Page 1

E2U0022-28-81
¡ Semiconductor MSM6895/6896
¡ Semiconductor
This version: Aug. 1998
Previous version: Nov. 1996
MSM6895/6896
Multi-Function PCM CODEC
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The MSM6895/MSM6896, developed especially for low-power and multi-function applications
in ISDN telephone terminals, are single +5 V power supply CODEC LSI devices. The devices
consist of the analog speech paths directly connectable to a handset, the calling circuit directly
connectable to a piezosounder, the push-button key scanning interface between push buttons
and control processors, the dial tone generator, the B-channel interface, the CODEC, and the
processor interface. The functions can be controlled via the 8-bit data bus.
FEATURES
• Single +5 V Power Supply
• Low Power Dissipation
Power ON Mode : 20 mW Typ. 53 mW Max.
CODEC Power Down Mode : 10 mW Typ. 21 mW Max.
• In compliance with ITU-T’s companding law
m-law : MSM6895
A-law : MSM6896
• Transmission clocks
Continuous CLK : 64, 128, 256 kHz
Burst CLK : 192, 384, 768, 1536, 2048 kHz
• Built-in PLL
• Built-in Reference Voltage Supply
• Ringing Tone : Controlled by processor, 9 modes
• Ringing Tone Combination : Controlled by processor, 6 modes
• Information Tone : Controlled by processor, 9 modes
• Built-in PB Tone Generator
• B-Channel Selectable
• General Latch Output for Speech path Control : 4 bits
• Watchdog Timer : 500 ms
• Key Scanning I/O
Output : 5 bits
Input : 8 bits
• Direct Connection to Handset
• Built-in Preamplifier for Loudspeaker
• Handfree Interface
• Digital and Analog Interface for the phone-conference speech paths
• Package:
80-pin plastic QFP (QFP80-P-1420-0.80-BK) (Product name : MSM6895GS-BK)
(Product name : MSM6896GS-BK)
1/43
Page 2
¡ Semiconductor MSM6895/6896
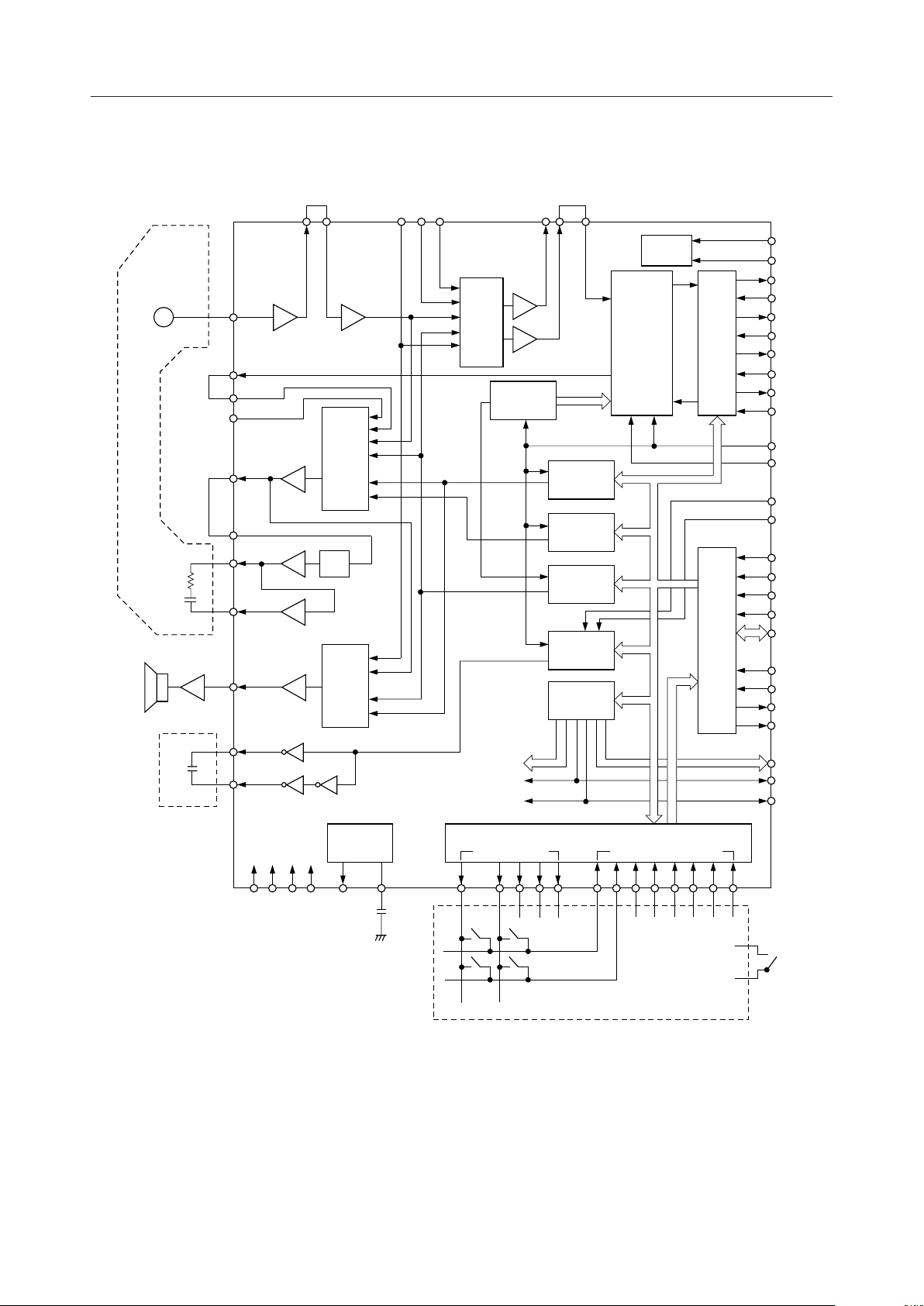
BLOCK DIAGRAM
TMX1I
TPAO MLDYTPBI
M
TPAI
CAO
R1I
R2I
TMX2I
T2O
SW
&
MIX
PLL
T1 O
CAI
AIN
CODEC
AOUT
TEST
CK1536
TEST
B1T
B1R
B2T
B2R
BR1
BT1
BR2
BT2
B1
B2
SP
HANDSET
BUZZER
RPO
RMI
RMO0
RMO1
SPO
SA0
SA1
SW
&
MIX
+
SW
F-TONE
GEN
R-TONE
GEN
DTMF TONE
GEN
–
S-TONE
SW
&
MIX
SW
CONT.
SGGEN
PO0 ~
VSGCVSG
PO4
VD VAG VDGVA
SCANNING
OUTPUT
GEN
LATCH
KEY INTF.
KEY DATA INPUT
CK8
8K
CK64
64K
SW0
SW1
WR
RD
CE
RESET
8BIT
LA ~
LD
PI0 to
PI7
7654321043210
Data Bus
AD0
AD1
INTT
TIME
4BIT
LOSS
LML
SWITCH
HOOK
MPU INTF. CHANNEL SELECTOR
PUSH-BOTTON SWITCH
2/43
Page 3
¡ Semiconductor MSM6895/6896
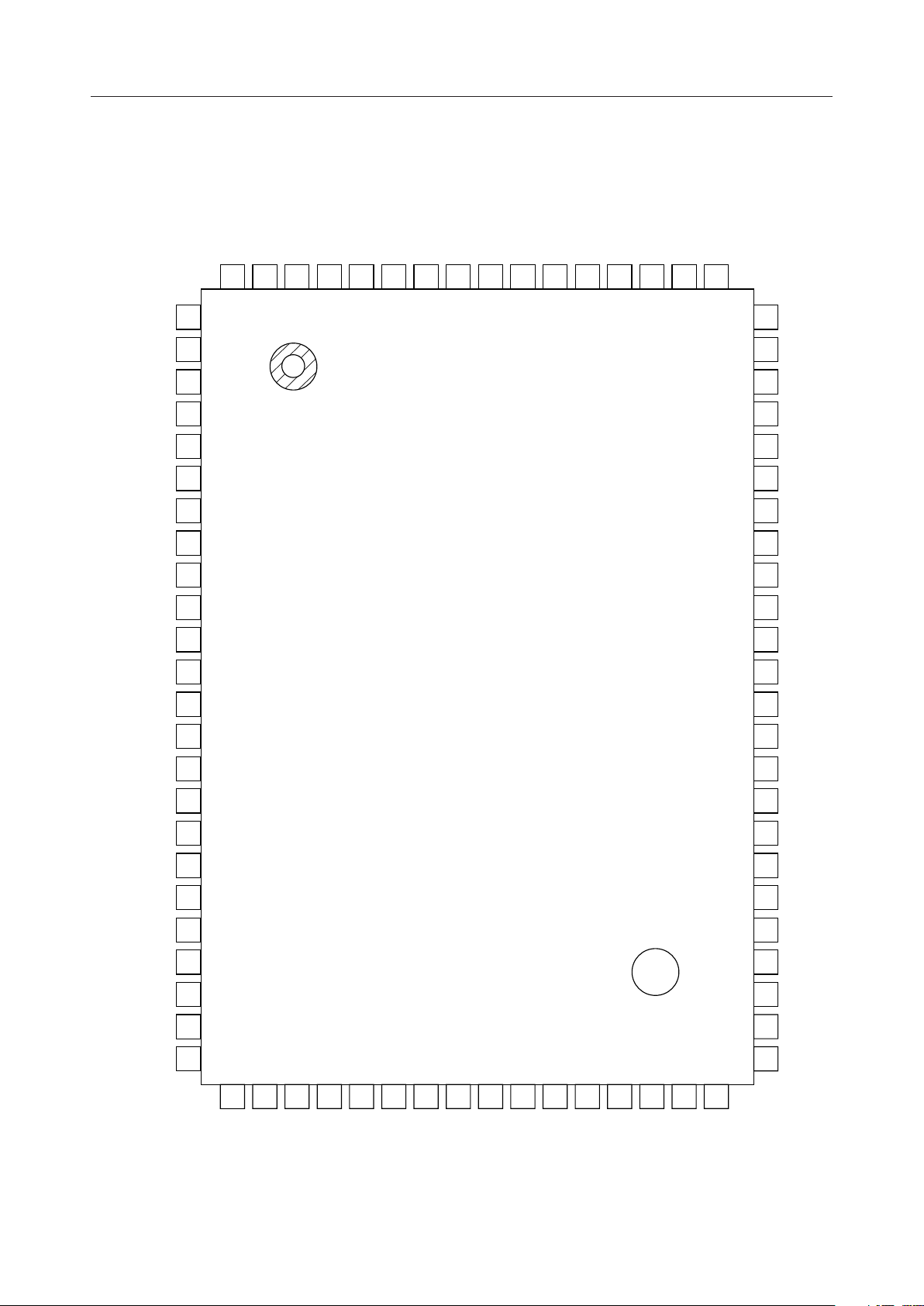
PIN CONFIGURATION (TOP VIEW)
LML
LA
80
79
TIME
78
RESET
77
BR2
76
BR1
75
BT2
74
BT1
73
B2R
72
B1R
71
B2T
70
B1T
69
CE
68
RD
67
WR
66
AD1
65
LB
LC
LD
SW0
SW1
VDG
VAG
SA0
SA1
NC
RM1
NC
RMO0
RMO1
10
11
12
13
14
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
64
63
62
61
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
51
VD
AD0
DB7
DB6
DB5
DB4
DB3
DB2
DB1
DB0
INTT
PI7
PI6
PI5
SPO
RPO
R2I
R1I
NC
NC
TMX2I
MLDY
TPBI
TMX1I
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
TPAI
26
VSG
27
TPAO
28
T1O
29
T2O
31
30
NC
NC : No connect pin
80-Pin Plastic QFP
NC
32
VA
33
CAI
34
VSGC
35
CA0
36
TEST
38
37
CK64
CK1536
39
CK8
40
LOSS
50
49
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
PI4
PI3
PI2
PI1
PI0
PO4
PO3
PO2
PO1
PO0
3/43
Page 4
¡ Semiconductor MSM6895/6896
PIN DESCRIPTION
Pin Symbol Type Description
1 LB DO Data Latch Output B
2 LC DO Data Latch Output C
3 LD DO Data Latch Output D
4 SW0 DI Sounder Tone Select (1)
5 SW1 DI Sounder Tone Select (2)
6 VDG — Digital Ground
7 VAG — Analog Ground
8 SA0 DO Sounder Output (+)
9 SA1 DO Sounder Output (–)
10 — — NC
11 RMI AI Receive Main Amp Input
12 — — NC
13 RMO0 AO
14 RMO1 AO
15 SPO AO Speaker Pre-Amp Output
16 RPO AO Receive Pre-Amp Output
17 R2I AI
18 R1I AI Receive Signal Input
19 — — NC
20 — — NC
21 TMX2I AI
22 MLDY AI Hold Tone Input
23 TPBI AI
24 TMX1I AI
25 TPAI AI
26 VSG AO Signal Ground
27 TPAO AO
28 T1O AO Transmit Signal Output (1)
29 T2O AO Transmit Signal Output (2)
30 — — NC
Receive MainAmp Output (+)
Receive MainAmp Output (–)
Receive Addition Signal Input
Transmit Addtion Signal Input (2)
Transmit Pre-Amp (B) Input
Transmit Addtion Signal Input (1)
Transmit Pre-Amp (A) Input
Transmit Pre-Amp (A) Output
Pin Symbol Type Description
31 —
32 VA
33 CAI
34 VSGC
35 CAO
36 TEST
37 CK1536
38 CK64
39 CK8
40 LOSS
41 PO0
42 PO1
43 PO2
44 PO3
45 PO4
46 PI0
47 PI1
48 PI2
49 PI3
50 PI4
51 PI5
52 PI6
53 PI7
54 INTT
55 DB0
56 DB1
57 DB2
58 DB3
59 DB4
60 DB5
—
—
AI
AO
AO
DI
DI
DI
DI
DO
DO
DO
DO
DO
DO
DI
DI
DI
DI
DI
DI
DI
DI
DO
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
NC
+5 V Analog Power Supply
Analog Signal Input to CODEC
Bypass Capacitor for Signal Ground
Analog Signal Output from CODEC
Control Input for Test
Clock Input for Test
Transmission Colck Input
Frame Synchronous Clock Input
Howler Tone Control Signal
Key Scanning Signal Output (0)
Key Scanning Signal Output (1)
Key Scanning Signal Output (2)
Key Scanning Signal Output (3)
Key Scanning Signal Output (4)
Key Scanned Data Input (0)
Key Scanned Data Input (1)
Key Scanned Data Input (2)
Key Scanned Data Input (3)
Key Scanned Data Input (4)
Key Scanned Data Input (5)
Key Scanned Data Input (6)
Key Scanned Data Input (7)
Interrupt Output
Data Bus (0)
Data Bus (1)
Data Bus (2)
Data Bus (3)
Data Bus (4)
Data Bus (5)
4/43
Page 5
¡ Semiconductor MSM6895/6896
PIN DESCRIPTION (Continued)
Pin Symbol Type Description
61 DB6 I/O Data Bus (6)
62 DB7 I/O Data Bus (7)
63 AD0 DI Address Data (0)
64 VD —
65 AD1 DI Address Data Input (1)
66 WR DI Write Signal Input
67 RD DI Read Signal Input
68 CE DI Chip Enable
69 B1T DO
70 B2T DO
+5 V Digital Power Supply
B1 Channel Transmit Output
B2 Channel Transmit Output
Pin Symbol Type Description
71 B1R B1 Channel Recive Input
72 B2R B2 Channel Recive Input
73 BT1
74 BT2
75 BR1
76 BR2
77 RESET Reset Input
78 TIME Timer Output
79 LML Hold Tone Control Output
80 LA Data Latch Output (A)
DI
DI
DI
DI
DO
DO
DI
DO
DO
DO
B Channel Selector Transmit Data (1)
B Channel Selector Transmit Data (2)
B Channel Selector Receive Data (1)
B Channel Selector Receive Data (2)
5/43
Page 6
¡ Semiconductor MSM6895/6896
PIN AND FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTIONS
LA, LB, LC, LD
General latch outputs for external control.
Statuses of these outputs are controlled via the processor interface. Refer to the description of the
control data for details.
SW0, SW1
External control signal inputs for setting the tone combination of the ringing tone.
When the external control for setting the tone combination is selected, the tone combination is
set by these pins.
SW0
0
0
1
1
VDG
Digital Ground.
SW1
0
1
0
1
Tone combination 1
Tone combination 2
Tone combination 3
Tone combination 1
1 / f1
Wambling Cycle
16 Hz
16 Hz
8 Hz
16 Hz
Wambling Cycle Time
1 / f2
f1
1000 Hz
800 Hz
800 Hz
1000 Hz
f2
1333 Hz
1000 Hz
1000 Hz
1333 Hz
VAG
Analog Ground.
6/43
Page 7
¡ Semiconductor MSM6895/6896
SA0, SA1
Sounder (ringing tone) driving outputs.
The output signal on SA1 is inverted against the signal on SA0. The sounder circuit can be easily
configured by connecting a piezo-sounder between SA0 and SA1. Through processor control, the
ringing tone volume is selectable from four levels and one of six tone combinations is selectable.
Initially, the ringing tone volume is set at a maximum and the tone combination is set externally.
If these pins are used with no-load, tone volume cannot be controlled.
When tone volume control is required, a load resistor must be connected between SA0 and SA1.
RMI, RMO0, RMO1
Receive main amplifier input and outputs.
RMI is the main amplifier input and RMO0 and RMO1 are the main amplifier outputs. The
output signal on RMO1 is inverted against RMO0, so the earphone of a piezo electric-type
handset is directly connected between RMO0 and RMO1. The RMI input pin is connected to the
receive preamplifier output pin (RPO).
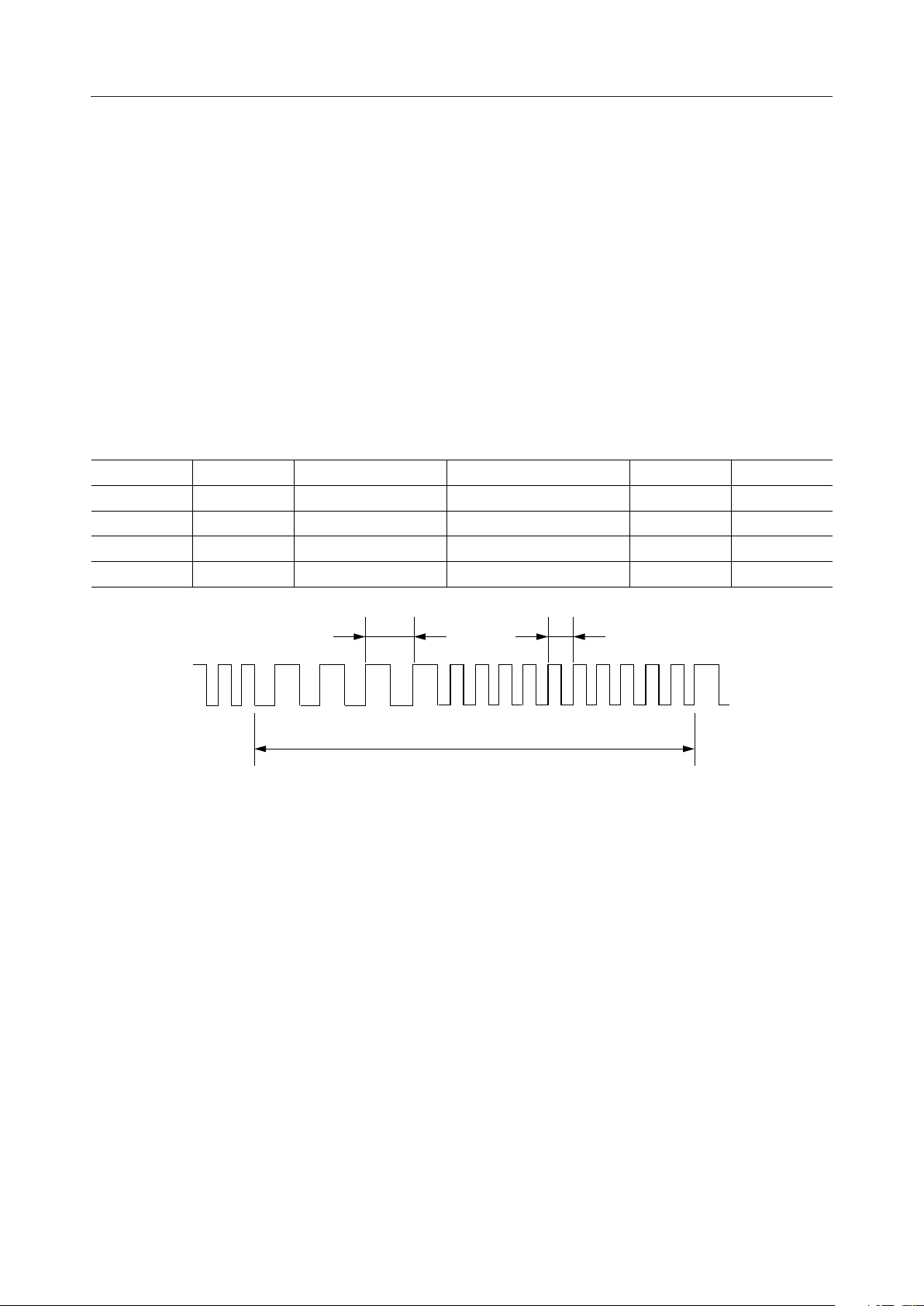
If the adjusting of receive path frequency characteristics is required, insert the following circuit
for adjustment. During initial setting, the speech path from RMI to RMO0 and RMO1 is
disconnected and the output of RMO0 and RMO1 is at the VSG level (VA/2). The speech path
is provided by processor control.
A circuit example for adjustment of frequency characteristics
RPO
R1
C1
RMI VSG
C2
R2
SPO
Output of preamplifier for speaker.
Since the driving capability is 2.4 VPP for the load of 20 kW, SPO can not directly drive a speaker.
During initial setting, SPO is in a non-signal state (VSG level), and a speech signal, RTONE0,
RTONE1, FTONE, hold acknowledge tone, and PB signal acknowledge tone are output through
processor control.
7/43
Page 8
¡ Semiconductor MSM6895/6896
R1I, R2I, RPO
Receive preamplifier inputs and output.
R1I and R2I are for the inputs and RPO is for the output of the receive preamplifier. Normally,
R1I is connected via an AC-coupling capacitor to the CODEC analog output (CAO), and R2I is
used as the mixing signal input pin.
During initial setting, the RPO output is in non-signal state (VSG level), and speech signal,
RTONE1, RTONE2, FTONE, PB acknowledge tone, and side tone signal are output through
processor control. And if the three-party speech function is required, the R2I pin is connected to
the analog output of the other CODEC.
MLDY
Hold tone signal input.
This pin is connected to the output of external melody IC. Through processor control, the signal
applied to MLDYI is output from the TO output pin as a hold tone on the transmit path, and from
the SPO output pin as a hold acknowledge tone on the receive path.
TPBI
Transmit signal input.
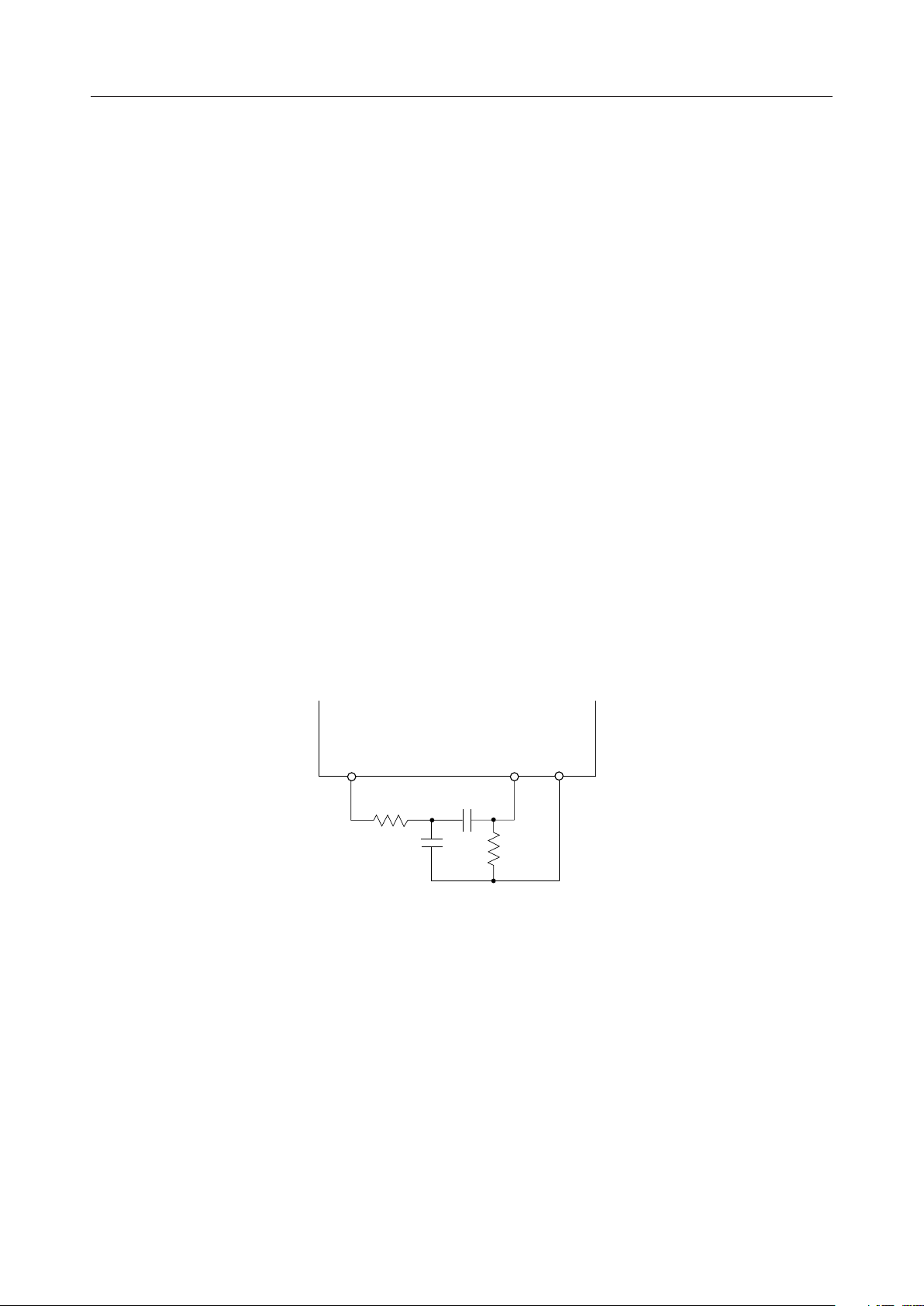
When the handset is used, TPBI is connected to the transmit preamplifier output pin (TPAO). If
adjustment of frequency characteristics on the transmit path is required, insert a circuit for
adjustment of characteristic between TPAO and TPBI. Through processor control, the signal
applied to this pin is output via the T1O and T2O pins on the transmit path output and its side
tone via the RPO pin.
A circuit example for adjustment of frequency characteristics
TPAO TPBI VSG
C3R3
R4
C4
TMX1I, TMX2I
Transmit addition signal inputs.
Through processor control, the input signals to TMX1I and TMX2I are added to the transmit
signal and are output to T1O and T2O respectively.
8/43
Page 9

¡ Semiconductor MSM6895/6896
TPAI, TPAO
The transmit preamplifier input and output.
TPAI is the input and TPAO is the output. Connect TPAI to the microphone of handset via an ACcoupling capacitor if the DC offset appears at a transmit signal (offset from SGT). The transmit
path from TPAI to TPAO is always established regardless of processor control.
VSG
Signal ground level output.
The output level is equal to a half of the power supply voltage.
VSGC
Bypass capacitor connecting pin for signal ground level.
Insert a 0.1 mF capacitor with good higher frequency characteristic, between VSGC and VAG.
VA, VD
+5 V power supply.
VA is for an analog circuit and VD is for digital supply. Connect both VA and VD to the +5 V
analog path of the system.
CAI
CODEC analog output.
Connect CAI to T1O.
CAO
CODEC analog output.
Connect CAO to R1I via an AC-Coupling capacitor.
9/43
Page 10

¡ Semiconductor MSM6895/6896
TEST, CK1536
External master clock inputs.
Since the MSM6895 and MSM6896 contain PLL internally, the external clock signal is eliminated.
But the device can operate with the external clock through these pins.
When these pins are not used, leave these pins open or at 0 V.
Mode
Internal PLL
External master clock
TEST pin
0 V
Digital "1"
CK1536 pin
open or 0 V
Input the signal of 1536 kHz
When the external clock is used, the CK1536 signal is required to be synchronized in phase with
the CK8 signal.
CK64
CODEC PCM data input and output shift clock input.
When the continuous clock is set, the frequency is one of 64 kHz, 128 kHz, and 256 kHz. When
the burst clock is used, one of 192, 384, 768, 1536, and 2048 kHz is available. If the BCLOCK signal
is not applied, PLL is out of synchronization and goes into the self-running mode.
CK8
Synchronous signal input.
CODEC PCM data is sent out sequencially from MSB at the rising edge of the CK64 signal in
synchronization with the rise of the synchronous signal. PCM data should be entered from MSB
in synchronization with the rise of the synchronous signal. PCM data is shifted in at the falling
edge of the CK64 signal.
Since the CK8 signal is used for a trigger signal for PLL and for a clock signal to the tone generator,
if this signal is not applied, not only any tone can not be output, but also PLL goes out of
synchronization and goes into self-running mode. This signal has to be synchronous with the
CK64 signal and its frequency must be within 8 kHz ±50 ppm to ensure the CODEC AC
characteristics (mainly frequency characteristics).
LOSS
Signal output for controlling the external circuits.
When the howler tone of sounder is selected through processor control, the output is in a digital
"1".
Initially, this output is set to a digital "0".
10/43
Page 11
¡ Semiconductor MSM6895/6896
PO0, PO1, PO2, PO3, PO4, PO5, PO6, PO7
Key scanning outputs.
These output pins need external pull-up resistors because of their open- drain circuits. Through
processor control, these outputs can be set open or to digital "0". Initially, these outputs are set
at an opened state.
PI0, PI1, PI2, PI3, PI4, PI5, PI6, PI7
Key scanning inputs.
In the READ mode, data on PI0 to PI7 can be read out of the processor via data bus (DB0 to DB7).
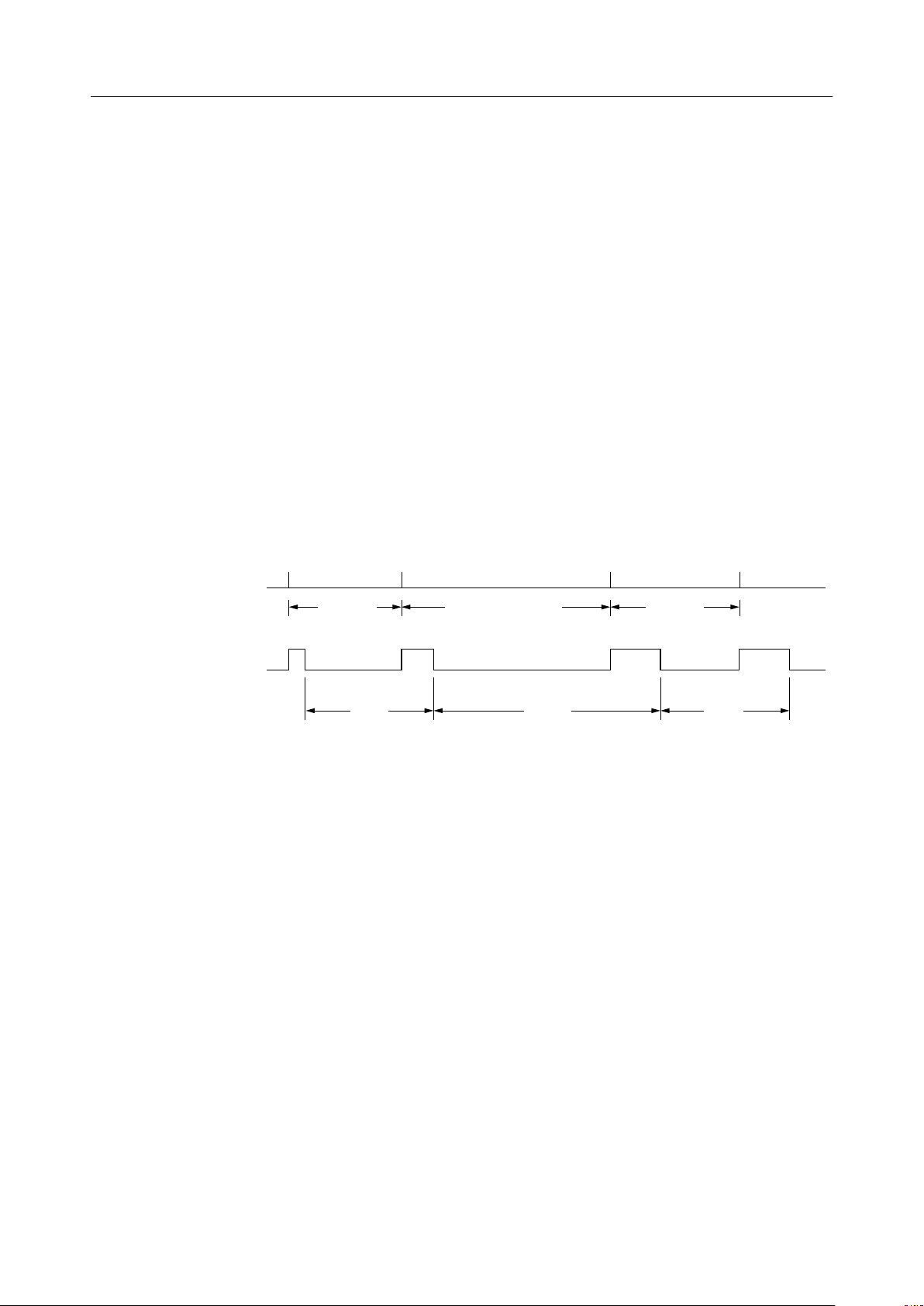
INTT
Interrupt signal output to the processor.
INTT outputs interrupt signals (digital "0") at intervals of 8 ms by the interrupt release control
signal from the processor. INTT does not output any signal while no CK8 signal is input.
Interrupt release signal
from processor
INTT output
t < 8 ms 8 ms < t < 16 ms t < 8 ms
8 ms 16 ms 8 ms
DB0, DB1, DB2, DB3, DB4, DB5, DB6, DB7
Data bus inputs and outputs.
11/43
Page 12
¡ Semiconductor MSM6895/6896
AD0, AD1
Address data inputs for the internal control registers.
Addressing of the internal control registers is executed by AD0 and AD1 and sub address data,
DB7 and DB6.
Write
Read
AD1 AD0 DB7 DB6
0000
0001
0010
0011
01——
10——
1100
1101
1110
1111
10——
Sounder Control
Control of function key acknowledge tone
PB tone control
Control of the internal control latch and the general-purpose latch,
Reset control of the watch dog timer.
Control of channel selector
Key scanning output control, interrupt release control
Volume control and tone combination control of sounder
CODEC power down control
Level control of transmit path, PB tone, and Hold tone, Gain control of
receive path
Frequency control of howler tone
Read of the key scanning data
Function
WR
Write signal for internal control registers.
Data on the data bus is written into the registers at the rising edge of WR under the condition of
digital "0" of CE (Chip Enable). While CE is in digital "1" state, WR becomes invalid. The Write
cycle is a minimum of 2 ms, but if the CK64 and CK8 signals are silent, the write cycle requires
a minimum of 50 ms.
A minimum of 2 ms specified as the write cycle is valid 10 ms after CK64 and CK8 signals are input.
RD
Read signal input to read PI0 to PI7 out of the processor.
When CE and RD are in digital "0" state, the digital values on PI0 to PI7 are output onto the data
buses DB0 to DB7. While CE is in digital "1" state, the RD signal becomes invalid.
12/43
Page 13

¡ Semiconductor MSM6895/6896
CE
Chip Enable signal input.
When CE is in digital "0" state, WR and RD are valid.
B1T, B2T, B1R, B2R
B channel interface inputs and outputs.
B1T and B2T are outputs, and B1R and B2R are inputs. Through channel control by the processor,
various data paths are set. The CODEC input and output signals are input and output via these
pins.
Initially the B1T and B2T outputs are fixed in a digital "1", and the B1R and B2R inputs are
neglected.
BR1, BR2, BT1, BT2
External digital inputs and outputs to the B-channel.
BR1 and BR2 are outputs, and BT1 and BT2 are inputs. Through channel control by processor,
the digital paths are set between these input and output pins and the B channel.
These signals are applied to another CODEC interface of three-party the speech path and to the
interface of 64 kbps at the rate adaptor circuit.
Initially the BR1 and BR2 outputs are fixed in a digital "1", and the BT1 and BT2 inputs are
neglected.
RESET
Reset signal input.
Digital "0" input to RESET makes all of internal control registers to be initialized. When powered
on, this RESET signal should be input for initializing the system.
TIME
Watchdog timer output.
When the processor does not reset the timer, the 500 ms period (Digital "0" : 4 ms) digital signal
is continuously output. When RESET is at digital "0", this timer is reset. And, in about 500 ms after
RESET goes to digital "1", the first timer output signal is issued and then the timer signal is output
at intervals of a 500 ms. If the CK8 signal is not input, the TIME signal is not output.
LML
Control signal output for external hold tone generator.
LML goes to digital "1" state when the hold tone transmit mode on transmit path or the hold
acknowledge tone mode on receive path is selected. During initialized state, LML is in digital "0"
state.
13/43
Page 14

¡ Semiconductor MSM6895/6896
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Parameter Symbol Condition Rating Unit
Power Supply Voltage V
Digital Input Voltage V
Storage Temperature T
DD
AIN
DIN
STG
VAG, VDG = 0 V
VAG, VDG = 0 V
VAG, VDG = 0 V
—
0 to 7
–0.3 to V
–0.3 to V
–55 to +150
DD
DD
+ 0.3
+ 0.3
V
VAnalog Input Voltage V
V
°C
RECOMMENDED OPERATING CONDITIONS
Min. Max.Parameter Symbol Condition Typ. Unit
Power Supply Voltage V
Operating Temperature °C
Input High Voltage
Input Low Voltage V
Digital Input Rise Time t
Digital Input Fall Time t
Digital Output Load
V
D
Ta — +25–10 +70
V
IH
IL
Ir
If
R
DL
C
DL
VA, VD (Voltage must be fixed) 5.04.75 5.25
All Digital Input Pins —2.2 V
DD
V
All Digital Input Pins —0 0.8 V
All Digital Input Pins ——50ns
All Digital Input Pins ——50ns
—10 —
kW
PO0 to PO4 Output
——
100
pF
Recommended Operating Conditions (CODEC Digital Interface)
Min. Max.Parameter Symbol Condition Typ. Unit
64
Clock Frequency kHz
Sync Pulse Frequency
Clock Duty Ratio
F
C
F
S
D
C
t
XS
Sync Pulse Setting Time
t
SX
Sync Pulse Width t
Data Setup Time
Data Hold Time t
WS
t
DS
DH
CK64
CK8
CK64
CK64ÆCK8
See Fig.1
CK8ÆCK64
See Fig.1
——1 CK64 100 ms
B1R, B2R —100 — ns
B1R, B2R —100 — ns
Allowable Jitter Width — CK8 —— 500 ns
128——
256
8.0——
kHz
5040 60 %
—— 100 ns
—— 100 ns
14/43
Page 15

¡ Semiconductor MSM6895/6896
Recommended Operating Conditions (Processor Digital Interface)
Min. Max.Parameter Symbol Condition Typ. Unit
Write Pulse Period nsWR —2000 —
Write Pulse Width nsWR —100 —
Read Pulse Width nsRD —200 —
Address Data
Setup Time
Address Data
Hold Time
CE Setup Time
CE Hold Time
Data Setup Time ns—110 —t
P
W
T
W
T
R
AW1
AR1
AW2
AR2
CW1
CR1
CW2
CR2
DW1
DW2
WRES
AD0, AD1ÆWR
AD0, AD1ÆRD ns—80 —t
WRÆAD0, AD1
RDÆAD0, AD1 ns—10 —t
CEÆWR
CEÆRD ns—80 —t
WRÆCE
RDÆCE ns—10 —t
DB0 to 7ÆWR
WRÆDB0 to 7Data Hold Time ns—20 —t
RESETReset Pulse Width ns—100 —t
See Fig.2
ns—10 —t
ns—50 —t
ns—10 —t
ns—50 —t
Recommend Operating Conditions (Analog Interface)
Min. Max.Parameter Symbol Condition Typ. Unit
— 0.24TPAI —
——
TMX1I, TMX2I
——
(Transmit Gain: Typ.)
MLDYI
AIN
(Transmit Gain: Typ.)
——
R1I, R2I
——
(Transmit Gain: Typ.)
——
——
TPAO, T1O, T2O,
—20 —
Analog Load Resistance kW
R
RPO, SPO, CAO
AL
RMO0, RMO1 —3—
Analog Load Capacitance
TPAO, T1O, T2O,
C
RPO, SPO, CAO
AL
—— 100
RMO0, RMO1 ——55
TPAI, TPBI, RMI —–10 +10
Allowable Analog
Input Offset Voltage
V
MLDYI, TMX1I, TMX2I —–50 +50
off
R1I, R2I —–25 +25
CAI —–100 +100
0.31TPBI
2.40
1.90Analog Input Voltage V
1.20
0.51RMI
2.40CAI
V
mV
PP
pF
nF
15/43
Page 16

¡ Semiconductor MSM6895/6896
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
DC and Digital Interface Characteristics
(V
= 5 V ±5%, Ta = –10°C to +70°C)
DD
Min. Max.Parameter Symbol Condition Typ. Unit
Power Supply Current
Input High Voltage V
Input Low Voltage V
High Input Leakage
Current
I
DD1
I
DD2
I
DD3
I
DD4
I
IH
Operating Mode (No Signal, Sounder OFF)
CODEC Receive Power Down 3.3— 8.0 mA
CODEC Transmit Power Down 2.8— 7.0 mA
CODEC Transmit/Receive Power Down
IH
IL
——2.2 V
——0.0 0.8 V
——— 2.0 mA
3.9— 10.0
mA
2.2— 4.0 mA
DD
V
Low Input Leakage
Current
Digital Output High
Voltage
Digital Output Low
Voltage
Digital Output Leakage
Current
Analog Output Offset
Voltage
Input Capacitance C
Analog Input Resistance R
I
IL
V
OH
V
OL
I
O
V
off
IN
TPAO, T1O, T2O,
CAO, RPO, RMO1, RMO2, SPO
TPAI, TPBI, MLDYI, RMI
IN
TMX1I, TMX2I, R1I, R2I —10 — kW
——— 0.5 mA
I
= 0.4 mA
OH
IOH = 1 mA
= –1.6 mA 0.0
I
OL
—
2.4
3.8
—
—
V
DD
V
DD
V
— 0.4 V
——10mA
—–100 +100 mV
—5——pF
10——MW
CAI (fin : < 4 kHz) 1——MW
VSG Voltage — — VA/2 V
I
VSG Drive Current mA
I
SGS
SGF
FORCE Current 1.51.0 —
SINK Current 0.50.3 —
VA/2
–0.05
VA/2
+0.05
16/43
Page 17

¡ Semiconductor MSM6895/6896
AC Characteristics 1 (CODEC)
(VDD = 5 V ±5%, Ta = –10°C to +70°C)
Parameter Symbol Condition Typ. UnitMin. Max.
Loss T1
Loss T2
Transmit Frequency
Response
Receive Frequency
Response
Transmit Signal to
Distortion Ratio
Receive Signal to
Distortion Ratio
Transmit Gain
Tracking
Receive Gain
Tracking
Loss T3
Loss T4
Loss T5
Loss T6
Loss R1
Loss R2
Loss R3
Loss R4
Loss R5
SD T1
SD T2
SD T3
SD T4
SD T5
SD R1
SD R2
SD R3
SD R4
SD R5
GT T1
GT T2
GT T3
GT T4
GT T5
GT R1
GT R2
GT R3
GT R4
GT R5
Freq.
(Hz)
300
1020
2020
3000
3400
300
1020
2020
3000
3400
1020
1020
1020
1020
60
Level
(dBm0)
0
3
0
–30
–40
–45
3
0
–30
–40
–45
3
–10
–40
–50
–55
3
–10
–40
–50
–55
*1
*1
*2
*2
*2
*2
20
–0.15
–0.15
–0.15
0.0
–0.15
–0.15
–0.15
0.0
35
35
35
29
28
24
23
37
37
37
31
30
26
25
–0.3
–0.3
–0.6
–1.5
–0.2
–0.2
–0.4
–0.8
+0.07
Reference
–0.03
+0.06
0.38
–0.03
Reference
–0.02
+0.15
0.56
43.0
41.0
38.0
31.0
26.5
43.0
41.0
40.0
34.0
31.0
+0.01
Reference
+0.13
+0.32
+0.64
Reference
–0.06
–0.20
–0.27
27
0.0
—
+0.20
+0.20
+0.20
0.80
+0.20
+0.20
+0.20
0.80
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
+0.3
+0.3
+0.6
+1.5
+0.2
+0.2
+0.4
+0.8
dB
dB0
dB
dB
dB
dB
Notes: *1 Psophometric filter is used
*2 Upper is specified for the MSM6895, lower for the MSM6896
17/43
Page 18

¡ Semiconductor MSM6895/6896
AC Characteristics 1 (CODEC) (Continued)
= 5 V ±5%, Ta = –10°C to +70°C)
(V
DD
S
Freq.
(Hz)
1020 0 Vrms
500
600
1000
2600
2800
500
600
1000
2600
2800
1020 0
4.6 kHz to
72 kHz
300 to
3400
fa = 470
fb = 320
0 to 50
kHz
Parameter Symbol Condition Typ. UnitMin. Max.
Nidle T ———
Idle Channel Noise
Nidle R —— — –77.8 –74
Absolute Amplitude
Absolute Delay Time
Transmit Group Delay
Receive Group Delay
Crosstalk Attenuation
Discrimination
Out-of-band Signal
Spurious
Intermodulation Distortion
Power Supply Noise
Rejection Ratio
AV T 0.5671 0.6007 0.6363
AV R 0.5671 0.6007 0.6363
Td 1020 0 — 0.58 0.60 ms
tgd T1
tgd T2
tgd T3
tgd T4
tgd T5
tgd R1
tgd R2
tgd R3
tgd R4
tgd R5
CR T
CR R
DIS
IMD
PSR T
PSR R
Level
(dBm0)
AIN = SG
*1
*1
*3
Transmit CODEC
Receive CODEC
A to A
CK64 = 64 kHz
0*4
0*4
Transmit Æ Receive
Receive Æ Transmit
–25 32.030 — dB
0 –37.5— –35 dBmO
–4 –52— –35 dBmO
100
mV
pp
0 to 4000 Hz
4.6 kHz to 100 kHz
2fa–fb
*2
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
*5 30——
–73.5
–71
0.19
0.12
0.02
0.05
0.08
0.0
0.0
0.0
0.09
0.12
8666 —
7870 —
0.125
0.125
0.125
0.125
–70
–69
dBmOp
0.75
0.35
ms
0.75
0.75
0.35
ms
0.75
dB
dB
Notes: *1 Psophometric filter is used
*2 Upper is specified for the MSM6895, lower for the MSM6896
*3 PCM data for MSM6895: All "1"
PCM data for MSM6896: "11010101"
*4 Minimum value of the group delay distortion
*5 The measurement under idle channel noise
18/43
Page 19

¡ Semiconductor MSM6895/6896
AC Characteristics 2 (Transmit Path)
= 5 V ±5%, Ta = –10°C to +70°C)
(V
DD
Parameter
Symbol
Freq.
(Hz)
Pre-Amp Gain –24.4
Transmit Path 1 Gain
GTPA 1020 22.0 dB
GTPB1
Level
(dBV)
Condition
TPAI-TPAO
TPBI-T1O
Min.
18.0
15.7
Typ.
20.0
17.7
Max. Unit
19.7
dB
1020 –22.1
Transmit Path 2 Gain
Transmit Addition Signal 1 Gain
GTPB2
GTMX1
TPBI-T2O
TMX1I-T1O
15.7
–2.0
17.7
0.0
19.7
+2.0
dB
dB
1020 –4.4
Transmit Addition Signal 2 Gain
GTMX2
TMX1I-T2O
–2.0
0.0
+2.0
dB
Set at
–17.4
–15.4
–13.4 dBV—
In-Channel PB Signal Output Level
VPBT1
—
T1O
typical gain
Set at
VPBT2
—
T2O
–17.4
–15.4
–13.4—
dBV
typical gain
In-Channel PB Signal Output
Level Setting
GPBT1
GPBT2
—
—
For
typical
setting
–
–
3 dB
6 dB
–5.0
–8.0
–3.0
–6.0
–1.0
–4.0
dB
dB
In-Channel PB Signal
DfPBT
—
T1O, T2O
–0.9
—
+0.9 %—
Frequency Deviation
In-Channel PB Signal Distortion — dB
THDPBT
—
In-Band Distortion
—
–35
–30
Hold Tone Path Gain
Hold Tone Path Gain Setting
GPAT1
GPAT2
RG1 PAT
RG2 PAT
Ni TPA
1020
–22.4
–22.41020
MLDYI-T1O
Set at
typical
MLDYI-T2O
For
gain
–
3 dB
typical
setting
TPAI: 510 W at termination
Meature at TPAO
–
6 dB
*6
–4.0
–4.0
–5.0
–8.0
—
–2.0
–2.0
–3.0
–6.0
–93
0.0
0.0
–1.0 dB
–4.0 dB
— dBV——
Idle Channel Noise
—
Ni TPB
T1O, T2O
*6
–91
— dBV——
TPAO, T1O,
Maximum Output Voltage Swing VOT — V
——
2.4
—
T2O, RL = 20 kW
Note: *6 Noise band width: 0.3 kHz to 3.4 kHz, non-weighted
dB
PP
19/43
Page 20

¡ Semiconductor MSM6895/6896
AC Characteristics 3 (Receive Path)
= 5 V ±5%, Ta = –10°C to +70°C)
(V
DD
Parameter
Receive Main Amp. Gain
Receive Main Amp.
Output Gain Difference
Receive Main Amp.
Output Phase Difference
Receive Signal Path Gain
Receive Signal Path Gain Setting
Receive Addition Signal Path Gain –4.0 dB–14.4
Receive Addition Signal Path
Gain Setting
Speaker Preamp. Gain
Hold Acknowledge Tone Path Gain –7.4
PB Acknowledge Tone Output Level
PB Acknowledge Tone Frequency
Difference
PB Acknowledge Tone Distortion —
Side Tone Path Gain –21.4
Idle Channel Noise
Symbol
GRMO0
GRMO1
DGRMO
DPRMO
GRPA –4.0–6.0–8.0R1I-RPO
RG RPA1
RG RPA2
RG RPA3
GRPB 1020
RG RPB1
RG RPB2
RG RPB3
GSP
GPAS 1020
VPBRP
VPBRP
DfPBR
THD PBR
GSIDE
Ni RPO
Ni SPO
Ni RMO
Freq.
(Hz)
1020
1020
1020 –19.4
1020 –14.4
1020 –4.4
—
—
—
1020
—
—
—
Level
(dBV)
–19.4
–19.4
–19.4
—
—
—
—
—
Condition Typ.Min.
RMI-RMO0
RMI-RMO1
RMO0/RMO1
RMO0/RMO1
Set at
typical
,
VSG
+3 dB
+6 dB
+9 dB
Set at
typical
+3 dB
+6 dB
+9 dB
Set at
typical
Set at
typical
*6
*6
*6
For
typical
setting
For
typical
setting
MLDYI-SPO
RMI
RMO0, RMO1
13.2
13.2
—
—
1.0
7.0
1.0
7.0
–5.0
–30.2
15.3
15.3
–0.01
179.6
–
3.0
9.0
–6.0–8.0R2I-RPO
3.0
9.0
–3.0
–28.2
Max. Unit
17.3 dB
17.3
—
—
5.0
8.0–23.4 dB1020 6.04.0
11.0
5.0
8.0–14.4 dB1020 6.04.0
11.0
–4.0–6.0–8.0R1I-SPO
–4.0–6.0–8.0R2I-SPO
–1.0 dB
–28.1–30.1–32.1 dBVRPO
–26.2
+0.9 %—–0.9RPO, SPO
–30 dB–35—RPO, SPO
12.9 dB10.98.9TPBI-RPO
— dBV–86—RPO
— dBV–86—SPO
— dBV–95—
dB
dB
deg
dB
dB
dBVSPO
Note: *6 Noise band width: 0.3 kHz to 3.4 kHz, non-weighted
20/43
Page 21

¡ Semiconductor MSM6895/6896
AC Characteristics 3 (Receive Path) (Continued)
= 5 V ±5%, Ta = –10°C to +70°C)
(V
DD
Parameter
Symbol
Freq.
(Hz)
VOR —
—
Level
(dBV)
Maximum Output Amplitude
VOM —
RTONE0 Output Amplitude —
RTONE1 Output Amplitude —
VRT0 —
*7
VRT1 —
*8
——
VFTRP
FTONE Output Amplitude —
—
VFTSP
Notes: *7 DT, PDT, SDT, CRBT, IIT
*8 RBT, DT, T250
—
Condition Typ.Min.
RPO, SPO
= 20 kW
R
L
RMO0, RMO1
RL = 3 kW +55 nF
RPO
RPO
SPO
2.4
3.0
132.0
159.0
—
—
91.777.2RPO
157.0
189.0
Max. Unit
V
PP
V
PP
109.0 mV
187.0 mV
191.5161.0135.5
mV
224.6
PP
PP
PP
21/43
Page 22

¡ Semiconductor MSM6895/6896
AC Characteristics 4 (Ringing Tone Output Circuit)
(V
= 5 V ±5%, Ta = –10°C to +70°C)
DD
Parameter
Symbol
Freq.
(Hz)
VST1
VST2
Calling Tone Output Amplitude —
*9
—
VST3
VST4
Howler Tone Output Amplitude —
VHOW
—
Level
(dBV)
Condition Typ.Min.
Volume 1
SA1
730 W
to
Volume 2
Volume 3
Volume 4
VDG
1.280.73
0.280.13
Max. Unit
—4.03.25SA0-
1.98
0.650.470.25
0.45
—4.03.25 V
Note: *9. IR-1, IR-2, SIR-1, SIR-2, CR, T1K, HR, SPT
Digital Interface Characteristics
= 5 V ±5%, Ta = –10°C to +70°C)
(V
DD
Parameter
Digital Output (Latch) Delay Time 1.9—0.5 msWRÆLA, LB, LC, LD, LML, LOSS
Symbol
t
PDLA
WRÆPO0, PO1, PO2, PO3, PO4
key Scanning Output Delay Time 1.9—0.5 ms
Digital Output (Data) Delay Time 1505220 nsRDÆDB0 to DB7
t
PDSCN
t
PDDATA
Pull-up resistor : 10 kW
BT1ÆBR1, BR2
Digital Path Delay Time
CODEC Data Output Delay Time 1005020 nsCK64ÆB1T, B2T
t
PDPATH
t
PDCOD
BT2ÆBR1, BR2
Condition
Typ.Min.
Max. Unit
1505220 ns
V
PP
PP
22/43
Page 23

¡ Semiconductor MSM6895/6896
TIMING DIAGRAM
CK64
CK8
B1T or
B2T
B1R or
B2R
A0, A1
CE
WR
RD
1 2 3 45678
t
SX
t
XS
t
WS
tpd cod
MSBB2 B3B4B5B6B7B8
MSB
t
DS
B2 B3 B4 B5 B6 B8B7
t
DH
Figure 1 CODEC Timing
t
AW1
t
CW1
t
AW2
t
CW2
T
W
t
t
AR1
CR1
t
AR2
t
CR2
T
R
DB0 to DB7
PO0 to PO4
Latch Output
t
DW1tDW2
t
PDSCN
t
PDLA
t
PDDATA
Figure 2 Processor Interface Timing
t
PDDATA
23/43
Page 24

¡ Semiconductor MSM6895/6896
24/43
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
Control Data Description
Sounder control
WRITE Mode
Address Data AD1 = 0, AD0 = 0
*1. PDC: This bit is used for the CODEC power-down control. For making this bit valid, "0"s must be written to the control data
bits
described in the later section.
PDC = 1: CODEC is in power-down mode. PDC = 0: CODEC is in operation mode.
*2. When the HOW is indicated, the LOSS output is "1". Otherwise it is "0".
*3. In the above specification, the data contents written later are valid. The signal of sounder path (SA0, SA1) and the signal
of receive path
(RPO) can not be output simultaneously.
Control Data Make/Break Timing *6
DB7 DB6 DB5 DB4 DB3 DB2 DB1 DB0
001PDC0000
*100001
0010
0011
0100
0101
0110
0111
1000
1000
1010
1011
1100
1101
1110
XXXX
Output Tone
(Hz)
Frequency
SPT
IR-1
IR-2
SIR-1
CR
HOW
SIR-2
T1K
HR
DT
SDT
RBT
BT
PDT
CRBT
*2
1
Wamble Tone
Wamble Tone
Wamble Tone
Wamble Tone
800 or
Wamble Tone
1
1
400
400
400/16
400
400
400/16
Wamble Tone
Make (Sec) Break1 (Sec) Break2 (Sec)
0.125
1
0.5
0.25
0.125
2
0.5
0.25
•
—
—
2.25
Continuous
Continuous
0.5
0.25
0.125
Continuous
0.125
1
0.5
0.25
0.5
1
0.25
0.125
0.125
2
0.5
0.25
•
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
Remarks
Tone Output:
SA0, SA1
Tone Output:
RPO, Refer to Table 2
and 4.
Suspends the tones above.
Page 25

¡ Semiconductor MSM6895/6896
25/43
Make
Break1 Break2
Control of function key acknowledge tone
WRITE Mode
Address Data AD1 = 0, AD0 = 0
*4. NTTC = 1 when the initial state is set. NTTC can be set as PBTC when the PB tone is set, but the data written into NTTC in l
ater is valid.
When NTTC = 1, the FTONE (1) and FTONE (2) signals are output from SPO. When NTTC = 0, these signals are output from RPO.
NTTC = 1 when FTONE and PB tone is stopped.
*5. When two or more signals are specified out of IIT, T250 and FTONE, the output signals are compounded by two or three tones.
*6. The definition of Make/Break Timing is as follows;
Make/Break Timing *6
Control Data
DB7 DB6 DB5 DB4 DB3 DB2 DB1 DB0
011XX001
XX010
X011
X100
0000
0001
011
Output Tone
(Hz)
Frequency
IIT
T250
FTONE (1)
FTONE (2)
400
250
1 k
1 k
Make (Sec) Break1 (Sec) Break2 (Sec)
0.25
Continuous
Continuous
0.1
0.25
•
2.25
—
Suspends the all above tones
Suspends the IIT tone
Suspends the FTONE
Remarks
Tone output:
RPO, SPO
NTTC
*4
0
0
0
0
0 1 0 Suspends the T250 tone
Page 26

¡ Semiconductor MSM6895/6896
26/43
PB tone control
WRITE Mode
Address Data AD1 = 0, AD0 = 0
Control Data Output PB Frequency
DB7 DB6 DB5 DB4 DB3 DB2 DB1 DB0 PB Low High
Remarks
1 0 1 PBTC 0 0 0 0
0001
0010
0011
0100
0101
0110
0111
1000
1001
1010
1011
1100
1101
1110
1111
XXXX00
1
2
3
A
4
5
6
B
7
8
9
C
*
0
#
D
697 Hz
697 Hz
697 Hz
697 Hz
770 Hz
770 Hz
770 Hz
770 Hz
852 Hz
852 Hz
852 Hz
852 Hz
941 Hz
941 Hz
941 Hz
941 Hz
1209 Hz
1336 Hz
1477 Hz
1633 Hz
1209 Hz
1336 Hz
1477 Hz
1633 Hz
1209 Hz
1336 Hz
1477 Hz
1633 Hz
1209 Hz
1336 Hz
1477 Hz
1633 Hz
Suspends the PB tone
When PBTC = 0, the PB tone is output from the transmit path and the
receive path RPO.
The conditions of internal control signals are MUTN = 0 and NTTC = 0.
When PBTC = 1, the PB tone is output only from the receive path
SPO.
The PB signal is not output from the transmit path.
The conditions of internal control signals are MUTN = 1 and NTTC = 1.
When the initial state is set and the PB tone is suspended,
the conditions of internal control signals are MUTN = 1 and NTTC = 1.
Page 27

¡ Semiconductor MSM6895/6896
27/43
Latch control and timer reset
WRITE Mode
Address Data AD1 = 0, AD0 = 0
Control data
Latch output
DB7 DB6 DB5 DB4 DB3 DB2 DB1 DB0
11100001
0010
0011
0101
0110
0111
1000
1001
1010
1011
1100
1101
1110
1111
0000
0000
00
1111
0 0 Latch codes described above
LT1 = 1
LML1 = 1
LMX1 = 1
LT2 = 1
LML2 = 1
LMX2 = 1
LR = 1
LS = 1
LMN = 1
LMR = 1
LA = 1
LB = 1
LC = 1
LD = 1
Remarks
These latch are for internal control and used for control of speech path.
Initially all latch are set to "0". For details of speech path control, refer to Table 1 to 4.
Each latch can be specified independently.
The output at the LML pin is in "1" when either LML1, LML2, or LMR is in "1".
These general latches are for external control. LA, LB, LC, and LD correspond to
the external pin symbols and are set independently. Initially, all latches are set to "0".
Sets the corresponding latches listed above to "0".
Sets all latches listed above to "0".
Resets the watch dog timer.
Page 28

¡ Semiconductor MSM6895/6896
28/43
Table 1. Transmit speech path setting list
Status Symbol
TA-1
TA-2
TA-3
TA-4
TA-5
TA-6
TA-7
TB-1
TB-2
TB-3
TB-4
TB-5
TB-6
TB-7
Control Symbol
LML1 LT1 LMX1 LML2 LT2 LMX2 LMN MUTN
00X———XX
010———01
010———11
011———01
011———11
01X———X0
1XX———XX
——— 0 0 X X X
——— 0 1 0 0 1
——— 0 1 0 1 1
——— 0 1 1 0 1
——— 0 1 1 1 1
——— 0 1 X X 0
——— 1 X X X X
SG T TMX1 PBt Ht
Output Signal at T1O
1————
—1———
1————
—1 1——
—— 1 ——
——— 1 —
———— 1
—————
—————
—————
—————
—————
—————
—————
SG T TMX2 PBt Ht
Output Signal at T2O
—————
—————
—————
—————
—————
—————
—————
1————
—1———
1————
—1 1——
—— 1 ——
——— 1 —
———— 1
Notes: 1. MUTN of Control Signal is set by PBTC (DB4).
MUTN = 1 when the initial state is set. MUTN = 0 when PBTC = 0. MUTN = 1 when PBTC= 1.
2. SG: Signal ground, T: Transmit signal, TMX1: Transmit addition signal 1, TMX2: Transmit addition signal 2, PBt: PB signal, Ht
: Hold
tone signal
3. The output signals of T1O and T2O are the signals added by the signals indicated in "1"s in each column.
Page 29

¡ Semiconductor MSM6895/6896
29/43
Table 2. Receive speech path setting list (RPO output)
Table 3. Control of receive
main amplifier
Notes: 4. R1: Receive signal 1, R2: Receive signal 2, Ts: Side tone signal, RT0: DT, PDT, SDT, CRBT, and IIT, RT1: RBT, BT, and T
250, FT:
FTONE and PBr: PB acknowledge signal.
5. Output Signal RPO is the signal added by the signal indicated in "1"s in each column.
6. "0"s of Control Signal NTTC are equivalent to "1"s of the Output Signals FT and PBr, and "1"s are equivalent to "0"s of Outpu
t Signals.
7. Control Signals MUTN and NTTC are the internal control signals. Initially, both signals are in "1"s. MUTN is controlled by PB
TC
of controlling the PB tone.
MUTN = 0 when PBTC = 0. MUTN = 1 when PBTC = 1.
NTTC is controlled by PBTC of controlling the PB tone or NTTC of controlling the function key acknowledge tone, but the NTTC
data written later is valid.
NTTC = 0 when PBTC = 0. NTTC = 1 when PBTC = 1.
Control Signal
LR
0
1
RMO0 and RMO1
SG
Input signal to RMI
Output signal of
Status Symbol
RP-1
RP-2
RP-3
RP-4
RP-5
RP-6
RP-7
RP-8
RP-9
RP-10
RP-11
RP-12
RP-13
RP-14
Control Signal
LS LT1 LT2 LMN MUTN NTTC
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
1
0
1
1
1
0
0
0
1
1
1
0
1
0
1
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
1
1
1
0
0
1
1
X
0
0
1
0
0
1
0
0
1
X
X
X
X
X
1
0
X
1
0
X
1
0
X
X
X
X
X
0/1
0/1
0/1
0/1
0/1
0/1
0/1
0/1
0/1
0/1
X
X
X
X
Output Signal at RPO
R2 Ts RT0 RT1 FT PBrR1
—
1
1
1
—
—
—
1
1
1
—
1
—
1
—
—
—
—
1
1
1
1
1
1
—
—
1
1
—
1
—
—
1
—
—
1
—
—
—
—
—
—
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1/0
1/0
1/0
1/0
1/0
1/0
1/0
1/0
1/0
1/0
—
—
—
—
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1/0
1/0
1/0
1/0
1/0
1/0
1/0
1/0
1/0
1/0
—
—
—
—
Page 30

¡ Semiconductor MSM6895/6896
30/43
Table 4. Receive speech path setting list (SPO)
Status Symbol
RS-1
RS-2
RS-3
RS-4
RS-5
RS-6
RS-7
RS-8
RS-9
RS-10
RS-11
Control Signal
LS LT1 LT2 NTTCLMR
0
0
0
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
0
0
1
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
1
X
X
X
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
X
X
X
0
0
1
1
0
0
1
1
0
1
0/1
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
Output Signal at SPO
SG
1
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
R1
—
—
—
—
1
—
1
—
1
—
1
R2
—
—
—
—
—
1
1
—
—
1
1
RT0
—
—
—
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
RT1
—
—
—
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
FT
—
1
0/1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
PBr
—
1
0/1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
Hr
—
—
1
—
—
—
—
1
1
1
1
Notes: 8. SG: Signal ground, R1: Receive signal 1, R2: Receive signal 2, Hr: Hold acknowledge tone, PBr: PB acknowledge tone, FT:
FTONE,
RT0: DT, PDT, SDT, CRBT, and IIT and RT1: RBT, BT, and T250.
9. An Output Signal at SPO is the signal added by the signal indicated in "1"s in each column.
10. The Control Signal NTTC is defined equally to Notes : 7.
Page 31

¡ Semiconductor MSM6895/6896
31/43
Channel selector control
WRITE Mode
Address Data AD1 = 0, AD0 = 1
Control Data
DB7 DB6 DB5 DB4 DB3 DB2 DB1 DB0
00000000
001
010
011
100
101
110
111
XXX
XXX
XXX
XXX
XXX
1
X
X
X
X
XX1
X1X
1XX
XXX
X
X
X
1
A1
A2
A3
A4
B1
B2
B3
B4
C
D1
D2
D3
D4
Symbol
Status
Main Connection Status
B1T¨"1"
B1T¨DOUT
B1T¨BT1
B1T¨BT2
B2T¨"1"
B2T¨DOUT
B2T¨BT1
B2T¨BT2
B1T¨B2R
B1T¨B1R
B2T¨B2R
BT1ÆBR1
BT2ÆBR2
B1RÆNo connection
B1RÆDIN
B1RÆBR1
B1RÆBR2
B2RÆNo connection
B2RÆDIN
B2RÆBR1
B2RÆBR2
B2T¨B1R
Remarks
Different groups (A, B, C, and D) are set
independently.
For setting the same group, the data written later is
valid.
Refer to Table 5 and 6 for details.
The initial statuses are A1 and B2.
Page 32

¡ Semiconductor MSM6895/6896
32/43
Table 6. Output pin status by the combination of A and B
Table 5. Output pin connection status by channel selector control
Notes: 11. *1. According to the combination of A and B (Table 6).
*2. One of statuses A1 to A4 is held.
*3. One of statuses B1 to B4 is held.
*4. One of statuses A1 to A4 or one of statuses B1 to B4,
whichever is written later, is held.
When the setting of C is performed before the setting
of D group, the setting of D must be performed after
the setting of the group A and B.
12. The statuses of the pins indicated by "—" is not
affected.
13. DIN is connected to the digital input of CODEC and
DOUT is connected to the digital output of CODEC.
*5. When writing is performed in the sequence of setting of A and
setting of B, the output status becomes B2R, and when writing
is performed in the sequence of setting of B and setting of A, the
output status becomes B1R.
Status
Symbol
A1
A2
A3
A4
B1
B2
B3
B4
C
D1
D2
D3
D4
1
DOUT
BT1
BT2
—
—
—
—
B2R
B1R
*2
*2
*2
—
—
—
—
1
DOUT
BT1
BT2
B1R
*3
B2R
*3
*3
*1
B1R
*1
*1
*1
B2R
*1
*1
—
—
—
—
—
*1
*1
B1R
*1
*1
*1
B2R
*1
—
*4
*4
BT1
*4
A1
A2
A3
BIT B2T DIN BR1
Setting of A
Output Pin Connection Status
Initial Setting
Initial Setting
Remarks
A4
Setting of B
B1
B2
B3
B4
B1
B2
B3
B4
B1
B2
B3
B4
B1
B2
B3
B4
1
B2R
1
1
B1R
B1R or B2R
B1R
B1R
1
B2R
1
1
1
B2R
1
1
1
1
B2R
1
1
1
B2R
1
B1R
B1R
B1R or B2R
B1R
1
1
B2R
1
1
1
1
B2R
1
1
1
B2R
1
1
1
B2R
B1R
B1R
B1R
B1R or B2R
DIN BR1 BR2
Output Pin Connection Status
Initial Setting
DIN *5
BR1 *5
BR2 *5
Remarks
*1
*1
*1
B1R
*1
*1
*1
B2R
—
*4
*4
*4
BT2
BR2
Page 33

¡ Semiconductor MSM6895/6896
33/43
key scanning output control and interrupt
WRITE Mode
Address Data AD1 = 1, AD0 = 0
Control Data
DB7 DB6 DB5 DB4 DB3 DB2 DB1 DB0
0 0 0 Output Data
1XXXXXXX
Remarks
Resets the INTT output and sets to "1".
This control data is valid only when written, it is not held.
Initially, PO4 to PO0 are left open.
When the data is "0", the output goes to "0", when the data is "1", the output is left open.
The output statuses are held until the data is rewritten.
The data set in DB4 to DB0 is output from output pins PO4 to PO0, respectively.
Page 34

¡ Semiconductor MSM6895/6896
34/43
Sounder, volume, and tone combination
WRITE Mode
Address Data AD1 = 1, AD0 = 1
Control Data
DB7 DB6 DB5 DB4 DB3 DB2 DB1 DB0
00XXXX00
01
10
11
000
001
010
011
101
110
111
XX
Remarks
The setting of volume and tone
combination is performed
simultaneously, not
independently.
Initially the high volume is set,
and tone combination is set
externally.
Control
Volume 1 (High)
Volume 2 (Medium)
Volume 3 (Low1)
Volume 4 (Low2)
Tone combination setting (Initial setting) by external control (SW0, SW1)
Tone combination 1 (1.0 kHz and 1.3 kHz, 16 Hz Wamble period)
Tone combination 2 (0.8 kHz and 1.0 kHz, 16 Hz Wamble period)
Tone combination 3 (0.8 kHz and 1.0 kHz, 8 Hz Wamble period)
Tone combination 4 (0.5 kHz and 0.65 kHz, 16 Hz Wamble period)
Tone combination 5 (0.4 kHz and 0.5 kHz, 16 Hz Wamble period)
Tone combination 6 (0.4 kHz and 0.5 kHz, 8 Hz Wamble period)
Page 35

¡ Semiconductor MSM6895/6896
35/43
CODEC power down control
WRITE Mode
Address Data AD1 = 1, AD0 = 1
Contorol Data
DB7 DB6 DB5 DB4 DB3 DB2 DB1 DB0
01XXX000
101
110
111
100
Remarks
CODEC power-down is controlled by PDC (DB4) during sounder
Control
control. (Initial setting)
PDC = 0 CODEC power-on
PDC = 1 CODEC power-down
CODEC Transmit power-down
CODEC Receive power-down
CODEC Transmit and Receive power-down
CODEC power-down release
Data written later is valid.
Page 36

¡ Semiconductor MSM6895/6896
36/43
Gain control
WRITE Mode
Address Data AD1 = 1, AD0 = 1
DB7 DB6 DB5 DB4 DB3 DB2 DB1 DB0
DB7
10XXXX00
01
1X
11XX
10XX
01XX
00XX
Remarks
The gain setting of the transmit path
and the receive path can be performed
simultaneously, not independently.
Control
Sets the transmit PB tone and hold tone level at the typical
value.(Initial setting)
Sets the transmit PB tone and hold tone level by 3 dB below the
typical value.
Sets the transmit PB tone and hold tone level by 6 dB below the
typical value.
Sets the receive gain at the typical value. (Initial setting)
Sets the receive gain by 3 dB above the typical value.
Sets the receive gain by 6 dB above the typical value.
Sets the receive gain by 9 dB above the typical value.
Page 37

¡ Semiconductor MSM6895/6896
37/43
Howler tone color combination
WRITE Mode
Address Data AD1 = 1, AD0 = 0
Key scanning data read out
READ Mode
Address Data AD1 = 1, AD0 = 0
Control Data
DB7 DB6 DB5 DB4 DB3 DB2 DB1 DB0
11XXXXX0
1
Control
Howler tone frequency: 0.8 kHz
Howler tone frequency: 1.0 kHz and 1.3 kHz, 16 Hz Wamble period
Remarks
Initial setting
DB7 DB6 DB5 DB4 DB3 DB2 DB1 DB0
PI7 PI6 PI5 PI4 PI3 PI2 PI1 PI0
Control
The data input to the pins PI7 to PI0 is output from DB7 to DB0, respectively.
Page 38

¡ Semiconductor MSM6895/6896
APPLICATION CIRCUIT
Line
CE
RD
AD1
MSM6895
Controller
AD0
INTT
TIME
DB7 to DB0
+5 V analog
0-20W
10 mF
+
1 mF
VA
VD
RESET
0 V analog
VAG
VDG
AG
0.1 mF
VSGC
PI7
PI6
PI5
PI4
PI3
PI2
PI1
PI0
PO4
PO3
PO2
+5 V
100 kW ¥ 8
Line Interface
BT1
CK64
BT2
DG
TEST
WR
CK1536
Swith the sounder
tone combination
DG
B1T
B2T
CK8
B1R
+5 V
SW1
100 kW ¥ 2
Tone
Melody
Generation
100 kW
SW0
LML
F
0.47 m
CAI
T1O
R2I
TPBI
B2R
MLDY
TMX2I
TMX1I
+
10 mF
+5 V analog
PO1
TPAO
TPAI
VSG
CAO
R1I
RPO
AG
100 kW
1 mF
0.47 mF
AG
Handset
RMI
RMO0
RMO1
AG
SPO
1 mF
Driver
Speaker
SAO
SA1LALB
Sounder
LED
PO0
DG
SW
Matrix
38/43
Page 39

¡ Semiconductor MSM6895/6896
Application circuit at the PCM Signal Data Rate of 192, 384, 768, 1536 and 2048
kbps.
BCLOCK signal
When the PCM signal data rate is one of 192, 384, 768, 1536, and 2048 kbps, input the 9-bit burst
clock corresponding to the frequency equivalent to each of the data rates, as CK64 signal.
125 mS
CK8
123456789
CK64
PCMIN/OUT
12345678
Burst clock generator
Continuous Clock
8 kHz
Syncronous Signal
+5 V
16 11 10 9
Equivalent to the 74LS161
12 78
MSM6895/6896
0 V
CK64
CK8
Continuous Clock
Syncronous Signal
Burst Clock
39/43
Page 40

¡ Semiconductor MSM6895/6896
Application Circuit of Three-party Speech Path
Speaker A
M
Handset
(A)
(B)
(A + B)
(C)
(B)
(C)
(B)
(B + C)
(A + B)
(C)
TPAI
TMX2I
T2O
TMX1I
CAO
R2I
R1I
RPO
RMI
RMO0
RMO1
AIN
AOUT
(A) (A + C)
TPAO
TPBI T1O CAI
MSM6895
MSM7508
AD
DA
AD
DA
B1T
B1R
B2T
B2R
BR2
BT2
PCMOUT
PCMIN
(A + C)
(B)
(A + B)
(C)
Note:
(A) indicates
the voice signal of
the A speaker
Speaker B
Speaker C
Speech path setting (Speech through a handset)
Transmit: TA-4 (LT1 = 1, LMX1 = 1, LMN = 0, MUTN = 1)
TB-4 (LT2 = 1, LMX2 = 1, LMN = 0, MUTN = 1)
Receive: RP-8 (LT1 = 1, LT2 = 1, LMN = 0, MUTN = 1, LR = 1)
Channel selector control
A2, B4
40/43
Page 41

¡ Semiconductor MSM6895/6896
41/43
SPEECH PATH GAIN
TPAI
R1I
R2I
RPO
RMI
RMO0
RMO1
SPO
+20 dB
–6 dB
–6 dB
+15.3 dB
X 1
X–1
–6.8 dB
0 dB
–3 dB
+
+
+
–
0, 3, 6, 9 dB
0, 3, 6, 9 dB
+17.7 dB
–2 dB
–8.8 dB
+6 dB
0 dB
0 dB
–2 dB
+6 dB
–6.8 dB
0, –3, –6dB
0, –3, –6dB
0, –3, –6 dB
0, –3, –6 dB
AD
0 dB
DA
0 dB
TPAO TPBI MLDY TMX2I TMX1I T1O T2O CAI
(Maximum input of
1.2 V
op
)
CAO
(Maximum input of
1.2 V
op
)
RTONE1
RTONE2
FTONE
91.7 mV
PP
(DT, PDT, SDT, CRBT)
157 mV
PP
(RBT, BT, T250)
161 mV
PP
189 mV
PP
–21.4 dBV (240 mVPP per signal)
PB
tone
Generator
FTONE
Page 42

¡ Semiconductor MSM6895/6896
RECOMMENDATIONS FOR ACTUAL DESIGN
• To assure proper electrical characteristics, use bypass capacitors with excellent high frequency
characteristics for the power supply and keep them as close as possible to the device pins.
• Connect the AG pin and the DG pin each other as close as possible. Connect to the system
ground with low impedance.
• Mount the device directly on the board when mounted on PCBs. Do not use IC sockets. If an
IC socket is unavoidable, use the short lead type socket.
• When mounted on a frame, use electro-magnetic shielding, if any electro-magnetic wave
source such as power supply transformers surround the device.
• Keep the voltage on the VDD pin not lower than –0.3 V even instantaneously to avoid latchup phenomenon when turning the power on.
• Use a low noise (particularly, low level type of high frequency spike noise or pulse noise)
power supply to avoid erroneous operation and the degradation of the characteristics of these
devices.
• Unused analog input pins must be connected to the VSG pin and unused digital pins must
be connected to the GND pin.
42/43
Page 43

¡ Semiconductor MSM6895/6896
PACKAGE DIMENSIONS
(Unit : mm)
QFP80-P-1420-0.80-BK
Mirror finish
Package material
Lead frame material
Pin treatment
Solder plate thickness
Package weight (g)
Epoxy resin
42 alloy
Solder plating
5 mm or more
1.27 TYP.
Notes for Mounting the Surface Mount Type Package
The SOP, QFP, TSOP, SOJ, QFJ (PLCC), SHP and BGA are surface mount type packages, which
are very susceptible to heat in reflow mounting and humidity absorbed in storage.
Therefore, before you perform reflow mounting, contact Oki’s responsible sales person for the
product name, package name, pin number, package code and desired mounting conditions
(reflow method, temperature and times).
43/43
 Loading...
Loading...