Page 1
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
DATA SH EET
TDA3857
Quasi-split sound processor with
two FM demodulators
Product specification
File under Integrated Circuits, IC02
June 1994
Page 2
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Quasi-split sound processor with two
TDA3857
FM demodulators
FEATURES
• Quasi-split sound processor for all FM standards e. g. B/G
• Reducing of spurious video signals by tracking function and AFC for the vision carrier reference circuit; (recommended
for NICAM)
• Automatic muting of the AF2 signal by the input level
• Stereo matrix correction
• Layout-compatible with TDA3856 (24 pins) and TDA3858 (32 pins).
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
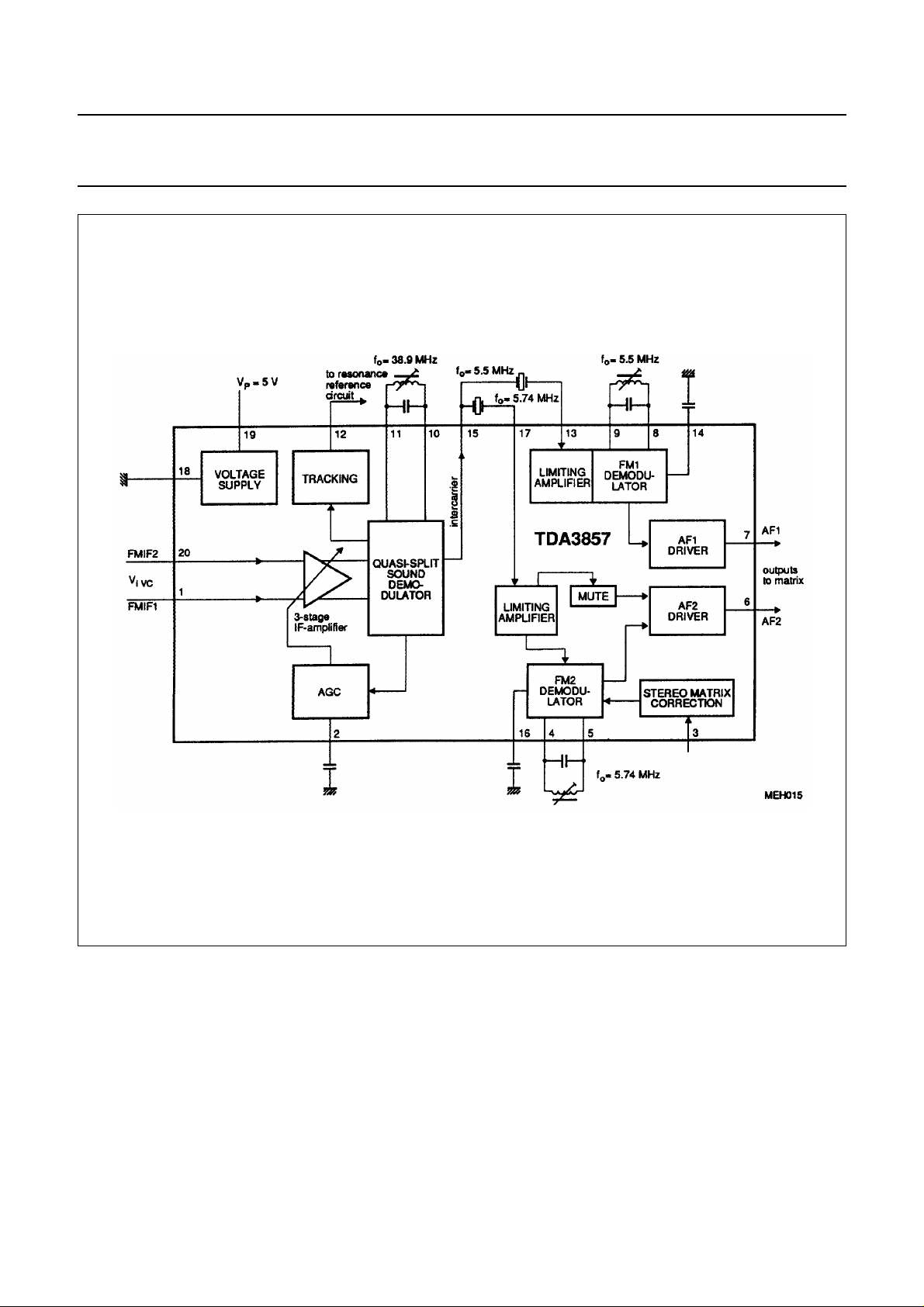
Symmetrical IF inputs. Gain controlled wideband IF amplifier.
AGC generation due to peak sync. Reference amplifier for the regeneration of the vision carrier. Optimized limiting
amplifier for AM suppression in the regenerated vision carrier signal and 90° phase shifter.
Intercarrier mixer for FM sound, output with low-pass filter.
Separate signal processing for 5.5 and 5.74 MHz intercarriers. Wide supply voltage range, only 300 mW power
dissipation at 5 V.
QUICK REFERENCE DATA
SYMBOL PARAMETER MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
V
P
I
P
V
i IF
V
o AF
THD total harmonic distortion − 0.5 − %
S/N (W) weighted signal-to-noise ratio − 68 − dB
ORDERING INFORMATION
EXTENDED
TYPE NUMBER
TDA3857 20 DIL plastic SOT146
Note
1. SOT 146-1; 1996 November 28.
supply voltage (pin 19) 4.5 5 8.8 V
supply current − 60 72 mA
IF input sensitivity (−3 dB) − 70 100 µV
audio output signal (RMS value) − 1 − V
PACKAGE
PINS
PIN
POSITION
MATERIAL CODE
(1)
June 1994 2
Page 3
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Quasi-split sound processor with two FM demodulators TDA3857
Fig.1 Block diagram (standard B/G).
June 1994 3
Page 4
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Quasi-split sound processor with two FM demodulators TDA3857
PINNING
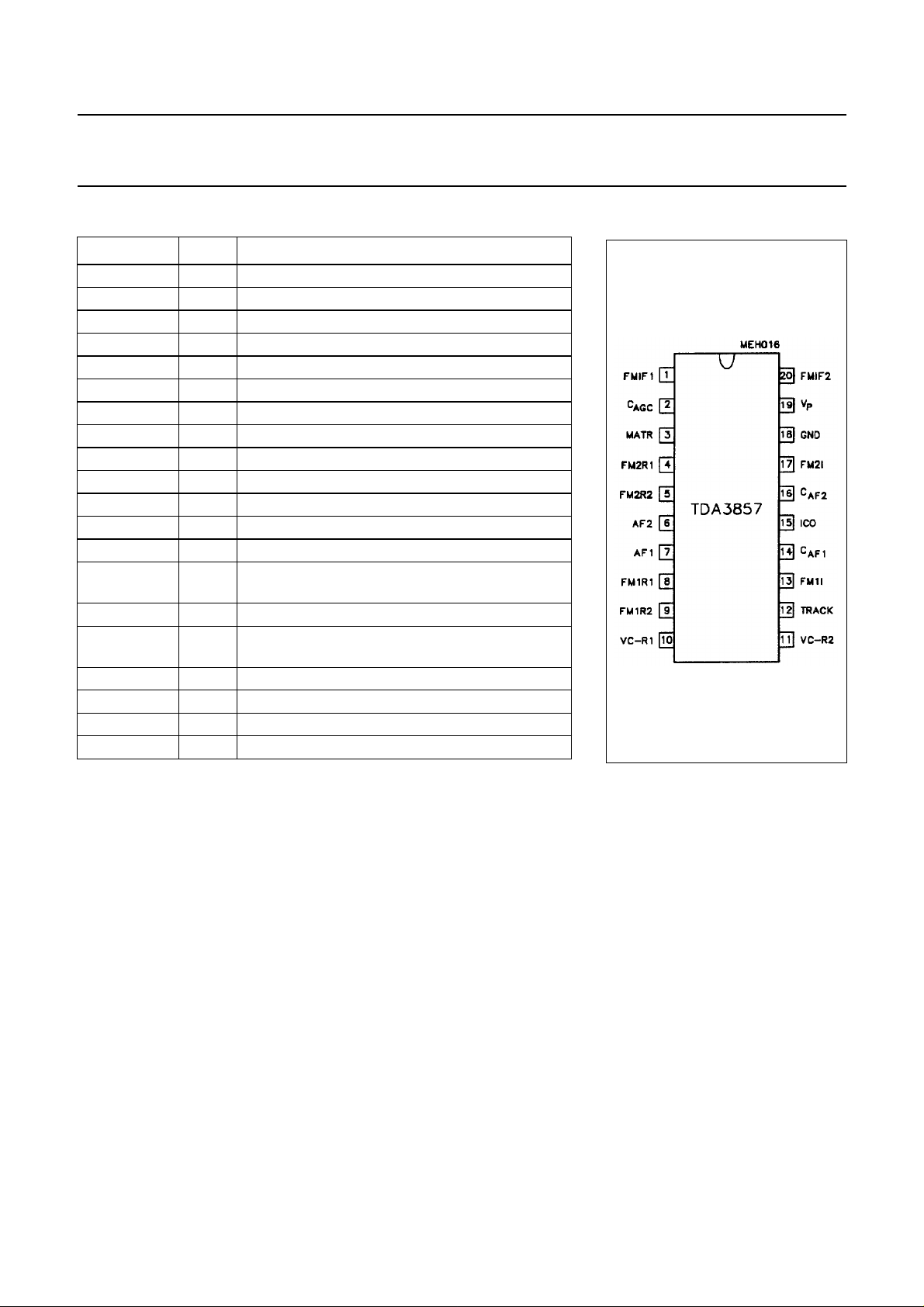
SYMBOL PIN DESCRIPTION
FMIF1 1 IF difference input 1 for B/G standard (38.9 MHz)
C
AGC
MATR 3 input for stereo matrix correction
FM2R1 4 reference circuit for FM2 (5.74 MHz)
FM2R2 5 reference circuit for FM2 (5.74 MHz)
AF2 6 AF2 output (AF out of 5.74 MHz)
AF1 7 AF1 output (AF out of 5.5 MHz)
FM1R1 8 reference circuit for FM1 (5.5 MHz)
FM1R2 9 reference circuit for FM1 (5.5 MHz)
VC-R1 10 reference circuit for the vision carrier (38.9 MHz)
VC-R2 11 reference circuit for the vision carrier (38.9 MHz)
TRACK 12 DC output level for tracking
FM1I 13 intercarrier input for FM1 (5.5 MHz)
C
AF1
ICO 15 intercarrier output signal (5.5/5.74 MHz)
C
AF2
FM2I 17 intercarrier input for FM2 (5.74 MHz)
GND 18 ground (0 V)
V
P
FMIF2 20 IF difference input 2 for B/G standard (38.9 MHz)
2 charge capacitor for AGC
14 DC decoupling capacitor for FM1 demodulator
(AF1)
16 DC decoupling capacitor for FM2 demodulator
(AF2)
19 +5 to +8 V supply voltage
Fig.2 Pin configuration.
June 1994 4
Page 5

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Quasi-split sound processor with two FM demodulators TDA3857
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
The quasi-split sound processor is suitable for all FM
standards (e. g. B/G).
B/G standard
AGC detector uses peak sync level. Sound carrier SC1
(5.5 MHz) provides AF1, sound carrier SC2 (5.74 MHz)
provides AF2.
Muting
With no sound carrier SC2 at pin 17, AF2 output is muted.
The mute circuit prevents false signal recognition in the
stereo decoder at high IF signal levels when no second
sound carrier exists (mono) and an AF signal is present in
the identification signal frequency range.
With 1 mV at pin 17, under measurement conditions, AF2
is switched on (see limiting amplifier). Weak input signals
at pins 1 and 20 generate noise at pin 17, which is present
in the intercarrier signal and passes through the 5.74 MHz
filter. Noise at pin 17 inhibits muting. No misinterpretation
due to white noise occurs in the stereo decoder, when
non-correlated noise masks the identification signal
frequencies, which may be present in sustained tone
signals. The stereo decoder remains switched to mono.
Sound carrier notch filter for an improved intercarrier
buzz
The series capacitor C
in the 38.9 MHz resonant circuit
s
provides a notch at the sound carrier frequency in order to
provide more attenuation for the sound carrier in the vision
carrier reference channel. The ratio of parallel/series
capacitor depends on the ratio of VC/SC frequency and
has to be adapted to other TV transmission standards if
necessary, according to the formula
C
Cpfvcfsc⁄()
s
2
C
–=
p
The result is an improved intercarrier buzz (up to 10 dB
improvement in sound channel 2 with 250 kHz video
modulation for B/G stereo) or suppression of 350 kHz
video modulated beat frequency in the digitally-modulated
NICAM subcarrier.
Intercarrier buzz fine tuning with 250 kHz square
wave video modulation
The picture carrier for quadrature demodulation in the
intercarrier mixer is not exactly 90 degrees due to the shift
variation in the integrated phase shift network. The tuning
of the LC reference circuit to provide optimal video
suppression at the intercarrier output is not the same as
that to provide optimal intercarrier buzz suppression. In
order to optimize the AF signal performance, a fine tuning
for the optimal S/N at the sound channel 2 (from 5.74 MHz)
may be performed with a 250 kHz square wave video
modulation.
Measurements at the demodulators
For all signal-to-noise measurements the generator must
meet the following specifications:
phase modulation errors < 0.5°for B/W-jumps intercarrier
signal-to-noise ratio as measured with ‘TV-demodulator
AMF2’ (weighted S/N) must be > 60 dB at 6 kHz sine
wave modulation of the B/W-signal.
Signal-to-noise ratios are measured with ∆f=±50 kHz
deviation and f
= 1 kHz; with a deviation of ±30 kHz the
mod
S/N ratio is deteriorated by 4.5 dB.
June 1994 5
Page 6

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Quasi-split sound processor with two FM demodulators TDA3857
LIMITING VALUES
In accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System (IEC 134).
SYMBOL PARAMETER MIN. MAX. UNIT
V
P
V
I
P
tot
T
stg
T
amb
V
ESD
Note to the Limiting Values
1. Equivalent to discharging a 200 pF capacitor through a 0 Ω series resistor.
supply voltage (pin 19) − 8.8 V
voltage (pins 1, 6, 7, 13, 15, 17 and 20) 0 V
P
V
total power dissipation 0 635 mW
storage temperature −25 +150 °C
operating ambient temperature 0 +70 °C
electrostatic handling (note 1)
all pins except pins 1 and 20 ±500 − V
pins 1 and 20 +400 − V
−500 − V
CHARACTERISTICS
= 5 V and T
V
P
f
= 33.158 MHz. Vision carrier (VC) modulated with different video signals, modulation depth 100% (proportional to
SC2
= +25 °C; measurements taken in Fig.3 with fVC= 38.9 MHz, f
amb
= 33.4 MHz and
SC1
10% residual carrier).
Vision carrier amplitude (RMS value) V
= 10 mV; vision to sound carrier ratios are VC/SC1 = 13 dB and
i VC
VC/SC2 = 20 dB. Sound carriers (SC1, SC2) modulated with f = 1 kHz and deviation ∆f = 50 kHz, unless otherwise
specified.
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
V
P
I
P
supply voltage (pin 19) 4.5 5 8.8 V
supply current (pin 19) 48 60 72 mA
IF amplifier (pins 1 and 20)
R
I
C
I
V
I
V
i IF (RMS)
input resistance 1.8 2.2 − kΩ
input capacitance − 2.0 2.6 pF
DC input voltage − 1.75 − V
maximum input signal (RMS value,
Vo=+1dB 70 100 − mV
pins 1-20)
input signal sensitivity (RMS value) −3 dB intercarrier signal
− 70 100 µV
reduction at pin 15
∆G
V
v
2
IF gain control 60 63 − dB
voltage for gain control (pin 2) 1.7 − 2.6 V
B IF bandwidth −3dB 50 70 − MHz
Resonance amplifier (pins 10-11)
V
o (p-p)
vision carrier amplitude
fo= 38.9 MHz − 270 − mV
(peak-to-peak value)
R
10-11
operating resistance − 4 − kΩ
L inductance Figs 3 and 4 − 0.247 −µH
C capacitance − 68 − pF
June 1994 6
Page 7

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Quasi-split sound processor with two FM demodulators TDA3857
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
Q
L
V
10, 11
Intercarrier mixer output (pin 15)
V
o (RMS)
B IF bandwidth −1 dB 6 8.5 − MHz
V
VID/V15
V
VC (RMS)
R
15
I
o
I
15
V
15
Q-factor of resonance circuit Qo=90 − 40 −
DC voltage (pins 10 and 11) − VP− 1 − V
output signal for 5.5 MHz (RMS value) 71 95 125 mV
output signal for 5.74 MHz (RMS
32 43 56 mV
value)
−3dB 7 10 − MHz
residual video AM on intercarrier note 1 − 310%
residual vision carrier (RMS value) 1st/2nd harmonic
− 0.5 1 mV
(38.9/77.8 MHz)
output resistance (emitter follower) 1 mA emitter current − 30 −Ω
allowable AC output current (pin 15) −−±0.7 mA
allowable DC output current −−−2mA
DC voltage LC-circuit at pin 10, 11
1.5 1.75 2.0 V
adjusted to minimum
video content at pin 15
Limiting amplifiers (pins 13 and 17)
V
i (RMS)
minimum input signal (RMS value) −3 dB AF signal − 300 450 µV
maximum input signal (RMS value) 200 −−mV
R
13, 17
V
13, 17
V
i (RMS)
input resistance 450 560 700 Ω
DC voltage − 0 − V
level detector threshold for no muting
only 5.74 MHz channel 0.8 1.2 1.7 mV
(RMS value, pin 17)
∆V
i
hysteresis of level detector 4 7 12 dB
FM1 and FM2 demodulators
Measurements with FM IF input signals of 5.5 MHz and 5.74 MHz with V
i IF (RMS)
= 10 mV (f
= 1 kHz, deviation
mod
∆f=±50 kHz) at pins 13 and 17 without ceramic filters, Rs=50Ω.
De-emphasis 50 µs.
QL-factor = 11 for resonant circuits at pins 4-5 and 8-9 (including IC).
V
IC (RMS)
intercarrier signals
− 100 − mV
(RMS values, pins 4-5 and 8-9)
V DC voltage (pins 4, 5, 8 and 9) − 1.8 − V
V
o (RMS)
AF output signals
0.84 0.95 1.07 V
(RMS values, pins 6 and 7)
∆V
o
difference of AF signals between
note 2 −−1dB
channels (pins 6 and 7)
R
6, 7
V
6, 7
output resistance 75 100 130 Ω
DC voltage 1.8 2.1 2.4 V
June 1994 7
Page 8

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Quasi-split sound processor with two FM demodulators TDA3857
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
I
6, 7 (M)
I
6, 7
THD total harmonic distortion − 0.5 1.0 %
V
o (RMS)
α
AM
S/N(W) weighted signal-to-noise ratio CCIR468-3 64 68 − dB
B AF bandwidth (−3 dB)
α
CR
V
3
∆G
AF2min
∆G
AF2max
V
14, 16
Tracking Automatic Frequency Control (AFC) of the vision carrier reference circuit
V
o 12
F
TR
S AFC steepness (open loop) for
allowed AC current of emitter output
note 3 −−±1.5 mA
(peak value)
maximum allowed DC output current −−−2mA
AF output signal (RMS value) THD = 1.5% 1.25 −−V
AM suppression 1 kHz; m = 0.3 48 54 − dB
lower limit −−20 Hz
upper limit 100 −−kHz
crosstalk attenuation (pins 6-7) 60 70 − dB
adjustment voltage for AF2 note 4
minimum output signal − 0 − V
maximum output signal − 5 − V
gain for minimum V
gain for maximum V
out
out
V3=0V −1.5 −2.5 − dB
V3= 5 V 1.0 1.5 − dB
DC voltage (pins 14 and 16) − 1.8 − V
tracking output voltage (pin 12) note 5 VP− 3.3 − VP− 1V
tracking reducing factor for
black picture − 9 −
white test picture − 4 −
50% grey picture − 6 −
black picture −−8−mV/kHz
white test picture −−3−mV/kHz
50% grey picture −−5.5 − mV/kHz
AF signal switches
input signals: FM intercarrier into pin 13 see part FM demodulator
no signal in pin 17 (AF2)
the output signals are related to the signals described in the demodulator part.
V
o/Vomute
dV
6
AF2 mute attenuation (pin 6) 70 −−dB
DC jump at the AF2 output switching to Mute − 525mV
June 1994 8
Page 9

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Quasi-split sound processor with two FM demodulators TDA3857
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
AF performance for FM operation (standard B/G)
input signals: B/G IF input signal (pin 1, 20)
unmodulated sound carriers
different video modulation (100%)
the output signals are related to the signals described in the demodulator part.
(S+N)/N(W) weighted signal-to-noise ratio CCIR468-3;
de-emphasis 50 µs
black picture f
2T/20T pulses with white bar f
6 kHz sine wave, B/W-modulated f
250 kHz square wave, B/W-modulated f
black picture f
2T/20T pulses with white bar f
6 kHz sine wave, B/W-modulated f
250 kHz square wave, B/W-modulated f
Ripple rejection of the AF outputs
RR ripple rejection
V
ripple
on VP/ V
ripple
on V
out
Notes to the characteristics
1. Spurious intercarrier AM: M = (A − B)/A (A = signal at sync; B = signal with 100% picture modulation).
2. AF signal can be adjusted by V3.
3. For larger current: RL> 2.2 kΩ (pin 6 or 7 to GND) in order to increase the bias current of the output emitter follower.
4. If not used, pin 3 should not be connected.
5. Automatic Frequency Control (AFC) of the vision carrier reference circuit (pins 10 and 11) for reducing spurious video
signals in the stereo/dual sound modes. The factor of reducing FTR at deviation ∆fVCspecifies the ratio of spurious
signals with/without tracking function.
= 5.5 MHz 59 63 − dB
i
= 5.5 MHz 57 61 − dB
i
= 5.5 MHz 52 56 − dB
i
= 5.5 MHz 50 54 − dB
i
= 5.742 MHz 57 61 − dB
i
= 5.742 MHz 55 59 − dB
i
= 5.742 MHz 50 54 − dB
i
= 5.742 MHz 48 52 − dB
i
V
R(p-p)
= 200 mV;
30 40 − dB
fR=70Hz
June 1994 9
Page 10

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Quasi-split sound processor with two FM demodulators TDA3857
Fig.3 Test and application circuit for standard B/G (for application SAW-filters must be used).
(1) simple resonant circuit
(2) resonant circuit with CP=68pF
CS=CP(f
CS= 27 pF (see Fig.3)
VC/fSC
)2− C
P
(1) CP= 47pF with optional use of tracking
(because of C
of the varicaps).
o
Fig.4 Frequency response of the 38.9 MHz reference circuit.
June 1994 10
Page 11

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Quasi-split sound processor with two FM demodulators TDA3857
APPLICATION INFORMATION
Fig.5 Internal circuits (continued in Fig.6).
June 1994 11
Page 12

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Quasi-split sound processor with two FM demodulators TDA3857
Fig.6 Internal circuits (continued from Fig.5).
June 1994 12
Page 13

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Quasi-split sound processor with two FM demodulators TDA3857
PACKAGE OUTLINE
DIP20: plastic dual in-line package; 20 leads (300 mil)
D
seating plane
L
Z
20
pin 1 index
e
b
SOT146-1
M
E
A
2
A
A
1
w M
b
1
11
E
c
(e )
1
M
H
1
0 5 10 mm
scale
DIMENSIONS (inch dimensions are derived from the original mm dimensions)
A
A
A
UNIT
inches
Note
1. Plastic or metal protrusions of 0.25 mm maximum per side are not included.
max.
mm
OUTLINE
VERSION
SOT146-1
1 2
min.
max.
1.73
1.30
0.068
0.051
IEC JEDEC EIAJ
b
b
1
0.53
0.38
0.021
0.015
0.36
0.23
0.014
0.009
REFERENCES
cD E e M
(1) (1)
26.92
26.54
1.060
1.045
SC603
June 1994 13
6.40
6.22
0.25
0.24
10
(1)
M
e
L
1
3.60
8.25
3.05
7.80
0.14
0.32
0.12
0.31
EUROPEAN
PROJECTION
H
E
10.0
0.2542.54 7.62
8.3
0.39
0.010.10 0.30
0.33
ISSUE DATE
w
92-11-17
95-05-24
Z
max.
2.04.2 0.51 3.2
0.0780.17 0.020 0.13
Page 14

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Quasi-split sound processor with two FM demodulators TDA3857
SOLDERING
Introduction
There is no soldering method that is ideal for all IC
packages. Wave soldering is often preferred when
through-hole and surface mounted components are mixed
on one printed-circuit board. However, wave soldering is
not always suitable for surface mounted ICs, or for
printed-circuits with high population densities. In these
situations reflow soldering is often used.
This text gives a very brief insight to a complex technology.
A more in-depth account of soldering ICs can be found in
“IC Package Databook”
our
Soldering by dipping or by wave
The maximum permissible temperature of the solder is
260 °C; solder at this temperature must not be in contact
DEFINITIONS
Data sheet status
Objective specification This data sheet contains target or goal specifications for product development.
Preliminary specification This data sheet contains preliminary data; supplementary data may be published later.
Product specification This data sheet contains final product specifications.
(order code 9398 652 90011).
with the joint for more than 5 seconds. The total contact
time of successive solder waves must not exceed
5 seconds.
The device may be mounted up to the seating plane, but
the temperature of the plastic body must not exceed the
specified maximum storage temperature (T
printed-circuit board has been pre-heated, forced cooling
may be necessary immediately after soldering to keep the
temperature within the permissible limit.
Repairing soldered joints
Apply a low voltage soldering iron (less than 24 V) to the
lead(s) of the package, below the seating plane or not
more than 2 mm above it. If the temperature of the
soldering iron bit is less than 300 °C it may remain in
contact for up to 10 seconds. If the bit temperature is
between 300 and 400 °C, contact may be up to 5 seconds.
stg max
). If the
Limiting values
Limiting values given are in accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System (IEC 134). Stress above one or
more of the limiting values may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only and operation
of the device at these or at any other conditions above those given in the Characteristics sections of the specification
is not implied. Exposure to limiting values for extended periods may affect device reliability.
Application information
Where application information is given, it is advisory and does not form part of the specification.
LIFE SUPPORT APPLICATIONS
These products are not designed for use in life support appliances, devices, or systems where malfunction of these
products can reasonably be expected to result in personal injury. Philips customers using or selling these products for
use in such applications do so at their own risk and agree to fully indemnify Philips for any damages resulting from such
improper use or sale.
June 1994 14
 Loading...
Loading...