Page 1
DATA SHEET
BIPOLAR ANALOG INTEGRATED CI RCUIT
µµµµ
PC8125GR
UP-CONVERTER WITH AGC FUNCTION
QUADRATURE
++++
MODULATOR IC FOR DIGITAL MOBILE COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS
DESCRIPTION
The µPC8125GR is a sillicon monolithic integrated circuit designing as indirect quadrature modulator for digital
mobile communication systems. This modulator consists of 1.8 GHz to 2.0 GHz up-converter with AGC function and
220 MHz to 270 MHz quadrature modulator which are packaged in 20-pin SSOP. The device has power save
function and can operate 2.7 to 5.5 V supply voltage. Therefore, it can contribute to make RF block small, high
performance and low power consumption.
FEATURES
• LPF is incorporated in the latter of 90° phase shifter for Lo1 Carrier leak and its Lo1 × n spurious level.
• Supply voltage: VCC = 2.7 to 5.5 V
• External IF filter can be applied between modulator output and up-converter input terminal.
• Equipped with power save function.
• Equipped with AGC function : Gain control range 40 dB TYP. @f = 1.9 GHz
APPLICATIONS
• Digital cordless phones: ex) PHS (Personal Handy Phone System)
ORDERING INFORMATION
Part Number Package Supplying Form
µ
PC8125GR-E1 20 pin plastic SSOP (225 m i l ) E m bossed tape, 12 mm wide.
Remark
Document No. P11486EJ2V0DS00 (2nd edition)
Date Published November 1999 N CP(K)
Printed in Japan
To order evaluation samples, please contact your local NEC sales office.
(Part number for sample order:
The information in this document is subject to change without notice. Before using this document, please
confirm that this is the latest version.
Not all devices/types available in every country. Please check with local NEC representative for
availability and additional information.
Pins 1 through 10 are in pull-out directi on.
Qty 2.5 kp/reel.
PC8125GR, Quantity: 20 pcs/unit)
µ
Caution Electro-static sensitive device
The mark shows major revised points.
©
1997, 1999
Page 2
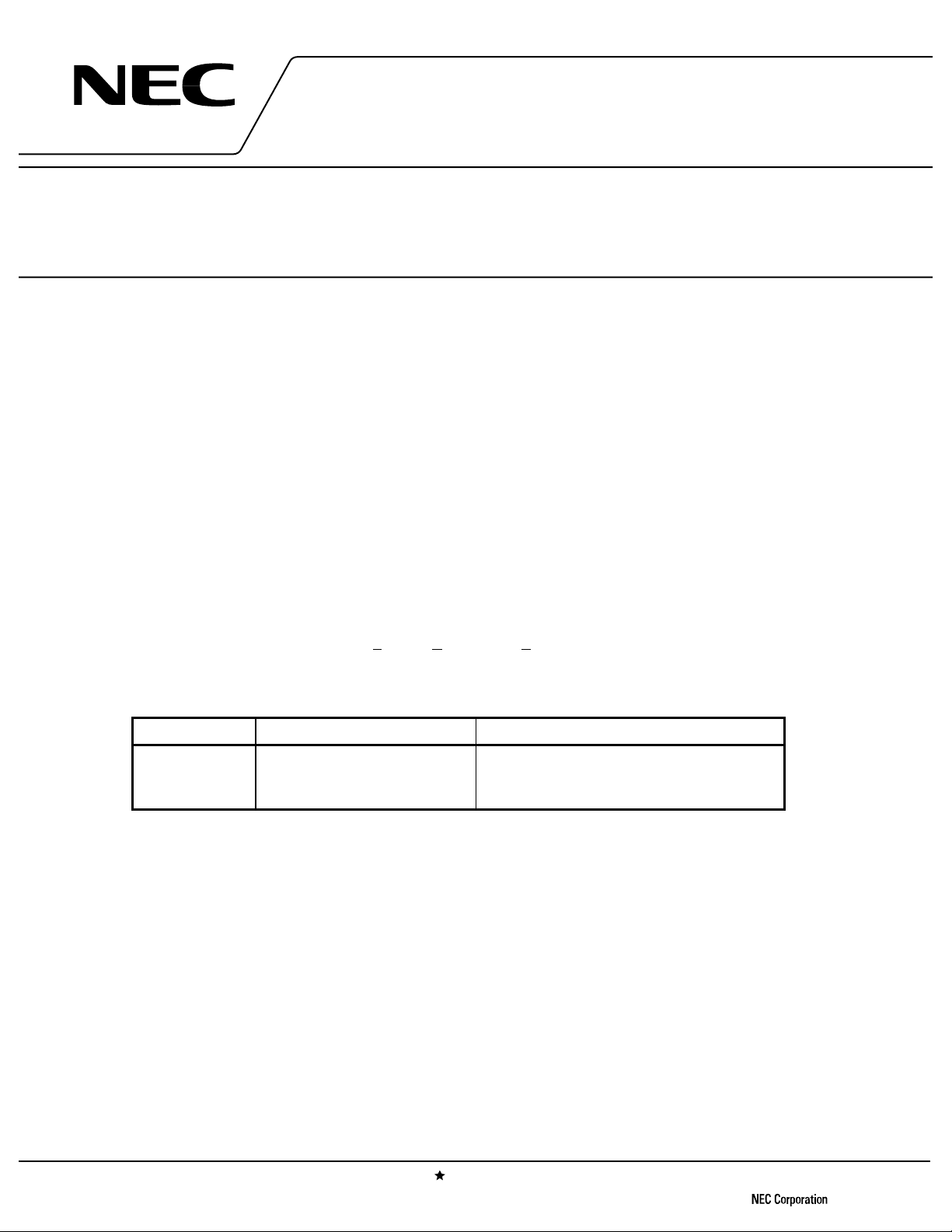
INTERNAL BLOCK DIAGRAM AND PIN CONNECTIONS (Top View)
V
CC
(MOD)
1
Reg. Reg.
20
CC
(Up-con.)
V
µµµµ
PC8125GR
Filter1
Filter2
Lo1 in
Lo1 inb
Qb
2
3
I
4
Ib
5
Q
6
7
8
× 2
9
LPF LPF
90 deg. Phase
Shifter (÷2)
GND
10
QUADRATURE MODULATOR SERIES PRODUCT
Part Number Functions
CC
I
(mA)
LO1in
f
(MHz)
MODout
f
(MHz)
RF Mixer
RFout
f
(MHz)
Phase
Shifter
RF
out
19
GND
18
GND
17
PS
V
16
V
AGC
15
GND
14
Lo2 in
13
Lo2 inb
12
GND
11
Package Application
PC8101GR 150 MHz Quad.Mod
µ
PC8104GR RF Up-Converter + IF
µ
15/@2.7 V
28/@3.0 V
100 to 300 50 to 150
100 to 400
External F/F CT-2 etc.
900 to 1 900
Quad.Mod
PC8105GR 400 MHz Quad.Mod
µ
PC8110GR 1 GHz Direct Quad.Mod
µ
PC8125GR RF Up-Converter + IF
µ
16/@3.0 V
24/@3.0 V
36/@3.0 V
100 to 400 External
800 to 1 000 External
220 to 270
1 800 to 2 000
Quad.Mod + AGC
PC8126GR 915 to 960 915 to 960
µ
PC8126K
µ
PC8129GR
µ
900 MHz Direct Quad.Mod
with Offset-Mixer
2LO IF Quad. Mod+RF
×
35/@3.0 V
28/@3.0 V
889 to 960 889 to 960
200 to 800 100 to 400
800 to 1 900
Up-Converter
µ
PC8139GR-7JH
PC8158K RF Up-Converter + IF
µ
Transceiver IC
(1.9 GHz Indirect Quad.
Mod + RX-IF + IF VCO)
TX: 32.5
RX: 4.8
/@3.0 V
28/@3.0 V
220 to 270
100 to 300
1 800 to 2 000
800 to 1 500
Quad.Mod + AGC
Remark
Please refer to the data sheet of each part number.
Doubler
+ F/F
F/F
CR
20-pin
SSOP (225 mil)
16-pin
SSOP (225 mil)
20-pin
SSOP (225 mil)
28-pin QFN
20-pin
SSOP (225 mil)
30-pin
TSSOP (225 mil)
28-pin QFN
Digital Comm.
PDC800 MHz, etc.
PHS
PDC800 MHz
GSM,
DCS1800, etc.
PHS
PDC800 M/1.5 G
2
Data Sheet P11486EJ2V0DS00
Page 3
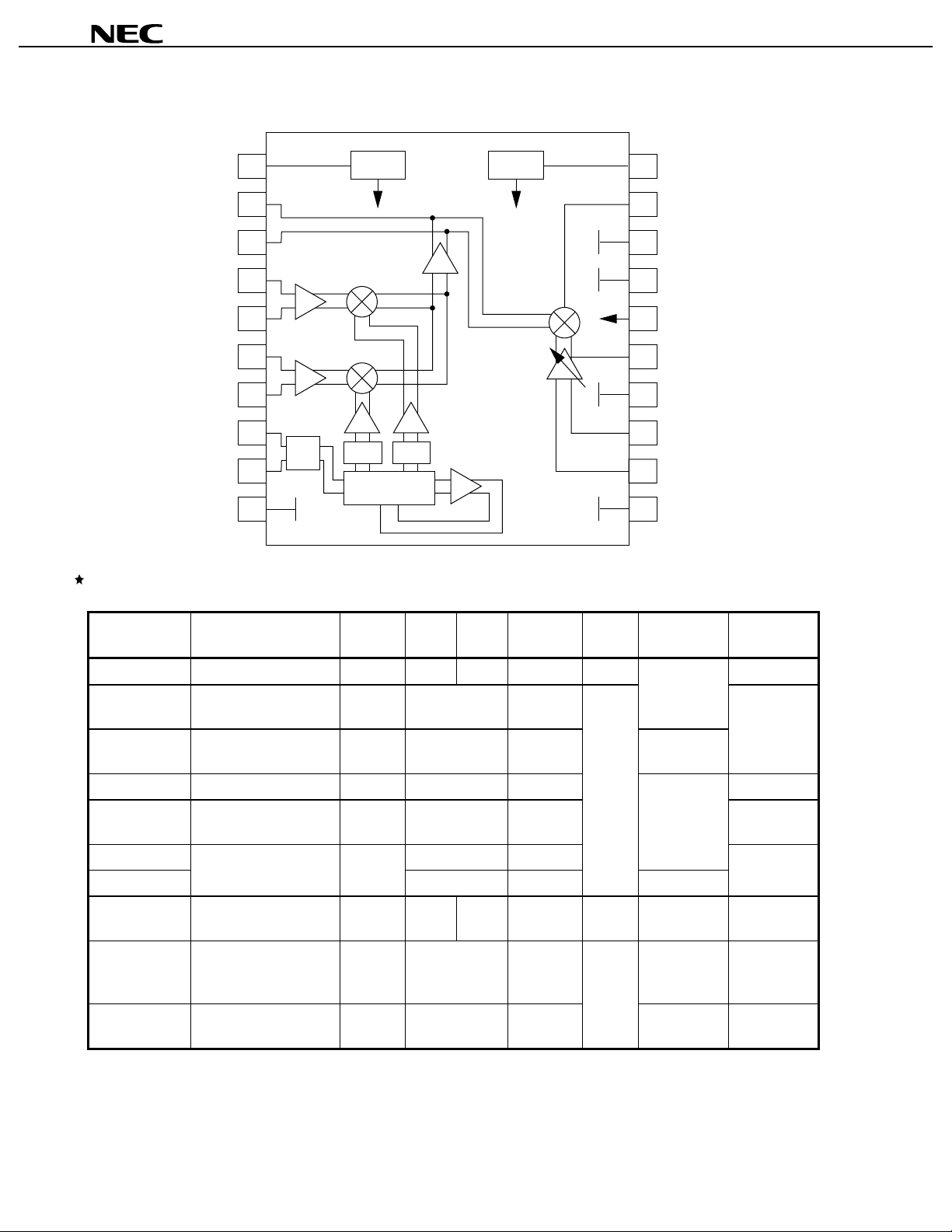
APPLICATION EXAMPLE (PHS)
µµµµ
PC8125GR
RX
TX
SW
PA
÷N
LC Filter
PLL
µ
PC8125GR
φ
0°
90°
DEMO.
PLL
I
Q
RSSI
I
Q
Data Sheet P11486EJ2V0DS00
3
Page 4

µµµµ
PC8125GR
CONTENTS
1. ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS................................................................................................. 5
2. RECOMMENDED OPERATING CONDITIONS ............................................................................ 5
3. ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS.............................................................................................. 6
4. STANDARD CHARACTERISTICS FOR REFERENCE............................................................... 6
5. PIN EXPLANATIONS ..................................................................................................................... 7
6. RELATIONS BETWEEN AMPLITUDE AND V
7. STANDARD TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS ............................................................................... 10
7.1 DC Performance................................................................................................................... 11
7.2 Output Performance ............................................................................................................ 12
7.3 Adjacent Channel Interference Power ............................................................................... 14
7.4 Error and Accuracy.............................................................................................................. 15
7.5 Power Save Response Time ............................................................................................... 16
7.6 Spectrum............................................................................................................................... 18
7.7 Input/output Impedance ...................................................................................................... 19
8. TEST CIRCUIT (SINGLE ENDED INPUT) .................................................................................. 20
9. APPLICATION CIRCUIT EXAMPLE (IN THE CASE OF SINGLE ENDED INPUT).............. 21
10. ASSEMBLED TEST BOARD ........................................................................................................ 22
11. PACKAGE DIMENSIONS............................................................................................................... 23
12. NOTE ON CORRECT USE........................................................................................................... 24
CC
/2 BIAS OF I/Q INPUT SIGNALS ............. 9
13. RECOMMENDED SOLDERING CONDITIONS ............................................................................ 24
4
Data Sheet P11486EJ2V0DS00
Page 5
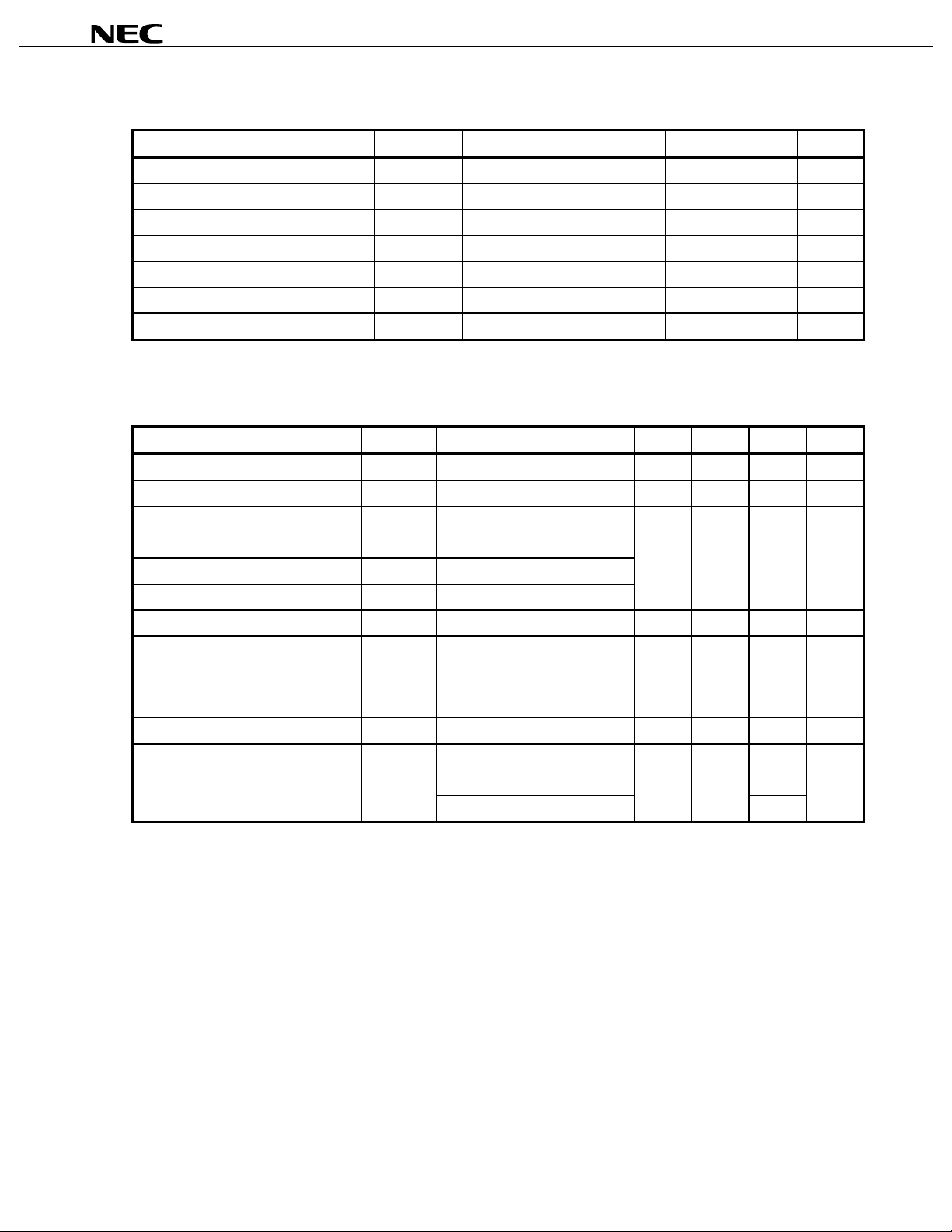
1. ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Parameter Symbol Conditions Rating Unit
µµµµ
PC8125GR
Supply Voltage V
Power Save Control Voltage V
AGC Control Voltage V
IQ DC Offset Voltage IQ
Power Dissipation P
Operating Ambient Temperature T
Storage Temperature T
Mounted on a 50 × 50 × 1.6 mm double copper clad epoxy glass PWB.
Note
CC
PS
AGC
(DC)
stg
TA = +25 °C 6.0 V
TA = +25 °C 6.0 V
TA = +25 °C 6.0 V
TA = +25 °C, 4 to 7 pins 4.0 V
D
A
TA = +85 °C
2. RECOMMENDED OPERATING CONDITIONS
Parameter Symbol Test Conditions MIN. TYP. MAX. Unit
Supply Voltage V
Operating Ambient Temperature T
Up-converter RF Frequency f
Up-converter Input Frequency f
Modulator Output Frequency f
Lo1 Input Frequency f
Lo2 Input Frequency f
I/Q Input Frequency f
Lo1 Input Level P
Lo2 Input Level P
I/Q Input amplitude V
CC
A
RFout
UPCONin
MODout
Lo1in
Lo2in
I/Qin
Lo1in
Lo2in
I/Qin
Lo1in
P
= −10 dBm
Lo2in
P
= −10 dBm 1 500
I/Qin
V
= 500 mVp-p max.
(Single ended Input)
I/Qin
= 250 mVp-p max.
V
(Differential Input)
Single ended Input
Differential Input 250
Note
430 mW
40 to +85
−
55 to +150
−
2.7 3.0 5.5 V
40
−
1 800
220
DC
11.5
−
15
−
−−
25
+
−
−
−
−
10
−
10
−
85
−
2 000 MHz
270 MHz
1 800 MHz
10 M Hz
5dBm
−
5dBm
−
500 mVp-p
C
°
C
°
C
°
Data Sheet P11486EJ2V0DS00
5
Page 6
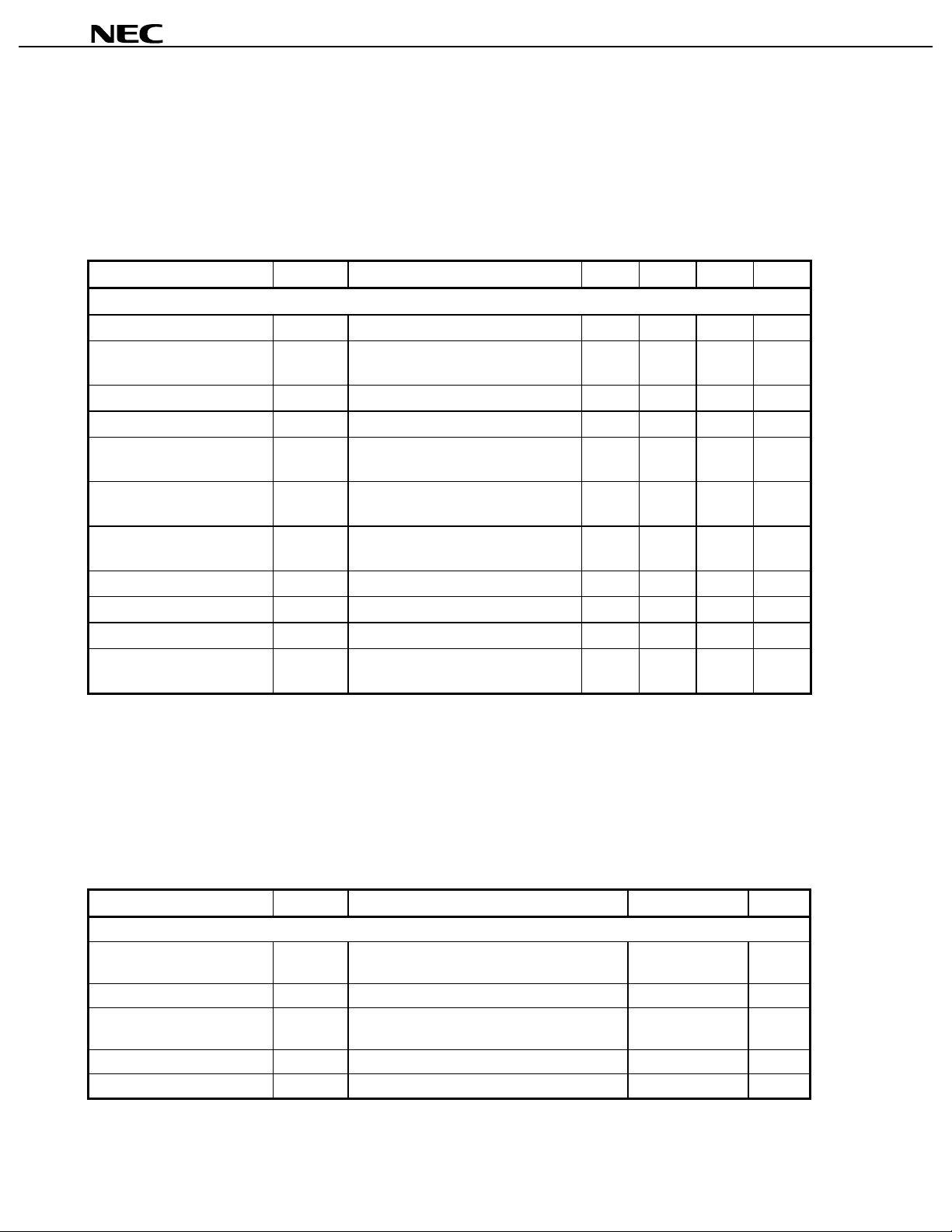
3. ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
µµµµ
PC8125GR
(TA = +25 °C, VCC = 3.0 V, unless otherwise specified V
I/Q (DC) = Ib/Qb (DC) = VCC/2 = 1.5 V, f
V
= 500 mVp-p (Single ended) or 250 mVp-p (Differential Input), π/4DQPSK modulation,
I/Qin
= 24 kHz,
I/Qin
Data rate: 384 kbps, Filter roll off: α = 0.5, MOD pattern: all zero [0000], f
f
= 1 650 MHz, P
Lo2in
= −10 dBm, f
Lo2in
= 1 900 MHz + f
RFout
AGC
= 3.0 V, Vps = 3.0 V, R
)
I/Qin
= 250 MHz, P
Lo1in
Parameter Symbol Test Conditions MIN. TYP. MAX. Unit
UP-CONVERTER + QUADRATURE MODULATOR TOTA L
Total Circuit Current ICC
Total Circuit Current at
TOTAL
CC(PS) TOTALVPS
I
No input signal 30 36 48 mA
≤ 0.5 V (Low)
Sleep Mode
Total Output Power 1 P
RFout 1
Lo Carrier Leakage LoL f
Image Rejection
ImR
V
Lo1
AGC
+ f
= 3.0 V
Lo2
(Side Band Leakage)
I/Q 3rd Order Intermodulation
IM
3(I/Q)
Distortion
AGC Amp. Gain control
GCR V
AGC
= 2.5 V to 0 V 28 40
range
Power Save Rise Time T
Power Save Fall Time T
PS(Rise)
PS(Fall)
PS(Low)
V
PS(Low)
V
→ V
→ V
PS(High)
PS(High)
Error Vector Magnitude EVM MOD Pattern: PN9
Adjacent Channel Power P
adj
f = 600 kHz
∆
MOD Pattern: PN9
AGC
= 10 kΩ, Rps = 1 kΩ,
= −10 dBm,
Lo1in
−
13
−
0.3 10
9
−
−−37−
−−35−
−−50−
−
−
−
25
510
2.5 4.5 %rms
−−68−
A
µ
5dBm
−
30 dBc
30 dBc
30 dBc
−
dB
s
µ
s
µ
60 dBc
4. STANDARD CHARACTERISTICS FOR REFERENCE
(TA = +25 °C, VCC = 3.0 V, unless otherwise specified V
I/Q (DC) = Ib/Qb (DC) = VCC/2 = 1.5 V, f
V
= 500 mVp-p (Single ended) or 250 mVp-p (Differential Input), π/4DQPSK modulation,
I/Qin
= 24 kHz,
I/Qin
Data rate: 384 kbps, Filter roll off: α = 0.5, MOD pattern: all zero [0000], f
f
= 1 650 MHz, P
Lo2in
Parameter Symbol Test Conditions Reference Unit
UP-CONVERTER + QUADRATURE MODULATOR TOTA L
Lo1 × n Spurious Level P
Total Output Power P
I/Q Input Inpedance Z
I/Q Bias Current I
Lo1 Input VSWR Z
6
= −10 dBm, f
Lo2in
= 1 900 MHz + f
RFout
SUP(Lo1)
RFout 2
I/Qin
I/Q
Lo1in
Lo1 × 7, Lo1 × 7 (Image)
Lo1 × 8, Lo1 × 8 (Image)
AGC
V
= 0.5 V
I/Qin
f
= 24 kHz,
I to Ib, Q to Qb
I, Ib, Q, Qb to GND (each) 5
Lo1
f
= 220 M to 270 MHz 1.2:1
Data Sheet P11486EJ2V0DS00
AGC
= 3.0 V, Vps = 3.0 V, R
)
I/Qin
= 250 MHz, P
Lo1in
AGC
= 10 kΩ, Rps = 1 kΩ,
= −10 dBm,
Lo1in
60 dBc
−
50 dBm
−
200 k
Ω
A
µ
Page 7
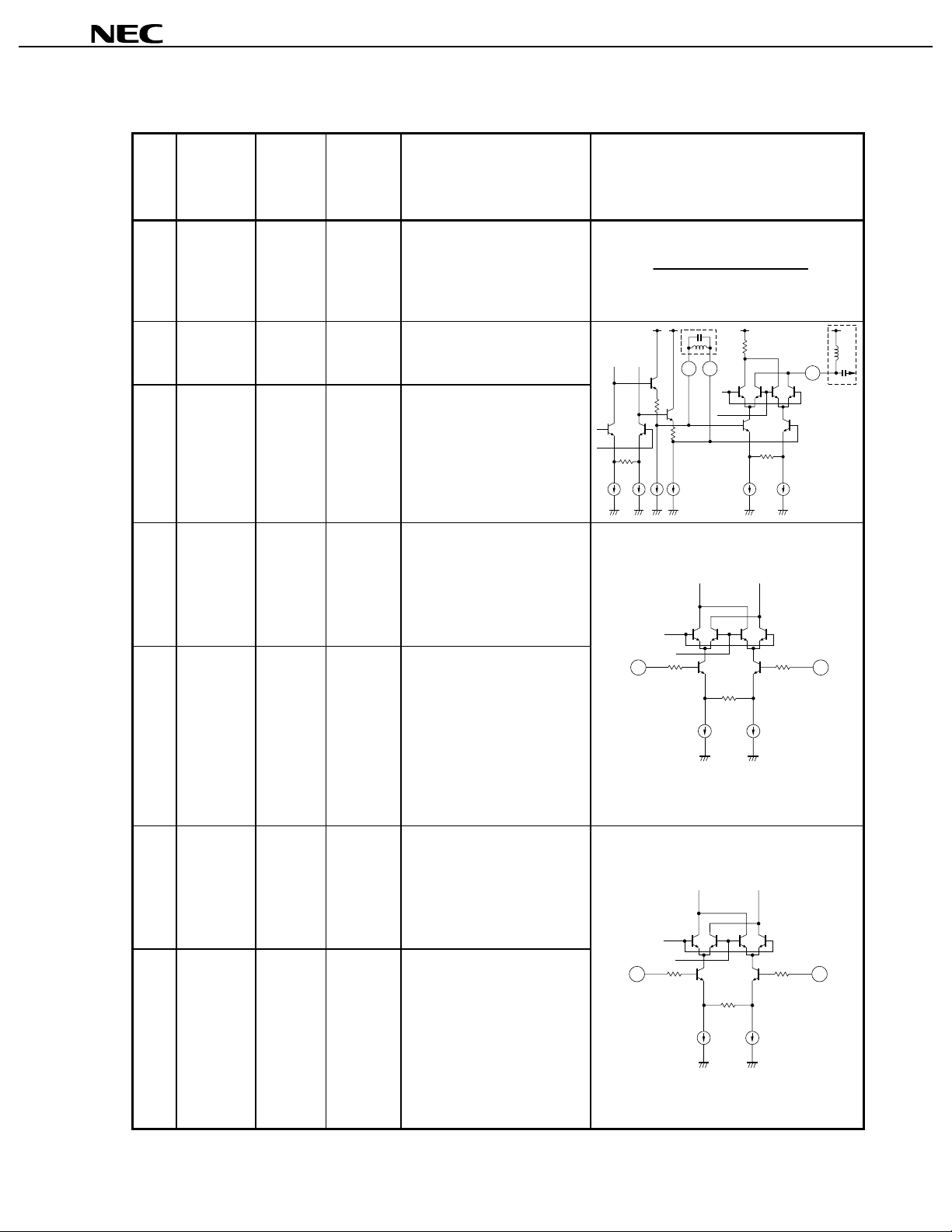
5. PIN EXPLANATIONS
µµµµ
PC8125GR
Pin
NO.
Symbol
Supply
Voltage
(V)
1VCC(MOD.) 2. 7 to
5.5
2 Filter1
3 Filter2
4IV
5IbV
6QV
7QbV
−
−
CC
/2
CC
/2
CC
/2
CC
/2
Pin
Voltage
Function and Description Internal Equivalent Circuit
Typ. (V)
CC
= 3 V
@V
−
Supply voltage pin for the
modulator. Internal regulator
can be kept stable condit i on
of supply bias against the
variable temperature or V
1.9 Filter pin can control
spurious (Lo1 × n) by insertion
BPF between Filter2 pin.
1.9 Filter pin can control
spurious (Lo1 × n) by insertion
BPF between Filter1 pin.
−
Input for I signal. This input
impedance is 200 kΩ. In case
of that I/Q input si gnal s are
single ended, amplitude of the
signal is 500 mVp-p max.
See
−
Input for I signal. This input
impedance is 200 kΩ. In case
of that I/Q input si gnal s are
single ended, V
signal should be input. In
case of the I/Q input signals
are differential, amplit ude of
the signal is 250 mVp-p max .
See
−
Input for Q signal. This i nput
impedance is 200 kΩ. In case
of that I/Q input si gnal s are
single ended, amplitude of the
signal is 500 mVp-p max.
See
−
Input for I signal. This input
impedance is 200 kΩ. In case
of that I/Q input si gnal s are
single ended, V
signal should be input. In
case of the I/Q input signals
are differential, amplit ude of
the signal is 250 mVp-p max .
See
Chapter 6
CC
/2 biased DC
Chapter 6
Chapter 6
CC
/2 biased DC
Chapter 6
CC
.
3192
.
2.1 k
2.1 k
54
2 k
.
.
2.1 k
6 7
2.1 k
2 k
.
Data Sheet P11486EJ2V0DS00
7
Page 8
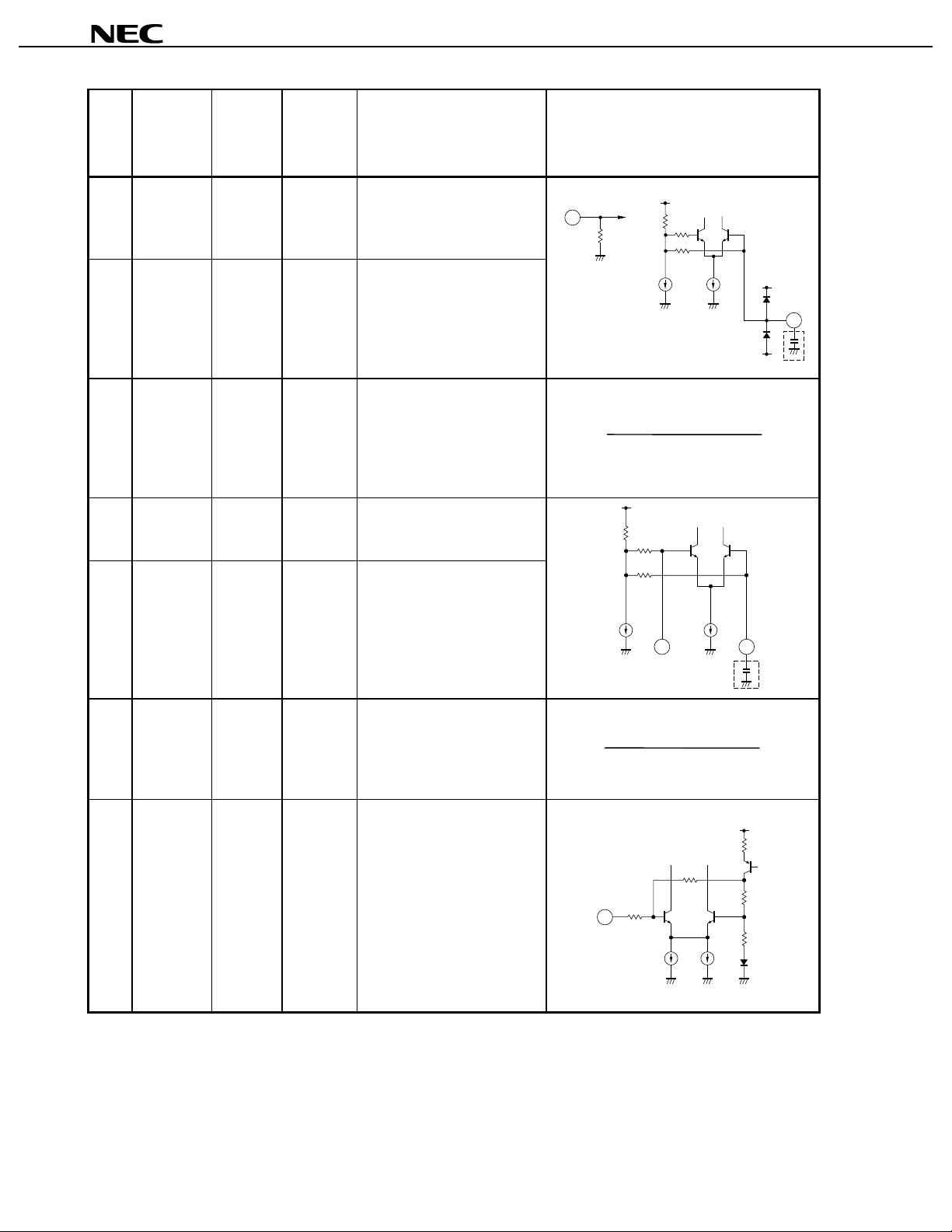
µµµµ
13 12
15
15 k
15 k
1 k
1 k
9 k
PC8125GR
Pin
NO.
Symbol
8 Lo1 in
9 Lo1 inb
10
11
12 Lo2 inb
13 Lo2 in
GND
(MOD.)
Supply
Voltage
(V)
−
−
−
−
−
Pin
Voltage
Typ. (V)
CC
= 3 V
@V
0 Lo input for the phase shi fter.
2.4 Bypass of the Lo1 input.
0 Ground pin for modulator
1.9 Bypass of the Lo2 input.
1.9 Lo input for the up-converter.
Function and Description Internal Equivalent Circuit
This input impedance is
internally matched to 50 Ω.
This pin is grounded through
external capacitor.
block. Connect to the ground
with minimum inductanc e.
Track length should be kept as
short as possible.
This pin is grounded through
external capacitor.
This pin is high impedance
input, and should be matched
external circuit.
8
50
9
14
17
18
15 V
8
GND
(Up-con.)
AGC
−
0 to V
0 Ground pin for up-Converter.
Connect to the ground with
minimum impedance.
Track length should be kept as
short as possible.
CC
−
Control voltage input pin for
AGC amplitude. RF output
level can be governed by
supply voltage to this pin.
AGC performance can be
AGC
adjustable R
Data Sheet P11486EJ2V0DS00
value.
Page 9
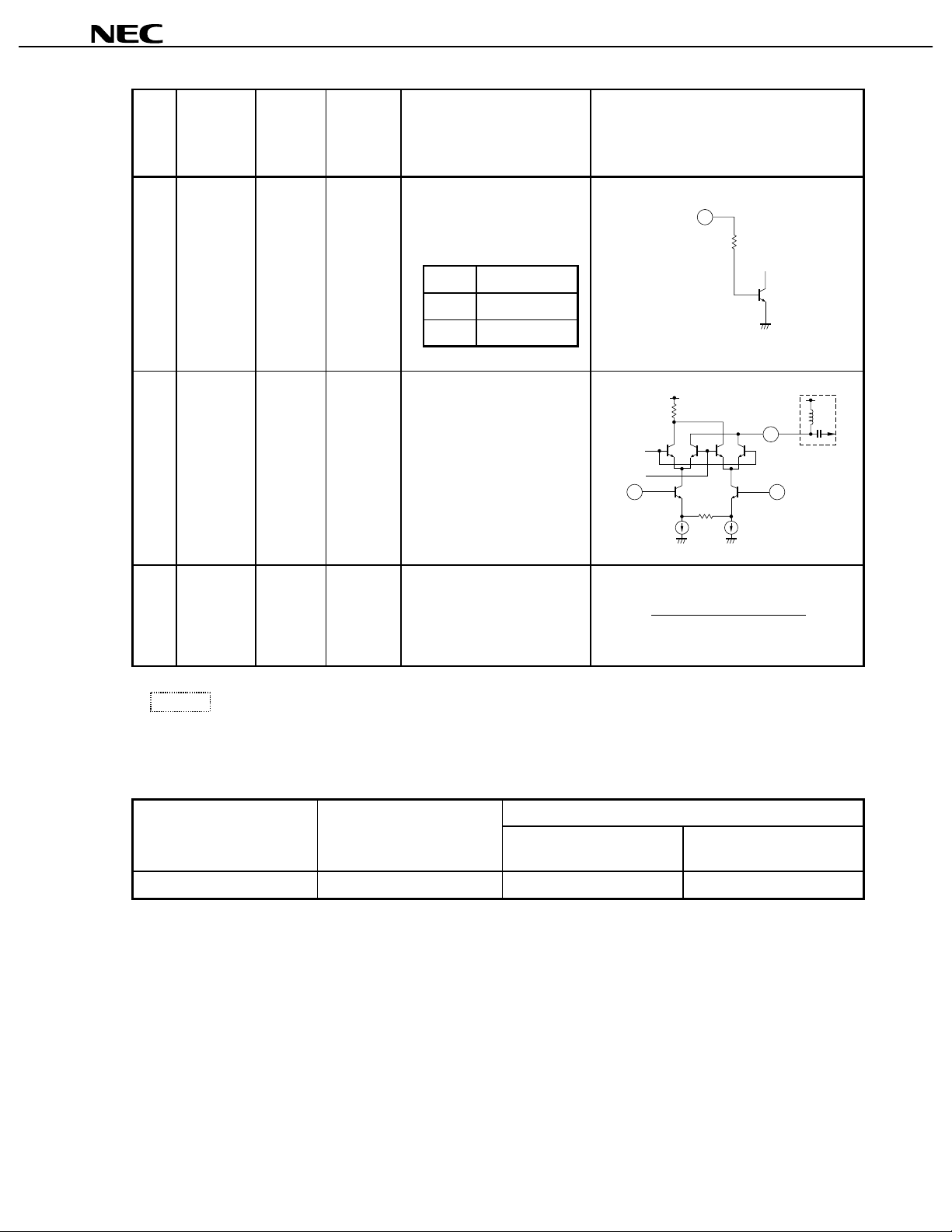
µµµµ
16
1.6 k
2 3
19
PC8125GR
Pin
NO.
Symbol
16 V
19 RF
Supply
Voltage
(V)
PS
0 to V
Voltage
Function and Description Internal Equivalent Circuit
Typ. (V)
CC
= 3 V
@V
CC
−
Power save control pin for
phase shifter and up-converter
can controlled the On/Sleep
state with bias as follows:
Pin
VPS(V) STATE
2 to VCCON (Active Mode)
0 to 0.5 OFF (Sleep Mode)
out
CC
V
−
RF output from up-converter.
This pin is open collect or
output and should be matched
external circuit.
20 V
(Up-con.)
CC
2.7 to
5.5
−
Supply voltage pin for the
up-converter.
An internal regulator helps
keep the device stable against
CC
temperature or V
variation.
: Externally
6. RELATIONS BETWEEN AMPLITUDE AND VCC/2 BIAS OF I/Q INPUT SIGNALS
Supply voltage
CC
V
(V)
I/Q DC Voltage(V)
CC
V
/2 = I = Ib = Q = Qb
2.7 to 3.0 to 5.5 1.35 to 1.5 to 2.75
Single ended input
I/Q Input signal (mVp-p)
I = Q
500
≤
Differential input
I = Ib = Q = Qb
≤
250
Data Sheet P11486EJ2V0DS00
9
Page 10

7. STANDARD TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS
µµµµ
PC8125GR
TA = +25 °C, VCC = Vps = 3 V, V
f
= 24 kHz, V
I/Qin
= 500 mVp-p (Single ended), Data rate: 384 kbps, Filter roll off: α = 0.5,
I/Qin
MOD pattern: all zero [0000], f
f
= 1 900 MHz + f
RFout
unless otherwise specified
I/Qin
AGC
= 3 V, R
= 250 MHz, P
Lo1in
AGC
= 10 kΩ, Rps = 1 kΩ, I/Q (DC) = Ib/Qb (DC) = VCC/2 = 1.5 V,
= −10 dBm, f
Lo1in
= 1 650 MHz, P
Lo2in
= −10 dBm,
Lo2in
10
Data Sheet P11486EJ2V0DS00
Page 11

7.1 DC Performance
µµµµ
PC8125GR
TOTAL CIRCUIT CURRENT vs. SUPPLY VOLTAGE
50
40
(mA)
CC TOTAL
30
No input signal
20
: TA = +25 °C
A
= −40 °C
: T
A
= +85 °C
10
Total Circuit Current I
0
1023
Supply Voltage V
: T
4
CC
(V)
5
TOTAL CIRCUIT CURRENT vs.
OPERATING AMBIENT TEMPERATURE
50
No input signal
45
40
(mA)
35
CC TOTAL
30
−40 °C
+25 °C
+85 °C
25
20
15
10
Total Circuit Current I
5
0
−50 0
Operating Ambient Temperature T
50
A
(°C) Operating Ambient Temperature TA (°C)
100
TOTAL CIRCUIT CURRENT vs. POWER SAVE VOLTAGE
50
40
(mA)
CC TOTAL
30
No input signal
20
: TA = +25 °C
A
= −40 °C
: T
A
= +85 °C
10
Total Circuit Current I
0
0123
Power Save Voltage V
: T
PS
(V)
TOTAL CIRCUIT CURRENT AT SLEEP MODE vs.
OPERATING AMBIENT TEMPERATURE
50
µ
( A)
VPS ≤ 0.5 V (Low)
45
40
CC(PS) TOTAL
35
30
25
20
15
10
5
0
Total Circuit Current at Sleep Mode I
−50 0 50
100
TOTAL CIRCUIT CURRENT AT SLEEP MODE vs.
SUPPLY VOLTAGE
µ
1
( A)
VPS ≤ 0.5 V (Low)
0.9
0.8
CC(PS) TOTAL
0.7
0.6
0.5
2.7 V
3.0 V
0.4
0.3
0.2
0.1
0
Total Circuit Current at Sleep Mode I
23
Supply Voltage V
456
CC
(V)
50
40
(mA)
5.5 V
CC TOTAL
30
20
10
Total Circuit Current I
0
Data Sheet P11486EJ2V0DS00
TOTAL CIRCUIT CURRENT vs.
POWER SAVE VOLTAGE
No input signal
: VCC = 3.0 V
CC
= 2.7 V
: V
CC
= 5.5 V
: V
012345
Power Save Voltage V
PS
(V)
11
Page 12

7.2 Output Performance
µµµµ
PC8125GR
TOTAL OUTPUT POWER, LO LEAKAGE, IMAGE REJECTION,
3 (I/Q)
vs. OPERATING AMBIENT TEMPERATURE
IM
0
−10
(dBm)Total Output Power P
−20
RFout1
−30
−40
−50
Total Output Power P
−60
−70
−40 0 +40
Operating Ambient Temperature T
ImR
LoL
P
IM
RFout
3 (I/Q)
1
+80 +120
A
0
−10
−20
−30
−40
−50
−60
−70
(°C)
TOTAL OUTPUT POWER, LO LEAKAGE, IMAGE REJECTION,
3 (I/Q)
vs. SUPPLY VOLTAGE
(dBc)Lo Leakage LoL, Image Rejection ImR, IM
3 (I/Q)
00
−10
(dBm)
−20
RFout1
−30
−40
IM
P
RFout
ImR
LoL
1
−50
IM
Total Output Power P
−60
−70
Lo Leakage LoL, Image Rejection ImR, IM
0123456
Supply Voltage V
3(I/Q)
CC
(V)
TOTAL OUTPUT POWER vs. AGC CONTROL VOLTAGE TOTAL OUTPUT POWER vs. AGC CONTROL VOLTAGE
0
0
: TA = +25 °C
A
= −40 °C
−10
(dBm)
−20
RFout1
−30
−40
−50
−60
GCR = 41.2 dB
(V
CC
= 3.0 V)
GCR = 41.0 dB
(V
CC
= 2.7 V)
GCR = 42.4 dB
(V
CC
= 5.5 V)
: VCC = 3.0 V
CC
: V
CC
: V
= 2.7 V
= 5.5 V
(dBm)Total Output Power P
RFout1
Total Output Power P
−10
−20
−30
−40
−50
−60
: T
: T
A
= +85 °C
GCR = 43.0 dB
(T
A
= −40
GCR = 41.2 dB
(T
A
= +25
GCR = 37.8 dB
(T
A
= +85
°C)
°C)
°C)
(dBc)
3 (I/Q)
−10
−20
−30
−40
−50
−60
−70
Lo Leakage LoL, Image Rejection ImR, IM
−70
0123
AGC Control Voltage V
45
AGC
(V) AGC Control Voltage V
TOTAL OUTPUT POWER, LO LEAKAGE, IMAGE REJECTION,
3 (I/Q)
vs. AGC CONTROL VOLTAGE
IM
0
P
−10
(dBm)
RFout1
−20
−30
−40
RFout
ImR
LoL
−50
Total Output Power P
−60
−70
12
10
IM
3 (I/Q)
23
AGC
(V)
Data Sheet P11486EJ2V0DS00
0
−10
−20
−30
−40
−50
−60
−70
−70
0123
AGC
(V)
TOTAL OUTPUT POWER vs. AGC CONTROL VOLTAGE
+10
(dBc)
3 (I/Q)
0
Slope : 118 dB/V
Slope : 41 dB/V
−10
R
AGC
(dBm)
−20
RFout1
= 80 kΩ
R
AGC
= 10 kΩ
−30
−40
−50
−60
−70
10
AGC Control Voltage V
23
AGC
(V)AGC Control Voltage V
Page 13

µµµµ
PC8125GR
TOTAL OUTPUT POWER, LO LEAKAGE,
IMAGE REJECTION, IM
3 (I/Q) vs. LO1 INPUT LEVEL
0
PRFout1
−10
−20
−30
ImR
−40
LoL
−50
Total Output Power PRFout1 (dBm)
−60
−70
−30 −20 −10 0 +10
Lo1 Input Level P
IM3 (I/Q)
Lo1in (dBm) I/Q Input Amplitude VI/Qin (mVp-p)
LO1 × N SPURIOUS LEVEL, TOTAL OUTPUT POWER
vs. SUPPLY VOLTAGE
−40
−50
0
−10
−20
−30
−40
−50
−60
−70
0
−10
TOTAL OUTPUT POWER vs. I/Q INPUT AMPLITUDE
0
VAGC = 3 V
−10
−20
RFout (dBm)
−30
AGC = 1.3 V
V
−40
Total Output Power P
−50
−60
Lo Leakage LoL, Image Rejection ImR, IM3 (I/Q) (dBc)
100 200 500 1 000 1 200
LO1 × N SPURIOUS LEVEL, TOTAL OUTPUT POWER
vs. OPERATING AMBIENT TEMPERATURE
−40
: PRFout
: 7fLo1
: 7fLo1 (Image)
Lo1
: 8f
: 8fLo1 (Image)
−50
0
−10
−60
: PRFout
: 7fLo1
Lo1 × n spurious Level PSUP (Lo1) (dBc)
: 7fLo1 (Image)
Lo1
: 8f
: 8fLo1 (Image)
−70
0123
Supply Voltage V
TOTAL OUTPUT POWER vs. LO2 INPUT LEVEL
+10
456
CC (V)
0
VAGC = 3 V
−10
−20
−30
VAGC = 1.3 V
−40
−50
Total Output Power PRFout (dBm)
−60
−70
−40 −30 −20 −10
Lo2 Input Level P
Lo2in (dBm)
0 +10
−20
−60
−20
Total Output Power PRFout1 (dBm)
Lo1 × n spurious Level PSUP (LO1) (dBc)
−30 −30
−70
−40 +40 +800
+120
Operating Ambient Temperature TA (°C)
Total Output Power PRFout1 (dBm)
Data Sheet P11486EJ2V0DS00
13
Page 14

7.3 Adjacent Channel Interference Power
µµµµ
PC8125GR
ADJACENT CHANNEL POWER vs. AGC CONTROL VOLTAGE
MOD pattern : PN 9
−40
(dBc)
adj
−50
−60
∆f = ±600 kHz
−70
∆f = ±900 kHz
−80
Adjacent Channel Power P
012
AGC
AGC Control Voltage V
(V)
3
ADJACENT CHANNEL POWER vs. SUPPLY VOLTAGE
−20
−25
−30
(dBc)
adj
−35
∆f = ±600 kHz,
MOD Pattern: PN9
−40
−45
−50
−55
−60
Adjacent Channel Power P
−65
−70
234
Supply Voltage V
56
CC
(V)
ADJACENT CHANNEL POWER vs. I/Q INPUT AMPLITUDE
MOD Pattern: PN9
−50
(dBc)
adj
−60
∆f = ±600 kHz
−70
∆f = ±900 kHz
−80
Adjacent Channel Power P
100 200 500
I/Q Input Amplitude V
I/Qin
(mV
1 000
P-P
)
ADJACENT CHANNEL POWER vs.
OPERATING AMBIENT TEMPERATURE
0
∆f = ±600 kHz,
MOD Pattern: PN9
−10
(dBc)
adj
−20
−30
−40
−50
Adjacent Channel Power P
−60
−70
−50 0 50
Operating Ambient Temperature T
A
(°C)
100
14
Data Sheet P11486EJ2V0DS00
Page 15

7.4 Error and Accuracy
µµµµ
PC8125GR
PHASE ERROR, MAGNITUDE ERROR, ERROR VECTOR
MAGNITUDE, I/Q OFFSET vs. AGC CONTROL VOLTAGE
10
8
6
4
φ
2
Phase Error ∆ (deg.), Magnitude Error ∆A(%rms),
Error Vector Magnitude EVM (%rms)
0
01
ERROR VECTOR MAGNITUDE vs. SUPPLY VOLTAGE
5
4.5
4
3.5
3
2.5
2
1.5
1
Error Vector Magnitude EVM (%rms)
0.5
0
AGC Control Voltage V
234
Supply Voltage V
MOD Pattern: PN9
I/Q Offset
EVM
∆A
∆
φ
23
AGC (V)
MOD Pattern: PN9
56
CC (V)
−20
−30
−40
−50
PHASE ERROR, MAGNITUDE ERROR, ERROR VECTOR
MAGNITUDE, I/Q OFFSET vs. I/Q INPUT AMPLITUDE
10
MOD Pattern: PN9
8
I/Q Offset
(off) (dB)
I/Q Offset I/Q
6
4
φ
2
Phase Error ∆ (deg.), Magnitude Error ∆A(%rms),
Error Vector Magnitude EVM (%rms)
0
5
4.5
4
3.5
3
2.5
2
1.5
1
Error Vector Magnitude EVM (%rms)
0.5
0
100 200 500 1 000
I/Q Input Amplitude VI/Qin (mV
ERROR VECTOR MAGNITUDE vs.
OPERATING AMBIENT TEMPERATURE
−50 0 50
Operating Ambient Temperature T
EVM
∆A
∆
φ
P-P
)
MOD Pattern: PN9
A (°C)
100
−20
−30
−40
−50
−60
I/Q Offset I/Q (off) (dB)
Data Sheet P11486EJ2V0DS00
15
Page 16

7.5 Power Save Response Time
µµµµ
PC8125GR
POWER SAVE RISE TIME vs. SUPPLY VOLTAGE
4
µ
3
2.7 V
2
3.0 V
VPS (LOW)
→
V
1
Power Save Rise Time TPS (Rise) ( s)
0
23
Supply Voltage V
4
56
CC (V)
POWER SAVE RISE TIME vs.
OPERATING AMBIENT TEMPERATURE
4
−40 ˚ C +85 ˚ C
3.5
µ
( s)
3
PS (Rise)
2.5
+25 ˚ C
2
1.5
1
Power Save Rise Time T
0.5
→
V
A (°C)
0
−50 0 50
VPS (LOW)
Operating Ambient Temperature T
PS (HIGH)
5.5 V
PS (HIGH)
100
POWER SAVE FALL TIME vs. SUPPLY VOLTAGE
8
VPS (HIGH)
V
→
7
µ
6
5
4
3
2
Power Save Fall Time TPS (Fall) ( s)
1
0
234
Supply Voltage V
56
CC (V)
POWER SAVE FALL TIME vs.
OPERATING AMBIENT TEMPERATURE
10
VPS (LOW)
→
V
9
8
µ
7
6
5
4
3
2
Power Save Fall Time TPS (Fall) ( s)
1
0
−50 0 50
Operating Ambienrt Temperature T
PS (LOW)
PS (HIGH)
100
A (°C)
16
Data Sheet P11486EJ2V0DS00
Page 17

µµµµ
PC8125GR
OUTPUT RESPONSE (1)
(V
CC
= 2.7 V)
ATTEN 10 dB
RL 0 dBm 10 dB/
RBW : 2.0 MHz VBW : 3.0 MHz SWP : 50 s
µ
OUTPUT RESPONSE (3)
(V
CC
= 5.5 V)
ATTEN 10 dB
RL 0 dBm 10 dB/
OUTPUT RESPONSE (2)
(V
CC
= 3.0 V)
ATTEN 10 dB
RL 0 dBm 10 dB/
RBW : 2.0 MHz VBW : 3.0 MHz SWP : 50 s
µ
RBW : 2.0 MHz VBW : 3.0 MHz SWP : 50 s
µ
Data Sheet P11486EJ2V0DS00
17
Page 18

7.6 Spectrum
µµµµ
PC8125GR
REF 0.0 dBm
10 dB/
MKR
1.900 GHz
RBW
300 kHz
VBW
3 MHz
SWP
10 s
REF 0.0 dBm
10 dB/
MKR
1.8986 GHz
TYPICAL SINE WAVE MODULATION
OUTPUT SPECTRUM
ATT 10 dB
MARKER
1.900 GHz
–8.53 dBm
2f
Lo1
f
Lo1
3f
Lo1
4f
Lo1
5f
START 0 Hz STOP 2.500 GHz
_
write B_blank
A
P
RFout
f
Lo2
Lo1
6f
Lo1
TYPICAL SINE WAVE MODULATION
OUTPUT SPECTRUM (IN BAND) (1)
MARKER
1.8986 GHz
–9.38 dBm
ATT 10 dB
P
RFout
_
write B_blank
A
REF 0.0 dBm
10 dB/
REF
0.0 GHz
RBW
3 kHz
VBW
10 MHz
SWP
2.0 s
REF 0.0 dBm
10 dB/
REF
0.0 dBm
TYPICAL SINE WAVE MODULATION
OUTPUT SPECTRUM
ATT 10 dB
LoL
ImR
IM
3 (I/Q)
CENTER 1.9000000 GHz SPAN 200.0 kHz
_
A
P
RFout
Å•
1.9000274 GHz
write B_blank
MARKER
–8.80 dBm
TYPICAL SINE WAVE MODULATION
OUTPUT SPECTRUM (IN BAND) (2)
LO1
= 233.15 MHz,f
(f
P
ATT 10 dB
RFout
LO2
= 1662 MHz)
_
write B_blank
A
RBW
300 kHz
VBW
3 MHz
SWP
10 s
REF 0.0 dBm
10 dB/
REF
0.0 dBm
RBW
100 kHz
VBW
10 kHz
SWP
10 s
8f
7f
LO1
1.75 GHz
–69.1 dBm
LO1
(Image)
1.8 GHz
–65.0 dBm
8f
LO1
2.0 GHz
–68.0 dBm
7f
LO1
(Image)
2.05 GHz
–67.5 dBm
START 1.6500 GHz STOP 2.1500 GHz
TYPICAL SINE WAVE MODULATION
OUTPUT SPECTRUM (IN BAND) (3)
(f
LO1
= 233.15 MHz, f
MARKER
1.91793 GHz
–8.02 dBm
1895.15 to 1917.95 MHz
START 1.88000 GHz STOP 1.93000 GHz
LO2
= 1684.8 MHz)
ATT 10 dB
Frequency Band
Width for PHS
_
write B_blank
A
P
RFout
RBW
100 kHz
VBW
10 kHz
SWP
10 s
REF –10.0 dBm
10 dB/
ADJ BS
192 kHz
DL –10.0 dBm
RBW 3 kHz
VBW 10 kHz
SWP 5.0 s
Frequency Band
Width for PHS
1895.15 to 1917.95 MHz
START 1.88000 GHz STOP 1.93000 GHz
TYPICAL /4 DQPSK MODULATION
π
OUTPUT SPECTRUM
ATT 0 dB
MARKER
1.900600 GHz
–68.00 dB
2
1
CENTER 1.900000 GHz SPAN 2.000 MHz
*** Multi Marker List ***
No.1 : 1.899100 GHz –71.00 dB
No.2 : 1.899400 GHz –68.00 dB
No.3 : 1.900600 GHz –68.00 dB
No.4 : 1.900900 GHz –71.25 dB
3
4
18
Data Sheet P11486EJ2V0DS00
Page 19

7.7 Input/output Impedance
RF OUTPUT (19 pin) IMPEDANCE
V
RFout
CH2 S
Connect to Inductor (L2 = 100 nH) between 19 pin to 20 pin.
22
MARKER 3
1.9 GHz
CC
= VPS = 3.0 V
3 : 9.1445 Ω –84.355 Ω 993.01 fF
1 900.000 000 MHz
Marker :
1 : 900 MHz
2 : 1.5 GHz
3 : 1.9 GHz
µµµµ
PC8125GR
3
START 800.000 000 MHz STOP 2 000.000 000 MHz
Lo1 INPUT (8 pin) IMPEDANCE V
Lo1in
CH1 S
11
1 : 50 Ω 0 Ω 0 H
1
2
CC
= VPS = 3.0 V
MARKER 3
250 MHz
1
START 50.000 000 MHz STOP 500.000 000 MHz
Lo2 INPUT (13 pin) IMPEDANCE
V
Lo2in
CH2 S
11
CC
= VPS = 3.0 V
2 : 10.053 Ω –44.049 Ω 2.1898 pF
1 650.000 000 MHz
250.000 000 MHz
MARKER 2
1.65 GHz
2
3
START 800.000 000 MHz STOP 2 000.000 000 MHz
Data Sheet P11486EJ2V0DS00
1
Marker
1 : 900 MHz
2 : 1.65 GHz
3 : 1.9 GHz
19
Page 20

8. TEST CIRCUIT (SINGLE ENDED INPUT)
µµµµ
PC8125GR
100 pF
1 000 pF
1 000 pF
1 000 pF
1 000 pF
1VCC (MOD.) VCC (UP-CON.)
2 19
Filter1
C1 = 7 pFL1 = 47 nH
Filter2 GND
3 18
l GND
4 17
lb V
5 16
QVAGC
6 15
Qb GND
7 14
8 13
Lo1in Lo2in
9 12
Lo1inb Lo2inb
10 11
GND GND
RFout
20
1 000 pF L2 = 100 nH
ps
ZL = 50 Ω
1 000 pF
ZL = 50 Ω
C2 = 2 pF
100 pF
1 kΩ (R
10 kΩ (R
ps)
100 pFC3 = 3 pF
AGC)
100 pF
20
Data Sheet P11486EJ2V0DS00
Page 21

9. APPLICATION CIRCUIT EXAMPLE (IN THE CASE OF SINGLE ENDED INPUT)
µµµµ
PC8125GR
1VCC (MOD.) VCC (UP-CON.)
1 000 pF
2 19
Filter1
C1 = 7 pFL1 = 47 nH
Filter2 GND
3 18
4 17
l GND
5 16
1 000 pF
1 000 pF
100 pF
1 000 pF
For the details of application circuit and its explanations, please refer to application note ‘
Note
PC8101, 8104, 8105, 8125, 8129
µµµµ
lb V
QV
6 15
Qb GND
7 14
8 13
Lo1in Lo2in
9 12
Lo1inb Lo2inb
10 11
GND GND
’ (Document No.
P13251E
RFout
AGC
).
20
1 000 pF L2 = 100 nH
ps
1 000 pF
C2 = 2 pF
100 pF
ZL = 50 Ω
50 Ω Matching circuit
at fRFout = 1 900 MHz
5 kΩ (R
ps
)
10 kΩ (R
50 Ω Matching circuit
at fLo2in = 1650 MHz
ZL = 50 Ω
AGC
100 pFC3 = 3 pF
)
100 pF
Usage of
Data Sheet P11486EJ2V0DS00
21
Page 22

10. ASSEMBLED TEST BOARD
RF OUT LO 2 IN
3 pF
100 pF
C 3
V
PS
µ
PC8125GR
5 kΩ 10 kΩ
1000 pF
µµµµ
PC8125GR
V
AGC
2 pF
100 pF
C 2
1000 pF
1000 pF
I
b
L 2
7 pF
100 pF
1000 pF
Q
1000 pF
b
LO 1 IN
100 pF
Q INI IN
2.5000
φ
φ
V
CC
V
CC
0.6000
Cut
100 nH
47 nH
1000 pF
Notes 1.
Remark
22
Double-sided patterning with 35
GND pattern on backside.
2.
Solder coating over patterns.
3.
indicate through-holes.
{,
{
4.
m thick copper on polyhimid board sizing 50 × 50 × 0.4 mm.
µ
The test circuits and board pattern on data sheet are for performance evaluation use only. (They are
not recommended circuits.) In the case of actual design-in, matching circuit should be determined
using S-parameter of desired frequency in accordance to actual mounting pattern.
Data Sheet P11486EJ2V0DS00
Page 23

11.
PACKAGE DIMENSIONS
20 PIN PLASTIC SSOP (225 mil) (UNIT: mm)
µµµµ
PC8125GR
20
110
6.7 ± 0.3
1.8 MAX.
1.5 ± 0.1
11
detail of lead end
3˚
6.4 ± 0.2
4.4 ± 0.1
+7˚
–3˚
1.0 ± 0.2
0.1 ± 0.1
NOTE
0.5 ± 0.2
0.65
0.22
+0.10
–0.05
0.10
0.15
M
0.575 MAX.
0.15
+0.10
–0.05
Each lead centerline is located within 0.10 mm of its true position (T.P.) at maximum material condition.
Data Sheet P11486EJ2V0DS00
23
Page 24

µµµµ
PC8125GR
12. NOTE ON CORRECT USE
(1) Observe precautions for handling because of electro-static sensitive devices.
(2) Form a ground pattern as widely as possible to minimize ground impedance (to prevent undesired oscillation).
(3) Keep the track length of the ground pins as short as possible.
(4) Connect a bypass capacitor (example: 1 000 pF) to the VCC pin.
13. RECOMMENDED SOLDERING CONDITIONS
This product should be soldered under the following recommended conditions. For soldering methods and
conditions other than those recommended below, contact your NEC sales representative.
Soldering Method Soldering Conditions
Infrared Reflow Package peak temperature: 235 °C or below
Time: 30 seconds or less (at 210 °C)
Count: 2, Exposure limi t: None
VPS Package peak temperature: 215 °C or below
Time: 40 seconds or less (at 200 °C)
Count: 2, Exposure limi t: None
Wave Soldering Soldering bath temperature: 260 °C or below
Time: 10 seconds or less
Count: 1, Exposure limi t: None
Partial Heating Pin temperature: 300 °C
Time: 3 seconds or less (per side of device)
Exposure limit: None
After opening the dry pack, keep it in a place below 25 °C and 65 % RH for the allowable storage period.
Note
Note
Note
Note
Note
Recommended Condition
Symbol
IR35-00-2
VP15-00-2
WS60-00-1
–
Caution Do not use different soldering methods together (except for partial heating).
For details of recommended soldering conditions for surface mounting, refer to information document
SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICE MOUNTING TECHNOLOGY MANUAL (C10535E).
24
Data Sheet P11486EJ2V0DS00
Page 25

[MEMO]
µµµµ
PC8125GR
Data Sheet P11486EJ2V0DS00
25
Page 26

[MEMO]
µµµµ
PC8125GR
26
Data Sheet P11486EJ2V0DS00
Page 27

[MEMO]
µµµµ
PC8125GR
Data Sheet P11486EJ2V0DS00
27
Page 28

µµµµ
PC8125GR
NESAT (NEC Silicon Advanced Technology) is a trademark of NEC Corporation.
• The information in this document is subject to change without notice. Before using this document, please
confirm that this is the latest version.
• No part of this document may be copied or reproduced in any form or by any means without the prior written
consent of NEC Corporation. NEC Corporation assumes no responsibility for any errors which may appear in
this document.
• NEC Corporation does not assume any liability for infringement of patents, copyrights or other intellectual property
rights of third parties by or arising from use of a device described herein or any other liability arising from use
of such device. No license, either express, implied or otherwise, is granted under any patents, copyrights or other
intellectual property rights of NEC Corporation or others.
• Descriptions of circuits, software, and other related information in this document are provided for illustrative
purposes in semiconductor product operation and application examples. The incorporation of these circuits,
software, and information in the design of the customer's equipment shall be done under the full responsibility
of the customer. NEC Corporation assumes no responsibility for any losses incurred by the customer or third
parties arising from the use of these circuits, software, and information.
• While NEC Corporation has been making continuous effort to enhance the reliability of its semiconductor devices,
the possibility of defects cannot be eliminated entirely. To minimize risks of damage or injury to persons or
property arising from a defect in an NEC semiconductor device, customers must incorporate sufficient safety
measures in its design, such as redundancy, fire-containment, and anti-failure features.
• NEC devices are classified into the following three quality grades:
"Standard", "Special", and "Specific". The Specific quality grade applies only to devices developed based on a
customer designated "quality assurance program" for a specific application. The recommended applications of
a device depend on its quality grade, as indicated below. Customers must check the quality grade of each device
before using it in a particular application.
Standard: Computers, office equipment, communications equipment, test and measurement equipment,
audio and visual equipment, home electronic appliances, machine tools, personal electronic
equipment and industrial robots
Special: Transportation equipment (automobiles, trains, ships, etc.), traffic control systems, anti-disaster
systems, anti-crime systems, safety equipment and medical equipment (not specifically designed
for life support)
Specific: Aircraft, aerospace equipment, submersible repeaters, nuclear reactor control systems, life
support systems or medical equipment for life support, etc.
The quality grade of NEC devices is "Standard" unless otherwise specified in NEC's Data Sheets or Data Books.
If customers intend to use NEC devices for applications other than those specified for Standard quality grade,
they should contact an NEC sales representative in advance.
M7 98. 8
 Loading...
Loading...