Page 1

Dell MD Storage Array VMware vStorage APIs For
Storage Awareness (VASA) Provider
User's Guide
Regulatory Model: E16S Series
Regulatory Type: E16S001
Page 2

Notes, Cautions, and Warnings
NOTE: A NOTE indicates important information that helps you make better use of your computer.
CAUTION: A CAUTION indicates either potential damage to hardware or loss of data and tells you how to avoid the
problem.
WARNING: A WARNING indicates a potential for property damage, personal injury, or death.
© 2013 Dell Inc.
Trademarks used in this text:
PowerConnect
Inc.
Intel
is a registered trademark and
Microsoft
or registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation in the United States and/or other countries.
Enterprise Linux
™
OpenManage
,
®
®
®
Pentium
,
Windows
,
Xeon
,
®
,
®
are registered trademarks of Red Hat, Inc. in the United States and/or other countries.
registered trademarks of Novell Inc. in the United States and other countries.
and/or its affiliates.
Citrix
the United States and/or other countries.
™
Dell
, the Dell logo,
™
EqualLogic
,
®
®
Core
,
and
AMD Opteron
Windows Server
®
®
,
,
Xen
XenServer
Dell Boomi
™
Compellent
,
®
Celeron
are registered trademarks of Intel Corporation in the U.S. and other countries.
™
AMD Phenom
,
®
Internet Explorer
,
®
and
XenMotion
®
VMware
trademarks of VMware, Inc. in the United States or other countries.
,
vMotion
™
Dell Precision
,
™
KACE
,
™
AMD Sempron
and
®
MS-DOS
,
®
are either registered trademarks or trademarks of Citrix Systems, Inc. in
®
,
vCenter
IBM
™
FlexAddress
,
®
Windows Vista
,
,
™
Oracle
®
,
vCenter SRM
®
is a registered trademark of International Business Machines
™
OptiPlex
,
™
Force10
,
™
are trademarks of Advanced Micro Devices, Inc.
®
and
®
is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation
™
and
Corporation.
2013 - 05
Rev. A08
™
Latitude
,
™
Vostro
and
Active Directory
®
Red Hat
®
vSphere
PowerEdge
™
PowerVault
,
™
are trademarks of Dell
™
AMD
®
are either trademarks
Red Hat
®
and
®
SUSE
®
are
and
Novell
are registered trademarks or
,
®
Page 3

Contents
1 Overview.......................................................................................................................................5
VASA Storage Capabilities....................................................................................................................................... 6
Profile-Driven And Policy-Based Storage................................................................................................................ 8
Storage Service-Level Agreements...................................................................................................................8
Storage Distributed Resource Scheduler.................................................................................................................8
VASA Session Communications............................................................................................................................... 8
2 Installing The VASA Provider....................................................................................................9
Before You Install..................................................................................................................................................... 9
Supported Operating Systems And Platforms................................................................................................... 9
Supported Host Operating Systems...................................................................................................................9
Required VMware Application Platforms.......................................................................................................... 9
Supported MD Series Storage Arrays............................................................................................................... 9
Required RAID Controller Module Firmware....................................................................................................10
Downloading The VASA Provider...........................................................................................................................10
Installing The VASA Provider................................................................................................................................. 10
Uninstalling The VASA Provider............................................................................................................................. 10
3 Using The VASA Provider........................................................................................................ 11
Bringing Storage Arrays Under VASA Management............................................................................................. 12
Adding Your Storage Arrays To VASA Control.................................................................................................12
To Register The VASA Provider In Your vSphere Client.................................................................................. 13
Verifying VASA Registration.............................................................................................................................15
Working with Storage Profiles................................................................................................................................16
Assigning VM Storage Profiles To Existing Virtual Machines......................................................................... 17
Checking Storage Profile Compliance............................................................................................................. 18
Storage Array Events And Alerts............................................................................................................................19
Troubleshooting Tips.............................................................................................................................................. 19
Troubleshooting Logs.......................................................................................................................................20
Configuration Reset..........................................................................................................................................20
4 Getting Help................................................................................................................................21
Locating Your System Service Tag.........................................................................................................................21
Contacting Dell....................................................................................................................................................... 21
Documentation Feedback.......................................................................................................................................21
Page 4

4
Page 5

1
Overview
VMware vStorage APIs for Storage Awareness (VASA) is a set of application program interfaces (APIs) that support Dell
PowerVault MD-Series iSCSI and Fibre Channel storage arrays. VASA enables vSphere vCenter to recognize MD
storage array features and corresponding datastores, which allows storage administrators to more easily set
virtualization and maintenance policies.
Using the VASA provider on an MD storage array also allows a vCenter-based storage administrator to:
• See information about MD-attached expansion storage.
• Discover and characterize an attached datastore’s static capabilities, which helps in selecting the appropriate
disk for virtual machine (VM) placement.
• Receive alert and event notifications from the MD storage arrays managed in vCenter.
The following figure shows the high-level VASA provider architecture and how it integrates with the vCenter
management environment.
5
Page 6
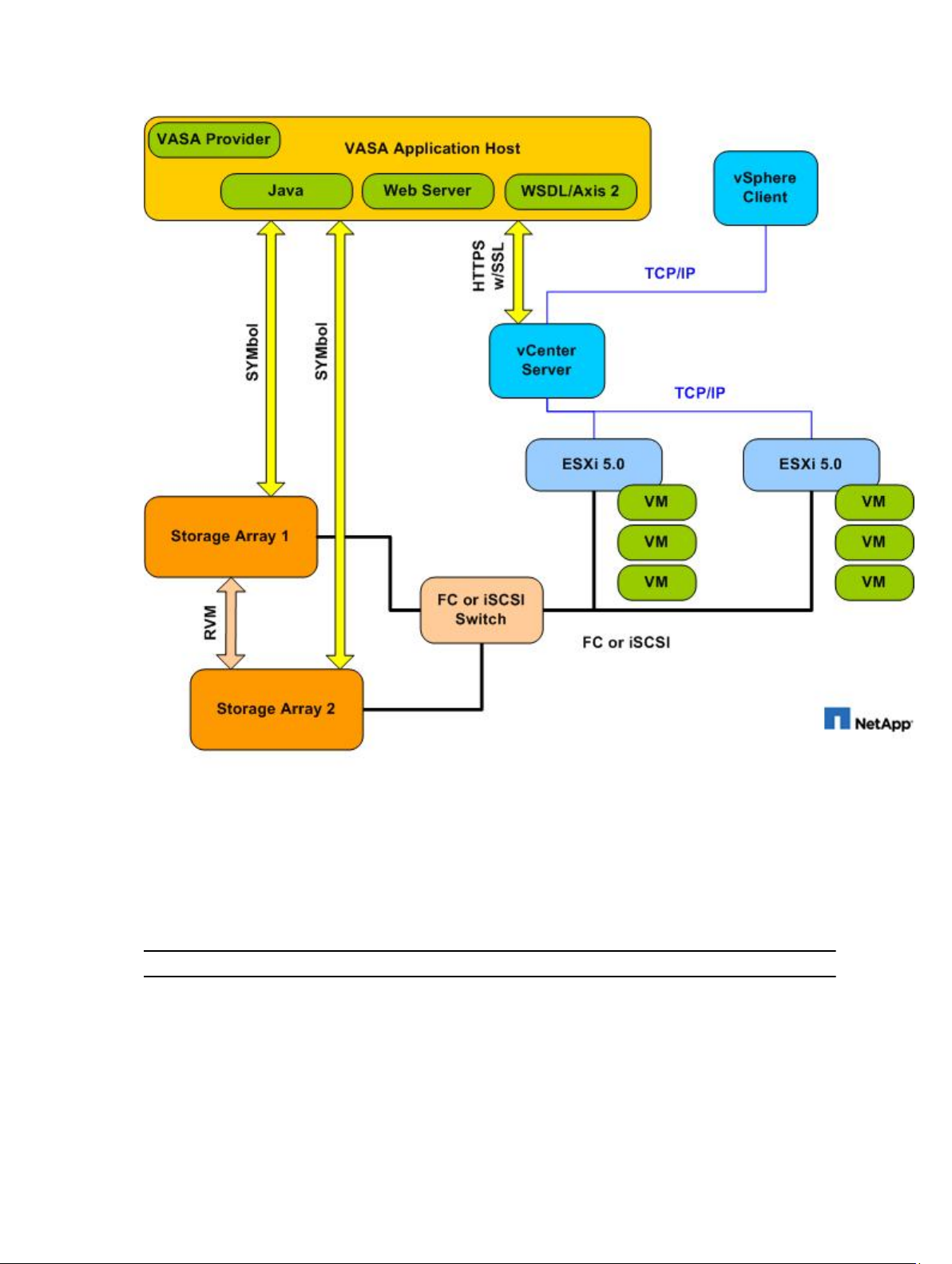
Figure 1. VASA Provider in a vCenter Storage Management Architecture
VASA Storage Capabilities
Storage provisioning operations available in vSphere allow VASA to monitor whether a storage array's physical
components can meet virtual machine needs according to defined capabilities. Available capabilities and their common
performance ranges are shown in table below.
Table 1. Available VASA Storage Capabilities
Storage Capabilities Common Use/Performance Range
SSD Drives
6
Storage Type Virtual disks comprised of solid-state physical disks
Page 7

Storage Capabilities Common Use/Performance Range
SSD Drives-Thin
10K/15K Drives
10K/15K Drives-Thin
NLSAS Drives
Performance
Level
Storage Type Thin-provisioned virtual disks comprised of solid-state physical
Performance
Level
Storage Type Virtual disks comprised of high-performance physical disks
Performance
Level
Storage Type Thin-provisioned virtual disks comprised of high-performance
Performance
Level
Storage Type Virtual disks comprised of Near-Line SAS (NL-SAS) physical disks
Performance
Level
Highest available
disks
Highest available
High (used in most standard environments)
physical disks
High (used in most standard environments)
10K RPM or less
Intermediate performance, good for bulk storage needs
NLSAS Drives-Thin
Replicated SSD Drives
Replicated 10K/15K
Drives
Replicated NLSAS
Drives
Steps for assigning these capabilities in vSphere are detailed in
Storage Type Thin-provisioned virtual disks comprised of Near-Line SAS (NL-
SAS) physical disks 10K RPM or less
Performance
Level
Storage Type Virtual disks comprised of solid-state physical disks
Performance
Level
Storage Type Virtual disks comprised of high-performance physical disks
Performance
Level
Storage Type Replicated virtual disks comprised of Near-Line SAS (NL-SAS)
Performance
Level
Intermediate performance, good for bulk storage needs
Highest available for replicated virtual disks
High (used in most standard replicated environments)
physical disks 10K RPM or less
Intermediate performance, good for bulk storage needs
Using the VASA Provider
later in this guide.
7
Page 8

Profile-Driven And Policy-Based Storage
The VASA provider supports profile-driven storage management by categorizing virtual disks by performance and
reporting performance capability to vCenter. This information can then be used to establish profiles based on specific
application performance requirements. Benefits of this approach include:
• Rapid, intelligent provisioning of applications
• Application service levels that match available storage
• Better visibility into the available storage pool
Policy-based storage management supported in vSphere 5.0 helps you further provision virtual machines (VMs) by
automating datastore placement decisions.
Storage Service-Level Agreements
Using the VASA provider replaces the need to maintain storage capability spreadsheets for each LUN. Instead, you can
deliver the best-matched resources to any service-level agreement (SLA) required by the VM.
The VASA provider allows you to discover and monitor storage array SLA properties based on availability, security and
performance. You can then use VASA to enforce storage VM SLAs and create end-to-end storage SLA guarantees for
each virtual machine.
Storage Distributed Resource Scheduler
The VASA provider extends VMware’s Distributed Resource Scheduler (DRS) functionality to data storage by enabling a
Storage Distributed Resource Scheduler (SDRS) to operate on a group of datastores with similar capabilities. With the
VASA provider, SDRS can determine whether a storage array can support SDRS migration, as well as whether migration
is recommended.
VASA Session Communications
All communications between the vCenter Server and the VASA provider use Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) certificates.
The VASA provider can use a self-signed certificate or a certificate issued by a certificate authority (CA).
8
Page 9

Installing The VASA Provider
This section describes prerequisites and installation steps for the VASA provider.
Before You Install
Before installing the VASA provider, review the supported and required shown in this section.
Supported Operating Systems And Platforms
The VASA provider is dependent on specific operating system and application platform requirements. Before installing
and configuring VASA, make sure your environment meets the requirements detailed in this section.
Supported Host Operating Systems
The VASA provider can be installed on one of the following Windows host operating systems:
• Windows Server 2003 SP2 (32-bit or 64-bit versions)
• Windows Server 2008 R2 (64-bit version)
• Windows Server 2012 (all editions)
2
NOTE: The VASA provider must be installed on a separate Windows host server than the vCenter Server platform.
Required VMware Application Platforms
The following VMware application platforms must be installed and properly configured before installing the VASA
provider:
• VMware vSphere Client 5.0 and 5.1
• VMware vCenter Server 5.0 and 5.1 (installed separately from the VASA provider)
For information on installing and configuring VMware platforms, see http://www.vmware.com/support/product-support.
For help on configuring your VMware environment, see
vmware.com/support/product-support.
VMware Fibre Channel SAN Configuration Guide
available at
Supported MD Series Storage Arrays
The VASA provider is supported on the following MD-series storage arrays:
• MD3200i, MD3220i, MD3260i, MD3600i, MD3620i, and MD3660i (iSCSI)
• MD3600f, MD3620f, and MD3660f (Fibre Channel)
9
Page 10

Required RAID Controller Module Firmware
The VASA provider is supported on MD Series RAID controller module firmware versions 7.35 and later. To verify your
firmware and operating system compatibility, see the
Support Matrix
available at dell.com/support/manuals.
Downloading The VASA Provider
The VASA provider is a self-extracting, self-installing file available from the Drivers and Download page at dell.com/
support.
To download the VASA provider:
1. Go to dell.com/support and select the Drivers and Download link.
2. Select your MD Series storage array model, then choose Select Model → Servers, Storage, Networking →
PowerVault Storage.
3. Select your model and click Confirm to show available downloads.
4. Choose the VASA provider download link and download the executable to your host server.
Installing The VASA Provider
1. Launch the VASA installation wizard.
2. Accept the license agreement and follow the installation prompts.
The default installation path on a 32-bit Windows OS is: C:\Program Files\Dell\Modular Disk Storage VASA Provider.
The default installation path on a 64-bit Windows OS is: C:\Program Files (x86)\Dell\Modular Disk Storage VASA
VASA Provider.
3. Once installation is complete, confirm the VASA provider appears in your programs list.
Uninstalling The VASA Provider
You can uninstall the VASA provider in one of two ways:
1. From the Windows Add and Remove Programs option.
2. Using the VASA provider uninstaller located at C:\Program Files (x86)\Dell\Modular Disk Storage VASA Provider
\Uninstall_ Modular Disk Storage VASA Provider.
Once the uninstall is complete, verify that all application files and folders are deleted.
10
Page 11

Using The VASA Provider
After installing the VASA provider, configure it for use in your environment:
1. From the installation directory, click on the VASAPConfigUI.exe file.
The application server starts and the Configuration Manager screen is displayed.
3
Figure 2. VASA Provider Configuration Manager Window
11
Page 12

2. In Configuration Manager, choose user IDs, passwords, and port settings for the host server.
NOTE: The default Admin User Password is
names and passwords. Passwords are verified dynamically and will display in a red text field background if
they do not match existing values.
3. To configure security between VASA and vSphere using a self-signed certificate, click Generate Self Signed
Certificate.
NOTE: Using this option requires a thorough understanding of the security requirements in place at your site.
Consult your local IT administrator before using this option.
4. Click Start Service to start the VASA provider.
NOTE: Any time you change passwords, you must stop and then re-start the VASA service before the
password change takes effect. Use the Stop Service and Start Service options in the Configuration Manager
window.
5. When you register the VASA provider with the vSphere Client in the next section, you will need the URL of the
server containing VASA. Click
into a text file.
Copy Provider URL to Clipboard to copy the server URL to your clipboard and paste it
password
. Enter SSL settings, including key store/trust store file
Bringing Storage Arrays Under VASA Management
Before you can use the capabilities of the VASA provider to manage your MD storage arrays, you need to do two things:
1. Add your storage arrays to VASA control (using VASA's Array Manager).
2. Register the VASA provider with your vSphere Client.
Adding Your Storage Arrays To VASA Control
1. From VASA's Configuration Manager, click Launch Array Manager. Alternately, you can start the array manager via
URL: http://<host_address>:8080/arraytree.
NOTE: If using static IP addressing, substitute a standard IP address for
substitute a DNS name for
<host_address>
<host_address>
. If using DHCP,
12
Page 13

Figure 3. Array Manager Window
2. From the Array Manager window, click Add Array in the Commands section. To first create a separate folder to
contain the storage arrays you intend to add, click Add Folder).
NOTE: vSphere 5.1 supports a Discover Arrays option to performs automatic array discovery based on a range
of RAID controller module IP addresses that you provide. Either method of specifying arrays -Add Array or
Discover Arrays (if available) - can be used.
3. In the Add Storage Device window, enter the IP addresses for the RAID controllers module in the storage arrays
you want to add to VASA.
4. Enter the RAID controller module password, if required.
5. Repeat step 2 through 4 to add more storage arrays.
6. Close the Array Manager window.
To Register The VASA Provider In Your vSphere Client
1. Start the vSphere Client and connect to your vCenter Server.
13
Page 14

Figure 4. vSphere Client Login Screen
2. From the vSphere Client window, click Storage Providers.
Figure 5. vSphere Client Home Screen
3. Above the Vendor Providers window, click Add.
14
Page 15

Figure 6. vSphere Add Vendor Provider Menu
4. In the Add Vendor Provider window, enter name, URL and login credentials to the server containing the VASA
provider you installed earlier.
Before you begin:
In the URL field, paste the URL you copied when you clicked Copy Provider URL to Clipboard in the VASA
Configuration Manager. Make sure the URL in the Add Vendor Provider window matches the following
requirements:
– /vasa/services/vasaService must be appended following your port number (for example, if the location of
your server containing the VASA provider is https://kswa-vasa3-prov:8443 the value in the URL field must
be: https://kswa-vasa3-prov:8443/vasa/services/vasaService where https specifies an SSL connection and
8443 is the default port number for the VASA provider.
– If you specified a different port number in the VASA Configuration Manager window than the default, make
sure you use your valid port number.
When entering a login and password value, make sure they match what you used in the VASA Configuration
Manager window.
5. If you require a vendor-signed security certificate, select Use Vendor Provider Certificate and enter the location of
the certificate. Otherwise, leave that checkbox empty.
6. When complete, click OK to register the VASA provider with your vCenter Server.
Verifying VASA Registration
Upon successfully registering the VASA provider, your managed storage arrays should appear in the Vendor Provider
Details window.
15
Page 16

Figure 7. vSphere Client VASA Provider Window
Working with Storage Profiles
In order for the storage capabilities to be recognized and reported the user must create a profile, and assign the
capability desired to said profile using the check box supplied with the corresponding system-defined capability. This
will allow the System Defined capabilities to be associated with the datastore and then displayed properly.
Using the VASA provider, you can create storage profiles that use datastores based on user-selected criteria. To enable
VM Storage Profiles:
1. From the vSphere Client Home window, select VM Storage Profiles.
2. Click Enable VM Storage Profiles.
3. In the Summary tab under Commands, click Create VM Storage Profile.
4. In the Create New VM Storage Profile Properties window, enter the properties for the new profile and click Next.
Figure 8. Create VM Storage Profile
5. In the Select Storage Capabilities window, select the storage capability to be associated with the profile and click
Next.
16
Page 17

Figure 9. Select Storage Capabilities
6. Review the summary information, then click Finish.
Assigning VM Storage Profiles To Existing Virtual Machines
After creating the storage profile, assign the profile to an existing virtual machine:
1. From the vSphere Hosts and Clusters view, select the virtual machine.
2. Right-click on the virtual machine and select VM Storage Profile → Manage Profiles.
3. From the Home VM Storage Profile drop-down menu, select the VM Storage Profile to be used and then click
Propagate to Disks.
4. Click OK to apply changes.
5. On the Summary tab of the VM Storage Profiles window, click Refresh.
The assigned profile should be displayed, along with the status under Compliance Status.
17
Page 18

Figure 10. Create VM Storage Profile
Figure 11. vSphere Storage Profile Summary
Checking Storage Profile Compliance
After assigning a storage profile to a virtual machine, you can verify its compliance by selecting the virtual machine from
the Host and Clusters view and selecting the Summary tab. The VM Storage Profiles box shows compliance details.
18
Page 19

Figure 12. vSphere Storage Profile Summary
Storage Array Events And Alerts
The VASA provider propagates storage array alerts to the vCenter Server Event Monitor. Alerts are displayed on two
separate views:
• Alert tab in the Tasks view
• Alarms view at the bottom of the vSphere Client
Events are viewed by clicking on the Events icon on the vSphere Client Home view.
Figure 13. Triggered Alarms View
Troubleshooting Tips
The table below shows some common issues and possible steps for resolution.
Table 2. Issues and Corrective Steps
Issue Possible Resolution
Unable to connect to the provider host
• Verify the proper URL for storage provider is registered.
• Verify that firewall settings allow for configured ports (default 8080
and 8443).
• Verify the VASA provider service is started on provider host.
No datastore capabilities being
displayed
• Verify that a valid vendor ID and model ID are listed for the registered
storage provider in vCenter Server.
19
Page 20

Issue Possible Resolution
• Verify that monitored storage arrays have been added to the array
manager.
• Verify the VASA provider service is running on the provider host.
Unable to access the Array Manager
Event messages do not display
description information
• Verify the URL for the Storage Array Manager is correct. (The default
provider host URL is http://localhost:8080/arraytree/)
• Verify that firewall settings allow configured ports.
• Verify the VASA provider service is running on the provider host.
This is a known issue with the VASA APIs and will be resolved in a future
release.
Troubleshooting Logs
If further troubleshooting is required, Dell technical support may require that a copy of the working log directory be sent
for analysis. The log directory is located on the VASA provider host at C:\Program Files (x86)\ Dell\Modular Disk Storage
VASA Provider\working\logs (64 bit) and C:\Program Files\ Dell\Modular Disk Storage VASA Provider\working\logs (32
bit).
Configuration Reset
If the VASA provider configuration needs to be reset to a clean configuration, perform the following steps:
1. Stop the Dell VASA provider application server service on provider host.
2. Delete the /db directory in the C:\Program Files (x86)\ Dell\Modular Disk Storage VASA Provider\working directory.
3. Delete the /tmp directory in the C:\Program Files (x86)\ Dell\Modular Disk Storage VASA Provider\working directory.
4. Start the Dell VASA Provider application server service on the provider host.
This will remove the alert information and cached data from the Dell VASA provider application server. However,
monitored storage array information is retained.
20
Page 21

Getting Help
Locating Your System Service Tag
Your system is identified by a unique Express Service Code and Service Tag number. The Express Service Code and
Service Tag are found on the front of the system by pulling out the information tag. This information is used by Dell to
route support calls to the appropriate personnel.
Contacting Dell
NOTE: Dell provides several online and telephone-based support and service options. If you do not have an active
Internet connection, you can find contact information on your purchase invoice, packing slip, bill, or Dell product
catalog. Availability varies by country and product, and some services may not be available in your area.
To contact Dell for sales, technical support, or customer-service issues:
1. Go to dell.com/contactdell.
2. Select your country or region from the interactive world map.
When you select a region, the countries for the selected regions are displayed.
3. Select the appropriate language under the country of your choice.
4. Select your business segment.
The main support page for the selected business segment is displayed.
5. Select the appropriate option depending on your requirement.
4
NOTE: If you have purchased a Dell system, you may be asked for the Service Tag.
Documentation Feedback
If you have feedback for this document, write to documentation_feedback@dell.com. Alternatively, you can click on the
Feedback link in any of the Dell documentation pages, fill up the form, and click Submit to send your feedback.
21
 Loading...
Loading...