
Index
Intel PROSet/Wireless 2915ABG Network
Connection User's Guide
With your wireless network card, you can access wireless networks, share files or
printers, or even share your Internet connection. All of these features can be explored
using a wireless network in your home or office. This wireless LAN solution is designed
for both home and business use. Additional users and features can be added as your
networking needs grow and change.
NOTE: This software is compatible with the Intel® PROSet/Wireless 2915ABG
Network Connection and the Intel® PROSet/Wireless 2200BG Network Connection.
Making a Basic Network Connection in Windows XP
Making a Basic Network Connection in Windows 2000
Using the Intel PROSet for Wireless Utility
Using Intel PROSet/WirelessProfiles
Security Overview
Configuring Advanced Network Security Settings in Windows XP
Configuring Advanced Network Security Settings in Windows 2000
Specifications
Regulatory Information
Troubleshooting
Glossary
Information in this document is subject to change without notice.
© 2000–2004 Dell Inc. All rights reserved.
The copying or reproducing of any material in this document in any manner whatsoever
without the written permission of Dell Inc. is strictly forbidden. The trademarks Dell,
Latitude, Inspiron, the DELL logo, and TrueMobile are trademarks of Dell Inc. Microsoft
and Windows are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
Other trademarks and trade names may be used in this document to refer to either the
file:///C|/Documents%20and%20Settings/pguillor/Desktop/w2k5/index.htm (1 of 2) [7/2/2004 12:27:06 PM]

Index
entities claiming the marks and names or their products. Dell disclaims any proprietary
interest in trademarks and trade names other than its own.
August 2004
file:///C|/Documents%20and%20Settings/pguillor/Desktop/w2k5/index.htm (2 of 2) [7/2/2004 12:27:06 PM]
Making a Basic Network Connection in Windows XP: Intel PRO/Wireless 2915ABG Network Connection User's Guide
Back to Contents
Making a Basic Network Connection in
Windows XP: Intel® PRO/Wireless 2915ABG
Network Connection User's Guide
Connecting to a Network in Windows XP
Viewing the Status of Your Wireless Connection
Connecting to a Network in Windows XP
The information in this User's Guide assumes that your wireless card and the software
are already installed in your system. If you did not receive your wireless card as part of a
system, refer to the Setup Guide that came with your wireless card for hardware and
software installation instructions. You can check your system to verify that the wireless
card is installed.
To see if you have a wireless card installed:
1. From your Windows desktop, right-click My Computer and select Properties.
2. From the Hardware tab, click Device Manager.
3. Double-click Network adapters.
If the wireless card is installed you will see Intel® PRO/Wireless 2915ABG
Network Connection. If the wireless card is not installed this name will not be
displayed.
If you are using Windows XP, it is recommended that you follow the steps below to
configure your wireless network connection. You can also choose to use Intel®
PROSet/Wireless to configure your wireless card. This is discussed in the
Making a
Basic Network Connection in Windows 2000 section.
file:///C|/Documents%20and%20Settings/pguillor/Desktop/w2k5/XPsetup.htm (1 of 9) [7/2/2004 12:29:13 PM]

Making a Basic Network Connection in Windows XP: Intel PRO/Wireless 2915ABG Network Connection User's Guide
NOTE:
If you are using Windows XP (Service Pack 2) Category View some of the
dialogs shown in the following examples may appear different from those on
your screen. To switch from Category View to Classic view, click Start
àControl Panel and on the navigation bar click Switch to Classic View.
Connecting to a Network
Before attempting to connect to your network, make sure that your access point or
wireless router is connected correctly. Please consult your access point or wireless
router documentation to configure your access point or wireless router. You should now
choose the type of security for your wireless network. Most home networks use either no
security or Wired Equivalent Privacy (
WEP) encryption. Additional security settings are
also available that are typically used in corporate environments or for advanced users
who require higher levels of security.
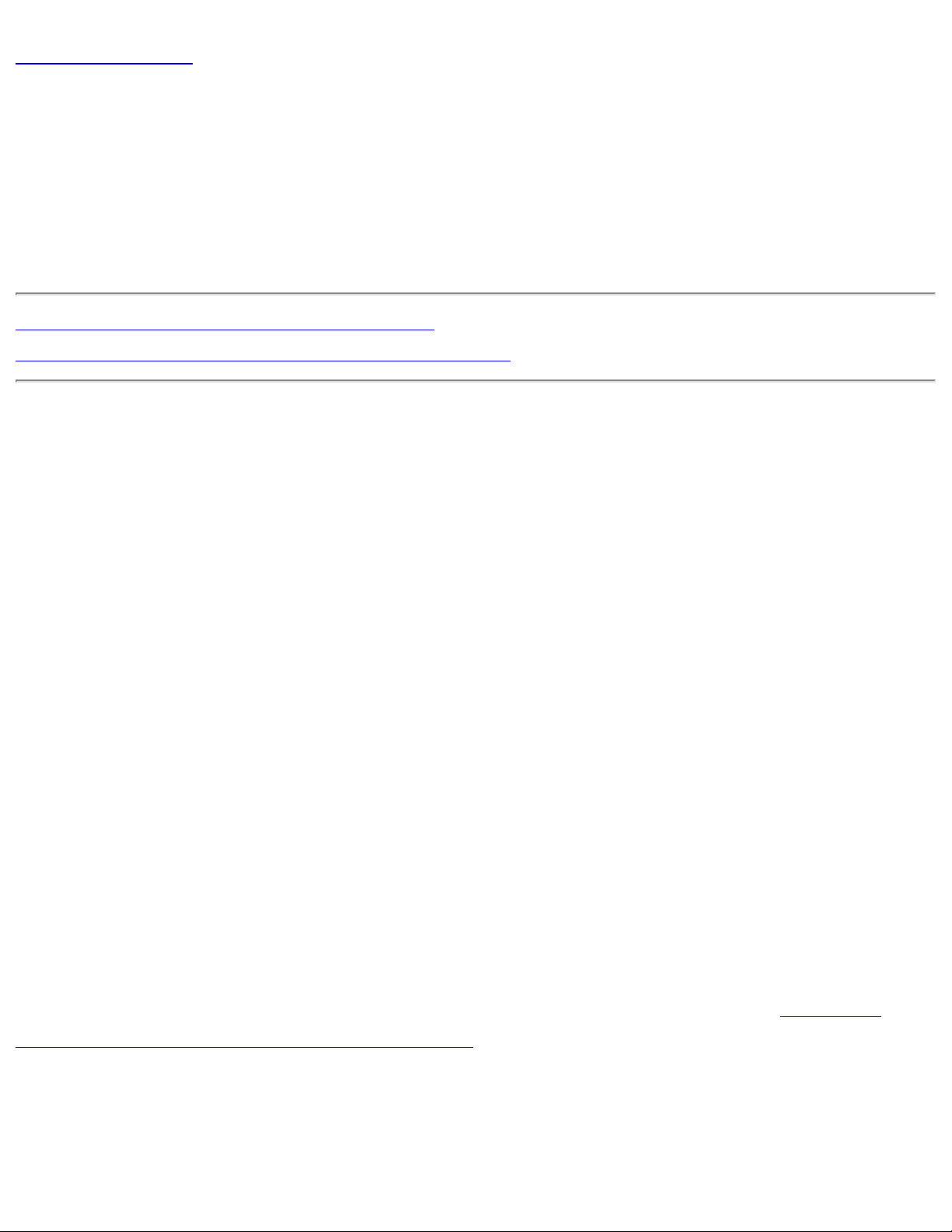
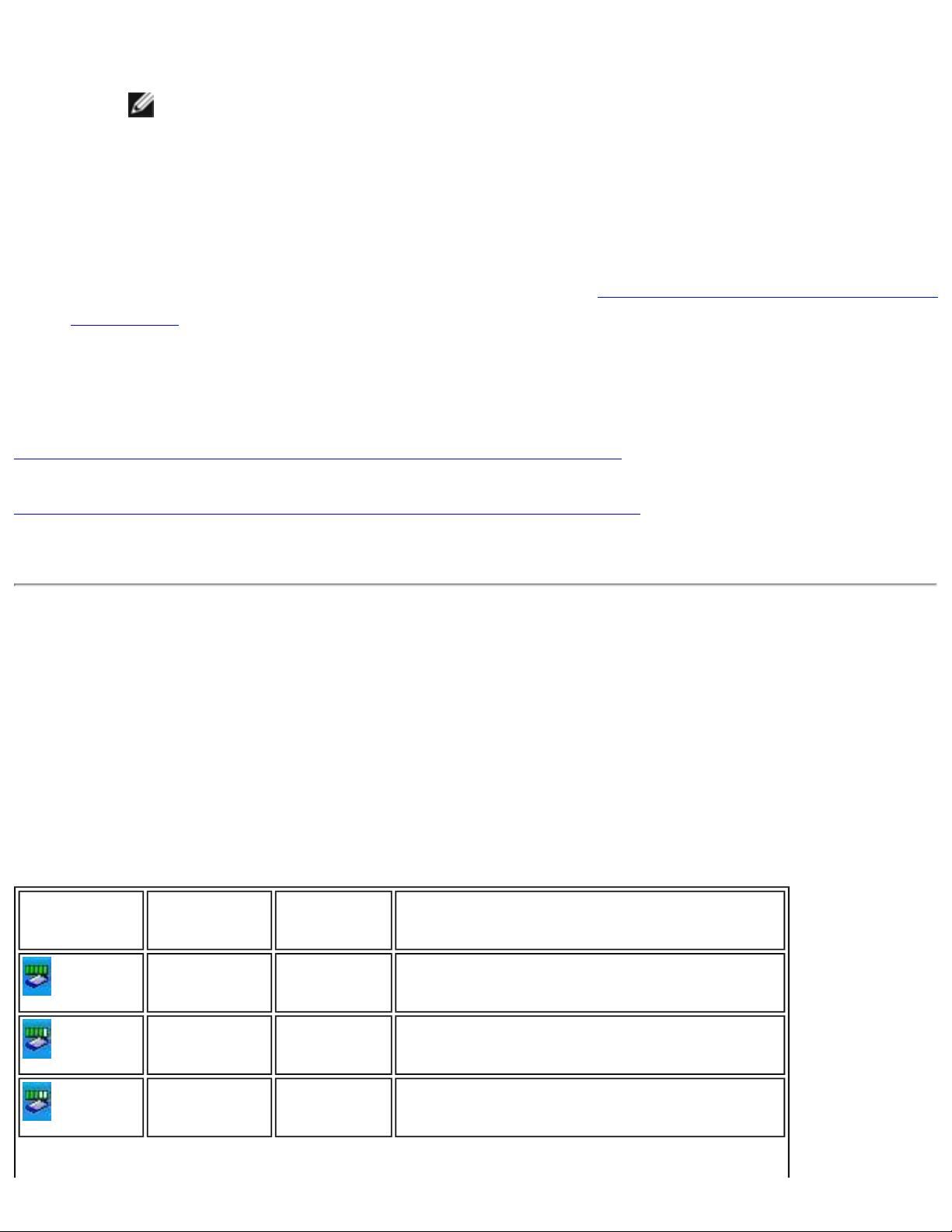
1. Right-click the Intel® PROSet/Wireless icon on the task tray and click Open
Microsoft client. The Wireless Network Connection Properties dialog opens:
file:///C|/Documents%20and%20Settings/pguillor/Desktop/w2k5/XPsetup.htm (2 of 9) [7/2/2004 12:29:13 PM]
Making a Basic Network Connection in Windows XP: Intel PRO/Wireless 2915ABG Network Connection User's Guide
NOTE:
The names of wireless networks your computer can see are
shown under Preferred networks. The name of your network is
usually shown here.
2. On the Wireless Networks tab, under Preferred networks, click Add. The
Wireless network properties dialog opens:
file:///C|/Documents%20and%20Settings/pguillor/Desktop/w2k5/XPsetup.htm (3 of 9) [7/2/2004 12:29:13 PM]
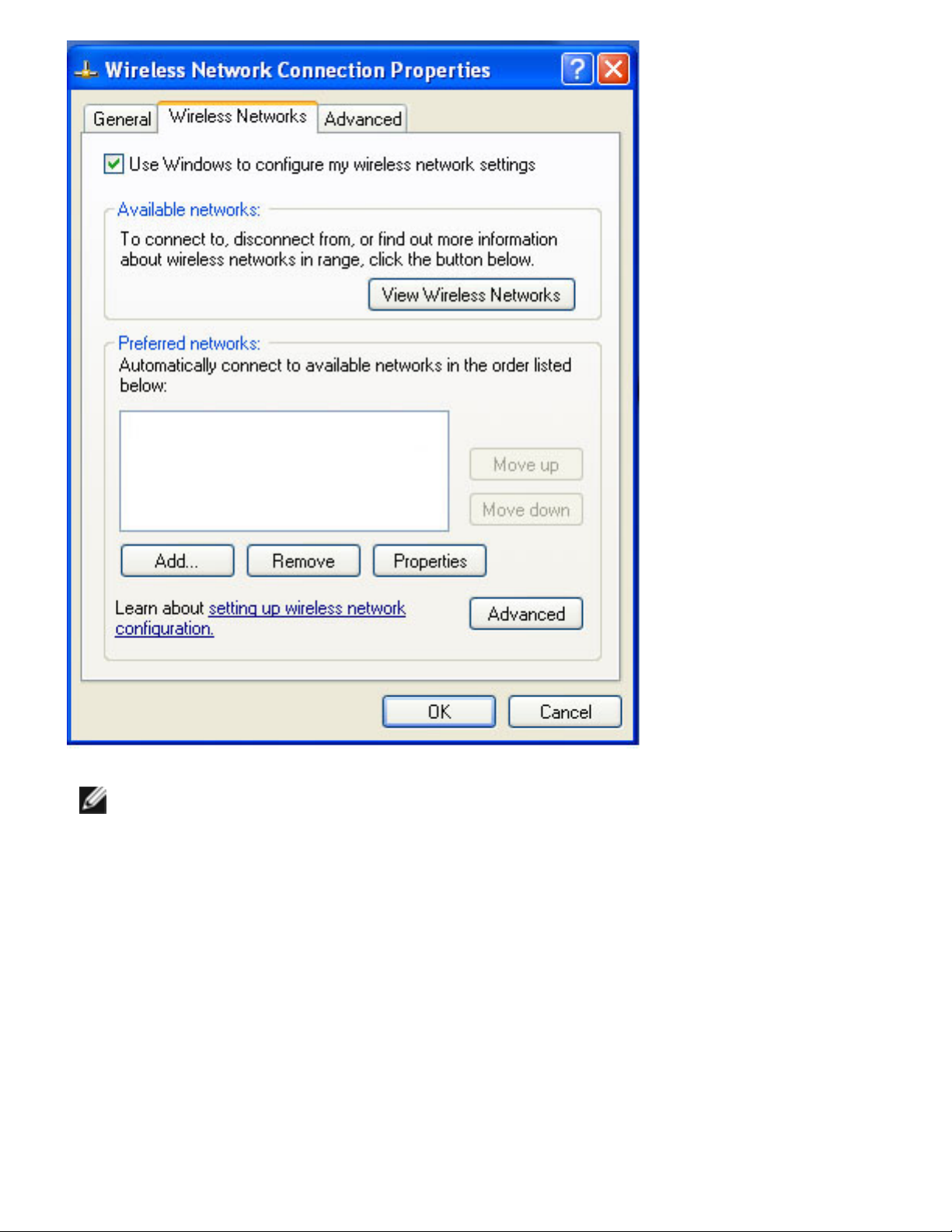
Making a Basic Network Connection in Windows XP: Intel PRO/Wireless 2915ABG Network Connection User's Guide
NOTE:
The names of wireless networks your computer can see are shown under
Available Networks. For Windows XP SP2, it is necessary to Click on View
Wireless Networks to see a list of available networks. The name of your
network is usually shown here. If a blank network name (SSID) is received
from a
silent mode wireless router, there will be no entry for that network in the
available networks list. To associate with a "silent mode" wireless router, a
new profile must first be created before connection. After connection, the
associated SSID can be viewed in the available networks list and in the
preferred networks list.
3. Enter the name of your network in the Network name (SSID) field.
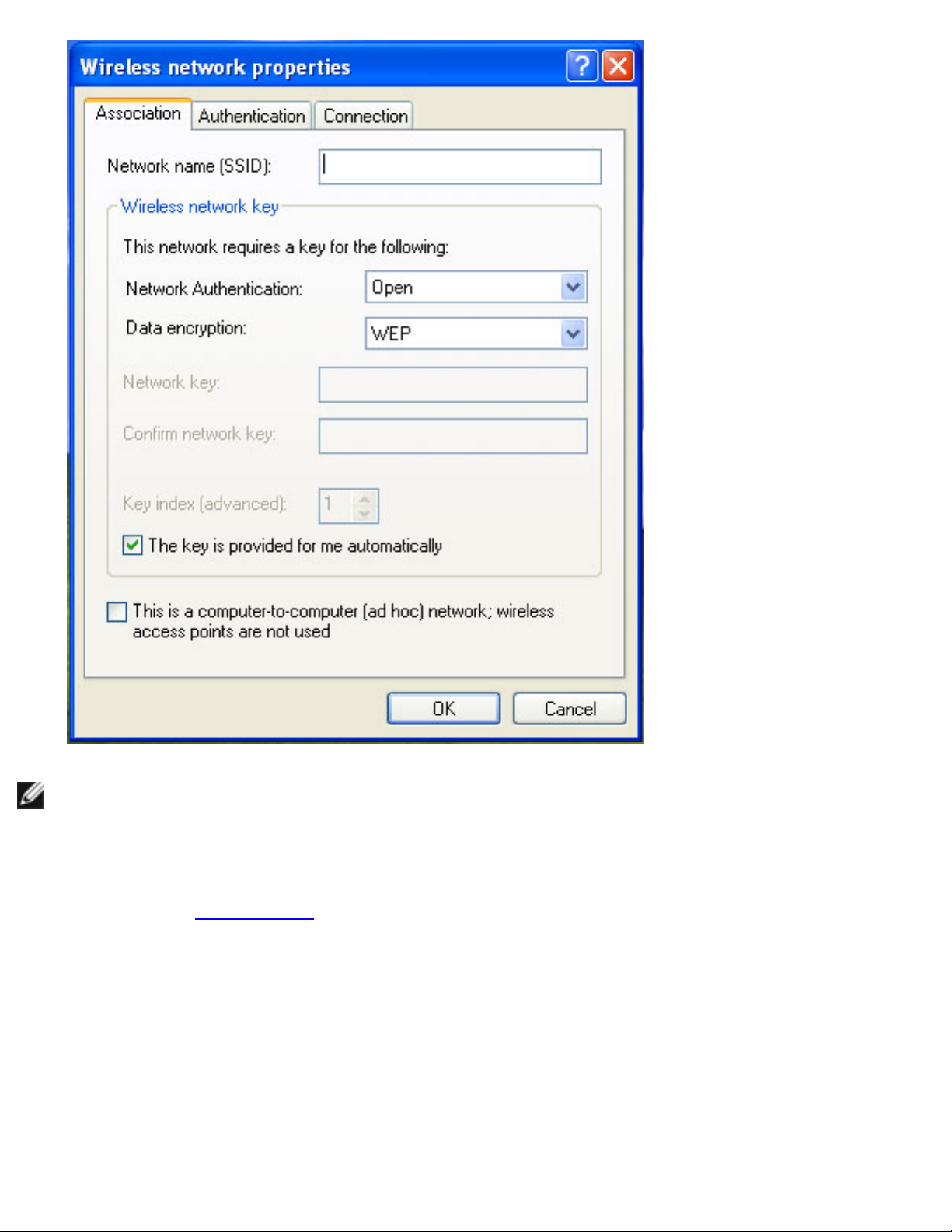
4. Click OK. The new network name appears in the Preferred networks list:
file:///C|/Documents%20and%20Settings/pguillor/Desktop/w2k5/XPsetup.htm (4 of 9) [7/2/2004 12:29:13 PM]
Making a Basic Network Connection in Windows XP: Intel PRO/Wireless 2915ABG Network Connection User's Guide
Adding an infrastructure network
Network security must now be configured. For a home wireless network, you can choose
not to have security, or you can configure your network for WEP security. If there is no
network security, anyone can access your wireless network. WEP security provides
some level of security for your wireless network. Additional advanced security settings
are also available that are typically used in corporate environments or for advanced
users who require higher security levels. You must ensure that the security settings on
the access point exactly match those chosen for the wireless connection. Choose the
appropriate link below for the security type you want to use.
● Configuring your Infrastructure Network with No Security
● Configuring your Infrastructure Network with WEP Security
● Configuring Advanced Network Security Settings in Windows XP
● Configuring Advanced Network Security Settings Using Intel® PROSet for
Wireless
Configuring your Infrastructure Network with No Security
1. Right-click the Intel® PROSet/Wireless Network icon on the task tray and click
Open Microsoft client. The Wireless Network connection Properties dialog opens
(see
Connecting to a Network).
2. On the Wireless Network Connection Properties dialog (see
Connecting to a
file:///C|/Documents%20and%20Settings/pguillor/Desktop/w2k5/XPsetup.htm (5 of 9) [7/2/2004 12:29:13 PM]
Making a Basic Network Connection in Windows XP: Intel PRO/Wireless 2915ABG Network Connection User's Guide
Network), click to select your wireless network in the Preferred networks
section.
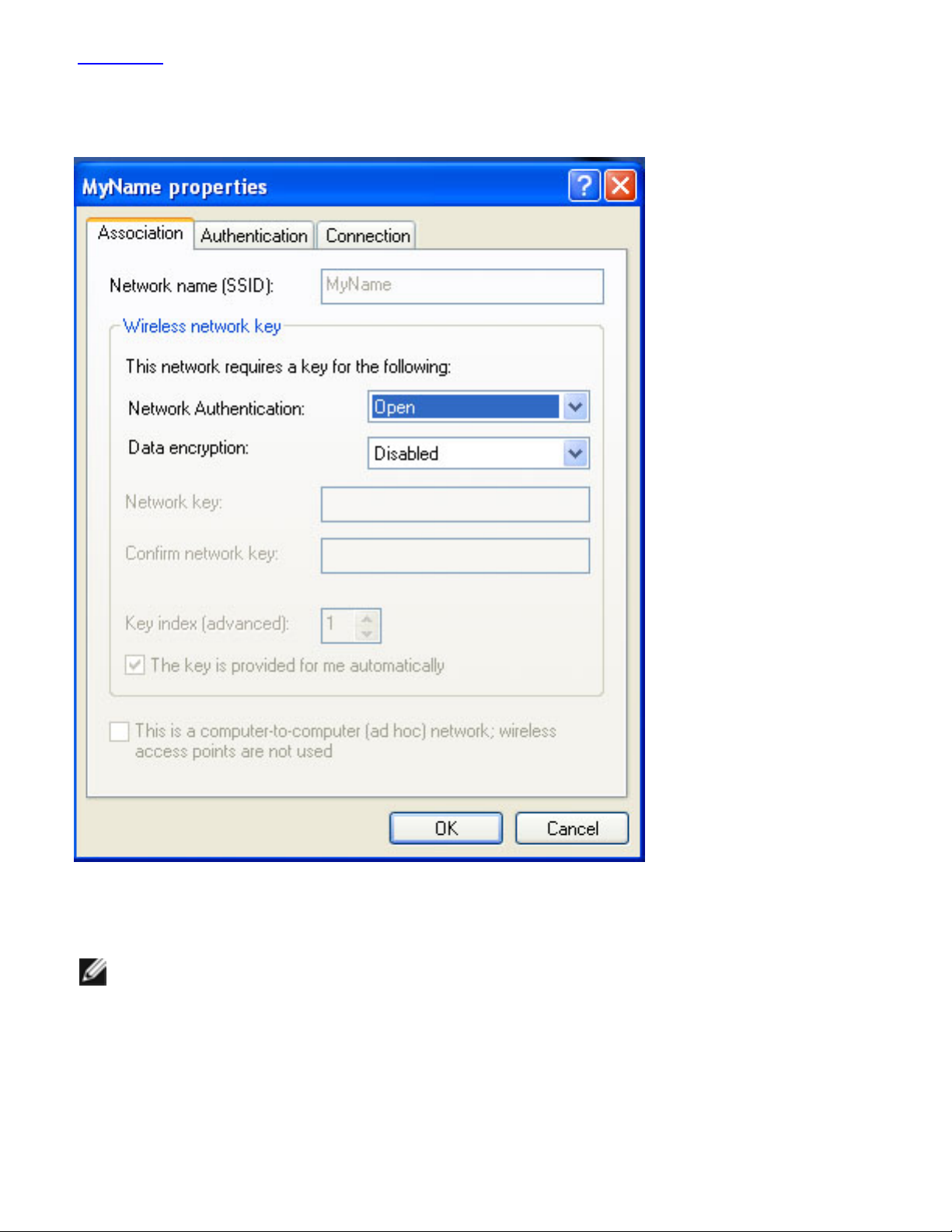
3. Click Properties. The your wireless network Properties dialog opens:
4. From the Network Authentication drop-down menu, click to select Open.
NOTE:
Earlier versions of Windows XP software may not contain these
drop-down menus. If you are using one of these earlier versions,
click to deselect the Data encryption (WEP enabled) checkbox
and skip to step 5.
5. From the Data encryption drop-down menu, click to select Disabled.
6. To save your settings on this dialog, click OK.
file:///C|/Documents%20and%20Settings/pguillor/Desktop/w2k5/XPsetup.htm (6 of 9) [7/2/2004 12:29:13 PM]

Making a Basic Network Connection in Windows XP: Intel PRO/Wireless 2915ABG Network Connection User's Guide
7. To close the Wireless Network Connection Properties dialog, click OK.
Your network configuration is now complete. Continue to
Viewing the Status of your
Wireless Connection.
Configuring your Infrastructure Network with WEP Security
1. On the Wireless Network Connection Properties dialog (see Connecting to a
Network), click to select your wireless network in the Preferred networks section.
2. Click Properties. The Wireless Network Properties dialog opens.
3. From the Network Authentication drop-down menu, select Open.
NOTE:
Earlier versions of Windows XP software may not contain these
drop-down menus. If you are using one of these earlier versions,
click to select the Data encryption (WEP enabled) checkbox and
skip to step 5.
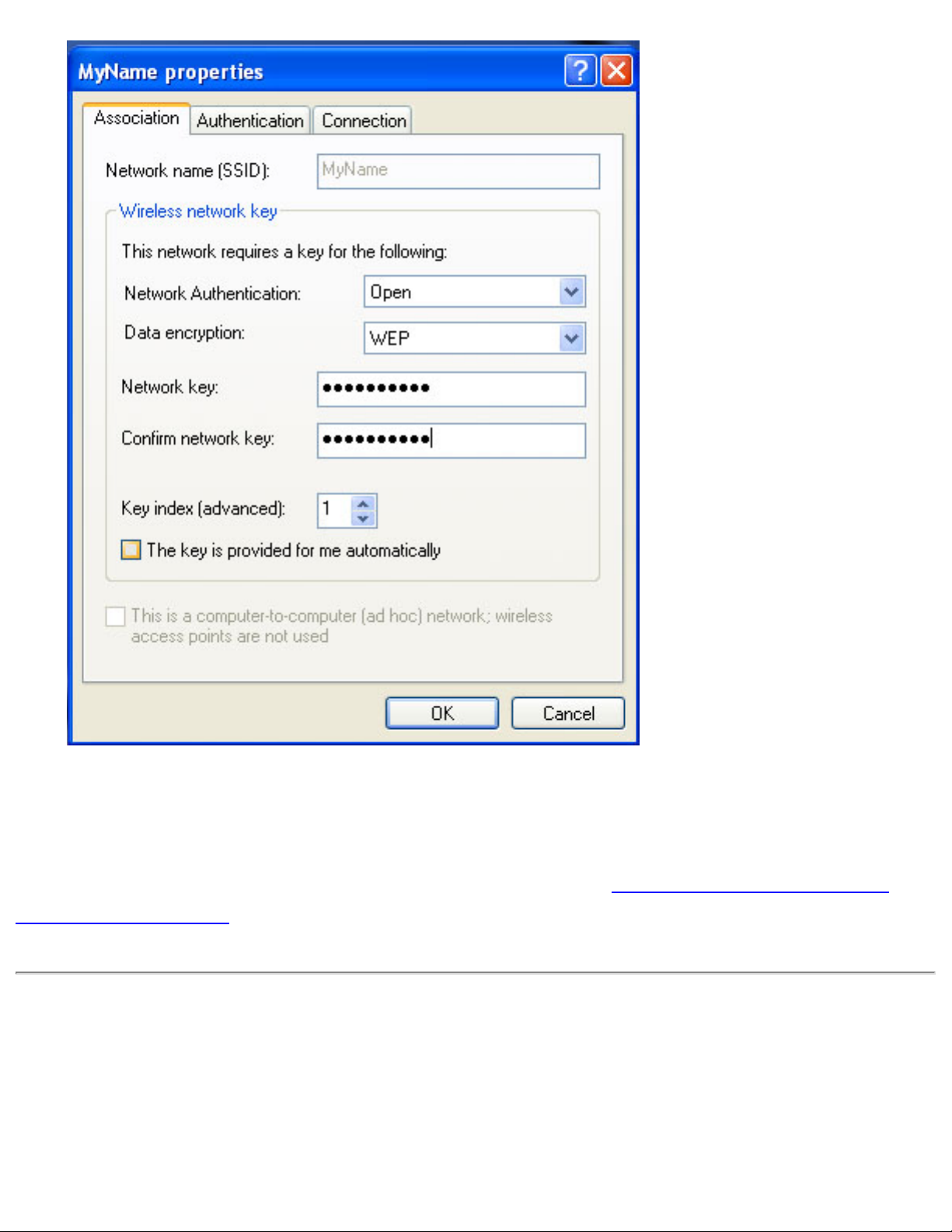
4. From the Data encryption drop-down menu, select WEP.
5. Click the checkbox to deselect The key is provided for me automatically.
6. Type the WEP network key in the Network key field. Your Network key must
exactly match the access point’s network key. Your Network key will be either 5 or
13 ASCII (text) characters, or 10 or 26 hexadecimal (0-9, A-F) characters. The
person who configured your access point is the only one who knows your network
key.
7. Type this key again in the Confirm network key field. The settings are shown in
the following illustration:
file:///C|/Documents%20and%20Settings/pguillor/Desktop/w2k5/XPsetup.htm (7 of 9) [7/2/2004 12:29:13 PM]
Making a Basic Network Connection in Windows XP: Intel PRO/Wireless 2915ABG Network Connection User's Guide
8. To save your settings, click OK.
9. To close the Wireless Network Connection Properties dialog, click OK.
Your network configuration is now complete. Continue to
Viewing the Status of your
Wireless Connection.
Viewing the Status of your Wireless Connection
The quality of your wireless connection is affected by:
● The strength of your wireless networking signal
file:///C|/Documents%20and%20Settings/pguillor/Desktop/w2k5/XPsetup.htm (8 of 9) [7/2/2004 12:29:13 PM]

Making a Basic Network Connection in Windows XP: Intel PRO/Wireless 2915ABG Network Connection User's Guide
● The level of noise created by other devices in your home or office
● The location and environment in your home or office
The quality of your wireless network is indicated by the Wireless Network Connection
icon, located in the lower right corner of your Windows desktop. Point to this icon for a
description of your signal quality.
NOTE
NOTE:
It is also possible to view the current status of your wireless connection
from the Intel® PROSet/Wireless main screen. To open PROSet/Wireless,
double-click the PROSet icon located in the lower right corner of your
Windows desktop.
Back to Top
Back to Contents
file:///C|/Documents%20and%20Settings/pguillor/Desktop/w2k5/XPsetup.htm (9 of 9) [7/2/2004 12:29:13 PM]

Making a Basic Network Connection in Windows 2000: Intel PRO/Wireless 2915ABG Network Connection User's Guide
Back to Contents
Making a Basic Network Connection in Windows
2000: Intel® PRO/Wireless 2915ABG Network
Connection User's Guide
Connect to a Network in Windows 2000
Viewing the Status of your Wireless Connection
Connecting to a Network using Windows 2000
This document assumes that your wireless card is already installed in your system and the
software has been installed. If you did not receive your wireless card as part of a system, refer to
the Setup Guide that came with your wireless card for hardware and software installation
instructions.
To see if you have a wireless card installed:
1. From your Windows desktop, right-click My Computer and select Properties.
2. From the Hardware tab, select the Device Manager button.
3. Double-click Network adapters.
4. If a supported wireless card is installed, you will see either Intel® PROSet/Wireless
2200BG Network Connection or Intel) PRO/Wireless 2915ABG Network Connection. If
a supported wireless card is not installed this name will not be displayed.
If you are using Windows 2000, you must use Intel® PROSet/Wireless to configure your
wireless card. This procedure is discussed in this section.
NOTE:
USING WINDOWS XP: It is recommended that you use Windows XP to configure
profiles for your network connections. However, you can also use Intel®
PROSet/Wireless to create your profiles. If you need to configure profiles using Cisco
specific settings such as
LEAP you will also need to use Intel® PROSet/Wireless.
Refer to
Making a Basic Network Connection in Windows XP for information about
configuring your wireless network profiles.
Configuring a Network Profile in Infrastructure Mode using Windows 2000
file:///C|/Documents%20and%20Settings/pguillor/Desktop/w2k5/W2Ksetup.htm (1 of 10) [7/2/2004 12:29:25 PM]

Making a Basic Network Connection in Windows 2000: Intel PRO/Wireless 2915ABG Network Connection User's Guide
To connect to a wireless network, you must first configure a network profile for that network on
your computer using Intel® PROSet/Wireless. Refer to
Using Intel® PROSet/Wireless for
instructions about how to launch Intel® PROSet/Wireless.
You can connect to a network by first creating a new profile using the Profile Wizard, and then
selecting that profile to connect to the network access point using the Connect button. Refer to
Creating a profile for more information.
Follow the applicable instruction set below, based on whether the network requires network
security key information (check with your network administrator or access point installer to see if
network key information is required).
● Configuring your Infrastructure Network with no security
● Configuring your Infrastructure Network with WEP Security
Configuring your Infrastructure Network with No Security
To configure a new profile with no security:
1. Double-click the Intel® PROSet/Wireless icon in the desktop task tray, or click Start
àPrograms àIntel® PROSet/Wireless àIntel® PROSet/Wireless. (Be sure you are
using Intel® PROSet/Wireless and not Microsoft Client to configure a new profile.)
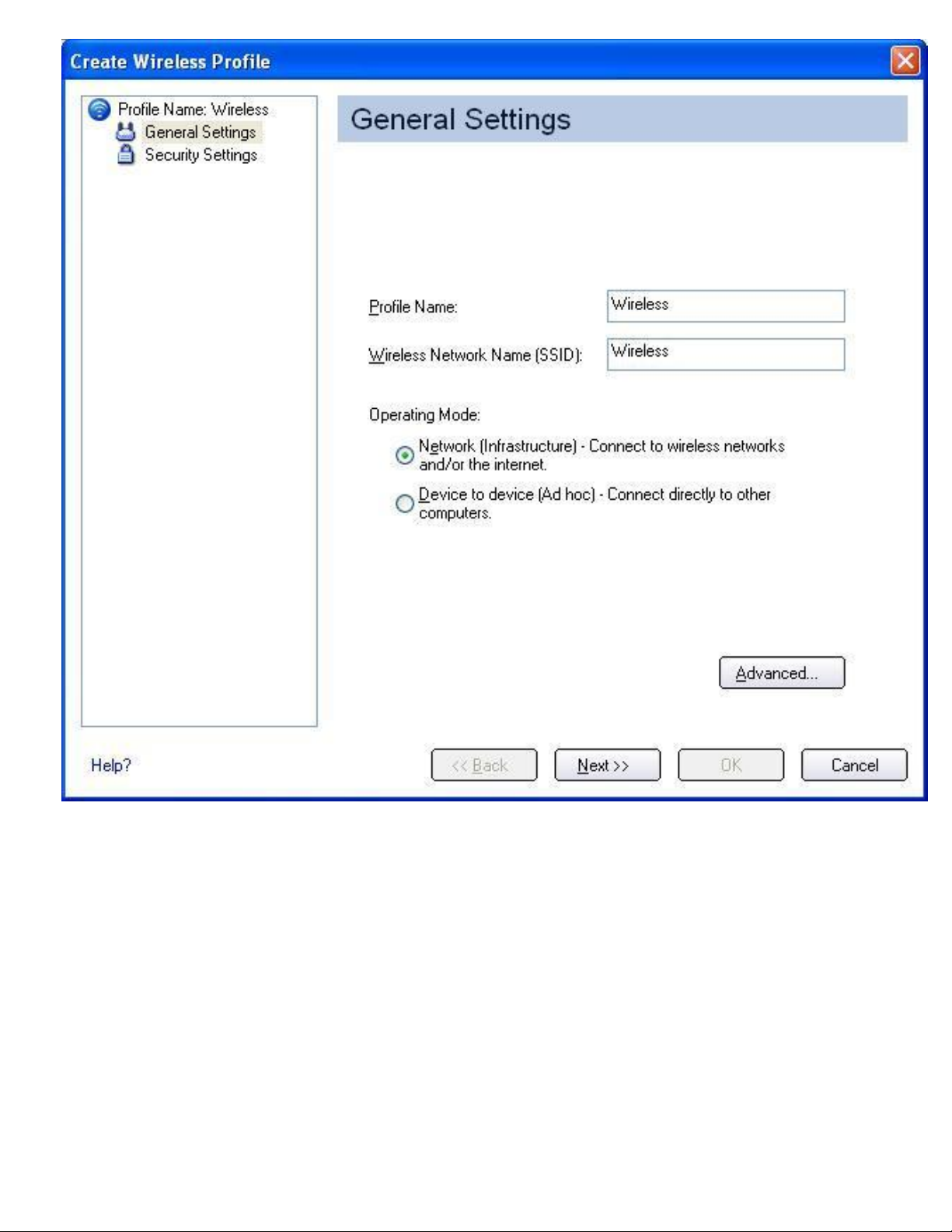
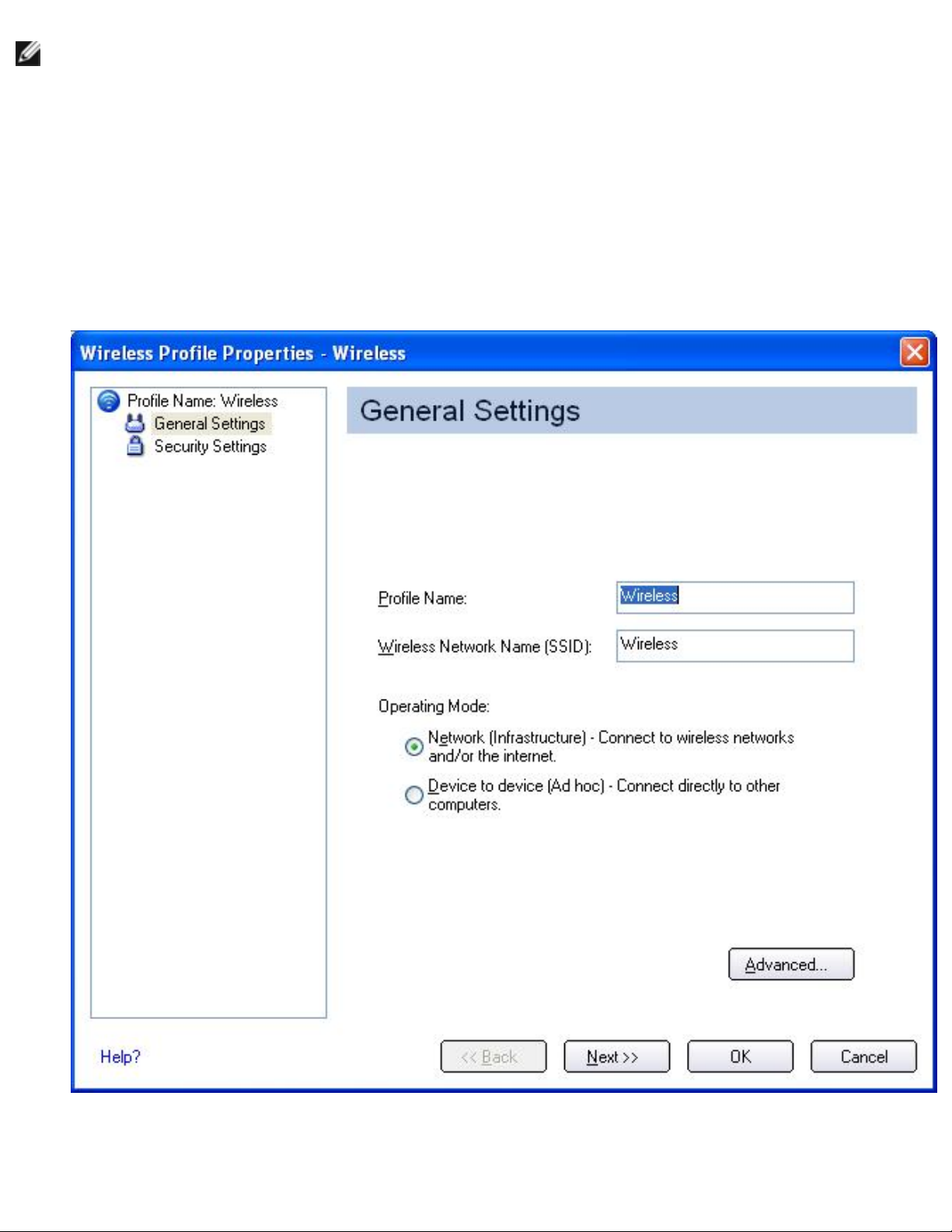
2. From the Intel® PROSet/Wireless dialog, under Profiles, click Add. The General Settings
dialog opens:
file:///C|/Documents%20and%20Settings/pguillor/Desktop/w2k5/W2Ksetup.htm (2 of 10) [7/2/2004 12:29:25 PM]
Making a Basic Network Connection in Windows 2000: Intel PRO/Wireless 2915ABG Network Connection User's Guide
3. Enter the Profile Name and Wireless Network Name (SSID) in the appropriate fields.
4. Select Network [Infrastructure]. If you want to assign a password for this profile, click
Advanced. The Advanced Settings dialog opens:
file:///C|/Documents%20and%20Settings/pguillor/Desktop/w2k5/W2Ksetup.htm (3 of 10) [7/2/2004 12:29:25 PM]
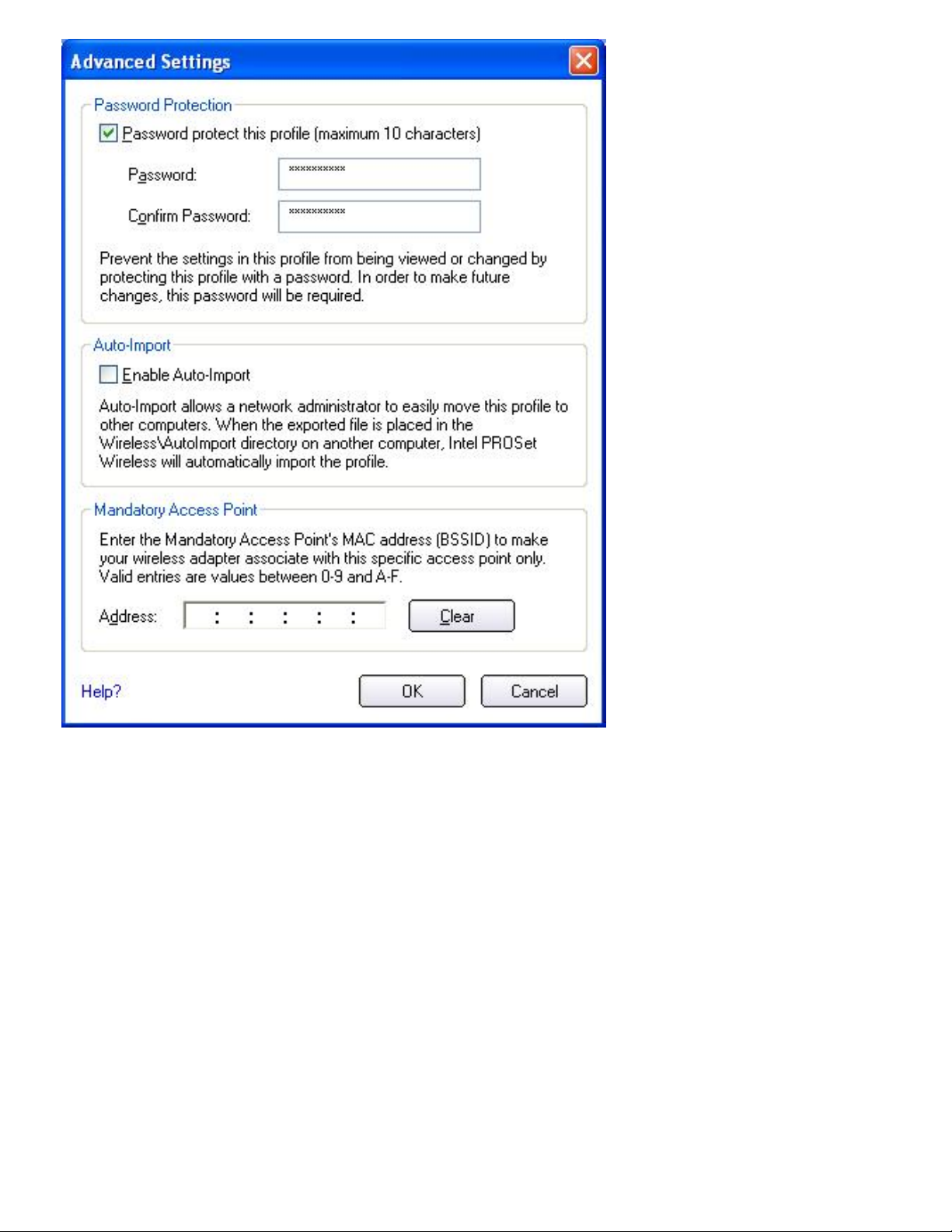
Making a Basic Network Connection in Windows 2000: Intel PRO/Wireless 2915ABG Network Connection User's Guide
5. Select Password protect this profile (maximum 10 characters).
6. Enter the password, then re-enter it in the Confirm Password box.
7. To close the dialog, click OK. The previous Create Wireless Profile dialog reopens:
file:///C|/Documents%20and%20Settings/pguillor/Desktop/w2k5/W2Ksetup.htm (4 of 10) [7/2/2004 12:29:25 PM]
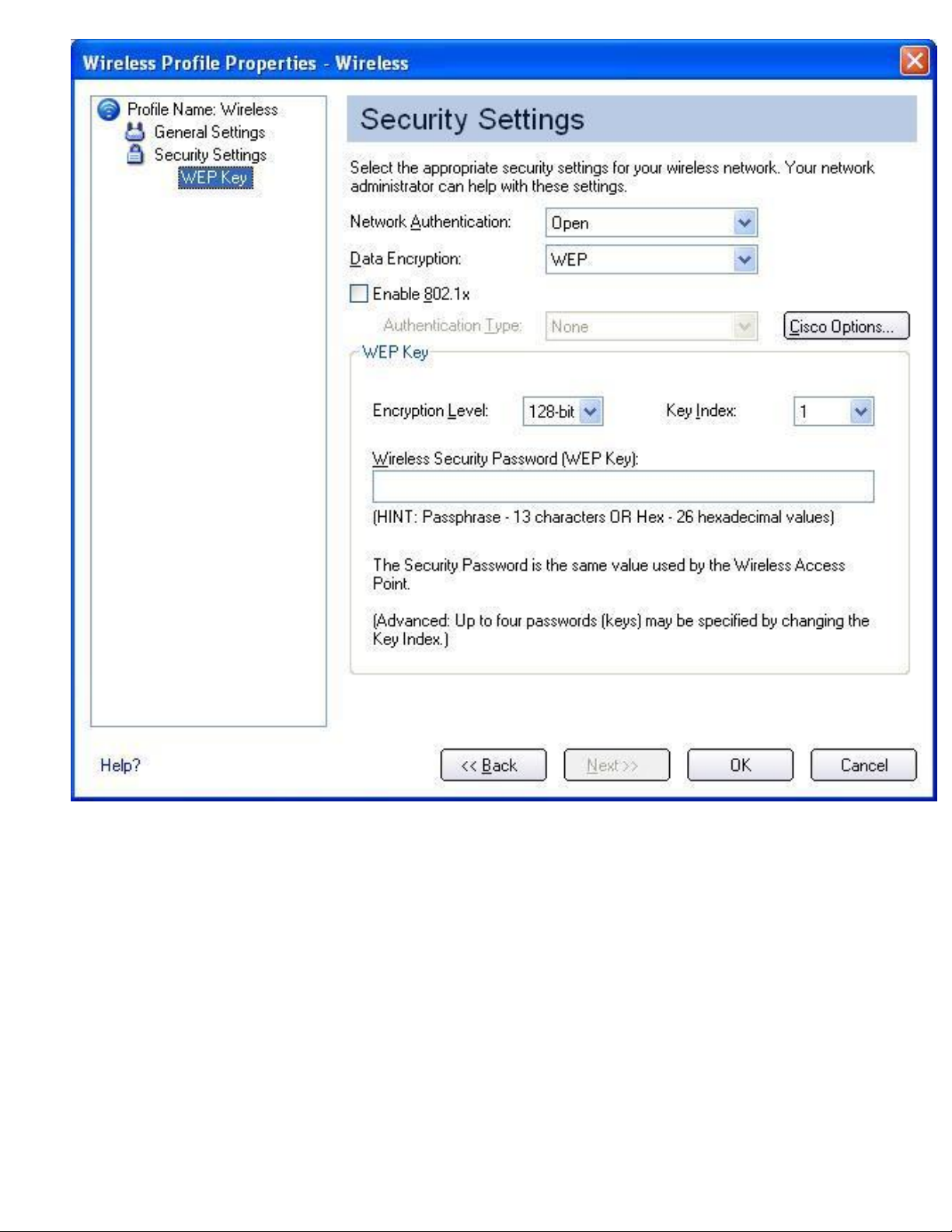
Making a Basic Network Connection in Windows 2000: Intel PRO/Wireless 2915ABG Network Connection User's Guide
8. Click Next.
9. For Network Authentication, select Open (recommended).
10. Select None as the Data Encryption.
11. To save your settings and close the Security Settings page, click OK. The Intel®
PROSet/Wireless dialog reopens.
file:///C|/Documents%20and%20Settings/pguillor/Desktop/w2k5/W2Ksetup.htm (5 of 10) [7/2/2004 12:29:25 PM]
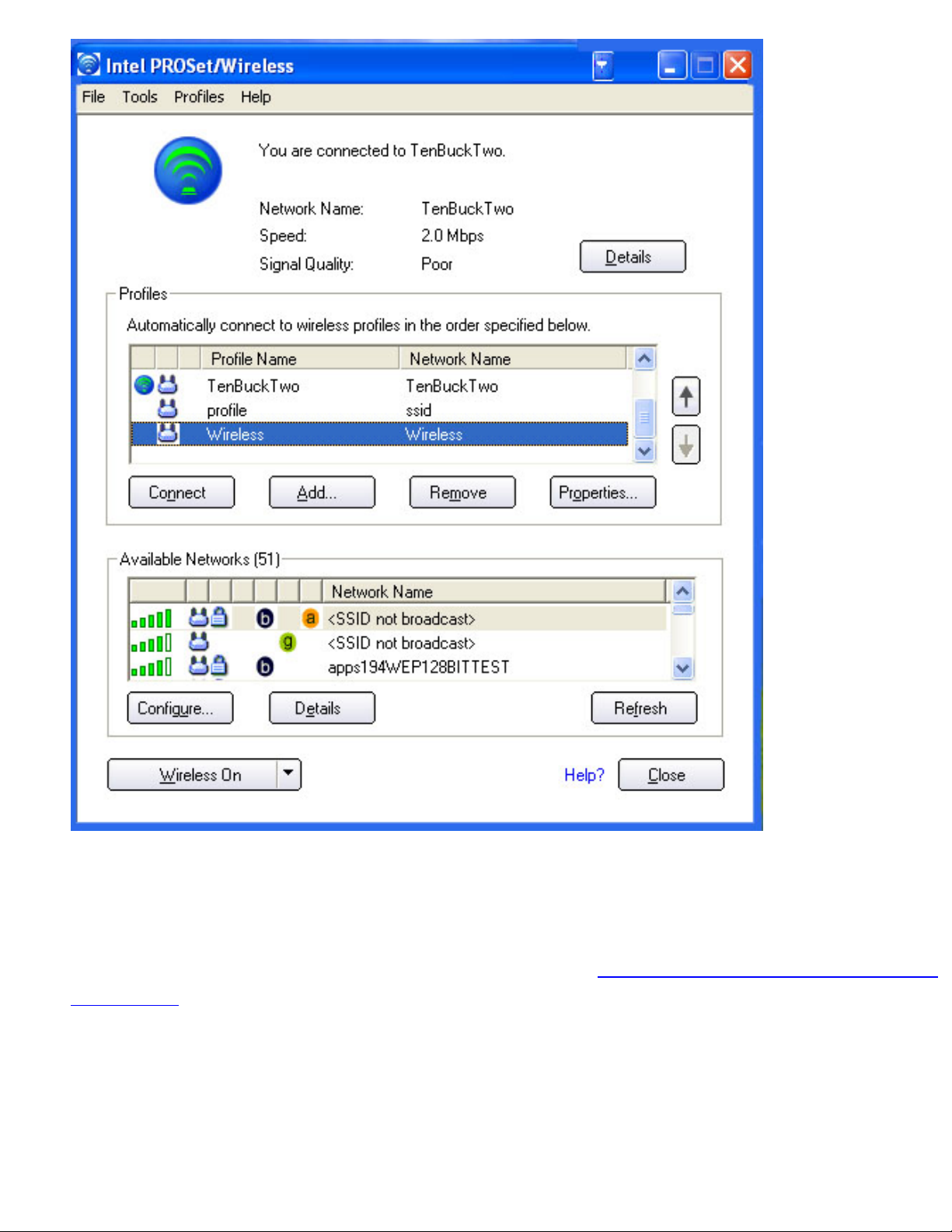
Making a Basic Network Connection in Windows 2000: Intel PRO/Wireless 2915ABG Network Connection User's Guide
12. The new profile is positioned at the bottom of the Profiles list. Use the up and down arrows
to position it at the top of the list.
13. To connect to the wireless network, select it and click Connect.
14. To verify the status of your wireless connection, refer to
Viewing the Status of your Wireless
Connection.
Configuring your Infrastructure Network with WEP security
The following describes how to edit an existing profile and apply Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP)
encryption.
file:///C|/Documents%20and%20Settings/pguillor/Desktop/w2k5/W2Ksetup.htm (6 of 10) [7/2/2004 12:29:25 PM]
Making a Basic Network Connection in Windows 2000: Intel PRO/Wireless 2915ABG Network Connection User's Guide
NOTE:
Before starting, have the security network key available for the access point (for home
use). If the access point is installed in a corporate environment, contact your system
administrator for the network key.
To configure a profile with WEP security:
1. Double-click the Intel® PROSet/Wireless icon in the desktop task tray, or click Start
àPrograms àIntel® PROSet/Wireless àIntel® PROSet/Wireless.
2. From the Intel® PROSet/Wireless dialog, select the profile from the Profiles list and click
Properties. The General Settings dialog opens:
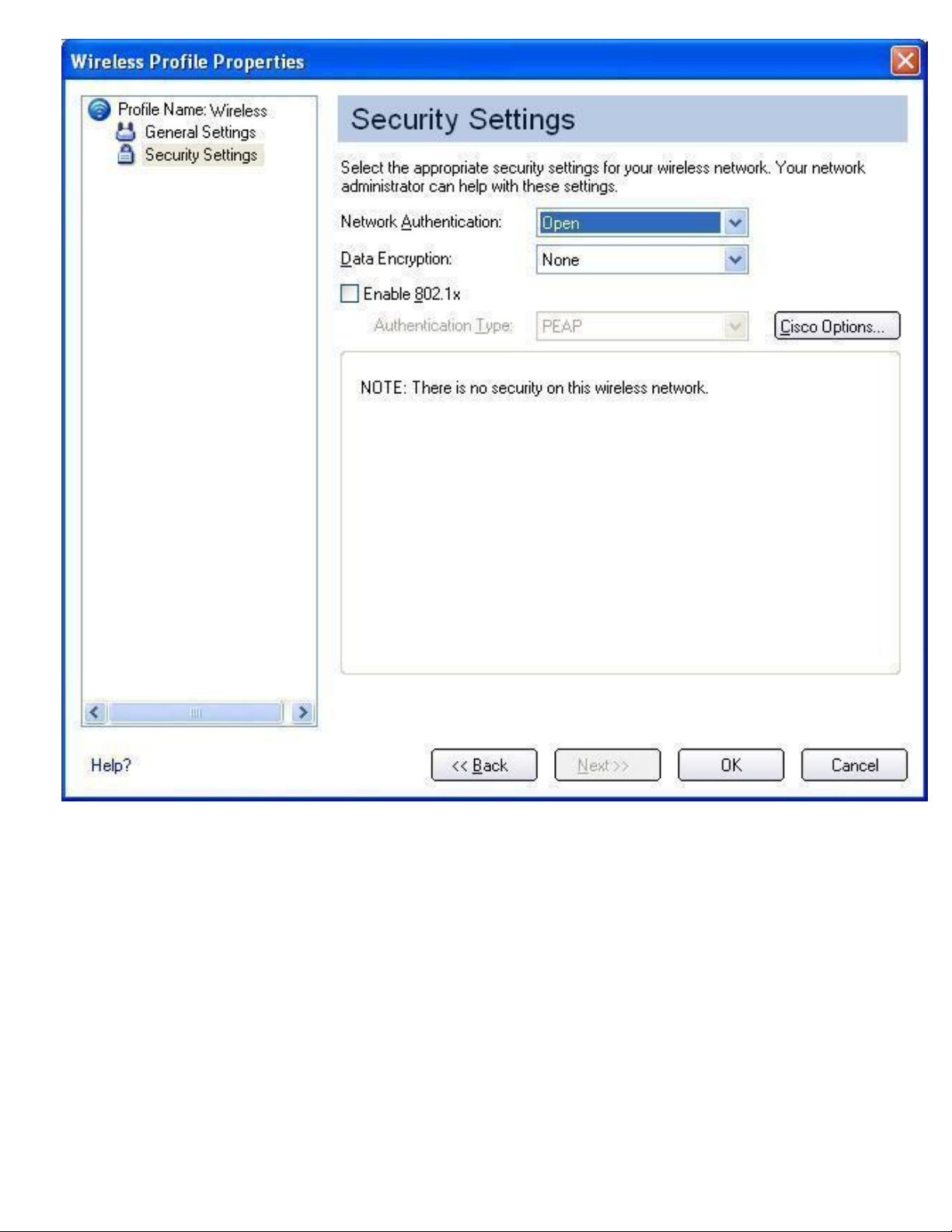
3. Click Next. The Security Settings dialog opens:
file:///C|/Documents%20and%20Settings/pguillor/Desktop/w2k5/W2Ksetup.htm (7 of 10) [7/2/2004 12:29:25 PM]
Making a Basic Network Connection in Windows 2000: Intel PRO/Wireless 2915ABG Network Connection User's Guide
4. For Network Authentication, select Open (recommended).
5. Select WEP as the Data Encryption.
6. For the Encryption Level, select 64-bit or 128-bit.
7. Select a key index number 1, 2, 3, or 4. Key selection must correspond to the network key
on the access point.
8. Enter the password characters in the Wireless Security Password (WEP Key) text box.
Select either of the following:
● Use ASCII characters: Click Use ASCII characters to enable. Enter a
text phrase, five (using 64-bit) or 13 (using 128-bit) alphanumeric
characters (0-9, a-z or A-Z), in the pass phrase field.
● Use hex Key: Click Use hex Key to enable. Enter ten (using 64-bit)
alphanumeric characters, 0-9, A-F, or twenty-six (using 128-bit)
file:///C|/Documents%20and%20Settings/pguillor/Desktop/w2k5/W2Ksetup.htm (8 of 10) [7/2/2004 12:29:25 PM]
Making a Basic Network Connection in Windows 2000: Intel PRO/Wireless 2915ABG Network Connection User's Guide
alphanumeric characters (0-9, A-F) in the hex key field.
NOTE:
Both the network name and the network key information are casesensitive.
9. To save the settings and close the Security Settings page, click OK.
10. The profile is positioned at the bottom of the Profiles list. Use the up and down arrows to
position it at the top of the list.
11. To connect to the wireless network, click Connect.
12. To verify the status of your wireless connection, refer to
Viewing the Status of your Wireless
Connection.
Your basic configuration is now complete. If your network required advanced security options,
click on the appropriate link below for advanced configuration instructions.
Configuring Advanced Network Security Settings in Windows XP: Using Windows XP Support.
Configuring Advanced Network Security Settings in Windows 2000: Using Intel®
PROSet/Wireless.
Viewing the Status of Your Wireless Connection
The wireless network connection icon in the bottom right corner of the windows desktop indicates
the current status of your wireless connection. There is also a signal quality icon on the Intel®
PROSet/Wireless main windows that provides the current status of your wireless connection. The
signal can vary from poor to excellent depending on the surroundings and quality of the signal
from the access point or computer (ad hoc mode). The following table shows how the signal
quality icon indicates the status of your wireless connection, and the suggested actions for low
signals.
Connection
Icon
Connection
Status
Bars/Color Suggested Action
Excellent 5 green
bars
No action required
Very Good 4 green
bars
No action required
Good 3 green
bars
No action required
file:///C|/Documents%20and%20Settings/pguillor/Desktop/w2k5/W2Ksetup.htm (9 of 10) [7/2/2004 12:29:25 PM]
Making a Basic Network Connection in Windows 2000: Intel PRO/Wireless 2915ABG Network Connection User's Guide
Low 2 green
bars
Move closer to the access point
Very Low 1 yellow
bar
Move closer to the access point
No
connection
no colored
bars
Computer is still trying to establish initial
connection or you have moved out of
the range of your access point.
Back to Top
Back to Contents
file:///C|/Documents%20and%20Settings/pguillor/Desktop/w2k5/W2Ksetup.htm (10 of 10) [7/2/2004 12:29:25 PM]

Using the Intel(R) PROSet Wireless Utility: Intel(R) PRO/Wireless 2200BG Network Connection User's Guide
Back to Contents
Using Intel® PROSet/Wireless: Intel
PROSet/Wireless 2915ABG Network
Connection User's Guide
Using Intel PROSet/Wireless as Your Wireless Manager
Enabling/Disabling the Wireless Radio
Intel PROSet/Wireless Main Window
Intel PROSet/Wireless Menus
Administrator Tool
Single Sign On Feature
Installing and Uninstalling the Software
Installing and Uninstalling the Single Sign On Feature
Window XP Zero Configuration
Using Intel PROSet/Wireless as Your Wireless Manager
The following information is for Windows XP users. If you are using Windows 2000 refer to
Making a Basic Network Connection in Windows 2000.
Intel PROSet/Wireless can be used to set up, edit, and manage network profiles to connect
to a network. It also includes advanced settings such as power management and channel
selection for setting up ad hoc networks. If you are using Windows XP, it is recommended
that you use Windows XP to manage your network profiles. However, if your network
requires
LEAP authentication, you will need to use Intel® PROSet/Wireless to configure
your LEAP profiles.
Disabling Windows XP Wireless Manager from the Windows Operating
System
To disable Windows XP as your wireless manager from Windows:
1. Click Start àSettings àControl Panel.
file:///C|/Documents%20and%20Settings/pguillor/Desktop/w2k5/UtilIntc.htm (1 of 39) [7/2/2004 12:29:31 PM]
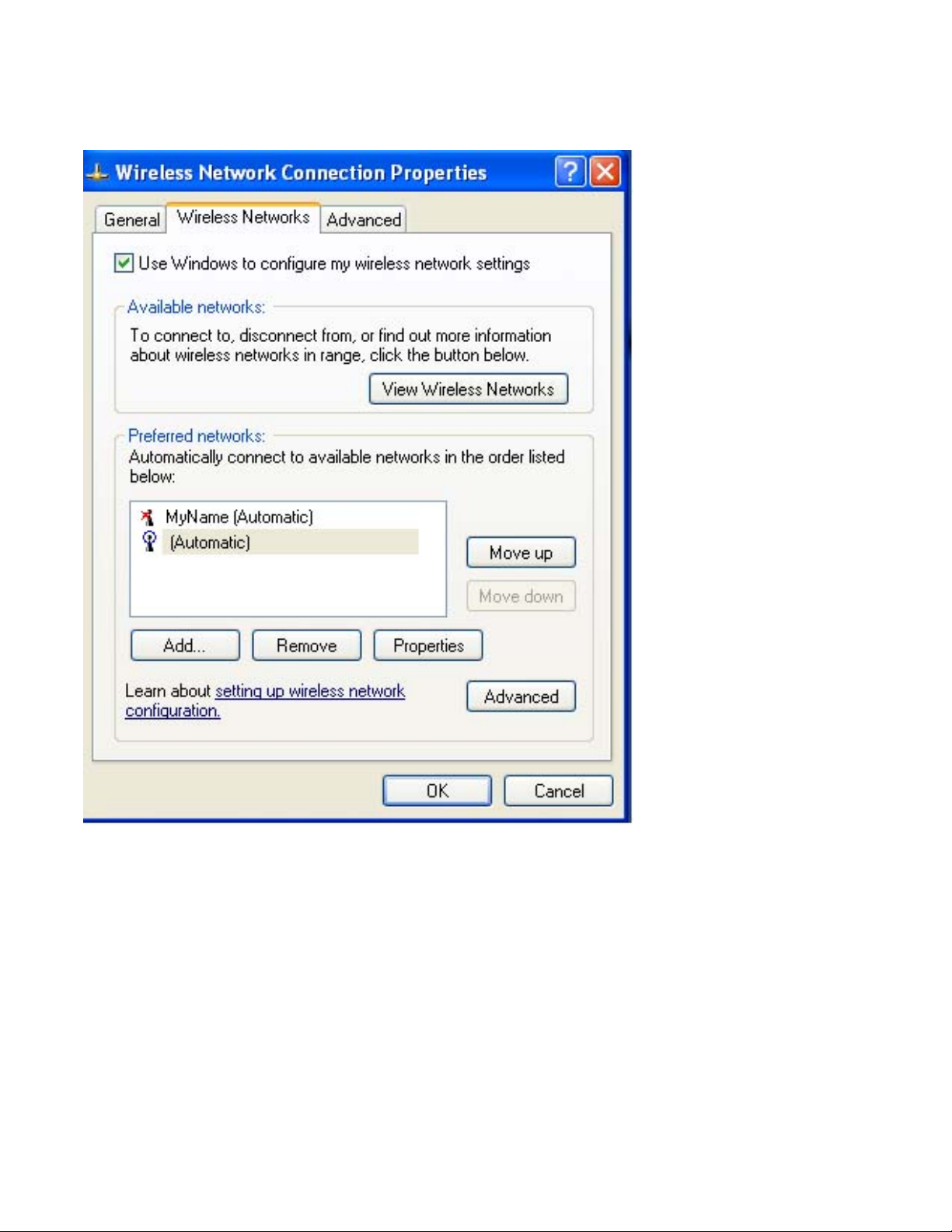
Using the Intel(R) PROSet Wireless Utility: Intel(R) PRO/Wireless 2200BG Network Connection User's Guide
2. Double-click Network Adapters.
3. Right-click Wireless Network Connection, and then click Properties. The Wireless
Network Connection Properties page opens:
2. On the Wireless Networks tab, click to clear the Use Windows to configure my
wireless network settings checkbox.
3. To save your settings, click OK.
This procedure configures Intel® PROSet/Wireless to manage your network profiles.
Disabling Windows XP from Intel® PROSet/Wireless
If Windows XP is enabled, the Intel® PROSet/Wireless main window is disabled. However,
you can still open the Intel® PROSet/Wireless window from the Start menu and disable
Windows XP.
file:///C|/Documents%20and%20Settings/pguillor/Desktop/w2k5/UtilIntc.htm (2 of 39) [7/2/2004 12:29:31 PM]
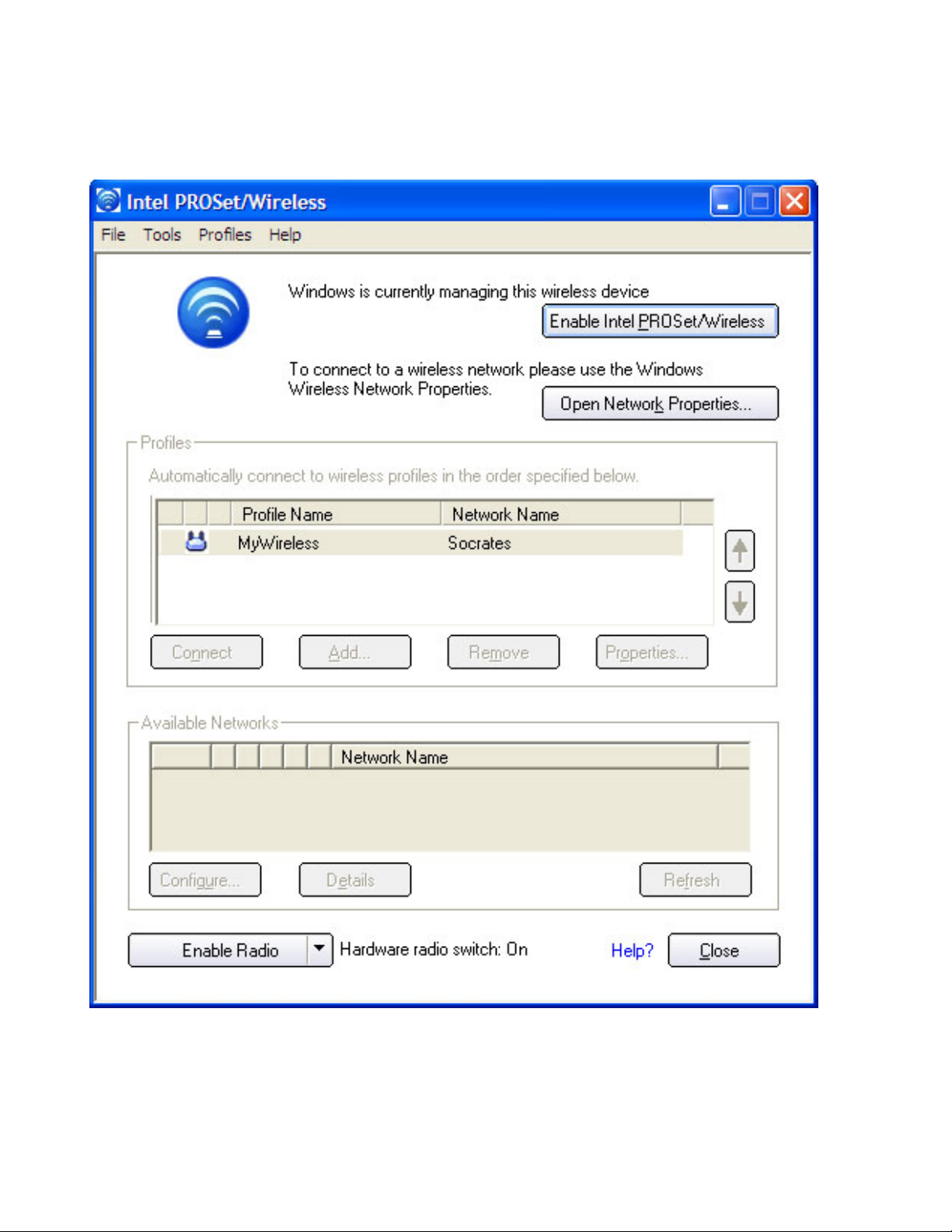
Using the Intel(R) PROSet Wireless Utility: Intel(R) PRO/Wireless 2200BG Network Connection User's Guide
To disable Windows XP from the Intel PROSet/Wireless window:
1. Click Start àPrograms àIntel PROSet/Wireless. The Intel PROSet/Wireless
window opens.
2. Click Enable Intel PROSet/Wireless. This procedure configures Intel
PROSet/Wireless to manage your network profiles.
file:///C|/Documents%20and%20Settings/pguillor/Desktop/w2k5/UtilIntc.htm (3 of 39) [7/2/2004 12:29:31 PM]
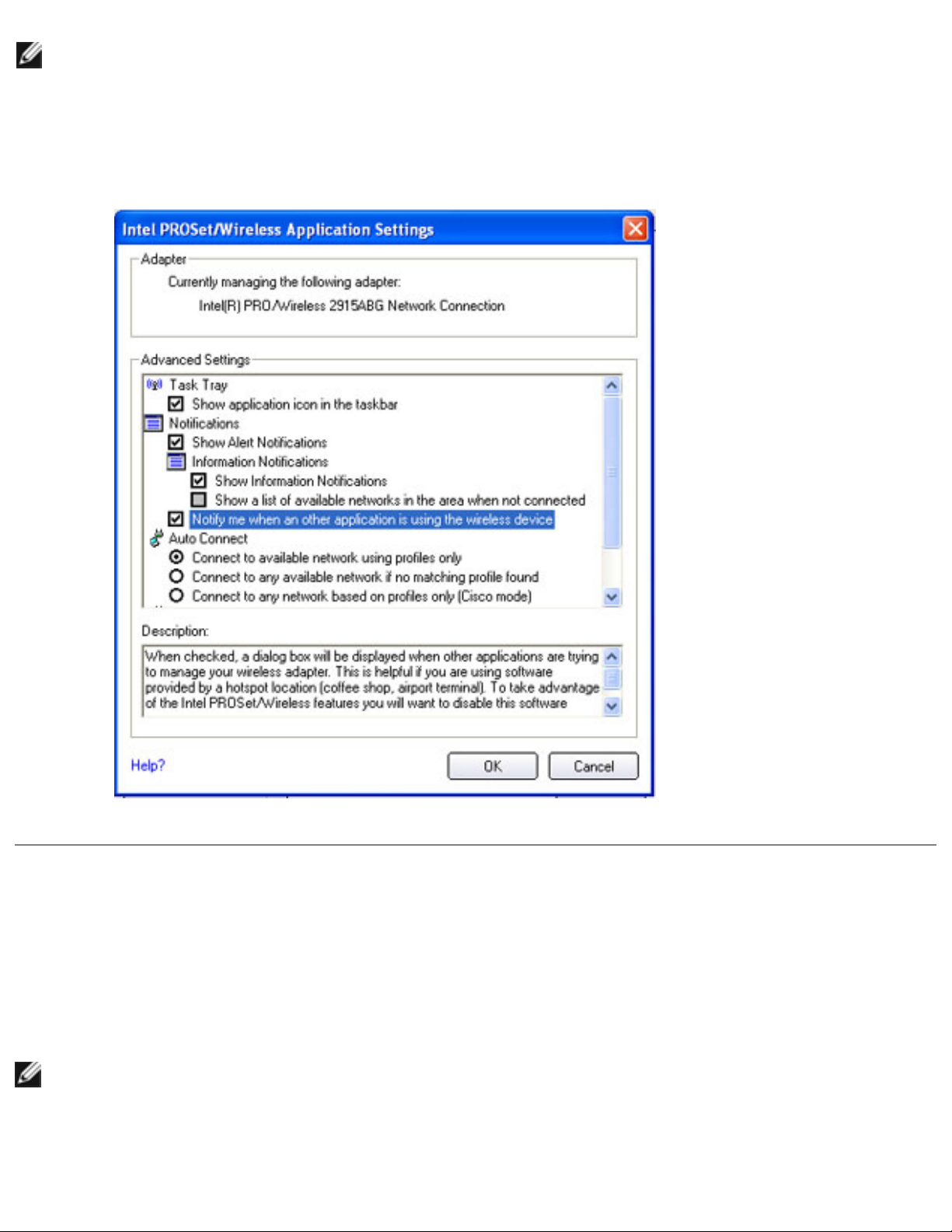
Using the Intel(R) PROSet Wireless Utility: Intel(R) PRO/Wireless 2200BG Network Connection User's Guide
NOTE:
To be notified when Windows XP or any other wireless manager starts to manage
your network profiles, select Applications Settings under the Tools menu on the
Intel PROSet/Wireless window box. Next, select Notify when another
application is using the wireless device checkbox, as shown in the following
illustration:
Enabling/Disabling the Wireless Radio
The wireless radio can be enabled/disabled from a hardware radio switch on your computer,
in conjunction with either the Intel PROSet/Wireless or with Windows.
NOTE: When your computer is switched on and the radio is enabled, the radio is capable
of constantly transmitting signals. In certain situations, such as in a plane, signals from the
radio may cause interference. The following methods describe how to disable the radio and
use your laptop without emitting radio signals.
file:///C|/Documents%20and%20Settings/pguillor/Desktop/w2k5/UtilIntc.htm (4 of 39) [7/2/2004 12:29:31 PM]
Using the Intel(R) PROSet Wireless Utility: Intel(R) PRO/Wireless 2200BG Network Connection User's Guide
Using the Fn + F2 radio off/on switch
To enable/disable the radio:
1. Press Fn + F2 to switch the radio on or off. This is known as the
hardware switch. If you have Intel PROSet/Wireless installed, the current state of
the radio is displayed in the Intel PROSet/Wireless
main window and in the task tray.
The hardware radio switch must be turned on before you can enable the radio using
the Intel PROSet/Wireless or Windows Device Manager:
Radio icon status: Using Fn + F2 displays a large wireless icon indicating that
the radio is enabled or disabled, as shown in the following illustration:
Radio Enabled using
Fn + F2
Radio Disabled
using Fn + F2
Using Intel PROSet/Wireless to enable/disable the radio
The radio can be enabled/disabled from Intel PROSet/Wireless. The status icon on the Intel
PROSet/Wireless main window displays the current state of the radio.
When the radio is on, an attempt is made to associate the network access point using the
last profile. If the adapter cannot connect to the access point, the Configuration Service
attempts to find an available network.
To enable/disable the radio using Intel PROSet/Wireless:
● To enable/disable the radio from the Intel PROSet/Wireless main window:
file:///C|/Documents%20and%20Settings/pguillor/Desktop/w2k5/UtilIntc.htm (5 of 39) [7/2/2004 12:29:31 PM]

Using the Intel(R) PROSet Wireless Utility: Intel(R) PRO/Wireless 2200BG Network Connection User's Guide
■ Open the Intel PROSet/Wireless main window.
■ To toggle the radio off and on, click Enable/Disable Radio.
● To enable/disable the radio off/on from the task tray:
■ Right-click the task tray icon .
■ From the menu that opens, select Enable Radio or Disable Radio.
When the radio is disabled, the task try shows the icon with a red X:
.
The icon is located in the lower right corner of Windows desktop.
Using Device Manager to enable/disable the radio
The radio can be enabled/disabled using Device Manager on the Windows operating
system. The wireless icon on the task tray will display the current state of the radio.
To enable/disable the radio from the Windows Device Manager:
1. From the Windows desktop, right-click My Computer and then click Properties.
2. Click the Hardware tab, and then click Device Manager.
3. Double-click Network adapters.
4. Right-click the installed wireless adapter in use.
5. From the pop-up menu, choose Enable/Disable (depending on whether the radio is
currently on or off).
6. When prompted, click Yes.
NOTE::
Make sure the radio is enabled on both the software and the hardware. If it
is not enabled on the hardware, you will receive this message when you try
to connect:
The Intel® PRO/Wireless 2915ABG (or the Intel
PROSet/Wireless 2200BG) network connection is still disabled.
Press Fn + F2 to enable it.
A red X indicates the radio is disabled.
Intel PROSet/Wireless Main Window
file:///C|/Documents%20and%20Settings/pguillor/Desktop/w2k5/UtilIntc.htm (6 of 39) [7/2/2004 12:29:31 PM]
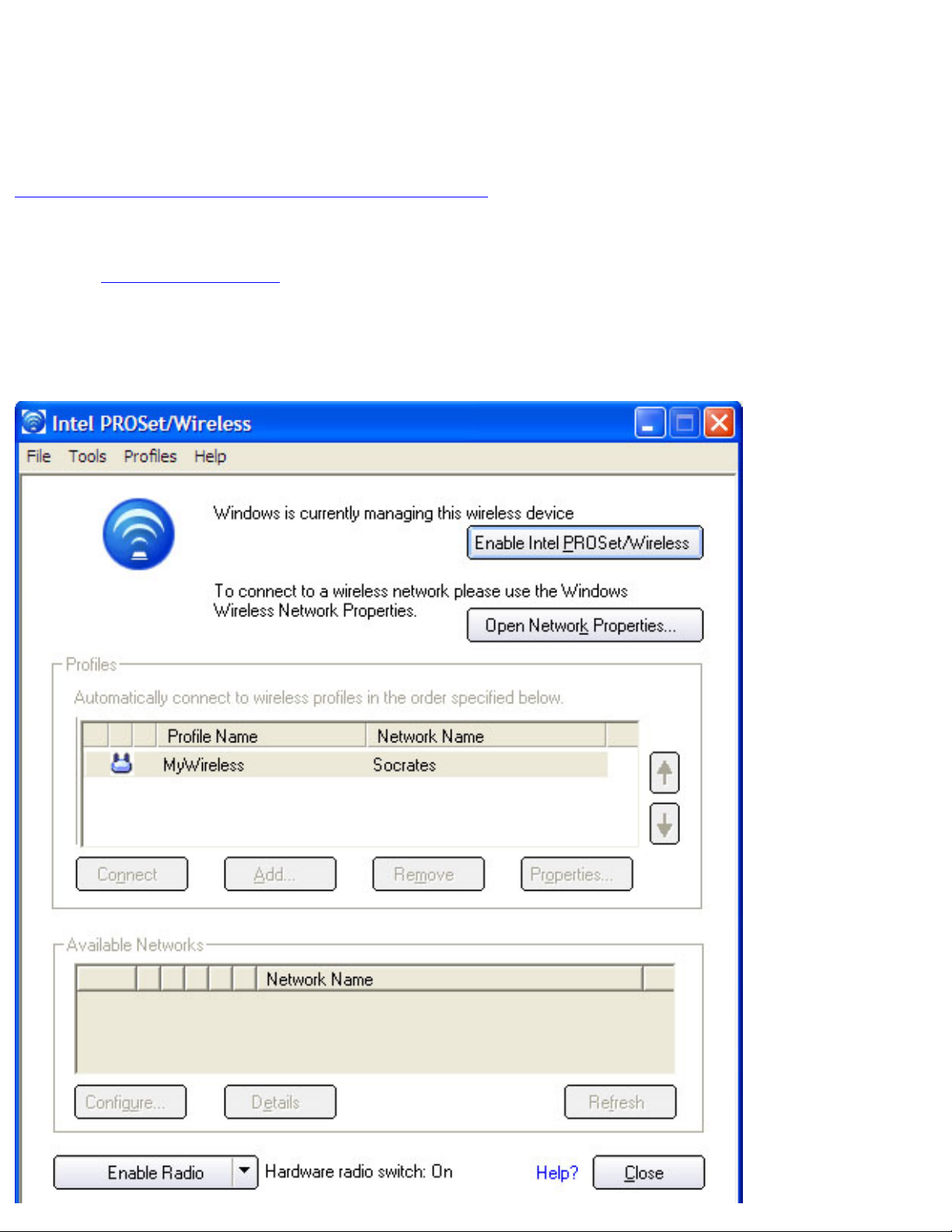
Using the Intel(R) PROSet Wireless Utility: Intel(R) PRO/Wireless 2200BG Network Connection User's Guide
The main window contains basic information about your connection. If you are associated to
a network, it will contain information such as SSID, profile name, and speed, and AP settings
such as 802.11 band, channel, and security mode. The Signal Quality icon provides visual
information about the quality of the wireless signal. It varies from poor to excellent,
depending on the surroundings and quality of the signal from the access point. Refer to
Viewing the Status of your Wireless Connection for more information.
The current status of the radio is also displayed in the Intel PROSet/Wireless main screen.
Refer to
enabling the radio for more information about how to enable/disable the wireless
radio.
Intel PROSet/Wireless Main Window:
file:///C|/Documents%20and%20Settings/pguillor/Desktop/w2k5/UtilIntc.htm (7 of 39) [7/2/2004 12:29:31 PM]
Using the Intel(R) PROSet Wireless Utility: Intel(R) PRO/Wireless 2200BG Network Connection User's Guide
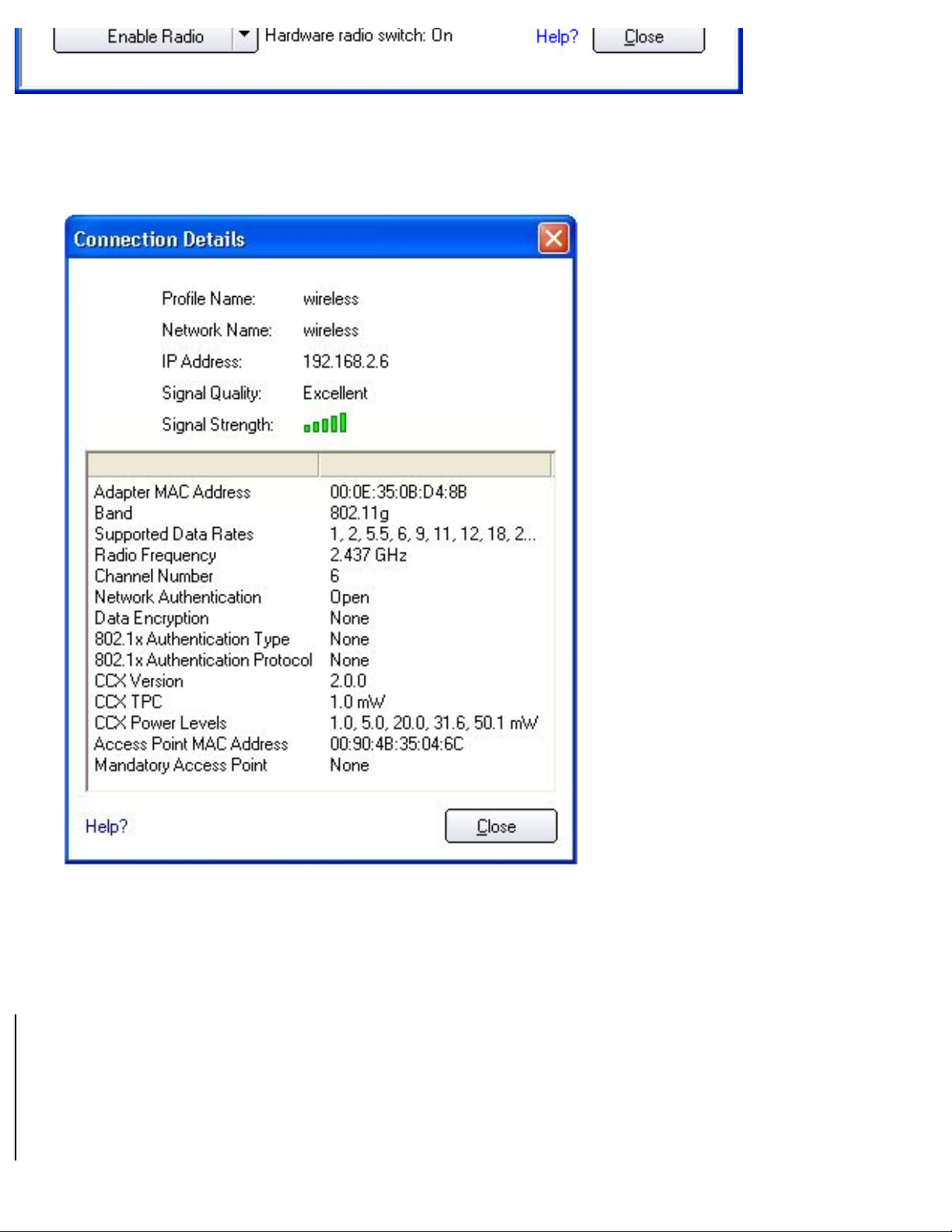
● To view detailed parameters of the access point and network adapter, as shown in the
following illustration, click Details.
The Connection Details window displays the current network connection information.
Connection Details description
Name Description
Profile Name
Name of the profile. If this is a one-time connection then <no active
profile> is displayed.
Network Name
Network Name (SSID) of the current connection.
IP address
Internet Protocol (IP) address for the current connection.
file:///C|/Documents%20and%20Settings/pguillor/Desktop/w2k5/UtilIntc.htm (8 of 39) [7/2/2004 12:29:31 PM]

Using the Intel(R) PROSet Wireless Utility: Intel(R) PRO/Wireless 2200BG Network Connection User's Guide
Signal Quality
A radio frequency (RF) signal can be assessed by basically two
components:
● strength (quantity) of the signal
● the quality of the signal
The quality of the signal is determined by a combination of factors but primarily is composed of signal strength and the ratio of the RF
noise present. RF noise occurs both naturally in nature and
artificially by electrical equipment. If the amount of the RF noise is
high, and/or the signal strength is low, it results in a lower signal to
noise ratio which causes poorer signal quality. With a low signal to
noise ratio it is more difficult for the radio receiver to discern the
data information contained in the signal from the noise itself.
Signal Strength
While adequate signal strength is required for good data
communications, even more important is the quality of the signal.
A strong signal of poor quality results in poor data
communications. If the signal quality is low, investigate sources of
noise nearby, such as interference from other wireless LANs, other
RF transmitters, electric motors or compressors. Also reflections of
the signal by metallic or other objects in the area can result in poor
signal quality.
Adapter MAC Address
The Media Access Control (MAC) address for the wireless adapter.
Band
Indicates the wireless band of the current connection.
● 802.11a
● 802.11b
● 802.11g
Supported Data rates
Rates at which the wireless adapter can send and receive data.
Displays the speed in Mbps for the frequency being used.
● 802.11g - 1, 2, 5.5, 6, 9, 11, 12, 18, 24, 36, 48, and 54
● 802.11b - 1, 2, 5.5, and 11
● 802.11a - 6, 9, 11, 12, 18, 24, 36, 48, and 54
Radio Frequency
Displays the channel frequency of the current wireless connection.
Channel Number
Displays the transmit and receive channel.
file:///C|/Documents%20and%20Settings/pguillor/Desktop/w2k5/UtilIntc.htm (9 of 39) [7/2/2004 12:29:31 PM]
 Loading...
Loading...