Page 1

Network Partition (NPAR) Technology and
VMware Virtual Switch comparison using
QLogic BCM57800
Dell Network Solutions Engineering
February 2016
This application note discusses the pros and cons of the QLogic BCM57800 series
network partition (NPAR) technology and VMware’s virtual standard switch (VSS) as
well as virtual distributed switch (VDS) with traffic shaping.
Page 2
Date
Version
Description
Authors
February 2016
1.0
Initial Release
Neal Beard
Revisions
Copyright © 2016 Dell Inc. or its subsidiaries. All Rights Reserved.
Except as stated below, no part of this document may be reproduced, distributed or transmitted in any form or by any
means, without express permission of Dell.
You may distribute this document within your company or organization only, without alteration of its contents.
THIS DOCUMENT IS PROVIDED “AS-IS”, AND WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED. IMPLIED
WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE SPECIFICALLY
DISCLAIMED. PRODUCT WARRANTIES APPLICABLE TO THE DELL PRODUCTS DESCRIBED IN THIS DOCUMENT
MAY BE FOUND AT: http://www.dell.com/learn/us/en/vn/terms-of-sale-commercial-and-public-sector-warranties
Performance of network reference architectures discussed in this document may vary with differing deployment conditions,
network loads, and the like. Third party products may be included in reference architectures for the convenience of the
reader. Inclusion of such third party products does not necessarily constitute Dell’s recommendation of those products.
Please consult your Dell representative for additional information.
Trademarks used in this text: Dell™, the Dell logo, Dell Boomi™, PowerEdge™, PowerVault™, PowerConnect™,
OpenManage™, EqualLogic™, Compellent™, KACE™, FlexAddress™, Force10™ and Vostro™ are trademarks of Dell
Inc. EMC VNX®, and EMC Unisphere® are registered trademarks of Dell. Other Dell trademarks may be used in this
document. Cisco Nexus®, Cisco MDS®, Cisco NX-0S®, and other Cisco Catalyst® are registered trademarks of Cisco
System Inc. Intel®, Pentium®, Xeon®, Core® and Celeron® are registered trademarks of Intel Corporation in the U.S. and
other countries. AMD® is a registered trademark and AMD Opteron™, AMD Phenom™ and AMD Sempron™ are
trademarks of Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. Microsoft®, Windows®, Windows Server®, Internet Explorer®, MS-DOS®,
Windows Vista® and Active Directory® are either trademarks or registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation in the
United States and/or other countries. Red Hat® and Red Hat® Enterprise Linux® are registered trademarks of Red Hat,
Inc. in the United States and/or other countries. Novell® and SUSE® are registered trademarks of Novell Inc. in the United
States and other countries. Oracle® is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates. VMware®, Virtual
SMP®, vMotion®, vCenter® and vSphere® are registered trademarks or trademarks of VMware, Inc. in the United States
or other countries. IBM® is a registered trademark of International Business Machines Corporation. Broadcom® and
NetXtreme® are registered trademarks of QLogic is a registered trademark of QLogic Corporation. Other trademarks and
trade names may be used in this document to refer to either the entities claiming the marks and/or names or their products
and are the property of their respective owners. Dell disclaims proprietary interest in the marks and names of others.
2 Network Partition (NPAR) Technology and VMware Virtual Switch comparison using QLogic BCM57800 | version 1.0
Page 3

Table of contents
Revisions............................................................................................................................................................................. 2
1 Overview ....................................................................................................................................................................... 4
2 QLogic BCM57800 Series NPAR with VMware’s VSS ................................................................................................ 5
3 VMware’s VSS with traffic shaping............................................................................................................................... 8
4 VMware VDS with traffic shaping ............................................................................................................................... 11
5 A VMware VDS with VM network resource pools ...................................................................................................... 14
6 Conclusion .................................................................................................................................................................. 16
A Component Revisions ................................................................................................................................................ 17
B Additional Information ................................................................................................................................................. 18
3 Network Partition (NPAR) Technology and VMware Virtual Switch comparison using QLogic BCM57800 | version 1.0
Page 4

1 Overview
When designing networks, one very important consideration is how much bandwidth to allocate to the
different devices that need varying levels of throughput. Where this bandwidth management occurs is
generally based on:
Where bottlenecks occur
What traffic types need prioritization (for example, Multicast, e-commerce applications, VoIP)
General business needs
Techniques for bandwidth management include:
Data compression to reduce the size of the data being transmitted
Caching to store frequently used data locally instead of transmitting it multiple times
Traffic shaping/bandwidth prioritization to optimize or guarantee performance, improve latency and/or
increase usable bandwidth for some kinds of packets by delaying other kinds
Numerous bandwidth management techniques can alleviate multiple throughput issues on a network. This
application note focuses on traffic shaping to achieve optimal throughput through prioritization using the tools
provided by the QLogic BCM57800 series Converged Network Adapter (CNA), VMware and VMware’s two
virtual switch types: the vSphere Standard Switch (VSS) and the vSphere Distributed Switch (VDS).
This document provides four configuration examples utilizing:
QLogic NPAR with a VMware VSS
VMware VSS with traffic shaping and NPAR
VMware VDS with traffic shaping and NPAR
VMware VDS with VM network resource pools and NPAR
Note: The QLogic BCM57800 series network adapter’s bandwidth allocation fields take precedence over
any VSS or VDS traffic shaping settings.
4 Network Partition (NPAR) Technology and VMware Virtual Switch comparison using QLogic BCM57800 | version 1.0
Page 5

2 QLogic BCM57800 Series NPAR with VMware’s VSS
QLogic’s NPAR technology helps simplify a data center’s network and storage infrastructure in two distinct
ways:
When using chassis-based blade servers that are limited to two or three PCIe slots, NPAR can
increase the uplink ports in VMware by a factor of eight
o Rack-based servers, which typically ship with up to eight PCIe slots, can supply enough
physical dual- or quad-port network adapters for uplink ports. Since VMware 6.0’s maximum
limitation per ESXi host of uplink ports is sixteen 10GbE ports and four 1GbE ports, NPAR is
not needed
When implementing bandwidth management, QLogic’s BCM57800 series network adapters have an
easy-to-use, transmit-based global bandwidth allocation configuration menu
QLogic’s NPAR technology also offers the following benefits:
Support for up to eight partitions per CNA and up to four partitions per CNA port
Support for monolithic operating systems and hypervisors—Microsoft Windows, Linux, and VMware
operating systems (OS)
No OS or BIOS changes required
Pre-OS operations for boot from SAN or PXE
Agnostic switch support for industry-standard 10 Gigabit Ethernet (10 GbE) switches
NIC control of the transmit flow rate from the server
Flexible and dynamic bandwidth allocation
Comprehensive support for standard network offload technologies including:
• Large send offload
• TCP/IP and TCP/UDP
• TCP checksum offload
• Receive-side scaling
• Transparent Packet Aggregation (TPA)
Support for the TCP/IP Offload Engine (TOE) and Internet SCSI (iSCSI) host bus adapters (HBAs).
Support for Fibre Channel over Ethernet (FCoE)
5 Network Partition (NPAR) Technology and VMware Virtual Switch comparison using QLogic BCM57800 | version 1.0
Page 6
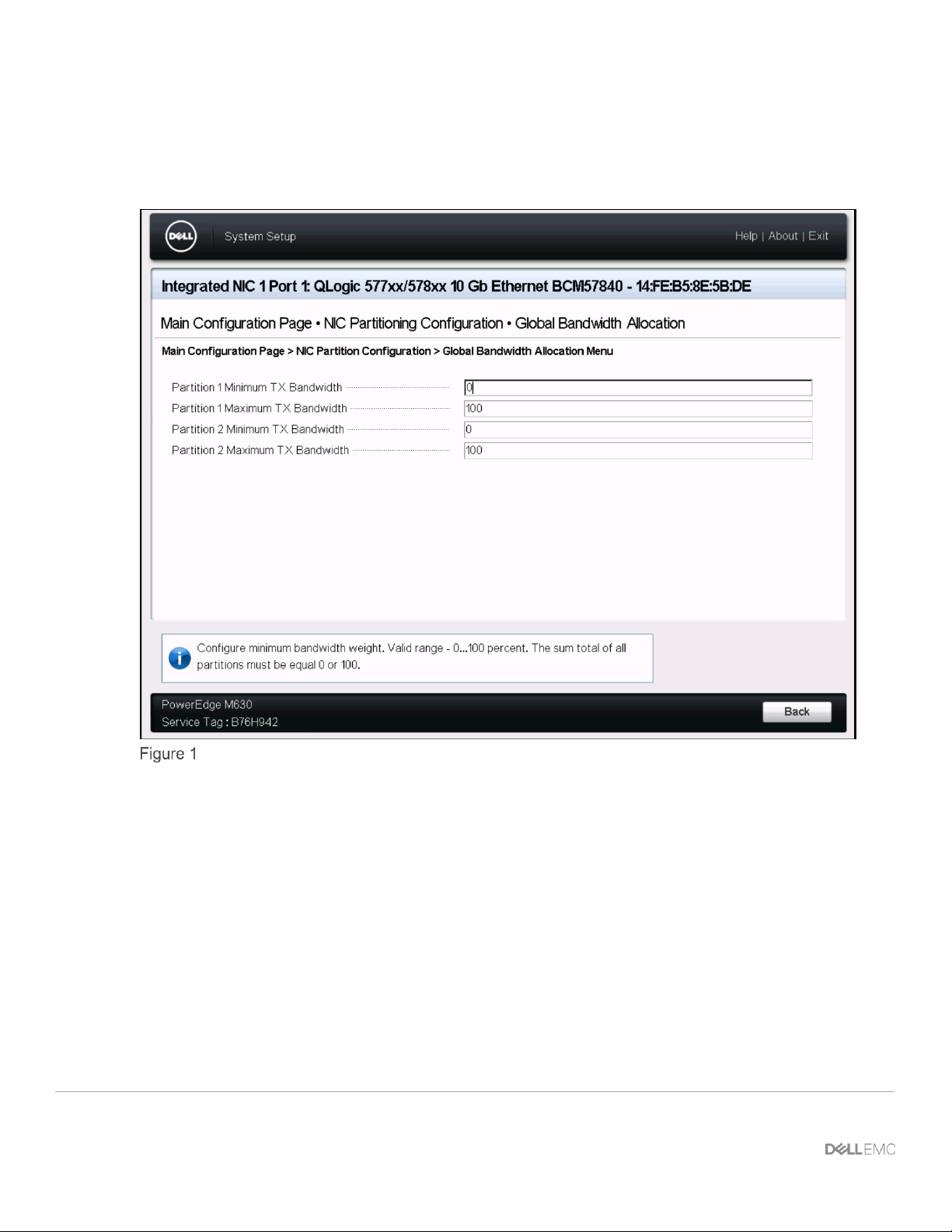
The QLogic BCM57840 network adapter provisioning in Figure 1 provides for no minimum traffic shaping
restrictions and full availability of the transmitted (TX) bandwidth. Administrators can tune these minimum and
maximum bandwidth allocation percentages after they know the I/O profile of the application using these NIC
partitions.
QLogic BCM57840 bandwidth allocation menu
6 Network Partition (NPAR) Technology and VMware Virtual Switch comparison using QLogic BCM57800 | version 1.0
Page 7
QLogic BCM57800 Series NPAR characteristics
PROs
CONs
Ease of use
Unable to adjust bandwidth allocation
within VMware ESXi
Reduced network cabling
Teaming support only available between
partitions of separate physical ports
Switch agnostic
Bandwidth allocation for TX traffic only
Up to 8 NPAR partitions per network
adapter
NPAR technology can only be enabled
per adapter not per port of the same
adapter
Superior solution for servers with limited
PCIe slots (ex. Blade servers)
Can be confusing if a server with a large
number of PCIe slots has NPAR enabled
on multiple adapters
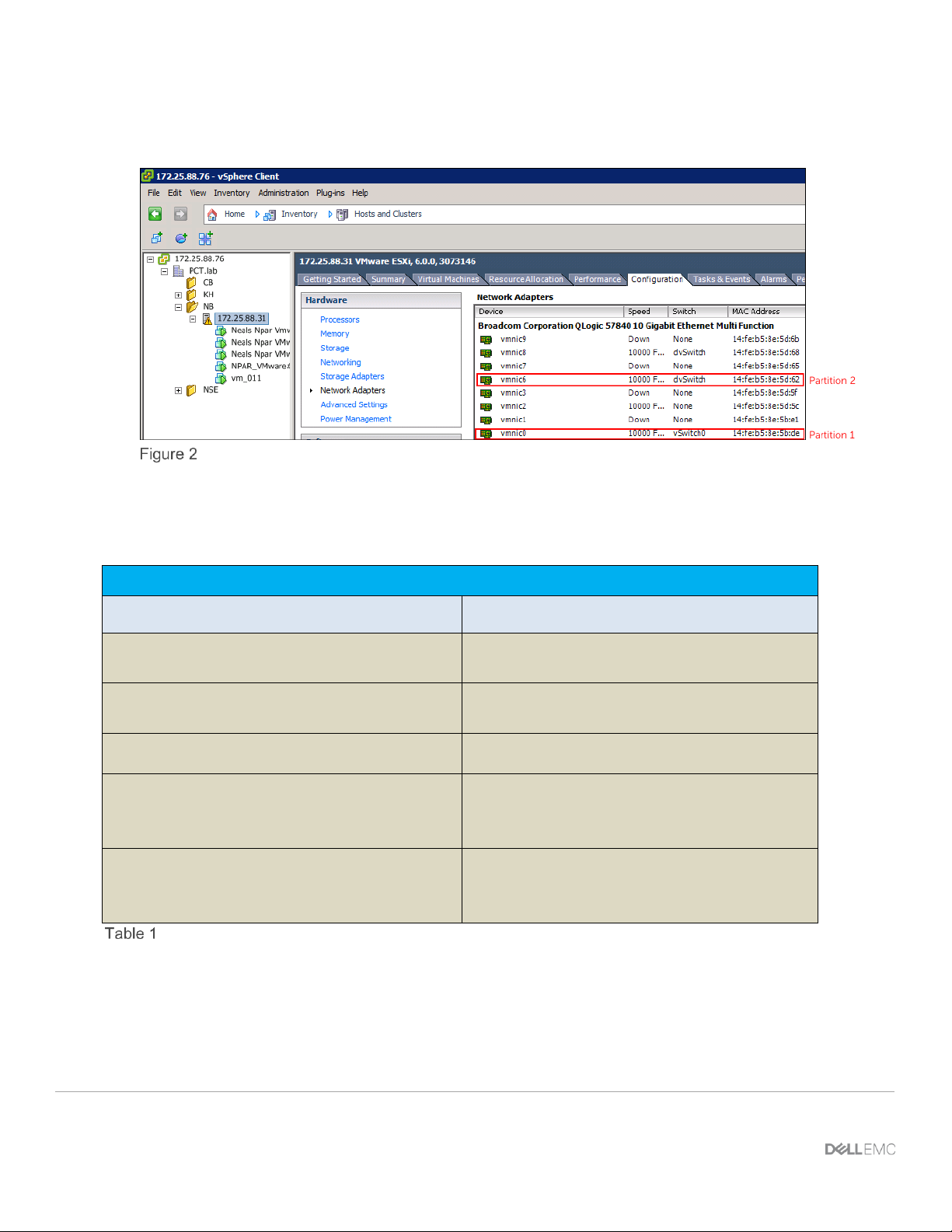
Figure 2 identifies the BCM57840 NPAR partitions 1 and 2 for port 1 assigned to the VMware ESXi host’s
VSS and VDS networking functions.
VMware Vmnic partition identification
Table 1 lists the pros and cons of the QLogic BCM57840 NPAR technology:
QLogic BCM57800 Series NPAR characteristics
7 Network Partition (NPAR) Technology and VMware Virtual Switch comparison using QLogic BCM57800 | version 1.0
Page 8

3 VMware’s VSS with traffic shaping
VMware’s VSS traffic shaping is allowed on outbound traffic from a VM, VMkernel port, or VSS port group.
The VMware vSphere client labels this “ingress/RX traffic” since it refers to data being transmitted to the VSS
from virtual devices. VSS traffic shaping includes three configurable settings per port group.
Average Bandwidth (Kbps) – sets an upper limit on how much data the port can transmit.
Peak Bandwidth (Kbps) – specified in Kbits/sec, allows the port to exceed the upper limit set by the
“Average Bandwidth” field up to the value set in the “Burst Size” field.
Burst Size (KB) –ensures that the “Peak Bandwidth” values do not create unnecessary congestion.
The VSS traffic shaping “Average Bandwidth,” “Peak Bandwidth” and “Burst Size” fields allow administrators
to set limits in increments of 100Mbps for a 10GbE NIC. This 100Mbps granularity allows bandwidth
adjustments for production environments to better service mission-critical application network I/O needs.
Figure 3 shows a graphical representation of the relationship between average bandwidth, peak bandwidth
and burst size traffic shaping fields.
Average Bandwidth, Peak Bandwidth, and Burst Size traffic shaping fields
8 Network Partition (NPAR) Technology and VMware Virtual Switch comparison using QLogic BCM57800 | version 1.0
Page 9
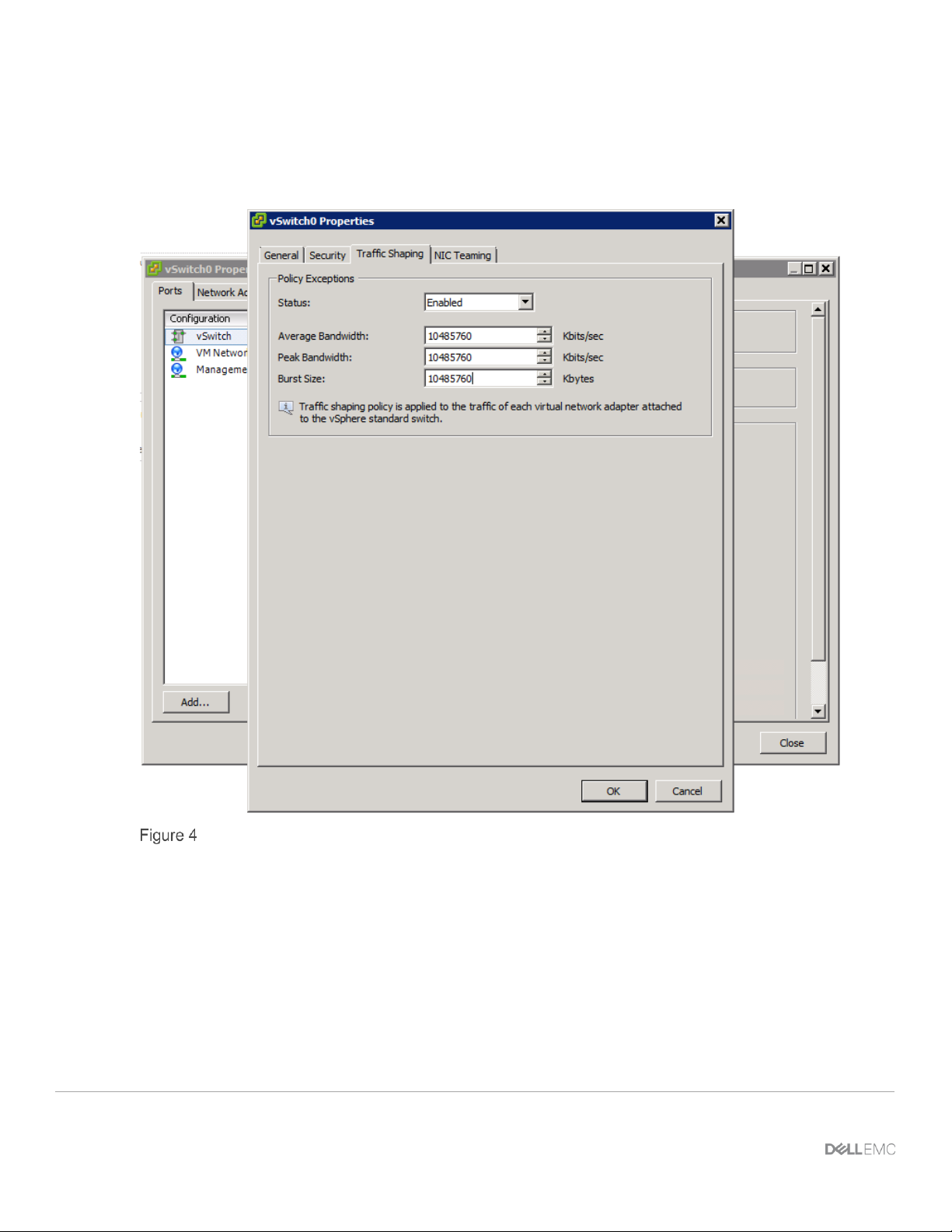
Figure 4 shows the VSS Traffic Shaping tab in VMware vSphere 6.0U1 with the status set to “enabled” and
the remaining three fields set to allow the maximum throughput of the network adapter. Adjust these fields in
production environments based on business needs after determining an I/O profile for the application(s)
utilizing the VM, VMkernel port or VSS port group.
VMware’s standard VSS traffic shaping policy
9 Network Partition (NPAR) Technology and VMware Virtual Switch comparison using QLogic BCM57800 | version 1.0
Page 10

VMware’s VSS traffic shaping characteristics
PROs
CONs
Able to adjust bandwidth allocation within
VMware vSphere
Bandwidth allocation for “ingress/RX”
VM/VMkernel traffic only
Able to change traffic shaping
parameters without rebooting ESXi host
Peak Bandwidth and Burst Size fields
difficult to understand
No VMware vSphere Enterprise Plus
license required
Additional NPAR complexity when
allocating uplinks to a VSS
Allows experienced VMware
administrators to manage traffic shaping
Table 2 lists the pros, and cons of the VMware VSS traffic shaping technology:
VMware VSS traffic shaping pros and cons
10 Network Partition (NPAR) Technology and VMware Virtual Switch comparison using QLogic BCM57800 | version 1.0
Page 11

4 VMware VDS with traffic shaping
VMs, VMkernel ports and VDS port groups support VMware VDS traffic shaping on outbound and inbound
traffic. VMware vSphere calls this “ingress or egress” traffic since it refers to the fact that data is being
transmitted to the VDS from virtual devices or from the VDS to virtual devices. Figure 5 shows a graphical
view of VMware vSphere’s “ingress and egress” traffic shaping model:
VMware egress and ingress traffic shaping view
Each dvportgroup includes the following three, configurable VDS traffic shaping settings:
Average Bandwidth – specified in Kbits/sec, sets an upper limit on how much data the port can
transmit.
Peak Bandwidth – specified in Kbits/sec, allows the port to exceed the upper limit set by the
“Average Bandwidth” field up to the value of “Burst Size.”
Burst Size – specified in Kbytes ensures that the “Peak Bandwidth” values do not create
unnecessary congestion.
The VDS traffic shaping “Average Bandwidth,” “Peak Bandwidth” and “Burst Size” fields allow administrators
to set limits in increments of 100Mbps for a 10GbE NIC. This 100Mbps granularity allows bandwidth
adjustments for production environments to better service mission-critical application network I/O needs.
11 Network Partition (NPAR) Technology and VMware Virtual Switch comparison using QLogic BCM57800 | version 1.0
Page 12

Figure 6 shows the VDS port group Traffic Shaping settings in VMware vSphere 6.0 with the top status set to
Enabled and the remaining three fields in each section configured to allow the maximum throughput possible.
Adjust these fields in production environments based on business needs after determining an I/O profile for
the application(s) utilizing the VM, VMkernel port or VDS port group.
VMware’s VDS Traffic Shaping Policy
12 Network Partition (NPAR) Technology and VMware Virtual Switch comparison using QLogic BCM57800 | version 1.0
Page 13

VMware’s VDS Traffic Shaping Characteristics
PROs
CONs
Able to adjust bandwidth allocation within
VMware vSphere ESXi
VMware vSphere Enterprise plus license
required
Able to change traffic shaping
parameters without rebooting ESXi host
Peak Bandwidth and Burst Size fields
difficult to understand
Bandwidth allocation for TX/RX
VM/VMkernel traffic
Additional complexity calculating TX/RX
traffic
Table 3 lists the pros and cons of the VMware VDS traffic shaping technology
VMware VDS traffic shaping pros and cons
13 Network Partition (NPAR) Technology and VMware Virtual Switch comparison using QLogic BCM57800 | version 1.0
Page 14

5 A VMware VDS with VM network resource pools
In VMware vSphere 6.0, Network I/O Control (NIOC) version 3 provides network resource pools to partition
network capacity during a resource contention event. These network resource pools provide predictable
networking performance while different network traffic streams contend for the same bandwidth. Following is
the list of the nine predefined system network-resource pools:
1. Fault Tolerance (FT) Traffic
2. Management Traffic
3. NFS Traffic
4. VM Traffic
5. Virtual SAN Traffic
6. iSCSI Traffic
7. vMotion Traffic
8. vSphere Data Protection Backup Traffic
9. vSphere Replication (VR) Traffic
NIOC guarantees traffic resource-pool bandwidth at the vNIC level. This allows vSphere administrators to
ensure that mission-critical VMs can effectively share the same upstream links.
VM traffic resource-pool configuration includes three editable options:
Shares: Shares, from 1 to 100, reflect the relative priority of a system traffic type against the other
system traffic types active on the same pNIC. Network I/O Resource Management totals up all the shares
and sets each in relation to the total. A system traffic type’s relative shares and the amount of data that
other system features transmit determine the traffic type’s available bandwidth. If a vNIC has a share
value of Normal (50 shares), that vNIC is not necessarily entitled to 50% of the bandwidth. Finally, unless
a congestion event is occurring on the vNIC that the traffic types are using, the Network I/O Resource
Management service allows other traffic types to use available bandwidth dynamically. Following are the
relative priorities indicated by the Shares option:
o High = 100
o Normal = 50
o Low = 25
o Custom = Any value between 1 and 100
Reservation: The minimum bandwidth, in Mbps, that must be guaranteed on a single physical adapter.
The total bandwidth reserved among all system traffic types cannot exceed 75 percent of the bandwidth
that the lowest capacity physical network adapter provides. For example, the Reservation value for a
10GbE network adapter is 7.5GbE.
Limit: The maximum bandwidth in Mbps or Gbps that a system traffic type can consume on a single
physical adapter.
Note: VM network resource pools only control outgoing traffic from the VM to the VDS.
14 Network Partition (NPAR) Technology and VMware Virtual Switch comparison using QLogic BCM57800 | version 1.0
Page 15
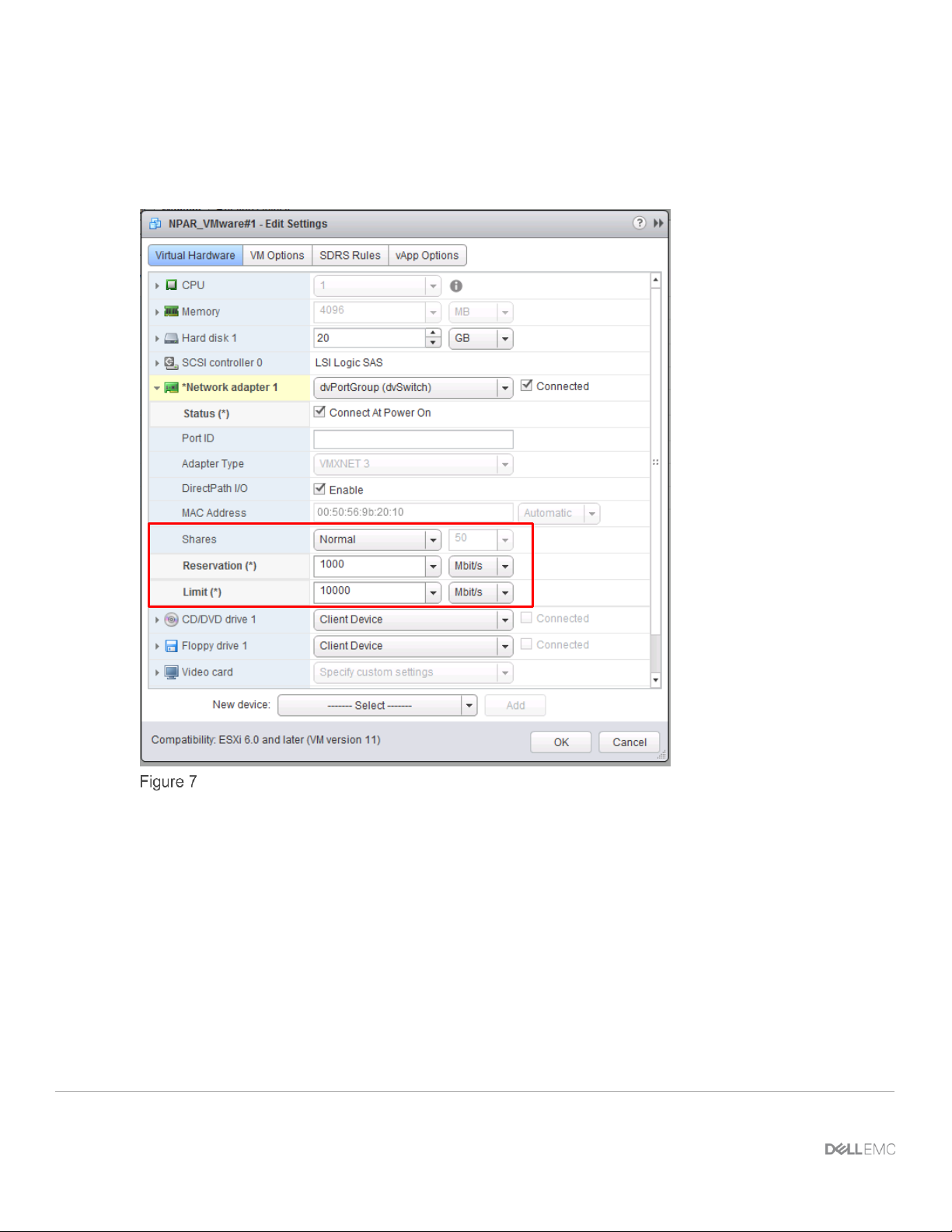
Figure 7 shows a Normal Share value of 50, a Reservation value of 1000Mbit/s (1GbE) and a Limit value of
10000 Mbit/s (10GbE). Based on the mission-criticality of virtual machines and their applications,
administrators can adjust these values to a Share value of High (100 shares), as well as increasing the
Reservation and Limit values.
VM Network Resource Pool Configuration
15 Network Partition (NPAR) Technology and VMware Virtual Switch comparison using QLogic BCM57800 | version 1.0
Page 16

6 Conclusion
Dell EMC’s standards-based NPAR technology in VMware’s vSphere ESXi 6.0 hypervisor provides the
opportunity to engineer bandwidth on a granular basis. This allows any enterprise to customize their network
to meet their traffic needs. Traffic shaping customization, along with a detailed I/O profile study, ensures that
administrators proactively address all aspects of bandwidth allocation rather than responding to them
reactively. This application note shows that, yes, NPAR adds another level of complexity to the initial
configuration and management of Dell blade servers. However, NPAR also allows the administrator to add
more uplink ports to the OS without requiring a server to have more PCIe slots. This can lower a data center’s
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) immediately if more ports are needed but not bandwidth. NPAR also can
increase Return on Investment (ROI), leveraging the advantages of Dell blade servers, including:
Scalable, flexible networking
Increased I/O control
Highly efficient shared-infrastructure solutions
16 Network Partition (NPAR) Technology and VMware Virtual Switch comparison using QLogic BCM57800 | version 1.0
Page 17
Component
Description/Firmware Versions
PowerEdge M1000e chassis
Chassis Management Controller (CMC) Firmware
4.5.A00
CMC Hardware Version
A03
Midplane Version
1.1
PowerEdge M630 Server
BIOS 1.2.5
QLogic BCM57800 Series Network Adapter
FW 7.12.17
A Component Revisions
Table 4 shows the hardware components and associated firmware revisions of the equipment used for the
examples in this document:
Components and Firmware Versions
17 Network Partition (NPAR) Technology and VMware Virtual Switch comparison using QLogic BCM57800 | version 1.0
Page 18

Support Contact Information
Web: http://Support.Dell.com/
Telephone: USA: 1-800-945-3355
B Additional Information
https://pubs.vmware.com/vsphere-60/topic/com.vmware.ICbase/PDF/vsphere-esxi-vcenter-server-60networking-guide.pdf
http://www.pearsonitcertification.com/articles/article.aspx?p=2190191&seqNum=7
http://kb.vmware.com/selfservice/microsites/search.do?language=en_US&cmd=displayKC&externalId=10225
85
http://www.virten.net/2015/09/vcp6-delta-part-7-network-enhancements/#Bandwidth-Allocation-for-Virtual-
Machine-Traffic
http://frankdenneman.nl/2013/01/17/a-primer-on-network-io-control/
Support and Feedback
Contacting Technical Support
Feedback for this document
We encourage readers of this publication to provide feedback on the quality and usefulness of this Application
Note by sending an email to Dell_Networking_Solutions@Dell.com
18 Network Partition (NPAR) Technology and VMware Virtual Switch comparison using QLogic BCM57800 | version 1.0
 Loading...
Loading...