Internal Use - Confidential
DellEMC Enterprise Systems Rail Sizing and Rack Compatibility Matrix
DellEMC
TM
Enterprise Systems Rail
Sizing and Rack Compatibility Matrix
This document provides mounting features and key dimensions of the
rack rails used for mounting many DellEMC enterprise systems and
peripheral devices in a rack enclosure.

DellEMC Enterprise Systems Rail Sizing and Rack Compatibility Matrix
ii
Internal Use - Confidential
This document is for informational purposes only and may contain typographical errors and technical
inaccuracies. The content is provided as is, without express or implied warranties of any kind.
©2021 DellEMC. All rights reserved. Reproduction of this material in any manner whatsoever without
the express written permission of DellEMC is strictly forbidden.
DellEMC, the DELLEMC logo, PowerEdge, PowerVault, ReadyRails, RapidRails, VersaRails, EqualLogic
and Compellent are trademarks of DellEMC. Other trademarks and trade names may be used in this
document to refer to either the entities claiming the marks and names or their products. DellEMC
disclaims any proprietary interest in trademarks and trade names other than its own.
June 2021 | Version 4.0

DellEMC Enterprise Systems Rail Sizing and Rack Compatibility Matrix
iii
Internal Use - Confidential
Contents
Introduction ............................................................................................................ 1
Considerations .......................................................................................................... 1
Mounting interface .................................................................................................... 2
Rail types - System Installation Method ............................................................................ 3
Cable Management Solutions ......................................................................................... 4
Backwards compatibility .............................................................................................. 5
Self-Adjusting Slide Feature .......................................................................................... 7
Definitions - Reference for Table 2 ................................................................................. 7
Figures
Tables
Table 1. DellEMC server rails compatibility chart ............................................................. 5
Table 2. DELLEMC Rail Sizing Matrix ............................................................................ 9
Table 3. DellEMC rack compatibility matrix .................................................................. 19

Dell Enterprise Systems Rail Sizing and Rack Compatibility Matrix
1
Internal Use - Confidential
Introduction
This document provides information about the mounting features and key dimensions of the rack rails used for mounting many
DellEMC™ enterprise systems and peripheral devices in a rack enclosure. This document also provides a compatibility summary
for select DellEMC racks as well as some common third-party racks. Note that the product list is not all-inclusive and updates will
be made as needed.
The dimensions provided in this document are for reference only. Some minor deviations due to manufacturing tolerances and
variances should be expected.
DellEMC rail kits may not be compatible with racks from other vendors, however, all DellEMC rail kits are designed for
compliance with all EIA-310-D and later revision specifications for 19-inch racks.
Considerations
Please pay attention to the footnotes indicated in the tables because they provide important information on using the rails i n
different racks and circumstances.
It is assumed that rack mount peripherals and cable bundles do not protrude into the space directly behind the systems.
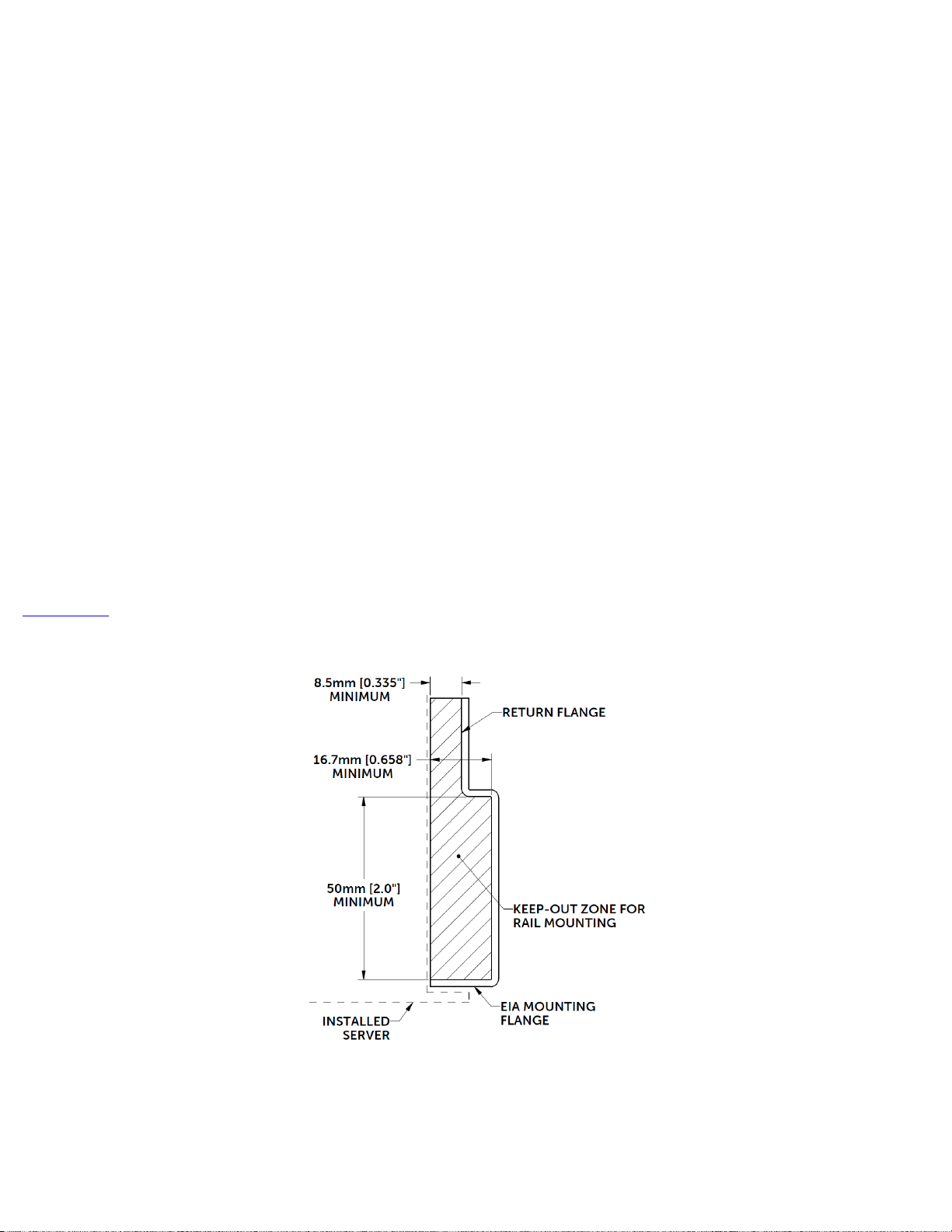
Note that DellEMC rail kits with a Rail Identifier code have been designed to be compliant with the Server System Infrastructure
(SSI) Specification for Computer Server Cabinet Enclosures & Racks, which specifies a minimum offset distance for return flanges
on the rack mounting flanges to allow sufficient room for mounting the rail kits, as indicated in Figure 1. For more information
about the Server System Infrastructure (SSI) Specification for Computer Server Cabinet Enclosures & Racks, see the SSI Forum at
ssiforum.org.
Figure 1. Top view of right front EIA mounting flange
Some third-party racks may not meet this requirement, and although DellEMC has made extensive efforts to accommodate as
many third-party racks as possible, it is not feasible to provide a solution for every circumstance.
DellEMC Enterprise Systems Rail Sizing and Rack Compatibility Matrix
2
Internal Use - Confidential
Rack Types – 2-post and 4-post
DellEMC rail kits install into two different rack types with various flange hole designs. These rack types are broken down in Table
2 into 4-post and 2-post styles. 4-post rack types contain vertical mounting flanges with either square-hole, unthreaded roundhole, or threaded round-hole designs as part of the rack and rail interface. 2-post rack types generally contain threaded roundhole designs and require users to mount the server in either the front or center mount orientations. Only stab-in static rail
designs that support 2-post rack configurations may be installed into a 2-post rack and commonly require additional hardware to
secure the rails to the rack. For more information, look at the definitions section for Table 2.
Mounting interface
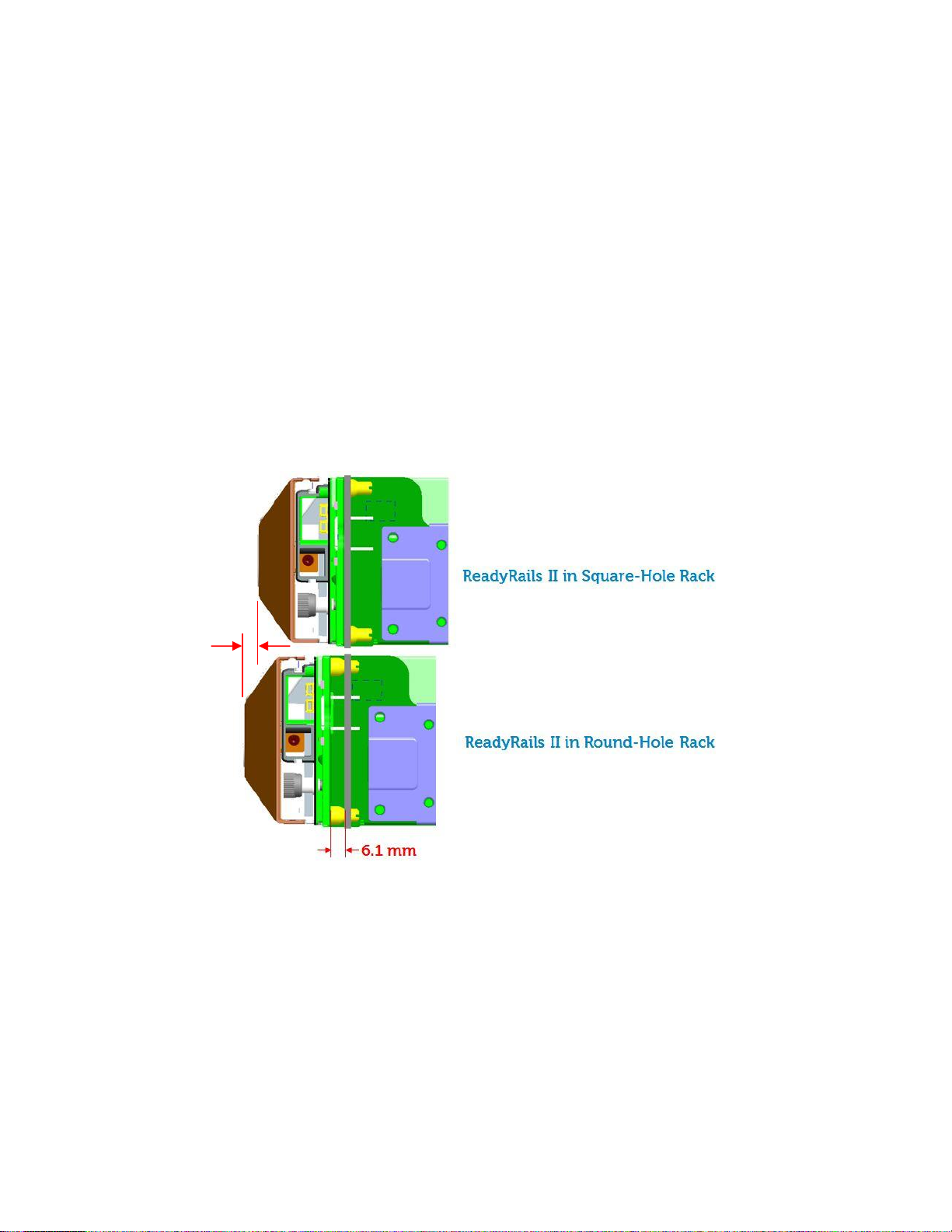
The ReadyRails™ II mounting interface supports tool-less installation in 4-post square-hole and unthreaded round-hole racks as
well as native support for tooled installation in threaded-hole racks. Note that installing this mounting interface in a square-hole
rack allows the bracket to be placed flush against the mounting post, while installation in a round-hole rack results in a slight
offset of approx. 6 mm from the mounting post, which also results in an approx. 6 mm bezel offset; refer to Figure 2.
Figure 2. System offset for round-hole racks
The original ReadyRails mounting interface is used for both static and sliding rails, and it supports tool-less installation in 4-post
square-hole and unthreaded round-hole racks. Static ReadyRails kits also support tooled installation in threaded-hole racks and
2-post racks. When installed in unthreaded round-hole racks, the original ReadyRails will also have the 6 mm offset from the
mounting post that was discussed in the previous ReadyRails II paragraph. In order to install sliding ReadyRails kits into a
threaded-hole rack, adapter brackets are required. 1U and 2U adapter bracket kits are available that support systems ranging
from 1U to 5U in height.
The adapter bracket kits include six brackets to accommodate different rail lengths, plus four sets of custom screws in 10-32,
12-24, M5 and M6 thread sizes. The design of the brackets has been optimized to limit the forward shift of the system in the rack
to only 17.3 mm. Depending on the depth of the rack used and the position of the mounting rails within the rack, it may be
6.1mm

DellEMC Enterprise Systems Rail Sizing and Rack Compatibility Matrix
3
Internal Use - Confidential
necessary to remove the system’s bezel in order to close the front door of the rack. For the front door to close with the system
bezel installed, a minimum clearance of 58 mm is needed between the back surface of the door panel and the front face of the
EIA flange.
The RapidRails™ mounting interface supports tool-less installation in 4-post square-hole racks only, while the VersaRails™
mounting interface supports tooled installation in 4-post square-hole and unthreaded round-hole racks. Mounting the VersaRails
in threaded-hole racks is not recommended and is not supported by DellEMC.
The Generic mounting interface encompasses all other mounting interfaces outside of the ones listed above. Unless indicated to
be tool-less, tools are required for installation.
Rail types - System Installation Method
Drop-in/Stab-in rails are a feature rich rail solution that allows a system to be fully extended out of the rack for service and the
user has the option to install the system into the rail using a drop-in method like the ReadyRails sliding rails, or a stab-in method
like the ReadyRails static rails. Drop-in/Stab-in rails support CMA or SRB applications. CMA and SRB applications must be
detached in order to remove the inner member from the rails.
A “drop-in” design means that the system is installed vertically into the rails by inserting the standoffs on the sides of the system
into the “J-slots” in the inner rail members with the rails in the fully extended position. The recommended method of
installation is to first insert the rear standoffs on the system into the rear J-slots on the rails to free up a hand and then rotate
the system down into the remaining J-slots while using the free hand to hold the rail against the side of the system.
A “stab-in” design means that the inner (chassis) rail members must first be attached to the sides of the system and then
inserted into the outer (cabinet) members installed in the rack. For systems that are 2U and larger, it is recommended that two
people perform this operation.
Sliding rails allow a system to be fully extended out of the rack for service. Most sliding rails support Cable Management Arms
(CMAs) which enable the system to be extended out of the rack without disconnecting data/power cables at the rear of the
system.
Unless otherwise indicated, all sliding rails are drop-in sliding rail design
Static rails typically do not support the ability to service the system in the rack and are not compatible with the CMA. However,
they do offer more flexibility in the types of racks and installations supported. Generally, there are two types of static rails:
stab-in static and L-bracket static.
Scan the QRL code for documentation and
trouble-shooting information regarding the
installation procedures for Drop-in/Stab-in rail
types.

DellEMC Enterprise Systems Rail Sizing and Rack Compatibility Matrix
4
Internal Use - Confidential
Stab-in static rails require the inner (chassis) rail members must first be attached to the sides of the system and then inserted
into the outer (cabinet) members installed in the rack. For systems that are 2U and larger, it is recommended that two people
perform this operation.
L-bracket static rails do not support the ability to fully extend a system out of the rack into a service position. These rails
typically are not compatible with cable management solutions unless otherwise indicated. Typically, equipment supported by L bracket are customer serviceable from the front or rear of the rack.
Cable Management Solutions
To help manage the numerous cables associated with rack-mounted servers, a Cable Management Arm (CMA) or Strain Relief Bar
(SRB) can be used. An optional CMA is offered with most sliding rails. CMAs attach on either the right or left side without tools.
Cable management arm (CMA) is a cable management accessory which connects to the rails behind the system. It allows a fully
cabled system to be extended out of the rack into a service position.
Strain relief bar (SRB) is a cable management solution, which in most cases, attaches to the back of the rails via the strain relief
bar brackets. Cables from the back of the chassis are placed across the top of the SRB and secured by straps.
SRBs are offered for select systems as an optional method for managing cables at the rear of the system due to the potential of a
cable bundle size that exceeds the capacity of the CMA. The rail depth with a SRB is significantly less than that of a CMA, which
in many cases, enables fitment of the rails in shallow racks. Cable service loops are required for systems on sliding rails to fully
extend out of the rack for service.
Note that using a CMA or SRB with a deeper system may interfere with access to power distribution units (PDUs) in certain racks.
If a configuration does not require CMA support, then the outer CMA mounting brackets can be removed from some of the sliding
rail kits to reduce the overall length of the rails and eliminate potential interference with rear-mounted PDUs or the rack rear
door.
DellEMC Enterprise Systems Rail Sizing and Rack Compatibility Matrix
5
Internal Use - Confidential
Backwards compatibility
Some systems may offer backward compatibility with the rail kits from previous-generation systems. This is not always possible,
because changes to chassis features, dimensions or weight can prevent older rail kits from being used with newer systems.
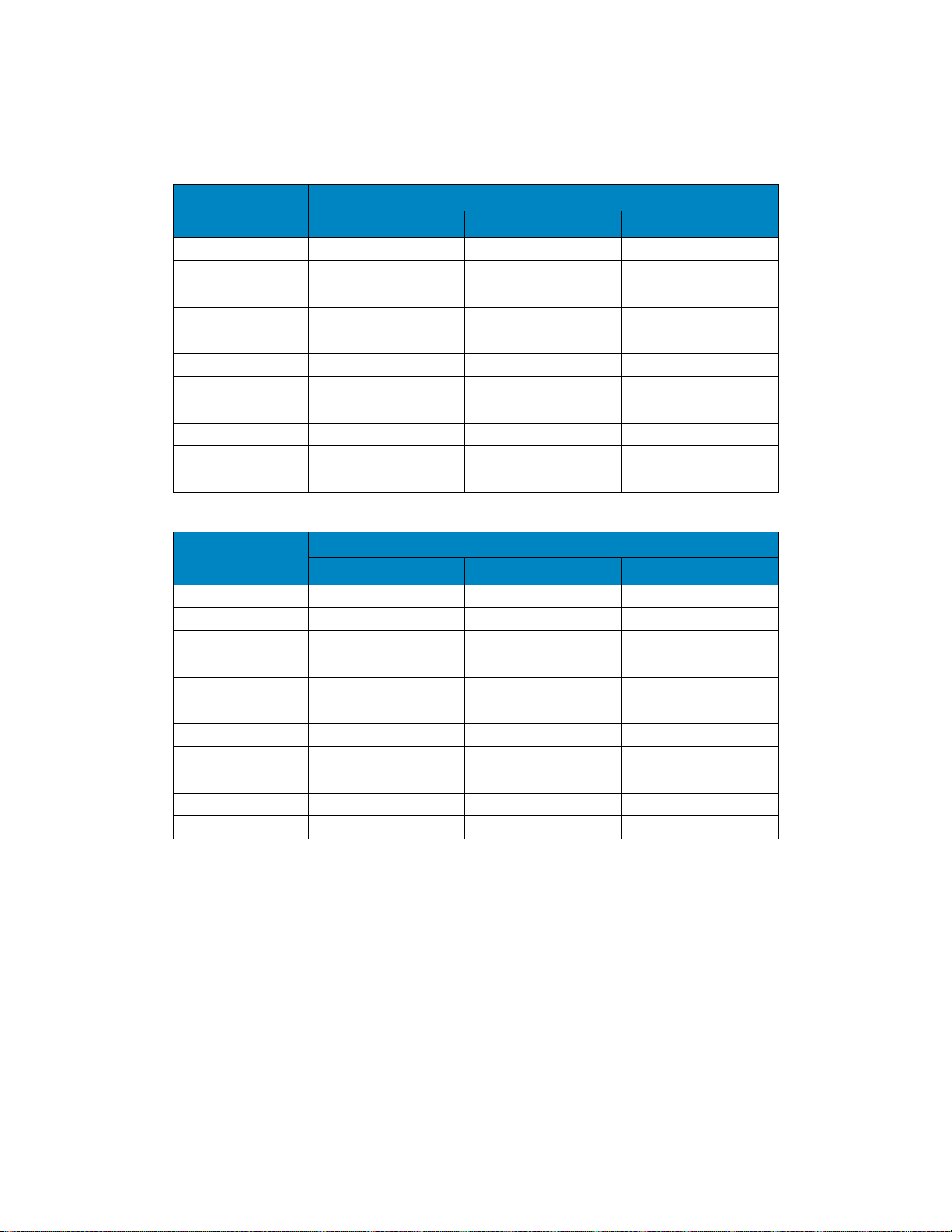
Please refer to Table 1 for cross-generational compatibility of DellEMC servers and rails.
Table 1. DellEMC server rails compatibility chart
15th Generation
product
Backwards compatibility with 14th generation rails/CMAs
Sliding rails
CMA
Static rails
R450/R450xs
✓ ✓ ✓
R550/R550xs
X ✓ X
R6515
✓ ✓ ✓
R6525
X ✓ X
R650
X ✓ X
R7515
✓ ✓ ✓
R7525
✓ ✓ ✓
R750
✓ ✓ ✓
R750xa
N/A
N/A
N/A
14th Generation
product
Backwards compatibility with 13th generation rails/CMAs
Sliding rails
CMA
Static rails
R240
N/A
N/A
✓
R340
X
✓
✓
R440
X
✓
✓
R540/R540xd
✓ ✓ ✓
R640
✓ ✓ ✓
R740/R740xd
✓ ✓ ✓
R740xd2
N/A
N/A
N/A
R840/940xa
X X X
R940
X ✓ N/A
C4140
N/A
N/A
✓
C64xx
N/A
N/A
✓
T440
X ✓ N/A
T640
✓
✓
N/A
DellEMC Enterprise Systems Rail Sizing and Rack Compatibility Matrix
6
Internal Use - Confidential
13th Generation
product
Backwards compatibility with 12th generation rails/CMAs
Sliding rails
CMA
Static rails
R230
N/A
N/A
✓
R330
✓ ✓ ✓
R430
✓ ✓ ✓
R530
✓ ✓ ✓
R630
✓ ✓ ✓
R730/R730xd
✓ ✓ ✓
R830
✓ ✓ ✓
R930
✓
✓
N/A
T330
✓
✓
N/A
T430
✓
✓
N/A
T630
X ✓ N/A
12th Generation
product
Backwards compatibility with 11th generation rails/CMAs
Sliding rails
CMA
Static rails
R220
N/A
N/A
✓ (R210 II)
R320
✓
✓
✓
R420
✓
✓
✓
R520
✓
✓
✓
R620 X X
X
R720/R720xd
X X X
R820 X X
N/A
R920 X X
N/A
T320
✓ (T610)
✓ (T610)
N/A
T420
✓ (T610)
✓ (T610)
N/A
T620
✓
✓
N/A
✓ - Compatible X – Not compatible
*Only with the previous generation sliding rail
 Loading...
Loading...