Page 1

Dell EMC Solutions for Microsoft Azure
Stack HCI
2-Node Hyperconverged Back-to-Back Connected
Infrastructure
June 2019
REV 08
Deployment Guide
Dell EMC Solutions
Page 2

Copyright © 2018-2019 Dell EMC All rights reserved.
Dell believes the information in this publication is accurate as of its publication date. The information is subject to change without notice.
THE INFORMATION IN THIS PUBLICATION IS PROVIDED “AS-IS.” DELL MAKES NO REPRESENTATIONS OR WARRANTIES OF ANY KIND WITH
RESPECT TO THE INFORMATION IN THIS PUBLICATION, AND SPECIFICALLY DISCLAIMS IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS
FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. USE, COPYING, AND DISTRIBUTION OF ANY DELL SOFTWARE DESCRIBED IN THIS PUBLICATION REQUIRES AN
APPLICABLE SOFTWARE LICENSE.
Dell Technologies, Dell, EMC, Dell EMC and other trademarks are trademarks of Dell Inc. or its subsidiaries. Other trademarks may be the property of their
respective owners. Published in the USA.
Dell EMC
Hopkinton, Massachusetts 01748-9103
1-508-435-1000 In North America 1-866-464-7381
www.DellEMC.com
2 Dell EMC Solutions for Microsoft Azure Stack HCI
Page 3

CONTENTS
Chapter 1
Chapter 2
Chapter 3
Chapter 4
Overview 5
Introduction..................................................................................................6
Audience and scope......................................................................................6
Assumptions................................................................................................. 6
Known issues................................................................................................ 7
Virtualization infrastructure with Dell EMC Ready Nodes 9
Overview.....................................................................................................10
R640 Storage Spaces Direct Ready Node...................................................12
Storage Spaces Direct................................................................................ 13
Solution component integration 15
Overview.....................................................................................................16
Network connectivity..................................................................................16
Virtualized infrastructure deployment by using Dell EMC Ready
Nodes 19
Overview.................................................................................................... 20
Deployment prerequisites...........................................................................20
Software versions..........................................................................20
Dell EMC validated firmware matrix............................................... 21
Deployment checklists................................................................................ 21
Management environment checklist...............................................21
Network configuration checklist.....................................................21
Host OS network checklist............................................................ 22
Predeployment configuration..................................................................... 23
Network switch configuration........................................................23
iDRAC and BIOS configuration...................................................... 24
QLogic NIC configuration.............................................................. 26
Firmware baselining....................................................................... 29
Chapter 5
Hyperconverged infrastructure deployment 31
Overview.................................................................................................... 32
Deploy operating system............................................................................ 32
Manual OS deployment..................................................................32
Factory-installed OS......................................................................32
Update out-of-box drivers.......................................................................... 33
Install roles and features.............................................................................34
Change hostname.......................................................................................34
Configure firewall....................................................................................... 34
Configure host networking......................................................................... 35
VM switch and adapter configuration............................................ 35
Dell EMC Solutions for Microsoft Azure Stack HCI 3
Page 4

Contents
AD domain join............................................................................................37
Create host cluster.....................................................................................38
Configuring Storage Spaces Direct............................................................ 38
Change RDMA mode on QLogic NICs—iWARP only.................................. 39
Update page file settings............................................................................39
Enabling jumbo frames............................................................................... 40
Remove host management network from Live Migration............................40
Update hardware timeout for Spaces port.................................................. 41
Configuring a cluster witness...................................................................... 41
Recommended next steps........................................................................... 41
Chapter 6
Appendix A
Appendix B
Appendix C
Deployment services 43
Overview.................................................................................................... 44
Additional resources 45
Firewall port requirements 47
Sample deployment checklists 49
4 Dell EMC Solutions for Microsoft Azure Stack HCI
Page 5

CHAPTER 1
Overview
This chapter presents the following topics:
l
Introduction......................................................................................................... 6
l
Audience and scope............................................................................................. 6
l
Assumptions.........................................................................................................6
l
Known issues........................................................................................................7
Dell EMC Solutions for Microsoft Azure Stack HCI 5
Page 6

Overview
Introduction
This guide focuses on deploying a 2-node back-to-back connected hyperconverged
infrastructure solution for Microsoft Azure Stack HCI. The guide includes an overview
of the solution infrastructure, guidance on how to integrate the solution components,
and instructions for preparing and deploying the solution infrastructure. This guide is
applicable only to infrastructure that is built by using the validated and certified Dell
EMC Microsoft Storage Spaces Direct Ready Nodes.
Audience and scope
The audience for this document includes systems engineers, field consultants, partner
engineering team members, and customers with a fair amount of knowledge in
deploying hyperconverged infrastructures with Microsoft Windows Server 2016 or
Windows Server 2019 Hyper-V and Storage Spaces Direct.
Customers who do not have Volume License agreements with Microsoft can order Dell
EMC Microsoft Storage Spaces Direct Ready Nodes with the operating system
preinstalled at the factory with OEM license or bare metal.
The Storage Spaces Direct Cluster deployment can be done in two ways:
l
Dell EMC Services led: Certified deployment engineers can deploy the solution,
which ensures accuracy and speed, reduced risk and down time.
l
Customer led: Customers can deploy the solution by referring to this deployment
guide, provided they have the qualified level of technical expertise.
Assumptions
Note:
Instructions in this deployment guide are applicable only to the generally
available OS build of Windows Server 2016 with the latest applicable updates and
Windows Server 2019 GA build with latest OS updates. These instructions are not
validated with Windows Server, version 1709. Storage Spaces Direct Ready nodes
do not support the Windows Server Semi-Annual Channel release. Dell EMC
recommends that you update the host OS with latest cumulative updates from
Microsoft before starting the cluster creation and configuration tasks.
Note: While the instructions in this deployment guide can be used with other Dell
EMC Microsoft Storage Spaces Direct Ready Nodes, R640 Storage Spaces Direct
Ready Node has been used as an example for the deployment instructions.
This deployment guide makes certain assumptions about the necessary prerequisite
knowledge of the deployment personnel. This includes the prerequisite knowledge of:
l
Dell EMC Microsoft Storage Spaces Direct Ready Nodes and deploying and
configuring BIOS and iDRAC settings
l
Deploying and configuring Windows Server 2016 and Windows Server 2019 HyperV infrastructure
6 Dell EMC Solutions for Microsoft Azure Stack HCI
Page 7

Known issues
Overview
Before starting the cluster deployment, ensure that you review the known issues and
workarounds. See https://www.dell.com/support/article/sln313305.
Dell EMC Solutions for Microsoft Azure Stack HCI 7
Page 8

Overview
8 Dell EMC Solutions for Microsoft Azure Stack HCI
Page 9

CHAPTER 2
Virtualization infrastructure with Dell EMC
Ready Nodes
This chapter presents the following topics:
l
Overview............................................................................................................ 10
l
R640 Storage Spaces Direct Ready Node.......................................................... 12
l
Storage Spaces Direct........................................................................................13
Dell EMC Solutions for Microsoft Azure Stack HCI 9
Page 10
Virtualization infrastructure with Dell EMC Ready Nodes
Overview
Dell EMC Solutions for Azure Stack HCI encompasses various configurations of
R740xd, R740xd2, and R640 Storage Spaces Direct Ready Node and PowerEdge
R440 servers to power the primary compute cluster deployed as a hyperconverged
infrastructure. This hyperconverged infrastructure built by using these Ready Nodes
uses a flexible solution architecture rather than a fixed component design. Figure 1
illustrates one of the flexible solution architectures consisting of compute cluster
alongside the redundant top-of-rack switches, a separate out-of-band (OOB)
network, and an existing management infrastructure in the data center.
The Dell EMC Solutions for Azure Stack HCI based on Dell EMC Storage Spaces
Direct Ready Nodes is available in both hybrid and all-flash configurations.
For more information on available configurations, see Dell EMC Ready Nodes for
Microsoft Storage Spaces Direct with Hyper-V Solution Overview.
Note: For the 2-node cluster deployment, it is mandatory that a cluster witness is
configured. See the section on configuring cluster witness for available options
and other references to deployment instructions.
10 Dell EMC Solutions for Microsoft Azure Stack HCI
Page 11
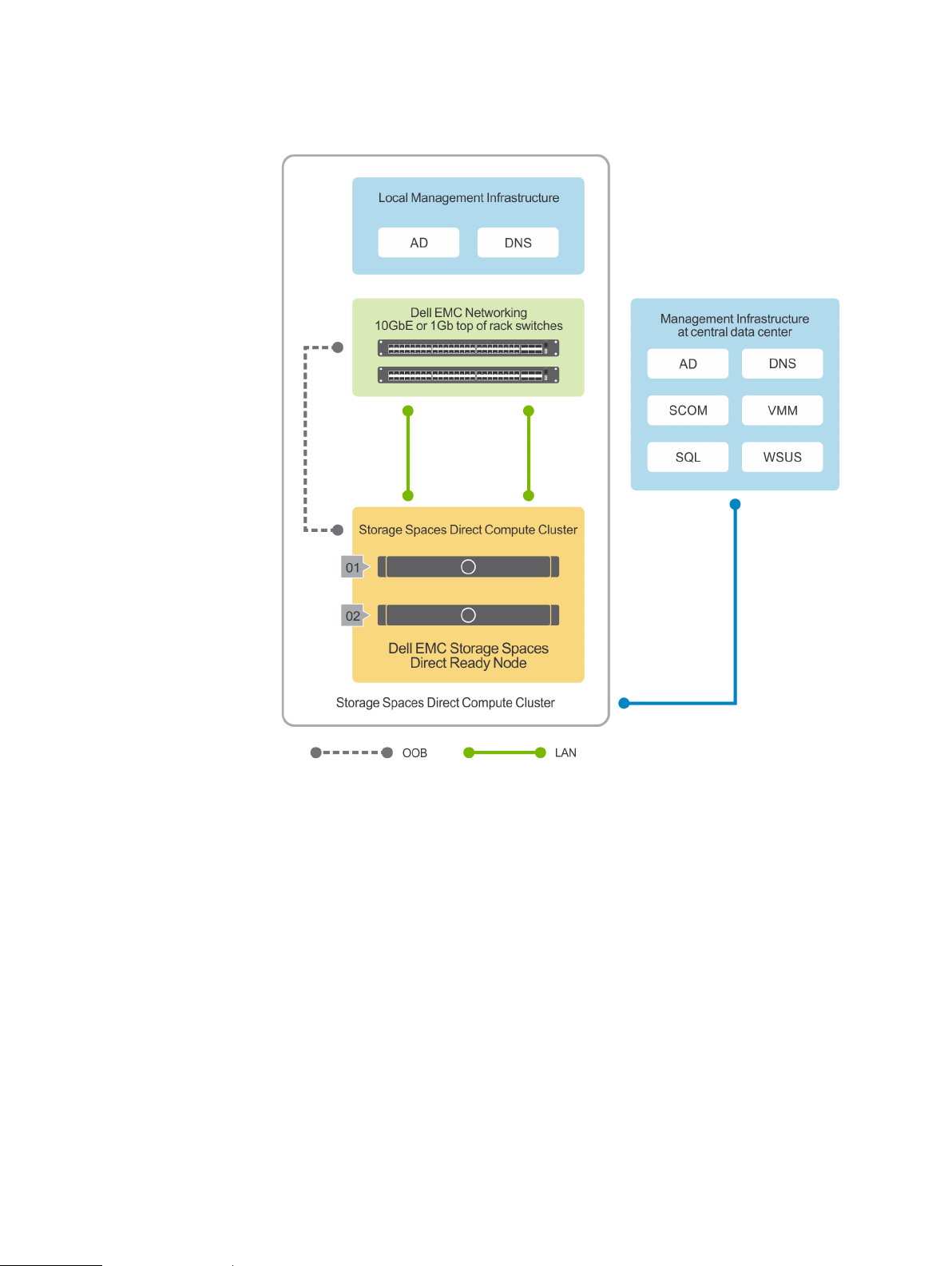
Virtualization infrastructure with Dell EMC Ready Nodes
Figure 1 2-Node hyperconverged virtualized solution using Dell EMC Ready Nodes
Dell EMC Solutions for Azure Stack HCI does not include management infrastructure
components such as a cluster for hosting management VMs and services such as
Active Directory (AD), Domain Name Service (DNS); Windows Server Update
Services (WSUS); and System Center components such as Operations Manager
(OM). Therefore, the instructions in this guide do not include deployment of any of
these services and components, and assume that at least an Active Directory domain
controller is available in the existing management infrastructure.
When deployed in a remote office scenario, Dell EMC recommends that you deploy
either an Active Directory replica or Ready-Only Domain Controller (RODC) at the
remote office. If you are using a RODC at the remote site, connectivity to the central
management infrastructure with a writeable domain controller is mandatory during
deployment of the 2-node cluster.
The subsequent sections provide an overview of the hardware and software
components in the virtualized solution based on Dell EMC Ready Nodes.
Dell EMC Solutions for Microsoft Azure Stack HCI 11
Page 12

Virtualization infrastructure with Dell EMC Ready Nodes
R640 Storage Spaces Direct Ready Node
R640 Storage Spaces Direct Ready Node, a 1U rack server based on the PowerEdge
R640, is optimized for software-defined storage implementations that enable
hyperconverged infrastructure (HCI) implementations. This Ready Node supports up
to two CPU sockets, with a wide range of options for the number of cores per CPU
socket, and 1.5 TB of memory when using DDR4 DIMMs.
The R640 Storage Spaces Direct Ready Node in a back-to-back connected
configuration is available only in a 10-drive chassis configuration in both hybrid and allflash configurations. For more details about the configuration, see https://
www.dell.com/learn/shared-content~data-sheets~en/documents~microsoftstorage-spaces-direct-ready-nodes-solution-overview-en.pdf.
Figure 2 Disk configuration in a Dell EMC Ready Node based on R640 Storage Spaces Direct
Ready Node with 10 drives (hybrid)
Figure 3 Disk configuration in a Dell EMC Ready Node based on R640 Storage Spaces Direct
Ready Node with 10 drives (all-flash)
The R640 Storage Spaces Direct Ready Node in a back-to-back connected
configuration supports only one add-in network adapter.
12 Dell EMC Solutions for Microsoft Azure Stack HCI
Page 13
Virtualization infrastructure with Dell EMC Ready Nodes
The following table provides an overview of the R640 Storage Spaces Ready Node in
the solution.
Table 1 System components
Component Specification
Compute cluster node R640 Storage Spaces Ready Node
NIC 1 x Mellanox Connectx-4 LX 25 GbE SFP add-in adapter
or
1 x QLogic FastLinQ 41262 25 GbE SFP28 add-in adapter
and
Dual-port 10 GbE or dual-port 1 GbE rNDC
Storage adapter HBA 330 Mini
Boot device BOSS S.1 with 2 x BOSS M.2 devices in RAID 1
Drives See Dell EMC Ready Nodes for Microsoft Storage
Spaces Direct with Hyper-V Solution Overview
Because this 2-node configuration implements back-to-back connectivity of the
servers using either the Mellanox or QLogic RDMA-capable NICs, a data center
bridging (DCB) policy or RoCE for RDMA configurations in the host operating system
are not needed.
If the nodes are configured with QLogic FastLinQ 41262 adapters, Dell EMC
recommends using iWARP for RDMA.
For a list of switches that are supported in this configuration, see the Support Matrix
at https://www.dell.com/azurestackhcimanuals.
Storage Spaces Direct
Storage Spaces Direct was first introduced in Windows Server 2016. This storage
feature uses the local disks within the nodes to create highly available softwaredefined storage. This feature is enhanced further in Windows Server 2019 with the
addition of support for deduplication among many other features and enhancements.
Two deployment options are possible for Storage Spaces Direct. In the first option,
the storage and compute cluster are kept separate. This method, which is known as
converged or disaggregated deployment, allows for scaling of storage and compute
clusters in a manner that is independent of each other. The second deployment
option, known as hyperconverged deployment, enables running the virtualization
services directly on top of the servers that host Storage Spaces Direct. This method
ensures that there is no need to configure and maintain file services separately in a
different cluster and, therefore, reduces the need for additional physical servers.
This deployment guide focuses on a hyperconverged deployment of Storage Spaces
Direct. For more information about Storage Spaces Direct and these deployment
options, see https://technet.microsoft.com/EN-US/windows-server-docs/storage/
storage-spaces/storage-spaces-direct-overview.
This guide provides the deployment instructions for implementing a Storage Spaces
Direct hyperconverged cluster that is built using Dell EMC Ready Nodes. The following
figure provides an overview of the deployment.
Dell EMC Solutions for Microsoft Azure Stack HCI 13
Page 14

Virtualization infrastructure with Dell EMC Ready Nodes
Figure 4 Deployment overview
14 Dell EMC Solutions for Microsoft Azure Stack HCI
Page 15

CHAPTER 3
Solution component integration
This chapter presents the following topics:
l
Overview............................................................................................................ 16
l
Network connectivity......................................................................................... 16
Dell EMC Solutions for Microsoft Azure Stack HCI 15
Page 16

Solution component integration
Overview
This section provides recommendations on server and network switch placement in
the racks and port mapping on the top-of-rack (TOR) switches.
Figure 5 Solution components integration for a 2-Node back-to-back connected configuration
Network connectivity
Each R640 Storage Spaces Direct Ready Node can be configured with either Mellanox
ConnectX-4 LX or QLogic FastLinQ 41262 25 GbE network adapters for storage
traffic and a dual-port 10 GbE or dual-port 1 GbE rNDC for host management and VM
traffic. Each port from the Mellanox or QLogic network adapters get connected
directly to the respective ports on the second server.
For host management and VM traffic, the ports on the rNDC can be used. The
following network connectivity diagrams illustrate using either 10 GbE SFP ports or 1
Gb BASE-T ports for host management and VM traffic.
16 Dell EMC Solutions for Microsoft Azure Stack HCI
Page 17

Solution component integration
Figure 6 Network connectivity when using 10 GbE ports on the rNDC for host management and
VM traffic
Note: Our-of-band (OOB) ports from the servers use Base-T connectivity.
Therefore, connecting these ports to a SFP+ switch port requires a 10 GbE SFP+
to Base-T transceiver.
Dell EMC Solutions for Microsoft Azure Stack HCI 17
Page 18

Solution component integration
Figure 7 Network connectivity when using 1 GbE ports on the rNDC for host management and
VM traffic
The dedicated iDRAC management ports can be connected to a separate 1 Gb Base-T
port at the remote site.
Note:
This topology supports both tagged and untagged VLANs for storage
traffic.
18 Dell EMC Solutions for Microsoft Azure Stack HCI
Page 19

CHAPTER 4
Virtualized infrastructure deployment by using
Dell EMC Ready Nodes
This chapter presents the following topics:
l
Overview............................................................................................................20
l
Deployment prerequisites.................................................................................. 20
l
Deployment checklists........................................................................................21
l
Predeployment configuration.............................................................................23
Dell EMC Solutions for Microsoft Azure Stack HCI 19
Page 20

Virtualized infrastructure deployment by using Dell EMC Ready Nodes
Overview
The 2-Node back-to-back connected configuration in Dell EMC Solutions for Azure
Stack HCI can be deployed in either of the following ways:
l
Manual OS deployment—A manual method of installation from OS deployment
through cluster creation
l
Factory OS deployment—Factory preinstallation of Windows Server 2016 or
Windows Server 2019 on the R640 Storage Spaces Direct Ready Node servers
Each of the methods has deployment prerequisites and predeployment configuration
requirements, including the network switch configuration.
Subsequent sections of this guide describe the deployment prerequisites for each of
these methods and also provide details on the supported software and firmware
versions.
Note: Storage Spaces Direct was first introduced in Windows Server 2016. This
storage feature uses the local disks within the nodes to create highly available
software-defined storage. This feature is enhanced further in Windows Server
2019 with the addition of support for deduplication, among many other features
and enhancements. Dell EMC recommends updating the host OS with the latest
cumulative updates from Microsoft before creating and configuring a cluster.
Deployment prerequisites
Deployment of this hyperconverged virtualized solution based on Dell EMC Ready
Nodes assumes that the management services that are required for the OS
deployment and cluster configuration are present in the existing infrastructure where
the Storage Spaces Direct cluster deployment is being done.
The following table describes management services, their purpose, and whether
deployment is required or optional.
Table 2
Software versions
The following table lists the software versions that are required for the Dell EMC
Ready Nodes deployment.
Management services
Management service Purpose Deployment—required/
Active Directory User authentication Required
Domain Name Service Name resolution Required
Windows Software Update
Service (WSUS)
Local source for Windows
Updates
optional
Optional
20 Dell EMC Solutions for Microsoft Azure Stack HCI
Page 21

Virtualized infrastructure deployment by using Dell EMC Ready Nodes
Table 3 Software versions
Component Version
Operating System Windows Server 2016 or Windows Server
2019 Data Center
Active Directory Forest/domain functional
level
Dell EMC validated firmware matrix
Dell EMC Solutions for Azure Stack HCI are validated and certified with certain
firmware versions that are related to solution infrastructure components. The support
matrix identifies the Dell EMC validated versions of software and firmware to be used
to ensure that the solution infrastructure remains supported and delivers optimal
performance.
The support matrix is available at https://www.dell.com/azurestackhcimanuals. It is
updated as software and firmware revisions are validated.
Deployment checklists
This section provides checklists for use in gathering information about the
management environment, network configuration, and host OS network. Fill in the
checklists before proceeding to the predeployment configuration.
Sample deployment checklists on page 49 provides completed examples of these
checklists for reference.
Windows Server 2008 R2 or later
Management environment checklist
This Dell EMC Ready Nodes deployment is a brownfield deployment and, therefore,
requires information such as Active Directory domain FQDN, DNS server addresses,
and so on.
The following table captures the necessary inputs as a checklist.
Table 4
Management environment checklist
Item Value
Active Directory domain FQDN
Domain administrator or equivalent
credentials
DNS server addresses
WSUS server FQDN (optional)
Network configuration checklist
Before starting the deployment, identify the IP scope and VLAN information for
various traffic classes in the solution infrastructure. The Minimum IP addresses
needed column in the following table can be used to identify the correct scope. The
Dell EMC Solutions for Microsoft Azure Stack HCI 21
Page 22

Virtualized infrastructure deployment by using Dell EMC Ready Nodes
value shown in that column is based on the number of components that require the
specified traffic class used in this solution. Ensure that the IP scope that is selected
for the traffic class meets the minimum IP addresses requirement.
The IP scope information in the following table is provided only an example. Select
values based on your existing data center architecture.
Consult with the customer network engineering team for VLAN ID and VLAN IP
addresses applicable to your solution.
Table 5 Network configuration
Traffic class Purpose Minimum IP
addresses
VLAN ID Tagged/
untagged
needed
Out of band Required for
OOB
management of
server nodes
and TOR
switches
Host
Management
Storage 1 SMB traffic 2 Tagged/
Storage 2 SMB traffic 2 Tagged/
Management of
cluster and
cluster nodes
2 Untagged /24
3 Tagged/
untagged
untagged
untagged
TOR and OOB switch configuration might also require configuring settings such as
hostnames, IP routes, and so on. The following table captures these requirements as a
checklist.
Table 6
Network configuration checklist
IP address
space
/25 TOR1:
/27 TOR1:
/27 TOR1:
VLAN IP
addresses
TOR2:
TOR2:
TOR2:
Item Value
OOB switch hostname
TOR1 switch hostname
TOR2 switch hostname
Enable password
Additional user/password
IP route on OOB (if needed)
IP route on TOR1/TOR2 (if needed)
Host OS network checklist
Dell EMC recommends having consistent host naming and IP addressing across
multiple nodes in the virtualized cluster deployment. The host OS network
22 Dell EMC Solutions for Microsoft Azure Stack HCI
Page 23

Node 1
Virtualized infrastructure deployment by using Dell EMC Ready Nodes
configuration includes naming for the virtual switches and adapters, and assigning
hostnames and IP addresses.
The following table provides the checklist for capturing the host OS network switch
and adapter details.
Table 7 Host OS network switch and adapter details
Item Value
Virtual switch (for management/VM traffic)
Management adapter name
For the host OS configuration in any deployment method, static IP address
assignment is recommended for all networks. The following table provides the
checklist for capturing the details of the host OS network.
Table 8 Host OS network checklist
Hostname ManagementIPStorage1 IP Storage2 IP OOB IP OOB
hostname
Node 2
Predeployment configuration
This section describes the predeployment configuration that must be performed
before deploying the hyperconverged virtualized solution based on Dell EMC
Microsoft Storage Spaces Direct Ready Nodes.
Network switch configuration
When considering the hyperconverged network topology of the Storage Spaces Direct
solution, network resiliency is a critical option that is achieved from both a physical
and logical standpoint.
Dell EMC recommends that you deploy a network topology that supports a dual
control plane while sharing a single data plane. The Dell EMC proprietary technology is
referred to as Virtual Link Trunking (VLT). This technology provides network resiliency
for data I/O.
For sample switch configurations for Dell EMC Networking switches, see https://
community.emc.com/docs/DOC-70310.
Because these Ready Nodes use back-to-back connections for storage traffic, only
three basic networks are needed for a standard Storage Spaces Direct infrastructure
—switch management, out-of-band (OOB) management, and host management.
Dell EMC Solutions for Microsoft Azure Stack HCI 23
Page 24

Virtualized infrastructure deployment by using Dell EMC Ready Nodes
Table 9 Solution network VLANs
VLAN network
type
OOB and switch
management
Host management
iDRAC and BIOS configuration
The R640 Storage Spaces Direct Ready Nodes are pre-configured at the factory for
Storage Spaces Direct optimized BIOS and iDRAC configuration setting. By default,
iDRACs are configured to use DHCP for IPv4 and IPv6 addresses.
Note: PowerEdge R440 servers are not factory configured with the Microsoft
Storage Spaces Direct optimized BIOS and iDRAC configuration settings. For
these servers, you must update the BIOS and iDRAC configuration settings before
deployment. The list of all optimized configuration settings is available at https://
www.dell.com/support/article/sln313842.
If static IPv4 configuration is needed for the iDRAC dedicated network interface,
follow the steps given below:
Minimal network
mask
/
24(255.255.255.0
)
/25
(255.255.255.128
)
Number of IP
addresses
4 Untagged
3 Tagged/untagged
VLAN ID tag/
untag
1. Press F2 during POST.
Figure 8
Enter iDRAC
2. Select iDRAC Settings.
24 Dell EMC Solutions for Microsoft Azure Stack HCI
Page 25

Virtualized infrastructure deployment by using Dell EMC Ready Nodes
Figure 9 System Setup main menu
3. Select Network.
Figure 10
Network Settings
4. In IPV4 Settings, against Enable DHCP, select Disabled and enter the static IP
address.
Dell EMC Solutions for Microsoft Azure Stack HCI 25
Page 26

Virtualized infrastructure deployment by using Dell EMC Ready Nodes
Figure 11 IPv4 Settings
5. Click Back, and then click Finish to return to the System Setup page.
6. Click Finish.
QLogic NIC configuration
QLogic FastLinQ 41262 network adapter supports both iWARP and RoCE for RDMA.
The Storage Spaces Direct Ready Nodes are validated with only iWARP for RDMA
when using the QLogic network adapters and therefore based on the network
configuration chosen, you must configure the adapter manually to enable iWARP for
RDMA.
About this task
Perform the following steps for each port to configure the QLogic network adapters.
Procedure
1. Press F2 during system boot to enter System Setup.
2. Click System BIOS and select Device Settings.
26 Dell EMC Solutions for Microsoft Azure Stack HCI
Page 27

Figure 12 Device settings
Virtualized infrastructure deployment by using Dell EMC Ready Nodes
3. Select the QLogic network adapter from the list of adapters.
Figure 13
System Setup
4. Click Device Level Configuration and ensure that Virtualization Mode is set to
None.
Dell EMC Solutions for Microsoft Azure Stack HCI 27
Page 28

Virtualized infrastructure deployment by using Dell EMC Ready Nodes
Figure 14 Virtualization mode
5. Click Back, and then click NIC Configuration.
6. Select the following options in the NIC Configuration page:
l
Link Speed—SmartAN
l
NIC + RDMA Mode—Enabled
l
RDMA Operational Mode—iWARP
l
Boot Protocol—None
l
Virtual LAN Mode—Disabled
Figure 15
NIC configuration options
28 Dell EMC Solutions for Microsoft Azure Stack HCI
Page 29

Virtualized infrastructure deployment by using Dell EMC Ready Nodes
7. Click Back and click Data Center Bridging (DCB) Settings.
8. In the Data Center Bridging (DCB) Settings page, set DCBX Protocol to
Disabled.
Figure 16 DCB settings
Firmware baselining
9. Click Back, and then click Finish. Click Yes to save the settings.
10. Click Yes to return to the Device Settings page.
11. Select the second port of the QLogic adapter and repeat the steps.
12. Click Finish to return to the System Setup page.
13. Click Finish to reboot the system.
Dell EMC Solutions for Azure Stack HCI have a validated set of firmware and driver
revisions, and the nodes in the HCI cluster must comply with the firmware matrix. It is
important to ensure that each server has the right firmware revisions for components
used within the server.
This can be verified by using the system inventory feature of iDRAC, or OpenManage
Essentials, or by using a command line interface such as RACADM.
The validated and supported firmware and driver version information for the Dell EMC
Microsoft Storage Spaces Direct Ready nodes is available at https://www.dell.com/
azurestackhcimanuals.
Dell EMC Solutions for Azure Stack HCI Operations Guide available at https://
www.dell.com/azurestackhcimanuals provides the steps for performing cluster-aware
firmware updates.
Dell EMC Solutions for Microsoft Azure Stack HCI 29
Page 30

Virtualized infrastructure deployment by using Dell EMC Ready Nodes
30 Dell EMC Solutions for Microsoft Azure Stack HCI
Page 31

CHAPTER 5
Hyperconverged infrastructure deployment
This chapter presents the following topics:
l
Overview............................................................................................................32
l
Deploy operating system....................................................................................32
l
Update out-of-box drivers..................................................................................33
l
Install roles and features.................................................................................... 34
l
Change hostname.............................................................................................. 34
l
Configure firewall...............................................................................................34
l
Configure host networking.................................................................................35
l
AD domain join................................................................................................... 37
l
Create host cluster............................................................................................ 38
l
Configuring Storage Spaces Direct....................................................................38
l
Change RDMA mode on QLogic NICs—iWARP only..........................................39
l
Update page file settings................................................................................... 39
l
Enabling jumbo frames.......................................................................................40
l
Remove host management network from Live Migration................................... 40
l
Update hardware timeout for Spaces port..........................................................41
l
Configuring a cluster witness..............................................................................41
l
Recommended next steps...................................................................................41
Dell EMC Solutions for Microsoft Azure Stack HCI
31
Page 32

Hyperconverged infrastructure deployment
Overview
This section describes the steps involved in installing OS on the bare metal servers
and deploying the hyperconverged infrastructure (HCI) with Storage Spaces Direct.
PowerShell commands are provided as relevant, to configure cluster deployment from
the command line.
Unless mentioned otherwise, the following steps should be performed on each
physical node in the infrastructure that will be a part of Storage Spaces Direct HCI.
Deploy operating system
There are two methods to deploy the operating system:
l
Manual OS deployment—A manual method of installation from OS deployment
through cluster creation
l
Factory OS deployment—Factory preinstallation of Windows Server 2016 or
Windows Server 2019 on Dell EMC Ready Nodes
Note: The steps in the subsequent sections are applicable to either full OS or
server core.
Manual OS deployment
Dell Lifecycle Controller and Integrated Dell Remote Access Controller provide various
options for operating systems deployment. This includes manual or unattended
installation by using the virtual media and OS deployment feature in the Unified Server
Configurator (USC).
The step-by-step procedure on how to deploy operating system is not within the
scope of this guide.
The subsequent steps in this guide assume that the Windows Server 2016 or Windows
Server 2019 Data Center edition deployment on the physical server is complete and
that you have access to the virtual console of the physical server.
Factory-installed OS
If the cluster nodes are shipped from the Dell EMC factory with Windows Server 2016
preinstalled or with a Windows Server 2019 Data Center edition OEM license,
complete the out-of-box experience (OOBE) by:
l
Selecting the language and locale settings
l
Accepting the Microsoft and OEM EULA
l
Setting up the password for the local administrator account
l
Updating the OS partition size and shrinking it as needed
Note: The command output shown in the subsequent sections might show only
QLogic adapters as physical adapters. The output is shown only as an example.
Note: For the PowerShell commands in this and subsequent sections that require
the network adapter name, use the Get-NetAdapter cmdlet to retrieve the
value for the associated physical network port. The network adapter names that
are used in the commands in this guide are shown only as examples and might not
represent the naming convention for what is installed in the system.
32 Dell EMC Solutions for Microsoft Azure Stack HCI
Page 33

The factory-installed OEM OS is preactivated, and the Hyper-V role is predeployed.
Therefore, after the OOBE steps are complete, perform the post-OS-deployment
steps as described in section Install roles and features on page 34 to complete the
cluster deployment and Storage Spaces Direct configuration.
Update out-of-box drivers
For certain system components, you might have to update the driver to the latest Dell
EMC supported version, as listed in the Supported Firmware and Software Matrix.
Run the following PowerShell command to retrieve a list of all driver versions that are
currently installed on the local system:
Get-PnpDevice | Select-Object Name, @{l='DriverVersion';e={(GetPnpDeviceProperty -InstanceId $_.InstanceId -KeyName
'DEVPKEY_Device_DriverVersion').Data}} -Unique
Before configuring host networking, ensure that the out-of-box (OOB) drivers are
updated. After identifying the required driver version, download the driver installers
from support.dell.com or by using the Dell EMC Solutions for Azure Stack HCI Update
Catalog.
Hyperconverged infrastructure deployment
Note: The QLogic FastLinQ adapter does not have an in-box driver in Windows
Server 2016. Install the driver before attempting host network configuration.
After you download the drivers, attach a folder containing the driver DUP files to the
system as a virtual media image. Attach the virtual media image folder as follows:
1. Click Virtual Media in the iDRAC virtual console menu.
2. Click Create Image.
Figure 17
Create new image
3. Click Browse, select the folder where the driver DUP files are stored, and, if
required, change the name of the image.
Figure 18
Virtual media image folder
4. Click Create Image.
5. Click Finish.
6. From the Virtual Media menu, click Connect Virtual Media.
Dell EMC Solutions for Microsoft Azure Stack HCI 33
Page 34

Hyperconverged infrastructure deployment
7. From the Virtual Media menu, click Map Removable Disk , click Browse, and select
the image that you created.
Figure 19 Map device
After the image is mapped, it appears as a drive in the host OS. You can then run the
driver DUP files to install the OOB drivers.
Install roles and features
Windows Server 2016 or Windows Server 2019 Storage Spaces Direct
hyperconverged Infrastructure (HCI) cluster deployment and configuration requires
enabling the following operating system roles and features.
l
Hyper-V service (not required if the OS is factory-installed)
l
Failover clustering
These features can be enabled using the Install-WindowsFeature PowerShell
cmdlet.
Install-WindowsFeature -Name Hyper-V, Failover-Clustering IncludeAllSubFeature -IncludeManagementTools –Verbose
Change hostname
By default, the OS deployment assigns a random name as the host computer name.
For easier identification and uniform configuration, Dell EMC recommends changing
the hostname to something that is easily identifiable and relevant. This can be done by
using the Rename-Computer cmdlet:
Rename-Computer –NewName S2D2Node01 -Restart
Configure firewall
Note:
Hyper-V role installation requires a reboot of the system. However, because
the subsequent procedures also require a reboot, the required reboots are
combined into a single reboot.
Note:
This command induces an automatic restart at the end of the rename
operation.
For the cluster operations post-deployment and optional monitoring configuration, you
must enable certain firewall rules on the cluster nodes. For a complete list of ports or
firewall rules that must be enabled, see Appendix B.
For configuring firewall rules at the command prompt, see https://
technet.microsoft.com/EN-US/library/jj554906(v=wps.630).aspx.
34 Dell EMC Solutions for Microsoft Azure Stack HCI
Page 35

Configure host networking
This section focuses on configuring the host networking such as VM switches, VM
network adapters, and RDMA configurations.
Note: All PowerShell commands in this section must be run at the local console to
ensure that there are no failures due to network disconnections during
configuration.
VM switch and adapter configuration
The two R640 Storage Spaces Direct Ready Nodes are connected to back-to-back
using either the Mellanox or QLogic 25 GbE network adapters for storage traffic. The
host management and virtual machine traffic will be configured as the VM Network
adapters in the host OS, connecting to a Switch embedded team created using the
integrated 10 GbE or 1 GbE ports.
Note: For specifics of configuration such as VM switch name, adapter names, and
VLAN IDs, see the Sample deployment checklists on page 49.
The following figure illustrates this host network configuration in a Storage Spaces
Direct Ready Node deployed in a back-to-back connected infrastructure.
Figure 20
Host network configuration
Hyperconverged infrastructure deployment
For this solution, only the management network has to have a VM SET (switchembedded teaming) switch, which you can configure as described in the following
procedure. Storage RDMA ports using default settings are directly configured with no
virtualization and no VLANs.
Note:
Repeat the steps in this host network configuration section on each server
in the 2-node infrastructure. When configuring the networks, avoid duplicating IP
addresses between the nodes.
Note: The rNDC is used solely as the management network adapter, whereas the
NICs are intended for storage.
Perform the following steps to configure the OS network:
Dell EMC Solutions for Microsoft Azure Stack HCI 35
Page 36

Hyperconverged infrastructure deployment
1. Run the following command to create a management VM switch in the SET
configuration by using the physical network ports from the rNDC in the system:
New-VMSwitch -Name Management -AllowManagementOS 0 -NetAdapterName 'NIC1','NIC2' MinimumBandwidthMode Weight -Verbose
The argument 0 in the AllowManagementOS parameter prevents the creation of
a VM network adapter in the host operating system.
This command creates a SET with Switch Independent teaming mode. Load
balancing algorithm settings used are OS defaults—Dynamic for Windows Server
2016 and Hyper-V port for Windows Server 2019.
These interface names can be retrieved by using the Get-NetAdapter cmdlet.
Note: The minimum Bandwidth Mode set to Weight can be used to shape the
VM Network traffic and it is not used for host OS network adapters. Setting
the minimum Bandwidth Mode is optional.
PS C:\> Get-NetAdapter
Name InterfaceDescription ifIndex Status
MacAddress LinkSpeed
---- -------------------- ------- ------
---------- --------SLOT 2 Port 1 QLogic FastLinQ QL41262-DE 25GbE A...#2 12 Up
00-0E-1E-F5-85-AE 25 Gbps
NIC2 Intel(R) Ethernet 10G X710 rNDC 6 Up
24-6E-96-79-97-EA 10 Gbps
SLOT 2 Port 2 QLogic FastLinQ QL41262-DE 25GbE A...#4 11 Up
00-0E-1E-F5-85-AF 25 Gbps
NIC4 Intel(R) I350 Gigabit Network Conn...#2 9 Disconnected
24-6E-96-79-98-09 0 bps
NIC3 Intel(R) I350 Gigabit Network Connec... 14 Disconnected
24-6E-96-79-98-08 0 bps
NIC1 Intel(R) Ethernet 10G 4P X710/I350 rNDC 16
Up 24-6E-96-79-97-E8 10 Gbps
2. Run the following command to create and configure the host management
adapter:
Add-VMNetworkAdapter -ManagementOS -Name 'Management' -SwitchName Management -Passthru
| Set-VMNetworkAdapterVlan -Access -VlanId 102 –Verbose
3. Run the following command to configure the management and storage IP
addresses:
#Host Management Adapter
New-NetIPAddress -InterfaceAlias ‘vEthernet (Management)’ -IPAddress 172.16.102.61 DefaultGateway 172.16.102.1 -PrefixLength 25 -AddressFamily IPv4 –Verbose
#DNS server address
Set-DnsClientServerAddress -InterfaceAlias ‘vEthernet (Management)’ -ServerAddresses
172.16.102.202
#Storage 1 Adapter
New-NetIPAddress -InterfaceAlias ‘SLOT 2 PORT 1’ -IPAddress 172.16.103.61 -PrefixLength
27 -AddressFamily IPv4 -Verbose
#Storage 2 Adapter
36 Dell EMC Solutions for Microsoft Azure Stack HCI
Page 37

Hyperconverged infrastructure deployment
New-NetIPAddress -InterfaceAlias ‘SLOT 2 PORT 2’ -IPAddress 172.16.104.51 -PrefixLength
27 -AddressFamily IPv4 –Verbose
After the network adapters are added to the host OS, static IP addresses can be
configured.
4. Retrieve the argument for the
NetAdapter
PS C:\> Get-NetAdapter
Name InterfaceDescription ifIndex Status
MacAddress LinkSpeed
---- -------------------- ------- ------
---------- --------vEthernet (Management) Hyper-V Virtual Ethernet Adapter 15 Up
00-15-5D-15-67-00 10 Gbps
SLOT 2 Port 1 QLogic FastLinQ QL41262-DE 25GbE A...#2 12 Up
00-0E-1E-F5-85-AE 25 Gbps
NIC2 Intel(R) Ethernet 10G X710 rNDC 6 Up
24-6E-96-79-97-EA 10 Gbps
SLOT 2 Port 2 QLogic FastLinQ QL41262-DE 25GbE A...#4 11 Up
00-0E-1E-F5-85-AF 25 Gbps
NIC4 Intel(R) I350 Gigabit Network Conn...#2 9 Disconnected
24-6E-96-79-98-09 0 bps
NIC3 Intel(R) I350 Gigabit Network Connec... 14 Disconnected
24-6E-96-79-98-08 0 bps
NIC1 Intel(R) Ethernet 10G 4P X710/I350 rNDC 16
Up 24-6E-96-79-97-E8 10 Gbps
cmdlet.
InterfaceAlias
parameter by using the
Get-
In this configuration, default gateway and DNS configuration is required only for
the host management network.
The assigned IP address configuration can be verified using the following
command:
Get-NetIPAddress -InterfaceAlias *vEthernet* -AddressFamily IPv4 | Select
InterfaceAlias, IPAddress
AD domain join
The cluster nodes must be a part of an Active Directory domain before you can create
a cluster. This domain join task can be performed by using the Add-Computer
cmdlet.
See the Deployment checklists on page 21 for the domain administrator or equivalent
credentials needed for the domain join.
Note:
Connecting to AD directory services by using the host management network
might require routing to the AD network. Ensure that this routing is in place before
proceeding to domain join.
$credential = Get-Credential
Add-Computer -DomainName S2dlab.local -Credential $credential Restart
Dell EMC Solutions for Microsoft Azure Stack HCI 37
Page 38

Hyperconverged infrastructure deployment
Note: This command induces an automatic restart at the end of the domain join
operation. Run this command on each host that will be a part of the Storage
Spaces Direct cluster.
Note: Optionally, you can add all newly created computer objects from the HCI
cluster deployment to a different Organizational Unit (OU) in the AD directory
services. In this case, you can use the -OUPath parameter along with the Add-
Computer cmdlet.
Create host cluster
Before creating a host cluster, ensure that the nodes that will be a part of the cluster
are configured as needed and are ready for the cluster creation. You can do this by
running the Test-Cluster cmdlet.
Note: Unless otherwise specified, you need only run the commands in this section
on just one node in the infrastructure.
Note: Before creating the host cluster, run the Get-PhysicalDisk command on
all cluster nodes and verify the output to ensure that all disks are in a healthy state
and the number of disks per node are equal.
Note: Validate that the nodes have homogeneous hardware configuration.
Test-Cluster -Node S2D2Node01, S2D2Node02 -Include 'System
Configuration','Inventory','Network','Storage Spaces Direct' Verbose
Note:
The Test-Cluster cmdlet generates an HTML report of all validations
that are performed and includes a summary of the validation. Review the report
before creating a cluster.
New-Cluster -Node S2D2Node01, S2D2Node02 -StaticAddress
172.16.102.63 -IgnoreNetwork '172.16.103.0/29','172.16.104.0/29' Name S2D2NodeCluster -NoStorage -Verbose
In the preceding command, the StaticAddress parameter is used to specify an IP
address for the cluster in the same IP subnet as the host management network. The
NoStorage switch parameter specifies that the cluster must be created without any
shared storage.
Note:
The New-Cluster cmdlet generates an HTML report of all configurations
that are performed and includes a summary of the validation. Review the report
before enabling Storage Spaces Direct.
Configuring Storage Spaces Direct
After creating the cluster, you can run the Enable-ClusterS2D cmdlet to create
the Storage Spaces Direct configuration on the cluster.
38 Dell EMC Solutions for Microsoft Azure Stack HCI
Page 39

Hyperconverged infrastructure deployment
Do not run this cmdlet in a remote session. Use the local console session instead.
Enable-ClusterS2D –Verbose
The Enable-ClusterS2D cmdlet generates an HTML report of all configurations
that are performed and includes a summary of the validation. Review the report, which
is typically stored in the local temporary folder on the node where you ran the
Enable-ClusterS2D cmdlet. The verbose output of the cmdlet shows the path to
the cluster report.
TAt the end of the operation, the cmdlet discovers and claims all the available disks
into an auto-created storage pool.
You can verify the cluster creation by using any of the following commands:
Get-ClusterS2D
Get-StoragePool
Get-StorageSubSystem -FriendlyName *Cluster* | GetStorageHealthReport
Change RDMA mode on QLogic NICs—iWARP only
In the predeployment configuration, the QLogic 41262 NICs are configured to use
iWARP for RDMA. However, the driver in the OS defaults to RoCE v2 for RDMA.
Change the setting by using the Set-NetAdapterAdvancedProperty cmdlet.
Note:
This change is required only for Ready Nodes with QLogic 41262 adapters
that are used for storage traffic.
Note: For QLogic 41262 driver versions earlier than 8.37.37.0, the display name of
the attribute is 'RDMA Mode'.
Set-NetAdapterAdvancedProperty -Name 'SLOT 1 PORT 1' -DisplayName
'NetworkDirect Technology' -DisplayValue 'iWarp'
Set-NetAdapterAdvancedProperty -Name 'SLOT 1 PORT 2' -DisplayName
'NetworkDirect Technology' -DisplayValue 'iWarp'
Update page file settings
To be able to capture the active memory dump when a fatal system error occurs,
allocate sufficient size for the page file. Dell EMC recommends that the size be at
least 40 GB plus the size of CSV block cache.
Determine the cluster CSV block cache size value by running the following command:
$blockCacheMB = (Get-Cluster).BlockCacheSize
Note:
On Windows Server 2016, the default block cache size is 0. On Windows
Server 2019, the block cache is set to a value 1024 (1 GB).
Dell EMC Solutions for Microsoft Azure Stack HCI 39
Page 40

Hyperconverged infrastructure deployment
To update the page file settings, run the following command:
$blockCacheMB = (Get-Cluster).BlockCacheSize
$pageFilePath = "C:\pagefile.sys"
$initialSize = [Math]::Round(40960 + $blockCacheMB)
$maximumSize = [Math]::Round(40960 + $blockCacheMB)
$system = Get-WmiObject -Class Win32_ComputerSystem EnableAllPrivileges
if ($system.AutomaticManagedPagefile) {
$system.AutomaticManagedPagefile = $false
$system.Put()
}
$currentPageFile = Get-WmiObject -Class Win32_PageFileSetting
if ($currentPageFile.Name -eq $pageFilePath)
{
$currentPageFile.InitialSize = $InitialSize
$currentPageFile.MaximumSize = $MaximumSize
$currentPageFile.Put()
}
else
{
$currentPageFile.Delete()
Set-WmiInstance -Class Win32_PageFileSetting -Arguments @{Name=
$pageFilePath; InitialSize = $initialSize; MaximumSize =
$maximumSize}
}
Enabling jumbo frames
Enabling jumbo frames specifically on the interfaces supporting the storage network
might help improve the overall read/write performance of the Storage Spaces Direct
cluster. It is important to note that an end-to-end configuration of jumbo frames is
required to take advantage of the technology. In addition, considerations need to be
made when configuring the technology because support for jumbo frame sizes varies
between software, NIC, and switch vendors. The lowest value within the data path
determines the maximum frame size used for that path.
For the storage network adapters in the host OS, enable jumbo frames by running the
Set-NetworkAdapterAdvancedProperty cmdlet.
Note:
Network adapters from different vendors support different jumbo packet
sizes. The configured value must be consistent across the host OS and network
switch configuration.
For information about configuring jumbo frames at the switch port level, see Sample
Switch Configurations.
Remove host management network from Live Migration
After you create the cluster, Live Migration is configured by default to use all available
networks. Disable Live Migration on the host management network by excluding the
host management network from the Live Migration settings.
40 Dell EMC Solutions for Microsoft Azure Stack HCI
Page 41

Run the following PowerShell commands to exclude the host management network:
$clusterResourceType = Get-ClusterResourceType -Name 'Virtual
Machine'
$hostNetworkID = Get-ClusterNetwork | Where-Object { $_.Address -eq
'172.16.102.0' } | Select -ExpandProperty ID
Set-ClusterParameter -InputObject $clusterResourceType -Name
MigrationExcludeNetworks -Value $hostNetworkID
In the preceding command, 172.16.102.0 represents the host management subnet.
Update hardware timeout for Spaces port
Note: For performance optimization and reliability, Dell EMC recommends that
you update the hardware timeout configuration for the Spaces port.
Run the following PowerShell commands on every node in the cluster to update the
configuration in the Windows registry:
Hyperconverged infrastructure deployment
Set-ItemProperty -Path HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services
\spaceport\Parameters -Name HwTimeout -Value 0x00002710 –Verbose
Restart-Computer –Force
This command induces a reboot of the node at the end of the registry update. Perform
this update on all Storage Spaces Direct nodes being deployed immediately after initial
deployment. Update one node at a time and wait until each node rejoins the cluster.
Configuring a cluster witness
Microsoft recommends configuring a cluster witness for a 4-node Storage Spaces
Direct cluster. A cluster witness must be configured for a 2-node cluster.
Cluster witness configuration helps maintain a cluster or storage quorum when there is
a node or network communication failure where nodes continue to operate but can no
longer communicate with one another.
A cluster witness can be either a file share or a cloud-based witness.
Note:
If you choose to configure a file share witness, it should exist outside the 2node cluster.
For information about configuring a file share witness, see https://
techcommunity.microsoft.com/t5/Failover-Clustering/New-File-Share-WitnessFeature-in-Windows-Server-2019/ba-p/372149.
For information about configuring a cloud-based witness, see https://
technet.microsoft.com/EN-US/windows-server-docs/failoverclustering/deploycloud-witness.
Recommended next steps
Dell EMC recommends that you perform the following steps after you create the host
cluster and enable Storage Spaces Direct:
Dell EMC Solutions for Microsoft Azure Stack HCI 41
Page 42

Hyperconverged infrastructure deployment
1. Generate a cluster validation report to ensure that all configuration is in order.
You can generate the report by running the test-Cluster cmdlet.
2. Conduct post-deployment verification to ensure that the infrastructure is
functional and ready for operations.
3. Activate the OS license.
By default, the OS is installed in the evaluation mode. Activate the license
immediately after OS installation.
For more information about these steps, see the operations guide at dell.com/
azurestackhcimanuals.
Dell EMC recommends that you provide a copy of the operating system media file
(ISO) to the Dell EMC Deployment Services Team to store in the remote site during
deployment. The Dell EMC Technical Support team can use the file to perform system
recovery, if required.
Test-Cluster -Node S2D2Node01, S2D2Node02, -Include ‘System
Configuration’, ‘Inventory', ‘Network’, ‘Storage Spaces Direct'
Note: The OS license activation step is not required if the OS is installed at the
factory.
42 Dell EMC Solutions for Microsoft Azure Stack HCI
Page 43

CHAPTER 6
Deployment services
This chapter presents the following topic:
l
Overview............................................................................................................44
Dell EMC Solutions for Microsoft Azure Stack HCI 43
Page 44

Deployment services
Overview
Issues that arise during installation and configuration are not covered even if you have
purchased Dell ProSupport or ProSupport Plus, as support for installation and
configuration issues come under a separate paid services package. When you call in
with a installation and configuration issue, Dell Tech Support will route you to your
Account Manager in Dell EMC Sales. The Account Manager will then help you in
purchasing the onsite deployment services package.
44 Dell EMC Solutions for Microsoft Azure Stack HCI
Page 45

APPENDIX A
Additional resources
l
iDRAC documentation
l
Supported firmware and software matrix
l
Storage Spaces Direct overview
Dell EMC Solutions for Microsoft Azure Stack HCI 45
Page 46

Additional resources
46 Dell EMC Solutions for Microsoft Azure Stack HCI
Page 47

APPENDIX B
Firewall port requirements
Table 10 Firewall port requirements
Source Target Protocol Port Comment
TCP/UDP 53 DNS
TCP/UDP 88 Kerberos
UDP 123 NTP
TCP 135 RPC, EMP
NetLogon,
UDP 137
NetBIOS Name
Resolution
Any
Domain
Controllers
DFSN,
NetLogon,
UDP 138
TCP 139
TCP/UDP 389 LDAP
TCP/UDP 445
TCP/UDP 464
TCP 636 LDAP (SSL)
TCP 3268 Global Catalog
TCP 3269
NetBIOS,
Datagram
Service
DSFN, NetBIOS
Session Service,
NetLogon
SMB, CIFS,
SMB2, DFSN,
LSARPC, NbtSS,
NetLogonR,
SAMR, SrvSvc
Kerberos
change/set
password
Global Catalog
(SSL)
TCP 5722
TCP 9389 SOAP
TCP 1025:5000
Dell EMC Solutions for Microsoft Azure Stack HCI 47
RPC, DFSR
(SYSVOL)
RPC, DCOM,
EPM, DRSUAPI,
Page 48

Firewall port requirements
Table 10 Firewall port requirements (continued)
Source Target Protocol Port Comment
NetLogon,
SamR, FRS
(2003)
UDP 1025:5000
DCOM, RPC,
EPM (2003)
RPC, DCOM,
EPM, DRSUAPI,
TCP 49152:65535
NetLogonR,
SamR, FRS
(2008)
DCOM, RPC,
EPM (2008)
Allow Name/
Share Resolution
Allow Name/
Share Resolution
Local Subnet
UDP 49152:65535
UDP 137:138
All Hosts and
VMs
TCP 139
Any Console VM TCP 3389 Remote Desktop
SWUS Updates
(HTTP)
SWUS Updates
(HTTPS)
WSUS (on VMM
VM)
TCP 80
Any
TCP 443
48 Dell EMC Solutions for Microsoft Azure Stack HCI
Page 49

APPENDIX C
Sample deployment checklists
Table 11 Sample checklist
Field Value
AD Domain FQDN hci.lab
Domain Administrator or equivalent
credentials
DNS Server addresses dns.s2dlab.local
WSUS Server FQDN (if needed) wsus.s2dlab.local
Table 12 Sample checklist
Traffic class Purpose Minimum IP
addresses
VLAN ID Tagged/
untagged
needed
Out of band Required for
OOB
management of
server nodes
and TOR
switches
Host
management
Storage 1 SMB traffic 2 Default Tagged/
Management of
cluster and
cluster nodes
2 100 Untagged /24 OOB:
3 102 Tagged/
untagged
untagged
Username: hci\administrator
Password: <DO NOT WRITE IT DOWN>
IP address
space
/25 TOR1: NA
/27 TOR1: NA
VLAN IP
addresses
172.16.100.1
TOR2: NA
TOR2: NA
Storage 2 SMB traffic 2 Default Tagged/
untagged
Table 13 Sample checklist
Field Value
TOR1 Switch hostname S2D-TOR1
TOR2 Switch hostname S2D-TOR2
Enable password <DO NOT WRITE IT DOWN>
Dell EMC Solutions for Microsoft Azure Stack HCI 49
/27 TOR1: NA
TOR2: NA
Page 50

Sample deployment checklists
Hostname ManagementIPStorage1 IP Storage2 IP OOB IP OOB
Table 13 Sample checklist (continued)
Field Value
Additional user/password NA
IP route on OOB (if needed) NA
IP route on TOR1/TOR2 (if needed) NA
Table 14 Sample checklist
Field Value
Virtual Switch S2DSwitch
Management Adapter Management
Table 15 Sample checklist
hostname
Node 1 S2D2Node01 172.16.102.61 172.16.103.61 172.16.104.61 172.16.100.61 S2D-DRAC-1
Node 2 S2D2Node02 172.16.102.62 172.16.103.62 172.16.104.62 172.16.100.62 S2D-DRAC-2
50 Dell EMC Solutions for Microsoft Azure Stack HCI
 Loading...
Loading...