Dell UCPE-900, UCPB-900, UCSE-900, UCSB-900, UCSA-901 User Manual
...
Dell PowerEdge RAID Controller (PERC) 9
User’s Guide
Regulatory Model: UCPA-901, UCPB-900, UCSA-901,
UCSB-900, UCSE-900, and UCPE-900

Notes, cautions, and warnings
NOTE: A NOTE indicates important information that helps you make better use of your computer.
CAUTION: A CAUTION indicates either potential damage to hardware or loss of data and tells you
how to avoid the problem.
WARNING: A WARNING indicates a potential for property damage, personal injury, or death.
Copyright © 2015 Dell Inc. All rights reserved. This product is protected by U.S. and international copyright and
intellectual property laws. Dell™ and the Dell logo are trademarks of Dell Inc. in the United States and/or other
jurisdictions. All other marks and names mentioned herein may be trademarks of their respective companies.
2015 - 04
Rev. A03

Contents
1 Overview.................................................................................................................9
Supported operating systems............................................................................................................. 14
PERC card specifications.....................................................................................................................15
Management applications for PERC cards......................................................................................... 17
Comprehensive embedded management ...................................................................................17
Dell OpenManage Storage Management..................................................................................... 17
Related documentation...................................................................................................................... 18
2 Getting started with your PERC card..............................................................19
Installing the operating system and the PERC card on a base system............................................. 19
Installing the PERC card on a system with the operating system pre-installed...............................20
Installing the operating system on a system with the PERC card pre-installed............................... 21
Setting up the system with the PERC card and the operating system pre-installed .......................22
Configuring settings of a replaced PERC card on a system with operating system pre-
installed................................................................................................................................................23
3 Features................................................................................................................ 25
PERC 9 personality management.......................................................................................................25
T10 protection information................................................................................................................ 25
Enabling T10 PI..............................................................................................................................25
Disabling T10 PI.............................................................................................................................26
Secure firmware update......................................................................................................................26
Improved RAID 10 configuration........................................................................................................26
4KB block size disk drives................................................................................................................... 26
Physical disk power management......................................................................................................26
Configured spin down delay.........................................................................................................27
Types of virtual disk initialization........................................................................................................ 27
Full initialization............................................................................................................................. 27
Fast initialization............................................................................................................................28
Background initialization.................................................................................................................... 28
Consistency checks............................................................................................................................ 28
Disk roaming....................................................................................................................................... 29
Using disk roaming........................................................................................................................29
FastPath............................................................................................................................................... 29
Configuring FastPath-capable virtual disks..................................................................................29
Virtual disk migration.......................................................................................................................... 30
Migrating virtual disks....................................................................................................................30
Virtual disk write cache policies..........................................................................................................31
3

Conditions under which write-back is employed........................................................................31
Conditions under which forced write-back with no battery is employed..................................31
Virtual disk read cache policies...........................................................................................................31
Reconfiguration of virtual disks.......................................................................................................... 32
Fault tolerance.................................................................................................................................... 34
The SMART Feature.......................................................................................................................34
Patrol Read.....................................................................................................................................35
Physical disk failure detection.......................................................................................................35
Using persistent hot spare slots....................................................................................................35
Physical disk hot swapping........................................................................................................... 36
Using replace member and revertible hot spares........................................................................36
Controller cache preservation......................................................................................................36
Battery Transparent Learn Cycle...................................................................................................37
Non-RAID disks support................................................................................................................37
4 Deploying the PERC card..................................................................................39
Removing the PERC 9 adapter........................................................................................................... 39
Installing the PERC 9 adapter..............................................................................................................41
Removing the PERC 9 mini monolithic controller.............................................................................41
Replacing the battery of a H730P mini monolithic card............................................................. 42
Installing the PERC 9 mini monolithic controller.............................................................................. 44
Removing a H730P slim card............................................................................................................. 45
Replacing the battery of a H730P slim card.................................................................................46
Installing a H730P slim card............................................................................................................... 48
Removing the PERC 9 mini blade controller.....................................................................................48
Replacing the tethered battery of a PERC 9 mini blade card......................................................49
Installing the PERC 9 mini blade controller....................................................................................... 53
Removing the PERC FD33xD Card.....................................................................................................54
Replacing the battery of a PERC FD33xD card............................................................................ 55
Installing the PERC FD33xD card....................................................................................................... 56
5 Driver installation............................................................................................... 58
Creating the device driver media....................................................................................................... 58
Downloading drivers from the Dell support website...................................................................58
Downloading drivers from the Dell systems service and diagnostic tools media .....................59
Windows driver installation.................................................................................................................59
Installing the driver during a Windows Server 2008 R2 and newer installation......................... 59
Installing the driver after Windows Server 2008 R2 and newer installation .............................. 59
Updating PERC 9 driver for existing Windows Server 2008 R2 and newer................................60
Linux driver installation.......................................................................................................................60
Installing or updating the RPM driver package with KMOD support...........................................61
Installing or updating the RPM driver package with KMP support.............................................. 61
4

6 BIOS Configuration Utility................................................................................62
Entering the BIOS Configuration Utility............................................................................................. 62
Exiting the Configuration Utility......................................................................................................... 62
Menu navigation controls...................................................................................................................63
Setting up virtual disks........................................................................................................................ 64
BIOS Configuration Utility menu options.......................................................................................... 66
Virtual disk management.............................................................................................................. 66
Virtual disk actions........................................................................................................................ 68
Physical disk management (PD Mgmt).........................................................................................69
Physical disk actions......................................................................................................................69
Rebuild...........................................................................................................................................70
Controller management (Ctrl Mgmt)........................................................................................... 70
Controller management actions...................................................................................................71
Foreign configuration view........................................................................................................... 72
Virtual Disk Management.................................................................................................................... 72
Creating virtual disks..................................................................................................................... 72
Selecting virtual disk parameters.................................................................................................. 73
Initializing virtual disks...................................................................................................................73
Checking data consistency...........................................................................................................74
Running a data consistency check...............................................................................................74
Importing or clearing foreign configurations using the VD mgmt menu...................................74
Importing or clearing foreign configurations using the foreign configuration view screen......75
Break mirror...................................................................................................................................76
Managing preserved cache........................................................................................................... 77
Managing dedicated hot spares....................................................................................................78
Deleting virtual disks......................................................................................................................78
Deleting disk groups......................................................................................................................79
Clearing the configuration............................................................................................................79
Physical Disk Management................................................................................................................. 79
Setting LED blinking...................................................................................................................... 79
Creating global hot spares............................................................................................................80
Removing global or dedicated hot spares...................................................................................80
Replacing an online physical disk.................................................................................................80
Restrictions and limitations........................................................................................................... 81
Stopping background initialization............................................................................................... 81
Performing a manual rebuild of an individual physical disk.........................................................81
Controller Management..................................................................................................................... 82
Enabling boot support.................................................................................................................. 82
Enabling boot support for a BIOS-enabled controller................................................................ 82
Enabling BIOS stop on error......................................................................................................... 83
Disabling BIOS stop on error........................................................................................................ 83
5

Enabling auto import.....................................................................................................................83
Disabling auto import....................................................................................................................83
Restoring factory default settings.................................................................................................84
7 UEFI/HII RAID configuration utility.................................................................85
Entering the UEFI configuration utility............................................................................................... 85
Exiting the UEFI configuration utility..................................................................................................85
Navigating to Dell PERC 9 configuration utility.................................................................................85
Configuration management...............................................................................................................86
Creating virtual disks.....................................................................................................................86
Creating profile based virtual disks...............................................................................................87
Converting physical disks to RAID capable disk...........................................................................87
Converting physical disks to non-RAID disk................................................................................ 87
Viewing disk group properties...................................................................................................... 87
Viewing disk group properties...................................................................................................... 87
Managing foreign configurations on a RAID controller.............................................................. 88
Deleting existing configurations on a RAID controller................................................................88
Controller management.....................................................................................................................88
Restoring factory settings for the controller................................................................................88
Saving controller events............................................................................................................... 88
Enabling security for the controller..............................................................................................89
Saving debug log...........................................................................................................................89
Switching the controller to HBA mode........................................................................................89
Switching the controller to RAID mode.......................................................................................90
Virtual disk management....................................................................................................................90
Viewing virtual disk properties......................................................................................................90
Viewing physical disks associated with a virtual disk...................................................................90
Physical disk management..................................................................................................................91
Viewing physical disk properties................................................................................................... 91
Hardware components management................................................................................................ 91
Viewing battery properties............................................................................................................ 91
Viewing physical disks associated with an enclosure..................................................................92
8 Security key and RAID management.............................................................. 93
Security key implementation..............................................................................................................93
Security key management in the BIOS configuration utility............................................................. 93
Local Key Management (LKM)...................................................................................................... 94
Creating a security key..................................................................................................................94
Changing the security key............................................................................................................ 94
Deleting a security key..................................................................................................................95
Creating secured virtual disks.......................................................................................................95
Securing pre-existing virtual disks................................................................................................95
6

Importing or clearing secured foreign configurations and secure disk migration.................... 96
Instant secure erase...................................................................................................................... 97
9 Troubleshooting.................................................................................................98
BIOS configuration utility error messages......................................................................................... 98
Discovery error message.............................................................................................................. 98
Extra enclosure error message.....................................................................................................98
Missing disks in virtual disk error message...................................................................................98
Previous configuration of disks removed error message............................................................99
Missing virtual disks error message.............................................................................................. 99
Dirty cache data error message....................................................................................................99
BIOS disabled error message......................................................................................................100
Drive Configuration Changes Error Message............................................................................ 100
Adapter at baseport not responding error message................................................................. 100
Offline or missing virtual drives with preserved cache error message......................................101
Virtual disks offline error message..............................................................................................101
Virtual disks degraded error message.........................................................................................101
Virtual disks partially degraded error message...........................................................................101
Memory or battery problem error message...............................................................................102
Firmware fault state error message............................................................................................102
Foreign configuration found error message..............................................................................102
Foreign configuration not found in <ctrl> <R> error message................................................. 102
Previous configuration cleared or missing error message........................................................103
Invalid SAS topology detected error message........................................................................... 103
Configured disks removed or not accessible error message....................................................103
Degraded state of virtual disks..........................................................................................................103
Memory errors...................................................................................................................................104
Preserved Cache State......................................................................................................................104
Security key errors............................................................................................................................ 104
Secured foreign import errors....................................................................................................104
Failure to select or configure non Self-Encrypting Disks (non-SED)........................................104
Failure to delete security key...................................................................................................... 105
Failure to instant secure erase task on physical disks................................................................105
General Issues................................................................................................................................... 105
PERC card has yellow bang in device manager.........................................................................105
PERC card not seen in device manager..................................................................................... 105
Physical disk issues............................................................................................................................105
Physical disk in failed state..........................................................................................................105
Unable to rebuild a fault tolerant virtual disk.............................................................................106
Fatal error or data corruption reported......................................................................................106
Physical disk displayed as blocked............................................................................................. 106
Multiple disks become inaccessible........................................................................................... 106
7

Rebuilding a failed physical disk................................................................................................. 107
Virtual disk fails during rebuild using a global hot spare............................................................107
Virtual disk fails during rebuild using a dedicated hot spare..................................................... 107
Physical disk fails during reconstruction on redundant virtual disk.......................................... 107
Virtual disk fails rebuild using a dedicated hot spare.................................................................107
Physical disk takes a long time to rebuild...................................................................................107
SMART errors.....................................................................................................................................108
Smart error detected on a physical disk in a redundant virtual disk......................................... 108
Smart error detected on a physical disk in a non-redundant virtual disk.................................108
Replace member errors....................................................................................................................108
Source disk fails during replace member operation..................................................................109
Target disk fails............................................................................................................................109
General disk fails......................................................................................................................... 109
Linux operating system errors..........................................................................................................109
Virtual disk policy is assumed as write-through error message................................................109
Unable to register SCSI device error message........................................................................... 110
Disk Carrier LED Indicators............................................................................................................... 110
UEFI error messages..........................................................................................................................110
Unhealthy Status of the Drivers...................................................................................................110
10 Appendix: RAID description..........................................................................112
Summary of RAID levels.................................................................................................................... 112
RAID terminology.............................................................................................................................. 112
Disk striping..................................................................................................................................112
Disk mirroring...............................................................................................................................113
Spanned RAID levels.................................................................................................................... 113
Parity data.....................................................................................................................................114
11 Getting help......................................................................................................115
Contacting Dell..................................................................................................................................115
Documentation feedback..................................................................................................................115
Locating your system Service Tag.................................................................................................... 115
8
1
Overview
The Dell PowerEdge Expandable RAID Controller (PERC) 9 Series of cards consist of the H330, H730,
H730P, and H830 cards.
• PERC H330: The PERC H330 is a general purpose RAID solution card. The card is available in Adapter
(low profile and full height), Mini Monolithic, and Mini Blade form factors for internal storage and tape
devices.
Figure 1. Features of PERC H330 adapter card
1. PERC H330 adapter 2. heat sink
3. SAS cable connectors
9
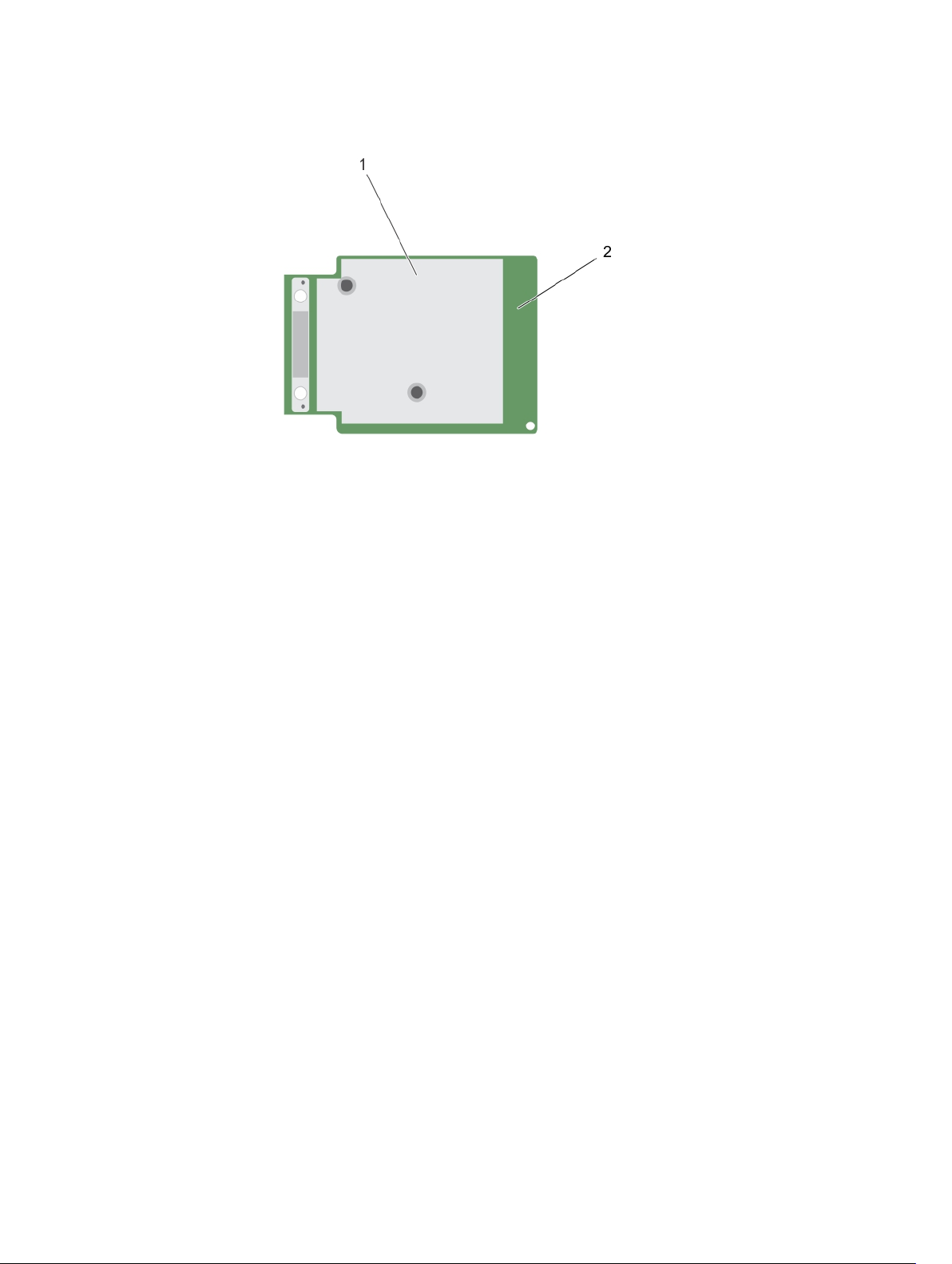
Figure 2. Features of PERC H330 mini monolithic card
1. heat sink 2. PERC H330 mini monolithic card
• PERC H730: The PERC H730 is a RAID solution card consisting of a minimum of 1 GB Non-Volatile
Cache and is available in the Adapter (low profile and full height), Mini Monolithic, and Mini Blade form
factors for internal storage.
10

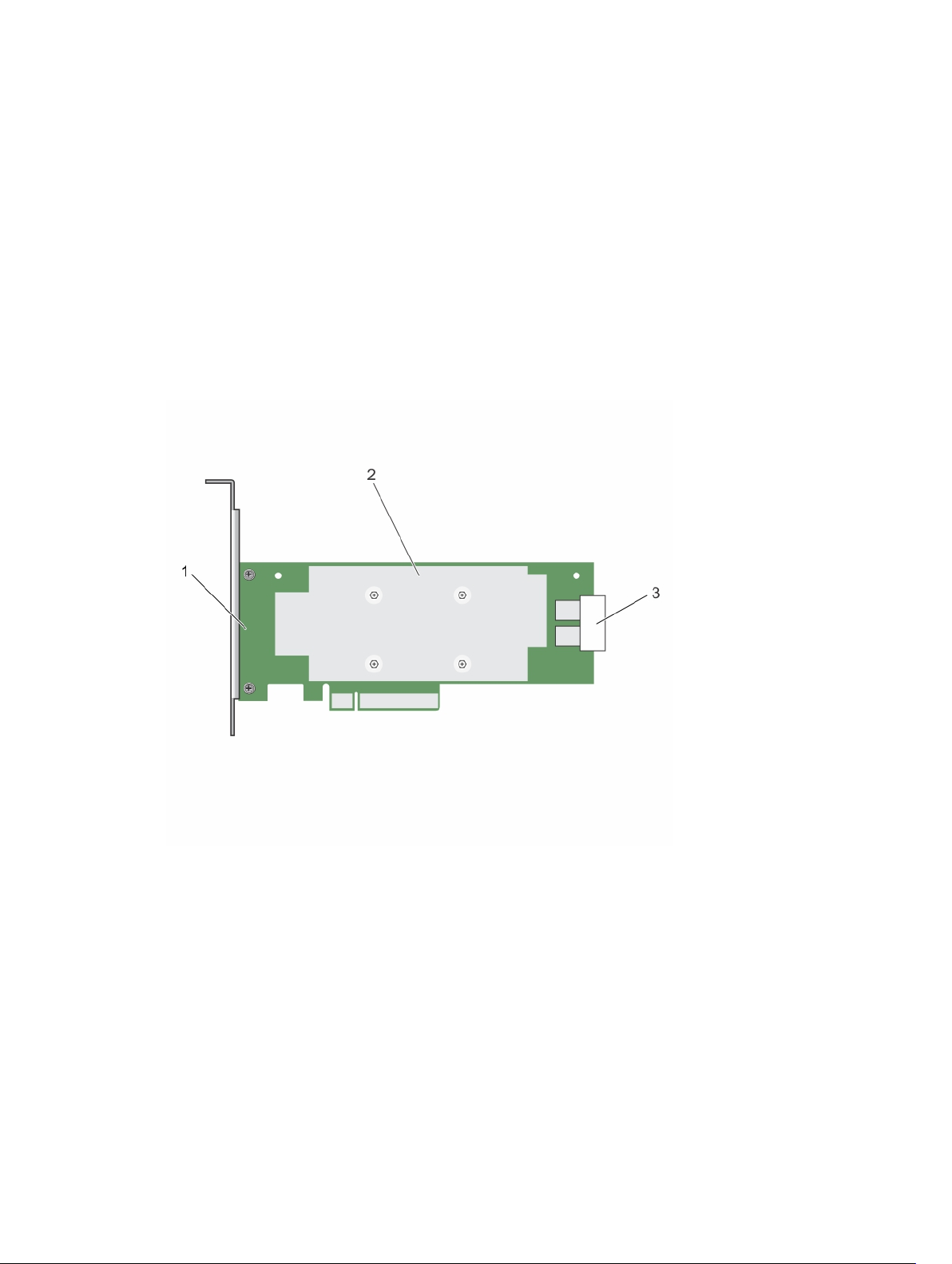
Figure 3. Features of PERC H730 card
1. PERC H730 card 2. heat sink
3. battery cable
4. battery carrier
5. SAS cable connectors
11
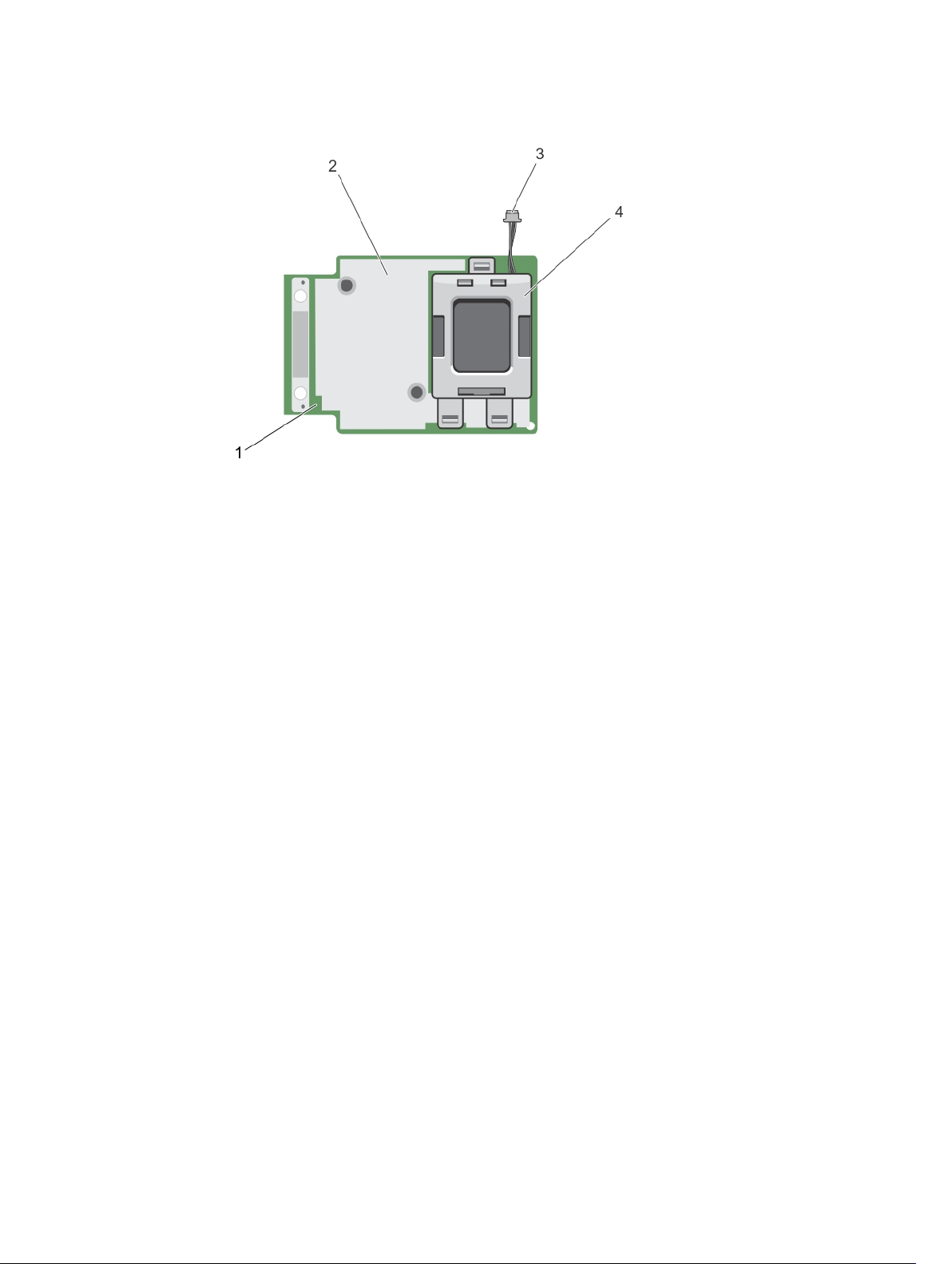
Figure 4. Features of PERC H730/H730P mini monolithic card
1. PERC H730/H730P card 2. heat sink
3. battery cable
4. battery carrier
• PERC H730P: The PERC H730P is the performance RAID solution card consisting of 2 GB Non-
Volatile Cache and is available in the Adapter (low profile and full height), Slim, and Mini Monolithic
form factors for internal storage.
12
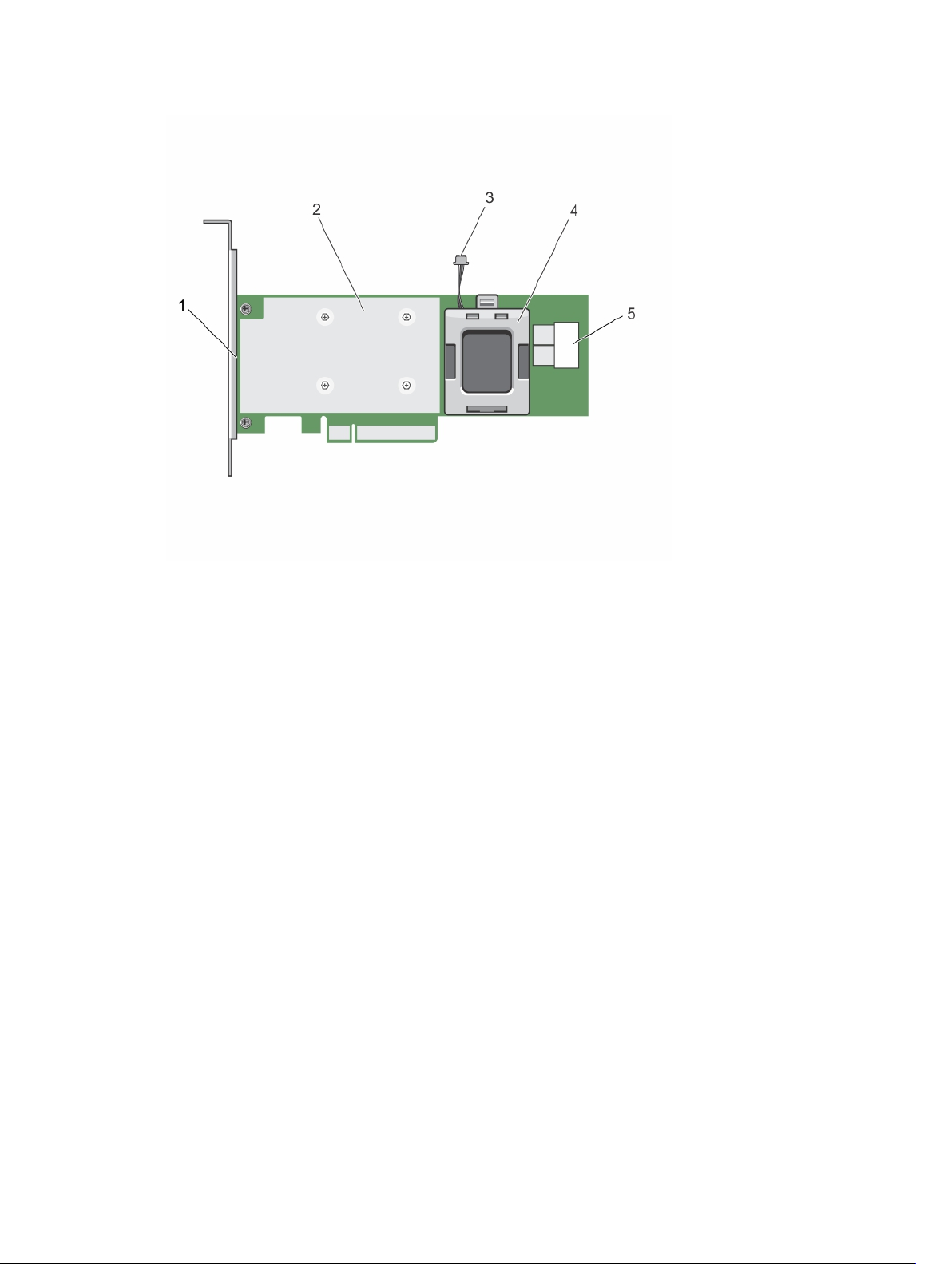
Figure 5. Features of PERC H730P adapter card
1. PERC H730P card 2. heat sink
3. battery cable
4. battery carrier
5. SAS cable connectors
• PERC H830: The PERC H830 is similar to the H730P solution, except that it supports external storage.
The PERC H830 is only available in the Adapter (low profile and full height) form factor.
13
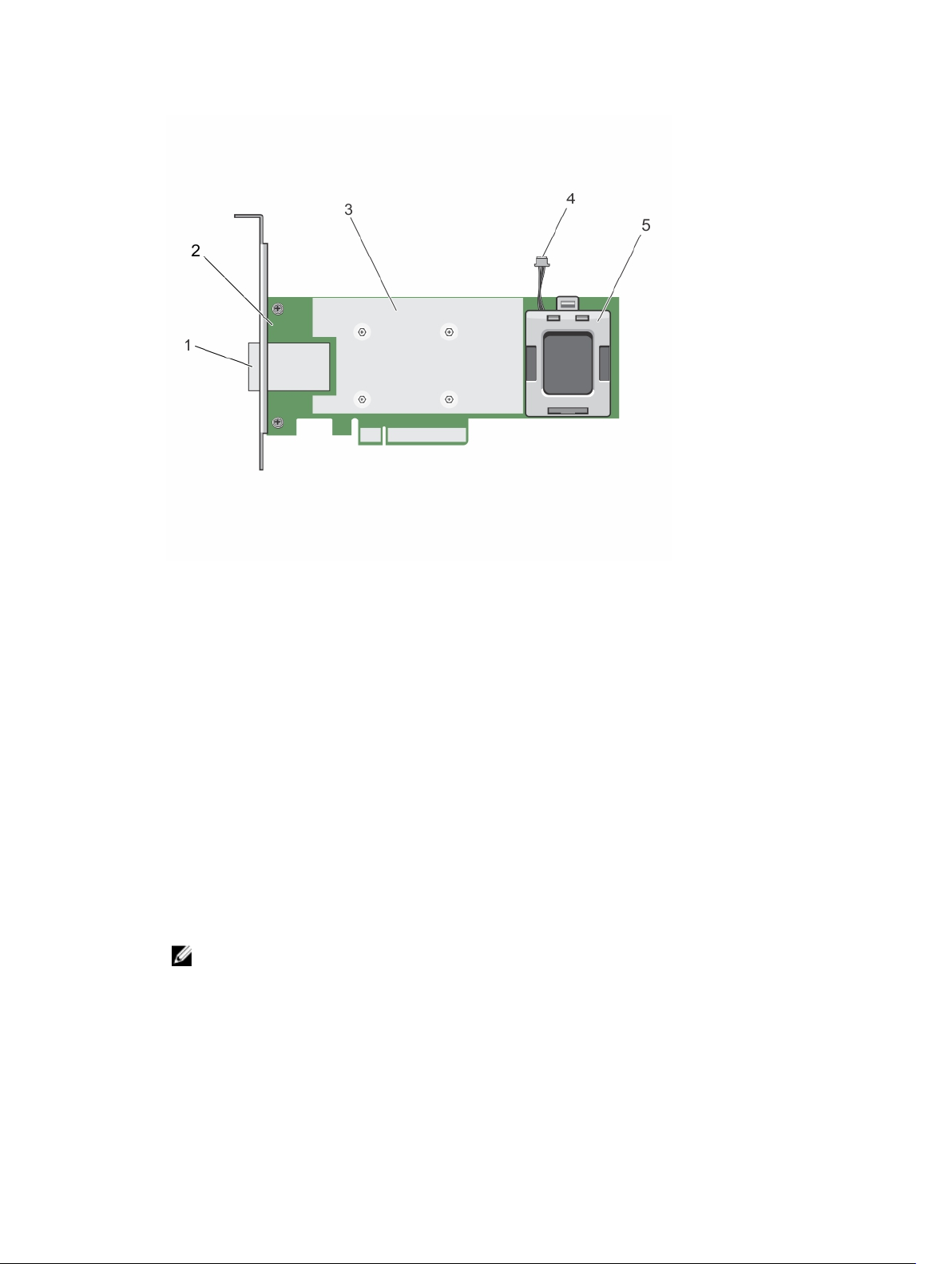
Figure 6. Features of PERC H830 adapter card
1. external SAS cable connectors 2. PERC H830 adapter
3. heat sink
5. battery carrier
4. battery cable
Supported operating systems
The PERC 9 series cards support the following operating systems:
• Microsoft Windows Server 2012
• Microsoft Windows Server 2012 R2
• Microsoft Windows Server 2008 R2
• Microsoft Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1
• VMware ESXi 5.1 Update 2
NOTE: The PERC 9 driver for VMware ESXi is bundled with the VMware ISO image available from
Dell. For more information, see dell.com/virtualizationsolutions.
• VMware ESXi 5.5 Update 2
• Red Hat Enterprise Linux version 6.5 (64-bit)
• Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6.5 for HPC Compute Node
• Red Hat Enterprise Virtualization 4.0 (64-bit)
14
• SUSE Linux Enterprise Server version 11 SP3 (64-bit)
• Red Hat Enterprise Linux version 7
NOTE: For the latest list of supported operating systems and driver installation instructions, see the
system documentation at dell.com/support/manuals. For specific operating system service pack
requirements, see the Drivers and Downloads section at dell.com/support/manuals.
PERC card specifications
The table below lists and describes the different PERC cards that comprise the PERC 9 series and their
specifications:
Feature PERC H330 PERC H730 PERC H730P PERC H830 PERC
RAID Levels 0, 1, 5, 10, 50 0, 1, 5, 6, 10, 50, 600, 1, 5, 6, 10,
50, 60
Enclosures per
port
Processor Dell Adapter
Battery Backup
Unit
Non-Volatile
cache
Cache policy No 1 GB DDR3
Not applicable Not applicable Not applicable 8 (4 per port) Not applicable
Dell Adapter
SAS RAID-onChip, 8-port
with LSI 3008
chipset
No Yes Yes Yes Yes
None Yes Yes Yes Yes
SAS RAID-on-
Chip, 8-port
with LSI 3108
chipset
1333 Mhz
cache
Dell Adapter
SAS RAID-onChip, 8-port
with LSI 3108
chipset
2 GB DDR3
1866 Mhz
cache
0, 1, 5, 6, 10,
50, 60
Dell Adapter
SAS RAID-onChip, 8- port
with LSI 3108
chipset
2 GB DDR3
1866 Mhz
cache
FD33xD/
FD33xS
0, 1, 5, 6, 10,
50, 60
Dell Adapter
SAS RAID-onChip, 8-port
with LSI 3108
chipset
2 GB DDR3
1866 Mhz
cache
15
Feature PERC H330 PERC H730 PERC H730P PERC H830 PERC
NOTE:
H330
does not
support
caching,
which
affects
performan
ce in RAID
5 and
RAID 50
arrays. For
performan
ce
sensitive
solutions,
caching is
recomme
nded.
FD33xD/
FD33xS
Cache function
Maximum number
of virtual disks
Maximum number
of virtual disks per
disk group
Hot swap devices
supported
Hardware XOR
Engine
Online capacity
expansion
Dedicated and
global hot spare
Drives Types 3 Gbps SATA, 6
Write Through
and No Read
Ahead
16 64 64 64 64
16 16 16 16 16
Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
No Yes Yes Yes Yes
Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
Gbps SATA/
SAS, and 12
Gbps SAS
Write Back,
Write Through,
No Read Ahead,
and Read
Ahead
3 Gbps SATA, 6
Gbps SATA/SAS,
and 12 Gbps
SAS
Write Back,
Write Through,
No Read
Ahead, and
Read Ahead
3 Gbps SATA, 6
Gbps SATA/
SAS, and 12
Gbps SAS
Write Back,
Write
Through, No
Read Ahead,
and Read
Ahead
6 Gbps SAS,
and 12 Gbps
SAS
Write Back,
Write
Through, No
Read Ahead,
and Read
Ahead
3 Gbps SATA,
6 Gbps SATA/
SAS, and 12
Gbps SAS
16
Feature PERC H330 PERC H730 PERC H730P PERC H830 PERC
PCIe Support Gen 3 Gen 3 Gen 3 Gen 3 Gen 3
FD33xD/
FD33xS
Non-RAID or pass
through mode
Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
Management applications for PERC cards
Dell OpenManage Storage Management applications enable you to manage and configure the RAID
system, create and manage multiple disk groups, control and monitor multiple RAID systems, and provide
online maintenance. The management applications for PERC H730P include:
• Comprehensive Embedded Management
• Dell OpenManage Storage Management
• BIOS Configuration Utility (<Ctrl> <R>)
• Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) RAID Configuration Utility
NOTE: Dell serial-attached SCSI (SAS) RAID Storage Manager is not supported for Self-Encrypting
Disks (SED) management.
Comprehensive embedded management
Comprehensive Embedded Management (CEM) is a storage management solution for Dell systems that
enables you to effectively monitor the RAID and network controllers installed on the system using iDRAC
without an OS installed on the system.
Using CEM enables you to perform the following:
• Monitor devices without an OS installed on the system.
• Provide a specific location to access monitored data of the storage devices and network cards.
• Allows controller configuration for all the PERC 9 cards (H330, H730, H730P, and H830).
NOTE:
The Comprehensive Embedded Management (CEM) feature is not supported on the Dell PowerEdge
R920 servers.
Dell OpenManage Storage Management
The Dell OpenManage Storage Management is a storage management application for Dell systems that
provides enhanced features for configuring a system's locally-attached RAID and Non-RAID disk storage.
The Dell OpenManage storage management application enables you to perform controller and enclosure
functions for all supported RAID controllers and enclosures from a single graphical or command-line
interface without using of the controller BIOS utilities. The graphical user interface (GUI) is wizard-driven
with features for novice and advanced users, and detailed online help. Using the Dell OpenManage
storage management application, you can protect your data by configuring data-redundancy, assigning
hot spares, or rebuilding failed physical disks. The command line interface available on selected operating
systems to perform RAID management tasks is fully featured and scriptable.
17

NOTE: For more information, see the Dell OpenManage Storage Management User's Guide at
dell.com/openmanagemanuals.
Related documentation
NOTE:
• For all storage controllers and PCIe SSD documents, go to dell.com/storagecontrollermanuals.
• For all Dell OpenManage documents, go to dell.com/openmanagemanuals.
• For all operating system documents, go to dell.com/operatingsystemmanuals.
• For all PowerEdge documentation, go to dell.com/poweredgemanuals.
• For all PowerVault documentation, go to dell.com/powervaultmanuals.
18

2
Getting started with your PERC card
The workflows outlined below list the procedures to getting started with the PERC card, based on your
system configuration:
• Installing the operating system and the PERC card on a base system
• Installing the PERC card on a system with the operating system pre-installed
• Installing the operating system on a system with the PERC card pre-installed
• Setting up the system with the PERC card and the operating system pre-installed
• Configuring settings of a replaced PERC card on a system with operating system pre-installed
Installing the operating system and the PERC card on a base system
1. Install the PERC 9 card in the system. For more information, see Deploying the PERC card.
2. Download the PERC 9 drivers from the Dell support site. For more information, see dell.com/
support.
3. Use any of the PERC management applications to create the virtual disks and RAID configurations
you require using the procedures listed below:
a. Importing Or Clearing Secured Foreign Configurations And Secure Disk Migration
b. Managing physical disks
1. Creating Global Hot Spares
2. Creating Security Key
3. Converting a RAID disk to a Non-RAID disk. For more information, see Controller
management.
4. Converting a Non-RAID disk to a RAID disk. For more information, see Controller
management.
c. Creating virtual disks
d. Managing virtual disks
1. Setting up virtual disks
2. Checking Data Consistency
3. Managing Preserved Cache
4. Initializing virtual disks
19

5. Performing Background Initialization
6. Creating Secured Virtual Disks
7. Securing Pre-Existing Virtual Disks
e. Managing controllers through BIOS
1. Enabling Boot Support
2. Enabling Boot Support For A BIOS-Enabled Controller
3. Enabling BIOS Stop On Error
4. Enabling Auto Import
4. Install the operating system. For more information, refer to your operating system documentation.
5. Install the operating system drivers for PERC 9.
• If your operating system is Windows, install the Windows drivers. For more information, see
Windows driver installation.
• If your operating system is Linux, install the Linux drivers. For more information, see Linux driver
installation.
6. Additionally, you can install and use OpenManage Storage Services to manage the PERC card(s),
after the operating system is installed.
Installing the PERC card on a system with the operating system pre-installed
1. Install the PERC 9 card in the system. For more information, see Deploying the PERC card.
2. Download the PERC 9 drivers from the Dell support site. For more information, see dell.com/
support.
3. Install the operating system drivers for PERC 9.
• If your operating system is Windows, install the Windows drivers. For more information, see
Windows driver installation.
• If your operating system is Linux, install the Linux drivers. For more information, see Linux driver
installation.
4. Use any of the PERC management applications to create the virtual disks and RAID configurations
you require using the procedures listed below:
a. Importing Or Clearing Secured Foreign Configurations And Secure Disk Migration
b. Managing physical disks
1. Creating Global Hot Spares
2. Creating Security Key
3. Converting a RAID disk to a Non-RAID disk. For more information, see Controller
management.
4. Converting a Non-RAID disk to a RAID disk. For more information, see Controller
management.
20

c. Creating virtual disks
• Setting up virtual disks
d. Managing virtual disks
1. Setting up virtual disks
2. Checking Data Consistency
3. Managing Preserved Cache
4. Initializing virtual disks
5. Performing Background Initialization
6. Creating Secured Virtual Disks
7. Securing Pre-Existing Virtual Disks
e. Managing Controllers through BIOS
1. Enabling Boot Support
2. Enabling Boot Support For A BIOS-Enabled Controller
3. Enabling BIOS Stop On Error
4. Enabling Auto Import
5. Additionally, you can install and use OpenManage Storage Services to manage the PERC card(s).
Installing the operating system on a system with the PERC card pre-installed
1. Use any of the PERC management applications to manage the virtual disks and RAID configurations
on your system, using the procedures listed below:
a. Importing Or Clearing Secured Foreign Configurations And Secure Disk Migration
b. Managing physical disks
1. Creating Global Hot Spares
2. Creating Security Key
3. Converting a RAID disk to a Non-RAID disk. For more information, see Controller
management.
4. Converting a Non-RAID disk to a RAID disk. For more information, see Controller
management.
c. Creating virtual disks
• Setting up virtual disks
d. Managing virtual disks
1. Setting up virtual disks
2. Checking Data Consistency
3. Managing Preserved Cache
21

4. Initializing virtual disks
5. Performing Background Initialization
6. Creating Secured Virtual Disks
7. Securing Pre-Existing Virtual Disks
e. Managing Controllers through BIOS
1. Enabling Boot Support
2. Enabling Boot Support For A BIOS-Enabled Controller
3. Enabling BIOS Stop On Error
4. Enabling Auto Import
2. Install the operating system. For more information, refer to your operating system documentation.
3. Install the operating system drivers for PERC 9.
• If your operating system is Windows, install the Windows drivers. For more information, see
Windows driver installation.
• If your operating system is Linux, install the Linux drivers. For more information, see Linux driver
installation.
4. Additionally, you can install and use OpenManage Storage Services to manage the PERC card(s),
after the operating system is installed.
Setting up the system with the PERC card and the operating system pre-installed
1. Use any of the PERC management applications to create the virtual disks and RAID configurations
you require using the procedures listed below:
a. Importing Or Clearing Secured Foreign Configurations And Secure Disk Migration
b. Manage physical disks.
1. Creating Global Hot Spares
2. Creating Security Key
3. Converting a RAID disk to a Non-RAID disk. For more information, see Controller
management.
4. Converting a Non-RAID disk to a RAID disk. For more information, see Controller
management.
c. Creating virtual disks
• Setting up virtual disks
d. Managing virtual disks
1. Setting up virtual disks
2. Checking Data Consistency
3. Managing Preserved Cache
22

4. Initializing virtual disks
5. Performing Background Initialization
6. Creating Secured Virtual Disks
7. Securing Pre-Existing Virtual Disks
e. Managing Controllers through BIOS
1. Enabling Boot Support
2. Enabling Boot Support For A BIOS-Enabled Controller
3. Enabling BIOS Stop On Error
4. Enabling Auto Import
2. Additionally, you can install and use OpenManage Storage Services to manage the PERC card(s).
Configuring settings of a replaced PERC card on a system with operating system pre-installed
1. Replace your existing PERC card with a new one and install the PERC 9 card in the system. For more
information, see Deploying the PERC card.
2. Download the PERC 9 drivers from the Dell support site. For more information, see dell.com/
support.
3. Use any of the PERC management applications to create the virtual disks and RAID configurations
you require using the procedures listed below:
a. Importing Or Clearing Secured Foreign Configurations And Secure Disk Migration
b. Managing physical disks
1. Creating Global Hot Spares
2. Creating Security Key
3. Converting a RAID disk to a Non-RAID disk. For more information, see Controller
management.
4. Converting a Non-RAID disk to a RAID disk. For more information, see Controller
management.
c. Creating virtual disks
• Setting up virtual disks
d. Managing virtual disks
1. Setting up virtual disks
2. Checking Data Consistency
3. Managing Preserved Cache
4. Initializing virtual disks
5. Performing Background Initialization
6. Creating Secured Virtual Disks
23

7. Securing Pre-Existing Virtual Disks
e. Managing Controllers through BIOS
1. Enabling Boot Support
2. Enabling Boot Support For A BIOS-Enabled Controller
3. Enabling BIOS Stop On Error
4. Enabling Auto Import
4. Additionally, you can install and use OpenManage Storage Services to manage the PERC card(s).
24

3
Features
PowerEdge RAID Controller (PERC) 9 series cards support the following features:
• Personality mode management
• T10 Protection Information (PI)
• secure firmware update
• improved RAID 10 configuration
• 4KB block size disk drives
PERC 9 personality management
PERC 9 series of cards support two personality modes.
• RAID mode: RAID mode is commonly used and the controllers are mostly shipped from the factory in
RAID mode. This mode allows the creation and operation of RAID virtual disks and non-RAID disks.
• HBA mode: In the HBA mode, PERC controller operates as Host Bus Adapter (HBA). This mode does
not contain virtual disks or the ability to create them. All physical disks function as non-RAID disks
under operating system control. The PERC card acts as a conduit between the host server and the
physical disks. Input and output requests originate from the host and are passed through the
controller to the physical drives. HBA mode is the approach used for Windows Storage Spaces.
NOTE: HBA mode should be enabled for customers, using Microsoft Storage Spaces or VMware
Virtual SAN. HBA mode allows the operating system to control backplane LED functionality on
supported systems.
T10 protection information
T10 Protection Information (PI) is an end-to-end data integrity feature of the PERC 9 series. When PI is
enabled, the PERC 9 series provides additional protection against silent data corruption, and ensures that
incomplete and incorrect data do not overwrite good data.
Only Dell certified PI disks are supported.
NOTE: PI is not supported on SAS disks with 512–byte native and 512–byte emulated block size and
SATA disks.
Enabling T10 PI
To enable T10 PI:
1. During host system boot, press <Ctrl> <R> to access the BIOs Configuration Utility.
25

The Virtual Disk Management screen is displayed in the BIOS Configuration Utility window.
If there is more than one controller, the main menu screen is displayed. Select a controller, and press
<Enter>. The Virtual Disk Management screen is displayed for the selected controller.
2. Use the arrow keys to highlight the PERC 9 series of cards or Disk Group # .
NOTE: The H330 PERC card does not support the T10 PI feature.
3. Press <F2>.
The list of available actions is displayed.
4. Click Enable Data Protection.
Disabling T10 PI
To disable T10 PI:
1. Press <F2>.
The list of available actions is displayed.
2. Click Disable Data Protection.
Secure firmware update
This feature provides a cryptographic method of updating the firmware using RSA encryption-decryption
algorithm.
Only Dell certified firmware is supported on your PERC controller.
Improved RAID 10 configuration
RAID 10 configuration has been simplified for easier management and deployment. Disks are selected in
mirrored pairs.
NOTE: An even number of drives is required to create RAID 10 virtual disks.
4KB block size disk drives
PERC H330, H730, H730P and H830 cards support 4KB block size disk drives, which enables you to
efficiently use the storage space.
NOTE: Mixing 512–byte native and 512–byte emulated drives in a virtual disk is allowed, but mixing
512–byte and 4KB native block size drives in a virtual disk is not allowed.
Physical disk power management
Physical disk power management is a power-saving feature of the PERC 9 series cards. The feature allows
disks to be spun down based on disk configuration and I/O activity. The feature is supported on all
rotating SAS and SATA disks and includes unconfigured, configured, and hot-spare disks. The physical
disk power management feature is disabled by default. The feature can be enabled in the Dell Open
Manage Storage Management application or Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) RAID
Configuration utility. For more information, see the Dell OpenManage documentation at dell.com/
support/manuals.
26
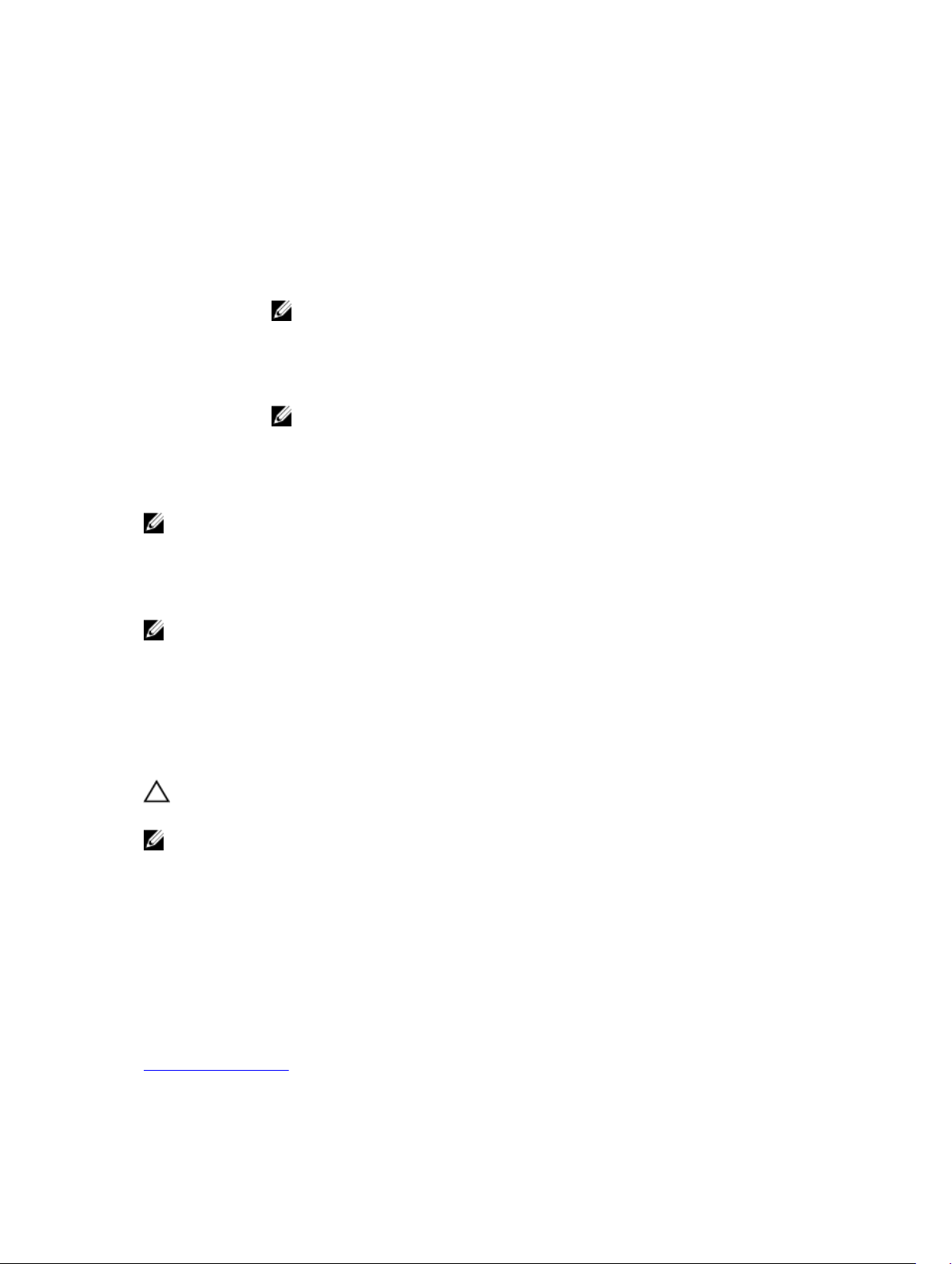
There are four power-saving modes:
No Power
Savings
(default mode)
Balanced
Power Savings
Maximum
Power Savings
Customized
Power Savings
All power savings features are disabled.
Spin down is enabled only for unconfigured and hot spare disks.
Spin down is enabled for configured, unconfigured, and hot spare disks.
NOTE: The maximum power savings mode is not supported by the H330
PERC card.
All power savings features are customizable. You can specify a Quality of Service
window during which the configured disks are excluded from spin-down.
NOTE: The customized power savings mode is not supported by the H330
PERC card.
Configured spin down delay
NOTE: The Configured Spin Down Delay option is not applicable for the No Power Savings mode.
The amount of time to wait before spinning down disks can be set using Configured Spin Down Delay.
The minimum value of the timer is 30 minutes (default) and the maximum is one day. Disks are spun
down automatically and spun up when accessed. All disks are spun up on reboot.
NOTE: There is a delay in I/O operations when a configured disk is being spun up.
Types of virtual disk initialization
PERC 9 series supports two types of virtual disk initialization:
• Full Initialization
• Fast Initialization
CAUTION: Initializing virtual disks erases files and file systems while keeping the virtual disk
configuration intact.
NOTE: The following initialization operations are not applicable for non-RAID disks.
Full initialization
Performing a full initialization on a virtual disk overwrites all blocks and destroys any data that previously
existed on the virtual disk. Full initialization of a virtual disk eliminates the need for the virtual disk to
undergo a Background initialization (BGI). Full initialization can be performed after the virtual disk is
created.
During full initialization, the host cannot access the virtual disk. You can start a full initialization on a
virtual disk by using the Slow Initialize option in the Dell OpenManage storage management application.
For more information on using the BIOS Configuration Utility to perform a full initialization, see
Initializing virtual disks.
27
NOTE: For better performance, you can perform full initialization on virtual disks. Full initialization
does not support RAID 6 and RAID 60 virtual disks with the PI feature enabled. BGI runs instead.
NOTE: If the system reboots during a full initialization, the operation aborts and a BGI begins on the
virtual disk.
Fast initialization
A fast initialization on a virtual disk overwrites the first and last 8 MB of the virtual disk, clearing any boot
records or partition information. The operation takes only 2–3 seconds to complete, but it is followed by
BGI, which takes a longer time to complete. To perform a fast initialization using the BIOS Configuration
Utility, see Initializing virtual disks.
NOTE: Fast initialization does not support RAID 6 and RAID 60 virtual disks with the PI feature
enabled.
Background initialization
Background Initialization (BGI) is an automated process that writes the parity or mirror data on newly
created virtual disks. BGI does not run on RAID 0 virtual disks. You can control the BGI rate in the Dell
OpenManage storage management application. Any change in the BGI rate does not take effect until the
next BGI run.
NOTE: BGI will run on RAID 0 virtual disks only with PI enabled.
NOTE: You cannot disable BGI permanently. If you cancel BGI, it automatically restarts within five
minutes. For information on stopping BGI, see Stopping Background Initialization.
NOTE: Unlike full or fast initialization of virtual disks, background initialization does not clear data
from the physical disks.
NOTE: Consistency Check (CC)/BGI typically causes some loss in performance until the operation
completes.
NOTE: VD with PI will have a longer background initialization when compared to non-PI virtual
disks.
Consistency Check (CC) and BGI perform similar functions in that they both correct parity errors.
However, CC reports data inconsistencies through an event notification, but BGI does not. You can start
CC manually, but not BGI.
Consistency checks
Consistency Check (CC) is a background operation that verifies and corrects the mirror or parity data for
fault tolerant virtual disks. It is recommended that you periodically run a consistency check on virtual
disks.
You can manually start a CC using the BIOS Configuration Utility or the Dell OpenManage storage
management application. You can schedule a CC to run on virtual disks using the Dell OpenManage
storage management application. To start a CC using the BIOS Configuration Utility, see Checking Data
Consistency .
NOTE: CC/BGI typically causes some loss in performance until the operation completes.
28

Consistency Check (CC) and BGI both correct parity errors. However, CC reports data inconsistencies
through an event notification, but BGI does not. You can start CC manually, but not BGI.
Disk roaming
Disk roaming is moving the physical disks from one cable connection or backplane slot to another on the
same controller. The controller automatically recognizes the relocated physical disks and logically places
them in the virtual disks that are part of the disk group. You can perform disk roaming only when the
system is turned off.
CAUTION: Do not attempt disk roaming during RAID level migration (RLM) or online capacity
expansion (OCE). This causes loss of the virtual disk.
Using disk roaming
Perform the following steps to use disk roaming:
1. Turn off the power to the system, physical disks, enclosures, and system components.
2. Disconnect power cables from the system.
3. Move the physical disks to desired positions on the backplane or the enclosure.
4. Perform a safety check. Make sure the physical disks are inserted properly.
5. Turn on the system.
The controller detects the RAID configuration from the configuration data on the physical disks.
FastPath
FastPath is a feature that improves application performance by delivering high I/O per second (IOPs) for
the Solid State Drives (SSD). The Dell PowerEdge RAID Controller (PERC) 9 series supports FastPath.
To enable FastPath on a virtual disk the Dell PowerEdge RAID Controller (PERC) 9 series cache policies
need to be set to Write-Through and No Read Ahead. This enables FastPath to use the proper data path
through the controller based on command (read/write), IO size, and RAID type.
For small random workloads, like OLTP, a RAID 10 array provides high performance and for sequential
read dominant workloads, a RAID5 array provides high performance.
NOTE: Only IO block sizes smaller than virtual disk’s stripe size are eligible for FastPath.
NOTE: The Physical Disk Power Management feature is not applicable to FastPath-capable virtual
disks.
Configuring FastPath-capable virtual disks
All simple virtual disks configured with write cache policy Write Through and read cache policy No Read
Ahead can utilize FastPath. Only IO block sizes smaller than virtual disk’s stripe size are eligible for
FastPath. In addition, there should be no background operations (rebuild, initialization) running on the
virtual disks. FastPath will not be used if these operations are active.
NOTE: RAID 50, and RAID 60 virtual disks cannot use FastPath.
29
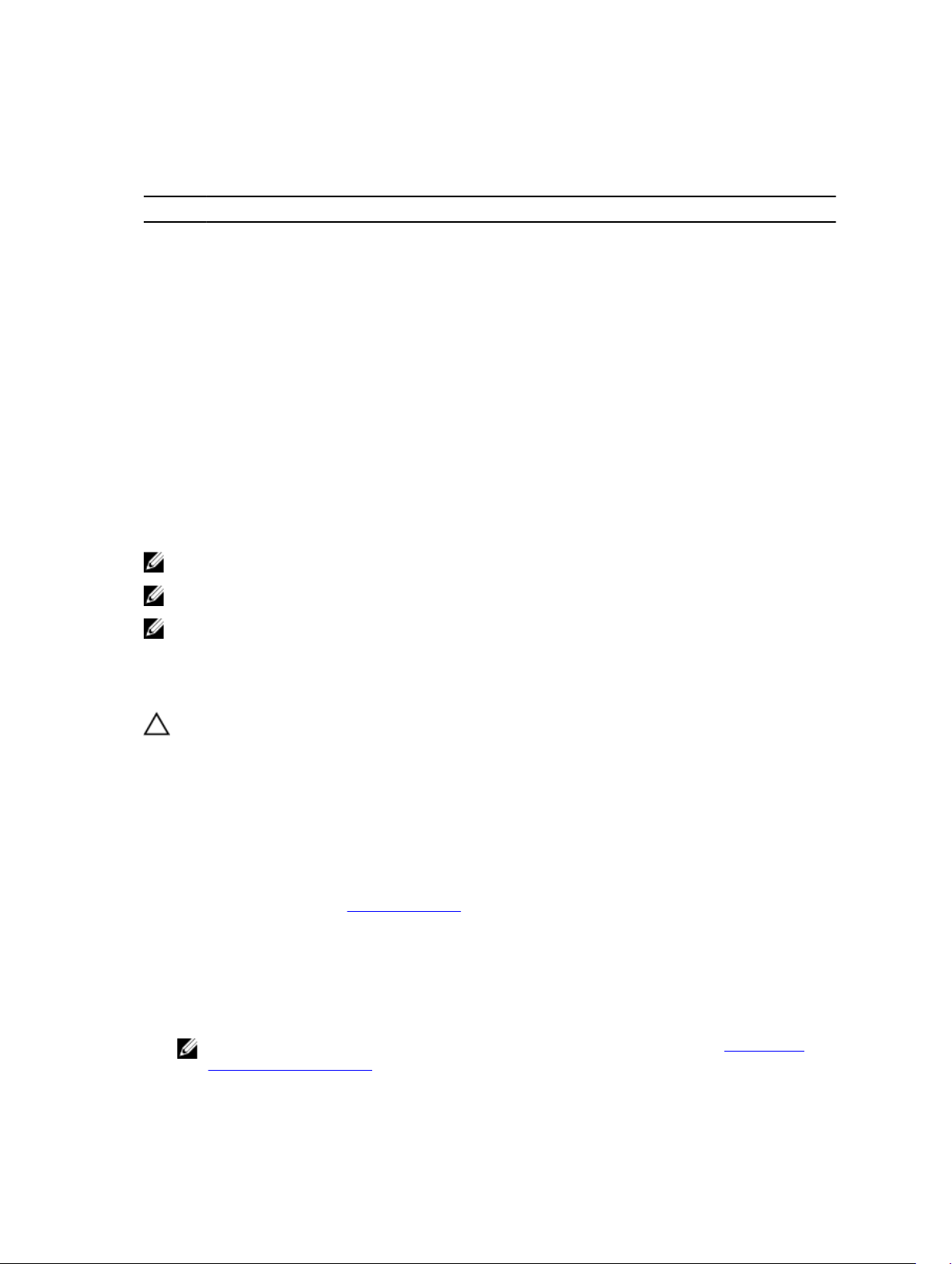
The following table summarizes the FastPath-eligibility of read and write IOs across the supported RAID
levels.
Table 1. FastPath eligibility across supported RAID levels
RAID 0 RAID 1 RAID 5 RAID 6 RAID 10
Read Yes
Write Yes No No No No
Yes
(Optimal and
Degraded)
Yes
(Optimal and
Degraded)
Yes
(Optimal and
Degraded)
Yes
(Optimal)
Virtual disk migration
The PERC 9 series supports migration of virtual disks from one controller to another without taking the
target controller offline. The controller can import RAID virtual disks in optimal, degraded, or partially
degraded states. You cannot import a virtual disk that is offline. Disk migration pointers:
• Supports migration of virtual disks from PERC H310, H710, H710P, and H810 to PERC 9 series
• Supports migration of volumes created within PERC 9 series
• Does not support migration from PERC 9 series to H310, H710, H710P, H810
NOTE: The source controller must be offline prior to performing the disk migration.
NOTE: Disks cannot be migrated to older generations of the PERC cards.
NOTE: Importing secured virtual disks is supported as long as the appropriate Local Key
Management (LKM) is supplied or configured.
When a controller detects a configured physical disk, it flags the physical disk as foreign, and generates
an alert indicating that a foreign disk was detected.
CAUTION: Do not attempt disk migration during RLM or online capacity expansion (OCE). This
causes loss of the virtual disk.
Migrating virtual disks
To migrate virtual disks from PERC H710, H710P, or H810 to PERC 9 series:
1. Turn off the system.
2. Ensure that all the latest firmware and drivers for the PERC H330, H730, H730P, or H830 card
(available at dell.com/support) are installed on the destination system.
For more information, see Driver installation.
3. Move the physical disks from PERC H310, H710, H710P, or H810 card to the PERC 9 series.
4. Boot the system and import the foreign configuration that is detected. You can do one of the
following:
• Press <F> to automatically import the foreign configuration.
• Enter the BIOS Configuration Utility and navigate to the Foreign Configuration View.
NOTE: For more information on accessing the BIOS Configuration Utility, see Entering the
BIOS configuration utility.
30
 Loading...
Loading...