Page 1

Dell Networking W-ClearPass Policy Model 6.0
An Introduction
From the point of view of a network device or other entities that need authentication services, Policy Manager
appears as a RADIUS, TACACS+ or Web Authentication server; however, its rich and extensible policy model
allows it to broker security functions across a range of existing network infrastructure, identity stores, health/posture
services and client technologies within the Enterprise.
Services Paradigm
Services
l Unique Categorization Rules (per Service) enable Policy Manager to test Access Requests ("Requests") against
NOTE: Policy Manager ships configured with a number of basic Service types. You can flesh out these Service types, copy them for
use as templates, import other Service types from another implementation (from which you have previously exported them), or
develop new Services from scratch.
l By wrapping a specific set of Policy Components, a Service can coordinate the flow of a request, from
Figure 1: Dell Networking W-ClearPass Policy Manager Flow of Control and Table 1: Policy Manager Service
Components illustrate and describe the basic Policy Manager flow of control and its underlying architecture.
are the highest level element in the Policy Manager policy model. They have two purposes:
available Services to provide robust differentiation of requests by access method, location, or other network
vendor-specific attributes.
authentication, to role and health evaluation, to determination of enforcement parameters for network access.
0511287-01 | Mar 2013 1
Page 2
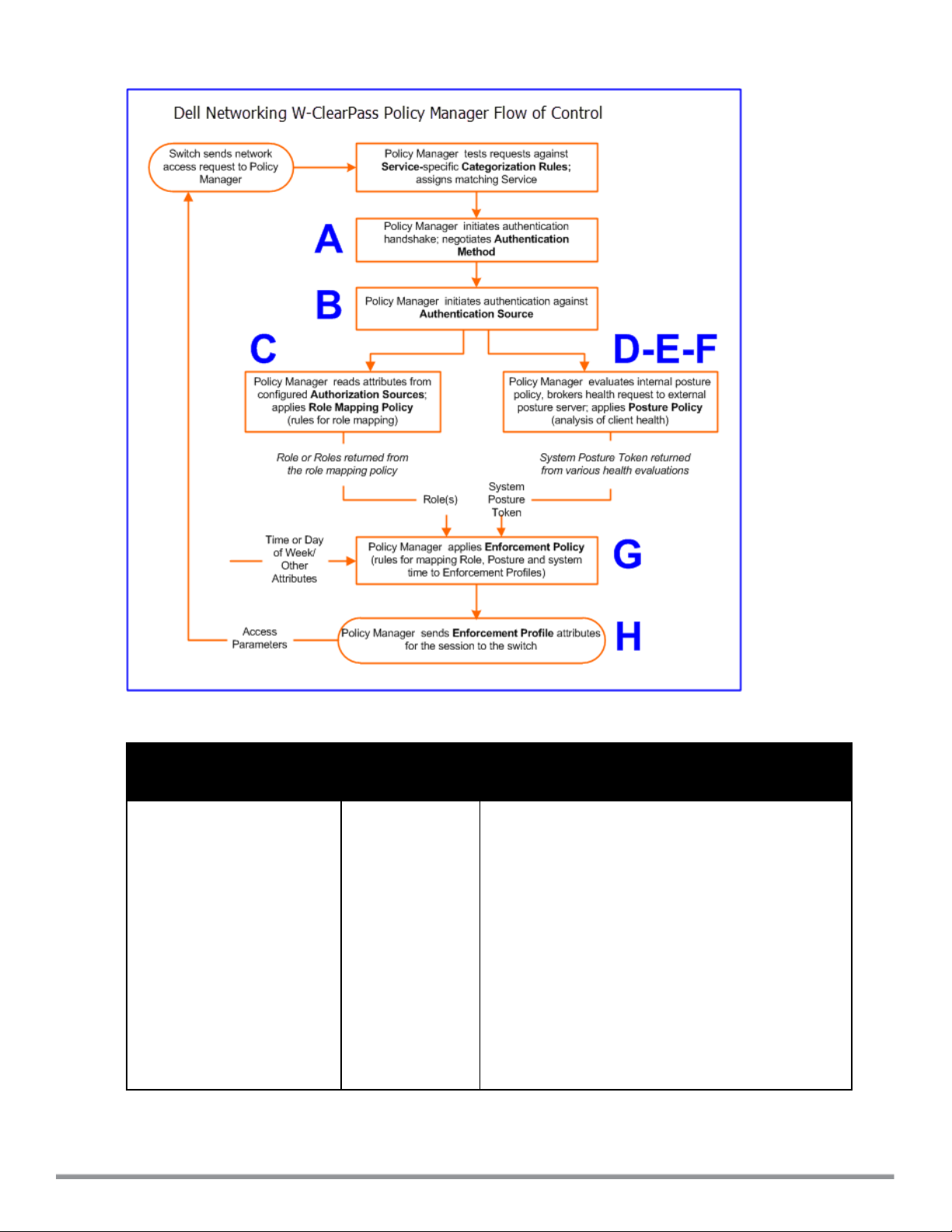
Figure 1: Dell Networking W-ClearPass Policy Manager Flow of Control
Table 1:
Policy Manager Service Components
Component Service:
component ratio
A - Authentication Method Zero or more per
service
Description
EAP or non-EAP method for client authentication.
Policy Manager supports four broad classes of authentication
methods:
l EAP, tunneled: PEAP, EAP-FAST, or EAP-TTLS.
l EAP, non-tunneled: EAP-TLS or EAP-MD5.
l Non-EAP, non-tunneled: CHAP, MS-CHAP, PAP, or MAC-
AUTH.
l MAC_AUTH must be used exclusively in a MAC-based
Authentication Service. When the MAC_AUTH method is
selected, Policy Manager: (1) makes internal checks to
verify that the request is indeed a MAC Authentication
request (and not a spoofed request) and (2) makes sure
that the MAC address of the device is present in the
authentication source.
2 Dell Networking W-ClearPass PolicyModel 6.0 | An Introduction
Page 3

Component Service:
component ratio
Description
Some Services (for example, TACACS+) contain internal
authentication methods; in such cases, Policy Manager does
not make this tab available.
B - Authentication Source Zero or more per
service
C - Authorization Source One or more per
Authentication
Source and zero or
more per service
C - Role Mapping Policy Zero or one per
service
An Authentication Source is the identity repository against
which Policy Manager verifies identity. It supports these
Authentication Source types:
l Microsoft Active Directory
l and LDAP compliant directory
l RSA or other RADIUS-based token servers
l SQL database, including the local user store.
l Static Host Lists, in the case of MAC-based Authentication
of managed devices.
An Authorization Source collects attributes for use in Role
Mapping Rules. You specify the attributes you want to collect
when you configure the authentication source. Policy
Manager supports the following authorization source types:
l Microsoft Active Directory
l any LDAP compliant directory
l RSA or other RADIUS-based token servers
l SQL database, including the local user store.
Policy Manager evaluates Requests against Role Mapping
Policy rules to match Clients to Role(s). All rules are evaluated
and Policy Manager may return more than one Role. If no
rules match, the request takes the configured Default Role.
Some Services (for example, MAC-based Authentication) may
handle role mapping differently:
D - Internal Posture Policies Zero or more per
service
E - Posture Servers Zero or more per
service
F - Audit Servers Zero or more per
service
l For MAC-based Authentication Services, where role
information is not available from an authentication source,
an Audit Server can determine role by applying post-audit
rules against the client attributes gathered during the
audit.
An Internal Posture Policy tests Requests against internal
Posture rules to assess health. Posture rule conditions can
contain attributes present in vendor-specific posture
dictionaries.
Posture servers evaluate client health based on specified
vendor-specific posture credentials, typically posture
credentials that cannot be evaluated internally by Policy
Manager (that is, not by internal posture policies).
Currently, Policy Manager supports two forms of posture
server interfaces: HCAP, RADIUS, and GAMEv2 posture
servers.
Audit servers evaluate the health of clients that do not have an
Dell Networking W-ClearPass PolicyModel 6.0 | An Introduction 3
Page 4

Component Service:
component ratio
Description
installed agent, or which cannot respond to Policy Manager
interactions. Audit servers typically operate in lieu of
authentication methods, authentication sources, internal
posture policies and posture server.
In addition to returning posture tokens, Audit Servers can
contain post-audit rules that map results from the audit into
Roles.
G - Enforcement Policy One per service
(mandatory)
H - Enforcement Profile One or more per
service
Policy Manager testsPosture Tokens, Roles (and system time)
against Enforcement Policy rules to return one or more
matching Enforcement Policy rules to return one or more
matching Enforcement Profiles (that define scope of access
for the client).
Enforcement Policy Profiles contain attributes that define a
client's scope of access for the session. Policy Manager
returns these Enforcement Profile attributes to the switch.
4 Dell Networking W-ClearPass PolicyModel 6.0 | An Introduction
 Loading...
Loading...