Page 1

DellTM PowerVaultTM 110T LTO-2 Tape Drive User's Guide
Information in this document is subject to change without notice.
(C) 2003 Dell Computer Corporation. All rights reserved.
(C) International Business Machines Corporation, 1999, 2003. All rights reserved.
Trademarks used in this text: Dell, PowerVault and the DELL logo are trademarks of Dell Computer Corporation. Linear Tape-Open, LTO, LTO Logo, Ultrium and Ultrium Logo
are U.S. trademarks of HP, IBM and Seagate. Microsoft and Windows are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
Other trademarks and trade names may be used in this document to refer to either the entities claiming the marks and names or their products. Dell Computer Corporation
disclaims any proprietary interest in trademarks and trade names other than its own.
Model Number LTO2-EX1
Initial release: May 2003
Introduction
Setting Up the Tape Drive
Using the Tape Drive
Using the Tape Backup Software
Troubleshooting
Specifications
Glossary
NOTE: A NOTE indicates important information that helps you make better use of your computer.
NOTICE: A NOTICE indicates either potential damage to hardware or loss of data and tells you how to avoid the problem.
CAUTION: A CAUTION indicates a potential for property damage, personal injury, or death.
Page 2

Back to Contents Page
Glossary: DellTM PowerVaultTM 110T LTO-2 Tape Drive User's Guide
- A - B - C - D - E - F - G - H - I - J - L - M - N - O - P - R - S - T - U - V - W
A
A. See ampere.
ampere (A). A unit of measure for electric current that is equivalent to a flow of one coulomb per second, or equivalent to the current produced by one volt applied across a
resistance of one ohm.
adapter. See adapter card.
adapter card. A circuit board that adds function to a computer.
B
backups. The short-term retention of records used for restoring essential business and server files when vital data has been lost because of program or server errors or
malfunctions.
backward compatible. Capable of being used with a previous product that was designed for a similar purpose. For example, a tape cartridge that is designed to be used
with a modern tape drive but can also be used with certain older tape drives. Synonymous with downward compatible.
bezel. The removable frame that fits over the front of the tape drive.
byte. A string that consists of a certain number of bits (usually 8) which are treated as a unit and represent a character. A byte is a fundamental unit of data.
C
C. See Celsius.
capacity. The amount of data that can be contained on storage media and expressed in bytes.
cartridge. See tape cartridge.
cartridge door. On a tape cartridge, the hinged barrier that can be opened to access, or closed to protect, the magnetic tape within the cartridge.
cartridge memory. See LTO cartridge memory.
Celsius (C). Having a thermostatic scale on which the interval between the freezing point and the boiling point of water is divided into 100 degrees, with 0 degrees representing
the freezing point and 100 degrees representing the boiling point.
cleaning cartridge. A tape cartridge that is used to clean the heads of a tape drive. Contrast with data cartridge.
clockwise. In the direction that the hands of a clock rotate, as viewed from the front.
compression. The process of eliminating gaps, empty fields, redundancies, and unnecessary data to shorten the length of records or blocks.
configure. To describe to a server the devices, optional features, and programs installed on the system.
counterclockwise. In a direction opposite to that in which the hands of a clock rotate, as viewed from the front.
current. The quantity of charge per unit of time. Current is measured in amperes.
cycle power. To apply and remove electrical power to a device within a short time span.
D
data. Any representations such as characters or analog quantities to which meaning is, or might be, assigned.
data cartridge. A tape cartridge that is dedicated to storing data. Contrast with cleaning cartridge.
data compression. See compression.
data transfer rate. The average number of bits, characters, or blocks per unit of time that pass between corresponding equipment in a data transmission system. The rate is
expressed in bits, characters, or blocks per second, minute, or hour.
Page 3

dc. See direct current.
degauss. To make a magnetic tape nonmagnetic by exposing the tape to electrical coils which carry currents that neutralize the magnetism of the tape.
device. Any hardware component or peripheral, such as a tape drive or tape library, that can receive and send data.
device driver. A file that contains the firmware that is needed to use an attached device.
diagnostic. A software program that is designed to recognize, locate, and explain faults in equipment or errors in programs.
direct current (dc). An electric current flowing in one direction only and substantially constant in value.
drive. A data-storage device that controls the movement of the magnetic tape in a tape cartridge. The drive houses the mechanism (drive head) that reads and writes data to
the tape.
drive dump. The recording, at a particular instant, of the contents of all or part of one storage device into another storage device, usually as a safeguard against faults or
errors, or in connection with debugging.
drive head. The component that records an electrical signal onto magnetic tape, or reads a signal from tape into an electrical signal.
drive sense data. See SCSI drive sense data.
dump. See drive dump.
E
eject. To remove or force out from within.
enclosure. A device, such as a desktop unit, tape cartridge autoloader, or tape library, into which you can install the tape drive.
error log. Maintained by the tape drive, a list that contains the ten most recent error codes. The codes identify errors that pertain to the drive.
F
file. A named set of records that are stored or processed as a unit.
firmware. The proprietary code that is usually delivered as part of an operating system. Firmware is more efficient than software that is loaded from an alterable medium, and
is more adaptable to change than pure hardware circuitry. An example of firmware is the Basic Input/Output System (BIOS) in read-only memory (ROM) on a PC
motherboard.
G
GB. See gigabyte.
Generation 1. The informal name for the Ultrium tape drive, which is the predecessor of the tape drive (Generation 2). The Generation 1 drive has a native storage capacity of
up to 100 GB per cartridge and a native sustained data transfer rate of 15 MB per second.
Generation 2. The informal name for the Ultrium 2 Tape Drive, which is the second-generation version of the Ultrium tape drive (Generation 1). The Generation 2 drive has a
native storage capacity of up to 200 GB per cartridge and a native sustained data transfer rate of 35 MB per second.
gigabyte. 1 000 000 000 bytes.
ground. An object that makes an electrical connection with the earth.
H
hardware. The physical equipment or devices that form a computer.
head. See drive head.
Head Resistance Measurements test. Part of the Test Head diagnostic, a procedure that determines whether the tape drive's head works correctly. The test measures the
head's ability to withstand cracks and other defects.
host. The controlling or highest-level system in a data communication configuration. Synonymous with server.
I
ID. Identifier.
in. See inch.
Page 4

inch. A unit of length equal to 1/36 yard or 25.4 mm.
input/output (I/O). Data that is provided to a computer or data that results from computer processing.
insertion guide. On the surface of the tape cartridge, a large, notched area that prevents you from inserting the cartridge incorrectly.
install. (1) To set up for use or service. (2) The act of adding a product, feature, or function to a server or device either by a singular change or by the addition of multiple
components or devices.
interposer. An adapter-like device that allows a connector of one size and style to connect to a mating connector of a different size and style. Data provided to the computer
or data resulting from computer processing.
I/O. See input/output.
J
jumper. (1) A tiny connector that fits over a pair of protruding pins in a connector. A jumper can be moved to change electrical connectors. When in place, the jumper
connects the pins electrically.
(2) To place a jumper on a connector pin.
L
label. A slip of paper with an adhesive backing that can be written on and affixed to a tape cartridge as a means of identification or description.
label area. On the LTO Ultrium Tape Cartridge, a recessed area next to the write-protect switch where a bar code label must be affixed.
leader block. Located within the tape drive, the part that engages the steel pin which is attached to the tape in an LTO Ultrium Tape Cartridge. Once engaged, the leader-pin
block pulls the tape from the cartridge into the drive.
leader pin. On the tape cartridge, a small metal column that is attached to the end of the magnetic tape. During tape processing the leader pin is grasped by a threading
mechanism, which pulls the pin and the tape out of the cartridge, across the drive head, and onto a takeup reel. The head can then read or write data from or to the tape.
LED. See light-emitting diode.
light-emitting diode. A semiconductor diode that emits light when subjected to an applied voltage and that is used in an electronic display.
Linear Tape-Open (LTO). A type of tape storage technology developed by the IBM Corporation, Hewlett-Packard, and Seagate. LTO technology is an "open format"
technology, which means that its users have multiple sources of product and media. The "open" nature of LTO technology enables compatibility between different vendors'
offerings by ensuring that vendors comply with verification standards.
load. Following the insertion of a tape cartridge into the tape load compartment, the act of positioning the tape (performed by the tape drive) for reading or writing by the drive's
head.
log sense data. See SCSI log sense data.
loop. (1) A series of instructions that is repeated until a terminating condition is reached.
(2) To connect so as to complete a loop.
Low Voltage Differential (LVD). A low-noise, low-power, and low-amplitude electrical signaling system that enables data communication between a supported server and
the tape drive. LVD signaling uses two wires to drive one signal over copper wire. The use of wire pairs reduces electrical noise and crosstalk.
LTO. See Linear Tape-Open.
LVD. See Low Voltage Differential.
M
magnetic tape. A tape with a magnetizable surface layer on which data can be stored by magnetic recording.
maintenance mode. The state of operation in which the tape drive must be before it can run diagnostics, verify write and read operations, verify a suspect tape cartridge,
update its own firmware, and perform other diagnostic and maintenance functions.
MB. See megabyte.
media. The plural of medium.
medium. A physical material in or on which data may be represented, such as magnetic tape.
megabyte (MB). 1 000 000 bytes.
N
Page 5

network. A configuration of data processing devices and software that is connected for information interchange.
O
oersted. The unit of magnetic field strength in the unrationalized centimeter-gram-second (cgs) electromagnetic system. The oersted is the magnetic field strength in the
interior of an elongated, uniformly wound solenoid that is excited with a linear current density in its winding of one abamper per 4 pi centimeters of axial length.
offline. The operating condition that the tape drive is in when the server's applications cannot interact with it.
online. The operating condition that the tape drive is in when the server's applications can interact with it.
Open Systems. Computer systems whose standards are not proprietary.
operating environment. The temperature, relative humidity rate, and wet bulb temperature of the room in which the tape drive routinely conducts processing.
P
parity. The state of being even-numbered or odd-numbered. A parity bit is a binary number that is added to a group of binary numbers to make the sum of that group always
odd (odd parity) or even (even parity).
parity error. A transmission error that occurs when the received data does not have the parity that is expected by the receiving system. This usually occurs when the
sending and receiving systems have different parity settings.
port. (1) A system or network access point for data entry or exit.
(2) A connector on a device to which cables for other devices such as display stations and printers are attached.
(3) The representation of a physical connection to hardware. A port is sometimes referred to as an adapter; however, there can be more than one port on an adapter.
power connector. Located at the rear of the tape drive, the connector to which the internal power cable of an enclosure connects.
power cord. A cable that connects a device to a source of electrical power.
power-off. To remove electrical power from a device.
power-on, powered-on. (1) To apply electrical power to a device.
(2) The state of a device when power has been applied to it.
R
read. To acquire or interpret data from a storage device, from a data medium, or from another source.
reboot. To reinitialize the execution of a program by repeating the initial program load (IPL) operation.
record. The smallest distinct set of data bytes that is supplied from a server for processing and recording by a tape drive, and the smallest distinct set of data to be read from
tape, reprocessed, and made available to a server by a tape drive.
relative humidity. The ratio of the amount of water vapor actually present in the air to the greatest amount possible at the same temperature.
reset. To return a device or circuit to a clear state.
S
s. See second.
scratch cartridge. A data cartridge that contains no useful data, but can be written to with new data.
SCSI. See Small Computer Systems Interface.
SCSI bus. (1) A collection of wires through which data is transmitted from one part of a computer to another.
(2) A generic term that refers to the complete set of signals that define the activity of the Small Computer Systems Interface (SCSI).
SCSI connector. Located at the rear of the tape drive, the connector that facilitates commands to and from the server, and to which the internal SCSI cable of an enclosure
connects.
SCSI device. Anything that can connect into the SCSI bus and actively participate in bus activity.
SCSI drive sense data. In response to inquiry from the server about an error condition, a packet of SCSI sense bytes that contains information about the error and that is
sent back to the server by the drive.
SCSI ID. The unique address (from 1 to 15) that you assign to a tape drive that uses a SCSI interface.
SCSI ID connector. Located at the rear of the tape drive, the connector that enables the drive's SCSI address to be set. Addresses are determined by the placement of
jumpers on the pins.
Page 6

SCSI interface. See Small Computer Systems Interface.
SCSI log sense data. In response to inquiry from the server about the tape drive's error logs and counters, a packet of SCSI sense bytes which contains that information and
which is sent back to the server by the drive. Log sense data is used to diagnose problems, especially if the problems are intermittent.
second. One sixtieth of a minute.
sense data. Data that describes an I/O error. Sense data is presented to a server in response to a Sense I/O command.
server. A functional unit that provides services to one or more clients over a network. Examples include a file server, a print server, or a mail server. The IBM pSeries, IBM
iSeries, HP, and Sun are servers. Synonymous with host.
single-character display. Located at the front of the tape drive, an LED that presents an alphabetical or numeric code which represents a diagnostic or maintenance
function, error condition, or informational message.
sleep mode. A power-management function that causes the tape drive's electronics to automatically enter a low-power mode by which to conserve energy.
Small Computer Systems Interface (SCSI). A standard used by computer manufacturers for attaching peripheral devices (such as tape drives, hard disks, CD-ROM
players, printers, and scanners) to computers (servers). Pronounced "scuzzy." Variations of the SCSI interface provide for faster data transmission rates than standard serial
and parallel ports (up to 160 megabytes per second). The variations include:
l Fast/Wide SCSI: Uses a 16-bit bus, and supports data rates of up to 20 MBps.
l SCSI-1: Uses an 8-bit bus, and supports data rates of 4 MBps.
l SCSI-2: Same as SCSI-1, but uses a 50-pin connector instead of a 25-pin connector, and supports multiple devices.
l Ultra SCSI: Uses an 8- or 16-bit bus, and supports data rates of 20 or 40 MBps.
l Ultra2 SCSI: Uses an 8- or 16-bit bus and supports data rates of 40 or 80 MBps.
l Ultra3 SCSI: Uses a 16-bit bus and supports data rates of 80 or 160 MBps.
l Ultra160 SCSI: Uses a 16-bit bus and supports data rates of 160 MBps.
software. Programs, procedures, rules, and any associated documentation pertaining to the operation of a computer system.
speed matching. A technique used by the tape drive to dynamically adjust its native (uncompressed) data rate to the slower data rate of a server. Speed matching improves
system performance and reduces backhitch.
status light. Located at the front of the tape drive, an LED that can be green or amber, and (when lit) solid or flashing. The condition of the light represents the state of the
drive.
T
TapeAlert. A patented technology and ANSI standard that defines conditions and problems that are experienced by tape drives.
TapeAlert flags. Status and error messages that are generated by the TapeAlert utility and display on the server's console.
tape cartridge. A removable storage case that houses belt-driven magnetic tape that is wound on a supply reel and a takeup reel.
tape drive. A data-storage device that controls the movement of the magnetic tape in a tape cartridge. The drive houses the mechanism (drive head) that reads and writes
data to the tape. Its native data capacity is 100 GB per cartridge; with 2:1 compression, its capacity is up to 200 GB.
tape path. Within a tape drive, the channel in which the media moves.
terminate. To prevent unwanted electrical signal reflections by applying a device (known as a terminator) that absorbs the energy from the transmission line. terminator. (1)
A part that is used to end a SCSI bus.
(2) A single-port, 75-&Omega. device that is used to absorb energy from a transmission line. Terminators prevent energy from reflecting back into a cable plant by absorbing
the radio frequency signals. A terminator is usually shielded, which prevents unwanted signals from entering or valid signals from leaving the cable system.
Test Head diagnostic. A test that determines whether the heads of the tape drive are operating properly and whether the drive can correctly read from and write to tape.
transfer rate. See data transfer rate.
U
Ultra160 LVD SCSI interface. See Small Computer Systems Interface.
unload. The act (performed by the drive) of unthreading tape from the drive's internal tape path and returning it (with the leader block) to the tape cartridge.
utility. See utility program.
utility program. A computer program that supports computer processes. For example, a diagnostic program, a trace program, or a sort program.
V
Vdc. Volts dc (direct current).
Page 7

volt. The SI (international) unit of potential difference and electromotive force. Formally defined as the difference of electric potential between two points of a conductor that
carries a constant current of one ampere when the power dissipated between these points is equal to one watt.
W
wet bulb temperature. The temperature at which pure water must be evaporated adiabatically at constant pressure into a given sample of air in order to saturate the air
under steady-state conditions. Wet bulb temperature is read from a wet bulb thermometer.
write. To make a permanent or transient recording of data in a storage device or on a data medium.
write protected. Applicable to a tape cartridge, the condition that exists when some logical or physical mechanism prevents a device from writing on the tape in that
cartridge.
write-protect switch. Located on the tape cartridge, a switch that prevents accidental erasure of data. Pictures of a locked and unlocked padlock appear on the switch.
When you slide the switch to the locked padlock, data cannot be written to the tape. When you slide the switch to the unlocked padlock, data can be written to the tape.
Write/Read test. Part of the Test Head diagnostic, a procedure that determines whether the tape drive can correctly read from and write to tape.
Back to Contents Page
Page 8
Back to Contents Page
Introduction: DellTM PowerVaultTM 110T LTO-2 Tape Drive User's Guide
- Overview - SCSI Bus Interface - Features - Tape Backup Software - The Front Panel - The Rear Panel
Overview
The DellTM PowerVaultTM 110T LTO-2 tape drive is a high-performance, high-capacity data-storage device that is designed to perform unattended backups, restore Open
Systems applications, and retrieve and archive files. The drive can be integrated into a server (internal model) or can be provided as a separately packaged desktop unit
(external model). The Dell PowerVault 110T LTO-2 tape drive (called Generation 2) is the second-generation tape drive in the LTO-2 series of products.
The Dell PowerVault 110 LTO-2 tape drive offers a formatted cartridge capacity of up to 200 GB (400 GB assuming 2:1 compression ratio) and a sustained data transfer rate of
35 MB per second (70 MB per second assuming 2:1 compression ratio).
Figure 1 shows a front view of the internal model of the tape drive. Figure 2 shows a front view of the separately purchased external model of the tape drive.
Figure 1. Front View (Internal Model)
Figure 2. Front View (External Model)
SCSI Bus Interface
These tape drives are designed to operate on an Ultra160 low voltage differential SCSI bus (LVD) with a burst transfer rate of 160 MB/sec. The interface is backward
compatible with older SCSI technology.
The tape drives contains a high density, 68-pin, D-Shell (HD-68) connector for attachment to the server. The drive supports LVD SCSI cables with HD-68 connectors.
Features
The tape drive has the following features:
l Capacity of 200GB (native), 400GB (compressed*) on a single LTO tape
l Built-in read-after-write verification for a high level of data integrity
l Sustained transfer rate of 35MB/s (native), 70MB/s(compressed*)
l Intelligent LTO-DC dual-mode compression algorithm
l Failsafe leader capture mechanism
l LTO-Cartridge Memory
l TapeAlert support for worry-free backup
l Ultra 160 Low Voltage Differential (LVD) SCSI interface
l Backward Read and Write Compatibility with Generation 1 Cartridges
l Speed matching (The tape drive can slow down to match the system data rate.)
Page 9
l Sleep mode for energy conservation
l Compatible with all cartridges that bear the official Ultrium LTO-2 logo
l Will interchange tapes with other LTO-2 tape drives that bear the official Ultrium LTO-2 logo
* Assumes 2:1 compression ratio. The capacity you realize in practice depends on the data set, which affects the actual compression ratio.
Tape Backup Software
You need backup software that supports the DELL PowerVault 110T LTO-2 tape drive. As a general rule, native backup applications (such as NTBackup and tar) do not
provide the required data streaming rate to get the full performance of your tape drive. We recommend using a backup application, which provides better memory management
as well as other useful features, such as TapeAlert. For the latest supported software versions, go to http://www.support.dell.com or visit the support site of your backup
software vendor.
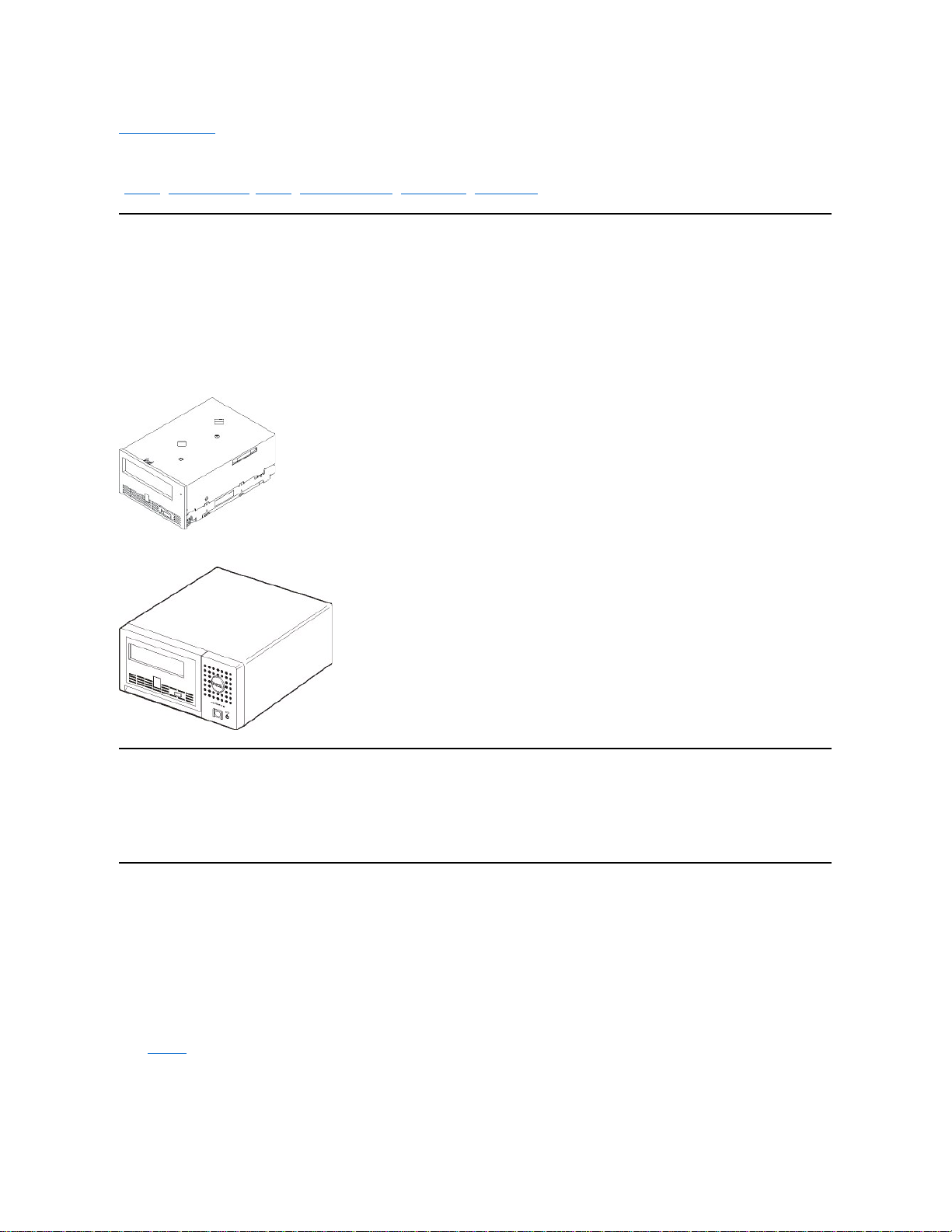
The Front Panel
Figure 3. Front Panel
1. Single-character display
2. Single red dot
3. Status light
4. Eject button
1. Single-character display. This LED presents a single-character code for diagnostic/maintenance functions, error conditions, and informational messages.
2. Single red dot. This single-character display is blank during normal operation. When a single red dot illuminates the display, the drive has created a dump of vital
technical data to drive memory.
3. Status Light. The front panel of your Dell PowerVault 110T LTO-2 tape drive has a status light that provides information about the state of the tape drive. The light can be
green or amber, and (when lit) solid or flashing. See Table 2 for descriptions.
Table 2. Status Light Descriptions
Color or Condition of
Status Light
Meaning
Off
The tape drive has no power or is powered off.
Green/Solid
The tape drive is powered on.
Green/Flashing
One of the following applies:
l If the light flashes less than once per second, the tape drive is in sleep mode.
l If the light flashes once per second, the tape drive is reading from the tape, writing to the tape, rewinding the tape, or locating data on
the tape.
Amber/Solid
One of the following applies:
l The tape drive is performing a selected operation.
l The tape drive is displaying the drive error code log.
l The tape drive is in maintenance mode or is exiting maintenance mode.
Amber/Flashing
One of the following applies:
l If the light flashes less than once per second, the tape drive is updating firmware through the field microcode replacement (FMR) tape,
or the SCSI, Fibre Channel, or RS-422 interface, or the drive has exceeded the recommended temperature.
l If the light flashes once per second, an error occurred and the tape drive or media may require service. Note the code on the single-
character display, then go to Table 16 on page 63 to determine the action that is required.
l If the light flashes once per second and a C displays in the character display, the tape drive needs to be cleaned.
l If the light flashes twice per second, the tape drive detected an error and is performing a firmware recovery. It resets automatically.
Page 10
4. Eject button. The eject button enables you to perform several functions. These functions are described in detail in Using the Tape Drive.
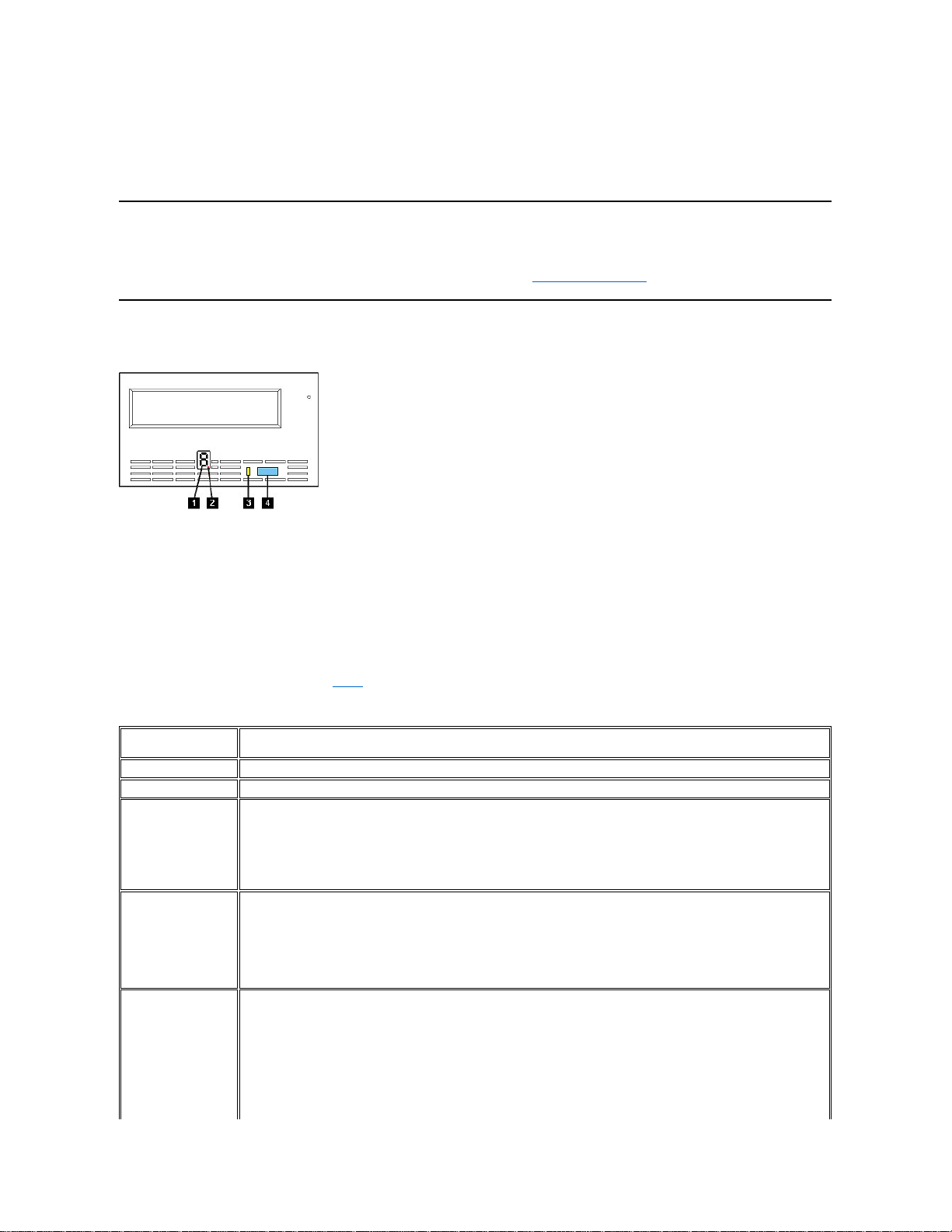
The Rear Panel
Figure 4. Rear Panel of Internal Tape Drive
The rear panel (see Figure 4) of your drive has the following features.
1. SCSI connector
2. SCSI ID connector
3. Power connector
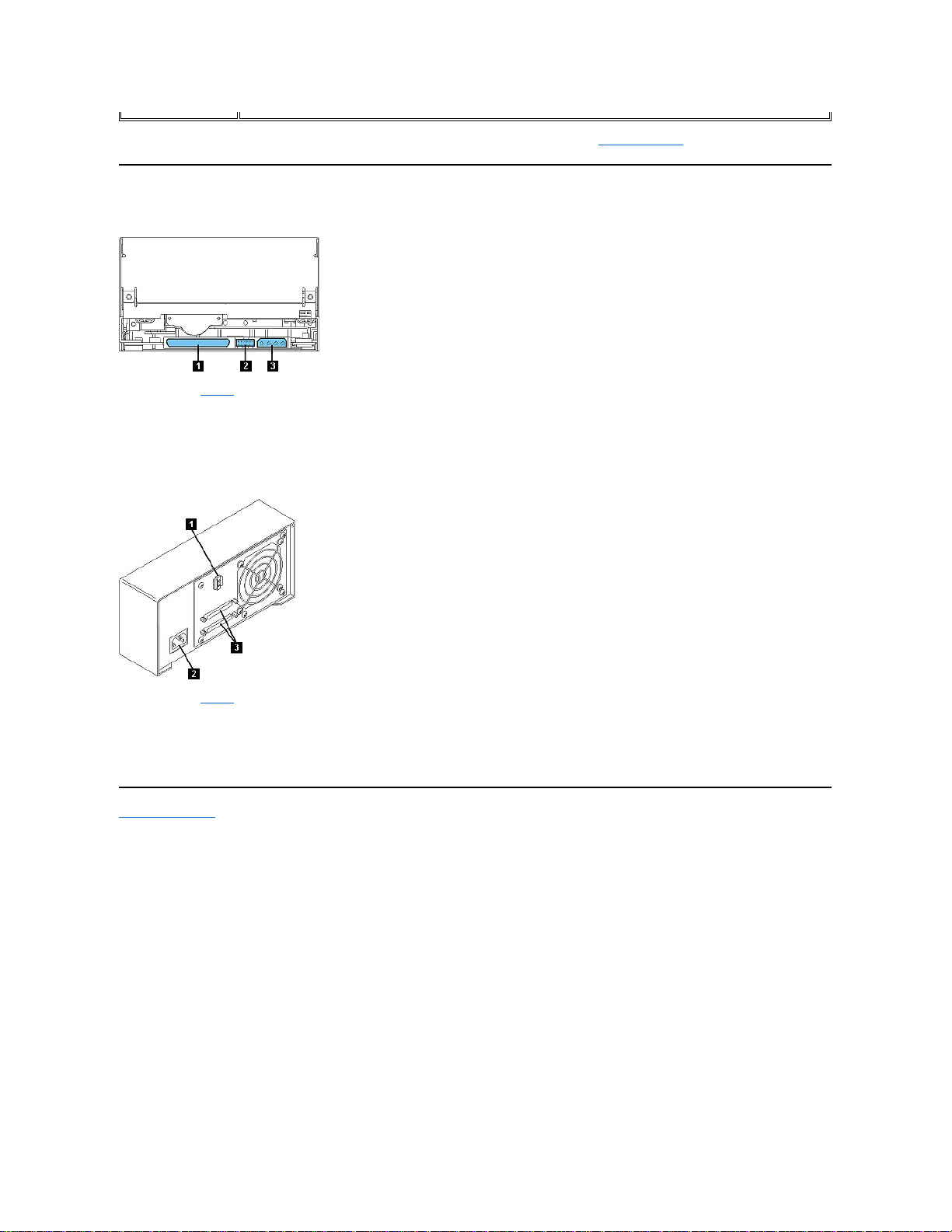
Figure 5. Rear Panel of External Tape Drive
The rear panel (see Figure 5) of your drive has the following features.
1. SCSI address switch
2. Power receptacle
3. External SCSI connectors
Back to Contents Page
Page 11

Back to Contents Page
Setup: DellTM PowerVaultTM 110T LTO-2 Tape Drive User's Guide
- Pre-installed Internal Drives - Installing Internal Drives - Installing External Drives - Loading Device Drivers - Verifying Drive Operation
Pre-installed Internal Drives
Dell performs the installation and setup of internal tape drives that are shipped as part of a system. Tape backup software normally is installed by Dell. If the software has
been recently upgraded, however, you may need to install the software. In this case, installation instructions are provided with the software.
For the latest supported software versions, go to http://www.support.dell.com or visit the support site of your backup software vendor
Installing Internal Drives
If your internal tape drive is not pre-installed, the installation instructions are as follows:
Installing the Tape Backup Software
Refer to your Tape Backup Software documentation for full details of how to install and operate your backup software application.
Installing the Drive - Prerequisites
DELL PowerVault 110T LTO-2 tape drives are Ultra160 LVD SCSI devices with a burst transfer rate of 160 MB/sec. Do not use the drive on a single-ended SCSI bus as
performance is restricted. Do not use on the same bus as other single-ended devices as this will switch the LVD host adapter into single-ended mode and restrict
performance. We recommend that a dedicated host bus adapter is used for the tape drive.
The tape drives have a 68-pin wide, high-density SCSI connector. If you are using a tape drive on an internal bus with other peripherals that run at Ultra2 speeds, it is important
that a 68-pin LVD-compatible ribbon cable is used.
Mounting Bay
You need one industry standard, 5 1/4-inch, full-height bay in which to install the PowerVault 110T LTO-2 tape drive. The drive may be mounted vertically or horizontally.
Install and configure the drive according to the instructions provided in the Dell documentation for your system.
Mounting Hardware
Most servers use trays or rails to mount the tape drive. For some servers, no tray or rails are required. Devices simply slide into the computer's chassis and are fixed with
screws.
Installing the Drive - Step-By-Step Instructions
Step 1 - Unpack the Drive. Unpack the tape drive and store the packaging. You may need the packaging if you return the unit for service.
A period of time is required if the temperature of the drive when unpacked is different than the temperature of its operating environment (measured at the front of the bezel near
the air intake area; see Figure 1). The recommended time is 4 hours after the drive has been unpacked or 1 hour after any condensation that you can see has evaporated,
whichever is greater. To allow the drive to adjust to its new environment, apply the following measures:
l If the drive is colder than its operating environment and the air contains sufficient humidity, condensation may occur in the drive and damage it. When the drive has
warmed to the operating temperature range (greater than 10 degrees C or 50 degrees F) and no danger of condensation is present (the air is dry), warm the drive more
quickly by powering it on for 30 minutes. Use a scratch tape to test the drive before inserting a tape that contains data.
l If the drive is hotter than its operating environment, the tape can stick to the drive head. When the drive has cooled to the operating temperature range (less than 40
degrees C or 104 degrees F), cool the drive more quickly by applying airflow for 30 minutes. Power on the drive and use a diagnostic tape to test it before inserting a
tape that contains data.
If you are uncertain about whether the temperature of the drive is within the recommended operating range or the humidity is sufficient to cause condensation, allow the drive
to adjust to its new environment for the full 4 hours.
Figure 1. Air Intake Area
Page 12

Step 2 - Remove Power from the Computer.
1. Power-off the computer.
2. Disconnect the power cord from both the electrical outlet and the computer.
Step 3 - Setting the SCSI ID. Your tape drive is shipped with a default SCSI ID of 6, but it can be assigned any unused ID between 0 and 15. Do not use SCSI ID 7, which is
reserved for the SCSI controller, or SCSI ID 0, which is typically assigned to the boot disk. We do not recommend installing the drive onto a narrow SCSI bus, as this will
restrict performance.
To set the SCSI ID:
1. Locate the SCSI ID connector (See number 3 on the rear panel diagram in the Introduction). The SCSI ID is set using jumpers on a set of pins at the rear of the drive.
2. Determine whether you need to change the SCSI ID from the default of 6. Make sure the ID is not used by another device.
3. Referring to Figure 2, find the ID number that you chose. Then, place jumpers on the connector pins as shown (use a pair of needle-nose pliers to connect the jumpers
to the pins that are shaded). Spare jumpers will be on the pin array itself (but only attached to a single pin).
Figure 2. SCSI Connector Pins
Step 4 - Prepare the Mounting Bay in Your Computer.
Refer to your computer system's documentation for instructions on how to prepare the mounting bay to receive the tape drive.
Step 5 - Attach Mounting Hardware
If your computer requires special rails or other hardware to install the tape drive, mount them on the tape drive in this step.
If your computer does not require special mounting hardware, proceed to step 6 now.
Figure 3. Install the Drive
Step 6 - Install the Drive
Slide the tape drive into the open bay, aligning the tray or rails with the slots in the bay, as shown in Figure 3.
Figure 4. Mounting Holes on Tape Drive
CAUTION: Static electricity can damage electronic components. Always wear an antistatic wriststrap if possible. If not, to equalize the
electromagnetic charges, touch a bare metal part of the computer (such as the back plate) before you remove the tape drive from its bag.
CAUTION: To avoid personal injury or damage to the computer or tape drive, ensure the computer power cord is disconnected before you install the
drive.
Page 13

1. 6-32 Mounting Screw Holes
2. M-3 Mounting Screw Holes
If your computer does not use mounting hardware, check that the holes in the chassis are aligned with the holes in the side of the tape drive.
Do not secure the drive with screws at this point because you may have to move the drive to get the cables in place.
Figure 5. Attach Power and SCSI Cables
1. Power Connector
2. SCSI Connector
Step 7 - Attach Power and SCSI Cables
Attach a spare power cable from the computer's internal power supply to the power connector, as shown in Figure 5, item 1.
Attach a spare SCSI cable on the computer's SCSI ribbon cable to the SCSI connector, as shown on Figure 5, item 2.
Figure 6. Secure the Drive
Step 8 - Secure the Drive
The tape drive can be mounted several ways. Ensure you have the proper mounting rails or drive mounting sled and the correct screws (6-32 for side mounting or M-3 for
bottom mounting). Some servers require the drive to be inserted into a media bay and attached directly to the server.
Step 9 - Connect Computer Power and Test Power to the Tape Drive.
Connect the power cord to the computer and to the electrical outlet. To ensure that the drive is receiving power, watch for the following while turning on the power to the
computer:
1. The single-character display presents a series of random characters.
NOTE: If the drive is the last device on the SCSI chain, it must be terminated.
Page 14

2. The single-character display becomes blank (not lit).
3. The status light briefly becomes solid amber, then becomes solid green.
Installing External Drives
Installing the Tape Backup Software
Refer to your Tape Backup Software documentation for full details of how to install and operate your backup software application. For the latest supported software versions,
go to http://www.support.dell.com or visit the support site of your backup software vendor
Installing the Drive - Prerequisites
The tape drives are Ultra160 SCSI devices designed to operate on a low voltage differential SCSI bus (LVD) with a burst transfer rate of 160 MB/sec. Do not use the drive on a
single-ended SCSI bus as performance is restricted. Do not use on the same bus as other single-ended devices as this will switch the LVD's host adapter into single-ended
mode and restrict performance. We recommend that a dedicated host bus adapter is used for the tape drive.
Your computer must have a properly installed and configured SCSI host adapter or a SCSI controller on the motherboard (SCSI-2 or SCSI-3 compliant) with driver software that
supports the tape drive. Check the server documentation for the specification of any built-in SCSI channels. Do not connect to a RAID controller channel; these are for disk
drives only. Consult your supplier for details.
The tape drive will attach to a computer with a HD-68 LVD SCSI connector (68 pins). If your server or host bus adapter is equipped with a very high density (VHD) wide SCSI
connector, you will need to order a 68-pin HD-to-VHD converter or 68-pin HD-to-VHD cable.
Installing the Drive - Step-By-Step Instructions
Figure 7. Rear Panel of the External Tape Drive
1. SCSI Address Switch
2. Power Receptacle
3. External SCSI Connectors
4. Power On/Off Button
Step 1 - Setting the SCSI ID. Your tape drive is shipped with a default SCSI ID of 6, but it can be assigned any unused ID between 0 and 15. Do not use SCSI ID 7, which is
reserved for the SCSI controller, or SCSI ID 0, which is typically assigned to the boot disk. We do not recommend installing the drive onto a narrow SCSI bus, as this will
restrict performance.
Determine whether you need to change the SCSI ID from the default of 6.
Change the tape drive's SCSI ID, if necessary. Use a small screwdriver or a ball-point pen to press the indented SCSI ID selector buttons on the rear panel (see number 1 in
Figure 7) until the required value is displayed. Do not use a pencil because small bits of lead could contaminate the drive. The computer and the tape drive SCSI IDs are only
checked at power-on. To change the SCSI ID after installation, power down both the computer and the tape drive, change the drive's SCSI ID, power up the tape drive, and
then power up the computer.
Step 2 - Positioning the Tape Drive. Position the tape drive anywhere that is convenient to the host. The only restrictions are the length of the power cord and the length of
the SCSI cable. Recommended locations are:
l Away from high-traffic areas, especially if the floor is carpeted.
l Out of computer rooms to avoid toner and paper dust. Do not store paper supplies next to any unit.
l Away from moving air, such as doorways, open windows, fans, and air conditioners.
l Off the floor.
l In a horizontal position.
l Where the tape cartridge can easily be inserted.
The tape drive should not be stacked. Do not place anything on top of the unit.
Step 3 - Connecting Power. An external DELL PowerVault 110T LTO-2 drive will operate using any voltage in the range 100-240 volts (50-60 Hz). No adjustment is needed.
To connect your drive to the power supply, proceed as follows:
Page 15

Ensure that the power on/off button is set to off by pressing it (See number 4 in Figure 7.
Plug the power cable securely into the socket on the rear panel of the drive. (See number 2 in Figure 7.)
Plug the other end of the power cable into a grounded power outlet.
Because the tape drive may not complete the Power-On Self Test (POST) without SCSI termination, ensure that the terminator (or SCSI bus with termination) is connected to
one of the two SCSI connectors at the rear of the unit.
Power on the tape drive by pressing the power on/off button (See number 4 in Figure 7. The tape drive runs the POST, which checks all hardware except the drive head.
Write the model name, product number, serial number, SCSI ID, and service tag number (external drives only) of your drive somewhere safe for future reference. The model
name is on the front of the drive and the product service tag, and serial numbers are on a label on the bottom of the drive.
Step 4 - Connecting the SCSI Cable. Perform a normal system shutdown and turn off the computer and any connected peripherals. Ensure that the tape drive is plugged
into an electrical outlet.
If the tape drive is the only device on the SCSI bus, attach one end of the SCSI cable to the host. Attach the other end of the SCSI cable to either SCSI connector on the rear
panel of the tape drive and secure it by tightening the screws. (See number 3 in Figure 7.) The cable can be up to 25 m (82 ft) long when the tape drive is the only device on
the bus. This configuration is shown in Figure 8.
Figure 8. Connecting One SCSI Device
1. Tape Drive
2. SCSI Connectors
3. Terminator
4. SCSI Bus Cable
5. SCSI Host Adapter Card
6. Host
If the tape drive is one of multiple devices on the SCSI bus, connect the SCSI cable to the next device on the bus, move the terminator to the last device on the bus, then
issue the host command to resume operation. This configuration is shown in Figure 9. The cable can be up to 12 m (39 ft) long.
Figure 9. Connecting Multiple SCSI Devices
1. Tape Drive
2. SCSI Connectors
3. Terminator
4. SCSI Bus Cable
5. SCSI Host Adapter Card
6. Host
7. Another Device
Step 5 - Configuring the Tape Drive to the Host. Power on the tape drive. Refer to your host and application software manuals to configure the tape drive for use.
Loading Device Drivers
Microsoft Windows 2000
This section describes how to install, remove, and disable the Microsoft Windows 2000 Device Driver for the tape drive.
Installation Procedures
CAUTION: To avoid damaging the computer or tape drive, ensure that both are powered off while you attach the SCSI cable. For optimum
performance, we recommend that your tape drive is installed on a dedicated SCSI bus.
Page 16

1. Make sure that you are logged on to the host server or workstation with Administrator privileges.
2. Insert the Dell Powervault 110T LTO-2 Drive Support CD into the CD drive on the host server or workstation.
3. Right-click the My Computer icon on the Windows desktop, click Manage, then click Device Manager.
4. The tape drive should be listed under the "? Other Devices" item as "IBM Ultrium-TD2 SCSI Sequential Device."
5. Right-click the IBM Ultrium-TD2 SCSI Sequential Device listing, click Uninstall, and then click the OK button to confirm that you want to remove the device.
6. Click the Action button in the upper-left corner of the Computer Management dialog box.
7. Click Scan for Hardware Changes. Windows 2000 now scans for the Dell PowerVault 110T LTO-2 drive. The tape drive appears under "? Other Devices" again.
8. Right-click the IBM Ultrium-TD2 SCSI Sequential Device listing and click Properties.
9. Click the Reinstall Driver button.
10. When the Upgrade Device Driver Wizard appears, click the Next button.
11. Click Display a list ... and then click the Next button.
12. Click the Tape Drives item in the list. You may have to scroll down to see this item. Click the Next button.
13. Click the Have Disk button, type d:\Drivers\W2K, replacing d: with the drive letter for the CD drive into which you inserted the support CD, and click the OK button.
14. Click the IBM Ultrium LTO Generation 2 W2K tape drive entry and click the Next button.
15. Click the Next button to install the driver.
16. You may get a warning that says "Installing this driver is not recommended ..." Click the Yes button anyway.
17. Click the Finish button.
18. Close the Device Properties dialog box.
19. The drive now appears in Device Manager under Tape drives and is ready to use.
Microsoft Windows Server 2003
1. Make sure that you are logged on to the host server or workstation with Administrator privileges.
2. Insert the Dell PowerVault 110T LTO-2 Drive Support CD into the CD drive on the host server or workstation.
3. Right-click the My Computer icon on the Windows desktop, click Manage, then click Device Manager.
4. The tape drive should be listed under the "? Other Devices" item as "IBM Ultrium-TD2 SCSI Sequential Device."
5. Right-click the IBM Ultrium-TD2 SCSI Sequential Device listing, click Uninstall, and then click the OK button to confirm that you want to remove the device.
6. Click the Action button in the upper-left corner of the Computer Management dialog box.
7. Click Scan for Hardware Changes. Windows .NET now scans for the Dell PowerVault 110T LTO-2 drive. The tape drive appears under "? Other Devices" again.
8. Right-click the IBM Ultrium-TD2 SCSI Sequential Device listing and click Properties.
9. Click the Reinstall Driver button. (If the Reinstall Driver button is not visible, you may have to click the Driver tab, then Update driver.)
10. The Upgrade Device Driver Wizard appears.
11. Click the Install from List or Specific Location radio button.
12. Click the Next button.
13. Click Include this location in the search.
14. Type d:\Drivers\W2K3 in the directory field, replacing d: with the drive letter for the CD drive into which you inserted the support CD and click the OK button.
15. You may have to click Continue to bypass a warning.
16. Click the Finish button.
17. Close the Device Properties dialog box.
18. The drive now appears in Device Manager under Tape drives and is ready to use.
Verifying Drive Operation
Once you have installed the drive hardware, you should verify that it is functioning properly before you store your valuable data. Switch on the computer. For external drives,
switch on the drive before you switch on the computer.
The tape drive will run its Power-On Self Test (POST) which checks all hardware except for the drive head. The single character display will present a series of random
characters, then become blank (not lit). The status light will briefly become solid amber, then become solid green.
Verify that the tape drive installation was successful. Following the instructions given with your Tape Backup Software application, write test data to a tape, read the test data
from the tape and compare the data read from the tape with the original data on disk.
Back to Contents Page
Page 17

Back to Contents Page
Using the Tape Backup Software: DellTM PowerVaultTM 110T LTO-2 Tape Drive User's
Guide
See the User's Operating Guide supplied with your Tape Backup application. For the latest supported software versions, go to http://www.support.dell.com or visit the support
site of your backup software vendor
Back to Contents Page
Page 18

Back to Contents Page
Specifications: DellTM PowerVaultTM 110T LTO-2 Tape Drive User's Guide
- General - External Drive - Internal Drive
General
External Drive
Physical specification
l dimensions: 24.9 cm (9.80 in.) width, 29.0 cm (11.42 in.) length, 12.5 cm (4.92 in.) height
l weight: 6.40 kg (14.1 lbs)
Power requirements
l power: 100-240 VAC, 50/60 Hz, .58A line current at 100 VAC, .24A line current at 240 VAC
Performance
l interface: Ultra160 LVD SCSI
l recording format: LTO Ultrium Generation 2
l media: LTO Ultrium
l capacity: 200 GB (native) 400 GB (compressed, assuming 2:1 compression)
l sustained transfer rate: native 35 MB/sec, compressed 70 MB/sec (assumes 2:1 compression)
l burst transfer rate: up to 160 MB/sec
Operating limits
l temperature: 10 degrees C to 35 degrees C (50 degrees F to 95 degrees F)
l humidity: 20% to 80% Relative Humidity (non-condensing)
l maximum wet bulb temperature: 28 degrees C (82.4 degrees F)
l maximum altitude: 3048 m (10000 ft)
Non-operating limits (Storage or Shipping)
l temperature: -40 degrees C to 65 degrees C (-40 degrees F to 149 degrees F)
l humidity: 5% to 95% Relative Humidity (non-condensing)
l maximum wet bulb temperature: 38 degrees C (100 degrees F)
Internal Drive
Physical specification
NOTE: These specifications are provided by the manufacturer for information purposes only and do not constitute an extension of Dell's warranty to you. Dell's
warranty is contained in the documentation for your system.
Specification
Value
Manufacturer
Manufactured for Dell
Model Number
DELL PowerVault 110T LTO-2 Tape Drive: LTO Internal; LTO External
Interface Type
Ultra160 Low-Voltage Differential (LVD) SCSI bus
Width
146.0 mm (5.75 in.) without bezel
148.3 mm (5.84 in.) with bezel
Length
205.5 mm (8.09 in.) without bezel
210.5 mm (8.29 in.) with bezel
Height
82.5 mm (3.25 in.) without bezel
84.8 mm (3.34 in.) with bezel
Weight (without a cartridge)
3 kg (6 lb 10 oz)
Page 19

Power requirements
Performance
l interface: Ultra160 LVD SCSI
l recording format: LTO Ultrium Generation 2
l media: LTO Ultrium
l capacity: 200 GB (native) 400 GB (compressed, assuming 2:1 compression)
l sustained transfer rate: native 35 MB/sec, compressed 70 MB/sec (assumes 2:1 compression)
l burst transfer rate: up to 160 MB/sec
Operating limits
l temperature: 10 degrees C to 35 degrees C (50 degrees F to 95 degrees F)
l humidity: 20% to 80% Relative Humidity (non-condensing)
l maximum wet bulb temperature: 29 degrees C (84.2 degrees F)
l maximum altitude: 3048 m (10,000 ft)
Non-operating limits (Storage)
l temperature: -40 degrees C to 65 degrees C (-40 degrees F to 149 degrees F)
l humidity: 5% to 95% Relative Humidity (non-condensing)
l maximum wet bulb temperature: 38 degrees C (100 degrees F)
Back to Contents Page
Tolerance
+ 5 Vdc and + 12 Vdc (plus or minus 10%)
Power supply current for 5 Vdc
1.3 A minimum/3.1 A maximum
Power supply current for 12 Vdc
0.2 A minimum/1.1 A maximum
Power supply peak for 5 Vdc (the instantaneous power by the power supply)
3.3 A for 100 ms15.5 W
Power supply peak for 12 Vdc (the instantaneous power by the power supply)
4.1 A for 2 ms49.2 W
Power usage for typical idle mode with no cartridge
10.9 W
Power usage for typical idle mode with a cartridge loaded
12.7 W
Power usage for reading and writing at 6.22 m/s
29 W
Power usage for sleep mode with no cartridge
9.0 W
Power usage for sleep mode with a cartridge loaded
10.8 W
Page 20

Back to Contents Page
Troubleshooting: DellTM PowerVaultTM 110T LTO-2 Tape Drive User's Guide
- Obtaining Drivers and Firmware Upgrades - Selecting a Diagnostic or Maintenance Function - General Guidelines - Methods of Receiving Errors and Messages -
Descriptions and Corrective Actions - Resolving Problems Reported by the Server - Resolving Media-Related Problems - Removing a Tape Drive - TapeAlert - Manually
Removing a Cartridge
Obtaining Drivers and Firmware Upgrades
Periodically check for updated levels of firmware by visiting the Web at http://support.dell.com.
Selecting a Diagnostic or Maintenance Function
The tape drive can run diagnostics, test write and read functions, test a suspect tape cartridge, and perform other diagnostic and maintenance functions. The drive must be in
maintenance mode to perform these functions. To place the drive in maintenance mode and select a diagnostic or maintenance function, see Table 1.
Table 1. Diagnostic and Maintenance Function Codes and Descriptions
CAUTION: When updating firmware, do not power off the tape drive until the update is complete, or the firmware may be lost.
Note: Maintenance functions cannot be performed concurrently with read or write operations. While in maintenance mode, the tape drive does not accept SCSI
commands from the server. Close all tape drive applications before entering maintenance mode.
Function Code 1 - Run SCSI Tape Drive Diagnostics
Causes the tape drive to run self tests.
Attention: Insert only a scratch data cartridge for this test. Data on the cartridge will be overwritten.
1. Make sure that no cartridge is in the drive.
2. Within a 1.5-second interval, press the eject button three times. The status light becomes solid amber, which means that the drive is in maintenance mode.
3. Press the eject button once per 1.5 seconds until 1 appears in the single-character display. If you cycle past 1, continue to press the eject button until it redisplays.
4. To select the function, press and hold the eject button for 3 seconds. After you select the function, 1 flashes, the drive runs diagnostics for approximately 90
seconds, then C flashes. When C flashes, the drive is waiting for a cartridge.
5. Within 60 seconds, insert a scratch data cartridge (or the tape drive exits maintenance mode). After you insert the cartridge, 1 flashes:
¡ If the diagnostic completes successfully, it begins again and runs for a maximum of 10 times. Each loop takes approximately 20 minutes to run. After the
tenth loop, the diagnostic stops and automatically exits maintenance mode. To halt the diagnostic, press the eject button within the first 20 minutes of the
test (or the diagnostic will run another 20 minutes). The drive acknowledges the request by slowing the length of time that the currently displayed character
flashes on the single-character display (from twice per second to once per second). The diagnostic continues to the end of its loop and then stops. The tape
drive then displays 0, rewinds and unloads the cartridge, and exits maintenance mode.
¡ If the diagnostics fail, the status light flashes amber and an error code displays. The tape drive unloads the tape cartridge and exits maintenance mode.
Function Code 2 - RESERVED (Service Function)
Function Code 3 - RESERVED (Service Function)
Function Code 4 - Force a Dump of Vital Data to Tape Drive Memory
Causes the tape drive to perform a collection (or dump) of of vital technical data to drive memory. (A drive dump is also known as a save of the firmware trace.)
1. Make sure that no cartridge is in the drive.
2. Within a 1.5-second interval, press the eject button three times. The status light becomes solid amber, which means that the drive is in maintenance mode.
3. Press the eject button once per 1.5 seconds until 4 appears in the single-character display. If you cycle past 4, continue to press the eject button until it redisplays.
4. To select the function, press and hold the eject button for 3 seconds. After you select the function, 4 displays, followed by 0. The single-character display then goes
blank, and the tape drive exits maintenance mode.
An illuminated red dot on the single-character display indicates that a drive dump has been created.
You can also perform this operation when the tape drive is in normal operating mode. Simply press and hold the eject button for 10 seconds.
Notice: When an error code displays, a red dot also displays to remind you that a dump already exists. If you perform Function Code 4, it will overwrite the
dump and cause the error information to be lost.
Function Code 5 - RESERVED (Service Function)
Function Code 6 - RESERVED (Service Function)
Function Code 7 - RESERVED (Service Function)
Function Code 8 - RESERVED (Service Function)
Function Code 9 - Display Error Code Log
Causes the tape drive to display the last 10 error codes, one at a time (the codes are ordered; the most recent is presented first and the oldest (tenth) is presented last).
Page 21

To view the drive error log:
1. Make sure that no cartridge is in the drive.
2. Within a 1.5-second interval press the eject button three times. The status light becomes solid amber, which means that the drive is in maintenance mode.
3. Press the eject button once per 1.5 seconds until 9 appears in the single-character display.
4. Press and hold the eject button for 3 seconds to view the most recent error code.
5. Refer to Descriptions and Corrective Actions to determine the meaning of the code and the action to take.
6. Press the eject button to view the next error code. (The codes are ordered; the most recent is presented first and the oldest (tenth) is presented last.)
7. Continue to press the eject button until "0" appears, indicating that no more error codes exist. If no errors have been encountered or the log has just been cleared, a
"0" will appear immediately and the drive will exit maintenance mode. A maximum of ten error codes are stored.
To redisplay the error codes, repeat steps 1 through 7.
Function Code A - Clear Error Code Log
Causes the tape drive to erase the contents of the error code log.
1. Make sure that no cartridge is in the drive.
2. Within a 1.5-second interval, press the eject button three times. The status light becomes solid amber, which means that the drive is in maintenance mode.
3. Press the eject button once per 1.5 seconds until A appears in the single-character display. If you cycle past A, continue to press the eject button until it
redisplays.
4. To select the function, press and hold the eject button for 3 seconds. After you select the function, the tape drive erases all errors from the error code log, displays
0, then exits maintenance mode.
Function Code C - Insert Cartridge into Tape Drive
This function cannot be selected by itself. It relates to other maintenance functions (such as Run Tape Drive Diagnostics) that require a scratch tape cartridge that is not
write protected.
Function Code E - Test Cartridge & Media
Causes the tape drive to perform a Write/Read test (on the edge bands) to ensure that a suspect cartridge and its magnetic tape are acceptable. The tape drive takes
approximately 10 minutes to run the test.
Attention: Data on the suspect tape will be overwritten.
1. Make sure that no cartridge is in the drive.
2. Within a 1.5-second interval, press the eject button three times. The status light becomes solid amber, which means that the drive is in maintenance mode.
3. Press the eject button once per 1.5 seconds until E appears in the single-character display. If you cycle past E, continue to press the eject button until it redisplays.
4. To select the function, press and hold the eject button for 3 seconds. After you select the function, C flashes. When C flashes, the drive is waiting for a cartridge.
Within 60 seconds, insert the suspect data cartridge (or the tape drive exits maintenance mode). After you insert the cartridge, E flashes and the test begins:
¡ If no error is detected, the test begins again and runs for a maximum of 10 times. After the tenth loop, the test stops and the drive automatically exits
maintenance mode. To halt the test, press the eject button. The drive acknowledges the request by slowing the length of time that the currently displayed
character flashes on the single-character display (from twice per second to once per second). The test continues to the end of its loop and then stops. The
tape drive then rewinds and unloads the cartridge, displays 0, and exits maintenance mode.
¡ If an error is detected, the tape drive displays 7, unloads the tape cartridge, and exits maintenance mode.
Function Code F - Fast Read/Write Test
Causes the tape drive to perform tests to ensure that the drive can read from and write to tape. This diagnostic performs fewer tests than the Run Tape Drive Diagnostics
test (Function Code 1). The tape drive takes approximately three minutes to run the test. The Fast Read/Write Test is not as comprehensive a test and is not
recommended for isolating errors between the drive and the media.
Attention: Data on the suspect tape will be overwritten.
1. Make sure that no cartridge is in the drive.
2. Within a 1.5-second interval, press the eject button three times. The status light becomes solid amber, which means that the drive is in maintenance mode.
3. Press the eject button once per 1.5 seconds until F appears in the single-character display. If you cycle past F, continue to press the eject button until it redisplays.
4. To select the function, press and hold the eject button for 3 seconds. After you select the function, C flashes. When C flashes, the drive is waiting for a cartridge.
Within 60 seconds, insert the suspect data cartridge (or the tape drive exits maintenance mode). After you insert the cartridge, F flashes and the test begins.
¡ If no error is detected, the test begins again and runs for a maximum of 10 times. Each loop takes approximately 3 minutes to run. After the tenth loop, the
test stops and the drive automatically exits maintenance mode. To halt the test, press the eject button. The drive acknowledges the request by slowing the
length of time that the currently displayed character flashes on the single-character display (from twice per second to once per second). The test continues to
the end of its loop and then stops. The tape drive then rewinds and unloads the cartridge, displays 0, and exits maintenance mode.
¡ If an error is detected, the tape drive displays an error code, unloads the tape cartridge, and exits maintenance mode.
Function Code H - Test Head
Causes the tape drive to perform the Head Resistance Measurements test and a Write/Read test (on the center of the tape). The drive runs these tests to ensure that the
tape drive's head and tape-carriage mechanics are working correctly. The tape drive takes approximately 10 minutes to run the test.
1. Make sure that no cartridge is in the drive.
2. Within a 1.5-second interval, press the eject button three times. The status light becomes solid amber, which means that the drive is in maintenance mode.
Page 22

General Guidelines
If you encounter problems when running the Dell PowerVault 110T LTO-2 Tape Drive, refer to Table 2 for common problems. If the problem is not identified, refer to Methods of
Receiving Errors and Messages. The color and condition of the status light may also indicate a problem.
Table 2. General Troubleshooting
Methods of Receiving Errors and Messages
Use the Table 3 as a guide for identifying error codes and message codes reported by the tape drive, its computer (if applicable), or the server.
Table 3. Methods of Receiving Errors and Messages
3. Press the eject button once per 1.5 seconds until H appears in the single-character display. If you cycle past H, continue to press the eject button until it
redisplays.
4. To select the function, press and hold the eject button for 3 seconds. After you select the function, C flashes. When C flashes, the drive is waiting for a cartridge.
Within 60 seconds, insert a scratch data cartridge (or the tape drive exits maintenance mode). After you insert the cartridge, H flashes and the test begins:
¡ If no error is detected, the test begins again and runs for a maximum of 10 times. Each loop takes approximately 10 minutes to run. After the tenth loop, the
test stops and the drive automatically exits maintenance mode. To halt the test, press the eject button. The drive acknowledges the request by slowing the
length of time that the currently displayed character flashes on the single-character display (from twice per second to once per second). The test continues to
the end of its loop and then stops. The tape drive then rewinds and unloads the cartridge, displays 0, and exits maintenance mode.
¡ If an error is detected, the tape drive displays 5, unloads the tape cartridge, and exits maintenance mode.
Function Code L - Reserved for Future Use
Reserved for future use.
Function Code P or U - RESERVED (Service Function)
If the problem is this....
Do this....
A code displays on the single-character
display and the status light flashes
amber.
The tape drive detected an error or is directing you to an informational message. See Methods of Receiving Errors and
Messages.
The status light or single-character
display never turns on.
The tape drive has no power. Check the power at the power source. Connect power to the tape drive. If the problem persists,
contact Dell technical support.
The tape drive will not load a tape
cartridge.
One of the following has occurred:
l A tape cartridge is already loaded. To remove the cartridge, press the eject button. If the cartridge does not eject, turn off
the power to the tape drive, then turn it back on. After the status light becomes solid green, press the eject button to
eject the cartridge.
l The tape cartridge was loaded incorrectly. To properly load a cartridge, see the Loading section in Using the Tape Drive.
l The tape cartridge may be defective. Load another tape cartridge. If the problem exists for multiple cartridges, the tape
drive is defective. Contact Dell technical support.
l The tape drive has no power. Connect power to the tape drive.
The tape drive will not unload the tape
cartridge.
The tape cartridge is stuck or is broken. Press the unload button. If the cartridge does not eject, turn off the power to the tape
drive, then turn it back on (note that the mid-tape recovery could take up to 5 minutes to complete). If the cartridge still does
not eject, manually remove it (see Manually Removing a Cartridge).
The server received TapeAlert flags.
See TapeAlert Flags.
The server reported SCSI problems (such
as selection or command time-outs, or
parity errors).
See Resolving Problems Reported by the Server.
Codes display on the single-character
display, but the status light does not turn
on.
The tape drive is defective. Contact Dell technical support.
The tape drive does not respond to server
commands.
Press and hold the eject button on the drive for 10 seconds to force a drive dump. The drive will save the dump and then reboot
to allow communication to the drive to occur. Do not cycle power, as this will erase the contents of the dump.
NOTE: The codes on the single-character display have different meanings, depending on whether they display during normal operations or while the drive is in
maintenance mode. Codes that occur during normal operations are defined in Descriptions and Corrective Actions. Codes that occur while in maintenance mode
are defined in Selecting a Diagnostic or Maintenance Function.
If the error or message was presented by....
Do this....
The computer's display (if the tape drive is enclosed in a
library or autoloader)
Refer to the documentation for the computer.
The tape drive's single-character display and the status
light flashes amber
See Descriptions and Corrective Actions. To determine the meaning of status light activity, see the Front Panel
section in the Introduction.
The tape drive's single-character display and the status
See Selecting a Diagnostic or Maintenance Function. To determine the meaning of status light activity, see the
Page 23

Descriptions and Corrective Actions
Table 4 gives descriptions of the errors and messages that pertain to the tape drive, and tells what to do when you receive them.
Table 4. Descriptions and Corrective Actions
light is solid amber
Front Panel section in the Introduction.
SCSI log sense data (such as TapeAlert flags) or SCSI
drive sense data
See TapeAlert Flags or Descriptions and Corrective Actions.
The tape drive's error log
See Descriptions and Corrective Actions.
Notice: If the tape drive detects a permanent error and displays an error code other than 0, it automatically performs a dump of vital data to drive memory. If you
force a dump, the existing dump will be overwritten and data will be lost. After you force a dump, do not turn off the power to the tape drive or you may lose the
dump data.
The single-character display clears if you power-off the drive.
Code
Cause and Action
0
No error occurred and no action is required. This code displays:
l When power is cycled (turned off, then on) to the tape drive.
l When diagnostics have finished running and no error occurred.
NOTE: The single-character display is blank during normal operation of the tape drive.
1
Cooling problem. The tape drive detected that the recommended operating temperature was exceeded. Perform the following action:
1. If a fan is present in the computer, ensure that it is rotating and is quiet. If not, replace the fan (for instructions about replacing the fan, see your
computer's documentation).
2. Remove any blockage that prevents air from flowing freely through the tape drive.
3. Ensure that the operating temperature and airflow is within the specified range (see Specifications).
4. If the operating temperature is within the specified range and the problem persists, contact Dell technical support.
The error code clears when you power-off the tape drive or place it in maintenance mode.
2
Power problem. The tape drive detected that the externally supplied power is either approaching the specified voltage limits (the drive is still operating) or is
outside the specified voltage limits (the drive is not operating). Perform the following action:
1. Ensure that the power connector is properly seated.
2. Ensure that the proper dc voltages are being applied within the tolerances allowed (see Specifications).
3. If the proper voltages are being applied but the problem persists, contact Dell technical support.
The error code clears when you power-off the tape drive or place it in maintenance mode.
3
Firmware problem. The tape drive determined that a firmware error occurred. Perform the following action:
1. Power the tape drive off and on, then retry the operation that produced the error. The error code clears when you power-off the tape drive or place it in
maintenance mode.
2. If the problem persists, download the latest firmware and retry the operation.
4
Firmware or tape drive problem. The tape drive determined that a firmware or tape drive hardware failure occurred. Perform the following action:
1. Power the tape drive off and on, then retry the operation that produced the error. The error code clears when you power-off the tape drive or place it in
maintenance mode.
2. If the problem persists, download the latest firmware and retry the operation; if new firmware is not available, contact Dell technical support.
5
Tape drive hardware problem. The drive determined that a tape path or read/write error occurred. To prevent damage to the drive or tape, the drive will not allow
you to insert a cartridge if the current cartridge was successfully ejected. The error code may clear when you cycle power to the tape drive or place it in
maintenance mode. If the problem persists, contact Dell technical support.
Tape drive or media error. The drive determined that an error occurred, but it cannot isolate the error to faulty hardware or to the tape cartridge. Perform the
following action:
For Problems with Writing Data:
If the problem occurred while the drive was writing data to the tape, and if you know the volume serial number (located on the cartridge label) of the tape
cartridge loaded in the drive when the problem occurred, retry the operation with a different cartridge:
l If the operation succeeds, the original cartridge was defective. Copy data from the defective cartridge and discard it.
l If the operation fails and another drive is available, insert the cartridge into the other drive and retry the operation.
Page 24

Resolving Problems Reported by the Server
6
¡ If the operation fails, discard the defective cartridge.
¡ If the operation succeeds, insert a scratch cartridge into the first drive and run the tape drive diagnostics (see Function Code 1 in Selecting a
Diagnostic or Maintenance Function).
n If the diagnostics fail, contact Dell technical support.
n If the diagnostics succeed, the error was temporary.
l If the operation fails and another drive is not available, insert a scratch cartridge into the drive and run the tape drive diagnostics (see Function Code 1 in
Selecting a Diagnostic or Maintenance Function).
¡ If the diagnostics fail, contact Dell technical support.
¡ If the diagnostics succeed, discard the cartridge.
If the problem occurs with multiple tape cartridges or if you do not know the tape cartridge's volume serial number, run the tape drive diagnostics (see Function
Code 1 in Selecting a Diagnostic or Maintenance Function):
l If the diagnostics fail, contact Dell technical support.
l If the diagnostics succeed, run the Test Head diagnostic (see Function Code H in Selecting a Diagnostic or Maintenance Function).
¡ If the Test Head diagnostic fails, contact Dell technical support.
¡ If the Test Head diagnostic succeeds, replace the cartridges that caused the problem.
The error code clears when you remove the tape cartridge or place the drive in maintenance mode.
For Problems with Reading Data:
If the problem occurred while the drive was reading data from the tape, and if you know the volume serial number of the tape cartridge, perform one of the
following procedures:
l If another drive is available, insert the cartridge into the other drive and retry the operation:
¡ If the operation fails, discard the defective cartridge.
¡ If the operation succeeds, insert a scratch cartridge into the first drive and run the tape drive diagnostics (see Function Code 1 in Selecting a
Diagnostic or Maintenance Function):
n If the diagnostics fail, contact Dell technical support.
n If the diagnostics succeed, the error was temporary.
l If another drive is not available, insert a scratch cartridge into the drive and run the tape drive diagnostics (see Function Code 1 in Selecting a
Diagnostic or Maintenance Function):
¡ If the diagnostics fail, contact Dell technical support.
¡ If the diagnostics succeed, discard the cartridge.
If the problem occurs with multiple tape cartridges or if you do not know the tape cartridge's volume serial number, run the tape drive diagnostics (see Function
Code 1 in Selecting a Diagnostic or Maintenance Function):
l If the diagnostics fail, contact Dell technical support.
l If the diagnostics succeed, run the Test Head diagnostic (see Function Code H in Selecting a Diagnostic or Maintenance Function).
¡ If the Test Head diagnostic fails, contact Dell technical support.
¡ If the Test Head diagnostic succeeds, replace the cartridges that caused the problem.
The error code clears when you remove the tape cartridge or place the drive in maintenance mode.
7
A high probability of media error. The tape drive determined that an error occurred because of a faulty tape cartridge. Try another tape cartridge. If the problem
occurs with multiple tape cartridges, see Resolving Media-Related Problems.
The error code clears when you remove the tape cartridge or place the drive in maintenance mode.
8
Tape drive or SCSI bus failure. The tape drive determined that a failure occurred in the tape drive's hardware or in the SCSI bus. See Resolving Problems
Reported by the Server. The error code clears 10 seconds after the drive detected the error or when you place the drive in maintenance mode.
9
Library to drive interface (RS-422) error. This interface is not used.
The error code clears when you place the drive in maintenance mode.
o, c, b, h,
d, E, or F
No error or message assigned. There may be a problem with the single-character display. Turn the power off, then on and determine whether all segments on
the single-character display are lit. If so, you may have a down-level version of the documentation (the documentation may not describe all of the available error
codes). Refer to the latest version of the documentation.
A
Tape drive hardware problem. The tape drive determined that a problem occurred which degraded the operation of the tape drive, but it did not restrict continued
use. If the problem persists, contact Dell technical support. The drive is usable, though the single-character display continues to indicate an error and the
status light flashes amber.
The error code may clear when you cycle power to the tape drive or place it in maintenance mode.
C
The tape drive needs to be cleaned. Clean the tape drive. See the Cleaning the Tape Mechanism section in Using the Tape Drive.
The error code clears when you clean the tape drive or place it in maintenance mode.
Page 25

The procedure for fixing SCSI bus errors varies, depending on whether the error is consistent or intermittent, and whether your configuration contains single or multiple tape
drives. The sections that follow describe how to fix each type of error.
Fixing a Consistent Error with a Single Drive on a SCSI Bus
1. Ensure that the power is on to the tape drive.
2. Ensure that the tape drive's SCSI address is the same as the SCSI address assigned by the server.
3. Replace the SCSI terminator and retry the failing operation.
4. Replace the SCSI cable and interposers, if any, and retry the failing operation
5. If these measures do not correct the problem, contact Dell customer support.
Fixing a Consistent Error with Multiple Drives on a SCSI Bus
When a consistent error occurs in a configuration that has multiple tape drives on the SCSI bus, you must determine if the problem exists with more than one tape drive. If the
problem is with all of the devices on the SCSI bus, the bus is stuck in a SCSI phase and cannot change to another phase or the SCSI cable from the server to the first device
is defective.
1. Ensure that the SCSI cable from the server to the first device is connected.
2. Disconnect all but the first tape drive on the SCSI bus. Move the terminator to the first SCSI device.
3. Run an application to determine whether the error will occur.
¡ If the error occurs, do the following:
n Replace the SCSI terminator and retry the failing operation.
n Replace the SCSI cable and interposers, if any, and retry the failing operation
n If these measures do not correct the problem, contact Dell customer support.
¡ If the error does not occur, connect one tape drive at a time back to the bus and repeat step 3 for each tape drive until you can identify which drive is defective.
4. Determine if the problem is with only one tape drive or with two or more tape drives.
¡ If the problem is with only one tape drive, do the following:
n Replace the SCSI terminator and retry the failing operation.
n Replace the SCSI cable and interposers, if any, and retry the failing operation
n If these measures do not correct the problem, contact Dell customer support.
¡ If the problem is with two or more tape drives, locate the first tape drive that has the error and replace the SCSI cable that connects the tape drive and the
interposer (if installed).
Fixing an Intermittent Error with a Single Drive on a SCSI Bus
1. Replace the SCSI terminator on the tape drive.
2. Run the operation that caused the error. If the problem persists, the problem may be with the cable.
3. Isolate which cable is causing the problem by replacing one cable at a time and running the operation that caused the error after each replacement.
4. If the problem persists, contact Dell technical support.
Fixing an Intermittent Error with Multiples Drives on a SCSI Bus
Refer to the server's error logs to determine which tape drive is the source of the problem:
l If only one tape drive is reporting a SCSI failure, contact Dell technical support.
l If multiple tape drives are reporting SCSI failures, the problem may be with the terminator or the SCSI cables:
¡ Replace the terminator and run the operation that caused the error. If the problem persists, the problem may be with the cables.
¡ Isolate which cable is causing the problem by replacing one cable at a time and run the operation that caused the error after each replacement.
Resolving Media-Related Problems
To resolve problems that are related to media, the tape drive's firmware includes:
l Test Cartridge & Media diagnostic that verifies whether a suspect cartridge and its magnetic tape are acceptable for use.
l Statistical Analysis and Reporting System (SARS) to assist in isolating failures between media and hardware. To determine the cause of failure, SARS uses the
cartridge performance history that is saved in the cartridge memory (CM) and the drive performance history that is kept in the drive's flash erasable programmable readonly memory (EPROM). Any failures that SARS detects are reported as TapeAlert flags on the server (see TapeAlert Flags).
If you encounter a media-related problem, use the following procedure:
1. If possible, run the tape cartridge in a different tape drive. If the operation in the other tape drive fails and 6 or 7 displays, replace the media. If the operation succeeds,
run the Test Cartridge & Media diagnostic (see Function Code E in Selecting a Diagnostic or Maintenance Function).
NOTE: Ensure that the SCSI terminator is always on the last tape drive on the SCSI bus.
When you run the Test Cartridge & Media diagnostic, data on the suspect tape is overwritten. If valuable data is on the tape, be sure to copy the data before running
this test.
Page 26

2. If the Test Cartridge & Media diagnostic fails, replace the media. If it runs successfully, clean the tape drive and run the tape drive diagnostics (see the Cleaning the
Tape Mechanism section in Using the Tape Drive and Function Code 1 in Selecting a Diagnostic or Maintenance Function).
3. If the tape drive diagnostics fail, contact Dell technical support. If the tape drive diagnostics run successfully, perform the operation that produced the initial media error.
Removing a Tape Drive
To remove the tape drive from a computer, perform the following steps:
1. Ensure that the tape drive does not contain a tape cartridge.
2. Deconfigure the drive from the server (for instructions, see your server's documentation).
3. Turn off the power to the computer. Disconnect the power cable from the computer and the electrical outlet.
4. Remove the cover of the computer.
5. Disconnect the internal power cable from the power connector (see number 3 in Figure 2).
6. Disconnect the internal SCSI cable from the SCSI connector (see number 1 in Figure 2).
7. Remove the tape drive from the computer and remove any mounting screws or rails from the side or bottom of the tape drive.
8. To reassemble, reverse these steps.
Figure 2. Rear view of the Tape Drive
Tape Alert
TapeAlert is a patented technology and standard of the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) that defines conditions and problems that are experienced by tape
drives. The technology enables a server to read TapeAlert flags from a tape drive through the SCSI interface. The server reads the flags from Log Sense Page 0x2E.
TapeAlert Flags
Table 5 lists the TapeAlert flags that are supported by the Dell PowerVault 110T LTO-2 Tape Drive.
Table 5. TapeAlert Flags and Descriptions
TapeAlert Flags Supported by the Tape Drive
Flag
Number
Flag
Parameter
(in hex)
Flag
Description
Action Required
3
03h
Hard error
Set for any unrecoverable read, write, or
positioning error. (This flag is set in
conjunction with flags 4, 5, or 6.)
See the Action Required column for Flag 4, 5, or 6 in this table.
4
04h
Media
Set for any unrecoverable read, write, or
positioning error that is due to a faulty tape
cartridge.
Contact Dell technical support.
5
05h
Read failure
Set for any unrecoverable read error where
isolation is uncertain and failure could be
due to a faulty tape cartridge or to faulty
drive hardware.
If Flag 4 is also set, the cartridge is defective. Contact Dell technical
support. If Flag 4 is not set, see error code 6 in Descriptions and Corrective
Actions.
6
06h
Write failure
Set for any unrecoverable write or
positioning error where isolation is uncertain
and failure could be due to a faulty tape
cartridge or to faulty drive hardware.
If Flag 9 is also set, make sure that the write-protect switch is set so that
data can be written to the tape (see the Setting the Write-Protect Switch
section in Using the Tape Drive). If Flag 4 is also set, the cartridge is
defective. Replace the tape cartridge. If Flag 4 is not set, see error code 6
in Descriptions and Corrective Actions.
8
08h
Not data grade
Set when severe servo errors occur while
loading a tape cartridge.
Replace the tape cartridge. If this error occurs with multiple tapes, see
error code 6 in Descriptions and Corrective Actions.
9
09h
Write protect
Set when the tape drive detects that the
tape cartridge is write-protected.
Make sure that the cartridge's write-protect switch is set so that the tape
drive can write data to the tape (see the Setting the Write-Protect Switch
section in Using the Tape Drive).
10
0Ah
No removal
Set when the tape drive receives an
UNLOAD command after the server
prevented the tape cartridge from being
Refer to the documentation for your server's operating system.
Page 27

Manually Removing a Cartridge
If problem-determination procedures identify the tape drive as the source of a problem, you can optionally perform one of the following:
l Manually remove the cartridge (see instructions below).
l If you are unable to manually remove the cartridge, contact trained service personnel for assistance.
removed.
11
0Bh
Cleaning media
Set when you load a cleaning cartridge into
the drive.
No action required.
12
0Ch
Unsupported format
Set when you load an unsupported cartridge
type into the drive or when the cartridge
format has been corrupted.
Use a supported tape cartridge.
15
0Fh
Cartridge memory
chip failure
Set when a cartridge memory (CM) failure is
detected on the loaded tape cartridge.
Replace the cartridge. If this error occurs on multiple tapes, see error code
6 in Descriptions and Corrective Actions.
16
10h
Forced eject
Set when you manually unload the tape
cartridge while the drive was reading or
writing.
No action required.
18
12h
Tape directory
corrupted in the
cartridge memory
Set when the drive detects that the tape
directory in the cartridge memory has been
corrupted.
Re-read all data from the tape to rebuild the tape directory.
20
14h
Clean now
Set when the tape drive detects that it
needs cleaning.
Clean the tape drive. See the Cleaning the Tape Mechanism section in
Using the Tape Drive.
21
15h
Clean periodic
Set when the drive detects that it needs
routine cleaning.
Clean the tape drive as soon as possible. The drive can continue to
operate, but you should clean the drive soon. See the Cleaning the Tape
Mechanism section in Using the Tape Drive.
22
16h
Expired clean
Set when the tape drive detects a cleaning
cartridge that has expired.
Replace the cleaning cartridge.
23
17h
Invalid cleaning
tape
Set when the drive expects a cleaning
cartridge and the loaded cartridge is not a
cleaning cartridge.
Use a valid cleaning cartridge.
30
1Eh
Hardware A
Set when a hardware failure occurs which
requires that you reset the tape drive to
recover.
If resetting the drive does not recover the error, use the error code from the
single-character display, library user interface, or SCSI drive sense data.
See Descriptions and Corrective Actions.
31
1Fh
Hardware B
Set when the tape drive fails its internal self
tests.
Use the error code on the single-character display, library user interface, or
SCSI drive sense data. See Descriptions and Corrective Actions.
32
20h
Interface
Set when the tape drive detects a problem
with the SCSI, Fibre Channel, or LDI (RS-
422) interface.
Locate error code 8 or 9 in Descriptions and Corrective Actions.
33
21h
Eject media
Set when a failure occurs that requires you
to unload the cartridge from the drive.
Unload and reload the tape cartridge.
34
22h
Download fail
Set when an FMR image is unsuccessfully
downloaded to the tape drive via the SCSI
interface.
Ensure that it is the correct image. Download the FMR image again.
36
24h
Drive temperature
Set when the drive's temperature sensor
indicates that the drive's temperature is
exceeding the recommended temperature of
the computer (see Specifications).
See error code 1 in Descriptions and Corrective Actions.
37
25h
Drive voltage
Set when the drive detects that the
externally supplied voltages are either
approaching the specified voltage limits or
are outside the voltage limits (see
Specifications).
See error code 2 in Descriptions and Corrective Actions.
39
27h
Diagnostics
required
Set when the drive detects a failure that
requires diagnostics to isolate the problem.
See error code 6 in Descriptions and Corrective Actions.
51
33h
Tape directory
invalid at unload
Set when the tape directory on the tape
cartridge that was previously unloaded is
corrupted. The file-search performance is
degraded.
Rebuild the tape directory by reading all the data
52
34h
Tape system area
write failure
Set when the tape cartridge that was
previously unloaded could not write its
system area successfully.
Copy the data to another tape cartridge, then discard the old cartridge.
53
35h
Tape system area
read failure
Set when the tape system area could not be
read successfully at load time.
Copy the data to another tape cartridge, then discard the old cartridge.
CAUTION: If you are not a trained service person, do not attempt to open the drive for repairs. Attempting a repair other than the manual removal of
a tape cartridge will void your warranty.
Page 28

Removing the Cartridge
If a tape cartridge fails to eject from the tape drive, you can manually remove the cartridge. The following tools are required for the procedure:
l 2.5-mm allen wrench
l Small-blade screwdriver or potentiometer-setting tool
l 2-mm hex wrench
l #3 Phillips screwdriver
l Needle-nose pliers
l Flashlight (optional)
To manually remove a tape cartridge, perform the following steps:
1. Place the drive so that the front faces you, then tilt it on its left side (see Figure 3).
2. Locate the access hole at the bottom of the unit (see number 1 in Figure 3).
3. Insert a 2.5-mm allen wrench into the access hole and position the wrench so that it is seated in the screw of the supply reel motor.
4. Push open the door of the tape load compartment and locate the flag (See number 2 in Figure 3) on the drive's takeup reel.
Figure 3. Determining whether the tape is broken
5. To determine whether the tape is broken, watch the flag (See number 2 in Figure 3) on the drive's takeup reel while you rotate the allen wrench (See number 1 in Figure
3) clockwise (do not let the wrench move counterclockwise):
¡ If you feel resistance to the allen wrench while attempting to turn the supply reel motor screw clockwise, go to step 7.
¡ If the takeup reel turns when you rotate the supply reel motor screw clockwise with the allen wrench, the tape is not broken. Go to step 6.
¡ If the takeup reel does not turn when you rotate the supply reel motor screw clockwise with the allen wrench and if supply reel motor screw rotates freely, the
tape is broken. You must determine the location of the leader block. To do so, insert a small-blade screwdriver or potentiometer-setting tool into the access hole
for the loader motor gear (See number 3 in Figure 3). Rotate the screwdriver counterclockwise. You may have to rotate for a lengthy period:
n If the cartridge moves up, the tape is completely in the cartridge and the leader block is in the home position. Continue rotating the screwdriver until the
cartridge ejects. Remove the cartridge.
n If you feel resistance and the cartridge does not move up, the leader block is not in the home position. Call your service representative.
6. Continue to rotate the allen wrench until you feel resistance. The tape has been rewound as far as it can go without unthreading.
7. With the allen wrench still inserted into the bottom access hole, insert a small-blade screwdriver or potentiometer-setting tool into the access hole for the loader motor
gear (See number 3 in Figure 3).
8. While keeping torque on the supply reel motor screw and rotating the allen wrench (See number 1 in Figure 3) clockwise, rotate the loader motor gear with the smallblade screwdriver (See number 3 in Figure 3) counterclockwise (see arrow). As you rotate the screwdriver, the allen wrench moves slightly.
CAUTION: Before performing this procedure, note the following:
l Ensure that you have attempted all normal methods of removing the tape cartridge from the drive.
l This procedure may damage the stuck tape cartridge. If you use this procedure, copy the data from the stuck cartridge to another cartridge. If
you believe the cartridge has been damaged, replace it.
l Do not use a power screwdriver to perform this procedure because it can destroy the tape.
l Never touch the head or electronic components within the drive. Touching may cause contamination or damage by electrostatic discharge.
CAUTION: In the following step, rotate the allen wrench clockwise, not counterclockwise. A counterclockwise motion may damage the tape.
NOTE: The number of required rotations depends on where the beginning of the tape is on the cartridge's takeup reel. You may have to rotate the allen wrench for
a lengthy period.
Page 29

9. With the small-blade screwdriver, continue to rotate the loader motor gear in the unload direction (counterclockwise):
¡ If you feel no resistance to the allen wrench and the cartridge slowly moves up and out of the tape load compartment to the fully ejected position, the procedure
was successful. Remove the small-blade screwdriver and go to step 10.
¡ If you feel resistance to the allen wrench and the cartridge does not move, the loader mechanism is jammed or the leader block is not at the home position.
10. Remove the tape cartridge.
11. To ensure that the drive operates properly, run tape drive diagnostics (see Function Code 1 in Selecting a Diagnostic or Maintenance Function).
Back to Contents Page
Page 30

Back to Contents Page
Using the Tape Drive: DellTM PowerVaultTM 110T LTO-2 Tape Drive User's Guide
- Operating the Drive - Loading, Unloading and Write-Protecting Cartridges - Caring for Tape Cartridges - Cleaning the Tape Mechanism
Operating the Drive
Switch on external drives by pushing the power on/off button on the front panel (See number 1 in Figure 1.) The tape drive will run its Power-On Self Test. At the end of the
hardware self-test, the status light should be solid green.
Figure 1. Switching on the Drive - The Power On/Off Button
Resetting the Drive
You can reset the drive without powering off the drive and computer. This may be necessary if the drive stops responding. To do this, press and hold the eject button on the
front panel of the tape drive for 10 seconds (See number 1 in Figure 2). The drive forces a dump of vital technical data to drive memory and overwrites the existing dump. The
drive then reboots to allow communication.
Figure 2. Resetting the Drive - The Eject Button
Loading, Unloading and Write-Protecting Cartridges
Only use LTO Ultrium format cartridges with your drive, as specified in the LTO ULTRIUM standard. Ensure that only one label is stuck to the label area of the cartridge. Never
use non-standard labels, and never stick anything to the cartridge other than in the label area.
The tape drive uses the following cartridge types:
l LTO Ultrium 100 GB Data Cartridge (Generation 1)
l LTO Ultrium 200 GB Data Cartridge (Generation 2)
l LTO Ultrium Universal Cleaning Cartridge
The Dell PowerVault 110T LT0-2 Tape Drive is compatible with the cartridges of its predecessor, the Dell PowerVault 110T LTO-2 Tape Drive. Cartridge compatibility for the
LTO-2 tape drive is as follows:
l Reads and writes Generation 2 format from Generation 2 cartridges.
l Reads and writes Generation 1 format from Generation 1 cartridges.
l Does not write Generation 2 format on Generation 1 cartridges.
l Does not reformat Generation 1 cartridges to Generation 2 format.
Figure 3 shows the LTO Ultrium 200 GB Data Cartridge and its components.
Figure 3. LTO Ultrium 200 GB Data Cartridge
Page 31

1. LTO cartridge memory
2. Label area
3. Write-protect switch
4. Insertion guide
5. Cartridge door
6. Leader pin
Loading a Tape Cartridge
Figure 4. Loading
1. Ensure that the tape drive is powered on (the status light is solid green).
2. Ensure that the write-protect switch (see number 1 in Figure 4) is properly set. (See Setting the Write-Protect Switch on Cartridges).
3. Grasp the cartridge so that the write-protect switch faces you.
4. Slide the cartridge into the tape load compartment (see Figure 4.
Notes:
a. If the cartridge is already in the ejected position and you want to reinsert it, remove the cartridge then insert it again.
b. If the cartridge is already loaded and you cycle the power (turn it off, then on), the tape will reload.
Unloading a Tape Cartridge
1. Ensure that the tape drive is powered on (the status light is solid green).
2. Press the eject button. The drive rewinds the tape and partially ejects the cartridge. The status light flashes green while the tape rewinds, then goes out before the
cartridge partially ejects.
3. After the cartridge partially ejects, grasp the cartridge and remove it.
Whenever you unload a tape cartridge, the tape drive writes any pertinent information to the cartridge memory.
Setting the Write-Protect Switch on Tape Cartridges
The position of the write-protect switch on the tape cartridge determines whether you can write to the tape:
l If the switch is set to locked (solid red padlock), data cannot be written to the tape.
l If the switch is set to unlocked (black void), data can be written to the tape.
CAUTION: Do not remove a tape cartridge while the drive activity indicator is on.
CAUTION:Write-protection will not prevent a cartridge being erased by bulk-erasure or degaussing. Do not bulk erase Ultrium format cartridges. This
will destroy pre-recorded servo information and render the cartridge unusable.
Page 32

Figure 5. Setting the Write-Protect Switch
To set the switch, slide it left or right to the desired position. If you slide the red tab after the cartridge is inserted in the drive, the change will not take effect until the cartridge
is removed and reinserted.
Caring for Tape Cartridges
Incorrect handling or an incorrect environment can damage the LTO Ultrium Tape Cartridge or its magnetic tape. To avoid damage to your tape cartridges and to ensure the
continued high reliability of your tape drive, use the following guidelines.
Provide Training
l Post procedures that describe proper media handling in places where people gather.
l Ensure that anyone who handles tape has been properly trained in handling and shipping procedures. This includes operators, users, programmers, archival services,
and shipping personnel.
l Ensure that any service or contract personnel who perform archiving are properly trained in media-handling procedures.
l Include media-handling procedures as part of any services contract.
l Define and make personnel aware of data recovery procedures.
Ensure Proper Packaging
l When you ship a cartridge, ship it in its original or better packaging.
l Always ship or store a cartridge in a jewel case.
l Use only a recommended shipping container that securely holds the cartridge in its jewel case during transportation.
l Never ship a cartridge in a commercial shipping envelope. Always place it in a box or package.
l If you ship the cartridge in a cardboard box or a box of a sturdy material, ensure the following:
¡ Place the cartridge in polyethylene plastic wrap or bags to protect it from dust, moisture, and other contaminants.
¡ Pack the cartridge snugly; do not allow it to move around.
¡ Double-box the cartridge (place it inside a box, then place that box inside the shipping box) and add padding between the two boxes
Provide Proper Acclimation and Environmental Conditions
l Before you use a cartridge, let it acclimate to the normal operating environment for 1 hour. If you see condensation on the cartridge, wait an additional hour.
l Ensure that all surfaces of a cartridge are dry before inserting it.
l Do not expose the cartridge to moisture or direct sunlight.
l Do not expose recorded or blank cartridges to stray magnetic fields of greater than 100 oersteds (for example, terminals, motors, video equipment, X-ray equipment, or
fields that exist near high-current cables or power supplies). Such exposure can cause the loss of recorded data or make the blank cartridge unusable.
l Maintain the following environmental conditions outlined in the Table 1.
Table 1. Environmental Specifications
CAUTION: Do not insert a damaged tape cartridge into your tape drive. A damaged cartridge can interfere with the reliability of the drive and may
void the warranties of the drive and the cartridge. Before inserting a tape cartridge, inspect the cartridge case, cartridge door, and write-
protect switch
for breaks.
Environmental Specifications
Environmental Factor
Operating
Operational Storage
Archival Storage
Shipping
Temperature
10 to 45 degrees C
(50 to 113 degrees F)
16 to 32 degrees C
(61 to 90 degrees F)
16 to 25 degrees C
(61 to 77 degrees F)
-23 to 49 degrees C
(-9 to 120 degrees F)
Relative humidity (noncondensing)
10 to 80%
20 to 80%
20 to 50%
5 to 80%
Wet bulb temperature
26 degrees C
(79 degrees F)
26 degrees C
(79 degrees F)
26 degrees C
(79 degrees F)
26 degrees C
(79 degrees F)
Notes:
1. Operational storage equals less than 1 year.
2. Archival storage equals 1 to 10 years.
Page 33

Perform a Thorough Inspection
l Inspect the cartridge's packaging to determine potential rough handling.
l When inspecting a cartridge, open only the cartridge door. Do not open any other part of the cartridge case. The upper and lower parts of the case are held together
with screws; separating them destroys the usefulness of the cartridge.
l Inspect the cartridge for damage before using or storing it.
l Inspect the rear of the cartridge (the part that you load first into the tape load compartment) and ensure that there are no gaps in the seam of the cartridge case. If there
are gaps in the seam, the leader pin may be dislodged.
l Check that the leader pin is properly seated.
l If you suspect that the cartridge has been mishandled but it appears useable, copy any data onto a good cartridge immediately for possible data recovery. Discard the
mishandled cartridge.
l Review handling and shipping procedures.
Handle the Cartridge Carefully
l Do not drop the cartridge. If the cartridge drops, slide the cartridge door back and ensure that the leader pin is properly seated in the pin-retaining spring clips.
l Do not handle tape that is outside the cartridge. Handling the tape can damage the tape's surface or edges, which may interfere with read or write reliability. Pulling on
tape that is outside the cartridge can damage the tape and the brake mechanism in the cartridge.
l Do not stack more than six cartridges.
l Do not degauss a cartridge that you intend to reuse. Degaussing makes the tape unusable.
Cleaning the Tape Mechanism
DELL PowerVault 110T LTO-2 tape drives have been developed to have a minimal cleaning requirement. The tape drive will display a C on the single-character display and the
status light will flash amber when the drive needs cleaning. Only insert a cleaning cartridge into the tape drive when the C is displayed.
An LTO Ultrium universal cleaning cartridge is supplied with each tape drive. Do not use swabs or other means of cleaning the heads. The cleaning cartridge uses a special
tape to clean the tape heads.
Though the number may vary according to the manufacturer, the universal cleaning cartridge is generally valid for 50 cleanings. If the cleaning cartridge is ejected immediately,
then it has expired or it is not a supported cleaning cartridge. Discard it and use a new one.
To use the LTO Ultrium universal cleaning cartridge:
1. Insert a cleaning cartridge into the tape drive. The tape drive performs the cleaning automatically. When the cleaning is finished, the drive ejects the cartridge.
2. Remove the cleaning cartridge from the drive.
Back to Contents Page
CAUTION: Only use LTO cleaning cartridges that are labeled "universal". Some Generation 1 cleaning cartridges may not be the universal type. The
Generation 2 tape drive is only compatible with the LTO Ultrium universal cleaning cartridges. Use of any other type of cleaning cartridge or method
can damage the read/write head in your drive. If you load any other type of cleaning cartridge, the tape drive ejects it immediately.
 Loading...
Loading...