Page 1

Dell™ Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point
User's Guide
Contents
Introduction
Overview
Wireless Networking Overview
A Look at the Hardware
Installation and Configuration
Configuration of the Access Point
Connecting the Access Point to the network
How to obtain the IP address of the Access Point
Setting Wireless Encryption in Your Access Point
Turning Off Broadcast SSID
Setting Up File and Printer Sharing
How to setup wireless clients to connect to the Access Point
Using Your Access Point
Overview
Factory Default Settings
Setup Wizard
Control Utility
Web- Based Configuration Tool
Technical Specifications and Regulatory Information
Technical Specifications
Regulatory Information
Limited Warranties and Return Policy
FAQs
Glossary
Online Customer Support
Information in this document is subject to change without notice.
© 2004 Dell Inc. All rights reserved.
Trademarks used in this text: Dell, the DELL logo; Microsoft and Windows are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
Other trademarks and trade names may be used in this document to refer to either the entities claiming the marks and names or
their products. Dell disclaims any proprietary interest in trademarks and trade names other than its own.
P/N G7992 Revision A00, Sept. 2004
Page 2
Back to Contents Page
Introduction: Dell™ Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point
User's Guide
Overview
Wireless Networking Overview
A Look at the Hardware
Overview
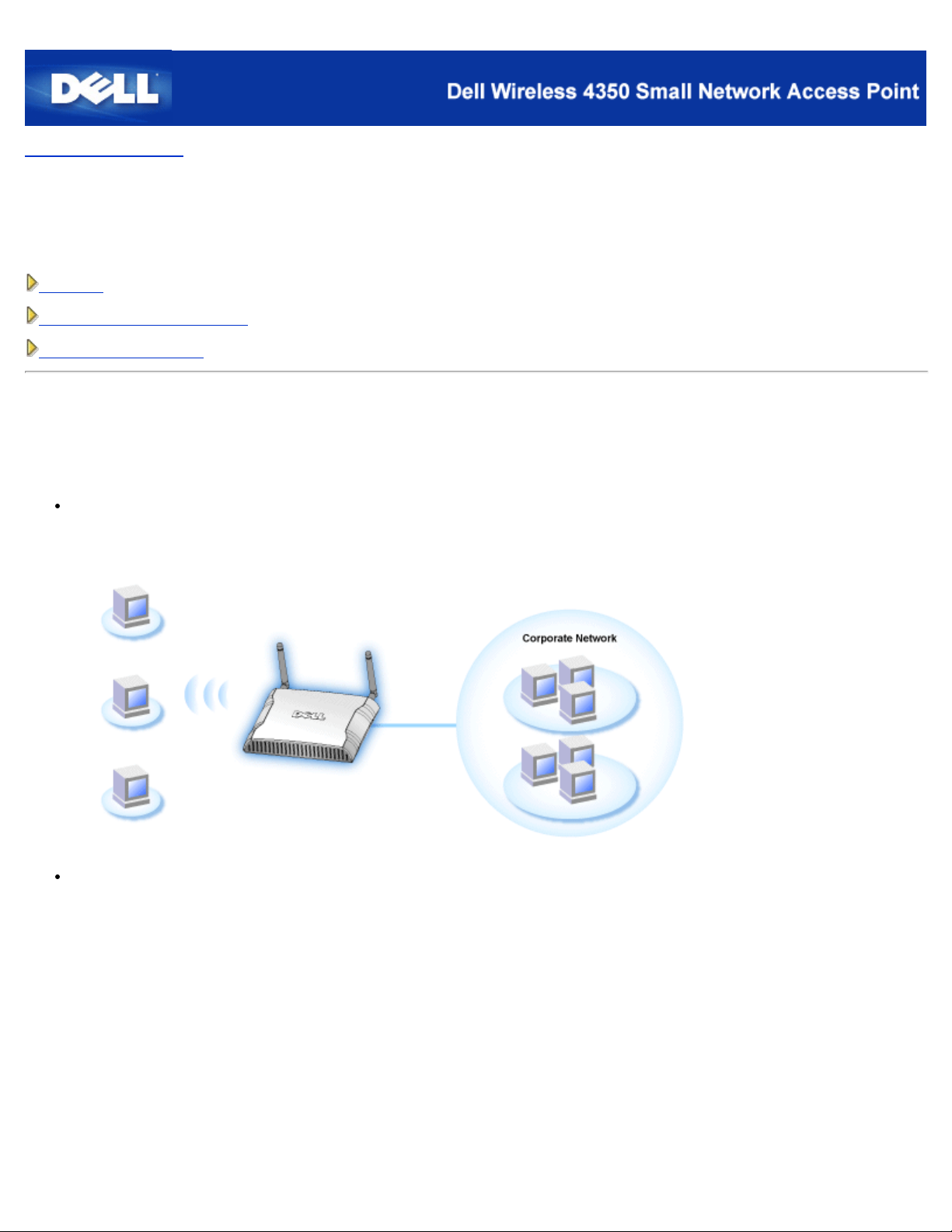
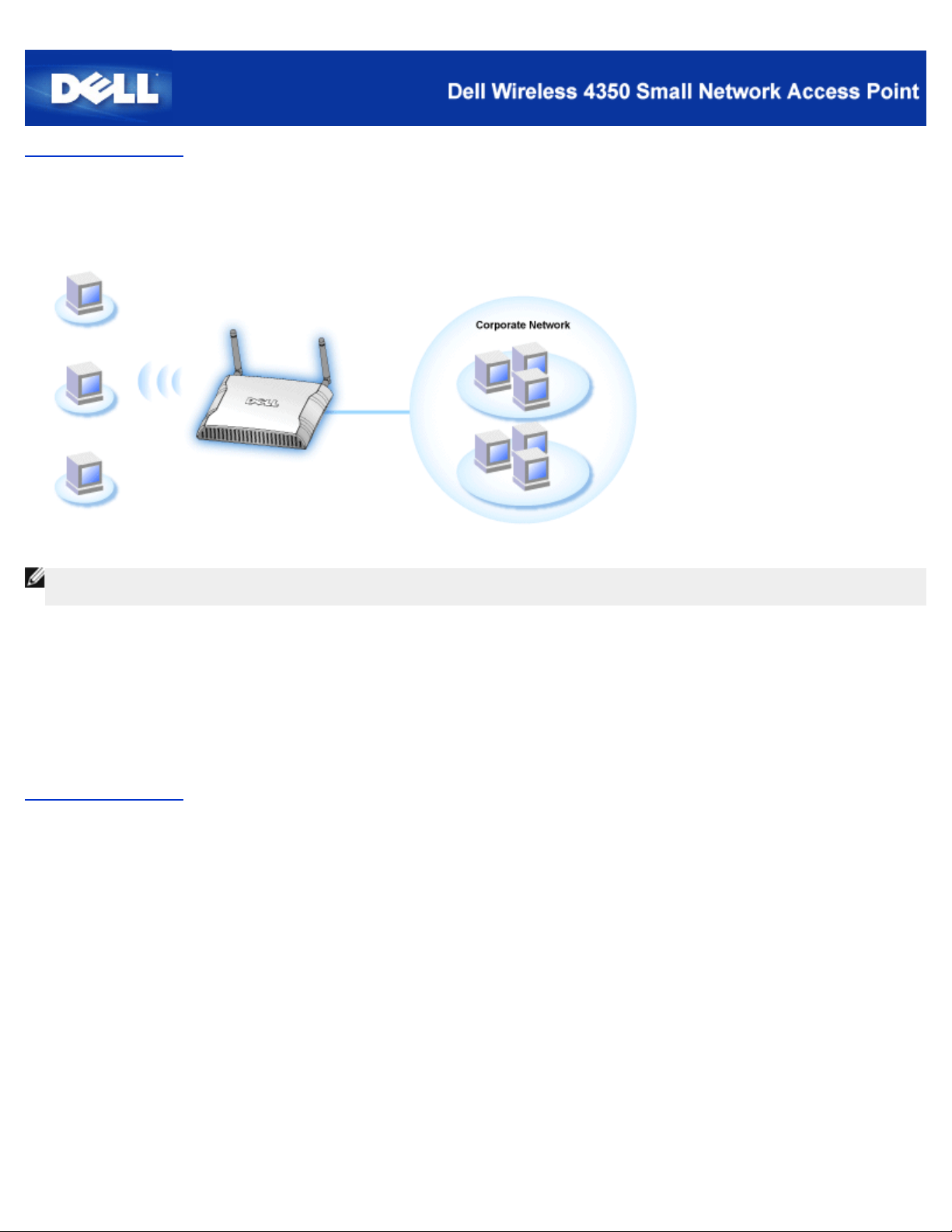
The Dell Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point is an 802.11b/g wireless access point that allows wireless clients access to a
corporate network. The Access Point can be configured in the following ways:
Wireless hub (Access Point): In this mode the Access Point connects wireless computers to the corporate network.
Wireless repeater: In this mode the Access Point is able to extend the wireless range of a root Access Point that is on the
corporate network to remote wireless computers.
Page 3

The Dell Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point supports up to 64 wireless clients. It runs at speeds up to 54 Megabits per
second (Mbps), and the LAN (wired) port runs at 10/100 Mbps. The maximum distance between the Access Point and each
Wireless computer is 300 feet. This distance may be less depending on your environment.
By default, the Dell Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point provides the following functionality:
a wireless access point using wireless as the wireless network name.
a bridge to an Ethernet hub.
Back to Contents Page
Page 4

Back to Contents Page
Wireless Networking Overview:
Dell™ Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point User's Guide
Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN)
Identifying a WLAN
Encryption
Automatic Rate Selection and Rate Scaling
Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN)
A Local Area Network (LAN) is a network in one location. Users at that location can share files, printers, and other services. In a
LAN, a networked computer that requests services is called a client. A Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN) is a type of LAN that
uses high frequency radio waves rather than wires to communicate and transmit data among the network clients and devices. It is
a flexible data communication system implemented as an extension to, or as an alternative for, a wired LAN.
In a WLAN, wireless adapters are installed in clients, also called wireless clients. The adapter allows the wireless client to
communicate with the WLAN without cables. Instead, wireless clients send and receive information through a path in the air called
a channel.
The standards for a WLAN are based on the IEEE 802.11b standard and IEEE 802.11g standard. All Dell 802.11b/g - compliant
devices interoperate with other 802.11b/g - compliant wireless devices from other vendors. The WiFi certification logo indicates that
the wireless device has been tested by an independent organization.
A wireless client operates in either infrastructure mode or peer-to-peer mode.
Back to Top
Identifying a WLAN
An ESSID and BSSID are both Service Set Identifiers (SSID) that identify and control the wireless client’s access to a given
WLAN. The SSID is sometimes referred to as the network name. The SSID indicates what WLAN you are referring to. In most
cases, the user interface displays the SSID.
When installing an access point or wireless adapter in a wireless client, the installation program asks you to enter the SSID. Dell
cannot provide you with this information, as it is specific to your network; but you may choose to use the default SSID, wireless,
for your Dell Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point. All wireless clients and access points in a WLAN must use the same
network name.
Back to Top
Encryption
In a WLAN, wireless clients and access points send and receive information through the air. Without implementing security, it is
possible for an unauthorized person to intercept the information.
Page 5

A common way of implementing security and protecting information is encryption. Encryption applies a set of instructions, called an
algorithm, to information. The instructions combine the plain or clear text of information with a sequence of hexadecimal numbers,
called an encryption key.
Before transmitting information over the airwaves, the wireless client or access point encrypts or scrambles the information. The
access point or wireless client receiving the information uses the same key to decrypt or unscramble the information. The
information is only readable to WLAN devices that have the correct encryption key. The longer the key is, the stronger the
encryption.
The Dell Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point supports both Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) and Wi-Fi Protected Access
(WPA).
WEP
WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) provides a way of creating an encrypted key that is shared between a wireless client (such as a
notebook with a wireless PC card) and the router. In the Dell Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point, WEP is an optional
feature that can be enabled or disabled. When WEP encryption is enabled, you must set the WEP key in the client to match the
WEP key used by the access point because you can ONLY connect to access points that have a matching WEP Key. The Dell
Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point Setup Wizard allows the user to gracefully configure WEP encryption on both the
access point and wireless clients.
NOTE:It is better to change keys frequently. The same algorithm is used for all the communications that should be protected. If
the same key is used, the same message will give exactly the same cipher text. Then, it will be possible for an
eavesdropper to break the encrypted data. For this reason, it is strongly recommended to change keys often.
There are two WEP encryption methods:
40(64)- bit Encryption
·
104(128) -bit Encryption
·
40- bit and 64 -bit encryption are identical. Some vendors use the term 40- bit; others use 64 -bit. A wireless device that claims to
have 40- bit encryption interoperates with a device that claims to have 64 -bit encryption; the same is true for the reverse. A 40(64) bit key consists of 10 hexadecimal numbers, arrayed as follows:
Key #1: 1011121314
Key #2: 2021222324
Key #3: 3031323334
Key #4: 4041424344
A 104(128)- bit key has several trillion times as many possible combinations than a 40(64) -bit key. It consists of 26 hexadecimal
numbers, arrayed as follows:
Key (#1): 101112131415161718191A1B1C
All wireless clients and access points in a WLAN must use the same encryption method and key. The following two examples
stress how important this point is.
Example 1
The encryption method for an access point is 40(64) -bit. The method for a wireless client is 104(128)- bit encryption. The client and
access point cannot communicate with each other, even though the selected key is the same. To resolve this problem, set the
access point to use 104(128)-bit encryption.
Example 2
The encryption method is the same for the access point and wireless client. You select key 1 for the access point and key 2 for
the wireless client. The wireless client cannot communicate with the WLAN. To resolve this problem, select key 1 for the wireless
client.
NOTE:Use the same key and encryption method for the wireless devices in the WLAN. Otherwise, they cannot communicate
Page 6

with each other.
The Dell Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point uses either hexadecimal digits or ASCII characters to create encryption keys.
Hexadecimal digits include the numbers 0 to 9 and the letters A to F. For example, the decimal number 15 is represented as F in
the hexadecimal numbering system.
ASCII is the acronym for the American Standard Code for Information Interchange. Pronounced ask-ee, ASCII is a code for
representing English characters as numbers, with each letter assigned a number from 0 to 127. For example, the ASCII code for
uppercase M is 77. Most computers use ASCII codes to represent text, which makes it possible to transfer data from one computer
to another.
WPA
WPA (Wi - Fi Protected Access) is an upgrade to the WEP standard for securing your wireless network. WPA is derived from and
will be forward- compatible with the future IEEE 802.11i standard. It provides improved data encryption and user authentication.
To enhance the level of security, WPA uses Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP) encryption to address the vulnerabilities of
the static keys used in WEP. TKIP includes four algorithms: message integrity check (MIC), to protect packets from tampering;
Per-Packet Key (PPK) hashing, to prevent weak key attacks; extended initialization vector (IV), to reduce IV reuse and the
possibility that a hacker will collect sufficient packets to crack the encryption; and a re -keying mechanism, to change the temporal
key dynamically. TKIP is the most commonly used encryption method; however, if your wireless clients do not support TKIP, the
Wireless 4350 also supports Advanced Encryption Security (AES) encryption. AES will replace 802.11's RC4-based encryption
under the 802.11i specification. AES, the gold -standard encryption algorithm, provides maximum security for wireless network.
For user authentication, WPA adopts an authentication scheme through 802.1x. 802.1x provides a framework for user
authentication and a key distribution management method. 802.1x consists of three main elements: an Authentication Server
(typically a RADIUS server), WPA -enabled router or AP (called Authenticator), and a WPA-enabled client (called Supplicant).
802.1x ensures only authorized users can access the network. The 802.1x protocols supported by the Dell Wireless 4350 Small
Network Access Point are PEAP, TTLS & TLS.
In enterprises, WPA will be used in conjunction with both a wireless router and authentication server. In a Small Office/Home
Office (SOHO) environment, where there is no authentication server, users can use pre- shared key (PSK) mode in place of the
authentication server.
The Dell Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point offers both WPA running in PSK mode and WPA with 802.1X authentication.
The mutual authentication and improved encryption technology of WPA allows wireless communication to achieve greater security.
Back to Top
Automatic Rate Selection and Rate Scaling
In 802.11g, wireless network adapters and access points can transmit data at one of the following rates: 54, 48, 36, 24, 18, 12, 9,
or 6 Mbps. In 802.11b, the data can be transmitted at a rate of 11, 5.5, 2, or 1 Mbps. As the distance between an adapter and
access point increases or decreases, the data rate automatically changes. Other factors, like interference, also affect the data rate.
The Dell Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point uses automatic rate selection and rate scaling to determine the most efficient
rate of communication. Rate scaling maintains optimal communication between wireless clients and the WLAN.
Back to Top
Back to Contents Page
Page 7
Back to Contents Page
A Look at the Hardware: Dell™ Wireless 4350 Small Network
Access Point
User's Guide
Front Panel
Back Panel
Front Panel
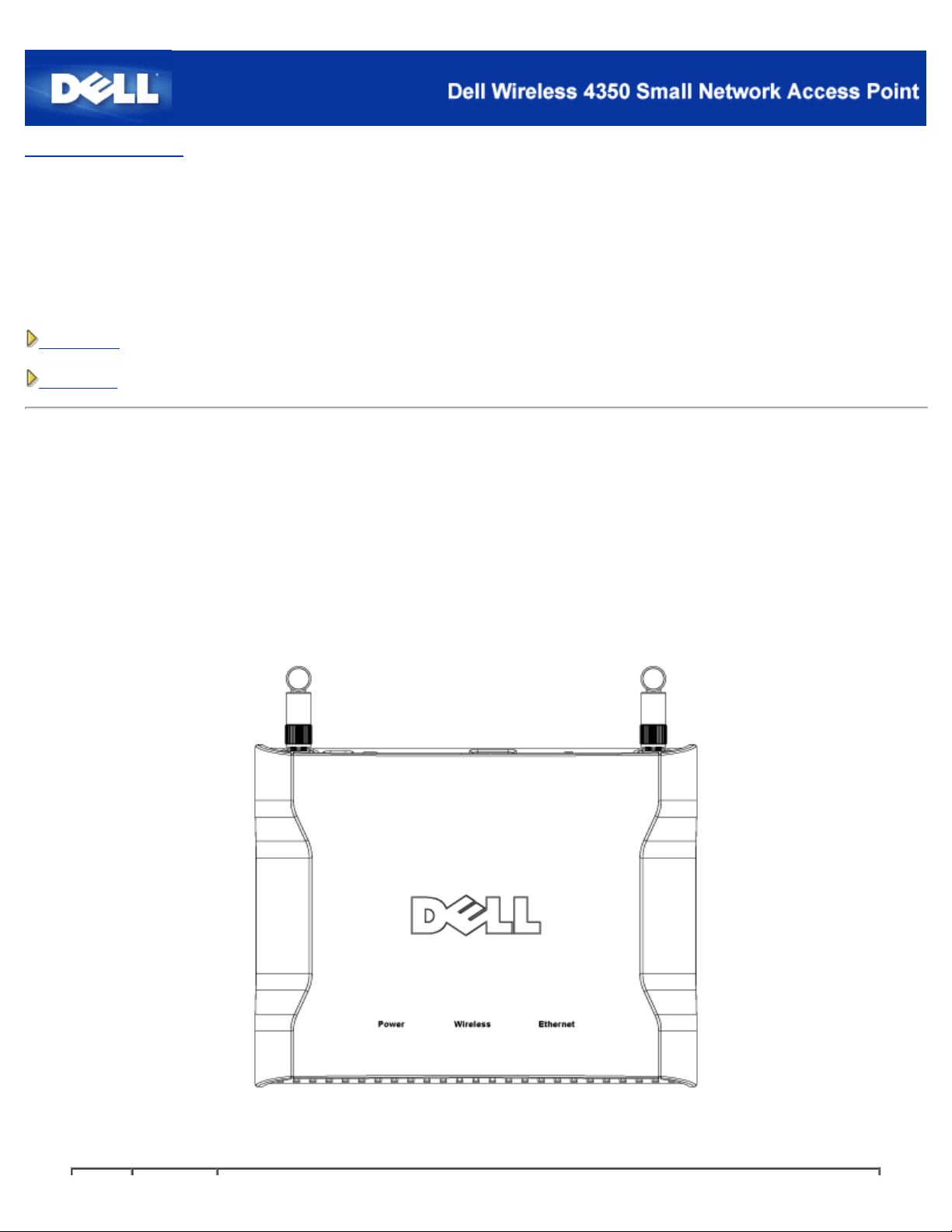
The Dell Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point has three Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs), or link lights, on its front side. The
following table defines the behaviour for each LED:
Front Panel
Page 8
LED Represents Activity
Power Power The Power LED will light up green when the device is powered on and ready for use. It will
blink when the device is powering up or when it is reset
WirelessWireless
LAN
Ethernet Intranet A steady green light indicates the connection is active, and blinks with data activity.
Back to Top
The LED alternates between on and off when wireless clients are attached. It will blink when
there is data activity on the wireless network. The rate of blinking will vary with the rate of data
transfer. It turns off when no wireless clients are associated with the Dell Wireless 4350 Small
Network Access Point.
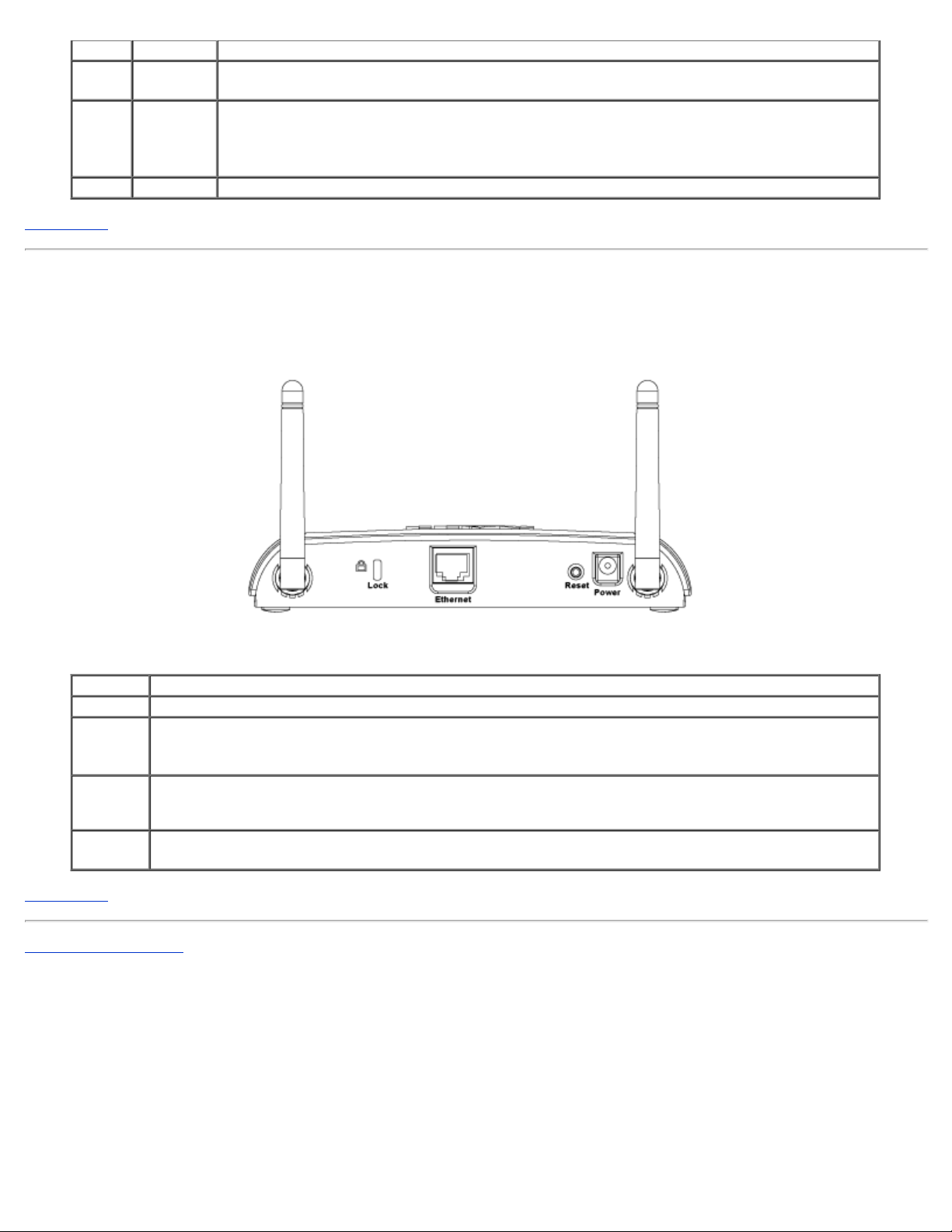
Back Panel
Back Panel
Connector Description
Lock This accepts locking devices for protecting the Dell Wireless 4350 from theft.
Reset Use an object, such as a paper clip, to press the button for at least 5 seconds. The Power LED will be off
for a short time and then light up again. You can then release the button to reset the device to its factorydefault settings.
Ethernet This accepts an RJ - 45 connector for network cabling.
*Also accepts power input from Ethernet port (Power Over Ethernet)
Power Connect the power adapter to this Power port, and then plug the other end of the power cable into a
power outlet.
Back to Top
Back to Contents Page
Page 9

Back to Contents Page
Installation and Configuration:
Dell™ Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point User's Guide
Configuration of the Access Point
Connecting the Access Point to the network
How to obtain the IP address of the Access Point
Setting Wireless Encryption in Your Access Point
Turning Off Broadcast SSID
Setting Up File and Printer Sharing
How to setup wireless clients to connect to the Access Point
Back to Contents Page
Page 10
Back to Contents Page
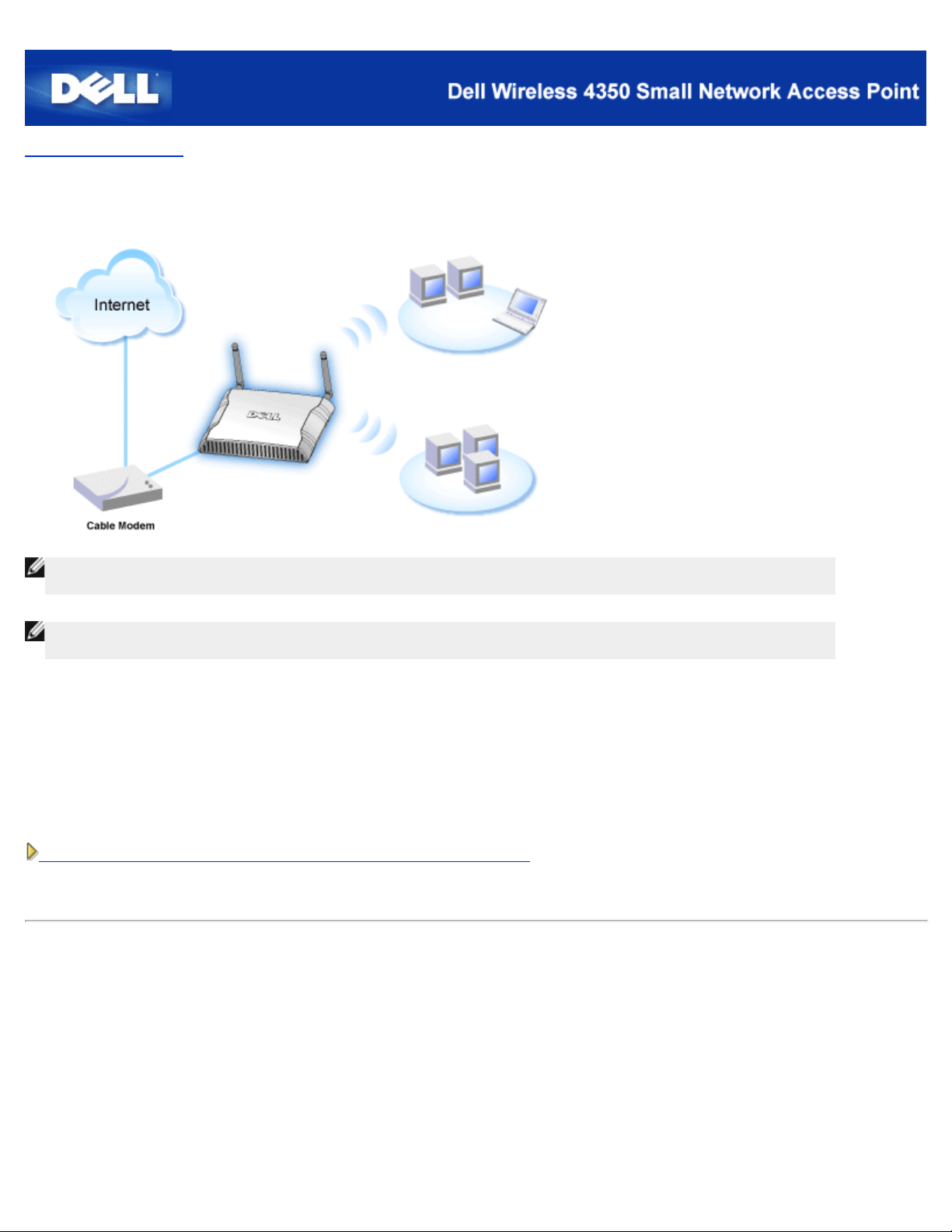
Configuration of the Access Point
NOTE:It is recommended that you configure the Dell Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point with the Setup
Wizard provided on the Dell Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point CD.
NOTE:Advanced users can configure the Dell Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point with the web - based
configuration utility which can be accessed by browsing to the IP address of the access point.
The Setup Wizard allows the user to configure the following parameters on the Dell Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point (a)
SSID, (b) wireless channel of operation, (c) WEP encryption (WEP encryption is optional) and (d) Static IP address.
In order to use the Setup Wizard to configure the Dell Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point, the access point must be
directly connected via an ethernet cable to the computer that is running the Setup Wizard. In this configuration, the Dell Wireless
4350 Small Network Access Point will have a default static IP address of 192.168.2.2 and the computer will have to be assigned a
static IP address in the same subnet.
How to assign a static IP address to the network card of your computer
This section contains information on how to assign a static IP address to the network card of your computer. This is required as
part of the access point configuration.
How to assign a static IP address to the network card of your computer
1. On your computer, click Start -- > Settings - -> Control Panel .
Double click the Network Connections icon.
2.
Right click the Local Area Connection icon.
3.
Select Properties from the pull- down menu.
4.
Click Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) and then Properties.
5.
Page 11

6.
Select Use the following IP address in the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties window.
7. Input your IP address and Sumnet mask in the appropriate fields. (The IP addresses on your network must be within the
same range (e.g. 192.168.2.3 or 192.168.2.4). The subnet mask must be the same for all computers on the network (i.e.
255.255.255.0).
Click OK.
8.
Back to Top
Back to Contents Page
Page 12
Back to Contents Page
Connecting the Access Point to the network
NOTE:It is recommended that you follow the instructions in the Quick Start Guide on connecting the Dell Wireless 4350 Small
Network Access Point to the network.
The following are the relevant steps on connecting the access point to your network.
1. Find the optimum location for your Access Point. The Access Point should be located at the center of your wireless network,
ideally with line of sight to all your mobile stations.
2. Fix the orientation of the antennas such that both antennas are perpendicular to the ground and parallel to each other
3. Connect the included Ethernet cable to the Access Point and the other end of the Ethernet cable to a switch or hub.
4. Connect the power adapter to the Access Point’s power port.
Back to Contents Page
Page 13

Back to Contents Page
How to obtain the IP Address of the Access Point
To browse to the Dell Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point's web - based configuration tool, you must known the access
point's IP address. The IP address of the access point can be either a static IP address or a dynamically assigned IP address. The
default configuration for the access point is with a static IP address of 192.168.2.2.
If the access point has been configured as a DHCP client, it will be dynamically assigned a IP address. In order to determine what
this IP address is, use the following method.
Find the Media Access Control (MAC) address of the wired port of the access point. This information can be derived from the
1.
product label which is located on the underside of the access point .
2. The product label contains the MAC address of the WLAN port of the access point. The MAC address of the wired port is
calculated by subtracting 0x1H from this address (i.e. If the MAC address on the product label is 00:90:4b:3c:12:10, then the MAC
address of the wired port is 00:90:4b:3c:12:10 - 0x1 = 00:90:4b:3c:12:0f)
Provide your organisation's network administrator with your access point's wired port MAC address (calculated in step 2).
3.
The network administrator will query the DHCP server using the MAC address to identify the IP address of the access point.
4.
Back to Contents Page
Page 14

Back to Contents Page
Setting Wireless Encryption in Your Access Point
Without wireless security options configured in your network, an eavesdropper within your wireless range may be able to access
the network and the data that is being transmitted over it. The Dell Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point provides Wired
Equivalent Privacy (WEP) and Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) encryption for wireless security.
WPA is an upgrade to the WEP standard for securing your wireless network.
If you would like to secure your wireless network using WPA, you must have WPA support for your wireless clients. If you are
using a Dell Wireless client, you can check for the availability of a WPA-enabled software update for your wireless client at
http://support.dell.com. The WPA -802.1x protocols supported by the Dell Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point are PEAP,
TTLS & TLS.
Log into the web configuration of your access point using it's IP address (for information on obtaining the access point's IP
1.
address see
Type the following text in the user name and password fields: "admin".
2.
Click Basic Settings and then select Wireless Security from the drop down menu.
3.
Click to select Enable Wireless Security.
4.
Select either WEP or WPA in the Network Encryption list.
5.
How to obtain the IP Address of the Access Point). The Enter Network Password login prompt appears.
WEP
1. Select hexadecimal or ASCII characters as the Key Format. You can use either as a string of hexadecimal digits (characters 0
through 9 and A through F ) or as ASCII characters (any key on the keyboard).
Select an encryption level from the Key Length list.
2.
Enter four different keys in the Key1, Key2, Key3, and Key4 fields to store on your router. For 40(64) -bit encryption, enter a
3.
5-character (or 10 hexadecimal digits) WEP key. For 104(128)- bit encryption, enter a 13 - character (or 26 hexadecimal digits) WEP
key.
Select only one key out of the four keys as the Default Key for encryption.
4.
Click the NEXT button, and then click Save and Restart to apply the changes.
5.
Set up the WEP on your wireless clients. Refer to the documentation that accompanied your wireless clients, or your wireless
6.
clients' on -line help systems, for information on how to set up WEP.
WPA
There are two options for network authentication (a) Pre -shared key or (b) 802.1x . Typically, in enterprises, WPA will be used in
conjunction with a RADIUS authentication server. In a Small Office/Home Office (SOHO) environment, where there is no
authentication server, users can use pre- shared key (PSK) mode in place of the authentication server.
WPA-PSK
Choose a key format by selecting either Hexadecimal Digits or ASCII Characters in the Key Format field. Hexadecimal digits
1.
are numbers 0- 9 and/or letters A-F. ASCII characters can be any key on the keyboard.
Enter your pre -shared key in the WPA Pre-Shared Key field. This key must match the key that is used by each wireless client
2.
computer associated to your Access Point
Page 15

3. The WPA Group Rekey Interval value specifies how often the key “rotates” or changes.
WPA Encryption allows you to select one of two possible encryption methods—TKIP and AES. Choose one that your wireless
4.
clients support.
Click the NEXT button, and then click Save and Restart to apply the changes.
5.
Set up WPA -PSK on your wireless clients. Refer to the documentation that accompanied your wireless clients, or your wireless
6.
clients' on -line help system, for information on how to setup WPA -PSK.
WPA-802.1x
WPA Encryption allows you to select one of two possible encryption methods—TKIP and AES. Choose one that your wireless
1.
clients support.
The Radius Server IP, Radius Server Port and Shared Secret fields required to be populated with the relevant information.
2.
This information regarding the Radius authentication server can be obtained from the network administrator.
The WPA Group Rekey Interval value specifies how often the key “rotates” or changes.
3.
Click the NEXT button, and then click Save and Restart to apply the changes.
4.
Set up WPA -802.1x on your wireless clients. Refer to the documentation that accompanied your wireless clients, or your
5.
wireless clients' on -line help system, for information on how to setup WPA with 802.1x authentication.
NOTE:The Dell Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point offers three ways to set the wireless encryption in your router. One
is the Wireless Security feature in the web configuration tool mentioned here. The other two are either through the
Windows-based
control utility or the Setup Wizard.
Back to Contents Page
Page 16

Back to Contents Page
Turning Off Broadcast SSID
1. Log into the web configuration of your Access Point using it's IP address (for information on obtaining the Access Point's IP
address see
2. Type the following text in the user name and password fields: "admin".
3. Click Advanced Settings and then select Advanced Wireless from the drop down menu.
4. Check Yes for Hide my wireless network
5. Click Submit.
Back to Contents Page
How to obtain the IP Address of the Access Point). The Enter Network Password login prompt appears.
Page 17
Back to Contents Page
Setting Up File & Printer Sharing
Installing File and Printer Sharing
Sharing a printer
Sharing files
Installing the File & Printer Sharing
Follow the instructions below to install the file and printer sharing service.
For Windows 2000 and XP
1. Right-click the My Network Places icon (on the desktop in Windows 2000 and in the Start button menu in Windows XP)
and left - click to select Properties in menu.
2. Right-click the Local Area Connection icon and select Properties in the menu.
3. If you can see the File and Printer Sharing for Microsoft Networks item, you can skip this section. The file and printer
sharing service had already been installed.
4. If the File and Printer Sharing for Microsoft Networks item is not present, click the Install button.
5. Click to select Service, and then click the Add button.
6. Click to select File and printer sharing for Microsoft Networks , and then click the OK button.
Sharing a Printer
To share a printer, perform the following steps on the computer that has the printer you wish to share.
1. Click the Start button, click Settings, and then click Printers.
2. Click the printer you want to share to highlight it.
3. On the File menu, click Properties.
4. Click the Sharing tab, and then click Shared As .
5. Follow the on - screen instructions to complete.
The printer is now available for the other computers to use.
Perform the following steps on the other computers:
1. Click the Start button, click Settings, and then click Printers.
2. Double-click the Add Printer icon.
3. Click Next on the first screen.
Page 18
4. On the next screen, select Network printer, and then click the Next button.
5. Click the Browse button and click to select the shared printer.
6. Follow the on - screen instructions to complete.
Sharing files
You can share files on your computer so that users on other computers on your network can view them.
1. In Microsoft Windows Explorer, right- click on the file, folder, or drive letter you wish to share and left- click Sharing.
2. Click Share As .
3. Type a name for the share and follow the on -screen instructions to complete.
Back to Contents Page
Page 19
Back to Contents Page
How to setup wireless clients to connect to the Access Point
NOTE:It is recommended that you connect wireless clients to the Dell Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point using the
Setup Wizard provided on the Dell Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point CD.
Back to Top
Back to Contents Page
Page 20

Back to Contents Page
Using Your Access Point:
Dell™ Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point User's Guide
Overview
Factory Default Settings
Setup Wizard
Control Utility
Web- Based Configuration Tool
Overview
Factory Default Settings: Your Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point came with factory default settings that should work for
the majority of the network usage scenarios. However, there are cases where your network environment may require a different
access point configuration.
Setup Wizard : Setup Wizard is a Windows -based software program included on your Dell Wireless 4350 Small Network Access
Point CD. You can use this program to 1) configure the access point before connecting it to the network, 2) add wireless clients to
the network, 3) install the Control Utility on your computer and 4) provide links to the user's guide and the
Control Utility: Control Utility is a Windows -based software program included on your Dell Wireless 4350 Small Network Access
Point CD. This utility can be installed on your computer by choosing the Install Control Utility option in the Setup Wizard. It provides
you with a useful configuration tool to manage your Dell Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point. Refer to the section
Utility for detailed information.
Web- Based Configuration Tool: The web- based configuration tool is for advanced configuration of the Dell Wireless 4350 Small
Network Access Point. It is a tool provided inside the access point which can be accessed via the web browser on your computer.
This tool includes every basic and advanced configuration option for the Dell Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point. For
instance, you can enable multiple virtual AP's or disable your wireless network.
NOTE:The Setup Wizard and Control Utility must be run on Windows 2000 or Windows XP computers. Microsoft Internet
Explorer 4.0 or higher or Netscape 4.0 or higher must be used for the web-based configuration tool.
Back to Contents Page
Dell support website.
Control
Page 21

Back to Contents Page
Factory Default Settings:
Dell™ Wireless 4350 Access Network Access Point User's Guide
Dell pre-configures the Dell Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point with the following settings:
NOTE:If you lose track of the device settings, you can reset the router by pushing the reset button to restore these settings back
to your router.
Setting Default
User Name admin
Password admin
AP Host Name Dell_4350_AP
IP Address Static IP address of 192.168.2.2
Subnet Mask 255.255.255.0
ESSID (wireless network name) wireless
Channel auto
Encryption No Encryption
Guest Mode Disabled
NOTE:Your Dell Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point comes with factory default settings that should work for the majority
of the network usage scenarios. However, there are cases where your network environment may require a different
configuration.
Back to Contents Page
Page 22

Back to Contents Page
Setup Wizard: Dell™ Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point
User's Guide
Introduction
Launch the Setup Wizard
Setup Wizard Screens
Introduction
The Setup Wizard is an easy -to-use program included on your Dell Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point CD. It provides
simplified steps for configuring the Access Point. The Setup Wizard displays a series of graphical illustrations on how to connect
the Access Point to your computer. It presents the user with the option of changing wireless parameters (such as SSID, channel
number, IP address) and enabling WEP security. Finally it applies these settings to your access point and validates its
configuration. At this point the access point is ready to be connected to the network. If the configuration cannot be completed
successfully, the Setup Wizard will display troubleshooting instructions to guide you through the configuration process.
In addition, the Setup Wizard also supports the installation of the Control Utility and provides links to the user's guide on the Dell
Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point CD and the Dell support website.
Back to Top
Launch the Setup Wizard
To run the Setup Wizard, perform the following steps:
Insert the CD
1. Insert the Dell Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point CD into the CD drive of a computer. Your CD should
automatically launch the Setup Wizard. If it does not, complete the following steps to start the Wizard.
Click the Start button, and then click Run.
a.
Type the following text in the Open: field:
b.
Page 23

X:\setup.exe
where X is the drive letter of your CD drive.
Once the Setup Wizard has been launched, you will be guided through a series of windows. These windows are illustrated below
along with an explanation on their functionalities.
Back to Top
Setup Wizard Screens
Welcome Menu
This menu offers several options to select from.
AP Configuration
·
Begin connecting your access point to the network, it's wireless and security parameters need to be configured.
Connect Wireless Computer
·
Configure wireless computers to connect to the wireless network.
Install Control Utility
·
Install the Control Utility on a computer
User's Guide
·
View the user's guide (this document)
Exit
·
End the Setup Wizard
Welcome
Page 24
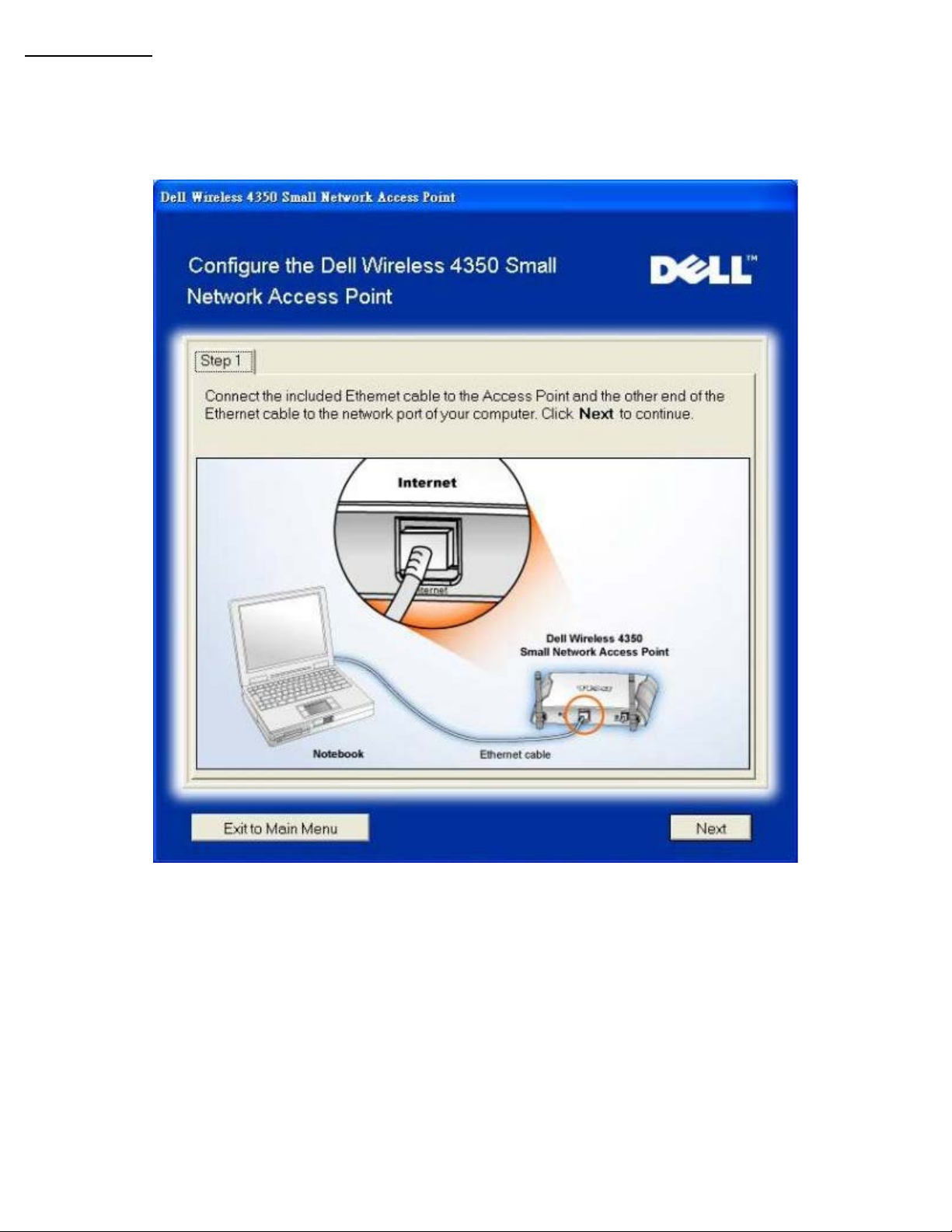
AP Configuration
Click AP Configuration if you want to configure the access point before connecting it to the network and follow the steps
described below.
Step 1 illustrates how the computer is to be connected to the Dell Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point.
Configure AP: Step 1
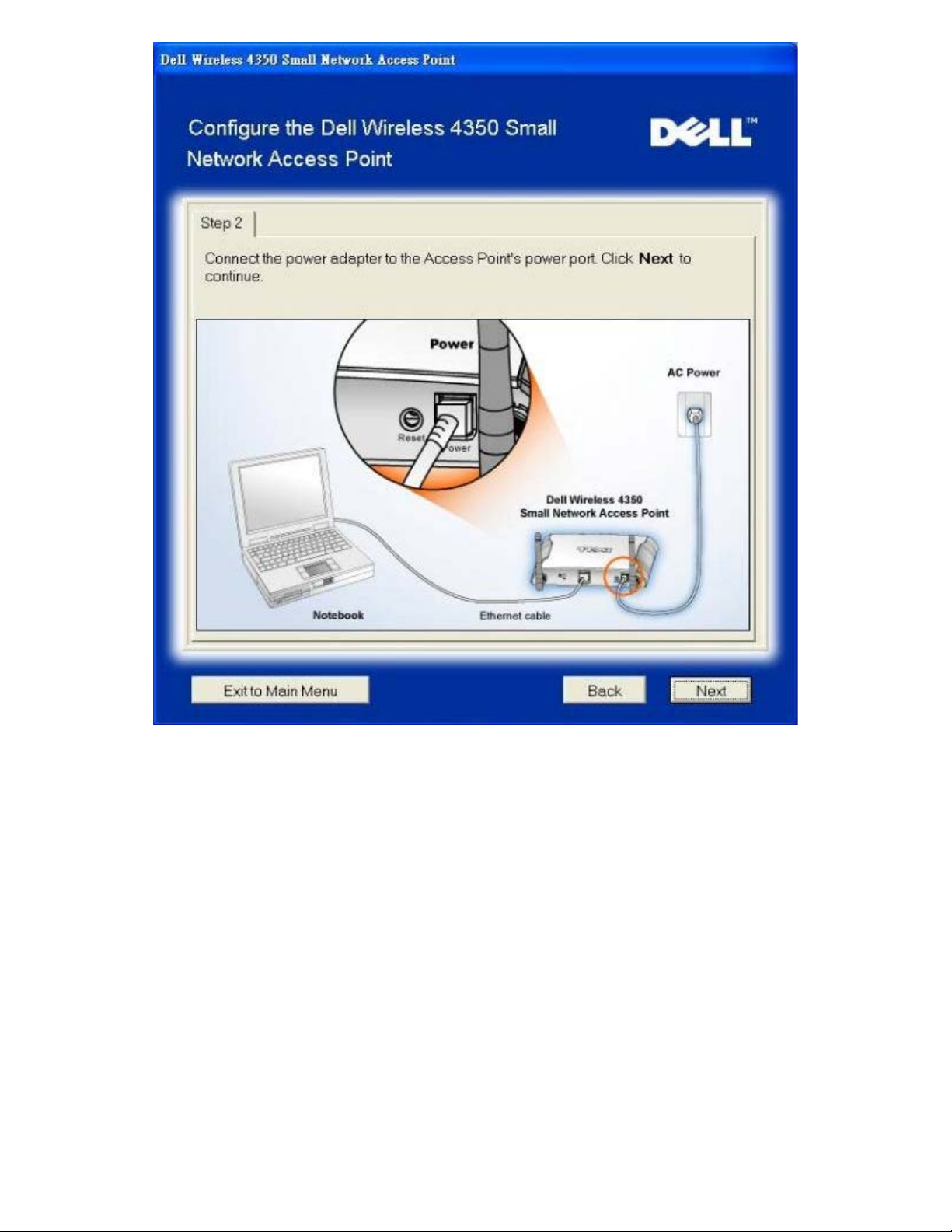
Step 2 illustrates how the Dell Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point is connected to the power supply.
Configure AP: Step 2
Page 25
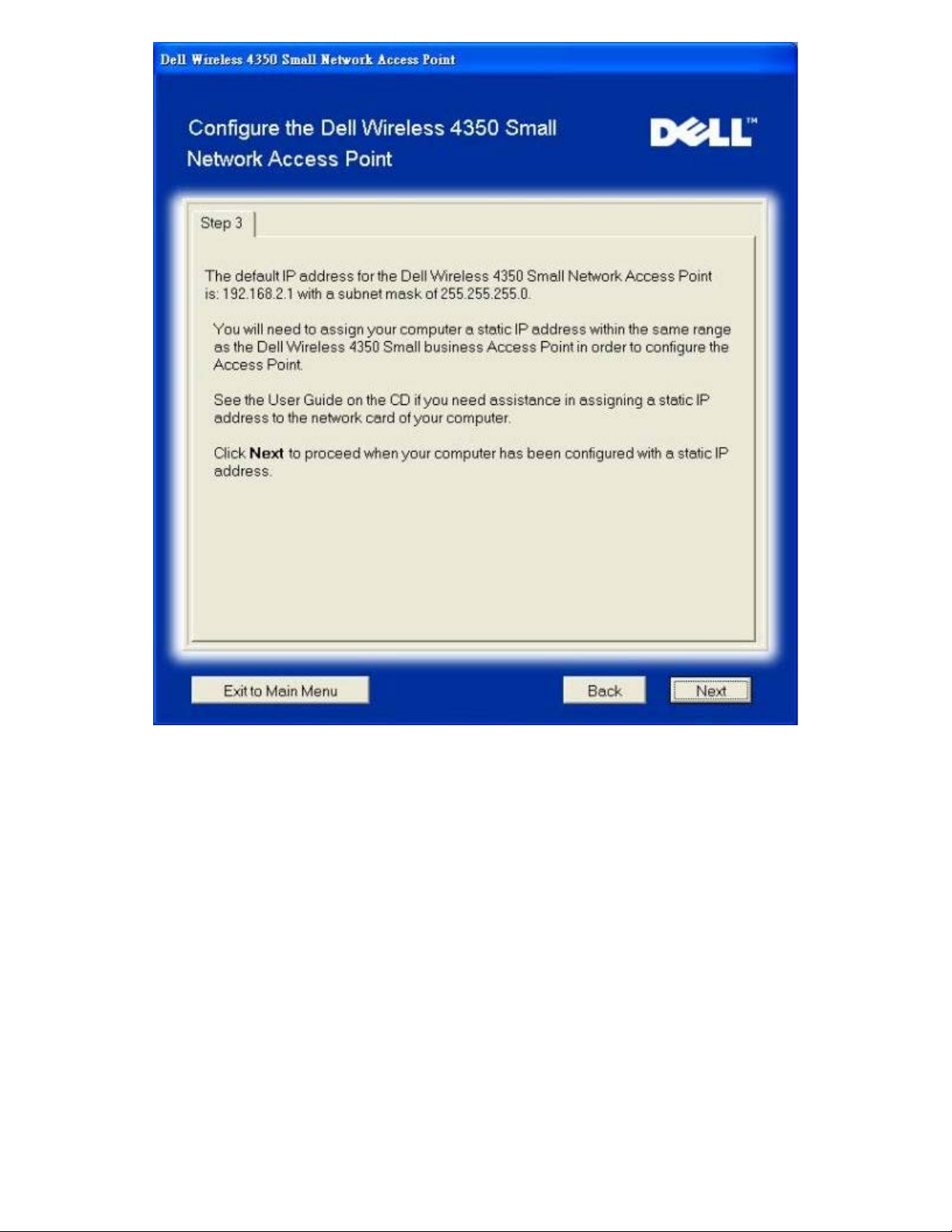
Step 3 informs the user that you need to assign your computer a static IP address within the same range as the access point. .
Configure AP: Step 3
Page 26
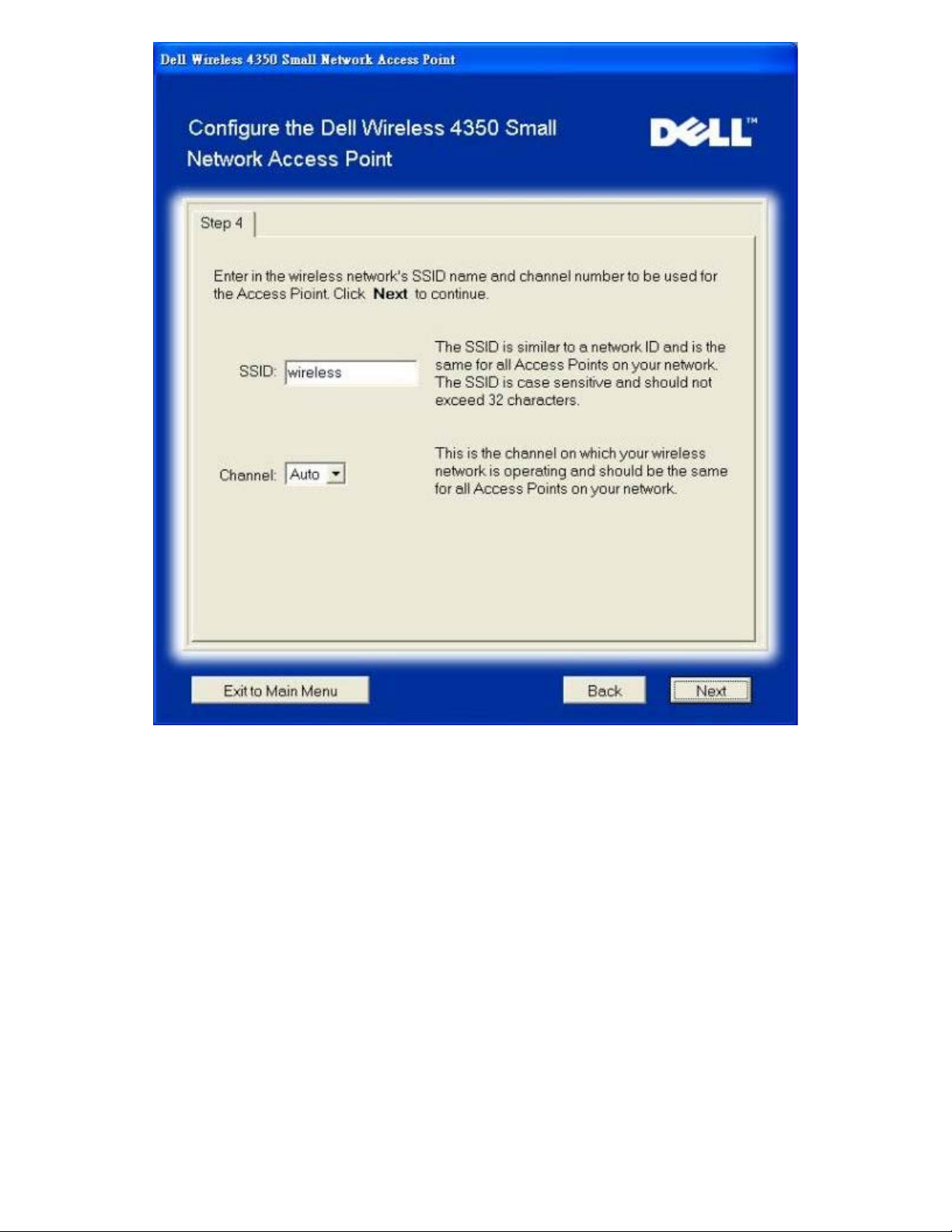
Step 4 gives the user the option to change the wireless network’s SSID and channel number.
Configure AP: Step 4
Page 27
Step 5 gives the user the option to enable WEP wireless encryption and to specify the WEP encryption key values.
Configure AP: Step 5
Page 28
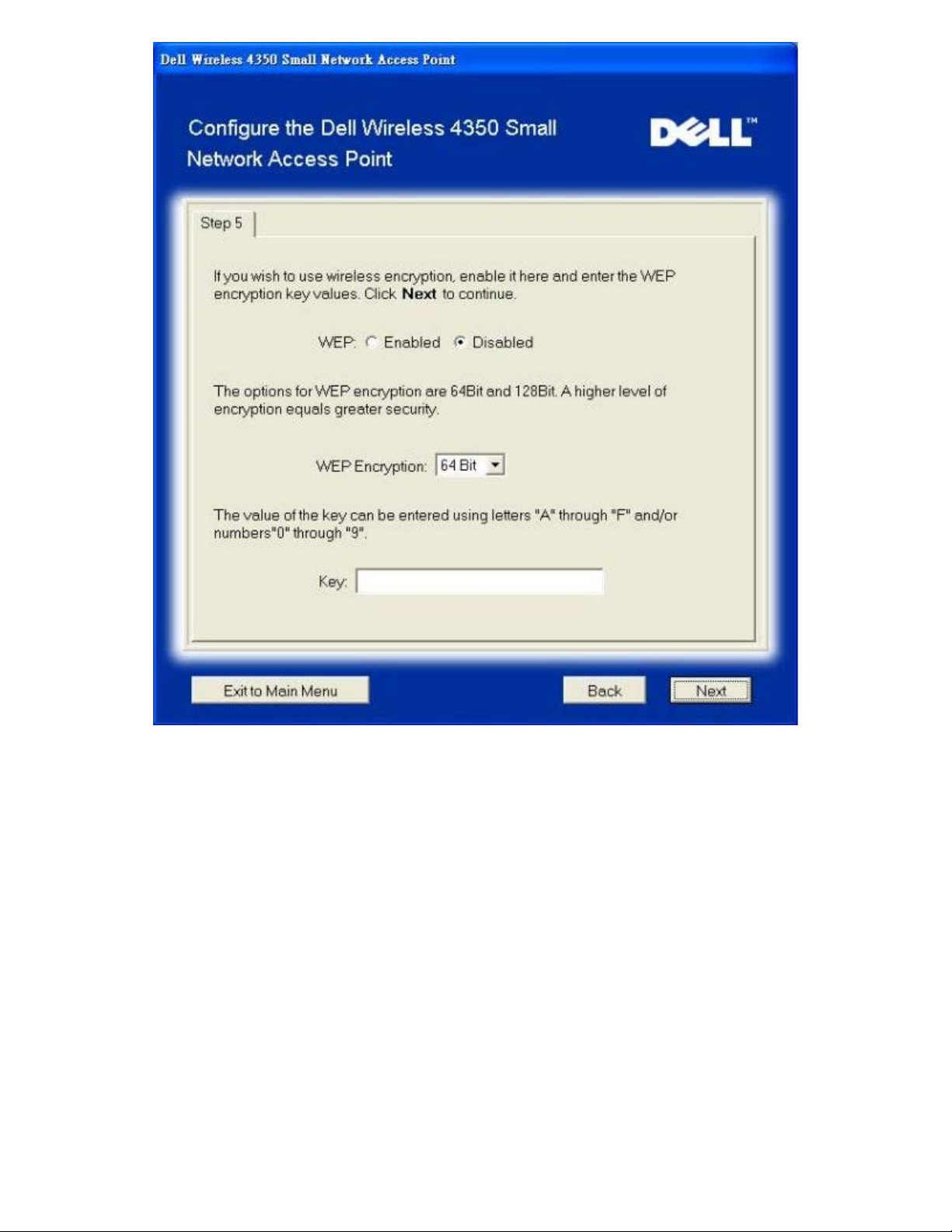
Step 6 gives the user the option to either change the static IP address or set the access point as a DHCP client.
Configure AP: Step 6
Page 29
Step 7 informs the user to wait until the Access Point configuration is finished.
Configure AP: Step 7
Page 30
.
Step 8 is a congratulations screen if the user has successfully configured the Dell Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point.
Configure AP: Step 8
Page 31

Step 9 is an optional screen that displays the configuration settings chosen by the user.
Configure AP: Step 9
Page 32

Back to Top
Connect Wireless Computer
To connect computers to your wireless network after you have successfully configured and installed the Access Point, place the
Dell Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point CD into each computer and run the Setup Wizard. Click Connect Wireless
Computer to add each wireless computer to your network.
Setup Wireless Computer - Win XP (No Encryption)
Pressing the Setup Wireless Computer button displays instructions to connect computers to the network through a wireless
connection.
Step 1 asks the user to enter the SSID of the wireless network that you wish to connect to.
Setup Wireless Computer: Step 1
Page 33

Step 2 asks the user to wait while the Setup Wizard does a site survey scanning for the requested wireless network.
Setup Wireless Computer: Step 2
Page 34

Step 3 guides the user through using the Windows wireless configuration utility to configure the wireless client.
Setup Wireless Computer: Step 3
Page 35

Step 4 guides the user through the remaining steps in using the Windows wireless configuration utility to configure the wireless
client.
Setup Wireless Computer: Step 4
Page 36

Step 5 informs the user to wait while the wireless client configuration is being verified.
Setup Wireless Computer : Step 5
Page 37

Step 6 informs the user that the wireless client is successfully configured and is now on the wireless network.
Setup Wireless Computer : Step 6
Page 38

Setup Wireless Computer - Win XP (WEP Encryption)
Pressing the Setup Wireless Computer button displays instructions to connect computers to the network through a wireless
connection.
Step 1 asks the user to enter the SSID of the wireless network that you wish to connect to.
Setup Wireless Computer: Step 1
Page 39

Step 2 asks the user to wait while the Setup Wizard does a site survey scanning for the requested wireless network.
Setup Wireless Computer: Step 2
Page 40

Step 3 asks the user to enter the WEP key of the wireless network that they wish to connect to.
Setup Wireless Computer: Step 3
Page 41

Step 4 guides the user through using the Windows wireless configuration utility to configure the wireless client.
Setup Wireless Computer: Step 4
Page 42

Step 5 guides the user through the remaining steps in using the Windows wireless configuration utility to configure the wireless
client.
Setup Wireless Computer: Step 5
Page 43

Step 6 informs the user to wait while the wireless client configuration is being verified.
Setup Wireless Computer : Step 6
Page 44

Step 7 informs the user that the wireless client is successfully configured and is now on the wireless network.
Setup Wireless Computer : Step 7
Page 45

Setup Wireless Computer - Win XP SP2 (No Encryption)
Pressing the Setup Wireless Computer button displays instructions to connect computers to the network through a wireless
connection.
Step 1 asks the user to enter the SSID of the wireless network that you wish to connect to.
Setup Wireless Computer: Step 1
Page 46

Step 2 asks the user to wait while the Setup Wizard does a site survey scanning for the requested wireless network.
Setup Wireless Computer: Step 2
Page 47

Step 3 informs the user to wait while the wireless client is being configured to join the network.
Setup Wireless Computer : Step 3
Page 48

Step 4 informs the user that the wireless client is successfully configured and is now on the wireless network.
Setup Wireless Computer : Step 4
Page 49

Setup Wireless Computer - Win XP SP2 (WEP Encryption)
Pressing the Setup Wireless Computer button displays instructions to connect computers to the network through a wireless
connection.
Step 1 asks the user to enter the SSID of the wireless network that you wish to connect to.
Setup Wireless Computer: Step 1
Page 50

Step 2 asks the user to wait while the Setup Wizard does a site survey scanning for the requested wireless network.
Setup Wireless Computer: Step 2
Page 51

Step 3 asks the user to enter the WEP key of the wireless network that they wish to connect to.
Setup Wireless Computer: Step 3
Page 52

Step 4 informs the user to wait while the wireless client is being configured to join the network.
Setup Wireless Computer : Step 4
Page 53

Step 5 informs the user that the wireless client is successfully configured and is now on the wireless network.
Setup Wireless Computer : Step 5
Page 54

Back to Top
Back to Contents Page
Page 55

Back to Contents Page
Control Utility
Control Utility:
Dell™ Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point User's Guide
The Control Utility is Windows -based software that allows you to configure your Access Point and monitor the status of your Dell
Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point.
Install the Control Utility
Uninstall the Control Utility
Start the Control Utility
Using the Control Utility to manage multiple Access Points
Exit the Control Utility
How to configure the Access Point via the Control Utility ?
Install the Control Utility
You can install the Control Utility on your computer from your Dell Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point CD .
Insert the Dell Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point CD into the CD drive. Your CD should automatically launch the
1.
Setup Wizard program. If it does not, complete the following steps to start the Wizard.
Click the Start button, and then click Run.
a.
Type the following text in the Open: field: X:\setup.exe (where X is the drive letter of your CD drive).
b.
Click the OK button.
c.
From the main menu, click the Install Control Utility button.
2.
Follow the on -screen instructions.
3.
Back to Top
Uninstall the Control Utility
1. If the Dell Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point icon is displayed in the system tray in the lower right corner of the
screen, right -click the icon and click Exit.
Click the Start button.
2.
Click Control Panel . The Control Panel window appears.
3.
Click the Add/Remove Programs icon.
4.
Click to select the
5.
from the program list and remove it as instructed.
Page 56

Back to Top
Start the Control Utility
The control utility program will run automatically upon each computer startup by default. If the utility does not start automatically,
run the Dell Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point Dell Control Utility from the Start menu.
Once running, a access point icon is created in the system tray in the lower right corner of your screen. If you have a connection
to the access point, the system tray icon looks gray and white
NOTE:
Back to Top
If the icon is red
, it indicates that the connection to the access point failed.
. You can double- click the icon to open the utility panel.
Using the Control Utility to manage multiple Access Points
The control utility program can be used to manage multiple Dell Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Points. When the Control
Utility launches it will connect to the last access point configured. If you wish to configure an alternative Dell Wireless 4350 Small
Network Access Point on the network, then follow the instructions below.
Start the Dell Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point Control Utility.
1.
In the My Network Overview tab, enable the Configure Alternative AP checkbox.
2.
Enter the IP address of the alternative Dell Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point that you wish to configure in the IP
3.
Address field.
Click Apply
4.
5. The Control Utility will then shutdown. After restarting the Control Utility, it will have connected to the alternative Dell Wireless
4350 Small Network Access Point.
Back to Top
Exit the Control Utility
When you start the control utility program, it will place a small gray and white icon in the system tray in the lower right corner of
your screen. If you want to exit the program, right-click the icon, and then left -click Exit to quit the program.
Back to Top
Back to Contents Page
Page 57

Back to Contents Page
Web-based Configuration Tool:
Dell™ Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point User's Guide
Overview
Basic Settings
Device Status
System Tools
Advanced Settings
Log Off
Overview
The web-based configuration tool enables you to set up advanced network configuration for your Dell Wireless 4350 Small Network
Access Point. Follow the instructions below to gain access to the web tool.
NOTE:Microsoft Internet Explorer 4.0 or higher or Netscape 4.0 or higher must be used for the web-based configuration tool.
Click the Start button, and then click Run.
1.
Type the IP address of the Dell Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point into the Open box: (for information on obtaining this IP
2.
address see
If this is the first time configuring your Dell Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point, or if the user name and password have not
3.
been changed, type admin in the User Name and Password fields.
Click the OK button. The Configuration screen appears.
4.
NOTE:Dell technical support representatives do not support the configuration options in the Advanced Settings portion of the
How to obtain the IP Address of the Access Point ).
configuration program. These options are provided for your convenience only. However, the advanced settings are fully
documented and explained in this guide.
Main Menu
Page 58

Back to Top
Log Off
The Log Off button logs the user off the web based configuration tool. This configuration tool only allows access to one user at a time.
Back to Top
Back to Contents Page
Page 59

Back to Contents Page
Technical Specifications and Regulatory Information:
Dell™ Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point User's Guide
Technical Specifications
Regulatory Information
Limited Warranties and Return Policy
Wireless Interoperability
The Dell Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point products are designed to be interoperable with any wireless LAN product that
is based on direct sequence spread spectrum (DSSS) and orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) radio technology and
to comply with the following standards:
IEEE 802.11b Standard on Wireless LAN
IEEE 802.11g Standard on Wireless LAN
Wireless Fidelity (WiFi) certification, as defined by the WECA (Wireless Ethernet Compatibility Alliance)
Wireless 802.11 and Your Health
The Dell Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point, like other radio devices, emits radio frequency electromagnetic energy. The
level of energy emitted by this device, however, is less than the electromagnetic energy emitted by other wireless devices such as
mobile phones. The Dell Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point device operates within the guidelines found in radio frequency
safety standards and recommendations. These standards and recommendations reflect the consensus of the scientific community
and result from deliberations of panels and committees of scientists who continually review and interpret the extensive research
literature. In some situations or environments, the use of the DDell Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point devices may be
restricted by the proprietor of the building or responsible representatives of the applicable organization. Examples of such situations
include the following:
Using the Dell Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point equipment on board airplanes, or
Using the Dell Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point equipment in any other environment where the risk of interference
with other devices or services is perceived or identified as being harmful.
If you are uncertain of the policy that applies to the use of wireless devices in a specific organization or environment (an airport, for
example), you are encouraged to ask for authorization to use the Dell Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point device before you
turn it on.
Back to Top
Technical Specifications
Standards supported IEEE 802.3, IEEE 802.3u, IEEE802.11b, 802.11g
Protocols TCP/ IP, IPX, UDP, DHCP Client, DHCP Proxy
Environment ·
Operating Humidity 10% to 85% (Non-Condensing)
Storage Humidity 5% to 90% (Non- Condensing)
·
Page 60

·
Operating Temperature 0° to 40° C (32° F to 104° F)
· Storage Temperature 0° to 70° C (32° F to 158° F)
Power specification Receive Sensitivity
11Mbps: 10-5 BER @ - 80 dBm, typical
·
54Mbps: 10-5 BER @ - 65 dBm, typical
·
Transmit Power
Normal Temp Range: ±12 dBm
·
DC power supply
Input: AC 100-250 50- 60 Hz 1A
·
Output: 5V DC 2A
·
Power over Ethernet
·
Radio specification
Range: "Up to 100m" indoors and "Up to 450m" outdoors (open range)
Specific features
Frequency range: 2.4 - 2.4835 GHz, direct sequence spread spectrum
Number of Channels:
Europe: 13 (1 -13)
·
US: 11 (1 -11 )
·
France: 2 (10-11 )
·
Japan: 11 (1- 13 )
·
Taiwan: 11 (1 -11)
·
Mobility: Seamless roaming across cell boundaries with handover
Supported bit rates:
For 802.11g:
54 Mbps
·
48 Mbps
·
36 Mbps
·
24 Mbps
·
18 Mbps
·
12 Mbps
·
9 Mbps
·
6 Mbps
·
For 802.11b:
11 Mbps
·
5.5 Mbps
·
2 Mbps
·
Page 61

· 1 Mbps
Data Encryption: WEP (64/128 bit) and WPA
Utility Software ·
Back to Top
Setup Wizard software
Control Utility software
·
Regulatory Information
The Dell Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point device must be installed and used in strict accordance with the manufacturer's
instructions as described in the user documentation that comes with the product. For country -specific approvals, see Radio
approvals. Dell Inc is not responsible for any radio or television interference caused by unauthorized modification of the devices
included with this Dell Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point kit, or the substitution or attachment of connecting cables and
equipment other than that specified by Dell Inc. The correction of interference caused by such unauthorized modification,
substitution or attachment is the responsibility of the user. Dell Inc and its authorized resellers or distributors are not liable for any
damage or violation of government regulations that may arise from the user failing to comply with these guidelines.
For the latest regulatory information, documentation, and other updates, please visit the Dell website at
support.dell.com.
Canada -- Industry Canada (IC)
This device complies with RSS210 of Industry Canada.
Back to Top
Europe -- EU Declaration of Conformity
This equipment complies with the essential requirements of the European Union directive 1999/5/EC.
Cet équipement est conforme aux principales caractéristiques définies dans la Directive européenne RTTE 1999/5/CE.
Die Geräte erfüllen die grundlegenden Anforderungen der RTTE-Richtlinie 1999/5/EG.
Questa apparecchiatura è conforme ai requisiti essenziali della Direttiva Europea R&TTE 1999/5/CE.
Este equipo cumple los requisitos principales de la Directiva 1999/5/CE de la UE, "Equipos de Terminales de Radio y
Telecomunicaciones".
Este equipamento cumpre os requisitos essenciais da Directiva 1999/5/CE do Parlamento Europeu e do Conselho (Directiva RTT).
Deze apparatuur voldoet aan de noodzakelijke vereisten van EU- richtlijn betreffende radioapparatuur en telecommunicatieeindapparatuur 1999/5/EG.
Dette udstyr opfylder de Væsentlige krav i EU's direktiv 1999/5/EC om Radio- og teleterminaludstyr.
Dette utstyret er i overensstemmelse med hovedkravene i R&TTE - direktivet (1999/5/EC) fra EU.
Utrustningen uppfyller kraven för EU-direktivet 1999/5/EC om ansluten teleutrustning och ömsesidigt erkännande av utrustningens
överensstämmelse (R&TTE).
Tämä laite vastaa EU:n radio- ja telepäätelaitedirektiivin (EU R&TTE Directive 1999/5/EC) vaatimuksia.
Back to Top
France
Some areas of France have a restricted frequency band. The worst- case maximum authorized power indoors is:
10 mW for the entire 2.4 GHz band (2400 MHz - 2483.5 MHz)
100 mW for frequencies between 2446.5 MHz and 2483.5 MHz (NOTE - Channels 10 through 13 inclusive operate in the band
2446.6 MHz - 2483.5 MHz)
Page 62

There are few possibilities for outdoor use: On private property or on the private property of public persons, use is subject to a
preliminary authorization procedure by the Ministry of Defence, with maximum authorized power of 100 mW in the 2446.5 - 2483.5
MHz band. Use outdoors on public property is not permitted.
In the departments listed below, for the entire 2.4 GHz band:
Maximum authorized power indoors is 100 mW
Maximum authorized power outdoors is 10 mW
Departements in which the use of the 2400 - 2483.5 MHz band is permitted with an EIRP of less than 100 mW indoors and less
than 10 mW outdoors:
01 Ain Orientales 36 Indre 66 Pyrénées
02 Aisne 37 Indre et Loire 67 Bas Rhin
03 Allier 41 Loir et Cher 68 Haut Rhin
05 Hautes Alpes 42 Loire 70 Haute Saône
08 Ardennes 45 Loiret 71 Saône et Loire
09 Ariège 50 Manche 75 Paris
11 Aude 55 Meuse 82 Tarn et Garonne
12 Aveyron 58 Nièvre 84 Vaucluse
16 Charente 59 Nord 88 Vosges
24 Dordogne 60 Oise 89 Yonne
25 Doubs 61 Orne 90 Territoire de Belfort
26 Drôme 63 Puy du Dôme 94 Val de Marne
32 Gers 64 Pyrénées Atlantique
This requirement is likely to change over time, allowing you to use your wireless LAN card in more areas within France. Please
check with ART for the latest information (
NOTE:Your Dell Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point transmits less than 100 mW, but more than 10 mW.
Back to Top
www.art-telecom.fr)
Italia
A license is required for indoor use. Outdoor use is prohibited.
E' necessaria la concessione ministeriale anche per l'uso interno. Verificare con i rivenditori la procedura da seguire. L'uso per
installazione in esterni non e' permessa.
Back to Top
USA -- Federal Communications Commission (FCC)
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation of the device is subject to the following two conditions:
This device may not cause harmful interference.
This device must accept any interference that may cause undesired operation.
Dell declares that WAPA-118GD ( FCC ID: MXF- A930909G ) is limited in CH1~CH11 for 2.4GHz by specified firmware controlled
in U.S.A.
Interference statement
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC
Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential installation. This
equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy. If the equipment is not installed and used in accordance with
the instructions, the equipment may cause harmful interference to radio communications. There is no guarantee, however, that such
Page 63

interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or television
reception (which can be determined by turning the equipment off and on), the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference
by taking one or more of the following measures:
Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
Increase the distance between the equipment and the receiver.
Connect the equipment to an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is connected.
Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
NOTE:This Dell Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point device must be installed and used in strict accordance with the
manufacturer's instructions as described in the user documentation that comes with the product. Any other installation or
use will violate FCC Part 15 regulations.
IMPORTANT NOTE
FCC RF Radiation Exposure Statement
This equipment complies with FCC RF radiation exposure limits set forth for an uncontrolled environment. This equipment should
be installed and operated with a minimum distance of 20 centimeters between the radiator and your body. This transmitter must
not be co - located or operating in conjunction with any other antenna or transmitter.
Radio approvals
To determine whether you are allowed to use your wireless network device in a specific country, please check to see if the radio
type number that is printed on the identification label of your device is listed on the radio approval list posted on the general Dell
support site at
Back to Top
support.dell.com.
Limited Warranties and Return Policy
Dell-branded hardware products purchased in the U.S. or Canada come with either a 90 day (U.S. only), one - year, two- year, three -year, or four -year limited warranty. To determine
which warranty you purchased, see the invoice that accompanied your hardware product(s).
The following sections describe the limited warranties and return policy for the U.S., the
limited warranties and return policy for Canada, and the manufacturer guarantee for Latin
America and the Caribbean.
Limited Warranty for the U.S.
What is covered by this limited warranty?
This limited warranty covers defects in materials and workmanship in your - our end-user
customer's - Dell- branded hardware products, including Dell -branded peripheral products.
What is not covered by this limited warranty?
This limited warranty does not cover:
• Software, including the operating system and software added to the Dell -branded
hardware products through our factory-integration system, third- party software, or the
reloading of software
• Non-Dell - branded products and accessories
• Problems that result from:
- External causes such as accident, abuse, misuse, or problems with electrical power
- Servicing not authorized by us
- Usage that is not in accordance with product instructions
- Failure to follow the product instructions or failure to perform preventive maintenance
Page 64

- Problems caused by using accessories, parts, or components not supplied by us
• Products with missing or altered service tags or serial numbers
• Products for which we have not received payment
THIS WARRANTY GIVES YOU SPECIFIC LEGAL RIGHTS, AND YOU MAY ALSO HAVE
OTHER RIGHTS WHICH VARY FROM STATE TO STATE (OR JURISDICTION TO
JURISDICTION). DELL'S RESPONSIBILITY FOR MALFUNCTIONS AND DEFECTS IN
HARDWARE IS LIMITED TO REPAIR AND REPLACEMENT AS SET FORTH IN THIS
WARRANTY STATEMENT. ALL EXPRESS AND IMPLIED WARRANTIES FOR THE
PRODUCT, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO ANY IMPLIED WARRANTIES AND
CONDITIONS OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE,
ARE LIMITED IN TIME TO THE TERM OF THE LIMITED WARRANTY PERIOD
REFLECTED ON YOUR INVOICE. NO WARRANTIES, WHETHER EXPRESS OR
IMPLIED, WILL APPLY AFTER THE LIMITED WARRANTY PERIOD HAS EXPIRED.
SOME STATES DO NOT ALLOW LIMITATIONS ON HOW LONG AN IMPLIED
WARRANTY LASTS, SO THIS LIMITATION MAY NOT APPLY TO YOU.
WE DO NOT ACCEPT LIABILITY BEYOND THE REMEDIES PROVIDED FOR IN THIS
LIMITED WARRANTY OR FOR CONSEQUENTIAL OR INCIDENTAL DAMAGES,
INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITATION, ANY LIABILITY FOR THIRD PARTY CLAIMS
AGAINST YOU FOR DAMAGES, FOR PRODUCTS NOT BEING AVAILABLE FOR USE,
OR FOR LOST DATA OR LOST SOFTWARE. OUR LIABILITY WILL BE NO MORE
THAN THE AMOUNT YOU PAID FOR THE PRODUCT THAT IS THE SUBJECT OF A
CLAIM. THIS IS THE MAXIMUM AMOUNT FOR WHICH WE ARE RESPONSIBLE. SOME
STATES DO NOT ALLOW THE EXCLUSION OR LIMITATION OF INCIDENTAL OR
CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES, SO THE ABOVE LIMITATION OR EXCLUSION MAY NOT
APPLY TO YOU.
How long does this limited warranty last ?
This limited warranty lasts for the time period indicated on your invoice, except that the
limited warranty on Dell- branded batteries lasts only one year and the limited warranty on
the lamps for Dell- branded projectors lasts only ninety days. The limited warranty begins on
the date of the invoice. The warranty period is not extended if we repair or replace a
warranted product or any parts. Dell may change the availability of limited warranties, at its
discretion, but any changes will not be retroactive.
What do I do if I need warranty service?
Before the warranty expires, please call us at the relevant number listed in the following
table. Please also have your Dell service tag number or order number available.
Individual Home Consumers:
Technical Support 1-800-624-9896
Customer Service 1-800-624-9897
Individual Home Consumers who purchased through an Employee Purchase
Program:
Technical Support and Customer Service 1-800-822-8965
Home and Small Business Commercial Customers:
Technical Support and Customer Service 1-800-456-3355
Medium, Large, or Global Commercial Customers, Healthcare Customers, and Value
Added Resellers (VARs):
Technical Support and Customer Service 1-800-822-8965
Government and Education Customers:
Technical Support and Customer Service 1-800-234-1490
Dell-Branded Memory 1-888-363-5150
What will Dell do?
During the first 90 days of the 90 -day limited warranty and the first year of all other
limited warranties : For the first 90 days of the 90- day limited warranty and the first year of
all other limited warranties, we will repair any Dell -branded hardware products returned to
us that prove to be defective in materials or workmanship. If we are not able to repair the
product, we will replace it with a comparable product that is new or refurbished.
Page 65

When you contact us, we will issue a Return Material Authorization Number for you to
include with your return. You must return the products to us in their original or equivalent
packaging, prepay shipping charges, and insure the shipment or accept the risk if the
product is lost or damaged in shipment. We will return the repaired or replacement products
to you. We will pay to ship the repaired or replaced products to you if you use an address in
the United States (excluding Puerto Rico and U.S. possessions and territories). Otherwise,
we will ship the product to you freight collect.
If we determine that the product is not covered under this warranty, we will notify you and
inform you of service alternatives that are available to you on a fee basis.
NOTE:Before you ship the product(s) to us, make sure to back up the data on the hard
drive(s) and any other storage device(s) in the product(s). Remove any
confidential, proprietary, or personal information and removable media such as
floppy disks, CDs, or PC Cards. We are not responsible for any of your
confidential, proprietary, or personal information; lost or corrupted data; or
damaged or lost removable media.
During the remaining years: For the remaining period of the limited warranty, we will
replace any defective part with new or refurbished parts, if we agree that it needs to be
replaced. When you contact us, we will require a valid credit card number at the time you
request a replacement part, but we will not charge you for the replacement part as long as
you return the original part to us within thirty days after we ship the replacement part to you.
If we do not receive the original part within thirty days, we will charge to your credit card
the then -current standard price for that part.
We will pay to ship the part to you if you use an address in the United States (excluding
Puerto Rico and U.S. possessions and territories). Otherwise, we will ship the part freight
collect. We will also include a prepaid shipping container with each replacement part for
your use in returning the replaced part to us.
NOTE:Before you replace parts, make sure to back up the data on the hard drive(s) and
any other storage device(s) in the product(s). We are not responsible for lost or
corrupted data.
What if I purchased a service contract ?
If your on -site service contract is with Dell, on- site service will be provided to you under the
terms of the on -site service agreement. Please refer to that contract for details on how to
obtain service.
If you purchased through us a service contract with one of our third -party service providers,
please refer to that contract for details on how to obtain service.
How will you fix my product?
We use new and refurbished parts made by various manufacturers in performing warranty
repairs and in building replacement parts and systems. Refurbished parts and systems are
parts or systems that have been returned to Dell, some of which were never used by a
customer. All parts and systems are inspected and tested for quality.
Replacement parts and systems are covered for the remaining period of the limited
warranty for the product you bought.
What do I do if I am not satisfied?
We pride ourselves on our great customer service. If you are not satisfied with the service
you receive under this limited warranty, please let us know. We have found that the best
way to resolve issues regarding our limited warranty is to work together. If, after those
discussions, you are still not satisfied, we believe arbitration is the most expeditious way to
resolve your concerns. Therefore, ANY CLAIM, DISPUTE, OR CONTROVERSY
Page 66

(WHETHER IN CONTRACT, TORT, OR OTHERWISE, WHETHER PREEXISTING,
PRESENT, OR FUTURE, AND INCLUDING STATUTORY, COMMON LAW,
INTENTIONAL TORT, AND EQUITABLE CLAIMS) AGAINST DELL arising from or relating
to this limited warranty, its interpretation, or the breach, termination, or validity thereof, the
relationships which result from this limited warranty (including, to the full extent permitted by
applicable law, relationships with third parties), Dell's advertising, or any related purchase
SHALL BE RESOLVED EXCLUSIVELY AND FINALLY BY BINDING ARBITRATION
ADMINISTERED BY THE NATIONAL ARBITRATION FORUM (NAF) under its Code of
Procedure then in effect (available via the Internet at
www.arb-forum.com or via telephone
at 1 - 800 -474-2371). The arbitration will be limited solely to the dispute or controversy
between you and Dell. Any award of the arbitrator(s) shall be final and binding on each of
the parties, and may be entered as a judgment in any court of competent jurisdiction.
Information may be obtained and claims may be filed with the NAF at P.O. Box 50191,
Minneapolis, MN 55405. This provision applies only to individual home consumers and
consumers who purchased through an employee purchase program. It does not apply to
small, medium, large, and global commercial customers or government, education, and
healthcare customers.
May I transfer the limited warranty?
Limited warranties on systems may be transferred if the current owner transfers ownership
of the system and records the transfer with us. The limited warranty on Dell -branded
memory may not be transferred. You may record your transfer by going to Dell's website:
• If you are an Individual Home Consumer, go to
www.dell.com/us/en/dhs/topics/sbtopic_015_ccare.htm
• If you are a Small, Medium, Large, or Global Commercial Customer, go to
www.dell.com/us/en/biz/topics/sbtopic_ccare_nav_015_ccare.htm
• If you are a Government, Education, or Healthcare Customer, or an Individual Consumer
who purchased through an employee purchase program, go to
www.dell.com/us/en/pub/topics/sbtopic_015_ccare.htm
If you do not have Internet access, call your customer care representative or call 1 -800624-9897.
"Total Satisfaction" Return Policy (U.S. Only)
We value our relationship with you and want to make sure that you're satisfied with your
purchases. That's why we offer a "Total Satisfaction" return policy for most products that
you, the end-user customer, purchase directly from Dell. Under this policy, you may return
to Dell products that you purchased directly from Dell for a credit or a refund of the
purchase price paid, less shipping and handling and applicable return fees as follows:
New Hardware Products and Accessories: Unless you have a separate agreement with
Dell, all hardware, accessories, peripherals, parts and unopened software still in its/their
sealed package,
excluding the products listed below, may be returned within twenty -one
(21) days from the date on the packing slip or invoice.
Exclusions from the foregoing return policy:
· New PowerEdgeTM , PowerConnectTM and PowerVaultTM products (excluding
PowerVault 160T tape libraries) may be returned within thirty (30) days from the date on
the packing slip or invoice, except that new PowerEdge
TM
SC servers and n series
products purchased from the Small and Medium Business Sales Division may only be
returned within fourteen (14) days from the date on the packing slip or invoice.
Application software or an operating system that has been installed by Dell may not be
·
returned unless you return the entire computer under the 21 -day return policy, if applicable
to your purchase (if not applicable to your purchase, you may not return application
software or an operating system).
Non-defective third party and Dell- branded software, peripheral, electronics and
·
Page 67

accessory products (for example: televisions, printers, projectors, MP3 players, PDAs,
battery chargers, un -preinstalled third party software, wireless cards/access points/routers),
including but not limited to those sold by or through Dell's "Software & Peripherals" or
"Electronics & Accessories" groups, may be returned within twenty - one (21) days from the
date on the packing slip or invoice, but a fifteen percent (15%) return fee may be deducted
from any refund or credit.
Dell | EMC storage products, EMC- branded products, Unisys- branded products,
·
PowerVault
TM
160T tape libraries, enterprise software, non -Dell branded enterprise
products, software and/or software licenses, or any non -Dell customized hardware and/or
software product(s) may not be returned at any time.
• Reconditioned or Refurbished Dell - Branded Hardware Products and Parts - All
reconditioned or refurbished PowerEdgeT , PowerConnectT and PowerVaultT products may
be returned within thirty (30) days from the date on the packing slip or invoice. All other
reconditioned or refurbished Dell- branded hardware products and parts may be returned
within fourteen (14) days of the date on the packing slip or invoice.
• How to Return - To return products, e- mail or call Dell customer service to receive a
Credit Return Authorization Number within the return policy period applicable to the product
you want to return. You must obtain a Credit Return Authorization Number in order to return
the product. See "Contacting Dell" or "Getting Help" in your customer documentation (or
www.dell.com/us/en/gen/contact.htm) to find the appropriate contact information for
obtaining customer assistance.
You must ship the products to Dell within five (5) days of the date that Dell issues the
Credit Return Authorization Number. You must also return the products to Dell in their
original packaging, in as -new condition along with any media, documentation, and all other
items that were included in the original shipment, prepay shipping charges, and insure the
shipment or accept the risk of loss or damage during shipment.
Limited Warranty Terms for Canada
What is covered by this limited warranty?
This limited warranty covers defects in materials and workmanship in your - - our end -user
customer's - - Dell -branded hardware products, including Dell -branded peripheral products.
What is not covered by this limited warranty?
This limited warranty does not cover:
• Software, including the operating system and software added to the Dell -branded
hardware products through our factory-integration system, or the reloading of the software
• Non-Dell branded products and accessories
• Problems that result from:
- External causes such as accident, abuse, misuse, or problems with electrical power
- Servicing not authorized by us
- Usage that is not in accordance with product instructions
- Failure to follow the product instructions or failure to perform preventive maintenance
- Problems caused by using accessories, parts, or components not supplied by us
• Products with missing or altered service tags or serial numbers
• Products for which we have not received payment
THIS WARRANTY GIVES YOU SPECIFIC LEGAL RIGHTS, AND YOU MAY ALSO HAVE
OTHER RIGHTS WHICH VARY FROM PROVINCE TO PROVINCE. DELL'S
RESPONSIBILITY FOR MALFUNCTIONS AND DEFECTS IN PRODUCT IS LIMITED TO
REPAIR AND REPLACEMENT AS SET FORTH IN THIS WARRANTY STATEMENT, FOR
THE TERM OF THE WARRANTY PERIOD REFLECTED ON YOUR INVOICE. EXCEPT
FOR THE EXPRESS WARRANTIES CONTAINED IN THIS WARRANTY STATEMENT,
DELL DISCLAIMS ALL OTHER WARRANTIES AND CONDITIONS, EXPRESS OR
IMPLIED, INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION IMPLIED WARRANTIES AND
Page 68

CONDITIONS OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE,
STATUTORY OR OTHERWISE. SOME PROVINCES DO NOT ALLOW THE EXCLUSION
inform you of service alternatives that are available to you on a fee basis
OF CERTAIN IMPLIED WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS, OR LIMITATIONS ON HOW
LONG AN IMPLIED WARRANTY OR CONDITION LASTS. THEREFORE, THE
FOREGOING EXCLUSIONS AND LIMITATIONS MAY NOT APPLY TO YOU.
WE DO NOT ACCEPT LIABILITY BEYOND THE REMEDIES PROVIDED FOR IN THIS
WARRANTY STATEMENT OR FOR SPECIAL, INDIRECT, CONSEQUENTIAL, OR
INCIDENTAL DAMAGES, INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITATION, ANY LIABILITY FOR
THIRD PARTY CLAIMS AGAINST YOU FOR DAMAGES, FOR PRODUCTS NOT BEING
AVAILABLE FOR USE, OR FOR LOST DATA OR LOST SOFTWARE. OUR LIABILITY
WILL BE NO MORE THAN THE AMOUNT YOU PAID FOR THE PRODUCT THAT IS THE
SUBJECT OF A CLAIM. THIS IS THE MAXIMUM AMOUNT FOR WHICH WE ARE
RESPONSIBLE.
SOME PROVINCES DO NOT ALLOW THE EXCLUSION OR LIMITATION OF SPECIAL,
INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES, SO THE ABOVE
LIMITATION OR EXCLUSION MAY NOT APPLY TO YOU.
How long does this limited warranty last ?
This limited warranty lasts for the time period indicated on your invoice, except that the
limited warranty on Dell- branded batteries lasts only one year and the limited warranty on
the lamps for Dell- branded projectors lasts only ninety days. The limited warranty begins on
the date of the invoice. The warranty period is not extended if we repair or replace a
warranted product or any parts. Dell may change the terms and availability of limited
warranties, at its discretion, but any changes will not be retroactive (that is, the warranty
terms in place at the time of purchase will apply to your purchase).
What do I do if I need warranty service?
Before the warranty expires, please call us at the relevant number listed in the following
table. Please also have your Dell service tag number or order number available.
Individual Home Consumers; Home Office and Small Business Customers:
Technical Support and Customer Service 1-800-847-4096
Medium, Large, and Global Commercial Customers; Government, Education, and
Healthcare Customers; and Value Added Resellers (VARs):
Technical Support 1-800-387-5757
Customer Service 1-800-326-9463
Government or Education Customers, or Individual Home Consumers who purchased
through an Employee Purchase Program:
Technical Support 1-800-387-5757
Customer Service
Dell-Branded Memory 1-888-363-5150
What will Dell do?
During the first year of all limited warranties: During the first year of all limited
warranties, we will repair any Dell- branded hardware products returned to us that prove to
be defective in materials or workmanship. If we are not able to repair the product, we will
replace it with a comparable product that is new or refurbished.
When you contact us, we will issue a Return Material Authorization Number for you to
include with your return. You must return the products to us in their original or equivalent
packaging, prepay shipping charges, and insure the shipment or accept the risk if the
product is lost or damaged in shipment. We will return the repaired or replacement products
to you. We will pay to ship the repaired or replaced products to you if you use an address in
Canada. Otherwise, we will ship the product to you freight collect.
1-800-326-9463 (Extension 8221 for
Individual Consumers)
If we determine that the problem is not covered under this warranty, we will notify you and
Page 69

.
NOTE:Before you ship the product(s) to us, make sure to back up the data on the hard
During the remaining years following the first year of all limited warranties : We will
replace any defective part with new or refurbished parts, if we agree that it needs to be
replaced. When you contact us, we will require a valid credit card number at the time you
request a replacement part, but we will not charge you for the replacement part as long as
you return the original part to us within thirty days after we ship the replacement part to you.
If we do not receive the original part within thirty days, we will charge to your credit card
the then -current standard price for that part.
We will pay to ship the part to you if you use an address in Canada. Otherwise, we will ship
the part freight collect. We will also include a prepaid shipping container with each
replacement part for your use in returning the replaced part to us.
NOTE:Before you replace parts, make sure to back up the data on the hard drive(s) and
drive(s) and any other storage device(s) in the product(s). Remove any
confidential, proprietary or personal information, removable media, such as floppy
disks, CDs, or PC Cards. We are not responsible for any of your confidential,
proprietary or personal information; lost or corrupted data; or damaged or lost
removable media.
any other storage device(s) in the product(s). We are not responsible for lost or
corrupted data.
What if I purchased an on- site service contract?
If your service contract is with Dell, service will be provided to you under the terms of the
service contract. Please refer to that contract for details on how to obtain service. Dell's
service contracts can be found online at
www.dell.ca or by calling Customer Care at 1- 800 -847-4096. If you purchased through us
a service contract with one of our third- party service providers, please refer to that contract
(mailed to you with your invoice) for details on how to obtain service.
How will you fix my product?
We use new and refurbished parts made by various manufacturers in performing warranty
repairs and in building replacement parts and systems. Refurbished parts and systems are
parts or systems that have been returned to Dell, some of which were never used by a
customer. All parts and systems are inspected and tested for quality.
Replacement parts and systems are covered for the remaining period of the limited
warranty for the product you bought. Dell owns all parts removed from repaired products.
What do I do if I am not satisfied?
We pride ourselves on our great customer service. If you are not satisfied with the service
you receive under this limited warranty, please let us know. We have found that the best
way to resolve issues regarding our limited warranty is to work together. If, after those
discussions, you are still not satisfied, we believe arbitration is the most expeditious way to
resolve your concerns. Therefore, ANY CLAIM, DISPUTE, OR CONTROVERSY
(WHETHER IN CONTRACT, TORT, OR OTHERWISE, WHETHER PREEXISTING,
PRESENT OR FUTURE, AND INCLUDING STATUTORY, COMMON LAW, INTENTIONAL
TORT, AND EQUITABLE CLAIMS) AGAINST DELL arising from or relating to this limited
warranty, its interpretation, or the breach, termination or validity thereof, the relationships
which result from this limited warranty (including, to the full extent permitted by applicable
law, relationships with third parties), Dell's advertising, or any related purchase SHALL BE
RESOLVED EXCLUSIVELY AND FINALLY BY BINDING ARBITRATION ADMINISTERED
BY THE NATIONAL ARBITRATION FORUM (NAF) under its Code of Procedure then in
effect (available via the Internet at
2371). The arbitration will be limited solely to the dispute or controversy between you and
Dell. Any award of the arbitrator(s) shall be final and binding on each of the parties, and
www.arb-forum.com, or via telephone at 1- 800 -474-
Page 70

may be entered as a judgment in any court of competent jurisdiction. Information may be
obtained and claims may be filed with the NAF at P.O. Box 50191, Minneapolis, MN 55405.
May I transfer the limited warranty?
Limited warranties on systems may be transferred if the current owner transfers ownership
of the system and records the transfer with us. The limited warranty on Dell -branded
memory may not be transferred. You may record your transfer by going to our website:
• If you are an Individual Home Consumer, go to
www.dell.com/us/en/dhs/topics/sbtopic_016_ccare.htm
• If you are a Home Office, Small, Medium, Large, or Global Commercial Customer, go to
www.dell.com/us/en/biz/topics/sbtopic_ccare_nav_016_ccare.htm
• If you are a Government, Education, or Healthcare Customer, or an Individual Home
Consumer who purchased through an Employee Purchase Program, go to
www.dell.com/us/en/pub/topics/sbtopic_016_ccare.htm
If you do not have Internet access, please call Dell at 1- 800 - 326 -9463.
"Total Satisfaction" Return Policy
If you are an end -user customer who bought new products directly from Dell, you may
return them to Dell up to 30 days after you receive them for a refund or credit of the product
purchase price. If you are an end-user customer who bought reconditioned or refurbished
products from Dell, you may return them to Dell within 14 days after the date of invoice for
a refund or credit of the product purchase price. In either case, the refund or credit will not
include any shipping and handling charges shown on your invoice and will be subject to a
fifteen percent (15%) restocking fee, unless otherwise prohibited by law. If you are an
organization that bought the products under a written agreement with Dell, the agreement
may contain different terms for the return of products than specified by this policy.
To return products, you must call Dell Customer Service at 1 -800 - 387 -5759 to receive a
Credit Return Authorization Number. To expedite the process of your refund or credit, Dell
expects you to return the products to Dell in their original packaging within five days of the
date that Dell issues the Credit Return Authorization Number. You must also prepay
shipping charges and insure the shipment or accept the risk of loss or damage during
shipment. You may return software for a refund or credit only if the sealed package
containing the floppy disk(s) or CD(s) is unopened. Returned products must be in as - new
condition, and all of the manuals, floppy disk(s), CD(s), power cables, and other items
included with a product must be returned with it. For customers who want to return, for
refund or credit only, either application or operating system software that has been installed
by Dell, the whole system must be returned, along with any media and documentation that
may have been included in the original shipment.
The "Total Satisfaction" Return Policy does not apply to Dell | EMC storage products. It also
does not apply to products purchased through Dell's Software and Peripherals division. For
those products, please instead refer to Dell's Software and Peripheral's then -current return
policy (see the following section, "Dell Software and Peripherals (Canada Only)").
Dell Software and Peripherals (Canada Only)
Third- Party Software and Peripherals Products
Similar to other resellers of software and peripherals, Dell does not warrant third- party
products. Third - party software and peripheral products are covered by the warranties
provided by the original manufacturer or publisher only. Third party manufacturer warranties
vary from product to product. Consult your product documentation for specific warranty
information. More information may also be available from the manufacturer or publisher.
While Dell offers a wide selection of software and peripheral products, we do not specifically
test or guarantee that all of the products we offer work with any or all of the various models
of Dell computers, nor do we test or guarantee all of the products we sell on the hundreds
of different brands of computers available today. If you have questions about compatibility,
Page 71

we recommend and encourage you to contact the third- party software and peripheral
product manufacturer or publisher directly.
Dell-Branded Peripheral Products
Dell does provide a limited warranty for new Dell -branded peripheral products (products for
which Dell is listed as the manufacturer) such as monitors, batteries, memory, docking
stations, and projectors). To determine which limited warranty applies to the product you
purchased, see the Dell invoice and/or the product documentation that accompanied your
product. Descriptions of Dell's limited warranties are described in preceding sections.
Return Policy
If you are an end -user customer who bought Dell Software and Peripherals products directly
from a Dell company, you may return Dell Software and Peripherals products that are in asnew condition to Dell up to 30 days from the date of invoice for a refund of the product
purchase price if already paid. This refund will not include any shipping and handling
charges shown on your invoice; you are responsible for those.
To return products, you must call Dell Customer Service at 1 -800 - 387 -5759 to receive a
Credit Return Authorization Number. You must ship the Dell Software and Peripherals
products back to Dell in their original manufacturer's packaging (which must be in as -new
condition), prepay shipping charges, and insure the shipment or accept the risk of loss or
damage during shipment.
To qualify for refund or replacement, returned products must be in as -new condition,
software products must be unopened, and all of the manuals, floppy disk(s), CD(s), power
cables, and other items included with a product must be returned with it.
One-Year End-User Manufacturer Guarantee (Latin America and the Caribbean Only)
Guarantee
Dell Inc ("Dell") warrants to the end user in accordance with the following provisions that its
branded hardware products, purchased by the end user from a Dell company or an
authorized Dell distributor in Latin America or the Caribbean, will be free from defects in
materials, workmanship, and design affecting normal use, for a period of one year from the
original purchase date. Products for which proper claims are made will, at Dell's option, be
repaired or replaced at Dell's expense. Dell owns all parts removed from repaired products.
Dell uses new and reconditioned parts made by various manufacturers in performing repairs
and building replacement products.
Exclusions
This Guarantee does not apply to defects resulting from: improper or inadequate
installation, use, or maintenance; actions or modifications by unauthorized third parties or
the end user; accidental or willful damage; or normal wear and tear.
Making a Claim
Claims must be made in Latin America or the Caribbean by contacting the Dell point of sale
within the guarantee period. The end user must always supply proof of purchase, indicating
name and address of the seller, date of purchase, model and serial number, name and
address of the customer, and details of symptoms and configuration at the time of
malfunction, including peripherals and software used. Otherwise, Dell may refuse the
guarantee claim. Upon diagnosis of a warranted defect, Dell will make arrangements and
pay for ground freight and insurance to and from Dell's repair/replacement center. The end
user must ensure that the defective product is available for collection properly packed in
original or equally protective packaging together with the details listed above and the return
number provided to the end user by Dell.
Limitation and Statutory Rights
Dell makes no other warranty, guarantee or like statement other than as explicitly stated
above, and this Guarantee is given in place of all other guarantees whatsoever, to the
Page 72

fullest extent permitted by law. In the absence of applicable legislation, this Guarantee will
be the end user's sole and exclusive remedy against Dell or any of its affiliates, and neither
Dell nor any of its affiliates shall be liable for loss of profit or contracts, or any other indirect
or consequential loss arising from negligence, breach of contract, or howsoever.
This Guarantee does not impair or affect mandatory statutory rights of the end user
against and/or any rights resulting from other contracts concluded by the end user
with Dell and/or any other seller.
Dell World Trade LP
One Dell Way, Round Rock, TX 78682, USA
Dell Computadores do Brasil Ltda (CNPJ No. 72.381.189/0001 -10) /
Dell Commercial do Brasil Ltda (CNPJ No. 03 405 822/0001- 40)
Avenida Industrial Belgraf, 400
92990-000 - Eldorado do Su - RS - Brasil
Dell Computer de Chile Ltda
Coyancura 2283, Piso 3 - Of.302,
Providencia, Santiago - Chile
Dell Computer de Colombia Corporation
Carrera 7 #115- 33 Oficina 603
Bogota, Colombia
Dell Computer de Mexico SA de CV
Paseo de la Reforma 2620 - 11° Piso
Col. Lomas Altas
11950 México, D.F.
Back to Top
Back to Contents Page
Page 73

FAQs
Hardware Installation:
How do I install the Dell Wireless 4350
Small Network Access Point for optimal
coverage?
Can the Dell Wireless 4350 Small Network
Access Point attach to a hub, switch, or
router?
What is the physical connection from the
Dell Wireless 4350 Small Network Access
Point to a wired network ?
Software Configuration
Wireless Attributes
Supported Features
Troubleshooting
Other
Glossary
Back to Contents
How do I install the Dell™ Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point for
optimal coverage?
Each Dell Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point supports up to about a 150 to 200 foot radius,
depending on obstacles and interference issues. For smaller installations a little experimentation
provides good placement of the Dell Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point.
Can the Dell Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point attach to a hub,
switch, or router?
Yes, via its LAN port, the Dell Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point provides the flexibility for a
wide variety of network configurations and connections.
What is the physical connection from the Dell Wireless 4350 Small Network
Access Point to a wired network?
Each Dell Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point has a 10/100 Ethernet (LAN port) connection,
which allows communication with a 10 megabit per second (Mbps), 100 Mbps, or 10/100 Mbps hub
or switch.
Page 74

Access Point
An Access Point is a device on the wireless network that receives and retransmits data. It allows computers with wireless network
adapters to be connected, typically, to an Ethernet network.
Client
A client is a computer on a network.
Domain Name System (or Service) (DNS)
DNS is an Internet service that translates domain names into IP addresses. A DNS server keeps a database of host computers,
their respective domain names, and IP addresses. When a domain name is requested, the DNS server uses this table to send the
user to the proper IP address.
The DNS system is really its own network. If one DNS server doesn't know how to translate a particular domain name, it asks
another one, and so on, until the correct IP address is returned.
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)
DHCP is the process of automatically configuring the TCP/IP settings for every computer on a network.
Encryption
Encryption is a common way of implementing security and protecting information. Encryption applies a set of instructions, called an
algorithm, to information. The instructions combine the plain or clear text of information with a sequence of hexadecimal numbers,
called an encryption key.
Before transmitting information over the airwaves, the wireless client or Access Point encrypts or scrambles the information. The
Access Point or wireless client receiving the information uses the same key to decrypt or unscramble the information. The
information is only readable to WLAN devices that have the correct encryption key. The longer the key is, the stronger the
encryption. All wireless clients and Access Points in a WLAN must use the same encryption method and key. An 802.11 - compliant
wireless network has Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) and Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) technologies for wireless security.
Ethernet
Ethernet is the most widely used local area networking technology. It is an industry- wide standard originally developed by Xerox
and formalized in 1980 by DEC, Intel, and Xerox. Ethernet networks transmit data at 10/100 Mbps using a specified
protocol.
Ethernet Address (MAC Address)
Page 75

An Ethernet address is a unique, pre -programmed address, sometimes referred to as a media access control (MAC) address. Each
computer on an Ethernet network has its own Ethernet address. This 12 - digit hexadecimal address is encoded into the circuitry of
the computer’s network adapter when it is manufactured. Other devices on the network use this address to identify the computer.
This address is not the same as the
address is associated with the MAC address to enable network communication.
IP address that is assigned to computers on TCP/IP networks. On these networks, the IP
Host
A host is any device that is connected to the network; for example, a computer, network printer, or router. Each host has a unique
name (called "Host Name") or IP address (called "Host IP") for identification on the network.
Internet Protocol (IP)
IP is the protocol used to send data from one computer to another over the Internet. The IP protocol describes how Internet
computers keep track of the
another.
IP address of each computer on the network and route packets of data from one IP address to
IP Address
An IP address provides unique identification for each computer on the Internet or on a local network. IP addresses are usually
expressed as a group of four numbers separated by periods, for example, 169.254.10.2. None of the numbers can be greater than
255. Each Ethernet interface has an IP address. For the Dell Wireless 2350 Broadband Router, there is a
WAN Ethernet interface; hence, there is a LAN IP address and a WAN IP address.
and a
LAN Ethernet interface
Link Light
A link light is a light on a network device that indicates a good network connection. Hubs typically have a link light for each port;
although, they may not be labelled as such, and the lights may show other information. These lights often blink for network activity.
Some hubs display different colored lights for 10 Mbps and 100 Mbps. For more information, see the documentation accompanying
your product.
Local Area Network (LAN)
A LAN is a network in one location. The network lets users at that location share files, printers and other services. See WAN.
Network Adapter
A network adapter is a device expansion card that provides the physical connection between a computer and the network. There
are many types of adapters. They include PC cards for laptops (a card that fits into a slot on your computer, like you might install a
sound card or modem card) and embedded cards, embedded USB adapters, USB dongle adapters, and USB desktop adapters.
Some newer computers have a network adapter already built into the system. PC cards or cards that fit into a slot in the desktop
are sometimes referred to as network interface cards, or NICs.
Network Name (SSID)
Access Points are grouped together by an identifier called an ESSID. The ESSID is also referred to as a Net ID. This identifier is a
combination of any letters or numbers that are appropriate for the network environment. ESSID is specifically for Access Points.
When you talk about peer- to-peer networks, you cannot use the term ESSID.
Page 76

Service Set Identifier (SSID) is more generic and is a 32 -character name that uniquely identifies all the computers and equipments
that make up a wireless network. A type of SSID is ESSID. Another type of SSID is Basic Service Set Identifier (BSSID). The
BSSID is the
MAC address of a wireless adapter or Access Point.
Port
A port is a connector on a networking device used to attach the network cable. Hubs and switches have numerous ports that
connect to computers on the network.
Protocol
Protocol refers to a set of rules for sending and receiving information on a network. The rules determine the format of the data that
is transmitted and other aspects of networking, such as how errors are detected and corrected. The protocol driver in each
computer is software that adheres to these rules when sending and receiving information. These drivers are also often called
protocols.
Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)
TCP/IP refers to the protocol that computers use to communicate over the Internet. TCP determines how a computer breaks up
data into small units, called "packets," to be sent to another computer and how the receiving computer reassembles the packets
into a single file. IP determines how the packets are routed across the Internet.
See Internet Protocol.
Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN)
A VLAN is a network of computers that behave as if they are connected to the same wire, even though they may be physically
located on different segments of a LAN. VLANs are configured through software rather than hardware, which makes them
extremely flexible. When a computer on a VLAN is physically moved to another location, it can stay on the same VLAN without any
hardware reconfigurations.
Virtual Server
A virtual server is a device that performs Internet protocol (IP) mapping. IP mapping allows remote client access to your network
via the Internet.
Wide Area Network (WAN)
A WAN is a communications network that uses devices such as telephone lines, satellite dishes, or radio waves to span a larger
geographic area than can be covered by a
LAN.
Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN)
A WLAN is a type of Local Area Network (LAN) that uses high frequency radio waves rather than wires to communicate and
transmit data among the network clients and devices. It is a flexible data communication system implemented as an extension to,
or as an alternative for, a wired LAN. Just like a LAN, the network lets users at that location share files, printers and other services.
Page 77

Dell™ Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point
User's Guide
Contents
Introduction
Overview
Wireless Networking Overview
A Look at the Hardware
Installation and Configuration
Configuration of the Access Point
Connecting the Access Point to the network
How to obtain the IP address of the Access Point
Setting Wireless Encryption in Your Access Point
Turning Off Broadcast SSID
Setting Up File and Printer Sharing
How to setup wireless clients to connect to the Access Point
Using Your Access Point
Overview
Factory Default Settings
Setup Wizard
Control Utility
Web- Based Configuration Tool
Technical Specifications and Regulatory Information
Technical Specifications
Regulatory Information
Limited Warranties and Return Policy
FAQs
Glossary
Online Customer Support
Information in this document is subject to change without notice.
© 2004 Dell Inc. All rights reserved.
Trademarks used in this text: Dell, the DELL logo; Microsoft and Windows are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
Other trademarks and trade names may be used in this document to refer to either the entities claiming the marks and names or
their products. Dell disclaims any proprietary interest in trademarks and trade names other than its own.
P/N G7992 Revision A00, Sept. 2004
Page 78

Back to Contents Page
Wireless Networking Overview:
Dell™ Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point User's Guide
Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN)
Identifying a WLAN
Encryption
Automatic Rate Selection and Rate Scaling
Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN)
A Local Area Network (LAN) is a network in one location. Users at that location can share files, printers, and other services. In a
LAN, a networked computer that requests services is called a client. A Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN) is a type of LAN that
uses high frequency radio waves rather than wires to communicate and transmit data among the network clients and devices. It is
a flexible data communication system implemented as an extension to, or as an alternative for, a wired LAN.
In a WLAN, wireless adapters are installed in clients, also called wireless clients. The adapter allows the wireless client to
communicate with the WLAN without cables. Instead, wireless clients send and receive information through a path in the air called
a channel.
The standards for a WLAN are based on the IEEE 802.11b standard and IEEE 802.11g standard. All Dell 802.11b/g-compliant
devices interoperate with other 802.11b/g - compliant wireless devices from other vendors. The WiFi certification logo indicates that
the wireless device has been tested by an independent organization.
A wireless client operates in either infrastructure mode or peer-to-peer mode.
Back to Top
Identifying a WLAN
An ESSID and BSSID are both Service Set Identifiers (SSID) that identify and control the wireless client’s access to a given
WLAN. The SSID is sometimes referred to as the network name. The SSID indicates what WLAN you are referring to. In most
cases, the user interface displays the SSID.
When installing an access point or wireless adapter in a wireless client, the installation program asks you to enter the SSID. Dell
cannot provide you with this information, as it is specific to your network; but you may choose to use the default SSID, wireless,
for your Dell Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point. All wireless clients and access points in a WLAN must use the same
network name.
Back to Top
Encryption
In a WLAN, wireless clients and access points send and receive information through the air. Without implementing security, it is
possible for an unauthorized person to intercept the information.
Page 79

A common way of implementing security and protecting information is encryption. Encryption applies a set of instructions, called an
algorithm, to information. The instructions combine the plain or clear text of information with a sequence of hexadecimal numbers,
called an encryption key.
Before transmitting information over the airwaves, the wireless client or access point encrypts or scrambles the information. The
access point or wireless client receiving the information uses the same key to decrypt or unscramble the information. The
information is only readable to WLAN devices that have the correct encryption key. The longer the key is, the stronger the
encryption.
The Dell Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point supports both Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) and Wi-Fi Protected Access
(WPA).
WEP
WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) provides a way of creating an encrypted key that is shared between a wireless client (such as a
notebook with a wireless PC card) and the router. In the Dell Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point, WEP is an optional
feature that can be enabled or disabled. When WEP encryption is enabled, you must set the WEP key in the client to match the
WEP key used by the access point because you can ONLY connect to access points that have a matching WEP Key. The Dell
Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point Setup Wizard allows the user to gracefully configure WEP encryption on both the
access point and wireless clients.
NOTE:It is better to change keys frequently. The same algorithm is used for all the communications that should be protected. If
the same key is used, the same message will give exactly the same cipher text. Then, it will be possible for an
eavesdropper to break the encrypted data. For this reason, it is strongly recommended to change keys often.
There are two WEP encryption methods:
40(64)- bit Encryption
·
104(128) -bit Encryption
·
40- bit and 64 -bit encryption are identical. Some vendors use the term 40- bit; others use 64 -bit. A wireless device that claims to
have 40- bit encryption interoperates with a device that claims to have 64 -bit encryption; the same is true for the reverse. A 40(64) bit key consists of 10 hexadecimal numbers, arrayed as follows:
Key #1: 1011121314
Key #2: 2021222324
Key #3: 3031323334
Key #4: 4041424344
A 104(128)- bit key has several trillion times as many possible combinations than a 40(64) -bit key. It consists of 26 hexadecimal
numbers, arrayed as follows:
Key (#1): 101112131415161718191A1B1C
All wireless clients and access points in a WLAN must use the same encryption method and key. The following two examples
stress how important this point is.
Example 1
The encryption method for an access point is 40(64) -bit. The method for a wireless client is 104(128)- bit encryption. The client and
access point cannot communicate with each other, even though the selected key is the same. To resolve this problem, set the
access point to use 104(128)-bit encryption.
Example 2
The encryption method is the same for the access point and wireless client. You select key 1 for the access point and key 2 for
the wireless client. The wireless client cannot communicate with the WLAN. To resolve this problem, select key 1 for the wireless
client.
NOTE:Use the same key and encryption method for the wireless devices in the WLAN. Otherwise, they cannot communicate
Page 80

with each other.
The Dell Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point uses either hexadecimal digits or ASCII characters to create encryption keys.
Hexadecimal digits include the numbers 0 to 9 and the letters A to F. For example, the decimal number 15 is represented as F in
the hexadecimal numbering system.
ASCII is the acronym for the American Standard Code for Information Interchange. Pronounced ask-ee, ASCII is a code for
representing English characters as numbers, with each letter assigned a number from 0 to 127. For example, the ASCII code for
uppercase M is 77. Most computers use ASCII codes to represent text, which makes it possible to transfer data from one computer
to another.
WPA
WPA (Wi - Fi Protected Access) is an upgrade to the WEP standard for securing your wireless network. WPA is derived from and
will be forward- compatible with the future IEEE 802.11i standard. It provides improved data encryption and user authentication.
To enhance the level of security, WPA uses Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP) encryption to address the vulnerabilities of
the static keys used in WEP. TKIP includes four algorithms: message integrity check (MIC), to protect packets from tampering;
Per-Packet Key (PPK) hashing, to prevent weak key attacks; extended initialization vector (IV), to reduce IV reuse and the
possibility that a hacker will collect sufficient packets to crack the encryption; and a re -keying mechanism, to change the temporal
key dynamically. TKIP is the most commonly used encryption method; however, if your wireless clients do not support TKIP, the
Wireless 4350 also supports Advanced Encryption Security (AES) encryption. AES will replace 802.11's RC4-based encryption
under the 802.11i specification. AES, the gold -standard encryption algorithm, provides maximum security for wireless network.
For user authentication, WPA adopts an authentication scheme through 802.1x. 802.1x provides a framework for user
authentication and a key distribution management method. 802.1x consists of three main elements: an Authentication Server
(typically a RADIUS server), WPA -enabled router or AP (called Authenticator), and a WPA-enabled client (called Supplicant).
802.1x ensures only authorized users can access the network. The 802.1x protocols supported by the Dell Wireless 4350 Small
Network Access Point are PEAP, TTLS & TLS.
In enterprises, WPA will be used in conjunction with both a wireless router and authentication server. In a Small Office/Home
Office (SOHO) environment, where there is no authentication server, users can use pre- shared key (PSK) mode in place of the
authentication server.
The Dell Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point offers both WPA running in PSK mode and WPA with 802.1X authentication.
The mutual authentication and improved encryption technology of WPA allows wireless communication to achieve greater security.
Back to Top
Automatic Rate Selection and Rate Scaling
In 802.11g, wireless network adapters and access points can transmit data at one of the following rates: 54, 48, 36, 24, 18, 12, 9,
or 6 Mbps. In 802.11b, the data can be transmitted at a rate of 11, 5.5, 2, or 1 Mbps. As the distance between an adapter and
access point increases or decreases, the data rate automatically changes. Other factors, like interference, also affect the data rate.
The Dell Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point uses automatic rate selection and rate scaling to determine the most efficient
rate of communication. Rate scaling maintains optimal communication between wireless clients and the WLAN.
Back to Top
Back to Contents Page
Page 81

Back to Contents Page
A Look at the Hardware: Dell™ Wireless 4350 Small Network
Access Point
User's Guide
Front Panel
Back Panel
Front Panel
The Dell Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point has three Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs), or link lights, on its front side. The
following table defines the behaviour for each LED:
Front Panel
Page 82

LED Represents Activity
Power Power The Power LED will light up green when the device is powered on and ready for use. It will
blink when the device is powering up or when it is reset
WirelessWireless
LAN
Ethernet Intranet A steady green light indicates the connection is active, and blinks with data activity.
Back to Top
The LED alternates between on and off when wireless clients are attached. It will blink when
there is data activity on the wireless network. The rate of blinking will vary with the rate of data
transfer. It turns off when no wireless clients are associated with the Dell Wireless 4350 Small
Network Access Point.
Back Panel
Back Panel
Connector Description
Lock This accepts locking devices for protecting the Dell Wireless 4350 from theft.
Reset Use an object, such as a paper clip, to press the button for at least 5 seconds. The Power LED will be off
for a short time and then light up again. You can then release the button to reset the device to its factorydefault settings.
Ethernet This accepts an RJ - 45 connector for network cabling.
*Also accepts power input from Ethernet port (Power Over Ethernet)
Power Connect the power adapter to this Power port, and then plug the other end of the power cable into a
power outlet.
Back to Top
Back to Contents Page
Page 83

Back to Contents Page
Introduction: Dell™ Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point
User's Guide
Overview
Wireless Networking Overview
A Look at the Hardware
Overview
The Dell Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point is an 802.11b/g wireless access point that allows wireless clients access to a
corporate network. The Access Point can be configured in the following ways:
Wireless hub (Access Point): In this mode the Access Point connects wireless computers to the corporate network.
Wireless repeater: In this mode the Access Point is able to extend the wireless range of a root Access Point that is on the
corporate network to remote wireless computers.
Page 84

The Dell Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point supports up to 64 wireless clients. It runs at speeds up to 54 Megabits per
second (Mbps), and the LAN (wired) port runs at 10/100 Mbps. The maximum distance between the Access Point and each
Wireless computer is 300 feet. This distance may be less depending on your environment.
By default, the Dell Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point provides the following functionality:
a wireless access point using wireless as the wireless network name.
a bridge to an Ethernet hub.
Back to Contents Page
Page 85

Back to Contents Page
Configuration of the Access Point
NOTE:It is recommended that you configure the Dell Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point with the Setup
Wizard provided on the Dell Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point CD.
NOTE:Advanced users can configure the Dell Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point with the web - based
configuration utility which can be accessed by browsing to the IP address of the access point.
The Setup Wizard allows the user to configure the following parameters on the Dell Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point (a)
SSID, (b) wireless channel of operation, (c) WEP encryption (WEP encryption is optional) and (d) Static IP address.
In order to use the Setup Wizard to configure the Dell Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point, the access point must be
directly connected via an ethernet cable to the computer that is running the Setup Wizard. In this configuration, the Dell Wireless
4350 Small Network Access Point will have a default static IP address of 192.168.2.2 and the computer will have to be assigned a
static IP address in the same subnet.
How to assign a static IP address to the network card of your computer
This section contains information on how to assign a static IP address to the network card of your computer. This is required as
part of the access point configuration.
How to assign a static IP address to the network card of your computer
1. On your computer, click Start -- > Settings - -> Control Panel .
Double click the Network Connections icon.
2.
Right click the Local Area Connection icon.
3.
Select Properties from the pull- down menu.
4.
Click Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) and then Properties.
5.
Page 86

6.
Select Use the following IP address in the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties window.
7. Input your IP address and Sumnet mask in the appropriate fields. (The IP addresses on your network must be within the
same range (e.g. 192.168.2.3 or 192.168.2.4). The subnet mask must be the same for all computers on the network (i.e.
255.255.255.0).
Click OK.
8.
Back to Top
Back to Contents Page
Page 87

Back to Contents Page
Connecting the Access Point to the network
NOTE:It is recommended that you follow the instructions in the Quick Start Guide on connecting the Dell Wireless 4350 Small
Network Access Point to the network.
The following are the relevant steps on connecting the access point to your network.
1. Find the optimum location for your Access Point. The Access Point should be located at the center of your wireless network,
ideally with line of sight to all your mobile stations.
2. Fix the orientation of the antennas such that both antennas are perpendicular to the ground and parallel to each other
3. Connect the included Ethernet cable to the Access Point and the other end of the Ethernet cable to a switch or hub.
4. Connect the power adapter to the Access Point’s power port.
Back to Contents Page
Page 88

Back to Contents Page
How to obtain the IP Address of the Access Point
To browse to the Dell Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point's web - based configuration tool, you must known the access
point's IP address. The IP address of the access point can be either a static IP address or a dynamically assigned IP address. The
default configuration for the access point is with a static IP address of 192.168.2.2.
If the access point has been configured as a DHCP client, it will be dynamically assigned a IP address. In order to determine what
this IP address is, use the following method.
Find the Media Access Control (MAC) address of the wired port of the access point. This information can be derived from the
1.
product label which is located on the underside of the access point .
2. The product label contains the MAC address of the WLAN port of the access point. The MAC address of the wired port is
calculated by subtracting 0x1H from this address (i.e. If the MAC address on the product label is 00:90:4b:3c:12:10, then the MAC
address of the wired port is 00:90:4b:3c:12:10 - 0x1 = 00:90:4b:3c:12:0f)
Provide your organisation's network administrator with your access point's wired port MAC address (calculated in step 2).
3.
The network administrator will query the DHCP server using the MAC address to identify the IP address of the access point.
4.
Back to Contents Page
Page 89

Back to Contents Page
Setting Wireless Encryption in Your Access Point
Without wireless security options configured in your network, an eavesdropper within your wireless range may be able to access
the network and the data that is being transmitted over it. The Dell Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point provides Wired
Equivalent Privacy (WEP) and Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) encryption for wireless security.
WPA is an upgrade to the WEP standard for securing your wireless network.
If you would like to secure your wireless network using WPA, you must have WPA support for your wireless clients. If you are
using a Dell Wireless client, you can check for the availability of a WPA-enabled software update for your wireless client at
http://support.dell.com. The WPA -802.1x protocols supported by the Dell Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point are PEAP,
TTLS & TLS.
Log into the web configuration of your access point using it's IP address (for information on obtaining the access point's IP
1.
address see
Type the following text in the user name and password fields: "admin".
2.
Click Basic Settings and then select Wireless Security from the drop down menu.
3.
Click to select Enable Wireless Security.
4.
Select either WEP or WPA in the Network Encryption list.
5.
How to obtain the IP Address of the Access Point). The Enter Network Password login prompt appears.
WEP
1. Select hexadecimal or ASCII characters as the Key Format. You can use either as a string of hexadecimal digits (characters 0
through 9 and A through F ) or as ASCII characters (any key on the keyboard).
Select an encryption level from the Key Length list.
2.
Enter four different keys in the Key1, Key2, Key3, and Key4 fields to store on your router. For 40(64) -bit encryption, enter a
3.
5-character (or 10 hexadecimal digits) WEP key. For 104(128)- bit encryption, enter a 13 - character (or 26 hexadecimal digits) WEP
key.
Select only one key out of the four keys as the Default Key for encryption.
4.
Click the NEXT button, and then click Save and Restart to apply the changes.
5.
Set up the WEP on your wireless clients. Refer to the documentation that accompanied your wireless clients, or your wireless
6.
clients' on -line help systems, for information on how to set up WEP.
WPA
There are two options for network authentication (a) Pre -shared key or (b) 802.1x . Typically, in enterprises, WPA will be used in
conjunction with a RADIUS authentication server. In a Small Office/Home Office (SOHO) environment, where there is no
authentication server, users can use pre- shared key (PSK) mode in place of the authentication server.
WPA-PSK
Choose a key format by selecting either Hexadecimal Digits or ASCII Characters in the Key Format field. Hexadecimal digits
1.
are numbers 0- 9 and/or letters A-F. ASCII characters can be any key on the keyboard.
Enter your pre -shared key in the WPA Pre-Shared Key field. This key must match the key that is used by each wireless client
2.
computer associated to your Access Point
Page 90

3. The WPA Group Rekey Interval value specifies how often the key “rotates” or changes.
WPA Encryption allows you to select one of two possible encryption methods—TKIP and AES. Choose one that your wireless
4.
clients support.
Click the NEXT button, and then click Save and Restart to apply the changes.
5.
Set up WPA -PSK on your wireless clients. Refer to the documentation that accompanied your wireless clients, or your wireless
6.
clients' on -line help system, for information on how to setup WPA -PSK.
WPA-802.1x
WPA Encryption allows you to select one of two possible encryption methods—TKIP and AES. Choose one that your wireless
1.
clients support.
The Radius Server IP, Radius Server Port and Shared Secret fields required to be populated with the relevant information.
2.
This information regarding the Radius authentication server can be obtained from the network administrator.
The WPA Group Rekey Interval value specifies how often the key “rotates” or changes.
3.
Click the NEXT button, and then click Save and Restart to apply the changes.
4.
Set up WPA -802.1x on your wireless clients. Refer to the documentation that accompanied your wireless clients, or your
5.
wireless clients' on -line help system, for information on how to setup WPA with 802.1x authentication.
NOTE:The Dell Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point offers three ways to set the wireless encryption in your router. One
is the Wireless Security feature in the web configuration tool mentioned here. The other two are either through the
Windows-based
control utility or the Setup Wizard.
Back to Contents Page
Page 91

Back to Contents Page
Turning Off Broadcast SSID
1. Log into the web configuration of your Access Point using it's IP address (for information on obtaining the Access Point's IP
address see
2. Type the following text in the user name and password fields: "admin".
3. Click Advanced Settings and then select Advanced Wireless from the drop down menu.
4. Check Yes for Hide my wireless network
5. Click Submit.
Back to Contents Page
How to obtain the IP Address of the Access Point). The Enter Network Password login prompt appears.
Page 92

Back to Contents Page
Setting Up File & Printer Sharing
Installing File and Printer Sharing
Sharing a printer
Sharing files
Installing the File & Printer Sharing
Follow the instructions below to install the file and printer sharing service.
For Windows 2000 and XP
1. Right-click the My Network Places icon (on the desktop in Windows 2000 and in the Start button menu in Windows XP)
and left - click to select Properties in menu.
2. Right-click the Local Area Connection icon and select Properties in the menu.
3. If you can see the File and Printer Sharing for Microsoft Networks item, you can skip this section. The file and printer
sharing service had already been installed.
4. If the File and Printer Sharing for Microsoft Networks item is not present, click the Install button.
5. Click to select Service, and then click the Add button.
6. Click to select File and printer sharing for Microsoft Networks , and then click the OK button.
Sharing a Printer
To share a printer, perform the following steps on the computer that has the printer you wish to share.
1. Click the Start button, click Settings, and then click Printers.
2. Click the printer you want to share to highlight it.
3. On the File menu, click Properties.
4. Click the Sharing tab, and then click Shared As .
5. Follow the on - screen instructions to complete.
The printer is now available for the other computers to use.
Perform the following steps on the other computers:
1. Click the Start button, click Settings, and then click Printers.
2. Double-click the Add Printer icon.
3. Click Next on the first screen.
Page 93

4. On the next screen, select Network printer, and then click the Next button.
5. Click the Browse button and click to select the shared printer.
6. Follow the on - screen instructions to complete.
Sharing files
You can share files on your computer so that users on other computers on your network can view them.
1. In Microsoft Windows Explorer, right- click on the file, folder, or drive letter you wish to share and left- click Sharing.
2. Click Share As .
3. Type a name for the share and follow the on -screen instructions to complete.
Back to Contents Page
Page 94

Back to Contents Page
How to setup wireless clients to connect to the Access Point
NOTE:It is recommended that you connect wireless clients to the Dell Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point using the
Setup Wizard provided on the Dell Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point CD.
Back to Top
Back to Contents Page
Page 95

Back to Contents Page
Installation and Configuration:
Dell™ Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point User's Guide
Configuration of the Access Point
Connecting the Access Point to the network
How to obtain the IP address of the Access Point
Setting Wireless Encryption in Your Access Point
Turning Off Broadcast SSID
Setting Up File and Printer Sharing
How to setup wireless clients to connect to the Access Point
Back to Contents Page
Page 96

Back to Contents Page
How to Configure the Access Point via the Control Utility:
Dell™ Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point User's Guide
My Network Overview
Wireless Settings
Network Access Control
Administration
Diagnostics
Advanced Settings
My Network Overview
This screen provides information about your network connection and settings. The left pane displays your connection status. The
right pane displays the following network settings:
Operation Mode
·
LAN IP Address
·
LAN Subnet Mask
·
Network Name (SSID)
·
Wireless Security
·
My Network Overview
Page 97

The Control Utility allows the user to manage multiple Dell Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Points on the network by allowing
the user to configure an alternative access point to the default access point presented by the Control Utility.
To configure an alternative access point, perform the following steps:
Click to select Configure Alternative AP.
1.
Enter the IP Address and Subnet Mask of the access point to be configured into the IP Address and Subnet Mask fields.
2.
3. Click Apply, the Control Utility will shutdown and after restarting will have connected to the desired Dell Wireless 4350 Small
Network Access Point.
Back to Top
Wireless Settings
· Network Name (SSID)
The SSID is a unique network name. It is used to identify the wireless network. This name is used when connecting wireless
clients to your wireless network.
Channel
·
This is the radio channel over which a communication transmission occurs between the access point and a wireless client.
Default Settings
·
Resets the wireless settings to its factory defaults.
Apply
·
Page 98

Saves current settings.
· Restore
Restores previous settings.
Your Dell Wireless 4350 Small Network Access Point has an advanced security mechanism. It ensures the confidentiality of data,
and also guards data against being modified. If you want to enable the security mechanism, click to select Enable Wireless
Security.
Wireless Settings WEP
WEP Settings
The Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) encryption defined in the 802.11 standard is used to protect wireless communication from
eavesdropping. WEP provides a way of creating an encrypted key that is shared between a wireless client (such as a notebook
with a wireless PC card) and the access point. This key encrypts data before it is transmitted. WEP can be implemented with a
40(64)- bit or 104(128)-bit key. For added security, change your key often. When you change the key on one wireless device, it
must be changed for all wireless devices and access points in the network.
Key Format
·
Can be ASCII or hexadecimal format. Hexadecimal format includes the numbers 0 through 9 and the letters A through F. ASCII
format includes all alphanumeric characters.
Key Length
·
Can be either 40(64) -bit or 104(128)- bit key length. Some wireless network cards are only able to use 40(64) -bit encryption. If all
your clients are able to communicate at 104(128)-bit, then choose 104(128)- bit. If any client is only able to communicate at 40(64) bit, choose 40(64) -bit.
Key1, Key2, Key3, and Key4
·
Type four different keys in the Key fields provided to store on the Wireless 2350. If you choose 40(64) -bit encryption, enter a 5-
Page 99

character (or 10 hexadecimal digits). For 104(128)-bit encryption, enter a 13 -character (or 26 hexadecimal digits) WEP key.
· Default Key
Select only one key out of the four provided in the Default Key field.
Wireless Settings WPA-PSK
WPA-PSK Settings
Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) is an upgrade to the WEP standard for securing your wireless network.
If you would like to secure your wireless network using WPA, you must have WPA support for your wireless clients. If you are
using a Dell wireless client, you can check for the availability of WPA -enabled software updates for your wireless client at
http://support.dell.com.
WPA Pre-shared Key
·
All wireless clients must use this key to gain access to the network. Note that the Key format must also match the setting for the
wireless clients.
Key Format
·
Can be ASCII or hexadecimal format. Hexadecimal format includes the numbers 0 through 9 and the letters A through F. ASCII
format includes all alphanumeric characters.
WPA Group Rekey Interval
·
WPA Group Rekey Interval is used to specify the frequency of encryption key rotations. The lower the number, the faster your
encryption key will rotate; however, setting this number too low may cause your wireless network to slow down.
WPA Encryption
·
TKIP (Temporal Key Integrity Protocol) is the most commonly used encryption method. AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) can
be used if your wireless clients do not support TKIP.
Page 100

Wireless Settings WPA 802.1x
WPA-802.1x Settings
· Radius Server IP, Radius Server Port and Shared Secret.
The Radius Server IP, Radius Server Port and Shared Secret fields required to be populated with the relevant information. This
information regarding the Radius authentication server can be obtained from the network administrator.
WPA Encryption
·
WPA Encryption allows you to select one of two possible encryption methods—TKIP and AES. Choose one that your wireless
clients support.
Back to Top
Network Access Control
· Add
Adds a new entry to the list.
Edit
·
 Loading...
Loading...