Page 1
53-1002576-02
53-1002576-02
December 2012
Brocade M6505 16 Gbps
Fibre Channel SAN I/O Module
Hardware Reference Manual
®
Page 2
Copyright © 2012 Brocade Communications Systems, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Brocade, Brocade Assurance, the B-wing symbol, BigIron, DCX, Fabric OS, FastIron, MLX, NetIron, SAN Health, ServerIron,
urboIron, VCS, and VDX are registered trademarks, and AnyIO, Brocade One, CloudPlex, Effortless Networking, ICX, NET Health,
T
OpenScript, and The Effortless Network are trademarks of Brocade Communications Systems, Inc., in the United States and/or in
other countries. Other brands, products, or service names mentioned may be trademarks of their respective owners.
Notice: This document is for informational purposes only and does not set f
any equipment, equipment feature, or service offered or to be offered by Brocade. Brocade reserves the right to make changes to
this document at any time, without notice, and assumes no responsibility for its use. This informational document describes
features that may not be currently available. Contact a Brocade sales office for information on feature and product availability.
Export of technical data contained in this document may require an export license from the United States government.
The authors and Brocade Communications Systems, Inc. shall have no liability or responsibility to any person or entity with
ct to any loss, cost, liability, or damages arising from the information contained in this book or the computer programs that
respe
accompany it.
The product described by this document may co
open source license agreements. To find out which open source software is included in Brocade products, view the licensing
terms applicable to the open source software, and obtain a copy of the programming source code, please visit
http://www.brocade.com/support/oscd.
ntain “open source” software covered by the GNU General Public License or other
orth any warranty, expressed or implied, concerning
Brocade Communications Systems, Incorporated
Corporate and Latin American Headquarters
Brocade Communications Systems, Inc.
130 Holger Way
San Jose, CA 95134
Tel: 1-408-333-8000
Fax: 1-408-333-8101
E-mail: info@brocade.com
European Headquarters
Brocade Communications Switzerland Sàrl
Centre Swissair
Tour B - 4ème étage
29, Route de l'Aéroport
Case Postale 105
CH-1215 Genève 15
Switzerland
Tel: +41 22 799 5640
Fax: +41 22 799 5641
E-mail: emea-info@brocade.com
Asia-Pacific Headquarters
Brocade Communications Systems China HK, Ltd.
No. 1 Guanghua Road
Chao Yang District
Units 2718 and 2818
Beijing 100020, China
Tel: +8610 6588 8888
Fax: +8610 6588 9999
E-mail: china-info@brocade.com
Asia-Pacific Headquarters
Brocade Communications Systems Co., Ltd. (Shenzhen WFOE)
Citic Plaza
No. 233 Tian He Road North
Unit 1308 – 13th Floor
Guangzhou, China
Tel: +8620 3891 2000
Fax: +8620 3891 2111
E-mail: china-info@brocade.com
Document History
Title Publication number Summary of changes Date
Brocade M6505 16 Gbps Fibre Channel
SAN I/O Module Hardware Reference
Manual
Brocade M6505 16 Gbps Fibre Channel
SAN I/O Module Hardware Reference
Manual
53-1002576-01 New document December 2012
53-1002576-02 Update Data Transmission
Ranges table
December 2012
Page 3

Contents
About This Document
In this chapter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . vii
How this document is organized . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . vii
Document conventions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . viii
Text formatting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . viii
Command syntax conventions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . viii
Notes, cautions, and warnings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ix
Key terms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .ix
Notice to the reader . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ix
Additional information. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . x
Brocade resources. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . x
Other industry resources. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . x
Product support documents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . x
Getting technical help. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xi
Document feedback . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xii
Chapter 1 Brocade M6505 Product Overview
In this chapter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
SAN I/O Module overview. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Operating system support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Hardware features and functionality . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Software features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Optional features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Ports on Demand . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
ISL trunking groups. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Access Gateway and Native Fabric modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Access Gateway mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Native Fabric mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Optional Brocade licenses . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Hardware description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
SAN I/O Module front panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
SAN I/O Module side view. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
SFP+ transceivers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Brocade M6505 16 Gbps Fibre Channel SAN I/O Module Hardware Reference Manual iii
53-1002576-02
Page 4

Chapter 2 Installing the SAN I/O Module
Unpacking the SAN I/O Module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Items included with the SAN I/O Module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
System reliability guidelines. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
Handling static-sensitive devices. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
Preparing the Blade Server Enclosure for the SAN I/O Module. . . .12
Inserting the SAN I/O Module in the Blade Server Enclosure . . . . .13
Handling SFP+ transceivers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Inserting an SFP+ transceiver in the SAN I/O Module port . . . . . . . 15
Cabling guidelines. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Data transmission ranges . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Chapter 3 Configuring the SAN I/O Module
In this chapter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .19
Items required . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .19
Modifying the SAN I/O Module IP address . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20
Using the CMC GUI to set the IP address. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20
Using the CMC CLI to set the IP address . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21
Using the SAN I/O Module CLI to set the IP address. . . . . . . . .22
Connecting the SAN I/O Module to the Ethernet network . . . . . . . . 24
Connecting to the SAN I/O Module using Web Tools . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Connecting the SAN I/O Module to the fabric. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Chapter 4 Operating the SAN I/O Module
In this chapter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .29
Interoperability . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .29
Activating Ports on Demand. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .30
Activating ports with a POD license . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .30
Changing from Access Gateway mode to Native Fabric mode. . . . . 31
Disabling Access Gateway mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .32
Changing from Native Fabric mode to Access Gateway mode. . . . .33
Access Gateway mode default port mapping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Accessing the SAN I/O Module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Interpreting POST results . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .34
Interpreting SAN I/O Module LED activity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .35
Power-on self-test LEDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Normal-operation LEDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .36
Removing and replacing SAN I/O Modules . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .37
Removing and replacing SFP+ transceivers and cables . . . . . . . . .39
iv Brocade M6505 16 Gbps Fibre Channel SAN I/O Module Hardware Reference Manual
53-1002576-02
Page 5

Switch management . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .40
Viewing the configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .40
Upgrading or downgrading firmware . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Changing the default account password. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Changing the default account password at login . . . . . . . . . . .42
Backing up the configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
Locating the serial number information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .43
Appendix A SAN I/O Module Specifications
In this appendix. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Processor and memory specifications. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .45
Weight and physical dimensions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .45
Environmental specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Electrical specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .46
Architectural specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Supported HBAs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Fibre Channel standards compliance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Regulatory compliance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
FCC warning (US only) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
BSMI statement (Taiwan) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
KC statement (Republic of Korea) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
VCCI statement (Japan) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .48
CE statement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .48
Canadian requirements. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Laser compliance. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .49
RTC battery. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .49
Regulatory compliance standards . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .49
Environmental regulation compliance. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .50
Environmental Protection Use Period (EPUP) Disclaimer . . . . . 50
China RoHS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .50
Index
Brocade M6505 16 Gbps Fibre Channel SAN I/O Module Hardware Reference Manual v
53-1002576-02
Page 6

vi Brocade M6505 16 Gbps Fibre Channel SAN I/O Module Hardware Reference Manual
53-1002576-02
Page 7

About This Document
In this chapter
•How this document is organized . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . vii
•Document conventions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . viii
•Notice to the reader . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ix
•Additional information. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . x
•Getting technical help . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xi
•Document feedback . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xii
How this document is organized
This document is organized to help you find information that you want as quickly and easily as
possible. The document contains the following components:
• Chapter 1, “Brocade M6505 Product Overview,”describes the Brocade M6505 16 Gbps Fibre
Channel SAN I/O Module and explains its basic concepts and features. This chapter also
provides instructions for unpacking the SAN I/O Module from its shipping container, references
to the appropriate publication for installing the SAN I/O Module into the Dell M1000e Blade
Server Enclosure, and Fibre Channel port cabling guidelines.
• Chapter 2, “Installing the SAN I/O Module,” describes the procedures needed to unpack and
install the Brocade M6505 16 Gbps Fibre Channel SAN I/O Module for the Dell M1000e Blade
Server Enclosure.
• Chapter 3, “Configuring the SAN I/O Module,” describes how to change the IP address of the
Brocade M6505 16 Gbps Fibre Channel SAN I/O Module, connect the module to the Ethernet
network and fabric, and connect to the Brocade M6505 16 Gbps Fibre Channel SAN I/O
Module using Web Tools.
• Chapter 4, “Operating the SAN I/O Module,” is a reference for understanding the power-on
diagnostics and LEDs supporting the Brocade M6505 16 Gbps Fibre Channel SAN I/O Module.
Also provided are details for operating and replacing the Brocade M6505 16 Gbps Fibre
Channel SAN I/O Module, removing and replacing SFP+ transceivers and cables, changing
between Access Gateway mode and Native Fabric mode, activating Ports on Demand (POD),
backing up the system, maintaining firmware, changing passwords, locating serial number
information, and viewing configurations.
• Appendix A, “SAN I/O Module Specifications,” provides product specifications and regulatory
compliance information.
Brocade M6505 16 Gbps Fibre Channel SAN I/O Module Hardware Reference Manual vii
53-1002576-02
Page 8

Document conventions
This section describes text formatting conventions and important notice formats used in this
document.
Text formatting
The narrative-text formatting conventions that are used are as follows:
bold text Identifies command names
italic text Provides emphasis
code text Identifies CLI output
For readability, command names in the narrative portions of this guide are presented in mixed
lettercase: for example, switchShow. In actual examples, command lettercase is all lowercase.
Identifies the names of user-manipulated GUI elements
Identifies keywords and operands
Identifies text to enter at the GUI or CLI
Identifies variables
Identifies paths and Internet addresses
Identifies document titles
Identifies command syntax examples
Command syntax conventions
Command syntax in this manual follows these conventions:
command Commands are printed in bold.
--option, option Command options are printed in bold.
-argument, arg Arguments.
[ ] Optional elements appear in brackets.
variable Variables are printed in italics. In the help pages, values are underlined
enclosed in angled brackets < >.
...
value Fixed values following arguments are printed in plain font. For example,
| Boolean. Elements are exclusive. Example:
Repeat the previous element, for example “member[;member...]”
--show WWN
--show -mode egress | ingress
or
viii Brocade M6505 16 Gbps Fibre Channel SAN I/O Module Hardware Reference Manual
53-1002576-02
Page 9

Notes, cautions, and warnings
NOTE
ATTENTION
CAUTION
DANGER
The following notices and statements are used in this manual. They are listed below in order of
increasing severity of potential hazards.
A note provides a tip, guidance, or advice, emphasizes important information, or provides a
reference to related information.
An Attention statement indicates potential damage to hardware or data.
A Caution statement alerts you to situations that can be potentially hazardous to you or cause
damage to hardware, firmware, software, or data.
A Danger statement indicates conditions or situations that can be potentially lethal or extremely
hazardous to you. Safety labels are also attached directly to products to warn of these conditions
or situations.
Key terms
For definitions specific to Brocade and Fibre Channel, see the technical glossaries on MyBrocade.
See
“Brocade resources” on page x for instructions on accessing MyBrocade.
For definitions of SAN-specific terms, visit the Storage Networking Industry Association online
dictionary at:
http://www.snia.org/education/dictionary
Notice to the reader
This document may contain references to the trademarks of the following corporations. These
trademarks are the properties of their respective companies and corporations.
These references are made for informational purposes only.
Corporation Referenced trademarks and products
Cisco Systems Cisco
Dell, Inc. PowerEdge
Microsoft Corporation Windows, Windows 2003, Windows 2008, Windows XP
Red Hat Inc. Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL)
Brocade M6505 16 Gbps Fibre Channel SAN I/O Module Hardware Reference Manual ix
53-1002576-02
Page 10

Corporation Referenced trademarks and products
The Open Group UNIX
VMware SUSE Linux Enterprise Server (SLES)
XenServer XEN 6.0
Additional information
This section lists additional Brocade and industry-specific documentation that you might find
helpful.
Brocade resources
To get up-to-the-minute information, go to http://my.brocade.com to register at no cost for a user ID
and password.
White papers, online demonstrations, and data sheets are available through the Brocade web site
at:
http://www.brocade.com/products-solutions/products/index.page
For additional Brocade documentation, visit the Brocade web site:
http://www.brocade.com
Release notes are available on the Brocade Connect Web site and are also bundled with the
Fabric
OS firmware.
Other industry resources
For additional resource information, visit the Technical Committee T11 web site. This web site
provides interface standards for high-performance and mass storage applications for Fibre
Channel, storage management, as well as other applications:
http://www.t11.org
For information about the Fibre Channel industry, visit the Fibre Channel Industry Association web
site:
http://www.fibrechannel.org
Product support documents
The following documentation is available from Dell.
• Dell PowerEdge M1000e Enclosure Owner’s Manual
• Dell Chassis Management Controller Firmware Version 4.x User Guide
The following support documentation is provided on the Brocade web site.
• Fabric OS Administrator’s Guide
• Fabric OS Command Reference
x Brocade M6505 16 Gbps Fibre Channel SAN I/O Module Hardware Reference Manual
53-1002576-02
Page 11

• Fabric OS MIB Reference
NOTE
• Fabric OS Message Reference
• Access Gateway Administrator’s Guide
• SAN TECH NOTE - Preparing to Install the Brocade Access Gateway
• Web Tools Administrator’s Guide
• Fabric Watch Administrator’s Guide
• Brocade M6505 16 Gbps Fibre Channel SAN I/O Module QuickStart Guide
• Release notes for the Fabric OS version running on the SAN I/O Module
• Release notes specific to the SAN I/O Module
Refer to the latest documentation version for the most up-to-date product information.
Getting technical help
Contact your switch support supplier for hardware, firmware, and software support, including
product repairs and part ordering. To expedite your call, have the following information available:
1. General Information
• Dell service tag (listed by the CMC)
• Switch model
• Switch operating system version
• Software name and software version, if applicable
• Error numbers and messages received
• supportSave command output
• Detailed description of the problem, including the switch or fabric behavior immediately
following the problem, and specific questions
• Description of any troubleshooting steps already performed and the results
• Serial console and Telnet session logs
• Syslog message logs
2. Switch serial number
The switch serial number and corresponding bar code are provided on the serial number label,
for example:
FT00X0054E9
FT00X0054E9
3. World Wide Name (WWN).
Use the wwn or switchShow commands to display the WWN.
4. Software licenses. Use the licenseIdShow command to display the list of licenses and
corresponding license IDs available on the unit.
Brocade M6505 16 Gbps Fibre Channel SAN I/O Module Hardware Reference Manual xi
53-1002576-02
Page 12

Document feedback
Quality is our first concern at Brocade and we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and
completeness of this document. However, if you find an error or an omission, or you think that a
topic needs further development, we want to hear from you. Forward your feedback to:
documentation@brocade.com
Provide the title and version number of the document, and as much detail as possible about your
comment, including the topic heading and page number and your suggestions for improvement.
xii Brocade M6505 16 Gbps Fibre Channel SAN I/O Module Hardware Reference Manual
53-1002576-02
Page 13

Chapter
NOTE
Brocade M6505 Product Overview
In this chapter
•SAN I/O Module overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
•Operating system support. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
•Hardware features and functionality . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
•Software features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
•Ports on Demand. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
•ISL trunking groups . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
•Access Gateway and Native Fabric modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
•Optional Brocade licenses . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
•Hardware description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
•SFP+ transceivers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
1
SAN I/O Module overview
The Brocade M6505 16 Gbps Fibre Channel SAN I/O Module is a nonblocking, embedded switch
with up to 8 external-facing Fibre Channel ports and up to 16 internal-facing Fibre Channel ports
that is custom built for the Dell PowerEdge M1000e Blade Server Enclosure. Although the product
may ship with a specific number of ports enabled, it can be upgraded to 24
on Demand (POD) license.
The Brocade M6505 16 Gbps Fibre Channel SAN I/O Module is also referred to as the SAN I/O
Module throughout this document.
The eight external ports of the Brocade M6505 16 Gbps Fibre Channel SAN I/O Module support
hot-pluggable Small Form Factor Pluggable plus (SFP+) optical transceivers. Only Brocade-branded
optical transceivers are supported.
Each external port is independently capable of supporting speeds of 16, 8, and 4 Gbps using
auto-sensing. Internal ports support speeds of 16 and 8 Gbps. The switch module operates in
either Brocade Access Gateway (AG) or Native Fabric (full-fabric switch) mode. The default mode is
AG, which utilizes NPIV for direct connectivity to Brocade, Cisco and/or McData SANs.
ports through a Ports
Brocade M6505 16 Gbps Fibre Channel SAN I/O Module Hardware Reference Manual 1
53-1002576-02
Page 14

Operating system support
1
Operating system support
Brocade Fabric OS has no specific host operating system (OS) dependencies. The Fabric OS in the
switches allows for any Fibre Channel-compliant device to attach to switches as long as it conforms
to the standards for device login, name service, and related Fibre Channel features.
The operating systems listed in Table 1 are for the host machine running Brocade management
applications outside the Fabric OS, such as Brocade Network Advisor (BNA). For the latest
information on operating system support for these applications, refer to the latest released
versions of BNA documentation.
TABLE 1 Supported operating systems for management server
Operating system Description
Microsoft • Windows 2003 SP1, 64-bit (Standard, Enterprise and Web)
Linux
VMWare VMWare ESX 4.0 (U2)
XenServer XEN 6.0
• Windows 2008 64-bit (Standard, Enterprise and Web)
• Windows Server 2008 Hyper-V R2
• Red Hat Enterprise Linux (EL) 5.5 32/64-bit (Standard and Advanced platform)
• SUSE Linux ES 11 (SP1 32/64-bit)
Hardware features and functionality
The SAN I/O Module ships in Access Gateway mode. It provides support for the following hardware
features and functionality:
• Twelve to 24 auto-negotiating Fibre Channel (FC) ports
• Diagnostic ports
• Up to eight small form-factor pluggable plus (SFP+) optical transceivers supporting speeds of
16
Gbps, 8 Gbps and 4 Gbps
• System LEDs noting system power, switch status, and management health status
• One RJ-45 connector for serial console management
• Hot pluggable—Up to 4 hot-pluggable SAN I/O Modules per Dell M1000e Blade Server
Enclosure chassis
• Runtime elements that include health monitoring, uptime, memory information, CPU usage,
user information, power, and licenses
• Two internal 100 Mbps full-duplex Ethernet ports to connect to the redundant Dell M1000e
Chassis Management Controllers (CMCs)
• One serial console port on the front panel.
2 Brocade M6505 16 Gbps Fibre Channel SAN I/O Module Hardware Reference Manual
53-1002576-02
Page 15

Software features
The Brocade M6505 16 Gbps Fibre Channel SAN I/O Module supports the following software
features. For updates to the supported feature set, refer to the Brocade Fabric OS Administrator’s
Guide and product release notes for additional information.
• Access Gateway (AG) mode and Native Fabric mode. (Refer to “Access Gateway and Native
Fabric modes” on page 5.)
The SAN I/O Module ships in Access Gateway mode, but it can support the standard Native
Fabric (Switch) mode. For detailed information about AG, refer to the Brocade Access Gateway
Administrator’s Guide.
• Brocade Fabric OS (FOS), which delivers distributed intelligence throughout the network and
enables a wide range of value-added applications, such as Brocade Advanced Web Tools and
Brocade Advanced Fabric Services (on certain models)
• Dynamic Ports on Demand (DPOD) offering the flexibility to scale from 12 ports on the
Base
• Inter-Switch Link (ISL) Trunking (licensable), which allows up to eight ports (at 16, 8, or 4 Gbps
speeds) to combine to form a single, logical ISL with a speed of up to 128 Gbps (each
direction, full duplex) for optimal bandwidth utilization, automatic path failover, and load
balancing.
• Enhanced Group Management, which enables the SAN I/O Module to be managed as a group
• Detection and resolution of duplicate WWNs
• Dell DMC, iDRAC, and CMC management
• Dual and redundant firmware images
• Service levels Class 2, Class 3, and Class F (inter-switch frames)
• Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) for managing user-permission levels
• Advanced zoning, which enables you to partition your storage area network (SAN) into logical
groups of devices that can access each other
• Zoning enhancements that allow a switch with the default zone “no access” to merge with a
fabric
• Buffer credit loss detection and automatic recovery on 16 Gbps ISLs
• Importing and exporting of configuration information, including port speeds and zoning
information
• Port mirroring to monitor ingress or egress traffic from any port within the switch
• SNMP v1, v2c, and v3. (SNMP traps log errors and alarms; logs can be exported)
• TACACS+ and RADIUS remote authentication for switch management access
• IPv4 support
• AG enhancements, such as detection of unreliable N_Port links, RADIUS and LDAP support,
Advanced Performance Monitoring (APM) capability, and F_Port static mapping
• Forward error correction (FEC), which provides method error control during data transmission
by sending redundant data to ensure error-free transmission on a specified port or port range
(enabled by default)
• IP address filtering for management access by way of Telnet, HTTP, HTTPS/SSL, SSH v2, and
SNMP
model up to 24 ports
Software features
1
Brocade M6505 16 Gbps Fibre Channel SAN I/O Module Hardware Reference Manual 3
53-1002576-02
Page 16

Ports on Demand
NOTE
1
• SNMP/MIB monitoring functionality contained within the Ethernet Control MIB-II
(RFC1213-MIB)
• NTP client support (NTP V3)
• FTP support for firmware upgrades
• End-to-end optics and link validation
• Registered State Change Notification (RSCN), which notifies a device of a change within the
fabric
• Switch banner support
• Syslog remote logging capabilities
• RASlogs to indicate invalid traffic isolation zones
• Four RMON groups: history, statistics, alarms, and events
Optional features
The following optional features are available, depending on whether the SAN I/O Module is
configured in Access Gateway mode or Native Fabric mode. For detailed information on any of
these features, refer to the Brocade Fabric OS Administrator’s Guide. You can also refer to
“Optional Brocade licenses” on page 6 for additional information.
• Ports on Demand (POD) licensing
• Inter-Switch Link (ISL) Trunking
• Fabric Watch
• Advanced Performance Monitoring
• Adaptive Networking
Ports on Demand
Depending on the model, the SAN I/O Module ships with either 12 or 24 active ports.
With Dynamic Ports on Demand (DPOD), physical ports are licensed as they come online. In the
Base model port set, the first 12 ports reporting (on a first-come, first-served basis) on boot-up are
assigned licenses. In the Full and ENT model port sets, the first 24 ports reporting (on a first-come,
first-served basis) on boot-up are assigned licenses. These ports may be any combination of
external or internal Fibre Channel (FC) ports. After all licenses have been assigned, you can
manually move those licenses from one port to another.
Ports 17 and 18 are prereserved for external/SAN connectivity.
• Base model—Ships with 12 active ports. You can allocate an optional POD license to activate
the additional 12 ports.
• Full model—Ships with 24 active ports. No additional POD license is needed.
• ENT (Enterprise) model—Ships with 24 active ports. No additional POD license is needed.
4 Brocade M6505 16 Gbps Fibre Channel SAN I/O Module Hardware Reference Manual
53-1002576-02
Page 17
ISL trunking groups
NOTE
NOTE
If your SAN I/O Module has an optional Brocade ISL Trunking license, external ports can form
trunking groups of ISLs between adjacent switches. ISL Trunking optimizes the performance and
availability of SAN fabrics while simplifying ISL management.
All external ports (0, 17 through 23) can be formed into a single 8-port trunk, or any combination of
2- to 7-port trunk. For details about Brocade ISL Trunking, refer to the Fabric OS Administrator’s
Guide.
Only the external ports are available for trunking.
Access Gateway and Native Fabric modes
The SAN I/O Module can function in either Native Fabric mode or Brocade Access Gateway mode.
The SAN I/O Module is shipped in Access Gateway (AG) mode by default.
Access Gateway simplifies SAN deployment by using NPIV (N_Port ID Virtualization) technology.
AG
mode improves SAN I/O Module scalability, manageability, and interoperability. For more
information on Access Gateway, refer to the Brocade Access Gateway Administrator’s Guide.
ISL trunking groups
1
Access Gateway cannot be connected directly into a storage array unless one of the external ports
is connected to a SAN network.
Access Gateway mode
The SAN I/O Module provides support for the following when operating in AG mode:
• Up to 8 auto-sensing (4, 8, and 16 Gbps) Fibre Channel ports. These are universal and
self-configuring ports that are capable of becoming the following types:
- F_Port (fabric-enabled)
- N_Port (NPIV-enabled)
• Up to 16 internal backplane F_Ports. Each port can automatically negotiate its speed at either
16 Gbps or 8 Gbps to match the speed of attached devices
• Dynamic fabric provisioning that supports fabric-assigned WWNs
Brocade M6505 16 Gbps Fibre Channel SAN I/O Module Hardware Reference Manual 5
53-1002576-02
Page 18

Optional Brocade licenses
1
Native Fabric mode
Native Fabric mode can be accessed by disabling the default AG mode. Once the SAN I/O Module is
in Native Fabric mode, it provides support for the following:
• Up to 8 external auto-sensing and auto-negotiating (4, 8, or 16 Gbps) Fibre Channel ports.
These universal and self-configuring ports are capable of becoming one of the following port
types:
- E_Port (expansion port)
- F_Port (fabric-enabled)
- U_Port (self-discovery based on switch type)
These external ports are capable of ISL trunking with appropriate licensing.
• Frame filtering that augments the hardware zoning capabilities of the Brocade ASIC, which
implements hardware zoning at the port level of the SAN I/O Module.
• Brocade ASIC expanded capabilities, including World Wide Name (WWN) and device-level
zoning.
• Hardware zoning implemented by firmware-accessible table per output port.
• Zoning enhancements that allow a switch with the default zone “no access” to merge with a
fabric.
• Buffer credit loss detection and automatic recovery on ISLs.
Optional Brocade licenses
Tab le 2 lists optional licenses that are available for use on the Brocade M6505 16 Gbps Fibre
Channel SAN I/O Module.
TABLE 2 Optional supported features
License Description
Adaptive Networking A suite of tools and capabilities that optimize behavior in the SAN. Even
Advanced Performance Monitoring Enables more effective end-to-end SAN performance analysis to enhance
Fabric Watch Continuously monitors SAN fabrics for potential faults based on thresholds
ISL Trunking Optimizes the performance and availability of SAN fabrics while simplifying
Ports on Demand Allows you to obtain additional ports by way of license key upgrade.
under the worst congestion conditions, Adaptive Networking features can
maximize the fabric behavior and provide necessary bandwidth for
high-priority, mission-critical applications and connections.
performance tuning, increase productivity, optimize resource utilization,
and reduce costs.
set for a variety of SAN fabric elements and events, automatically alerting
administrators to potential problems before they become costly failures.
ISL management.
6 Brocade M6505 16 Gbps Fibre Channel SAN I/O Module Hardware Reference Manual
53-1002576-02
Page 19

Hardware description
This section describes the Brocade M6505 16 Gbps Fibre Channel SAN I/O Module as shipped
from the factory. For specifications, such as installed memory, weight and physical dimensions,
facility requirements, and architectural specifications, refer to
Specifications”.
SAN I/O Module front panel
All external ports and LEDs are accessible from the front panel of the Brocade M6505 16 Gbps
Fibre Channel SAN I/O Module. The front panel faces out when the SAN I/O Module is inserted in
the I/O
module bays B or C of the Dell M1000e Blade Server Enclosure. Each external port has a
dedicated LED that identifies port status and port diagnostics. For a complete description of the
locations and interpretations of the LEDs, refer to
page 35.
Figure 1 shows details of the front panel and includes the release lever. Pressing the release latch
to open the release lever enables you to insert and remove the SAN I/O Module in and out of the
Dell M1000e Blade Server Enclosure.
Hardware description
Appendix A, “SAN I/O Module
“Interpreting SAN I/O Module LED activity” on
1
Brocade M6505 16 Gbps Fibre Channel SAN I/O Module Hardware Reference Manual 7
53-1002576-02
Page 20
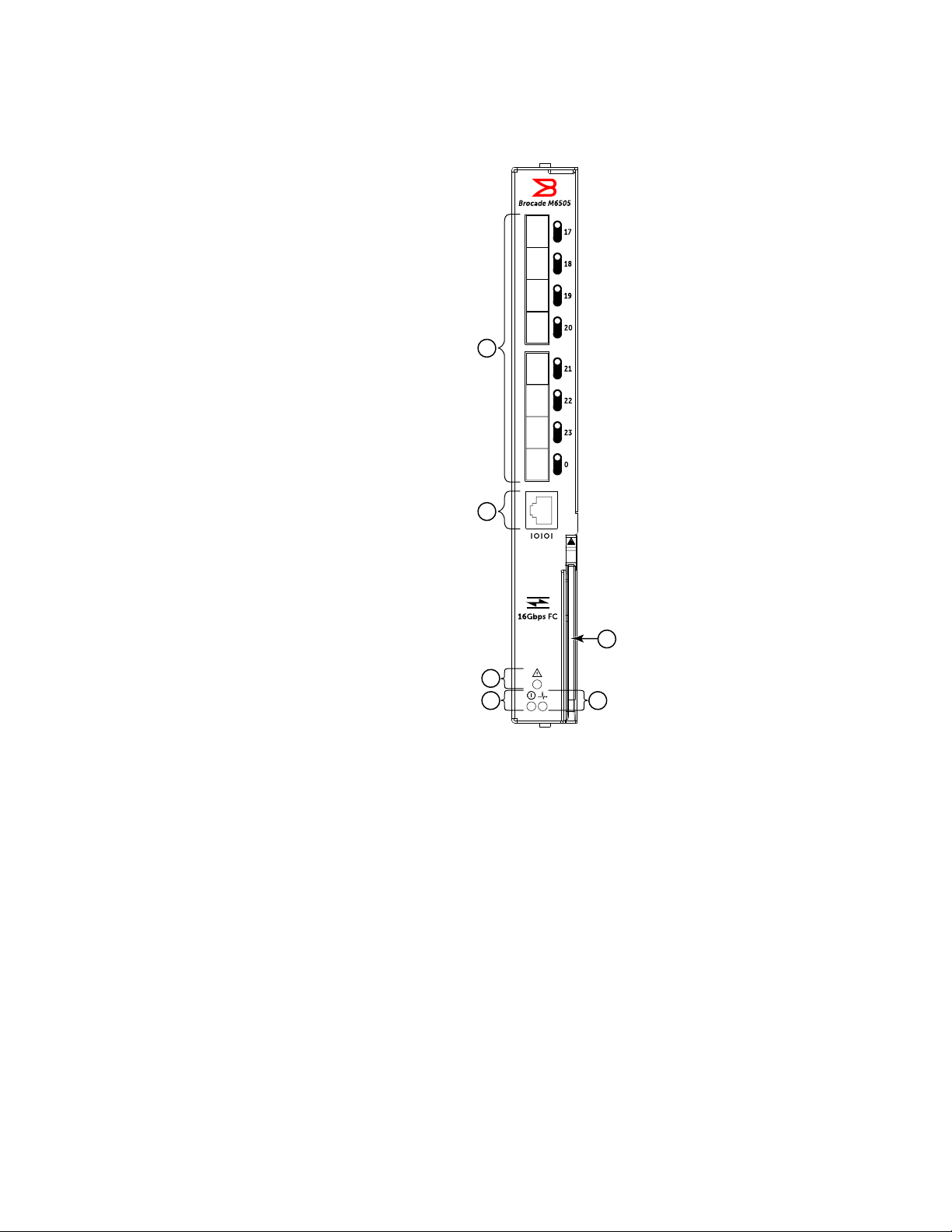
Hardware description
4
5
3
2
1
6
1
1 Ports with port status LEDs 4 Power status LED
2 RJ-45 console port 5 Server management status/indicator LED
3 SAN I/O Module status LED 6 SAN I/O Module release lever
FIGURE 1 Brocade M6505 16 Gbps Fibre Channel SAN I/O Module front panel
For more information on SAN I/O Module front panel LEDs, refer to “Interpreting SAN I/O Module
LED activity” on page 35.
8 Brocade M6505 16 Gbps Fibre Channel SAN I/O Module Hardware Reference Manual
53-1002576-02
Page 21
Hardware description
1
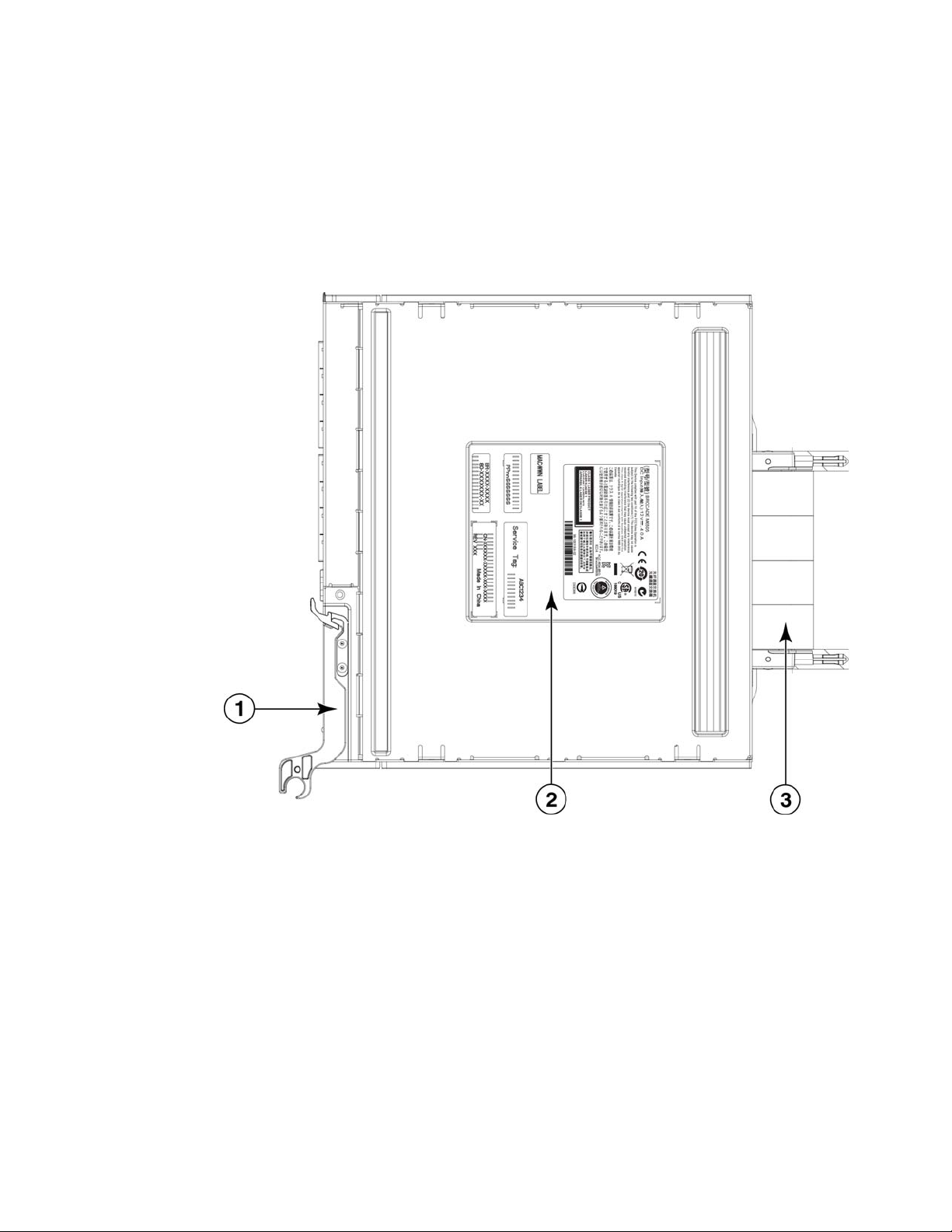
SAN I/O Module side view
The SAN I/O Module connects to the I/O module bay of the Dell M1000e Blade Server Enclosure by
way of the backplane connectors. (Refer to
the release lever is closed securely.
Once the SAN I/O Module is securely seated, the backplane connectors become active, allowing
the SAN I/O Module to be configured in the Dell M1000e Blade Server Enclosure.
Figures 2.) The SAN I/O Module seats correctly when
1Release lever
2 Product labels
3 Backplane connectors
FIGURE 2 SAN I/O Module side view
Brocade M6505 16 Gbps Fibre Channel SAN I/O Module Hardware Reference Manual 9
53-1002576-02
Page 22

SFP+ transceivers
NOTE
1
SFP+ transceivers
The SAN I/O Module is designed to work exclusively with Brocade-branded small form-factor
pluggable plus (SFP+) optical transceivers. The SFP+ transceivers are hot-swappable, thus allowing
for connection to external devices without removing the SAN I/O Module from the Dell M1000e
Blade Server Enclosure.
For information on inserting or removing SFP+ transceivers, refer to “Removing and replacing SAN
I/O Modules” on page 37.
SFP+ transceivers provide optical connections to external devices for both short wavelength (SWL)
and long wavelength (LWL) connections. You can replace SFP+ transceivers with a new pluggable
SFP+ transceiver rather than replacing the SAN I/O Module.
The SAN I/O Module is shipped with 16 Gbps Brocade-branded transceivers.
• Base model—Ships with two pre-installed SFP+ transceivers. Six additional SFP+ transceivers
can be installed.
• Full model—Ships with four pre-installed SFP+ transceivers. Four additional SFP+ transceivers
can be installed.
• ENT model—Ships fully loaded with eight pre-installed SFP+ transceivers.
You can also insert pre-qualified 8 Gbps SFP+ transceivers in the SAN I/O Module.
For a list of supported SFP+ transceivers on the SAN I/O Module, refer to Table 3 on page 15.
For a complete list of Brocade-branded SFP+ transceivers and other interoperable hardware, visit
the MyBrocade website at:
http://my.brocade.com
To register at MyBrocade, go to http://my.brocade.com/wps/portal/registration.
From the main page at my.brocade.com, select the Product Portfolio tab, then select Small
Form-Factor Pluggables (SFP) from the Filter by list box. Click Brocade Optical Transceiver Modules.
10 Brocade M6505 16 Gbps Fibre Channel SAN I/O Module Hardware Reference Manual
53-1002576-02
Page 23

Chapter
Installing the SAN I/O Module
In this chapter
•Unpacking the SAN I/O Module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
•Items included with the SAN I/O Module. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
•System reliability guidelines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
•Handling static-sensitive devices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
•Preparing the Blade Server Enclosure for the SAN I/O Module. . . . . . . . . . 12
•Inserting the SAN I/O Module in the Blade Server Enclosure . . . . . . . . . . . 13
•Handling SFP+ transceivers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
•Inserting an SFP+ transceiver in the SAN I/O Module port . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
•Cabling guidelines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
•Data transmission ranges. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
2
Unpacking the SAN I/O Module
Perform the following steps to remove the Brocade Product Name from its shipping package:
1. Open the shipping box and inspect the contents for damage.
2. Remove the foam layer that sits on top of the SAN I/O Module.
3. Remove the switch from the surrounding protective foam.
4. After ensuring that standard electrostatic discharge (ESD) precautions have been taken, slide
the SAN I/O Module from the antistatic sleeve.
Items included with the SAN I/O Module
• SFP+ transceivers: Each SAN I/O Module includes pre-installed SFP+ transceivers. The
number of pre-installed SFP+ transceivers varies based on the SAN I/O Module. The
transceivers can be activated directly out of the box.
- Base model: Two 16 Gbps SFP+ transceivers
- Full model: Four 16 Gbps SFP+ transceivers
- ENT (Enterprise) model: Eight 16 Gbps SFP+ transceivers
• Brocade M6505 16 Gbps Fibre Channel SAN I/O Module QuickStart Guide
Brocade M6505 16 Gbps Fibre Channel SAN I/O Module Hardware Reference Manual 11
53-1002576-02
Page 24

System reliability guidelines
ATTENTION
2
System reliability guidelines
To help ensure proper cooling, performance, and system reliability, make sure the following
requirements are met:
• Each of the I/O module bays at the rear of the Dell M1000e Blade Server Enclosure contains
either a SAN I/O Module or a filler panel.
• A removed hot-swappable SAN I/O Module is replaced with an identical SAN I/O Module or
filler panel within 60
seconds of removal.
• You have followed the reliability guidelines in the documentation that comes with the Dell
M1000e Blade Server Enclosure.
Handling static-sensitive devices
Static electricity can damage the Dell M1000e Blade Server Enclosure and other electronic devices.
To avoid damage, keep static-sensitive devices in their static-protective packages until you are ready
to install them.
To reduce the possibility of electrostatic discharge, observe the following precautions:
• Limit your movement. Movement can cause static electricity to build up around you.
• Handle the device carefully, holding it by its edges or its frame.
• Do not touch solder joints, pins, or exposed printed circuitry.
• Do not leave the device where others can handle and damage it.
• While the device is still in its static-protective package, touch it to an unpainted metal surface
of the Dell M1000e Blade Server Enclosure or an unpainted metal surface on any other
grounded rack component in the rack in which you are installing the device for at least two
seconds. This drains static electricity from the package and from your body.
• Remove the device from its package and install it directly into the Dell M1000e Blade Server
Enclosure without setting down the device. If it is necessary to set down the device, put it back
into its static-protective package. Do not place the device on the Dell M1000e Blade Server
Enclosure or on a metal surface.
• Take additional care when you handle devices during cold weather. Heating reduces indoor
humidity and increases static electricity.
• Some types of chassis come with electrostatic discharge (ESD) connectors. If the chassis is
equipped with an ESD connector, see the documentation that comes with the Dell M1000e
Blade Server Enclosure for using the ESD connector.
Preparing the Blade Server Enclosure for the SAN I/O Module
Before the SAN I/O Module can be inserted in the Dell M1000e Blade Server Enclosure, make sure
the following conditions are met:
• The I/O module bay into which the SAN I/O Module will be inserted is ready to receive the SAN
I/O Module.
• All power requirements specific to the Dell M1000e Blade Server Enclosure are met.
12 Brocade M6505 16 Gbps Fibre Channel SAN I/O Module Hardware Reference Manual
53-1002576-02
Page 25

Inserting the SAN I/O Module in the Blade Server Enclosure
NOTE
• Any protective cover on the SAN I/O Module backside connector is removed.
• If you are replacing an existing SAN I/O Module with a new module, the new SAN I/O Module
should be ready to be inserted within 60
maintain the proper cooling level in the chassis.
seconds from the removal of the old module to
Inserting the SAN I/O Module in the Blade Server Enclosure
Complete the following steps to insert the SAN I/O Module in the Dell M1000e Blade Server
Enclosure.
1. Unpack the SAN I/O Module from its shipping box, as described in “Unpacking the SAN I/O
Module” on page 11.
2. Verify that the Dell M1000e Blade Server Enclosure I/O module bay into which the SAN I/O
Module is being inserted is empty and that any filler panel or dust cover is removed.
A maximum of four SAN I/O Modules can be installed in the Dell M1000e Blade Server
Enclosure.
The SAN I/O Module is designed to work only in I/O module bays B1/B2 and C1/C2 of the Dell
M1000e Blade Server Enclosure. Make sure to comply with installation requirements stated in
the Dell PowerEdge M1000e Enclosure Owner’s Manual.
2
3. Press the release latch on the SAN I/O Module to free the release lever, as shown in Figure 3.
1 Release latch 2 Release lever
FIGURE 3 SAN I/O Module latching mechanism (closed position)
Brocade M6505 16 Gbps Fibre Channel SAN I/O Module Hardware Reference Manual 13
53-1002576-02
Page 26

Inserting the SAN I/O Module in the Blade Server Enclosure
NOTE
1
2
2
4. Ensure that the release lever is fully extended so the SAN I/O Module can be seated properly in
the Dell M1000e Blade Server Enclosure, as shown in
Figure 4.
1 Release latch 2 Release lever
FIGURE 4 SAN I/O Module latching mechanism (open position)
5. With the port side facing you and the release lever fully extended, slide the SAN I/O Module in
the Dell M1000e Blade Server Enclosure I/O module bay.
6. Press the release lever upward until the release latch clicks and locks the lever in place.
This locks the SAN I/O Module into the Dell M1000e Blade Server Enclosure I/O module bay.
Locking the SAN I/O Module into the I/O module bay provides power (if the power is on in the
Blade Server Enclosure) and activates (powers on) the switch and switch LEDs.
The switch then runs self-diagnostic tests (such as POST).
When the SAN I/O Module is inserted in the Dell M1000e Blade Server Enclosure, the physical
Ethernet connection is established through the Dell M1000e Blade Server Enclosure Chassis
Management Controller (CMC). Also, the SAN I/O Module serial port connection becomes
available through the CMC CLI connect switch-x interface.
Once inserted, the SAN I/O Module can be accessed remotely. Ensure that the SAN I/O Module
is not being modified from any other connection until configuration is complete. Refer to
Chapter 3, “Configuring the SAN I/O Module,” for additional information about configuring the
SAN I/O Module.
14 Brocade M6505 16 Gbps Fibre Channel SAN I/O Module Hardware Reference Manual
53-1002576-02
Page 27

Handling SFP+ transceivers
DANGER
DANGER
ATTENTION
Before installing an SFP+ transceiver, be aware of the following:
• The housing on the SFP+ transceiver includes an integral guide key that is designed to prevent
you from inserting the transceiver incorrectly.
• Use minimal pressure when you insert an SFP+ transceiver in the port. Forcing the transceiver
into the port can cause damage to the transceiver or the SAN I/O Module port.
• You can insert or remove an SFP+ transceiver while the Dell M1000e Blade Server Enclosure
is powered on.
• You must first insert the SFP+ transceiver in the port before connecting the cables.
• You must remove the cable from the SFP+ transceiver before you remove the SFP+ transceiver
from the SAN I/O Module.
Tab le 3 lists Brocade-branded SFP+ transceivers that are supported on the SAN I/O Module.
TABLE 3 Brocade-branded SFP+ transceivers and part numbers
Transceiver type Device support Device description Brocade part number Dell part number
SFP+ 16 Gbps FC SWL, 1-pack, BR XDL-000192 2D0N2
SFP+ 16 Gbps FC SWL, 8-pack, BR XDL-000193 MTW83
SFP+ 8 Gbps FC SWL, 1-pack, BR XDL-000163 KP1HM
SFP+ 8 Gbps FC SWL, 8-pack, BR XDL-000164 X3T03
Handling SFP+ transceivers
2
To order SFP+ transceivers, contact your sales representative.
Inserting an SFP+ transceiver in the SAN I/O Module port
All fiber-optic interfaces use Class 1 lasers.
Laser radiation. Do not view directly with optical instruments. Class 1 laser products.
Your SAN I/O Module ships from the factory with a certain number of pre-installed SFP+
transceivers. The number of pre-installed transceivers will vary based on your SAN I/O Module
model.
To insert additional SFP+ transceivers in your SAN I/O Module, complete the following procedure. If
you are replacing an SFP+ transceiver, refer to
cables” on page 39.
“Removing and replacing SFP+ transceivers and
Be sure to use only Brocade-branded SFP+ transceivers. (Refer to Table 3).
Brocade M6505 16 Gbps Fibre Channel SAN I/O Module Hardware Reference Manual 15
53-1002576-02
Page 28

Cabling guidelines
NOTE
CAUTION
2
1. Review the section “Handling SFP+ transceivers” on page 15.
2. If your SAN I/O Module ships with insert plugs in the unused external ports, remove the insert
plugs from the ports to be used.
3. Insert the SFP+ transceiver into a port until it is firmly seated and the latching mechanism
clicks.
SFP+ Transceivers are keyed to ensure correct orientation. If an SFP+ transceiver does not
install easily, ensure that it is correctly oriented.
4. Connect the cable to the SFP+ transceiver. Refer to “Cabling guidelines” on page 16.
For instructions specific to the type of transceiver, visit the MyBrocade web site at:
http://my.brocade.com
The cables used in trunking groups must meet specific requirements. For a list of these
requirements, refer to the Brocade Fabric OS Administrator’s Guide.
5. After the diagnostics have completed, cable the SAN I/O Module according to instructions
provided by the manufacturer. For more information, refer to the documentation that came
with your embedded switch.
6. Configure the Ethernet IP address on the SAN I/O Module as described in “Connecting to the
SAN I/O Module using Web Tools” on page 24.
Cabling guidelines
After modifying the IP address of the SAN I/O Module, it is recommended that you cable all external
ports to fabric connections before bringing the SAN I/O Module online.
Begin by cabling the ports from the top (ports 17 and 18) and working down as needed (ports 19,
20, 21, 22, 23, and 0). At a minimum, for all licensed variants of the SAN I/O Module, ports 17 and
18 are pre-licensed at the factory as part of Dynamic Ports On Demand (DPOD).
To avoid damage to the fiber-optic cables, follow these guidelines:
• Do not route the cable along a folding cable-management arm.
• When you attach the cable to a device on slide rails, leave enough slack in the cable so that it
does not bend to a radius of less than 38 mm (1.5 in.) when the device is extended, or
becomes pinched when the device is retracted.
• Tie wraps are not recommended for optical cables because they are easily overtightened.
A 50-micron cable should not be bent to a radius less than 2 inches under full tensile load and
1.2 inches with no tensile load.
16 Brocade M6505 16 Gbps Fibre Channel SAN I/O Module Hardware Reference Manual
53-1002576-02
Page 29

Data transmission ranges
Data transmission ranges
Tab le 4 provides the data transmission ranges for the transceivers, port speeds, and cable types.
TABLE 4 Supported optical tranceivers, speeds, cables, and distances
Transceiver
type
SWL SFP+ 2 Gbps 150 m (492 ft.) 300 m (984 ft.) 500 m (1640 ft.) N/A N/A
SWL SFP+ 4 Gbps 70 m (229 ft.) 150 m (492 ft.) 380 m (1264 ft.) 400 m (1312 ft.) N/A
SWL SFP+ 8 Gbps 21 m (68 ft.) 50 m (164 ft.) 150 m (492 ft.) 190 m (623 ft.) N/A
SWL SFP+ 16 Gbps 15 m (49 ft.) 35 m (115 ft.) 100 m (328 ft.) 125 m (410 ft.) N/A
1. 16Gb SFP+ optical transceivers support 16/8/4 Gbps speeds, and 8Gb SFP+ optical transceivers support 8/4/2 Gbps speeds.
Form
factor
Link Speed
1
Multi-node media
(50 microns)
(OM1)
Multi-mode media
(50 microns)
(OM2)
Multi-mode media
(50 microns)
(OM3)
Multi-mode media
(50 microns)
(OM4)
Single-mode
media
2
Brocade M6505 16 Gbps Fibre Channel SAN I/O Module Hardware Reference Manual 17
53-1002576-02
Page 30

Data transmission ranges
2
18 Brocade M6505 16 Gbps Fibre Channel SAN I/O Module Hardware Reference Manual
53-1002576-02
Page 31

Chapter
NOTE
NOTE
Configuring the SAN I/O Module
In this chapter
•Items required . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
•Modifying the SAN I/O Module IP address . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
•Connecting to the SAN I/O Module using Web Tools . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
•Connecting the SAN I/O Module to the Ethernet network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
•Connecting the SAN I/O Module to the fabric . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Although the SAN I/O Module is configured at the factory for Access Gateway (AG) mode, you can
enable it for Fabric OS Native mode. For more information, refer to
mode to Native Fabric mode” on page 31.
Items required
3
“Changing from Access Gateway
The following items are required for configuring and connecting the SAN I/O Module for use in a
network and fabric:
• The SAN I/O Module to be installed in the Dell M1000e Blade Server Enclosure.
• If required, a management workstation (computer) that has a terminal emulator (such as
HyperTerminal) or a keyboard, video, and mouse (KVM) device. This is only required if you are
not changing the SAN I/O Module IP address through the Dell M1000e Blade Server Enclosure
GUI or CLI management programs.
• An unused IP address and corresponding subnet mask and gateway address, unless DHCP is
used.
• If required, a serial cable to connect to the SAN I/O Module serial console port.
The serial cable is only required if you are not changing the SAN I/O Module IP address through
the Dell M1000e Blade Server Enclosure GUI or CLI management programs.
• Access to an FTP server for backing up the SAN I/O Module configuration.
Brocade M6505 16 Gbps Fibre Channel SAN I/O Module Hardware Reference Manual 19
53-1002576-02
Page 32

Modifying the SAN I/O Module IP address
NOTE
3
• Access to the following publications:
- Dell PowerEdge M1000e Enclosure Owner’s Manual
- Dell Chassis Management Controller Firmware Version 4.x User Guide
- Brocade Fabric OS Command Reference
- Brocade Fabric OS Message Reference
- Brocade SAN TECH NOTE – Preparing to Install the Brocade Access Gateway
- Brocade Access Gateway Administrator’s Guide
- Brocade Web Tools Administrator’s Guide
- Release notes for the Fabric OS version running on the SAN I/O Module
- Release notes specific to the SAN I/O Module
Modifying the SAN I/O Module IP address
By default, the IP address for the SAN I/O Module is configured as 10.77.77.77 with a default
Ethernet subnetmask of 255.255.255.0.
Reset the IP address using any of the following three methods. The IP address values are stored on
the SAN I/O Module.
• “Using the CMC GUI to set the IP address” on page 20
• “Using the CMC CLI to set the IP address” on page 21
• “Using the SAN I/O Module CLI to set the IP address” on page 22
It is recommended that you set the IP address using the Dell M1000e Blade Server Chassis
Management Controller (CMC). From the CMC, you can set the IP address using either the GUI or the
CLI.
Using the CMC GUI to set the IP address
To modify the SAN I/O Module IP address using the CMC GUI, perform the following steps:
1. Select I/O Module Overview from the left navigation panel.
2. Click the Setup tab.
3. Enter the new information in the IP Address, Subnet Mask, and Gateway fields as appropriate,
then click Apply.
4. To enable DHCP, select DHCP Enabled, then click Apply.
Refer to Figure 5 on page 21.
20 Brocade M6505 16 Gbps Fibre Channel SAN I/O Module Hardware Reference Manual
53-1002576-02
Page 33

FIGURE 5 CMC Setup tab
Modifying the SAN I/O Module IP address
3
Refer to the Dell PowerEdge M1000e Enclosure Owner’s Manual that comes with your Dell
M1000e Blade Server Enclosure for more information.
Using the CMC CLI to set the IP address
To modify the SAN I/O Module IP address through the Chassis Management Controller (CMC) CLI,
perform the following steps:
1. Establish a Telnet session to the CMC CLI.
2. At the command prompt, enter connect switch-x where x is the bay in which the SAN I/O
Module is installed. For example, switch-x can be one of the following values:
• Switch-3 for SAN I/O Module installed in bay B1.
• Switch-4 for SAN I/O Module installed in bay B2.
• Switch-5 for SAN I/O Module installed in bay C1.
• Switch-6 for SAN I/O Module installed in bay C2.
3. Log in to the default administrative account using the following default settings:
Login: admin
Password: password
4. When prompted, either change the administrative password, or press Ctrl-C to bypass.
5. Enter the ipAddrSet command to change the IP address of the selected SAN I/O Module.
switch:admin> ipaddrset
6. Follow on-screen instructions and supply the correct information, as shown in the following
example:
switch:admin> ipaddrset
Ethernet IP Address [10.77.77.77]:10.32.53.47
Ethernet Subnetmask [255.255.255.0]:255.255.240.0
Brocade M6505 16 Gbps Fibre Channel SAN I/O Module Hardware Reference Manual 21
53-1002576-02
Page 34

Modifying the SAN I/O Module IP address
3
Fibre Channel IP Addresss [none]:
Fibre Channel Subnetmask [none]:
Gateway IP Address [0.0.0.0]:10.32.48.1
DHCP [Off]:
IP address is being changed...Done.
7. E n t er ipAddrShow to verify the IP address was correctly set.
switch:admin> ipaddrshow
Ethernet IP Address: 10.32.53.47
Ethernet Subnetmask: 255.255.240.0
Fibre Channel IP Addresss: none
Fibre Channel Subnetmask: none
Gateway IP Address 10.32.48.1
DHCP: Off
Refer to the Dell PowerEdge M1000e Enclosure Owner’s Manual that comes with your Blade
Server Enclosure for information on using the CMC connect command.
Using the SAN I/O Module CLI to set the IP address
Perform the following tasks to change the IP address on the Brocade M6505 16 Gbps Fibre
Channel SAN I/O Module using the SAN I/O Module’s CLI.
Task 1: Establish a terminal session with the SAN I/O Module
Complete the following steps to establish a terminal emulation session between the SAN I/O
Module and a management workstation used for managing the SAN I/O Module. Once this session
is established, you can log in to the SAN I/O Module and use its CLI commands to manage the
module.
1. Connect a serial cable between the serial console port on the SAN I/O Module and the
management workstation that can establish a terminal emulation session with the SAN I/O
Module.
2. Disable any serial communication programs that are running on the workstation.
3. Using a terminal emulator application (such as HyperTerminal or PuTTY connection manager
on a PC or TERM in a LINUX or UNIX environment), establish a terminal session to the SAN I/O
Module from the management workstation. You will use this connection if you want to reset the
IP address of the SAN I/O Module using CLI commands and perform other configuration tasks.
For Windows 2003, 2008
a. Click Start and select Programs > Accessories > Communications.
b. Select HyperTerminal and enter a name for the connection.
c. From the HyperTerminal window, click the Connect menu and select an available COM
port.
d. Click OK.
22 Brocade M6505 16 Gbps Fibre Channel SAN I/O Module Hardware Reference Manual
53-1002576-02
Page 35

Modifying the SAN I/O Module IP address
e. From the COM Port Properties window, select the following configuration values.
Bits per second 9600
Databits 8
Parity None
Stop bits 1
Flow control None
f. Log in using the default administrative account:
Login: admin
Password: password
g. When prompted, either change the administrative password, or press Ctrl-C to bypass.
For LINUX or UNIX
a. Enter the following command at the command prompt:
tip /dev/ttyb -9600
3
b. When the terminal application stops reporting information, press Enter to display the login
prompt.
c. Log in using the default administrative account:
Login: admin
Password: password
d. When prompted, either change the administrative password, or press Ctrl-C to bypass.
Task 2: Change the IP address
1. Verify that the SAN I/O Module has completed power-on self-test (POST). When POST is
complete, the port status and SAN I/O Module power and status LEDs return to a standard
healthy state.
2. Enter the ipAddrSet command.
switch:admin> ipaddrset
3. Follow on-screen instructions and supply the correct information, as shown in the following
examples.
switch:admin> ipaddrset
Ethernet IP Address [10.77.77.77]:10.32.53.47
Ethernet Subnetmask [255.255.255.0]:255.255.240.0
Fibre Channel IP Addresss [none]:
Fibre Channel Subnetmask [none]:
Gateway IP Address [0.0.0.0]:10.32.48.1
DHCP [Off]:
IP address is being changed...Done.
Brocade M6505 16 Gbps Fibre Channel SAN I/O Module Hardware Reference Manual 23
53-1002576-02
Page 36

Connecting the SAN I/O Module to the Ethernet network
NOTE
NOTE
NOTE
3
4. Enter ipAddrShow at the prompt to verify that the address was set correctly.
switch:admin> ipaddrshow
Ethernet IP Address: 10.32.53.47
Ethernet Subnetmask: 255.255.240.0
Fibre Channel IP Addresss: none
Fibre Channel Subnetmask: none
Gateway IP Address 10.32.48.1
DHCP: Off
Connecting the SAN I/O Module to the Ethernet network
Once you have successfully set the appropriate IP address of the SAN I/O Module, you can
establish an Ethernet connection through the Dell M1000e Blade Server Enclosure Chassis
Management Controller (CMC) to a remote management workstation for any additional
configuration. The management workstation must be on the same Ethernet subnet as the CMC.
Ensure that the SAN I/O Module is not being modified from any other connection until configuration
is complete.
Once an Ethernet connection is established, you can configure the SAN I/O Module by way of
Telnet/SSH using the switch CLI, or by launching Web Tools.
Connecting to the SAN I/O Module using Web Tools
Complete the following steps to connect to the Brocade M6505 16 Gbps Fibre Channel SAN I/O
Module using Web Tools.
1. On the management console, open a web browser such as Internet Explorer.
The web browser must be connected to the same network as the SAN I/O Module.
2. Enter the IP address of the SAN I/O Module in the Address field, then press Enter.
Web Tools requires any browser that conforms to HTML version 4.0, JavaScript version 1.0, and Java
Plug-in 1.6.0_24 or later.
For more information about using Web Tools, refer to the Brocade Web Tools Administrator’s Guide.
Connecting the SAN I/O Module to the fabric
Refer to “Cabling guidelines” on page 16 before beginning the following procedure.
Before beginning the following steps, determine whether the SAN I/O Module is in Brocade Access
Gateway or Native Fabric mode. This affects the configuration process. Using the Brocade M6505
16 Gbps Fibre Channel SAN I/O Module CLI, enter the ag
current operating mode.
24 Brocade M6505 16 Gbps Fibre Channel SAN I/O Module Hardware Reference Manual
––modeShow command to determine the
53-1002576-02
Page 37

Connecting the SAN I/O Module to the fabric
If you are in AG mode and want to change to Native Fabric mode before connecting the SAN I/O
Module to the fabric, refer to
“Changing from Access Gateway mode to Native Fabric mode” on
page 31.
1. If the Brocade M6505 16 Gbps Fibre Channel SAN I/O Module is in Native Fabric mode,
continue to
step 2 and step 3. If the Module is in Access Gateway mode, go on to step 4.
2. Log in to the SAN I/O Module through a Telnet connection using the admin account.
3. Modify the domain ID if required using Brocade M6505 16 Gbps Fibre Channel SAN I/O
Module CLI commands.
The default domain ID is 1. If the SAN I/O Module is not powered on until after it is connected
to the fabric and the default domain ID is already in use, the domain ID for the new SAN I/O
Module is automatically reset to a unique value. If the SAN I/O Module is connected to the
fabric after it has been powered on and the default domain ID is already in use, the fabric
segments.
To find the domain IDs that are currently in use, run the fabricShow command on another SAN
I/O Module or switch in the fabric. Identify an unused domain ID:
a. Disable the SAN I/O Module being configured using the switchDisable command.
b. Enter the configure command at the root prompt.
3
The command prompts display sequentially. Enter a new value at the Domain prompt or
press Enter to accept the default value. The SAN I/O Module now has a unique domain ID
and can join the fabric. The following sample is an example of command output.
Fabric parameters (yes, y, no, n): [no] y
Data field size: (256..2112) [2112]
Sequence Level Switching: (0..1) [0]
Disable Device Probing: (0..1) [0]
Suppress Class F Traffic: (0..1) [0]
Switch PID Format: (1..2) [1]Configure...
Domain: (1..239) [1] 155
R_A_TOV: (4000..120000) [10000]
E_D_TOV: (1000..5000) [2000]
WAN_TOV: (0..30000) [0]
MAX_HOPS: (7..19) [7]
Per-frame Route Priority: (0..1) [0]
Long Distance Fabric: (0..1) [0]
BB credit: (1..27) [16]
Insistent Domain ID Mode (yes, y, no, n): [no]
Virtual Channel parameters (yes, y, no, n): [no]
F-Port login parameters (yes, y, no, n): [no]
Zoning Operation parameters (yes, y, no, n): [no]
RSCN Transmission Mode (yes, y, no, n): [no]
Arbitrated Loop parameters (yes, y, no, n): [no]
System services (yes, y, no, n): [no]
Portlog events enable (yes, y, no, n): [no]
ssl attributes (yes, y, no, n): [no]
http attributes (yes, y, no, n): [no]
snmp attributes (yes, y, no, n): [no]
rpcd attributes (yes, y, no, n): [no]
cfgload attributes (yes, y, no, n): [no]
webtools attributes (yes, y, no, n): [no]
Brocade M6505 16 Gbps Fibre Channel SAN I/O Module Hardware Reference Manual 25
53-1002576-02
Page 38

Connecting the SAN I/O Module to the fabric
NOTE
NOTE
ATTENTION
3
System (yes, y, no, n): [no]
WARNING: The domain ID will be changed. The port level zoning may be
affected.
c. Re-enable the SAN I/O Module by entering the switchEnable command.
It can take up to 20 seconds for the newly added SAN I/O Module to appear in the fabric
display with its newly assigned domain ID.
4. If you must install SFP+ transceivers, install them in the external Fibre Channel ports, as
required.
a. If necessary, remove the end caps from the SFP+ transceiver.
b. Orient the SFP+ transceiver correctly and insert it in a port until it is firmly seated and the
latching mechanism clicks.
c. Repeat substeps a, b, and c for the remaining ports, as required.
Only Brocade-branded SFP+ transceivers are supported for use with the SAN I/O Module.
5. Connect the cables to the transceivers.
The transceivers are keyed to ensure correct orientation. If a transceiver does not install easily,
ensure that it is correctly oriented and that the end caps have been removed. The cables used
in trunking groups must meet specific requirements. For a list of these requirements, see the
Brocade Fabric OS Administrator’s Guide.
A cable should not be bent to a radius less than 5.08 cm (2 inches) under full tensile load and
3.048 cm (1.2 inches) with no tensile load.
Tie wraps are not recommended for optical cables because they are easily overtightened.
a. Orient a cable connector so that the key (the ridge on one side of connector) aligns with
the slot in the transceiver.
b. Insert the cable into the transceiver until the latching mechanism clicks. For instructions
specific to cable type, refer to the cable manufacturer’s documentation.
c. Repeat substeps a and b for the remaining transceivers, as required.
6. Check the LEDs to verify that all components are functional.
For information about LED patterns, refer to the “Interpreting SAN I/O Module LED activity” on
page 35.
7. Verify the correct operation of the SAN I/O Module by entering the switchShow command from
the switch Telnet session.
This command provides information about SAN I/O Module and port status.
8. Verify the correct operation of the SAN I/O Module in the fabric by entering the fabricShow
command from the switch Telnet session.
26 Brocade M6505 16 Gbps Fibre Channel SAN I/O Module Hardware Reference Manual
53-1002576-02
Page 39

Connecting the SAN I/O Module to the fabric
9. Back up the SAN I/O Module configuration to an FTP server by typing the configUpload
command and following the prompts.
This command uploads the SAN I/O Module configuration to the server, making it available for
downloading to a replacement SAN I/O Module if necessary. Brocade recommends backing up
the configuration on a regular basis to ensure that a complete configuration is available for
downloading to a replacement SAN I/O Module.
For specific instructions about how to back up the configuration, see the Brocade Fabric OS
Administrator’s Guide. The switchShow, fabricShow, and configUpload commands are
described in detail in the Brocade Fabric OS Command Reference.
3
Brocade M6505 16 Gbps Fibre Channel SAN I/O Module Hardware Reference Manual 27
53-1002576-02
Page 40

Connecting the SAN I/O Module to the fabric
3
28 Brocade M6505 16 Gbps Fibre Channel SAN I/O Module Hardware Reference Manual
53-1002576-02
Page 41

Chapter
Operating the SAN I/O Module
In this chapter
•Interoperability. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
•Activating Ports on Demand . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
•Changing from Native Fabric mode to Access Gateway mode . . . . . . . . . . . 33
•Changing from Access Gateway mode to Native Fabric mode . . . . . . . . . . . 31
•Access Gateway mode default port mapping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
•Accessing the SAN I/O Module. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
•Interpreting POST results . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
•Interpreting SAN I/O Module LED activity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
•Interpreting POST results . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
•Removing and replacing SAN I/O Modules . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
•Removing and replacing SFP+ transceivers and cables. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
•Switch management . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
•Viewing the configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
•Upgrading or downgrading firmware . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
•Changing the default account password . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
•Backing up the configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
•Locating the serial number information. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
4
Interoperability
The SAN I/O Module supports interoperability for the features and functions listed in Tab le 5.
TABLE 5 Interoperability
Feature/Function Description
Link initialization The SAN I/O Module comes online automatically after it is seated securely in
one of the Dell M1000e Blade Server Enclosure I/O module bays.
Routing Fabric Shortest Path First (FSPF)—A link state path selection protocol that
directs traffic along the shortest path between the source and destination
based upon the link cost.
Registered state change
notification (RSCN)
SNMP facilities v1, v2c, and v3
Translative mode Private target support on fabrics.
Brocade M6505 16 Gbps Fibre Channel SAN I/O Module Hardware Reference Manual 29
53-1002576-02
Notifies a device of a change within the fabric.
Page 42

Activating Ports on Demand
NOTE
NOTE
4
TABLE 5 Interoperability (Continued)
Feature/Function Description
Trunking Supported only between two Brocade switches.
Advanced Performance
Monitoring
Activating Ports on Demand
Ports on Demand (POD) licensing allows you to enable up to 24 ports from the initial 12 ports on
the Base model. You can add optional Ports on Demand (POD) licenses using either Brocade Web
Tools or a Telnet connection. Do not use the Dell M1000e Blade Server Enclosure Chassis
Management Controller (CMC) software.
Enhancements include:
• Coexistence of Top Talkers and APM on 16 Gbps platforms
• E_Port Top Talkers support and E_Port end-to-end monitor support on
16 Gbps platforms
• APM support on AG that provides end-to-end monitors and frame
monitors
Only the Base model requires the use of POD licensing to increase the amount of active ports. The
Full model and ENT model already have all ports enabled.
Ports on Demand is ready to be unlocked in the SAN I/O Module firmware. A POD license may be
supplied with the SAN I/O Module software, or you can purchase the license separately from your
SAN I/O Module vendor, who will provide you with a key to unlock it.
Once you have installed the license key, you must enable the ports. You can do so without
disrupting SAN I/O Module operation, or you can disable and re-enable the SAN I/O Module to
activate all ports.
If you remove a POD license, ports that were enabled by that license are disabled.
Activating ports with a POD license
You can activate ports with a POD license while the SAN I/O Module is connected to existing SANs,
or before connecting to an existing SAN.
For SAN I/O Modules already connected to existing storage networks, complete the following steps:
1. Add the POD license using Web Tools or the CLI.
2. Enable each newly licensed port using Web Tools or the CLI.
This method is non-disruptive to existing servers and storage connecting to the SAN I/O
Module.
30 Brocade M6505 16 Gbps Fibre Channel SAN I/O Module Hardware Reference Manual
53-1002576-02
Page 43

Changing from Access Gateway mode to Native Fabric mode
ATTENTION
NOTE
NOTE
For new SAN I/O Module installations, perform the following procedure before connecting to an
existing SAN.
Do not use this method if the SAN I/O Module is operating in an existing SAN because traffic will be
disrupted.
1. Disable the SAN I/O Module.
If Secure Fabric OS is enabled, you cannot use Telnet or SSH to disable the SAN I/O Module.
For details about using Web Tools, refer to the Brocade Web Tools Administrator’s Guide. For
details about the CLI, refer to the Brocade Fabric OS Command Reference.
2. Add the POD license using Web Tools or the CLI.
3. Enable the SAN I/O Module using Web Tools or the CLI. When the SAN I/O Module is enabled,
the newly added POD ports become enabled.
Changing from Access Gateway mode to Native Fabric mode
4
The SAN I/O Module ships from the factory in Access Gateway (AG) mode. If your SAN I/O Module is
currently configured in AG mode, you can enable the module for Native Fabric (fabric switch) mode
by disabling AG mode. When you do this, the module automatically reboots in Native Fabric mode.
Note that once the switch reboots to Native Fabric mode, it will not join the SAN automatically.
Refer to the Access Gateway Administrator’s Guide for instructions on how to join the switch into
your SAN fabric.
Determine if the SAN I/O Module is running in AG mode by entering the switchShow command to
display the current switch configuration. If running in Native Fabric mode, the switchMode
parameter should display Access Gateway Mode.
For complete instructions on disabling Access Gateway mode using the CLI and joining the switch
to the fabric, refer to the “Disabling Access Gateway Mode” section in the Brocade Access Gateway
Administrator’s Guide.
Disabling Access Gateway mode is disruptive because the switch is disabled and rebooted. Always
back up the current configuration before enabling or disabling Access Gateway mode. Enabling
Access Gateway mode clears the security and zone databases. Disabling Access Gateway mode
clears the F_Port to N_Port mapping.
Brocade M6505 16 Gbps Fibre Channel SAN I/O Module Hardware Reference Manual 31
53-1002576-02
Page 44

Changing from Access Gateway mode to Native Fabric mode
NOTE
4
Disabling Access Gateway mode
To disable AG mode on the SAN I/O Module, perform the following procedure.
1. Before disabling a switch in AG mode, save the current configuration file using the
configUpload command in case you need this configuration again.
2. Enter the switchDisable command.
switch:admin> switchdisable
This command disables all user ports on a switch. All Fibre Channel ports are taken offline. If
the switch is part of a fabric, the remaining switches reconfigure. You must disable the switch
before making configuration changes.
3. Enter the ag --modeDisable command.
switch:admin> ag --modedisable
WARNING 1: Changing from Access Gateway mode to Switch mode will set zoning to
"all access".
WARNING 2: Disabling agmode will remove all the configuration data on the
switch including N_Port configuration and F_Port to N_Port mapping. Please
backup your configuration using configupload.
This operation will reboot the switch.
Do you want to continue? (yes, y, no, n): [no] y
Access Gateway mode was disabled successfully
Switch is being rebooted...Wait for the switch to come up in “Native”mode.
4. Log in to the switch and verify that the switch is set to Native Fabric mode using the
switchShow command.
switch:admin> switchshow
The switch mode should display “Native.”
SH3_1737:root> switchshow
switchName: SH3_1737
switchType: 130.0
switchState: Online
switchMode: Native
switchRole: Subordinate
switchDomain: 2
switchId: fffc02
switchWwn: 10:00:00:27:f8:0a:d8:83
zoning: ON (cfg_sh3_sanblaze)
switchBeacon: OFF
FC Router: OFF
FC Router BB Fabric ID: 1
Address Mode: 0
You can also use the ag --modeShow command. The console will display the message,
“Access Gateway mode is NOT enabled.”
Refer to the Access Gateway Administrator’s Guide for more information on changing from
AG
mode to Native Fabric mode.
32 Brocade M6505 16 Gbps Fibre Channel SAN I/O Module Hardware Reference Manual
53-1002576-02
Page 45

Changing from Native Fabric mode to Access Gateway mode
NOTE
Changing from Native Fabric mode to Access Gateway mode
Converting to Access Gateway (AG) mode allows you to use the module as a device management
tool that transparently connects hosts to the fabric. Refer to the Brocade Access Gateway
Administrator’s Guide for information on changing from Native Fabric mode to AG mode.
Access Gateway mode default port mapping
The SAN I/O Module can contain 24 total ports. Of these, F_Ports are ports 1 through 16 and
N_Ports are ports 0 and 17 through 23.
In Access Gateway mode, the SAN I/O Module F_Ports are mapped to N_Ports. The following table
lists the factory-default F_Port to N_Port mapping for Access Gateway mode. For more information
on changing port mapping and managing ports in Access Gateway mode, refer to the Brocade
Access Gateway Administrator’s Guide.
Tab le 6 shows Access Gateway mapping information.
Automatic failover and automatic failback are enabled on all N_Ports.
4
TABLE 6 AG mapping
N_Port 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 0
F_Port 1, 2 3, 4 5, 6 7, 8 9, 10 11, 12 13, 14 15, 16
Accessing the SAN I/O Module
The SAN I/O Module is managed as a single element. It has a single IP address and appears as a
separate entity to the Telnet protocol and the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP).
When SNMP devices send SNMP messages to a management console running SAN management
software, the information is stored in a Management Information Base (MIB). The SAN I/O Module
Fabric OS supports the FibreAlliance Fibre Channel Management (FCMGMT) MIBs, allowing the
provision of needed information to a SAN administrator.
In addition, the Brocade Fabric Access Layer (API) and the Storage Management Initiative (SMI)
provide facilities for the discovery and management of physical and logical elements in a SAN.
Using the Fabric Access interface to the Fabric OS, a client application can retrieve information and
modify the configuration of Brocade switches in the fabric.
Secure Telnet access is available using Secure Shell (SSH), a network security protocol for secure
remote login and other secure network services over an insecure network.
Brocade Web Tools management is available through a secure browser using Secure Sockets Layer
(SSL) and Transport Layer Security (TLS). The SSL/TLS security protocol provides data encryption,
server authentication, message integrity, and optional client authentication for a TCP/IP
connection. Because SSL/TLS is built into all major browsers and web servers, installing a digital
certificate enables the SSL/TLS capabilities.
Brocade M6505 16 Gbps Fibre Channel SAN I/O Module Hardware Reference Manual 33
53-1002576-02
Page 46

Interpreting POST results
4
Interpreting POST results
The power-on self-test (POST) system check is performed each time the SAN I/O Module is powered
on, rebooted, or reset. Refer to the following sample output:
POST1: Started running Tue Nov 9 20:27:57 GMT 2004
POST1: Test #1 - Running turboramtest
POST1: Test #2 - Running centralmemorytest
POST1: Test #3 - Running cmitest
POST2: Running diagshow
POST1: Script PASSED with exit status of 0 Tue Nov 9 20:28:10 GMT 2004 took
(0:
0:13)
POST2: Started running Tue Nov 9 20:28:12 GMT 2004
POST2: Test #1 - Running camtest
POST2: Test #2 - Running txdpath
POST2: Test #3 - Running spinsilk (SERDES)
POST2: Running diagshow
POST2: Script PASSED with exit status of 0 Tue Nov 9 20:29:11 GMT 2006 took
(0:
0:59)
Initializing Ports ....
Port Initialization Completed
Enabling switch...
Perform the following steps to determine POST completion status.
1. Verify the LEDs on the SAN I/O Module indicate that switch status is healthy. LED patterns are
described in
“Interpreting SAN I/O Module LED activity” on page 35.
If any of the LEDs does not display a healthy state, verify the LEDs are not set to beacon. Use
the switchShow command or Web Tools to verify the LED state. For information about how to
enable and disable beaconing, refer to the Brocade Fabric OS Administrator’s Guide or the
Brocade Web Tools Administrator’s Guide.
2. Use the Dell M1000e Blade Server Enclosure’s Chassis Management Controller (CMC) GUI to
verify that the SAN I/O Module is working correctly.
For details, refer to the Dell PowerEdge M1000e Enclosure Owner’s Manual that comes with
your Dell M1000e Blade Server Enclosure.
3. Review the system log for errors.
Any errors detected during POST are written to the system log. Access this log using the
errShow command. For more information, refer to the Brocade Fabric OS Command
Reference. For information about error messages, see the Brocade Fabric OS Message
Reference.
34 Brocade M6505 16 Gbps Fibre Channel SAN I/O Module Hardware Reference Manual
53-1002576-02
Page 47

Interpreting SAN I/O Module LED activity
3
4
2
1
Interpreting SAN I/O Module LED activity
The SAN I/O Module uses LEDs to indicate status, as shown in Figure 6.
4
1 FC external port status 3 SAN I/O Module power status
2 SAN I/O Module status 4 Server management status/indicator
FIGURE 6 SAN I/O Module front panel LEDs
LEDs are used to indicate switch health, status of the external ports, and power to the SAN I/O
Module. LEDs are also used to indicate diagnostics and test results.
For details about the meaning of each LED state, refer to the following sections:
• “Power-on self-test LEDs” on page 36
• “Normal-operation LEDs” on page 36
Brocade M6505 16 Gbps Fibre Channel SAN I/O Module Hardware Reference Manual 35
53-1002576-02
Page 48

Interpreting SAN I/O Module LED activity
NOTE
4
Power-on self-test LEDs
The SAN I/O Module LEDs flash in various patterns during bootup, power-on self-test (POST), or
other diagnostic tests. This is normal and does not indicate a problem unless the LEDs do not
indicate a healthy state after all boot processes and diagnostic tests are complete.
• If POST fails, LEDs appear yellow.
• If POST is successful, LEDs appear green.
The SAN I/O Module will continue to operate after POST indicates a fatal error. Although the SAN I/O
Module continues to operate, it will not operate normally. It is therefore recommended that you
check the Dell M1000e Blade Server Enclosure Chassis Management Controller (CMC) error log and
resolve the condition as soon as possible.
Normal-operation LEDs
After POST is complete and if no diagnostics are being run, LEDs are used to monitor the state and
health of the SAN I/O Module, which are listed in
shown as steady, flashing, or flickering, depending on the SAN I/O Module operating mode. When
LEDs are off, there is no light or signal carrier (for example, no module or cable) for the media
interface. The green and amber switch LEDs are shown as steady or flashing depending on
whether the SAN I/O Module has power, is up and running, or results in an error.
Tab le 7. The green and amber port LEDs are
TABLE 7 Interpreting front panel LEDs during normal operation
LED type LED color and state Description
LED (diagnostic) Off (no light) • No light or signal carrier (no module or no cable
for media interface)
• No license
Steady amber Receiving light or signal carrier, but not yet online
Slow flashing amber
(2-second intervals)
Fast flashing amber
(1/2- second intervals)
FC external port status LED Off (no light)
Disabled (result of diagnostics or portDisable
command)
Error (fault with port)
• No light or signal carrier (no module or no cable
for media interface)
• No license
Steady green
• Online (connected with external device over
cable)
• Normal active port, but no activity
Slow flashing green Online, but segmented (loopback cable or
incompatible switch)
Fast flashing green Internal loopback (diagnostic)
Flickering green Normal active port (frames flowing through port)
Steady amber Signal is present but not online
Slow flashing amber Disabled port (less than 2-second interval)
Fast flashing amber Error or fault with port (less than 1/2-second interval)
36 Brocade M6505 16 Gbps Fibre Channel SAN I/O Module Hardware Reference Manual
53-1002576-02
Page 49

Removing and replacing SAN I/O Modules
NOTE
NOTE
TABLE 7 Interpreting front panel LEDs during normal operation (Continued)
SAN I/O Module status LED Off (no light) SAN I/O Module is off or power supplies for the Blade
Server or onboard DCC have failed
Steady green No errors and all ports are ready for use
Steady amber Boot-up state, port(s) offline, or in reset state
Blinking (green or amber) One or more environmental ranges are exceeded, or
error log contains diagnostic error messages
NOTE: The LED may blink during testing.
SAN I/O Module power LED Off (no light) SAN I/O Module is off or power supplies for the Dell
M1000e Blade Server Enclosure or onboard DCC
have failed
Green Normal operation and power supply is functioning.
properly. Power is supplied by the Dell M1000e Blade
Server Enclosure
Server management LED Blue or Amber Indicates management health status; controlled by
Dell M1000e Blade Server Enclosure CMC
For details, refer to the Dell PowerEdge M1000e
Enclosure Owner’s Manual.
4
Removing and replacing SAN I/O Modules
Complete the following steps to remove and replace a failed SAN I/O Module.
Before beginning this procedure, ensure that you have a replacement SAN I/O Module or filler panel
available because you do not want to leave the slot on the Dell M1000e Blade Server Enclosure
open for an extended period of time. The slot must be filled with either a replacement SAN I/O
Module or a filler panel to maintain proper air flow.
1. Back up the SAN I/O Module configuration to an FTP server using the copy configUpload
command, then complete the prompts that follow. For more information on backing up a
configuration, refer to the Brocade Fabric OS Administrator’s Guide.
The configUpload command uploads the SAN I/O Module configuration to the server, making it
available for downloading to a replacement SAN I/O Module, if necessary.
It is recommended that you back up the configuration on a regular basis to ensure that a
complete configuration is available for downloading to a replacement SAN I/O Module.
2. Using the Dell M1000e Blade Server Enclosure, ensure that all port activity used in the SAN
I/O Module and all services are stopped.
For details about port management, refer to the documentation that comes with your Dell
M1000e Blade Server Enclosure. Verify there is no activity by viewing the SAN I/O Module
LEDs. For details about LED activity, refer to
page 35.
“Interpreting SAN I/O Module LED activity” on
3. Disconnect all cables from the SFP+ transceivers, then remove the transceivers from the
external ports. For more information, refer to
“Removing and replacing SFP+ transceivers and
cables” on page 39.
Brocade M6505 16 Gbps Fibre Channel SAN I/O Module Hardware Reference Manual 37
53-1002576-02
Page 50

Removing and replacing SAN I/O Modules
ATTENTION
SFP
Bale
3
1
Cable
Release
2
SFP
4
4
For added convenience, you can refer to Figure 7, which provides the generic process for
removing an SFP+ transceiver from a port.
1 Cable release clip 3 Opening the bale on the SFP+
2 Disconnecting the cable 4 Removing the SFP+
FIGURE 7 Removing an SFP+ transceiver from a port
4. Disconnect the RJ-45 Ethernet cable from the COM serial port.
5. Press the release latch to free the release lever. Refer to Figure 3 on page 13.
6. Gently pull the release lever down and toward you to release the SAN I/O Module.
You will feel the SAN I/O Module unseat and move out of the I/O module bay approximately
0.6
cm (0.25 inch).
7. Slide the SAN I/O Module out of the I/O module bay and set it aside.
8. Insert the replacement SAN I/O Module in the I/O module bay of the Dell M1000e Blade
Server Enclosure. You must complete this step within 60
If you are not inserting a replacement SAN I/O Module in the I/O module bay, use a filler panel
to fill the empty slot to maintain proper air flow and cooling. Do not leave the slot empty.
seconds.
9. Reinsert the SFP+ transceivers that you removed in step 3.
38 Brocade M6505 16 Gbps Fibre Channel SAN I/O Module Hardware Reference Manual
53-1002576-02
Page 51

Removing and replacing SFP+ transceivers and cables
NOTE
ATTENTION
NOTE
CAUTION
10. Reconnect the cables that you disconnected in step 3.
For additional information about connecting cables, refer to “Installation and safety guidelines
when handling cables” on page 16, and the documentation that comes with the SFP+
transceivers to which the cables have been connected.
11. (Optional) Reconnect the RJ-45 Ethernet cable that you disconnected in step 4.
12. Establish a connection to the Dell M1000e Blade Server Enclosure from the Chassis
Management Controller (CMC).
Removing and replacing SFP+ transceivers and cables
1. Review “Installation and safety guidelines when handling cables” on page 16.
2. Disconnect the cable from the SFP+ transceiver.
3. Remove the SFP+ transceiver according to the manufacturer’s instructions, or as shown in
Figure 7.
The figure illustrates the process for removing the cable from the transceiver, and then
removing the transceiver from the port.
4
The appearance of your SFP+ transceivers might differ slightly from the transceiver shown in
Figure 7, but the steps for removal are the same.
4. Insert the replacement SFP+ transceiver in the external port on the SAN I/O Module until it is
firmly seated and the latching mechanism clicks.
SFP+ transceivers are keyed to ensure correct orientation. If a transceiver does not install
easily, ensure that it is correctly oriented.
Be sure to use only Brocade-branded SFP+ transceivers. If unapproved products are used, a
fault will occur on the port.
For instructions specific to the type of transceiver, visit the MyBrocade web site at:
http://my.brocade.com
5. Insert the cable in the SFP+ transceiver until the latching mechanism clicks.
Before inserting the cables, it is recommended that you refer to “Installation and safety
guidelines when handling cables” on page 16.
A 50-micron cable should not be bent to a radius less than 2 inches under full tensile load and
1.2 inches with no tensile load.
Brocade M6505 16 Gbps Fibre Channel SAN I/O Module Hardware Reference Manual 39
53-1002576-02
Page 52

Switch management
4
Switch management
You can access the SAN I/O Module from either the Dell M1000e Blade Server Enclosure Chassis
Management Controller (CMC), or directly from the SAN I/O Module.
Managing the SAN I/O Module can be performed using Web Tools, through Brocade Network
Advisor (BNA) management software, which offers a holistic view of the SAN, or through the CLI,
which is accessible using Telnet/SSH, or the local RJ-45 serial port.
• Brocade Web Tools—An embedded graphical user interface (GUI) that enables administrators
to monitor and manage single or small fabrics, switches, and ports. Web Tools is launched
directly from a web browser or from the Brocade Network Advisor. Refer to the Brocade Web
Tools Administrator’s Guide for details about using the application.
• Brocade Network Advisor (BNA)—A management application that provides centralized
management of the network using a graphical user interface (GUI), as well as quick access to
all product configuration applications. Refer to the Brocade Network Advisor SAN User Manual
for details about using the application.
• Command-line interface (CLI)—The command-line interface uses Fabric OS. (Refer to the
product release notes for version information.) Refer to the Brocade Fabric OS Command
Reference Manual for supported commands.
From the Dell M1000e Blade Server Enclosure CMC, you can connect to the SAN I/O Module by:
• Entering the connect switch-x command at the command prompt, which connects by way of an
internal serial port.
• From the CMC GUI by selecting I/O Module Overview from the left navigation panel, which
launches the Web Tools application.
• Using Telnet or SSH to access the SAN I/O Module CLI.
• Through the CMC Ethernet physical connection after assigning an IP address to the SAN I/O
Module.
Viewing the configuration
Use the configShow -all command to display all configuration data for the SAN I/O Module.
A sample configuration is provided.
switch :admin> configshow -all
[Configuration upload Information]
Configuration Format = 2.0
date = Tue Oct 7 14:54:20 2008
FOS version = v6.2.0.0
Number of LS = 3
[Chassis Configuration Begin]
[fcRouting]
fcRoute.backboneFabricId:100
fcRoute.fcrState:2
fcRouteParam.maxLsanCount:3000
fcRoute.port.8.xportAdmin:DISABLED
fcRoute.port.8.fabricId:4
fcRoute.port.8.ratov:10000
fcRoute.port.8.edtov:2000
fcRoute.port.8.frontConfigDid:160
fcRoute.port.8.portType:400
40 Brocade M6505 16 Gbps Fibre Channel SAN I/O Module Hardware Reference Manual
53-1002576-02
Page 53

fcRoute.port.8.portMode:0
fcRoute.port.8.autoElp:7
fcRoute.port.9.xportAdmin:DISABLED
fcRoute.port.9.fabricId:5
fcRoute.port.9.ratov:10000
fcRoute.port.9.edtov:2000
fcRoute.port.9.frontConfigDid:160
fcRoute.port.9.portType:400
fcRoute.port.9.portMode:0
fcRoute.port.9.autoElp:7
fcRouteParam.port.8.rportCost:0
fcRouteParam.port.9.rportCost:0
fcRoute.xlate.persistxdState:1
fcRouteParam.lsan.tagCnt:0
For more information on command options, refer to the Brocade Fabric OS Command Reference.
Upgrading or downgrading firmware
Use the firmwareDownload command to download firmware from a remote host. You can download
firmware interactively. A sample configuration is provided.
switch:admin> firmwaredownload
Server Name or IP Address: 192.168.32.10
User Name: admin
File Name: ~admin/dist/FOS7.0.0/
Network Protocol(1-auto-select, 2-FTP, 3-SCP, 4-SFTP) [1]:
Password:********
Upgrading or downgrading firmware
4
For more information on command options, refer to the Brocade Fabric OS Command Reference.
Changing the default account password
The SAN I/O Module automatically prompts you to change the default account password after
logging in for the first time. If you do not change the password, you are prompted to do so after
each subsequent login until the default password has been changed.
The default account password can be changed from its original value only when prompted
immediately following the login; the password cannot be changed using the passwd command later
in the session. If you skip the prompt and then later decide to change the password, you must log
out and then log in again.
The passwd command changes the password for your own account.
Use the “admin” account to log in to the switch for the first time and to perform the basic
configuration tasks. The default password for all of these accounts is “password”.
Brocade M6505 16 Gbps Fibre Channel SAN I/O Module Hardware Reference Manual 41
53-1002576-02
Page 54

Backing up the configuration
NOTE
4
Changing the default account password at login
1. Connect to the SAN I/O Module and log in using the default administrative account.
2. At each of the “Enter new password” prompts, enter a new password.
User-defined passwords can have from 8 through 40 characters. They must begin with an
alphabetic character and can include numeric characters, the period (.), and the
underscore ( _ ). Passwords are case-sensitive.
A sample output of changing passwords is provided.
login: admin
Password:
Please change your passwords now.
Use Control-C to exit or press 'Enter' key to proceed.
for user - root
Changing password for root
Enter new password: <hidden>
Password changed.
Saving password to stable storage.
Password saved to stable storage successfully.
(output truncated)
For more information on setting passwords, refer to the Brocade Fabric OS Administrator’s Guide.
Backing up the configuration
Prior to backing up a configuration for the SAN I/O Module, you can check the configuration by
initiating the configShow and fabricShow commands.
• The configShow command displays switch and port status.
• The fabricShow command displays fabric membership information.
Complete the following steps to back up the switch configuration to an FTP server.
1. Open a Telnet or SSH session to the SAN I/O Module.
2. Enter configUpload, which uploads the switch configuration to the server, making it available
for downloading to a replacement SAN I/O Module, if necessary.
3. Follow the prompts to upload the configuration.
It is recommended that you back up the configuration on a regular basis to ensure that a complete
configuration is available for downloading to a replacement SAN I/O Module.
For specific instructions about how to back up a configuration, refer to the Brocade Fabric OS
Administrator’s Guide. For detailed information about the commands used in backing up a
configuration, refer to the Brocade Fabric OS Command Reference.
42 Brocade M6505 16 Gbps Fibre Channel SAN I/O Module Hardware Reference Manual
53-1002576-02
Page 55

Locating the serial number information
NOTE
Before contacting service support, be sure to obtain the SAN I/O Module serial number.
When contacting service support, you will also need the Dell service tag. The service tag label is
located on the outside of SAN I/O Module; however, the label is not visible when the SAN I/O Module
is inserted in the Dell M1000e Blade Server Enclosure. You can access the service tag number using
cli commands.
To locate the serial number, invoke the chassisShow command. The SAN I/O Module serial number
is displayed, along with other data.
If your SAN I/O Module was shipped as a single unit, the service tag and serial number are one and
the same when viewing the command output. In the sample configuration output provided below,
the serial number and service tag are shown as 8RTYJN1.
CHASSIS/WWN Unit: 1
Header Version: 2
Factory Part Num: 40-1000789-04
Factory Serial Num: CFU0428H00W
Manufacture: Day: 12 Month: 7 Year: 2012
Update: Day: 30 Month: 8 Year: 2012
Time Alive: 21 days
Time Awake: 3 days
ID: BRD0000CA
Part Num: SLKWRM0000E14
Serial Num: 8RTYJN1
Locating the serial number information
4
For additional Dell service tag information, refer to Dell Chassis Management Controller Firmware
Version 4.x User Guide.
Brocade M6505 16 Gbps Fibre Channel SAN I/O Module Hardware Reference Manual 43
53-1002576-02
Page 56

Locating the serial number information
4
44 Brocade M6505 16 Gbps Fibre Channel SAN I/O Module Hardware Reference Manual
53-1002576-02
Page 57

Appendix
SAN I/O Module Specifications
In this appendix
•Processor and memory specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
•Weight and physical dimensions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
•Environmental specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
•Electrical specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
•Architectural specifications. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
•Supported HBAs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
•Fibre Channel standards compliance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
•Regulatory compliance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
•Environmental regulation compliance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
Processor and memory specifications
A
Tab le 8 lists processor and memory used in the SAN I/O Module.
TABLE 8 Processor and memory specifications
Memory type Value
PowerPC 440EPX processor 667 MHz
SDRAM 1 GB DDR2 - for system memory at 64 bits with
8 ECC operating at 166 MHz
Boot Flash 4 MB
Compact Flash 1 GB
Weight and physical dimensions
Tab le 9 lists the weight and physical dimensions of the SAN I/O Module.
TABLE 9 Weight and physical dimensions
Dimension Measurement
Height 32.48 mm (1.27 in)
Width 272.75 mm (10.74 in)
Depth 307.24 mm (12.09 in)
Weight 2.10 kg (4.65 pounds) without media
Brocade M6505 16 Gbps Fibre Channel SAN I/O Module Hardware Reference Manual 45
53-1002576-02
Page 58

Environmental specifications
A
Environmental specifications
Tab le 10 lists the environmental specifications for the SAN I/O Module.
TABLE 10 Environmental specifications
Condition Operating Non-operating
Temperature 0°C to 40°C (32°F to 104°F) -20°C to 70°C (-4°F to 158°F)
Humidity 10% to 90%, non-condensing at
29°C (84.2°F)
Altitude Up to 3,048 m (10,000 ft) 10,668 m (35,000 ft)
Shock 20 G for 6 ms 50 G with velocity change of 4216
Vibration 0.4 G at 5–500 Hz for 60 minutes 0.5 G at 2–200 Hz for 15 minutes
Air flow 30°C (86 °F) Ambient: Approx. 3CFM
40°C (104°F) Ambient: Approx. 9CFM
5% to 95%, non-condensing at
38°C (100.4 °F)
mm/sec squared
None required
Electrical specifications
Tab le 11 lists the electrical specifications for the SAN I/O Module.
TABLE 11 Electrical specifications
Feature Description
DC input 12V and 3.3V from chassis
Power consumption 30W (idle) to 40W (maximum)
Architectural specifications
The SAN I/O Module meets the specifications shown in Tab le 12.
TABLE 12 Architectural specifications
Feature Description
Scalability Refer to the current Brocade Scalability Guidelines publication.
Certified maximum Refer to the current Brocade Scalability Guidelines publication.
Performance 4.25/8.50/14.025 Gbps line speed, full duplex
Fabric latency
(Native Fabric mode only)
Maximum frame size 2112-byte payload
Class of service Class 2
<1.2 µsec with no contention
Class 3
Class F (interswitch frames)
46 Brocade M6505 16 Gbps Fibre Channel SAN I/O Module Hardware Reference Manual
53-1002576-02
Page 59

TABLE 12 Architectural specifications (Continued)
Feature Description
Port types Fabric OS Native mode
Fabric services
(Native Fabric mode only)
Supported HBAs
For information regarding supported Fibre Channel mezzanine adapters, refer to Dell-specific
product information.
For additional information, refer to your Dell PowerEdge documentation.
Supported HBAs
• E_Port (expansion port)
• F_Port (fabric-enabled port)
• U_Port (self-discovery based on switch type)
AG mode
• F_Port (fabric-enabled port)
• N_Port (NPIV-enabled port)
Simple Name Server, Registered State Change Notification (RSCN)
A
Fibre Channel standards compliance
The SAN I/O Module meets or exceeds the Fibre Channel standards for compliance, performance,
and feature capabilities as defined in the Brocade standards compliance list. This information is
available at:
http://www.brocade.com/products/interop/standards_compliance.jsp
Regulatory compliance
This section describes the regulatory compliance requirements for the Product Name.
FCC warning (US only)
This equipment has been tested and complies with the limits for a Class A computing device
pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection
against harmful interference when the equipment is operated in a commercial environment.
This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy, and if not installed and
used in accordance with the instruction manual, might cause harmful interference to radio
communications. Operation of this equipment in a residential area is likely to cause harmful
interference, in which case the user will be required to correct the interference at the user’s own
expense.
Brocade M6505 16 Gbps Fibre Channel SAN I/O Module Hardware Reference Manual 47
53-1002576-02
Page 60

Regulatory compliance
ATTENTION
A
BSMI statement (Taiwan)
KC statement (Republic of Korea)
VCCI statement (Japan)
This is a Class A product based on the standard of the Voluntary Control Council for Interference by
Information Technology Equipment (VCCI). If this equipment is used in a domestic environment,
radio disturbance might arise. When such trouble occurs, the user might be required to take
corrective actions.
CE statement
This is a Class A product. In a domestic environment, this product might cause radio interference,
and the user might be required to take corrective measures.
The standards compliance label on the SAN I/O Module contains the CE mark which indicates that
this system conforms to the provisions of the following European Council directives, laws, and
standards:
• Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Directive 89/336/EEC and the Complementary Directives
92/31/EEC and 93/68/EEC
• Low Voltage Directive (LVD) 73/23/EEC and the Complementary Directive 93/68/EEC
• EN50082-2/EN55024:1998 (European Immunity Requirements)
- EN61000-3-2/JEIDA (European and Japanese Harmonics Spec)
- EN61000-3-3
48 Brocade M6505 16 Gbps Fibre Channel SAN I/O Module Hardware Reference Manual
53-1002576-02
Page 61

Regulatory compliance
CAUTION
ATTENTION
Canadian requirements
This Class A digital apparatus meets all requirements of the Canadian Interference-Causing
Equipment Regulations, ICES-003 Class A.
Laser compliance
This equipment contains Class 1 laser products and complies with FDA Radiation Performance
Standards, 21 CFR Subchapter I and the international laser safety standard EN60825-1:1994
+A1+A2.
Use only optical transceivers that are qualified by Brocade Communications Systems, Inc. and
comply with the FDA Class 1 radiation performance requirements defined in 21 CFR Subchapter
I, and with IEC825-2 to EN60825-1:1994 +A1+A2. Optical products that do not comply with
these standards might emit light that is hazardous to the eyes.
A
RTC battery
Do not attempt to replace the real-time clock (RTC) battery. There is danger of explosion if the battery
is incorrectly replaced or disposed of. Contact your switch supplier if the real-time clock begins to
lose time.
Regulatory compliance standards
Tab le 13 lists the regulatory compliance standards for which the SAN I/O Module is certified.
TABLE 13 Regulatory compliance standards
Country Standards Agency Certifications and Markings
Safety EMC Safety EMC
United States Bi-Nat UL/CSA 60950-1
2nd Ed or latest
Canada Bi-Nat UL/CSA 60950-1
2n
d Ed or latest
Japan CISPR22 and JEIDA
European Union EN60950-1 or latest EN55022 and
Australia, New Zealand EN55022 or CISPR22
Korea KN22 and KN24 KC mark Class A
ANSI C63.4 cCSAus FCC Class A and
Statement
ICES-003 Class A cCSAus ICES A and Statement
VCCI-A and Statement
(H
armonics)
TUV Type CE marking
EN5502
4
C-Tick mark
or
AS/NZS CISPR22
Brocade M6505 16 Gbps Fibre Channel SAN I/O Module Hardware Reference Manual 49
53-1002576-02
Page 62

Environmental regulation compliance
⦃ֱՓ⫼ᳳ䰤 (EPUP) ܡ䋷ໄᯢ˖
EPUP ᖫϡӮߎ⦄ѻક FRU ⱘᬍ㺙ѻકЁˈгϡӮᇍ Brocade
᠔ᦤկⱘⳌ݇ѻકֱׂᴵℒ˄䆹ֱׂᴵℒ Brocade
ঞ݊ᅶ᠋䯈䖒៤ⱘ䗖⫼ড়ৠЁ߫ߎ˅䖯㸠㸹DŽᇍѢℸ CD
ϞࣙⱘⳌֵ݇ᙃˈབ䗖䫔ᗻǃ䩜ᇍ⡍ᅮ⫼䗨ⱘ䗖⫼ᗻ䴲։ᴗᗻⱘᱫ⼎ֱ䆕ˈBr
ocade ℸ䚥䞡ໄᯢᴀ݀ৌᇍѢϢϞ䗄ֵᙃⳌ݇ⱘ᠔᳝݊Ҫֱ䆕䰜䗄ὖϡ䋳䋷DŽ
EPUP ؛䆒Āѻક᪡ݠāЁ⊼ᯢⱘᐌ㾘ᴵӊϟՓ⫼䆹ѻકDŽ
A
Environmental regulation compliance
This section describes the China ROHS environmental regulatory compliance requirements for the
SAN I/O Module.
Environmental Protection Use Period (EPUP) Disclaimer
In no event do the EPUP logos shown on the product and field-replaceable units (FRUs) alter or
expand that warranty that Brocade provides with respect to its products as set forth in the
applicable contract between Brocade and its customer. Brocade hereby disclaims all other
warranties and representations with respect to the information contained on this CD including the
implied warranties of merchantability, fitness for a particular purpose, and non-infringement.
The EPUP assumes that the product will be used under normal conditions in accordance with the
operating manual of the product.
China RoHS
The contents included in this section are per the requirements of the People's Republic of ChinaManagement Methods for Controlling Pollution by Electronic Information products.
䙉ᅜ⦃๗⊩㾘
Ё RoHS
ᴀ㡖Ёࣙⱘݙᆍ䛑䙉ᅜњЁҎ⇥݅lj⬉ᄤֵᙃѻક∵ᶧࠊㅵ⧚ࡲ⊩NJⱘ
㽕∖DŽ
Names and Contents of the Toxic and Hazardous Substances or Elements
In accordance with China's Management Measures on the Control of Pollution caused by Electronic
Information products (Decree No. 39 by the Ministry of Information Industry), the following
information is provided regarding the names and concentration level of Hazardous substances (HS)
which may be contained in this product.
50 Brocade M6505 16 Gbps Fibre Channel SAN I/O Module Hardware Reference Manual
53-1002576-02
Page 63

Environmental regulation compliance
CHINA ROHS᳝ᆇ⠽䋼/᳝↦⠽䋼(HS/TS)䰤䞣߫㸼
᳝↦Ϣ᳝ᆇ⠽䋼ܗ㋴ⱘৡ⿄ঞ䞣
ḍЁⱘ<<⬉ᄤֵᙃѻક∵ᶧࠊㅵ⧚ࡲ⊩>>
(ֵᙃѻϮ䚼39োҸ)ˈᴀ݀ৌᦤկҹϟ᳝݇ѻકЁৃ㛑᳝ⱘ᳝ᆇ⠽䋼(HS)ⱘৡ⿄ঞ䞣∈ᑇⱘ
ֵᙃDŽ
᳝ᆇ/᳝↦⠽䋼ܗ㋴Џ㽕䚼ӊৡ⿄
䪙
˄PB
˅
∲
Hg
˅
䬝
CD
˅
݁Ӌ䫀
˄C
R6+˅
⒈㘨㣃
˄PBB˅
⒈Ѡ㣃䝮
PB
DE˅
˅
ܝ㑸䗮䘧Ѹᤶᴎ
XOO O O O
XOO O O O
㒓䏃ᵓ䚼ӊ
XOO O O O
SFP˄ܝ㑸
༈˅
XOO O O O
䩷䞥ӊ
OOOOOO
XOO O O O
ᴎẄᬃᶊঞ⒥䔼
䕃ӊ/᭛ḷܝⲬ
X 㸼⼎ℸ㉏䚼ӊݙৠ䋼ᴤ᭭Ёⱘ᳝ᆇ/᳝↦䞣催ѢSJ/T11363-2006ⱘ䰤䞣㽕∖DŽ
O 㸼⼎Փ⫼ℸ㉏⠽䋼݊䞣ԢѢϞ䗄䰤䞣㽕∖DŽ
˄
˄
China ROHS Hazardous Substances/Toxic Substances (HS/TS) Concentration Chart
A
Name of the
Component
Fibre Channel
Switch
PCBA cards X O O O O O
SFPs (optical
cable
connectors)
Sheet Metal X O O O O O
Mechanical
brackets and
Slides
Software/
Documentation
CDs
Hazardous/Toxic Substance/Elements
Lead (PB) Mercury
(Hg)
XOOO O O
XOOO O O
XOOO O O
OO O O O O
Cadium
(CD)
Hexavalent
Chromium
(CR6+)
Polybrominated
Biphenyl (PBB)
Polybrominated
Diphenyl Ether
(PBDE)
X indicates that the concentration of such hazardous/toxic substance in all the units of
homogeneous material of such component is higher than the SJ/T11363-2006 Requirements for
Concentration Limits.
O indicates that no such substances are used or that the concentration is within the
aforementioned limits.
Brocade M6505 16 Gbps Fibre Channel SAN I/O Module Hardware Reference Manual 51
53-1002576-02
Page 64

Environmental regulation compliance
A
52 Brocade M6505 16 Gbps Fibre Channel SAN I/O Module Hardware Reference Manual
53-1002576-02
Page 65

Index
A
access gateway
enhancements, 3
storage arrays, 5
access gateway mode, 1, 3, 5
default port mapping, 33
Adaptive Networking
license, 6
Advanced Performance Monitoring
enhancements, 30
license, 6
ag --modeShow command, 32
ag --modeDisable command, 32
architectural specifications, 46
ASIC, 6
Australia
regulatory compliance, 50
B
backplane connectors, 9
base model, 11
battery statement, 49
beacon, 34
boot, 36
Brocade ASIC, 6
Brocade Fabric OS cli, 40
Brocade ISL Trunking
license, 5
Brocade Network Advisor, 40
Brocade Web Tools, 40
BSMI statement (Taiwan), 48
C
cables
caution, 16, 39
guidelines, 16
part numbers, 17
radius, 16
Canada
regulatory compliance, 49
Canadian requirements, 49
caution
indicator, ix
CE statement, 48
chassisShow command, 43
China RoHS, 50, 52
commands
ag --modeDisable, 32
ag --modeShow, 32
chassisShow, 43
configShow, 40, 42
configUpload, 27, 32, 37, 42
configure, 25
connect, 22
connect switch, 21
connect switch-x, 14, 21, 40
errShow, 34
fabricShow, 27, 42
firmwareDownload, 41
ipAddrSet, 23
ipAddrShow, 22
licenseIdShow, xi
passwd, 41
supportSave, xi
switchDisable, 25, 32
switchShow, xi, 27, 31, 32, 34
wwn, xi
configShow command, 40, 42
configUpload command, 27, 32, 37, 42
configuration
backing up, 42
configure command, 25
connect command, 22
connect switch-x command, 14, 21, 40
Brocade M6505 16/8 Gbps Fibre Channel SAN I/O Module Hardware User’s Guide 53
53-1002576-02
Page 66

Index
D
diagnostics, 16
LED operation, 36
dimensions, 45
DPOD (see dynamic ports on demand)
dynamic ports on demand, 3, 4
licensing, 4
E
electrostatic discharge, 11
enhanced group management, 3
enterprise model, 11
EPUP disclaimer, 50
errShow command, 34
ESD, 11
Ethernet connection, 14
European Union
regulatory compliance, 50
external ports, 1
F
Fabric OS, 2, 33
native mode, 5
release notes, x
fabric OS, 3
fabric OS native mode
changing from access gateway mode, 31
Fabric Watch
license, 6
fabricShow command, 27, 42
FCC warning (US only), 47
Fibre Channel
auto-negotiating ports, 2
auto-sensing ports, 5
ports, 1
Fibre Channel standards compliance, 47
firmwareDownload command, 41
FSPF, 29
FTP
firmware upgrades, 4
FTP server, 42
full model, 11
full-duplex
Ethernet ports, 2
G
guidelines
reliability, 12
static-sensitive devices, 12
H
handling
optical transceivers, 15
static-sensitive devices, 12
hazardous substances, 51
host OS, 2
I
internal ports, 1
Internet Explorer, 24
interoperability, 29
interpreting
LED activity, 35
POST results, 35
IP address
filtering, 3
modify using CMC CLI, 21
modify using CMC GUI, 21
modify using module CLI, 22
modifying default, 20
ipAddrSet command, 23
ipAddrShow command, 22
ISL Trunking, 3
groups, 5, 6
license, 6
J
Japan
regulatory compliance, 50
Java, 24
54 Brocade M6505 16/8 Gbps Fibre Channel SAN I/O Module Hardware User’s Guide
53-1002576-02
Page 67

Index
K
KC statement (Republic of Korea), 48
Korea
regulatory compliance, 50
L
laser compliance, 49
LED, 34, 35
LED activity
interpreting, 35
LEDs
ACT led, 36
diagnostics, 36
LINK led, 36
management health status, 2
normal operation, 36
port and port status, 8
POST, 36
power status, 8
server management status, 8
switch status, 2, 8
system power, 2
licenseIdShow command, xi
licenses
Adaptive Networking, 6
Advanced Performance Monitoring, 6
BNA, 6
Fabric Watch, 6
ISL Trunking, 6
Ports on Demand, 6
link initialization, 29
N
native fabric mode, 1
port types, 6
New Zealand
regulatory complaince, 50
NPIV, 1, 5
NTP
client support, 4
O
operating system support, 33
operating systems
supported, 2
optical cabling, 16
optical transceivers
connection types, 10
guidelines, 15
handling, 15
inserting, 16
orientation, 16, 39
part numbers, 15
pre-installed, 10
removing, 39
replacing, 39
SFP+, 2
speed, 17
wavelength, 10
optional features
access gateway mode, 7
P
M
management
Brocade Network Advisor, 40
cli, 40
Web Tools, 40
management tool, 34
media
multi-mode, 17
models
base, 11
enterprise, 11
full, 11
multi-mode media, 17
Brocade M6505 16/8 Gbps Fibre Channel SAN I/O Module Hardware User’s Guide 55
53-1002576-02
passwd command, 41
password
changing initial prompt, 42
port mapping, 33
port mirroring, 3
port negotiation, 33
ports
external, 1
internal, 1
serial console, 2
speed, 1
Ports on Demand
license, 6
Page 68

Index
ports on demand
dynamic, 4
POST, 16, 34
LEDs
bootup, 36
results, 35
R
RBAC, 3
RCSN, 29
regulatory compliance, 47
Australia, 50
BSMI statement (Taiwan), 48
Canada, 49
Canadian requirements, 49
CE statement, 48
environmental, 50
European Union, 50
FCC warning (US only), 47
Japan, 50
KC statement (Republic of Korea), 48
Korea, 50
laser compliance, 49
New Zealand, 50
RTC battery, 49
United States, 49
VCCI staetment (Japan), 48
release latch, 13
locking, 14
operating, 14
release lever, 7, 13, 14
operating, 14, 38
reliability guidelines, 12
remote access, 14
role-based access control, 3
routing, 29
RTC battery statement, 49
runtime elements, 2
S
SAN I/O Module
accessing, 33
backplane connectors, 9
characteristics, 7
connecting to Ethernet, 24
connecting to fabric, 24
front panel, 7
hardware description, 7
nonport side, 9
physical dimensions and weight, 45
release latch, 13
release lever, 7, 13
removing, 37
replacing, 37
side view, 9
status, 35
serial console port, 2
serial number, xi
locating, 43
service level classes, 3
service tag, xi, 43
SFP+ (see also optical transceivers), 2, 10
SNMP
supported versions, 3
SNMP facilities, 29
specifications, 45
SSH, 42
static-sensitive devices, handling, 12
substances
hazardous, 51
hazardous concentration chart, 51
toxic, 51
supported HBAs, 47
supportSave command, xi
switch
serial number, xi
switch management
Brocade Network Advisor, 40
cli, 40
Web Tools, 40
switchDisable command, 25, 32
switchShow command, xi, 27, 31, 32, 34
system LEDs, 2
56 Brocade M6505 16/8 Gbps Fibre Channel SAN I/O Module Hardware User’s Guide
53-1002576-02
Page 69

T
Telnet, 42
terminal session with I/O module, 22
toxic substances, 51
transceivers (see also optical transceivers), 10
translative mode, 29
trunking, 30
U
United States
regulatory compliance, 49
V
VCCI statement, 48
Index
W
warning
indicator, ix
web browser, 24
Web Tools, 24
Java, 24
using to connect SAN I/O Module, 24
weight, 45
wwn command, xi
Z
zoning, 3, 6, 33
Brocade M6505 16/8 Gbps Fibre Channel SAN I/O Module Hardware User’s Guide 57
53-1002576-02
Page 70

Index
58 Brocade M6505 16/8 Gbps Fibre Channel SAN I/O Module Hardware User’s Guide
53-1002576-02
 Loading...
Loading...