................................39
Page 6

1
About The Shared PERC 8 Card
The Dell Shared PowerEdge RAID Controller (PERC) 8 card installed on the Dell PowerEdge VRTX system
supports Single Root Input Output Virtualization (SR-IOV). This feature allows multiple systems to share
available hardware resources.
The PERC 8 card allows four server modules to access a local shared storage. Each server module's
operating system loads a Virtual Function (VF) driver that allows the server module to communicate with
the Shared PERC 8 firmware. The server module can then be mapped to either a single virtual disk or
multiple virtual disks that are located on the shared storage. From a single server module, you can only
access the virtual disks that are mapped to that server module.
Configurations of the Shared PERC 8 card
The PowerEdge VRTX system is available in two configurations of the Shared PERC 8 card:
Single Shared PERC 8 Card Configuration — In this configuration, the PowerEdge VRTX system is installed
with a single Shared PERC 8 card. The default cache policy for virtual disks created in this configuration is
write-back. In this mode, write completion information is returned to the host after the data is written to
the Shared PERC 8 controller’s cache.
Fault Tolerant Shared PERC 8 Card Configuration — In this configuration, the PowerEdge VRTX system is
installed with two Shared PERC 8 cards. The shared PERC cards are configured in an active-passive
mode. Both the cards can access the storage subsystem. However, only the active controller will provide
the data access. If one Shared PERC 8 card fails, the other Shared PERC 8 card takes control in a
seamless transition.
Checkpoints are created for all background operations. After a failover, operations are restored from the
last checkpoint. The default cache policy for virtual disks created in this configuration is write-back. In
this mode, write completion information is returned to the host after the data is written to the peer
shared PERC 8 controller’s cache.
Host data is also mirrored to the peer controller's cache to allow seamless operation in case of a primary
card failure.
Important information regarding the Fault Tolerant Shared PERC 8 Card Configuration:
• Multipath support must be enabled in the operating system for the Fault Tolerant Shared PERC 8 card
configuration to function.
• In the event of a controller failover, a Background Initialization (BGI) starts automatically on each
virtual disk.
• An ongoing full initialization does not restart in the event of a failover.
6
Page 7

• Currently, Linux drivers do not support the fault tolerance feature of the PowerEdge VRTX system.
Host servers running Linux are only supported in single-controller configuration.
Specifications of a Shared PERC 8 card
The characteristics of a Shared PERC 8 card are as follows:
Table 1. Shared PERC 8 card specifications
Specification Description
Supported drives Dell-qualified SAS hard drives and SAS solid state drives (SSDs).
Mixing disks of different speeds (7,200 rpm, 10,000 rpm, or
15,000 rpm) and bandwidth (3 Gbps or 6 Gbps) while
maintaining the same drive type (SAS) and technology (HDD or
SSD) is supported. However, this may affect data transfer
performance.
NOTE: Mixing HDDs and SSDs within a virtual disk is not
supported. SATA drives are not supported.
RAID levels 0, 1, 5, 6, 10, 50, and 60
NOTE: Non-RAID drives are not supported.
Virtual functions Four virtual functions to support up to four host servers
Management application Dell Chassis Management Controller (CMC).
NOTE: Option ROM (OP-ROM) is not supported. Booting
from a shared storage is not supported. You can only boot
from the storage located on the server module.
Enclosure per port Not applicable
Processor Dell Adapter SAS RAID-on-Chip, 8-Port with LSI 2208 Chipset
Battery backup unit Yes
Non-volatile cache Yes
Cache memory 1 GB DDR3, 1333 MHz
Cache policies Write Back, Forced Write-Back, Write Through, Adaptive Read-
Ahead, No Read-Ahead, and Read Ahead
NOTE: Note that write-back caching in a dual controller
configuration is not supported on the earlier versions of the
Shared PERC 8 solution.
NOTE: For the Shared PERC 8 card to support write-back
feature, ensure that you download the updated firmware
and driver version available at dell.com/support/home.
NOTE: For more information, see the PowerEdge VRTX
Storage Subsystem Compatibility Matrix at dell.com/
support/home.
7
Page 8

Specification Description
Maximum number of spans per disk
group
Maximum number of virtual disks per
disk group
Maximum number of virtual disks 64
Dedicated and global hot spares Yes
Hot swap devices supported Yes
Hardware XOR engine Yes
Virtual disk initialization; background,
full, and fast
Consistency check Yes
Disk roaming Yes
FastPath Yes
Virtual disk migration between two
Shared PERC 8 cards
Virtual disk migration from PERC
H310, H710, or H710P cards to a
Shared PERC 8 card
8
16
Yes
Yes
No
NOTE: The target Shared PERC 8 card firmware level must
be either higher or equal to the source Shared PERC 8 card
firmware level.
SMART detection Yes
Patrol Read Yes
Automatic replace member Yes
SAS (HDD/SSD) hard drive Yes
Physical disk power management IDLE-C for compliant HDDs only. No support for balanced,
maximum, and customized power savings.
SATA (HDD/SSD) hard drive No
Manual replace member No
Online capacity expansion No
Cachecade No
Local Key Management (LKM) No
PCIe hot-plug of controller No
8
Page 9
Specification Description
Multipath support Required for systems with Fault Tolerant Shared PERC 8 card
configuration.
NOTE: Multipath is not supported on systems running Linux
operating system.
Controller failover Available only for systems with Fault Tolerant Shared PERC 8
card configuration.
Supported Operating Systems
The Shared PERC 8 card supports the following operating systems:
• Microsoft Windows Server 2012 R2
• Microsoft Windows Server 2012
• Microsoft Windows Server 2008 including Hyper-V virtualization
• Microsoft Windows Server 2008 R2
• Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 Update 5
• SUSE Enterprise Linux 11 SP3
• VMware ESXi 5.1 UP1 and above
• VMware ESXi 5.5, ESXi, 5.5 UP1 and above
NOTE: For information on supported software and hardware for the PowerEdge VRTX system,
see the PowerEdge VRTX Storage Subsystem Compatibility Matrix at dell.com/support/manuals.
Best Practices For Shared PERC 8
• Always use the latest firmware and drivers from dell.com/support/drivers.
• Always keep a copy of your virtual disk configuration and server node mapping information. To
document your virtual drive configuration and mapping information, perform the following steps:
a. Open CLI terminal and run the command racadm raid get vdisks –o. Take a screen shot of the
results page and save the captured screen shot to a location of choice, or write down the
information and store it in a safe, secure location.
b. Click Chassis Overview → Storage → Virtual Disks → Assign to view the virtual disk mapping by
the CMC GUI. Take a screen shot of the results page and save the captured screen shot to a
location of choice, or write down the information and store it in a safe, secure location.
c. Click Chassis Overview → Storage → Virtual Disks to get the virtual disk configuration
information by the CMC GUI. Take a screen shot of the results page and save the captured
screen shot to a location of choice, or write down the information and store it in a safe, secure
location.
Related Documentation
WARNING: See the safety and regulatory information that shipped with your system. Warranty
information may be included within this document or as a separate document.
• The Dell PowerEdge VRTX Getting Started Guide shipped with your system provides an overview of
system features, setting up your system, and technical specifications.
9
Page 10

• The PowerEdge VRTX Storage Subsystem Compatibility Matrix provides information on the minimum
driver and firmware requirements for the components of the Dell PowerEdge VRTX storage
subsystem.
• The setup placemat shipped with your system provides information on the initial system setup and
configuration.
• The server module Owner's Manual provides information about the server module features and
describes how to troubleshoot the server module and install or replace the server module
components. This document is available online at dell.com/poweredgemanuals.
• The Updating Servers of M1000e Chassis and Using in VRTX Chassis provides information on updating
M1000e server modules to be used in the VRTX chassis, using the Chassis Management Controller.
This document is available online at dell.com/esmmanuals.
• The rack documentation included with your rack solution describes how to install your system into a
rack, if required.
• The I/O module documentation at dell.com/poweredgemanuals describes the features of the I/O
module installed in the VRTX enclosure.
• The Dell Shared PowerEdge RAID Controller (PERC) 8 User's Guide provides information about
deploying the Shared PERC 8 card and managing the storage subsystem. This document is available
online at dell.com/storagecontrollermanuals.
• The Dell Chassis Management Controller for Dell PowerEdge VRTX User’s Guide provides information
on installing, configuring and using the Chassis Management Controller (CMC). This document is
available online at dell.com/esmmanuals.
• The Dell PowerEdge VRTX Chassis Management Controller Firmware Event Message Reference Guide
provides information on the error and event messages generated by the firmware or other agents that
monitor system components. This document is available at dell.com/esmmanuals.
• The CMC Online Help provides information and instructions for the current page on the CMC web
interface. To access the Online Help, click Help on the CMC web interface.
• The Integrated Dell Remote Access Controller (iDRAC) User’s Guide provides information about
installation, configuration and maintenance of the iDRAC on managed systems. This document is
available online at dell.com/esmmanuals.
• Dell systems management application documentation provides information about installing and using
the systems management software.
• For the full name of an abbreviation or acronym used in this document, see the Glossary at dell.com/
support/manuals.
• Any media that ships with your system that provides documentation and tools for configuring and
managing your system, including those pertaining to the operating system, system management
software, system updates, and system components that you purchased with your system.
NOTE: Always check for updates on dell.com/support/manuals and read the updates first because
they often supersede information in other documents.
Locating your system Service Tag
Your system is identified by a unique Express Service Code and Service Tag number. The Express Service
Code and Service Tag are found on the front of the system by pulling out the information tag.
Alternatively, the information may be on a sticker on the chassis of the system. This information is used
by Dell to route support calls to the appropriate personnel.
Contacting Dell
Dell provides several online and telephone-based support and service options. If you do not have an
active Internet connection, you can find contact information on your purchase invoice, packing slip, bill,
10
Page 11

or Dell product catalog. Availability varies by country and product, and some services may not be
available in your area. To contact Dell for sales, technical support, or customer-service issues:
1. Go to dell.com/support.
2. Select your country from the drop-down menu on the bottom right corner of the page.
3. For customized support:
a. Enter your system Service Tag in the Enter your Service Tag field.
b. Click Submit.
The support page that lists the various support categories is displayed.
4. For general support:
a. Select your product category.
b. Select your product segment.
c. Select your product.
The support page that lists the various support categories is displayed.
Documentation Feedback
If you have feedback for this document, write to documentation_feedback@dell.com. Alternatively, you
can click on the Feedback link in any of the Dell documentation pages, fill up the form, and click Submit
to send your feedback.
11
Page 12

2
Shared PERC 8 Card Features
Some of the features of the Shared PERC 8 card are as follows:
• Physical disk power management
• Consistency checks
• Virtual disk initialization
• Disk roaming
• FastPath
• Virtual disk migration
• Virtual disk cache policies
• Fault tolerance
• Patrol read
• Multipath support
Physical Disk Power Management
Physical disk power management is a power saving feature of the Shared PERC 8 card. Idle-C feature, as
defined by the T10 organization, is auto-enabled for physical disk power management. Physical disks that
support Idle-C feature, spin at lower RPMs upon timer expiration when there is no I/O activity.
NOTE: There is a delay to I/O operations when a configured disk is being spun up.
NOTE: For detailed information about power management, see the Dell Chassis Management
Controller for Dell PowerEdge VRTX User’s Guide at dell.com/poweredgemanuals.
Consistency Checks
Consistency Check (CC) is a background operation that verifies and corrects the mirror or parity data for
fault tolerant virtual disks. It is recommended that you periodically run a consistency check on virtual
disks. You can manually start a CC in the Dell Chassis Management Controller (CMC).
NOTE: For more information about consistency checks, see the Dell Chassis Management
Controller for Dell PowerEdge VRTX Online Help.
Virtual Disk Initialization
CAUTION: Initializing virtual disks erases the files and file systems but keeps the virtual disk
configuration intact. Initializing a virtual disk destroys all data on the virtual disk.
You can initialize virtual disks as described in the following sections.
12
Page 13

Background Initialization Of Virtual Disks
Both Consistency Check (CC) and Background Initialization (BGI) correct parity errors. However, CC
reports data inconsistencies through an event notification, whereas BGI is an automatic process.
BGI does not run on RAID 0 virtual disks. You cannot disable BGI permanently. If you cancel BGI, it
automatically restarts within five minutes. Unlike full or fast initialization of virtual disks, BGI does not clear
data from the physical disks. CC or BGI typically causes some loss in performance until the operation
completes.
NOTE: In systems with Fault Tolerant Shared PERC 8 card configuration, in the event of controller
failover, a BGI starts automatically on each virtual disk. If a BGI operation was in progress at the time
of controller failover, then the BGI resumes on the new active Shared PERC 8 controller from the
last recorded checkpoint.
Full Initialization Of Virtual Disks
CAUTION: Performing a full initialization on a virtual disk overwrites all blocks and destroys any
data that previously existed on the virtual disk. Full initialization of a virtual disk eliminates the
need for the virtual disk to undergo a BGI. Full initialization can be performed after the creation
of a virtual disk.
During full initialization, the host is not able to access the virtual disk. You can start a full initialization on a
virtual disk in the CMC.
In the event of a controller failover in systems with Fault Tolerant Shared PERC 8 card configuration, full
initialization does not continue on the active controller. You must start full initialization again through
CMC. For more information on virtual disk initialization, see the Dell Chassis Management Controller for
Dell PowerEdge VRTX User’s Guide at dell.com/poweredgemanuals and the Dell Chassis Management
Controller for Dell PowerEdge VRTX Online Help.
In the event of controller failover or system reboot during a full initialization, the operation terminates
and a BGI begins on the virtual disk.
NOTE: Performing a full initialization prevents a BGI from starting automatically on virtual disks.
Fast Initialization Of Virtual Disks
A fast initialization on a virtual disk overwrites the first and last 8 MB of the virtual disk, clearing any boot
records or partition information. The operation takes only 2-3 seconds to complete and is recommended
when you are recreating virtual disks. You can perform a fast initialization in the CMC.
NOTE: A BGI starts five minutes after the Fast Initialization is completed.
Physical Disk Roaming
Physical disk roaming is moving the physical disks from one backplane slot to another on the same
controller. The controller automatically recognizes the relocated physical disks and logically places them
in the virtual disks that are part of the disk group. You can perform disk roaming only when the system is
turned off.
13
Page 14

Using Physical Disk Roaming
Perform the following steps to use disk roaming:
1. Turn off the power to the system, physical disks, enclosures, and system components.
2. Disconnect power cables from the system.
3. Move the physical disks to the required positions on the backplane or the enclosure.
4. Perform a safety check. Make sure the physical disks are inserted properly.
5. Turn on the system.
The controller detects the RAID configuration from the configuration data on the physical disks.
FastPath
The Shared PERC 8 card supports FastPath feature, which improves application performance by
delivering high I/O per second (IOPS).
Under specific conditions with FastPath, the I/O bypasses the controller cache and is committed directly
to the physical disk from the host memory or directly from the physical disk. All simple non-spanned
virtual disks configured with Write-Through write-cache policy and No Read-Ahead read-cache policy
can utilize FastPath.
Workloads on SSD volumes provide the most performance improvement with FastPath.
The following conditions support FastPath:
• Random workloads with small blocks.
• I/O block sizes smaller than virtual disk’s stripe size.
• Sequential read workloads on unspanned RAID volumes (RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 5, and RAID 6).
• Sequential read and write workloads on RAID 0 virtual disks.
The following conditions do not support FastPath
• Virtual disks running background operations like rebuild, initialization, and so on.
• Spanned RAID volumes like RAID 10, RAID 50, and RAID 60.
Virtual Disk Migration
The Shared PERC 8 card supports migration of virtual disks from one controller to another without taking
the target controller offline. The controller can import RAID virtual disks in optimal, degraded, or partially
degraded states.
Conditions that do not support virtual virtual disk migration:
• Does not support migration of virtual disk that is in a failed state.
• Does not support migration of virtual disk when the source system is turned on.
Conditions that support virtual virtual disk migration:
• Supports migration of virtual disks from a similar Shared PERC 8 card.
14
Page 15

• Does not support migration from any other PERC cards such as PERC H310, H700, H710, H800, and
H810.
• Supports migration of virtual disks from the Single Shared PERC 8 card configuration to the Fault
Tolerant Shared PERC 8 card configuration, but does not support migration from a newer firmware
version to an older firmware version system.
• Supports migration of virtual disks from another system's Shared PERC 8 controller when the target
system is either turned on or off
NOTE: When a controller detects a physical disk with an existing configuration, it flags the physical
disk as a foreign disk and generates an alert indicating that a foreign disk was detected.
Migrating Virtual Disks If The Target System Is Turned Off
1. If installed, remove the front bezel (optional) from the PowerEdge VRTX enclosure.
2. Power down the server module using the operating system commands or the CMC, and ensure that
the server module's power is off.
3. Turn off the chassis using CMC.
NOTE: For information about the chassis shutdown, refer to the Dell Chassis Management
Controller for Dell PowerEdge VRTX User’s Guide at dell.com/esmmanuals.
4. Move the appropriate physical disks from the source system to the target system with a similar
Shared PERC 8 controller.
5. Turn on the target system.
The system discovers and automatically imports the detected foreign configuration.
Migrating Virtual Disks If The Target System Is Turned On
1. Turn off the source system.
2. Move the appropriate physical disks from the source system to the target system with a similar
Shared PERC 8 card.
3. Access the Dell Chassis Management Controller (CMC) to import and clear the foreign configuration.
NOTE: For more information on importing or clearing the foreign configuration, see the Dell
Chassis Management Controller for Dell PowerEdge VRTX User’s Guide at dell.com/
poweredgemanuals.
NOTE: If write cache is enabled for these virtual disks, ensure that all cache is flushed to the
hard drives on the source system before migrating them. This can be accomplished by stopping
all applications, powering down the blades, and waiting 30 seconds before powering down the
chassis.
Virtual Disk Cache Policies
The following Virtual Disk Cache policies are supported on Shared PERC 8:
• Virtual disk write cache policies
• Virtual disk read cache policies
15
Page 16

Virtual Disk Write Cache Policies
The write cache policy of a virtual disk determines how the controller handles writes to the virtual disk.
Write-Back and Write-Through are the two write cache policies that can be set on virtual disks
individually.
All RAID volumes are presented as Write-Through to the operating system independent of the actual
write cache policy of the virtual disk. The Shared PERC 8 cards manage data in the cache independently
of the operating system or any applications.
NOTE: Use the Dell Chassis Management Controller (CMC) to view and manage virtual disk cache
settings.
Write-Back
In Write-Back caching, the controller sends a data transfer completion signal to the host when the
controller cache has received all the data in a transaction. The controller then writes the cached data to
the storage device in the background.
The risk of using Write-Back cache is that the cached data can be lost if there is a power failure during or
when the data is written to the storage device. This risk is mitigated by using a Non-Volatile Cache on the
Shared PERC 8 card.
NOTE: The default cache setting for virtual disks in single and dual controller systems is Write-Back
caching.
Conditions Under Which Write-Back Is Employed
Write-Back caching is the default caching mode for single and dual Shared PERC 8 card configurations.
Write-Back caching can be configured under all conditions in which the battery is present and in good
condition.
If a virtual disk is already created on the VRTX system with the firmware version that does not support
write-back caching, then the default will remain as write-through. The virtual disk must be manually
changed to write-back before it goes to write-back mode, even if the system has been updated to a
write-back supported firmware version.
Conditions Under Which Forced Write-Back With No Battery Is Employed
CAUTION: It is recommended that you use a power backup system when forcing Write-Back to
ensure there is no loss of data if the system loses power.
Write-Back mode is available when you select Write-Back Force. When Write-Back Force mode is
selected, the virtual disk is in Write-Back mode even if the battery is not present.
Write-through
In Write-Through caching, the controller sends a data transfer completion signal to the host system
when the disk subsystem has received all the data in a transaction.
NOTE: Most configurations and workloads experience some reduction in performance when
configured with Write-Through cache, as compared to Write-Back cache.
16
Page 17

NOTE: If the virtual drives are created with write-through as selected mode, make sure that the
virtual drives are changed to write-back mode.
Conditions under which write-through is employed
Write-through caching is used under conditions in which the battery fails or is not present.
Virtual Disk Read Cache Policies
The read policy of a virtual disk determines how the controller handles reads to that virtual disk. The read
policies are:
• Read Ahead — Allows the controller to read sequentially ahead of the requested data and store the
additional data in cache memory. This speeds up reads for sequential data, but there is little
improvement when accessing random data.
• No Read Ahead — Disables the Read-Ahead capability.
• Adaptive Read Ahead — Begins using Read-Ahead if the two most recent disk accesses occurred in
sequential sectors. If the read requests are random, the controller reverts to No Read Ahead mode.
NOTE: The default read cache setting for virtual disks is Adaptive Read Ahead.
Physical Disk Write Cache Policy
Management utilities provide the option to modify disk cache policies for physical disks associated with a
virtual disk. The following options are available for the Shared PERC controller:
Option
Enabled Enables physical disk cache for drives associated with the selected virtual disk.
Disabled Disables physical disk cache for drives associated with the selected virtual disk.
Default The default cache policy on the physical disk is used. See the physical disk
WARNING: Enabling physical disk cache is not recommended for disks with critical data as a
power failure may result in the loss of data prior to it being flushed to the persistent media.
NOTE: Any changes to the physical disk cache applies to all virtual disks in an entire disk group. It is
not possible to have different cache policies on virtual disks from the same disk group.
Description
documentation for details on the default setting.
Fault Tolerance
The fault tolerance features of Shared PERC 8 are as follows:
• Support for Self Monitoring and Reporting Technology (SMART)
• Support for Patrol Read
• Physical disk failure detection
• Physical disk rebuild using hot spares
• Controller Cache Preservation
• Battery and Non-Volatile Cache backup of controller cache to protect data
• Detection of batteries with low charge after boot up
17
Page 18

• Support for controller failover in systems with Fault Tolerant Shared PERC 8 card configuration.
The following sections describe some methods to achieve fault tolerance.
The SMART Feature
The SMART feature monitors certain physical aspects of all motors, heads, and physical disk electronics
to help detect predictable physical disk failures. Data on SMART-compliant physical disks can be
monitored to identify changes in values and determine whether the values are within threshold limits.
Many mechanical and electrical failures display some degradation in performance before failure.
A SMART failure is also referred to as predicted failure. There are numerous factors that are predicted
physical disk failures, such as a bearing failure, a broken read/write head, and changes in spin-up rate. In
addition, there are factors related to read/write surface failure, such as seek error rate and excessive bad
sectors.
NOTE: For detailed information on SCSI interface specifications, see t10.org and for detailed
information on SATA interface specifications, see t13.org.
Patrol Read
The Patrol Read feature is designed as a preventive measure to ensure physical disk health and data
integrity. Patrol Read scans for and resolves potential problems on configured physical disks. The Dell
Chassis Management Controller (CMC) can be used to start and control the features of Patrol Read.
The following is an overview of Patrol Read:
• Patrol Read runs on all disks on the controller that are configured as part of a virtual disk, including
hot spares.
• Patrol Read does not run on physical disks that are not part of a virtual disk or are in Ready state.
• Patrol Read adjusts the amount of controller resources dedicated to Patrol Read operations based on
outstanding disk I/O. For example, if the system is busy processing I/O operation, then Patrol Read
uses fewer resources to allow the I/O to take a higher priority.
• Patrol Read does not run on disks involved in any of the following operations:
– Rebuild
– Replace Member
– Full or Background Initialization
– Consistency Check (CC)
NOTE: By default, Patrol Read automatically runs every seven days on configured SAS hard
drives. Patrol Read is not necessary on SSD and is disabled by default.
NOTE: In the event of a controller failover in systems with Fault Tolerant Shared PERC 8 card
configuration, Patrol Read does not continue on the active controller. You must start Patrol
Read again through CMC. If you do not start Patrol Read, it automatically starts on the active
controller within seven days of the failover.
For more information on Patrol Read, see the Dell Chassis Management Controller for PowerEdge VRTX
Online Help.
18
Page 19

Physical disk failure detection
Failed physical disks are detected and rebuilds automatically start to new disks that are inserted into the
same slot. Automatic rebuilds can also occur with hot spares. If you have configured hot spares, the
controllers automatically try to use them to rebuild failed physical disks.
Physical Disk Hot Swapping
NOTE: Shared PERC 8 supports physical disk hot-swapping, however this should only be
implemented for unconfigured or failed drives.
Hot swapping is the manual replacement of a disk while the Shared PERC 8 card is online and performing
the normal functions. The following requirements must be fulfilled before performing a hot swap of a
physical disk:
• The replacement disk must be of the same protocol and disk technology. For example, only a SAS
hard drive can replace a SAS hard drive.
• The replacement disk must be of equal or greater capacity than the one it is replacing.
Auto Replacement Of A Virtual Disk Member And Revertible Hot Spares
The automatic Replace Member functionality allows a previously commissioned hot spare to be reverted
to a usable hot spare. When a disk failure occurs within a virtual disk, an assigned hot spare (dedicated or
global) is commissioned and begins rebuilding until the virtual disk is optimal. After the failed physical disk
is replaced (in the same slot) and the rebuild is complete, the Shared PERC 8 card automatically starts to
copy data from the commissioned hot spare to the newly-inserted disk. After the data is copied, the new
disk is a part of the virtual disk and the hot spare is reverted to a ready hot spare. This allows hot spares to
remain in specific enclosure slots. While the Shared PERC 8 card is reverting the hot spare, the virtual disk
remains optimal.
NOTE: The Shared PERC 8 card automatically reverts a hot spare only if the failed disk is replaced
with a new disk in the same slot.
NOTE: A Replace Member operation typically has a temporary impact on disk performance. After
the operation completes, the disk performance returns to normal.
Shared PERC 8 Card Cache Preservation
The Shared PERC 8 card is capable of preserving its cache in the event of a system power outage or
improper system shutdown. The Shared PERC 8 card is attached to a Battery Backup Unit (BBU) that
provides backup power to transfer contents of the DRAM to the Non-Volatile Cache (NVC) during system
power loss.
NOTE: The Controller Cache Preservation feature is applicable only for virtual disks in write-back
mode. Virtual disks in write-through mode do not have any data in cache.
Cache Preservation With Non-Volatile Cache
The Cache Preservation With Non-Volatile Cache (NVC) module allows controller cache data to be
stored indefinitely. If the controller has data in the cache memory during a power outage or improper
system shutdown, a small amount of power from the battery is used to transfer cache data to a nonvolatile flash storage where it remains until power is restored and the system is booted.
19
Page 20

Recovering cache data
If a system power loss or improper system shutdown has occurred:
1. Ensure all online physical disks are still connected.
2. Restore the system power.
3. Boot the system.
Virtual disks are automatically imported and preserved cache (if any) will be flushed to the physical
disks of appropriate virtual disks. If preserved cache is still present, there could be situations
preventing the flushing of preserved cache data.
NOTE: For more information on recovering the cache data, see the Dell Chassis Management
Controller for Dell PowerEdge VRTX User’s Guide at dell.com/poweredgemanuals.
NOTE: If there is preserved cache in Shared PERC 8, you can clear the preserved cache in the
CMC. If there is no preserved cache, this option is not displayed in CMC which indicates that
the preserved cache data is recovered and written to the physical disks successfully.
NOTE: If preserved cache is discarded, preserved cache data is not written to the physical disks.
Ensure that the preserved cache data is not critical before discarding.
Battery Transparent Learn Cycle
A transparent learn cycle is a periodic operation that calculates the charge that is remaining in the battery
to ensure there is sufficient energy. The operation runs automatically, and causes no impact to the
system or Shared PERC 8 card performance. The Shared PERC 8 card automatically performs the
Transparent Learn Cycle (TLC) on the battery to calibrate and gauge its charge capacity once every 90
days.
NOTE: Virtual disks stay in Write-Back mode, if enabled, during transparent learn cycle. If the TLC
completes, the Shared PERC 8 card sets the next TLC to +90 days.
TLC Time Frame
The time frame for completion of a learn cycle is a function of the battery charge capacity and the
discharge and charge currents used. For Shared PERC 8 card, the expected time frame for completion of
a learn cycle is approximately seven hours.
Conditions For Replacing The Battery
The Shared PERC 8 battery is marked Failed in the Battery Status in the CMC, when the state or health of
the battery is declared bad. If battery is declared failed, then the firmware runs learn cycles in subsequent
reboots until the battery is replaced. After the battery is replaced, the virtual disk then transitions to WriteBack mode.
The Controller Failover Feature
The dual-controller configuration of the VRTX system has two shared-PERC controllers configured in an
active-passive mode. A single active controller monitors all the storage related processes. When the
active controller stops functioning, the passive controller acts as a peer hot-spare, and takes over the
functions of the active controller in a seamless manner. Although the transition is seamless with respect
to the operating system, there may be some temporary performance impact in the course of the failover.
20
Page 21

Multipath Support
Multipathing solutions use redundant physical path components such as adapters, cables, and switches
to create logical paths between the server and the storage device. In the event that one or more of these
components fails, multipathing logic uses an alternate path for I/O so that applications can still access
their data.
In the Fault Tolerant Shared PERC 8 card configuration, the PowerEdge VRTX system has two Shared
PERC 8 cards in an active-passive mode. In this configuration, each host server can access the same
virtual disk through both cards. In the absence of a multipath driver, the operating system identifies the
single disk as two identical disks. The multipath driver aggregates the two disks into a single disk with
redundant access that is then presented to the operating system. The MPIO driver determines the path
chosen for any I/O sent to the virtual disk. Any I/O directed to the passive card is internally redirected to
the active card for completion.
Configuring Multipath Support In Windows
In Windows, multipath support is enabled by installing the MPIO driver. The Shared PERC 8 device must
be added to the list of devices that are aggregated by MPIO after the device driver is installed. Perform the
following steps to add the Shared PERC 8 card:
1. Open the MPIO control panel.
2. Click the Discover Multi-Paths tab.
3. Select DELL Shared PERC8 and click Add.
This is only a one time setup procedure. After the Shared PERC 8 device is added to the list of devices,
the MPIO driver aggregates all instances of the same virtual disk into a single one. The recommended
multipath policy for Windows is round-robin (with subset).
Configuring Multipath Support In VMWare
In VMWare, multipath support is automatically enabled using Native Multipathing (NMP) for all Shared
PERC 8 cards in Dell versions of the ESXi operating systems.
NOTE: The recommended multipath policy is Most Recently Used (MRU).
Multipath support in Linux
Currently, Linux support is not offered by Dell on fault tolerant VRTX configurations.
21
Page 22

3
Deploying The Shared PERC 8 Card
Follow the documentation in this section to remove or install a Shared PERC 8 card under different
scenarios.
Installing A New Shared PERC 8 Card
For information on how to install a Shared PERC 8 card, see Installing The Shared PERC 8 Card.
For information on the post-installation tasks, see Post-Installation Tasks For Shared 8 Card.
Replacing A Shared PERC 8 Card
When replacing an existing Shared PERC8 card in the PowerEdge VRTX system, perform the steps in this
chapter to ensure proper functionality of the shared storage after the replacement process is complete.
CAUTION: The Shared PERC 8 cards are not hot-swappable. Do not remove or install the Shared
PERC 8 cards from the system board while the PowerEdge VRTX system is powered-on.
In the Single Shared PERC 8 card configuration, the shared PERC slot is labeled as INT_STORAGE_1 on
the PowerEdge VRTX system board. In the Fault Tolerant Shared PERC 8 card configuration, the shared
PERC slots are labeled as INT_STORAGE_1 and INT_STORAGE_2 on the PowerEdge VRTX system board.
To locate the Shared PERC slots, see System Board Connectors in the Dell PowerEdge VRTX Enclosure
Owner's Manual at dell.com/poweredgemanuals.
Controller firmware package 23.8.10-0059 is the minimum firmware package version required for fault
tolerant Shared PERC 8 configurations on PowerEdge VRTX.
NOTE: Write-back caching in a fault tolerant configuration is not supported with firmware version
23.8.10-0061 and the earlier versions.
NOTE: For write-back caching capability, ensure that all the storage solution components are
updated with the latest firmware.
For more information, see the storage subsystem compatibility matrix document at dell.com/support/
home
For information on removing and reinstalling system parts, see the VRTX Enclosure Owner's Manual of
the system at dell.com/poweredgemanuals.
22
Page 23

Prerequisites For Removing The Shared PERC 8 Card
CAUTION: Many repairs may only be done by a certified service technician. You should only
perform troubleshooting and simple repairs as authorized in your product documentation, or as
directed by the online or telephone service and support team. Damage due to servicing that is
not authorized by Dell is not covered by your warranty. Read and follow the safety instructions
that came with the system.
Perform the following steps to enable recovery in the event the part replacement process fails:
1. Follow the operating system procedure to back up all data from the shared storage drives
CAUTION: The part replacement procedure is complex and can put your data at risk if
mistakes are made. It is imperative that critical data is backed up prior to starting the
procedure.
2. Document your virtual drive configuration and mapping information by performing the following
steps:
a. Open CLI terminal and run the command racadm raid get vdisks –o. Take a screen shot of the
results page and save the captured screen shot to a location of choice, or write down the
information and store it in a safe, secure location.
b. Click Chassis Overview → Storage → Virtual Disks → Assign to view the virtual disk mapping by
the CMC GUI. Take a screen shot of the results page and save the captured screen shot to a
location of choice, or write down the information and store it in a safe, secure location.
c. Click Chassis Overview → Storage → Virtual Disks to get the virtual disk configuration
information by the CMC GUI. Take a screen shot of the results page and save the captured screen
shot to a location of choice, or write down the information and store it in a safe, secure location.
3. Click Chassis Overview → Storage → Controllers to view the firmware version of the current Shared
PERC 8 card. If your system has two Shared PERC 8 cards installed, the firmware version must be the
same for both the cards.
4. Turn off the server modules using operating system commands or the CMC.
5. Turn off the enclosure, including any attached peripherals, and disconnect the enclosure from the
electrical outlet and peripherals.
6. Remove the server modules and the shared storage hard drives from the PowerEdge VRTX system.
WARNING: To prevent damage to system components, do not stack system components
together after removal. For information on electrostatic discharge (ESD) compliance, see
dell.com/regulatory_compliance.
NOTE: Label all server modules and hard drives before removal so that they can be replaced in
the same slots.
7. If applicable, rotate the system feet inward and lay the system on its side on a flat stable surface, with
the cover release latch side on top.
8. Open the system.
Removing The Shared PERC 8 Card
CAUTION: Many repairs may only be done by a certified service technician. You should only
perform troubleshooting and simple repairs as authorized in your product documentation, or as
directed by the online or telephone service and support team. Damage due to servicing that is
not authorized by Dell is not covered by your warranty. Read and follow the safety instructions
that came with the system.
CAUTION: The Shared PERC 8 cards are not hot-swappable. Do not remove or install the Shared
PERC 8 cards from the system board while the PowerEdge VRTX system is powered on.
23
Page 24

To remove the Shared PERC 8 card:
1. Push down the two release levers at the edge of the Shared PERC 8 card to disengage the card from
the storage-controller card holder.
2. Orient the card so that the other end of the card disengages from the storage-controller card holder
on the system board.
CAUTION: When removing or replacing the Shared PERC 8 card, hold the card by its edges.
Do not handle the card while holding the battery or the heatsink.
Figure 1. Removing and Installing the Shared PERC 8 Card
1. release lever (2) 2. storage-controller card holder
3. storage controller card 4. battery
5. heatsink 6. touch points (2)
7. storage-controller card connector on the
system board
24
8. guide pins (2)
Page 25

Installing The Shared PERC 8 Card
CAUTION: Many repairs may only be done by a certified service technician. You should only
perform troubleshooting and simple repairs as authorized in your product documentation, or as
directed by the online or telephone service and support team. Damage due to servicing that is
not authorized by Dell is not covered by your warranty. Read and follow the safety instructions
that came with the product.
1. Align one end of the card with the card holder on the system board.
2. Lower the other end of the card into the storage-controller card holder on the system board.
CAUTION: Applying pressure on the heat sink or battery while seating the Shared PERC 8
card may cause damage to the card. Use only the touch points to seat the card.
3. Press the touch-points on the card and push the card down until it is fully seated.
When the card is fully seated, the release levers snap over the edge of the card.
NOTE: Before closing the system, ensure the release levers have snapped over the edge of the
card.
4. Close the system.
Post-Installation Tasks For Shared PERC 8 Card
1. Turn on the PowerEdge VRTX system without hard drives and server modules inserted.
It may take up to 25 minutes for the PowerEdge VRTX storage subsystem to completely power on.
2. Log in to the CMC GUI.
3. Click Overview → Power → Control, and view the Power State to ensure that it is ON.
4. Click Chassis Overview → Storage → Controllers to view the firmware version of the replaced
Shared PERC 8 card.
The firmware version must be same for both the cards.
NOTE: If the Shared PERC 8 cards have different versions of their firmware, download and
update the firmware to the latest version from dell.com/drivers.
5. If the system has two Shared PERC 8 cards, ensure that the Fault Tolerance Status is Healthy/
Normal. This is necessary to ensure that any new firmware has been initialized and is compatible
before you reinsert the shared hard drives and modular servers.
6. Turn off the PowerEdge VRTX system.
7. Insert the shared storage hard drives that you had removed earlier. Insert the shared hard drives in
the original slots.
8. Turn on the PowerEdge VRTX system.
9. Check the Virtual Disk Layout and the Virtual Disk Assignments in the CMC GUI. If the virtual disks
are not imported, not present, or the virtual disk assignments are not present or are incorrect,
contact Dell Technical Support.
10. Turn off the PowerEdge VRTX system.
11. Insert the server modules that you had removed earlier. Insert the server modules in the original slots.
12. Turn on the PowerEdge VRTX system.
13. Turn on the server modules.
25
Page 26

Firmware installation or update
The VRTX storage subsystem comprises of Shared PERC firmware, drivers, Chassis Infrastructure firmware
and the CMC. When updating any of these components, make sure that all the component versions are
at a compatible baseline.
NOTE: For more information, see the PowerEdge VRTX Storage Subsystem Compatibility Matrix at
dell.com/support/home.
Updating firmware
Before you begin, download the windows update package for the firmware.
1. Log in to the VRTX CMC.
2. Make sure that you turn off all the server modules.
3. Navigate to Storage and click the Update tab.
4. Browse to the location where you downloaded the file and select the new file.
5. Click Upload.
6. After the file transfer, select the check box next to the release version, and click Update.
NOTE: Shared PERC8 firmware can only be updated from the VRTX Chassis Management
Controller. The firmware DUP will not respond if it is run in Windows from a server.
NOTE: The firmware upgrade may fail if the RAID controller in the system is performing an I/O
background task (that is, consistency check, background initialization, rebuild, or
reconstruction). Ensure that you allow the background task to complete before attempting to
upgrade the firmware.
NOTE: Patrol Read tasks will not affect a firmware upgrade.
26
Page 27

4
Driver Installation
The Dell Shared PowerEdge RAID Controller (PERC) 8 card requires software drivers to operate with the
supported operating systems.
This chapter contains the procedures for installing the drivers for the Shared PERC 8 card.
NOTE: To check operating system compatibility, see dell.com/ossupport.
NOTE: Shared PERC 8 does not support booting to the shared storage.
Downloading Drivers and Firmware For Shared PERC 8 From The Dell Support Website For All Operating Systems
1. Go to dell.com/drivers.
2. In the Product Selection section, enter the service tag of your system in the Service Tag or Express
Service Code field.
NOTE: If you do not have the service tag, select Automatically detect my Service Tag for me to
allow the system to automatically detect your service tag, or select Choose from a list of all
Dell products to select your product from the Product Selection page.
NOTE: To download the latest firmware and drivers for a server module (for example Dell
PowerEdge M520, M620, and M820), enter the service tag or the model number of the server
module. To download the latest firmware and driver for components inside the PowerEdge
VRTX chassis (for example Shared PERC 8 firmware and driver), enter the service tag or the
model number of the PowerEdge VRTX chassis.
3. Select the Operating System, Category, Release Date, and Importance from the respective dropdown lists.
The drivers that are applicable to your selection are displayed.
4. Download the drivers that you require to a diskette drive, USB drive, CD, or DVD.
5. During the operating system installation, use the media that you created with the Load Driver option
to load mass storage drivers. For more information on reinstalling the operating system, see the
operating system document at
dell.com/operatingsystemmanuals.
Downloading Drivers From The Dell Systems Service And Diagnostic Tools Media For Windows
To download drivers from the Dell Systems Service and Diagnostic Tools media:
1. Insert the Dell Systems Service and Diagnostics Tools media in a system.
The Welcome to Dell Service and Diagnostic Utilities screen is displayed.
2. Select your system model and operating system.
27
Page 28

For the list of supported operating systems, see Supported Operating Systems.
3. Click Continue.
4. From the list of drivers displayed, select the driver you require.
5. Select the self-extracting zip file and click Run.
6. Copy the driver to a diskette drive, CD, DVD, or USB drive.
Repeat this step for all the drivers you require.
7. During the operating system installation, use the media that you created with the Load Driver option
to load mass storage drivers.
For more information on reinstalling the operating system, see the relevant document at dell.com/
support/manuals.
Installing Or Updating Windows Drivers For Shared PERC 8
This procedure is applicable for updating existing Windows Server 2008 R2 or Windows Server 2012/2012
R2 drivers.
NOTE: PERC H310/H710/H710P/H810 controllers use the same driver as Shared PERC 8 and do not
require separate driver installations.
NOTE: For more information, see the PowerEdge VRTX Storage Subsystem Compatibility Matrix at
dell.com/support/home.
NOTE: Close all applications on your system before you update the driver.
1. Insert the media (CD, DVD, or USB drive) containing the driver.
2. Select Start → Settings → Control Panel → System.
The System Properties screen is displayed.
NOTE: The path to System Properties may vary depending on the operating system family.
3. Click on the Hardware tab.
4. Click Device Manager.
The Device Manager screen is displayed.
NOTE: The path to Device Manager may vary depending on the operating system family.
5. Expand SCSI and RAID Controllers by double-clicking the entry or by clicking on the plus symbol
next to
6. Double-click the RAID controller for which you want to update the driver.
7. Click the Driver tab and click Update Driver.
The screen to update the device driver wizard is displayed.
8. Select Install from a list or specific location.
9. Click Next.
10. Follow the steps in the wizard and browse to the location of the driver files.
11. Select the INF file from the driver media (CD, DVD, or other media).
12. Click Next and continue with the installation steps in the wizard.
13. Click Finish to exit the wizard and reboot the system for the changes to take place.
SCSI and RAID Controller.
NOTE: In Windows Server 2012 or Windows Server 2008, the Shared PERC 8 card is listed
under Storage Controllers.
28
Page 29

NOTE: Dell provides the Dell Update Package (DUP) to update drivers on systems running
Windows Server 2012/2012 R2 or Window Server 2008/2008 R2 operating systems. DUP is an
executable application that updates drivers for specific devices. DUP supports command line
interface and silent execution. For more information, see dell.com/support.
Installing Or Updating Linux Drivers For Shared PERC 8
Use the procedures in this section to update the driver for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 Update 5 and SUSE
Enterprise Linux 11 SP3. To ensure that you have the current version of the driver, download the updated
Linux driver from dell.com/support.
NOTE: PERC H310/H710/H710P/H810 controllers use the same driver as Shared PERC 8 and do not
require separate driver installations.
Installing Or Updating The Driver Package On RHEL Using KMOD Support
NOTE: This procedure is applicable for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 SP5.
Perform the following steps to install the RPM package with KMOD support:
1. Uncompress the gzipped tarball driver release package.
2. Install the driver package using the command rpm –ihv kmod-megaraid_ sas-
<version>.x86_64.rpm
NOTE: Use rpm -Uvh <package name> when upgrading an existing package.
3. Reboot the system for the updated driver to take effect.
4. Verify that the driver has been loaded using the command modinfo megaraid_sas
5. View the list of controllers installed on your system using the command lspci | grep IOV
Installing Or Updating The Driver Package On SLES Using KMP Support
NOTE: This procedure is applicable for SUSE Enterprise Linux 11 SP3.
Perform the following steps to install the RPM package with KMP support:
1. Uncompress the gzipped tarball driver release package.
2. Install the driver package using the command rpm –ihv kmod-megaraid_ sas-
<version>.x86_64.rpm
NOTE: Use rpm -Uvh <package name> when updating an existing package.
3. Reboot the system for the updated driver to take effect.
4. Verify that the driver is loaded using the command modinfo megaraid_sas
5. View the list of controllers installed on your system using the command lspci | grep IOV
Installing Or Updating VMware Drivers For Shared PERC 8
For information on how to install drivers on VMware ESXi 5.1 and 5.5, see kb.vmware.com/kb/2005205.
For information on VMware ESXi drivers, see the VMware ESXi documentation at dell.com/
virtualizationsolutions.
29
Page 30

5
Management Applications For Shared PERC 8 Card
The Dell Chassis Management Controller (CMC) enables you to:
• Configure the shared RAID system
• Create and manage multiple disk groups
• Control and monitor multiple RAID systems
• Provide online maintenance through a web interface or Command Line Interface (CLI)
NOTE: Dell OpenManage Storage Management, BIOS Configuration Utility (<Ctrl> <L>), or Unified
Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) RAID Configuration Utility does not support the Shared PERC 8
and may only be used to manage non-shared PERC cards. For non-shared PERC cards, see the
system-specific PERC User's Guide at dell.com/storagecontrollermanuals.
For more information on the CMC web interface or CLI commands available for Shared PERC 8, see the
Dell Chassis Management Controller for Dell PowerEdge VRTX User’s Guide at dell.com/esmmanuals.
NOTE: Ensure that all the software components are upgraded to the latest versions. For information
on the latest supported firmware and driver versions, see the Drivers and Downloads link on
dell.com/support/drivers for your system.
30
Page 31

6
Troubleshooting
To get help with your Dell Shared PowerEdge RAID Controller Shared (PERC) 8 card, you can contact
your Dell Technical Service representative or see dell.com/contactdell.
Performance variations between write-back and writethrough cache modes
Performance is highly variable across configurations, drive type, applications and IO workloads. The write
performance of write-through mode is typically lower than that of write-back mode. Some
configurations and workloads exhibit significant performance deltas.
Evaluate your needs for maximum I/O performance (a single Shared PERC 8 configuration) versus
maximum data protection (a Fault Tolerant Shared PERC 8 configuration).
Shared PERC 8 Card Boots Into Safe Mode
In the event of some failure conditions encountered at boot, Shared PERC 8 boots with restricted
capability in safe mode without user intervention. In such a condition Shared PERC 8 reports all
configured disk drives as Foreign to the management application. The Dell Chassis Management
Controller (CMC) displays events generated by the Shared PERC 8 card indicating the reason for booting
into safe mode. The following table details the conditions and the corresponding event notifications that
are reported to the CMC.
Table 2. Conditions and the Corresponding Event Notifications Reported to the CMC
Category Event Reported To the CMC Description of the
Pinned
Cache
SAS
Discovery
Controller cache pinned
for missing or offline
VDs: %s
Controller booted to safe
mode due to critical
errors Critical Error
during boot - On-board
expander FW or mfg image
is corrupted - reflash
image
Failure
The Shared PERC 8 card
preserves dirty cache for
a virtual disk that
transitioned to offline or
was deleted due to
missing physical disks.
This issue occurs if
expanders are not
detected.
Corrective Action
You can restore the
preserved cache to the
virtual disk once the
original drives are reinserted and the foreign
configuration is imported.
Reseat and cable the
expanders.
31
Page 32

Category Event Reported To the CMC Description of the
Failure
Corrective Action
Critical Error during
boot - NVDATA image is
invalid - reflash NVDATA
image
The NVData image is
invalid.
Contact Dell Technical
Support.
Degraded State Of Virtual Disks
A redundant virtual disk is in a degraded state when one or more physical disks have failed or are
inaccessible. For example, if a RAID 1 virtual disk consists of two physical disks and one of them fails or
becomes inaccessible, the virtual disk becomes degraded.
To recover a virtual disk from a degraded state, you must replace the failed physical disk and rebuild it.
After the rebuilding process is complete, the virtual disk state changes from degraded to optimal.
General Issues
Shared PERC 8 Card Has Yellow Exclamation Mark In Device Manager
Issue: The device is displayed in Device Manager but has a yellow exclamation mark (!).
Corrective
Action:
Reinstall the driver. For more information on reinstalling drivers, see Driver
Installation. If reinstalling the driver does not resolve the yellow exclamation mark,
perform a shutdown of all server modules and power cycle the chassis.
Shared PERC 8 Card Not Seen In Device Manager
Issue: The device does not appear in the Device Manager.
Corrective
Action:
In the Dell Chassis Management Controller (CMC) application, verify if the Shared
PERC 8 is correctly mapped to the server module. For more information on
assigning virtual adapters to server slots, see the Dell Chassis Management
Controller for Dell PowerEdge VRTX User’s Guide at dell.com/poweredgemanuals.
NOTE: Make changes to Virtual Adapter to Server Slot mapping only when
the server modules are turned off.
If the Virtual Adapter to Server Slot mapping is correct and the device still does
not appear in the Device Manager, turn off the system and reseat the Shared PERC
8 card.
Critical Errors Or Disk Warning Messages Seen In The Windows Event Log
Issue:
Error messages such as Critical Event11, PERCSAS2The driver detected
a controller error on \Device\RaidPort...
or,
32
Page 33

Warning event: Event 153, Disk
The IO operation at logical block address xxxxxx for Disk x was
retried
referring to the PercSAS2 driver is seen in the Windows Event log .
Corrective
Action:
NOTE: Event 153 or Event 11 seen in the Windows Event log do not require any corrective action.
These error messages may be triggered under some non-critical cases. See the
system status and the CMC logs to identify any persistent failures.
Shared PERC 8 Cards Fail To Function
Issue: Shared PERC 8 cards fail to function in systems with the Fault Tolerant Shared
PERC 8 card configuration.
Corrective
Action:
This issue may occur if the Shared PERC 8 card property settings between the two
Shared PERC 8 cards is not compatible. Make sure that the firmware packages are
identical for both the Shared PERC 8 cards.
Physical disk issues
Incorrect Number of Virtual Disks Displayed In Windows Disk Manager
Issue: The number of disks displayed in Windows Disk Manager is more than the actual
number of virtual disks assigned to the server.
Corrective
Action:
This issue occurs if the MPIO feature is not installed in systems with the Fault
Tolerant Shared PERC 8 card configuration. Install MPIO services from the list of
features that can be installed on the server. For instructions on how to install MPIO,
see Installing and Configuring MPIO at technet.microsoft.com.
Physical Disk In Failed State
Issue: One of the physical disks in the disk array is in the failed state.
Corrective
Action:
Update the Shared PERC 8 cards to the latest firmware available on dell.com/
support. Replace the physical disk with a working one which is compatible with the
old physical disk and is of equal or greater capacity.
Unable to rebuild a fault tolerant virtual disk
Issue: Cannot rebuild a fault tolerant virtual disk. For more information, see the alert log
for virtual disks.
Corrective
Action:
The replacement disk is too small or not compatible with the virtual disk. Replace
the failed disk with a compatible good physical disk with equal or greater capacity.
33
Page 34

Fatal Error Or Data Corruption Reported
Issue: Fatal error(s) or data corruption(s) is reported when accessing virtual disks.
Corrective
Action:
Contact Dell Technical Support.
Physical Disk Displayed As Blocked By Management Application
Issue: One or more physical disks are displayed as Blocked and cannot be configured.
Corrective
Action:
NOTE: If you are using the Dell Update Package (DUP) to update the physical disk, shutdown all the
server modules and power cycle the chassis after the update is completed.
Ensure the physical disk is supported by SCSI-3 Persistent Reservation (PR). Update
the physical disk and Shared PERC 8 to the latest firmware available on dell.com/
support.
Multiple Disks Become Inaccessible
Issue: Multiple disks become simultaneously inaccessible.
Corrective
Action:
Multiple physical disk errors in a single array indicate a failure in cabling or
connection and can involve loss of data. Perform the following steps to recover the
virtual disk:
CAUTION: Follow the safety precautions to prevent electrostatic discharge.
1. Turn off the system, check the cable connections, and reseat the physical
disks.
2. Ensure that all the disks are present in the enclosure.
3. Turn on the system and enter the Chassis Management Controller (CMC).
4. Use the CMC to import the foreign configuration that is detected or clear the
foreign configuration.
NOTE: For information about importing or clearing foreign configuration, see
the Dell Chassis Management Controller for Dell PowerEdge VRTX User’s
Guide at dell.com/poweredgemanuals.
If the virtual disk is redundant and transitioned to Degraded state before going
Offline, a rebuild operation starts automatically after the configuration is imported.
If the virtual disk has gone directly to the Offline state due to a cable pull or power
loss situation, the virtual disk is imported in its Optimal state without a rebuild
occurring.
Rebuilding A Failed Physical Disk
Issue: Rebuilding a physical disk after one of them is in a failed state.
Corrective
Action:
34
If you have configured hot spares, the Shared PERC 8 card automatically tries to
rebuild a physical disk that is in a failed state. The automatic rebuild is not available
if there is no hot spare with enough capacity to rebuild the failed physical disk. You
Page 35

must make sure a physical disk with enough storage in the subsystem is set as a
hot spare for rebuilding the physical disk.
Virtual Disk Fails During Rebuild Using A Global Hot Spare
Issue: A virtual disk fails during rebuild while using a global hot spare. The global hot
spare reverts to Hotspare state and the virtual disk is in Failed state.
Corrective
Action:
Check whether the original virtual disk has failed or has been removed.
Virtual Disk Fails During Rebuild Using A Dedicated Hot Spare
Issue: A virtual disk fails during rebuild while using a dedicated hot spare. The dedicated
hot spare goes to Ready state and the virtual disk goes to Failed state.
Description: Check whether the original virtual disk has failed or has been removed.
Physical disk takes a long time to rebuild
Issue: A physical disk is taking longer than expected to rebuild.
Description: A physical disk takes longer to rebuild when under high stress. For example, there is
one rebuild I/O operation for every five host I/O operations. You cannot add a
second virtual disk to a disk group while the virtual disk in that disk group is
undergoing a rebuild. The firmware does not allow you to create a virtual disk using
the free space available in a disk group if a physical disk in a virtual disk group is
undergoing a rebuild operation.
Controller cache issues
For certain conditions virtual drives will be either not configured to write-back caching or if configured, it
will transition to write-through caching. The status of write-back caching can be viewed through CMC
storage logs.
The following table details the conditions and the corrective actions.
Table 3. Conditions and the corrective actions
Conditions Actions
During the VRTX power on with no failing
conditions, the virtual drive temporarily transitions
to write-through as part of the Shared PERC 8
firmware initialization. After the system power on,
the virtual drive transitions back to write-back.
During VRTX power on or reset, unresolved pinned
cache is present.
There is no intervention required.
Perform the following:
• Insert the drives that caused the virtual drive to
go offline, that resulted in the cache being
pinned to recover the virtual drive.
OR
• Clear the pinned cache through CMC.
35
Page 36
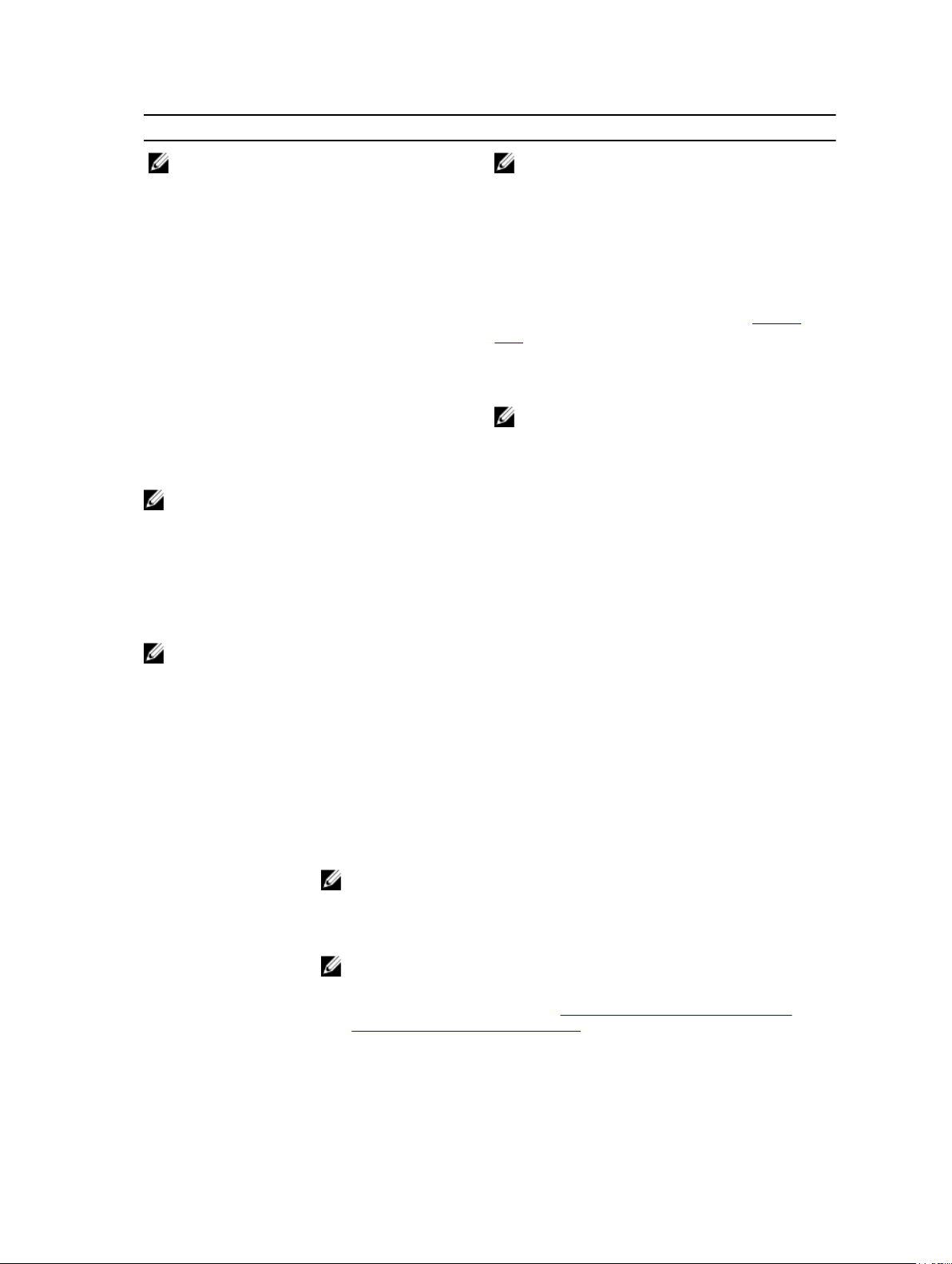
Conditions Actions
NOTE: Unresolved pinned cache can occur if
a virtual drive goes offline for any reason while
there is uncommitted cache data in memory.
During a Shared PERC firmware flash, virtual drive
transitions to write-through until chassis is
recycled.
Virtual drives permanently transition to writethrough when Hardware failure occurs.
In the event of a firmware mismatch, in the dual
fault tolerant Shared PERC 8 configurations, if one
controller has write-through capability and the
other does not, virtual drives on the controller with
write-through capability reverts to write-through.
NOTE: Virtual drives configured with forced write-back caching will not transition to write-through
in the above conditions.
NOTE: Clearing pinned cache means that the
pinned data is lost.
Allow the chassis reset to complete after the
firmware flash.
If hardware failure occurs, contact Dell technical
support. For more information, see the Getting
help.
Update the firmware such that both cards are
running the latest supported versions available.
NOTE: Ensure that you download the updated
firmware and driver version available at
dell.com/support/home.
SMART Errors
Self Monitoring and Reporting Technology (SMART) monitors the internal performance of all motors,
heads, and physical disk electronics and detects predictable physical disk failures.
NOTE: For information about where to find reports of SMART errors that can indicate hardware
failure, see the Dell Chassis Management Controller for Dell PowerEdge VRTX User’s Guide at
dell.com/esmmanuals.
SMART Error Detected On A Physical Disk In A Redundant Virtual Disk
Issue: A SMART error is detected on a physical disk in a redundant virtual disk.
Corrective
Action:
Perform the following steps:
1. Back up your data.
2. Physically remove the physical disk that detected the SMART error.
NOTE: If a hot spare is present, the rebuild starts with the hot spare after
the disk is removed.
3. Replace the disk with a new physical disk of equal or higher capacity.
4. Perform the Auto Replacement of a Virtual Disk operation.
NOTE: The Auto Replacement of Virtual Disk operation allows you to
copy data from a source physical disk of a virtual disk to a target physical
disk that is not a part of the virtual disk. For more information about the
Auto Replacement feature, see Auto Replacement Of A Virtual Disk
Member And Revertible Hot Spares.
36
Page 37

SMART Error Detected On A Physical Disk In A Non-Redundant Virtual Disk
Issue: A SMART error is detected on a physical disk in a non-redundant virtual disk.
Corrective
Action:
Perform the following steps:
1. Back up your data.
2. Physically remove the physical disk that detected the SMART error.
NOTE: The virtual disk will be in a Failed state after the physical disk is
removed. Ensure you back up your data before performing this operation.
3. Replace the affected physical disk with a new physical disk of equal or higher
capacity.
4. Delete the failed virtual disk and recreate the virtual disk with the same
members.
NOTE: For information on creating and deleting virtual disks, see the Dell
Chassis Management Controller for Dell PowerEdge VRTX User’s Guide at
dell.com/esmmanuals.
5. Restore from the backup.
Auto Replacement Member Errors
NOTE: For more information about the Auto Replacement Member feature, see Auto Replacement
Of A Virtual Disk Member And Revertible Hot Spares.
Source Disk Fails
Issue: The source disk fails during the Auto Replacement Member operation.
Description: If the source data is available from other disks in the virtual disk, the rebuild begins
automatically on the target disk, using the data from the other disks.
Target Disk Fails
Issue: The target disk fails.
Description: If the target disk fails, the Auto Replacement Member operation is terminated.
General Disk Fails
Issue: A general disk fails.
Description: If the target disk fails and the Auto Replacement Member operation terminates but
the source data is still available, then the Auto Replacement Member operation
continues as Auto Replacement Member.
37
Page 38

Hard-Drive Indicator Patterns
Figure 2. Hard-Drive Indicators
1. hard-drive activity indicator (green) 2. hard-drive status indicator (green and amber)
Drive-Status Indicator Pattern Condition
Blinks green two times per second Identifying drive or preparing for removal
Off Drive ready for insertion or removal
NOTE: The drive status indicator remains off
until all hard drives are initialized after the
system is turned on. Drives are not ready for
insertion or removal during this time.
Blinks green, amber, and off Predicted drive failure
Blinks amber four times per second Drive failed
Blinks green slowly Drive rebuilding
Steady green Drive online
Blinks green three seconds, amber three seconds,
and off six seconds
Rebuild aborted
38
Page 39

7
Getting help
Contacting Dell
Dell provides several online and telephone-based support and service options. If you do not have an
active Internet connection, you can find contact information on your purchase invoice, packing slip, bill,
or Dell product catalog. Availability varies by country and product, and some services may not be
available in your area. To contact Dell for sales, technical support, or customer-service issues:
1. Go to dell.com/support.
2. Select your country from the drop-down menu on the bottom right corner of the page.
3. For customized support:
a. Enter your system Service Tag in the Enter your Service Tag field.
b. Click Submit.
The support page that lists the various support categories is displayed.
4. For general support:
a. Select your product category.
b. Select your product segment.
c. Select your product.
The support page that lists the various support categories is displayed.
Locating your system Service Tag
Your system is identified by a unique Express Service Code and Service Tag number. The Express Service
Code and Service Tag are found on the front of the system by pulling out the information tag.
Alternatively, the information may be on a sticker on the chassis of the system. This information is used
by Dell to route support calls to the appropriate personnel.
Documentation feedback
If you have feedback for this document, write to documentation_feedback@dell.com. Alternatively, you
can click on the Feedback link in any of the Dell documentation pages, fill out the form, and click Submit
to send your feedback.
39
 Loading...
Loading...