Page 1

Dell PowerEdge M520 Systems
Owner's Manual
Regulatory Model: HHB
Regulatory Type: HHB004
Page 2

Notes, Cautions, and Warnings
NOTE: A NOTE indicates important information that helps you make better use of your computer.
CAUTION: A CAUTION indicates either potential damage to hardware or loss of data and tells you how to avoid the
problem.
WARNING: A WARNING indicates a potential for property damage, personal injury, or death.
© 2013 Dell Inc.
Trademarks used in this text:
PowerConnect
Inc.
Intel
is a registered trademark and
Microsoft
or registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation in the United States and/or other countries.
Enterprise Linux
™
OpenManage
,
®
®
®
Pentium
,
Windows
,
Xeon
,
®
,
®
are registered trademarks of Red Hat, Inc. in the United States and/or other countries.
registered trademarks of Novell Inc. in the United States and other countries.
and/or its affiliates.
Citrix
the United States and/or other countries.
™
Dell
, the Dell logo,
™
EqualLogic
,
®
®
Core
,
and
AMD Opteron
Windows Server
®
®
,
,
Xen
XenServer
Dell Boomi
™
Compellent
,
®
Celeron
are registered trademarks of Intel Corporation in the U.S. and other countries.
™
AMD Phenom
,
®
Internet Explorer
,
®
and
XenMotion
®
VMware
trademarks of VMware, Inc. in the United States or other countries.
,
vMotion
™
Dell Precision
,
™
KACE
,
™
AMD Sempron
and
®
MS-DOS
,
®
are either registered trademarks or trademarks of Citrix Systems, Inc. in
®
,
vCenter
IBM
™
FlexAddress
,
®
Windows Vista
,
,
™
Oracle
®
,
vCenter SRM
®
is a registered trademark of International Business Machines
™
OptiPlex
,
™
Force10
,
™
are trademarks of Advanced Micro Devices, Inc.
®
and
®
is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation
™
and
Corporation.
2013 - 09
Rev. A02
™
Latitude
,
™
Vostro
and
Active Directory
®
Red Hat
®
vSphere
PowerEdge
™
PowerVault
,
™
are trademarks of Dell
™
AMD
®
are either trademarks
Red Hat
®
and
®
SUSE
®
are
and
Novell
are registered trademarks or
,
®
Page 3

Contents
1 About Your System......................................................................................................................7
Front-Panel Features And Indicators....................................................................................................................... 7
Using USB Diskette or USB DVD/CD Drives............................................................................................................. 7
Hard-Drive/SSD Indicator Patterns.......................................................................................................................... 8
Other Information You May Need.............................................................................................................................9
2 Using The System Setup And Boot Manager.......................................................................11
Choosing The System Boot Mode.......................................................................................................................... 11
Entering System Setup............................................................................................................................................12
Responding To Error Messages.......................................................................................................................12
Using The System Setup Navigation Keys....................................................................................................... 12
System Setup Options.............................................................................................................................................12
System Setup Main Screen..............................................................................................................................13
System BIOS Screen........................................................................................................................................13
System Information Screen..............................................................................................................................13
Memory Settings Screen................................................................................................................................. 14
Processor Settings Screen.............................................................................................................................. 14
SATA Settings Screen......................................................................................................................................15
Boot Settings Screen....................................................................................................................................... 16
Integrated Devices Screen.............................................................................................................................. 16
Serial Communications Screen........................................................................................................................17
System Profile Settings Screen........................................................................................................................18
System Security Screen...................................................................................................................................18
Miscellaneous Settings....................................................................................................................................19
System And Setup Password Features.................................................................................................................. 20
Assigning A System And/Or Setup Password..................................................................................................20
Using Your System Password To Secure Your System....................................................................................21
Deleting Or Changing An Existing System And/Or Setup Password................................................................21
Operating With A Setup Password Enabled.................................................................................................... 22
Entering The UEFI Boot Manager........................................................................................................................... 22
Using The Boot Manager Navigation Keys......................................................................................................22
Boot Manager Screen......................................................................................................................................23
UEFI Boot Menu............................................................................................................................................... 23
Embedded System Management............................................................................................................................23
iDRAC Settings Utility..............................................................................................................................................24
Entering The iDRAC Settings Utility..................................................................................................................24
3 Installing Blade Components.................................................................................................. 25
Page 4

Recommended Tools.............................................................................................................................................. 25
Removing And Installing A Blade........................................................................................................................... 25
Removing The Blade........................................................................................................................................ 25
Installing The Blade..........................................................................................................................................26
Opening And Closing The Blade............................................................................................................................. 27
Opening The Blade...........................................................................................................................................27
Closing The Blade............................................................................................................................................ 28
Inside The Blade.....................................................................................................................................................28
Cooling Shroud....................................................................................................................................................... 29
Removing The Cooling Shroud......................................................................................................................... 29
Installing The Cooling Shroud.......................................................................................................................... 30
System Memory......................................................................................................................................................30
General Memory Module Installation Guidelines............................................................................................ 31
Mode-Specific Guidelines................................................................................................................................32
I/O Module Mezzanine Cards................................................................................................................................. 36
Mezzanine Card Installation Guidelines...........................................................................................................36
Removing A Mezzanine Card........................................................................................................................... 36
Installing A Mezzanine Card.............................................................................................................................37
Management Riser Card.........................................................................................................................................38
Replacing The SD Card.................................................................................................................................... 38
Internal USB Key.............................................................................................................................................. 39
SD vFlash Card........................................................................................................................................................40
Replacing The SD vFlash Card......................................................................................................................... 40
Processors..............................................................................................................................................................41
Removing A Processor.....................................................................................................................................41
Installing A Processor......................................................................................................................................43
Hard Drives/SSDs................................................................................................................................................... 45
Hard Drive/SSD Installation Guidelines........................................................................................................... 45
Removing A Hard Drive/SSD............................................................................................................................ 45
Installing A Hard Drive/SSD............................................................................................................................. 46
Shutdown Procedure For Servicing a Hard Drive/SSD....................................................................................46
Configuring The Boot Drive.............................................................................................................................. 46
Removing A Hard Drive/SSD From A Hard-Drive/SSD Carrier.........................................................................46
Installing A Hard Drive/SSD In A Hard-Drive/SSD Carrier...............................................................................47
Hard-Drive/SSD Backplane.................................................................................................................................... 47
Removing The Hard-Drive/SSD Backplane......................................................................................................47
Installing The Hard-Drive/SSD Backplane.......................................................................................................48
System Board..........................................................................................................................................................49
Removing The System Board........................................................................................................................... 49
Installing The System Board............................................................................................................................ 50
NVRAM Backup Battery......................................................................................................................................... 51
Replacing The NVRAM Backup Battery.......................................................................................................... 51
Page 5

Storage Controller Card..........................................................................................................................................52
Removing The Storage Controller Card............................................................................................................52
Installing The Storage Controller Card.............................................................................................................53
4 Troubleshooting Your System................................................................................................. 55
Safety First—For You and Your System..................................................................................................................55
Troubleshooting System Memory...........................................................................................................................55
Troubleshooting Hard Drives..................................................................................................................................56
Troubleshooting USB Devices................................................................................................................................56
Troubleshooting An Internal SD Card.....................................................................................................................57
Troubleshooting Processors...................................................................................................................................57
Troubleshooting The Blade System Board.............................................................................................................57
Troubleshooting The NVRAM Backup Battery.......................................................................................................58
5 Using System Diagnostics....................................................................................................... 59
Dell Online Diagnostics...........................................................................................................................................59
Dell Embedded System Diagnostics....................................................................................................................... 59
When To Use The Embedded System Diagnostics.......................................................................................... 59
Running The Embedded System Diagnostics...................................................................................................59
System Diagnostic Controls............................................................................................................................. 60
6 Jumpers And Connectors........................................................................................................ 61
System Board Jumper Settings.............................................................................................................................. 61
System Board Connectors......................................................................................................................................62
Disabling A Forgotten Password............................................................................................................................ 63
7 Technical Specifications......................................................................................................... 65
8 System Messages.....................................................................................................................69
LCD Status Messages.............................................................................................................................................69
Viewing LCD Messages................................................................................................................................... 69
Removing LCD Messages.................................................................................................................................69
System Error Messages..........................................................................................................................................69
Warning Messages...............................................................................................................................................138
Diagnostic Messages........................................................................................................................................... 138
Alert Messages.....................................................................................................................................................138
9 Getting Help..............................................................................................................................139
Contacting Dell..................................................................................................................................................... 139
Page 6

6
Page 7
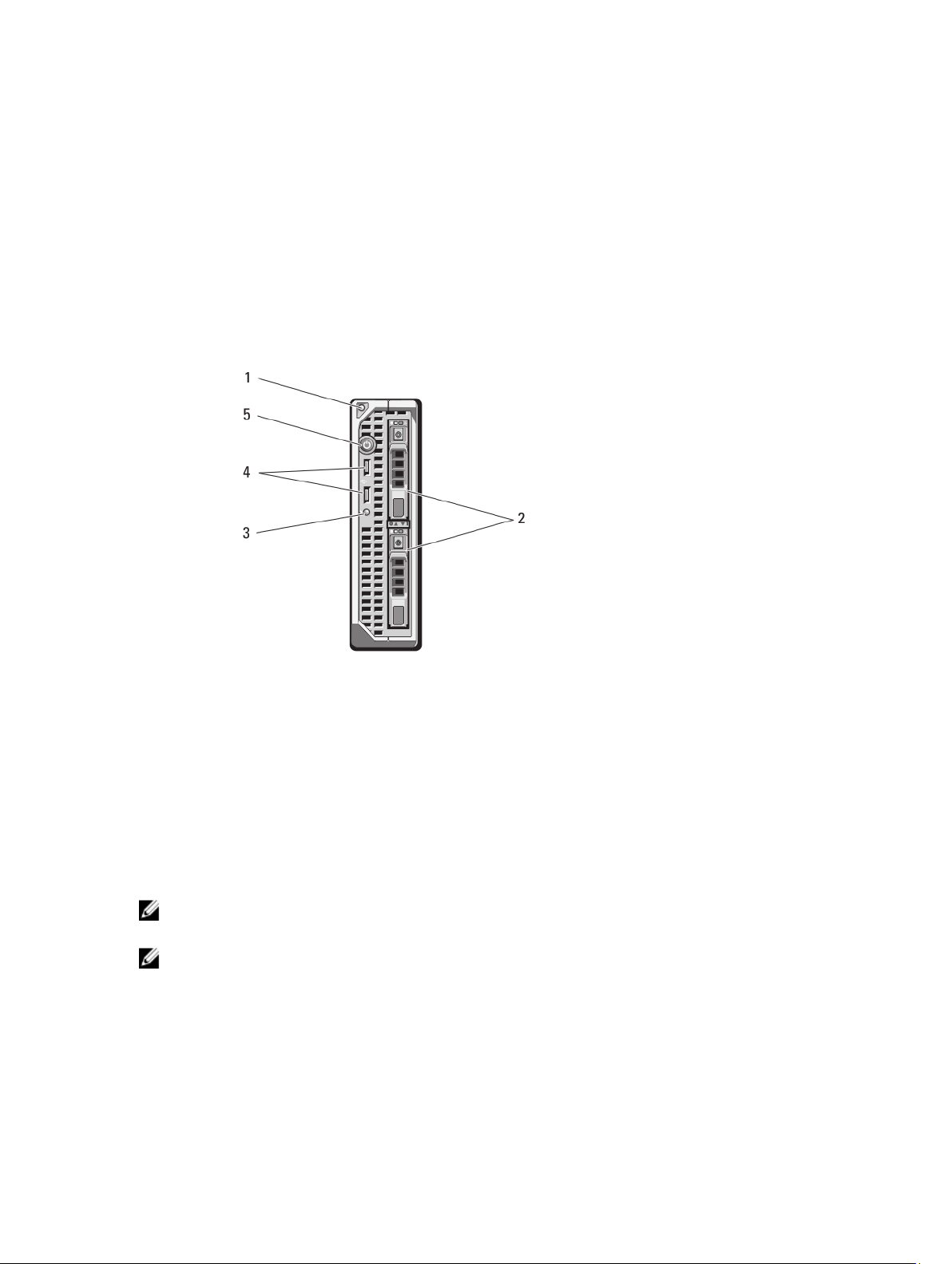
About Your System
Front-Panel Features And Indicators
1
Figure 1. Front-Panel Features and Indicators
1. blade handle release button
2. hard drives/SSDs (2)
3. status/identification indicator
4. USB connectors (2)
5. blade power button
Using USB Diskette or USB DVD/CD Drives
The blade has USB ports on the front which allow you to connect a USB diskette drive, USB flash drive, USB DVD/CD
drive, keyboard, or mouse. The USB drives can be used to configure the blade.
NOTE: Your blade supports only Dell-branded USB 2.0 drives. Use the optional external drive storage tray to
support the drive while in use.
NOTE: If the drive must be designated as the boot drive, connect the USB drive, restart the system, then enter the
System Setup and set the drive as first in the boot sequence. The USB device is displayed in the boot order setup
screen only if it is attached to the system before you run the System Setup. You can also select the boot device by
pressing <F11> during system start-up and selecting a boot device for the current boot sequence.
7
Page 8
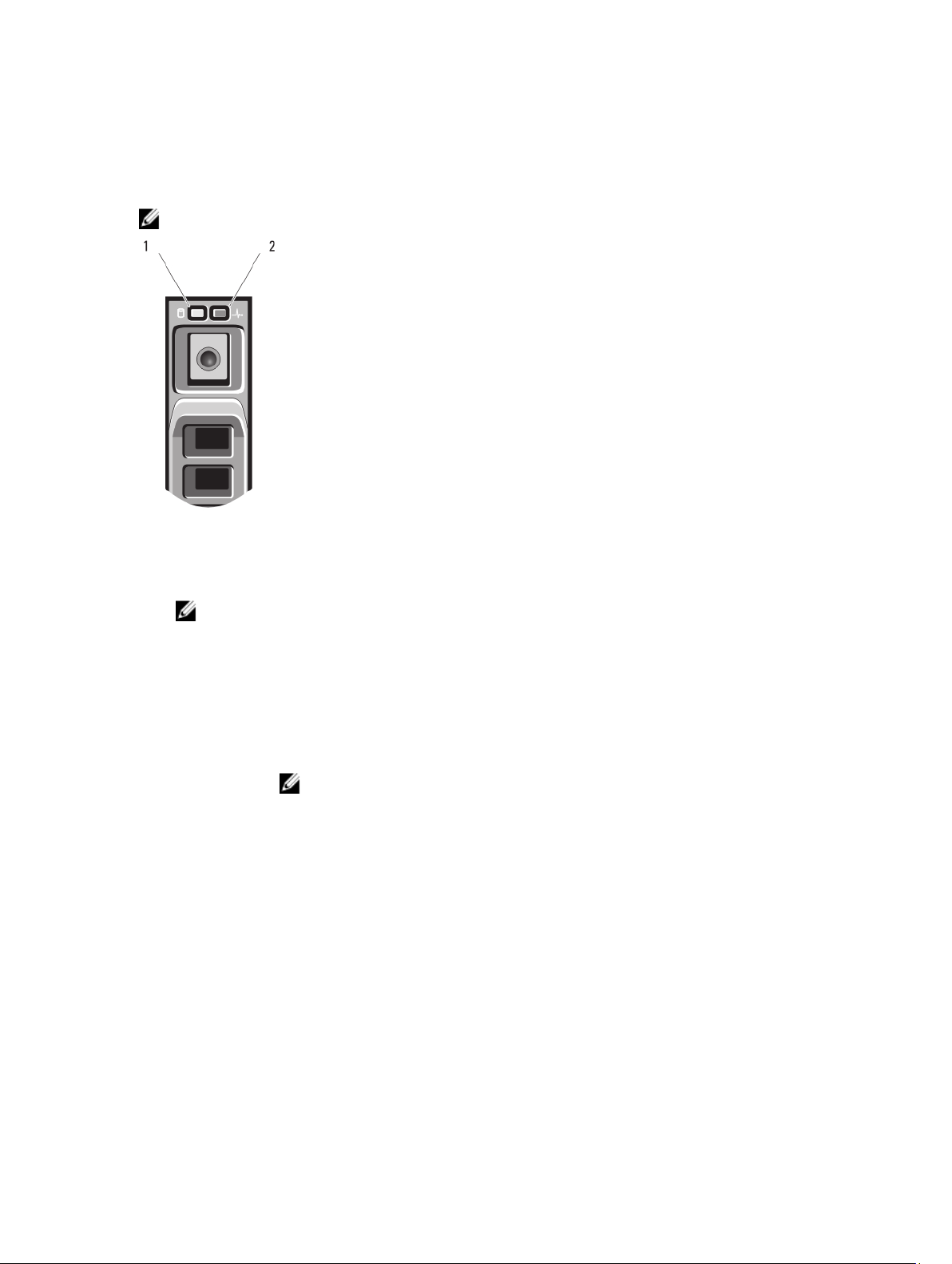
Hard-Drive/SSD Indicator Patterns
The hard-drive/SSD indicators display different patterns as drive events occur in the system.
NOTE: The blade must have a hard drive/SSD or a hard-drive blank installed in each drive bay.
Figure 2. Hard-Drive/SSD Indicators
1. drive activity indicator (green)
2. drive status indicator (green and amber)
NOTE: If the drive is in Advanced Host Controller Interface (AHCI) mode, the status LED (on the right side)
does not function and remains off.
Drive-Status
Indicator Pattern
Blinks green two
times per second
Off Drive ready for insertion or removal
Blinks green, amber,
and off
Blinks amber four
times per second
Blinks green slowly Drive rebuilding
Steady green Drive online
Blinks green three
seconds, amber three
seconds, and off six
seconds
Condition
Identifying drive or preparing for removal
NOTE: The drive status indicator remains off until all drives are initialized after system
power is applied. Drives are not ready for insertion or removal during this time.
Drive predicted failure
Drive failed
Rebuild aborted
8
Page 9
Other Information You May Need
WARNING: See the safety and regulatory information that shipped with your system. Warranty information may be
included within this document or as a separate document.
• The
Getting Started Guide
specifications.
• The
Rack Installation Instructions
rack.
• The
Dell PowerEdge M1000e Enclosure Owner’s Manual
describes how to troubleshoot the enclosure and install or replace the enclosure's components.
• The
Dell Chassis Management Controller User’s Guide
the Chassis Management Controller (CMC).
• For the full name of an abbreviation or acronym used in this document, see the Glossary at www.dell.com/
support/manuals.
• Dell systems management application documentation provides information about installing and using the
systems management software.
• Any media that ships with your system that provides documentation and tools for configuring and managing your
system, including those pertaining to the operating system, system management software, system updates, and
system components that you purchased with your system.
NOTE: Always check for updates on www.dell.com/support/manuals and read the updates first because they often
supersede information in other documents.
provides an overview of system features, setting up your system, and technical
included with your rack solution describes how to install your system into a
provides information about enclosure features and
provides information on installing, configuring and using
9
Page 10

10
Page 11

Using The System Setup And Boot Manager
System Setup enables you to manage your system hardware and specify BIOS-level options.
The following keystrokes provide access to system features during startup:
Keystroke Description
<F2> Enters the System Setup.
<F10> Enters System Services, which opens the Dell Lifecycle Controller 2 (LC2). The Dell LC2
supports systems management features such as operating system deployment, hardware
diagnostics, platform updates, and platform configuration, using a graphical user interface. The
exact LC2 feature set is determined by the iDRAC license purchased. For more information, see
the Dell LC2 documentation.
<F11> Enters the BIOS Boot Manager or the Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) Boot
Manager, depending on the system's boot configuration.
<F12> Starts Preboot eXecution Environment (PXE) boot.
From the System Setup, you can:
• Change the NVRAM settings after you add or remove hardware
• View the system hardware configuration
• Enable or disable integrated devices
• Set performance and power management thresholds
• Manage system security
2
You can access the System Setup using the:
• Standard graphical browser, which is enabled by default
• Text browser, which is enabled using Console Redirection
To enable Console Redirection, in System Setup, select System BIOS → Serial Communication screen → Serial
Communication, select On with Console Redirection.
NOTE: By default, help text for the selected field is displayed in the graphical browser. To view the help text in the
text browser, press <F1>.
Choosing The System Boot Mode
System Setup enables you to specify the boot mode for installing your operating system:
• BIOS boot mode (the default) is the standard BIOS-level boot interface.
• UEFI boot mode is an enhanced 64-bit boot interface based on Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI)
specifications that overlays the system BIOS.
You must select the boot mode in the Boot Mode field of the Boot Settings screen of System Setup. Once you specify the
boot mode, the system boots in the specified boot mode and you then proceed to install your operating system from that
11
Page 12

mode. Thereafter, you must boot the system in the same boot mode (BIOS or UEFI) to access the installed operating
system. Trying to boot the operating system from the other boot mode will cause the system to halt at startup.
NOTE: Operating systems must be UEFI-compatible to be installed from the UEFI boot mode. DOS and 32-bit
operating systems do not support UEFI and can only be installed from the BIOS boot mode.
NOTE: For the latest information on supported operating systems, go to dell.com/ossupport.
Entering System Setup
1. Turn on or restart your system.
2. Press <F2> immediately after you see the following message:
<F2> = System Setup
If your operating system begins to load before you press <F2>, allow the system to finish booting, and then restart
your system and try again.
Responding To Error Messages
If an error message is displayed while the system is booting, make a note of the message. For more information, see
System Error Messages.
NOTE: After installing a memory upgrade, it is normal for your system to display a message the first time you start
your system.
Using The System Setup Navigation Keys
Keys Action
Up arrow Moves to the previous field.
Down arrow Moves to the next field.
<Enter> Allows you to type in a value in the selected field (if applicable) or follow the link in the field.
Spacebar Expands or collapses a drop-down list, if applicable.
<Tab> Moves to the next focus area.
NOTE: For the standard graphics browser only.
<Esc> Moves to the previous page till you view the main screen. Pressing <Esc> in the main screen
displays a message that prompts you to save any unsaved changes and restarts the system.
<F1> Displays the System Setup help file.
NOTE: For most of the options, any changes that you make are recorded but do not take effect until you restart the
system.
System Setup Options
12
Page 13

System Setup Main Screen
NOTE: Press <Alt><F> to reset the BIOS or UEFI settings to their default settings.
Menu Item Description
System BIOS This option is used to view and configure BIOS settings.
iDRAC Settings This option is used to view and configure iDRAC settings.
Device Settings This option is used to view and configure device settings.
System BIOS Screen
NOTE: The options for System Setup change based on the system configuration.
NOTE: System Setup defaults are listed under their respective options in the following sections, where applicable.
Menu Item Description
iDRAC Settings This option is used to view and configure iDRAC settings.
Device Settings This option is used to view and configure device settings.
System Information Displays information about the system such as the system model name, BIOS version, Service
Tag, and so on.
Memory Settings Displays information and options related to installed memory.
Processor Settings Displays information and options related to the processor such as speed, cache size, and so
on.
SATA Settings Displays options to enable or disable the integrated SATA controller and ports.
Boot Settings Displays options to specify the boot mode (BIOS or UEFI). Enables you to modify UEFI and BIOS
boot settings.
Integrated Devices Displays options to enable or disable integrated device controllers and ports, and to specify
related features and options.
Serial Communication Displays options to enable or disable the serial ports and specify related features and options.
System Profile
Settings
System Security Displays options to configure the system security settings like, system password, setup
Miscellaneous
Settings
Displays options to change the processor power management settings, memory frequency,
and so on.
password, TPM security, and so on. It also enables or disables support for local BIOS update
and the power button on the system.
Displays options to change the system date, time, and so on.
System Information Screen
Menu Item
System Model Name Displays the system model name.
Description
13
Page 14

Menu Item Description
System BIOS Version Displays the BIOS version installed on the system.
System Service Tag Displays the system Service Tag.
System Manufacturer Displays the name of system manufacturer.
System Manufacturer
Contact Information
Displays the contact information of the system manufacturer.
Memory Settings Screen
Menu Item Description
System Memory Size Displays the amount of memory installed in the system.
System Memory Type Displays the type of memory installed in the system.
System Memory
Speed
System Memory
Voltage
Video Memory Displays the amount of video memory.
System Memory
Testing
Memory Operating
Mode
Displays the system memory speed.
Displays the system memory voltage.
Specifies whether system memory tests are run during system boot. Options are Enabled and
Disabled. By default, the System Memory Testing option is set to Disabled.
Specifies the memory operating mode. The options available depending on the memory
configuration of your system are Optimizer Mode, Advanced ECC Mode, Mirror Mode, Spare
Mode, Spare with Advanced ECC Mode, and Dell Fault Resilient Mode. By default, the Memory
Operating Mode option is set to Optimizer Mode.
NOTE: The Memory Operating Mode can have different defaults and available options
based on the memory configuration.
NOTE: The Dell Fault Resilient Mode establishes an area of memory that is fault resilient.
This mode can be used by an operating system that supports the feature to load critical
applications or enables the operating system kernel to maximize system availability.
Node Interleaving If this field is Enabled, memory interleaving is supported if a symmetric memory configuration is
installed. If Disabled, the system supports Non-Uniform Memory architecture (NUMA)
(asymmetric) memory configurations. By default, Node Interleaving option is set to Disabled.
Serial Debug Output By default, it is set to disabled.
Processor Settings Screen
Menu Item Description
Logical Processor Allows you to enable or disable logical processors and display the number of logical
processors. If the Logical Processor option is set to Enabled, the BIOS displays all the logical
processors. If this option is set to Disabled, the BIOS only displays one logical processor per
core. By default, the Logical Processor option is set to Enabled.
14
Page 15

Menu Item Description
QPI Speed Allows you to set the QuickPath Interconnect data rate settings. By default, the QPI Speed
option is set to Maximum data rate.
NOTE: The QPI Speed option is displayed only when both the processors are installed.
Alternate RTID
(Requestor
Transaction ID)
Setting
Virtualization
Technology
Adjacent Cache Line
Prefetch
Hardware Prefetcher Allows you to enable or disable hardware prefetcher. By default, the Hardware Prefetcher
DCU Streamer
Prefetcher
DCU IP Prefetcher Allows you to enable or disable DCU IP prefetcher. By default, the DCU IP Prefetcher option is
Execute Disable Allows you enable or disable execute disable memory protection technology. By default, the
Number of Cores per
Processor
Processor 64-bit
Support
Allows you to allocate more RTIDs to the remote socket increasing cache performance
between the sockets or work in normal mode for NUMA. By default, the Alternate RTID
(Requestor Transaction ID) Setting is set to Disabled.
Allows you enable or disable the additional hardware capabilities provided for virtualization. By
default, the Virtualization Technology option is set to Enabled.
Allows you to optimize the system for applications that require high utilization of sequential
memory access. By default, the Adjacent Cache Line Prefetch option is set to Enabled. You can
disable this option for applications that require high utilization of random memory access.
option is set to Enabled.
Allows you to enable or disable DCU streamer prefetcher. By default, the DCU Streamer
Prefetcher option is set to Enabled.
set to Enabled.
Execute Disable option is set to Enabled.
Allows you to control the number of enabled cores in each processor. By default, the Number
of Cores per Processor option is set to All.
Specifies if the processor(s) support 64-bit extensions.
Processor Core
Speed
Processor Bus Speed Displays the bus speed of the processors.
Processor X FamilyModel-Stepping
Displays the maximum core frequency of the processor.
NOTE: The processor bus speed option is displayed only when both the processors are
installed.
Displays the family and model number of each processor. A submenu displays the core speed,
the amount of cache memory, and the number of cores of the processor(s).
SATA Settings Screen
Menu Item Description
Embedded SATA Allows the embedded SATA to be set to Off, ATA, AHCI, or RAID modes. By default, Embedded
SATA is set to AHCI.
Port A Auto enables BIOS support for the device attached to SATA port A. Off disables BIOS support
for the device. By default, Port A is set to Auto.
15
Page 16

Menu Item Description
Port B Auto enables BIOS support for the device attached to SATA port B. Off disables BIOS support
for the device. By default, Port B is set to Auto.
Boot Settings Screen
Menu Item Description
Boot Mode Allows you to set the boot mode of the system.
CAUTION: Switching the boot mode may prevent the system from booting if the operating
system is not installed in the same boot mode.
If the operating system supports UEFI, you can set this option to UEFI. Setting this field to BIOS
allows compatibility with non-UEFI operating systems. By default, the Boot Mode option is set
to BIOS.
NOTE: Setting this field to UEFI disables BIOS Boot Settings menu. Setting this field to
BIOS disables the UEFI Boot Settings menu.
Boot Sequence Retry Allows you to enable or disable the boot sequence retry feature. If this field is enabled and the
system fails to boot, the system reattempts the boot sequence after 30 seconds. By default, the
Boot Sequence Retry option is set to Disabled.
BIOS Boot Settings Allows you to enable or disable BIOS Boot options.
NOTE: This option is enabled only if the boot mode is BIOS.
UEFI Boot Settings Allows you to enable or disable UEFI Boot options. The Boot options include IPv4 PXE and IPv6
PXE. By default, the UEFI PXE boot protocol is set to IPv4.
NOTE: This option is enabled only if the boot mode is UEFI.
One-Time Boot Allows you to enable or disable a one-time boot from a selected device.
Integrated Devices Screen
Menu Item Description
Integrated RAID
Controller
User Accessible USB
Ports
Internal USB Port Allows you to enable or disable the internal USB port. By default, the Internal USB Port option
Internal SD Card Port Enables or disables the system’s internal SD card port. By default, Internal SD Card Port option
Allows you to enable or disable the integrated RAID controller. By default, the Integrated RAID
Controller option is set to Enabled.
Allows you enable or disable the user accessible USB ports. Selecting Only Back Ports On
disables the front USB ports and selecting All Ports Off disables both front and back USB ports.
By default, the User Accessible USB Ports option is set to All Ports On.
is set to On.
is set to On.
NOTE: This option is displayed only if IDSDM is installed on the system board.
16
Page 17

Menu Item Description
Internal SD Card
Redundancy
Integrated Network
Card 1
OS Watchdog Timer Allows you to enable or disable the OS watchdog timer. When this field is enabled, the
Embedded Video
Controller
SR-IOV Global Enable Allows you to enable or disable the BIOS configuration of Single Root I/O Virtualization (SR-
Memory Mapped I/O
above 4GB
Slot Disablement Allows you to enable or disable available PCIe slots on your system. The Slot Disablement
If set to Mirror mode, data is written on both SD cards. If any one of the SD card fails, data is
written to the active SD card. Data from this card is copied to the replacement SD card at the
next boot. By default, Internal SD Card Redundancy option is set to Mirror.
NOTE: This option is displayed only if IDSDM is installed on the system board.
Allows you to enable or disable the integrated network card 1. By default, the Integrated
Network Card 1 option is set to Enabled.
operating system initializes the timer and the OS watchdog timer helps in recovering the
operating system. By default, the OS Watchdog Timer option is set to Disabled.
Allows you to enable or disable the Embedded Video Controller. By default, the embedded
video controller is Enabled.
IOV) devices. By default, the SR-IOV Global Enable option is set to Disabled.
Allows you to enable support for PCIe devices that require large amounts of memory. You can
enable this option only on 64-bit operating systems. By default, the option is set to Disabled.
feature controls the configuration of PCIe cards installed in the specified slot.
CAUTION: Slot disablement must be used only when the installed peripheral card is
preventing booting into the Operating System or causing delays in system startup. If the
slot is disabled, both the Option ROM and UEFI driver are disabled.
Serial Communications Screen
Menu Item Description
Serial Communication Allows you to enable the COM port or Console Redirection options.
Serial Port Address Allows you to set the port address for serial devices. By default, the Serial Port Address option
is set to COM1.
NOTE: Only Serial Device 2 can be used for Serial Over LAN (SOL). To use console
redirection by SOL, configure the same port address for console redirection and the serial
device.
Failsafe Baud Rate Displays the failsafe baud rate for console redirection. The BIOS attempts to determine the
baud rate automatically. This failsafe baud rate is used only if the attempt fails and the value
must not be changed. By default, the Failsafe Baud Rate option is set to 11520.
Remote Terminal
Type
Redirection After
Boot
Allows you to set the remote console terminal type. By default, the Remote Terminal Type
option is set to VT 100/VT220.
Allows you to enable or disable to the BIOS console redirection when the operating system is
loaded. By default, the Redirection After Boot option is set to Enabled.
17
Page 18

System Profile Settings Screen
Menu Item Description
System Profile Allows you to set the system profile. If you set the System Profile option to a mode other than
Custom, the BIOS automatically sets the rest of the options. You can only change the rest of the
options if the mode is set to Custom. By default, the System Profile option is set to Performance
Per Watt Optimized (DAPC). DAPC is Dell Active Power Controller.
NOTE: The following parameters are available only when the System Profile is set to
Custom.
CPU Power
Management
Memory Frequency Allows you to set the memory frequency. By default, the Memory Frequency option is set to
Turbo Boost Allows you to enable or disable the processor to operate in turbo boost mode. By default, the
C1E Allows you to enable or disable the processor to switch to a minimum performance state when
C States Allows you to enable or disable the processor to operate in all available power states. By
Monitor/Mwait Allows you to enable Monitor/Mwait instructions in the processor. By default, the Monitor/
Memory Patrol Scrub Allows you to set the memory patrol scrub frequency. By default, the Memory Patrol Scrub
Memory Refresh Rate Allows you to set the memory refresh rate. By default, the Memory Refresh Rate option is set to
Allows you to set the CPU power management. By default, the CPU Power Management option
is set to System DBPM (DAPC). DBPM is Demand-Based Power Management.
Maximum Performance.
Turbo Boost option is set to Enabled.
it is idle. By default, the C1E option is set to Enabled.
default, the C States option is set to Enabled.
Mwait option is set to Enabled for all system profiles, except Custom.
NOTE: This option can be disabled only if the C States option in Custom mode is disabled.
NOTE: When C States is enabled in Custom mode, changing the Monitor/Mwait setting
does not impact system power/performance.
option is set to Standard.
1x.
Memory Operating
Voltage
Collaborative CPU
Performance Control
Allows you to set the DIMM voltage selection. When set to Auto, the system automatically sets
the system voltage to the optimal setting based on the DIMM capacity and the numbers of
DIMMs installed. By default, the Memory Operating Voltage option is set to Auto.
When set to enabled, the CPU power management is controlled by the OS DBPM and the
System DBPM (DAPC). By default, the option is set to Disabled
System Security Screen
Menu Item
Intel AES-NI The Intel AES-In option improves the speed of applications by performing encryption and
18
Description
decryption using the Advanced Encryption Standard set and is set to Enabled by default.
Page 19

Menu Item Description
System Password Allows you to set the system password. This option is read-only if the password jumper is not
installed in the system.
Setup Password Allows you to set the setup password. This option is read-only if the password jumper is not
installed in the system.
Password Status Allows you to lock the system password. By default, the Password Status option is set to
Unlocked.
TPM Security Allows you to control the reporting mode of the Trusted Platform Module (TPM). By default, the
TPM Security option is set to Off. You can only modify the TPM Status, TPM Activation , and
Intel TXT fields if the TPM Status field is set to either On with Pre-boot Measurements or On
without Pre-boot Measurements.
TPM Activation Allows you to change the operational state of the TPM. By default, the TPM Activation option is
set to No Change.
TPM Status Displays the TPM status.
TPM Clear
Intel TXT Allows you enable or disable Intel Trusted Execution Technology. To enable Intel TXT,
BIOS Update Control Allows you to update the BIOS using either DOS or UEFI shell-based flash utilities. For
Power Button Allows you to enable or disable the power button on the front of the system. By default, the
AC Power Recovery Allows you to set how the system reacts after AC power is restored to the system. By default,
CAUTION: Clearing the TPM results in loss of all keys in the TPM. The loss of TPM keys
may affect booting to the operating system.
Allows you to clear all the contents of the TPM. By default, the TPM Clear option is set to No.
Virtualization Technology must be enabled and TPM Security must be enabled with Pre-boot
measurements. By default, the Intel TXT option is set to Off.
environments that do not require local BIOS updates, it is recommended to set this field to
Limited. By default, the Local BIOS Update Support option is set to Unlocked.
NOTE: BIOS updates using Dell Update Package is not affected by this option.
Power Button option is set to Enabled.
the AC Power Recovery option is set to Last.
Miscellaneous Settings
Menu Item Description
System Time Allows you to set the time on the system.
System Date Allows you to set the date on the system.
Asset Tag Displays the asset tag and allows you to modify it for security and tracking purposes.
Keyboard NumLock Allows you to set whether the system boots with the NumLock enabled or disabled. By default
the Keyboard NumLock is set to On.
NOTE: This field does not apply to 84-key keyboards.
19
Page 20

Menu Item Description
Report Keyboard
Errors
F1/F2 Prompt on Error Allows you to enable or disable the F1/F2 prompt on error. By default, F1/F2 Prompt on Error is
In-System
Characterization
Allows you to set whether keyboard-related error messages are reported during system boot.
By default, the Report Keyboard Errors field is set to Report.
set to Enabled.
This field enables or disables In-System Characterization. By default, In-System
Characterization is set to Enabled.
System And Setup Password Features
You can create a system password and a setup password to secure your system. To enable creation of the system and
setup password, the password jumper must be set to enabled. For more information on the password jumper settings,
see System Board Jumper Settings.
System password This is the password that you must enter before you can boot your system.
Setup password This is the password that you must enter to access and make changes to the BIOS or UEFI
settings of your system.
CAUTION: The password features provide a basic level of security for the data on your system.
CAUTION: Anyone can access the data stored on your system if the system is running and unattended.
NOTE: Your system is shipped with the system and setup password feature disabled.
Assigning A System And/Or Setup Password
NOTE: The password jumper enables or disables the System Password and Setup Password features. For more
information on the password jumper settings, see System Board Jumper Settings.
You can assign a new System Password and/or Setup Password or change an existing System Password and/or Setup
Password only when the password jumper setting is enabled and Password Status is Unlocked. If the Password Status
is Locked, you cannot change the System Password and/or Setup Password.
If the password jumper setting is disabled, the existing System Password and Setup Password is deleted and you need
not provide the system password to boot the system.
To assign a system and/or setup password:
1. To enter System Setup, press <F2> immediately after a power-on or reboot.
2. In the System Setup Main Menu, select System BIOS and press <Enter>.
The System BIOS screen is displayed.
3. In the System BIOS screen, select System Security and press <Enter>.
The System Security screen is displayed.
4. In the System Security screen, verify that Password Status is Unlocked.
5. Select System Password , enter your system password, and press <Enter> or <Tab>.
Use the following guidelines to assign the system password:
– A password can have up to 32 characters.
– The password can contain the numbers 0 through 9.
– Only lower case letters are valid, upper case letters are not allowed.
20
Page 21

– Only the following special characters are allowed: space, (”), (+), (,), (-), (.), (/), (;), ([), (\), (]), (`).
A message prompts you to re-enter the system password.
6. Re-enter the system password that you entered earlier and click OK.
7. Select Setup Password, enter your system password and press <Enter> or <Tab>.
A message prompts you to re-enter the setup password.
8. Re-enter the setup password that you entered earlier and click OK.
9. Press <Esc> to return to the System BIOS screen. Press <Esc> again, and a message prompts you to save the
changes.
NOTE: Password protection does not take effect until the system reboots.
Using Your System Password To Secure Your System
NOTE: If you have assigned a setup password , the system accepts your setup password as an alternate system
password.
1. Turn on or reboot your system by pressing <Ctrl<Alt><Delete>.
2. Type your password and press <Enter>.
When Password Status is Locked, you must type the password and press <Enter> when prompted at reboot.
If an incorrect system password is entered, the system displays a message and prompts you to re-enter your password.
You have three attempts to enter the correct password. After the third unsuccessful attempt, the system displays an
error message that the system has halted and will shut down.
Even after you shut down and restart the system, the error message continues to be displayed until the correct
password is entered.
NOTE: You can use the Password Status option in conjunction with the System Password and Setup Password
options to protect your system from unauthorized changes.
Deleting Or Changing An Existing System And/Or Setup Password
Ensure that the Password jumper is set to enabled and the Password Status is Unlocked before attempting to delete or
change the existing System and/or Setup password. You cannot delete or change an existing System or Setup password
if the Password Status is Locked.
To delete or change the existing System and/or Setup password:
1. To enter System Setup, press <F2> immediately after a power-on or reboot.
2. In the System Setup Main Menu, select System BIOS and press <Enter>.
The System BIOS screen is displayed.
3. In the System BIOS Screen, select System Security and press <Enter>.
The System Security screen is displayed.
4. In the System Security screen, verify that Password Status is Unlocked.
5. Select System Password, alter or delete the existing system password and press <Enter> or <Tab>.
6. Select Setup Password, alter or delete the existing setup password and press <Enter> or <Tab>.
NOTE: If you change the System and/or Setup password a message prompts you to re-enter the new
password. If you delete the System and/or Setup password, a message prompts you to confirm the deletion.
7. Press <Esc> to return to the System BIOS screen. Press <Esc> again, and a message prompts you to save the
changes.
21
Page 22

NOTE: You can disable password security while logging on to the system. To disable the password security, turn on
or reboot your system, type your password and press <Ctrl><Enter>.
Operating With A Setup Password Enabled
If Setup Password is Enabled, enter the correct setup password before modifying most of the System Setup options.
If you do not enter the correct password in three attempts, the system displays the message
Invalid Password! Number of unsuccessful password attempts: <x> System Halted!
Must power down.
Even after you shut down and restart the system, the error message is displayed until the correct password is entered.
The following options are exceptions:
• If System Password is not Enabled and is not locked through the Password Status option, you can assign a
system password.
• You cannot disable or change an existing system password.
NOTE: You can use the Password Status option in conjunction with the Setup Password option to protect the
system password from unauthorized changes.
Entering The UEFI Boot Manager
NOTE: Operating systems must be 64-bit UEFI-compatible (for example, Microsoft Windows Server 2008 x64
version) to be installed from the UEFI boot mode. DOS and 32-bit operating systems can only be installed from the
BIOS boot mode.
The Boot Manager enables you to:
• Add, delete, and arrange boot options
• Access System Setup and BIOS-level boot options without rebooting
To enter the Boot Manager:
1. Turn on or restart your system.
2. Press <F11> after you see the following message:
<F11> = UEFI Boot Manager
If your operating system begins to load before you press <F11>, allow the system to finish booting, and then restart
your system and try again.
Using The Boot Manager Navigation Keys
Key Description
Up arrow Moves to the previous field.
Down arrow Moves to the next field.
<Enter> Allows you to type in a value in the selected field (if applicable) or follow the link in the field.
Spacebar Expands or collapses a drop-down list, if applicable.
<Tab> Moves to the next focus area.
22
Page 23

Key Description
NOTE: For the standard graphics browser only.
<Esc> Moves to the previous page till you view the main screen. Pressing <Esc> in the main screen
exits the Boot Manager and proceeds with system boot.
<F1> Displays the System Setup help file.
NOTE: For most of the options, any changes that you make are recorded but do not take effect until you restart the
system.
Boot Manager Screen
Menu Item Description
Continue Normal
Boot
BIOS Boot Menu Displays the list of available BIOS boot options (marked with asterisks). Select the boot option
UEFI Boot Menu Displays the list of available UEFI boot options (marked with asterisks). Select the boot option
Driver Health Menu Displays a list of the drivers installed on the system and their health status.
Launch System Setup Enables you to access the System Setup.
System Utilities Enables you to access the BIOS Update File Explorer, run the Dell Diagnostics program, and
The system attempts to boot to devices starting with the first item in the boot order. If the boot
attempt fails, the system continues with the next item in the boot order until the boot is
successful or no more boot options are found.
you wish to use and press <Enter>.
you wish to use and press <Enter>. The UEFI Boot Menu enables you to Add Boot Option,
Delete Boot Option, or Boot From File.
reboot the system.
UEFI Boot Menu
Menu Item Description
Select UEFI Boot
Option
Add Boot Option Adds a new boot option.
Delete Boot Option Deletes an existing boot option.
Displays the list of available UEFI boot options (marked with asterisks), select the boot option
you wish to use and press <Enter>.
Boot From File Sets a one-time boot option not included in the boot option list.
Embedded System Management
The Dell Lifecycle Controller provides advanced embedded systems management throughout the server’s lifecycle. The
Lifecycle Controller can be started during the boot sequence and can function independently of the operating system.
NOTE: Certain platform configurations may not support the full set of features provided by the Lifecycle Controller.
For more information about setting up the Lifecycle Controller, configuring hardware and firmware, and deploying the
operating system, see the Lifecycle Controller documentation at dell.com/support/manuals.
23
Page 24

iDRAC Settings Utility
The iDRAC Settings utility is an interface to setup and configure the iDRAC parameters using UEFI. You can enable or
disable various iDRAC parameters using the iDRAC Settings Utility.
NOTE: Accessing some of the features on the iDRAC Settings Utility requires the iDRAC7 Enterprise License
upgrade.
For more information on using iDRAC, see the
Remote Access Controllers, at dell.com/support/manuals.
iDRAC7 User's Guide
Entering The iDRAC Settings Utility
1. Turn on or restart the managed system.
2. Press <F2> during Power-on Self-test (POST).
3. In the System Setup Main Menu page, click iDRAC Settings.
The iDRAC Settings screen is displayed.
under Software → Systems Management → Dell
24
Page 25

Installing Blade Components
Recommended Tools
You may need the following items to perform the procedures in this section:
• #1 and #2 Phillips screwdrivers
• T8 and T10 Torx drivers
• Wrist grounding strap
Removing And Installing A Blade
CAUTION: Many repairs may only be done by a certified service technician. You should only perform
troubleshooting and simple repairs as authorized in your product documentation, or as directed by the online or
telephone service and support team. Damage due to servicing that is not authorized by Dell is not covered by your
warranty. Read and follow the safety instructions that came with the product.
Removing The Blade
1. Power down the blade using OS commands or the CMC, and ensure that the blade's power is off.
When a blade is powered off, its front-panel power indicator is off.
2. Before removing half-height blades 11 or 12, rotate the LCD panel to the storage position to prevent accidental
damage to the LCD screen.
3. Press the release button on the handle.
4. Pull out the handle to unlock the blade from the enclosure.
5. Slide the blade out of the enclosure.
3
CAUTION: To protect the I/O connector pins, install the I/O connector cover any time a blade is removed from
the enclosure.
6. Install the I/O connector cover over the I/O connector.
CAUTION: If you are permanently removing the blade, install a blade blank. Operating the system for extended
periods of time without a blade blank installed can cause the enclosure to overheat.
25
Page 26
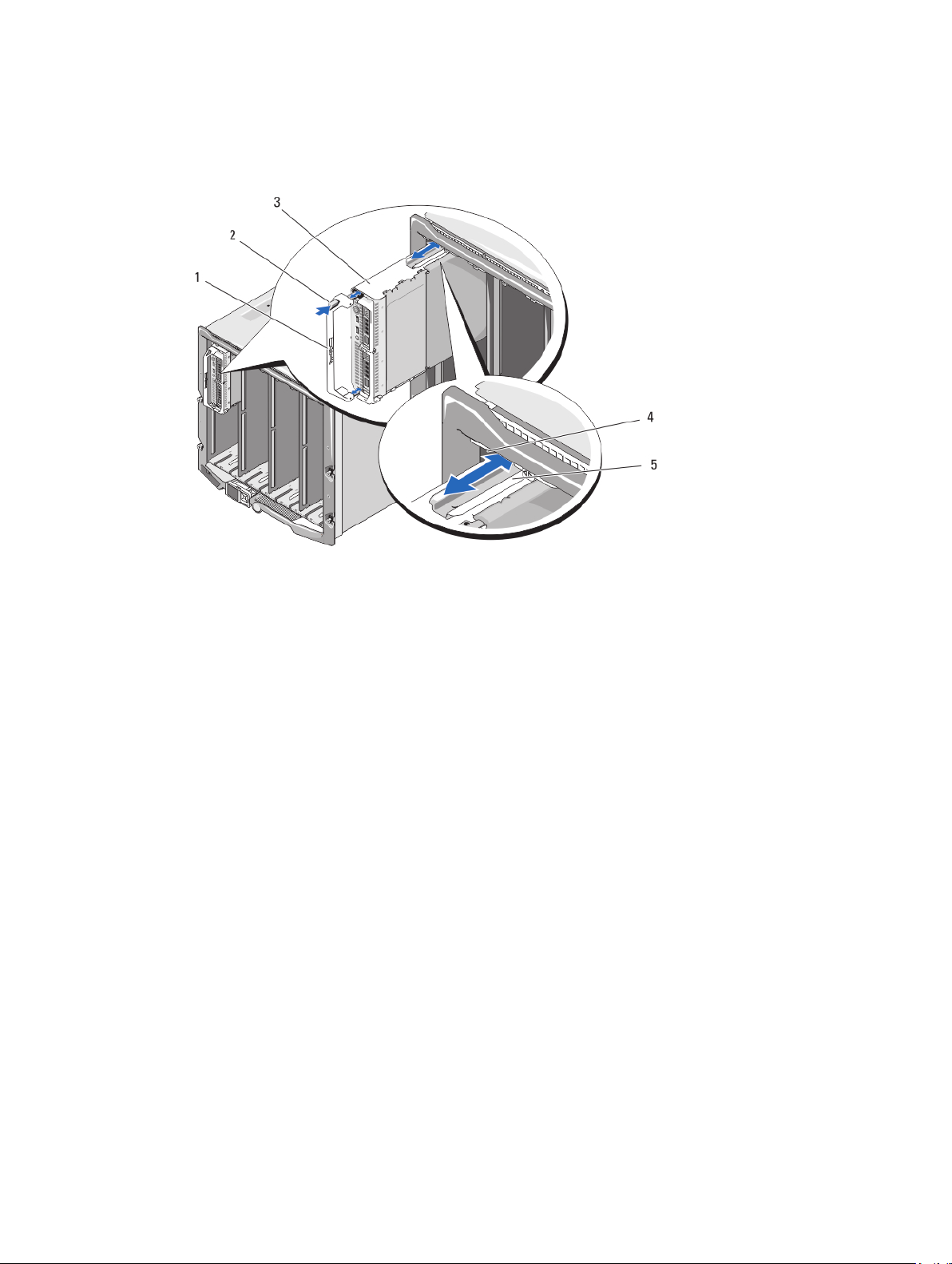
Figure 3. Removing or Installing the Blade
1. blade handle
2. release button
3. blade
4. guide rail on enclosure
5. guide rail on blade (or blade blank)
Installing The Blade
1. If you are installing a new blade, remove the plastic cover from the I/O connector(s) and save for future use.
2. Orient the blade so that the handle is on the left side of the blade.
3. If you are installing a half-height blade in bays 11 or 12, rotate the LCD module to the horizontal storage position to
prevent accidental damage to the LCD screen.
4. If you are installing a half-height blade in one of the eight upper bays, align the guide rail on the upper edge of the
blade so that the rail fits between the plastic guides on the enclosure.
If you are installing a half-height blade in one of the eight lower bays, align the edge of the blade with the guide rail
on the floor of the M1000e enclosure.
5. Slide the blade into the enclosure until the handle engages and locks the blade in place.
26
Page 27
Opening And Closing The Blade
Opening The Blade
CAUTION: Many repairs may only be done by a certified service technician. You should only perform
troubleshooting and simple repairs as authorized in your product documentation, or as directed by the online or
telephone service and support team. Damage due to servicing that is not authorized by Dell is not covered by your
warranty. Read and follow the safety instructions that came with the product.
NOTE: It is recommended that you always use a static mat and static strap while working on components in the
interior of the system.
1. Remove the blade from the enclosure.
2. Install the I/O connector cover.
3. Press the release button and slide the cover toward the back of the blade.
4. Carefully lift the cover away from the blade.
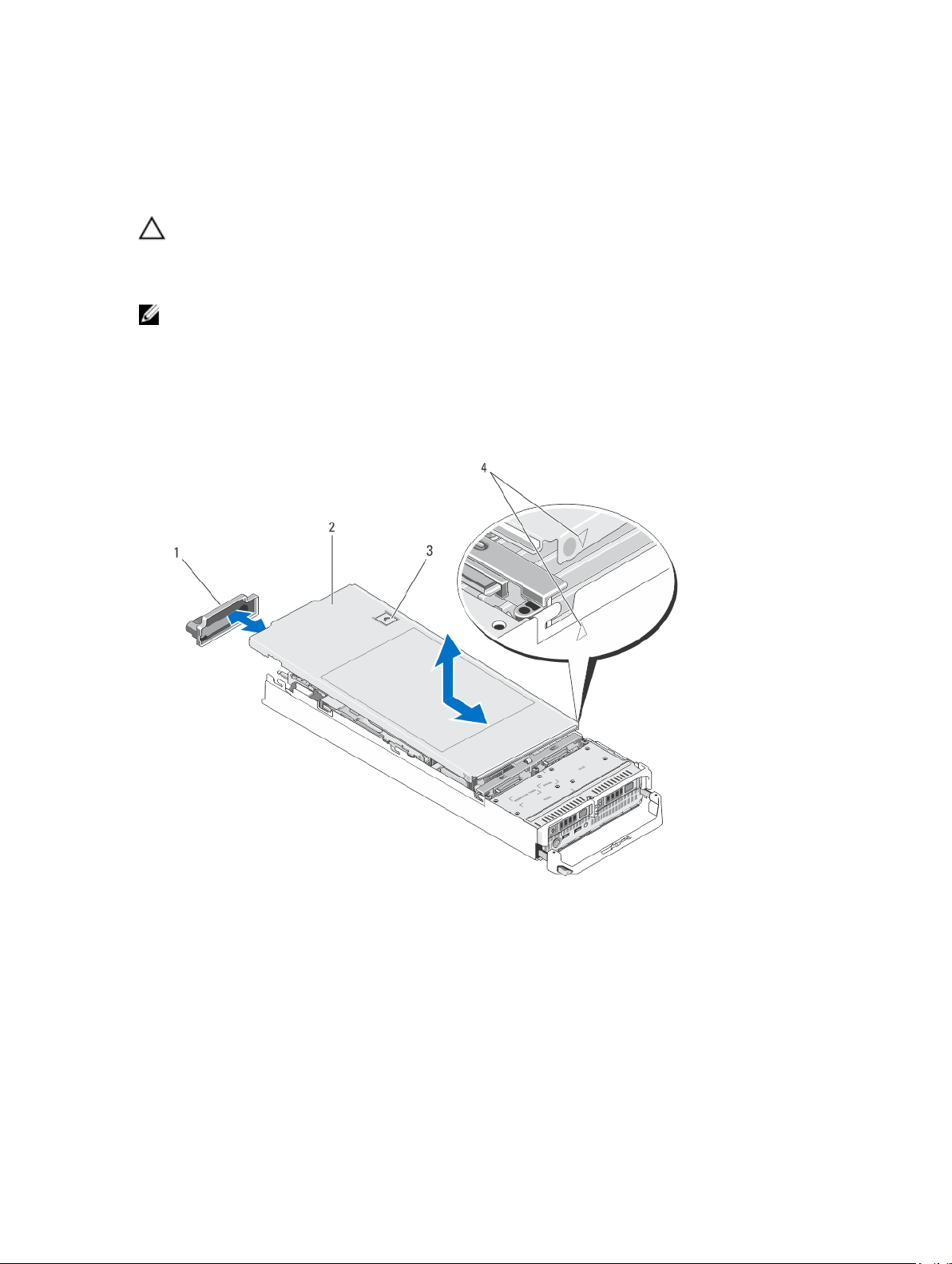
Figure 4. Opening and Closing the Blade
1. I/O connector cover
2. blade cover
3. release button
4. cover alignment pins and notches
27
Page 28
Closing The Blade
1. Ensure that no tools or parts are left inside the blade.
2. Align the notches in the edges of the chassis with the cover alignment pins on the inner sides of the cover.
3. Lower the cover onto the chassis.
4. Slide the cover until it clicks into position.
A properly seated cover is flush with the surface of the chassis.
Inside The Blade
CAUTION: Many repairs may only be done by a certified service technician. You should only perform
troubleshooting and simple repairs as authorized in your product documentation, or as directed by the online or
telephone service and support team. Damage due to servicing that is not authorized by Dell is not covered by your
warranty. Read and follow the safety instructions that came with the product.
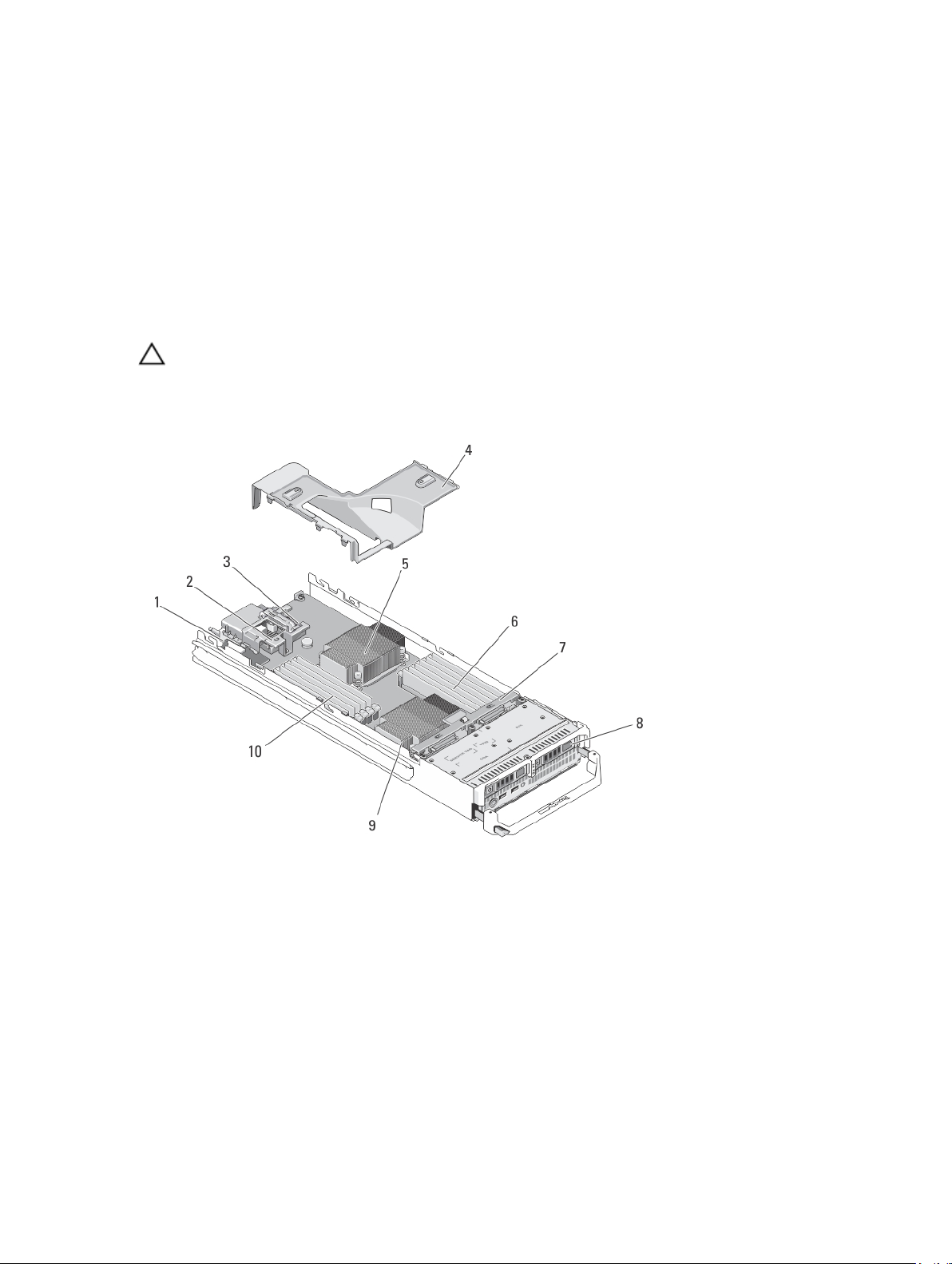
Figure 5. Inside the Blade
1. management riser card
2. optional mezzanine card 1 - Fabric C
3. optional mezzanine card 2 - Fabric B
4. cooling shroud
5. processor 1 and heat sink
6. memory modules (B1 - B6)
28
7. hard-drive/SSD backplane
8. hard drives/SSDs (2)
9. processor 2 and heat sink
10. memory modules (A1 - A6)
Page 29
Cooling Shroud
The cooling shroud covers the memory modules and directs air flow in the system.
Removing The Cooling Shroud
CAUTION: Many repairs may only be done by a certified service technician. You should only perform
troubleshooting and simple repairs as authorized in your product documentation, or as directed by the online or
telephone service and support team. Damage due to servicing that is not authorized by Dell is not covered by your
warranty. Read and follow the safety instructions that came with the product.
CAUTION: Never operate your system with the cooling shroud removed. The system may get overheated quickly,
resulting in shutdown and loss of data.
1. Remove the blade from the enclosure.
2. Open the blade.
3. Hold the cooling shroud at both ends near the blade chassis and lift it up and away from the blade.
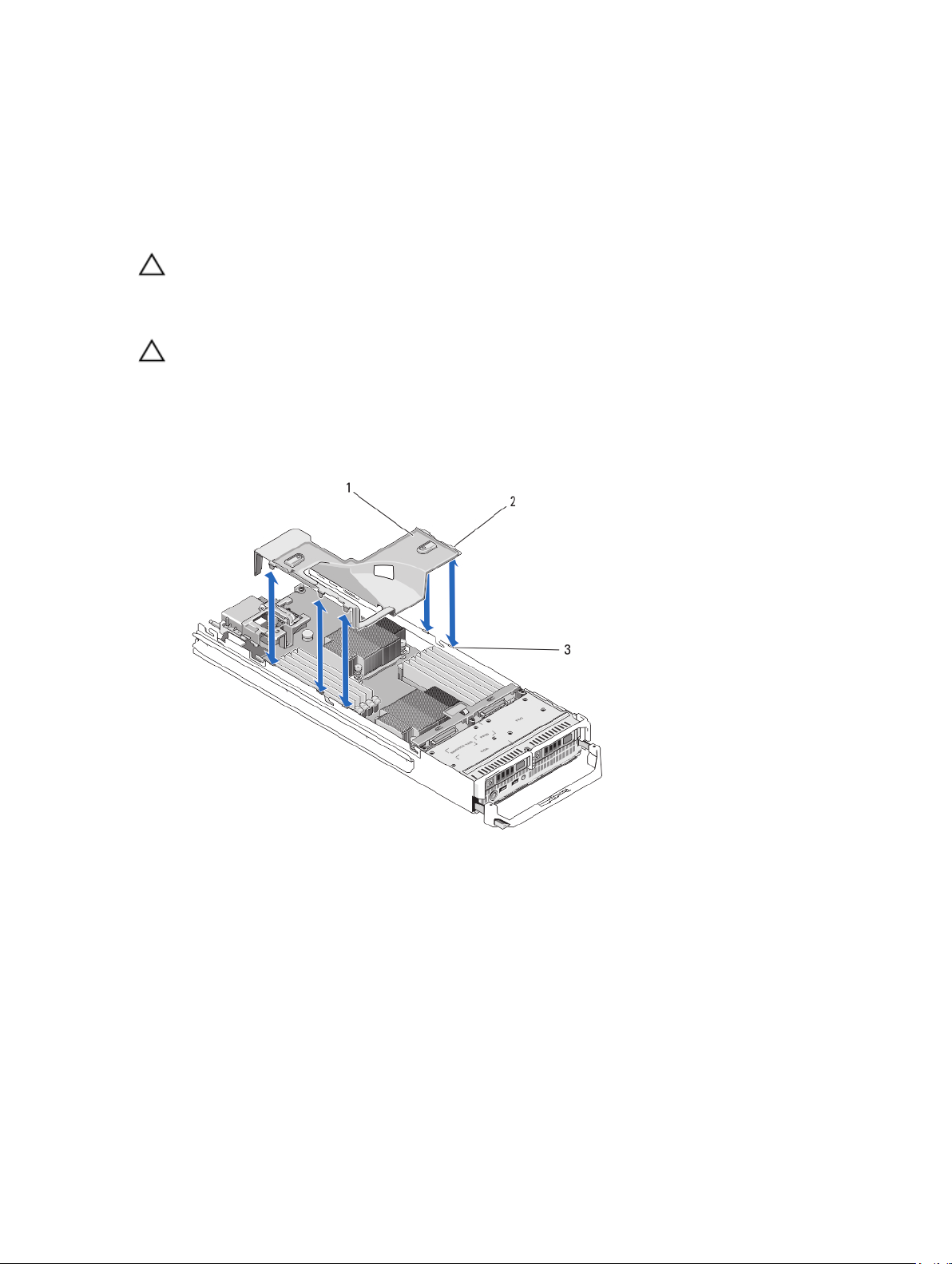
Figure 6. Removing and Installing a Cooling Shroud
1. cooling shroud
2. tabs (5)
3. slots on the chassis (5)
29
Page 30
Installing The Cooling Shroud
CAUTION: Many repairs may only be done by a certified service technician. You should only perform
troubleshooting and simple repairs as authorized in your product documentation, or as directed by the online or
telephone service and support team. Damage due to servicing that is not authorized by Dell is not covered by your
warranty. Read and follow the safety instructions that came with the product.
1. Align the tabs on the cooling shroud with the slots on the chassis.
2. Lower the cooling shroud into the system until the tabs seat securely on the slots on the blade chassis.
3. Close the blade.
4. Install the blade in the enclosure.
System Memory
Your system supports DDR3 unbuffered ECC DIMMs (UDIMM ECC) and registered DIMMs (RDIMMs). It supports DDR3
and DDR3L voltage specifications.
NOTE: MT/s indicates DIMM speed in MegaTransfers per second.
Memory bus operating frequency can be 1600 MT/s, 1333 MT/s, 1066 MT/s, or 800 MT/s depending on:
• DIMM type (UDIMM or RDIMM)
• DIMM configuration (number of ranks)
• maximum frequency of the DIMMs
• number of DIMMs populated per channel
• DIMM operating voltage
• system profile selected (for example, Performance Optimized, Custom, or Dense Configuration Optimized)
• maximum supported DIMM frequency of the processors
The following table shows the memory populations and operating frequencies for the supported configurations.
DIMM Type DIMMs
Populated/
Channel
UDIMM ECC 1 1333, 1066, and 800 1333, 1066, and 800 Dual rank
2 1333, 1066, and 800 1333, 1066, and 800 Dual rank
RDIMM 1
2
The system contains 12 memory sockets split into two sets of six sockets, one set per processor. Each six-socket set is
organized into three channels. In each channel, the release levers of the first socket is marked white and the second
black.
NOTE: DIMMs in sockets A1 to A6 are assigned to processor 1 and DIMMs in sockets B1 to B6 are assigned to
processor 2.
30
Operating Frequency (in MT/s) Maximum DIMM Rank/
1.5 V 1.35 V
1600, 1333, 1066 and 800
1333
1600, 1333, and 1066
1066
1333, 1066 and 800
1066
1333 and 1066
1066
Channel
Dual rank
Quad rank
Dual rank
Quad rank
Page 31

Figure 7. Memory Socket Locations
Memory channels are organized as follows:
Processor 1 channel 1: memory sockets A1 and A4
channel 2: memory sockets A2 and A5
channel 3: memory sockets A3 and A6
Processor 2 channel 1: memory sockets B1 and B4
channel 2: memory sockets B2 and B5
channel 3: memory sockets B3 and B6
General Memory Module Installation Guidelines
This system supports Flexible Memory Configuration, enabling the system to be configured and run in any valid chipset
architectural configuration. The following are the recommended guidelines for best performance:
• UDIMMs and RDIMMs must not be mixed.
• x4 and x8 DRAM based DIMMs can be mixed. For more information, see Mode-Specific Guidelines.
• A maximum of two UDIMMs can be populated in a channel.
• A maximum of two quad-rank RDIMMs can be populated in a channel.
• A maximum of two single- or dual-rank RDIMMs can be populated in a channel.
• One quad-rank RDIMM and one single- or dual-rank RDIMM can be populated per channel.
• Populate DIMM sockets only if a processor is installed. For single-processor systems, sockets A1 to A6 are
available. For dual-processor systems, sockets A1 to A6 and sockets B1 to B6 are available.
• Populate all sockets with white release tabs first and then black.
31
Page 32

• Populate the sockets by highest rank count in the following order - first in sockets with white release levers and
then black. For example, if you want to mix quad-rank and dual-rank DIMMs, populate quad-rank DIMMs in the
sockets with white release tabs and dual-rank DIMMs in the sockets with black release tabs.
• In a dual-processor configuration, the memory configuration for each processor must be identical. For example,
if you populate socket A1 for processor 1, then populate socket B1 for processor 2, and so on.
• Memory modules of different sizes can be mixed provided that other memory population rules are followed (for
example, 2 GB and 4 GB memory modules can be mixed).
• Depending on mode-specific guidelines, populate two or three DIMMs per processor (one DIMM per channel)
at a time to maximize performance. For more information, see Mode-Specific Guidelines.
• If memory modules with different speeds are installed, they will operate at the speed of the slowest installed
memory module(s) or slower depending on system DIMM configuration.
Mode-Specific Guidelines
Three memory channels are allocated to each processor. The allowable configurations depend on the memory mode
selected.
NOTE: x4 and x8 DRAM based DIMMs can be mixed providing support for (Reliability, Availability, and
Serviceability) RAS features. However, all guidelines for specific RAS features must be followed. x4 DRAM based
DIMMs retain Single Device Data Correction (SDDC) in either memory optimized (independent channel) or
Advanced ECC modes. x8 DRAM based DIMMs require Advanced ECC mode to gain SDDC.
The following sections provide additional slot population guidelines for each mode.
Advanced ECC (Lockstep)
Advanced ECC mode extends SDDC from x4 DRAM based DIMMs to both x4 and x8 DRAMs. This protects against single
DRAM chip failures during normal operation.
Memory installation guidelines:
• Memory sockets A1, A4, B1, and B4 are disabled and do not supported Advanced ECC mode.
• DIMMs must be installed in matched pairs — DIMMs installed in memory sockets (A2, B2) must match DIMMs
installed in memory sockets (A3, B3) and DIMMs installed in memory sockets (A5, B5) must match DIMMs
installed in memory sockets (A6, B6).
NOTE: Advanced ECC with mirroring is not supported.
Memory Optimized (Independent Channel) Mode
This mode supports SDDC only for memory modules that use x4 device width and does not impose any specific slot
population requirements.
Memory Sparing
NOTE: To use memory sparing, this feature must be enabled in the System Setup.
In this mode, one rank per channel is reserved as a spare. If persistent correctable errors are detected on a rank, the
data from this rank is copied to the spare rank and the failed rank is disabled.
With memory sparing enabled, the system memory available to the operating system is reduced by one rank per
channel. For example, in a system with three 8 GB dual-rank DIMMs, the available system memory is: 1/2 (ranks/
channel) × 3 (DIMMs) × 8 GB = 12 GB, and not 3 (DIMMs) × 8 GB = 24 GB.
NOTE: Memory sparing does not offer protection against a multi-bit uncorrectable error.
NOTE: Both Advanced ECC/Lockstep and Optimizer modes support Memory Sparing.
Memory Mirroring
Memory Mirroring offers the strongest DIMM reliability mode compared to all other modes, providing improved
uncorrectable multi-bit failure protection. In a mirrored configuration, the total available system memory is one half of
32
Page 33

the total installed physical memory. Half of the installed memory is used to mirror the active DIMMs. In the event of an
uncorrectable error, the system will switch over to the mirrored copy. This ensures SDDC and multi-bit protection.
Memory installation guidelines:
NOTE: The first memory channel for each processor (Channel 1) is disabled and not available for Memory
Mirroring.
• Memory channels 2 and 3 must be populated.
• Memory modules must be identical in size, speed, and technology.
• DIMMs installed in memory sockets with white release tabs must be identical and similar rule applies for
sockets with black release tabs. For example, DIMMs installed in sockets A2 and A3 must be identical.
Sample Memory Configurations
The following tables show sample memory configurations that follow the appropriate memory guidelines stated in this
section.
NOTE: 16 GB quad-rank RDIMMs are not supported.
NOTE: 1R, 2R, and 4R in the following tables indicate single-, dual-, and quad-rank DIMMs respectively.
Table 1. Memory Configurations — Single Processor
System Capacity
(in GB)
2 2 1
4 2 2
10 2 5
12 4 3
20 4 5
24 8 3
32 8 4
48 16 3
96 16 6
128 32 4
192 32 6
DIMM Size (in
GB)
Number of
DIMMs
Organization and
Speed
1R x8, 1333 MT/s
1R x8, 1600 MT/s
1R x8, 1333 MT/s
1R x8, 1600 MT/s
1R x8, 1333 MT/s
1R x8, 1600 MT/s
1R x8, 1333 MT/s
1R x8, 1600 MT/s
1R x8, 1333 MT/s
1R x8, 1600 MT/s
2R x4, 1333 MT/s
2R x4, 1600 MT/s
2R x4, 1333 MT/s
2R x4, 1600 MT/s
2R x4, 1333 MT/s
2R x4, 1600 MT/s
2R x4, 1333 MT/s
2R x4, 1600 MT/s
4R x4, 1333 MT/s
4R x4, 1333 MT/s
DIMM Slot Population
A1
A1, A2
A1, A2, A3, A4, A5
A1, A2, A3
A1, A2, A3, A4, A5
A1, A2, A3
A1, A2, A3, A4
A1, A2, A3
A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6
A1, A2, A3, A4
A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6
33
Page 34

Table 2. Memory Configurations — Two Processors
System Capacity (in
GB)
4 2 2
8 2 4
12 2 6
24 4 6
48 8 6
96 16 6
128 16 8
160 16 10
192 16 12
256 32 8
384 32 12
DIMM Size (in
GB)
Number of
DIMMs
Organization and
Speed
1R x8, 1333 MT/s
1R x8, 1600 MT/s
1R x8, 1333 MT/s
1R x8, 1600 MT/s
1R x8, 1333 MT/s
1R x8, 1600 MT/s
2R x8, 1333 MT/s
2R x8, 1600 MT/s
2R x4, 1333 MT/s
2R x4, 1600 MT/s
2R x4, 1333 MT/s
2R x4, 1600 MT/s
2R x4, 1333 MT/s
2R x4, 1600 MT/s
2R x4, 1333 MT/s
2R x4, 1600 MT/s
2R x4, 1333 MT/s
2R x4, 1600 MT/s
4R x4, 1333 MT/s
4R x4, 1333 MT/s
DIMM Slot Population
A1, B1
A1, A2, B1, B2
A1, A2, A3, B1, B2, B3
A1, A2, A3, B1, B2, B3
A1, A2, A3, B1, B2, B3
A1, A2, A3, B1, B2, B3
A1, A2, A3, A4, B1, B2, B3, B4
A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, B1, B2, B3,
B4, B5
A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6, B1, B2,
B3, B4, B5, B6
A1, A2, A3, A4, B1, B2, B3, B4
A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6, B1, B2,
B3, B4, B5, B6
Removing Memory Modules
WARNING: The DIMMs are hot to touch for some time after the blade has been powered down. Allow time for the
DIMMs to cool before handling them. Handle the DIMMs by the card edges and avoid touching the DIMM
components.
CAUTION: Many repairs may only be done by a certified service technician. You should only perform
troubleshooting and simple repairs as authorized in your product documentation, or as directed by the online or
telephone service and support team. Damage due to servicing that is not authorized by Dell is not covered by your
warranty. Read and follow the safety instructions that came with the product.
CAUTION: To ensure proper system cooling, memory-module blanks must be installed in any memory socket that is
not occupied. Remove memory-module blanks only if you intend to install memory modules in those sockets.
CAUTION: If you are permanently removing a processor, you must install a socket protective cap and a processor/
DIMM blank in the vacant socket to ensure proper system cooling. The processor/DIMM blank covers the vacant
sockets for the DIMMs and the processor.
1. Remove the blade from the enclosure.
2. Open the blade.
3. Remove the cooling shroud.
4. Locate the memory module socket(s).
34
Page 35

CAUTION: Handle each memory module only by the card edges, making sure not to touch the middle of the
memory module or gold contacts.
5. Press down and out on the ejectors on each end of the socket until the memory module pops out of the socket.
6. Install the cooling shroud.
7. Close the blade.
8. Install the blade in the enclosure.
Figure 8. Installing and Removing a Memory Module or Memory Module Blank
1. memory module or memory blank
2. edge connector
3. ejectors (2)
4. socket
5. alignment key
Installing Memory Modules
WARNING: The memory modules are hot to the touch for some time after the system has been powered down.
Allow time for the memory modules to cool before handling them. Handle the memory modules by the card edges
and avoid touching the components or metallic contacts on the memory module.
CAUTION: Many repairs may only be done by a certified service technician. You should only perform
troubleshooting and simple repairs as authorized in your product documentation, or as directed by the online or
telephone service and support team. Damage due to servicing that is not authorized by Dell is not covered by your
warranty. Read and follow the safety instructions that came with the product.
CAUTION: To ensure proper system cooling, memory-module blanks must be installed in any memory socket that is
not occupied. Remove memory-module blanks only if you intend to install memory modules in those sockets.
CAUTION: If you are permanently removing a processor, you must install a socket protective cap and a processor/
DIMM blank in the vacant socket to ensure proper system cooling. The processor/DIMM blank covers the vacant
sockets for the DIMMs and the processor.
1. Remove the blade from the enclosure.
2. Open the blade.
3. Remove the cooling shroud.
4. Locate the appropriate memory module socket(s).
5. Press the ejectors on the memory module socket down and out to allow the memory module to be inserted into the
socket.
35
Page 36

If a memory module blank is installed in the socket, remove it. Retain removed memory-module blank(s) for future
use.
CAUTION: Handle each memory module only on either card edge, making sure not to touch the middle of the
memory module.
6. Align the memory module's edge connector with the alignment key on the memory module socket, and insert the
memory module in the socket.
NOTE: The memory module socket has an alignment key that allows you to install the memory module in the
socket in only one way.
7. Press down on the memory module with your thumbs to lock the memory module into the socket.
When the memory module is properly seated in the socket, the ejectors on the memory module socket align with
the ejectors on the other sockets that have memory modules installed.
8. Repeat step 5 through step 7 of this procedure to install the remaining memory modules.
9. Install the cooling shroud.
10. Close the blade.
11. Install the blade in the enclosure.
12. (Optional) Press <F2> to enter the System Setup, and check the System Memory setting.
The system should have already changed the value to reflect the newly installed memory.
13. If the value is incorrect, one or more of the memory modules may not be installed properly. Check to ensure that the
memory modules are firmly seated in their sockets.
14. Run the system memory test in the system diagnostics.
I/O Module Mezzanine Cards
The blade supports a variety of optional mezzanine cards. If installed, the mezzanine card(s) must be used in conjunction
with a matching I/O module(s).
For more information on I/O modules, see "Guidelines for Installing I/O Modules" in the
Manual
at support.dell.com/manuals.
Mezzanine Card Installation Guidelines
The blade supports two mezzanine cards:
• Mezzanine card slot C supports Fabric C. This card must match the fabric type of I/O modules installed in I/O
module bays C1 and C2.
• Mezzanine card slot B supports Fabric B. This card must match the fabric type of I/O modules installed in I/O
module bays B1 and B2.
The blade supports SFF mezzanine cards. x8 PCIe Gen 3 cards are supported.
Removing A Mezzanine Card
CAUTION: Many repairs may only be done by a certified service technician. You should only perform
troubleshooting and simple repairs as authorized in your product documentation, or as directed by the online or
telephone service and support team. Damage due to servicing that is not authorized by Dell is not covered by your
warranty. Read and follow the safety instructions that came with the product.
1. Remove the blade from the enclosure.
2. Open the blade.
M1000e Enclosure Owner's
36
Page 37

3. Open the mezzanine card latch by pressing the ridged area on the latch with your thumb, and lifting the end of the
latch.
NOTE: Hold the mezzanine card by its edges only.
4. Lift the mezzanine card up and away from the system board.
5. Close the retention latch.
6. Close the blade.
7. Install the blade in the enclosure.
Figure 9. Removing and Installing a Mezzanine Card
1. mezzanine cards (2)
2. Fabric B mezzanine card slot
3. Fabric C mezzanine card slot
4. retention latch
Installing A Mezzanine Card
CAUTION: Many repairs may only be done by a certified service technician. You should only perform
troubleshooting and simple repairs as authorized in your product documentation, or as directed by the online or
telephone service and support team. Damage due to servicing that is not authorized by Dell is not covered by your
warranty. Read and follow the safety instructions that came with the product.
1. Remove the blade from the enclosure.
2. Open the blade.
3. Open the retention latch by pressing the ridged area on the latch with your thumb and lifting the end of the latch.
37
Page 38

4. If present, remove the connector cover from the mezzanine card bay.
NOTE: Hold the mezzanine card by its edges only.
5. Mezzanine cards are designed to fit in either card slot. Rotate the card to align the connector on the bottom of the
mezzanine card with the corresponding socket on the system board.
6. Lower the card into place until it is fully seated and the plastic clip on the outer edge of the card fits over the side of
the blade chassis.
7. Close the retention latch to secure the mezzanine card.
8. Close the blade.
9. Install the blade in the enclosure.
Management Riser Card
The management riser card provides two SD card slots and a USB interface dedicated for the embedded hypervisor.
This card offers the following features:
• Internal Dual SD interface — maintains a mirrored configuration using SD cards in both slots and provides
redundancy.
• Single card operation — single card operation is supported, but without redundancy.
Replacing The SD Card
NOTE: The SD card in the lower card slot is the primary card (SD1) and the SD card in the upper card slot is the
secondary card (SD2).
1. Enter the System Setup and ensure that the Internal SD Card Port is enabled.
CAUTION: If the Internal SD Card Redundancy option is set to Mirror Mode in the Integrated Devices screen
of the system setup, you must follow the instructions in step 4 through step 6 to avoid loss of data.
NOTE: When an SD card failure occurs, the Internal SD Card Redundancy option in the System Setup is set to
disabled and the internal dual SD module controller notifies the system. On the next reboot, the system
displays a message indicating the failure.
2. Remove the blade from the enclosure.
3. If the Internal SD Card Redundancy option is set to Disabled, replace the failed SD card with a new SD card.
4. Install the blade in the enclosure.
5. Enter the System Setup and ensure that the Internal SD Card Port and Internal SD Card Redundancy mode is
enabled.
6. Check if the new SD card is functioning properly.
If the problem persists, see Getting Help.
38
Page 39

Figure 10. Replacing the SD Card
1. SD card 1
2. SD card 2
3. management riser card
4. USB connector
5. SD card slot identification label
Internal USB Key
The blade provides an internal USB connector for a USB flash memory key. The USB memory key can be used as a boot
device, security key, or mass storage device. To use the internal USB connector, the Internal USB Port option must be
enabled in the Integrated Devices screen of the System Setup.
To boot from the USB memory key, you must configure the USB memory key with a boot image, and then specify the
USB memory key in the boot sequence in the System Setup. For information on creating a bootable file on the USB
memory key, see the user documentation that accompanied the USB memory key.
Replacing The Internal USB Key
CAUTION: Many repairs may only be done by a certified service technician. You should only perform
troubleshooting and simple repairs as authorized in your product documentation, or as directed by the online or
telephone service and support team. Damage due to servicing that is not authorized by Dell is not covered by your
warranty. Read and follow the safety instructions that came with the product.
CAUTION: To avoid interference with other components in the blade, the maximum allowable dimensions of the
USB key are 15.9 mm wide x 57.15 mm long x 7.9 mm high.
1. Remove the blade from the enclosure.
2. Open the blade.
3. Locate the USB connector / USB key.
4. If installed, remove the USB key.
5. Insert the new USB memory key into the USB connector.
39
Page 40

6. Close the blade.
7. Install the blade in the enclosure.
8. Enter the System Setup and verify that the USB key is detected by the system.
Figure 11. Replacing the USB Memory Key
1. USB memory key connector
2. USB memory key
SD vFlash Card
Replacing The SD vFlash Card
1. Remove the blade from the enclosure.
2. If installed, remove the SD vFlash card from the card slot.
NOTE: The SD vFlash card slot is located underneath the system board at the back of the blade and can be
identified by the SD vFlash card slot identification label.
3. To install the SD vFlash card, insert the contact-pin end of the SD card into the card slot on the vFlash media unit
with the card label side facing up.
NOTE: The slot is keyed to ensure correct insertion of the card.
4. Press inward on the card to lock it into the slot.
5. Install the blade in the enclosure.
40
Page 41

Figure 12. Replacing the SD vFlash Card
1. SD vFlash card
2. SD vFlash card slot
3. SD vFlash card slot identification label
Processors
Use the following procedure when:
• Installing an additional processor
• Replacing a processor
Removing A Processor
CAUTION: Many repairs may only be done by a certified service technician. You should only perform
troubleshooting and simple repairs as authorized in your product documentation, or as directed by the online or
telephone service and support team. Damage due to servicing that is not authorized by Dell is not covered by your
warranty. Read and follow the safety instructions that came with the product.
1. Remove the blade from the enclosure.
2. Open the blade.
WARNING: The processor and heat sink can become extremely hot. Be sure the processor has had sufficient
time to cool before handling.
3. If required, remove the cooling shroud.
41
Page 42

CAUTION: Never remove the heat sink from a processor unless you intend to remove the processor. The heat
sink is necessary to maintain proper thermal conditions.
4. Loosen the retention sockets that secure the heat sink to the blade system board.
5. Remove the heat sink.
Figure 13. Removing and Installing a Heat Sink
1. retention sockets (4)
2. heat sink
3. retention screws (4)
6. Use a clean, lint-free cloth to remove any thermal grease from the surface of the processor shield.
CAUTION: The processor is held in its socket under strong pressure. Be aware that the release lever can
spring up suddenly if not firmly grasped.
7. Position your thumb firmly over the processor socket-release lever and release the lever from the locked position.
Rotate the lever 90 degrees upward until the processor is released from the socket.
8. Hold the tab on the processor shield and rotate it upward and out of the way.
9. If applicable, remove the socket protective cap from the processor shield. To remove the socket protective cap,
push the cap from the inside of the processor shield and move it away from the socket pins.
NOTE: It is recommended that you install/remove the socket protective cap from the processor shield with the
processor shield in the open position.
42
Page 43

CAUTION: The socket pins are fragile and can be permanently damaged. Be careful not to bend the pins in the
socket when removing the processor out of the socket.
10. Lift the processor out of the socket and leave the release lever up so that the socket is ready for the new
processor.
CAUTION: If you are permanently removing a processor, you must install a socket protective cap and a
processor/DIMM blank in the vacant socket to ensure proper system cooling. The processor/DIMM blank
covers the vacant sockets for the DIMMs and the processor.
Figure 14. Removing and Installing a Processor
1. processor
2. processor shield
3. notches in processor (2)
4. socket keys (2)
5. socket-release lever
Installing A Processor
CAUTION: Many repairs may only be done by a certified service technician. You should only perform
troubleshooting and simple repairs as authorized in your product documentation, or as directed by the online or
telephone service and support team. Damage due to servicing that is not authorized by Dell is not covered by your
warranty. Read and follow the safety instructions that came with the product.
NOTE: If you are installing just one processor, it must be installed in socket CPU1.
1. If applicable, remove the processor/DIMM blank.
2. Unlatch and rotate the socket-release lever 90 degrees upward and ensure that the socket-release lever is fully
open.
3. Use the tab on the processor shield to rotate the processor shield upward and out of the way.
43
Page 44

4. If applicable, remove the socket protective cap from the processor shield. To remove the socket protective cap,
push the cap from the inside of the processor shield and move it away from the socket pins.
NOTE: It is recommended that you install/remove the socket protective cap from the processor shield with the
processor shield in the open position.
CAUTION: Positioning the processor incorrectly can permanently damage the system board or the processor.
Be careful not to bend the pins in the socket.
CAUTION: Do not use force to seat the processor. When the processor is positioned correctly, it engages
easily into the socket.
5. Install the processor in the socket:
a) Align the processor with the socket keys on the ZIF socket.
b) Set the processor lightly in the socket.
Because the system uses a ZIF processor socket, do not use force. When the processor is positioned correctly,
it drops down into the socket with minimal pressure.
c) Close the processor shield.
d) Rotate the socket release lever down until it is locked in position.
CAUTION: Applying too much thermal grease can result in excess grease coming in contact with and
contaminating the processor socket.
6. Install the heat sink:
If you are:
Reinstalling a
heat sink
Upgrading a
processor
Reinstalling a
processor
a) Open the grease applicator included with your processor kit and apply all of the thermal grease in the
applicator to the center of the topside of the new processor.
b) Place the heat sink on the processor.
c) Tighten the four retention sockets to secure the heat sink to the blade system board.
NOTE: Do not over-tighten the heat sink retention screws when installing the heat sink. To prevent overtightening, tighten the retention screw until resistance is felt, and stop once the screw is seated. The
screw tension should be no more than 6 in-lb (6.9 kg-cm).
7. If applicable, install the cooling shroud.
8. Close the blade.
9. Install the blade in the enclosure.
As the system boots, it detects the presence of the new processor and automatically changes the system
configuration information in the System Setup.
10. Press <F2> to enter the System Setup and check that the processor information matches the new system
configuration.
Use a clean, lint-free cloth to remove the existing thermal grease from the heat sink.
If a new heat sink was supplied with the processor, install it.
Clean any remnants of thermal grease from the processor.
11. Run the system diagnostics to verify that the new processor operates correctly.
12. Update the system BIOS.
44
Page 45

Hard Drives/SSDs
• The system supports up to two 2.5 inch SSD, SAS, or SATA hard drives.
• All drives connect to the blade system board through the SAS/SATA/SSD backplane board.
• Hard drives/SSDs are supplied in special hot-swappable drive carriers that fit in the drive bays.
• SSD/SAS/SATA hard drives cannot be mixed within a blade.
Hard Drive/SSD Installation Guidelines
For a single-drive configuration, a hard-drive blank must be installed in the other drive bay to maintain proper cooling
airflow.
Removing A Hard Drive/SSD
NOTE: Not all operating systems support hot-swappable drive installation. See the documentation supplied with
your operating system.
1. Take the hard drive/SSD offline and wait until the hard-drive/SSD indicator codes on the drive carrier signal that
the drive may be removed safely.
When all indicators are off, the drive is ready for removal.
See your operating system documentation for more information on taking the drive offline.
2. Open the hard-drive/SSD carrier handle to release the drive.
3. Slide the hard drive/SSD out until it is free of the drive bay.
If you are permanently removing the hard drive/SSD, install a blank insert.
Figure 15. Removing and Installing a Hard Drive/SSD
1. release button
2. hard drive/SSD
45
Page 46

3. hard-drive/SSD connector (on backplane)
4. hard-drive/SSD carrier handle
Installing A Hard Drive/SSD
CAUTION: When a replacement hot-swappable hard drive/SSD is installed and the blade is powered on, the drive
automatically begins to rebuild. Make absolutely sure that the replacement hard drive/SSD is blank or contains
data that you wish to have over-written. Any data on the replacement hard drive/SSD is immediately lost after the
drive is installed.
NOTE: Not all operating systems support hot-swappable drive installation. See the documentation supplied with
your operating system.
1. Open the hard-drive/SSD carrier handle.
2. Insert the hard-drive/SSD carrier into the drive bay. Carefully align the channel on the hard-drive/SSD carrier with
the appropriate drive slot on the blade.
3. Push the drive carrier into the slot until the handle makes contact with the blade.
4. Rotate the carrier handle to the closed position while pushing the carrier into the slot until it locks into place.
The status LED indicator displays a steady green light if the drive is installed correctly. The drive carrier LED green
indicator flashes as the drive rebuilds.
Shutdown Procedure For Servicing a Hard Drive/SSD
NOTE: This section applies only to situations where the blade must be powered down to service a hard drive/SSD.
In many situations, the hard drive/SSD can be serviced while the blade is powered on.
CAUTION: If you need to power off the blade to service a hard drive/SSD, wait 30 seconds after the blade’s power
indicator turns off before removing the hard drive/SSD. Otherwise, the hard drive/SSD may not be recognized after
it is reinstalled and the blade is powered on again.
Configuring The Boot Drive
The drive or device from which the system boots is determined by the boot order specified in the System Setup.
Removing A Hard Drive/SSD From A Hard-Drive/SSD Carrier
1. Remove the four screws from the slide rails on the hard-drive/SSD carrier.
2. Lift the hard drive/SSD out of the hard-drive/SSD carrier.
46
Page 47

Figure 16. Removing and Installing a Hard Drive/SSD in a Hard-Drive/SSD Carrier
1. hard drive/SSD
2. screw holes (4)
3. hard-drive/SSD carrier
4. screws (4)
Installing A Hard Drive/SSD In A Hard-Drive/SSD Carrier
1. Insert the hard drive/SSD into the hard-drive/SSD carrier with the drive’s controller board’s connector end of the
drive at the back of the carrier.
2. From the back of the carrier, slide the drive into the carrier.
3. Align the screw holes on the hard drive/SSD with the holes on the hard-drive/SSD carrier.
CAUTION: To avoid damaging the drive or the carrier, do not overtighten the screws.
4. Attach the four screws to secure the hard drive/SSD to the hard-drive/SSD carrier.
Hard-Drive/SSD Backplane
Removing The Hard-Drive/SSD Backplane
CAUTION: Many repairs may only be done by a certified service technician. You should only perform
troubleshooting and simple repairs as authorized in your product documentation, or as directed by the online or
telephone service and support team. Damage due to servicing that is not authorized by Dell is not covered by your
warranty. Read and follow the safety instructions that came with the product.
1. Remove the blade from the enclosure.
2. Open the blade.
47
Page 48

CAUTION: You must note the number of each hard drive/SSD and temporarily label them before removal so
that you can replace them in the same locations.
CAUTION: To prevent damage to the hard drives/SSDs and the hard-drive/SSD backplane, you must remove
the hard drives/SSDs from the blade before removing the hard-drive/SSD backplane.
3. Remove the hard drive(s)/SSD(s).
4. Hold both edges of the hard-drive/SSD backplane near the blade chassis and lift the backplane away from the
blade.
Figure 17. Removing and Installing the Hard-Drive/SSD Backplane
1. guide pins (3)
2. guides (3)
3. hard-drive/SSD backplane
4. hard-drive/SSD connectors (2)
5. hard-drive backplane/SSD connector
Installing The Hard-Drive/SSD Backplane
1. Open the blade.
2. Align the guides on the hard-drive/SSD backplane with the guide pins on the system board.
3. Press down the backplane until the connectors on the backplane and the system board are fully engaged.
4. Install the hard drives/SSDs in their original locations.
48
Page 49

5. Close the blade.
6. Install the blade in the enclosure.
System Board
Removing The System Board
CAUTION: Many repairs may only be done by a certified service technician. You should only perform
troubleshooting and simple repairs as authorized in your product documentation, or as directed by the online or
telephone service and support team. Damage due to servicing that is not authorized by Dell is not covered by your
warranty. Read and follow the safety instructions that came with the product.
1. Remove the blade from the enclosure.
2. Open the blade.
3. Install an I/O connector cover on the I/O connector(s) at the back of the board.
WARNING: The processor and heat sink can become extremely hot. Be sure the processor has had sufficient
time to cool before handling.
WARNING: The memory modules are hot to the touch for some time after the system has been powered
down. Allow time for the memory modules to cool before handling them. Handle the memory modules by the
card edges and avoid touching the components.
NOTE: If you are removing more than one hard drive/SSD, label them so you can replace them in their original
locations.
4. Remove the hard drives/SSDs.
5. Remove the hard-drive/SSD backplane.
6. Remove the cooling shroud.
7. If present, remove both mezzanine cards.
CAUTION: Do not lift the system board assembly by grasping a memory module, processor, or other
components.
8. Hold the blade chassis with one hand, lift and pull the system board retention latch with the other hand, and then
slide the system board out of the open end of the chassis.
9. Ensure that the I/O connector cover is still in place on the I/O connector at the back of the board.
10. Remove the memory modules and memory module blanks.
11. Remove the processor(s).
12. Remove the storage controller card.
49
Page 50

Figure 18. Removing and Installing the System Board
1. I/O connector cover
2. retention latch
3. system board
4. tabs on system chassis
5. slots in system board tray
Installing The System Board
1. Transfer the following components to the new system board:
a. internal USB key
b. storage controller card
c. SD vFlash card
d. memory modules and memory module blanks
e. processor(s) and heat sink(s), or processor filler blank
CAUTION: Ensure that the system board plate is parallel with the chassis.
2. Slide the new system board into the open end of the blade chassis until the retention latch engages.
When the board assembly is installed correctly, the tabs on the system board pan snap into the corresponding
openings in the floor of the blade chassis.
3. Replace the mezzanine card(s) in their original locations.
4. Reinstall the hard-drive/SSD backplane.
5. Replace the hard drive(s)/SSD(s).
If there are two drives, ensure that you reinstall them in their original locations.
6. Reinstall the cooling shroud.
7. Close the blade.
50
Page 51

8. Remove the plastic I/O connector covers from the back of the blade.
9. Install the blade in the enclosure.
10. Import your new or existing iDRAC Enterprise license. For more information, see the
support.dell.com/manuals.
iDRAC7 User's Guide
, at
NVRAM Backup Battery
Replacing The NVRAM Backup Battery
WARNING: There is a danger of a new battery exploding if it is incorrectly installed. Replace the battery only with
the same or equivalent type recommended by the manufacturer. Discard used batteries according to the
manufacturer's instructions. See the safety instructions that came with your system for additional information.
CAUTION: Many repairs may only be done by a certified service technician. You should only perform
troubleshooting and simple repairs as authorized in your product documentation, or as directed by the online or
telephone service and support team. Damage due to servicing that is not authorized by Dell is not covered by your
warranty. Read and follow the safety instructions that came with the product.
1. Remove the blade from the enclosure.
2. Open the blade.
3. Remove the system board to access the battery.
4. To remove the battery, press down firmly on the positive side of the connector and lift the battery out of the
securing tabs at the negative side of the connector.
5. To install a new system battery:
a) Support the battery connector by pressing down firmly on the positive side of the connector.
b) Hold the battery with the "+" facing up and slide it under the securing tabs at the positive side of the connector.
6. Press the battery straight down into the connector until it snaps into place.
7. Reinstall the system board.
8. Close the blade.
9. Install the blade in the enclosure.
10. Enter the System Setup to confirm that the battery is operating properly.
11. Enter the correct time and date in the System Setup's Time and Date fields.
12. Exit the System Setup.
13. To test the newly installed battery, remove the blade for at least an hour.
14. After an hour, reinstall the blade.
15. Enter the System Setup and if the time and date are still incorrect, see Getting Help.
51
Page 52

Figure 19. Replacing the NVRAM Backup Battery
1. positive side of battery
2. negative side of battery connector
Storage Controller Card
Your system includes a dedicated expansion-card slot on the blade system board for the storage controller card that
provides the integrated storage subsystem for your system’s hard drives. The storage controller card supports SAS and
SATA hard drives.
NOTE: The storage controller card is located underneath the drive bays.
Removing The Storage Controller Card
CAUTION: Many repairs may only be done by a certified service technician. You should only perform
troubleshooting and simple repairs as authorized in your product documentation, or as directed by the online or
telephone service and support team. Damage due to servicing that is not authorized by Dell is not covered by your
warranty. Read and follow the safety instructions that came with the product.
CAUTION: To ensure proper system cooling, a storage controller blank must be installed on the storage controller
card connector that is not occupied. Remove the storage controller blank only if you intend to install a storage
controller card.
1. Remove the blade from the enclosure.
2. Open the blade.
3. Remove the blade system board and place it on the work surface.
4. Remove the two screws from the storage controller card.
5. Pull the storage controller card straight up and out of the connector.
52
Page 53

Figure 20. Removing and Installing a Storage Controller Card
1. storage controller card
2. screws (2)
3. tabs (2)
4. connector
Installing The Storage Controller Card
1. If installed, remove the storage controller blank.
2. Holding by its edges, position the storage controller card so that the card-connector aligns with the system board
connector.
3. Adjust the other end of the card so that the card edge is secured under the two tabs on the plastic bracket.
4. Insert the controller card-connector firmly into the system board connector until the card is fully seated.
5. Install the two screws to secure the storage controller card to the blade system board.
6. Reinstall the system board.
7. Install the blade in the enclosure.
53
Page 54

54
Page 55

Troubleshooting Your System
Safety First—For You and Your System
CAUTION: Many repairs may only be done by a certified service technician. You should only perform
troubleshooting and simple repairs as authorized in your product documentation, or as directed by the online or
telephone service and support team. Damage due to servicing that is not authorized by Dell is not covered by your
warranty. Read and follow the safety instructions that came with the product.
NOTE: For troubleshooting information on the M1000e enclosure components, see “Troubleshooting The
Enclosure” in the
Troubleshooting System Memory
CAUTION: Many repairs may only be done by a certified service technician. You should only perform
troubleshooting and simple repairs as authorized in your product documentation, or as directed by the online or
telephone service and support team. Damage due to servicing that is not authorized by Dell is not covered by your
warranty. Read and follow the safety instructions that came with the product.
NOTE: Before performing the following procedure, ensure that you have installed the memory modules according
to the memory installation guidelines for the blade.
1. Restart the blade:
a) Press the power button once to turn off the blade
b) Press the power button again to apply power to the blade.
If no error messages appear, go to step 8.
Dell PowerEdge M1000e Enclosure Owner's Manual
at support.dell.com/manuals.
4
2. Enter the System Setup and check the system memory setting.
If the amount of memory installed matches the system memory setting, go to step 8.
3. Remove the blade from the enclosure.
4. Open the blade.
CAUTION: The memory modules are hot to touch for some time after the blade has been powered down. Allow
time for the memory modules to cool before handling them. Handle the memory modules by the card edges
and avoid touching the components.
5. Reseat the memory modules in their sockets.
6. Close the blade.
7. Install the blade in the enclosure.
8. Run the appropriate diagnostic test. For more information, see Using System Diagnostics.
If the test fails, see Getting Help.
55
Page 56

Troubleshooting Hard Drives
CAUTION: Many repairs may only be done by a certified service technician. You should only perform
troubleshooting and simple repairs as authorized in your product documentation, or as directed by the online or
telephone service and support team. Damage due to servicing that is not authorized by Dell is not covered by your
warranty. Read and follow the safety instructions that came with the product.
CAUTION: This troubleshooting procedure can destroy data stored on the hard drive. Before you proceed, back up
all the files on the hard drive, if possible.
1. Run the appropriate controllers test and the hard drive tests in system diagnostics.
If the tests fail, go to step 3.
2. Take the hard drive offline and wait until the hard-drive indicator codes on the drive carrier signal that the drive
may be removed safely, then remove and reseat the drive carrier in the blade.
3. Restart the blade, enter the System Setup and confirm that the drive controller is enabled.
4. Ensure that any required device drivers are installed and are configured correctly.
NOTE: Installing a hard drive into another bay may break the mirror if the mirror state is optimal.
5. Remove the hard drive and install it in the other drive bay.
6. If the problem is resolved, reinstall the hard drive in the original bay.
If the hard drive functions properly in the original bay, the drive carrier could have intermittent problems. Replace
the drive carrier.
7. If the hard drive is the boot drive, ensure that the drive is configured and connected properly.
8. Partition and logically format the hard drive.
9. If possible, restore the files to the drive.
If the problem persists, see Getting Help.
Troubleshooting USB Devices
CAUTION: Many repairs may only be done by a certified service technician. You should only perform
troubleshooting and simple repairs as authorized in your product documentation, or as directed by the online or
telephone service and support team. Damage due to servicing that is not authorized by Dell is not covered by your
warranty. Read and follow the safety instructions that came with the product.
1. Ensure that the blade is turned on.
2. Check the USB device connection to the blade.
3. Swap the USB device with a known-working USB device.
4. Connect the USB devices to the blade using a powered USB hub.
5. If another blade is installed, connect the USB device to that blade. If the USB device works with a different blade,
the first blade may be faulty. See
Getting Help.
56
Page 57

Troubleshooting An Internal SD Card
CAUTION: Many repairs may only be done by a certified service technician. You should only perform
troubleshooting and simple repairs as authorized in your product documentation, or as directed by the online or
telephone service and support team. Damage due to servicing that is not authorized by Dell is not covered by your
warranty. Read and follow the safety instructions that came with the product.
1. Enter the System Setup and ensure that the Internal SD Card Port is enabled.
2. Note the Internal SD Card Redundancy option enabled in the Integrated Devices screen of the System Setup
(Mirror or Disabled).
3. Remove the blade from the enclosure.
4. If the Internal SD Card Redundancy option in the Integrated Devices screen of the System Setup is set to Mirror
mode and SD card 1 has failed:
a) Remove the SD card from SD card slot 1.
b) Remove the SD card present in SD card slot 2 and insert it into SD card slot 1.
c) Install a new SD card in slot 2.
5. If the Internal SD Card Redundancy option in the Integrated Devices screen of the System Setup is set to Mirror
mode and SD card 2 has failed, insert the new SD card into SD card slot 2.
6. If the Internal SD Card Redundancy option in Integrated Devices screen of the System Setup is set to Disabled,
replace the failed SD card with a new SD card.
7. Install the blade in the enclosure.
8. Enter the System Setup and ensure that the Internal SD Card Port option is enabled and Internal SD Card
Redundancy option is set to Mirror mode.
9. Check if the SD card is functioning properly.
If the problem persists, see Getting Help.
Troubleshooting Processors
1. Remove the blade from the enclosure.
2. Open the blade.
3. Ensure that the processor(s) and heat sink(s) are properly installed.
4. If your system only has one processor installed, ensure that it is installed in the primary processor socket (CPU1).
5. Close the blade.
6. Install the blade in the enclosure.
7. Run the appropriate diagnostic test. For more information, see Using System Diagnostics.
If the problem persists, see Getting Help.
Troubleshooting The Blade System Board
CAUTION: Many repairs may only be done by a certified service technician. You should only perform
troubleshooting and simple repairs as authorized in your product documentation, or as directed by the online or
telephone service and support team. Damage due to servicing that is not authorized by Dell is not covered by your
warranty. Read and follow the safety instructions that came with the product.
1. Remove the blade from the enclosure.
2. Open the blade.
3. Clear the blade NVRAM.
57
Page 58

4. If there is a still a problem with the blade, remove and reinstall the blade in the enclosure.
5. Turn on the blade.
6. Run the appropriate diagnostic test. For more information, see Using System Diagnostics.
If the tests fail, see Getting Help.
Troubleshooting The NVRAM Backup Battery
CAUTION: Many repairs may only be done by a certified service technician. You should only perform
troubleshooting and simple repairs as authorized in your product documentation, or as directed by the online or
telephone service and support team. Damage due to servicing that is not authorized by Dell is not covered by your
warranty. Read and follow the safety instructions that came with the product.
The battery maintains the blade configuration, date, and time information in the NVRAM when the blade is turned off.
You may need to replace the battery if an incorrect time or date is displayed during the boot routine.
You can operate the blade without a battery; however, the blade configuration information maintained by the battery in
NVRAM is erased each time you remove power from the blade. Therefore, you must re-enter the system configuration
information and reset the options each time the blade boots until you replace the battery.
1. Re-enter the time and date through the System Setup.
2. Remove the blade from the enclosure for at least one hour.
3. Install the blade in the enclosure.
4. Enter the System Setup.
If the date and time are not correct in the System Setup, replace the battery. If the problem is not resolved by
replacing the battery, see Getting Help.
NOTE: If the blade is turned off for long periods of time (for weeks or months), the NVRAM may lose its system
configuration information. This situation is caused by a defective battery.
NOTE: Some software may cause the blade’s time to speed up or slow down. If the blade operates normally
except for the time maintained by the System Setup, the problem may be caused by a software rather than by
a defective battery.
58
Page 59

5
Using System Diagnostics
If you experience a problem with your system, run the system diagnostics before contacting Dell for technical
assistance. The purpose of running system diagnostics is to test your system hardware without requiring additional
equipment or risking data loss. If you are unable to fix the problem yourself, service and support personnel can use the
diagnostics results to help you solve the problem.
Dell Online Diagnostics
Dell Online Diagnostics, a stand-alone suite of diagnostic programs or test modules, allows you to run diagnostic tests
on the systems in a production environment, and helps you ensure maximum uptime of your systems. Online Diagnostics
allows you to run diagnostic tests on chassis and storage components such as hard drives, physical memory, and
network interface cards (NICs). You can use the graphical user interface (GUI) or the command line interface (CLI) to run
diagnostic tests on the hardware that Online Diagnostics discovers on your system. For information about using
diagnostics, see the
dell.com/support/manuals.
Dell Online PowerEdge Diagnostics User’s Guide
Dell Embedded System Diagnostics
NOTE: Also known as Enhanced Pre-boot System Assessment (ePSA) diagnostics.
The embedded system diagnostics provides a set of options for particular device groups or devices allowing you to:
under Software → Serviceability Tools, at
• Run tests automatically or in an interactive mode
• Repeat tests
• Display or save test results
• Run thorough tests to introduce additional test options to provide extra information about the failed device(s)
• View status messages that inform you if tests are completed successfully
• View error messages that inform you of problems encountered during testing
When To Use The Embedded System Diagnostics
If a major component or device in the system does not operate properly, running the embedded system diagnostics may
indicate component failure.
Running The Embedded System Diagnostics
The embedded system diagnostics program is run from the Dell Lifecycle Controller.
CAUTION: Use the embedded system diagnostics to test only your system. Using this program with other systems
may cause invalid results or error messages.
1. As the system boots, press <F11>.
2. Use the up and down arrow keys to select System Utilities → Launch Dell Diagnostics .
59
Page 60

The ePSA Pre-boot System Assessment window is displayed, listing all devices detected in the system. The
diagnostics starts executing the tests on all the detected devices.
System Diagnostic Controls
Menu Description
Configuration Displays the configuration and status information of all detected devices.
Results Displays the results of all tests that are executed.
System Health Provides the current overview of the system performance.
Event Log Displays a time-stamped log of the results of all tests run on the system. This is displayed if at
least one event description is recorded.
For information about embedded system diagnostics, see the
dell.com/support/manuals.
Dell Enhanced Pre-boot System Assessment User Guide
at
60
Page 61

Jumpers And Connectors
System Board Jumper Settings
CAUTION: Many repairs may only be done by a certified service technician. You should only perform
troubleshooting and simple repairs as authorized in your product documentation, or as directed by the online or
telephone service and support team. Damage due to servicing that is not authorized by Dell is not covered by your
warranty. Read and follow the safety instructions that came with the product.
For information on resetting the password jumper to disable a password, see Disabling A Forgotten Password.
Table 3. System Board Jumper Settings
Jumper Setting Description
PWRD_EN
(default)
The password feature is enabled.
The password feature is disabled.
6
NVRAM_CLR
(default)
The configuration settings are retained at system boot.
The configuration settings are cleared at the next system boot.
(If the configuration settings become corrupted to the point
where the system does not boot, install the jumper and boot
the system. Remove the jumper before restoring the
configuration information.)
61
Page 62

System Board Connectors
Figure 21. System Board Connectors
Table 4. System Board Connectors
Item Connector Description
1 PWRD_EN, NVRAM_CLR System configuration jumpers
2 CPU2 Processor socket 2
3 A1, A4, A2, A5, A3, A6 Memory module sockets (for processor 1)
4 MANAGEMENT RISER Management riser card connector
5 MEZZ1_FAB_C Mezzanine card connector for Fabric C
6 MEZZ2_FAB_B Mezzanine card connector for Fabric B
7 - SD vFlash card connector
NOTE: The SD vFlash card connector is located underneath the system
board.
8 CPU1 Processor socket 1
9 B1, B4, B2, B5, B3, B6 Memory module sockets (for processor 2)
10 HD_BP Hard-drive backplane connector
11 STORAGE storage controller card connector
12 USB2 USB connector
62
Page 63

Item Connector Description
13 USB1 USB connector
14 BATTERY Connector for the 3.0 V coin cell battery
Disabling A Forgotten Password
The blade's software security features include a system password and a setup password. The password jumper enables
these password features or disables them, and clears any password(s) currently in use.
CAUTION: Many repairs may only be done by a certified service technician. You should only perform
troubleshooting and simple repairs as authorized in your product documentation, or as directed by the online or
telephone service and support team. Damage due to servicing that is not authorized by Dell is not covered by your
warranty. Read and follow the safety instructions that came with the product.
1. Remove the blade from the enclosure.
2. Open the blade.
3. Remove the system board to gain access to the jumpers.
4. Relocate the jumper plug to disable the password feature.
5. Reinstall the system board.
6. Close the blade.
7. Install the blade in the enclosure.
When the blade is on, the power-on indicator is solid green. Allow the blade to finish booting.
The existing passwords are not disabled (erased) until the system boots with the password removed. However,
before you assign a new system and/or setup password, you must reinstall the password jumper.
NOTE: If you assign a new system and/or setup password with the jumper removed, the system disables the
new password(s) the next time it boots.
8. Remove the blade from the enclosure.
9. Open the blade.
10. Remove the system board to gain access to the jumpers.
11. Relocate the jumper plug to enable the password feature.
12. Reinstall the system board.
13. Close the blade.
14. Install the blade in the enclosure.
15. Assign a new system and/or setup password.
63
Page 64

64
Page 65

Technical Specifications
Processor
Processor type One or two Intel Xeon processor E5-2400 product family
Memory
Architecture 1600 MT/s, 1333 MT/s, or 1066 MT/s DDR3 and LV-DDR3
DIMMs
Memory module sockets Twelve 240-pin
Memory module capacities
RDIMMs 2 GB (single-rank), 4 GB (single- and dual-rank), 8 GB
(dual-rank), 16 GB (dual-rank), and 32 GB (quad-rank)
UDIMMs 2 GB (single-rank) and 4 GB (dual-rank)
Minimum RAM 2 GB (single processor configuration)
Maximum RAM 384 GB
Drives
7
Hard drives Up to two 2.5-inch, hot-pluggable SSD/SAS/SATA hard
drives
Optical drive External optional USB DVD
NOTE: DVD devices are data only.
Flash drive
Connectors
Front
USB Two 4-pin, USB 2.0-compliant
Internal
SD
Internal optional USB
Internal optional SD card
Optional vFlash card (with integrated iDRAC7 Enterprise)
Two internal SD cards dedicated for the hypervisor
One dedicated for future vFlash support
65
Page 66

Mezzanine Cards
Mezzanine slots Two mezzanine PCIe x8 Gen 3 slots supporting dual-port
Gb Ethernet, 10 Gb Ethernet, FC8 Fibre Channel, or
Infiniband mezzanine cards
Video
Video type Matrox G200 integrated with iDRAC
Video memory 8 MB shared with iDRAC application memory
Battery
NVRAM backup battery CR 2032 3.0 V Lithium coin cell
Environmental
NOTE: For additional information about environmental measurements for specific system configurations, see
dell.com/environmental_datasheets.
Storage temperature –40 °C to 65 °C (–40 °F to 149 °F) with a maximum
temperature gradation of 20 °C per hour.
Standard operating temperature Continuous operation: 10 °C to 35 °C at 10% to 80%
relative humidity (RH), with 26 °C max dew point. De-rate
maximum allowable dry bulb temperature at 1 °C per 300
m above 900 m (1 °F per 550 ft).
Expanded operating temperature
NOTE: When operating in the expanded temperature
range, system performance may be impacted.
NOTE: When operating in the expanded temperature
range, ambient temperature warnings may be
reported on the LCD and in the System Event Log.
≤ 10% of annual operating hours 5 °C to 40 °C at 5% to 85% RH with 26 °C dew point.
NOTE: Outside the standard operating temperature
(10 °C to 35 °C), the system can operate down to 5 °C
or up to 40 °C for a maximum of 10% of its annual
operating hours.
For temperatures between 35 °C and 40 °C, de-rate
maximum allowable dry bulb temperature by 1 °C per 175
m above 950 m (1 °F per 319 ft).
≤ 1% of annual operating hours –5 °C to 45 °C at 5% to 90% RH with 26 °C dew point.
NOTE: Outside the standard operating temperature
(10 °C to 35 °C), the system can operate down to –5
°C or up to 45 °C for a maximum of 1% of its annual
operating hours.
66
Page 67

Environmental
For temperatures between 40 °C and 45 °C, de-rate
maximum allowable dry bulb temperature by 1 °C per 125
m above 950 m (1 °F per 228 ft).
67
Page 68

68
Page 69

8
System Messages
LCD Status Messages
The LCD messages consist of brief text messages that refer to events recorded in the System Event Log (SEL). For
information on the SEL and configuring system management settings, see the systems management software
documentation.
Viewing LCD Messages
If a system error occurs, the LCD screen will turn amber. Press the Select button to view the list of errors or status
messages. Use the left and right buttons to highlight an error number, and press Select to view the error.
Removing LCD Messages
For faults associated with sensors, such as temperature, voltage, fans, and so on, the LCD message is automatically
removed when that sensor returns to a normal state. For other faults, you must take action to remove the message from
the display:
• Clear the SEL — You can perform this task remotely, but you will lose the event history for the system.
• Power cycle — Turn off the system and disconnect it from the electrical outlet; wait approximately 10 seconds,
reconnect the power cable, and restart the system.
System Error Messages
System messages appear on the monitor to notify you of a possible problem with the system. These messages refer to
events recorded in the System Event Log (SEL). For information on the SEL and configuring system management settings,
see the systems management software documentation.
Some messages are also displayed in abbreviated form on the system's LCD, if the system includes that feature.
NOTE: The LCD error messages listed here are displayed in the simple format. See Setup Menu to select the format
in which the messages are displayed.
NOTE: If you receive a system message not listed here, check the documentation for the application that was
running when the message was displayed or the operating system's documentation for an explanation of the
message and recommended action.
NOTE: In some messages, a particular system component is identified by name (“<name>”), component number
(“<number>”), or location (“bay”).
Error Code Message Information
AMP0300
Message The system board <
threshold.
Details System board <
name
name
> current is less than the lower warning
> current is outside of the optimum range.
69
Page 70

Error Code Message Information
AMP0301
AMP0302
Action
Message The system board <
LCD Message System board <
Details System board <
Action
Message The system board <
Details System board <
1. Review system power policy.
2. Check system logs for power related failures.
3. Review system configuration changes.
4. If the issue persists, see Getting Help.
threshold.
name
name
1. Review system power policy.
2. Check system logs for power related failures.
3. Review system configuration changes.
4. If the issue persists, see Getting Help.
threshold.
name
name
> current is less than the lower warning
> current is outside of range.
> current is outside of the optimum range.
name
> current is greater than the upper warning
> current is outside of the optimum range.
AMP0303
AMP0304
Action
Message The system board <
LCD Message System board <
Details System board <
Action
Message The system board <
LCD Message System board <
1. Review system power policy.
2. Check system logs for power related failures.
3. Review system configuration changes.
4. If the issue persists, see Getting Help.
threshold.
name
name
1. Review system power policy.
2. Check system logs for power related failures.
3. Review system configuration changes.
4. If the issue persists, see Getting Help.
name
name
> current is greater than the upper critical
> current is outside of range.
> current is outside of the optimum range.
name
> current is outside of range.
> current is outside of range.
70
Page 71

Error Code Message Information
AMP0306
AMP0307
Details System board <
Action
1. Review system power policy.
2. Check system logs for power related failures.
3. Review system configuration changes.
4. If the issue persists, see Getting Help.
Message Disk drive bay <
threshold.
Details Disk drive bay <
Action
1. Review system power policy.
2. Check system logs for power related failures.
3. Review system configuration changes.
4. If the issue persists, see Getting Help.
Message Disk drive bay <
threshold.
LCD Message Disk drive bay <
name
> current is outside of the optimum range.
name
> current is less than the lower warning
name
> current is outside of the optimum range.
name
> current is less than the lower critical
name
> current is outside of range.
AMP0308
AMP0309
Details Disk drive bay <
Action
1. Review system power policy.
2. Check system logs for power related failures.
3. Review system configuration changes.
4. If the issue persists, see Getting Help.
Message Disk drive bay <
threshold.
Details Disk drive bay <
Action
1. Review system power policy.
2. Check system logs for power related failures.
3. Review system configuration changes.
4. If the issue persists, see Getting Help.
Message Disk drive bay <
threshold.
name
> current is outside of the optimum range.
name
> current is greater than the upper warning
name
> current is outside of the optimum range.
name
> current is greater than the upper critical
71
Page 72

Error Code Message Information
AMP0310
AMP0312
LCD Message Disk drive bay <
Details Disk drive bay <
Action
1. Review system power policy.
2. Check system logs for power related failures.
3. Review system configuration changes.
4. If the issue persists, see Getting Help.
Message Disk drive bay <
LCD Message Disk drive bay <
Details Disk drive bay <
Action
1. Review system power policy.
2. Check system logs for power related failures.
3. Review system configuration changes.
4. If the issue persists, see Getting Help.
Message System level current is less than the lower warning threshold.
name
> current is outside of range.
name
> current is outside of the optimum range.
name
> current is outside of range.
name
> current is outside of range.
name
> current is outside of the optimum range.
AMP0313
AMP0314
Details System level current is outside of the optimum range.
Action
1. Review system power policy.
2. Check system logs for power related failures.
3. Review system configuration changes.
4. If the issue persists, see Getting Help.
Message System level current is less than the lower warning threshold.
LCD Message System level current is outside of range.
Details System level current is outside of the optimum range.
Action
1. Review system power policy.
2. Check system logs for power related failures.
3. Review system configuration changes.
4. If the issue persists, see Getting Help.
Message System level current is greater than the upper warning threshold.
Details System level current is outside of the optimum range.
72
Page 73

Error Code Message Information
AMP0315
AMP0316
Action
1. Review system power policy.
2. Check system logs for power related failures.
3. Review system configuration changes.
4. If the issue persists, see Getting Help.
Message System level current is greater than the upper critical threshold.
LCD Message System level current is outside of range.
Details System level current is outside of the optimum range.
Action
1. Review system power policy.
2. Check system logs for power related failures.
3. Review system configuration changes.
4. If the issue persists, see Getting Help.
Message System level current is outside of range.
LCD Message System level current is outside of range.
Details System level current is outside of the optimum range.
AMP0318
AMP0319
Action
1. Review system power policy.
2. Check system logs for power related failures.
3. Review system configuration changes.
4. If the issue persists, see Getting Help.
Message Chassis power level current is less than the lower warning threshold.
Details Chassis power level current is outside of the optimum range.
Action
1. Review system power policy.
2. Check system logs for power related failures.
3. Review system configuration changes.
4. If the issue persists, see Getting Help.
Message Chassis power level current is less than the lower critical threshold
Details Chassis power level current is outside of the optimum range.
Action
1. Review system power policy.
2. Check system logs for power related failures.
73
Page 74

Error Code Message Information
3. Review system configuration changes.
4. If the issue persists, see Getting Help.
AMP0320
AMP0321
AMP0322
Message Chassis power level current is greater than the upper warning
threshold.
Details Chassis power level current is outside of the optimum range.
Action
1. Review system power policy.
2. Check system logs for power related failures.
3. Review system configuration changes.
4. If the issue persists, see Getting Help.
Message Chassis power level current is greater than the upper critical
threshold.
Details Chassis power level current is outside of the optimum range.
Action
1. Review system power policy.
2. Check system logs for power related failures.
3. Review system configuration changes.
4. If the issue persists, see Getting Help.
Message Chassis power level current is outside of range.
ASR0000
ASR0001
74
Details Chassis power level current is outside of the optimum range.
Action
1. Review system power policy.
2. Check system logs for power related failures.
3. Review system configuration changes.
4. If the issue persists, see Getting Help.
Message The watchdog timer expired.
Details The operating system or an application failed to communicate within
the time-out period.
Action Check the operating system, application, hardware, and system event
log for exception events.
Message The watchdog timer reset the system.
Page 75

Error Code Message Information
Details The operating system or an application failed to communicate within
Action Check the operating system, application, hardware, and system event
the time-out period. The system was reset.
log for exception events.
ASR0002
ASR0003
ASR0008
ASR0100
Message The watchdog timer powered off the system.
Details The operating system or an application failed to communicate within
the time-out period. The system was shut down.
Action Check the operating system, application, hardware, and system event
log for exception events.
Message The watchdog timer power cycled the system.
Details The operating system or an application failed to communicate within
the time-out period. The system was power-cycled.
Action Check the operating system, application, hardware, and system event
log for exception events.
Message The watchdog timer interrupt was initiated.
Details The operating system or an application failed to communicate within
the time-out period. No action was taken.
Action Check the operating system, application, hardware, and system event
log for exception events.
Message The BIOS watchdog timer reset the system.
ASR0101
ASR0102
Details The operating system or an application failed to communicate within
the time-out period. The system was reset.
Action Check the operating system, application, hardware, and system event
log for exception events.
Message The OS watchdog timer reset the system.
Details The operating system or an application failed to communicate within
the time-out period. The system was reset.
Action Check the operating system, application, hardware, and system event
log for exception events.
Message The OS watchdog timer shutdown the system.
75
Page 76

Error Code Message Information
Details The operating system or an application failed to communicate within
Action Check the operating system, application, hardware, and system event
the time-out period. The system was shutdown.
log for exception events.
ASR0103
ASR0104
ASR0105
ASR0106
Message The OS watchdog timer powered down the system.
Details The operating system or an application failed to communicate within
the time-out period. The system was powered down.
Action Check the operating system, application, hardware, and system event
log for exception events.
Message The OS watchdog timer power-cycled the system.
Details The operating system or an application failed to communicate within
the time-out period. The system was power-cycled.
Action Check the operating system, application, hardware, and system event
log for exception events.
Message The operating system watchdog timer powered off the system.
Details The operating system or an application failed to communicate within
the time-out period. The system was powered off.
Action Check the operating system, application, hardware, and system event
log for exception events.
Message The watchdog timer expired.
ASR0107
BAT0000
76
Details The operating system or an application failed to communicate within
the time-out period.
Action Check the operating system, application, hardware, and system event
log for exception events.
Message The watchdog timer pre-timeout interrupt was initiated.
Details The operating system or an application failed to communicate within
the time-out period.
Action Check the operating system, application, hardware, and system event
log for exception events.
Message The system board battery is low.
Page 77

Error Code Message Information
Details The system board battery is either missing, bad, or unable to charge
Action Check system fans. Replace the system board battery.
due to thermal issues.
BAT0002
BAT0004
BAT0005
BAT0007
Message The system board battery has failed.
LCD Message The system board battery has failed. Check battery.
Details The system board battery is either missing or bad.
Action See Getting Help.
Message The system board battery is absent.
LCD Message The system board battery is absent. Check battery.
Action Reinstall the system board battery.
Message The storage battery is low.
Details System has to remain powered on to charge the battery.
Action Allow the battery to charge. If the issue persists, see Getting Help.
Message The storage battery has failed.
LCD Message The storage battery has failed. Check battery.
Details Verify the cable connection between the storage battery and the
controller.
BAT0010
BAT0012
BAT0014
Action Verify the storage battery installation.
Message The storage battery for disk drive bay <
Details System has to remain powered on to charge the storage battery.
Action Allow the storage battery to charge. If the issue persists, see Getting
Help.
Message The storage battery for disk drive bay <
LCD Message Battery for disk drive bay <
Details Verify the cable connection between the storage battery and the
controller.
Action Verify the storage battery installation.
Message The storage battery for disk drive bay <
bay
> has failed. Check battery.
bay
> is low.
bay
> has failed.
bay
> is absent.
77
Page 78

Error Code Message Information
BAT0015
BAT0017
BAT0019
LCD Message Battery for disk drive bay <
Details Verify the cable connection between the storage battery and the
controller.
Action Verify the storage battery installation.
Message The <
Details The low <
Action Recharge the <
Message The <
LCD Message The <
Details The <
Action Check system fans. Replace the <
Message The <
LCD Message The <
name
> battery is low.
name
replace the <
name
> battery has failed.
name
> battery has failed. Check battery.
name
> battery is either missing, bad, or unable to charge due to
thermal issues.
name
> battery is absent.
name
> battery is absent. Check battery.
> battery may impact system performance negatively.
name
name
bay
> is absent. Check battery.
> battery if possible. If the problem continues
> battery.
name
> battery.
CBL0006
CPU0000
CPU0001
Details The failed or missing <
performance.
Action Check system fans. Replace the <
Message Multiple storage controllers are incorrectly connected to the same
backplane <
Details Unsupported backplane configuration.
Action Check backplane configuration. Reconnect cable. If the issue
persists, see Getting Help.
Message CPU <
LCD Message CPU <
Details System event log and OS logs may indicate that the exception is
external to the processor.
Action Review System Event Log and Operating System Logs. If the issue
persists, see Getting Help.
Message CPU <
Bay ID
number
> has an internal error (IERR).
number
> has an internal error (IERR).
number
> has a thermal trip (over-temperature) event.
name
> battery may reduce system
name
> battery.
>.
78
Page 79

Error Code Message Information
CPU0002
CPU0003
LCD Message CPU <
Details The processor temperature increased beyond the operational range.
Action Review logs for fan failures, replace failed fans. If no fan failures are
Message CPU <
Action
Message CPU <
Action
number
> has a thermal trip. Check CPU heat sink.
detected, check inlet temperature (if available) and reinstall
processor heat-sink.
number
> has failed the built-in self-test (BIST).
1. Turn system off and remove input power for one minute.
Reapply input power and turn system on.
2. Make sure the processor is seated correctly.
3. If the issue persists, see Getting Help.
number
> is stuck in POST.
1. Turn system off and remove input power for one minute.
Reapply input power and turn system on.
2. Reduce system configuration to minimum memory and remove
all PCI devices. If system completes POST, update system BIOS.
reinstall memory and PCI one component at a time to meet the
original configuration.
3. If the issue persists, see Getting Help.
CPU0004
CPU0005
CPU0006
Message CPU <
Action
Message CPU <
LCD Message CPU <
Details System is unable to boot or may run in a degraded state.
Action Review the technical specifcations for supported processor types.
Message Unrecoverable CPU complex error detected on CPU <
Details System is unable to boot or may run in a degraded state.
number
> failed to initialize.
1. Turn system off and remove input power for one minute.
Reapply input power and turn system on.
2. Make sure the processor is seated correctly.
3. If the issue persists, see Getting Help.
number
> configuration is unsupported.
number
> configuration is unsupported. Check CPU or BIOS
revision.
number
>.
79
Page 80

Error Code Message Information
CPU0008
CPU0010
CPU0023
Action
Message CPU <
Details System is unable to boot or may run in a degraded state.
Action If unexpected, check presence, and system setup (BIOS)
Message CPU <
Details The CPU is throttled due to thermal or power conditions.
Action Review system logs for power or thermal exceptions.
Message CPU <
LCD Message CPU <
Action Verify processor installation. If present, re-seat the processor.
1. Turn system off and remove input power for one minute.
Reapply input power and turn system on.
2. Make sure the processor is seated correctly.
3. If the issue persists, see Getting Help.
number
> is disabled.
configuration.
number
> is throttled.
number
> is absent.
number
> is absent. Check CPU.
CPU0100
CPU0101
CPU0102
CPU0103
Message CPU <
Details System performance may be degraded.
Action Check system operating environment.
Message CPU <
LCD Message CPU <
Details System performance may be degraded.
Action Check system operating environment, fans, and heat-sinks.
Message CPU <
Details System performance may be degraded.
Action Check system operating environment, fans, and heat-sinks.
Message CPU <
number
number
number
number
threshold.
number
threshold.
> temperature is less than the lower warning threshold.
> temperature is less than the lower critical threshold.
> temperature is outside of range.
> temperature is greater than the upper warning
> temperature is greater than the upper critical
80
Page 81

Error Code Message Information
CPU0104
CPU0200
LCD Message CPU <
Details System performance may be degraded.
Action Check system operating environment, fans, and heat-sinks.
Message CPU <
LCD Message CPU <
Details System performance may be degraded.
Action Check system operating environment, fans, and heat-sinks.
Message CPU <
Details Low voltages may be the result of a problem with the voltage
Action
number
> temperature is outside of range. Check fans.
number
> temperature is outside of range.
number
> temperature is outside of range. Check fans.
number
> <
name
> voltage is less than the lower warning
threshold.
regulator or a problem with the processor. The low voltage may
cause the processor to fail to operate.
1. Turn system off and remove input power for one minute.
2. Reapply input power and turn system on.
3. Ensure the processor is seated correctly.
4. If the issue persists, see Getting Help.
CPU0201
CPU0202
Message CPU <
LCD Message CPU <
Details Low voltages may be the result of a problem with the voltage
Action
Message CPU <
Details High voltages may be the result of problem with the voltage regulator
number
> <
name
> voltage is less than the lower critical
threshold.
number
> <
name
> voltage is outside of range. Re-seat CPU.
regulator or a problem with the processor. When the critical
threshold is crossed, the processor will fail to operate. The system
may power down.
1. Turn system off and remove input power for one minute.
2. Reapply input power and turn system on.
3. Ensure the processor is seated correctly.
4. If the issue persists, see Getting Help.
number
> <
name
> voltage is greater than the upper warning
threshold.
or a problem with the processor. Elevated voltages may result in
81
Page 82

Error Code Message Information
damage to the processor or other electronic components in side the
system.
CPU0203
CPU0204
Action
Message CPU <
LCD Message CPU <
Details High voltages may be the result of problem with the voltage regulator
Action
Message CPU <
1. Turn system off and remove input power for one minute.
2. Reapply input power and turn system on.
3. Ensure the processor is seated correctly.
4. If the issue persists, see Getting Help.
number
> <
name
> voltage is greater than the upper critical
threshold.
number
> <
name
> voltage is outside of range. Re-seat CPU.
or a problem with the processor. Elevated voltages may result in
damage to the processor or other system electrical components. The
system may power down.
1. Turn system off and remove input power for one minute.
2. Reapply input power and turn system on.
3. Ensure the processor is seated correctly.
4. If the issue persists, see Getting Help.
number
> <
name
> voltage is outside of range.
CPU0700
82
LCD Message CPU <
Details Voltages outside the allowable range may damage electrical
Action
Message CPU <
LCD Message CPU <
Details System BIOS was unable to initialize the processor.
Action
number
> <
name
> voltage is outside of range. Re-seat CPU.
components or may cause the system to shutdown.
1. Turn system off and remove input power for one minute.
2. Ensure the processor is seated correctly.
3. Reapply input power and turn system on.
4. If the issue persists, see Getting Help.
number
> initialization error detected.
number
> initialization error detected. Power cycle system.
1. Turn system off and remove input power for one minute.
2. Ensure the processor is seated correctly.
3. Reapply input power and turn system on.
Page 83

Error Code Message Information
4. If the issue persists, see Getting Help.
CPU0701
CPU0702
Message CPU <
LCD Message CPU <
Details System event log and operating system logs may indicate that the
Action
Message CPU bus parity error detected.
LCD Message CPU bus parity error detected. Power cycle system.
Details System event log and operating system logs may indicate that the
Action
number
> protocol error detected.
number
> protocol error detected. Power cycle system.
exception is external to the processor.
1. Check system and operating system logs for exceptions. If no
exceptions are found, continue.
2. Turn system off and remove input power for one minute.
3. Ensure the processor is seated correctly.
4. Reapply input power and turn system on.
5. If the issue persists, see Getting Help.
exception is external to the processor.
1. Check system and operating system logs for exceptions. If no
exceptions are found, continue.
2. Turn system off and remove input power for one minute.
3. Ensure the processor is seated correctly.
4. Reapply input power and turn system on.
5. If the issue persists, see Getting Help.
CPU0703
Message CPU bus initialization error detected.
LCD Message CPU bus initialization error detected. Power cycle system.
Details System event log and operating system logs may indicate that the
exception is external to the processor.
Action
1. Check system and operating system logs for exceptions. If no
exceptions are found, continue.
2. Turn system off and remove input power for one minute.
3. Ensure the processor is seated correctly.
4. Reapply input power and turn system on.
5. If the issue persists, see Getting Help.
83
Page 84

Error Code Message Information
CPU0704
CPU0801
Message CPU <
LCD Message CPU <
Details System event log and operating system logs may indicate that the
Action
Message CPU <
LCD Message CPU <
Details System performance may be degraded or the system may fail to
Action
number
> machine check error detected.
number
> machine check error detected. Power cycle system.
exception is external to the processor.
1. Check system and operating system logs for exceptions. If no
exceptions are found, continue.
2. Turn system off and remove input power for one minute.
3. Ensure the processor is seated correctly.
4. Reapply input power and turn system on.
5. If the issue persists, see Getting Help.
number
> voltage regulator module failed.
number
> voltage regulator module failed. Re-seat module.
operate.
1. Turn system off and remove input power for one minute.
2. Reapply input power and turn system on.
3. Ensure the processor is seated correctly.
4. If the issue persists, see Getting Help.
CPU0802
CPU0803
84
Message A predictive failure detected on CPU <
module.
Details System performance may be degraded or the system may fail to
operate.
Action
Message The power input for CPU <
LCD Message Lost power input for CPU <
Details System performance may be degraded or the system may fail to
1. Turn system off and remove input power for one minute.
2. Reapply input power and turn system on.
3. Ensure the processor is seated correctly.
4. If the issue persists, see Getting Help.
number
number
module.
operate.
number
> voltage regulator
> voltage regulator module is lost.
>voltage regulator module. Re-seat
Page 85

Error Code Message Information
CPU0804
CPU0805
Action
Message The power input for CPU <
LCD Message The power input for CPU <
Details System performance may be degraded or the system may fail to
Action
Message The power input for CPU <
1. Turn system off and remove input power for one minute.
2. Reapply input power and turn system on.
3. Ensure the processor is seated correctly.
4. If the issue persists, see Getting Help.
number
> voltage regulator module is
outside of range.
number
> voltage regulator module is
outside of range. Re-seat module.
operate.
1. Turn system off and remove input power for one minute.
2. Reapply input power and turn system on.
3. Ensure the processor is seated correctly.
4. If the issue persists, see Getting Help.
number
> voltage regulator module is
outside of range, but it is attached to the system.
CPU0806
CPU0816
Details System performance may be degraded or the system may fail to
operate.
Action
Message CPU <
LCD Message CPU <
Details System performance may be degraded or the system may fail to
Action Review this manual for proper configuration and installation
Message CPU <
LCD Message CPU <
1. Turn system off and remove input power for one minute.
2. Reapply input power and turn system on.
3. Ensure the processor is seated correctly.
4. If the issue persists, see Getting Help.
number
> voltage regulator module is incorrectly configured.
number
> voltage regulator module incorrectly configured.
Check configuration.
operate.
procedures.
number
> voltage regulator module is absent.
number
> voltage regulator module absent. Check module.
85
Page 86

Error Code Message Information
Details System performance may be degraded or the system may fail to
Action If removal was unintended, check presence and reinstall.
operate.
HWC1001
HWC1002
HWC1005
HWC1006
Message The <
LCD Message The <
Details The absent device may be necessary for proper operation. System
Action Reinstall or reconnect the hardware.
Message The <
Action If device disabled unexpectedly, re-enable device.
Message The storage adapter is absent.
LCD Message The storage adapter is absent. Check hardware.
Details The storage adapter may be necessary for proper operation. System
Action Install storage adapter.
Message The storage adapter is disabled.
Action If adapter disabled unexpectedly, re-enable the storage adapter.
name
> is absent.
name
> is absent. Check hardware.
functionality may be degraded.
name
> is disabled.
functionality may be degraded.
HWC1009
HWC1010
HWC1015
86
Message The backplane is absent.
LCD Message The backplane is absent. Check hardware.
Details The backplane may be necessary for proper operation. System
functionality may be degraded.
Action If removal was unintended, check presence, then reinstall or
reconnect.
Message The backplane is disabled.
Action If disabled unexpectedly, re-enable backplane.
Message The mezzanine card <
Details The mezzanine card may be necessary for proper operation. System
functionality may be degraded.
number
> is absent.
Page 87

Error Code Message Information
Action If removal was unintended, check presence, then reinstall or
reconnect.
HWC2006
HWC2008
HWC2011
Message The <
LCD Message The <
Details The device may be necessary for proper operation. System
Action Check presence, then re-install or reconnect.
Message A fabric mismatch detected between IOM and mezzanine card
Details The fabric type for the IOM and mezzanine cards must match.
Action Check chassis fabric type in CMC GUI and compare to the type of
Message The riser board cable or interconnect is not connected, or is
LCD Message Riser board cable or interconnect failure. Check connection.
Details The riser blade cable may be necessary for proper operation. System
Action Check the riser board or interconnect presence, then reinstall or
name
> is not installed correctly.
name
> is not installed correctly. Check connection.
functionality may be degraded.
<
number
>.
IOM or mezzanine card.
improperly connected.
functionality may be degraded.
reconnect.
HWC3000
HWC3002
HWC3004
Message The <
Details The removed device may be necessary for proper operation. System
Action If removal was unintended, check presence of the removed device,
Message Server <
Action If removal was unintended, check presence of the server, then
Message IO module <
Action If removal was unintended, check presence of the IO module, then
name
> is removed.
functionality may be degraded.
then reinstall or reconnect
number
> is removed.
reinsert.
number
> is removed.
reinsert.
87
Page 88

Error Code Message Information
HWC4000
HWC4002
HWC4011
Message A hardware incompatibility detected between BMC/iDRAC firmware
and CPU.
LCD Message Incompatibility between BMC/iDRAC firmware and CPU. Update
firmware.
Details A hardware incompatibility was detected between BMC/iDRAC
firmware and Processor(s). An iDRAC or BMC firmware update is
needed.
Action Update the BMC/iDRAC firmware. If the issue persists, see Getting
Help.
Message A hardware incompatibility detected between BMC/iDRAC firmware
and other hardware.
Details A hardware incompatibility was detected between BMC/iDRAC
firmware and other hardware. An iDRAC or BMC firmware update is
needed.
Action Update the BMC/iDRAC firmware. If the issue persists, see Getting
Help.
Message Hardware unsuccessfully updated for mezzanine card <
number
>.
HWC4013
HWC4015
HWC5001
HWC5002
Action Check presence of the hardware, reinstall or reconnect, then
reattempt the update. If the issue persists, see Getting Help.
Message Hardware unsuccessfully updated for embedded NIC.
Action Check presence, reinstall or reconnect, then reattempt the update. If
the issue persists, see Getting Help.
Message Link Tuning error detected.
Details CMC has old firmware. After updating the firmware the CMC will
recognize the device.
Action Update the CMC firmware. If the issue persists, see Getting Help.
Message <
Action If unexpected, check presence, then reinstall or reconnect.
Message A fabric mismatch detected on <
Details The fabric type for the IOM and mezzanine cards must match.
name
> is offline.
name
>.
88
Page 89

Error Code Message Information
Action Check chassis fabric type in CMC GUI and compare to the type of
IOM or mezzanine card.
HWC5004
HWC5006
HWC5008
HWC5010
HWC5014
HWC5031
Message A link tuning failure detected on <
Details CMC has old firmware. After updating the firmware the CMC will
recognize the device.
Action Update the CMC firmware. If the issue persists, see Getting Help.
Message A failure is detected on <
Action If the issue persists, see Getting Help.
Message Console is not available for the <
Action If the issue persists, see Getting Help.
Message <
Action If the issue persists, see Getting Help.
Message <
Action If the issue persists, see Getting Help.
Message IO module <
name
> cannot detect any hosts.
name
> is not functional and is powered off.
number
name
> is offline.
>.
name
name
>.
>.
HWC5032
HWC5034
HWC5036
Details The CMC has powered off the IOM.
Action If the issue persists, see Getting Help.
Message A fabric mismatch detected on IO module <
Details The fabric type for IOM's on the same chassis fabric must match.
Action Check chassis fabric type in CMC GUI and compare to the type of
both IOM's.
Message A link tuning failure detected on IO module <
Details Link tuning table not supported for this IO modular.
Action Update the CMC firmware. If the issue persists, see Getting Help.
Message A failure is detected on IO module <
number
number
number
>.
>.
>.
89
Page 90

Error Code Message Information
Details The IOM module performance may be impacted.
Action If the issue persists, see Getting Help.
HWC6000
HWC6002
HWC6003
HWC6004
HWC7002
Message The <
Details Information and status from the controller is unavailable.
Action Remove and reapply input power. If the issue persists, see Getting
Message The <
Details Information and status from the controller is unavailable.
Action Remove and reapply input power. If the issue persists, see Getting
Message The <
Message Cannot communicate with <
Details Information and status from the controller is unavailable.
Action Remove and reapply input power. If the issue persists, see Getting
Message Server <
Help.
Help.
Help.
state.
name
> controller is offline.
name
> controller is stuck in boot mode.
name
> controller is booting.
name
number
> health changed to a warning state from a normal
> controller.
HWC7004
HWC7006
90
Details Server <
state.
Action Review System Log or front panel for additional information.
Message Server <
normal or warning state.
Details Server <
state.
Action Review System Log or front panel for additional information.
Message Server <
less severe state.
Details Server <
state.
number
> health changed to a warning state from a normal
number
> health changed to a critical state from either a
number
> health changed to a warning state from a normal
number
> health changed to a nonrecoverable state from a
number
> health changed to a warning state from a normal
Page 91

Error Code Message Information
Action Review System Log or front panel for additional information.
HWC7008
HWC7010
HWC7012
LNK2700
Message Server <
severe state. Server <
a non-recoverable state.
Details Server <
state.
Action Review System Log or front panel for additional information.
Message Server <
nonrecoverable state.
Details Server <
state.
Action Review System Log or front panel for additional information.
Message Server <
Details Server <
state.
Action Review System Log or front panel for additional information.
Message The <
number
> health changed to a warning state from more
number
> health changed to a warning state from a normal
number
> health changed to a critical state from a
number
> health changed to a warning state from a normal
number
> health changed to a nonrecoverable state.
number
> health changed to a warning state from a normal
name
> LAN heartbeat is lost.
number
> health changed to a critical state from
MEM0000
MEM0001
Details CMC has lost network connection.
Action Check network cable and network connections.
Message Persistent correctable memory errors detected on a memory device
at location(s) <
Details This is an early indicator of a possible future uncorrectable error.
Action Re-seat the memory modules. If the issue persists, see Getting Help .
Message Multi-bit memory errors detected on a memory device at location(s)
<
location
LCD Message Multi-bit memory error on <
Details The memory module has encountered a uncorrectable error. System
performance may be degraded. The operating system and/or
applications may fail as a result.
Action Re-seat the memory modules. If the issue persists, see Getting Help.
>.
location
>.
location
>. Re-seat memory.
91
Page 92

Error Code Message Information
MEM0002
MEM0003
MEM0004
MEM0005
Message Parity memory errors detected on a memory device at location
<
location
>.
Details The memory is operational. This an early indicator of a possible future
uncorrectable error.
Action Re-seat the memory modules. If the issue persists, see Getting Help.
Message Stuck bit memory error detected on a memory device at location
<
location
>.
Details This is an early indicator of a possible future uncorrectable error.
Action Re-seat the memory modules. If the issue persists, see Getting Help.
Message Memory device at location <
Details The memory may not be seated correctly, misconfigured, or has
failed. Memory size is reduced.
Action Re-seat the memory modules. If the issue persists, see Getting Help.
Message Persistent correctable memory error limit reached for a memory
device at location(s) <
location
location
>.
> is disabled.
MEM0007
MEM0009
LCD Message Persistent correctable memory error limit reached for <
seat memory.
Details The memory is operational. This an early indicator of a possible future
uncorrectable error.
Action Re-seat the memory modules. If the issue persists, see Getting Help.
Message Unsupported memory configuration; check memory device at location
<
location
>.
LCD Message Unsupported memory configuration. Check memory <
Details The memory may not be seated correctly, misconfigured, or has
failed. Memory size is reduced.
Action Check the memory configuration. Re-seat the memory modules. If the
issue persists, see Getting Help.
Message Memory device at location <
Details System performance is degraded.
Action If unexpected, review system logs for power or thermal exceptions.
location
> is throttled.
location
location
>. Re-
>.
92
Page 93

Error Code Message Information
MEM0010
MEM0022
MEM0701
MEM0702
Message Memory device at location <
LCD Message Memory device <
Details System performance is degraded.
Action If unexpected, review system logs for power or thermal exceptions.
Message Memory device at location <
Details The memory may not be seated correctly, misconfigured, or has
failed. Memory size is reduced.
Action Re-seat the memory modules. If the issue persists, see Getting Help.
Message Correctable memory error rate exceeded for <
Details The memory may not be operational. This an early indicator of a
possible future uncorrectable error.
Action Re-seat the memory modules. If the issue persists, see Getting Help.
Message Correctable memory error rate exceeded for <
LCD Message Correctable memory error rate exceeded for <
memory.
location
location
> is over heating.
> is over heating. Check fans.
location
> is absent.
location
location
location
>.
>.
>. Re-seat
MEM1001
MEM1003
Details The memory may not be operational. This an early indicator of a
possible future uncorrectable error.
Action Re-seat the memory modules. If the issue persists, see Getting Help.
Message Memory device at location <
state.
LCD Message Memory device <
seat memory
Details The memory may not be operational. This an early indicator of a
possible future uncorrectable error.
Action Re-seat the memory modules. If the issue persists, see Getting Help.
Message Memory device at location <
Details The memory may not be operational. This an early indicator of a
possible future uncorrectable error.
Action Re-seat the memory modules. If the issue persists, see Getting Help.
location
location
> failed to transition to a running
> failed to transition to a running state. Re-
location
> failed to transition to in test.
93
Page 94

Error Code Message Information
MEM1012
MEM1016
MEM1205
Message Memory device at location <
Details The memory may not be operational. This an early indicator of a
possible future uncorrectable error.
Action Re-seat the memory modules. If the issue persists, see Getting Help.
Message Memory device at location <
LCD Message Memory <
Details The memory may not be seated correctly, misconfigured, or has
failed. Memory size is reduced.
Action Check the memory configuration. Re-seat the memory modules. If the
issue persists, see Getting Help.
Message Memory mirror redundancy is lost. Check memory device at
location(s) <
LCD Message Memory mirror lost on <
Details The memory may not be seated correctly, misconfigured, or has
failed.
Action Check the memory configuration. Re-seat the memory modules. If the
issue persists, see Getting Help.
location
> is not installed correctly. Reinstall.
location
>.
location
> is in a degraded state.
location
> is not installed correctly.
location
>. Power cycle system.
MEM1206
MEM1208
MEM1212
Message Memory mirror redundancy is degraded. Check memory device at
location <
Details The memory may not be seated correctly, misconfigured, or has
failed.
Action Check the memory configuration. Re-seat the memory modules. If the
issue persists, see Getting Help.
Message Memory spare redundancy is lost. Check memory device at location
<
location
LCD Message Memory spare lost on <
Details Memory sparing is no longer available.
Action Re-seat the memory modules. If the issue persists, see Getting Help.
Message Memory redundancy is lost.
Details The memory may not be seated correctly, misconfigured, or has
failed.
location
>.
>.
location
>. Power cycle system.
94
Page 95

Error Code Message Information
Action Review system logs for memory exceptions. reinstall memory at
location <
location
>
MEM1214
MEM7002
MEM8000
Message Memory redundancy is degraded.
Details The memory may not be seated correctly, misconfigured, or has
failed.
Action Check the memory configuration. Re-seat the memory modules. If the
issue persists, see Getting Help.
Message A hardware mismatch detected for memory riser.
LCD Message Memory riser mismatch detected. Check memory riser.
Details Memory riser is installed incorrectly, or failed.
Action Check that the memory riser is installed correctly. If the issue
persists, see Getting Help.
Message Correctable memory error logging disabled for a memory device at
location <
LCD Message SBE log disabled on <
Details Errors are being corrected but no longer logged.
Action Review system logs for memory exceptions. reinstall memory at
location <
location
location
>.
>.
location
>. Re-seat memory.
OSE0000
OSE0001
OSE0004
Message A critical stop occurred during OS load.
Details The system halted due to an exception during operating system load
or operating system initialization.
Action Review operating system logs and system video for additional
information.
Message A runtime critical stop occurred.
Details The system halted due to an exception while the operating system
was running. This is a kernel panic or bug check event.
Action Review operating system logs and system video for additional
information.
Message A soft shut-down initiated by platform event filter.
Details A separate exception or status condition shutdown the operating
system. (IPMI sensor type 20h - offset 04h).
95
Page 96

Error Code Message Information
Action Review system event log for platform events capable of shutting the
system down.
OSE0005
OSE1001
OSE1003
OSE1005
OSE1007
Message Agent is not responding.
Details Graceful shutdown request to an agent via the BMC did not occur
due to a system hardware or software exception.
Action Review operating system logs and system video for additional
information.
Message Failed to boot from A.
Action Review system boot configuration and boot media. Verify the media in
a: is bootable. See system video for additional information.
Message Failed to boot from C.
Action Review system boot configuration and boot media. Verify the media in
C: is bootable. See system video for additional information.
Message PXE boot failed.
Action Review system boot configuration, local PXE configuration, and PXE
server configuration.
Message Diagnostic boot failed.
OSE1009
OSE1011
OSE1013
96
Action Review system boot configuration and boot media. See system video
for additional information.
Message Failed to boot from CD-ROM.
Action Review system boot configuration and boot media. Verify the media in
the CDROM is bootable. See system video for additional information.
Message Failed to boot from ROM.
Action Check system event logs for additional exception information. Power
down the system and attempt to boot again.
Message Failed to boot.
Action Review system boot configuration and boot media. See system video
for additional information.
Page 97

Error Code Message Information
PCI1302
PCI1304
PCI1306
PCI1308
Message A bus time-out was detected on a component at bus
<
bus
>device<
Details System performance may be degraded. The device has failed to
respond to a transaction.
Action Cycle input power, update component drivers, if device is removable,
reinstall the device.
Message An I/O channel check error was detected.
LCD Message I/O channel check error detected. Power cycle system.
Action Cycle input power, update component drivers, if device is removable,
reinstall the device.
Message A software error was detected on a component at bus
<
bus
>device<
Action Reboot the system and update the component drivers.
Message A PCI parity error was detected on a component at bus
<
bus
>device<
LCD Message PCI parity error on bus <
Power cycle system.
device
device
device
>function <
>function <
>function <
bus
> device <
func
func
func
>.
>.
>.
device
> function <
func
>.
PCI1310
PCI1314
Details System performance may be degraded, PCI device may fail to
operate, or system may fail to operate.
Action Cycle input power, update component drivers, if device is removable,
reinstall the device.
Message A PCI system error was detected on a component at bus
<
bus
>device<
LCD Message PCI system error on bus <
Power cycle system.
Details System performance may be degraded, or system may fail to operate.
Action Cycle input power, update component drivers, if device is removable,
reinstall the device.
Message A bus correctable error was detected on a component at bus
<
bus
>device<
Details System performance may be degraded.
device
device
>function <
bus
> device <
>function <
func
func
>.
>.
device
> function <
func
>.
97
Page 98

Error Code Message Information
Action Cycle input power, update component drivers, if device is removable
reinstall the device at the next scheduled service time.
PCI1316
PCI1318
PCI1320
Message A bus uncorrectable error was detected on a component at bus
<
bus
>device<
Details System performance may be degraded, or system may fail to operate.
Action Cycle input power, update component drivers, if device is removable,
reinstall the device.
Message A fatal error was detected on a component at bus
<
bus
>device<
LCD Message Fatal error on bus <
cycle system.
Details System performance may be degraded, or system may fail to operate.
Action Cycle input power, update component drivers, if device is removable,
reinstall the device.
Message A bus fatal error was detected on a component at bus
<
bus
>device<
LCD Message Bus fatal error on bus <
cycle system.
Details System performance may be degraded, or system may fail to operate.
device
device
device
>function <
>function <
bus
> device <
>function <
bus
> device <
func
func
device
func
>.
>.
> function <
>.
device
func
> function <
>. Power
func
>. Power
PCI1322
PCI1342
98
Action Cycle input power, update component drivers, if device is removable,
reinstall the device.
Message Bus performance degraded for a component at bus
<
bus
>device<
Details System performance may be degraded. The bus is not operating at
maximum speed or width.
Action Cycle input power, update component drivers, if device is removable,
reinstall the device.
Message A bus time-out was detected on a component at slot <
Details System performance may be degraded, or system may fail to operate.
Action Cycle input power, update component drivers, if device is removable,
reinstall the device.
device
>function <
func
>.
number
>.
Page 99

Error Code Message Information
PCI1344
PCI1346
PCI1348
PCI1350
Message An I/O channel check error was detected.
LCD Message An I/O channel check error was detected. Power cycle system.
Action Cycle input power, update component drivers, if device is removable,
reinstall the device.
Message A software error was detected on a component at slot <
Action Reboot the system and update the component drivers.
Message A PCI parity error was detected on a component at slot <
LCD Message PCI parity error on slot <
Details System performance may be degraded, or system may fail to operate.
Action Cycle input power, update component drivers, if device is removable,
reinstall the device.
Message A PCI system error was detected on a component at slot <
LCD Message PCI parity error on slot <
Details System performance may be degraded, or system may fail to operate.
number
>. Re-seat PCI card.
number
>. Re-seat PCI card.
number
number
number
>.
>.
>.
PCI1354
PCI1356
PCI1358
Action Cycle input power, update component drivers, if device is removable,
reinstall the device.
Message A bus correctable error was detected on a component at slot
<
number
>.
Details System performance may be degraded.
Action Cycle input power, update component drivers, remove and reinstall
the device at the next scheduled service time.
Message A bus uncorrectable error was detected on a component at slot
<
number
>.
Details System performance may be degraded, or system may fail to operate.
Action Cycle input power, update component drivers, if device is removable,
reinstall the device.
Message A fatal error was detected on a component at slot <
LCD Message Fatal error on slot <
Details System performance may be degraded, or system may fail to operate.
number
>. Re-seat PCI card.
number
>.
99
Page 100

Error Code Message Information
Action Cycle input power, update component drivers, if device is removable,
reinstall the device.
PCI1360
PCI1362
PCI2000
Message A bus fatal error was detected on a component at slot <
LCD Message Bus fatal error on slot <
Details System performance may be degraded, or system may fail to operate.
Action Cycle input power, update component drivers, if device is removable,
reinstall the device.
Message Bus performance degraded for a component at slot <
Details System performance may be degraded. The bus is not operating at
maximum speed or width.
Action Cycle input power, update component drivers, remove and reinstall
the device at the next scheduled service time.
Message A fatal IO error detected on a component at bus
<
bus
>device<
LCD Message Fatal IO error on bus <
Details System performance may be degraded, or system may fail to operate.
Action Cycle input power, update component drivers, remove and reinstall
the device.
device
number
>function <
bus
> device <
>. Re-seat PCI card.
func
>.
device
> function <
number
number
func
>.
>.
>.
PCI2002
PCI3000
PCI3002
100
Message A fatal IO error detected on a component at slot <
LCD Message Fatal IO error on slot <
Details System performance may be degraded, or system may fail to operate.
Action Cycle input power, update component drivers, remove and reinstall
the device.
Message Device option ROM on embedded NIC failed to support Link Tuning or
FlexAddress.
Details Either the BIOS, BMC/iDRAC, or LOM firmware is out of date and does
not support FlexAddress.
Action Update BIOS, BMC/iDRAC, and LOM firmware. If the issue persists,
see Getting Help.
Message Failed to program virtual MAC address on a component at bus
<
bus
>device<
device
number
>function <
>.
func
>.
number
>.
 Loading...
Loading...