Page 1
Open Automation Guide
Configuration and Command Line Reference
February 2013
Page 2

Notes, Cautions, and Warnings
NOTE: A NOTE indicates important information that helps you make better use of your computer.
CAUTION: A CAUTION
WARNING: A WARNING indicates a potential for property damage, personal injury, or death.
Information in this publication is subject to change without notice.
© 2013 Dell Force10. All rights reserved.
Reproduction of these materials in any manner whatsoever without the written permission of Dell Inc. is strictly forbidden.
Trademarks used in this text: Dell™, the DELL logo, Dell Precision™, OptiPlex™, Latitude™, PowerEdge™, PowerVault™,
PowerConnect™, OpenManage™, EqualLogic™, KACE™, FlexAddress™ and Vostro™ are trademarks of Dell Inc. Intel, Pentium, Xeon,
Core™ and Celeron are registered trademarks of Intel Corporation in the U.S. and other countri es. AMD is a regist ered trademark and AMD
®
Opteron™, AMD Phenom™, and AMD Sempron™ are trademarks of Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. Microsoft
®
, MS-DOS® and Windows V ista® are either trademarks or registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation in the United States and/or
Server
other countries. Red Hat Enterprise Linux
other countries. Novell
®
is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its af filiates. Citrix®, Xen®, XenServer® and XenMotion® are either registered
Oracle
®
is a registered trademark and SUSE ™ is a trademark of Novell Inc. in the United States and other countries.
®
and Enterprise Linux® are registered trademarks of Red Hat, Inc. in the United State s and/or
, Windows®, Windows
trademarks or trademarks of Citrix Systems, Inc. in the United States and/or other countries. VMware®, Virtual SMP®, vMotion®, vCenter®,
®
and vSphere
are registered trademarks or trademarks of VMWare, Inc. in the United States or other countries.
Other trademarks and trade names may be used in this publication to refer to either the entities claiming the marks and names or their
products. Dell Inc. disclaims any proprietary interest in trademarks and trade names other than its own.
February 2013
Page 3

1 About this Guide . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5
Objectives . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5
Audience . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5
Supported Platforms and Required FTOS Versions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5
Conventions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6
Information Symbols . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6
Related Documents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7
2 Open Automation Framework. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9
Bare Metal Provisioning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10
Smart Scripting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
Virtual Server Networking . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
Programmatic Management . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
Web Graphical User Interface and HTTP Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
3 Smart Scripting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13
Use Cases . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
Downloading the Smart Scripting Package . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
Installing Smart Scripting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .16
Displaying Installed Packages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .17
Uninstalling Smart Scripting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .17
Limits on System Usage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .17
Supported UNIX Utilities . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .18
Creating PERL, Python and UNIX Scripts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20
Creating a User Name and Password for Smart Scripting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20
Running a Script from the FTOS CLI . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21
Logging in to a NetBSD UNIX Shell . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .22
Running a Script from the UNIX Shell . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .22
Using the PERL API . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .23
Creating a PERL API Script . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .23
Running a PERL API Script . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .26
Using the Python API . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .27
Creating a Python API Script . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .27
Running a Python API Script . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .30
Using UNIX Shell Scripting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .31
Creating a UNIX API Script . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .31
Running a UNIX API Script . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .33
4 Smart Scripting CLI. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .35
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .35
Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .35
| 3
Page 4

www.dell.com | support.dell.com
5 Virtual Server Networking . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .43
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .43
Hypervisor Modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .45
VSN Persistency . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .45
VLAN configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .45
Management VLAN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .45
Data VLANS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .45
Hypervisor-unaware VLANs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .46
Installing VSN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .46
Enabling VSN in a Hypervisor Session . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .48
Discovery . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .50
Connectivity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .50
Running VSN Scripts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .51
Stopping a Hypervisor Session . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .52
Disabling a Session . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .52
Removing a Session . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .52
Uninstalling VSN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .53
Viewing VSN information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .53
6 Virtual Server Networking CLI. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .57
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .57
Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .57
7 Programmatic Management . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .69
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .69
Using the REST API . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .70
Plug-In Modules . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .73
8 Web GUI and HTTP Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .75
HTTP Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .75
Web Graphical User Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .76
Getting Started . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .76
Menu Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .77
9 Web Graphical User Interface. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .79
10 Index . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .97
4 |
Page 5

About this Guide
Objectives
This document describes the components and uses of the Open Automation
Framework designed to run on the Force10 Operating Syste m (FTOS), including:
• Smart Scripting
• Virtual Server Networking (VSN)
• Programmatic Management
• Web graphic user interface (GUI) and HTTP Server
Information another feature, Bare Metal Provisioning (BMP) that interacts with the
Open Automation Framework can be found in the
1
FTOS Configuration Guide.
Audience
This document is intended for data center managers and network administrators
responsible for virtualization or system management. It assumes basic knowledge
about virtualization technology and networking.
Note: Although this document contains information on protocols, it is not intended to provide complete
information on protocol configuration and usage. For this information, refer to the document listed in
Related Documents on page 7 and the IETF Requests for Comment (RFCs).
Supported Platforms and Required FTOS Versions
The Open Automation 2.0 release is supported on the following Dell Force10
switches and minimum FTOS versions:
• S55 switches require FTOS version 8.3.5.2 or later.
• S60 switches require FTOS version of 8.3.3.7 or later.
About this Guide | 5
Page 6
Conventions
Convention Description
• S4810 switches require FTOS version 8.3.10.1 or later.
• Z9000 switches require FTOS version 9.0.0.0 or later. (SmartScripts and
SmartUtil support only).
This document uses the following conventions to describe command syntax:
www.dell.com | support.dell.com
keyword Keywords are shown in bold and should be entered in the CLI as listed.
parameter Parameters are shown in italics and require a number or word to be ent e red in the CLI.
{X} Keywords and parameters within braces are required entries and must be entered in the CLI.
[X] Keywords and parameters within brackets are optional.
x | y Keywords and parameters separated by bar require you to choose one.
Information Symbols
Table 1-1 describes the symbols used in this document.
Table 1-1. Information Symbols
Symbol Type Description
Note Informs you about important operational information.
FTOS Behavior Informs you about an FTOS behavior. These behaviors are inherent to the Dell
Force10 system or FTOS feature and are non-configurable.
z
6 | About this Guide
Platform-specific
Feature
Exception A note associated with some other text on the page that is marked with an
Informs you of the platform supporting the Open Automation features.
For example, the S55, S60, and S4810 platforms support all Open Automation
2.0 features. The Z9000 platform supports the SmartScripts and SmartUtil
features.
asterisk.
Page 7

Related Documents
For more information about the Dell Force10 Networks switches discussed in this
document, refer to the following documents:
•S55
• FTOS Command Line Reference Guide for the S55 System
• FTOS Configuration Guide for the S55 System
• Installing the S55 System
•S60
• FTOS Command Line Reference Guide for the S60 System
• FTOS Configuration Guide for the S60 System
• Installing the S60 System
• S4810
• FTOS Command Line Reference Guide for the S4810 System
• FTOS Configuration Guide for the S4810 System
• Installing the S4810 System
• Z9000
• FTOS Command Line Reference Guide for the Z9000 System
• FTOS Configuration Guide for the Z9000 System
• Installing the Z9000 System
• FTOS Release Notes for the platform and version you are using.
About this Guide | 7
Page 8

www.dell.com | support.dell.com
8 | About this Guide
Page 9

Open Automation Framework
Open Automation Framework is supported on
platforms:
Dell Force10’s Open Automation Framework is designed to provide an open,
industry standards-based automation technology that simplifies the management of
dynamic virtual data centers and reduces risk and overhead.
With the Open Automation Framework, resources in a virtualized data center are
managed more flexibly and efficiently without requiring the manual reconfiguration
of virtual switches (vSwitches), virtual machines (VMs) on network servers, and VM
control software each time there is a change in the network. Automated provisioning
of network resources during virtual machine migration ensures that connectivity and
security policies are maintained.
z
2
Industry-standard scripting languages, such as Perl and Python, are used to automate
the monitoring and management of network devices. Virtual resources can be quickly
allocated to adapt to configuration changes. Failure of a network device is more
quickly detected and resolved. As a result, network uptime increases.
Automated bare metal provisioning allows you to reduce operational overhead by
automatically configuring Force10 switches, accelerating switch installation, and
simplifying operating system upgrades.
Support for multiple, industry-standard hypervisors, virtual switches, and system
management tools ensure that automated solutions work within an established
data-center environment in which heterogeneous server, storage, and networking
equipment interoperate. In addition, Open Automation allows you to customize
automated solutions for your current multi-vendor virtualization environment.
An onboard Web-based graphical user interface (GUI) provides a user-friendly way
to monitor and manage a data center network. HTTP and HTTPS daemons run on
supported switches to provide additional management capability, such as the REST
application programming interface (API).
The Open Automation Framework consists of the following network management
tools:
• Bare Metal Provisioning
• Smart Scripting
• V irtual Server Networking
Open Automation Framework | 9
Page 10

www.dell.com | support.dell.com
Web GUI and
HTTP Server
Programmatic
Management
Bare Metal
Provisioning
Smart
Scripting
Virtual Ser ver
Networking
• Programmatic Management
• Web GUI and HTTP server
You can use these components together or independently to extend and add
functionality to the FTOS operating system without requiring updates to an FTOS
release.
Figure 2-1. Open Automation Framework
Note: The Open Automation Framework is referred to as Open Automation in the rest of this document.
Bare Metal Provisioning
Bare Metal Provisioning (BMP) provides the following features:
• Automatic network switch configuration and automated configuration updates
• Enforced standard configurations
• Reduced installation time
• Simplified operating system upgrades
Automated bare metal provisioning reduces operational expenses, accelerates switch
installation, simplifies upgrades and increases network availability by automatically
configuring Dell Force10 switches. BMP eliminates the need for a network
administrator to manually configure a switch, resulting in faster installation,
elimination of configuration errors and enforcement of standard configurations.
With bare metal provisioning, after a switch is installed, the switch searches the
network for a DHCP server. The DHCP server provides the switch with an IP address
and the location of a file server, such as TFTP. The file server maintains a
configuration file and an approved version of FTOS, the operating system for Dell
Force10 switches. The switch automatically configures itself by loading and
installing an embedded FTOS image with the startup configuration file.
10 | Open Automation Framework
Page 11

Smart Scripting
Smart Scripting provides:
• Support for industry-standard languages, such as Perl and Python, avoiding the
need to learn a new proprietary scripting language
• Customization of device monitoring and management to suit your network needs,
including custom maintenance tasks, discovery programs, and event logging for
faster problem resolution
Smart scripting increases network availability and manageability by allowing
network administrators to deploy custom monitoring and management scripts on Dell
Force10 switches. Using custom scripts, network administrators can implement
version control systems, automatically generate alerts, create custom logging tools
and automate management of network devices. Any function that can be performed
through the FTOS command-line interface (CLI) can be performed with smart
scripting.
The scripting environment provided by Smart Scripting (Perl, Python, and UNIX
shell scripts) makes it easy for IT administrators to quickly develop scripts without
having to learn a new scripting language.
Virtual Server Networking
Virtual Server Networking (VSN) provides:
• Automatic re-provisioning of VLANs when you migrate virtual machines (VMs).
• Support for multiple hypervisors, such as VMware and Citrix XenServer.
Virtual data centers require network infrastructure to be dynamic to ensure that
network connectivity and QoS and security policies are maintained when VMs are
migrated. VSN facilitates communication between Dell Force10 switches and VM
management software to automatically re-provision VMs and associated VLANs
during virtual machine migration.
As a result, VSN greatly simplifies many of the tasks associated with virtualized
computing environments. Network administrators can manage the network while
server administrators manage the servers. No manual VLAN reconfiguration is
required when you migrate VMs.
VSN software supports the following hypervisors:
• VMware vSphere 4.0/4.1/5.0
• Citrix XenServer 5.6/6.0
Open Automation Framework | 11
Page 12

www.dell.com | support.dell.com
Programmatic Management
Programmatic Management provides application programming interfaces (APIs) so
that FTOS switches can be managed by in-house or third-party system management
tools.
• Common third-party management tool sets are supported as plug-ins to the Open
Automation Framework, including Dell AIM, EMC Smarts Ionix, IBM Systems
Director, HP Network Automation (NA), CA Spectrum Infrastructure Manager,
and Oracle Enterprise Manager (OEM).
• Industry-standard management protocols are supported, such as SNMP (Get and
Set) and Representational State Transfer (REST).
• User protocols are supported, such as CLI/CLI-script, XML (Get and Set), and
Web-based command.
Programmatic management greatly improves network manageability by allowing
Dell Force10 switches to be managed by third-party system management tools via
standard programmatic interfaces.
The programmatic management environment and set of interfaces communicate
directly with third-party system management tools, avoiding the need for a dedicated
network management tool. As a result, network management is simplified and the
number of management tools is minimized.
Web Graphical User Interface and HTTP Server
The Open Automation Framework supports Web connectivity through its Web
interface and HTTP server:
• The Web-based GUI allows you to retrieve and update switch attributes and
characteristics.
• The HTTP Server consists of both HTTP and HTTPS daemons running on a
switch and communicating with the Web GUI.
12 | Open Automation Framework
Page 13

Smart Scripting
Smart Scripting is supported on platforms: z
Smart Scripting allows you to add functionality to the FTOS operating system
without requiring updates to the FTOS release. Smart Scripting is available as a
separate installable package that supports TCL, ZCL, Expect, PERL, Python, and
UNIX scripting and various FTOS functions.
The Smart Scripting package supports smart utility APIs (SmartUtils) to provide
developers with an easier way to invoke switch operations by creating and running
PERL, Python, and UNIX shell scripts on the FTOS operating system. API library
files describe the functions supported in TCL, ZSH, Expect, PERL, Python, and
UNIX scripts.
A separate package has been extended with HTTP and HTTPS daemons to support a
REST-like API based on CGI scripts and a Web-based graphical user interface. For
information on the HTTP Get requests supported by the REST API, see Chapter 7,
Programmatic Management.
3
Overview
Using Smart Scripting, network administrators can create custom TCL, ZCL, Expect,
PERL, Python, and UNIX shell scripts to manage and interact with Dell Force10
switches/routers in the network. Smart Scripting provides support for:
• Modules required to run PERL scripts, such as the software development kits
(SDKs) for VMware and vCenter/vSphere.
• Modules that implement requested Python features, such as AMQP (message
queuing), XML-RPC (arbitrary data exchange), and Twisted (event-driven
networking engine).
• BMP module that implement scripts written in TCL, ZSH, or Expect. For more
information, see the
Provisioning 3.0 (BMP 3.0).
With Smart Scripting, there is no need to learn proprietary scripting languages,
allowing for the faster development and deployment of custom scripts.
FTOS Configuration Guide, Chapter 9, Bare Metal
Smart Scripting | 13
Page 14

www.dell.com | support.dell.com
Smart Scripting also offers solutions in a UNIX environment that are useful to cloud
administrators who are familiar with working directly in a UNIX shell. Script support
in a UNIX environment allows you to invoke standard UNIX utilities, such as netstat,
tcpdump, ls, chmod, chown, and so on.
Smart Scripting includes a convenient set of API function libraries to which script
developers can refer when they create PERL, Python, and UNIX scripts. A
representation of CLI functions to retrieve data from the FTOS operating system and
change configuration parameters on Dell Force10 switches is provided in the API
libraries. Script writers include API function calls made directly on the FTOS
command-line interface in their PERL, Python, and UNIX scripts.
For example, the API functions used in a script include setting up a telnet session,
gathering data on the switch, sending information to the CLI, and closing telnet
sessions. By using simple function calls, script writers do not have to include the
parsing code required for telnet sessions and retrieving configuration information.
Smart Scripting supports running a script either from the FTOS CLI or directly from
a UNIX shell.
This chapter includes the following sections:
• Use Cases
• Downloading the Smart Scripting Package
• Installing Smart Scripting
• Limits on System Usage
• Supported UNIX Utilities
• Creating a User Name and Password for Smart Scripting
• Running a Script from the FTOS CLI
• Logging in to a NetBSD UNIX Shell
• Running a Script from the UNIX Shell
• Using the PERL API
• Using the Python API
• Using UNIX Shell Scripting
14 | Smart Scripting
Use Cases
Smart Scripting allows you to automate common management and maintenance
tasks, such as:
• Building visibility and/or discovery programs.
• Creating custom logging.
• Reporting configuration information.
Page 15

• Reporting switch memory usage, configured VLANs, and other operating and
configuration parameters.
• Creating custom APIs for external applications to access the switch.
• Automating custom provisioning of network devices to support server
virtualization.
For example, you can automate any of the following tasks:
• Monitor the configuration of switch ports to verify that no change occurs and
generate an alarm if a configuration change is detected as part of a
cloud-computing deployment.
• Stage CLI command requests received from a customer. If a link flaps, the
command completion status is held in the script so you can see when the
management plane reconnects.
• Generate time-based reports to receive updates on network status on a periodic
basis.
• Query an external, configuration management database on a remote server to
retrieve information on port operation, and reconfigure switch ports based on the
data received.
• Apply additional time-based access-control lists (ACLs) to limit after hours
access.
• Monitor network requests; for example, “find a specified MAC address” or
“generate a health-check heartbeat”.
• Create a simple menu of options that a non-network administrator can use to
create requests to be sent to the network.
Smart Scripting consolidates management data inside a switch and sends it to
management consoles, databases or applications – reducing polling and network
traffic. For example, you can use a script as part of a cloud-computing deployment to
detect when the network has changed, query a database server for Configuration
Management Database (CMDB) information, and ultimately apply network changes
based on the data.
Downloading the Smart Scripting Package
The SmartScripts package ca n be down load ed from the Dell Force10 website as a file
named SmartScripts2.0.x.tar.gz for platforms such as S4810, S55, and S60; for
Z9000 the file name is SmartScripts-Z.2.0.x.tar.gz. The Smart Scripting package is
downloaded with the following files and functionality:
• PERL interpreter and associated files
• Python interpreter and associated files
• Expanded set of UNIX utilities
• REST-like API based on CGI scripts (see Using the REST API)
• Web-based graphical user interface (see Web Graphical User Interface)
• HTTP and HTTPS daemons (see HTTP Server)
Smart Scripting | 15
Page 16
Installing Smart Scripting
You install the Smart Scripting file in the same way as you install an FTOS release:
directly from local flash memory on a switch or from an external drive on a network
server. Because the installation takes time, it is performed in the background. When
the download is complete, a message is displayed on the console. The package
installation updates the running-configuration file.
www.dell.com | support.dell.com
CAUTION
You can modify (e.g. edit or rename) the files downloaded with the Smart
Scripting package only in the directory in which you install the package. Never
modify the files in other system directories.
To install the Smart Scripting package, you must download it from the Dell Force10
web portal:
1. On a PC or other network device, go to the Dell Force10 web po rtal at
https://www.force10networks.com/CSPortal20/Main/SupportMain.aspx. Click
Login, enter your user ID and password, and click the Login button.
2. On the Customer Support page, click the Software Center tab.
3. In the left hand column, click Automation Software.
4. At the bottom of the Terms and Conditions page, click I agree.
5. On the Automation Software page, under Software, click the
SMARTSCRIPTS2.0.x.tar.gz file for S55, S60 and S4810 switches. Click the
SMARTSCRIPTS-Z.2.0.x.tar.gz file for Z9000 switches.
6. In the dialog box, select the path for the local flash on the switch or a directory
path on a network server where you want to download the
SMARTSCRIPTS2.0.x.tar.gz file for S55, S60 and S4810 switches or the
SMARTSCRIPTS-Z.2.0.x.tar.gz file for Z9000 switches.
Command Syntax Command Mode Task
package install {flash://filename |
ftp://userid:password@host-ipaddress/dir-path | tftp://
host-ipaddress/dir-path}
Where:
•
flash://filename installs the Smart Scripting file
stored in flash memory on the switch.
•
ftp://userid:password@host-ipaddress/filepath logs
in and installs Smart Scripting from a file stored on
an FTP server.
•
tftp://host-ipaddress/filepath installs Smart Scripting
from a file stored on a TFTP server.
16 | Smart Scripting
7. When the download is complete, enter the
package install command from the
FTOS CLI on a switch to install the Smart Scripting package.
EXEC Privilege Install the Smart Scripting package
from local flash memory or a network
server.
Page 17
T o remove an installed Open Automation package, such as Smart Scripting, enter the
package uninstall command.
To follow the progress of a package installation (or removal), enter the
packages
command.
Displaying Installed Packages
To view the Open Automation packages currently installed on a switch, including
version numbers and content, enter the
Command Syntax Command Mode Task
show packages
EXEC Privilege View package information.
show packages command.
Uninstalling Smart Scripting
Caution: Before you uninstall the Smart Scripting package, you must first stop all scripts
that are currently running using the
manually stop the http server daemon.
Uninstalling the Smart Scripting package removes it from the internal flash memory.
no script script-name command. You must also
show
Command Syntax Command Mode Task
package uninstall package-name
Enter the name of the Smart Scripting package,
exactly as it appears in the
list.
show packages
EXEC Privilege Uninstall the Smart Scripting package stored on
the switch.
Limits on System Usage
Smart Scripting establishes limits on system processes for the following attributes
(regardless of the user-privilege level or scripting method) to restrict CPU and
memory usage:
Table 3-1. Limits on System Attributes
System
Attribute Value Description
cputime unlimited Maximum amount of time used by a process.
filesize unlimited Largest file size that can be created.
Smart Scripting | 17
Page 18
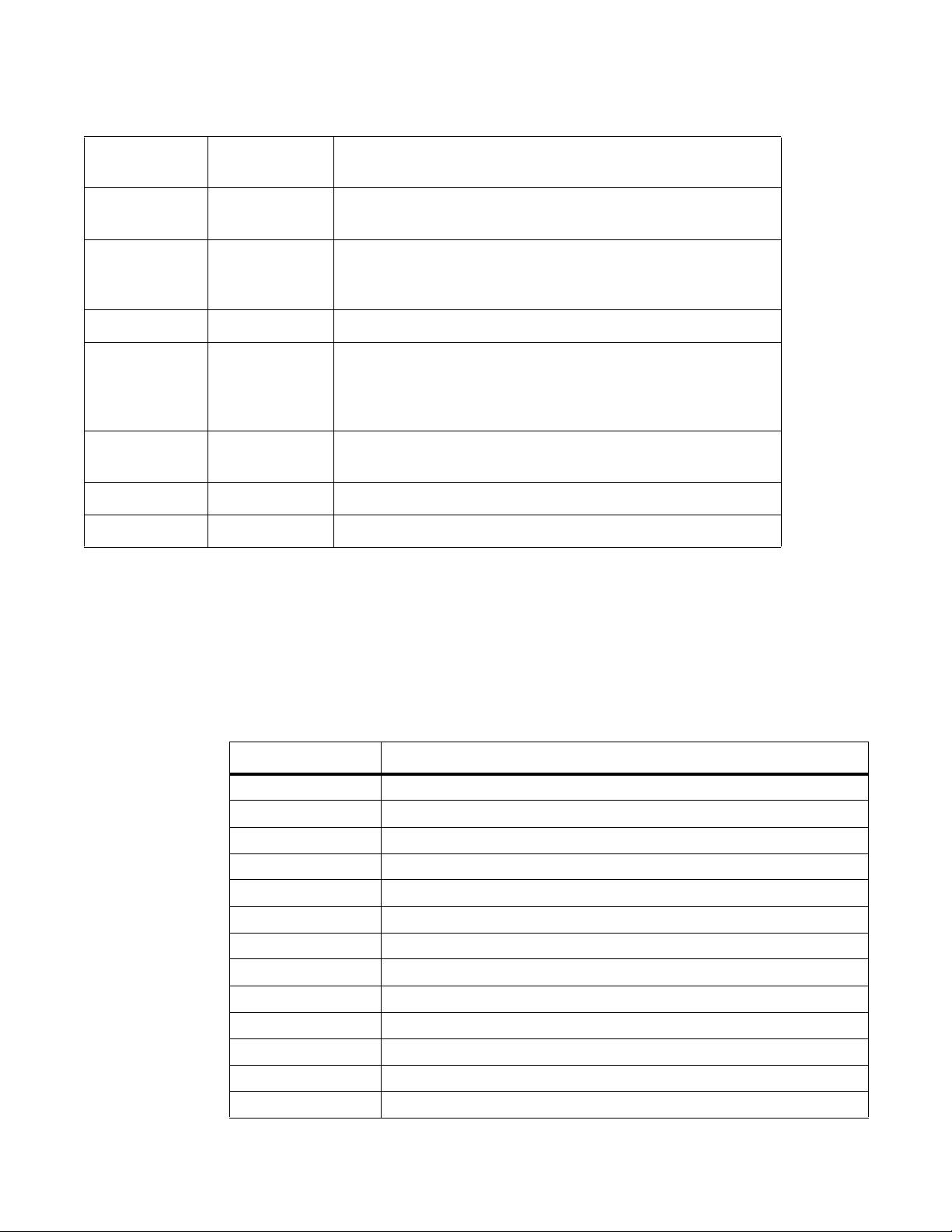
Table 3-1. Limits on System Attributes
System
Attribute Value Description
datasize 131,072 KB Maximum size of the data segment for a process; this value defines
how far a program may extend its break with the sbrk(2) system call.
stacksize 2,048 KB Maximum size of the stack segment for a process; this value defines
how far a program's stack segment may be extended. Stack extension
is performed automatically by the system.
coredumpsize unlimited Largest size of a core file that may be created
memory use 233,244 KB Maximum size to which a process’s resident set size may grow. This
www.dell.com | support.dell.com
memorylocked 77,741 Maximum size (in bytes) which a process may lock into memory using
maxproc 160 Maximum number of simultaneous processes allowed for the user ID.
openfiles 64 Maximum number of open files for this process.
value imposes a limit on the amount of physical memory to be given to
a process; if memory is tight, the system will prefer to take memory
from processes that are exceeding their declared resident set size.
the mlock(2) function.
Supported UNIX Utilities
Smart Scripting supports the invocation of the following UNIX utilities in the scripts
you run:
Table 3-2. Supported UNIX Utilities
UNIX Utility Function
arp Address resolution display and control.
awk Pattern scanning and processing language.
basename Return filename or directory portion of pathname.
cat Concatenate and print files.
chmod Change file modes.
chown Change fi le own er and group.
cksum Display file checksums and block counts.
cut Select portions of each line of a file.
date Display or set date and time.
dd Convert and copy a file.
df Display free disk space.
env Set and print environment.
18 | Smart Scripting
expr Evaluate expression.
Page 19
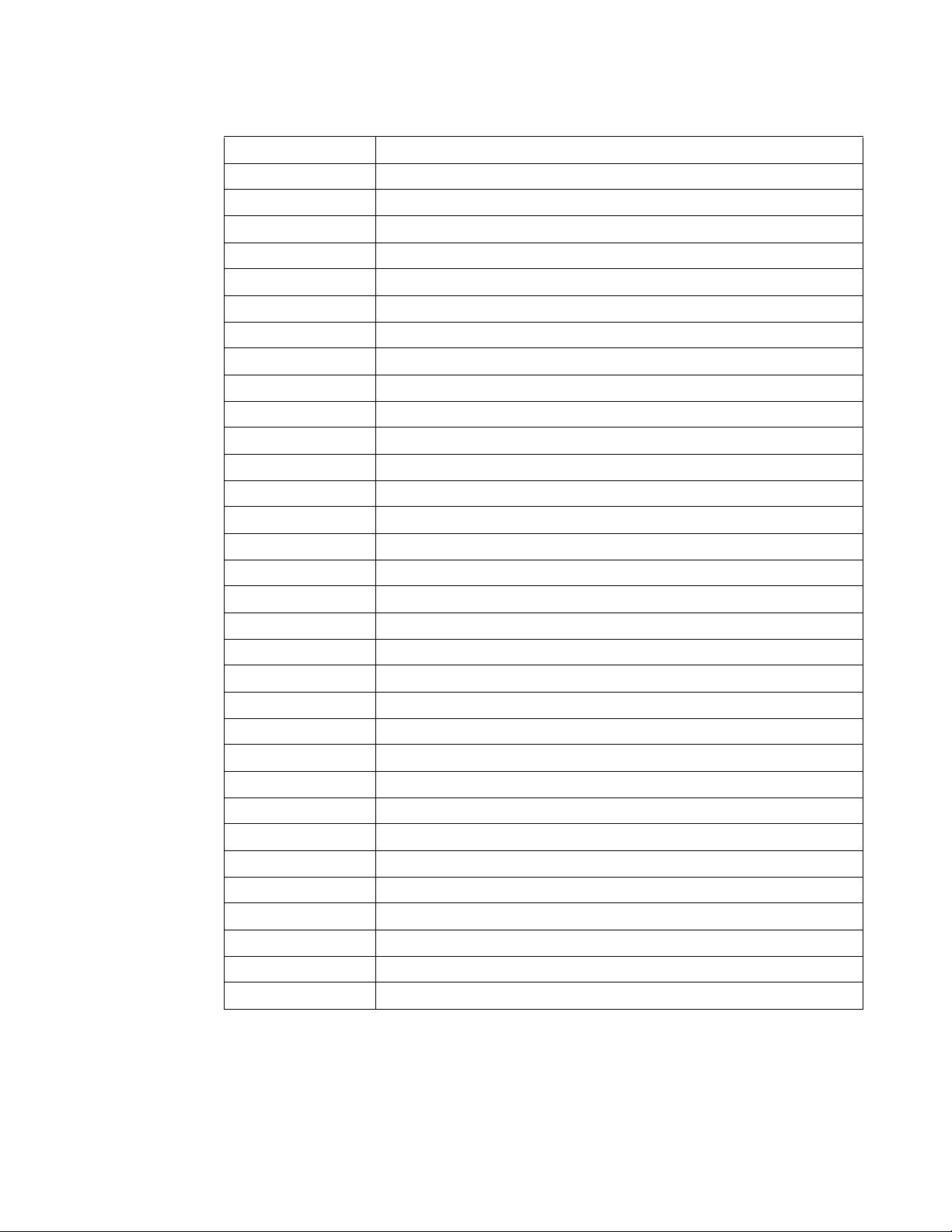
Table 3-2. Supported UNIX Utilities (continued)
fc List the history of commands on the computer.
fg Change the background process to foreground.
file Determine file type.
find Walk a file hierarchy.
ftp Internet file transfer program.
getopts Called each time you want to process an argument.
grep Print lines matching a pattern.
hostname Set or print name of current host system.
ifconfig Configure network interface parameters.
iostat Report I/O statistics.
ln Make links.
ls List directory contents.
md5 Calculates and verifies 128-bit MD5 hashes.
more A filter for browsing text files.
netstat Show network status
nice Execute a utility with an altered scheduling priority.
nohup Invoke a command immune to hangups.
ping Send ICMP ECHO_REQUEST packets to network hosts.
ps Process status.
pwd Return working directory name.
sed Stream editor.
sleep Suspend execution for an interval of time.
sort Sort or merge text files.
ssh Open SSH client (remote login program).
stty Used for changing the settings of a UNIX computer terminal.
tail Display the last part of a file.
test Condi tion evaluation utility.
ulimit Get and set process limits.
umask Set file creation mode mask.
vmstat Report virtual memory statistics.
wait Await process completion.
wc Word, line, and byte count.
who Display the users who are current ly lo gged in.
Smart Scripting | 19
Page 20

www.dell.com | support.dell.com
Creating PERL, Python and UNIX Scripts
When you install the Smart Scripting package, sample PERL and Python scripts are
installed in the /usr/pkg/scripts/sample_scripts directory. You can also create your
own customized scripts and store them anywhere on the switch, such as in a /f10/
flash_ scripts directory.
In addition, you can use the PERL, Python, and UNIX APIs to create scripts that
invoke function calls directly in the FTOS CLI. These APIs provide a shortcut when
writing scripts. Refer to the following sections for more information:
• Using the PERL API
• Using the Python API
• Using UNIX Shell Scripting
For instructions on how to run a PERL, Python, or UNIX script from the FTOS CLI,
see Running a Script from the FTOS CLI.
For information on how to run a PERL, Python, or UNIX script directly from a UNIX
shell, see Running a Script from the UNIX Shell.
Creating a User Name and Password for Smart Scripting
Before you run a script from the FTOS CLI, you may want to configure an additional
user name and password to be used only to run scripts on a switch. The user name and
password are used to log in to a UNIX shell and apply the read-write privileges
assigned to the user name when a script is run with the
FTOS CLI.
The user name is an optional entry in the
the FTOS CLI). To satisfy the requirements for a UNIX BSD login, the username
must be less than 16 characters. A username used to run scripts cannot contain special
characters.
Command Syntax Command Mode Task
username name password password CONFIGURATION Create an additional user name and password
script command (see Running a Script from
that are used to log in to a shell and apply
read-write privileges when a script is run.
script command from the
20 | Smart Scripting
Page 21
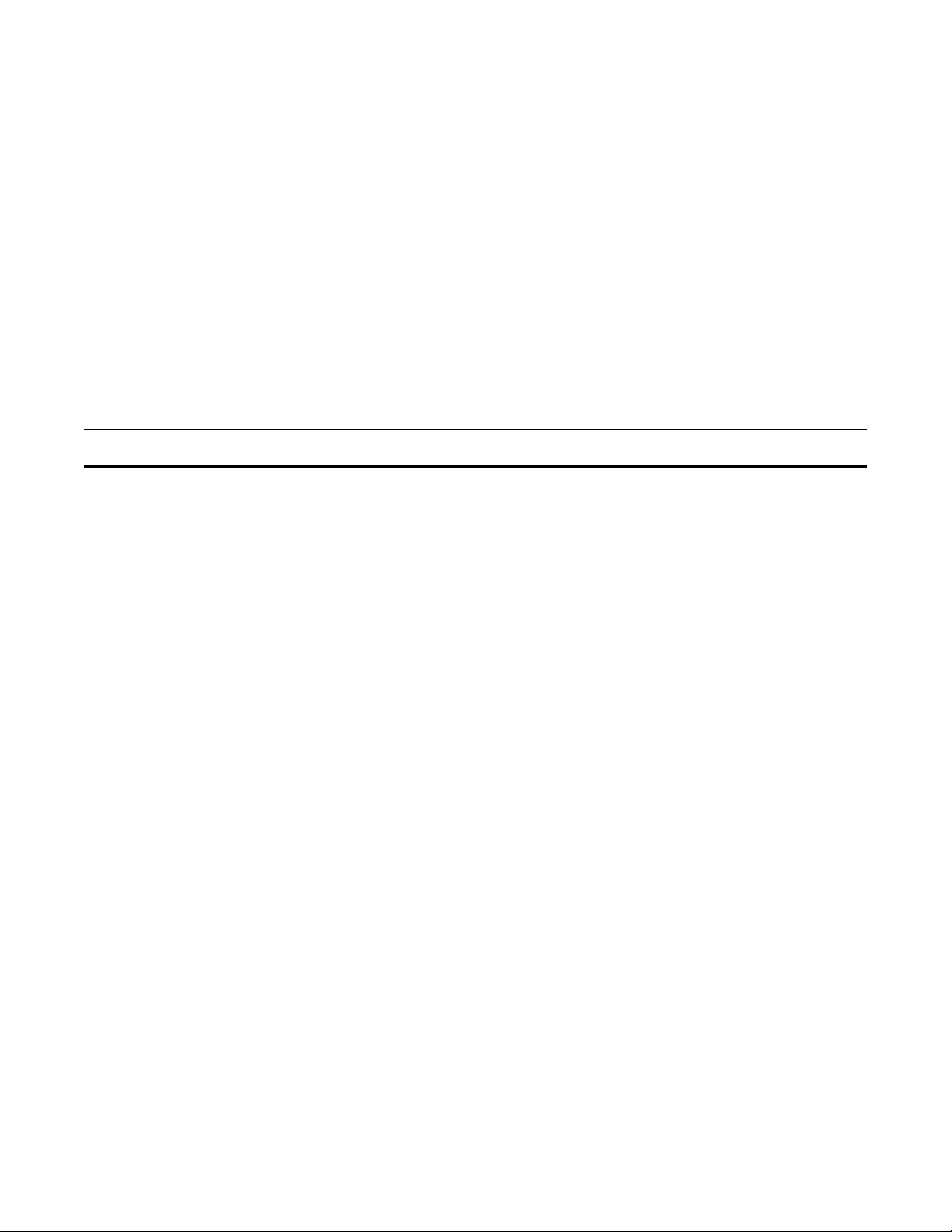
Running a Script from the FTOS CLI
f)# script /usr/pkg/scripts/sample_scripts/cmd-server.pl
f)# no script /usr/pkg/scripts/sample_scripts/cmd-server.pl
f)# script username admin /usr/pkg/scripts/sample_scripts/DisplayAlarms.py
f)# no script username admin /usr/pkg/scripts/sample_scripts/DisplayAlarms.py
You can run any PERL, Python, and UNIX script that is stored on the switch from the
FTOS CLI.
When you run a script from the FTOS CLI, you can specify an optional user name to
apply the associated read-write privileges when the script is run (see Creating a User
Name and Password for Smart Scripting). If you do not specify a user name, the
script is run with the privileges of the current user.
To run a PERL, Python, or UNIX script from the FTOS CLI, enter the
command. You must enter the script name and directory path to start the script. The
script can invoke any of the supported UNIX utilities listed in Table 3-2. You can
enter the command multiple times to run more than one script at the same time.
Command Syntax Command Mode Task
script [username name]
script-path [script-parameter
script-parameter ...]
CONFIGURATION Run an installed script; for examples, see Figure 3-1.
For script-path, enter the directory path and filename.
(Optional) For username name, enter the user name
whose read-write privileges will be applied when the script
is run. A username used to run scripts cannot contain
special characters.
(Optional) For script-parameter, enter the values of up to
three parameters to be applied when the script is run. Enter
a blank space between parameter values; for example:
script username admin /f10/flash/createVlans.py 1 2
To stop a script that is running. enter the
example:
no script admin.pl.
To display the scripts that are currently running, including the scripts you have
stopped, enter the
show running-config | grep command.
script
no version of the script command; for
Figure 3-1. Starting and Stopping PERL and Python Scripts: Examples
Tip: For information on how to run a script directly from a UNIX shell without using
the FTOS CLI, see Running a Script from the UNIX Shell.
Smart Scripting | 21
Page 22

Logging in to a NetBSD UNIX Shell
To log in to the NetBSD UNIX shell on a switch to directly enter any of the UNIX
commands described in Table 3-2 or to run a script, enter the
You are prompted to enter a user name and password before you can access the shell.
Login is performed using SSHv2.
Command Syntax Command Mode Task
start shell command.
www.dell.com | support.dell.com
start shell
EXEC Privilege Access the shell to run UNIX commands or a
script (see Running a Script from the UNIX
Shell).
Running a Script from the UNIX Shell
You can run any PERL, Python, and UNIX script stored on a switch from either the
FTOS CLI (see Running a Script from the FTOS CLI on page 21) or directly from a
NetBSD shell on the switch.
When you run a script from a UNIX shell, you must first access the shell by entering
start shell command (see Logging in to a NetBSD UNIX Shell). You are
the
prompted to enter a user name and password configured with the
(see Creating a User Name and Password for Smart Scripting).
Figure 3-2 shows examples of how to execute a PERL, Python, and UNIX shell script
directly from a NetBSD shell on the FTOS operating system.
username command
22 | Smart Scripting
Page 23

Figure 3-2. Execution of a PERL, Python, and Shell Script from a UNIX Shell: Example
The NetBSD Foundation, Inc. All rights reserved.
The Regents of the University of California. All rights reserved.
Using the PERL API
Use the information in this section to create a PERL script using the PERL API and
run the script on a Dell Force10 switch. For information on how to create and run a
Python script using the Python API, see Using the Python API.
Creating a PERL API Script
The Programmatic Management package provides a PERL API library containing the
supported functions (described in Table 3-2), which can be used in a PERL script to
invoke FTOS operations on a switch. The PERL API library is stored in the
F10SmartUtils.pl file at /usr/pkg/scripts/smartutils.
You code FTOS API functions in a PERL script as shown in the following example:
Smart Scripting | 23
Page 24

www.dell.com | support.dell.com
#!/usr/pkg/bin/perl -w
require '/usr/pkg/scripts/smartutils/F10SmartUtils.pl'; <------ Load the PERL API
usage() if ($#ARGV < 1);
($start,$end)=@ARGV;
$startVlan = $start;
$endVlan = $end;
for (my $i=$startVlan;$i<=$endVlan;$i++) {
my $createvlanId = F10CreateVlanId($i); <-------------------- Invoke a PERL API function
}
sub usage {
print "usage: createVlans.pl <start> <end>\n";
exit;
}
Figure 3-3. PERL Script with API function call: Example
Table 3-2 describes the supported functions and required arguments that you can use
in PERL scripts run on a Dell Force10 switch to connect through a telnet session and
gather information or configure parameters through the CLI.
24 | Smart Scripting
Page 25
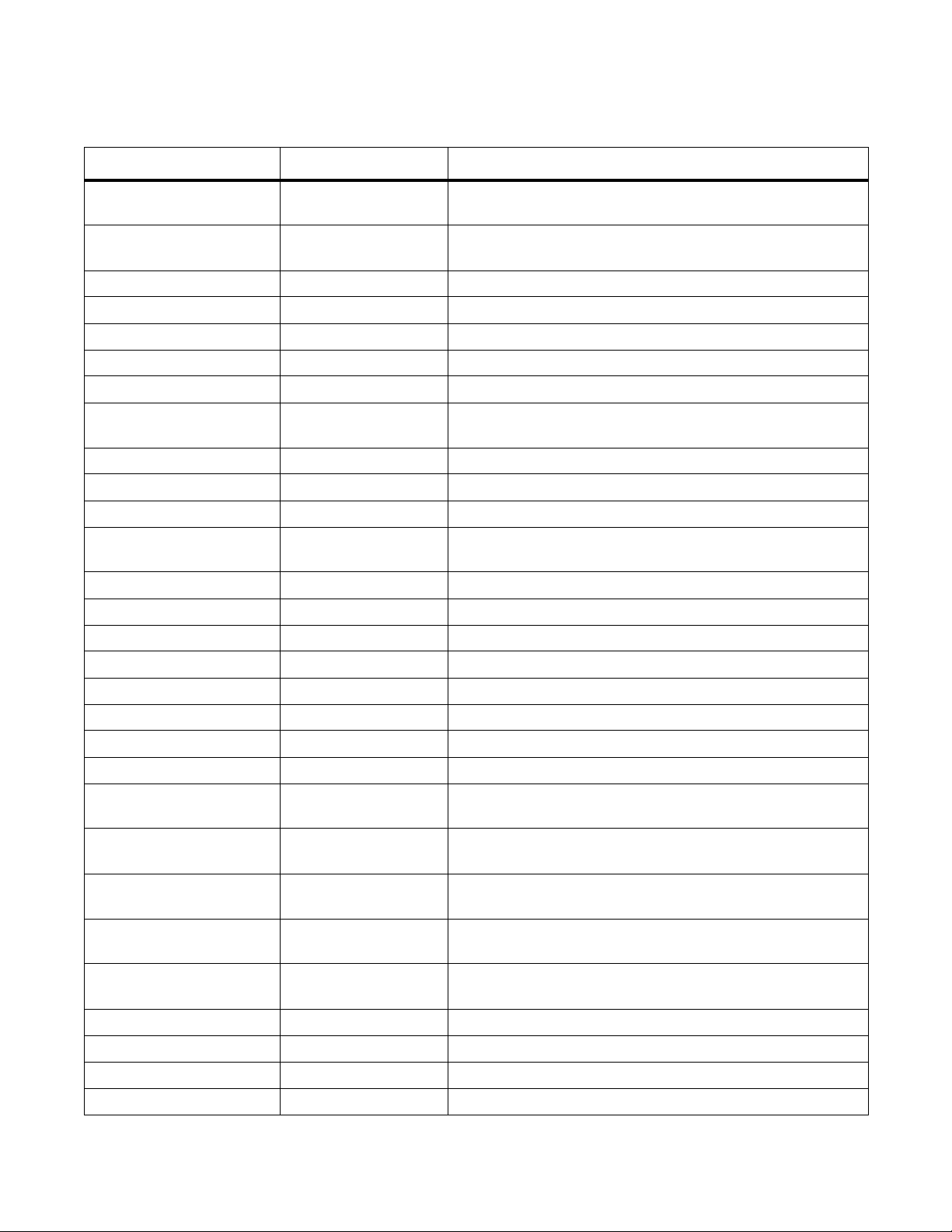
Table 3-3. Supported FTOS API Functions in PERL Scripts
PERL API Function Arguments Description
F10AddLagIntToVlan (lagId, vlanId, tagFlag) Adds a LAG interface to a VLAN as either tagged or untagged.
tagFlag values: 1 (tagged) or 0 (untagged).
F10AddPhyIntToVlan (stackUnitNum, portId,
vlanId, tagFlag)
Adds a physical interface to a VLAN as either tagged or untagged.
tagFlag values: 1 (tagged) or 0 (untagged).
F10CreateVlanId (vlanId) Creates a VLAN on the switch.
F10DeleteVlanId (vlanId) Deletes a VLAN on the switch.
F10ExecShowCmd (command) Executes a specified show command.
F10MakeLagIntNoShutdown (lagId) Enables the specified port channel.
F10MakeLagIntShutdown (lagId) Disables the specified port channel.
F10MakeLagIntSwitch (lagId) Configures the specified port channel (LAG) as a Layer 2
switchport.
F10MakePhyIntNoShutdown (stackUnitNum, portId) Enables the specified port.
F10MakePhyIntShutdown (stackUnitNum, portId) Disables the specified port.
F10MakePhyIntSwitch (stackUnitNum, portId) Configures the specified port as a Layer 2 switchport.
F10MakeVlanIntNoShutdown(vlanId) Enables the specified VLAN interface.
F10MakeVlanIntShutdown (vlanId) Disables the specified VLAN interface.
F10Ping (ipAddress) Pings (via ICMP) an IP address from the switch.
F10ShowArpTbl None Returns the table of learned ARP entries.
F10ShowBGPNeighbors None Returns list of BGP neighbors.
F10ShowBGPRoute None Returns the table of BGP-l earned routes.
F10ShowBGPSummary None Returns summary information on BGP sessions.
F10ShowBootVar None Returns system boot variables.
F10ShowEnvironment None Returns environment-monitoring variable values.
F10ShowIntBrief None Returns brief interface status (up/down/admin up/admin down) of
all interfaces.
F10ShowIntBriefLag None Returns brief interface status (up/down/ admin up/down) of all
port-channel interfaces.
F10ShowIntBriefMan None Returns brief interface status (up/down/ admin up/down) of all
management interfaces.
F10ShowIntBriefPhy None Returns brief interface status (up/down/ admin up/down) of all
physical interfaces.
F10ShowIntBriefVlan None Returns brief interface status (up/down/ admin up/down) of all
VLAN interfaces.
F10ShowIPRoute None Returns routing table info rmation.
F10ShowISISNeighbors None Returns list of ISIS neighbors.
F10ShowISISRoute None Returns the table of ISIS-learned routes.
F10ShowLagIntStatus (lagId) Returns the detailed status of a specified port-channel interface.
Smart Scripting | 25
Page 26
Table 3-3. Supported FTOS API Functions in PERL Scripts (continued)
F10ShowLagIntVlanMembers(lagId) Returns information on VLAN membership for a specified
port-channel interface.
F10ShowLog None Returns the switch log buffer.
F10ShowMacAddrTbl None Returns the table of learned MAC addresses.
F10ShowMem (lagId) Returns switch memory usage.
F10ShowOSPFNeighbors None Returns list of OSPF neighbors.
F10ShowOSPFRoute None Returns the table of OSPF-learned routes.
F10ShowPhyIntBand (stackUnitNum, portId) Returns in/out bandwidth average for a specified port.
F10ShowPhyIntStatus (stackUnitNum, portId) Returns the detailed status of a specified physical interface.
F10ShowPhyIntVlanMembers(stackUnitNum, portId) Returns information on VLAN membership for a specified
www.dell.com | support.dell.com
physical interface.
F10ShowProcCpu None Returns switch CPU usage and running processes.
F10ShowRun None Returns the running configuration (in memory).
F10ShowVer None Returns software version information.
F10ShowVlan None Returns the
F10ShowVlanId (vlanId) Returns the
F10ShowVlanIntStatus (vlanId) Returns the detailed status of a specified VLAN interface.
F10ShowVrrp None Returns the full VRRP status output.
F10ShowVrrpBrief None Returns a brief VRRP session summary.
show vlan output for all VLANs.
show vlan output for a specific vlan.
F10Traceroute (ipAddress, timeout) Performs a traceroute operation to an IP address from the switch.
F10WriteMem None Write the running configuration to the startup configuration file.
Running a PERL API Script
When you run a PERL script that invokes the API functions in Table 3-2, logon
credentials are read from the smartutils.cfg file, and a telnet session is opened on the
switch in which function calls are executed in the FTOS CLI. The script closes the
telnet session after running all the CLI commands.
The smartutils.cfg file is the configuration file used by the Programmatic
Management package. It contains the user name and passwords required to log on to
a switch via telnet and access the CLI to execute the function calls in a PERL API
script. The smartutils.cfg file is downloaded with the Programmatic Management
package and is stored at /usr/pkg/scripts/smartutils.
Note: The user name and passwords contained in the smartutils.cfg file are used to
log in and run only the scripts created using the PERL, Python, and UNIX APIs
described in this chapter
characters.
. A username used to run scripts cannot contain special
26 | Smart Scripting
Page 27

To configure the username and passwords in the smartutils.cfg file that are used to
run PERL API scripts, do one of the following:
• From the Web user interface, select
Options).
• From a UNIX shell, use the UNIX text editor to open the smartutils.cfg file, enter
a user name and password, and save the file.
To run a PERL API script:
• From the FTOS CLI, use the
from the FTOS CLI.
• From a UNIX shell, follow the procedure described in Running a Script from the
UNIX Shell.
Using the Python API
Use the information in this section to create a Python script using the Python API and
run the script on a Dell Force10 switch. For information on how to create and run a
PERL script using the PERL API, see Supported UNIX Utilities.
Creating a Python API Script
Settings > SmartUtils Credentials (see Menu
script command as described in Running a Script
Use the information in this section to create a Python script to be run on a Dell
Force10 switch. For information on how to run a Python script from the FTOS CLI,
see Running a Script from the FTOS CLI.
F10SmartUtils.py is the Python API library containing the supported functions
(described in Table 3-4), which can be used in a Python script to invoke FTOS
operations on a switch. This file is downloaded with the Programmatic Management
package and is stored at /usr/pkg/scripts/smartutils.
You code FTOS API functions in a Python script as shown in the following example:
Smart Scripting | 27
Page 28
www.dell.com | support.dell.com
Figure 3-4. Python Script with API function call: Example
#!/usr/pkg/bin/python
import sys
sys.path.append('/usr/pkg/scripts/smartutils') <--------------- Load the Python API
import F10SmartUtils
def create_vlans(startId,endId):
for vlanId in range(startId,endId+1):
result = F10SmartUtils.F10CreateVlanId(vlanId) <------- Invoke a Python API function
print result
def main(args):
try:
startId = int(args[0])
endId = int(args[1])
if(startId<=endId):
create_vlans(startId, endId)
else :
print "Invalid range: startId cannot be larger than endId",startId,endId
except ValueError:
print "Invalid arguments",args
if __name__=="__main__":
if len(sys.argv)>2:
main(sys.argv[1:])
else:
print "Please supply valid arguments"
print "createVlans.py <startId> <endId>"
Table 3-4 describes the supported functions and required arguments that you can use
in Python scripts run on a Dell Force10 switch to connect through a telnet session and
gather information or configure parameters through the CLI.
Table 3-4. Supported FTOS API Functions in Python Scripts
Python API Function Arguments Description
F10AddLagInttoVlan (lagId, vlanId, tagFlag) Adds a LAG interface to a VLAN as either tagged or untagged.
tagFlag values: 1 (tagged) or 0 (untagged).
F10AddPhyInttoVlan (stackUnitNum, portId,
vlanId, tagFlag)
F10CreateVlanId (vlanId) Creates a VLAN on the switch.
F10DeleteVlanId (vlanId) Deletes a VLAN on the switch.
F10ExecShowCmd (command) Executes a specified show command.
F10MakeLagIntNoShutdown (lagId) Enables the specified port channel.
F10MakeLagIntShutdown (lagId) Disables the specified port channel.
F10MakeLagIntSwitch (lagId) Configures the specified port channel (LAG) as a Layer 2
F10MakePhyIntNoShutdown (stackUnitNum, portId) Enables the specified port.
F10MakePhyIntShutdown (stackUnitNum, portId) Disables the specified port.
Adds a physical interface to a VLAN as either tagged or untagged.
tagFlag values: 1 (tagged) or 0 (untagged).
switchport.
F10MakePhyIntSwitch (stackUnitNum, portId) Configures the specified port as a Layer 2 switchport.
28 | Smart Scripting
Page 29
Table 3-4. Supported FTOS API Functions in Python Scripts (continued)
F10MakeVlanIntNoShutdown (vlanId) Enables the specified VLAN interface.
F10MakeVlanIntShutdown (vlanId) Disables the specified VLAN interface.
F10Ping (ipAddress) Pings (via ICMP) an IP address from the switch.
F10ShowArpTbl None Returns the table of learned ARP entries.
F10ShowBGPNeighbors None Returns list of BGP neighbors.
F10ShowBGPRoute Non e Returns the table of BGP-learned routes.
F10ShowBGPSummary None Returns summary information on BGP sessions.
F10ShowBootVar None Returns system boot variables.
F10ShowEnvironment None Returns environment-monitoring variable values.
F10ShowIntBrief None Returns brief interface status (up/down/admin up/admin down) of
all interfaces.
F10ShowIntBriefLag None Returns brief interface status (up/down/ admin up/down) of all
port-channel interfaces.
F10ShowIntBriefMan None Returns brief interface status (up/down/ admin up/down) of all
management interfaces.
F10ShowIntBriefPhy None Returns brief interface status (up/down/ admin up/down) of all
physical interfaces.
F10ShowIntBriefVlan None Returns brief interface status (up/down/ admin up/down) of all
VLAN interfaces.
F10ShowIPRoute None Returns routing table information.
F10ShowISISNeighbors None Returns list of ISIS neighbors.
F10ShowISISRoute None Returns the table of ISIS-learned routes.
F10ShowLagIntStatus (lagId) Returns the detailed status of a specified port-channel interface.
F10ShowLagIntVlanMembers (lagId) Returns information on VLAN membership for a specified
port-channel interface.
F10ShowLog None Returns the switch log buffer.
F10ShowMacAddrTbl None Returns the table of learned MAC addresses.
F10ShowMem (lagId) Returns switch memory usage.
F10ShowOSPFNeighbors None Returns list of OSPF neighbors.
F10ShowOSPFRoute None Returns the table of OSPF-learned routes.
F10ShowPhyIntBand (stackUnitNum, portId) Returns in/out bandwidth average for a specified port.
F10ShowPhyIntStatus (stackUnitNum, portId) Returns the detailed status of a specified physical interface.
F10ShowPhyIntVlanMembers (stackUnitNum, portId) Returns information on VLAN membership for a specified
physical interface.
F10ShowProcCpu None Returns switch CPU usage and running processes.
F10ShowRun None Returns the running configuration (in memory).
F10ShowVer None Returns so ftware version information.
F10ShowVlan None Returns the show vlan output for all VLANs.
F10ShowVlanId (vlanId) Returns the show vlan output for a specific vlan.
Smart Scripting | 29
Page 30
Table 3-4. Supported FTOS API Functions in Python Scripts (continued)
F10ShowVlanIntStatus (vlanId) Returns the detailed status of a specified VLAN interface.
F10ShowVrrp None Returns the full VRRP status output.
F10ShowVrrpBrief None Returns a brief VRRP session summary.
F10Traceroute (ipAddress, timeout) Performs a traceroute operation to an IP address from the switch.
F10WriteMem None Write the running configuration to the startup configuration file.
Running a Python API Script
When you run a Python script that invokes the API functions in Table 3-4, logon
www.dell.com | support.dell.com
credentials are read from the smartutils.cfg file, and a telnet session is opened on the
switch in which function calls are executed in the FTOS CLI. The script closes the
telnet session after running all the CLI commands.
The smartutils.cfg file is the configuration file used by the Programmatic
Management package. It contains the user name and passwords required to log on to
a switch via telnet and access the CLI to execute the function calls in a Python API
script. The smartutils.cfg file is downloaded with the Programmatic Management
package and is stored at /usr/pkg/scripts/smartutils.
Note: The user name and passwords contained in the smartutils.cfg file are used to
log in and run only the scripts created using the PERL, Python, and UNIX APIs
described in this chapter
characters.
. A username used to run scripts cannot contain special
To configure the username and passwords in the smartutils.cfg file that are used to
run Python API scripts, do one of the following:
• From the Web user interface, select
Settings > SmartUtils Credentials (see Menu
Options).
• From a UNIX shell, use the UNIX text editor to open the smartutils.cfg file, enter
a user name and password, and save the file.
To run a Python API script:
• From the FTOS CLI, use the
script command as described in Running a Script
from the FTOS CLI.
• From a UNIX shell, follow the procedure described in Running a Script from the
UNIX Shell.
30 | Smart Scripting
Page 31

Using UNIX Shell Scripting
echo $i
/usr/pkg/bin/python /usr/pkg/scripts/smartutils/F10SmartScriptUtils.py createvlanid $i
(( i++ ))
Use the information in this section to create a UNIX script using the UNIX API and
run the script on a Dell Force10 switch. For information on how to create and run a
PERL or Python script using the PERL or Python API, see Supported UNIX Utilities
and Using the Python API.
Creating a UNIX API Script
Use the information in this section to create a UNIX shell script to be run on a Dell
Force10 switch.
The F10SmartScriptUtils.py file is the main API library file that contains the
functions that you can include in a UNIX shell script. The F10SmartScriptUtils.py
file is downloaded with the Programmatic Management package and is stored at /usr/
pkg/scripts/smartutils. Table 3-5 describes the FTOS operations that you can invoke
from a UNIX shell script, including the supported functions and required arguments.
Figure 3-5 shows an example of how to write a script in the UNIX shell scripting
language. You can store a UNIX shell script anywhere on the switch.
Figure 3-5. Script Written in the UNIX Shell Scripting Language: Example
Table 3-5. Supported API Functions in UNIX Shell Scripts
Function Arguments Description
addlaginttovlan lagId, vlanId, tagFlag Adds a port channel (LAG) to a VLAN.
tagFlag values: 1 (tagged) or 0 (untagged).
addphyinttovlan stackunitNum, portId
vlanId, tagFlag
createvlanid vlanId Creates a VLAN with a specified VLAN ID.
deletevlanid vlanId Deletes a VLAN with a specified VLAN ID
makelagintnoshutdown lagId Enables the specified port channel.
makelagintshutdown lagId Disables the specified port channel.
makelagintswitch lagId Configures the specified port channel (LAG) as a Layer 2
Adds an interface to a VLAN.
tagFlag values: 1 (tagged) or 0 (untagged).
switchport.
Smart Scripting | 31
Page 32

Table 3-5. Supported API Functions in UNIX Shell Scripts (continued)
makephyintnoshutdown stackUnitNum, portId Enables the specified port.
makephyintshutdown stackUnitNum, portId Disables the specified port.
makephyintswitch stackun itNum, portId Configures the specified port as a Layer 2 switchport.
makevlanintnoshutdown vlanId Enables the specified VLAN interface.
makevlanintshutdown vlanId Disables the specified VLAN interface.
ping ipAddress Pings (via ICMP) an IP address from the switch.
showarptbl None Returns the table of learned ARP addresses.
showbgpneighbors None Returns detailed BGP neighbor information.
showbgproute None Returns BGP-learned routes.
www.dell.com | support.dell.com
showbgpsummary None Returns BGP peer summary and status.
showbootvar None Returns system boot variables.
showcmd command Executes a specified show command.
showenvironment None Returns environment-monitoring variable values.
showipintbrief None Returns full interface list with up/down status.
showipintbrieflag None Returns brief interface status (up/down/ admin up/down) of all
port-channel interfaces.
showipintbriefman None Returns brief interface status (up/down/ admin up/down) of all
management interfaces.
showipintbriefphy None Returns brief interface status (up/down/ admin up/down) of all
physical interfaces.
showipintbriefvlan None Returns brief interface status (up/down/ admin up/down) of all
VLAN interfaces.
showiproute None Returns switch routing table.
showisisneighbors None Returns detailed ISIS neighbor information.
showisisroute None Returns ISIS-learned routes.
showlagintstatus lagId Returns detailed status information for a specified port channel.
showlagintvlanmembers lagId Returns VLAN membership of a specified port channel.
showlog None Returns system log output.
showmacaddrtbl None Returns the table of learned MAC addresses.
showmem lagId Returns switch memory usage.
showospfneighbors None Returns detailed OSPF neighbor information.
showospfroute None Returns OSPF-learned routes.
showphyintband stackunitN um , portId Returns in/out bandwidth average for a specified port.
showphyintstatus stackunitNum, portId Returns detailed status information fo r a specified port
showphyintvlanmembers stackunitNum, portId Returns VLAN membership of a specified port.
showproccpu None Returns switch CPU usage and running processes.
showrun None Returns the running configuration (in memory).
showver None Returns software version information.
32 | Smart Scripting
Page 33

Table 3-5. Supported API Functions in UNIX Shell Scripts (continued)
showvlan None Returns information on all VLANs, including membership.
showvlanid vlanId Returns detailed interface information for a specified VLAN.
showvlanintstatus vlanId Returns VLAN interface status.
showvrrp None Returns the full VRRP status output.
showvrrpbrief None Returns a brief VRRP session summary.
traceroute ipAddress, timeout Performs a traceroute operation to an IP address from the switch.
writemem None Write the running configuration to the startup configuration file.
Running a UNIX API Script
When you run a UNIX shell script that invokes the API functions in Table 3-5, logon
credentials are read from the smartutils.cfg file, and a telnet session is opened on the
switch in which function calls are executed in the FTOS CLI. The script closes the
telnet session after running all the CLI commands.
The smartutils.cfg file is the configuration file used by the Programmatic
Management package. It contains the user name and passwords required to log on to
a switch via telnet and access the CLI to execute the function calls in a UNIX API
script. The smartutils.cfg file is downloaded with the Programmatic Management
package and is stored at /usr/pkg/scripts/smartutils.
Note: The user name and passwords cont ained in th e sma rtutils.cfg file a re used to
log in and run only the scripts created using the PERL, Python, and UNIX APIs
described in this chapter
characters.
. A username used to run scripts cannot contain special
To configure the username and passwords in the smartutils.cfg file that are used to
run UNIX API scripts, do one of the following:
• From the Web user interface, select
Settings > SmartUtils Credentials (see Menu
Options).
• From a UNIX shell, use the UNIX text editor to open the smartutils.cfg file,
enter a user name and password, and save the file.
To run a UNIX API script:
• From the FTOS CLI, use the
script command as described in Running a Script
from the FTOS CLI.
• From a UNIX shell, follow the procedure described in Running a Script from the
UNIX Shell.
Smart Scripting | 33
Page 34

www.dell.com | support.dell.com
34 | Smart Scripting
Page 35

Smart Scripting CLI
Overview
Smart Scripting CLI is supported on platforms: z
Commands
• package install
• package uninstall
• script
• show packages
• start shell
• username
4
package install
z
Syntax
Parameters
Defaults
Command Modes
Command
History
location Enter the location from where you will download and install an Open Automation
Version 9.0.0.0 Introduced on the Z9000.
Version 8.3.8.0 Introduced on the S4810.
Install the Smart Scripting package. This command downloads the package from the
specified location, and installs it in the internal flash memory on a switch.
package install location
package, where location is one of the following values:
•
From the local flash: flash://filename
•
From an FTP server: ftp://userid:password@host-ipaddress/filepath
•
From a TFTP server: tftp://host-ipaddress/filepath
None
EXEC Privilege
Smart Scripting CLI | 35
Page 36

Version 8.3.5.1 Introduced on the S55.
Version 8.3.3.4 Introduced on the S60.
Usage
Information
package uninstall
www.dell.com | support.dell.com
z
Syntax
Parameters
Defaults
Command Modes
Command
History
Because the installing of an Open Automation package may take time, the installation
is performed in the background when the download finishes. A message is displayed
on the console when the installation is complete.
To follow the progress of a package installation, enter the
show packages command.
Remove an installed Open Automation package, such as Smart Scripting, from the
system.
package uninstall package-name
package-name Enter the name of an Open Automation automation package, exactly
as it appears in the show packages list.
None
EXEC Privilege
Version 9.0.0.0 Introduced on the Z9000.
Version 8.3.8.0 Introduced on the S4810.
Version 8.3.5.1 Introduced on the S55.
Version 8.3.3.4 Introduced on the S60.
Usage
Information
Related
commands
36 | Smart Scripting CLI
When you uninstall an Open Automation package, it is removed from the local flash
Caution: Before you uninstall the Smart Scripting package, you must first stop all scripts
that are currently running using the
no script script-name command.
memory.
To follow the progress when uninstalling an Open Automation package installation,
enter the
show packages Display all Open Automation packages installed on the
show packages command.
switch.
Page 37

script
Run a Perl, Python, or UNIX shell script from the FTOS CLI.
z
Syntax
Parameters
Defaults
Command Modes
Command
History
script [username name] script-name [script-parameter script-parameter ...]
username name (Optional) Enter the user name whose read-write privileges will be
applied when the script is run. A username used to run scripts cannot
contain special characters.
script-name Enter the name of the script to run, including the directory path and
filename; for example:
Perl script: /usr/pkg/scripts/sample_scripts/cmd-server.pl
Python script: /usr/pkg/scripts/sample_scripts/DisplayAlarms.p y
UNIX shell script: /usr/pkg/home/admin/test.sh
script-parameter (Optional) Enter the values of up to three parameters to be applied
when the script is run. Enter a blank space between parameter
values; for example:
script username admin /f10/flash/createVlans.py 1 2
None
CONFIGURATION
Version 9.0.0.0 Introduced on the Z9000.
Version 8.3.8.0 Introduced on the S4810.
Version 8.3.5.1 Introduced on the S55.
Version 8.3.3.4 Introduced on the S60.
Usage
Information
You can enter the script command multiple times to run more than one script at the
same time; for example:
FTOS(conf)#script username root /usr/pkg/scripts/sample_scripts/
DisplayAlarms.py
FTOS(conf)#script username root /usr/pkg/bin/python /usr/pkg/scripts/VSNAgent/
Xen/hpAgtMain.py
When you run a script from the FTOS CLI with the script command, you can specify an
optional user name to apply the read-write privileges assigned to the user name when
the script is run (see Running a Script from the FTOS CLI). You configure the
username and password with the username command. If you do not specify a user name
with the script command, the script is run with the privileges of the current user.
For information on how to run a script directly from a UNIX shell, see Running a
Script from the UNIX Shell.
Smart Scripting CLI | 37
Page 38

show packages
z
Enter the no script script-name command to stop a running script.
To display the scripts that are currently running, including the scripts you have
stopped, enter the show running-config | grep command.
Display the installed Open Automation packages, including version number and
contents.
www.dell.com | support.dell.com
Command Modes
Syntax
Defaults
Command
History
show packages
None
EXEC
EXEC Privilege
Version 9.0.0.0 Introduced on the Z9000.
Version 8.3.8.0 Introduced on the S4810.
Version 8.3.5.1 Introduced on the S55.
Version 8.3.3.4 Introduced on the S60.
38 | Smart Scripting CLI
Page 39

Example
FTOS# show packages
* Package Name: SMARTSCRIPTS Version: 2.0.0
Python 2.6.5
Perl 5.8.8
Data::Dumper 2.126
Class::MethodMaker 2.16
ExtUtils::MakeMaker 6.56
XML::NamespaceSupport 1.11
XML::SAX 0.96
XML::LibXML 1.70
Compress::Raw::Bzip2 2.027
Compress::Raw::Zlib 2.027
IO::Compress 2.027
URI 1.54
HTML::Tagset 3.20
HTML::Parser 3.65
LWP 5.836
Net::Telnet 3.03
OSSP::uuid 1.0602
UUID 0.02
version 0.82
Class::Inspector 1.24
Task::Weaken 1.03
Algorithm::Diff 1.1902
Text::Diff 1.37
SOAP::Lite 0.712
Crypt::SSLeay 0.57
URI::urn::uuid 0.03
UUID 0.03
Crypt::SSLeay 0.57
Net::SNMP 6.0.0
Net::Telnet::Cisco 1.10
HTTP Server
mini_httpd 1.19
Perl and Python function library for Force10 SmartScripts
smartutils 2.0.0
WebConnect Web UI and CGI scripts
htdocs 2.0.0
Smart Scripting CLI | 39
Page 40

www.dell.com | support.dell.com
Example
FTOS# show packages
* Package Name:SMARTSCRIPTS-Z Version: 2.0.0
Python 2.6.5
Perl 5.8.8
Data::Dumper 2.126
Class::MethodMaker 2.16
ExtUtils::MakeMaker 6.56
XML::NamespaceSupport 1.11
XML::SAX 0.96
XML::LibXML 1.70
Compress::Raw::Bzip2 2.027
Compress::Raw::Zlib 2.027
IO::Compress 2.027
URI 1.54
HTML::Tagset 3.20
HTML::Parser 3.65
LWP 5.836
Net::Telnet 3.03
OSSP::uuid 1.0602
UUID 0.02
version 0.82
Class::Inspector 1.24
Task::Weaken 1.03
Algorithm::Diff 1.1902
Text::Diff 1.37
SOAP::Lite 0.712
Crypt::SSLeay 0.57
URI::urn::uuid 0.03
UUID 0.03
Crypt::SSLeay 0.57
Net::SNMP 6.0.0
Net::Telnet::Cisco 1.10
HTTP Server
mini_httpd 1.19
Perl and Python function library for Force10 SmartScripts
smartutils 2.0.0
WebConnect Web UI and CGI scripts
htdocs 2.0.0
40 | Smart Scripting CLI
Page 41

start shell
z
Start a NetBSD UNIX shell.
Syntax
Defaults
Command Modes
Command
History
Usage
Information
Related
commands
start shell
None
EXEC Privilege
Version 9.0.0.0 Introduced on the Z9000.
Version 8.3.8.0 Introduced on the S4810.
Version 8.3.5.1 Introduced on the S55.
Version 8.3.3.4 Introduced on the S60.
You must start an NetBSD shell on a switch before you can enter UNIX commands
(Table 3-2) or run a script directly from the shell to invoke FTOS operations (see
Running a Script from the UNIX Shell).
After you start a shell, you are prompted to enter a user name and password.
show packages Display all Open Automation packages installed on the
switch.
Smart Scripting CLI | 41
Page 42

username
z
Configure an additional user name and password to be used only to run scripts on a
switch. The user name and password are used to log in to a UNIX shell and apply the
read-write privileges assigned to the user name when a script is run.
www.dell.com | support.dell.com
Command Modes
Syntax
Defaults
Parameters
Command
History
Usage
Information
username name password password
Enter no username to remove the user name and password.
none
name Enter a username to access the UNIX shell. The user name must be
less than 16 characters to satisfy the BSD UNIX login requirements.
A username used to run scripts cannot contain special characters.
password password Enter a password to access the UNIX shell.
CONFIGURATION
Version 9.0.0.0 Introduced on the Z9000.
Version 8.3.8.0 Introduced on the S4810.
Version 8.3.5.1 Introduced on the S55.
Version 8.3.3.4 Introduced on the S60.
When you run a script from the FTOS CLI with the script command, you can specify
an optional user name to apply the read-write privileges assigned to the user name
when the script is run (see Running a Script from the FTOS CLI).
42 | Smart Scripting CLI
Page 43

Virtual Server Networking
Virtual Server Networking is supported on platforms:
As a part of the Open Automation package, Virtual Switch Networking (VSN)
provides real-time communication between the Dell Force10 network fabric and
virtual servers to automate network management and configuration tasks throughout
the data center. VSN provides a closed-loop provisioning system to enable, for
example, the automatic re-provisioning of VLANs and port profiles across multiple
switches simultaneously, thereby increasing employee productivity and minimizing
human error.
Because Open Automation supports hypervisors from multiple vendors, data center
managers can use a single mechanism to simultaneously support multiple hypervisors
and their current management tools.
5
VSN is installed as a self-contained package, and requires the Smart Scripting
package.
Note: VSN is not supported in stacked configurations; it is supported only on standalone switches.
This chapter includes the following:
• Hypervisor Modes
• VLAN configuration
• Installing VSN
• Enabling VSN in a Hypervisor Session
• Running VSN Scripts
• Stopping a Hypervisor Session
• Uninstalling VSN
• V iewing VSN information
Overview
Virtual Server Networking is an Open Automation tool that enables Dell Force10
switch/routers in a data center network to retrieve configuration information from
hypervisors. VMware vSphere and Citrix Xen hypervisors are supported.
Virtual Server Networking | 43
Page 44

Both VMware and Citrix Xen provide SDKs and APIs for accessing their
vCenter
Citrix Xen
S60 FTOS
VMVMVMVM
VM
VM
vSphere
VM
VM
vSphere
vSphere
VM
VM
configuration objects. VSN requires Layer 3 connectivity to access a hypervisor.
Figure 5-1 shows an example of the network architecture in which a Dell FTOS
switch is connected to multiple servers, each of which may run a different type of
hypervisor. The vCenter hypervisor from VMware is a centralized server
management system that can manage multiple vSphere operating systems on which
multiple virtual machines (VMs) can run. The VMware ESX server is a single unit,
that may be managed by the hypervisor or act as an independent unit. The Citrix Xen
hypervisor uses a distributed management methodology under which a number of
XenServers are grouped in a management domain, with a master server managing the
other units in the domain.
www.dell.com | support.dell.com
Minimal packet drops may be seen when migrating VMS from one server to another.
THe drops may vary from one second or higher, depending on the load on the server
and network.
FTOS supports up to eight hypervisor sessions. A hypervisor session can consist of a
single hypervisor unit (ESX, ESXi, XenServer) or a centralized hypervisor (vCenter,
Xenpool). A vSphere client is used to manage a single VMware hypervisor. A
vCenter server is a centralized management server for managing multiple VMware
hypervisors.
Figure 5-1. Virtual Server Networking example
44 | Virtual Server Networking
VSN subscribes to hypervisor for any change to be notified to switch. Depending on
the hypervisor mode configured, FTOS may automatically update its configuration,
provide provisioning for configuration changes, or require system administrator
intervention.
Page 45

Hypervisor Modes
There are two modes for retrieving configuration information from a hypervisor on a
virtual server:
• Check: VSN retrieves configuration information from a hypervisor and notifies
the system administrator when there is a change in the network configuration; for
example, when a VLAN is added or removed. A system administrator must make
manual updates to the FTOS configuration.
• Config: VSN retrieves configuration information from a hypervisor and
automatically makes the required configuration changes in FTOS on the switch.
VSN Persistency
VSN installation and configuration is persistent in the FTOS configuration and
remains after a system reload. However, the configuration information retrieved
through a hypervisor is not persistent. If the system reloads, when it boots up the
VSN application will retrieve the network configuration of virtual servers again and
reconfigure FTOS accordingly.
VLAN configuration
Management VLAN
The management interface between a switch and a hypervisor can be a single port or
VLAN interface. If the connection with a hypervisor is through a VLAN, you must
manually configure the VLAN interface on the switch before VSN can establish a
connection with the hypervisor and retrieve information from it about virtual-server
configuration.
A hypervisor's management interface can also be a data interface, which means both
management traffic and data traffic can use the same interface.
Manually configured VLANs are not removed by VSN after application or
configuration changes are made in FTOS on a switch.
Data VLANS
Hypervisor-aware VLANs used for data traffic are automatically configured
according to the configuration parameters retrieved from the hypervisor by VSN as
part of the VLAN trunk on the switch port.
Virtual Server Networking | 45
Page 46

www.dell.com | support.dell.com
Enter the show vlan command to display the VSN hypervisor-learned VLANs on the
switch. As shown in Figure 5-2, VSN VLANs that have been automatically
configured are displayed with a
ports marked with an
H tag. If a VSN VLAN has been manually configured on the
G tag in the left-most column and are associated with
switch, the VLAN has no tag; the associated ports are displayed with an
Figure 5-2. Display VSN Hypervisor-learned VLANs: show vlan
FTOS(conf-hypervisor)#show config
!
Codes: * - Default VLAN, G - GVRP VLANs, R - Remote Port Mirroring VLANs,
P - Primary, C - Community, I - Isolated
tagged
Q: U - Untagged, T - Tagged
x - Dot1x untagged, X - Dot1x tagged
G - GVRP tagged, M - Vlan-stack, H - VSN tagged
i - Internal untagged, I - Internal tagged, v - VLT untagged, V - VLT
NUM Status Description Q Ports
* 1 Active U Te 0/0,15,25,27,29,42-43
U Te 11/35-36
G 4001 Active H Te 0/35
G 4002 Active H Te 0/35
4003 Active H Te 0/35
T Te 0/15
Hypervisor-unaware VLANs
H tag.
VSN cannot discover VLAN configurations from a hypervisor. If an application
requires a hypervisor-unaware VLAN, you must configure the VLAN manually.
User-configured VLANs are not removed when VSN retrieves and updates a network
configuration.
Installing VSN
VSN is installed as a separate Open Automation package, apart from the FTOS image
and the downloaded Smart Scripting package. When you install the VSN package,
VSN is loaded into FTOS.
Note: VSN is not supported in stacked configurations; it is only supported on
standalone switches.
You install the VSN package file in the same way as you install an FTOS release:
directly from local flash memory on a switch or from an external drive on a network
server. Because the installation takes time, it is performed in the background. When
the download is complete, a message is displayed on the console. The package
installation updates the running-configuration file.
You must manually configure the interfaces used to connect to hypervisors. Refer to
the FTOS Configuration Guide, Interfaces chapter for information on how to
configure a VLAN or physical interface.
46 | Virtual Server Networking
Page 47

Prerequisites:
- Smart Scripting is a prerequisite for using V irtual Server Network ing. You must first
install the Smart Scripting package before you can run the VSN application (see
Installing Smart Scripting)
To install the VSN package:
1. On a PC or other network device, go to the Dell Force10 web portal at
https://www.force10networks.com/CSPortal20/Main/SupportMain.aspx. Click
Login, enter your user ID and password, and click the Login button.
2. On the Customer Support page, click the Software Center tab.
3. In the left-hand column, click Automation Software.
4. At the bottom of the Terms and Conditions page, click I agree.
5. On the Automation Software page, under Software, click the
VSNAGENT2.0.x.tar.gz file.
6. In the dialog box, select the path for the local flash on the switch or a directory
path on a network server where you want to download the
VSNAGENT2.0.x.tar.gz file.
7. When the download is complete, enter the
package install command from the
FTOS CLI on a switch to install the VSN package in the internal flash memory.
Command Syntax Command Mode Task
package install {flash://filename |
ftp://userid:password@host-ipaddress/dir-path | tftp://
host-ipaddress/dir-path}
Where:
• flash://filename installs the VSN file stored in flash
memory on the switch.
• ftp://userid:password@host-ipaddress/filepath logs
in and installs VSN from a file stored on an FTP
server.
• tftp://host-ipaddress/filepath installs VSN from a
file stored on a TFTP server.
EXEC Privilege Install the VSN package in the running
configuration of the switch from local
flash memory or a network server.
8. Enter the following command to configure the Perl script (VSNAgent.pl) used for
VSN operations on VMware hypervisors: script /usr/pkg/scripts/VSNAgent/
VMWare/VSNAgent.pl.
To follow the progress of a package installation (or removal), enter the
packages
command.
show
Virtual Server Networking | 47
Page 48

www.dell.com | support.dell.com
Enabling VSN in a Hypervisor Session
Restrictions:
- VSN is not supported in stacked configurations; it is only supported on standalone
units.
- VSN supports connections only with VMware and Xen hypervisors
- You can define up to eight hypervisor sessions on a switch.
- To connect with a VMware hypervisor running on an ESXi 5.0 server, you must
configure the server's firewall to allow connections only through the management IP
address. You can reconfigure the firewall by using the
command to create a rule set that allows the IP address of a Dell Force10 switch to
pass the firewall. For detailed information, refer to How to Create Custom Firewall
Rules in ESXi 5.0.
- When you establish a VSN session with a Citrix Xen hypervisor (
command) that operates as a slave in a pool, the connection is established with the
master. Configuration and access information is retrieved from the entire pool. If the
slave is removed from the pool and operates as a standalone hypervisor, the VSN
session is still active with the master. In this case, information is retrieved from the
pool and not from the standalone hypervisor.
To enable VSN on an interface and connect to hypervisors on network servers:
esxcli network firewall
access
Step Task Command Syntax Command Mode
1
Enable VSN on an interface. vsn enable
2
Specify the name of a hypervisor
session and enter hypervisor
configuration mode.
3
Define the hypervisor type to which
you want to connect. Use the show
hypervisor supported command
to display the currently supported
hypervisor types.
VSN is disabled by default on switch
interfaces.
hypervisor name
Enter up to 40 characters to define the
hypervisor session.
type {vmware | xen-citrix}
There is no default value.
INTERFACE
CONFIGURATION
HYPERVISOR
48 | Virtual Server Networking
Page 49

Step Task Command Syntax Command Mode
4
Establish the connection between the
switch and a hypervisor
5
Set the mode for retrieving virtual
server configurations and updating
FTOS settings on the switch.
access url username username
password password
Where url is one of the following values:
For a VMware hypervisor:
https://[ip-address]/sdk/vimService
username [name] password [password]
For an Xen hypervisor:
http://ip-address username [name]
password [password]
username name: Username to be used for
authentication on the server.
password password: Password to be used for
authentication shown in clear text.
mode {check | config}
check: Retrieve configuration information
from the hypervisor, and notify the system
administrator of any configuration
changes. The configuration changes need
to be entered manually on the switch.
config: Retrieve configuration information
and automatically update the configuration
parameters in FTOS on the switch.
Default: config.
HYPERVISOR
HYPERVISOR
6
Enable the defined hypervisor
connection.
no disable HYPERVISOR
After you enable VSN on an interface and enable a hypervisor session that connects
to hypervisors on network servers, you can change the
is active. You cannot, however, change the
type and access settings if the session is
mode setting when the session
active. To change these settings, you must:
1. In hypervisor configuration mode, stop the session by entering the
disable
command.
2. Enter the
password password
3. Enter the
password
no type {vmware | xen-citrix} or no access url username username
command to remove a configured setting.
type {vmware | xen-citrix} or access url username username password
command to configure a new setting.
Virtual Server Networking | 49
Page 50

Discovery
The discovery process starts after you enter the no disable command on the interface
and ends 10 minutes after connectivity is established between the switch and
hypervisor. If no connectivity is established, the switch attempts to connect for three
minutes and then stops. Refer to Connectivity for more details on this process.
After you enable the link between a switch and a hypervisor, the switch uses a
discovery mechanism to learn VMAC and VLAN information from the hypervisor.
The discovery process also starts in the following conditions:
www.dell.com | support.dell.com
• You enter the
shutdown and no shutdown commands on a VSN-enabled port.
The discovery process resumes on the individual port only, not on all enabled
ports.
• You enter the
disable and no disable commands in hypervisor configuration
mode for a specified type of hypervisor connection. The discovery process is
resumed on all enabled ports.
• An update arrives from a hypervisor. The discovery process resumes on all
VSN-enabled ports.
In order for a switch to learn VLAN information from a hypervisor:
• Incoming traffic must be received on the VSN-enabled ports.
• There must be at least one VMAC configured on the hypervisor so that the VCAP
table can capture the VMAC entries for each VSN-enabled port.
The following log messages are displayed when the discovery process is interrupted
and when it starts again.
Message 1
Nov 28 11:34:19: %STKUNIT0-M:CP %VSNMGR-5-VSN_DISCOVERY_SUSPENDED:
Hypervisor macs not seen on Te 0/25. Discovery suspended.
Message 2
Nov 28 11:40:36: %STKUNIT0-M:CP %VSNMGR-5-VSN_DISCOVERY_RESUMED: Detected
config change in Hypervisor. Discovery of Hypervisor macs resumed on Te 0/25.
Message 3
Xen-Citrix:Connection error for hypervisor testing:LOGIN FAILURE
50 | Virtual Server Networking
Connectivity
If a network server is not reachable, a log message is displayed and the VSN agent
tries periodically to establish the connection with the hypervisor. The initial log
message is:
Page 51

If connectivity to a hypervisor is lost after information is retrieved and used to
reconfigure a switch, the following log message is displayed. The VSN agent tries to
connect to the hypervisor in the background. The information that was retrieved from
the hypervisor is not deleted.
Message 4
Xen-Citrix:Lost connection to hypervisor xen217. Retrying...
Afterwards, one of the following actions is performed:
• If connectivity with the hypervisor is re-established within three minutes after the
loss of connectivity, the following log message is displayed and the retrieved
information is retained:
Message 5
Xen-Citrix:Reestablished connection with hypervisor xen217.
• If connectivity with the hypervisor is not re-established within three minutes after
the loss of connectivity , the fol lowing log message is displayed. The information
retrieved from the hypervisor is deleted and the VLANs from the hypervisor are
unconfigured:
Message 6
Xen-Citrix:Lost connection to hypervisor xen217. Removing learnt
information.
Running VSN Scripts
The VSN package contains the SDKs for VMware and Citrix Xen hypervisors. The
Perl and Python scripts required for VSN functionality are stored with the VSN 2.0.x
package in the
• For VMware hypervisors, the Perl script is stored is at
VSNAgent/VMWare/
• For Citrix Xen hypervisors, the Python script is stored is at /usr/pkg/scripts/
VSNAgent/Xen/hpAgtMain.py
Caution: The Dell Open Automation Virtual Server Networking™ software package (the
“Product”) may contain the VMware SDK for Perl, which is licensed by VMware, Inc.
VMware will not provide technical support for the VMware SDK included in the Product.
Users interested in writing scripts for VMware products must obtain the VMware SDK
directly from VMware. You may not create scripts for VMware products through use of the
VMware SDK included in the Virtual Server Networking package. End Users may use the
Dell Virtual Server Networking according to the terms, conditions, and limitation of the
pertinent Dell End User License Agreement only.
/usr/pkg/scripts/VSNAgent directory as follows:
VSNAgent.pl.
/usr/pkg/scripts/
Virtual Server Networking | 51
Page 52

To run a VSN script (Perl or Python) in all connected hypervisor sessions to retrieve
virtual server configurations and update FTOS settings on the switch, enter the
command in configuration mode.
Command Syntax Command Mode Task
script
www.dell.com | support.dell.com
script script-name
CONFIGURATION Run a VSN script in active sessions on VMware and
Xen hypervisors.
For script-name, enter the directory path and
filename where the VSN script is stored on the
switch; for example: script /usr/pkg/
scripts/VSNAgent/VMWare/VSNAgent.pl.
Note: The script command is not supported on S55 switches to run VSN scripts.
To stop a VSN script that is running. enter the
no version of the script script-name
command; for example: no script /usr/pkg/scripts/VSNAgent/VMWare/
VSNAgent.pl
.
Stopping a Hypervisor Session
Disabling a Session
Enter the disable command in HYPERVISOR mode to stop VSN in a hypervisor
session. The
remove the session information from the system configuration.
disable command does not remove connectivity with the hypervisor or
Command Syntax Command Mode Task
disable HYPERVISOR Shut down VSN in a hypervisor session.
Command Syntax Command Mode Task
no hypervisor name CONFIGURATION Delete a session from the system.
52 | Virtual Server Networking
Removing a Session
Use the no hypervisor command in CONFIGURATION mode to delete the
configuration of a hypervisor session from the running configuration. The
hypervisor
command deletes the specified configuration and closes an active
hypervisor session, but does not remove the VSN agent from your system.
Enter the name of the hypervisor session that
you want to remove.
no
Page 53

Uninstalling VSN
Caution: Before you uninstall the VSN package, you must first stop all VSN scripts that are
currently running using the no script script-name command.
Uninstalling the VSN package removes it from the internal flash memory on a
switch.
Command Syntax Command Mode Task
package uninstall name
Enter the name of the VSN package, exactly as
it appears in show packages output.
EXEC Privilege Uninstall the VSN package from the system.
Viewing VSN information
To view the configuration of currently active hypervisor sessions, enter the show
configuration
Command Syntax Command Mode Task
show configuration HYPERVISOR Display configuration of current hypervisor
Figure 5-3. Display a Hypervisor Session: show configuration
FTOS(conf-hypervisor)#show config
!
hypervisor LocalNetwork
mode config
access https://10.10.10.10 username admin password 7 1d28e9f33f99cf5c
command in HYPERVISOR mode.
sessions.
To display a list of currently supported hypervisors, enter the show hypervisors
supported
Command Syntax Command Mode Task
show hypervisor supported EXEC Privilege Display a list of supported hypervisors.
Figure 5-4. Display Supported Hypervisors: show hypervisor supported
FTOS#show hypervisor supported
vmware
xen-citrix
command.
Virtual Server Networking | 53
Page 54

To display the components of current hypervisor sessions, including the link, virtual
switch, and hypervisor to which the switch is connected, enter the
virtualswitch
Command Syntax Command Mode Task
command.
show
www.dell.com | support.dell.com
show virtualswitch [interface]
[virtualswitch-name]
Figure 5-5. Display All Hypervisor Sessions: show virtualswitch
FTOS#show virtualswitch
Interface VSwitch Hypervisor
Gi 0/32 vSwitch3 VMWare_vmware207
Po 7 vSwitch1 VMWare_vmware206
Figure 5-6. Display a Specified Hypervisor Sessions: show virtualswitch
FTOS#show virtualswitch GigabitEthernet 0/32 vSwitch3
Interface :Gi 0/32
Hypervisor Type :vmware
Hypervisor Name :vmware207
Hypervisor Version :4.1.0
Virtual Switch :vSwitch3
Port groups :
Name :VLAN 3
Vlan Id :138
VIFs:
MAC MTU
00:50:56:92:00:77 8000
Name :VM Network 4
Vlan Id : VIFs:
MAC MTU
00:0c:29:4f:66:19 8000
PIFs:
MAC MTU
00:26:55:dd:01:4f 8000
EXEC Privilege Display general information on current hypervisor
sessions. To display detailed information on a
hypervisor session, enter the VSN interface and/or
virtual-switch name generated by the hypervisor as
displayed in
show virtualswitch output (Figure 5-6).
Command Syntax Command Mode Task
show vmmap interface EXEC Privilege Display the virtual machines accessed on a switch
54 | Virtual Server Networking
To display information on the virtual machines accessed on a switch interface,
including the virtual machine name, VMAC address, and corresponding VLAN ID,
enter the
show vmmap command.
interface.
Page 55

Figure 5-7. Display Virtual Machines Accessed on an Interface: show vmmap
FTOS#show vmmap gigabitethernet 0/32
VM Name VIF Vlan ID
Redhat_207_03_nfs 00:0c:29:4f:66:19 Redhat_207_03_nfs 00:50:56:92:00:77 138
Note: In show vmmap and show virtualswitch output, VLAN 1 is displayed as VLAN ID 1;
VLAN 4095 is displayed without a VLAN ID as "- "
Virtual Server Networking | 55
Page 56

www.dell.com | support.dell.com
56 | Virtual Server Networking
Page 57

Virtual Server Networking CLI
Overview
Virtual Server Networking CLI is supported on
platforms:
Note: VSN is not supported in stacked configurations; it is only supported on
standalone switches.
Commands
6
• access
• disable
• hypervisor
• mode
• package install
• package uninstall
• script
• show hypervisor supported
• show packages
• show virtualswitch
• show vmmap
• type
• vsn enable
Virtual Server Networking CLI | 57
Page 58

access
Configure the connection to access a hypervisor.
www.dell.com | support.dell.com
Command Modes
Syntax
Parameters
Defaults
Command
History
Usage
Information
[no] access url username name password password
url Enter the URL location of the desired hypervisor.
For a VMware hypervisor, enter:
https://[ip-address]/sdk/vimService username [name] password
[password]
For a Xen hypervisor, enter:
http://ip-address username [name] password [password]
username name Enter the user name to be used for authentication.
password password Enter the password to be used for authentication in clear text.
None
HYPERVISOR
Version 8.3.8.0 Introduced on the S4810.
Version 8.3.5.1 Introduced on the S55.
Version 8.3.3.4 Introduced on the S60.
VSN tries to establish a connection with a hypervisor only after the user credentials
(user name and password) are configured with the
access command.
disable
Syntax
Defaults
Command Modes
Command
History
Usage
Information
Stop a hypervisor session.
[no] disable
disable
HYPERVISOR
Version 8.3.8.0 Introduced on the S4810.
Version 8.3.5.1 Introduced on the S55.
Version 8.3.3.4 Introduced on the S60.
Entering the disable command in hypervisor configuration mode disables VSN in the
current hypervisor session. It does not remove connectivity with the hypervisor or
remove the session information from the system configuration.
Enter
no disable to re-enable a configured hypervisor session.
58 | Virtual Server Networking CLI
Page 59

hypervisor
Specify the name of a hypervisor session with which VSN will connect.
Syntax
Parameters
Defaults
Command Modes
Command
History
Usage
Information
[no] hypervisor name
name Enter up to 40 characters to specify the name of a hypervisor session
to which you want to connect on network servers.
None
CONFIGURATION
Version 8.3.8.0 Introduced on the S4810.
Version 8.3.5.1 Introduced on the S55.
Version 8.3.3.4 Introduced on the S60.
After you enter the command, you are placed in hypervisor configuration mode to
configure settings for the session.
Enter the
no hypervisor name command to remove the configuration of a specified
hypervisor session from the running configuration and close active hypervisor
sessions without removing the VSN agent from the system.
mode
Syntax
Defaults
Parameters
Command Modes
Command
History
Set the hypervisor mode used to retrieve configuration information on virtual servers.
[no] mode {check | config}
config
check VSN retrieves configuration information about virtual servers from a
hypervisor and notifies the system administrator if the configuration
has changed (for example, a VLAN has been added or removed).
Changes in FTOS configuration parameters must be entered
manually on the switch.
config VSN retrieves configuration information from the Hypervisor and
implements any necessary configuration changes automatically.
HYPERVISOR
Version 8.3.8.0 Introduced on the S4810.
Version 8.3.5.1 Introduced on the S55.
Version 8.3.3.4 Introduced on the S60.
Virtual Server Networking CLI | 59
Page 60

Usage
Information
You can use the mode command to change the way in which virtual-server
information is retrieved in an existing hypervisor session.
www.dell.com | support.dell.com
package install
Syntax
Parameters
The following log messages are displayed when the hypervisor mode
check is used to
retrieve configuration information on virtual servers:
Message 1
Dec 1 04:57:48: %STKUNIT0-M:CP %VSNMGR-5-VSN_VLAN_DISCOVERY: Te 0/35, Vlan:
4001-4008,4011-4012
Message 2
Dec 1 04:56:46: %STKUNIT0-M:CP %VSNMGR-5-VSN_VLAN_WITHDRAWAL: Te 0/35, Vlan:
4001-4008,4011-4012
Install an Open Automation package, such as Virtual Server Networking. This
command downloads the package from the specified location, and installs it in the
internal flash memory on a switch.
package install location
location Enter the location where you want to install an Open Automation
package, where location is one of the following values:
• flash://filename installs the VSN package file stored in flash
memory on the switch.
• ftp://userid:password@host-ip-address/file-path logs in and
installs VSN from a file stored on an FTP server.
• tftp://host-ip-address/file-path installs VSN from a file stored on
a TFTP server.
Defaults
Command Modes
Command
History
Version 8.3.8.0 Introduced on the S4810.
Version 8.3.5.1 Introduced on the S55.
Version 8.3.3.4 Introduced on the S60.
Usage
Information
60 | Virtual Server Networking CLI
None
EXEC Privilege
Because the installation of the VSN package takes time, the installation is performed
in the background. When the download is complete, a message is displayed on the
console.
To follow the progress of a package installation, enter the show packages command.
Page 61

package uninstall
Remove an installed Open Automation package, such as Virtual Server Networking,
from the system.
Syntax
Parameters
Defaults
Command Modes
Command
History
Usage
Information
Related
commands
package uninstall name
name Enter the name of the Open Automation package, exactly as it
appears in the show packages list.
None
EXEC Privilege
Version 8.3.8.0 Introduced on the S4810.
Version 8.3.5.1 Introduced on the S55.
Version 8.3.3.4 Introduced on the S60.
Uninstalling the VSN package removes it from the internal flash memory on the
switch. To follow the progress when removing a package from the system, enter the
show packages command.
Caution: Before you uninstall the V irtual Server Networking package, you must first stop all
scripts that are currently running using the
show packages Display all the packages installed in the system.
no script script-name command.
Virtual Server Networking CLI | 61
Page 62

script
Run an installed VSN script (Perl or Python) on active hypervisor links to retrieve
virtual server configurations and update FTOS settings on the switch.
www.dell.com | support.dell.com
Command Modes
Syntax
Parameters
Defaults
Command
History
Usage
Information
[no] script script-name
Enter the no script script-name to stop a running script.
script-name Enter the di rectory path and filename of where the VSN script is
stored; for example, /usr/pkg/scripts/VSNAgent/VMWare/
VSNAgent.pl.
None
CONFIGURATION
Version 8.3.8.0 Introduced on the S4810.
Version 8.3.3.4 Introduced on the S60.
For VMware hypervisors, the VSNAgent.pl Perl script is stored in the /usr/pkg/
scripts/VSNAgent/VMWare directory.
For Xen Citrix hypervisors, the hpAgtMain.py Python script is stored in the /usr/pkg/
scripts/VSNAgent/Xen directory .
Note: The script command used to run VSN scripts is not supported on S55 switches.
62 | Virtual Server Networking CLI
Page 63

show hypervisor supported
Display the types of hypervisors currently supported by VSN.
Syntax
Defaults
Command Modes
Command
History
Usage
Information
Related
Commands
Example FTOS#show hypervisor supported
Version 8.3.8.0 Introduced on the S4810.
Version 8.3.5.1 Introduced on the S55.
Version 8.3.3.4 Introduced on the S60.
hypervisor Define a hypervisor instance.
vmware
xen-citrix
show packages
show hypervisor supported
None
EXEC Privilege
Use this information when defining types of hypervisor connections with the
hypervisor command.
Display all Open Automation packages installed on a switch.
Syntax
Defaults
Command Modes
Command
History
show packages
None
EXEC Privilege
Version 8.3.8.0 Introduced on the S4810.
Version 8.3.5.1 Introduced on the S55.
Version 8.3.3.4 Introduced on the S60.
Virtual Server Networking CLI | 63
Page 64

www.dell.com | support.dell.com
Example
FTOS#show packages
****************************************
* Package Name:SMARTSCRIPTS Version: 2.0.0
Python 2.6.5
Perl 5.8.8
Data::Dumper 2.126
Class::MethodMaker 2.16
ExtUtils::MakeMaker 6.56
XML::NamespaceSupport 1.11
XML::SAX 0.96
XML::LibXML 1.70
Compress::Raw::Bzip2 2.027
Compress::Raw::Zlib 2.027
IO::Compress 2.027
URI 1.54
HTML::Tagset 3.20
HTML::Parser 3.65
LWP 5.836
Net::Telnet 3.03
OSSP::uuid 1.0602
UUID 0.02
version 0.82
Class::Inspector 1.24
Task::Weaken 1.03
Algorithm::Diff 1.1902
Text::Diff 1.37
SOAP::Lite 0.712
Crypt::SSLeay 0.57
URI::urn::uuid 0.03
UUID 0.03
Crypt::SSLeay 0.57
Net::SNMP 6.0.0
Net::Telnet::Cisco 1.10
HTTP Server
mini_httpd 1.19
Perl and Python function library for Force10 SmartScripts
smartutils 2.0.0
WebConnect Web UI and CGI scripts
htdocs 2.0.0
****************************************
****************************************
* Package Name:VSNAGENT Version: 2.0.0
Python 2.6.5
XenAPI
Perl 5.8.8
VIPerlToolkit 4.1
VSNAgent Scripts
****************************************
64 | Virtual Server Networking CLI
Page 65

show virtualswitch
Display the components of current hypervisor sessions, including the virtual switch
and name of the hypervisor session to which a switch interface is connected,
Syntax
Defaults
Parameters
Command Modes
Command
History
Usage
Information
show virtualswitch [interface] [virtualswitch-name]
None
interface Display info rm ation on the hypervisor session established on a
specified interface. Enter one of the following interface types:
• For a 100/1000 Ethernet interface or 1-Gigabit Ethernet interface,
enter: GigabitEthernet slot/port
• For a 10-Gigabit Ethernet interface, enter:
TenGigabitEthernet slot/port
• For a port-channel interface, enter: port-channel number
Where the valid port-channel numbers are 1 to 128.
virtualswitch-name Display information on a specified virtual switch by entering the
name generated by the hypervisor.
EXEC Privilege
Version 8.3.8.0 Introduced on the S4810.
Version 8.3.5.1 Introduced on the S55.
Version 8.3.3.4 Introduced on the S60.
Use the show virtualswitch command to display the interface, virtual-switch name,
and hypervisor-session name for all current hypervisor connections on the switch.
Example
To display detailed information on a hypervisor session, re-enter the command with
the interface and virtual-switch name for the session from the
output as shown in the example below.
The following command output displays information on the hypervisor sessions
established on all virtual switches on network servers connected to switch interfaces.
FTOS#show virtualswitch
Interface VSwitch Hypervisor
Gi 0/32 vSwitch3 VMWare_vmware207
Po 7 vSwitch1 VMWare_vmware206
show virtualswitch
Virtual Server Networking CLI | 65
Page 66

www.dell.com | support.dell.com
The following command output displays information on the hypervisor session
established on virtual switch vSwitch3 on a VMware server connected to the
interface 0/32.
FTOS#show virtualswitch Gigabitethernet 0/32 vSwitch3
Interface :Gi 0/32
Hypervisor Type :vmware
Hypervisor Name :vmware207
Hypervisor Version :4.1.0
Virtual Switch :vSwitch3
Port groups :
Name :VLAN 3
Vlan Id :138
VIFs:
MAC MTU
00:50:56:92:00:77 8000
Name :VM Network 4
Vlan Id : VIFs:
MAC MTU
00:0c:29:4f:66:19 8000
PIFs:
MAC MTU
00:26:55:dd:01:4f 8000
Note: In show virtualswitch output, VLAN 1 is displayed as VLAN ID 1; VLAN 4095 is
displayed without a VLAN ID as "- "
66 | Virtual Server Networking CLI
Page 67

show vmmap
Display the virtual machines accessed on a switch interface.
Syntax
Defaults
Parameters
Command Modes
Command
History
Usage
Information
show vmmap interface
None
interface Display information on the virtual machines accessed on a specified
interface. Enter one of the following interface types:
• For a 100/1000 Ethernet interface or 1-Gigabit Ethernet interface,
enter: GigabitEthernet slot/port
• For a 10-Gigabit Ethernet interface, enter the keyword
TenGigabitEthernet slot/port
• For a port-channel interface, enter:
port-channel number
Where the valid port-channel numbers are 1 to 128.
EXEC Privilege
Version 8.3.8.0 Introduced on the S4810.
Version 8.3.5.1 Introduced on the S55.
Version 8.3.3.4 Introduced on the S60.
The show vmmap command displays information on the virtual machines accessed on a
switch interface, including the virtual machine name, VMAC address, and
corresponding VLAN ID
Related
Commands
Example
hypervisor Define a hypervisor instance.
FTOS#show vmmap gigabitethernet 0/32
VM Name VIF Vlan ID
Redhat_207_03_nfs 00:0c:29:4f:66:19 Redhat_207_03_nfs 00:50:56:92:00:77 138
Note: In show vmmap output, VLAN 1 is displayed as VLAN ID 1; VLAN 4095 is
displayed without a VLAN ID as "- "
Virtual Server Networking CLI | 67
Page 68

type
Set the hypervisor type to which you want to connect.
Parameters
Command Modes
www.dell.com | support.dell.com
Information
Command
vsn enable
Syntax
Defaults
Usage
History
[no] type {vmware | xen-citrix}
None
vmware Set the hypervisor type as VMware.
xen-citrix Set the hypervisor type as Xen-Citrix.
HYPERVISOR
You must configure a hypervisor type in order to enable VSN connections with
virtual servers. Use the
show hypervisor supported command to display the currently
supported hypervisor types.
Version 8.3.8.0 Introduced on the S4810.
Version 8.3.5.1 Introduced on the S55.
Version 8.3.3.4 Introduced on the S60.
Enable VSN on an interface.
Syntax
Defaults
Command Modes
Command
History
Usage
Information
[no] vsn enable
VSN is disabled by default on switch interfaces.
INTERFACE
Version 8.3.8.0 Introduced on the S4810.
Version 8.3.5.1 Introduced on the S55.
Version 8.3.3.4 Introduced on the S60.
Enter the vsn enable command only on hypervisor-facing interfaces. DO NOT enter
this command on an interface used for inter-switch links.
Enter the
no vsn enable command to remove the VSN configuration from the system.
You must reconfigure VSN to re-enable a hypervisor session.
68 | Virtual Server Networking CLI
Page 69

Programmatic Management
Programmatic Management is supported on
platforms: and is downloaded with the SmartScripts
package (see Downloading the Smart Scripting Package).
Note: This feature is not currently supported on the Z9000 platform.
Overview
In the Open Automation framework, Programmatic Management allows you to
remotely manage Dell Force10 switches by invoking “out-of-the-box” scripts using
the Representational State Transfer (REST) application programming interface
(API).
7
The REST API takes advantage of Perl and Python scripts to add switch functionality
outside of FTOS. You can run scripts from a remote device to access a switch and
perform FTOS operations through a REST-based HTTP call.
Script writers can use the REST API to access the FTOS CLI on switches without
having to code individual CLI commands and telnet connections for each command.
This API allows Open Automation to remain independent of changes in the FTOS
CLI.
In addition to using the REST API, you can use third-party management tools and
other industry-standard management protocols, such as SNMP (Get and Set) and
XML, to manage Dell Force10 switches.
• For information on the third-party management tools supported to manage Dell
Force10 switches, see Plug-In Modules.
• For information on the SNMP and XML functions supported on Dell Force10
switches, refer to the FTOS Configuration Guides for the S55, S60, and S4810
systems.
Programmatic Management | 69
Page 70

www.dell.com | support.dell.com
print $response->decoded_content;
die $response->status_line;
Using the REST API
The script-based REST API allows you to remotely access a switch that supports
Open Automation from a network management device through programmatic HTTP
requests to directly perform FTOS functions.
The REST API operates by invoking the CGI scripts within the HTTP server on the
switch. The HTTP server passes an HTTP request to the backend CGI scripts. For
more information on the HTTP server, see HTTP Server.
The CGI scripts are shared with the W eb GUI to retrieve data through th e FTOS CLI.
The CGI script functions are stored on the switch under the main Web GUI directory
at /htdocs/cgi-bin.
Note: In Open Automation 2.0, the REST API supports only CGI script s that perform
HTTP read (get) requests. HTTP write (post) requests that make configuration
changes will be supported in future releases.
All REST-based API calls return plain text output.
Prerequisites: You must know the IP address of the switch to which you want to
connect and there must be network connectivity from your remote device to the
switch.
Table 7-1 describes the CGI scripts supported in an HTTP get request to access the
REST API and return data from a remote Dell Force10 switch.
The following example shows how to embed a REST-based HTTP get request in a
Perl script run from a remote device.
Figure 7-1. Perl Sample with HTTP Get Request that Invokes the REST API
70 | Programmatic Management
Page 71

The following example shows how to embed an HTTP get request in Python script.
# Handle response data
data = response.read()
print data
# Handle error
print "Operation failed",response.status,response.reason
Figure 7-2. Python Sample with HTTP Get Request that Invokes the REST API
Programmatic Management | 71
Page 72

Table 7-1. Supported Get Requests Invoked through the REST API
HTTP Get Request FTOS CLI Operation
F10Ping?IpAddress={ip-address} Pings a remote host from the switch using HTTP and returns the output.
F10ShowArpTbl Returns a formatted table of known MAC address-to-IP address bindings.
F10ShowBGPNeighbors Returns information on currently running BGP instances and discovered
(configured or connected) BGP neighbors.
F10ShowBGPSummary Returns summary information on BGP sessions.
F10ShowBootVar Returns the FTOS images that are loaded on the switch and the order in which
the are used to reload the switch.
F10ShowDate Returns the current system date and time.
www.dell.com | support.dell.com
F10ShowIntBrief Returns brief status (up/down/ admin) of all interfaces.
F10ShowIntBriefLag Returns brief interface status (up/down/ admin) of all port-channel interfaces.
F10ShowIntBriefMan Returns brief interface status (up/down/ admin) of all management interfaces.
F10ShowIntBriefPhy Returns brief interface status (up/down/ admin) of all physical interfaces.
F10ShowIntBriefVlan Returns brief status (up/down/ admin) of all VLAN interfaces.
F10ShowIPRoute Ret urns information from the switch’s routing table.
F10ShowISISNeighbors Returns information on currently running ISIS instances and discovered
(configured or connected) ISIS neighbors.
F10ShowLog Returns the contents of the event log in the switch memory buffer.
F10ShowMacAddrTbl Returns a table of learned MAC addresses from the switch’s forwarding table.
F10ShowMem Returns information on switch memory consumption.
F10ShowOSPFNeighbors Returns information on configured OSPF instances and discovered OSPF
neighbors.
F10ShowPhyIntBand?StackSlot={slot-
Returns the amount of bandwidth used for a specified port.
number}&Port={port-number}
F10ShowProcCpu Returns information on CPU util ization and the processes running on the
switch.
F10ShowRun Returns the contents of the running configuration file.
F10ShowVersion Returns information on the version of the currently runnin g switch software.
F10ShowVlan Returns the table of known VLANs and their member interfaces.
F10ShowVlanId?VlanId={vlan-id} Returns a list of the member interfaces that belong to a specified VLAN.
F10ShowVrrp Returns information on the currently configured VRRP instances, sessions,
and their status.
F10ShowVrrpBrief Returns information on VRRP sessions and their status.
F10Traceroute?IpAddress={ip-address}&
Timeout={timeout}
Performs a traceroute operation to a remote host from the switch and returns
output to the client device from which the HTTP request was sent for a
specified timeout period.
72 | Programmatic Management
Page 73

Plug-In Modules
Programmatic Management are third-party management tools and applications that
run on host devices in a data center network.
Plug-in modules running on remote hosts work together to provide a framework that
may invoke SNMP get and set requests, XML queries, and Telnet CLI commands on
Dell Force10 switches. For example, the Oracle OEM plug-in can retrieve status
information on network interfaces, and CPU and memory usage via SNMP walks,
resulting in timely detection of possible switch problems.
Table 7-2 describes the plug-in modules that are supported to access Dell Force10
switches.
Table 7-2. Supported Plug-In Modules to Access Dell Force10 Switches
Management Tool and Required Version Supported Devices
CA Spectrum Infrastructure Manager S55, S60, and S4810
EMC Smarts Ionix S55, S60, and S4810
Dell AIM S55, S60, and S4810
HP Network Automation (NA) S55, S60, and S4810
IBM Systems Director S55, S60, and S4810
Oracle Enterprise Manager (OEM) version 12c S55, S60, and S4810
For more information on a plug-in module, refer to the third-party web site for the
management tool.
Programmatic Management | 73
Page 74

www.dell.com | support.dell.com
74 | Programmatic Management
Page 75

Web GUI and HTTP Server
Web GUI and HTTP Server are supported on platforms
and are downloaded with the SmartScripts package (see Downloading the Smart
Scripting Package).
This chapter describes the Web-based components in the Open Automation package:
• HTTP Server
• Web Graphical User Interface
HTTP Server
8
In the Open Automation package, the HTTP web server runs on a switch and handles
HTTP requests from the Web-based graphical user interface (GUI). You can start the
HTTP web server in a non-secure (HTTP) or secure (HTTPS) mode.
To start the web server in a non-secure (without SSL) mode for receiving HTTP
requests and write the configuration to the running configuration, enter the
http-server http command:
Command Syntax Command Mode Task
http-server http CONFIGURATION Starts the web-server application in non-secure mode
to receive HTTP requests.
To start the web server in a secure mode for receiving HTTP requests and write the
configuration to the running configuration, enter the
command:
Command Syntax Command Mode Task
http-server secure-http CONFIGURATION Starts the web-server application in secure mode
using SSL to receive HTTP requests.
http-server secure-http
Enter the
remove the configuration from the running-configuration file.
no http-server {http | secure-http} command to stop the web server and
Web GUI and HTTP Server | 75
Page 76

www.dell.com | support.dell.com
Web Graphical User Interface
In the Open Automation package, the Web graphical user interface (GUI) provides a
user-friendly way to retrieve configuration information from a switch by choosing a
menu option.
Getting Started
To open the Web interface and get started on switch operations, follow these steps:
Step Task
Prerequisites: Only the following web browsers are supported:
• Internet Explorer 7.0 or later
• Firefox 3.6 or later
1. Open a web browser and enter the http://ip-address command to access the Open Automation web-based
interface for a switch. The main screen of the Web GUI is displayed as shown below:
76 | Web GUI and HTTP Server
Page 77

2 To retrieve or change configuration parameters on the switch, click a menu name and then click a menu option.
You may be prompted to enter more information.
Refer to Table 8-1 for a list of the tasks you can perform by choosing each menu option.
Refer to the Web Graphical User Interface for examples of the output of each menu option.
Menu Options
Table 8-1 describes the switch operation performed by each menu option.
Table 8-1. Web User Interface: Supported Operations
Menu Option Task
System > Software Version Displays information on the FTOS version currently running on the switch.
System > Time/Date Displays the system date and time.
System > Memory Usage Displays information on memory usage.
System > CPU Usage Displays information on CPU usage for the processes running on the switch.
System > Boot Variables Displays the FTOS images loaded on a switch and the order in which they are used when
the system boots up.
System > Running Config Displays the currently runni ng configuration on a switch.
Interfaces > All Displays brief status information (up, down, administratively up or down) on all
interfaces.
Interfaces > Physical Displays the status and IP address of physical port interfaces.
Interfaces > LAGs Displays the status and IP address of port-channel interfaces.
Interfaces > VLANs Displays the status and IP address of VLAN interfaces.
Web GUI and HTTP Server | 77
Page 78

Table 8-1. Web User Interface: Supported Operations (continued)
Interfaces > Management Displays the status and IP address of management interfaces.
Protocols > VRRP Displays the currently configured VRRP instances on a switch, including status and
session information.
Protocols > VRRP Brief Displays summary information on BGP sessions and status.
Protocols > BGP Summary Displays summary information on BGP sessions.
Protocols > BGP Neighbors Displays detailed information on current BGP sessions, including connected neighbors.
Protocols > OSPF Neighbors Displays detailed information on current OSPF sessions, including connected neighbors.
Protocols > ISIS Neighbors Displays detailed information on current ISIS sessions, including connected neighbors.
Diagnostics > ARP Table Displays the learned MAC address-to-IP address bindings from the ARP table.
Diagnostics > MAC Address Table Displays the learned MAC addresses from the forwarding table.
www.dell.com | support.dell.com
Diagnostics > Routing Table Displays information on learned IP routes from the routing table.
Diagnostics > System Log Displays the current events from the switch log buffer.
Diagnostics > VLANs Displays the currently configured VLANs and thei r po rt members.
Diagnostics > VLAN Members Displays the current membership of a specified VLAN ID.
Utilities > Ping Ping a remote host at the specified IP address via HTTP and display returned output.
Utilities > Traceroute Trace the route to a remote host at the specified IP address using the specified timeout
value (in seconds) and display returned output.
Settings > SmartUtils Credentials Reconfigure the user name, password, and enable password used to log on to FTOS on a
switch and run a script.
Important: Use this option to ensure that the user credentials applied by Smart Scripting
to run scripts on a switch are the same values as those configured on the FTOS CLI with
the username command.
78 | Web GUI and HTTP Server
Page 79

System Menu
System > Software Version
Appendix A
Web Graphical User Interface
This appendix contains examples of the output displayed for each menu option in the
Web interface used in the Open Automation Framework for the menus:
•System
• Interfaces
•Protocols
• Diagnostics
• Utilities
• Settings
System > Time/Date
System > Memory Usage
Web Graphical User Interface | 79
Page 80

www.dell.com | support.dell.com
System > CPU Usage
80 | Web Graphical User Interface
Page 81

System > Boot Variables
System > Running Config
Web Graphical User Interface | 81
Page 82

www.dell.com | support.dell.com
System > Information
82 | Web Graphical User Interface
Page 83

Interfaces Menu
Interfaces > All
Web Graphical User Interface | 83
Page 84

www.dell.com | support.dell.com
Interfaces > Physical
Interfaces > LAGs
Interfaces > VLANs
84 | Web Graphical User Interface
Page 85

Interfaces > Management
Web Graphical User Interface | 85
Page 86

www.dell.com | support.dell.com
Protocols Menu
Protocols > VRRP
86 | Web Graphical User Interface
Page 87

Protocols > VRRP Brief
Protocols > BGP Summary
Web Graphical User Interface | 87
Page 88

www.dell.com | support.dell.com
Protocols > BGP Neighbors
Protocols > OSPF Neighbors
88 | Web Graphical User Interface
Page 89

Protocols > ISIS Neighbors
Web Graphical User Interface | 89
Page 90

www.dell.com | support.dell.com
Diagnostics Menu
Diagnostics > Arp Table
Diagnostics > Mac Address Table
Diagnostics > Routing Table
90 | Web Graphical User Interface
Page 91

Diagnostics > System Log
Web Graphical User Interface | 91
Page 92

www.dell.com | support.dell.com
Diagnostics > VLANs
Diagnostics > VLAN Members
92 | Web Graphical User Interface
Page 93

Diagnostics > Int Bandwidth
Web Graphical User Interface | 93
Page 94

www.dell.com | support.dell.com
Utilities Menu
Utilities > Ping
Utilities > Traceroute
94 | Web Graphical User Interface
Page 95

Settings Menu
Settings > SmartUtils Credentials
Web Graphical User Interface | 95
Page 96

www.dell.com | support.dell.com
96 | Web Graphical User Interface
Page 97

Index
A
APIs
Perl
25
Python 28
REST 72
UNIX 31
B
Bare Metal Provisioning
description
switch autoconfiguration 10
10
D
displaying installed OA packages 17
Document conventions 6
E
ESX hypervisor 44
H
HTTP server
description
starting in secure mode 75
starting without SSL 75
hypervisors
check and config modes
connecting to 51
discovering VMACs and VLANs 50
displaying a session 53
displaying virtual machines 54
displaying VSN VLANs 46
enabling a session 48
removing a session 52
running a script 51
stopping a session 52
supported with VSN 11
12, 75
45
M
menu options, for Web interface 77, 79
minimum software versions required 5
O
Open Automation
components
description 9
display installed packages 17
10
P
PERL
application programming interface
Perl 13
creating a script 23
running a script 26
supported API functions 25
Plug-in modules
as third-party management tools
description 73
supported modules 73
Programmatic Management
description
protocols supported 12
REST API 70
third-party tools supported 12, 69
Python 13
application programming interface 27
creating a script 27
running a script 30
supported API functions 28
12, 69
23
73
R
REST API
description
supported CGI scripts 72
70
S
scripts 52
adding functionality with Smart Scripting 13
creating a Perl API script 23
creating a Python API script 27
creating a UNIX API script 31
creating a user name 20
logging in to a UNIX shell 22
running a perl API script 26
running a Python API script 30
running a script 37
running a UNIX API script 33
running from a UNIX shell 22
running from FTOS CLI 21
samples installed with Smart Scripting 20
stopping a running script 21
shell
logging in to UNIX
starting 41
Smart Scripting
description
installation 16
package contents 15
PERL API 23
Perl scripts 13
11, 13
22
Index | 97
Page 98

Python API 27
Python scripts 13
REST API 69
restrictions on CPU and memory usage 17
running scripts from a UNIX shell 22
scripting languages supported 11
supported UNIX utilities 18
UNIX scripts 13, 31
use cases 14
username for running scripts 20
Smart Scripting commands
package install
package uninstall 36
www.dell.com | support.dell.com
script 37
show packages 38
start shell 41
username 42
SmartUtils 13
stopping a hypervisor session 52
35
T
third-party management tools supported 73
U
UNIX
creating a shell script
logging in to shell 22
running a UNIX script 33
running scripts from a shell 22
supported API functions 31
UNIX scripts 13
UNIX utilities 18
user name
for running scripts
31
20
V
vCenter hypervisor 44
vCenter server 44
virtual machines 44
displaying in a hypervisor session 54
Virtual Server Networking
connecting to a hypervisor
description 11, 43
discovering hypervisor configuration 50
displaying a hypervisor session 53
displaying VSN VLANs 46
enabling on an interface 48
hypervisors supported 11
installation 46
removing a hypervisor session 52
51
running a script in a hypervisor session 51
stopping a hypervisor session 52
stopping a script 52
supported hypervisors 43
VLAN configuration 45
Virtual Server Networking commands
access
disable 58
hypervisor 59
mode 59
package install 60
package uninstall 61
script 62
show hypervisor supported 63
show packages 63
show virtualswitch 65
show vmmap 67
type 68
vsn enable 68
VLAN configuration
displaying VSN VLANs
with VSN 45
VMware hypervisors 51
VSN. See Virtual Server Networking.
vSphere client
58
46
44
W
Web interface
description
menu options 77, 79
opening and using 76
supported web browsers 76
12
X
Xenpool hypervisor 44
XenServer hypervisor 44
98 | Index
 Loading...
Loading...