Page 1

Dell Networking W-
ClearPass Guest 6.0
Deployment Guide
Page 2

Copyright
© 2013 Aruba Networks, Inc. Aruba Networks trademarks include , Aruba Networks®, Aruba Wireless Networks®, the registered Aruba the Mobile Edge Company logo, and Aruba Mobility Management System®.
Dell™, the DELL™ logo, and PowerConnect™ are trademarks of Dell Inc.
All rights reserved. Specifications in this manual are subject to change without notice.
Originated in the USA. All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
Open Source Code
Certain Aruba products include Open Source software code developed by third parties, including software code
subject to the GNU General Public License (GPL), GNU Lesser General Public License (LGPL), or other Open
Source Licenses. Includes software from Litech Systems Design. The IF-MAP client library copyright 2011
Infoblox, Inc. All rights reserved. This product includes software developed by Lars Fenneberg, et al. The Open
Source code used can be found at this site:
http://www.arubanetworks.com/open_source
Legal Notice
The use of Aruba Networks, Inc. switching platforms and software, by all individuals or corporations, to terminate
other vendors’ VPN client devices constitutes complete acceptance of liability by that individual or corporation for
this action and indemnifies, in full, Aruba Networks, Inc. from any and all legal actions that might be taken against it
with respect to infringement of copyright on behalf of those vendors.
2 | Dell Networking W-ClearPassGuest 6.0 | Deployment Guide
Page 3

Contents
About this Guide 13
Audience 13
Conventions 13
Contacting Support 14
Dell Networking W-ClearPass Guest Overview 15
About Dell Networking W-ClearPass Guest 15
Visitor Access Scenarios 16
Reference Network Diagram 16
Key Interactions 17
AAA Framework 18
Key Features 19
Visitor Management Terminology 20
ClearPass Guest Deployment Process 21
Operational Concerns 21
Network Provisioning 21
Site Preparation Checklist 22
Security Policy Considerations 23
AirGroup Deployment Process 23
Documentation and User Assistance 24
Deployment Guide and Online Help 24
Context-Sensitive Help 24
Field Help 25
Quick Help 25
If You Need More Assistance 25
Use of Cookies 25
Guest Manager 27
Accessing Guest Manager 27
About Guest Management Processes 28
Sponsored Guest Access 28
Self Provisioned Guest Access 28
Using Standard Guest Management Features 29
Creating a Guest Account 29
Creating a Guest Account Receipt 30
Creating Multiple Guest Accounts 30
Creating Multiple Guest Account Receipts 31
Creating a Single Password for Multiple Accounts 32
Managing Guest Accounts 34
Dell Networking W-ClearPassGuest 6.0 | Deployment Guide | 3
Page 4

Managing Multiple Guest Accounts 38
Importing Guest Accounts 40
Exporting Guest Account Information 43
About CSV and TSV Exports 43
About XML Exports 43
MAC Authentication in ClearPass Guest 44
MAC Address Formats 44
Managing Devices 44
Changing a Device’s Expiration Date 46
Disabling and Deleting Devices 47
Activating a Device 47
Editing a Device 47
Viewing Current Sessions for a Device 49
Viewing and Printing Device Details 49
MAC Creation Modes 49
Creating Devices Manually in ClearPass Guest 50
Creating Devices During Self-Registration - MAC Only 51
Creating Devices During Self-Registration - Paired Accounts 52
AirGroup Device Registration 53
Registering Groups of Devices or Services 53
Registering Personal Devices 55
Automatically Registering MAC Devices in ClearPass Policy Manager 56
Importing MAC Devices 57
Advanced MAC Features 57
2-Factor Authentication 57
MAC-Based Derivation of Role 57
User Detection on Landing Pages 58
Click-Through Login Pages 58
Active Sessions Management 59
Session States 60
RFC 3576 Dynamic Authorization 61
Filtering the List of Active Sessions 61
Disconnecting Multiple Active Sessions 62
Sending Multiple SMS Alerts 63
About SMS Guest Account Receipts 63
Onboard 65
Accessing Onboard 65
About ClearPass Onboard 65
Onboard Deployment Checklist 66
Onboard Feature List 67
Supported Platforms 68
Public Key Infrastructure for Onboard 68
Certificate Hierarchy 69
Certificate Configuration in a Cluster 70
Revoking Unique Device Credentials 70
4 | Dell Networking W-ClearPassGuest 6.0 | Deployment Guide
Page 5

Revoking Credentials to Prevent Network Access 70
Re-Provisioning a Device 71
Network Requirements for Onboard 71
Using Same SSID for Provisioning and Provisioned Networks 71
Using Different SSID for Provisioning and Provisioned Networks 71
Configuring Online Certificate Status Protocol 72
Configuring Certificate Revocation List (CRL) 72
Network Architecture for Onboard 72
Network Architecture for Onboard when Using ClearPass Guest 74
The ClearPass Onboard Process 75
Devices Supporting Over-the-Air Provisioning 75
Devices Supporting Onboard Provisioning 76
Managing Provisioned Applications 78
Configuring the User Interface for Device Provisioning 79
Customizing the Device Provisioning Web Login Page 79
Using the {nwa_mdps_config} Template Function 80
Configuring the Certificate Authority 81
Setting Up the Certificate Authority 81
Setting Up a Root Certificate Authority 82
Setting Up an Intermediate Certificate Authority 84
Obtaining a Certificate for the Certificate Authority 86
Using Microsoft Active Directory Certificate Services 86
Installing a Certificate Authority’s Certificate 88
Renewing the Certificate Authority’s Certificate 90
Configuring Data Retention Policy for Certificates 90
Uploading Certificates for the Certificate Authority 91
Creating a Certificate 93
Specifying the Identity of the Certificate Subject 93
Issuing the Certificate Request 95
Managing Certificates 95
Searching for Certificates in the List 96
Working with Certificates in the List 97
Working with Certificate Signing Requests 99
Importing a Code-Signing Certificate 101
Importing a Trusted Certificate 103
Requesting a Certificate 104
Providing a Certificate Signing Request in Text Format 104
Providing a Certificate Signing Request File 105
Specifying Certificate Properties 106
Configuring Provisioning Settings 106
Configuring Basic Provisioning Settings 107
Configuring Certificate Properties for Device Provisioning 107
Configuring Revocation Checks and Authorization 109
Configuring Provisioning Settings for iOS and OS X 110
Configuring Instructions for iOS and OS X 111
Dell Networking W-ClearPassGuest 6.0 | Deployment Guide | 5
Page 6

Configuring Reconnect Behavior for iOS and OS X 111
Configuring Provisioning Settings for Legacy OS X Devices 112
Configuring Provisioning Settings for Windows Devices 113
Configuring Provisioning Settings for Android Devices 114
Configuring Options for Legacy OS X, Windows, and Android Devices 116
Configuring Network Settings for Device Provisioning 117
Configuring Basic Network Access Settings 118
Configuring 802.1X Authentication Network Settings 120
Configuring Device Authentication Settings 121
Configuring Mutual Authentication Settings 122
Configuring Trust Settings Automatically 122
Configuring Trust Settings Manually 123
Configuring Windows-Specific Network Settings 124
Configuring Proxy Settings 125
Configuring an iOS Device VPN Connection 125
Configuring an iOS Device Email Account 127
Configuring an iOS Device Passcode Policy 129
Resetting Onboard Certificates and Configuration 130
Onboard Troubleshooting 131
Configuration 133
Accessing Configuration 133
Configuring ClearPass Guest Authentication 134
Content Manager 134
Uploading Content 135
Downloading Content 135
Additional Content Actions 136
Customizing Guest Manager 137
Default Settings for Account Creation 137
About Fields, Forms, and Views 141
Business Logic for Account Creation 141
Verification Properties 141
Basic User Properties 141
Visitor Account Activation Properties 142
Visitor Account Expiration Properties 142
Other Properties 143
Standard Forms and Views 143
Customizing Fields 145
Creating a Custom Field 145
Duplicating a Field 147
Editing a Field 147
Deleting a Field 147
Displaying Forms that Use a Field 147
Displaying Views that Use a Field 147
Customizing AirGroup Registration Forms 147
Configuring the Shared Locations and Shared Role Fields 147
6 | Dell Networking W-ClearPassGuest 6.0 | Deployment Guide
Page 7

Example: 149
Customizing Forms and Views 150
Editing Forms and Views 151
Duplicating Forms and Views 151
Editing Forms 152
Form Field Editor 152
Form Validation Properties 162
Examples of Form field Validation 163
Advanced Form Field Properties 165
Form Field Validation Processing Sequence 166
Editing Views 169
View Field Editor 169
Customizing Self-Provisioned Access 171
Self-Registration Sequence Diagram 171
Creating a Self-Registration Page 172
Editing Self-Registration Pages 173
Configuring Basic Properties for Self-Registration 174
Using a Parent Page 174
Paying for Access 175
Requiring Operator Credentials 175
Editing Registration Page Properties 176
Editing the Default Self-Registration Form Settings 177
Creating a Single Password for Multiple Accounts 177
Editing Guest Receipt Page Properties 178
Editing Receipt Actions 178
Enabling Sponsor Confirmation for Role Selection 179
Editing Download and Print Actions for Guest Receipt Delivery 181
Editing Email Delivery of Guest Receipts 181
Editing SMS Delivery of Guest Receipts 182
Enabling and Editing NAS Login Properties 183
Editing Login Page Properties 184
Self-Service Portal Properties 186
Resetting Passwords with the Self-Service Portal 187
Email Receipts and SMTP Services 189
About Email Receipts 189
Configuring Email Receipts 190
Email Receipt Options 190
About Customizing SMTP Email Receipt Fields 192
Customizing Print Templates 194
Creating New Print Templates 194
Print Template Wizard 196
Modifying Wizard-Generated Templates 196
Setting Print Template Permissions 197
Customize SMS Receipt 198
SMS Receipt Fields 199
Dell Networking W-ClearPassGuest 6.0 | Deployment Guide | 7
Page 8

Configuring Access Code Logins 199
Customize Random Username and Passwords 199
Create the Print Template 199
Customize the Guest Accounts Form 201
Create the Access Code Guest Accounts 201
Hotspot Manager 203
Accessing Hotspot Manager 203
About Hotspot Management 203
Managing the Hotspot Sign-up Interface 204
Captive Portal Integration 205
Web Site Look-and-Feel 206
SMS Services 206
Managing Hotspot Plans 206
Editing or Creating a Hotspot Plan 207
Managing Transaction Processors 209
Creating a New Transaction Processor 209
Managing Existing Transaction Processors 210
Managing Customer Information 210
Managing Hotspot Invoices 210
Customizing the User Interface 211
Customizing Visitor Sign-Up Page One 212
Customizing Visitor Sign-Up Page Two 212
Customizing Visitor Sign-Up Page Three 215
Viewing the Hotspot User Interface 217
Administration 219
AirGroup Services 220
Configuring the AirGroup Services Plugin 220
Creating AirGroup Administrators 221
Creating AirGroup Operators 221
Authenticating AirGroup Users via LDAP 221
Data Retention 221
Import Configuration 222
Plugin Manager 223
Viewing Available Plugins 223
Configuring Plugins 224
Configuring the Kernel Plugin 225
Configuring the Dell W-ClearPass Skin Plugin 226
Configuring the SMS Services Plugin 227
SMS Services 228
Viewing SMS Gateways 228
Creating a New SMS Gateway 229
Editing an SMS Gateway 231
Sending an SMS 232
About SMS Credits 233
8 | Dell Networking W-ClearPassGuest 6.0 | Deployment Guide
Page 9

About SMS Guest Account Receipts 233
SMS Receipt Options 234
Working with the SMTP Carrier List 234
Support Services 236
Viewing the Application Log 237
Exporting the Application Log 238
Contacting Support 239
Viewing Documentation 239
Operator Logins 241
Accessing Operator Logins 241
About Operator Logins 241
Role-Based Access Control for Multiple Operator Profiles 242
Operator Profiles 242
Creating an Operator Profile 242
Configuring the User Interface 245
Customizing Forms and Views 245
Operator Profile Privileges 246
Managing Operator Profiles 247
Configuring AirGroup Operator Device Limit 247
Local Operator Authentication 247
Creating a New Operator 248
External Operator Authentication 248
Manage LDAP Operator Authentication Servers 249
Creating an LDAP Server 249
Advanced LDAP URL Syntax 251
Viewing the LDAP Server List 251
LDAP Operator Server Troubleshooting 252
Testing Connectivity 252
Testing Operator Login Authentication 252
Looking Up Sponsor Names 253
Troubleshooting Error Messages 253
LDAP Translation Rules 254
Custom LDAP Translation Processing 256
Operator Logins Configuration 257
Custom Login Message 258
Advanced Operator Login Options 259
Automatic Logout 259
Reference 261
Basic HTML Syntax 261
Standard HTML Styles 262
Smarty Template Syntax 264
Basic Template Syntax 264
Text Substitution 264
Template File Inclusion 264
Dell Networking W-ClearPassGuest 6.0 | Deployment Guide | 9
Page 10

Comments 264
Variable Assignment 264
Conditional Text Blocks 264
Script Blocks 265
Repeated Text Blocks 265
Foreach Text Blocks 265
Modifiers 266
Predefined Template Functions 266
dump 266
nwa_commandlink 267
nwa_iconlink 267
nwa_icontext 268
nwa_quotejs 269
nwa_radius_query 269
ChangeToRole() 270
GetCallingStationCurrentSession() 270
GetCallingStationSessions() 270
GetCallingStationTime() 270
GetCallingStationTraffic() 271
GetCurrentSession() 271
GetIpAddressCurrentSession() 272
GetIpAddressSessions() 272
GetIpAddressTime() 272
GetIpAddressTraffic() 272
GetSessions() 273
GetSessionTimeRemaining() 273
GetTime() 273
GetTraffic() 274
GetUserActiveSessions() 274
GetUserActiveSessionCount() 274
GetUserCumulativeUsage() 274
GetUserCurrentSession() 274
GetUserFirstLoginTime() 274
GetUserSessions() 275
GetUserTraffic() 275
Advanced Developer Reference 275
nwa_assign 275
nwa_bling 275
nwa_makeid 276
nwa_nav 276
nwa_plugin 277
nwa_privilege 278
nwa_replace 278
nwa_text 278
nwa_userpref 279
10 | DellNetworking W-ClearPass Guest 6.0 | Deployment Guide
Page 11

nwa_youtube 279
Date/Time Format Syntax 279
nwadateformat Modifier 279
nwatimeformat Modifier 280
Date/Time Format String Reference 281
Programmer’s Reference 282
NwaAlnumPassword 282
NwaBoolFormat 282
NwaByteFormat 283
NwaByteFormatBase10 283
NwaComplexPassword 283
NwaCsvCache 283
NwaDigitsPassword($len) 283
NwaDynamicLoad 283
NwaGeneratePictureString 283
NwaGenerateRandomPasswordMix 284
NwaLettersDigitsPassword 284
NwaLettersPassword 284
NwaMoneyFormat 284
NwaParseCsv 284
NwaParseXml 285
NwaPasswordByComplexity 285
NwaSmsIsValidPhoneNumber 286
NwaStrongPassword 286
NwaVLookup 286
NwaWordsPassword 287
Field, Form, and View Reference 287
GuestManager Standard Fields 287
Hotspot Standard Fields 294
SMS Services Standard Fields 295
SMTP Services Standard Fields 296
Format Picture String Symbols 297
Form Field Validation Functions 298
Form Field Conversion Functions 301
Form Field Display Formatting Functions 301
View Display Expression Technical Reference 303
LDAP Standard Attributes for User Class 304
Regular Expressions 305
Glossary 307
Index 311
Dell Networking W-ClearPassGuest 6.0 | Deployment Guide | 11
Page 12

12 | DellNetworking W-ClearPass Guest 6.0 | Deployment Guide
Page 13

Chapter 1
About this Guide
Dell Networking W-ClearPass Guest provides a simple and personalized user interface through which operational
staff can quickly and securely manager visitor network access.
Audience
This deployment guide is intended for system administrators and people who are installing and configuring Dell
Networking W-ClearPass Guest as their visitor management solution. It describes the installation and configuration
process.
Conventions
The following conventions are used throughout this guide to emphasize important concepts:
Table 1:
Typographical Conventions
Type Style Description
Italics
System items
Commands
<
Arguments
[Optional]
{Item A |
Item B}
>
This style is used to emphasize important terms and to mark the titles of books.
This fixed-width font depicts the following:
l Sample screen output
l System prompts
l Filenames, software devices, and specific commands when mentioned in the text
In the command examples, this bold font depicts text that you must type exactly as shown.
In the command examples, italicized text within angle brackets represents items that you should
replace with information appropriate to your specific situation. For example:
# send <text message>
In this example, you would type “send” at the system prompt exactly as shown, followed by the text of
the message you wish to send. Do not type the angle brackets.
Command examples enclosed in brackets are optional. Do not type the brackets.
In the command examples, items within curled braces and separated by a vertical bar represent the
available choices. Enter only one choice. Do not type the braces or bars.
Dell Networking W-ClearPassGuest 6.0 | Deployment Guide About thisGuide | 13
Page 14

The following informational icons are used throughout this guide:
NOTE: Indicates helpful suggestions, pertinent information, and important things to remember.
CAUTION: Indicates a risk of damage to your hardware or loss of data.
WARNING: Indicates a risk of personal injury or death.
Contacting Support
Web Site Support
Main Website dell.com
Support Website dell.com/support
Documentation Website dell.com/support/manuals
14 | Contacting Support Dell Networking W-ClearPassGuest 6.0 | Deployment Guide
Page 15

Chapter 2
Dell Networking W-ClearPass Guest Overview
This chapter explains the terms, concepts, processes, and equipment involved in managing visitor access to a
network, and helps you understand how Dell Networking W-ClearPass Guest can be successfully integrated into your
network infrastructure. It is intended for network architects, IT administrators, and security consultants who are
planning to deploy visitor access, or who are in the early stages of deploying a visitor access solution.
This chapter includes the following sections:
l "About Dell Networking W-ClearPass Guest" on page 15
l "Visitor Access Scenarios " on page 16
l "Reference Network Diagram " on page 16
l "Key Interactions" on page 17
l "AAA Framework" on page 18
l "Key Features" on page 19
l "Visitor Management Terminology" on page 20
l "ClearPass Guest Deployment Process " on page 21
l "AirGroup Deployment Process " on page 23
l "Documentation and User Assistance " on page 24
l "Use of Cookies " on page 25
About Dell Networking W-ClearPass Guest
Dell Networking W-ClearPass Guest provides a simple and personalized user interface through which operational
staff can quickly and securely manage visitor network access. It gives your non-technical staff controlled access to a
dedicated visitor management user database. Through a customizable Web portal, your staff can easily create an
account, reset a password, or set an expiry time for visitors. Access permissions to ClearPass Guest functions are
controlled through an operator profile that can be integrated with an LDAP server or Active Directory login.
Visitors can be registered at reception and provisioned with an individual guest account that defines their visitor
profile and the duration of their visit. The visitor can be given a printed customized receipt with account details, or
the receipt can be delivered wirelessly using the integrated SMS services. Companies are also able to pre-generate
custom scratch cards, each with a defined network access time, which can then be handed out in a corporate
environment or sold in public access scenarios.
You can use the customization features to define settings that allow your visitors to self-provision their own guest
accounts. Visitors register through a branded and customized Web portal, ensuring a streamlined and professional
experience. Surveys can also be presented during the self-registration process and the data stored for later analysis and
reporting, providing additional insight to your visitors and their network usage.
Dell Networking W-ClearPassGuest 6.0 | Deployment Guide Dell Networking W-ClearPassGuest Overview | 15
Page 16
ClearPass Guest integrates with all leading wireless and NAC solutions through a flexible definition point, ClearPass
Policy Manager. This ensures that IT administrators have a standard integration with the network security
framework, but gives operational staff the user interface they require.
Visitor Access Scenarios
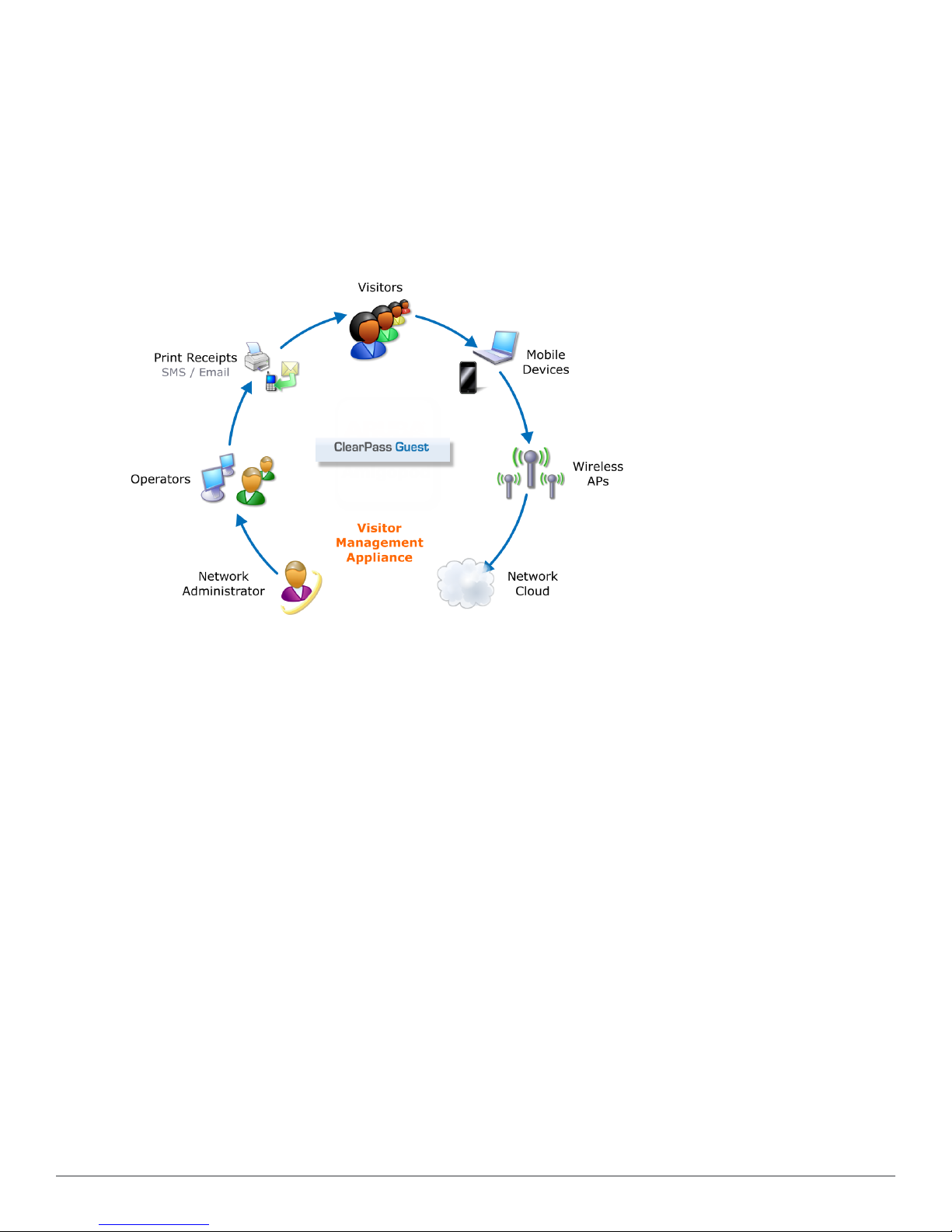
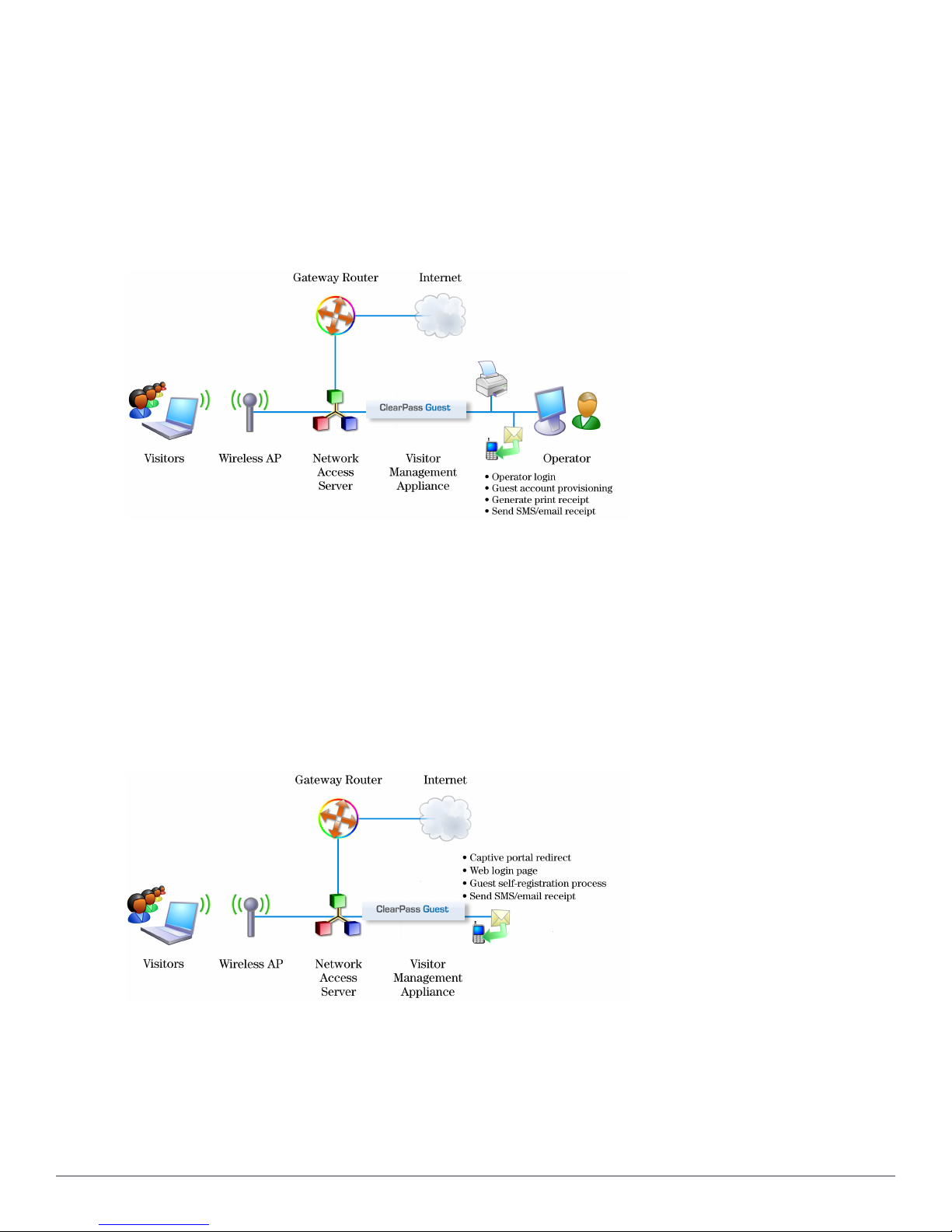
The following figure shows a high-level representation of a typical visitor access scenario.
Figure 1: Visitor access using ClearPass Guest
In this scenario, visitors are using their own mobile devices to access a corporate wireless network. Because access to
the network is restricted, visitors must first obtain a username and password. A guest account may be provisioned by
a corporate operator such as a receptionist, who can then give the visitor a print receipt that shows their username
and password for the network.
When visitors use self-registration, as might be the case for a network offering public access, the process is broadly
similar but does not require a corporate operator to create the guest account. The username and password for a selfprovisioned guest account may be delivered directly to the visitor’s Web browser, or sent via SMS or email.
Reference Network Diagram
The following figure shows the network connections and protocols used by ClearPass Guest.
16 | Visitor AccessScenarios Dell Networking W-ClearPassGuest 6.0 | Deployment Guide
Page 17
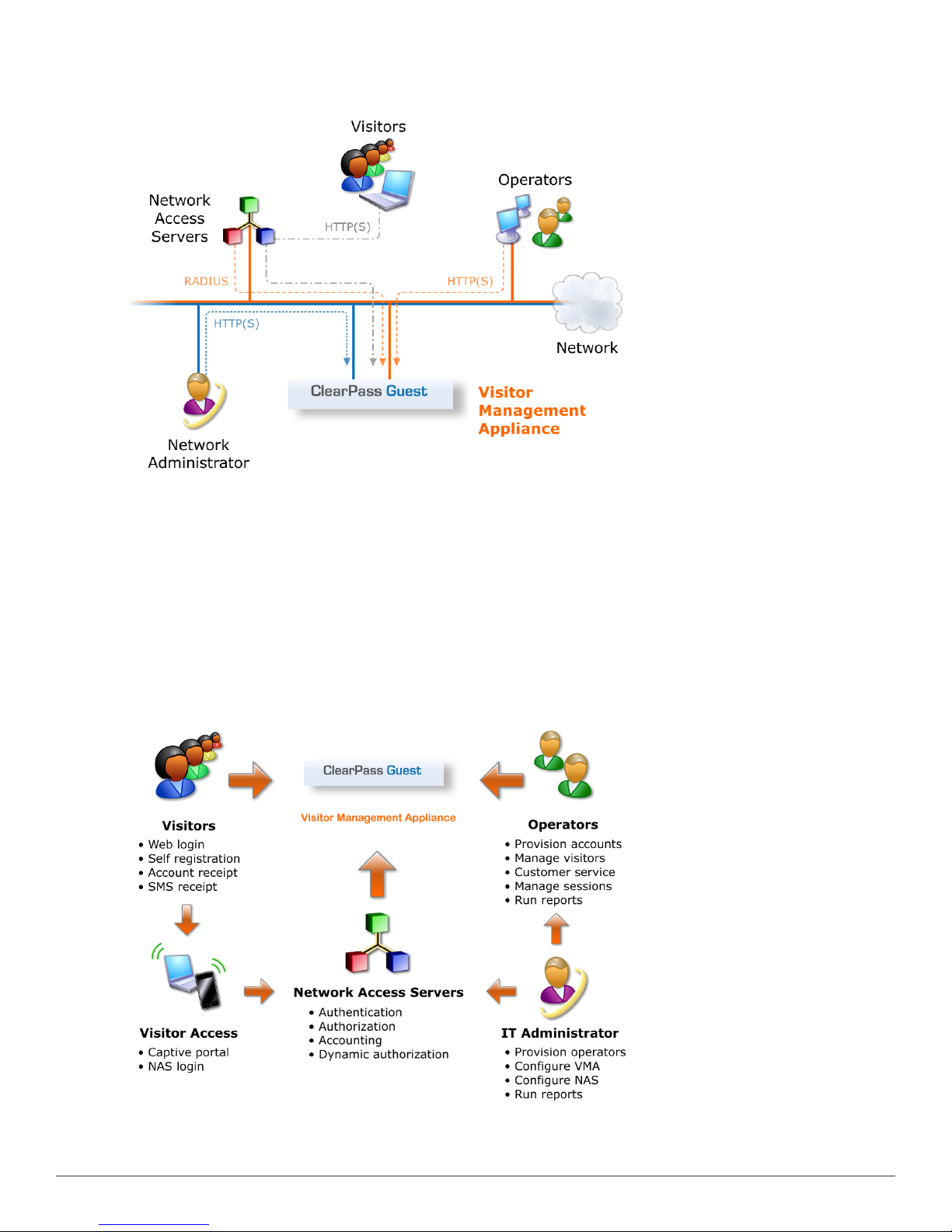
Figure 2: Reference network diagram for visitor access
The network administrator, operators, and visitors may use different network interfaces to access the visitor
management features. The exact topology of the network and the connections made to it will depend on the type of
network access offered to visitors and the geographical layout of the access points.
Key Interactions
The following figure shows the key interactions between ClearPass Guest and the people and other components
involved in providing guest access.
Figure 3: Interactions involved in guest access
Dell Networking W-ClearPassGuest 6.0 | Deployment Guide Key Interactions | 17
Page 18
ClearPass Guest is part of your network’s core infrastructure and manages guest access to the network.
NAS devices, such as wireless access points and wired switches on the edge of the network, use the RADIUS
protocol to ask ClearPass Policy Manager to authenticate the username and password provided by a guest logging in
to the network. If authentication is successful, the guest is then authorized to access the network.
Roles are assigned to a guest as part of the context ClearPass Policy Manager uses to apply its policies. RADIUS
attributes that define a role’s access permissions are contained within Policy Manager’s Enforcement Profile.
Additional features such as role mapping for ClearPass Guest can be performed in ClearPass Policy Manager.
The network usage of authorized guests is monitored by the NAS and reported in summary form to ClearPass Policy
Manager using RADIUS accounting, which allows administrators to generate network reports in ClearPass Insight.
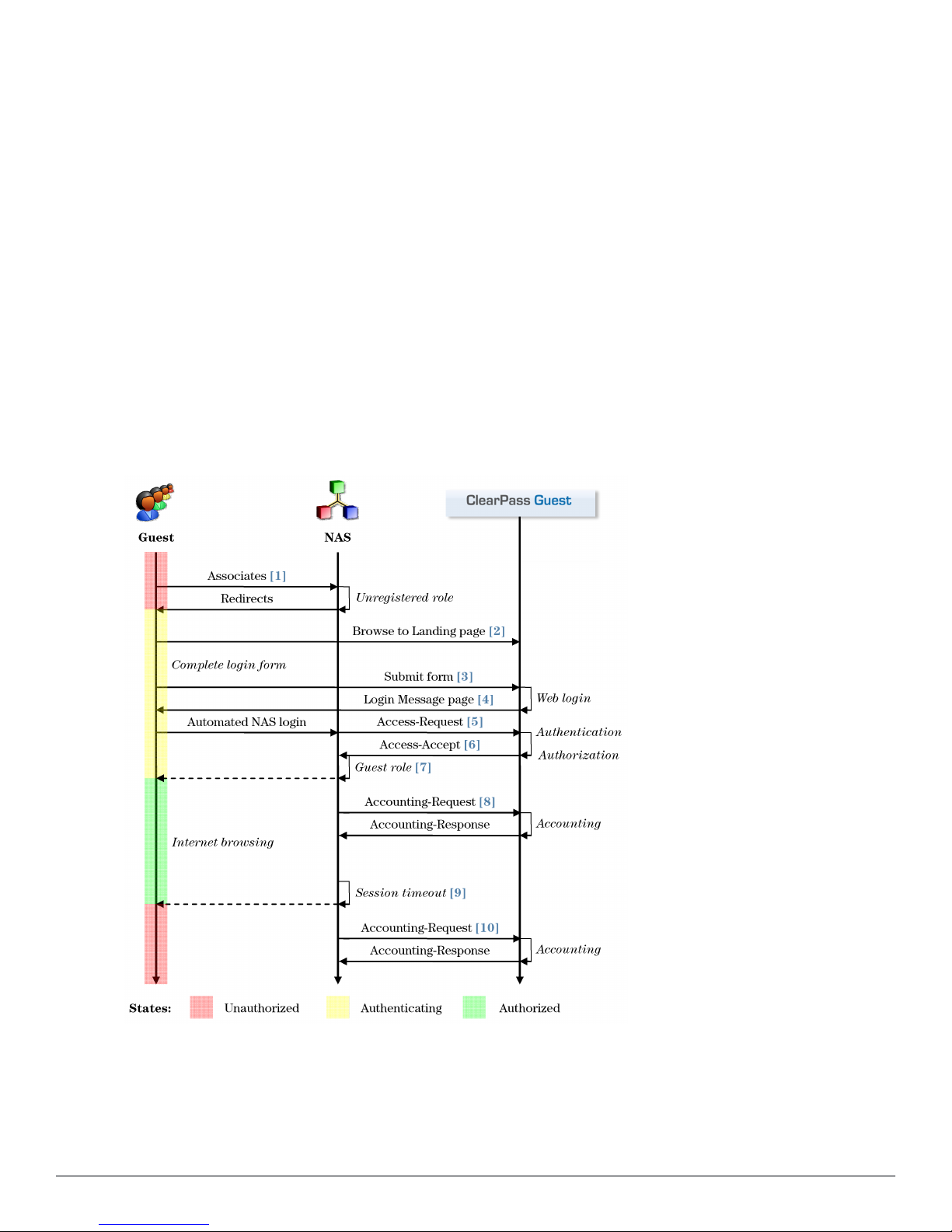
AAA Framework
ClearPass Guest is built on the industry standard AAA framework, which consists of authentication, authorization,
and accounting components.
The following figure shows how the different components of this framework are employed in a guest access scenario.
Figure 4: Sequence diagram for network access using AAA
In the standard AAA framework, network access is provided to a user according to the following process:
l The user connects to the network by associating with a local access point [1].
18 | AAA Framework Dell Networking W-ClearPassGuest 6.0 | Deployment Guide
Page 19

l A landing page is displayed to the user [2] which allows them to log in to the NAS [3], [4] using the login name
and password of their guest account.
l The NAS authenticates the user with the RADIUS protocol [5].
l ClearPass Policy Manager determines whether the user is authorized, and, if so, returns vendor-specific attributes
[6] that are used to configure the NAS based on the user’s role and other policies [7].
l If the user’s access is granted, the NAS permits the guest access to the network based on the settings provided by
the ClearPass Policy Manager server.
l The NAS reports details about the user’s session to the ClearPass Policy Manager server using RADIUS
accounting messages [8].
l After the user’s session times out [9], the NAS will return the user to an unauthorized state and finalize the
details of the user’s session with an accounting update [10].
Key Features
Refer to the table below for a list of key features and a cross-reference to the relevant section of this deployment
guide.
Table 2:
List of Key features
Feature Refer to…
Visitor Access
Web server providing content delivery for guests
Guest self-registration
Visitor Management
Create and manage visitor accounts, individually or in groups
Manage active RADIUS sessions using RFC 3576 dynamic authorization support
Import and export visitor accounts
Create guest self-registration forms
"Content Manager " on page
134
"Customizing Self-Provisioned
Access " on page 171
"Using Standard Guest
Management Features" on
page 29
"Active Sessions Management "
on page 59
"Importing Guest Accounts "
on page 40
"Creating a Self-Registration
Page " on page 172
Configure a self-service portal for guests
Local printer, SMS or email delivery of account receipts
Visitor Account Features
Independent activation time, expiration time, and maximum usage time
Dell Networking W-ClearPassGuest 6.0 | Deployment Guide Key Features | 19
"Self-Service Portal Properties"
on page 186
"Editing Guest Receipt Page
Properties" on page 178
"Business Logic for Account
Page 20
Feature Refer to…
Creation" on page 141
Define unlimited custom fields
Username up to 64 characters
Customization Features
Create new fields and forms for visitor management
Use built-in data validation to implement visitor survey forms
Create print templates for visitor account receipts
Administrat ive Management Features
Operators defined and authenticated locally
Operators authenticated via LDAP
Role based access control for operators
"Customizing Fields " on page
145
"GuestManager Standard
Fields" on page 287
"Customizing Forms and Views
" on page 150
"Form Validation Properties" on
page 162
"Editing Guest Receipt Page
Properties" on page 178
"Local Operator
Authentication" on page 247
"External Operator
Authentication" on page 248
"Operator Profiles " on page
242
Plugin-based application features, automatically updated by ClearPass Policy
Manager
User Interface Features
Context-sensitive help with searchable online documentation
"Plugin Manager " on page 223
"Documentation and User
Assistance " on page 24
Visitor Management Terminology
The following table describes the common terms used in ClearPass Guest and this guide.
Table 3:
Common Terms
Term Explanation
Accounting Process of recording summary information about network access by users and devices.
Authentication Verification of a user’s credentials; typically a username and password.
Authorization Controls the type of access that an authenticated user is permitted to have.
Captive Portal
Implemented by a Network Access Server to restrict network access to authorized users
only.
20 | Visitor Management Terminology Dell Networking W-ClearPassGuest 6.0 | Deployment Guide
Page 21

Term Explanation
Field In a user interface or database, a single item of information about a user account.
Form In a user interface, a collection of editable fields displayed to an operator.
Device that provides network access to users, such as a wireless access point, network
Network Access Server
switch, or dial-in terminal server. When a user connects to the NAS device, a RADIUS
access request is generated by the NAS.
Operator Profile
Operator/Operator Login User of ClearPass Guest to create guest accounts or perform system configuration.
Print Template Formatted template used to generate guest account receipts.
Role
Sponsor Operator
User Database Database listing the guest accounts in ClearPass Guest.
View
Visitor/Guest Someone who is permitted to access the Internet through your Network Access Server.
Visitor Account
Web Login/NAS Login Login page displayed to a guest user.
Characteristics assigned to a class of operators, such as the permissions granted to
those operators.
Type of access being granted to visitors. You can define multiple roles. Such roles could
include employee, guest, team member, or press.
In a user interface, a table displaying data, such as visitor account information, to
operators.
Settings for a visitor stored in the user database, including username, password and
other fields.
ClearPass Guest Deployment Process
As part of your preparations for deploying a visitor management solution, you should consider the following areas:
l Management decisions about security policy
l Decisions about the day-to-day operation of visitor management
l Technical decisions related to network provisioning
Operational Concerns
When deploying a visitor management solution, you should consider these operational concerns:
l Who is going to be responsible for managing guest accounts? What privileges will the guest account manager
have? Will this person only create guest accounts or will this person also be permitted access to reports?
l Do you want guests to be able to self-provision their own network access? What settings should be applied to
self-provisioned visitor accounts?
l How will operator logins be provisioned? Should operators be authenticated against an LDAP server?
l Who will manage reporting of guest access? What are the reports of interest? Are any custom reports needed?
Network Provisioning
Deploying ClearPass Guest requires provisioning the following:
Dell Networking W-ClearPassGuest 6.0 | Deployment Guide ClearPass Guest Deployment Process | 21
Page 22
l Physical location – rack space, power and cooling requirements; or deployment using virtualization
l Network connectivity – VLAN selection, IP address, and hostname
l Security infrastructure – SSL certificate
Site Preparation Checklist
The following is a checklist of the items that should be considered when setting up ClearPass Guest.
Table 4:
Site Preparation Checklist
ü
Security Policy
Operational Concerns
Policy Decision
Segregated guest accounts?
Type of network access?
Time of day access?
Bandwidth allocation to guests?
Prioritization of traffic?
Different guest roles?
IP address ranges for operators?
Enforce access via HTTPS?
Who will manage guest accounts?
Guest account self provisioning?
What privileges will the guest managers have?
Who will be responsible for printing reports?
Network Management Policy
Password format for guest accounts?
Shared secret format?
Operator provisioning?
Network Provisioning
Physical location?
Network connectivity?
Security infrastructure?
22 | Site Preparation Checklist Dell Networking W-ClearPassGuest 6.0 | Deployment Guide
Page 23
Security Policy Considerations
To ensure that your network remains secure, decisions have to be made regarding guest access:
l Do you wish to segregate guest access? Do you want a different VLAN, or different physical network
infrastructure to be used by your guests?
l What resources are you going to make available to guests (for example, type of network access; permitted times
of day; bandwidth allocation)?
l Will guest access be separated into different roles? If so, what roles are needed?
l How will you prioritize traffic on the network to differentiate quality of service for guest accounts and non-guest
accounts?
l What will be the password format for guest accounts? Will you be changing this format on a regular basis?
l What requirements will you place on the shared secret, between NAS and the RADIUS server to ensure network
security is not compromised?
l What IP address ranges will operators be using to access the server?
l Should HTTPS be required in order to access the visitor management server?
AirGroup Deployment Process
AirGroup allows users to register their personal mobile devices on the local network and define a group of friends or
associates who are allowed to share them. You use ClearPass Guest to define AirGroup administrators and operators.
AirGroup administrators can then use ClearPass Guest to register and manage an organization’s shared devices and
configure access according to username, role, or location. AirGroup operators (end users) can use ClearPass Guest to
register their personal devices and define the group who can share them.
Table 5 summarizes the steps for configuring AirGroup functionality in ClearPass Guest. Details for these steps are
provided in the relevant sections of this Guide. This table does not include the configuration steps performed in
ClearPass Policy Manager or the W-Series controller. For complete AirGroup deployment information, refer to the
AirGroup Deployment Guide and the ClearPass Policy Manager documentation.
Table 5:
Summary of AirGroup Configuration Steps in ClearPass Guest
Step Section in this Guide
Create AirGroup administrators "Creating a New Operator" on page 248
Create AirGroup operators "Creating a New Operator" on page 248
Configure an operator’s device limit "Configuring AirGroup Operator Device Limit " on page 247
To authenticate AirGroup users via LDAP:
l Define the LDAP server
l Define appropriate translation rules
AirGroup administrator: Register devices or groups of
devices
AirGroup operator: Register personal devices "AirGroup Device Registration " on page 53
(Optional) Configure device registration form with dropdown lists for existing locations and roles
"External Operator Authentication" on page 248
"LDAP Translation Rules " on page 254
"AirGroup Device Registration " on page 53
"Customizing AirGroup Registration Forms " on page 147
Dell Networking W-ClearPassGuest 6.0 | Deployment Guide Security Policy Considerations | 23
Page 24

Documentation and User Assistance
This section describes the variety of user assistance available for ClearPass Guest.
Deployment Guide and Online Help
This Deployment Guide provides complete information for all ClearPass Guest features. The following quick links
may be useful in getting started.
Table 6:
Quick Links
For information about... Refer to...
What visitor management is and how it works
Using the guest management features
Role-based access control for operators "Operator Profiles " on page 242
Setting up LDAP authentication for operators "External Operator Authentication" on page 248
Guest self-provisioning features "Self Provisioned Guest Access" on page 28
Dynamic authorization extensions "RFC 3576 Dynamic Authorization" on page 61
SMS receipts for guest accounts "SMS Services " on page 228
Email receipts for guest accounts "Email Receipts and SMTP Services" on page 189
Network administration of the appliance "Administration " on page 219
"About Dell Networking W-ClearPass Guest" on
page 15
"Using Standard Guest Management Features" on
page 29
Context-Sensitive Help
For more detailed information about the area of the application you are using, click the context-sensitive Help link
displayed at the top right of the page. This opens a new browser tab showing the relevant section of this deployment
guide.
The deployment guide may be searched using the Search box in the top right corner.
Type in keywords related to your search and click the Search button to display a list of matches. The most relevant
matches will be displayed first. Words may be excluded from the search by typing a minus sign directly before the
word to exclude (for example-exclude). Exact phrase matches may also be searched for by enclosing the phrase in
double quotes (for example, “word phrase”).
24 | Documentation and User Assistance
Dell Networking W-ClearPassGuest 6.0 | Deployment Guide
Page 25
Field Help
The ClearPass Guest user interface has field help built into every form. The field help provides a short summary of
the purpose of the field at the point you need it most. In many cases this is sufficient to use the application
without further assistance or training.
Quick Help
In list views, click the Quick Help tab located at the top left of the list to display additional information about
the list you are viewing and the actions that are available within the list.
On some forms and views, the Quick Help icon may also be used to provide additional detail about a field.
If You Need More Assistance
If you encounter a problem using ClearPass Guest, your first step should be to consult the appropriate section in this
Deployment Guide.
If you cannot find an answer here, the next step is to contact your reseller. The reseller can usually provide you with
the answer or obtain a solution to your problem.
If you still need information, you can refer to the Contact Support command available under Support Services in
the user interface, or see "Contacting Support" on page 14.
Use of Cookies
Cookies are small text files that are placed on a user’s computer by Web sites the user visits. They are widely used in
order to make Web sites work, or work more efficiently, as well as to provide information to the owners of a site.
Session cookies are temporary cookies that last only for the duration of one user session.
When a user registers or logs in via a W-Series captive portal, Dell uses session cookies solely to remember between
clicks who a guest or operator is. Dell uses this information in a way that does not identify any user-specific
information, and does not make any attempt to find out the identities of those using its W-Series ClearPass
products. Dell does not associate any data gathered by the cookie with any personally identifiable information (PII)
from any source. Dell uses session cookies only during the user’s active session and does not store any permanent
cookies on a user’s computer. Session cookies are deleted when the user closes his/her Web browser.
Dell Networking W-ClearPassGuest 6.0 | Deployment Guide Field Help | 25
Page 26

26 | Use of Cookies Dell Networking W-ClearPassGuest 6.0 | Deployment Guide
Page 27
Chapter 3
Guest Manager
The ability to easily create and manage guest accounts is the primary function of Dell Networking W-ClearPass
Guest. The Guest Manager module provides complete control over the user account creation process.
Guest Manager features for managing guest accounts let you:
l Create single or multiple guest accounts and receipts
l List guest accounts and edit individual or multiple accounts
l View and manage active sessions
l Import new accounts from a text file
l Export a list of accounts
l View MAC devices
l Create new MAC devices
Many features can also be customized. For information on customizing Guest Manager settings, forms and views,
guest self-registration, and print templates, see "Configuration " on page 133.
Accessing Guest Manager
To access Dell Networking W-ClearPass Guest’s guest management features, click the Guest link in the left
navigation.
Dell Networking W-ClearPassGuest 6.0 | Deployment Guide Guest Manager | 27
Page 28
About Guest Management Processes
There are two major ways to manage guest access – either by your operators provisioning guest accounts, or by the
guests self-provisioning their own accounts. Both of these processes are described in the next sections.
Sponsored Guest Access
The following figure shows the process of sponsored guest access.
Figure 5: Sponsored guest access with guest created by operator
The operator creates the guest accounts and generates a receipt for the account.
The guest logs on to the Network Access Server (NAS) using the credentials provided on her receipt. The NAS
authenticates and authorizes the guest’s login in ClearPass Guest. Once authorized, the guest is able to access the
network.
Self Provisioned Guest Access
Self-provisioned access is similar to sponsored guest access, but there is no need for an operator to create the
account or to print the receipt. The following figure shows the process of self-provisioned guest access.
Figure 6: Guest access when guest is self-provisioned
The guest logs on to the Network Access Server (NAS), which captures the guest and redirects them to a captive
portal login page. From the login page, guests without an account can browse to the guest self-registration page,
where the guest creates a new account. At the conclusion of the registration process, the guest is automatically
redirected to the NAS to log in.
The guest can print or download a receipt, or have the receipt information delivered by SMS or email.
28 | About Guest Management Processes Dell Networking W-ClearPassGuest 6.0 | Deployment Guide
Page 29
The NAS performs authentication and authorization for the guest in ClearPass Guest. Once authorized, the guest is
then able to access the network.
See"Customizing Self-Provisioned Access " on page 171 for details on creating and managing self-registration pages.
Using Standard Guest Management Features
This section describes:
l How to create a single guest account and a guest account receipt
l How to create multiple guest accounts and multiple guest account receipts
l How to create a single password for multiple accounts
l How to list and edit single and multiple guest accounts
To customize guest self-registration, please see Configuration on page 133.
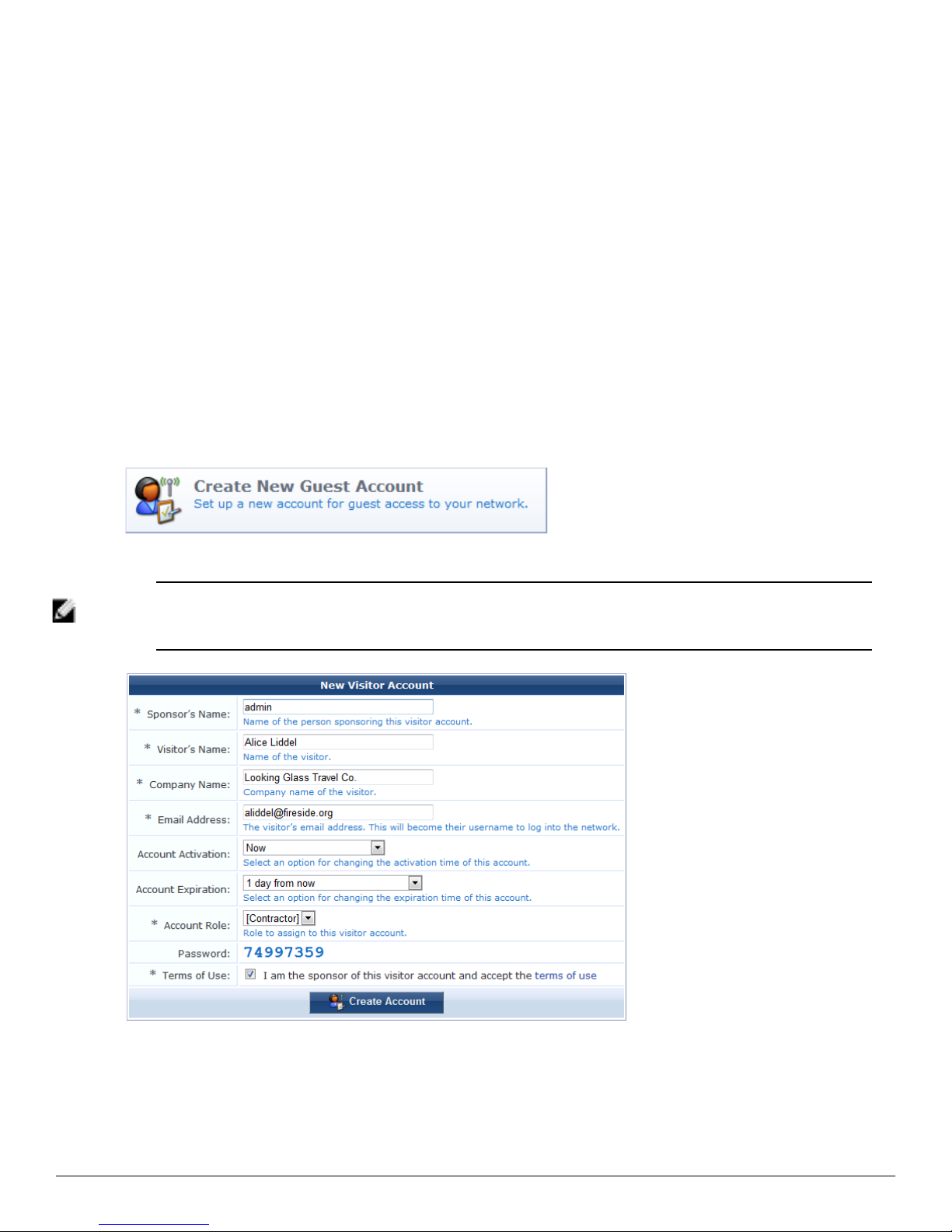
Creating a Guest Account
To create a new account, go to Guest > Create Account, or click the Create New Guest Account command link on
the Guest Manager page. The New Visitor Account form opens.
NOTE: The New Visitor Account form (create_user) may be customized by adding new fields, or modifying or removing the
existing fields. See"Customizing Self-Provisioned Access " on page 171 for details about the customization process. The
default settings for this form are described below.
To complete the form, first enter the visitor’s details into the Sponsor’s Name, Visitor Name, Company Name and
Email Address fields. The visitor’s email address will become their username to log into the network.
Dell Networking W-ClearPassGuest 6.0 | Deployment Guide Using Standard Guest Management Features | 29
Page 30
You can specify the account activation and expiration times. The visitor account cannot be used before the
activation time, or after the expiration time.
The Account Role specifies what type of account the visitor should have.
A random password is created for each visitor account. This is displayed on this form, but will also be available on
the guest account receipt.
You must mark the Terms of Use check box in order to create the visitor account.
Click the Create Account button after completing the form.
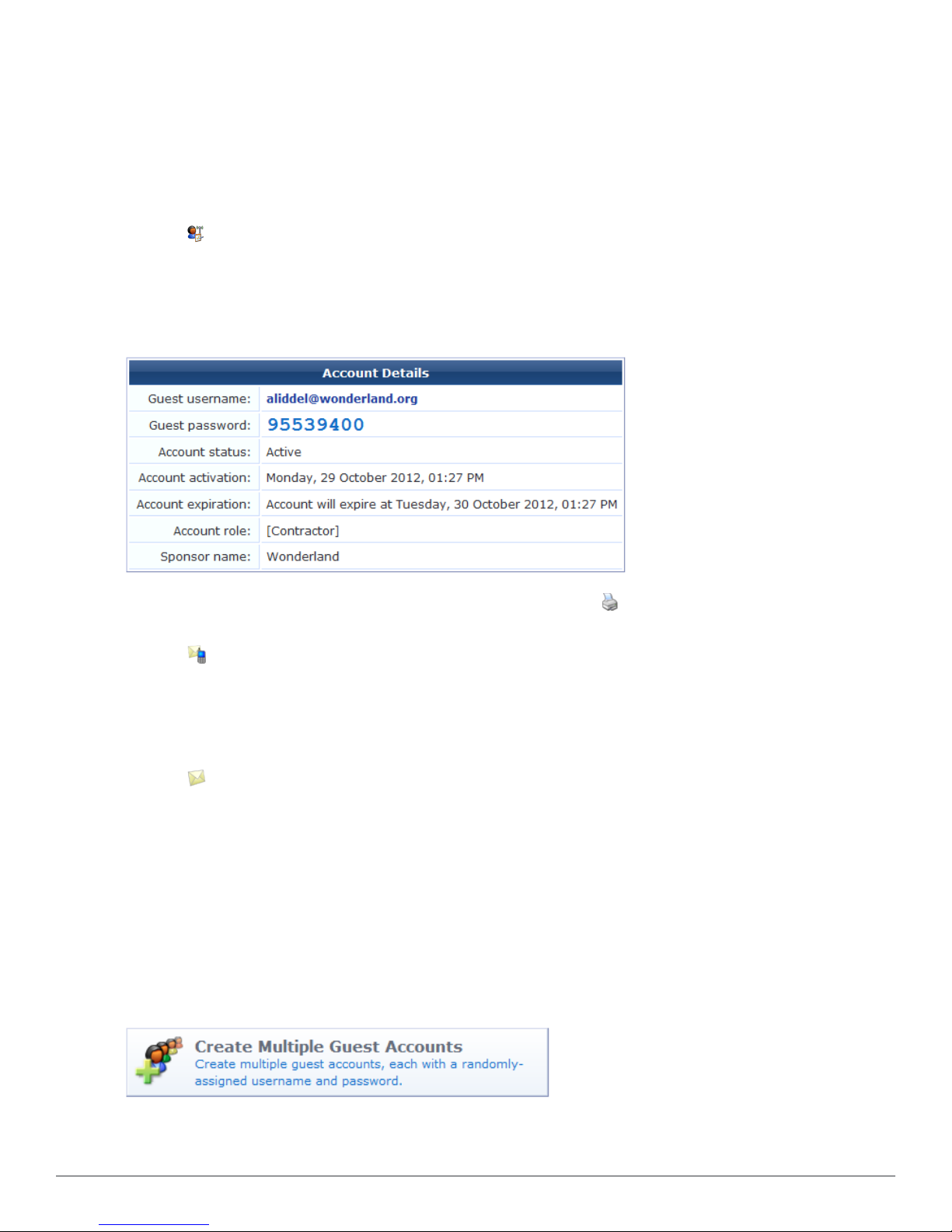
Creating a Guest Account Receipt
After you click the Create Account button on the New Visitor Account form, the details for that account are
displayed.
To print a receipt for the visitor, select an appropriate template from the Open print window using template…
list. A new Web browser window will open and the browser’s Print dialog box will be displayed.
Click the Send SMS receipt link to send a guest account receipt via text message. Use the SMS Receipt form to
enter the mobile telephone number to which the receipt should be sent.
Sending SMS receipts requires the SMS Services plugin. If the administrator has enabled automatic SMS, and the
visitor’s phone number was typed into the New Visitor Account form, an SMS message will be sent automatically. A
message is displayed on the account receipt page after an SMS message has been sent.
Click the Send email receipt link to send an email copy of the guest account receipt. Use the Email Receipt form
to enter the email address to which the receipt should be sent. You can also specify the subject line for the email
message. If the administrator has enabled automatic email for guest account receipts, and the visitor’s email address
was typed into the New Visitor Account form, an email receipt will be sent automatically. A message is displayed on
the account receipt page after an email has been sent.
Creating Multiple Guest Accounts
The Create Guest Accounts form is used to create a group of visitor accounts.
To create multiple accounts, go to Guest > Create Multiple, or click the Create Multiple Guest Accounts
command link on the Guest Manager page. The Create Guest Accounts form opens.
30 | Creating a Guest Account Receipt
Dell Networking W-ClearPassGuest 6.0 | Deployment Guide
Page 31

NOTE: The Create Guest Accounts form (create_multi) may be customized by adding new fields, or modifying or removing the
existing fields. See "Customizing Self-Provisioned Access " on page 171 for details about the customization process. The
default settings for this form are described below.
To complete the form, you must enter the number of visitor accounts you want to create.
A random username and password will be created for each visitor account. This is not displayed on this form, but
will be available on the guest account receipt.
The visitor accounts cannot be used before the activation time, or after the expiration time.
The Account Role specifies what type of accounts to create.
Click the Create Accounts button after completing the form.
Creating Multiple Guest Account Receipts
Once a group of guest accounts has been created, the details for the accounts are displayed.
Dell Networking W-ClearPassGuest 6.0 | Deployment Guide
CreatingMultiple Guest Account Receipts
| 31
Page 32

To print the receipts, select an appropriate template from the Open print window using template… drop-down
list. A new browser window opens with the Print dialog displayed.
To download a copy of the receipt information in CSV format, click the Save list for scratch cards (CSV file)
link. You will be prompted to either open or save the spreadsheet (CSV) file. The fields available in the CSV file are:
l Number – the sequential number of the visitor account, starting at one
l Username – the username for the visitor account
l Password – the password for the visitor account
l Role – the visitor account’s role
l Activation Time – the date and time at which the account will be activated, or N/A if there is no activation
time
l Expiration Time – the date and time at which the account will expire, or N/A if there is no activation time
l Lifetime – the account lifetime in minutes, or N/A if the account does not have a lifetime specified
l Successful – “Yes” if the account was created successfully, or “No” if there was an error creating the account
Creating a Single Password for Multiple Accounts
You can create multiple accounts that have the same password. In order to do this, you first customize the Create
Multiple Guest Accounts form to include the Password field.
32 | Creating a Single Password for Multiple Accounts Dell Networking W-ClearPassGuest 6.0 | Deployment Guide
Page 33

To include the Password field on the Create Multiple Guest Accounts form:
1. Go to Configuration > Forms & Views. Click the create_multi row, then click its Edit Fields link. The
Customize Form Fields view opens, showing a list of the fields included in the Create Multiple Guest Accounts
form and their descriptions.
At this point, the Password field is not listed because the Create Multiple Guest Accounts form (create_multi)
has not yet been customized to include it. You will create it for the form in the next step.
2. Click on any field in the list to expand a row, then click the Insert After link (you can modify this placement
later). The Customize Form Field form opens.
3. In the Field Name row, choose password from the drop-down list. The form displays configuration options for
this field.
4. In the Field row, mark the Enable this field check box.
5. To adjust the placement of the password field on the Create Multiple Guest Accounts form, you may change the
number in the Rank field.
6. In the User Interface row, choose Password text field from the drop-down list. The Field Required check box
should now be automatically marked, and the Validator field should be set to IsNonEmpty.
7. Click Save Changes. The Customize Form Fields view opens again, and the password field is now included and
can be edited.
To create multiple accounts that all use the same password:
1. Go to Guest > Create Multiple. The Create Guest Accounts form opens, and includes the Visitor Password
field.
2. In the Number of Accounts field, enter the number of accounts you wish to create.
3. In the Visitor Password field, enter the password that is to be used by all the accounts.
4. Complete the other fields with the appropriate information, then click Create Accounts. The Finished Creating
Guest Accounts view opens. The password and other account details are displayed for each account.
Dell Networking W-ClearPassGuest 6.0 | Deployment Guide Creatinga Single Password for Multiple Accounts | 33
Page 34

Managing Guest Accounts
Use the Guest Manager Accounts list view to work with individual guest accounts. To open the Guest Manager
Accounts list, go to Guest > List Accounts.
The Guests Manager Accounts view opens.This view (guest_users) may be customized by adding new fields or
modifying or removing the existing fields. See "Customizing Fields " on page 145 for details about this
customization process. The default settings for this view are described below.
34 | Managing Guest Accounts
Dell Networking W-ClearPassGuest 6.0 | Deployment Guide
Page 35

The Username, Role, State, Activation, and Expiration columns display information about the visitor accounts that
have been created:
l The value in the Expiration column is colored red if the account will expire within the next 24 hours. The
expiration time is additionally highlighted in boldface if the account will expire within the next hour.
l In addition, icons in the Username column indicate the account’s activation status:
n —Visitor account is active
n —Visitor account was created but is not activated yet
n —Visitor account was disabled by Administrator
n —Visitor account has expired
n —Visitor account was deleted
You can use the Filter field to narrow the search parameters. You may enter a simple substring to match a portion of
the username or any other fields that are configured for search, and you can include the following operators:
Table 7:
Operators supported in filters
Operator Meaning Additional Information
= is equal to
!= is not equal to
> is greater than
>= is greater than or equal to
< is less than
<= is less than or equal to
You may search for multiple values when using the equality
(=) or inequality !=) operators. To specify multiple values, list
them separated by the pipe character ( | ).
For example, specifying the filter "role_id=2|3, custom_
field=Value" restricts the accounts displayed to those with
role IDs 2 and 3 (Guest and Employee), and with the field
named "custom_field" set to "Value".
~ matches the regular expression
!~ does not match the regular expression
To restore the default view, click the Clear Filter link.
Use the paging control at the bottom of the list to jump forwards or backwards by one page, or to the first or last
page of the list. You can also click an individual page number to jump directly to that page.
Dell Networking W-ClearPassGuest 6.0 | Deployment Guide
Managing Guest Accounts
| 35
Page 36

NOTE: When the list contains numerous user accounts, consider using the Filter field to speed up finding a specific user
account.
Use the Create tab to create new visitor accounts using the New Visitor Account form. See "Creating a Guest
Account " on page 29 for details about this form.
Use the More Options tab for additional functions, including import and export of guest accounts and the ability
to customize the view.
Click a user account’s row to select it. You can then select from one of these actions:
l Reset password – Changes the password for a guest account. A new randomly generated password is displayed
on the Reset Password form.
Click Update Account to reset the guest account’s password. A new account receipt is displayed, allowing you
to print a receipt showing the updated account details.
l Change expiration – Changes the expiration time for a guest account.
.
NOTE: This form (change_expiration) may be customized by adding new fields, or modifying or removing the existing fields.
See "Customizing Forms and Views " on page 150 for details about this customization process.
Select an option from the drop-down list to change the expiration time of the guest account.
Click Update Account to set the new expiration time for the guest account. A new account receipt is
displayed, allowing you to print a receipt showing the updated account details.
l Remove – Disables or deletes a guest account.
36 | Managing Guest Accounts
Dell Networking W-ClearPassGuest 6.0 | Deployment Guide
Page 37

Select the appropriate Action radio button, and click Make Changes to disable or delete the account.
If you wish to have automatic disconnect messages sent when the enabled value changes, you can specify this in
the Configuration module. See"Configuring ClearPass Guest Authentication " on page 134.
l Activate – Re-enables a disabled guest account, or specifies an a ctivation time for the guest account.
Select an option from the drop-down list to change the activation time of the guest account. To re-enable an
account that has been disabled, choose Now. Click Enable Account to set the new activation time for the
guest account. A new account receipt is displayed, allowing you to print a receipt showing the updated account
details.
l Edit – Changes the properties of a guest account.
NOTE: This form may be customized by adding new fields, or modifying or removing the existing fields. See "Customizing
Forms and Views " on page 150 for details about this customization process. This is the guest_edit form.
Dell Networking W-ClearPassGuest 6.0 | Deployment Guide
Managing Guest Accounts
| 37
Page 38

Click Update Account to update the properties of the guest account. A new account receipt is displayed,
allowing you to print a receipt showing the updated account details.
l Sessions – Displays the active sessions for a guest account. See "Active Sessions Management " on page 59 in
this chapter for details about managing active sessions.
l Print – Displays the guest account’s receipt and the delivery options for the receipt. For security reasons, the
guest’s password is not displayed on this receipt. To recover a forgotten or lost guest account password, use the
Reset password link.
Managing Multiple Guest Accounts
Use the Edit Accounts list view to work with multiple guest accounts. This view may be accessed by clicking the
Edit Multiple Guest Accounts command link.
This view (guest_multi) may be customized by adding new fields or by modifying or removing the existing fields.
See "Customizing Self-Provisioned Access " on page 171 for details about this customization process. The default
settings for this view are described below.
The Username, Role, State, Activation, and Expiration columns display information about the visitor accounts that
have been created:
l The value in the Expiration column is colored red if the visitor account will expire within the next 24 hours. The
expiration time is additionally highlighted in boldface if the visitor account will expire within the next hour.
l In addition, icons in the Username column indicate the account’s activation status:
n —Visitor account is active
n —Visitor account was created but is not activated yet
n —Visitor account was disabled by Administrator
n —Visitor account has expired
You can use the Filter field to narrow the search parameters. You may enter a simple substring to match a portion of
the username or any other fields that are configured for search, and you can include the following operators:
38 | Managing Multiple Guest Accounts
Dell Networking W-ClearPassGuest 6.0 | Deployment Guide
Page 39

Table 8:
Operators supported in filters
Operator Meaning Additional Information
= is equal to
!= is not equal to
> is greater than
>= is greater than or equal to
< is less than
<= is less than or equal to
~ matches the regular expression
!~ does not match the regular expression
You may search for multiple values when using the equality
(=) or inequality !=) operators. To specify multiple values, list
them separated by the pipe character ( | ).
For example, specifying the filter "role_id=2|3, custom_
field=Value" restricts the accounts displayed to those with
role IDs 2 and 3 (Guest and Employee), and with the field
named "custom_field" set to "Value".
To restore the default view, click the Clear Filter link.
Use the paging control at the bottom of the list to jump forwards or backwards by one page, or to the first or last
page of the list. You can also click an individual page number to jump directly to that page.
To select guest accounts, click the accounts you want to work with. You may click either the check box or the row
to select a visitor account. To select or unselect all visible visitor accounts, click the check box in the header row of
the table.
Use the selection row at the top of the table to work with the current set of selected accounts. The number of
currently selected accounts is shown. When a filter is in effect, the “All Matching” link can be used to add all pages
of the filtered result to the selection.
Use the Create tab to create new visitor accounts using the Create Guest Accounts form. See "Managing
Multiple Guest Accounts " on page 38 in this chapter for details about this form.
Use the Delete tab to delete the visitor accounts that you have selected. This option is not active if there are no
visitor accounts selected.
Use the Edit tab to make changes to multiple visitor accounts at once. This option is not active if there are no
visitor accounts selected.
Dell Networking W-ClearPassGuest 6.0 | Deployment Guide
Managing Multiple Guest Accounts
| 39
Page 40

The Edit Guest Accounts form may be customized by adding new fields, or modifying or removing the existing
fields. See "Customizing Self-Provisioned Access " on page 171 for details about this customization process. This is
the guest_multi_form form.
The Results tab will be automatically selected after you have made changes to one or more guest accounts. You
can create new guest account receipts or download the updated guest account information. See "Creating Multiple
Guest Account Receipts " on page 31 in this chapter for more information.
The More Options tab includes the Choose Columns command link. You can click this link to open the
Configuration module’s Customize View Fields form, which may be used to customize the Edit Guest Accounts
view.
Importing Guest Accounts
Guest accounts may be created from an existing list by uploading the list to ClearPass Guest. To upload a list of
existing accounts, go to Guest > Import Accounts, or click the Import Guest Accounts command link on the
Guest Manager page. The Upload User List form opens.
The Upload User List form provides you with different options for importing guest account data.
To complete the form, you must either specify a file containing account information, or type or paste in the account
information to the Accounts Text area.
Select the Show additional import options check box to display the following advanced import options:
l Character Set: ClearPass Guest uses the UTF-8 character set encoding internally to store visitor account
information. If your accounts file is not encoded in UTF-8, the import may fail or produce unexpected results if
non-ASCII characters are used. To avoid this, you should specify what character set encoding you are using.
l Import format: The format of the accounts file is automatically detected. You may specify a different encoding
type if automatic detection is not suitable for your data. The Import Format drop-down list includes the
following options:
40 | Importing Guest Accounts
Dell Networking W-ClearPassGuest 6.0 | Deployment Guide
Page 41

n Automatically detect format (This default option recognizes guest accounts exported from ClearPass Policy
Manager in XML format)
n XML
n Comma separated values
n Tab separated values
n Pipe (|) separated values
n Colon (:) separated values
n Semicolon (;) separated values
l Select the Force first row as header row check box if your data contains a header row that specifies the field
names. This option is only required if the header row is not automatically detected.
Click Next Step to upload the account data.
In step 2 of 3, ClearPass Guest determines the format of the uploaded account data and matches the appropriate
fields are m to the data. The first few records in the data will be displayed, together with any automatically detected
field names.
In this example, the following data was used:
username,visitor_name,password,expire_time
demo005,Demo five,secret005,2011-06-10 09:00
demo006,Demo six,secret006,2011-06-11 10:00
demo007,Demo seven,secret007,2011-06-12 11:00
demo008,Demo eight,secret008,2011-06-13 12:00
demo009,Demo nine,secret009,2011-06-13 12:00
demo010,Demo ten,secret010,2011-06-13 12:00
demo011,Demo eleven,secret011,2011-06-13 12:00
Because this data includes a header row that contains field names, the corresponding fields have been automatically
detected in the data:
Use the Match Fields form to identify which guest account fields are present in the imported data. You can also
specify the values to be used for fields that are not present in the data.
Dell Networking W-ClearPassGuest 6.0 | Deployment Guide
Importing Guest Accounts
| 41
Page 42

To complete the Match Fields form, make a selection from each of the drop-down lists. Choose a column name to
use the values from that column when importing guest accounts, or select one of the other available options to use a
fixed value for each imported guest account.
Click the Next Step button to preview the final result. Import Step 3 of 3, the Import Accounts form, opens and
shows a preview of the import operation. The values of each guest account field are determined, and any conflicts
with existing user accounts are shown.
The icon displayed for each user account indicates if it is a new entry ( ) or if an existing user account will be
updated ( ).
By default, this form shows ten entries per page. To view additional entries, click the arrow button at the bottom of
the form to display the next page, or click the 10 rows per page drop-down list at the bottom of the form and select
the number of entries that should appear on each page.
Click the check box by the account entries you want to create, or click one of the following options to select the
desired accounts:
l Click the ThisPage link to select all entries on the current page.
l Click the All link to select all entries on all pages
l Click the None link to deselect all entries
l Click the New link to select all new entries
42 | Importing Guest Accounts
Dell Networking W-ClearPassGuest 6.0 | Deployment Guide
Page 43

l Click the Existing link to select all existing user accounts in the list.
Click the Create Accounts button to finish the import process. The selected items will be created or updated.
You can then print new guest account receipts or download a list of the guest accounts. See "Creating Multiple
Guest Account Receipts " on page 31 in this chapter for more information.
Exporting Guest Account Information
Guest account information may be exported to a file in one of several different formats.
Click the appropriate command link to save a list of all guest accounts in comma-separated values (CSV), tabseparated values (TSV), or XML format.
The Export Accounts view (guest_export) may be customized by adding new fields, or by modifying or removing the
existing fields. See "Customizing Self-Provisioned Access " on page 171 for details about this customization process.
About CSV and TSV Exports
In CSV and TSV format, the following default fields are included in the export:
l Number – Sequential number of the guest account in the exported data
l User ID – Numeric user ID of the guest account
l Username – Username for the guest account
l Role – Role for the guest account
l Activation – Date and time at which the guest account will be activated, or “N/A” if there is no activation time
l Expiration – Date and time at which the guest account will expire, or “N/A” if there is no expiration time
l Lifetime – The guest account’s lifetime in minutes after login, or 0 if the account lifetime is not set
l Expire Action – Number specifying the action to take when the guest account expires (0 through 4)
About XML Exports
The default XML format consists of a <GuestUsers> element containing a <GuestUser> element for each
exported guest account. The numeric ID of the guest account is provided as the “id” attribute of the <GuestUser>
element. This format is compatible with the ClearPass Policy Manager XML format for guest users.
The values for both standard and custom fields for guest accounts are exported as the contents of an XML tag, where
the tag has the same name as the guest account field.
An example XML export is given below:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="true"?>
<TipsContents xmlns="http://www.avendasys.com/tipsapiDefs/1.0">
<TipsHeader version="6.0" exportTime="Sun, 16 Dec 2012 16:36:03 PST"/>
<GuestUsers>
<GuestUser guestType="USER" enabled="true" sponsorName="55480025"
expiryTime="2012-12-04 13:39:25" startTime="1969-12-31 16:00:00"
password="08654361" name="55480025">
<GuestUserTags tagValue="Hotspot Services self-provisioned guest account
Source IP: 10.11.10.254 MAC: unknown Plan: Free Access x 1 Transaction
Amount: $0.00 Invoice Number: P-15 Transaction ID: " tagName="notes"/>
<GuestUserTags tagValue="2" tagName="[Role ID]"/>
<GuestUserTags tagValue="1" tagName="do_expire"/>
<GuestUserTags tagValue="1" tagName="simultaneous_use"/>
Dell Networking W-ClearPassGuest 6.0 | Deployment Guide
Exporting Guest Account Information
| 43
Page 44

<GuestUserTags tagValue="ff" tagName="Company Name"/>
<GuestUserTags tagValue="2012-12-04 12:39:14" tagName="Create Time"/>
<GuestUserTags tagValue="fff@df" tagName="Email"/>
<GuestUserTags tagValue="ff" tagName="first_name"/>
<GuestUserTags tagValue="plan0" tagName="hotspot_plan_id"/>
<GuestUserTags tagValue="Free Access" tagName="hotspot_plan_name"/>
<GuestUserTags tagValue="ff" tagName="last_name"/>
<GuestUserTags tagValue="ff ff" tagName="Visitor Name"/>
<GuestUserTags tagValue="ff" tagName="zip"/>
</GuestUser>
MAC Authentication in ClearPass Guest
ClearPass Guest supports a number of options for MAC Authentication and the ability to authenticate devices.
The advanced features described in this section generally require a WLAN capable of MAC authentication with
captive portal fallback. Please refer to your WLAN documentation for setting up the controller appropriately.
To verify that you have the most recent MAC Authentication Plugin installed and enabled before you configure
these advanced features, go to Administration > Plugin Manager > List Available Plugins. For information on
plugin management, see "Plugin Manager " on page 223.
MAC Address Formats
Different vendors format the client MAC address in different ways—for example:
l 112233AABBCC
l 11:22:33:aa:bb:cc
l 11-22-33-AA-BB-CC
ClearPass Guest supports adjusting the expected format of a MAC address. To configure formatting of separators
and case in the address, as well as user detection and device filtering for views, go to Administration > Plugin
Manager > Manage Plugins and click the Configuration link for the MAC Authentication plugin. The MAC
Authentication Configuration page opens.
Figure 7: MAC Authentication Plugin—Configuration
On the controller, the fields look as follows:
Figure 8: MAC Authentication Profile
Managing Devices
To view the list of current MAC devices, go to Guest > List Devices.
44 | MAC Authentication in ClearPassGuest Dell Networking W-ClearPassGuest 6.0 | Deployment Guide
Page 45

The Guest Manager Devices page opens.
All devices created by one of methods described in the following section are listed. Options on the form let you
change a device’s account expiration date; remove, activate, or edit the device; view active sessions or details for the
device; or print details, receipts, confirmations, or other information.
The MAC Address, Role, State, Activation, and Expiration columns display information about the device accounts
that have been created:
l The value in the Expiration column is colored red if the device account will expire within the next 24 hours. The
expiration time is additionally highlighted in boldface if the device account will expire within the next hour.
l In addition, icons in the MAC Address column indicate the device account’s activation status:
n —Device account is active
n —Device account was created but is not activated yet
n —Device account was disabled by Administrator
n —Device account has expired
n —Device account was deleted
You can use the Filter field to narrow the search parameters. You may enter a simple substring to match a portion of
any fields that are configured for search, and you can include the following operators:
Dell Networking W-ClearPassGuest 6.0 | Deployment Guide Managing Devices | 45
Page 46

Table 9:
Operators supported in filters
Operator Meaning Additional Information
= is equal to
!= is not equal to
> is greater than
>= is greater than or equal to
< is less than
<= is less than or equal to
~ matches the regular expression
!~ does not match the regular expression
You may search for multiple values when using the equality
(=) or inequality !=) operators. To specify multiple values, list
them separated by the pipe character ( | ).
For example, specifying the filter "role_id=2|3, custom_
field=Value" restricts the accounts displayed to those with
role IDs 2 and 3 (Guest and Employee), and with the field
named "custom_field" set to "Value".
To restore the default view, click the Clear Filter link.
Use the paging control at the bottom of the list to jump forwards or backwards by one page, or to the first or last
page of the list. You can also click an individual page number to jump directly to that page.
To select a device, click the device you want to work with.
Changing a Device’s Expiration Date
To change a device’s expiration date, click the device’s row in the Guest Manager Devices list, then click its Change
expiration link. The row expands to include the Change Expiration form.
1. In the Account Expiration row, choose one of the options in the drop-down list to set an expiration date:
l If you choose Account expires after, the Expires After row is added to the form. Choose an interval of hours,
days, or weeks from the drop-down list.
46 | Changing a Device’sExpiration Date Dell Networking W-ClearPassGuest 6.0 | Deployment Guide
Page 47

l If you choose Account Expires at a specified time, the Expiration Time row is added to the form. Click the
button to open the calendar picker. In the calendar, use the arrows to select the year and month, click the
numbers in the Time fields to increment the hours and minutes, then click a day to select the date.
2. If you choose any option other than “will not expire” or “now” in the Account Expiration field, the Expire
Action row is added to the table. Use the drop-down list in this row to specify one of the following actions:
delete, delete and log out, disable, or disable and log out.
3. Click Update Account to commit your changes.
Disabling and Deleting Devices
To remove a device’s account by disabling or deleting it, click the device’s row in the Guest Manager Devices list,
then click its Remove link. The row expands to include the Remove Account form.
You may choose to either disable or delete the account. If you disable it, it remains in the device list and you may
activate it again later. If you delete the account, it is removed from the list permanently.
Activating a Device
To activate a disabled device’s account, click the device’s row in the Guest Manager Devices list, then click its
Activate link. The row expands to include the Enable Guest Account form.
1. In the Activate Account row, choose one of the options in the drop-down list to specify when to activate the
account. You may choose an interval, or you may choose to specify a time.
2. If you choose Activate at specified time, the Activation Time row is added to the form. Click the button to
open the calendar picker. In the calendar, use the arrows to select the year and month, click the numbers in the
Time fields to increment the hours and minutes, then click a day to select the date.
3. Click Enable Account to commit your changes.
Editing a Device
To edit a device’s account, click the device’s row in the Guest Manager Devices list, then click its Edit link. The row
expands to include the Edit MAC form.
Dell Networking W-ClearPassGuest 6.0 | Deployment Guide Disabling and Deleting Devices | 47
Page 48

1. You can change the device’s address in the MAC Address row.
If you need to modify the configuration for expected separator format or case, go to Administration > Plugin
Manager > Manage Plugins and click the Configuration link for the MAC Authentication plugin.
2. If you need to change the activation time, choose one of the options in the Account Activation drop-down list.
You may choose to activate the account immediately, at a preset interval of hours or days, or at a specified time.
l If you choose Activate at a specified time, the Activation Time row is added to the form. Click the button
to open the calendar picker. In the calendar, use the arrows to select the year and month, click the numbers in
the Time fields to increment the hours and minutes, then click a day to select the date.
3. If you need to change the expiration time, choose one of the options in the Account Expiration drop-down list.
You may terminate the account immediately, at a preset interval of hours or days, or at a specified time.
l If you choose any time in the future, the Expire Action row is added to the form. Use this drop-down list to
indicate the expiration action for the account—either delete, delete and log out, disable, or disable and log
out. The action will be applied at the time set in the Account Expiration row.
l If you choose Account expires after, the Expires After row is added to the form. Choose an interval of hours,
days, or weeks from the drop-down list. The maximum is two weeks.
48 | Editing a Device DellNetworking W-ClearPass Guest 6.0 | Deployment Guide
Page 49

l If you choose Account Expires at a specified time, the Expiration Time row is added to the form. Click the
button to open the calendar picker. In the calendar, use the arrows to select the year and month, click the
numbers in the Time fields to increment the hours and minutes, then click a day to select the date.
4. To change the maximum usage allowed for the account, choose an option from the Total Allowed Usage dropdown list. You may set the total usage to one or two hours, add one or two hours to the existing setting, or
subtract one or two hours from the existing setting.
5. You can use the Account Role drop-down list to change the visitor’s assigned role.
6. (Optional) In the Notes row, you may enter additional information.
7. To commit your changes, click Update MAC.
Viewing Current Sessions for a Device
To view any sessions that are currently active for a device, click the Sessions link in the device’s row on the Guest
Manager Devices form. The Active Sessions list opens. For more information, see "Active Sessions Management " on
page 59.
Viewing and Printing Device Details
To print details, receipts, confirmations, or other information for a device, click the device’s row in the Guest
Manager Devices list, then click its Print link. The row expands to include the Account Details form and a dropdown list of information that can be printed for the device.
Choosing an option in the Open print window using template drop-down list opens a print preview window and
the printer dialog. Options include account details, receipts in various formats, a session expiration alert, and a
sponsorship confirmation notice.
MAC Creation Modes
MAC device accounts may be created in three ways:
l Manually in ClearPass Guest using the Create Device form
l During guest self-registration by a mac parameter passed in the redirect URL, if the process is configured to
create a MAC device account
l During guest self-registration by a mac parameter passed in the redirect URL, creating a parallel account paired
with the visitor account
Dell Networking W-ClearPassGuest 6.0 | Deployment Guide Viewing Current Sessionsfor a Device | 49
Page 50

Creating Devices Manually in ClearPass Guest
If you have the MAC address, you can create a new device manually. You do this on the New MAC Authentication
form.
To create a new device:
1. Go to Guest > List Devices and click the Create link, or you can go to the Guest navigation page and click the
Create Device command.
The New MAC Authentication page opens.
2. In the Sponsor’s Name row, enter the name of the person sponsoring the visitor account.
3. Enter the name for the device in the Device Name row.
4. Enter the address in the MAC Address row.
If you need to modify the configuration for expected separator format or case, go to Administration > Plugin
Manager > Manage Plugins and click the Configuration link for the MAC Authentication Plugin.
5. Choose one of the options in the Account Activation drop-down list. You may choose to activate the account
immediately, at a preset interval of hours or days, at a specified time, or leave the account disabled.
l If you choose Activate at a specified time, the Activation Time row is added to the form. Click the button
to open the calendar picker. In the calendar, use the arrows to select the year and month, click the numbers in
the Time fields to increment the hours and minutes, then click a day to select the date.
50 | Creating DevicesManuallyin ClearPass Guest DellNetworking W-ClearPass Guest 6.0 | Deployment Guide
Page 51

6. To set the account’s expiration time, choose one of the options in the Account Expiration drop-down list. You
may set the account to never expire, or to expire at a preset interval of hours or days, or at a specified time.
l If you choose any time in the future, the Expire Action row is added to the form. Use this drop-down list to
indicate the expiration action for the account—either delete, delete and log out, disable, or disable and log
out. The action will be applied at the time set in the Account Expiration row.
l If you choose Account expires after, the Expires After row is added to the form. Choose an interval of hours,
days, or weeks from the drop-down list. The maximum is two weeks.
l If you choose Account Expires at a specified time, the Expiration Time row is added to the form. Click the
button to open the calendar picker. In the calendar, use the arrows to select the year and month, click the
numbers in the Time fields to increment the hours and minutes, then click a day to select the date.
7. Use the Account Role drop-down list to assign the visitor’s role.
8. In the Terms of Use row, first click the terms of use link and read the agreement, then mark the check box to
agree to the terms.
9. To commit your changes and create the device, click Create MAC. The Account Details and print options are
displayed. For more information, see "Viewing and Printing Device Details " on page 49.
Creating Devices During Self-Registration - MAC Only
This section describes how to configure a guest self-registration so that it creates a MAC device account. Once the
guest is registered, future authentication can take place without the need for the guest to enter their credentials. A
registration can be converted to create a MAC device instead of standard guest credentials.
This requires a vendor passing a mac parameter in the redirect URL. ClearPass Guest does not support querying the
controller or DHCP servers for the client's MAC based on IP.
To edit the registration form fields, go to Configuration > Forms and Views. In the guest_register row, click the
Edit Fields link. The Customize Form Fields page opens. If you do not see mac or mac_auth in the list, click the
Customize fields link above the list. Click the Edit link in the field’s row. In the Define Custom Field form, edit the
registration form fields:
l Add or enable mac
n UI: Hidden field
n Field Required: checked
n Validator: IsValidMacAddress
l Add or enable mac_auth
n UI: Hidden field
l Any other expiration options, role choice, surveys, and so on can be entered as usual.
Dell Networking W-ClearPassGuest 6.0 | Deployment Guide Creating DevicesDuring Self-Registration - MAC Only | 51
Page 52

Figure 9: Modify fields
l Edit the receipt form fields:
n Edit username to be a Hidden field
n Edit password to be a Hidden field
l Adjust any headers or footers as needed.
When the visitor registers, they should be able to still log in via the Log In button. The MAC will be passed as their
username and password via standard captive portal means.
The account will only be visible on the List Devices page.
If the guest logs out and reconnects, they should be immediately logged in without being redirected to the captive
portal page.
Creating Devices During Self-Registration - Paired Accounts
Paired accounts is a means to create a standard visitor account with credentials, but to have a MAC account created
in parallel that is directly tied to the visitor account. These accounts share the same role, expiration and other
properties.
This requires a vendor passing a mac parameter in the redirect URL. ClearPass Guest does not support querying the
controller or DHCP servers for the client's MAC based on IP.
To edit the registration form fields, go to Configuration > Forms and Views. In the guest_register row, click the
Edit Fields link. The Customize Form Fields page opens. If you do not see mac or mac_auth_pair in the list, click
the Customize fields link above the list. Click the Edit link in the field’s row. In the Define Custom Field form, edit
the registration form fields:
l Add or enable mac
n UI: Hidden field
n Field Required: optional
n Validator: IsValidMacAddress
l Add or enable mac_auth_pair
n UI: Hidden field
n Initial Value: -1
l Any other expiration options, role choice, surveys and so on can be entered as usual.
You will see an entry under both List Accounts and List Devices. Each should have a View Pair action that cross
links the two.
52 | Creating DevicesDuring Self-Registration - Paired Accounts Dell Networking W-ClearPassGuest 6.0 | Deployment Guide
Page 53

NOTE: If you delete the base account, all of its pairings will also be deleted. If RFC-3576 has been configured, all pairs will be logged
out.
AirGroup Device Registration
AirGroup allows users to register their personal mobile devices on the local network and define a group of friends or
associates who are allowed to share them. If AirGroup Services is enabled, AirGroup administrators can provision
their organization’s shared devices and manage access, and AirGroup operators can register and provision a limited
number of their own personal devices for sharing. For complete AirGroup deployment information, refer to the
AirGroup Deployment Guide and the ClearPass Policy Manager documentation.
Registering Groups of Devices or Services
This functionality is only available to AirGroup administrators.
To register and manage an organization’s shared devices and configure device access:
1. Log in as the AirGroup administrator and go to Guest > Create Device. The Register Shared Device form
opens.
2. In the Device Name field, enter the name used to identify the device.
3. In the MAC Address field, enter the device’s MAC address.
4. In the Shared Locations field, enter the locations where the device can be shared. To allow the device to be
shared with all locations, leave this field blank.
Each location is entered as a tag=value pair describing the MAC address of the access point (AP) closest to the
registered device. Use commas to separate the tag=value pairs in the list. Tag=value pair formats are shown in
the following table.
Table 10:
Tag=Value Pair Formats
AP Type Tag=Value Format
Name-based AP ap-name=<name>
Group-based AP ap-group=<group>
FQLN-based AP fqln=<fqln>
Dell Networking W-ClearPassGuest 6.0 | Deployment Guide AirGroup Device Registration | 53
Page 54

l AP FQLNs should be configured in the format <ap name>.<floor>.<building>.<campus>
l Floor names should be in the format floor <number>
l The <ap-name> should not include periods ( . )
Example:
AP105-1.Floor 1.TowerD.Mycompany
5. In the Shared With field, enter the usernames of your organization’s staff or students who are allowed to use the
device. Use commas to separate usernames in the list.
l If the Share With field is left blank, this device can be accessed by all devices.
l If users are entered in the Shared With field, the device can only be accessed by the specified users.
6. In the Shared Roles field, enter the user roles that are allowed to use the device. Use commas to separate the
roles in the list.
l To make the device available to all roles, leave this field blank.
l If roles are entered in the Shared Roles field, the device can only be accessed by users with matching roles.
7. Click Register Shared Device. The Finished Creating Guest Account page opens. This page displays Account
Details and provides printer options.
To view and edit your organization’s shared AirGroup devices:
1. Go to Guest > List Devices, or click the Manage my AirGroup Devices link on the Create AirGroup Device
page. The AirGroup Devices page opens. This page lists all the shared AirGroup devices for the organization. You
can remove a device; edit a device’s name, MAC address, shared locations, shared-user list, or shared roles; print
device details; or add a new device.
2. To work with a device, click the device’s row in the list. The form expands to include the Remove, Edit, and
Print options.
54 | Registering Groups of Devicesor Services DellNetworking W-ClearPass Guest 6.0 | Deployment Guide
Page 55

3. To edit properties of a shared device, click the Edit link for the device. The row expands to include the Edit
Shared Device form. You can modify the device’s name, MAC address, shared locations, group of users, and
shared roles.
4. When your edits are complete, click Save Changes.
Registering Personal Devices
This functionality is available to AirGroup operators.
To register your personal devices and define a group who can share them:
1. Log in as the AirGroup operator and go to Guest > Create Device. The Register Device form opens.
2. In the Your Name field, enter your username for your organization.
3. In the Device Name field, enter the name used to identify the device.
4. In the MAC Address field, enter the device’s MAC address.
5. In the Shared With field, enter the usernames of your friends or colleagues who are allowed to use the device. Use
commas to separate usernames in the list. You may enter up to ten usernames.
l If the Shared With field is left blank, this device can only be accessed by devices registered by the same
operator or with a dot1x username that matches the operator’s name.
l If users are entered in the Shared With field, the device can be accessed by the device owner and by the
specified users.
6. Click Register Device. The Finished Creating Guest Account page opens. This page displays Account Details
and provides printer options.
To view and edit your personal AirGroup devices, go to Guest > List Devices, or click the Manage my AirGroup
Devices link on the Create AirGroup Device page. The List Device page lets you remove a device; edit a device’s
name, MAC address, or shared-user list; print device details; or add a new device.
To view and edit your personal AirGroup devices:
Dell Networking W-ClearPassGuest 6.0 | Deployment Guide Registering PersonalDevices | 55
Page 56

1. Go to Guest > List Devices, or click the Manage my AirGroup Devices link on the Create AirGroup Device
page. The AirGroup Devices page opens. This page lists all your personal AirGroup devices. You can remove a
device; edit a device’s name, MAC address, or shared-user list; print device details; or add a new device.
2. To work with a device, click the device’s row in the list. The form expands to include the Remove, Edit, and
Print options.
3. To edit properties of a device, click the Edit link for the device. The row expands to include the Edit Device
form. You can modify the device’s name, MAC address, and group of users.
4. When your edits are complete, click Save Changes.
Automatically Registering MAC Devices in ClearPass Policy Manager
If ClearPass Policy Manager is enabled, you can configure a guest MAC address to be automatically registered as an
endpoint record in ClearPass Policy Manager when the guest uses a Web login page or a guest self-registration
workflow. This customization option is available if a valid Local or RADIUS pre-authentication check was
performed.
To configure auto-registration for an address through a Web login page:
1. Go to Configuration > Web Logins, click the row of the page you wish to configure, then click its Edit link.
The RADIUS Web Login Editor form opens.
2. Scroll down to the Post-Authentication area.
56 | Automatically Registering MAC Devices in ClearPassPolicyManager Dell Networking W-ClearPassGuest 6.0 | Deployment Guide
Page 57

3. In the Policy Manager row, mark the check box to register the guest’s MAC address with ClearPass Policy
Manager. The Advanced row is added to the form.
4. In the Advanced row, mark the check box to enable advanced options in ClearPass Policy Manager. The
Endpoint Attributes row is added to the form.
5. In the Endpoint Attributes row, enter name|value pairs for the user fields and Endpoint Attributes to be passed.
6. Click Save Changes to complete this configuration and continue with other tasks, or click Save and Reload to
proceed to Policy Manager and apply the network settings.
Importing MAC Devices
The standard Guest > Import Accounts form supports importing MAC devices. At a minimum the following two
columns are required: mac and mac_auth.
mac_auth,mac,notes
1,aa:aa:aa:aa:aa:aa,Device A
1,bb:bb:bb:bb:bb:bb,Device B
1,cc:cc:cc:cc:cc:cc,Device C
Any of the other standard fields can be added similar to importing regular guests.
Advanced MAC Features
2-Factor Authentication
2-factor authentication checks against both credentials and the MAC address on record.
Tying the MAC to the visitor account will depend on the requirements of your deployment. In practice you would
probably add mac as a text field to the create_user form. When mac is enabled in a self-registration it will be
included in the account as long as mac is passed in the URL. Relying on self-registration may defeat the purpose of
two-factor authentication, however.
The 2-factors are performed as follows:
1. Regular RADIUS authentication using username and password
2. Role checks the user account mac against the passed Calling-Station-Id.
Edit the user role and the attribute for Reply-Message or Aruba-User-Role. Adjust the condition from Always to
Enter conditional expression.
return !MacEqual(GetAttr('Calling-Station-Id'), $user['mac']) && AccessReject();
There is an alternative syntax where you keep the condition at Always and instead adjust the Value.
<?= MacEqual(GetAttr('Calling-Station-Id'), $user['mac'])? $role["name"] : AccessReject()
or
<?= MacEqual(GetAttr('Calling-Station-Id'), $user['mac'])? 'Employee' : AccessReject()
MAC-Based Derivation of Role
Depending on whether the MAC address matches a registered value, you can also adjust which role is returned. The
controller must be configured with the appropriate roles and the reply attributes mapping to them as expected.
Edit the Value of the attribute within the role returning the role to the controller.
If you are on the registered MAC, apply the Employee role, otherwise set them as Guest.
<?= MacEqual(GetAttr('Calling-Station-Id'), $user['mac'])? 'Employee' : 'Guest'
Dell Networking W-ClearPassGuest 6.0 | Deployment Guide Importing MAC Devices | 57
Page 58

This can be expanded if you create multiple MAC fields. Navigate to Customize > Fields and duplicate mac.
Rename it as mac_byod and then add it to the 'create_user and guest_edit forms. In this example the account has a
registered employee device under mac, and a registered BYOD device under mac_byod.
<?= MacEqual(GetAttr('Calling-Station-Id'), $user['mac_byod'])? 'BYOD' : (MacEqual(GetAttr('
Calling-Station-Id'), $user['mac'])? 'Employee' : 'Guest')
User Detection on Landing Pages
When mac is passed in the redirect URL, the user is detected and a customized message displays on the landing
page.
Navigate to Administration > Plugin Manager > Manage Plugins: MAC Authentication: Configuration and
enable MAC Detect.
Edit the header of your redirect landing page (login or registration) and include the following:
<p>{if $guest_receipt.u.visitor_name}
Welcome back to the show, {$guest_receipt.u.visitor_name|htmlspecialchars}!
{else}
Welcome to the show!
{/if}</p>
For debugging purposes, include the following to see all the fields available:
{dump var=$guest_receipt export=html}
Click-Through Login Pages
A click-through login page will present a splash or terms screen to the guest, yet still provide MAC-auth style
seamless authentication. Under this scenario, you could have people create an account, with a paired MAC, yet still
have them click the terms and conditions on every new connection.
Disable MAC authentication on the controller.
Navigate to Administration > Plugin Manager > Manage Plugins: MAC Authentication: Configuration and
enable MAC Detect.
Create a Web Login
l Authentication: Anonymous
l Anonymous User: _mac
l Pre-Auth Check: Local
l Terms: Require a Terms and Conditions confirmation
(_mac is a special secret value)
Set the Web login as your landing page and test. Using a registered device the 'Log In' button should be enabled,
otherwise it will be disabled.
You may also want to add a message so visitors get some direction.
<p>{if $guest_receipt.u.username}
{if $guest_receipt.u.visitor_name}
Welcome back, {$guest_receipt.u.visitor_name|htmlspecialchars}!
{else}
Welcome back.
{/if}
Please accept the terms before proceeding.
{else}
You need to register...
{/if}</p>
You can hide the login form by having the final line of the header be:
{if!$guest_receipt.u.username}<div style="display:none">{/if}
58 | User Detection on Landing Pages DellNetworking W-ClearPass Guest 6.0 | Deployment Guide
Page 59

and the first line of the footer be:
{if!$guest_receipt.u.username}</div>{/if}
Active Sessions Management
The RADIUS server maintains a list of active visitor sessions. If your NAS equipment has RFC 3576 support, the
RADIUS dynamic authorization extensions allow you to disconnect or modify an active session.
To view and manage active sessions for the RADIUS server, go to Guest > Active Sessions. The Active Sessions list
opens. You can use this list to modify, disconnect or reauthorize, or send SMS notifications for active visitor
sessions; manage multiple sessions; or customize the list to include additional fields.
l To view details for an active session, click the session’s row in the list, then click its Show Details link. The form
expands to include the Session Details view.
Dell Networking W-ClearPassGuest 6.0 | Deployment Guide
Active SessionsManagement
| 59
Page 60

l If the NAS equipment has RFC 3576 support, you can disconnect or dynamically reauthorize active sessions. See
"RFC 3576 Dynamic Authorization" on page 61 for more information.
n To disconnect an active session, click the session’s row in the list, then click its Disconnect link. A message
is displayed to show that the disconnect is in progress and acknowledge when it is complete.
n To reauthorize a session that was disconnected, click the session’s row in the list, then click its Reauthorize
link. The Reauthorize Session form opens. Click Reauthorize Session. A message is displayed to show that
the disconnect is in progress and acknowledge when it is complete.
n To disconnect multiple sessions, click the Manage Multiple tab. The form expands to include the Manage
Multiple Sessions form. For more information, see "Disconnecting Multiple Active Sessions " on page 62.
l To view and work with the guest accounts associated with a session, click the session’s row in the list, then click
its List Accounts link. The Guest Manager Accounts view opens. See "Managing Guest Accounts " on page 34 for
more information.
l To display only sessions that meet certain criteria, click the Filter tab. For more information, see "Filtering the
List of Active Sessions" on page 61.
l To send SMS notifications to visitors, click the SMS tab. For more information, see "Sending Multiple SMS
Alerts " on page 63.
l To include additional fields in the Active Sessions list, or delete fields from it, click the More Options tab.
The Customize View Fields page opens. For more information, see "Editing Forms " on page 152.
l You can use the paging control at the bottom of the list to jump forwards or backwards by one page, or to the
first or last page of the list. You can also click an individual page number to jump directly to that page.
Session States
A session may be in one of three possible states:
l Active—An active session is one for which the RADIUS server has received an accounting start message and
has not received a stop message, which indicates that service is being provided by a NAS on behalf of an
authorized client.
While a session is in progress, the NAS sends interim accounting update messages to the RADIUS server. This
maintains up-to-date traffic statistics and keeps the session active. The frequency of the accounting update
messages is configurable in the RADIUS server.
l Stale—If an accounting stop message is never sent for a session—for example, if the visitor does not log out—
that session will remain open. After 24 hours without an accounting update indicating session traffic, the session
is considered ‘stale’ and is not counted towards the active sessions limit for a visitor account. To ensure that
accounting statistics are correct, you should check the list for stale sessions and close them.
l Closed—A session ends when the visitor logs out or if the session is disconnected. When a session is
explicitly ended in either of these ways, the NAS sends an accounting stop message to the RADIUS server. This
closes the session. No further accounting updates are possible for a closed session.
60 | Session States DellNetworking W-ClearPass Guest 6.0 | Deployment Guide
Page 61

RFC 3576 Dynamic Authorization
Dynamic authorization describes the ability to make changes to a visitor account’s session while it is in progress.
This includes disconnecting a session, or updating some aspect of the authorization for the session.
The Active Sessions page provides two dynamic authorization capabilities that apply to currently active sessions:
l Disconnect causes a Disconnect-Request message to be sent to the NAS for an active session, requesting that
the NAS terminate the session immediately. The NAS should respond with a Disconnect-ACK message if the
session was terminated or Disconnect-NAK if the session was not terminated.
l Reauthorize causes a Disconnect-Request message to be sent to the NAS for an active session. This message
will contain a Service-Type attribute with the value ‘Authorize Only’. The NAS should respond with a
Disconnect-NAK message, and should then reauthorize the session by sending an Access-Request message to the
RADIUS server. The RADIUS server’s response will contain the current authorization details for the visitor
account, which will then update the corresponding properties in the NAS session.
If the NAS does not support RFC 3576, attempts to perform dynamic authorization will time out and result in a
‘No response from NAS’ error message.
Refer to RFC 3576 for more details about dynamic authorization extensions to the RADIUS protocol.
Filtering the List of Active Sessions
You can use the Filter tab to narrow the search parameters and quickly find all matching sessions:
Enter a username or IP address in the Filter field. Additional fields can be included in the search if the “Include
values when performing a quick search” option was selected for the field within the view. To control this option, use
the Choose Columns command link on the More Options tab.
You may enter a simple substring to match a portion of the username or any other fields that are configured for
search, and you can include the following operators:
Dell Networking W-ClearPassGuest 6.0 | Deployment Guide RFC 3576 DynamicAuthorization | 61
Page 62

Table 11:
Operators supported in filters
Operator Meaning Additional Information
= is equal to
!= is not equal to
> is greater than
>= is greater than or equal to
< is less than
<= is less than or equal to
~ matches the regular expression
!~ does not match the regular expression
You may search for multiple values when using the equality
(=) or inequality !=) operators. To specify multiple values, list
them separated by the pipe character ( | ).
For example, specifying the filter "role_id=2|3, custom_
field=Value" restricts the accounts displayed to those with
role IDs 2 and 3 (Guest and Employee), and with the field
named "custom_field" set to "Value".
To restore the default view, click the Clear Filter link.
Click the Apply Filter button to save your changes and update the view, or click the Reset button to remove
the filter and return to the default view.
Disconnecting Multiple Active Sessions
To disconnect multiple sessions, click the Manage Multiple tab. The Manage Multiple Sessions form opens.
l To close all active sessions, leave the Start Time and End Time fields empty and click Make Changes. All active
sessions are closed and are removed from the Active Sessions list.
You can specify sessions in a time range.
1. To close all sessions that started after a particular time, click the button in the Start Time row. The calendar
picker opens. Use the calendar to specify the year, month, and day, and click the numbers in the Time fields to
increment the hours and minutes. All sessions that started after the specified date and time will be disconnected.
2. To close all sessions that started before a particular time, click the button in the End Time row. The calendar
picker opens. Use the calendar to specify the year, month, and day, and click the numbers in the Time fields to
increment the hours and minutes. All sessions that started before the specified date and time will be
disconnected.
3. Click Make Changes. The specified sessions are closed and are removed from the Active Sessions list.
62 | Disconnecting Multiple Active Sessions
Dell Networking W-ClearPassGuest 6.0 | Deployment Guide
Page 63

Sending Multiple SMS Alerts
The SMS tab on the Active Sessions page lets you send an SMS alert message to all active sessions that have a valid
phone number. An SMS alert during an active session can be used to send a group of visitors information you might
want them to have immediately—for example, a special offer that will only be available for an hour, a change in a
meeting’s schedule or location, or a public safety announcement.
To create an SMS message:
1. Click the SMS tab on the Active Sessions page. The Send SMS Notification form opens.
2. Use the filter to specify the group of addresses that should receive the message. See "Filtering the List of Active
Sessions" on page 61. Only accounts with valid phone numbers can be sent SMS alerts.
3. Enter the message in the Message text box. Messages may contain up to 160 characters.
4. Click Send.
About SMS Guest Account Receipts
You can send SMS receipts for guest accounts that are created using either sponsored guest access or self-provisioned
guest access. This is convenient in situations where the visitor may not be physically present to receive a printed
receipt.
ClearPass Guest may be configured to automatically send SMS receipts to visitors, or to send receipts only on
demand.
To manually send an SMS receipt:
1. Navigate to the Guest > List Accounts and click to expand the row of the guest to whom you want to send a
receipt.
2. Click Print to display the Account Details view, then click theSend SMS receipt link. The SMS Reciept form
opens. Use the fields on this form to enter the service to use, the recipient’s mobile phone number, the mobile
carrier, and the message text.
For more information on SMS services, see "SMS Services " on page 228.
Dell Networking W-ClearPassGuest 6.0 | Deployment Guide Sending Multiple SMS Alerts | 63
Page 64

64 | About SMS Guest Account Receipts
Dell Networking W-ClearPassGuest 6.0 | Deployment Guide
Page 65

Chapter 4
Onboard
Onboarding is the process of preparing a device for use on an enterprise network by creating the appropriate access
credentials and setting up the network connection parameters. Dell Networking W-ClearPass Onboard automates
802.1X configuration and provisioning for “bring your own device” (BYOD) and IT-managed devices—Windows,
Mac OS X, iOS and Android—across wired, wireless, and VPNs.
ClearPass Onboard includes the following key features:
l Automatic configuration of network settings for wired and wireless endpoints.
l Provisioning of unique device credentials for BYOD and IT-managed devices.
l Support for Windows, Mac OS X, iOS, and Android devices.
l Enables the revocation of unique credentials on a specific user’s device.
l Leverages ClearPass profiling to identify device type, manufacturer, and model.
Accessing Onboard
To access Dell Networking W-ClearPass Onboard’s device provisioning features, click the Onboard link in the left
navigation.
About ClearPass Onboard
This section provides important information about Dell Networking W-ClearPass Onboard.
Dell Networking W-ClearPassGuest 6.0 | Deployment Guide Onboard | 65
Page 66

Onboard Deployment Checklist
Table 12 lists planning, configuration, and testing procedures. Use this checklist to complete your Onboard
deployment.
Onboard events are stored in the Application Log for seven days by default. After seven days, significant runtime
events are listed in the Audit Viewer in Dell Networking W-ClearPass Policy Manager’s Monitoring module.
Onboard events that are listed include:
l Changing the CA certificate
l Issuing a new certificate
l Signing a certificate signing request
l Revoking a certificate
l Deleting a certificate
l Importing a trusted certificate
l Uploading a code-signing or other certificate
Table 12:
Onboard Deployment Checklist
Deployment Step Reference
Planning and Preparat ion
Review the Onboard feature list to identify the major areas of interest for
your deployment.
Review the list of platforms supported by Onboard, and identify the
platforms of interest for your deployment.
Review the Onboard public key infrastructure, and identify any certificate
authorities that will be needed during the deployment.
Review the network requirements and the network architecture
diagrams to determine how and where to deploy the Onboard solution.
Configuration
Configure the hostname and networking properties of the Onboard
provisioning server.
l DNS is required for SSL.
l Ensure that hostname resolution will work for devices being
provisioned.
"Onboard Feature List " on page 67
"Supported Platforms" on page 68
"Public Key Infrastructure for Onboard" on page
68
Refer to the ClearPass Policy Manager
documentation, and "Network Architecture for
Onboard" on page 72 in this chapter
Refer to the ClearPass Policy Manager
documentation
Configure SSL certificate for the Onboard provisioning server.
A commercial SSL certificate is required to enable secure device
provisioning for iOS devices.
Configure the Onboard certificate authority.
l Decide whether to use the Root CA or Intermediate CA mode of
operation.
Create the certificate for the certificate authority.
Configure the data retention policy for the certificate authority.
66 | Onboard Deployment Checklist DellNetworking W-ClearPass Guest 6.0 | Deployment Guide
Refer to the ClearPass Policy Manager
documentation
"Configuring the Certificate Authority " on
page 81
"Configuring Data Retention Policy for
Certificates" on page 90
Page 67

Deployment Step Reference
Configure device provisioning settings.
l Select certificate options for device provisioning.
Select which device types should be supported.
Configure network settings for device provisioning.
l Set network properties.
l Upload 802.1X server certificates.
Set device-specific networking settings.
Configure networking equipment for non-provisioned devices.
l Set authentication for the provisioning SSID, if required.
Ensure the captive portal redirects non-provisioned devices to the device
provisioning page.
Configure networking equipment to authenticate provisioned devices.
l Ensure 802.1X authentication methods and trust settings are
configured correctly for all EAP types that are required.
Configure OCSP or CRL on the authentication server to check for client
certificate validity.
Configure the user interface for device provisioning.
l Set display options for iOS devices.
l Set user interface options for other Onboard devices.
Setup the device provisioning Web login page.
Testing and Verification
"Configuring Provisioning Settings " on page
106
"Configuring Network Settings for Device
Provisioning " on page 117
"Network Requirements for Onboard" on page
71
"Network Requirements for Onboard" on page
71
"Configuring the User Interface for Device
Provisioning" on page 79
Test device provisioning.
l Verify that each type of device can be provisioned successfully.
Verify that each type of device can join the provisioned network and is
authenticated successfully.
Test device revocation.
l Revoke a device’s certificate.
l Verify that the device is no longer able to authenticate.
Verify that re-provisioning the device fails.
Onboard Feature List
The following features are available in Dell Networking W-ClearPass Onboard.
Table 13:
Feature Uses
Automatic configuration of network settings for
wired and wireless endpoints.
Secure provisioning of unique device
credentials for BYOD and IT-managed devices.
Onboard Features
l Configure wired networks using 802.1X
l Configure Wi-Fi networks using either 802.1X or pre-shared key (PSK)
l Configure trusted server certificates for 802.1X
l Configure Windows-specific networking settings
l Configure HTTP proxy settings for client devices (Android, OS X only)
l Configure EAP-TLS and PEAP-MSCHAPv2 without user interaction
l Revoke unique device credentials to prevent network access
Support for Windows, Mac OS X, iOS, and l Leverage ClearPass Profiling to identify device type, manufacturer,
Dell Networking W-ClearPassGuest 6.0 | Deployment Guide Onboard Feature List | 67
Page 68

Feature Uses
Android devices.
Certificate authority enables the creation and
revocation of unique credentials on a specific
user’s device.
Provision additional settings specific to iOS
devices
and model
l Control the user interface displayed during device provisioning
l Root and intermediate CA modes of operation
l Supports SCEP enrollment of certificates
l Supports CRL generation to list revoked certificates
l Supports OCSP responder to query for certificate status
l Approve certificate signing request
l Reject certificate signing request
l Sign certificate from uploaded certificate signing request (CSR)
l Issue certificate
l Revoke certificate
l Display certificates
l Export certificate
l Renew root certificate
l Exchange ActiveSync
l Passcode policy
l VPN settings
Supported Platforms
The platforms supported by Dell Networking W-ClearPass Onboard and the version requirements for each platform
are summarized in the following table.
Table 14:
Platforms Supported by ClearPass Onboard
Platform Example Devices Version Required for Onboard Support Notes
iPhone
Apple iOS
iPad
iPod Touch
Apple Mac OS X
MacBook Pro
MacBook Air
Samsung Galaxy S
Android
Samsung Galaxy Tab
Motorola Droid
Microsoft Windows
Note 1: Uses the “Over-the-air provisioning” method.
Note 2: Uses the “Onboard provisioning” method.
Note 3: Onboard mayalsobe used to provisionVPN settings, Exchange ActiveSyncsettings, and passcode policyon these devices.
Laptop
Netbook
iOS 4
iOS 5
Mac OS X 10.8 “Mountain Lion”
Mac OS X 10.7 “Lion”
Mac OS X 10.6 “Snow Leopard”
Mac OS X 10.5 “Leopard”
Android 2.2 (or higher) 2
Windows XP with Service Pack 3
Windows Vista with Service Pack 3
Windows 7
1, 3
1
2
2
Public Key Infrastructure for Onboard
During the device provisioning process, one or more digital certificates are issued to the device. These are used as
the unique credentials for a device. To issue the certificate, Dell Networking W-ClearPass Onboard must operate as
68 | Supported Platforms Dell Networking W-ClearPassGuest 6.0 | Deployment Guide
Page 69

a certificate authority (CA). The following sections explain how the certificate authority works, and which
certificates are used in this process.
Certificate Hierarchy
In a public key infrastructure (PKI) system, certificates are related to each other in a tree-like structure.
Figure 10: Relationship of Certificates in the Onboard Public Key Infrastructure
The root certificate authority (CA) is typically an enterprise certificate authority, with one or more intermediate
CAs used to issue certificates within the enterprise.
Onboard may operate as a root CA directly, or as an intermediate CA. See "Configuring the Certificate Authority "
on page 81. For information on setting up certificates when using Onboard in a cluster, see "Certificate
Configuration in a Cluster " on page 70.
The Onboard CA issues certificates for several purposes:
l The Profile Signing Certificate is used to digitally sign configuration profiles that are sent to iOS devices.
n The identity information in the profile signing certificate is displayed during device provisioning.
l One or more Server Certificates may be issued for various reasons – typically, for an enterprise’s authentication
server.
n The identity information in the server certificate may be displayed during network authentication.
l One or more Device Certificates may be issued – typically, one or two per provisioned device.
n The identity information in the device certificate uniquely identifies the device and the user that provisioned
the device.
You do not need to manually create the profile signing certificate; it is created when it is needed See "Configuring
Provisioning Settings for iOS and OS X" on page 110 to control the contents of this certificate.
You may revoke the profile signing certificate; it will be recreated when it is needed for the next device provisioning
attempt.
Dell Networking W-ClearPassGuest 6.0 | Deployment Guide Certificate Hierarchy | 69
Page 70

Certificate Configuration in a Cluster
When you use Onboard in a cluster, you must use one common root certificate authority (CA) to issue all CPPM
server certificates for the cluster. This allows the “verified” message in iOS and lets you verify that the CPPM server
certificate is valid during EAP-PEAP or EAP-TLS authentication.
In a cluster of CPPM servers, devices can be onboarded through any node or authenticated through any node. Each
CPPM server has a different certificate, used for both SSL and RADIUS server identity. In the default configuration,
these are self-signed certificates—that is, they are not issued by a root CA. This configuration of multiple self-signed
certificates will not work for Onboard: Although a single self-signed certificate can be trusted, multiple self-signed
certificates are not.
There are two ways to configure a common root CA to issue all the CPPM server certificates for a cluster:
l Use the Onboard certificate authority. Create a certificate signing request on each CPPM node, sign the
certificates using Onboard, and install them in CPPM. You can then onboard devices on any node in the cluster,
and can perform secure EAP authentication from a provisioned device to any node in the cluster.
l Use a commercial certificate authority to issue CPPM server certificates. Verify that the same root CA is at the
top of the trust chain for every server certificate, and that it is the trusted root certificate for Onboard.
Provisioning and authentication will then work across the entire cluster.
Revoking Unique Device Credentials
Because each provisioned device uses unique credentials to access the network, it is possible to disable network
access for an individual device. This offers a greater degree of control than traditional user-based authentication —
disabling a user’s account would impact all devices using those credentials.
To disable network access for a device, revoke the TLS client certificate provisioned to the device. See "Working
with Certificates in the List " on page 97.
NOTE: Revoking access for a device is only possible when using an enterprise network. Personal (PSK) networks do not support this
capability.
Revoking Credentials to Prevent Network Access
NOTE: Revoking a device's certificate will also prevent the device from being re-provisioned.
This is necessary to prevent the user from simply re-provisioning and obtaining a new certificate. To re-provision the
device, the revoked certificate must be deleted.
If the device is provisioned with an EAP-TLS client certificate, revoking the certificate will cause the certificate
authority to update the certificate’s state. When the certificate is next used for authentication, it will be recognized
as a revoked certificate and the device will be denied access.
NOTE: When using EAP-TLS authentication, you must configure your authentication server to use either OCSP or CRL to check the
revocation status of a client certificate. OCSP is recommended as it offers a real-time status update for certificates. If the device is
provisioned with PEAP unique device credentials, revoking the certificate will automatically delete the unique username and
password associated with the device. When this username is next used for authentication, it will not be recognized as valid and the
device will be denied access.
NOTE: OCSP and CRL are not used when using PEAP unique device credentials. The ClearPass Onbord server automatically
updates the status of the username when the device's client certificate is revoked.
70 | Certificate Configuration in a Cluster Dell Networking W-ClearPassGuest 6.0 | Deployment Guide
Page 71

Re-Provisioning a Device
Because “bring your own” devices are not under the complete control of the network administrator, it is possible for
unexpected configuration changes to occur on a provisioned device.
For example, the user may delete the configuration profile containing the settings for the provisioned network,
instruct the device to forget the provisioned network settings, or reset the device to factory defaults and destroy all
the configuration on the device.
When these events occur, the user will not be able to access the provisioned network and will need to re-provision
their device.
The Onboard server detects a device that is being re-provisioned and prompts the user to take a suitable action
(such as connecting to the appropriate network). If this is not possible, the user may choose to restart the
provisioning process and re-provision the device.
Re-provisioning a device will reuse an existing TLS client certificate or unique device credentials, if these credentials
are still valid.
If the TLS client certificate has expired then the device will be issued a new certificate. This enables re-provisioning
to occur on a regular basis.
If the TLS client certificate has been revoked, then the device will not be permitted to re-provision. The revoked
certificate must be deleted before the device is able to be provisioned.
Network Requirements for Onboard
For complete functionality to be achieved, Dell Networking W-ClearPass Onboard has certain requirements that
must be met by the provisioning network and the provisioned network:
l The provisioning network must use a captive portal or other method to redirect a new device to the device
provisioning page.
l The provisioning server (Onboard server) must have an SSL certificate that is trusted by devices that will be
provisioned. In practice, this means a commercial SSL certificate is required.
l The provisioned network
l must support EAP-TLS and PEAP-MSCHAPv2 authentication methods.
l The provisioned network must support either OCSP or CRL checks to detect when a device has been revoked
and deny access to the network.
Using Same SSID for Provisioning and Provisioned Networks
To configure a single SSID to support both provisioned and non-provisioned devices, use the following guidelines:
l Configure the network to use both PEAP and EAP-TLS authentication methods.
l When a user authenticates via PEAP with their domain credentials, place them into a provisioning role.
l The provisioning role should have limited network access and a captive portal that redirects users to the device
provisioning page.
l When a user authenticates via PEAP with unique device credentials, place them into a provisioned role.
l When a user authenticates via EAP-TLS using an Onboard client certificate, place them into a provisioned role.
For provisioned devices, additional authorization steps can be taken after authentication has completed to
determine the appropriate provisioned role.
Using Different SSID for Provisioning and Provisioned Networks
To configure dual SSIDs to support provisioned devices on one network, and non-provisioned devices on a separate
network, use the following guidelines:
Dell Networking W-ClearPassGuest 6.0 | Deployment Guide Re-Provisioning a Device | 71
Page 72

l Configure the provisioning SSID to use PEAP, or another suitable authentication method.
l When a user connects to the provisioning SSID, place them into a provisioning role.
n The provisioning role should have limited network access and a captive portal that redirects users to the
device provisioning page.
l When a user connects to the provisioned SSID, authenticate based on the type of credentials presented.
n For PEAP authentication with unique device credentials, place them into a provisioned role.
n For EAP-TLS authentication using an Onboard client certificate, place them into the provisioned role.
n In all other cases, deny access.
As for the single-SSID case, additional authorization steps may be taken after authentication has completed to
determine the appropriate provisioned role.
Configuring Online Certificate Status Protocol
Onboard supports the Online Certificate Status Protocol (OCSP) to provide a real-time check on the validity of a
certificate.
To configure OCSP for your network, you will need to provide the URL of an OCSP service to your network
equipment. This URL can be constructed by using the relative path mdps_ocsp.php/1.
For example, if the Onboard server’s hostname is onboard.example.com, the OCSP URL to use is:
http://onboard.example.com/mdps_ocsp.php/1.
NOTE: OCSP does not require the use of HTTPS and can be configured to use HTTP.
Configuring Certificate Revocation List (CRL)
Onboard supports generating a Certificate Revocation List (CRL) that lists the serial numbers of certificates that
have been revoked.
To configure a CRL, you will need to provide its URL to your network equipment. This URL can be constructed by
using the relative path mdps_crl.php?id=1.
For example, if the Onboard server’s hostname is onboard.example.com, the location of the CRL is:
http://onboard.example.com/mdps_crl.php?id=1.
NOTE: A certificate revocation list does not require the use of HTTPS and can be configured to use HTTP.
Network Architecture for Onboard
The high-level network architecture for the Onboard solution is shown in the following figure.
72 | Configuring Online Certificate Status Protocol Dell Networking W-ClearPassGuest 6.0 | Deployment Guide
Page 73

Figure 11: ClearPass Onboard Network Architecture
The sequence of events shown in Figure 11 is:
1. Users bring their own device to the enterprise.
2. The Dell Networking W-ClearPass Onboard workflow is used to provision the user’s device securely and with a
minimum of user interaction.
3. Once provisioned, the device re-authenticates to the network using a set of unique device credentials. These
credentials uniquely identify the device and user and enable management of provisioned devices.
4. Administrators can configure all aspects of the provisioning workflow – including the devices that have been
provisioned, policies to apply to devices and the overall user experience for BYOD.
A more detailed view of the network architecture is shown in Figure 12. This diagram shows different types of client
devices using the Onboard workflow to gain access to the network. Some of the components that may be configured
by the network administrator are also shown.
Figure 12: Detailed View of the ClearPass Onboard Network Architecture
The components shown in Figure 12 are:
Dell Networking W-ClearPassGuest 6.0 | Deployment Guide Network Architecture for Onboard | 73
Page 74

1. Users bring different kinds of client device with them. Onboard supports “smart devices” that use the iOS or
Android operating systems, such as smartphones and personal tablets. Onboard also supports the most common
versions of Windows and Mac OS X operating systems found on desktop computers, laptops and netbooks.
2. The Onboard workflow is used to provision the user’s device securely and with a minimum of user interaction.
The provisioning method used depends on the type of device.
a. Newer versions of Mac OS X (10.7 and later) and iOS devices use the “over-the-air” provisioning method.
b. Other supported platforms use the “Onboard provisioning” method.
3. Once provisioned, client devices use a secure authentication method based on 802.1X and the capabilities best
supported by the device.
a. The unique device credentials issued during provisioning are in the form of an EAP-TLS client certificate for
iOS devices and OS X (10.7+) devices.
b. Other supported devices are also issued a client certificate, but will use the PEAP-MSCHAPv2 authentication
method with a unique username and strong password.
4. Administrators can manage all Onboard devices using the certificate issued to that device.
Network Architecture for Onboard when Using ClearPass Guest
ClearPass Guest supports the provisioning, authentication, and management aspects of the complete Onboard
solution. Figure 13 shows the high-level network architecture for the Onboard solution when using ClearPass Guest
as the provisioning and authentication server.
Figure 13: ClearPass Onboard Network Architecture when Using ClearPass Guest
The user experience for device provisioning is the same in Figure 13 and Figure 11, however there are
implementation differences between these approaches:
l When using the ClearPass Guest RADIUS server for provisioning and authentication, EAP-TLS and PEAP
authentication must be configured.
Navigate to RADIUS> Authentication> EAP & 802.1X to configure a server certificate and the appropriate
EAP types for the ClearPass Guest RADIUS server.
l ClearPass Policy Manager supports a rich policy definition framework. If you have complex policies to enforce,
multiple authentication or authorization sources that define user accounts, or you need features beyond those
available in the ClearPass Guest RADIUS server, you should deploy Policy Manager for authentication.
74 | Network Architecture for Onboard when Using ClearPassGuest Dell Networking W-ClearPass Guest 6.0 | Deployment Guide
Page 75

The ClearPass Onboard Process
Devices Supporting Over-the-Air Provisioning
Dell Networking W-ClearPass Onboard supports secure device provisioning for iOS 4, iOS 5, and recent versions of
Mac OS X (10.7 “Lion” and later). These are collectively referred to as “iOS devices”. The Onboard process for iOS
devices is shown in Figure 14.
Figure 14: ClearPass Onboard Process for iOS Devices
The Onboard process is divided into three stages:
1. Pre-provisioning. The enterprise’s root certificate is installed on the iOS device.
2. Provisioning. The user is authenticated at the device provisioning page and then provisions their device with the
Onboard server. The device is configured with appropriate network settings and a device-specific certificate.
3. Authentication. Once configuration is complete, the user switches to the secure network and is authenticated
using an EAP-TLS client certificate.
A sequence diagram showing the interactions between each component of this workflow is shown in Figure 15.
Figure 15: Sequence Diagram for the Onboard Workflow on iOS Platform
Dell Networking W-ClearPassGuest 6.0 | Deployment Guide The ClearPass Onboard Process | 75
Page 76

1. When a BYOD device first joins the provisioning network it does not have a set of unique device credentials.
This will trigger the captive portal for that device, which brings the user to the mobile device provisioning page.
2. A link on the mobile device provisioning page prompts the user to install the enterprise’s root certificate.
Installing the enterprise’s root certificate enables the user to establish the authenticity of the provisioning server
during device provisioning.
3. The user then authenticates with their provisioning credentials – these are typically the user’s enterprise
credentials from Active Directory. If the user is authorized to provision a mobile device, the over-the-air
provisioning workflow is then triggered (see Figure 16, below).
4. After provisioning has completed, the device switches to EAP-TLS authentication using the newly provisioned
client certificate. Mutual authentication is performed (the authentication server verifies the client certificate, and
the client verifies the authentication server’s certificate).
5. The device is now onboard and is able to securely access the provisioned network.
Over-the-air provisioning is used to securely provision a device and configure it with network settings. Figure 16
shows a sequence diagram that explains the steps involved in this workflow.
Figure 16: Over-the-Air Provisioning Workflow for iOS Platform
1. The only user interaction required is to accept the provisioning profile. This profile is signed by the Onboard
server, so that the user can be assured of its authenticity.
2. An iOS device will have two certificates after over-the-air provisioning is complete:
a. A Simple Certificate Enrollment Protocol (SCEP) certificate is issued to the device during the provisioning
process. This certificate identifies the device uniquely, and is used to encrypt the device configuration profile
so that only this device can read its unique settings.
b. A Transport Layer Security (TLS) client certificate is issued to the device. This certificate identifies the
device and the user that provisioned the device. It is used as the device’s network identity during EAP-TLS
authentication.
Devices Supporting Onboard Provisioning
Dell Networking W-ClearPass Onboard supports secure device provisioning for Microsoft Windows XP (service pack
3 and later), Microsoft Windows Vista, Microsoft Windows 7, Apple Mac OS X 10.5 and 10.6, and Android devices
(smartphones and tablets). These are collectively referred to as “Onboard-capable devices”. The Onboard process for
these devices is shown in Figure 17.
76 | DevicesSupporting Onboard Provisioning Dell Networking W-ClearPassGuest 6.0 | Deployment Guide
Page 77

Figure 17: ClearPass Onboard Process for Onboard-Capable Devices
The Onboard process is divided into three stages:
1. Pre-provisioning. This step is only required for Android devices; the W-Series QuickConnect app must be
installed for secure provisioning of the device.
2. Provisioning. The device provisioning page detects the device type and downloads or starts the QuickConnect
app. The app authenticates the user and then provisions their device with the Onboard server. The device is
configured with appropriate network settings and credentials that are unique to the device. See Figure 18 for
details.
3. Authentication. Once configuration is complete, the user switches to the secure network and is authenticated
using PEAP-MSCHAPv2 unique device credentials.
Figure 18: Sequence Diagram for the Onboard Workflow on Android Platform
1. When a BYOD device first joins the network it does not have a set of unique device credentials. This will trigger
the captive portal for that device, which brings the user to the mobile device provisioning page.
Dell Networking W-ClearPassGuest 6.0 | Deployment Guide Devices Supporting Onboard Provisioning | 77
Page 78

2. The Onboard portal is displayed. The user’s device type is detected, and a link is displayed depending on the
device type:
a. For Android devices, the link is to a file containing the Onboard configuration settings; downloading this file
will launch the QuickConnect app on the device.
b. For Windows and Mac, the link is to a executable file appropriate for that operating system that includes
both the QuickConnect app and the Onboard configuration settings.
3. The QuickConnect app uses the Onboard provisioning workflow to authenticate the user and provision their
device with the Onboard server. The device is configured with appropriate network settings and credentials that
are unique to the device.
4. After provisioning has completed, the app switches the device to PEAP authentication using the newly
provisioned unique device credentials. Mutual authentication is performed (the authentication server verifies the
client’s username and password, and the client verifies the authentication server’s certificate).
5. The device is now onboard and is able to securely access the network.
The Onboard provisioning workflow is used to securely provision a device and configure it with network settings.
Figure 19 shows a sequence diagram that explains the steps involved in this workflow.
Figure 19: Onboard Provisioning Workflow in the QuickConnect App
Managing Provisioned Applications
The Applications form lets you mark individual applications for installation during device provisioning, and specify
whether they should be restarted when the device is provisioned. If restart is selected, you can specify whether the
restart should take effect when the installation is complete or at a later time.
To manage your applications:
1. Go to Onboard > Applications. The Applications form opens.
78 | Managing Provisioned Applications
Dell Networking W-ClearPassGuest 6.0 | Deployment Guide
Page 79

2. To upload applications, click the Content Manager link above the form.
3. To select applications to install, mark their check boxes, then click Save Changes.
Configuring the User Interface for Device Provisioning
The user interface for device provisioning can be customized in three different ways:
l Customizing the Web login page used for device provisioning.
All devices will reach the device provisioning Web login page as the first step of the provisioning process.See
"Customizing the Device Provisioning Web Login Page" on page 79 to make changes to the content or
formatting of this page.
l Customizing the properties of the device provisioning profile for iOS and OS X devices.
After starting the provisioning process, users of iOS and OS X are prompted to accept a configuration profile. See
"Configuring Provisioning Settings for iOS and OS X" on page 110 to make changes to the content of this profile.
l Customizing the user interface of the QuickConnect app for Windows, Mac OS X and Android devices.
The provisioning process for Windows, Mac OS X and Android devices uses a separate app, which has a
customizable user interface. See "Configuring Options for Legacy OS X, Windows, and Android Devices " on
page 116 to make changes to the user interface.
Customizing the Device Provisioning Web Login Page
Onboard creates a default Web login page that is used to start the device provisioning process.
To edit this page, navigate to Configuration > Start Here, then click the Web Logins command link. Click to
expand the Onboard Provisioning row in the list, and then click Edit. The RADIUS Web Login Editor form for
Onboard opens. Scroll to the Onboard Device Provisioning rows of the form.
The Onboard-specific settings required for a device provisioning page are described below:
Mark the Enable device provisioning check box to activate the Onboard features for this Web login page.
NOTE: If this check box is not marked, device provisioning will be inoperative.
Select the appropriate Onboard configuration from the Configuration drop-down list.
Dell Networking W-ClearPassGuest 6.0 | Deployment Guide Configuring the User Interface for Device Provisioning | 79
Page 80

To modify the instructions provided to users on the device provisioning page, edit the contents of the Header
HTML text area.
The default instructions are displayed to the user as:
This corresponds to the following text prepopulated in the Header HTML text area:
<p>
Please configure security and network settings on your device to allow secure<br>
access to the internal network. Please follow the instructions listed below:<br>
<br>
<strong>1.</strong> {nwa_iconlink icon="images/icon-certificate22.png"
text="Install root certificate (click here)"}{nwa_mdps_config name=root_cert}{/nwa_iconlink}<
br>
<strong>2.</strong> Login below using your {nwa_mdps_config name=organ
ization_name} credentials<br>
<strong>3.</strong> Install the certificate when prompted<br>
<strong>4.</strong> Go to your Wi-Fi settings and connect to SSID: <st
rong>{nwa_mdps_config name=wifi_ssid}</strong>
<br>
</p>
Using the {nwa_mdps_config} Template Function
Certain properties can be extracted from the Onboard configuration and used in the device provisioning page.
To obtain these properties, use the {nwa_mdps_config} Smarty template function. The “name” parameter specifies
which property should be returned, as described in Table 15.
Table 15:
Name Description
root_cert
80 | Using the {nwa_mdps_config} Template Function Dell Networking W-ClearPassGuest 6.0 | Deployment Guide
Properties Available with the
URL of the Onboard certificate authority’s root certificate.
Browsing to this URL will install the root certificate on the device, which is required as part of
the pre-provisioning step.
Example:
<a href="{nwa_mdps_config name=root_cert}"> Install Onboard root
certificate</a>
(nwa_mdps_config)
Smarty Template Function
Page 81

Name Description
Name of the wireless network. See "Configuring Basic Network Access Settings " on page
wifi_ssid
organization_name
118.
Example:
Connect to the network named {nwa_mdps_config name=wifi_ssid}
The organization name. See "Configuring Basic Provisioning Settings " on page 107.
Example:
<h2> Welcome to {nwa_mdps_config name=organization_name}</h2>
Configuring the Certificate Authority
To configure certificate authority settings, Navigate to Onboard > Certificate Authority Settings, or click the
Certificate Authority Settings command link.
The Certificate Authority Settings form opens.
This page is used to configure the Onboard certificate authority and to perform maintenance tasks for the CA.:
l Set up a root or intermediate certificate authority (See "Setting Up the Certificate Authority" on page 81)
l Determine the OCSP URL for the certificate authority
l View the trust chain for the certificate authority (See "Uploading Certificates for the Certificate Authority " on
page 91)
l Renew the certificate authority’s certificate (See "Renewing the Certificate Authority’s Certificate " on page 90)
l Configure the data retention policy applied to certificates issued by the authority (See "Configuring Data
Retention Policy for Certificates" on page 90)
l Import a private key/certificate pair (See "Installing a Certificate Authority’s Certificate " on page 88)
NOTE: For information on setting up certificates when using Onboard in a cluster, see "Certificate Configuration in a Cluster "
on page 70.
Setting Up the Certificate Authority
The Certificate Authority Settings form is used to set up the mode of operation for the certificate authority.
Dell Networking W-ClearPassGuest 6.0 | Deployment Guide
Configuring the Certificate Authority
| 81
Page 82

The Name and Description fields are used internally to identify this certificate authority for the network
administrator. These values are never displayed to the user during device provisioning.
Select the appropriate mode for the certificate authority:
l Root CA – The Onboard certificate authority issues its own root certificate. The certificate authority issues
client and server certificates using a local signing certificate, which is an intermediate CA that is subordinate to
the root certificate. Use this option when you do not have an existing public-key infrastructure (PKI), or if you
want to completely separate the certificates issued for Onboard devices from your existing PKI.
Click the Root CA image in the Mode area, then click Continue to proceed to the second step. See "Setting
Up a Root Certificate Authority " on page 82.
l Intermediate CA – The Onboard certificate authority is issued a certificate by an external certificate authority.
The Onboard certificate authority issues client and server certificates using this certificate. Use this option when
you already have a public-key infrastructure (PKI), and would like to include the certificate issued for Onboard
devices in that infrastructure.
Click the Intermediate CA image in the Mode area, then click Continue to proceed to the second step. See
"Setting Up an Intermediate Certificate Authority" on page 84.
Setting Up a Root Certificate Authority
If you already have a certificate and private key for the certificate authority, see "Installing a Certificate Authority’s
Certificate " on page 88.
After you choose Root CA on the Certificate Authority Settings form and click Continue, the Root Certificate
Settings form opens. The Root Certificate Settings form is used to configure the distinguished name and properties
for the certificate authority’s root (self-signed) certificate.
82 | Setting Up a Root Certificate Authority DellNetworking W-ClearPass Guest 6.0 | Deployment Guide
Page 83

NOTE: If you intend to change any of the root certificate's distinguished name properties, and you have previously created any client
or server certificates or performed device provisioning using the existing root certificate, these certificates will be invalidated and
deleted because the root certificate's distinguished name has changed. To avoid the complication of revoking and reissuing
certificates, it is recommended that you configure the certificate authority before any device provisioning or other configuration is
done.
In the Identity section of the form:
l Enter values in the Country, State, Locality, Organization, and Organizational Unit text fields that correspond
to your organization. These values form part of the distinguished name for the root certificate.
l Enter a descriptive name for the root certificate in the Common Name text field. This value will be used to
identify the root certificate as the issuer of other certificates, notably the signing certificate.
l Enter a descriptive name for the signing certificate in the Signing Common Name text field. This value will be
used to identify the signing certificate as the issuer of client and server certificates from this certificate authority.
The other identity information in the signing certificate will be the same as for the root certificate.
l Enter a contact email address in the Email Address text field. This email address will be included in the root and
signing certificates, and provides a way for users of the certificate authority to contact your organization.
In the Private Key section:
l To create a new private key for the root certificate, mark the Generate a new private key check box. The form
expands to include the Key Type drop-down list. Creating a new private key is only necessary if you are recreating
the entire certificate authority from the beginning.
NOTE: If you have previously created any client or server certificates or performed device provisioning using the existing root
certificate, these certificates will be invalidated when changing the root certificate's private key.
Dell Networking W-ClearPassGuest 6.0 | Deployment Guide Setting Up a Root Certificate Authority | 83
Page 84

l The Key Type drop-down list specifies the type of private key that should be created for the certificate. You can
select one of these options:
n 1024-bit RSA – not recommended for a root certificate
n 2048-bit RSA – recommended for general use
n 4096-bit RSA – higher security
In the Self-Signed Certificate section:
l Use the CA Expiration field to specify the lifetime of the root certificate in days. The default value of 3653 days
is a 10-year lifetime.
l The Clock Skew Allowance field adds a small amount of time to the start and end of the root certificate’s
validity period. This permits a newly issued certificate to be recognized as valid in a network where not all
devices are perfectly synchronized.
l The Digest Algorithm drop-down list allows you to specify which hash algorithm should be used.
NOTE: MD5 is not recommended for use with root certificates.
Mark the Generate CA certificate and invalidate all other certificates check box to confirm the changes.
Click the Create Root Certificate button to save the settings and generate a new root certificate.
Setting Up an Intermediate Certificate Authority
After you choose Intermediate CA on the Certificate Authority Settings form and click Continue, the Intermediate
Certificate Settings form opens. The Intermediate Certificate Settings form is used to configure the distinguished
name and properties for the certificate authority’s certificate, which will be issued by an external certificate
authority.
NOTE: If you intend to change any of the intermediate certificate's distinguished name properties, and you have previously created
any client or server certificates or performed device provisioning using the existing intermediate certificate, these certificates will
be invalidated because the intermediate certificate's distinguished name has changed. In this case, you should use the Reset to
Factory Defaults form (see "Resetting Onboard Certificates and Configuration " on page 130) to delete all client certificates and re-
provision all devices. You will also need to reissue any server or subordinate CA certificates.
To avoid the complication of revoking and reissuing certificates, it is recommended that you configure the
certificate authority before any device provisioning or other configuration is done.
84 | Setting Up an Intermediate Certificate Authority Dell Networking W-ClearPassGuest 6.0 | Deployment Guide
Page 85

In the Identity section of the form:
l Enter values in the Country, State, Locality, Organization, and Organizational Unit text fields that correspond
to your organization. These values form part of the distinguished name for the certificate authority.
l Enter a descriptive name for the certificate authority in the Common Name text field. This value will be used to
identify the intermediate certificate as the issuer of client and server certificates from this certificate authority.
l Enter a contact email address in the Email Address text field. This email address will be included in the
certificate authority’s certificate, and provides a way for users of the certificate authority to contact your
organization.
In the Private Key section:
l To create a new private key for the intermediate certificate, mark the Generate a new private key check box. The
form expands to include the Key Type drop-down list. Creating a new key is only necessary if you are recreating
the entire certificate authority from the beginning.
NOTE: If you have previously created any client or server certificates or performed device provisioning using the existing
intermediate CA certificate, these certificates will be invalidated when changing the intermediate CA's private key.
l The Key Type drop-down list specifies the type of private key that should be created for the certificate. You can
select one of these options:
n 1024-bit RSA – not recommended for a certificate authority
n 2048-bit RSA – recommended for general use
n 4096-bit RSA – higher security
In the Intermediate Certificate section:
l The Digest Algorithm drop-down list allows you to specify which hash algorithm should be used.
NOTE: MD5 is not recommended for use with certificate authority certificates.
Mark the Generate CA certificate request and invalidate all other certificates check box to confirm the changes.
Dell Networking W-ClearPassGuest 6.0 | Deployment Guide Setting Up an Intermediate Certificate Authority | 85
Page 86

Click the Create Certificate Request button to save the settings and generate a new certificate signing request.
Obtaining a Certificate for the Certificate Authority
The Intermediate Certificate Request page displays the certificate signing request for the certificate authority’s
intermediate certificate. This page is also used to renew the certificate authority’s intermediate certificate when it is
close to expiring.
You can copy the certificate signing request in text format using your Web browser. Use this option when you can
paste the request directly into another application to obtain a certificate.
You can click the Download the current CSR link to download the certificate signing request as a file. Use this
option when you need to provide the certificate signing request as a file to obtain a certificate.
Once you have obtained the certificate, click the Install a signed certificate link to continue configuring the
intermediate certificate authority. See "Installing a Certificate Authority’s Certificate " on page 88.
You can also click the Change CA settings link to return to the main Certificate Authority Settings form. Use
this option to switch to a root CA, or to change the name or properties of the intermediate CA and reissue the
certificate signing request.
Using Microsoft Active Directory Certificate Services
Navigate to the Microsoft Active Directory Certificate Services Web page. This page is typically found at
https://yourdomain/certsrv/. The Welcome page opens.
Click the Request a Certificate link on this page. The Request a Certificate page opens.
Click the link to submit an advanced certificate request. The Advanced Certificate Request page opens.
86 | Obtaining a Certificate for the Certificate Authority Dell Networking W-ClearPassGuest 6.0 | Deployment Guide
Page 87

Click the link to submit a request using a base-64-encoded CMC or PKCS #10 file. The Submit a Certificate
Request or Renewal Request page is displayed.
Copy and paste the certificate signing request text into the Saved Request text field.
Because this certificate is for a certificate authority, select the “Subordinate Certificate Authority” in the
Certificate Template drop-down list.
Click the Submit button to issue the certificate. Either the Certificate Pending or the Certificate Issued page is
displayed.
Figure 20: The Certificate Pending Page
Dell Networking W-ClearPassGuest 6.0 | Deployment Guide Using Microsoft Active Directory Certificate Services | 87
Page 88

If the Certificate Pending page is displayed, follow the directions on the page to retrieve the certificate when it is
issued.
Figure 21: The Certificate Issued Page
If the Certificate Issued page is displayed, select the Base 64 encoded option and then click the Download
certificate chain link. A file containing the intermediate certificate and the issuing certificates in the trust chain will
be downloaded to your system.
Refer to the instructions in "Installing a Certificate Authority’s Certificate " on page 88 for information on
uploading the certificate file to Onboard.
Installing a Certificate Authority’s Certificate
You can import a private key and certificate pair to use for the root certificate or intermediate certificate. The CA
Certificate Import page may be used to:
l Upload a certificate that has been issued by another certificate authority. This process is required when
configuring an intermediate certificate authority.
n A private key is not required, as the certificate authority has already generated one and used it to create the
certificate signing request.
l Upload a certificate and private key to be used as the certificate authority’s certificate. This process may be used
to configure a root certificate authority.
n A private key is required, as the certificate authority’s existing private key will be replaced.
NOTE: This form may be used multiple times in order to import each of the certificates in the trust chain. Check the message
displayed above the form to determine which certificate or type of file must be uploaded next.
To upload a certificate:
1. Go to Onboard > Certificate Authority Settings, and choose either Root CA or Intermediate CA, as
appropriate. For more information, see "Setting Up the Certificate Authority" on page 81.
2. On either the Root Certificate Settings or Intermediate Certificate Settings page, click the Import Certificate
link above the form. The Step 1 area of the CA Certificate Import form opens.
88 | Installing a Certificate Authority’s Certificate Dell Networking W-ClearPassGuest 6.0 | Deployment Guide
Page 89

3. Select one of the radio buttons to either copy and paste the certificate as encoded text or browse to the file to
upload. The form expands to include options for that method.
4. If you selected Copy and paste certificate as text:
l To upload a single certificate, copy and paste the certificate into the Certificate text field. The text must
include the “BEGIN CERTIFICATE” and “END CERTIFICATE” lines. Leave the passphrase fields blank.
l To upload a certificate and private key, copy and paste the certificate and private key into the Certificate
text field. The text must include the “BEGIN CERTIFICATE” and “END CERTIFICATE” lines, as well as
the “BEGIN RSA PRIVATE KEY” and “END RSA PRIVATE KEY” lines.
5. If you selected Upload certificate file, click Choose File in the Certificate row to browse to the file and select
it.
l To upload a single certificate, choose a certificate file in PEM (base-64 encoded) or binary format (.crt or
PKCS#7). Leave the passphrase fields blank.
l To upload a certificate’s private key as a separate file, choose the private key file in PEM (base-64 encoded)
format. If the private key has a passphrase, enter it in the Private Key Passphrase and Confirm Passphrase
fields. The private key will be automatically matched to its corresponding certificate when uploaded.
l To upload a combined certificate and private key, choose a file in either PEM (base-64 encoded) or
PKCS#12 format. If the private key has a passphrase, enter it in the Private Key Passphrase and Confirm
Passphrase fields.
Dell Networking W-ClearPassGuest 6.0 | Deployment Guide Installing a Certificate Authority’sCertificate | 89
Page 90

6. Click the Upload Certificate button to save your changes.
If additional certificates are required, you will remain at the same page. Check the message displayed above the form
to determine which certificate or type of file must be uploaded next. When the trust chain is complete, it will be
displayed. This completes the initialization of the certificate authority.
Renewing the Certificate Authority’s Certificate
When a root certificate is close to expiration, it must be renewed.
Navigate to Onboard> Certificate Authority Settings and click the Renew Root Certificate link. The Root
Certificate Renewal form is displayed.
Select an option in the Renewal Type drop-down list:
l Basic Renewal – Uses the same private key for the root certificate, but reissues the root CA certificate with an
updated validity period. Use this option to maintain the validity of all certificates issued by the CA.
l Replacement Renewal – Generates a new private key for the root certificate, and reissues the root CA certificate
with an updated validity period. Use this option if the root certificate has been compromised, or if you want to
invalidate all certificate that were previously issued by the CA.
Whether you renew or replace the root certificate, you should distribute a new copy of the root certificate to all
users of that certificate.
Click the Renew Root Certificate button to perform the renewal action.
Configuring Data Retention Policy for Certificates
The data retention policy for certificates and certificate requests can be configured by navigating to Onboard>
Certificate Authority Settings and clicking the Configure data retention link.
The Manage Data Retention form is displayed.
90 | Renewing the Certificate Authority’s Certificate Dell Networking W-ClearPassGuest 6.0 | Deployment Guide
Page 91

In the Onboard Device Certificates section of the form, specify a value in the Minimum Period and Maximum
Period fields that is appropriate for your organization’s retention policy.
NOTE: Use a blank value for Minimum Period to enable the Delete Certificate and Delete Request actions in the Certificate
Management list view. This is useful for testing and initial deployment.
The default data retention policy specifies the values:
l Minimum Period of 12 weeks
l Maximum Period of 52 weeks
Uploading Certificates for the Certificate Authority
The Certificate Authority Trust Chain page is used to view the certificate authority’s current trust chain, or to
upload a new certificate in the trust chain when configuring a certificate authority.
To view the Certificate Authority’s trust chain, go to Onboard > Certificate Authority Settings and click the View
CA Certificate link at the top of the page. The Certificate Authority Trust Chain page is displayed. This page
shows a graphical representation of the certificates that make up the trust chain.
The first certificate listed is the root certificate. Root certificates are always self-signed and are explicitly trusted by
clients.
Each additional certificate shown is an intermediate certificate. The last certificate in the list is the signing
certificate that is used to issue client and server certificates.
To view the properties of a certificate in the trust chain, click the Show certificate link. The Certificate
Information view opens.
Dell Networking W-ClearPassGuest 6.0 | Deployment Guide
Uploading Certificates for the Certificate Authority
| 91
Page 92

To export a certificate:
1. Click the Download Bundle link. The Export Certificate form opens.
2. In the Format row, choose the certificate format. The form expands to include configuration options for that
format.
3. Complete the fields with the appropriate information, then click Export Certificate.
92 | Uploading Certificatesfor the Certificate Authority
Dell Networking W-ClearPassGuest 6.0 | Deployment Guide
Page 93

Creating a Certificate
From the Certificate Management page, click the Generate a new certificate signing request link to access the
Certificate Request form.
To create a new certificate or certificate signing request, first select the type of certificate you want to create from
the Certificate Type drop-down list:
l TLS Client Certificate—Use this option when the certificate is to be issued to a client, such as a user or a user’s
device.
n When this option is selected, the issued certificate’s extended key usage property will contain a value of
“Client Auth”, indicating that the certificate may be used to identify a client.
l Trusted Certificate—Use this option when the certificate is to be issued to a network server, such as a Web
server or as the EAP-TLS authentication server.
n When this option is selected, the issued certificate’s extended key usage property will contain a value of
“Server Auth”, indicating that the certificate may be used to identify a server.
l Certificate Authority—Use this option when the certificate is for a subordinate certificate authority.
n When this option is selected, the issued certificate will contain an extension identifying it as an intermediate
certificate authority, and the extended key usage property will contain the three values “Client Auth”, “Server
Auth” and “OCSP Signing”.
l Code Signing—Use this option for signing the Windows provisioning application.
Specifying the Identity of the Certificate Subject
In the first part of the form, provide the identity of the person or device for which the certificate is to be issued (the
“subject” of the certificate). Together, these fields are collectively known as a distinguished name, or “DN”.
l Country
l State
l Locality
l Organization
Dell Networking W-ClearPassGuest 6.0 | Deployment Guide
Creatinga Certificate
| 93
Page 94

l Organizational Unit
l Common Name – this is the primary name used to identify the certificate
l Email Address
The Key Type drop-down list specifies the type of private key that should be created for the certificate. You can
select one of these options:
l 1024-bit RSA – lower security
l 2048-bit RSA – recommended for general use
l 4096-bit RSA – higher security
NOTE: Using a private key containing more bits will increase security, but will also increase the processing time required to create
the certificate and authenticate the device. The additional processing required will also affect the battery life of a mobile device. It
is recommended to use the smallest private key size that is feasible for your organization.
If you have selected TLS Client as the certificate type, the Subject Alternative Name section is also shown. The
alternative name can be used to specify additional identification details for the certificate’s subject. If one or more
of these options are provided, the issued certificate will contain a subjectAltName extension with the specified
values.
Table 16 explains the fields that may be included as part of the subject alternative name.
Table 16:
Subject Alternative Name Fields Supported When Creating a TLS Client Certificate Signing
Request
Name Description
Device Type Type of device, such as “iOS”, “Android”, etc.
Device UDID
Device IMEI International Mobile Equipment Identity (IMEI) number allocated to this device.
Device ICCID
Unique device identifier (UDID) for this device. This is typically a 64-bit, 128-bit or 160bit number represented in hexadecimal (16, 32 or 40 characters, respectively).
Integrated Circuit Card Identifier (ICCID) number from the Subscriber Identity Module
(SIM) card present in the device.
94 | Specifying the Identity of the Certificate Subject Dell Networking W-ClearPassGuest6.0 | Deployment Guide
Page 95

Name Description
Device Serial Serial number of the device.
MAC Address IEEE MAC address of this device.
Product Name
Product Version Software version number for the device.
User Name Username of the user who provisioned the device.
Product string identifying the device and often including the hardware version
information.
Issuing the Certificate Request
Mark the Issue this certificate immediately check box to automatically create the certificate.
Click the Create Certificate Request button to save your changes.
l If the “Issue this certificate immediately” check box is marked, the certificate will be issued immediately and will
be displayed in the Certificate Management list view.
l If the “Issue this certificate immediately” check box is not marked, the certificate request will be displayed in
the Certificate Management list view. The certificate can then be issued or rejected at a later time.
Managing Certificates
To view the list of certificates and work with them, go to Onboard > Certificate Management, or click the
Certificate Management command link.
The Certificate Management list view opens. This list displays all of the certificates and certificate requests in the
Onboard system.
Information provided in the Certificate Management list includes common name, serial number (if available),
certificate type, validity date range, and device type—iOS, Android, Windows, or None (if not associated with a
device type). Table 17 lists the types of certificate that are displayed in this list.
Dell Networking W-ClearPassGuest 6.0 | Deployment Guide Issuing the Certificate Request | 95
Page 96

Table 17:
Types of Certificate Supported by Onboard Certificate Management
Certificate Type “Type” Column Notes
Root certificate ca
Intermediate certificate ca
Profile signing certificate profile-signing Issued by the certificate authority
Certificate signing request tls-client or trusted
Rejected certificate signing request tls-client or trusted
Device certificate scep-client Issued to iOS and OS X (10.7+) devices only
Client certificate tls-client
Server certificate trusted Identity certificate issued to a server
Code-signing certificate ca
Revoked certificate --
Self-signed certificate for the certificate
authority
Issued by the root CA or another intermediate
CA
The type shown depends on the kind of
certificate requested
Certificate request that was rejected due to an
administrator decision
Identity certificate issued to a specific user’s
device
Used for signing the Windows provisioning
application
Certificate that has been administratively
revoked and is no longer valid
Expired certificate --
Certificate that is outside its validity period and
is no longer valid
Searching for Certificates in the List
The Filter field can be used to quickly search for a matching certificate. Type a username into this field to locate all
certificates matching that username quickly.
The filter is applied to all columns displayed in the list view. To search by another field, such as MAC address,
device type, or device serial number, click the Columns tab, select the appropriate column(s), and then click the
Save and Reload button. The list view will refresh to update the results of the filter.
Click the Clear Filter link to restore the default view.
Use the paging control at the bottom of the list to jump forwards or backwards by one page, or to the first or last
page of the list. You can also click an individual page number to jump directly to that page.
NOTE: When the list contains many thousands of certificates, consider using the Filter field to speed up finding a specific certificate.
Click the column headers to sort the list view by that column. Click the column header a second time to reverse the
direction of the sort.
96 | Searching for Certificates in the List Dell Networking W-ClearPassGuest 6.0 | Deployment Guide
Page 97

Working with Certificates in the List
Click on a certificate to select it. You can then select from one of these actions:
l View certificate – Displays the properties of the certificate. Click the Cancel button to close the
certificate properties.
l Export certificate – Displays the Export Certificate form.
Use the Format drop-down list to select the format in which the certificate should be exported. The following
formats are supported:
l PKCS#7 Certificates (.p7b)—Exports the certificate, and optionally the other certificates forming the trust
chain for the certificate, as a PKCS#7 container.
l Base-64 Encoded (.pem)—Exports the certificate as a base-64 encoded text file. This is also known as “PEM
format”. You may optionally include the other certificates forming the trust chain for the certificate.
l Binary Certificate (.crt)—Exports the certificate as a binary file. This is also known as “DER format”.
l Open SSL Text Format—Exports the certificate as a full openssl text-format output, allowing you to view
advanced details such as X509v3 extensions. It also includes the certificate in .pem format appended to the
.txt file.
l PKCS#12 Certificate & Key (.p12)—Exports the certificate and its associated private key, and optionally
any other certificates required to establish the trust chain for the certificate, as a PKCS#12 container. This
option is only available if the private key for the certificate is available to the server. If you select the
PKCS#12 format, you must enter a passphrase to protect the private key stored in the file.
NOTE: To protect against brute-force password attacks and ensure the security of the private key, you should use a strong
passphrase – one consisting of several words, mixed upper- and lower-case letters, and punctuation or other symbol characters.
Click the Export Certificate button to download the certificate file in the selected format.
l Revoke certificate – Displays the Revoke Certificate form.
Dell Networking W-ClearPassGuest 6.0 | Deployment Guide Working with Certificatesin the List | 97
Page 98

Mark the Revoke this client certificate check box to confirm that the certificate should be revoked, and then
click the Revoke Certificate button.
Once the certificate has been revoked, future checks of the certificate’s validity using OCSP or CRL will indicate
that the certificate is no longer valid.
NOTE: Due to the way in which certificate revocation lists work, a certificate cannot be un-revoked. A new certificate must be
issued if a certificate is revoked in error.
NOTE: Revoking a device’s certificate will also prevent the device from being re-provisioned. This is necessary to prevent the user
from simply re-provisioning and obtaining a new certificate. To re-provision the device, the revoked certificate must be deleted.
l Delete certificate – Removes the certificate from the list. Trusted certificates that were imported into
Onboard may be deleted at any time after import. For all other certificates, this option is only available if the
data retention policy is configured to permit the certificate’s deletion. See "Configuring Data Retention Policy
for Certificates" on page 90.
98 | Working with Certificatesin the List Dell Networking W-ClearPassGuest 6.0 | Deployment Guide
Page 99

The Delete Certificate form is displayed. Mark the Delete this client certificate check box to confirm the
certificate’s deletion, and then click the Delete Certificate button.
Working with Certificate Signing Requests
Certificate signing requests can be managed through the Certificate Management list view. This allows for server
certificates, subordinate certificate authorities, and other client certificates not associated with a device to be issued
by the Onboard certificate authority.
Click on a certificate request to select it. You can then select from one of these actions:
l View request – Displays the properties of the certificate request. Click the Cancel button to close the
certificate request properties.
l Export request – Displays the Export Certificate Request form.
Use the Format drop-down list to select the format in which the certificate signing request should be exported.
The following formats are supported:
n PKCS#10 Certificate Request (.p10) – Exports the certificate signing request in binary format.
n Base-64 Encoded (.pem) – Exports the certificate signing request as a base-64 encoded text file. This is also
known as “PEM format”.
If you choose Base-64 Encoded, the form expands to include the Trust Chain row. You can use this option to
create and export a certificate bundle that includes the Intermediate CA and Root CA and can be imported in
Dell Networking W-ClearPassGuest 6.0 | Deployment Guide Working with Certificate Signing Requests | 99
Page 100

ClearPass Policy Manager as the server certificate (ClearPass Policy Manager does not accept PKCS#7). To
include the trust chain in a certificate bundle that can be imported as the server certificate in ClearPass Policy
Manager, mark the Include certificate trust chain check box, then click the Export Certificate button.
Click the Export Request button to download the certificate signing request file in the selected format.
l Sign request – Displays the Sign Request form. Use this action to approve the request for a certificate and
issue the certificate.
Use the Expiration text field to specify how long the issued certificate should remain valid.
Mark the Sign this request check box to confirm that the certificate should be issued, and then click the Sign
Request button. The certificate will be issued and will then replace the certificate signing request in the list view.
l Reject request – Displays the Reject Request form. Use this action to reject the request for a certificate.
Rejected requests are automatically deleted according to the data retention policy.
100 | Working with Certificate Signing Requests DellNetworking W-ClearPass Guest 6.0 | Deployment Guide
 Loading...
Loading...