Page 1

1.8cm (0.7 Type) Black-and-White LCD Panel
Description
The LCX034ALT is a 1.8cm diagonal active matrix
TFT-LCD panel addressed by polycrystalline silicon
super thin film transistors with a built-in peripheral
driving circuit. Use of three LCX034ALT panels
provides a full-color representation. The striped
arrangement suitable for data projectors is capable
of displaying fine text and vertical lines.
The adoption of DMS∗1structure and high light
resistance structure realizes a high luminance
screen. And cross talk free circuit and ghost free
circuit contribute to high picture quality.
This panel has a polysilicon TFT high-speed
scanner and built-in function to display images
up/down and/or right/left inverse. The built-in 5V
interface circuit leads to lower voltage of timing and
control signals.
The panel contains an active area variable circuit
which supports SVGA/VGA/PC98∗2data signals by
changing the active area according to the type of
input signal. In addition, double-speed processed
NTSC/PAL can also be supported.
∗1
Dual Metal Shield
∗2
“PC98” is a treadmark of NEC Corporation.
Features
• Number of active dots: 485,000 (0.7 Type, 1.8cm in diagonal)
• Accepts the computer requirements of SVGA (804 × 604), VGA (644 × 484) and PC98 (644 × 404) platforms
• Supports NTSC (644 × 484) and PAL (762 × 572) by processing the video signal at double speed
• High optical transmittance: 13% (typ.)
• Built-in cross talk free circuit and ghost free circuit
• High contrast ratio with normally white mode
• Built-in H and V drivers (built-in input level conversion circuit, 5V driving possible)
• Up/down and/or right/left inverse display function
• Dust-proof glass used
Element Structure
• Dots: 804 (H) × 604 (V) = 485,616
• Built-in peripheral driver using polycrystalline silicon super thin film transistors
Applications
• Liquid crystal data projectors
• Liquid crystal projectors, etc.
– 1 –
E99665A04
Sony reserves the right to change products and specifications without prior notice. This information does not convey any license by
any implication or otherwise under any patents or other right. Application circuits shown, if any, are typical examples illustrating the
operation of the devices. Sony cannot assume responsibility for any problems arising out of the use of these circuits.
LCX034ALT
Page 2
– 2 –
LCX034ALT
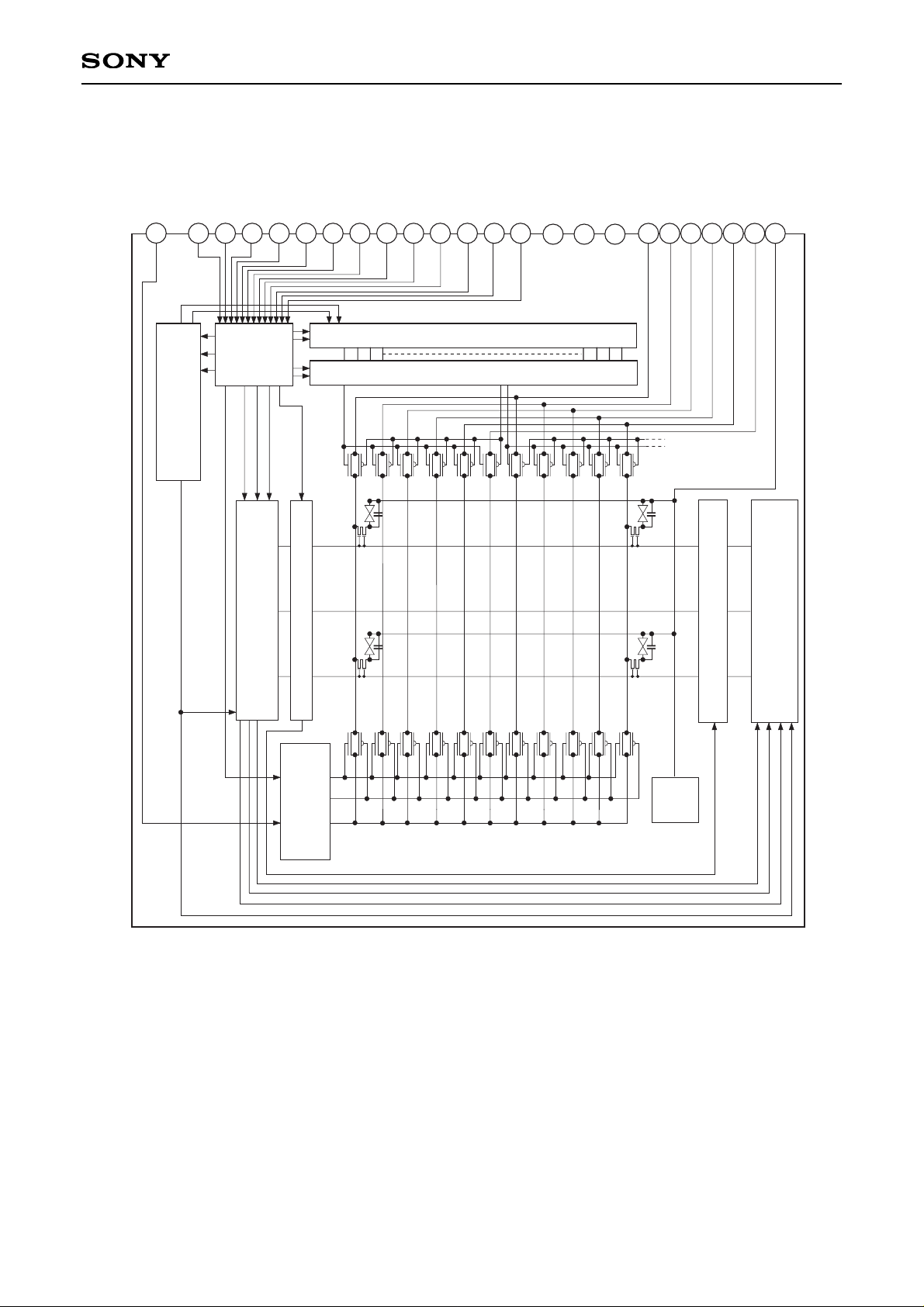
Block Diagram
1
18
H Shift Register (Bidirectional Scanning)
Up/Down and/or Right/Left
Inversion Control Circuit
V Shift Register
(Bidirectional Scanning)
Precharge Control
Circuit
COM
PAD
V Shift Register
(Bidirectional Scanning)
COM
SIG6
SIG5
SIG4
SIG3
SIG2
SIG1
Vss
VV
DD
HV
DD
MODE1
ENB
DWN
PCG
VCK
VST
RGT
BLK
HCK2
HCK1
HST
PSIG
14 15
17
9
20
19
21
22
12
11
10
8
23
16
7
6
4
3
5
2
24
Black Frame Control Circuit
Black Frame Control Circuit
13
Black Frame Control Circuit
MODE2
MODE3
Input Signal
Level Shifter
Circuit
Page 3
– 3 –
LCX034ALT
Pin
No.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
PSIG
SIG4
SIG3
SIG5
SIG2
SIG6
SIG1
HVDD
RGT
MODE3
MODE2
MODE1
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
HST
HCK1
HCK2
Vss
BLK
ENB
VCK
VST
PCG
DWN
VVDD
COM
Start pulse for H shift register
drive
Clock pulse for H shift register
drive
Clock pulse for H shift register
drive
GND (H, V drivers)
Black Frame display pulse
Enable pulse for gate selection
Clock pulse for V shift register
drive
Start pulse for V shift register
drive
Improvement pulse for uniformity
Drive direction pulse for V shift
register (H: normal, L: reverse)
Power supply for V driver
Common voltage of panel
Symbol Description
Pin
No.
Symbol Description
Uniformity improvement signal
Video signal 4 to panel
Video signal 3 to panel
Video signal 5 to panel
Video signal 2 to panel
Video signal 6 to panel
Video signal 1 to panel
Power supply for H driver
Drive direction pulse for H shift
register (H: normal, L: reverse)
Display area switching 3
Display area switching 2
Display area switching 1
Absolute Maximum Ratings (VSS = 0V)
• H driver supply voltage HVDD –1.0 to +20 V
• V driver supply voltage VVDD –1.0 to +20 V
• Common pad voltage COM –1.0 to +17 V
• H shift register input pin voltage HST, HCK1, HCK2, –1.0 to +17 V
RGT
• V shift register input pin voltage VST, VCK, PCG, –1.0 to +17 V
BLK, ENB, DWN
MODE1, MODE2, MODE3
• Video signal input pin voltage SIG1, SIG2, SIG3, SIG4, –1.0 to +15 V
SIG5, SIG6, PSIG
• Operating temperature
∗
Topr –10 to +70 °C
• Storage temperature Tstg –30 to +85 °C
∗
Panel temperature inside the antidust glass
Operating Conditions (VSS = 0V)
• Supply voltage
HVDD 15.5 ± 0.5V
VVDD 15.5 ± 0.5V
• Input pulse voltage (Vp-p of all input pins except video signal and uniformity improvement signal input pins)
Vin 5.0 ± 0.5V
Pin Description
Page 4
– 4 –
LCX034ALT
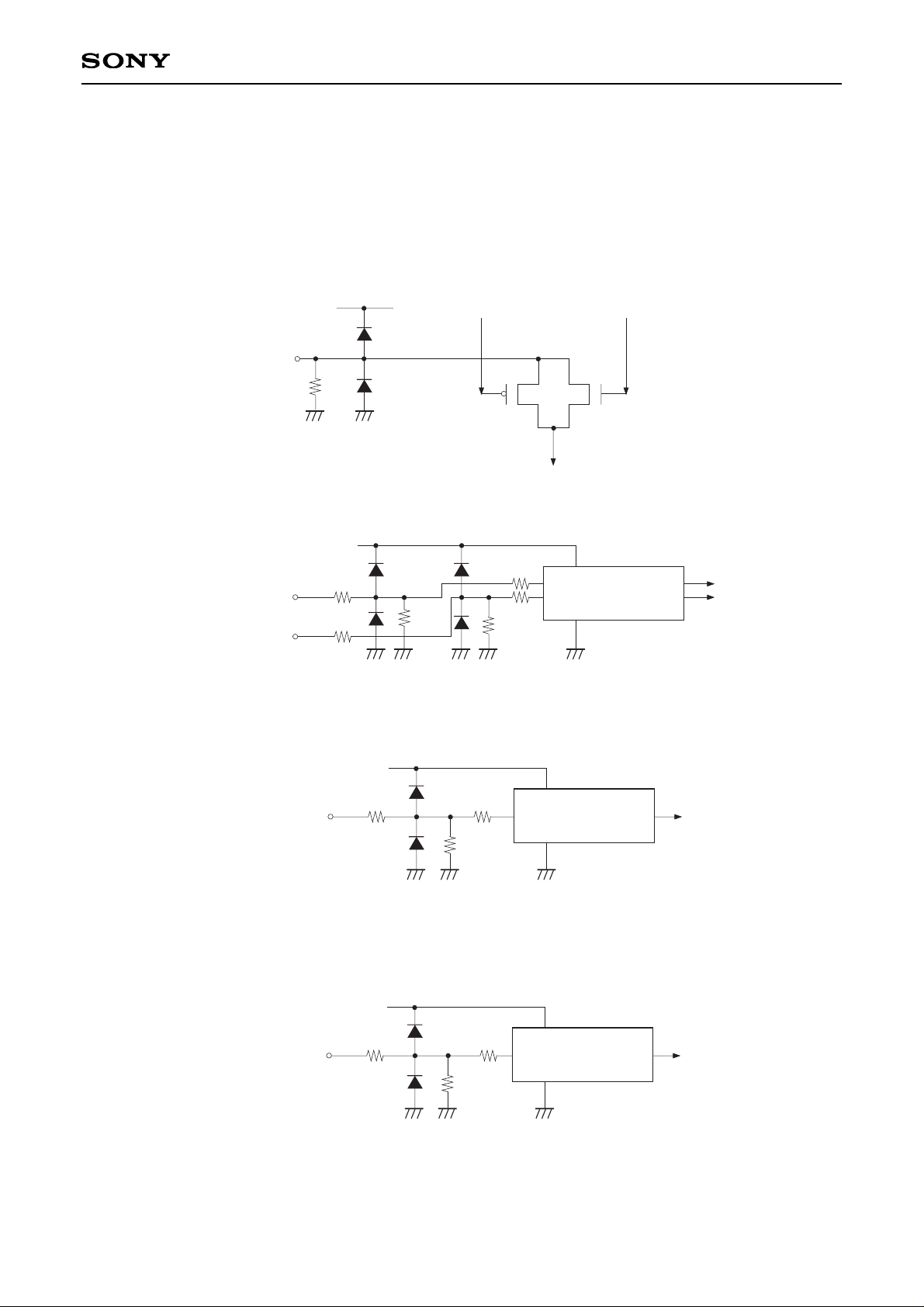
Input Equivalent Circuit
To prevent static charges, protective diodes are provided for each pin except the power supplies. In addition,
protective resistors are added to all pins except the video signal inputs. All pins are connected to VSS with a
high resistor of 1MΩ (typ.). The equivalent circuit of each input pin is shown below: (Resistance value: typ.)
(1) SIG1, SIG2, SIG3, SIG4, SIG5, SIG6, PSIG
Input
HV
DD
Signal line
1MΩ
(2) HCK1, HCK2
HVDD
250Ω
250Ω
250Ω
250Ω
Level conversion circuit
(2-phase input)
Input
1MΩ
1MΩ
(3) RGT, MODE1, MODE2, MODE3
Level conversion circuit
(single-phase input)
2.5kΩ2.5kΩ
HVDD
Input
1MΩ
(4) HST
Level conversion circuit
(single-phase input)
250Ω250Ω
HV
DD
Input
1MΩ
Page 5
– 5 –
LCX034ALT
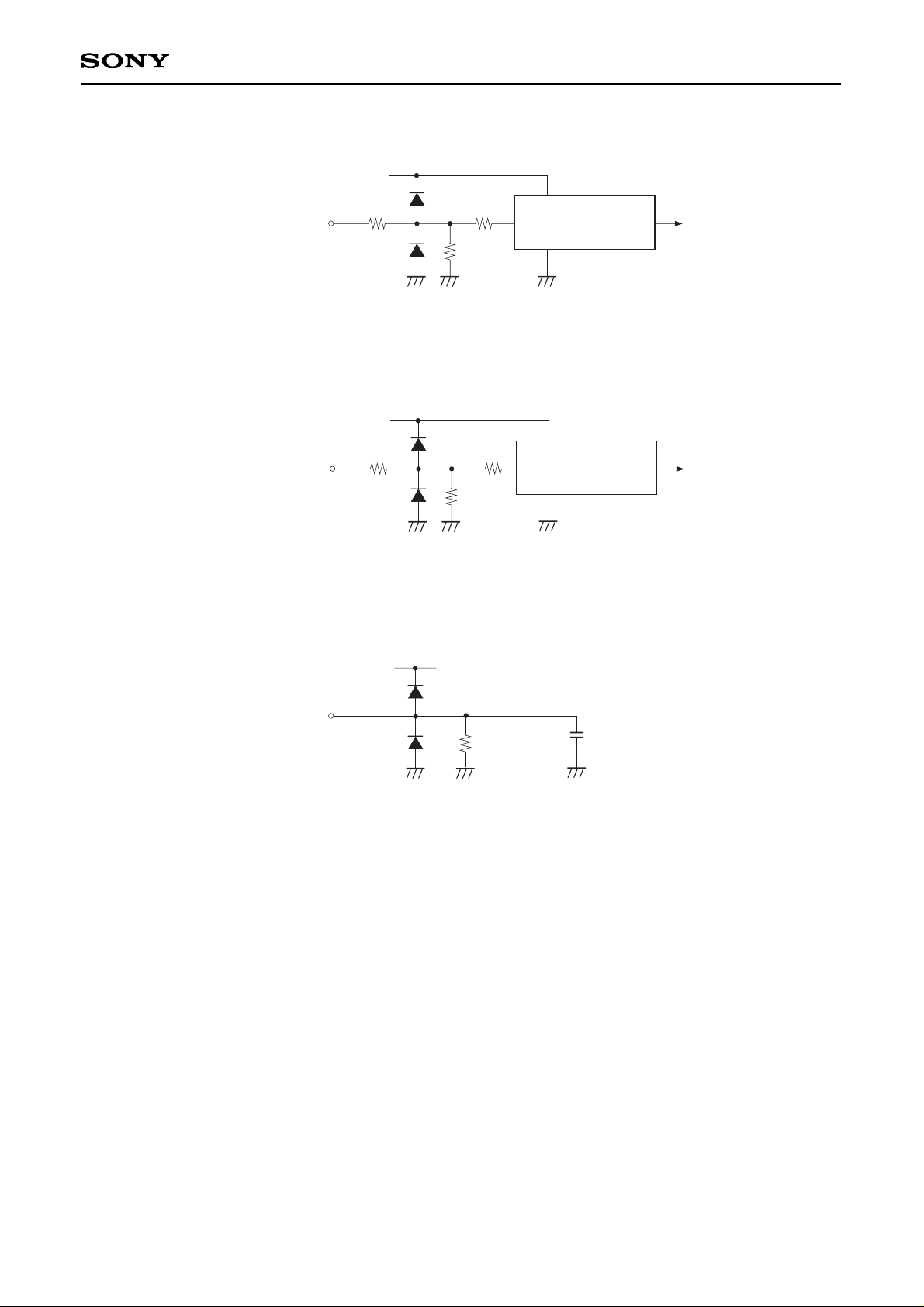
(5) PCG, VCK
Level conversion circuit
(single-phase input)
250Ω250Ω
VV
DD
Input
1MΩ
(6) VST, BLK, ENB, DWN
Level conversion circuit
(single-phase input)
2.5kΩ2.5kΩ
VV
DD
Input
1MΩ
(7) COM
Input
LC
1MΩ
VVDD
Page 6
– 6 –
LCX034ALT
Input Signals
1. Input signal voltage conditions (VSS = 0V)
Item
H shift register input voltage
HST, HCK1, HCK2, RGT
(Low)
(High)
(Low)
(High)
VHIL
VHIH
VVIL
VVIH
VVC
Vsig
Vcom
VpsigB
VpsigG
–0.5
4.5
–0.5
4.5
6.8
VVC – 4.5
VVC – 0.6
VVC ± 4.4
VVC ± 1.8
0.0
5.0
0.0
5.0
7.0
7.0
VVC – 0.5
VVC ± 4.5
VVC ± 1.9
0.4
5.5
0.4
5.5
7.2
VVC + 4.5
VVC – 0.4
VVC ± 4.6
VVC ± 2.0
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V shift register input voltage
MODE1, MODE2, MODE3,
BLK, VST, VCK, PCG,
ENB, DWN
Video signal center voltage
Video signal input range
∗1
Common voltage of panel
∗2
Uniformity improvement signal
input voltage (PSIG)
∗3
Symbol Min. Typ. Max. Unit
∗1
Input video signal shall be symmetrical to VVC.
∗2
The typical value of the common pad voltage may lower its suitable voltage according to the set
construction to use. In this case, use the voltage of which has maximum contrast as typical value.
When the typical value is lowered, the maximum and minimum values may lower.
∗3
Input a uniformity improvement signal PSIG in the same polarity with video signals VSIG1 to VSIG6 and
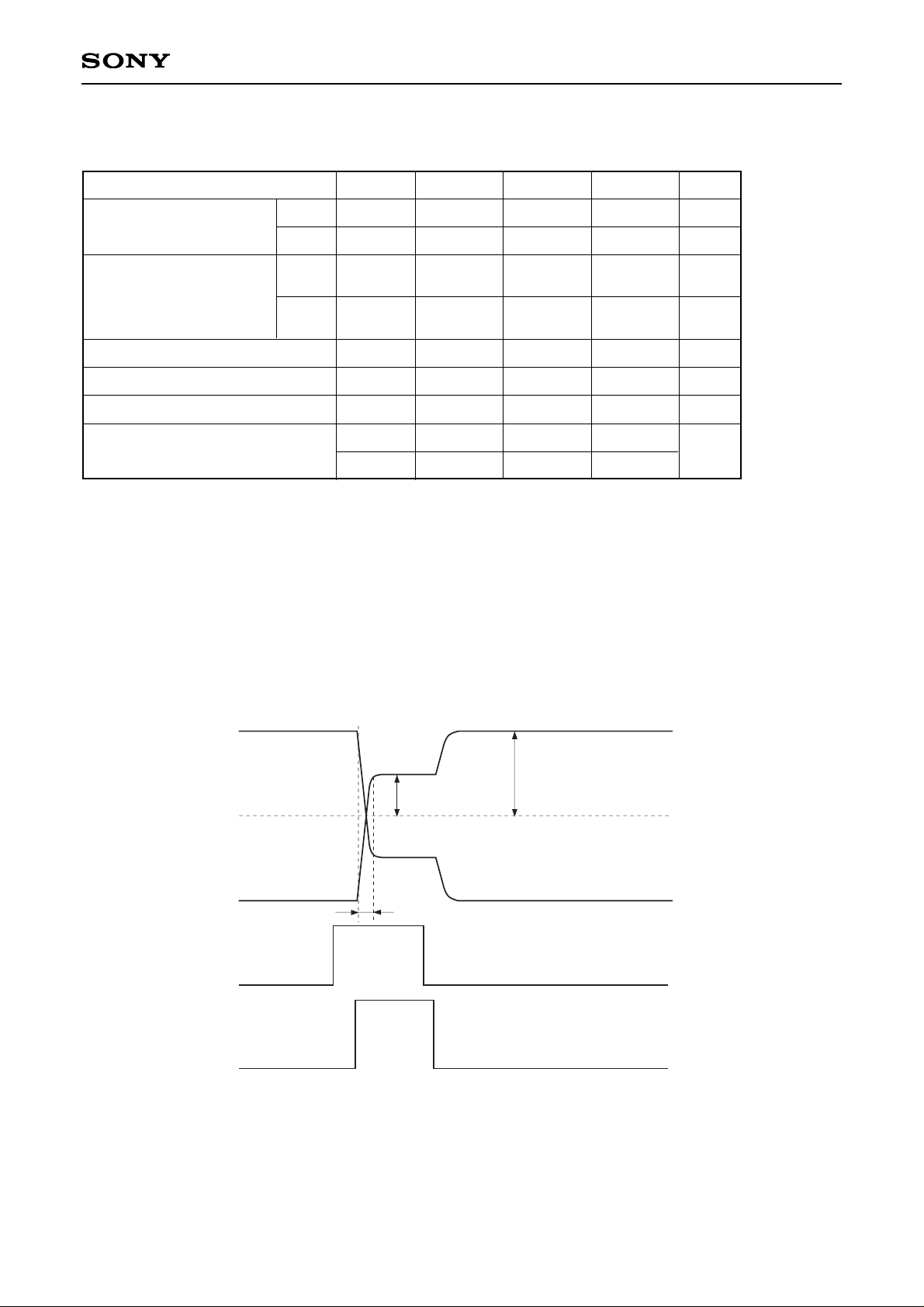
which is symmetrical to VVC. PSIG wave form is 2 steps like below, in the upper chart, lower shows signal
level of the 1st step, upper shows signal level of the 2nd step. Also, the rising and falling of PSIG are
synchronized with the rising of PRG pulse, and the rise time trPSIG and fall time tfPSIG are suppressed
within 450ns (as shown in a diagram below).
The optimum input voltage of PSIG may be changed according as drive conditions of the drive side.
∗4
PRG shows the time of the 1st step of PSIG signal, and it is not input to the panel.
Level Conversion Circuit
The LCX034ALT has a built-in level conversion circuit in the clock input unit on the panel. The input signal
level increases to HVDD or VVDD. The VCC of external ICs are applicable to 5 ± 0.5V.
90%
10%
PsigB
PsigG
trPSIG, tfPSIG
PSIG
PCG
PRG
∗
4
VVC
Input waveform of uniformity improvement signal PSIG
Page 7
– 7 –
LCX034ALT
2. Clock timing conditions (Ta = 25°C) (SVGA mode: fHCKn = 4.0MHz, fVCK = 24.0kHz)
∗5
Hckn means Hck1 and Hck2.
∗6
Blk is set to positive polarity pulse for other than SVGA mode ; Low level for SVGA mode.
Hst rise time
Hst fall time
Hst data set-up time
Hst data hold time
Hckn rise time
∗5
Hckn fall time
∗5
Hck1 fall to Hck2 rise time
Hck1 rise to Hck2 fall time
Vst rise time
Vst fall time
Vst data set-up time
Vst data hold time
Vck rise time
Vck fall time
Enb rise time
Enb fall time
Vck rise/fall to Enb rise time
Horizontal video period completed to Enb fall time
Enb fall to Pcg rise time
Pcg rise time
Pcg fall time
Pcg rise to Prg rise time
Pcg rise to Prg rise time
Prg rise to Pcg fall time
Pcg fall to horizontal video period start time
Pcg pulse width
Prg rise to Vck rise/fall time
Blk rise time
Blk fall time
Blk fall to Vst rise time
trHst
tfHst
tdHst
thHst
trHckn
tfHckn
to1Hck
to2Hck
trVst
tfVst
tdVst
thVst
trVck
tfVck
trEnb
tfEnb
toEnb
tdEnb
toPcg
trPcg
tfPcg
toPrgr
toPrgf
toPcg
toVideo
twPcg
toVck
trBlk
tfBlk
toVst
—
—
50
50
—
—
–15
–15
—
—
5
5
—
—
—
—
300
900
630
—
—
300
200
1050
300
1350
0
—
—
32
—
—
60
60
—
—
0
0
—
—
10
10
—
—
—
—
500
1000
700
—
—
500
250
1100
350
1600
1000
—
—
—
30
30
70
70
30
30
15
15
100
100
15
15
100
100
100
100
—
—
—
30
30
—
—
—
—
—
—
100
100
—
ns
µs
ns
Item Symbol Min. Typ. Max. Unit
HST
HCK
VST
VCK
ENB
PCG
PRG
BLK
∗6
µs
Page 8
– 8 –
LCX034ALT
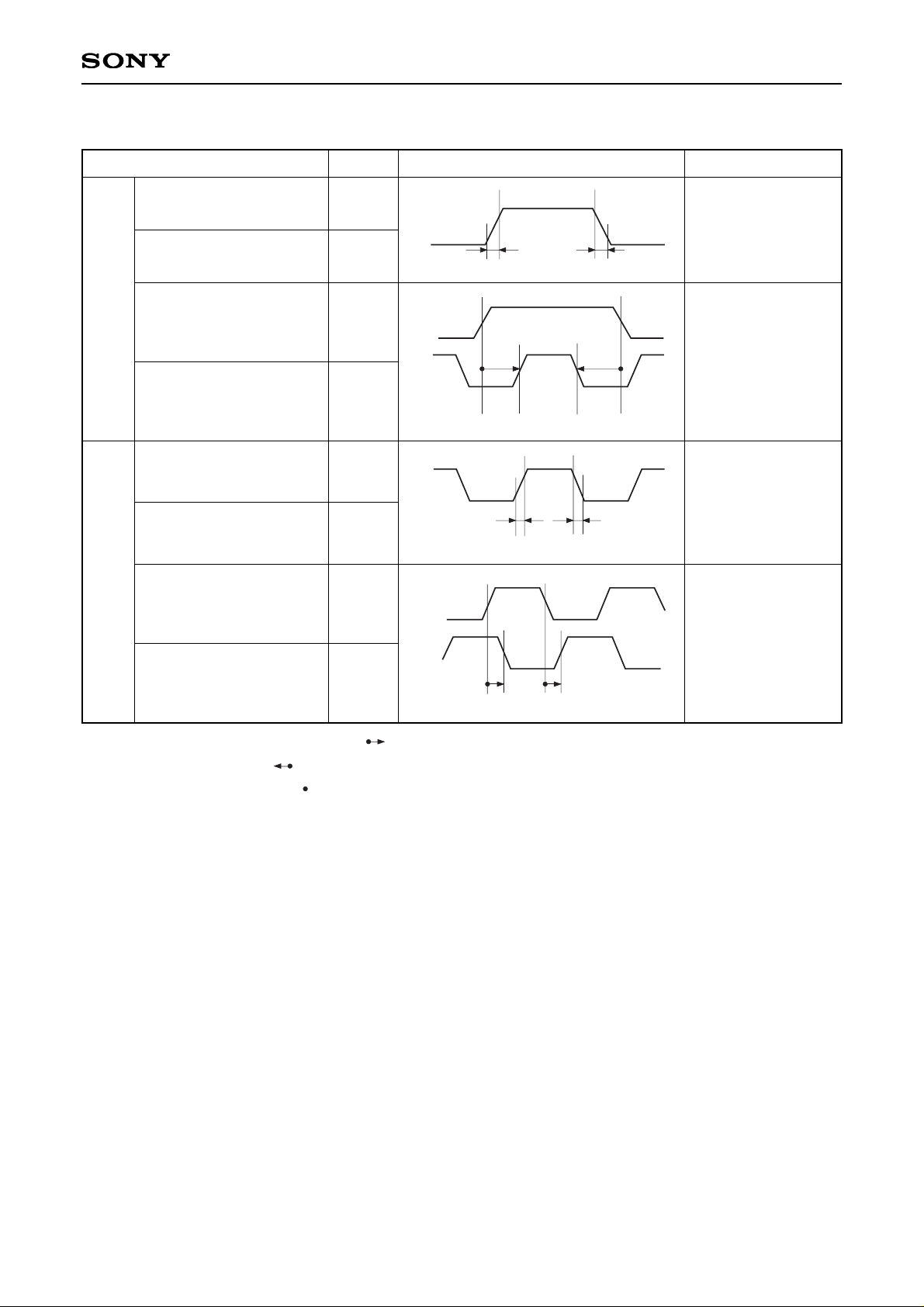
∗7
Definitions: The right-pointing arrow ( ) means +.
The left-pointing arrow ( ) means –.
The black dot at an arrow ( ) indicates the start of measurement.
<Horizontal Shift Register Driving Waveform>
Hst rise time
HST
HCK
Hst fall time
Hst data set-up time
Hst data hold time
Hckn rise time
∗3
Hckn fall time
∗3
Hck1 fall to Hck2 rise time
Hck1 rise to Hck2 fall time
• Hckn
∗5
duty cycle 50%
to1Hck = 0ns
to2Hck = 0ns
• Hckn
∗5
duty cycle 50%
to1Hck = 0ns
to2Hck = 0ns
• Hckn
∗5
duty cycle 50%
to1Hck = 0ns
to2Hck = 0ns
trHst
tfHst
tdHst
thHst
trHckn
tfHckn
to1Hck
to2Hck
Item Symbol Waveform Conditions
90%
10%
10%
90%
Hst
trHst tfHst
50%
50%
∗
7
Hst
Hck1
tdHst thHst
50%
50%
∗
5
Hckn
10%
10%
90%
90%
trHckn tfHckn
50%
50%
∗
7
Hck1
to2Hck to1Hck
50%
50%
Hck2
Page 9

– 9 –
LCX034ALT
<Vertical Shift Register Driving Waveform>
VCK
ENB
Vck rise time
Vck fall time
Enb rise time
Enb fall time
trVck
tfVck
trEnb
tfEnb
Vck rise/fall to
Enb rise time
toEnb
Horizontal video period
completed to Enb fall time
tdEnb
Enb fall to Pcg rise time toPcg
Item Symbol Waveform Conditions
Vck
10%
10%
90%
90%
trVckn tfVckn
Vst rise time
VST
Vst fall time
Vst data set-up time
Vst data hold time
trVst
tfVst
tdVst
thVst
90%
10%
10%
90%
Vst
trVst tfVst
50%
50%
∗
7
Vst
Vck
tdVst thVst
50%
50%
90%
10%
10%
90%
Enb
tfEnb trEnb
50%
50%
toEnb
Vck
H. blanking periodH. video period
tdEnb
toPcg
50% 50%
Enb
Pcg
∗
7
Page 10

– 10 –
LCX034ALT
tfBlk
toVst
BLK
Blk rise time
Blk fall time
Blk fall to Vst rise time
trBlk
Blk
50%
50%
toVst
Vst
∗
7
50%
∗8
Input the pulse obtained by taking the OR of the above pulse (PCG) and BLK to the PCG input pin.
Item Symbol Waveform Conditions
Pcg rise time
PCG
∗8
PRG
trPcg
Pcg fall time tfPcg
Pcg rise to Prg rise time
toPrgr
Pcg fall to Prg fall time
toPrgf
Prg rise to Pcg fall time
toPcg
Pcg fall to horizontal
video period start time
toVideo
Pcg pulse width
twPcg
Prg rise to
Vck rise/fall time
toVck
90%
10%
10%
90%
Pcg
tfEnb trEnb
50%
H. video period startH. blanking period
toPcg
toVideo
50%
Pcg
50%
toPrgr
toPrgf
50%
Prg
twPcg
∗
7
50%
50%
toVck
Prg
Vck
∗
7
Page 11

– 11 –
LCX034ALT
Electrical Characteristics (Ta = 25°C, HVDD = 15.5V, VVDD = 15.5V)
1. Horizontal drivers
Item
Input pin capacitance HCKn
HST
Input pin current HCK1
HCK2
HST
RGT
Video signal input pin capacitance
Current consumption
CHckn
CHst
Csig
IH
HCK1 = GND
HCK2 = GND
HST = GND
RGT = GND
HCKn: HCK1, HCK2 (4.0MHz)
—
—
–500
–1000
–500
–150
—
—
7
7
–250
–300
–150
–30
130
10.0
12
12
—
—
—
—
200
15.0
pF
pF
µA
µA
µA
µA
pF
mA
Symbol Min. Typ. Max. Unit Condition
2. Vertical drivers
Item
Input pin capacitance VCK
VST
Input pin current VCK
PCG, VST, ENB, DWN, BLK, MODE1,
MODE2, MODE3
Current consumption
CVck
CVst
IV
—
—
–1000
–150
—
7
7
–150
–30
3.0
12
12
—
—
6.0
pF
pF
µA
µA
mA
Symbol Min. Typ. Max. Unit Condition
3. Total power consumption of the panel
Item
Total power consumption of the
panel
PWR — 200 300 mW
Symbol Min. Typ. Max. Unit
4. Pin input resistance
Item
Pin – VSS input resistance Rpin 0.4 1 — MΩ
Symbol Min. Typ. Max. Unit
VCK = GND
PCG, VST, ENB, DWN,
BLK, MODE1, MODE2,
MODE3 = GND
VCK: (24.0kHz)
5. Uniformity improvement signal
Item
Input pin capacitance for uniformity
improvement signal
CPSIGo 8 nF
Symbol Min. Typ. Max. Unit
—
12
Page 12

– 12 –
LCX034ALT
Reflection Preventive Processing
When a retardation film which rotates the polarization axis is used to adjust to the polarization direction of a
polarization screen or prism, use a retardation film with reflection preventive processing on the surface. This
prevents characteristic deterioration caused by luminous reflection.
Electro-optical Characteristics (SVGA mode)
Item
Contrast ratio
25°C
25°C
25°C
60°C
25°C
60°C
25°C
60°C
0°C
25°C
0°C
25°C
60°C
25°C
25°C
CR
T
RV90-25
GV90-25
BV90-25
RV90-60
GV90-60
BV90-60
RV50-25
GV50-25
BV50-25
RV50-60
GV50-60
BV50-60
RV10-25
GV10-25
BV10-25
RV10-60
GV10-60
BV10-60
ton0
ton25
toff0
toff25
F
YT60
CTK
120
11
1.0
1.1
1.2
1.0
1.0
1.1
1.4
1.5
1.6
1.4
1.4
1.5
1.9
2.0
2.1
1.9
1.9
1.9
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
150
13
1.3
1.5
1.6
1.3
1.4
1.5
1.7
1.8
1.9
1.6
1.7
1.8
2.2
2.3
2.4
2.1
2.2
2.3
30
12
100
30
–65
—
—
—
—
1.7
1.9
2.0
1.6
1.7
1.9
2.0
2.1
2.2
1.9
2.0
2.1
2.5
2.6
2.7
2.4
2.5
2.6
80
40
200
70
–40
0
5
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
—
%
V
ms
dB
s
%
Optical transmittance
V-T
characteristics
V90
V50
ON time
OFF time
V10
Response time
Flicker
Image retention time
Cross talk
Symbol Measurement method Min. Typ. Max. Unit
Page 13

– 13 –
LCX034ALT
<Electro-optical Characteristics Measurement>
• Measurement system I
• Measurement system II
Luminance
Meter
Measurement
Equipment
Light Detector
Measurement
Equipment
Screen: Made by Sony (VPS-120FH: Gain 2.8, Glass Beaded Type) or equivalent
Projection lens: Focal distance 80mm, F1.9
Light source: 155W metal Haloid arc lamp (Color temperature 7500K ± 500)
(× 24, Sensor area: 7mmφ)
Polarizer: Side of incidence – Nitto Denko’s EG-1224DU or Polatechno’s SKN-1824ZT or equivalent
Side of output light – Polatechno's SHC-128 or equivalent
Optical fiber
LCD panel
Light receptor lens
Drive Circuit
Light
Source
Basic measurement conditions
(1) Driving voltage
HVDD = 15.5V, VVDD = 15.5V
VVC = 7.0V, Vcom = 6.5V
(2) Measurement temperature
25°C unless otherwise specified.
(3) Measurement point
One point in the center of the screen unless otherwise specified.
(4) Measurement systems
Two types of measurement systems are used as shown below.
(5) Video input signal voltage (Vsig)
Vsig = 7.0 ± VAC [V] (VAC = signal amplitude)
Screen
LCD Projector
Approx. 2000mm
1. Contrast Ratio
Contrast Ratio (CR) is given by the following formula (1).
L (White)
CR = ... (1)
L (Black)
L (White): Surface luminance of the center of the screen at the input signal amplitude VAC = 0.5V.
L (Black): Surface luminance of the center of the screen at VAC = 4.5V.
Both luminosities are measured by System I.
Page 14

– 14 –
LCX034ALT
2. Optical Transmittance
Optical Transmittance (T) is given by the following formula (2).
White luminance
T = × 100 [%] ... (2)
Luminance of light source
"White luminance" means the maximum luminance on the screen at the input signal amplitude VAC = 0.5V
on Measurement System I.
3. V-T Characteristics
V-T characteristics, or the relationship between signal
amplitude and the transmittance of the panels, are
measured by System II by inputting the same signal
amplitude VAC to each input pin. V90, V50, and V10
correspond to the voltages which define 90%, 50%,
and 10% of transmittance respectively.
4. Response Time
Response time ton and toff are defined by
formulas (5) and (6) respectively.
ton = t1 – tON ...(5)
toff = t2 – tOFF ...(6)
t1: time which gives 10% transmittance of
the panel.
t2: time which gives 90% transmittance of
the panel.
The relationships between t1, t2, tON and
tOFF are shown in the right figure.
90
50
10
V
90 V50 V10
VAC – Signal amplitude [V]
Transmittance [%]
Input signal voltage (Waveform applied to the measured pixels)
4.5V
0.5V
7.0V
0V
Optical transmittance output waveform
100%
90%
10%
0%
tON t1
ton
tOFF t2
toff
Page 15

– 15 –
LCX034ALT
5. Flicker
Flicker (F) is given by formula (7). DC and AC (SVGA/VGA/PC98/NTSC: 30Hz, rms, PAL: 25Hz, rms)
components of the panel output signal for gray raster∗mode are measured by a DC voltmeter and a spectrum
analyzer in System II.
F [dB] = 20log
{
AC component
}
...(7)
DC component
6. Image Retention Time
Apply the monoscope signal to the LCD panel for 60 minutes and then change this signal to the gray scale
of Vsig = 7.0 ± VAC (VAC: 3 to 4V). Judging by sight at the VAC that holds the maximum image retention,
measure the time till the residual image becomes indistinct.
∗
Monoscope signal conditions:
Vsig = 7.0 ± 4.5 or ±2.0 [V]
(shown in the right figure)
Vcom = 6.6V
7. Cross Talk
Cross talk is determined by the luminance differences between adjacent areas represented by Wi' and
Wi (i = 1 to 4) around a black window (Vsig = 4.5 V/1V).
Cross talk value CTK = × 100 [%]
∗
Each input signal voltage for gray raster mode
is given by Vsig = 7.0 ± V50 [V]
where: V50 is the signal amplitude which gives
50% of transmittance in V-T characteristics.
Black level
White level
Vsig waveform
7.0V
0V
4.5V
2.0V
4.5V
2.0V
W1
W1
'
W3
W3
'
W2
W2
' W4'
W4
Wi' – Wi
Wi
Page 16

– 16 –
LCX034ALT
Viewing angle characteristics (Reference Value)
90
270
180
0
Theta
Phi
30 70
θ
φ
φ180°
X
φ270°
Y
φ0°
φ90°
Z
θ0°
Measurement method
5010
Page 17

– 17 –
LCX034ALT
Optical transmittance of LCD panel (Reference Value)
20
10
0
400 500 600 700
Wavelength [nm]
Trans. [%]
Measurement method: Measurement system ΙΙ
Page 18

– 18 –
LCX034ALT
1. Dot Arrangement
The dots are arranged in a stripe. The shaded area is used for the dark border around the display.
612 dots
4 dots
604 dots (Effective 10.87mm)
Active area
Photo-Shielding
Gate SW Gate SW Gate SW
6 dots
816 dots
6 dots
4 dots
804 dots (Effective 14.47mm)
Page 19

– 19 –
LCX034ALT
2. LCD Panel Operations
[Description of basic operations]
• A vertical driver, which consists of vertical shift registers, enable-gates and buffers, applies a selected pulse
to every 604 gate lines sequentially in a single horizontal scanning period. (in SVGA mode)
• A horizontal driver, which consists of horizontal shift registers, gates and CMOS sample-and-hold circuits,
applies selected pulses to every 804 signal electrodes sequentially in a single horizontal scanning period.
These pulses are used to supply the sampled video signal to the row signal lines.
• Vertical and horizontal shift registers address one pixel, and then Thin Film Transistors (TFTs; two TFTs) turn
on to apply a video signal to the dot. The same procedures lead to the entire 604 × 804 dots to display a
picture in a single vertical scanning period.
• The data and video signals shall be input with the 1H-inverted system.
[Description of operating mode]
This LCD panel can change the active area by displaying a black frame to support various computer or video
signals. The active area is switched by MODE1, 2 and 3. However, the center of the screen is not changed.
The active area setting modes are shown below.
MODE1 MODE2 MODE3 Display mode
L
H
H
L
H
L
H
L
SVGA
804 × 604
PAL
762 × 572
VGA/NTSC
644 × 484
PC98
644 × 404
L
L
L
H
This LCD panel has the following functions to easily apply to various uses, as well as various broadcasting
systems.
• Right/left inverse mode
• Up/down inverse mode
These modes are controlled by two signals (RGT and DWN). The right/left and/or up/down setting modes are
shown below.
Right/left and/or up/down mean the direction when the Pin 1 marking is located at the right side with the pin
block upside.
To locate the active area in the center of the panel in each mode, polarity of the start pulse and clock phase for
both the H and V systems nust be varied. The phase relationship between the start pulse and the clock for
each mode is shown on the following pages.
RGT
Mode
Right scan
Left scan
H
L
DWN Mode
Down scan
Up scan
H
L
Page 20

– 20 –
LCX034ALT
VST (DWN = H)
VST (DWN = L)
(1.2) PAL
VD
1
2
VCK
569 570 571 572
VST (DWN = H)
VST (DWN = L)
(1.1) SVGA
VD
1 2
VCK
601 602 603 604
VD
1 2
VCK
482 483 484
(1.3) VGA/NTSC
VD
1 2
VCK
401 402 403 404
(1.4) PC98
VST (DWN = H)
VST (DWN = L)
VST (DWN = H)
VST (DWN = L)
481
Vertical display cycle 572H
Vertical display cycle 604H
Vertical display cycle 484H
Vertical display cycle 404H
(1) Vertical direction display cycle
Page 21

– 21 –
LCX034ALT
(2.1.1) SVGA, RGT = H
Horizontal display cycle
HST
HCK1
1 2 3 4 131 132 133 134
HCK2
HD
(2.1.2) SVGA, RGT = L
Horizontal display cycle
HST
HCK1
HCK2
HD
1
2
3 4 131
132 133
134
1 2 3 4
Horizontal display cycle
HST
HCK1
125 126 127 128
(2.2.1) PAL, RGT = H
HCK2
Horizontal display cycle
HST
HCK1
1 2 3 4 125 126 127 128
(2.2.2) PAL, RGT = L
HCK2
HD
HD
(2) Horizontal direction display cycle
Page 22

– 22 –
LCX034ALT
Horizontal display cycle
HST
HCK1
105 106 107 108
(2.3.1) VGA/NTSC/PC98, RGT = H
HCK2
Horizontal display cycle
HST
HCK1
1 2 3 4
105 106
107 108
(2.3.2) VGA/NTSC/PC98, RGT = L
HCK2
HD
HD
1 2 3 4
Page 23

– 23 –
LCX034ALT
3. 6-dot Simultaneous Sampling
The horizontal shift register samples signals SIG1 to SIG6 simultaneously. This requires phase matching
between signals SIG1 to SIG6 to prevent the horizontal resolution from deteriorating. Thus, phase matching
between each signal is required using an external signal delaying circuit before applying the video signal to
the LCD panel.
The block diagram of the delaying procedure using the sample-and-hold method is as follows. The following
phase relationship diagram indicates the phase setting for right scan (RGT = High level). For left scan (RGT =
Low level), the phase settings for signals SIG1 to SIG6 are exactly reversed.
S/H
CK1
CK2
SIG3
SIG6
SIG1
LCX034ALT
SIG3
SIG6
SIG1
SIG2
SIG2
SIG4
SIG4
SIG5
SIG5
CK3
CK4
CK5
S/H
S/H
S/H
S/H
S/H
CK6
S/H
S/H
S/H
S/H
S/H
5
3
2
4
6
7
HCKn
CK1
CK3
CK5
CK2
CK4
CK6
<Phase relationship of delaying sample-and-hold pulses> (right scan)
Page 24

– 24 –
LCX034ALT
Display System Block Diagram
An example of display system is shown below.
R-IN
G-IN
B-IN
Vsync
Hsync
CLP, PRG
MCK1
FRP, S/H Control
6
HST, HCK, VST, VCK, PCG, ENB
Pre Driver
CXA2111R
Timing
Generator
CXD3500R
PLL
CXA3106Q
S/H Driver
CXA2112R
S/H Driver
CXA2112R
S/H Driver
CXA2112R
LCX034
R
LCX034
G
LCX034
B
6
6
Page 25

– 25 –
LCX034ALT
Notes on Handling
(1) Static charge prevention
Be sure to take the following protective measures. TFT-LCD panels are easily damaged by static charges.
a) Use non-chargeable gloves, or simply use bare hands.
b) Use an earth-band when handling.
c) Do not touch any electrodes of a panel.
d) Wear non-chargeable clothes and conductive shoes.
e) Install conductive mats on the working floor and working table.
f) Keep panels away from any charged materials.
g) Use ionized air to discharge the panels.
(2) Protection from dust and dirt
a) Operate in a clean environment.
b) When delivered, the panel surface (glass panel) is covered by a protective sheet. Peel off the protective
sheet carefully so as not to damage the glass panel.
c) Do not touch the glass panel surface. The surface is easily scratched. When cleaning, use a clean-
room wiper with isopropyl alcohol. Be careful not to leave a stain on the surface.
d) Use ionized air to blow dust off the glass panel.
(3) Light resistance
Orientation film and organic matter such as liquid crystal used inside of the LCD panel deteriorate by the
light chemical reaction. As a result, its indication characteristic may irreversible change. The progress of its
chemical reaction is influenced by short wavelength side's light (characteristics of UV cut filter) and
temperature when quantitiy of light is constant. To control its progress, attach suitable UV cut filter between
light source and LCD panel. (Sharp characteristic's filter of λ > 425nm is recommended.) Also, use suitable
IR cut filter to lower the temperature of LCD panel and cool the panel carefully.
(4) Other handling precautions
a) Do not twist or bend the flexible PC board especially at the connecting region because the board is
easily deformed.
b) Do not drop the panel.
c) Do not twist or bend the panel or panel frame.
d) Keep the panel away from heat sources.
e) Do not dampen the panel with water or other solvents.
f) Avoid storing or using the panel at a high temperature or high humidity, which may result in panel
damages.
g) Minimum radius of bending curvature for a flexible substrate must be 1mm.
h) Torque required to tighten screws on a panel must be 0.098N · m (measurement screw : JCIS Type 1,
M1.7 flat head screw) or less.
i) Do not pressure the portion other than mounting hole (cover).
Page 26

– 26 –
LCX034ALT
Package Outline Unit: mm
Active Area
1
2
3
4
5
7
8
9
Output light
Polarizing Axis
25.0 ± 0.15
(14.47)
(10.87)
12.0 ± 0.15
(75.5)
101.5 ± 1.4
23.0 ± 0.1
26.0 ± 0.15
8-R1.0
12.5 ± 0.05
4.9 ± 0.2
Thickness of the connector
0.3 ± 0.05
2.2 ± 0.1
1.5 ± 0.1
12.5 ± 0.15
2.0 ± 0.1
21.0 ± 0.1
Incident
light
5-φ1.8 ± 0.05
electrode (enlarged)
PIN24
PIN1
P 0.5 ± 0.02 × 23 = 11.5 ± 0.03
0.5 ± 0.1
0.5 ± 0.15
4.0 ± 0.4
0.35 ± 0.03
The rotation angle of the active area relative to H and V is ± 1°.
Incident light
Polarizing Axis
6
weight 5.6g
Description
Molding material
Outside frame
Reinforcing board
Reinforcing material
F P C
No
1
2
3
4
5
6
Cover 1
7
8
Cover 2
9
Glass 1
Glass 2
Sony Corporation
 Loading...
Loading...