Dell SonicPoint-N Dual Radio Getting Started Manual
Getting Started Guide
Dell SonicWALL Clean Wireless Appliances
Wireless Network Security
SonicPoint-N Dual Radio
SonicPoint-N Dual Radio Getting Started Guide | 1
Notes, Cautions, and Warnings
© 2013 Dell, Inc.
Trademarks: Dell™, the DELL logo, SonicWALL™, SonicWALL GMS™, SonicWALL Analyzer™, Reassembly-Free Deep Packet
Inspection™, Dynamic Security for the Global Network™, SonicWALL SuperMassive™ Appliances, SonicWALL Dynamic Support
24x7™, SonicWALL Comprehensive Gateway Security Suite™, SonicWALL McAfee Client/Server Anti-Virus Suite™, and all other
SonicWALL product and service names and slogans are trademarks of Dell, Inc.
Microsoft Windows, Internet Explorer, and Active Directory are trademarks or registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
The Wi-Fi CERTIFIED Logo is a registered mark of the Wi-Fi Alliance.
Other product and company names mentioned herein may be trademarks and/or registered trademarks of their respective companies
and are the sole property of their respective manufacturers.
2013 – 06 P/N 232-001939-52 Rev. A
NOTE: A NOTE indicates important information that helps you make better use of your system.
CAUTION: A CAUTION indicates potential damage to hardware or loss of data if instructions are not followed.
WARNING: A WARNING indicates a potential for property damage, personal injury, or death.

2 | SonicPoint-N Dual Radio Getting Started Guide
SonicPoint-N Dual Radio Getting Started Guide
This Dell SonicWALL Getting Started Guide provides the network administrator with setup instructions for creating an enterprise-class
secure wireless network with the SonicPoint-N Dual Radio appliance, all in about 60 minutes. More than just the basics, this guide
provides a concise overview of both general wireless deployment concepts and specific network configurations.
Setup
Additional Configuration and Information
• Optimizing Wireless with RF Analysis - page 29
• Support and Training Options - page 33
• Product Safety and Regulatory Information - page 37
Step Procedure Est. Time
Before You Begin - page3
Introduction to Secure Wireless - page 7
Registering Your Appliance - page 11
Configuring the Wireless Zone and Interface - page 15
Setting Up Your SonicPoint - page 21
12345

SonicPoint-N Dual Radio Getting Started Guide | 3
Before You Begin
In this Section:
This section provides a basic checklist of materials and information you will need before you begin.
• Check Package Contents - page4
• What You Need to Begin - page 5
• Ports and Status LEDs - page 6
1
4 | Check Package Contents
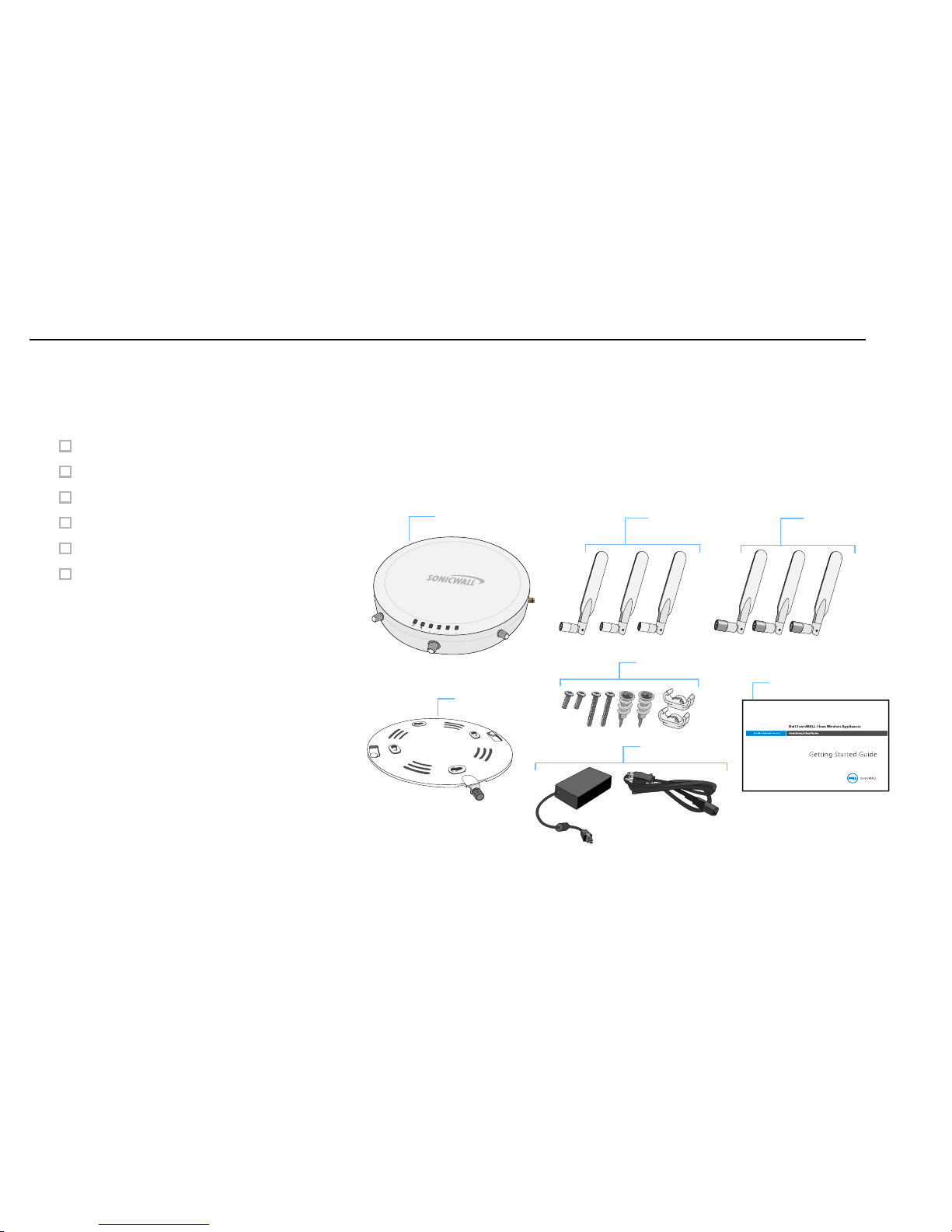
Check Package Contents
Before continuing, ensure that your SonicPoint package contains the following materials:
SonicPoint-N Dual Radio Appliance
Six (6) Antennas (2.4 GHz x 3), (5GHz x 3)
Mounting Plate
Anchor Kit (Screw Kit, Ceiling Braces)
This Getting Started Guide
Power Adaptor and Cord*
*The included power cord is approved for use only in specific
countries or regions. Before using a power cord, verify that it is
rated and approved for use in your location.
Missing Items?
If any of the items corresponding to your product
are missing from the package, please contact
Dell SonicWALL support.
A listing of the most current support documents
are available online at:
<http://www.sonicwall.com/us/support.html>
Getting Started Guide
SonicPoint N Dual-Radio
Mounting Plate
2.4Ghz Antennas (3)
5Ghz Antennas (3)
Anchor/Screw Kit
Power Adaptor
and Cord*
5GHz
wlan
lan
2.4GHz
link
act
What You Need to Begin | 5
What You Need to Begin
This page provides basic network hardware and software
prerequisites as a baseline for SonicPoint-N Dual Radio
deployments. More specific requirements are detailed in the
remainder of this guide.
Hardware / Firmware Requirements
The Dell SonicWALL SonicPoint-N Dual Radio access points
are centrally managed by any of the following Dell SonicWALL
appliances running SonicOS 5.8.0.2 or higher:
• SuperMassive 9000 Series
• NSA E-Class Series
• NSA Series (Except NSA 2400MX)
• TZ 215/205/105 Series
• TZ 210/200/100 Series
Network Deployment Requirements
• An active broadband Internet connection
• At least one free network interface on the Dell SonicWALL
security appliance, configured with a zone type of “WLAN”
• A single point placement or distributed wireless placement
plan for your SonicPoint(s)
• Wireless clients capable of 802.11n wireless
communications
1
• A network infrastructure capable of sustaining 802.1 1n dat a
rates to the number of clients you intend to support
• An 802.3at compliant PoE injector or PoE-capable switch
(if powering your deployment using PoE)
Note: For more network deployment recommendations and
tips, see the Hardware Decisions section, on page 9.
1. Although clients with 802.11a/b/g hardware are supported,
the presence of these legacy clients within range of your network may affect the connection speed of your 802.11n clients.
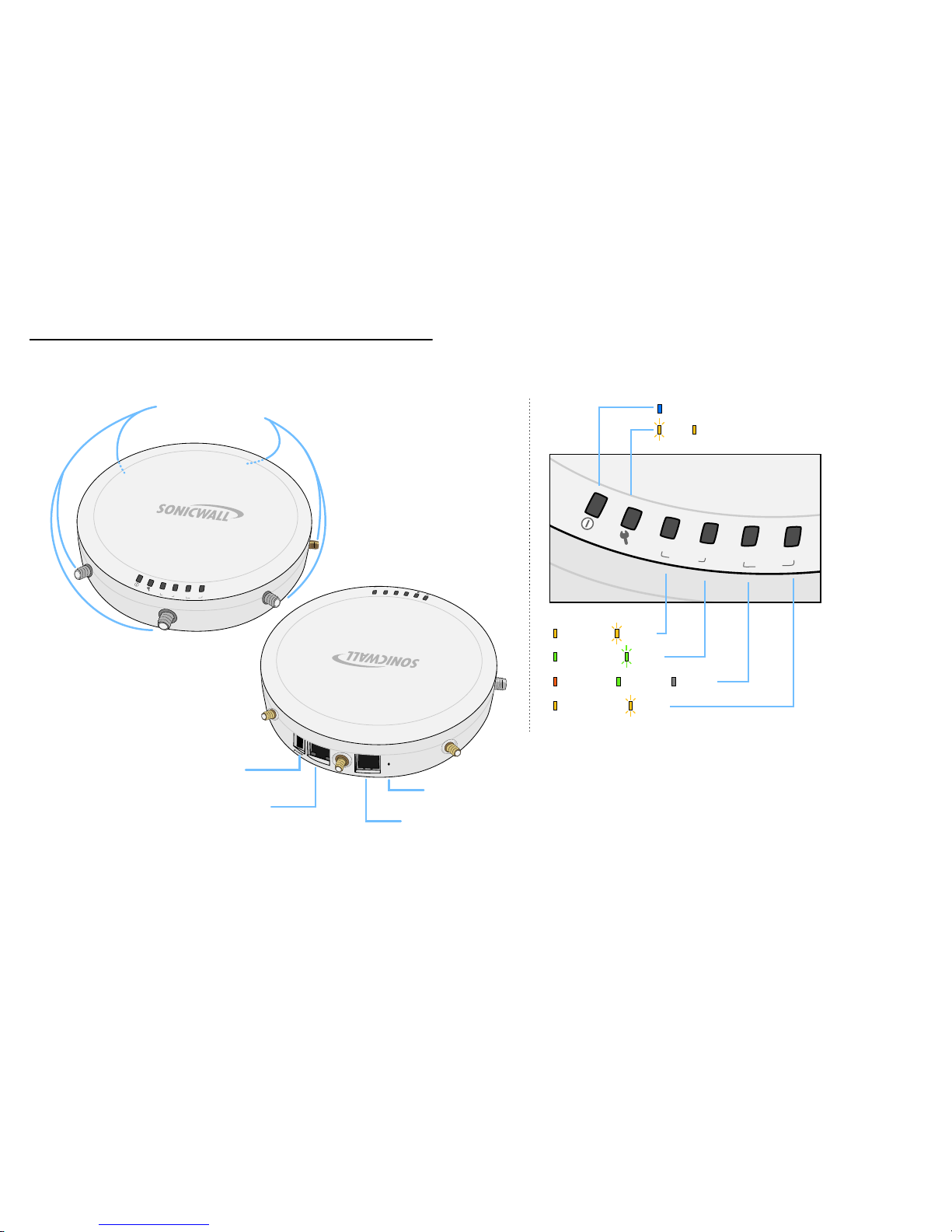
6 | Ports and Status LEDs
Ports and Status LEDs
5GHz
wlan
lan
2.4GHz
link
act
5GHz
wlan
lan
2.4GHz
link
act
A
n
t
e
n
n
a
C
o
n
n
e
c
t
i
o
n
s
Status LEDs
Power
Test SafeMode
5GHz Link Activity
2.4GHz Link Activity
1000Mbps 100Mbps 10Mbps
Ethernet Link Activity
c
o
n
s
o
l
e
l
a
n
Power Port
Provides 12VDC power connection
LAN/PoE Port
Provides Ethernet connection and
802.3at Power over Ethernet (PoE)
Console Port
Provides management connection using
CLI->DB9 cable (for command line management only)
Reset Button
Press and hold to manually reset
5GHz
wlan
lan
2.4GHz
link
act
SonicPoint-N Dual Radio Getting Started Guide | 7
Introduction to Secure Wireless
In this Section:
This section contains excerpts from the SonicWALL Secure Wireless Network Integrated Solutions Guide.
The content is meant to provide a brief introduction to Radio Frequency (RF) technology as it pertains to different deployment scenarios.
• Wireless RF Introduction - page 8
• Access Points and Network Design - page 9
2
8 | Wireless RF Introduction
Wireless RF Introduction
There are currently four widely adopted standards for 802.11
wireless network types: a, b, g, and n. Although 802.11n is the
newest and highest capacity standard, each of the four
standards has its own strengths and weaknesses. This section
provides overviews of these standards.
See the following sections for a brief overview of Radio
Frequency technologies:
• 802.11 Comparison Chart - page 8
• Radio Frequency Barriers - page 8
• RF Interference - page 8
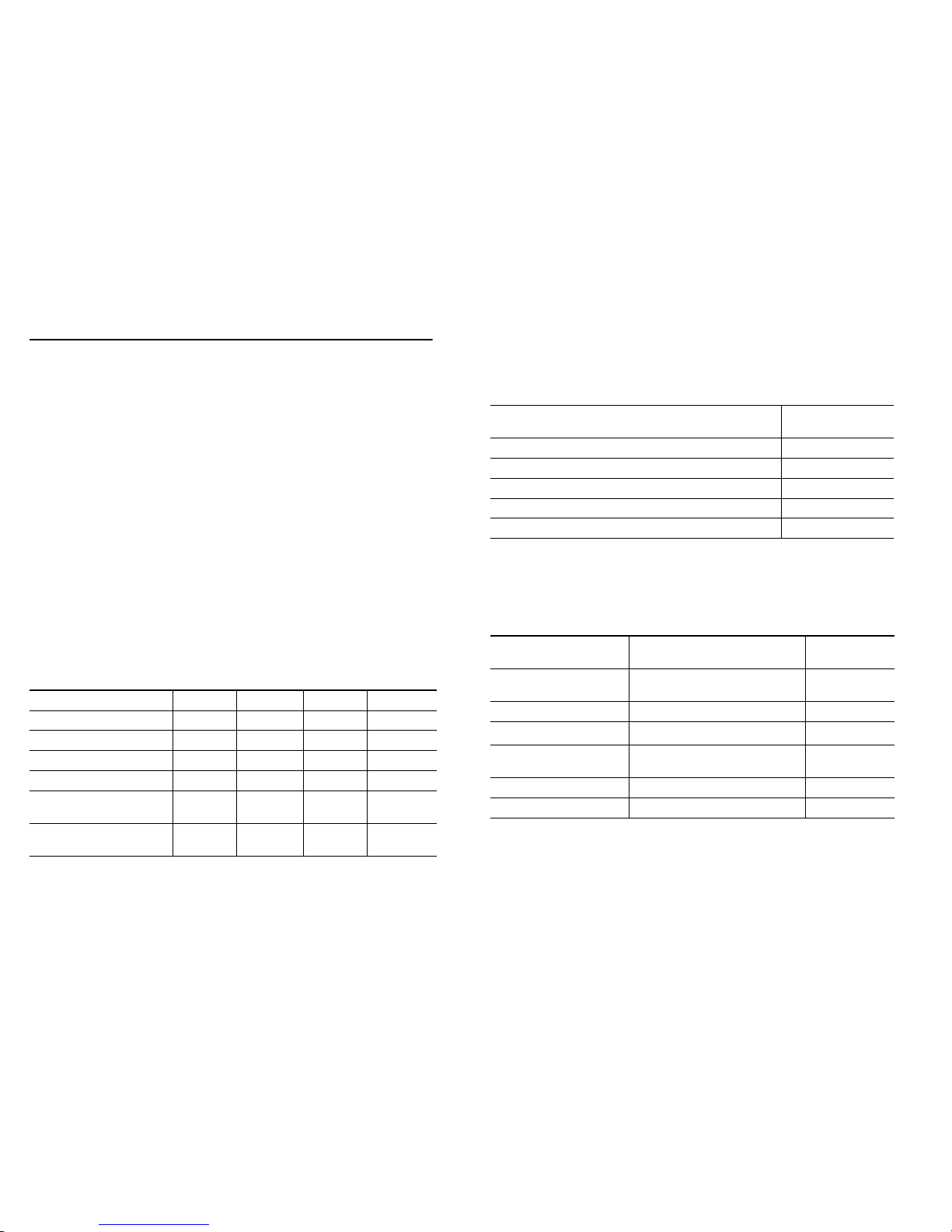
802.11 Comparison Chart
The following table compares signal characteristics as they
apply to the current 802.11standards:
Radio Frequency Barriers
The following tables list some common RF barrier types:
RF Interference
The following table lists several common interference sources:
802.11a 802.11b 802.11g 802.11n
# of Channels in USA 23 11 11 11
# of Channels in EU 23 13 13 13
# of Channels in Japan 15 14 14 14
Frequency Band 5GHz 2.4GHz 2.4GHz 2.4/5GHz
Max. Data Rate 54Mbps 1 1Mbps 54Mbps 150Mbps
300Mbps
Radius (Range) 90ft/25m 120ft/
35m
120ft/
35m
300ft/90m
Barrier Type RF Signal
Blocking
Open air Very Low
Glass, drywall, cubicle partitions Low
Stone floors and walls (brick/marble/granite) Medium
Concrete, security glass, stacked books/paper High
Metal, metal mesh, reinforced concrete, water Very High
Interference Source Possible RF Interference Band(s)
Affected
2.4GHz phones Entire range (hundreds of
feet)
802.11b/g/n
Bluetooth devices Within 30 feet 802.11b/g/n
Microwave oven
a
a.Most newer model microwave ovens have sufficient shielding
to negate possible RF interference.
Within 10-20 feet 802.11b/g/n
Scientific and medical
equipment
Short distance, varies 802.1 1b/g/n
Other wireless devices Entire range All
RF reflective objects Long-range wireless bridging All
Access Points and Network Design | 9
Access Points and Network Design
Physical placement of an access point has a measurable effect
on who can and cannot access your wireless signal. The
following sections provide an overview of wireless access point
placement, signal strength, and signal direction in common
wireless deployment situations:
• Hardware Decisions - page 9
• Solutions to RF Interference and Barriers - page 10
Tip: For the latest SonicPoint wireless deployment
information from switching recommendations to
site survey, see the SonicWALL SonicPoint
Deployment Best Practices Guide at:
<http://www.sonicwall.com/us/support.html>
Hardware Decisions
The first decision in hardware is the access point. While access
point technology (802.11a/b/g/n) is one factor in determining
your placement, based on distance served and bandwidth
needed, taking note of other hardware-based factors is just as
important.
Some hardware factors to take into consideration:
• Number of access points versus user density – If too
many users are serviced by a single access point,
maximum transfer rates are reached and that point may
become a bottleneck for the whole system.
• Bandwidth – How much data is moving upstream and
downstream for a given type of user?
• Eth ernet cabling – Where are you running the powered
Ethernet (PoE) cable to and how are you securing that
cable? Is your PoE switch able to power all access points?
• Hubs / Switches / Security Appliance – Your wireless
deployment has to tie back into your SonicWALL security
appliance and LAN resources at some point. What speed is
needed for your Ethernet connection to accommodate the
number of access points you are installing? Also consider
where your key networking devices are deployed and how
they will connect efficiently with your wireless appliances.
• Eth ernet connections for 802.11n – In most cases,
802.1 1n wireless hardware requires more bandwidth than a
single (or even dual) 10/100 Ethernet connection can
handle. Gigabit Ethernet connectivity between the WLAN
and the LAN is required to take full advantage of 802.11n
speed.
• Power Over Ethernet (PoE) – Part of your wireless
network planning should include verifying that your PoE
equipment is 802.3at compliant, and that full power can be
supplied to each SonicPoint.
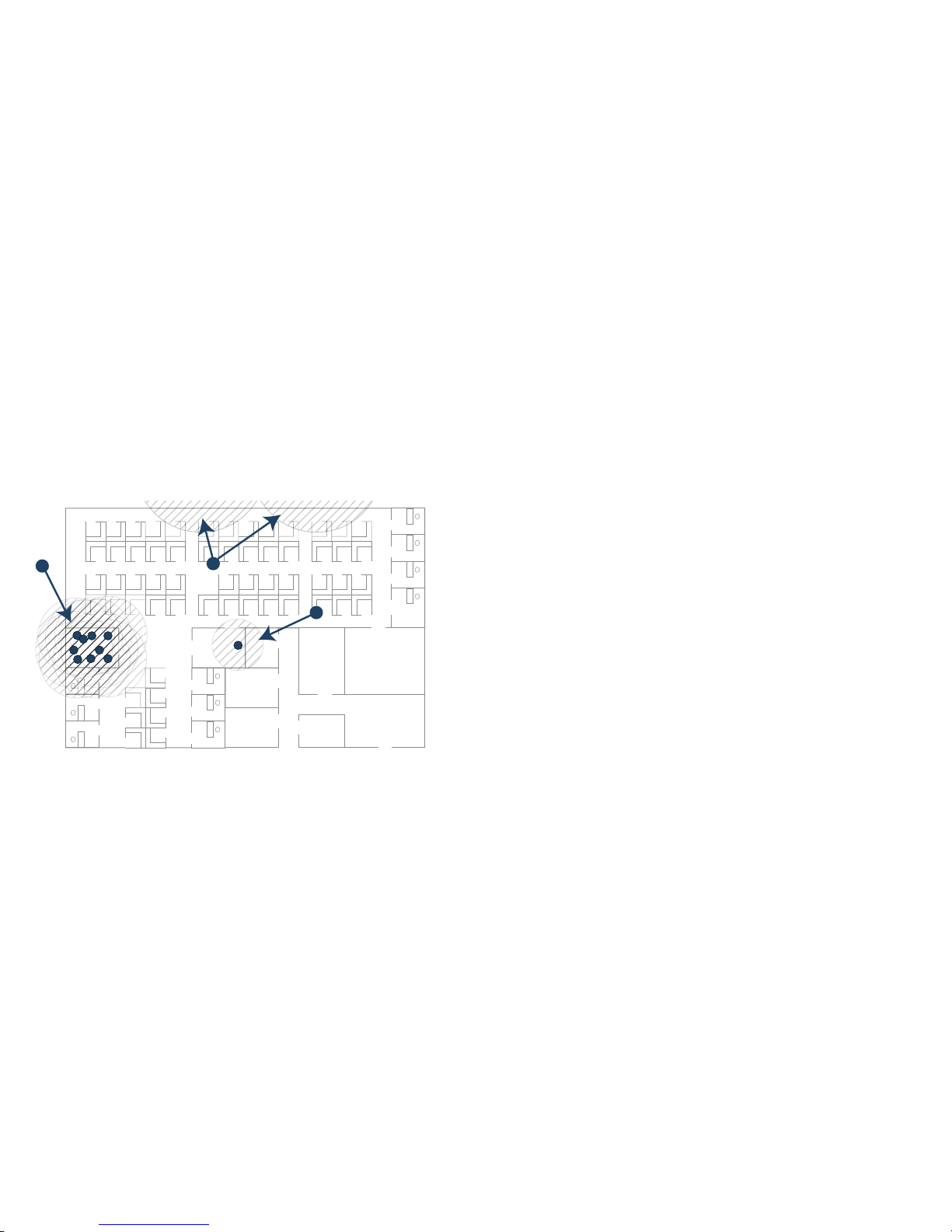
10 | Access Points and Networ k D e sign
Solutions to RF Interference and Barriers
These days, finding an environment with no RF interference or
noise is nearly impossible. Only if you are setting up an office in
a secluded redwood grove can you count on RF interference to
be a non-issue. Even then, the redwood trees might just be
among those fitted with high-gain cellular antennas, an all-toocommon occurrence today. Regardless, you should expect to
deal with some level of signal interference in your deployment.
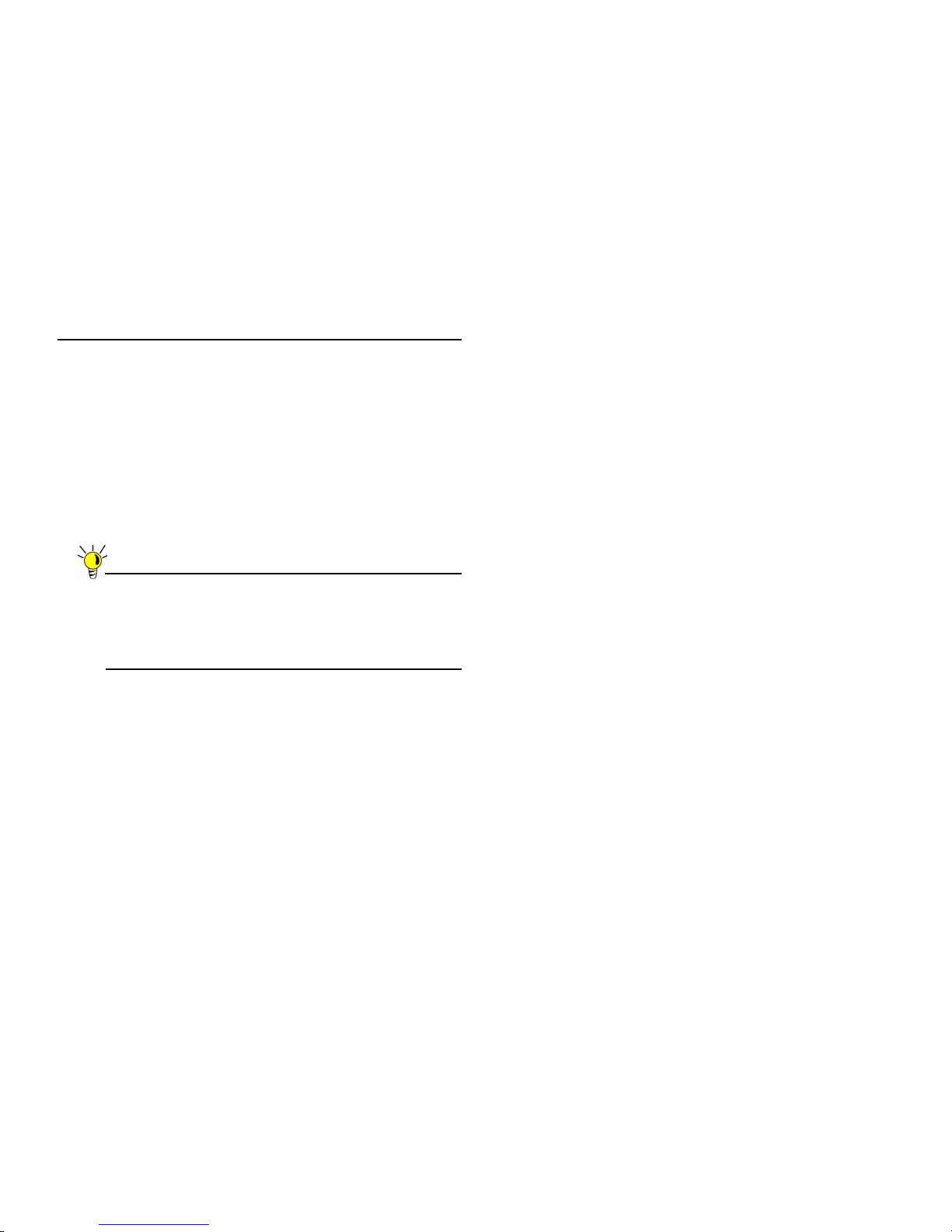
Location A – Rogue access points
• Problem – Wi reless product test labs and other (nonmalicious) rogue access points are problems in many Wi-Fi
deployments.
• Solution – Either eliminate all rogue access points, or
force their owners to use a set channel that does not
overlap with your distributed wireless solution.
Location B – Spectrum noise for 2.4 GHz
and 5 GHz
• Problem – Your phone system is partially wireless and
uses the 2.4GHz or 5GHz spectrum.
• Solution – Give VoIP a try. VoIP will work in tandem with
your wireless network, instead of against it. For more on
SonicWALL VoIP implementation and capabilities, refer to
the Configuring VoIP SonicOS feature module available at:
http://www.sonicwall.com/us/support.html
Location C – Off-network access points
• Problem – Your neighbors need wireless, too!
Unfortunately, only a few sheets of drywall separate you.
Solution – Overpowering your neighbors with high-gain
antennas is an option, but not a particularly neighborly one.
Instead, you could simply use a different channel for
wireless access points bordering this wall and ensure that
your neighbors do the same. Performance in some dualchannel wireless devices may take a hit, but it is better
than dropped connections—or unhappy neighbors.
A
C
B
SonicPoint-N Dual Radio Getting Started Guide | 11
Registering Your Appliance
In this Section:
This section provides instructions for registering your Dell SonicWALL SonicPoint appliance.
• Registering and Licensing Your Appliance on MySonicWALL - page 12
• Using De ll SonicWALL Security Services for Wireless Clients - page 13
Note: Registration is an important part of the setup process and is necessary to receive the full benefits of Dell SonicWALL security
services, automatic SonicPoint firmware updates, and technical support.
3
12 | Registering and Licensing Your Appliance on MySonicWALL
Registering and Licensing Your
Appliance on MySonicWALL
You must register your SonicPoint on MySonicWALL to enable
full functionality.
Note: Registration is an important part of the setup process
and is necessary in order to receive the benefits of
Dell SonicWALL security services, firmware update s,
and technical support.
To register your SonicPoint, perform the following tasks:
1. Log in to your MySonicWALL account. If you do not have
an account, you can create one at www.mysonicwall.com.
2. Enter the serial number of your product in the Register a
Product field and click the Next button.
3. Type a friendly name for the appliance, select the Product
Group if any, type the authentication code into the
appropriate text boxes, and then click Register.
4. On the Product Survey page, fill in the requested
information and then click Continue.
5. To pair your SonicPoint with a Dell SonicWALL security
appliance, navigate to the Service Management page by
clicking on the device you wish to pair with your
SonicPoint.
6. Scroll to the Associated Products section and click the
SonicWALL SonicPoint link to associate your SonicPoint
with the appliance.

Using Dell SonicWALL Security Services for Wireless Clients | 13
Using Dell SonicW ALL Security Services
for Wireless Clients
Any security services you purchased for your Dell SonicWALL
security appliance can also be applied to wireless clients.
Simply enable the security services on the WLAN zone or on
a custom wireless zone, and your wireless traffic will be
protected along with your wired traffic.
If you have not yet purchased a security service
subscription for your Dell SonicWALL security appliance,
please speak with a sales representative or visit
www.mysonicwall.com to register for free trials.
T o license a security service, complete one of the following from
the Service Management page for your product on
MySonicWALL:
• Free Trial of Service—Click the Try icon in the Action
column for the security service you wish to try for a 30-day
free trial. The free trial immediately activates and notifies
you of the trial expiration date. The Service Management
page displays updated information about the free trial
service.
• Purchase a Service—Click the Cart icon to purchase a
security service. In the Buy Service page, specify the
quantity of licenses wanted, then click Add to Cart. Once
the item(s) have been added, click the Checkout button.
Follow the instructions to complete your purchase.

14 | Using Dell SonicWALL Security Services for Wireless Clients
 Loading...
Loading...