Page 1

Dell Server Deployment Pack Version 2.1 for
Microsoft System Center Configuration Manager
User's Guide
Page 2

Notes, Cautions, and Warnings
NOTE: A NOTE indicates important information that helps you make better use of your computer.
CAUTION: A CAUTION indicates either potential damage to hardware or loss of data and tells you how to avoid the
problem.
WARNING: A WARNING indicates a potential for property damage, personal injury, or death.
Copyright © 2014 Dell Inc. All rights reserved. This product is protected by U.S. and international copyright and intellectual property
laws.
mentioned herein may be trademarks of their respective companies.
2014- 04
Rev. A01
™
and the Dell logo are trademarks of Dell Inc. in the United States and/or other jurisdictions. All other marks and names
Dell
Page 3

Contents
1 Introduction..................................................................................................................................5
What's New in This Release.....................................................................................................................................5
Dell Server Deployment Pack Features Overview....................................................................................................5
2 Before Using Configuration Manager......................................................................................7
Recommended DTK Version for DSDP..................................................................................................................... 7
3 Using the Dell Server Deployment Pack on Systems Running Configuration
Manager 2012 and Configuration Manager 2012 SP1..............................................................9
Importing a DTK Package......................................................................................................................................... 9
Upgrading a DTK Package........................................................................................................................................9
Creating a Boot Image for Deploying Dell PowerEdge Servers............................................................................. 10
Enabling Command Prompt for Debugging Boot Images....................................................................................... 11
Importing Dell Server Driver Packages.................................................................................................................. 11
Distributing Content and Updating Distribution Points...........................................................................................11
Configuring Your Servers Hardware Components................................................................................................. 12
Creating a Task Sequence............................................................................................................................... 12
Creating a Dell Specific Task Sequence..........................................................................................................12
Creating a Custom Task Sequence.................................................................................................................. 13
Editing a Task Sequence..................................................................................................................................13
Adding Diskpart Clean To Task Sequence.......................................................................................................14
Configuring Task Sequence Actions...................................................................................................................... 14
Configuring System BIOS.................................................................................................................................14
Configuring Set Boot Order.............................................................................................................................. 15
Retrieving Boot Device IDs.............................................................................................................................. 16
Configuring RAID Using RAID Config (wizard)................................................................................................. 16
Using the Array Builder.......................................................................................................................................... 17
How Array Builder Works................................................................................................................................ 17
Controllers........................................................................................................................................................17
Variable Conditions.......................................................................................................................................... 18
Arrays...............................................................................................................................................................19
Logical Drives (also known as Virtual Disks)................................................................................................... 20
Disks (also known as Array Disks)................................................................................................................... 21
Exporting to XML.............................................................................................................................................. 21
Importing XML..................................................................................................................................................21
Saving to Package............................................................................................................................................22
Creating Task Sequences for RAID, DRAC, and iDRAC..........................................................................................22
Variable Replacement......................................................................................................................................23
Page 4

Configuring Variable Replacement Tab........................................................................................................... 23
Log/Return Files ...............................................................................................................................................24
Configuring the Task Sequence Steps to Apply Operating System Image And Driver Package........................... 24
Applying the Operating System Image.............................................................................................................24
Adding Dell Driver Packages........................................................................................................................... 24
Advertising a Task Sequence.................................................................................................................................25
Best Practices for Advertising a Task Sequence............................................................................................ 25
Deploying a Task Sequence................................................................................................................................... 25
4 Using the Dell Server Deployment Pack on Systems Running Configuration
Manager 2007............................................................................................................................... 27
Importing a DTK Package....................................................................................................................................... 27
Upgrading a DTK Package......................................................................................................................................27
Creating a Boot Image for Deploying Dell PowerEdge Servers............................................................................. 28
Updating and Managing Distribution Points...........................................................................................................29
Importing Dell Server Driver Packages.................................................................................................................. 30
Enabling Command Prompt for Debugging Boot Images....................................................................................... 30
Configuring Your Servers Hardware Components................................................................................................. 30
Creating a Task Sequence............................................................................................................................... 30
Creating a Dell Specific Task Sequence..........................................................................................................31
Creating a Custom Task Sequence.................................................................................................................. 31
Editing a Task Sequence..................................................................................................................................32
Rebooting to PXE USB Custom Action on Systems Running Configuration Manager 2007 ............................32
Advertising a Task Sequence.................................................................................................................................33
Best Practices for Advertising a Task Sequence............................................................................................ 33
Deploying a Task Sequence................................................................................................................................... 33
5 Troubleshooting.........................................................................................................................35
Task Sequences Fail or Act Incorrectly After an Upgrade on Configuration Manager 2007 SP2..........................35
Operating System Deployment Fails in Microsoft Windows Server 2003.............................................................. 35
DTK Configuration wizard completes with errors...................................................................................................36
6 Command Line Options.............................................................................................................37
7 Other Dell Documents You Might Need................................................................................ 39
Contacting Dell....................................................................................................................................................... 39
Accessing Documents From Dell Support Site.......................................................................................................39
Page 5

1
Introduction
This document describes the activities that you can perform with the Dell Server Deployment Pack (DSDP) Version 2.1
for Microsoft System Center Configuration Manager (Configuration Manager).
NOTE: This document contains information on requirements and the supported software necessary for working
with DSDP. If you are installing this version of DSDP after a long time after its release date, check to see if there is
an updated version of this document on the support site. For accessing documents on support site, see Accessing
Documents From The Dell Support Site or see dell.com/support/Manuals/us/en/04/Product/dell-srvr-dplymnt-pck-
v2.1-for-systm-center-config-mangr.
What's New in This Release
• Support for Microsoft System Center 2012 SP1 Configuration Manager installed on Microsoft Windows Server 2012
Standard Edition 64–bit, Microsoft Windows Server 2012 Datacenter Edition 64–bit, and other earlier releases of
Windows Servers.
• Support for Microsoft System Center 2012 SP1 Configuration Manager Admin console installed on Microsoft
Windows 8 Pro and Windows 8 Enterprise, 32–bit and 64–bit.
• Support for Dell Deployment Toolkit (DTK) version 4.4 and later.
• Support for deploying Windows Server 2012.
• Support for remote SMS Provider.
Dell Server Deployment Pack Features Overview
You can perform the following tasks using the Dell Server Deployment Pack:
• Configure the server's Dell Remote Access Controller (DRAC), integrated Dell Remote Access Controller (iDRAC),
RAID, and BIOS using INI files and Command Line Interface (CLI) options. You can also configure RAID using the
Array Builder Wizard.
• Create a Dell-specific boot image that is used in the operating system deployment.
• Import and apply driver installation packages for specific Dell servers.
• Consolidated launch points to various wizards, to perform a typical server deployment on site server installation.
• Enhanced support for up to sixteen global and dedicated RAID hot spares.
• Support for Microsoft System Center Configuration Manager 2012, 2012 SP1, 2007 R2, SP2, and R3 releases.
• Support for importing of Dell Deployment ToolKit (DTK) using the PowerEdge Deployment ToolKit Configuration
Wizard. Make sure that you import DTK package only from the site server and not from the admin console.
• Support for importing Dell driver packages from the Configuration Manager Admin Console.
• Support for deployment using x64 boot images (DTK with 64-bit support is required).
5
Page 6

6
Page 7

2
Before Using Configuration Manager
Before you begin using the Configuration manager, ensure the following:
• Import the DTK packages if you are upgrading DSDP using the option Remove Dell Deployment ToolKit (DTK) utilities
and Windows PE drivers or installing DSDP for the first time.
NOTE: You can import the DTK package only from a Configuration Manager site server and not from the admin
console.
For more information on importing a DTK package for Configuration Manager 2012 SP1, 2012, or 2007, see Importing
a DTK Package.
• Create distribution points or update the appropriate packages to Configuration Manager distribution points. The
Update Distribution Points operation ensures that all packages of the Dell Server Deployment Pack that you installed
are updated on the distribution points. The Distribution operation ensures that the packages are available on the
distribution points for the client systems to access them. To add a distribution point, see the Configuration Manager
Online Help
Dell Server Deployment Pack provides consolidated launch points to various wizards to perform a typical server
deployment. To access the wizards sequentially, right-click the Operating System Deployment node and select Dell
PowerEdge Server Deployment. You can use DSDP for Configuration Manager to perform the following tasks:
• Import a Dell Deployment ToolKit (DTK)
• Create Dell boot images for server deployment
• Import Dell driver packages from
• Create an operating system deployment task sequence
.
Dell Systems Management
DVD
Recommended DTK Version for DSDP
DSDP with DTK version 4.4 supports the following Configuration Manager versions:
• Configuration Manager 2007 SP2 R3
• Configuration Manager 2007 SP2
• Configuration Manager 2012
• Configuration Manager 2012 SP1
NOTE: In Configuration Manager 2012 SP1, there are only Windows PE 4.0 drivers , so only 64–bit operating
systems' deployment is supported as DTK 4.4 does not support 32–bit version of Windows PE 4.0 drivers.
In Configuration Manager 2012, there are only Windows PE 3.x drivers, so both 32–bit and 64–bit operating
systems' deployments are supported as DTK 4.4 supports 32–bit version and 64–bit version of Windows PE 3.x
drivers.
7
Page 8

8
Page 9
3
Using the Dell Server Deployment Pack on Systems Running Configuration Manager 2012 and Configuration Manager 2012 SP1
This section provides information on how to use Dell Server Deployment Pack on systems running Configuration
Manager 2012 and Configuration Manager 2012 SP1.
Importing a DTK Package
NOTE: Download the latest DTK pack from support.dell.com. Make sure that you import a DTK Package from the
site server and not from the admin console.
To import a DTK Package:
1. Launch the Configuration Manager Console.
2. From the left pane of the Configuration Manager Console, select Software Library → Overview → Application
Management → Packages.
3. Right-click Packages and select Dell PowerEdge Server Deployment → Launch Deployment Toolkit Configuration
Wizard.
The PowerEdge Deployment ToolKit Configuration Wizard screen is displayed.
4. Click Browse and navigate to the DTK self-extractable zip file that you downloaded.
The selected DTK version, Windows PE version, and architecture is displayed under DTK selected for import.
5. Follow steps 3 to 8 in the Creating a Boot Image for Deploying Dell PowerEdge Servers section for creating a boot
image.
Upgrading a DTK Package
To upgrade a DTK package:
1. Launch Configuration Manager Console.
2. From the left pane of the Configuration Manager Console, select Software Library → Overview → Application
Management
3. Right-click Packages and select Dell PowerEdge Server Deployment → Launch Deployment Toolkit Configuration
Wizard.
The PowerEdge Deployment ToolKit Configuration Wizard screen is displayed. If there is an existing DTK package
on the server, then the DTK version, Windows PE version, and architecture is displayed under DTK present on
system.
4. Click Browse and navigate to the DTK self-extractable zip file that you downloaded.
The selected DTK version, Windows PE version, and architecture is displayed under DTK selected for import.
5. Click Next.
The Boot Image Selection screen is displayed.
→ Packages.
9
Page 10

6. In Boot Image Properties, follow steps 3 to 8 in the Creating a Boot Image for Deploying Dell PowerEdge Servers
section for creating a boot image.
Creating a Boot Image for Deploying Dell PowerEdge Servers
To create boot image for deploying Dell PowerEdge Server:
1. Launch Configuration Manager Console.
2. From the left pane of the Configuration Manager Console, select Software Library → Overview → Operating
Systems → Boot Images.
3. Right-click Boot Images and select Dell PowerEdge Server Deployment → Create Dell Server Boot Image.
4. In Boot Image Selection, select any one of the following options:
NOTE: Make sure that you import a 64-bit version of DTK before selecting x64 boot images in any of the
following options.
Use Boot Image
from WAIK/ADK
tools
Use existing Boot
Image from
Configuration
Manager
Use a custom
Boot Image
NOTE: Only finalized images are supported if you select the Use a Custom Boot Image option for Windows PE
version 2.x.
NOTE: The Windows PE custom boot image should have XML, Scripting, and WMI packages installed on it.
For more information on how to install these packages, see the
available on your system.
5. Click Next.
The Boot Image Property screen is displayed.
6. Enter a name for the Dell boot image.
The Version and Comments fields are optional.
7. Click Create.
The boot image creation process begins. A progress bar shows the status of the boot image creation. Once the
boot image is created, the boot image details are displayed on the Summary screen, the information includes DTK
details, and success state.
8. Right-click each of the newly created boot images and perform the update and manage distribution points
operations.
Select this option to create both x64 and x86 Dell boot images. The source for the boot
image creation is obtained from Windows Automated Installation Kit (WAIK) and all the
Windows PE custom install packages are added to the boot image.
This option allows you to select an existing boot image in Configuration Manager. Select
the existing boot image from the drop-down list and use it to create a Dell boot image.
Select this option to import a custom boot image from any other location. Specify the
Universal Naming Convention (UNC) path of the Windows Imaging (WIM) file and select
the boot image from the drop-down list.
Microsoft Windows AIK documentation
NOTE: You can view the DTK configuration details only by using the PowerEdge Deployment ToolKit
Configuration Wizard.
10
Page 11
Enabling Command Prompt for Debugging Boot Images
NOTE: To display the debug console during deployment, press <F8>.
To enable command prompt to debug boot images:
1. Launch Configuration Manager Console.
2. From the left pane of the Configuration Manager Console, select Software Library → Overview → Operating
Systems → Boot Images.
3. Right-click on the boot image and select Properties.
4. In the Properties window, select the Customization tab and select Enable Command Prompt (testing only) check
box.
5. Click Apply, and proceed with distribute content and updating distribution points. For more information, see
Distributing Content and Updating Distribution Points.
Importing Dell Server Driver Packages
Dell Server Deployment Pack provides a wizard to create driver packages in Configuration Manager based on the
server-operating system combination, out of the drivers available in the
Documentation
DVD. These packages are used in the task sequences that are used for operating system deployment.
Dell Systems Management Tools and
1. Insert the
can download the latest ISO image of the DVD from
2. Launch Configuration Manager Console.
3. From the left pane of the Configuration Manager Console, select Software Library → Overview → Operating
Systems → Driver Packages.
4. Right-click Driver Packages, select Dell Server Driver Package → Import Dell PowerEdge Server Driver Packages.
The Dell PowerEdge Server Driver Package Import Wizard displays asking for the location of the Systems
Management DVD.
5. Select the drive in which you inserted the DVD and click Next.
A list of the driver packages for a combination of the servers and operating systems is displayed.
6. Select the required packages and click Finish.
A progress bar displays the status of the import. After the import is complete, the import summary is displayed.
7. Click Close.
Dell Systems Management Tools and Documentation
support.dell.com.
NOTE: If you have downloaded an ISO image, then create a physical disk or mount it on a virtual drive.
NOTE: Sections involving importing of drivers may take more time without updating the progress bar.
DVD version 6.2 (or later) in your system drive. You
Distributing Content and Updating Distribution Points
To update and manage distribution points:
1. Launch Configuration Manager Console.
2. From the left pane of the Configuration Manager Console, select Software Library → Overview → Application
Management
3. Right-click PowerEdge Deployment Toolkit Integration and click Update Distribution Points.
A message box prompting for a confirmation is displayed.
4. Click OK to update the distribution points.
→ Packages → Dell PowerEdge Deployment.
11
Page 12

5. Right-click PowerEdge Deployment Toolkit Integration and click Distribute Content.
The Distribute Content Wizard is displayed.
6. Click Next and proceed through the wizard to manage the distribution points. For more information, see the
Configuration Manager
7. Go to Overview → Boot Images → Operating Systems.
8. Right-click the boot image you created and click Distribute Content.
The Distribute Content Wizard screen is displayed.
9. Follow the instructions in the wizard to manage the distribution points.
10. To update and manage distribution points for the driver packages you imported, go to Driver Packages → Dell
PowerEdge Driver Packages <Dell OpenManage Version>.
The driver packages window is displayed.
11. Right-click each of the newly imported driver packages and perform the distribute content and update distribution
points operations.
Online Help
or the Configuration Manager documentation.
Configuring Your Servers Hardware Components
Configure the various components of the hardware on your server.
Creating a Task Sequence
You can create a task sequence to configure your server in two ways:
• Create a Dell-specific task sequence using PowerEdge Server Deployment template.
• Create a custom task sequence.
Creating a Dell Specific Task Sequence
To create a Dell-specific task sequence using PowerEdge Server Deployment template:
1. Launch Configuration Manager Console.
The Configuration Manager Console screen is displayed.
2. From the left pane of the Configuration Manager Console, select Software Library → Overview → Operating
Systems
3. Right-click Task Sequences, and then click Bare Metal Server Deployment → Create Dell PowerEdge Server
Deployment Template.
The Dell PowerEdge Server Deployment Task Sequence Wizard is displayed.
4. Type the name of the task sequence in Task Sequence Name field.
5. Select the boot image to use from the drop-down list.
6. Under Server Hardware Configuration, select the hardware items that you want to configure in this task sequence.
7. Under Operating System Installation, select the operating system installation type. The options are:
– Use an OS WIM image
– Scripted OS install
8. Select an operating system package from the Operating system package to use drop-down menu.
9. If you have a package with unattend.xml, then select it from the Package with unattend.xml info menu. Else, select
<do not select now>.
→ Task Sequences.
NOTE: It is recommended that you use the Dell custom boot image that you created.
12
Page 13

10. If Dell Lifecycle Controller Integration for Configuration Manager is installed on the server, select the Apply Drivers
from Dell Lifecycle Controller check box. For more information, see the
Configuration Manager User’s Guide
The Apply Drivers from Dell Lifecycle Controller option is enabled only when DLCI is installed and this option is
useful when a deployment is done using DLCI.
11. Click Create.
Click Close on the confirmation message box that is displayed.
.
Dell Lifecycle Controller Integration for
Creating a Custom Task Sequence
To create a custom task sequence:
1. Launch the Configuration Manager Console.
The Configuration Manager Console screen is displayed.
2. From the left pane of the Configuration Manager Console, select Software Library → Overview → Operating
Systems → Task Sequences.
3. Right-click Task Sequences, and then click Create Task Sequence.
The Create Task Sequence Wizard is displayed.
4. Select Create a new custom task sequence, and click Next.
5. Type Task sequence name and Description for the task sequence.
6. Browse for the Dell boot image that you had created, and click Next.
The Confirm the Settings screen is displayed.
7. Review your settings and click Next.
8. Click Close on the confirmation message box that is displayed.
Editing a Task Sequence
To edit a new task sequence or an existing task sequence:
1. Launch the Configuration Manager Console.
The Configuration Manager Console screen is displayed.
2. From the left pane of the Configuration Manager Console, select Software Library → Overview → Operating
Systems → Task Sequence.
3. Right-click the task sequence and click Edit.
The Task Sequence Editor window is displayed.
4. Click Add → Dell Deployment → PowerEdge Server Configuration.
This loads the custom action for your Dell server deployment.
NOTE: When editing a task sequence for the first time, an error message Setup Windows and ConfigMgr is
displayed, create and select the Configurations Manager Client Upgrade package to resolve the error. For
more information on creating packages, see the Configuration Manager 2012 documentation at
technet.microsoft.com.
You can now make changes to the task sequence accordingly. For more information on configuring task sequence
actions like system BIOS, RAID, DRAC, and iDRAC, see Configuring Task Sequence Actions.
13
Page 14

Adding Diskpart Clean To Task Sequence
To add diskpart clean to Task Sequence:
1. In Task Sequence Editor, click Add → General → Command Line.
2. Name it as Diskpart Clean.
3. Select input command line option diskpartclean.bat.
4. Select package Dell PowerEdge Deployment → Dell PowerEdge Custom Reboot Script 2.1.
Configuring Task Sequence Actions
When you select PowerEdge Server Configuration from the Task Sequence Editor, the following tabs are displayed:
• Action Settings
• Variable Replacement
• Logs/Return Files
This section explains about the Action Settings tab. For information on Variable Replacement tab, see Variable
Replacement. For information on Logs/Return Files tab, see Log/Return Files .
Configuring System BIOS
To configure your system BIOS:
1. Right-click the task sequence and click Edit.
2. From the left hand side of the Task Sequence Editor, under Configure Hardware → Step 1 , click Set BIOS Config
→ Action Settings tab.
(ini file)
3. Select BIOS Config (ini file) from the Configuration action type: drop-down menu.
The View button is enabled.
NOTE: You can also select BIOS Config (command line) if you want configure system using the CLI option. For
more information on the CLI option usage, see Command Line Options.
4. Click View to open the ini file. Make modifications as per the configurations required and save the file.
For information on the ini file format, see “Sample File Formats” in the
Version 4.4 Command Line Interface Reference Guide
5. Select Save to a file in the toolkit package for this custom action when I click OK, in the pop-up message, click OK,
and then click
6. Save the file in the default directory.
An example of default directory: \\<site server hostname>\sms_<site code>\OSD\lib\Packages\Deployment\Dell
\PowerEdge\DTK\Template\Configs\Syscfg.
7. Click Apply to save the edited file to the task sequence.
8. Select Set from the Action: drop-down menu.
The Configuration file/Command line parameters field is enabled. For more information see, Configuration file/
Command line Parameter Options.
Alternatively, you can select the <Create configuration file> option from the drop-down to create an ini file from the start.
14
OK.
available at dell.com/support/manuals.
Dell OpenManage Deployment Toolkit
Page 15

Configuration file/Command line Parameter Options
There are three options you can choose from:
• <Create configuration file>
• <Import configuration file>
• Edit <syscfg.ini>
CAUTION: When you update or save a new file in the package, it is not automatically updated on all of its
distribution points. To make sure that the new file is available to systems that need it, you must update the
distribution points from the Software Distribution→ Packages→ Dell PowerEdge Deployment→ Dell PowerEdge
Deployment ToolKit Integration <version> node.
<Create configuration file>
On selecting the <Create configuration file> option, the Create button is displayed.
1. Click Create.
2. Select one of the following options in the Configuration File Editor :
– Import File: Click this button to import an existing .ini file from a directory.
– You can also create an online .ini file in the Configuration File Editor field and click OK. This prompts you to save
the .ini file you created to a local drive or network share of your choice.
3. If you select the Save these changes to the existing file in the toolkit package when I click OK option, your
configuration is exported to a file when you click OK.
<Import configuration file>
On selecting the <Import configuration file> option, the Import button is displayed. Click Import to import an existing .ini
file.
Edit <syscfg.ini>
This is a sample BIOS.ini file.
NOTE: See the DTK documentation to get the appropriate values for the profiles.
1. Click View to see the existing syscfg.ini file.
2. In the Configuration File Editor window, you can edit the syscfg.ini file, select the Save these changes to the
existing file in the toolkit package when I click OK option and click OK.
After creating the .ini file using any of the preceding options listed, click Apply in the Task Sequence Editor window. The
task sequence for Set BIOS Config (ini file) is created.
Configuring Set Boot Order
To add a new set boot order step to a task sequence:
1. Right-click the task sequence and click Edit.
The Task Sequence Editor window is displayed.
2. Click Add → Dell Deployment → PowerEdge Server Configuration.
This loads the custom action for your Dell server deployment.
3. Select the Configuration action type as Boot Order and Action as Set.
4. Under Configuration file/Command line parameters, select --bootseq=virtualcd.slot.1. This sets the
boot order to boot from a virtual CD. To retrieve the boot device ids for a device, see Retrieving Boot Device IDs.
NOTE: See the
Dell Deployment Toolkit CLI Guide
for information on parameters for --bootseq option.
15
Page 16

Retrieving Boot Device IDs
To retrieve boot device IDs for a device:
1. Create a task sequence using DSDP:
a) Launch the Create Dell Task Sequence wizard.
b) In Server Hardware, select Set BIOS config.
c) Select the appropriate boot image, credentials and other inputs.
d) Click Create and Save the Task Sequence.
2. Edit the task sequence and set the details to get BIOS config.
a) Right-click on the task sequence and click Edit.
b) Delete the step Build the Reference Machine step as deploying OS is not required.
c) Click Set BIOS Config (ini file).
d) Change the action to Get.
e) In Configuration File/Command line parameters provide a filename. This filename is assigned to the BIOS config
file that is created after running the task sequence.
f) In the Log/Return Files tab, provide the share path and credentials of the location where you want to create the
file.
g) Save the task sequence.
3. Run the task sequence on the target for which you need to set the boot order.
A file is created in the mentioned share location with the specified file name.
4. Select a value for the bootseq attribute from the config file. For example: bootseq=nic.emb.1,cdrom.emb.
0,hdd.emb.0,virtualfloppy.slot.1,virtualcd.slot.1
Values separated by comma are the individual bootable devices in the target.
5. Select the device ID of the device which you want to set in the boot order. For example, hdd.emb.0.
Configuring RAID Using RAID Config (wizard)
The RAID Config (wizard) allows you to either create a new configuration file or import an existing configuration to
configure RAID on your systems.
For instance, to configure RAID by creating a new configuration file using the RAID Config (wizard). From the left-hand
side of the Task Sequence Editor, under Configure Hardware → Step1, click Set RAID Config (wizard).
Under Configuration file/Command line parameters there are three options you can choose from:
• <Create configuration file>
• <Import configuration file>
• <sample.xml>
<Create configuration file>
To create steps for RAID:
1. Select the sample ini file from the drop-down.
The View button is enabled.
2. Click View to open the ini file. Make modifications per the configurations required and save the file.
For information on the ini file format, see “Sample File Formats” in the
Version 4.4 Command Line Interface Reference Guide
Manuals.
3. Select Save to a file in the toolkit package for this custom action when I click OK, in the pop-up message, click OK,
and then click OK.
. You access guide from this URL: www.dell.com/support/
Dell OpenManage Deployment Toolkit
16
Page 17

4. Save the file in the default directory.
An example of default directory: \\<site server hostname>\sms_<site code>\OSD\lib\Packages\Deployment\Dell
\PowerEdge\DTK\Template\Configs\Raidcfg.
5. Click Apply to save the edited file to the task sequence.
Alternatively, you can select the <Create configuration file> option from the drop-down to create an ini file from the start.
<Import configuration file>
1. Select <Import configuration file> from the Configuration file/Command line parameters drop-down menu.
2. Click Import.
3. Specify the location of the configuration file you want to import and click Open.
<sample.xml>
1. Select <sample.xml> from the Configuration file / Command line parameters drop-down menu.
2. Click View.
The Array Builder wizard for the sample.xml is displayed.
3. To edit the sample.xml, see <Create configuration file>.
Using the Array Builder
Using Array Builder, you can define arrays/disk sets with all available RAID settings, logical drives/virtual disks of
varying sizes or use all available space, and assign hot spares to individual arrays or assign global hot spares to the
controller.
How Array Builder Works
When you run the task sequence on a target server, the array configuration utility detects the existing controller(s) on
the server as well as the disks attached to each controller. The custom action then tries to match the physical
configuration(s) the utility detected to the logical configurations you defined in the configuration rules. These array
configuration rules are defined using a graphical, logical layout that allows you to visualize how your array controllers
are configured. Rules are processed in the order displayed in the Array Builder tree, so you know exactly which rules
have priority.
You can define rules to match configurations based on detected slot number that the controller is in (or just the
embedded controller, if any), how many disks are attached to the controller, or simply apply a blanket configuration to
any controller the Array Builder finds. You can also apply configuration rules based on task sequence variables detected
on the server. This allows you to define different configurations to different servers even if the detected hardware is
identical.
Controllers
Controller elements contain variable condition elements. Controllers are one of several configuration types:
• The embedded controller
• A controller in slot "X"
• Any controller with "X" disks
• Any controller with "X" disks or more
• All remaining controllers
17
Page 18

When launching Array Builder from a <Create configuration file> selection in the deployment action, a default embedded
controller is created.
When a controller is created, a default variable condition, array and disk(s) are created to ensure a valid configuration.
You can choose to leave the controller unconfigured - with disks set to non-RAID, or you can add arrays or do other
actions.
Adding a Controller
1. To add a new controller, select a controller from the list, or select an embedded controller.
The Controllers drop-down menu is enabled.
2. Click Controllers → New Controller.
The Controller Configuration window is displayed.
3. Under Controller Selection Criteria, select from the following options:
Select the
controller located
in slot
Select any
controller with
<exactly, atleast>
<number of>
disks attached
Select all
remaining
controllers in the
system
regardless of
configuration
4. Under Variable Matching Criteria, you can set a rule to apply this configuration only if it matches certain criteria
that you select. Select
5. Click OK.
Type the slot number of the controller.
Set a rule to select any controller which matches exactly, or at least the number of disks
you have selected.
Set a rule to select all remaining controllers in the system regardless of configuration.
Apply this configuration only when variable to enable the rule setting options.
Editing a Controller
To edit a controller, select the controller and click Controllers → Edit Controller. On the Controller Configuration window,
you can make changes to your controller.
Deleting a Controller
1. To delete a controller, select the controller and click Controllers → Delete Controller.
A warning message that all the attached arrays and disks are deleted is displayed.
2. Click Yes to delete or No to cancel.
NOTE: On a server, you require at least one controller. If there is only one controller and you delete it, then a
message that the default controller was inserted because the last controller was deleted is displayed.
Variable Conditions
To provide the ability to use the same hardware configuration in multiple logical configurations, variable evaluation is
provided so that you can apply different configuration for arrays and logical drives to different situations.
18
Page 19

Variable condition elements contain arrays and global hot spares, and are of two types:
• No variables defined: This is the default configuration inserted with every controller, and you cannot remove or
move it from last in the order.
• Variables defined: This is where any variable is compared to a value using one of the pre-defined operators.
Adding a New Variable Condition
To add a new variable condition under an embedded controller:
1. Expand Embedded Controller, and select [No variable conditions defined].
2. Click Variables → New Variable Condition.
The Variable Condition Configuration window is displayed.
3. Under Variable Matching Criteria, you can set a rule to apply this variable only if it matches certain criteria that you
select.
4. Click OK to apply the variable condition, or Cancel to return to Array Builder.
Editing a Variable Condition
To edit a variable condition:
1. Select the variable condition and click Variables → Edit Variable Condition.
The Variable Condition Configuration window is displayed where you can make changes to your variable condition.
2. Click OK to apply the variable condition, or Cancel to return to Array Builder.
Deleting a Variable Condition
To delete a variable condition:
1. Select the variable condition and click Variables → Delete Variable Condition.
A message that all the attached arrays and disks are deleted is displayed.
2. Click Yes to delete or No to cancel.
Arrays
Array nodes include both RAID arrays and non-RAID disk groups (indicated by the different icons for RAID arrays and
non-RAID disks). By default, a non-RAID disk group is created when a controller is created. If the controller
configuration specifies the number of disks required, then the same number of disks are added to the non-RAID group.
• Arrays are added, modified or deleted depending on the controller configuration and number of disks available.
• Array elements contain logical drives and physical disks.
Adding a New Array
To add a new array under a variable condition:
1. Select a variable condition and click Arrays → New Array.
The Array Settings window is displayed.
2. Set the required RAID level from the Desired RAID Level drop-down menu.
3. Click OK to apply the array, or Cancel to return to the Array Builder.
19
Page 20

Editing an Array
To edit an array:
1. Select the array and click Arrays → Edit Array.
The Array Settings window is displayed. Here you can select a different RAID level for the array.
2. Click OK to apply the changes, or Cancel to return to the Array Builder.
Deleting an Array
To delete an array:
1. Select the array and click Arrays → Delete Array.
A message that all the attached disks will be deleted is displayed.
2. Click Yes to delete or No to cancel.
Logical Drives (also known as Virtual Disks)
Logical drives are present on RAID arrays and non-RAID groups. You can configure them by specifying the size (in GB)
or to consume all available (or remaining) space in the array. By default, a single logical drive is created for all new
arrays and is set to use all the available space.
When specific-size logical drives are defined, the using all remaining space logical drive will consume any remaining
space after other logical drive(s) are allocated their space on the array.
NOTE: Array Builder does not support creating logical drives under Non-RAID groups.
NOTE: You cannot delete a logical drive under Non-RAID disks in Array Builder.
Adding a New Logical Drive
To add a new logical drive under an array:
1. Select the array and click Logical Drives → New Logical Drive.
The Logical Drive Settings window is displayed.
2. Under Create a logical drive, enter the exact number of gigabytes the logical drive must contain.
3. Click OK to create the logical drive, or click Cancel to return to Array Builder.
Editing a Logical Drive
To edit a logical drive:
1. Select the logical drive and click Logical Drives → Edit Logical Drive.
The Logical Drive Settings window is displayed. Here you can change the size of the logical drive.
2. Click OK to apply the changes, or click Cancel to return to the Array Builder.
Deleting a Logical Drive
To delete a logical drive:
1. Select the logical drive and click Logical Drives → Delete Logical Drive.
A message to confirm the delete operation is displayed.
2. Click Yes to delete or No to cancel.
20
Page 21

Disks (also known as Array Disks)
You can include disks as part of the arrays (or the non-RAID disks node). These disks can be classified as:
• Standard disks — These are the basic, non-defined disk type that make up the storage on arrays.
• Hot Spares — These disks provide online redundancy if a RAID disk fails, and are assigned to a specific array.
• All Remaining Disks — These disks provide an option to define an array without specifying the exact number of disks
in it.
If the controller configuration specifies a number of disks required, then an equivalent number of disks are added to the
non-RAID group. If the controller specifies an exact quantity, then you cannot add or remove disks from the controller,
you can move them from array to array (or the non-RAID group). If the controller specifies a minimum number of disks,
then you can add or remove disks, else you cannot remove disks below the lower limit of the controller configuration.
Adding a New Disk
To add a new disk to an array, select the array and click Disks → New Disk.
You can choose from the following:
• Single disk
• Multiple disks
• Hot spare (only for the current array)
• Global hot spare (all arrays)
Changing a Disk
To change a disk, click on the disk and select Disks → Change Disk.
You can change a disk to:
• Standard disk
• Hot spare (only for the current array)
• Global hot spare (all arrays)
Deleting a Disk
To delete a disk, click on the disk and select Disks → Delete Disk.
Exporting to XML
This menu item allows you to save the current configuration in an XML file to a location of your choice. To make sure
that this configuration file is used, save it into the package. Else, the configuration is saved to a variable.
To export the current configuration to an XML file, click Export to XML.
Importing XML
This menu item allows you to search for and import an existing Array Builder XML file. Format the XML file properly, else
Configuration Manager automatically modifies the XML file and sends a notification of the change.
To import an existing Array Builder XML file from another location, click Import XML.
21
Page 22
Saving to Package
1. Select the Save these changes to the existing file in the toolkit package when I click OK option.
2. Click OK to save the configuration to an XML file.
CAUTION: When you update or save a new file in the package, it is not automatically updated on all of its
distribution points. To make sure that the new file is available to servers that need it, update the distribution points
from the Software Distribution → Packages → Dell PowerEdge Deployment → Dell PowerEdge Deployment
ToolKit Integration <version> node.
Creating Task Sequences for RAID, DRAC, and iDRAC
From the Configuration action type menu you can select the options listed in following table to create task sequences for
RAID, DRAC, and iDRAC.
Option Suboptions Description
RAID Configuration (.ini file) 5i-raid0.ini Sample file for RAID 0.
5i-raid1.ini Sample file for RAID 1.
5i-raid5.ini Sample file for RAID 5.
raidcfg.ini Use the existing raidcfg.ini file to
configure RAID. For a similar example,
see <Edit syscfg.ini>.
iscsicfg.ini Use the existing iscsicfg.ini file to
configure RAID. For a similar example,
see <Edit syscfg.ini>.
RAID Configuration (command line) None Use this option if you want to manually
configure the RAID tokens using the
CLI.
RAC Configuration (DRAC 5) <Create configuration file> For more information about the BIOS
option, see <Create configuration file>.
<Import configuration file> For more information about the BIOS
option, see <Import configuration file>.
rac5cfg.ini Use the existing rac5cfg.ini file to
configure DRAC 5. For a similar
example, see <Edit syscfg.ini>.
NOTE: Use DRAC configuration
(DRAC5) to configure Integrated
Dell Remote Access Controller
(iDRAC) on Dell PowerEdge
modular servers.
iDRAC Configuration (iDRAC 6) <Create configuration file> See <Create configuration file> for the
BIOS option.
xx0x
22
Page 23

Option Suboptions Description
<Import configuration file> For more information about the BIOS
option, see <Import configuration file>.
idrac6cfg.ini Use the existing idrac6cfg.ini file to
configure iDRAC 6. For a similar
example, see <Edit syscfg.ini>.
iDRAC Configuration (iDRAC 7) <Create configuration file> For more information about the BIOS
option, see <Create configuration file>.
<Import configuration file> For more information about the BIOS
option, see <Import configuration file>.
idrac7cfg.ini Use the existing idrac7cfg.ini file to
configure iDRAC 7. For a similar
example, see <Edit syscfg.ini>.
The hardware component sequences are displayed in the Task Sequence Editor after configuring the system BIOS,
RAID, DRAC, and iDRAC.
Variable Replacement
The Variable Replacement tab allows you to use and configure task variables like:
• System Variables
• Task Sequence Variables
• Machine Variables
• Collection Variables
Configuring Variable Replacement Tab
To configure the options on the Variable Replacement tab:
1. Select one of the following options under the Action to take when a variable is unintialized or the value is null or
blank section:
Use a null/blank
value
Fail the task Fails an action that cannot retrieve a valid variable value. This allows you to view what is
2. Select Search all text input files for variables to replace to do the following:
– Enable client-side scripts to search for and replace variables in the command line or within files specified.
– Replace variables with values found in the task sequence environment or the Windows system environment.
For optimum performance of the action clear the Search all text input files for variables to replace check box.
3. Select Replace %PASSWORD% variables with this password to replace any instances of a password in the Actions
with the password provided and confirmed
Uses a variable that has not been initialized or has a blank value. This allows the clients to
continue processing the action even if the variable is undefined or blank.
wrong with an action instead of trying to debug a failed command line or a incorrectly
configured system.
dialog box.
23
Page 24

4. Select Manually define additional variables to set additional variables on the system. To define the additional
variables:
a) Type a variable Name.
b) Type the variable Value.
c) Select the variable Type from the drop-down menu.
5. Click Apply and OK.
Log/Return Files
To retrieve the log files or capture configuration files:
1. Select Retrieve the task sequence log file from the client after this action runs.
2. Select Enable extended / debug logging by this action to get extensive information in the log files.
3. Select Retain network folder settings from a prior step, if available to copy any available network folder settings
from the previous step or to configure the network folder settings proceed to step 4.
4. Provide a valid network/local path to save the file.
5. Provide the domain and account name to access the path.
6. Provide and confirm the password.
7. If you have specified a network path on step 4, then select Map a drive letter to the network share above and then
select a drive letter from the drop-down menu.
8. Click Apply and OK.
Configuring the Task Sequence Steps to Apply Operating System Image And Driver Package
The scope of this document includes information only on the Dell Server Deployment Pack feature to apply operating
system image and add Dell drivers.
Applying the Operating System Image
NOTE: Before you begin this task, make sure that you have the required operating system image file (.wim file)
within the Operating System Images tree in the Configuration Manager.
To apply the operating system image:
1. From the left-hand side of the Task Sequence Editor, under Deploy Operating System, click Apply Operating System
Image.
2. Select from the following options:
– Apply operating system from a captured image
– Apply operating system from an original installation source
3. Browse and select the operating system location and click OK.
Adding Dell Driver Packages
To add Dell driver packages:
1. From the left-hand side of the Task Sequence Editor, under Deploy Operating System, click Apply Driver Package.
2. Click Browse.
The Select a Package window is displayed.
24
Page 25

3. Click Dell PowerEdge Driver Packages<OM Version>.
The list of driver packages available in the Dell Server Deployment Pack is displayed.
4. Select a package for a Dell PowerEdge server, such as, Dell R720-Microsoft Windows 2008x86 OM7.0.
5. Click Apply.
NOTE: After operating system deployment, make sure that the mass-storage driver installed is same as that
specified in the Task Sequence. If you find any differences, then update the driver manually.
Advertising a Task Sequence
After saving the task sequence, assign it to the collection of servers by advertising it. To advertise a task sequence:
Right-click the task sequence and select Deploy.
The Deploy Software Wizard is displayed.
Refer the Configuration Manager
NOTE: In the New Advertisement Wizard, select the Make this task sequence available to boot media and Preboot
Execution Environment (PXE) option.
Online Help
on how to advertise a task sequence.
Best Practices for Advertising a Task Sequence
• Always configure advertisements with the following settings when using PXE:
– Make the task sequence available to boot media and PXE.
– Distribution Points: Access content directly from a distribution point when needed by the running task sequence.
– Interaction: Show task sequence progres.
• Always configure Windows PE boot images with the following settings:
– Windows PE: Enable command support (testing only)
• For the following packages, right-click and select Properties, click on the Data Access tab and select the Copy the
Contents of this Package to a package share on distribution points check box, then click on the Distribution Settings
tab and select the Automatically download content when packages are assigned to distribution points radio button.
– Dell PowerEdge Deployment Toolkit Integration 2.0
– Configuration Manager Client Upgrade Package
– Boot images
– Operating System Images
– Driver Packages
Deploying a Task Sequence
NOTE: DSDP does not support the Standalone Media method to create Task Sequence Media
Now that the task sequence is ready, use any of the following methods to deploy the task sequence you have created:
• Deploy through a CD
• Deploy through a USB
• Deploy through PXE
For more information on how to deploy a task sequence using the preceding methods, see the Configuration Manager
Online Help
.
25
Page 26

26
Page 27

Using the Dell Server Deployment Pack on Systems Running Configuration Manager 2007
The chapter will help you to use Dell Server Deployment Pack on systems running Configuration Manager 2007.
Importing a DTK Package
NOTE: Download the latest DTK pack from support.dell.com.
To import a DTK package and create a Dell boot image:
1. Launch Configuration Manager by clicking Start → Microsoft System Center → Configuration Manager 2007 →
Configuration Manager Console.
The Configuration Manager Console screen is displayed.
2. From the left pane of the Configuration Manager Console, select Site Database → Computer Management →
Software Distribution → Packages → Dell PowerEdge Server Deployment.
3. Right-click Dell PowerEdge Server Deployment and select Dell PowerEdge Server Deployment → Launch
Deployment ToolKit Configuration Wizard.
The PowerEdge Deployment ToolKit Configuration Wizard screen is displayed. If there is an existing DTK package
on the server, then the DTK version is displayed in the DTK Zip Details field.
4. Click Browse and navigate to the DTK self-extractable zip file that you downloaded.
The selected DTK version, Windows PE version, and architecture is displayed under DTK Zip Details.
5. If there is no existing DTK package present in the server, or if the version selected is newer than the existing
version, click Next.
The Boot Image Property screen is displayed.
4
NOTE: Dell Server Deployment Pack 2.1 does not support downgrading or re-importing the same version of
DTK.
6. Follow step 3 to 11 under the Creating a Boot Image for Deploying Dell PowerEdge Servers section for creating a
boot image.
Upgrading a DTK Package
To upgrade a DTK package:
1. Launch Configuration Manager by clicking Start → Microsoft System Center → Configuration Manager 2007 →
Configuration Manager Console.
The Configuration Manager Console screen is displayed.
2. From the left pane of the Configuration Manager Console, select Site Database → Computer Management →
Software Distribution → Packages → Dell PowerEdge Server Deployment.
27
Page 28

3. Right-click Dell PowerEdge Server Deployment and select Dell PowerEdge Server Deployment → Launch
Deployment ToolKit Configuration Wizard.
The PowerEdge Deployment ToolKit Configuration Wizard screen is displayed. The existing DTK version present on
the server is displayed in the DTK Zip Details field.
4. Click Browse and navigate to the DTK self-extractable zip file that you downloaded. The selected DTK version,
Windows PE version, and architecture is displayed under DTK Zip Details.
5. Click Next.
The Boot Image Property screen is displayed.
6. Follow steps 3 to 8 under the Creating a Boot Image for Deploying Dell PowerEdge Servers section for creating a
boot image.
Creating a Boot Image for Deploying Dell PowerEdge Servers
To create a boot image for deploying Dell PowerEdge servers:
1. Launch Configuration Manager by clicking Start → Microsoft System Center → Configuration Manager 2007 →
Configuration Manager Console.
The Configuration Manager Console screen is displayed.
2. From the left pane of the Configuration Manager Console, select Site Database → Computer Management →
Operating System Deployment → Boot Images.
3. Right-click Boot Images and select Dell PowerEdge Server Deployment → Create Dell Server Boot Image.
4. In Boot Image Selection, select any one of the following options:
NOTE: Make sure that you import a 64-bit version of DTK before selecting x64 boot images in any of the
following options.
Obtain the Boot
Image from WAIK
Use Existing Boot
Image from
Configuration
Manager
Use a Custom
Boot Image
NOTE: Only finalized images are supported if you select the Use a Custom Boot Image option for Windows PE
version 2.x.
NOTE: The Windows PE custom boot image should have XML, Scripting, and WMI packages installed on it.
For more information on how to install these packages, see the
available on your system.
5. Click Next.
The Boot Image Property screen is displayed.
6. Type a name for the Dell boot image.
NOTE: The Version and Comments fields are optional.
7. Select Enable Unknown Computer Support for this Boot Image to enable unknown computer support.
A warning that the boot image is used only for unknown computer deployment is displayed.
Select this option to create both x64 and x86 Dell boot images. The source for the boot
image creation is obtained from Windows Automated Installation Kit (WAIK) and all the
Windows PE custom install packages are added to the boot image.
This option allows you to select an existing boot image in Configuration Manager. Select
the existing boot image from the drop-down list to create a Dell boot image.
Select this option to import a custom boot image from any other location. Specify the
Universal Naming Convention (UNC) path of the Windows Imaging (WIM) file and select
the boot image from the drop-down list.
Microsoft Windows AIK documentation
28
Page 29

8. Click OK.
9. Click Browse. In the Collection selector screen, select the collection to which the unknown computer is added
during the operating system deployment.
NOTE: Make sure that you do not select the Configuration Manager created All Unknown Computers
collection.
10. Click Create. The boot image creation process begins. A progress bar displays the status of the boot image
creation. Once the boot image is created, the boot image details, DTK details, and success state is displayed in the
Summary screen.
11. Right-click each of the newly created boot images and perform the update and manage distribution points
operations.
NOTE: You can view the DTK configuration details only by using the PowerEdge Deployment ToolKit
Configuration Wizard.
Updating and Managing Distribution Points
To update and manage distribution points:
1. Launch Configuration Manager by clicking Start → Microsoft System Center → Configuration Manager 2007 →
Configuration Manager Console.
The Configuration Manager Console screen is displayed.
2. From the left pane of the Configuration Manager Console, select Site Database → Computer Management →
Software Distribution → Packages → Dell PowerEdge Deployment.
3. Under Dell PowerEdge Deployment, two packages are available — Dell PowerEdge Custom Reboot Script and Dell
PowerEdge Deployment ToolKit Integration
Distribution Points.
The Confirm Update Distribution Points screen is displayed.
4. Confirm to update the distribution points.
5. Right-click Dell PowerEdge Custom Reboot Script → Manage Distribution Points.
The Manage Distribution Point Wizard is displayed.
6. Click Next and proceed through the wizard to manage the distribution points. See the Configuration Manager online
help or the Configuration Manager documentation for details.
7. Repeat step 1 through step 6 for Dell PowerEdge Deployment ToolKit Integration and ConfigMgr Client Package
(under Packages).
8. From the left pane of the Configuration Manager Console, select Site Database → Computer Management →
Operating System Deployment → Boot Images → Dell Deployment.
9. Right-click on the boot image that you created, and click Manage Distribution Points.
The Manage Distribution Point Wizard screen is displayed.
10. Proceed through the wizard to manage the distribution points.
11. Repeat step 8 and step 9 for all the other boot images that you created.
Similarly, use the Manage and Update Distribution Points wizard to update and manage the operating system
images to distribution points.
. Right-click Dell PowerEdge Custom Reboot Script and click Update
29
Page 30

Importing Dell Server Driver Packages
Dell Server Deployment Pack provides a wizard to create driver packages in Configuration Manager based on the
server-operating system combination, out of the drivers available in the
Documentation
DVD. These packages are used in the operating system deployment task sequences.
Dell Systems Management Tools and
1. Insert the
can download the latest ISO image of the DVD from www.support.dell.com.
2. From the left pane of the Configuration Manager Console, select Site Database → Computer Management →
Operating System Deployment → Driver Packages.
3. Right-click Driver Packages → Dell Server Driver Package. Select Import Dell PowerEdge Server Driver Packages.
4. On the Dell PowerEdge Server Driver Package Import Wizard screen you can:
– Select the drive in which you inserted the
– Browse and select the
A list of the driver packages for a combination of the servers and operating systems is displayed.
5. Select the required packages and click Finish.
A progress bar displays the status of the import. After the import is complete, the import summary is displayed.
6. Click Close.
7. To update and manage distribution points for the driver packages you imported, go to Driver Packages → Dell
PowerEdge Driver Packages <Dell OpenManage Version>
The driver packages window is displayed.
8. Right-click each of the newly imported driver packages and perform the update and manage distribution points
operations.
Dell Systems Management Tools and Documentation
Dell Systems Management Tools and Documentation
Next.
Dell Systems Management Tools and Documentation DVD
NOTE: Sections involving importing of drivers may take more time without updating the progress bar.
DVD version 6.2 (or later) in your system drive. You
DVD and click
ISO image and click Next.
.
Enabling Command Prompt for Debugging Boot Images
To enable command prompt to debug boot images:
1. On the left-hand pane, click Operating System Deployment → Boot Images.
2. Right-click on the boot image and select Properties.
3. In the Properties window, select Windows PE tab and select Enable Command Prompt check box.
4. Click Apply, and proceed with updating and managing the distribution points. For more information, see Updating
and Managing Distribution Points.
NOTE: To display the debug console during deployment, press <F8>.
Configuring Your Servers Hardware Components
Configuring the various components of the hardware on your server.
Creating a Task Sequence
You can create a task sequence to configure your server in two ways:
• Create a Dell-specific task sequence using PowerEdge Server Deployment template.
30
Page 31

• Create a custom task sequence.
Creating a Dell Specific Task Sequence
To create a Dell-specific task sequence using PowerEdge Server Deployment template:
1. Launch Configuration Manager by clicking Start → Microsoft System Center → Configuration Manager 2007 →
Configuration Manager Console.
The Configuration Manager Console screen is displayed.
2. From the left pane of the Configuration Manager Console, select Site Database Computer Management Operating
System Deployment.
3. Right-click Task Sequences, and then click Bare Metal Server Deployment → Create Dell PowerEdge Server
Deployment Template.
The Dell PowerEdge Server Deployment Task Sequence Wizard is displayed.
4. Type the name of the task sequence in Task Sequence Name field.
5. From the drop-down list, select the boot image to use.
NOTE: It is recommended that you use the Dell custom boot image that you created.
6. Under Server Hardware Configuration, select the hardware items that you want to configure in this task sequence.
7. Under Operating System Installation, select the operating system installation type. The options are:
– Use an OS WIM image
– Scripted OS install
8. Select an operating system package from the Operating system package to use drop-down menu.
9. If you have a package with unattend.xml, then select it from the Package with unattend.xml info menu. Else, select
<do not select now>.
10. If Dell Lifecycle Controller Integration for Configuration Manager is installed on the server, then select the Apply
Drivers from Dell Lifecycle Controller check box. For more information, see the
for Configuration Manager User’s Guide
11. Click Create.
A confirmation message is displayed.
.
Dell Lifecycle Controller Integration
Creating a Custom Task Sequence
To create a custom task sequence:
1. Launch Configuration Manager by clicking Start → Microsoft System Center → Configuration Manager 2007 →
Configuration Manager Console.
The Configuration Manager Console screen is displayed.
2. From the left pane of the Configuration Manager Console, select Site Database → Computer Management →
Operating System Deployment.
3. Right-click Task Sequences, then New → Task Sequence.
The New Task Sequence Wizard is displayed.
4. Select Create a new custom task sequence and click Next.
5. Type Task sequence name and Description for the task sequence.
6. Browse for the Dell boot image that you had created, and click Finish.
A confirmation message is displayed.
31
Page 32

Editing a Task Sequence
To edit a new task sequence or an existing task sequence:
1. Launch Configuration Manager by clicking Start → Microsoft System Center → Configuration Manager 2007 →
Configuration Manager Console.
The Configuration Manager Console screen is displayed.
2. From the left pane of the Configuration Manager Console, select Site Database → Computer Management →
Operating System Deployment → Task Sequences.
3. Right-click the task sequence and click Edit.
The Task Sequence Editor window is displayed.
4. Click Add → Dell Deployment → PowerEdge Server Configuration.
This loads the custom action for your Dell server deployment.
If you are creating a task sequence for the first time, then a message asking you whether you are adding any array
configuration task to this task sequence is displayed.
5. Click Yes to use the Dell specific template and avoid any potential Windows Preinstallation Environment (Windows
PE) issue.
A description of the potential Windows PE issue is displayed.
6. Click OK to continue or Cancel to quit.
7. Click OK.
The Dell PowerEdge Server Deployment Task Sequence Wizard is displayed.
You can now make changes to the task sequence accordingly. Next, you can configure your system BIOS, RAID, DRAC,
and iDRAC. For more information, see Configuring Task Sequence Actions.
Rebooting to PXE USB Custom Action on Systems Running Configuration Manager 2007
Windows Preinstallation Environment (Windows PE) may have an issue when you add a system hardware configuration
action to a task sequence. Windows PE will not correctly recognize any newly-created disk partitions or any significant
change to the disk structure created after the initial Windows PE boot. This will cause the task sequence to fail at any
task that writes data to the disk (including the standard Configuration Manager reboot task).
To resolve this issue, you must insert custom reboot actions after you create and partition a disk. If you are using Preboot eXecution Environment (PXE) instead of boot media, then you must reset the PXE advertisement in order to reboot
back into PXE.
You can insert the Reboot to PXE/USB Custom Action into a task sequence in one of the following ways:
• Reboot to PXE/USB Custom Action is created automatically when a task sequence is created using the Dell
PowerEdge Server Deployment template.
• Reboot to PXE/USB Custom Action is created automatically when you edit a task sequence. For more information,
see Editing a Task Sequence.
• Reboot to PXE/USB Custom Action is created manually when from the Task Sequence Editor you click Add → Dell
Deployment → Reboot to PXE/USB.
To automate the reboot process, insert a Set Boot Order step before the Reboot to PXE/USB Custom Action step. To
insert the step automatically, select the Set Boot Order check box from the Dell PowerEdge Server Task Sequence
Wizard. For more information on configuring Set Boot Order, see the Configuring Set Boot Order section.
CAUTION: It is recommended that you do not move or delete the Set RebootStep, Reboot to PXE/USB, and Reset
RebootStep Custom Action steps in the task sequence.
32
Page 33

CAUTION: It is recommended that you delete the computer variable for any computer that has failed the task
sequence. This ensures that the task sequence restarts from the beginning.
Advertising a Task Sequence
After saving the task sequence, assign it to the collection of servers by advertising it. To advertise a task sequence:
Right-click on the task sequence and select Advertise.
The New Advertisement Wizard window is displayed.
Refer the Configuration Manager
NOTE: In the New Advertisement Wizard, make sure that you check the option Make this task sequence available
to boot media and Preboot Execution Environment (PXE).
Online Help
on how to advertise a task sequence.
Best Practices for Advertising a Task Sequence
• Always configure advertisements with the following settings when using PXE:
– Make the task sequence available to boot media and PXE.
– Schedule: Mandatory assignment: As soon as possible.
– Schedule: Program rerun behavior: Always rerun program.
– Distribution Points: Access content directly from a distribution point when needed by the running task sequence.
– Interaction: Show task sequence progress.
• Always configure Windows PE boot images with the following settings:
– Windows PE: Enable command support (testing only).
– Two advertisements are required while using a PXE boot media with the Unknown Computer support feature.
One for the All Unknown Computers collection, and one for the known collection that you specified during boot
image creation. The second advertisement will typically contain all the steps for hardware configuration and
operating system deployment. Make sure that you clear the last PXE advertisement from the All Unknown
Computers collection to boot to Windows PE successfully.
Deploying a Task Sequence
Now that the task sequence is ready, use any of the following methods to deploy the task sequence you have created:
• Deploy through a CD
• Deploy through a USB
• Deploy through PXE
For more information on how to deploy a task sequence using the above methods, see the Configuration Manager
Help
.
Online
33
Page 34

34
Page 35

Troubleshooting
NOTE: Before you run the sample commands provided in the troubleshooting section, see the DTK documentation
and if required recreate the commands based on machine configuration.
Task Sequences Fail or Act Incorrectly After an Upgrade on Configuration Manager 2007 SP2
In order for the task sequences to function correctly on systems running Configuration Manager 2007 SP2:
1. Launch the task sequence editor. For more information see, Editing a Task Sequence.
2. Remove the Set RebootStep Variable step in the task sequence.
3. Remove all the Reboot to PXE/USB steps in the task sequence.
4. Remove Reset RebootStep Variable step in the task sequence.
5. Remove the Step 2 group.
6. Remove the RebootStep variable condition present in Step 1, Step 3, and Deploy Operating System groups.
Operating System Deployment Fails in Microsoft Windows Server 2003
When the operating system deployment fails in Microsoft Windows Server 2003:
5
1. Make sure that you select the appropriate mass storage controller driver in the Apply Driver Package step of the
task sequence.
2. Uninstall and reinstall the Dell Server Deployment Pack Version 2.0, and then use the PowerEdge Deployment
ToolKit Configuration Wizard to re-import the same version, or import an older version of Deployment ToolKit into
Configuration Manager.
3. After uninstalling the Dell Server Deployment Pack, delete the shortcuts from the Start menu, if available.
If you are upgrading the Dell Server Deployment Pack, delete the shortcuts of the previous version from the Start
menu, if available.
NOTE: While importing a computer, make sure that the computer name you enter starts with a letter. Else, the
deployment will fail.
35
Page 36

DTK Configuration wizard completes with errors
When the DTK configuration wizard completes with errors, while importing the DTK package on systems running
Configuration Manager 2007:
1. Check if the log file contains text similar to Utilities::ExtractDTK: Exception occurred during
extraction.
When the preceding text exists, it is due to a driver catalog file that is in use by the WMI process.
2. Restart the WMI process.
CAUTION: The WMI process is a common service used by other applications.
3. Retry the DTK package import operation to import it successfully.
36
Page 37
Command Line Options
DSDP supports the command line options supported in Dell Deployment Toolkit.
For more information on the command line options, usage guidelines, and syntax, see
Toolkit Version 4.4 Command Line Interface Reference Guide
syntax, for the commands to run in DSDP.
The SYSCFG and RAIDCFG commands are supported in DSDP
• SYSCFG — The Deployment Toolkit (DTK) system configuration utility SYSCFG commands enable you to run
commands to get information on configuration file format, and individual executables used to configure server BIOS,
DTK state settings, and system information including PCI device detection.
• RAIDCFG — The Deployment Toolkit (DTK) RAID configuration utility RAIDCFG provides commands to configure all
supported RAID controllers.
When using the SYSCFG commands, do the following changes to the commands, for example:
NOTE: To get correct results, it is recommended that you type command line options in the Task Sequence wizard.
—acpower
. However, you must do the following changes to the
Dell OpenManage Deployment
6
Option
Valid Arguments on, off, last
Description Sets the behavior for the system after AC power is lost. This option specifies
Applicable Systems All Dell PowerEdge systems prior to PowerEdge 12G systems.
When using this command in DSDP, remove syscfg and run the command
--acpower=on acpower=on
When using the RAIDCFG commands, do the following changes to the commands, for example:
The following table lists the RAIDCFG options, parameters, and pre-defined arguments for setting the name of a virtual
disk on a controller.
Mandatory Options
and Arguments
-vd -vd=id ac=svdn - vdn=
<string> -
Optional Parameters Valid Parameters
NA NA
--acpower
how the system responds to the restoration of AC power and is particularly
useful in systems that are turned off using a power strip. When set to on, the
system turns on after AC is restored. When set to off, the system does not turn
on after AC is restored. When set to
on when AC power was lost; if the system was off when AC power was lost, the
system remains off when power is restored. This option can be replicated.
Example:
A:>syscfg --acpower=on acpower=on
Arguments
last, the system turns on if the system was
Description
Sets the name of the specified virtual disk on
the specified controller.
37
Page 38
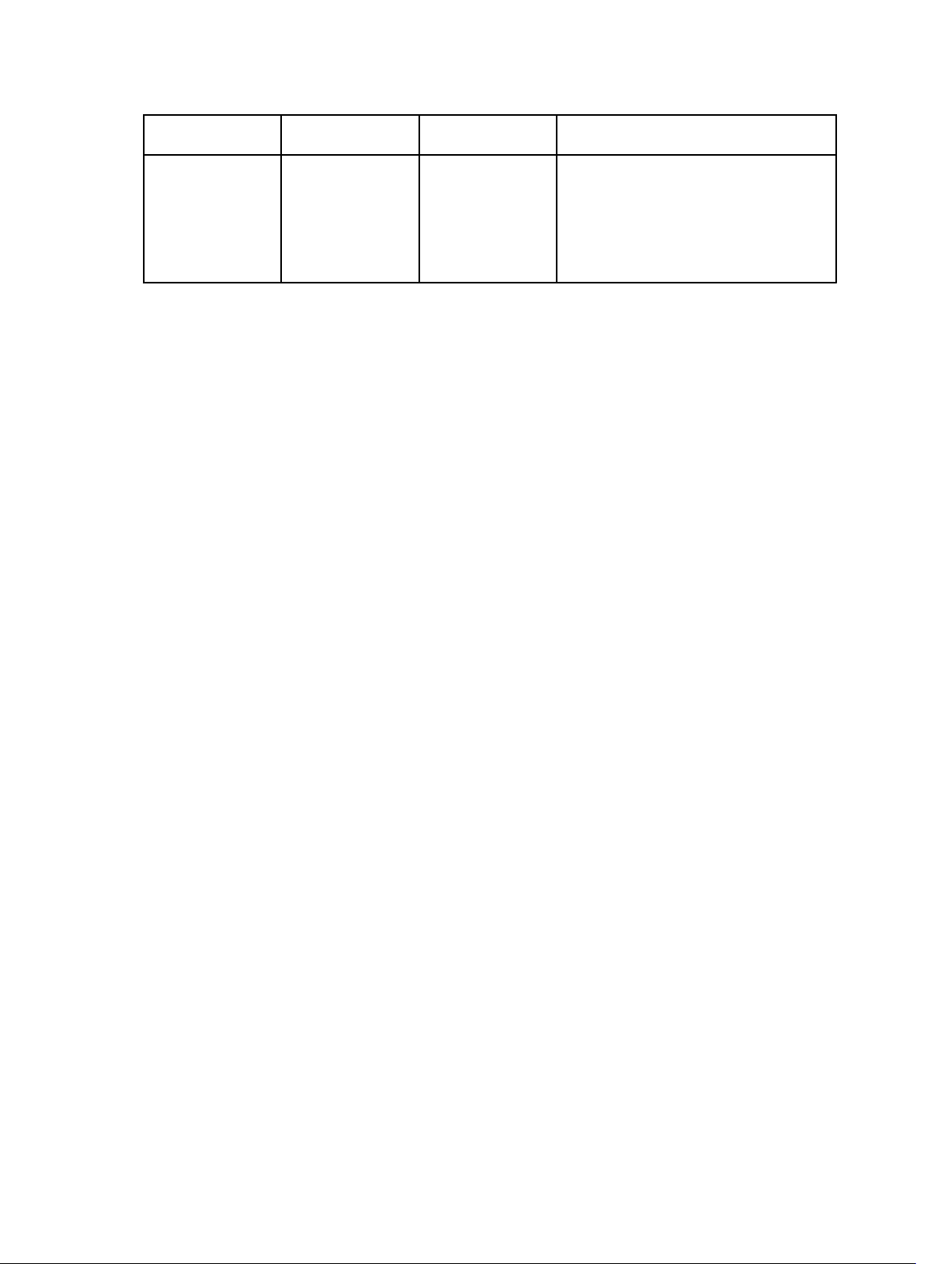
Mandatory Options
and Arguments
c=id or vdisk
vdisk= id
action=
setvdname
vdname=<string
>
controllerid=
id
When using this command in DSDP, remove raidcfg and run the command.
-vd -vd=2 -ac=svdn -vdn=xxx -c=2 RAIDCFG Command successful!
Optional Parameters Valid Parameters
Arguments
Description
Example:
A:>raidcfg -vd -vd=2 -ac=svdn vdn=xxx -c=2
RAIDCFG Command successful!
38
Page 39

Other Dell Documents You Might Need
In addition to this guide and the online help, you might need to refer the following documents to get details on specific
Dell OpenManage products. These documents are available at dell.com/support/manuals.
• The
Dell Server Deployment Pack Version 2.1 for Microsoft System Center Configuration Manager Installation Guide
provides information about installing DSDP 2.1 on your system.
• The
Dell Remote Access Controller 5 Firmware User's Guide
RACADM command line utility to configure DRAC 5.
• The
Dell Chassis Management Controller User's Guide
controller that manages all modules in the chassis containing your Dell server.
• The
Integrated Dell Remote Access Controller User's Guide
and maintenance of the Integrated Dell Remote Access Controller (iDRAC) on management and managed systems.
• The
Dell Remote Access Controller/Modular Chassis User's Guide
configuration, and maintenance of the Dell Remote Access Controller/Modular Chassis (DRAC/MC).
• The
Command Line Reference Guide for iDRAC6 and CMC
RACADM command line utility.
• The
Dell OpenManage Deployment ToolKit User's Guide
the basic tasks for a successful deployment using Windows Preinstallation Environment (Windows PE) or embedded
Linux.
• The
Dell OpenManage Deployment ToolKit version 4.4 Command Line Interface Reference Guide
information on the command line utilities to configure system features.
• The
Server Update Utility User's Guide
• The
Dell Repository Manager User’s Guide
repositories for servers running on Microsoft Windows operating systems.
• The
Glossary
for information on terms used in this document.
provides information on how to identify and apply updates to your system.
provides information on how to create customized bundles and
provides comprehensive information about using the
provides comprehensive information about using the
provides information about installation, configuration,
provides information about installation,
provides comprehensive information about using the
provides general, best practices procedures that focus on
provides
7
Contacting Dell
NOTE: If you do not have an active Internet connection, you can find contact information on your purchase
invoice, packing slip, bill, or Dell product catalog.
Dell provides several online and telephone-based support and service options. Availability varies by country and
product, and some services may not be available in your area. To contact Dell for sales, technical support, or customer
service issues:
1. Go to dell.com/contactdell.
2. Verify your country or region from the drop-down menu at the top left corner of the page.
3. Select your support category: Technical Support, Customer Support, Sales, or International Support Services.
4. Select the appropriate service or support link based on your requirement.
NOTE: If you have purchased a Dell system, you may be asked for the Service Tag.
Accessing Documents From Dell Support Site
You can access the required documents in one of the following ways:
39
Page 40

• From the following links:
– For all Systems Management documents — dell.com/softwaresecuritymanuals
– For Enterprise Systems Management documents — dell.com/openmanagemanuals
– For Remote Enterprise Systems Management documents — dell.com/esmmanuals
– For Serviceability Tools documents — dell.com/serviceabilitytools
– For Client Systems Management documents — dell.com/OMConnectionsClient
– For OpenManage Connections Enterprise Systems Management documents — dell.com/
OMConnectionsEnterpriseSystemsManagement
– For OpenManage Connections Client Systems Management documents — dell.com/OMConnectionsClient
• From Dell Support site as follows:
– Go to dell.com/support/manuals.
– In the Tell us about your Dell system section, under No, select Choose from a list of all Dell products and click
Continue.
– In the Select your product type section, click Software and Security.
– In the Choose your Dell Software section, click the required link from the following:
* Client System Management
* Enterprise System Management
* Remote Enterprise System Management
* Serviceability Tools
– To view the document, click the required product version.
• Using search engines as follows:
– Type the name and version of the document in the Search box.
40
 Loading...
Loading...