Page 1

Color Television Chassis
TC5.1U
CA
G_16340_000.eps
100306
Contents Page
1. Technical Specifications, Connections and Chassis
Overview 2
2. Safety Instructions, Warnings, and Notes 3
3. Directions for Use 6
4. Mechanical Instructions 6
5. Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding 7
6. Block Diagrams, Test Point Overviews, and
Waveforms
Chassis Block Diagram 9
7. Circuit Diagrams and CBA Layouts Diagram CBA
Main Board 10 11-12
CRT Panel 13 14
Layout Side AV Board 14
Layout Keyboard Panel 40-P25207-KEA1X 14
Layout Keyboard Panel 40-P25207-KEB1XG 14
8. Alignments 15
9. Circuit Descriptions, Abbreviation List, and IC Data
Sheets 18
10. Spare Parts List 24
11. Revision List 26
©
Copyright 2006 Philips Consumer Electronics B.V. Eindhoven, The Netherlands.
All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a
retrieval system or transmitted, in any form or by any means, electronic,
mechanical, photocopying, or otherwise without the prior permission of Philips.
Published by WS 0663 TV Service Printed in the Netherlands Subject to modification EN 3122 785 16340
Page 2
EN 2 TC5.1U CA1.
Technical Specifications, Connections and Chassis Overview
1. Technical Specifications, Connections and Chassis Overview
1.1 Technical Specifications
Tuning - technology : PLL
Tuning - presets/channels : 181
Freq Bands : Full-Cable
TV Systems Off Air/ Cable : NTSC M (3.58 - 4.5)
TV Systems Multi : NTSC
Mains voltage : 90-140V
Mains frequency : 50/60Hz
Standby Power consumption : <1W
Sound Systems : BTCS SAP
Audio output (RMS) : 2x3W
Scan Modes : 4:3
Sound Features : AVL, Mute
Sound Control : 4 sound modes
: Balance
: Bass Boost
: Treble Boost,
Menu Languages : American English,
: Volume
French, Spanish
Clock/Timer Function : Sleep timer
Terrestrial Antenna in : 75 Ohm (F type)
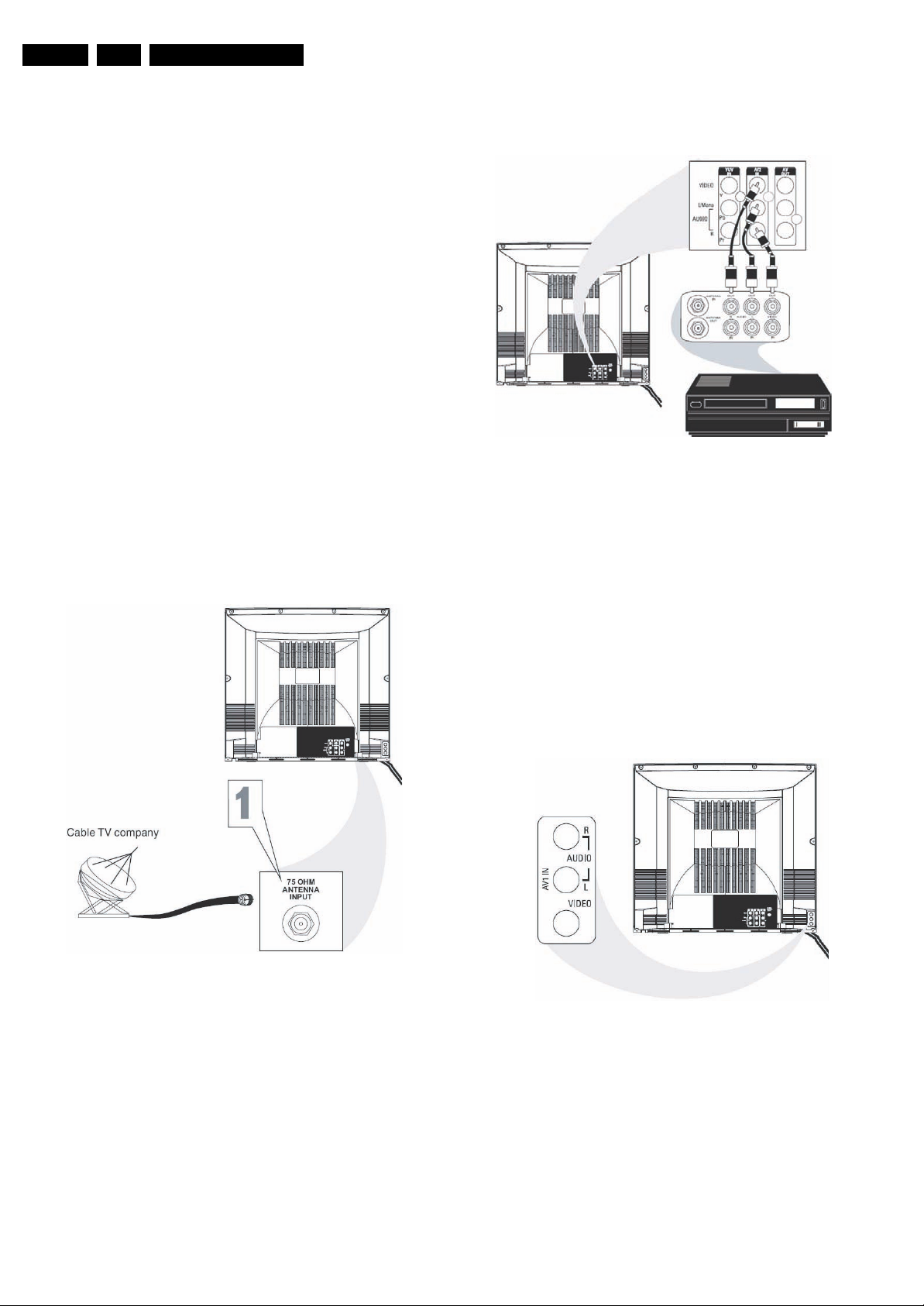
Figure 1-2 Rear audio and video connections
G_16340_002.eps
100306
1.2 Connection overview
1.2.1 Connections
G_16340_001.eps
100306
Cinch: Video CVBS - Out, Audio - Out
Ye - Video CVBS 1 V
Wh - Audio L 0.5 V
Rd - Audio R 0.5 V
/ 75 ohm kq
PP
/10 kohm kq
RMS
/ 10 kohm kq
RMS
Cinch: Video YUV- In
Gn - Video Y 1 V
Bu - Video U 0.7 V
Rd - Video V 0.7 V
/ 75 ohm jq
PP
/ 75 ohm jq
PP
/ 75 ohm jq
PP
Cinch: Audio - Out
Rd - Audio - R 0.5 V
Wh - Audio - L 0.5 V
/ 10 kohm kq
RMS
/ 10 kohm kq
RMS
Figure 1-1 Aerial connection
Aerial - In
- - F-type Coax, 75 ohm D
Figure 1-3 Side audio and video connections
Cinch: Video CVBS - In, Audio - In
Ye - Video CVBS 1 V
Wh - Audio L 0.5 V
Rd - Audio R 0.5 V
1.3 Chassis Overview
See Chapter 10, Parts List.
G_16340_003.eps
/ 75 ohm jq
PP
/ 10 kohm jq
RMS
/ 10 kohm jq
RMS
100306
Page 3
Safety Instructions, Warnings, and Notes
2. Safety Instructions, Warnings, and Notes
EN 3TC5.1U CA 2.
Index of this chapter:
2.1 Safety Instructions
2.2 Maintenance Instructions
2.3 Warnings
2.4 Notes
2.1 Safety Instructions
Safety regulations require the following during a repair:
• Connect the set to the Mains/AC Power via an isolation
transformer (> 800 VA).
• Replace safety components, indicated by the symbol h,
only by components identical to the original ones. Any
other component substitution (other than original type) may
increase risk of fire or electrical shock hazard.
• Wear safety goggles when you replace the CRT.
Safety regulations require that after a repair, the set must be
returned in its original condition. Pay in particular attention to
the following points:
• General repair instruction: as a strict precaution, we advise
you to re-solder the solder connections through which the
horizontal deflection current flows. In particular this is valid
for the:
1. Pins of the line output transformer (LOT).
2. Fly-back capacitor(s).
3. S-correction capacitor(s).
4. Line output transistor.
5. Pins of the connector with wires to the deflection coil.
6. Other components through which the deflection current
flows.
Note: This re-soldering is advised to prevent bad connections
due to metal fatigue in solder connections, and is therefore only
necessary for television sets more than two years old.
• Route the wire trees and EHT cable correctly and secure
them with the mounted cable clamps.
• Check the insulation of the Mains/AC Power lead for
external damage.
• Check the strain relief of the Mains/AC Power cord for
proper function, to prevent the cord from touching the CRT,
hot components, or heat sinks.
• Check the electrical DC resistance between the Mains/AC
Power plug and the secondary side (only for sets that have
a Mains/AC Power isolated power supply):
1. Unplug the Mains/AC Power cord and connect a wire
between the two pins of the Mains/AC Power plug.
2. Set the Mains/AC Power switch to the "on" position
(keep the Mains/AC Power cord unplugged!).
3. Measure the resistance value between the pins of the
Mains/AC Power plug and the metal shielding of the
tuner or the aerial connection on the set. The reading
should be between 4.5 Mohm and 12 Mohm.
4. Switch "off" the set, and remove the wire between the
two pins of the Mains/AC Power plug.
• Check the cabinet for defects, to prevent touching of any
inner parts by the customer.
2.2 Maintenance Instructions
We recommend a maintenance inspection carried out by
qualified service personnel. The interval depends on the usage
conditions:
• When a customer uses the set under normal
circumstances, for example in a living room, the
recommended interval is three to five years.
• When a customer uses the set in an environment with
higher dust, grease, or moisture levels, for example in a
kitchen, the recommended interval is one year.
• The maintenance inspection includes the following actions:
1. Perform the “general repair instruction” noted above.
2. Clean the power supply and deflection circuitry on the
chassis.
3. Clean the picture tube panel and the neck of the picture
tube.
2.3 Warnings
• In order to prevent damage to ICs and transistors, avoid all
high voltage flashovers. In order to prevent damage to the
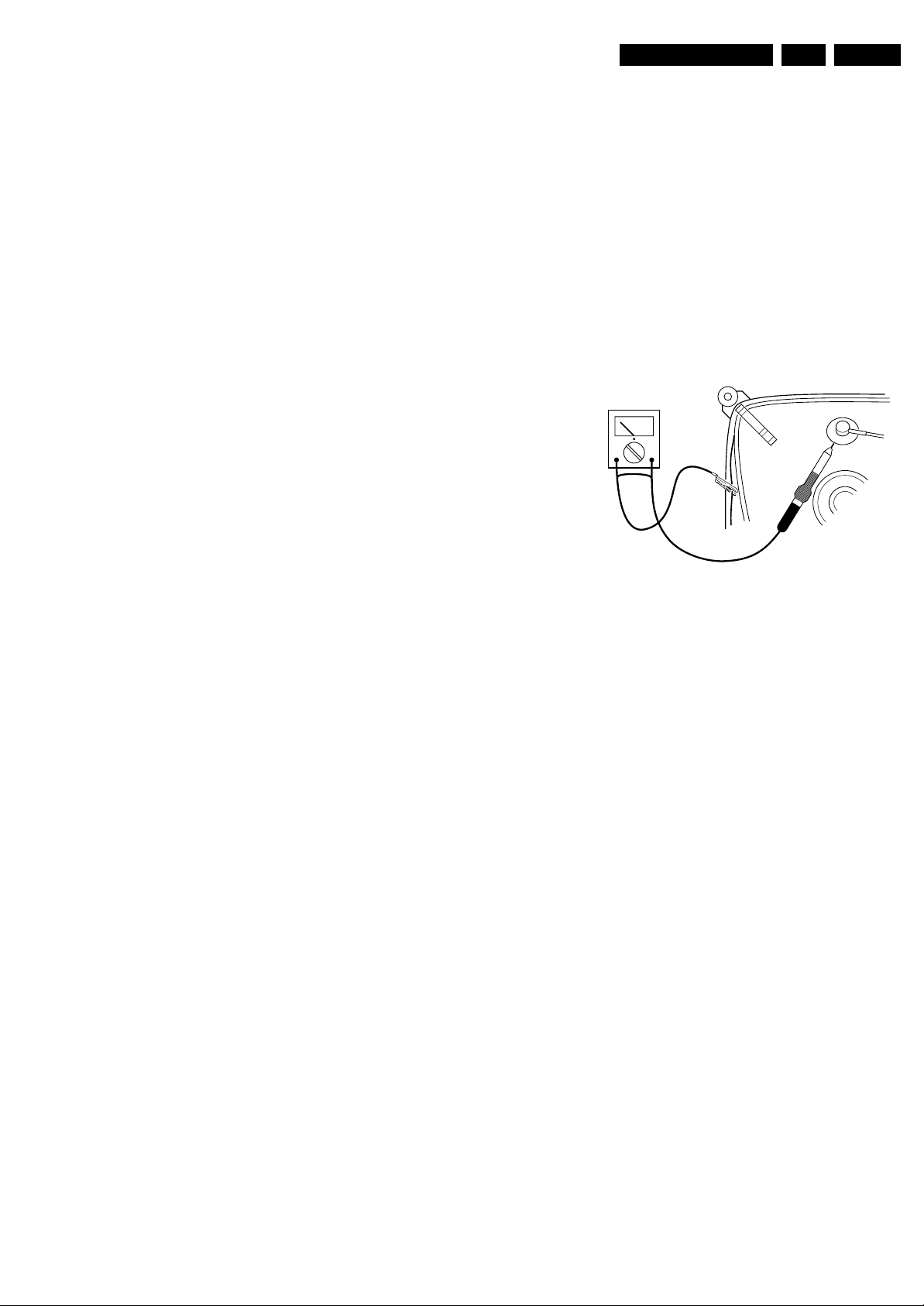
picture tube, use the method shown in figure “Discharge
picture tube”, to discharge the picture tube. Use a high
voltage probe and a multi-meter (position V
until the meter reading is 0 V (after approx. 30 s).
V
Figure 2-1 Discharge picture tube
• All ICs and many other semiconductors are susceptible to
electrostatic discharges (ESD w). Careless handling
during repair can reduce life drastically. Make sure that,
during repair, you are connected with the same potential as
the mass of the set by a wristband with resistance. Keep
components and tools also at this same potential. Available
ESD protection equipment:
– Complete kit ESD3 (small tablemat, wristband,
connection box, extension cable and earth cable) 4822
310 10671.
– Wristband tester 4822 344 13999.
• Be careful during measurements in the high voltage
section.
• Never replace modules or other components while the unit
is switched "on".
• When you align the set, use plastic rather than metal tools.
This will prevent any short circuits and prevents circuits
from becoming unstable.
2.4 Notes
2.4.1 General
• Measure the voltages and waveforms with regard to the
chassis (= tuner) ground (H), or hot ground (I), depending
on the tested area of circuitry. The voltages and waveforms
shown in the diagrams are indicative. Measure them in the
Service Default Mode (see chapter 5) with a color bar
signal and stereo sound (L: 3 kHz, R: 1 kHz unless stated
otherwise) and picture carrier at 475.25 MHz for PAL, or
61.25 MHz for NTSC (channel 3).
• Where necessary, measure the waveforms and voltages
with (D) and without (E) aerial signal. Measure the
voltages in the power supply section both in normal
operation (G) and in stand-by (F). These values are
indicated by means of the appropriate symbols.
• The semiconductors indicated in the circuit diagram and in
the parts lists, are interchangeable per position with the
). Discharge
DC
E_06532_007.eps
250304
Page 4

EN 4 TC5.1U CA2.
Safety Instructions, Warnings, and Notes
semiconductors in the unit, irrespective of the type
indication on these semiconductors.
• Manufactured under license from Dolby Laboratories.
“Dolby”, “Pro Logic” and the “double-D symbol”, are
trademarks of Dolby Laboratories.
2.4.2 Schematic Notes
• All resistor values are in ohms, and the value multiplier is
often used to indicate the decimal point location (e.g. 2K2
indicates 2.2 kohm).
• Resistor values with no multiplier may be indicated with
either an "E" or an "R" (e.g. 220E or 220R indicates 220
ohm).
• All capacitor values are given in micro-farads (µ= x10
nano-farads (n= x10
• Capacitor values may also use the value multiplier as the
decimal point indication (e.g. 2p2 indicates 2.2 pF).
• An "asterisk" (*) indicates component usage varies. Refer
to the diversity tables for the correct values.
• The correct component values are listed in the Spare Parts
List. Therefore, always check this list when there is any
doubt.
2.4.3 Rework on BGA (Ball Grid Array) ICs
General
Although (LF)BGA assembly yields are very high, there may
still be a requirement for component rework. By rework, we
mean the process of removing the component from the PWB
and replacing it with a new component. If an (LF)BGA is
removed from a PWB, the solder balls of the component are
deformed drastically so the removed (LF)BGA has to be
discarded.
-9
), or pico-farads (p= x10
-12
2.4.4 Lead-free Solder
Philips CE is producing lead-free sets (PBF) from 1.1.2005
onwards.
Identification: The bottom line of a type plate gives a 14-digit
serial number. Digits 5 and 6 refer to the production year, digits
7 and 8 refer to production week (in example below it is 1991
week 18).
-6
),
).
E_06532_024.eps
230205
Figure 2-2 Serial number example
Regardless of the special lead-free logo (which is not always
indicated), one must treat all sets from this date onwards
according to the rules as described below.
P
b
Figure 2-3 Lead-free logo
Device Removal
As is the case with any component that is being removed, it is
essential when removing an (LF)BGA, that the board, tracks,
solder lands, or surrounding components are not damaged. To
remove an (LF)BGA, the board must be uniformly heated to a
temperature close to the reflow soldering temperature. A
uniform temperature reduces the risk of warping the PWB.
To do this, we recommend that the board is heated until it is
certain that all the joints are molten. Then carefully pull the
component off the board with a vacuum nozzle. For the
appropriate temperature profiles, see the IC data sheet.
Area Preparation
When the component has been removed, the vacant IC area
must be cleaned before replacing the (LF)BGA.
Removing an IC often leaves varying amounts of solder on the
mounting lands. This excessive solder can be removed with
either a solder sucker or solder wick. The remaining flux can be
removed with a brush and cleaning agent.
After the board is properly cleaned and inspected, apply flux on
the solder lands and on the connection balls of the (LF)BGA.
Note: Do not apply solder paste, as this has been shown to
result in problems during re-soldering.
Device Replacement
The last step in the repair process is to solder the new
component on the board. Ideally, the (LF)BGA should be
aligned under a microscope or magnifying glass. If this is not
possible, try to align the (LF)BGA with any board markers.
So as not to damage neighboring components, it may be
necessary to reduce some temperatures and times.
More Information
For more information on how to handle BGA devices, visit this
URL: www.atyourservice.ce.philips.com (needs subscription,
not available for all regions). After login, select “Magazine”,
then go to “Repair downloads”. Here you will find Information
on how to deal with BGA-ICs.
Due to lead-free technology some rules have to be respected
by the workshop during a repair:
• Use only lead-free soldering tin Philips SAC305 with order
code 0622 149 00106. If lead-free solder paste is required,
please contact the manufacturer of your soldering
equipment. In general, use of solder paste within
workshops should be avoided because paste is not easy to
store and to handle.
• Use only adequate solder tools applicable for lead-free
soldering tin. The solder tool must be able:
– To reach a solder-tip temperature of at least 400°C.
– To stabilize the adjusted temperature at the solder-tip.
– To exchange solder-tips for different applications.
• Adjust your solder tool so that a temperature of around
360°C - 380°C is reached and stabilized at the solder joint.
Heating time of the solder-joint should not exceed ~ 4 sec.
Avoid temperatures above 400°C, otherwise wear-out of
tips will increase drastically and flux-fluid will be destroyed.
To avoid wear-out of tips, switch “off” unused equipment or
reduce heat.
• Mix of lead-free soldering tin/parts with leaded soldering
tin/parts is possible but PHILIPS recommends strongly to
avoid mixed regimes. If this cannot be avoided, carefully
clean the solder-joint from old tin and re-solder with new
tin.
• Use only original spare-parts listed in the Service-Manuals.
Not listed standard material (commodities) has to be
purchased at external companies.
• Special information for lead-free BGA ICs: these ICs will be
delivered in so-called "dry-packaging" to protect the IC
against moisture. This packaging may only be opened
shortly before it is used (soldered). Otherwise the body of
the IC gets "wet" inside and during the heating time the
structure of the IC will be destroyed due to high (steam-)
pressure inside the body. If the packaging was opened
before usage, the IC has to be heated up for some hours
(around 90°C) for drying (think of ESD-protection!).
Do not re-use BGAs at all!
Page 5

Safety Instructions, Warnings, and Notes
• For sets produced before 1.1.2005, containing leaded
soldering tin and components, all needed spare parts will
be available till the end of the service period. For the repair
of such sets nothing changes.
In case of doubt whether the board is lead-free or not (or with
mixed technologies), you can use the following method:
• Always use the highest temperature to solder, when using
SAC305 (see also instructions below).
• De-solder thoroughly (clean solder joints to avoid mix of
two alloys).
Caution: For BGA-ICs, you must use the correct temperatureprofile, which is coupled to the 12NC. For an overview of these
profiles, visit the website www.atyourservice.ce.philips.com
(needs subscription, but is not available for all regions)
You will find this and more technical information within the
"Magazine", chapter "Repair downloads".
For additional questions please contact your local repair help
desk.
2.4.5 Alternative BOM identification
In September 2003, Philips CE introduced a change in the way
the serial number (or production number, see Figure 2-1) is
composed. From this date on, the third digit in the serial
number (example: AG2B0335000001) indicates the number of
the alternative BOM (Bill of Materials used for producing the
specific model of TV set). It is possible that the same TV model
on the market is produced with e.g. two different types of
displays, coming from two different O.E.M.s.
By looking at the third digit of the serial number, the service
technician can see if there is more than one type of B.O.M.
used in the production of the TV set he is working with. He can
then consult the At Your Service Web site, where he can type
in the Commercial Type Version Number of the TV set (e.g.
28PW9515/12), after which a screen will appear that gives
information about the number of alternative B.O.M.s used.
If the third digit of the serial number contains the number 1
(example: AG1B033500001), then there is only one B.O.M.
version of the TV set on the market. If the third digit is a 2
(example: AG2B0335000001), then there are two different
B.O.M.s. Information about this is important for ordering the
correct spare parts!
For the third digit, the numbers 1...9 and the characters A...Z
can be used, so in total: 9 plus 26 = 35 different B.O.M.s can
be indicated by the third digit of the serial number.
EN 5TC5.1U CA 2.
2.4.6 Practical Service Precautions
• It makes sense to avoid exposure to electrical shock.
While some sources are expected to have a possible
dangerous impact, others of quite high potential are of
limited current and are sometimes held in less regard.
• Always respect voltages. While some may not be
dangerous in themselves, they can cause unexpected
reactions that are best avoided. Before reaching into a
powered TV set, it is best to test the high voltage insulation.
It is easy to do, and is a good service precaution.
Page 6

EN 6 TC5.1U CA3.
3. Directions for Use
Directions for Use
You can download this information from the following websites:
http://www.philips.com/support
4. Mechanical Instructions
See Chapter 10, Parts List.
http://www.p4c.philips.com
Page 7
Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding
5. Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding
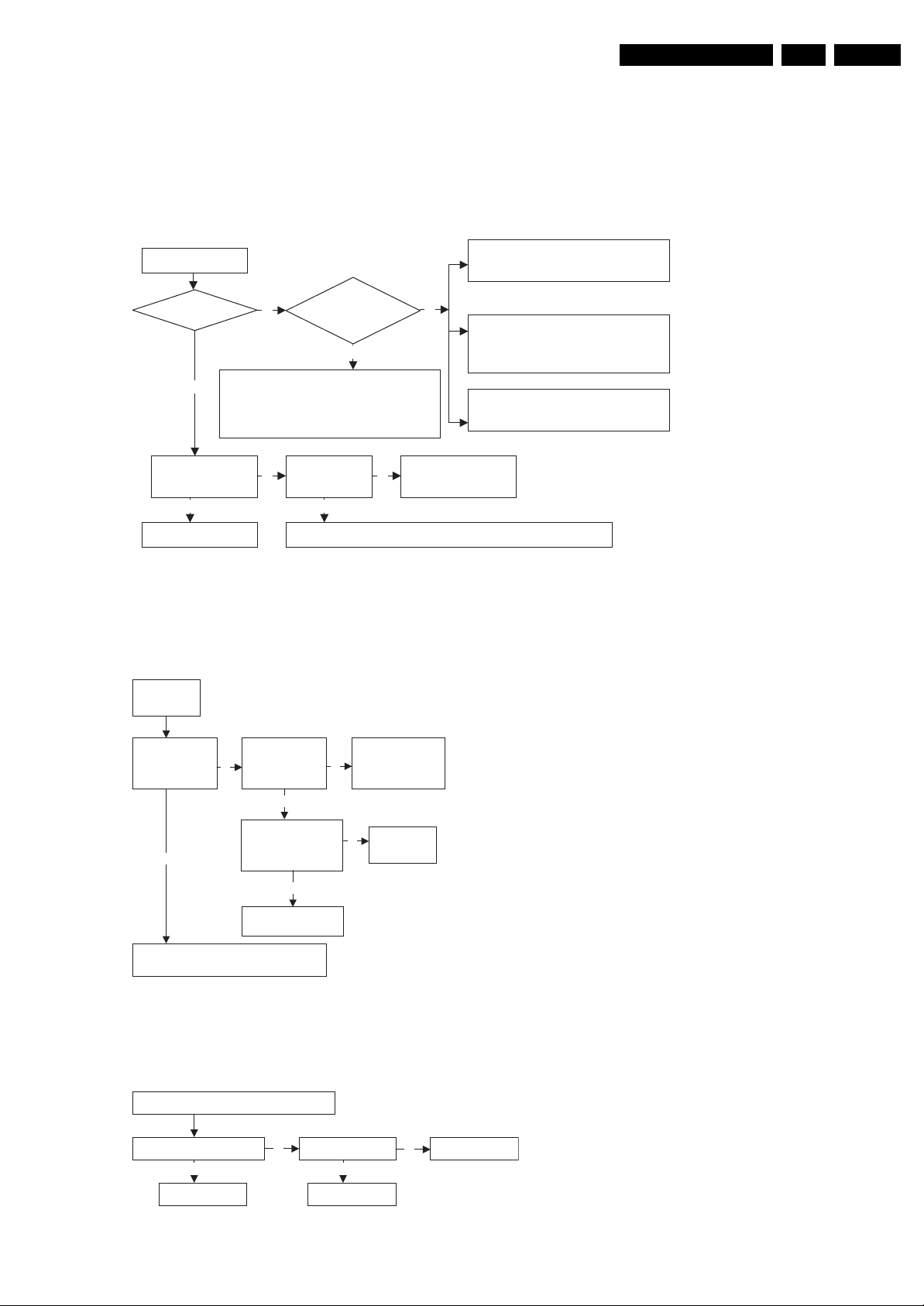
5.1 Trouble Shooting
5.1.1 Can not Power On
EN 7TC5.1U CA 5.
Can not Power On
Fuse OK?
(1) Check if B+ shorted to earth.
(2) To check whether D822 and R821 are
N
(3) To check whether D823 and R823 are
Is it IC801 Pin 1
shorted to earth?
Y
Check/Replace IC801
5.1.2 No Raster, Sound OK
No Raster
Sound OK
Check B+,
Y Y
turnoff.
turnoff. And whether C836 shorted.
+12V, Ok?
N
Is DB801 OK?
NN
Y
Check the components such as C801, C802, C806, C807 and C815
Is power supply for IC101 correct?
If not, check Q820, Q821, Q007, Q008,
D001
Check Horizontal Scan circuit:
Check H-Vcc and H-out of IC 101
Check Q401, T401 and Q411
Check standby circuit: Check Pin64 of
IC101, Check Q825, Q824, Q823, Q822.
Replace DB801
Figure 5-1 Can not Power On
G_16340_004.eps
100306
Is the power
supply of Q401
and Q411 ok?
N
To check whether R404, C401, T401,
Q401, R422 are ok?
Check Pin 13
(H-OUT) voltage
ok?
Y
Is there any shorted
in the scan part of
the circuit?
Change IC101
Y
N
Y
N
5.1.3 Raster OK, Sound OK, No TV/AV picture
Raster OK, Sound OK, No TV/AV picture
Check whether Q917 is
ok?
N
Replace Q917
Y Y
Replace C238
N
Check each
output voltage of
FBT
Change the
shorted part.
G_16340_005.eps
100306
Figure 5-2 No Raster, Sound OK
Change IC901 Check C238, ok?
G_16340_008.eps
100306
Figure 5-3 Raster OK, Sound OK, No TV/AV picture
Page 8
EN 8 TC5.1U CA5.
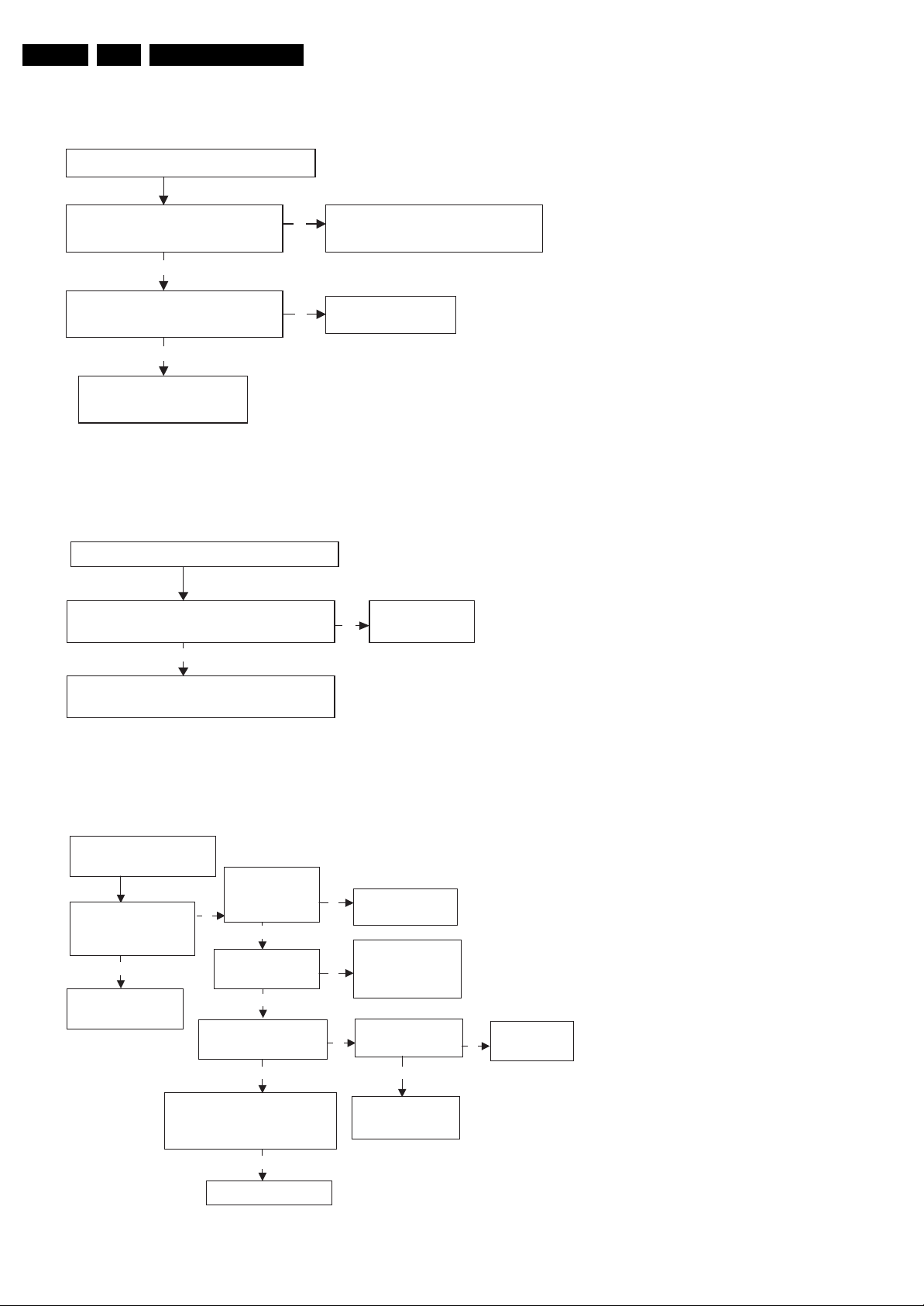
5.1.4 Raster OK, Sound OK, No AV picture
Raster OK, Sound OK, No AV picture
Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding
Is the signal waveform at Pin 12 and
Pin 14 of IC901 right?
Y
Check Q917, Q918, Q919, ok?
N
Replace the fail component.
5.1.5 Raster OK, Sound OK, No TV picture
Raster OK, Sound OK, No TV picture
Is the signal waveform at Pin 15 of IC901
right?
N
To check whether R903, C903, R902
N
and R905, C908, R908 are ok?
Replace IC901
Y
G_16340_006.eps
100306
Figure 5-4 Raster OK, Sound OK, No AV picture
Replace
IC901
Y
Check R234, Q204, R235, C229
5.1.6 No picture, dense noise dots
No picture, dense noise
dots
Is the antenna feed line
or the adapter broken?
Y
Handing the antenna
fault
N
Is the signal at IF
pin of the tuner ok?
Is the signal at Pin SCL,
SDA of tuner ok?
Check signal at P5, P57, P58,
P59, and P60 of IC101 and
replace the abnormal relative
circuit
Figure 5-5 Raster OK, Sound OK, No TV picture
Is the signal at
Pin41, Pin42 of
IC101 ok?
N
N
N N
Y
Y
Y
Y
G_16340_007.eps
Check/Replace
IC101
Check the relative
circuit of Q101,
Z141 etc
Is the supply
voltage of tuner ok?
Check/Replace
IC201, IC202,
D101.
100306
Y
Check/Replace
Tuner
Check EEPROM
G_16340_009.eps
Figure 5-6 No picture, dense noise dots
100306
Page 9

Block Diagrams, Test Point Overviews, and Waveforms
6. Block Diagrams, Test Point Overviews, and Waveforms
Chassis Block Diagram
EN 9TC5.1U CA 6.
G_16340_010.eps
100306
Page 10

Circuit Diagrams and CBA Layouts
7. Circuit Diagrams and CBA Layouts
Main Board
12
23MT2336/37
A
B
C
P501
1
S501
CRT
!
EHT
EHT
1
2
SCREEN
S
FOCUS
3
1 342
P502
HEATER
200V
FOCUS
L502
*JUMP
SCREEN
CRT BOARO.
GND
C505
1000P
2KV
*10uH
L503
!
L504
0
KR
KG
KB
40-02501C-CRG
2.7K 1/2W
2.7K 1/2W
2.7K 1/2W
R519
R520
R521
R518
15K
2W
1
R517
2
15K
2W
3
R516
15K 2W
C504
10u
+
250V
C508
10n
L505
D
TU101
AGC
E
VT
+
C101
4.7u
50V
R903
22K
D
SDA
VCC
SCL
+5VA
L101
+
47uH
F
C903
47u
P902
V1
R1
G
L1
V2
R2
H
L2
Y
Cr
Cb
I
*P904
V0
J
R0
L0
*P905
K
16V
+
+9V
R902
82
R904
1K
R906
1K
P903
R910
R912
+9V
R923
75
R924
1K
R925
1K
F
R932A
1K
F
C904
R954
10u
22k
16V
+
F
C905
10u
16V
+
Q902
C1815
C908
47u
16V
R908
82
C909
10u
16V
1K
F
C910
10u
16V
1K
+
Q903
C1815
R914
82
R915
82
R920
47
C926
220u
16V
+
C927
10u
16V
+
Q914
C1815
+
C928
10u
16V
Q901
C1815
+9V
R953
22k
R916
D
1K
R917
R905
1K
+
F
+
+9V
R951
22k
R913
1K
22K
+9V
R952
22k
Q904
C1815
R911
1K
R937
+
C930
100u
16V
Q913
C1815
R926
1K
R936
100
Q912
A1015
C929
0.01u
Q911
C1815
R931
R930
220
R929
1K
220
D
+9V
+
R934A
C912
C911
100u
0.01u
16V
R932
1K
+
C914
C913
100u
1K
0.01u
16V
3
Q501
C4544
1
Q502
C1815
R503
680
2
Q503
C4544
Q504
C1815
R508
3
680
Q505
C4544
Q506
C1815
R513
680
L506
C105
C106
100u
0.01
50V
76 8
5
34
1 2
C
IC901
4052
R501
560
R502
680
R504
0
C501
390P
C506
470u
+
R505
16V
560
R506
R509
680
R507
0
C511
C502
220u
390P
16V
R510
560
R511
680
R512
0
R523
1K
C503
470P
Q507
A562
33V
10 9
11
V1
12
0
3
V_OUT
3
1
1
V2
2
14 13
2
TV
0
+9V
16 15
4
D504
1N4001
L501
0
C509
10n
680
+
IF33V
C107
0.01
R947
100K
B
G
R514
2.7K
R
4132
54312
D501
1N4148
D502
1N4148
R515
R101
100
R101A
100
5
P503
R522
680
1K
L102
C108
0.01
R106
1K
R107
56
R108
Q101
150
C3779
R945
10K
R944
10K
+9V
+9V
Q917
C1815
R948
1K
P201
R102
150
R103
1uH
470
C109
1000
Z101
F1859
1
3
2
4
Q919
DTC124
Q918
DTC124
R946A
2.2k
+
R946
2.2k
+9V
L950
+9V
22uH
R942
R940
2K2
Cr
680
Q916
A1015
Cb
+
R935
C924
22K
10u/16V
1K
R933
C925
15K
33p
C1024
1n
+9V
R934
1K
C922
180
R941
68K
+
C923
Q915
1u
A1015
50V
R939
560K
R938
12K
R1023
1K
R1022
C1023
1K
1n
56
+5V
SDA0
1
2
P002
R005
+5V
22K
C002
R007
C003
1500
3.9K
RESET
ROTAT E
SDA0
SCL0
MUTE
R
G
B
MUTE
RESET
C1016
2SA817A
SIF
10u
C1011
100n
C1008
100n
SIF
S-SW
S-SW
R209
Q208
10K
C211
0.1u
16V
R1006
C1013
1
2
3
4
47
+
10u
C1009
10u
+
+5VA
2700
R008
3.9K
Q003
C1815
C009
R009
10K
10u
+
R026
87
IC001
24C08
6
5
C023
C024
22P
22P
C209
+12V
+
16V10u
+
C212
R212
4.7K
1N4148
RGB
D202-D204
1N4148X3
R219
30K
+
C216
0.22u
50V
+9V
R222
100K
R223
100K
Q1003
C1815
R1005
C
1015
10u
3k3
+
R1007
1k5
+
34
NC
VCC
CAPL-M
35
GND
36 37
AGNDC
IN-L2
38
IN-R2
39
GND
40
IN-L1
41
IN-R1
42
REF
43
MONOIN
44
GND
VCC
SIF IN+
1
2 3 4 5 6 7 8 91011
C1006
100n
C1005
56p
10K
+9V
R211
4K7
DTC124
+5VA
C1012
C1004
R025
10K
Q209
C217
2200p
+5VA
1.5n
C1025
470P
S-OUT-L
SIF IN-
56p
SYNC
+9V
B
G
R
STD-BY
D215
1N4148
+
C210
47u
16V
R213
10K
AGC
SCL0
SDA0
+9V
AGC
5
AV1/AV 2
TV/AV
+9V
C229
47u
16V
SYNC
+9V
C1010
3u3
+
EN 10TC5.1U CA 7.
7
8
9
CIRCUIT CONTAINS AND CIRCUIT ITSELF ARE SUBJECT TO CHANGE WITHOUT NOTICE.
S001A
S003A
S002A
TV/AV
VOL DN VOL UP
MENU
R024A
R023A
1.8K
1K5
R030
Q007
4.7
C1815
1/4W
+
C028
R031
10u
1K
16V
R033
Q008
1K
R247
330
C248
0.47u
16V
+
R244
10
R032
A1015
1K
D001
5V1
9V
Y
9V
C281
0.1u
+
L209
10uH
X201
10n
D209
2V4
D208
1N4148
L208
22uH
+9V
+9V
R235A
***
R235
120
Q204
C1815
R258
150
R255
22K
C624
470u
R611
25V
0.47 2W
+
+13V
C627
R612
1K
R608
1K
+12V
R605
47K
Q601
C1815
0.22u
R607
C626
4.7K
3300P
C631
0.22u
R609
C630
4.7K
3300P
+
R610
Q603
47K
C124
4
3
R006
+5V
R018
C021
10u
+
R220
220K
L205
22uH
L204
22uH
C226
680P
+
GND
S-OUT-R
IC1001
MSP 3425G
GND
XT-IN
C1001
1.5p
X1001
18.432M
+5V
SCL0
R001
R001A
10K
64
STD BY
63
RMT-IN
62
TV Sync
S-SW
61
R023
100
60
ROTATE
SW
59
+5V
58
SCL0
57
SDA0
56
EXT.MUTE
55
5V
54
GND
53
TV AGND
R214
270
52
B-OUT
R215
270
51
G-OUT
R216
270
50
R-OUT
C214
0.01
+
49
49
RGB 9V
RGB 9V
48
48
IK-IN
U COM PORT
47
APC FIL
BLACK DET
46
SVM OUT
45
Y/C 5V
44
C220
0.01
RF AGC
43
IF IN
42
IF IN
41
IF GND
40
+
IF AGC
39
SF OUT
38
C223
4.7u
16V
+
S-Reg
IF VCC(5V)
36
C225
0.01
PIF PLL
35
DC NF
34
+
SIF-IN
33 32
10u
C230
16V
R229
0.1
R228
10K
C1037
10n
2333 32 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24
NC
NC
RESET
GND
I2S
DVSS
D-VCC
ADR
I2S
I2S
I2S
I2S
SDA
SCL
IO
ST BY
ADR-SEL
+5VA
+5VA
R1011
100
C1034
10n
R003
1K
IC101
TMPA8859
TCL-A27V01-TO
V/C/D
47K
+9V
22
2120
9
1
181716
15
4
1
R1002
100
13
12
R1001
100
C1017
470n
C1035
22P
10K
C008
10K
100P/27P
R019
10K
10K
C022
10n
R024
47
R027
22
R028
22
C026
+5V
0.1u
+
C025
10u
16V
B
G
R
C213
+9V
47u
L212
10uH
C215
R217
4K7
180
+
C218
1u
50V
+
C219
100u
16V
C221
1u
16V
+
C224
100u
25V
C227
+
0.47
50V
R227
C228
270
C1038
10n
1014
C
10u
ROLONC
IO
TP
XT-OUT
10n
C1031
C1002
1.5p
R1010
100
C1033
10n
R043
10K
TV AGND
SCP-OUT
TV-DGND
DVCC(3.3V)
Fsc OUT
ABCL-IN
EW-OUT
IF-VCC(9V)
SIF-OUT
EHT IN
R230
24K
C1036
TV/AV
FBP-IN
V-SAW
TV-OUT
22P
X-RAY
RESET
X-TAL
X-TAL
H-OUT
H-AFC
V-OUT
H-VCC
Cb IN
Cr IN
V2-IN
TV/AV
STD-BY
R004
+5V
C041
R044
C043
2.2K
10u
+
1
2
R036
470
KEY
3
GND
4
5
C031
X001
39P
8M
6
C032
39P
7
TEST
8
L002
C034
10uH
0.01
5V
9
+
C033
10u
GND
Ys IN
Y-I N
C-IN
C253
47
R1004
100K
R1003
***
16V
10
11
12
13
14
C246
0.47u
50V
+
15
16
17
C244
R248
10n
1K
18
C243
+
19
1u
50V
C242
100n
20
C241
+
21
1u
50V
22
23
C238
100n
24
25
C236
10n
26
C280
27
+
C235
D205
33u
1N4148
16V
2837
29
R232
100
30
Q203
C1815
31
R233A
3K3
C231
R231
33K
2200
C254
R226
47
100
X202
L206
4.5MBF
22uH
L1001
C1018
22uH
100n
+
C1019
47u
16V
D602
+9V
1N4148
SDA0
SCL0
R656
*1K
0.1u
R036A
10K
C027
220p
+5V
C029
10n
C030
220P
R034
10K
+5V
C247
R246
8K2
8200p
R245
470
L201
22uH
+
C245
2200u
16V
R243
100
Cb
R242
100
Cr
R241
100
+
C237
10u
50V
0.1u
R239
1K
R238
470
C233
C234
100u
10n
16V
R234
R233
330
330
4.5MBF
+9V
R225
330
+5VA
C626A
C630A
C661
10n
100u
25V
+
10K
R606
10K
Q602
A1015
01-2336PH-MA2
2006-01-11
10
S005A
S004A
S006A
CH DN
CH UP
R026A
R027A
R025A
2K7
4K3
6K2
R0334
470
4K7
4
4
C263
100u
16V
LIN
IC602
TDA7266
RIN
ST-BY
MUTE
P-GND
3
3
+5V
R010
Q006
C1815
uPC574J
+
C833
4700u
16V
Q825
C1815
7805
+
R254
100K
313
VCC1 VCC2
LOUT+
LOUT-
ROUT+
ROUT-
S-GND
8
NC
+33V
+12V
1N4148
D214
Q202
C1815
12
12
D101
Q824
C1815
9
P001B
P001
Q821
4544
R829
10K
R832
1K
R262
1K2
D834
9V1
R833
1K
C262
220u
16V
IN4148
C250
R256
5K6
D206
IN4148
1
2
15
14
1
+12V
D02
IN4148
C104
100n
R826
10 2W
Q820
C2230
R827
4K7/5W
D826
8V2
C834
0.01u
R837
10K
+9V
+
R261
D261
330
R260
OPEN
D213
47u
3V9
50V
+
R249
0
R250
150
9V
R257
4K7
P601 P602
2
W601
L
+5VA
5
5
J025
R838
10K
C264
0.1u
50V
C625
100n
12
4
7
6
C634
0.1u
50V
11
12
10
11
12
!
S008
POWER
IR001A
R0333
3
R070A
120K
47
+
C070A
47u
16V
+
C01
100u
D01
IN4001
R01
4K7
R02
27K
R266
22K
2W
C261
10n
R828
22K/2W
D210
24V
RL01
Q01
C2236
+130V
L801
100uH
R830
1K
1
IC802
!
615A
2
R836
1K
1/4W
Q822
C1815
D828
6V2
Q823
D827
1N4148
C1815
C834A
0.1u
IC201IC202
7809
Q205
A1015
D262
IN4148
+14V
D212
220u
IN4148
D211
C251
IN4148
4.7u
50V
R251
470
+
C249
R253
4u7
100K
50V
R311
4.7k
+130V
1 2
C401
+
4.7u
160V
Q401
2482
R401
!
220
L411
1uH
18
D1001A
D1001B
LED
LED
12
R033B
NC
C821
1000u
25V
+
+13V
+
C828
330u
160V
R835
120K
1/2W
C835
R831
0.1u
33K
VR802
R834A
C836
6K8
820K
470u
R834
16V
R834B
+
*470
D829
1N4148
D824
+12V
1N4001
+
C260
47u
16V
INPUT
VCC
1 2
+
C301
C302
100u
35V
35V
+
D301
IN4001
+
C303
50V
-14V
10u
3
R404
4K7
7W
S702
MOF
2 3
R402
2K4
C403
1W
390P
500V
1 4
C402
3n3
16
500V
C411
Q411
*3300p
3DD3402
1.6KV
!
!
D412
FR104
19
L412
0.6uH
R418
6.8K
Q413
A1015
Q412
R417
A1015
2.2K
R420
2.2K
C822
0.1u
C827
330
+
C422
220u
160V
!
!
R412
2K
R420A
2.2K
10n
500V
POMP UP
T401
D411
RS3FS
C832
1000u
16V
*6800P
D820
!
RU4YX
C820
220P
500V
C826
470P
2KV
D822
RU4AM
C829
10u
50V
D823
RU4YX
C830
+
220P
500V
C831
100n
IC301
TDA8172
OUT
GND
43 75 6
R304
1.5 1W
C305
0.33
C308
100u
+
35V
C306
R314
10K
+
C421
10u
200V
!
C412
*8200p
1.6KV
C413
*0.022
400V
PPN
R413
15K
R416
4.7K
D410
1N4148
+
!
!
R414
47K
IRF630MFP
AC 120V
+14V
Q414
5A/250V
3A/250V
+
2A/250V
Vp
R315
5K6
R432
*6K8
C432
1000u
35V
+9V
!
R820
R821
R823
!
R302
3.9K
R312
22K
C414
*7200p
1.6KV
S801
33
11
!
BCK-4201-78
16
17
18
10
12
15
14
8.2M 1/2W
!
Vref
D311
***
+
C304
4.7u
16V
D303
8V2
C311
2700P
100V
R422
0.33
R421
10K/2W
D421
FR104
-14V
D431
!
FR105
L431
+
C431
220p
500V
!
L413
*600uH
R415
3.9
2W
+
C415
4u7
50V
P801
22
T803
R840
C840
2200P
AC400V
R303
33K
R313
1.5
2W
R316
10K
2W
L432
A1
!
F801
-14V
+33V
1/2W
C435
1000u
+
25V
A4
C419
*470n
400v
!
!
T801
36-LIF007-XX0
!
1M
C801
R801
220n
1/2W
AC250V
!
C807
10n
15 1/2W
1K5 1/4W
*S237-479
500V
R813
D810
FR104
C814
D811
10uF
FR104
35V
R814
C812
1000p
7
9
1
4
!
D309
1.3W 51V
R310
D310
10K
1N4148
-14V
C441
220P 500V
!
D441
+
FR104
C442
22u
250V
A3
+
C443
C433
220P
500V
D432
FR104
2W FUS
A1`
R433
0.68
2W FUS
R431
0.68
!
20
NO D.F
A2
C802
+
MF
D420
FR104
4u7
50V
220n
AC250V
RT802
+
!
IC802(1/2)
SFH615A-3
D813
6V2
R812
1K
C813
100n
R308
120
MOF
1/2W
+200V
!
-14V
+14V
COL
AFC
A6
250V AC
C806
680u
200V
B+
C804-C805
3 4
C309
330n
100V
400V
PTC
!
!
R811
1K
!
D812
IN4148
1
11
2
7
10
8
4
5
P803
100n
C803
RT801
!
4n7
FB
6
OLP/SS
R309
120
MOF
2W
R461
1.5
1W FUS
!
T802
36-LIF007-XX0
C804A
470p
AC400V
C805A
470p
AC400V
!
DB801
D3SB60
!
R810
68K/2W
IC801
STR-W6735
4 1
VCC
OCP/BD
S/GND
5 37
C810
220P
+
C811
R815
3.3uF
100
50V
L301
35-332220-00X
L414
21uH
680
R419
2W
MOF
HV
T402
!
A
!
B
!
D
C815
1500p
2KV
C
D
R816
0.12/2W
P411
E
VERT
COIL
!
HOR
COIL
EHT
Q402
C1815
R453
1K
C451
100n
FOCUS
A5
SCREEN
ABL
9
HEATER
1
F
G
2
3
4
200V
3
H
2
1
P421
I
J
1
W602
2
G_16340_011.eps
R
140306
K
Page 11

Circuit Diagrams and CBA Layouts
Layout Main Board (Top Side)
EN 11TC5.1U CA 7.
G_16340_012.eps
100306
Page 12

Circuit Diagrams and CBA Layouts
Layout Main Board (Bottom Side)
EN 12TC5.1U CA 7.
G_16340_013.eps
100306
Page 13

CRT Panel
Circuit Diagrams and CBA Layouts
EN 13TC5.1U CA 7.
G_16340_014.eps
100306
Page 14

Circuit Diagrams and CBA Layouts
EN 14TC5.1U CA 7.
Layout CRT Panel
Layout Side AV Board
Layout Keyboard Panel 40-P25207-KEA1X
G_16340_017.eps
100306
Layout CRT Panel
G_16340_015.eps
150306
Layout Keyboard Panel 40-P25207-KEB1XG
G_16340_018.eps
100306
G_16340_019.eps
100306
G_16340_016.eps
130306
Page 15

8. Alignments
Alignments
EN 15TC5.1U CA 8.
8.1 How to Put the Set into Factory Mode
• Press the “VOL-” button to minimize the volume.
• Hold the “VOL-” button and simultaneously press the
“DISPLAY” button on the remote control.
• Press the “CH+” or the “CH-” button to select the parameter
you want to adjust.
• Press the “VOL+” or the “VOL-” button to adjust the
selected parameter.
• To put the new values into the memory, leave the factory
mode with the “STANDBY” button on the remote control, or
switch the set off with the “ON/OFF” button.
2
8.2 Adjustment of the B+ (BAT) voltage
1. Apply the Philips standard test pattern to the RF input.
2. Connect a DC voltmeter (range >200 Volt) to pins 1 (GND)
and 3 (+) of S804 [1].
3. Adjust potentiometer VR802 [2] in STANDARD mode in
such a way the voltage reading is 130 +/- 0.5 Volt.
1
Figure 8-1 Test pin & potentiometer position
8.3 RF AGC Alignment:
1. Apply an 8-scale gray signal (60dB).
2. Adjust the AGC data in Factory Mode in such a way the
noise just disappears.
3. Change the signal to 90dB.
4. Measure the voltage at test Pin C of Q101 (this is the PreAmplifier output).
5. Write down this voltage, and call it V1P-P.
6. Apply an 8-scale gray signal with Color Bar (90Db)
7. Adjust the AGC data in Factory Mode in such a way the
picture is without distortion and interference.
8. Change the signal to 8-scale gray signal (90dB).
9. Measure the voltage at test Pin C of Q101 (Pre-Amplifier
output)
10. Write down this voltage and call it V2P-P.
11. Calculate the value VP-P with the following formula: VPP={(V2P-P)-(V1P-P)}/3.
G_16340_020.eps
100306
12. Apply 8-scale gray signal (90dB).
13. Measure the voltage at test Pin C of Q101 (Pre-Amplifier
output)
14. Adjust AGC data until the voltage of Pin C of Q101 reaches
the value of VP-P (=(V2P-P-V1P-P)/3)
G_16340_021.eps
100306
Figure 8-2 Test circuit
Page 16

EN 16 TC5.1U CA8.
Alignments
8.4 Screen & Focus Voltage Adjustment
1. Apply the test pattern signal in normal status.
2. Enter the Factory mode
3. Press the "AV/CH" button to stop the vertical scan (Note:
the RC/GC/BC is preset to 80, GD/BD to 40)
4. Adjust the SCREEN potentiometer on the line output
transformer in such a way the horizontal line is just visible
on the screen.
5. Turn on the vertical output, and adjust the "FOCUS"
potentiometer on the line output transformer in such a way
the focus is maximized.
8.5 White Balance Adjustment (NORMAL)
1. Apply the black and white pattern in normal status.
2. Alignment of the normal color temperature
a. Change the Color Temperature to the normal status
b. Use a color analyzer to measure the black side of the
screen.
c. By changing the value of RC, GC and BC, set the
reading of the color analyzer to PHILIPS standard
– x=285+/-4
– y=296+/-4.
d. Use a color analyzer to measure the white side of the
screen.
e. By changing the value of GD, BD, set the reading of the
color analyzer to PHILIPS standard
– x=285+/-4
– y=296+/-4.
f. Separately set the brightness and contrast from
minimum to maximum, repeat the step -b- up to and
including -e- until the reading of the color analyzer is
correct.
The PHILIPS standard is:
– Warm:X=315+/-10, Y=321+/-10
– Cool:X=269+/-10, Y=275+/-10
8.6 Adjustment of Sub-brightness
1. Apply the Grey-scale / Color bar (NTSC signal) to the AV
input, in normal status.
2. Enter factory alignment menu 5.
3. Select BRTC
4. Adjust the sub-brightness, until the 2nd dark bar of 8 level
Grey scales can just be seen.
8.7 Picture Geometry Adjustment
1. Apply the Philips standard testing pattern in normal status
2. Then enter menu 3
3. Adjust the following data to get the minimum distortion:
a. HPOS6 (Horizontal Centre)
b. PARA6 (Level)
c. TRAP6 (Trapezium)
d. HSIZE6 (Horizontal Size)
e. CNRT6 (Top)
f. CNRB6 (Bottom)
4. Apply the Philips standard testing pattern in normal status.
5. Enter menu 3.
6. Adjust the following data to get the minimum distortion:
a. HIGH6 (Height)
b. VP60 (Vertical Center)
c. VLIN6 (Linearity)
d. VSC6 (Vertical-S Correction)
Page 17

Alignments
EN 17TC5.1U CA 8.
8.8 Initialization
Put the set into “Factory Mode” (see “How to Put the Set into
Factory Mode”, the first item of this chapter). Press the
"SOUND" button, the screen displays "WAIT". When the
screen displays FGSFGSFGSFG "OK", the initialization is
finished. Now you can enter the following working procedure.
Table 8-1 EEPROM Data
FAC 01 FAC 02
RC* GC* BC* GD* BD* HIGH5 VP50 VLIN5 VSC5 VBLK5 VCEN5
80 80 80 40 40 13 03 0A 0C 00 18
FAC 02
HIGH6* VP60* VLIN6* VSC6* VBLK6 VCEN6 VP60*
27 04 0A 0B 00 2C 04
FAC 03
HPOS5 PARA5 TRAP5 HSIZE5 CNRT5 CNRB5 VEHT5 HEHT5
0C 10 29 13 0A 06 03 03
FAC 03
HPOS6* PARA6* TRAP6* HSIZE6* CNRT6* CNRB6* VEHT6 HEHT6
13 15 12 1D 0B 0C 03 03
FAC 04
CNCX CNTX BRTX BRTN COLX COLN TNTX TNTN
7F 08 20 20 35 00 28 28
FAC 05
BRTC* COLC COLP SCOL SCNT CNTC TNTCT TNTCV
40 2C 00 07 0C 4C 40 40
FAC 06
ST3 SV3 SV4 SVD ASSH SHPN SHPN
20 20 19 19 07 10 2A
FAC 07
MOD1 MOD2 MOD3 OPT OPTM1 OPTM2 HDCNT HSTOP
60 B0 70 37 C0 00 00 FF
FAC 08
RFAGC* BRTS OSD OSDF CCD OSD CCD OSDF TXCN RGCN
25 00 21 53 4A 65 1F 16
FAC 09
V01 V25 V50 V100 VOLMAX CURTCEN GATE COL-OUT
46 64 68 6E 32 A5 2A 73
FAC 10
MODE4 MODE5 MODE6 MODE7 MODE8 MODE9
22 0B 19 54 2D 02
FAC 11
MPB-STR MPB-HMC MPB-HP MPB-LP MPB-LIM SUB-FRE SUB-HP VOL-MAI
43 0D 07 11 00 28 02 00
FAC 12
SVM SVM1 OSD2 OSDF2 PYNX PYNN PYXS PYNS
05 05 20 64 28 18 22 10
FAC 13
CLTM CLVO CLVS ABL DCBS FLG0 FLG1
44 43 43 27 14 82 0D
FAC 14 FAC 15
HAFC AGCC NOIS ONTM NSHP PVLVL PLMT RC-C GC-C BC-C GD-C
09 1C 01 08 1A 80 80 00 00 00 00
FAC 16 FAC 17
RC-W GC-W BC-W GD-W BD-W YUVGC YUVBC D-COL D-BRI D-CON D-SHP
00 00 00 00 00 03 03 32 32 5A 32
FAC 18 FAC 19
S-COL S-BRI S-CON S-SHP M-COL M-BRI M-CON M-SHP
32 32 32 32 32 32 1E 32
FAC 20
SEG-PO INT1 SEG-POINT2 DATA-VL DATA-VH DATA-UF SPE-POS1 SPE-DATA1 SENSI-ON SENSI -OFF
173 407 01 02 08 06 05 00 00
FAC 21 FAC 22
T-Hz120 -BAS T-Hz500 -TRE T-Hz1K5 T-Hz5K T-Hz10K C-Hz120-BAS C-Hz500 -TRE C-Hz1K5 C-Hz1K C-Hz10K
2D 4A 0C 0C 0C 38 3E 0C 0C 0C
FAC 23 FAC 24
B-Hz120-BAS B-Hz500-TRE B-Hz1K5 B-Hz5K B-Hz10K COMB1 COMB2 COMB3 AV GAIN OPTM3
19 2C 0C 0C 0C 00 05 00 19 08
8.9 EEPROM Data:
Note: although all items are adjustable, we only recommend to
adjust the items with an asterisk (*). The other items are
adjustable as well, but we strongly discourage adjusting them.
EEPROM data
Page 18

EN 18 TC5.1U CA9.
Circuit Descriptions, Abbreviation List, and IC Data Sheets
9. Circuit Descriptions, Abbreviation List, and IC Data Sheets
9.1 Brief Introduction of the Chassis
9.1.1 Chassis block diagram
9.1.2 Power Supply Section
This section mainly consists of
• IC STR-W6735 (IC801).
• Transformer (T803).
• Bridge rectifier (DB801).
• Accessory circuits.
The supply voltage for this chassis should be AC 110V. The
allowed voltage range is 90V to 140V, the frequency range is
50/60Hz.
The AC power with high/low frequency interference goes
through an RC filter, consisting of C801, T801, C802, R801,
and T802. The filter removes the high/low frequency
interference. Then DB801 transforms the AC power to DC
power. T803 and IC 801 work in standby state. T803 will
provide a power voltage to IC101. IC101 scans for the "KEY IN"
signal (Pin 3 of IC101) from the ON/OFF switch on the
keyboard. If "KEY IN" = "power on" signal, pin 64 (IC101) will
generate a signal to drive the photo coupler (IC8021). It acts as
a feed back circuit (feed back to Pin 6 of IC801) for controlling
IC801 to adjust MOSFET.
Transformer T803 provides the following voltages:
• +13V voltage from Pin16.
Figure 9-1 Chassis block diagram
• +130V (B+) voltage from Pin1.
• +12V from Pin 15.
• Pin 15 is also connected to two Positive Voltage
The picture below shows IC201 and IC202:
G_16340_010.eps
100306
Regulators (IC201, IC202) in-series. The outputs of these
regulators are +9V and +5V respectively.
G_16340_022.eps
100306
Figure 9-2 IC 201/202
Page 19

Circuit Descriptions, Abbreviation List, and IC Data Sheets
6
9.1.3 Tuning Section
This section mainly consists of the tuner (TU101), the IF preamplifier circuit and the SAWFILTER.
Table 9-1 Tuning section 1
Pin Symbol Description
1 AGC Auto gain control
2 AS I2C bus address select
3 SCL I2C bus serial clock
4 SDA I2C bus serial data
5
6 BP Supply voltage tuner section +5V
7 BT Supply voltage tuning section +31V
8 IF Intermediate frequency out
Table 9-2 Short specification of the tuner
Receiving
Channel
Receiving
System
Intermediate
Frequency
Antenna Input
Impedance
Output Impedance
Band changeover system
VHF LOW BAND: CH2~B(55.25~127.25MHz)
VHF HIGH BAND: CH C~CH W+11(133.25~361.25MHz)
CH W+12~69(367.25~801.25MHz)
NTSC
Picture carrier: 47.74MHz
Colour carrier: 42.17MHz
Sound carrier: 41.25MHz
Unbalanced 75Ohms
Unbalanced 75Ohms
Digital change by PLL IC
G_16340_023.eps
10030
Figure 9-3 Pre-amplifier circuit
9.1.4 Sound Process Section
The SIF signal is sent out together with the TV signal from
Pin30 of IC101. It passes through Q203, R225. X202 and a
High-pass filter (consisting of C254, L206, C253) filters out the
video signal and low frequency interference.
G_16340_024.eps
100306
EN 19TC5.1U CA 9.
From Pin58 of IC101 the I2C bus clock signal goes to the tuner.
The tuner works during the clock time. IC101 will send out a
data signal from Pin57 to control the tuner's working state by
controlling the +33V voltage. +33V is provided from Pin10 of
T803. That voltage is put into the tuner at Pin7. A circuit inside
the tuner transforms +33V into a voltage between 0 and +33V
(as a function of the data, sent by IC101).
The AGC signal is a close loop control voltage that keeps the
amplitude of the signal constant.
Output of tuner is the Intermediate Frequency signal (IF signal).
The IF signal will pass pre-amplifier circuit (refer to the picture
below). The amplified IF signal passes the SAW filter and is
then sent to IC101 Pin41/42.
IC101 creates a CVBS signal and sends it out from Pin30.
CVBS will be selected by IC901, and then pass from Pin13 of
IC901 to Pin20/24 if IC101. IC101 will demodulate the CVBS
signal into an R, G, B signal. Next IC101 will send this R, G, B
signal from Pin50/51/52 to the CRT board.
Figure 9-4 Sound process section 1
SIF will be finally sent into Pin2 of IC1001. An analog automatic
gain control circuit (AGC) allows a wide range of input levels.
The analog-to-digital conversion of the IF sound signal is done
by an A/D-converter. The high pass filter, formed by a coupling
capacitor at SIF_IN1+ suppresses video components.
IC1001 is controlled via the I2C bus slave interface.
The AV sound signal will be directly sent to Pin37/38 or Pin40/
41 of IC1001. Q901/2 and Q903/4 form Emitter-Follower
circuits to provide a better load ability.
The (analog) sound signal will go from Pin26/27 of IC1001 to
Pin4/12 of IC602. IC602 is a dual bridge amplifier. The output
voltage of IC602 drives the speakers. The volume is adjusted
via the I2C bus.
G_16340_025.eps
100306
Figure 9-5 Sound process section 2
Page 20

EN 20 TC5.1U CA9.
Circuit Descriptions, Abbreviation List, and IC Data Sheets
9.1.5 Vertical Output Section
This section mainly consists of IC301 (TDA8172), the Vertical
Coil and the related circuit. The supply voltage of IC301 are
+14V and -14V. These two voltages are provided by the LOT
section. For the vertical scan, IC101 creates a Saw-tooth
waveform at Pin16. This is the input signal of IC301. The main
task of IC101 is to create the vertical scan waveform. The
output signal of IC301 drives the Vertical Coil. If IC301 works in
normal state, Pin6 will send a square-signal to maintain a high
voltage at D214. If it does not, D214 will get a low voltage, Pin2
of IC101 senses this change and IC101 sends out a standby
signal.
9.1.6 Horizontal Output and LOT Section
The horizontal drive pulse is a square wave. IC101 creates this
waveform at Pin13. Via Q401 the signal goes to the input of
Q411. Q411 is a horizontal output triode with a damper inside.
The signal from Pin C of Q411 drives the Horizontal Coil.
When Q411 goes into cut-off state, a sub-coil inside the LOT
will generate an EHT by inductance.
9.2 IC description
9.2.1 Main IC (IC101)
Description:
The main IC is a TMPA8857CSNG, provided by TOSHIBA. It is
an integrated circuit, suited for PAL, NTSC and SECAM TV. An
MCU and a TV signal processor are integrated in a 64 pin DIP
package.
The MCU contains an 8-bit CPU, ROM, RAM, I/O-ports, timer/
counters, A/D-converters, an on-screen display controller,
remote control interfaces, IIC bus interfaces, and the closed
caption decoder.
The TV signal processor contains PIF, SIF, Video, multistandard chroma, deflection, and RGB processors.
TV Processor
IF
• Integrated PIF VCO, aligned automatically
• Negative demodulation PIF
• Multi-frequency SIF demodulator, without external tankcoil
Video
• Integrated chroma traps
• Black stretch
• Y-gamma
Chroma
• Integrated chroma BPF’s
• PAL/NTSC/SECAM demodulation
RGB/Base-band
• Integrated 1 H base-band delay line
• Base-band TINT control
• Internal OSD interface
• Half-tone and transparent for OSD
• External YCbCr interface for DVD
• RGB cut-off/drive controls by bus
• ABCL (ABL and ACL combined)
Synchronization
• Integrated fH x 640 VCO
• DC coupled vertical ramp output (single)
• EW correction with EHT output
•Sync out
Features:
MCU:
• High speed 8-bit CPU
• 12 I/O ports
• I2C bus interface (multi-master)
• 14-bit PWM output, 1 channel, for a voltage synthesizer
• 7-bit PWM output, 1 channel
• 8-bit A/D converter, 3 channels
• Remote control signal preprocessor
• Two 16-bit internal timer/counters, 2 channels
• Two 8-bit internal timer/counters, 2 channels
• Time base timer
• Watchdog timer
• 16 interrupt sources: 5 external, 11 internal
• Stop and Idle power saving modes
CCD decoder
• Digital data slicer for NTSC
OSD
• Clock generation for OSD display
• Font ROM characters: 384 characters
• Characters display: 32 columns x 12 lines
• Composition: 16 x 18 dots
• Size of character: 3 (line by line)
• Color of character: 8 (character by character)
• Display position: H 256 / V 512 steps
• BOX function
• Fringing, smoothing, italic, underline function
• Conform to CCD regulation
• Jitter elimination
Page 21

Circuit Descriptions, Abbreviation List, and IC Data Sheets
EN 21TC5.1U CA 9.
Figure 9-6 Block Diagram Main IC 1
G_16340_026.eps
100306
Page 22

EN 22 TC5.1U CA9.
Circuit Descriptions, Abbreviation List, and IC Data Sheets
9.2.2 Vertical Deflection Booster (IC 301)
The STV8172A is a vertical deflection booster, designed for TV
and monitor applications.
This device, supplied with up to 35 V, provides a maximum
output current of 2.5 A, to drive the vertical deflection yoke.
The internal fly back generator delivers fallback voltages of up
to 75 V.
Figure 9-8 Vertical Deflection Booster
Figure 9-7 Block Diagram Main IC 2
G_16340_028.eps
100306
G_16340_027.eps
100306
Page 23

Circuit Descriptions, Abbreviation List, and IC Data Sheets
EN 23TC5.1U CA 9.
9.2.3 Demultiplexer (IC 901)
The HCF4052B is a monolithic integrated circuit, fabricated in
Metal Oxide Semiconductor technology, available in DIP and
SOP packages.
The HCF4052B analog multiplexer/demultiplexer is a digitally
controlled analog switch, having low ON impedance, and very
low OFF leakage current. This multiplexer circuit dissipates
extremely low quiescent power over the full supply voltage
range, independent of the logic states of the control signals.
When a logic “1” is present at the inhibit input, all channels are
off. This device is a differential 4-channel multiplexer, having 2
binary control inputs, A and B, and an inhibit input. The two
binary input signals select 1 of 4 pairs of channels to be turned
on and connect the analog inputs to the outputs.
G_16340_029.eps
100306
Figure 9-9 Demultiplexer
Table 9-3 Demultiplexer
PIN Symbol
1 and 2 Y CHANNELS IN/OUT
3 COMMON "Y" OUT/IN
4 and 5 Y CHANNELS IN/OUT
6INH
7 VEE
8 VSS
9B
10 A
11 and 12 X CHANNELS IN/OUT
13 COMMON "X" OUT/IN
14 and 15 X CHANNELS IN/OUT
16 VDD
9.2.4 Sound Processor (IC1001)
Pin No. Pin Name Type Short Description
19 DVSUP Digital power supply +5
V
20 DVSS Digital ground
21 I2S_DA_IN2 I2S2 data input
22 RESETQ IN Power-on-reset
23 NC Not connected
24 NC Not connected
25 VREF2 Reference ground 2
High-voltage part
26 DACM_R OUT Loudspeaker out, right
27 DACM_L OUT Loudspeaker out, left
28 NC Not connected
29 VREF1 Reference Ground 1
High voltage part
30 SC1_OUT_R OUT Audio 1 output, right
31 SC1_OUT_L OUT Audio 1 output, left
32 NC Not connected
33 AHVSUP Analog power supply
8.0V
34 CAPL_M Volume capacitor MAIN
35 AHVSS Analog ground
36 AGNDC Analog reference voltage
High-voltage part
37 SC2_IN_L IN Audio 2 input, left
38 SC2_IN_R IN Audio 2 input, right
39 ASG Analog shield Ground
40 SC1_IN_L IN Audio 1 input, left
41 SC1_IN_R IN Audio 1 input, right
42 VREFTOP Reference voltage IF A/D
converter
43 MONO_IN IN Mono input
44 AVSS Analog ground
9.2.5 Dual Bridge Amplifier (IC 602)
The TDA7266SA is a dual bridge amplifier, specially designed
for LCD monitor, PC motherboard, TV, and portable radio
applications.
Table 9-4 Sound Processor
Pin No. Pin Name Type Short Description
1 AVSUP Analog power supply
+5V
2 ANA_IN+ IN IF Input 1
3 ANA_IN- IN IF common
4 TESTEN IN Test pin
5 XTAL_IN IN Crystal oscillator
6 XTAL_OUT OUT Crystal oscillator
7 TP Test pin
8 D_CTR_I/O_1 IN/OUT D_CTR_I/O_1
9 D_CTR_I/O_0 IN/OUT D_CTR_I/O_0
10 ADR_SEL IN I2C BUS address select
11 STANDBYQ IN Stand-by ( Low-active)
12 I2C_CL IN/OUT I2C clock
13 I2C_DA IN/OUT I2C data
14 I2S_CL I2S clock
15 I2S_WS I2S word strobe
16 I2S_DA_OUT I2S data output
17 I2S_DA_IN1 I2S1 data input
18 ADR_CL ADR clock
G_16340_031.eps
100306
Figure 9-10 Dual Bridge Amplifier
Page 24

EN 24 TC5.1U CA10.
10. Spare Parts List
Spare Parts List
G_16340_032.eps
Figure 10-1 Spare Parts
Table 10-1 Spare Parts List
ITEM NAME QTY. REMARK
1 Side AV PWB 1
2 S/T Screw W 3 X 10 AB 2 MGT Side AV PWB.
3 Speaker 2
4 Speaker Rubber Cushion 8
5 S/T Screw W 3 X 14 HS 4 MGT Speaker
6 Side AV Inlay 1
7 Plate Model NO. 1
8 S/T Screw F 3 X 10 BT 2 MGT Rear AV Jack
9 Rear AV Inlay 1
10 S/T Screw B 4 X 20 AB 8 MGT Rear and Front Cabinet
11 Rear Cabinet 1
12 Cushion (25mm X 7mm) 2
13 S/T Screw W 3 X 10 AB 3 MGT Main Board
14 Main Board 1
15 Main Board Bracket 1
16 CRT Screw HA 6 X 30 4 MGT CRT & Front Cabinet
17 Metal Cushion 4
18 CRT 1
19 Fibre Sheet 4
20 S/T Screw W 3 X 10 AB 6 MGT KEY Board & Front Cabinet
21 Key Board 1
22 S/T Screw W 3 X 10 AB 4 MGT Push Button
100306
Page 25

Spare Parts List
ITEM NAME QTY. REMARK
23 Push Button 1
24 S/T Screw W 3 X 10 AB 1 MGT Lens
25 Lens 1
26 Decorative Piece for Power Knob 1
27 Power Knob 1
28 Power Spring 1
29 Logo 1
30 Front Cabinet 1
31 S/T Screw W 3 X 10 AB 4 MGT CRT Support
32 S/T Screw W 3 X 10 AB 4 MGT Guide Rail
33 Cushion (25mm X 7mm) 2
34 Power Line Block 1
35 Guide Rail (Left) 1
36 CRT Support 2
37 Guide Rail (Right) 1
EN 25TC5.1U CA 10.
Page 26

EN 26 TC5.1U CA11.
11. Revision List
Manual xxxx xxx xxxx.0
• First release.
Revision List
 Loading...
Loading...