Page 1

INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
74F193
Up/down binary counter with separate
up/down clocks
Product specification
IC15 Data Handbook
1995 Jul 17
Page 2
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
74F193Up/down binary counter with separate up/down clocks
FEA TURES
•Synchronous reversible 4-bit counting
•Asynchronous parallel load capability
•Asynchronous reset (clear)
•Cascadable without external logic
DESCRIPTION
The 74F193 is a 4-bit synchronous up/down counter in the binary
mode. Separate up/down clocks, CP
simplify operation. The outputs change state synchronously with the
Low-to-High transition of either clock input. If the CP
pulsed while CP
is pulsed while CP
is held High, the device will count up. If CPD clock
D
is held High, the device will count down. The
U
device can be cleared at any time by the asynchronous reset pin. It
may also be loaded in parallel by activating the asynchronous
parallel load pin.
Inside the device are four master-slave JK flip-flops with the
necessary steering logic to provide the asynchronous reset,
asynchronous preset, load, and synchronous count up and count
down functions.
Each flip-flop contains JK feedback from slave to master, such that a
Low-to-High transition on the CP
one, while a similar transition on the CP
count by one.
One clock should be held High while counting with the other,
because the circuit will either count by twos or not at all, depending
on the state of the first JK flip-flop, which cannot toggle as long as
either clock input is Low. Applications requiring reversible operation
must make the reversing decision while the activating clock is High
to avoid erroneous counts.
The Terminal Count Up (TC
) and Terminal Count Down (TCD)
U
outputs are normally High. When the circuit has reached the
maximum count state of 15, the next High-to-Low transition of CP
will cause TCU to go Low. TCU will stay Low until CPU goes High
again, duplicating the count up clock, although delayed by two gate
delays. Likewise, the TC
the zero state and the CP
output will go Low when the circuit is in
D
goes Low. The TC outputs can be used
D
as the clock input signals to the next higher order circuit in a
multistage counter, since they duplicate the clock waveforms.
and CPD respectively,
U
clock is
U
input will decrease the count by
D
input will advance the
U
U
Multistage counters will not be fully synchronous since there is a
two-gate delay time difference added for each stage that is added.
The counter may be preset by the asynchronous parallel load
capability of the circuit. Information present on the parallel Data
inputs (D0 - D3) is loaded into the counter and appears on the
outputs regardless of the conditions of the clock inputs when the
Parallel Load (PL
) input is Low. A High level on the Master Reset
(MR) input will disable the parallel load gates, override both clock
inputs, and set all Q outputs Low. If one of the clock inputs is Low
during and after a reset or load operation, the next Low-to-High
transition of the clock will be interpreted as a legitimate signal and
will be counted.
TYPICAL
TYPE
TYPICAL f
MAX
SUPPLY CURRENT
(TOTAL)
74F193 125MHz 32mA
ORDERING INFORMATION
COMMERCIAL RANGE
DESCRIPTION
VCC = 5V ±10%,
T
= 0°C to +70°C
amb
PKG DWG #
16-pin plastic DIP N74F193N SOT38-4
16-pin plastic SO N74F193D SOT109-1
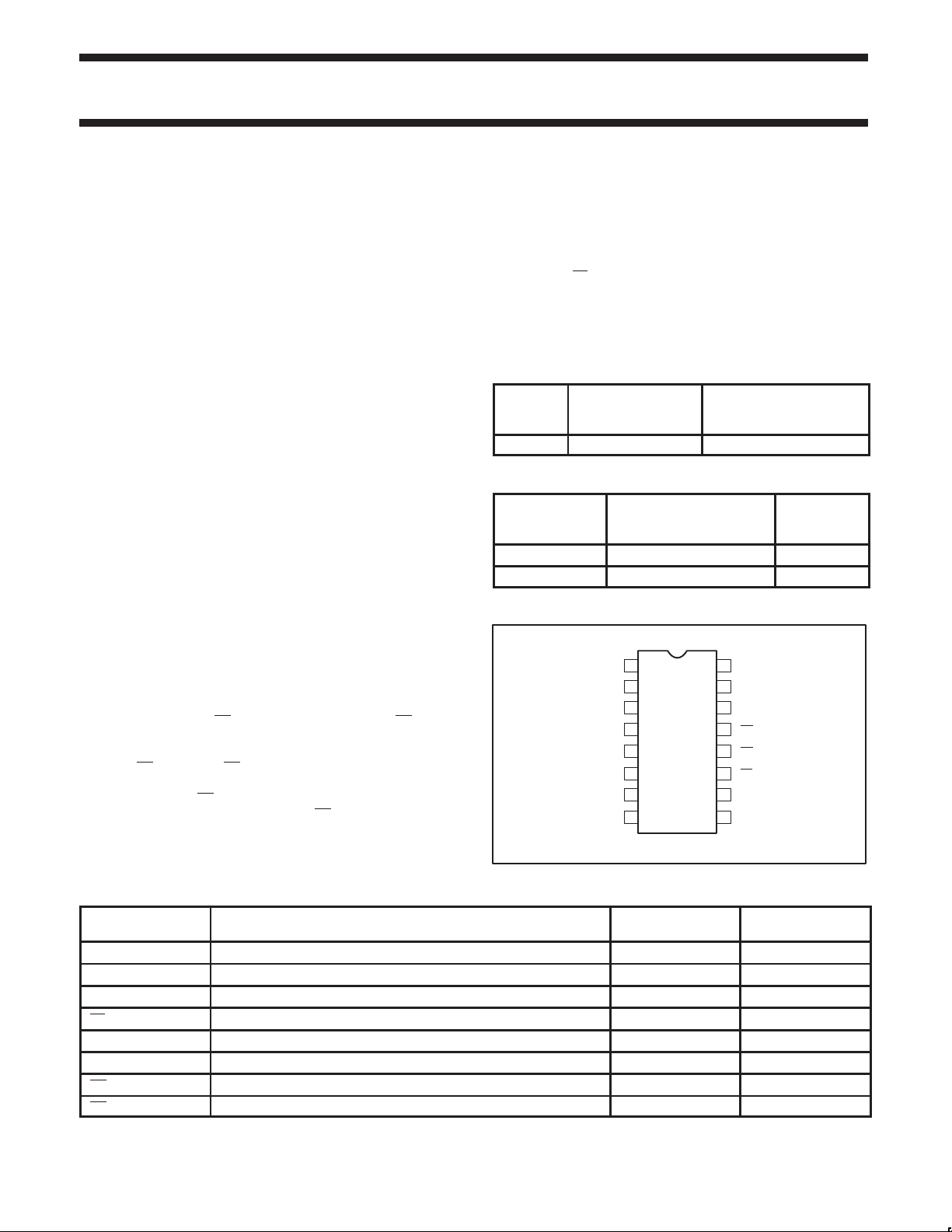
PIN CONFIGURATION
16
V
CC
D0
15
MR
14
13
TC
D
12
TC
U
PL
11
D2
10
D3
98
SF00745
Q1
Q0
CP
CP
Q2
Q3
GND
1D1
2
3
4
D
5
U
6
7
INPUT AND OUTPUT LOADING AND FAN-OUT TABLE
PINS DESCRIPTION
74F(U.L.)
HIGH/LOW
D0 - D3 Data inputs 1.0/1.0 20µA/0.6mA
CP
CP
U
D
Count up clock input (active rising edge) 1.0/3.0 20µA/1.8mA
Count down clock input (active rising edge) 1.0/3.0 20µA/1.8mA
PL Asynchronous parallel load control input (active Low) 1.0/1.0 20µA/0.6mA
MR Asynchronous master reset input 1.0/1.0 20µA/0.6mA
Q0 - Q3 Flip-flop outputs 50/33 1.0mA/20mA
TC
TC
U
D
Terminal count up (carry) output (active Low) 50/33 1.0mA/20mA
Terminal count down (borrow) output (active Low) 50/33 1.0mA/20mA
NOTE: One (1.0) FAST Unit Load (U.L.) is defined as: 20µA in the High state and 0.6mA in the Low state.
1995 Jul 17
2
LOAD VALUE
HIGH/LOW
853-0353 15459
Page 3
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
74F193Up/down binary counter with separate up/down clocks
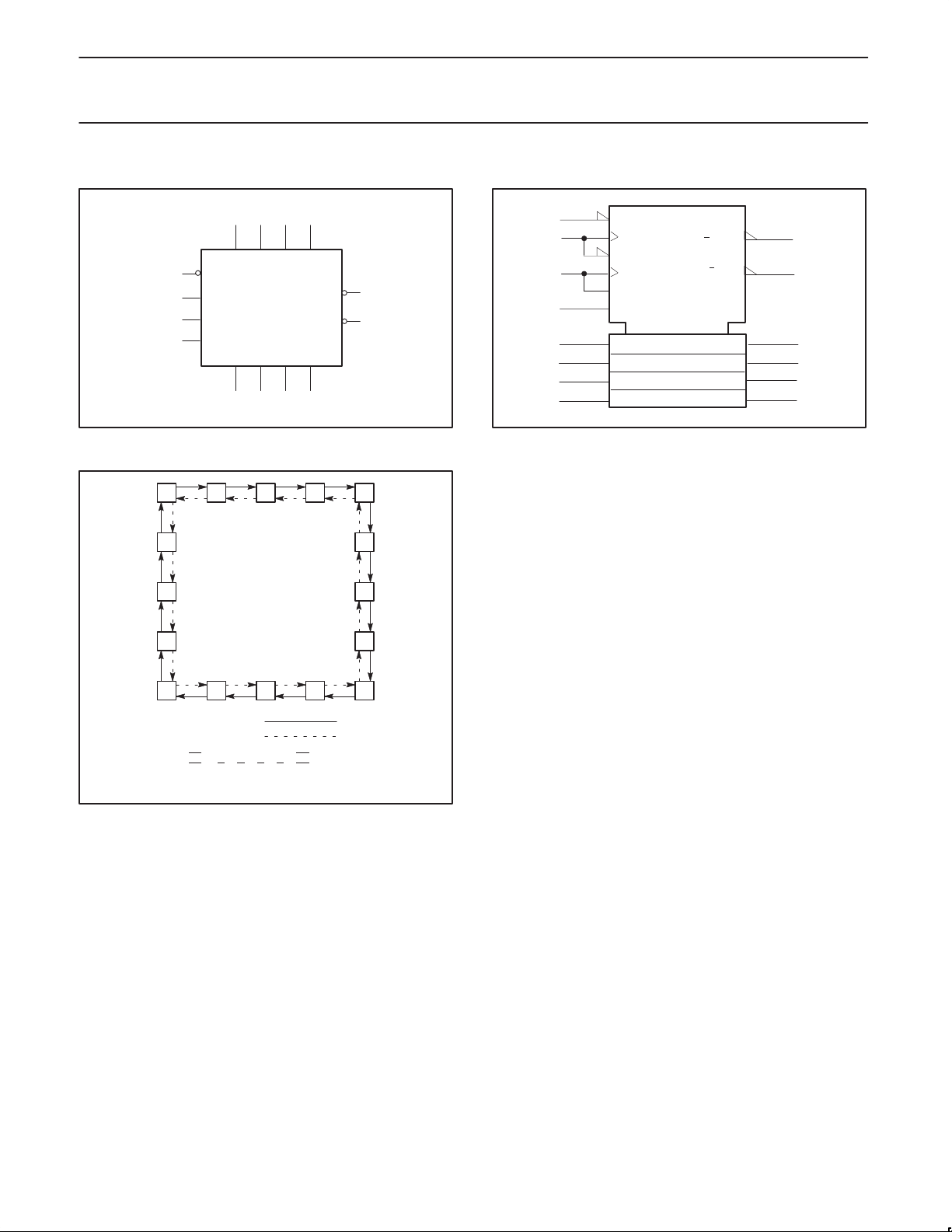
LOGIC SYMBOL
11
5
4
14
VCC = Pin 16
GND = Pin 8
STATE DIAGRAM
01234
15
14
15 1 10 9
D0 D1Q1D2
PL
CP
U
CP
D
MR
Q0
D3
Q2 Q3
LOGIC SYMBOL (IEEE/IEC)
11
5
4
U
D
SF00746
12
13
5
6
14
15
1
10
9
TC
TC
7623
C3
G1
G2
R
2+
1–
3D
CTR DIV 16
[1]
[2]
[4]
[8]
CT=15
1
2CT=0
12
13
3
2
6
7
SF00747
13
COUNT UP
COUNT DOWN
TCU = Q0 . Q1 . Q2 . Q3 . CP
TCD = Q0 . Q1 . Q2 . Q3 . CP
Logic Equations for Terminal Count
7
89101112
U
D
SF00748
1995 Jul 17
3
Page 4

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
74F193Up/down binary counter with separate up/down clocks
LOGIC DIAGRAM
CP
CP
D0 D1 D3
11
PL
5
U
4
D
15 1
KJ
CP
S
R
D
D
Q
Q
J
CP
S
R
D
D
Q
Q
D2
10
KJ
CP
S
R
D
D
Q
Q
9
12
TC
U
13
TC
D
K
JQCP
S
R
D
D
Q
14
MR
V
= Pin 16
CC
GND = Pin 8
23
Q1Q0
Q1
6
7
Q1
FUNCTION TABLE
INPUTS OUTPUTS OPERATING
MR PL CPUCP
H X X L X X X X L L L L H L Reset (clear)
H X X H X X X X L LLLHH
L L X L L L L L L L L L H L
L L X H L L L L L LLLHH Parallel load
L L L X H H H H H HHHLH
L L H X H H H H H HHHHH
L H ↑ H X X X X Count up H
L H H ↑ X X X X Count down H H2Count down
H = High voltage level
L = Low voltage level
X = Don’t care
↑ = Low-to-High clock transition
D0 D1 D2 D3 Q0 Q1 Q2 Q3 TCUTC
D
NOTES:
TC
=CPU at terminal count up (HHHH)
U
=CPD at terminal count down (LLLL)
TC
D
1
D
H Count up
SF00749
MODE
1995 Jul 17
4
Page 5

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
SYMBOL
PARAMETER
UNIT
NO TAG
VOHHigh-level output voltage
V
CC
MIN, V
IL
MAX,
VOLLow-level output voltage
V
CC
MIN, V
IL
MAX,
Low level in ut
V
MAX, V
5V
74F193Up/down binary counter with separate up/down clocks
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
(Operation beyond the limits set forth in this table may impair the useful life of the device. Unless otherwise noted these limits are over the
operating free-air temperature range.)
SYMBOL PARAMETER RATING UNIT
V
CC
V
IN
I
IN
V
OUT
I
OUT
T
amb
T
stg
RECOMMENDED OPERATING CONDITIONS
V
CC
V
IH
V
IL
I
IK
I
OH
I
OL
T
amb
Supply voltage –0.5 to +7.0 V
Input voltage –0.5 to +7.0 V
Input current –30 to +5.0 mA
Voltage applied to output in High output state –0.5 to +V
CC
V
Current applied to output in Low output state 40 mA
Operating free-air temperature range 0 to +70
Storage temperature –65 to +150
°
C
°
C
LIMITS
MIN NOM MAX
Supply voltage 4.5 5.0 5.5 V
High-level input voltage 2.0 V
Low-level input voltage 0.8 V
Input clamp current –18 mA
High-level output current –1 mA
Low-level output current 20 mA
Operating free-air temperature range 0 +70
°
C
DC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
(Over recommended operating free-air temperature range unless otherwise noted.)
LIMITS
SYMBOL PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS
V
= MIN, V
p
p
V
IK
I
I
I
IH
I
IL
I
OS
I
CC
Input clamp voltage VCC = MIN, II = I
Input current atmaximum
input voltage
High-level input current VCC = MAX, VI = 2.7V 20 µA
Low-level input
current
Short-circuit output current
Supply current (total)
4
CPU, CP
NO TAG
D
Others
=
I
= MAX, VIH = MIN
OH
V
= MIN, V
=
IOL = MAX, VIH = MIN
VCC = MAX, VI = 7.0V 100 µA
=
CC
VCC = MAX –60 –150 mA
VCC = MAX 32 50 mA
= MAX,
=
= MAX,
=
IK
= 0.
I
10%V
5%V
10%V
5%V
CC
CC
MIN
2.5 V
CC
2.7 3.4 V
CC
TYP
NO TAG
MAX
0.35 0.50 V
0.35 0.50 V
–0.73 –1.2 V
–1.8 mA
–0.6 mA
NOTES:
1. For conditions shown as MIN or MAX, use the appropriate value specified under recommended operating conditions for the applicable type.
2. All typical values are at V
3. Not more than one output should be shorted at a time. For testing I
= 5V, T
CC
techniques are preferable in order to minimize internal heating and more accurately reflect operational values. Otherwise, prolonged shorting
amb
= 25°C.
, the use of high-speed test apparatus and/or sample-and-hold
OS
of a High output may raise the chip temperature well above normal and thereby cause invalid readings in other parameter tests. In any
sequence of parameter tests, I
4. Measure I
with parallel load and Master reset inputs grounded, all other inputs at 4.5V and all outputs open.
CC
tests should be performed last.
OS
UNIT
1995 Jul 17
5
Page 6

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
74F193Up/down binary counter with separate up/down clocks
AC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
LIMITS
T
SYMBOL PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS
f
MAX
t
PLH
t
PHL
t
PLH
t
PHL
t
PLH
t
PHL
t
PLH
t
PHL
t
PHL
t
PLH
t
PHL
t
PLH
t
PHL
t
PLH
t
PHL
Maximum clock frequency Waveform 1 100 125 90 MHz
Propagation delay
CPU or CPD to TCU or TC
Propagation delay
CPU or CPD to Qn
Propagation delay
Dn to Qn
Propagation delay
PL to Qn
Propagation delay
MR to Qn
Propagation delay
MR to TC
U
Propagation delay
MR to TC
D
Propagation delay
PL
to TCU or TC
D
Propagation delay
Dn to TCU or TC
D
D
Waveform 2
Waveform 1
Waveform 4
Waveform 3
Waveform 5 5.0 7.5 11.0 5.0 12.0 ns
Waveform 5 6.0 8.5 12.0 5.5 13.0 ns
Waveform 5 5.0 7.5 11.0 5.0 12.0 ns
Waveform 3
Waveform 4
= +25°C
amb
VCC = +5.0V
CL = 50pF, RL = 500Ω
MIN TYP MAX MIN MAX
2.5
3.0
2.5
5.0
2.0
6.0
4.5
5.5
6.0
6.0
5.5
4.5
5.5
5.0
5.5
8.5
4.0
9.5
6.5
8.5
9.5
9.0
9.0
8.5
8.5
8.0
8.5
12.0
7.0
13.5
10.0
12.0
13.5
12.0
13.0
12.5
T
= 0°C to +70°C
amb
VCC = +5.0V ± 10%
CL = 50pF, RL = 500Ω
2.5
3.0
2.5
5.0
1.5
6.0
4.0
5.0
6.0
6.0
5.0
4.5
9.0
9.0
9.0
13.0
8.0
15.0
11.0
13.0
15.0
13.0
14.0
13.5
UNIT
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
AC SETUP REQUIREMENTS
SYMBOL PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS
ts(H)
ts(L)
th(H)
th(L)
tw(L)
tw(H)
tw(L)
tw(L)
tw(H)
t
rec
t
rec
Setup time, High or Low
Dn to PL
Hold time, High or Low
Dn to PL
PL Pulse width
Low
CPU or CPD Pulse width
High or Low
CPU or CPD Pulse width
Low (Change of direction)
MR Pulse width
High
Recovery time,
PL to CPU or CP
D
Recovery time
MR to CPUor CP
D
Waveform 6
Waveform 6
Waveform 3 6.0 6.0 ns
Waveform 1
Waveform 1 10.0 10.0 ns
Waveform 5 6.0 6.0 ns
Waveform 3 6.0 6.0 ns
Waveform 5 4.0 4.0 ns
LIMITS
T
= +25°C
amb
VCC = +5.0V
C
= 50pF, RL = 500Ω
L
T
= 0°C to +70°C
amb
VCC = +5.0V ± 10%
C
= 50pF, RL = 500Ω
L
MIN TYP MAX MIN MAX
4.5
4.5
2.0
2.0
3.5
5.0
5.0
5.0
2.0
2.0
3.5
5.0
UNIT
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
1995 Jul 17
6
Page 7

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
74F193Up/down binary counter with separate up/down clocks
AC WAVEFORMS
For all waveforms Vm = 1.5V
1/f
MAX
CPU, CP
Qn
t
PHL
V
M
tW(H)
V
M
D
V
M
t
PLH
Waveform 1. Propagation Delay, Clock Input to Output,
Clock Pulse Width and Maximum Clock Frequency
tW(L)
tW(L)
PL
CPU, CP
TCU, TCD, Qn
V
M
t
PLH
D
VMV
M
t
PHL
V
M
V
M
Waveform 3. Parallel Pulse Width,
Parallel Load to Output Delays, and Parallel Load
to Clock Recovery Time
CPU, CP
MR
V
M
tW(H) t
D
V
M
rec
V
M
V
M
SF00750
V
M
t
rec
V
M
SF00751
CPU, CP
TCU, TC
D
D
t
PHL
V
M
V
V
M
t
PLH
M
V
M
SF00753
Waveform 2. Propagation Delay, Clock to Terminal Count
Qn
Qn
,
,
TC
TC
Dn
, TC
U
D
, TC
U
D
V
M
t
PLH
t
PHL
V
M
t
PHL
V
M
t
PLH
V
M
V
M
V
M
SF00754
Waveform 4. Propagation Delay, Data to Flip-Flop Outputs,
Terminal Count Up and Down Outputs
Dn
PL
The shaded areas indicate when the input is permitted
to change for predictable output performance.
tS(H)
V
M
th(H)
tS(L)
V
M
(L)
t
h
V
M
SF00755
Waveform 6. Data Setup and Hold Times
t
PLH
V
TC
Qn, TC
U
t
PHL
D
M
V
M
SF00752
Waveform 5. Master Reset Pulse Width, Master Reset to Output
Delay and Master Reset to Clock Recovery Time
1995 Jul 17
7
Page 8

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
74F193Up/down binary counter with separate up/down clocks
Timing Diagram (Typical clear, load, and count sequence)
1
LOAD
MR
PL
D0
D1
D2
D3
2
CP
U
2
CP
D
Q0
CLEAR
DATA
COUNT UP
COUNT DOWN
OUTPUTS
SEQUENCE
NOTES:
1. Clear overrides load, data, and count inputs.
2. When counting up, count-down input must be High; when counting down, count-up input must be High.
Q1
Q2
Q3
TC
U
TC
D
0 13 14 15 0 1 2 1 0 15 14 13
CLEAR PRESET
COUNT UP COUNT DOWN
Binary Counter
TEST CIRCUIT AND WAVEFORMS
V
CC
NEGATIVE
PULSE
V
PULSE
GENERATOR
IN
R
T
Test Circuit for Totem-Pole Outputs
D.U.T.
V
OUT
R
C
L
L
POSITIVE
PULSE
90%
10%
SF00756
t
w
THL (tf
10%
)
)
90%
V
M
V
M
V
M
10%
t
V
90%
M
THL (tf
t
TLH (tr
)
)
t
TLH (tr
t
t
w
90%
10%
AMP (V)
0V
AMP (V)
0V
DEFINITIONS:
R
= Load resistor;
L
see AC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS for value.
C
= Load capacitance includes jig and probe capacitance;
L
see AC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS for value.
= Termination resistance should be equal to Z
R
T
pulse generators.
1995 Jul 17
OUT
of
family
74F
8
Input Pulse Definition
INPUT PULSE REQUIREMENTS
V
amplitude
3.0V 1.5V
rep. rate
M
1MHz 500ns
t
w
t
TLHtTHL
2.5ns 2.5ns
SF00006
Page 9

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Up/down binary counter with separate up/down clocks
DIP16: plastic dual in-line package; 16 leads (300 mil) SOT38-4
74F193
1995 Juk 17
9
Page 10

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Up/down binary counter with separate up/down clocks
SO16: plastic small outline package; 16 leads; body width 3.9 mm SOT109-1
74F193
1995 Juk 17
10
Page 11

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Up/down binary counter with separate up/down clocks
NOTES
74F193
1995 Juk 17
11
Page 12

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Up/down binary counter with separate up/down clocks
Data sheet status
Data sheet
status
Objective
specification
Preliminary
specification
Product
specification
Product
status
Development
Qualification
Production
Definition
This data sheet contains the design target or goal specifications for product development.
Specification may change in any manner without notice.
This data sheet contains preliminary data, and supplementary data will be published at a later date.
Philips Semiconductors reserves the right to make chages at any time without notice in order to
improve design and supply the best possible product.
This data sheet contains final specifications. Philips Semiconductors reserves the right to make
changes at any time without notice in order to improve design and supply the best possible product.
[1]
74F193
[1] Please consult the most recently issued datasheet before initiating or completing a design.
Definitions
Short-form specification — The data in a short-form specification is extracted from a full data sheet with the same type number and title. For
detailed information see the relevant data sheet or data handbook.
Limiting values definition — Limiting values given are in accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System (IEC 134). Stress above one
or more of the limiting values may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only and operation of the device at these or
at any other conditions above those given in the Characteristics sections of the specification is not implied. Exposure to limiting values for extended
periods may affect device reliability.
Application information — Applications that are described herein for any of these products are for illustrative purposes only. Philips
Semiconductors make no representation or warranty that such applications will be suitable for the specified use without further testing or
modification.
Disclaimers
Life support — These products are not designed for use in life support appliances, devices or systems where malfunction of these products can
reasonably be expected to result in personal injury . Philips Semiconductors customers using or selling these products for use in such applications
do so at their own risk and agree to fully indemnify Philips Semiconductors for any damages resulting from such application.
Right to make changes — Philips Semiconductors reserves the right to make changes, without notice, in the products, including circuits, standard
cells, and/or software, described or contained herein in order to improve design and/or performance. Philips Semiconductors assumes no
responsibility or liability for the use of any of these products, conveys no license or title under any patent, copyright, or mask work right to these
products, and makes no representations or warranties that these products are free from patent, copyright, or mask work right infringement, unless
otherwise specified.
Philips Semiconductors
811 East Arques Avenue
P.O. Box 3409
Sunnyvale, California 94088–3409
Telephone 800-234-7381
Copyright Philips Electronics North America Corporation 1998
All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A.
print code Date of release: 10-98
Document order number: 9397-750-05094
yyyy mmm dd
12
 Loading...
Loading...