Page 1
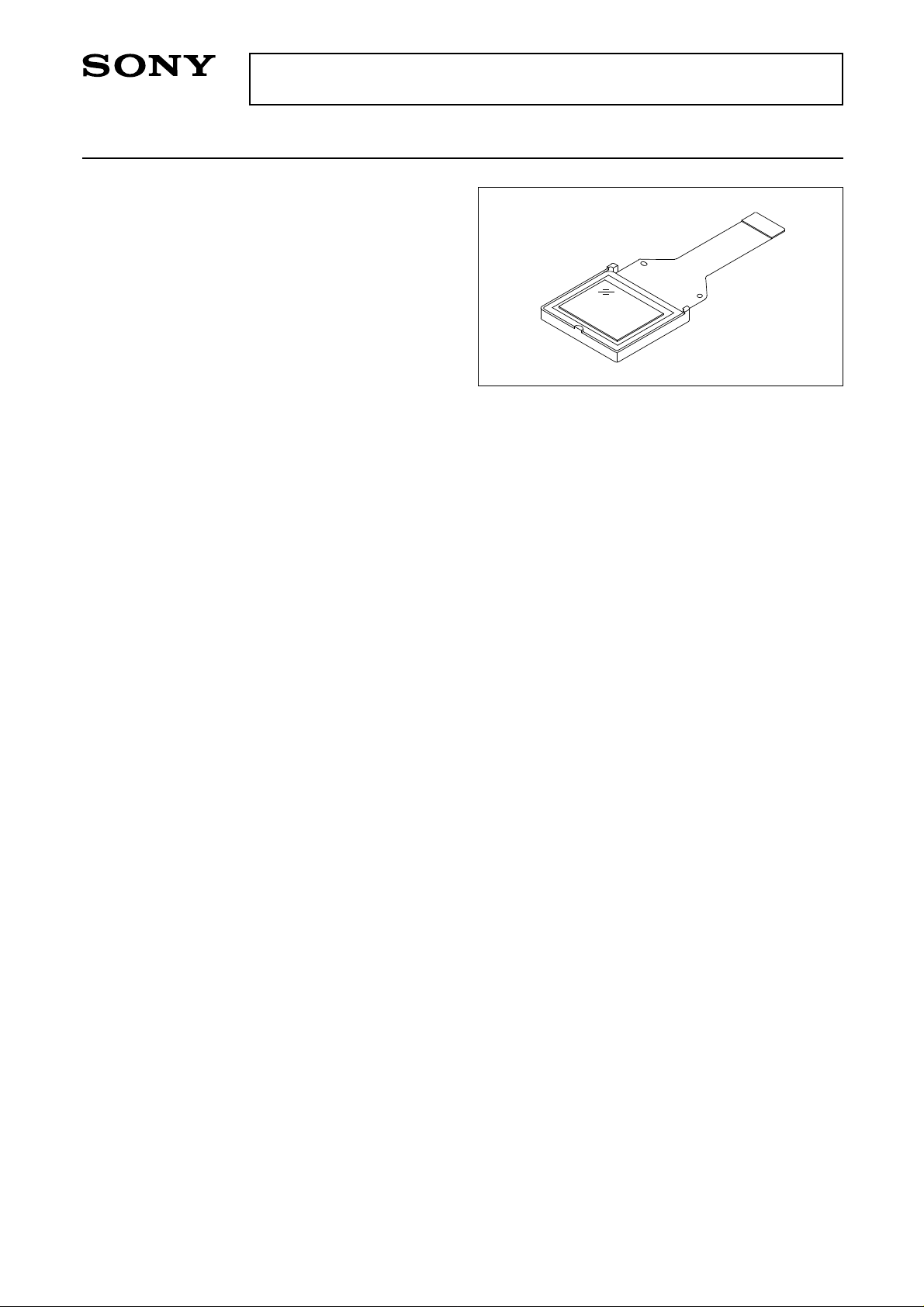
LCX009AKB
For the availability of this product, please contact the sales office.
1.8cm (0.7-inch) NTSC/PAL Color LCD Panel
Description
The LCX009AKB is a 1.8cm diagonal active matrix
TFT-LCD panel addressed by the polycrystalline
silicon super thin film transistors with built-in
peripheral driving circuit. This panel provides fullcolor representation in NTSC/PAL mode. RGB dots
are arranged in a delta pattern featuring high picture
quality of no fixed color patterns, which is inherent in
vertical stripes and mosaic pattern arrangements.
Features
• The number of active dots: 180,000 (0.7-inch; 1.8cm in diagonal)
• Horizontal resolution: 400 TV lines
• High optical transmittance: 3.5% (typ.)
• High contrast ratio with normally white mode: 200 (typ.)
• Built-in H and V driving circuit (built-in input level conversion circuit, TTL drive possible)
• High quality picture representation with RGB delta arranged color filters
• Full-color representation
• NTSC/PAL compatible
• Right/left inverse display function
Element Structure
• Dots
Total dots : 827 (H) × 228 (V) = 188,556
Active dots : 800 (H) × 225 (V) = 180,000
• Built-in peripheral driving circuit using the polycrystalline silicon super thin film transistors.
Sony reserves the right to change products and specifications without prior notice. This information does not convey any license by
any implication or otherwise under any patents or other right. Application circuits shown, if any, are typical examples illustrating the
operation of the devices. Sony cannot assume responsibility for any problems arising out of the use of these circuits.
– 1 –
E94501C64-ST
Page 2
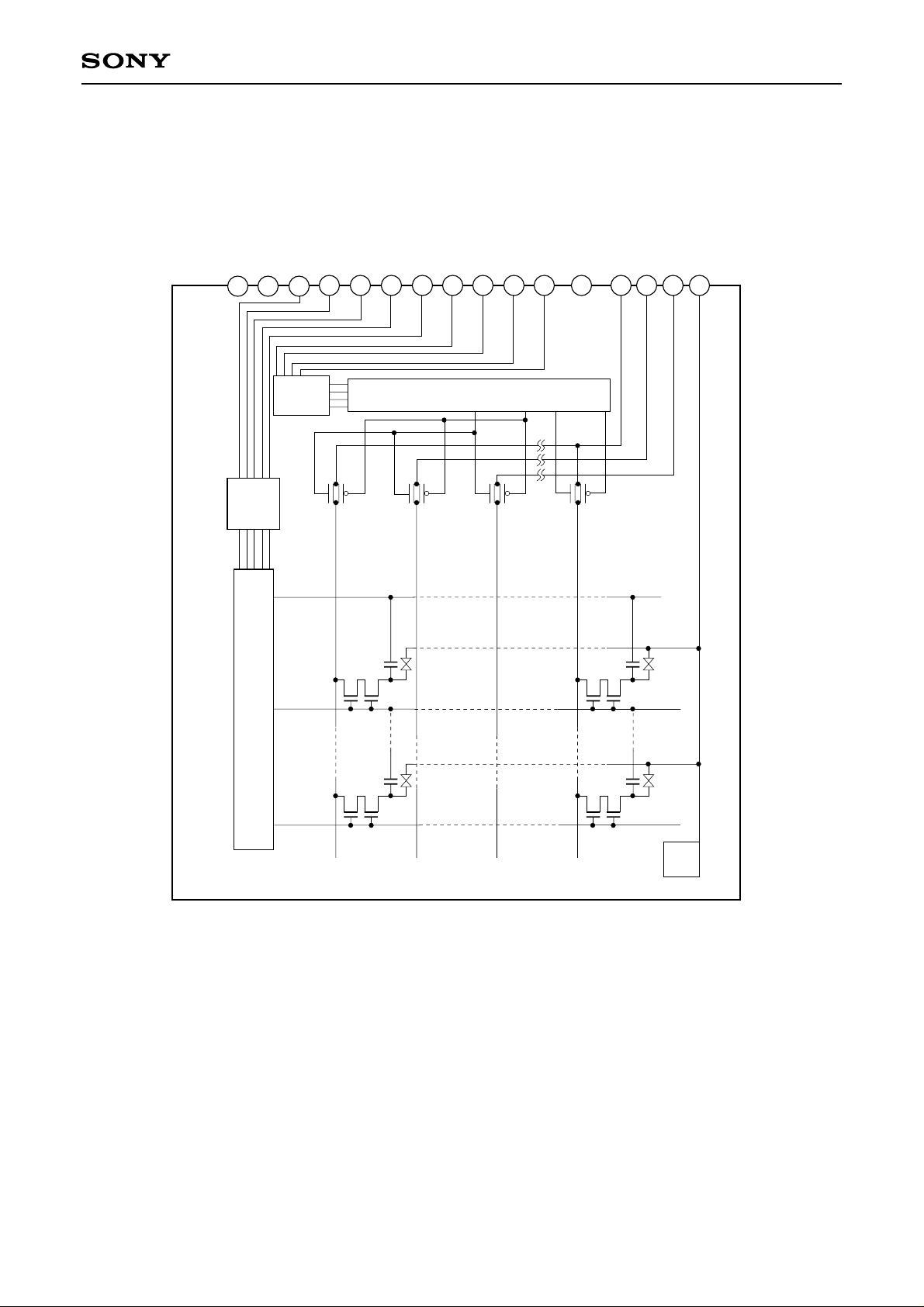
Block Diagram
LCX009AKB
DD
VV
16
V Level
Shifter
15
SS
V
H Level
Shifter
14
VST
VCK1
VCK2
13
12
CS LC
11
EN
CLR
10
HST
RGT
9
8
H Shift Register
HCK2
7
HCK1
6
DD
RED
BLUE
HV
5
4
GREEN
COM
1
2
3
V Shift Register
COM
Pad
– 2 –
Page 3
Absolute Maximum Ratings (Vss = 0V)
• H driver supply voltage HVDD –1.0 to +17 V
• V driver supply voltage VVDD –1.0 to +17 V
• H driver input pin voltage HST, HCK1, HCK2 –1.0 to +17 V
RGT
• V driver input pin voltage VST, VCK1, VCK2 –1.0 to +17 V
CLR, EN
• Video signal input pin voltage GREEN, RED, BLUE –1.0 to +15 V
• Operating temperature Topr –10 to +70 °C
• Storage temperature Tstg –30 to +85 °C
Operating Conditions (Vss = 0V)
• Supply voltage
HVDD 13.5 ± 0.5 V
VVDD 13.5 ± 0.5 V
• Input pulse voltage (Vp-p of all input pins except video signal input pins)
Vin 3.0V or more
LCX009AKB
Pin Description
Pin
No.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
Symbol Description
COM
GREEN
RED
BLUE
HVDD
HCK1
HCK2
HST
Common voltage of panel
Video signal (G) to panel
Video signal (R) to panel
Video signal (B) to panel
Power supply for H driver
Clock pulse for
H shift register drive
Clock pulse for
H shift register drive
Start pulse for
H shift register drive
Pin
No.
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
Symbol Description
RGT
CLR
EN
VCK1
VCK2
VST
Vss
VVDD
Drive direction pulse for H shift
register (H: normal, L: reverse)
Improvement pulse
for uniformity
Enable pulse for gate selection
Clock pulse for
V shift register drive
Clock pulse for
V shift register drive
Start pulse for
V shift register drive
GND (H, V drivers)
Power supply for V driver
– 3 –
Page 4
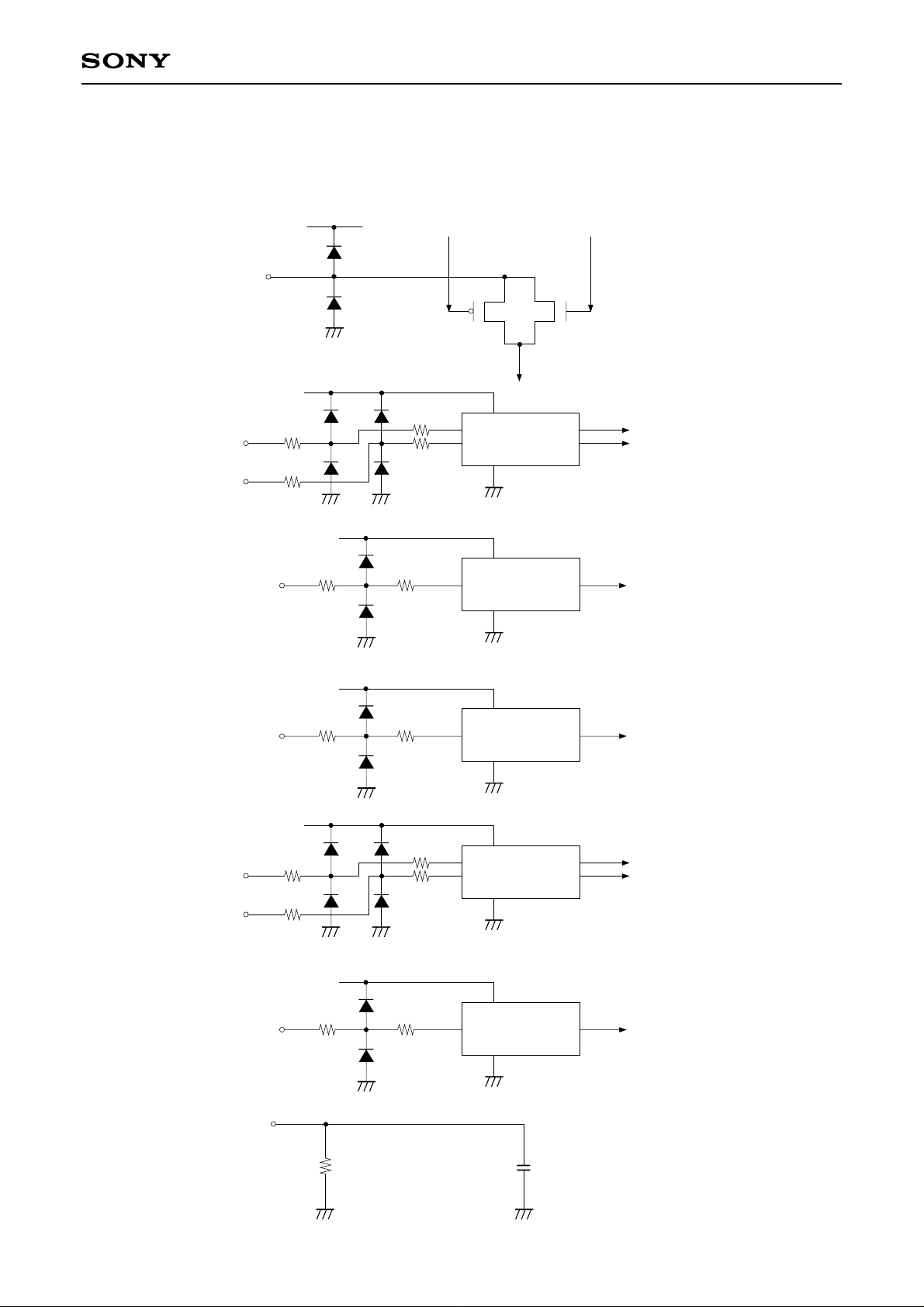
LCX009AKB
Input Equivalent Circuit
To prevent static charges, protective diodes are provided for each pin except the power supply. In addition,
protective resistors are added to all pins except video signal input. The equivalent circuit of each input pin is
shown below. (The resistor value: typ.)
(1) Video signal input
From H driver
Input
HV
DD
(2) HCK1, HCK2
(3) HST
(4) RGT
(5) VCK1, VCK2
HCK1
HCK2
VCK1
VCK2
Input
Input
HV
250Ω
250Ω
VV
2.5kΩ
DD
DD
1kΩ
HV
HV
DD
DD
250Ω250Ω
2.5kΩ2.5kΩ
250Ω
250Ω
2.5kΩ
1kΩ
Signal line
Level conversion
circuit
(2-phase input)
Level conversion
circuit
(single-phase input)
Level conversion
circuit
(single-phase input)
Level conversion
circuit
(2-phase input)
(6) VST, CLR, EN
(7) COM
Input
Input
VV
DD
1MΩ
2.5kΩ2.5kΩ
Level conversion
circuit
(single-phase input)
LC
– 4 –
Page 5
LCX009AKB
Level Conversion Circuit
The LCX009AKB has a built-in level conversion circuit in the clock input unit located inside the panel. The
circuit voltage is stepped up to 13.5V. This level conversion circuit meets the specifications of a 3.0V to 5.0V
power supply of the externally-driven IC mainly. However, this circuit can operate even with a 12V power
supply of the IC.
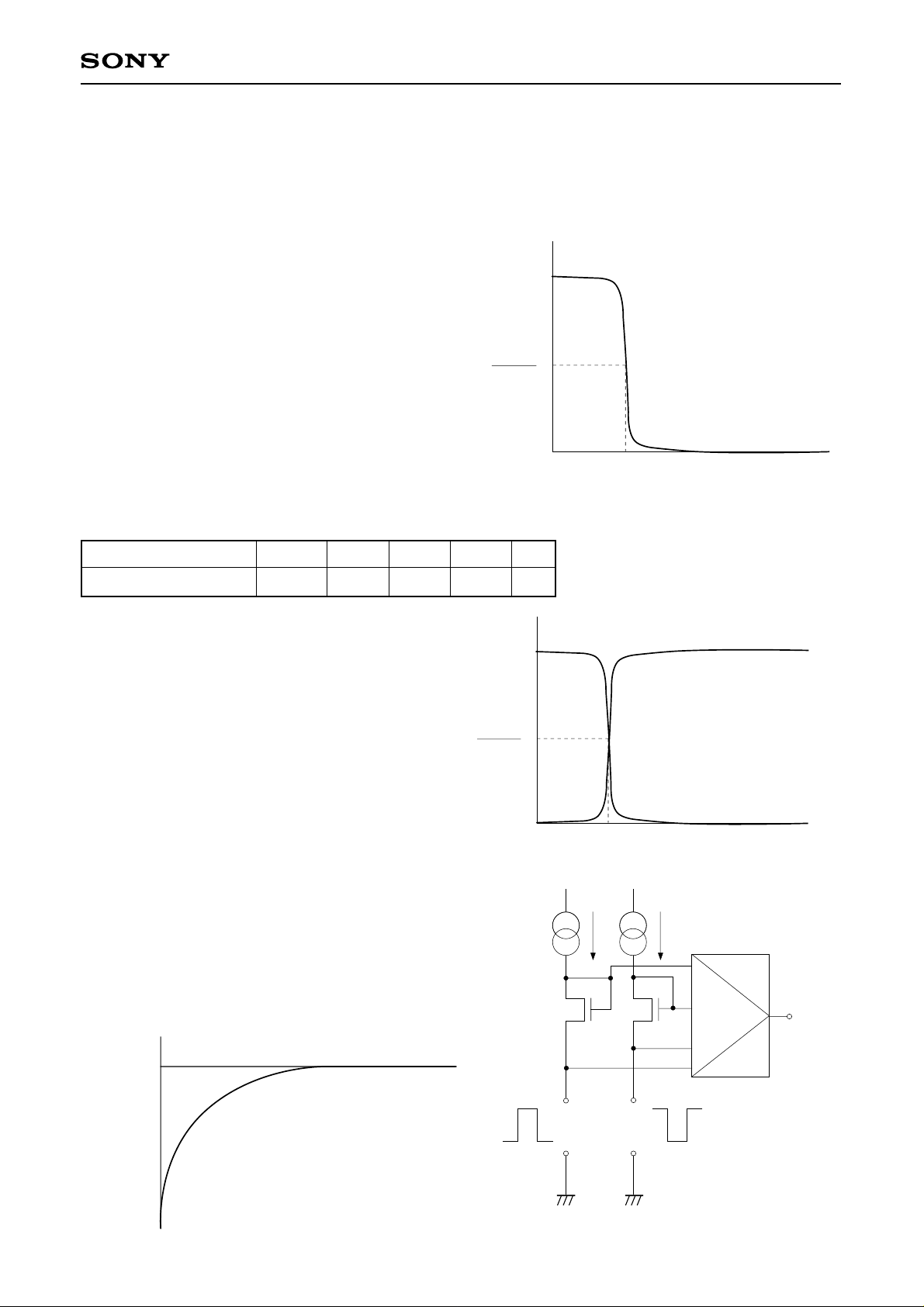
1. I/O characteristics of level conversion circuit
HVDD
(For a single-phase input unit)
An example of the I/O voltage characteristics of a
level conversion circuit is shown in the figure to the
right. The input voltage value that becomes half the
HVDD
2
Example of single-phase
I/O characteristics
output voltage (after voltage conversion) is defined
as Vth.
Output voltage (inside panel)
The Vth value varies depending on the HVDD and
VVDD voltages.
The Vth values under standard conditions are
Vth
Input voltage [V]
indicated in the table below. (HST, VST, EN, CLR, and RGT in the case of a single-phase input)
HVDD = VVDD = 13.5V
Item
Symbol Min. Typ. Max. Unit
Vth voltage of circuit Vth 0.35 1.50 2.70 V
(For a differential input unit)
An example of I/O voltage characteristics of a
HVDD
level conversion circuit for a differential input is
shown in the figure to the right. Although the
characteristics, including those of the Vth voltage,
are basically the same as those for a singlephased input, the two-phased input phase is
defined. (Refer to clock timing conditions.)
HVDD
2
Output voltage (inside panel)
Example of differential
I/O characteristics
2. Current characteristics at the input pin of level
conversion circuit
A slight pull-in current is generated at the input
pin of the level conversion circuit. (The equivalent
circuit diagram is shown to the right.) The current
volume increases as the voltage at the input pin
decreases, and is maximized when the pin is
grounded.) (Electrical characteristics are defined
by the grounded input.)
0
0
Input pin current
Max. value
Input pin voltage [V]
Pull-in current
characteristics at the
input pin
10
– 5 –
HCK1
input
Vth
Input voltage [V]
VDD
Output
HCK2
input
Level conversion equivalent circuit
Page 6
Input Signals
1. Input signal voltage conditions (Vss = 0V)
LCX009AKB
Item
(Low)
Symbol Min. Typ. Max. Unit
VHIL
H driver input voltage
(High)
(Low)
VHIH
VVIL
V driver input voltage
(High)
Video signal center voltage
Video signal input range
∗1
Common voltage of panel
∗1
Video input signal should be symmetrical to VVC.
VVIH
VVC
Vsig
Vcom
2. Clock timing conditions (Ta = 25°C)
Item Symbol Min. Typ. Max. Unit
Hst rise time
Hst fall time
HST
Hst data set-up time
Hst data hold time
Hckn∗2rise time
–0.3
3.0
–0.3
3.0
5.8
VVC – 4.5
VVC – 0.55
trHst
tfHst
tdHst
thHst
trHckn
0.0
5.0
0.0
5.0
6.0
VVC – 0.40
–100
–200
0.3
5.5
0.3
5.5
6.2
VVC + 4.5
VVC – 0.25
60
–120
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
30
30
100
–50
30
HCK
CLR
VST
VCK
EN
Hckn∗2fall time
Hck1 fall to Hck2 rise time
Hck1 rise to Hck2 fall time
Clr rise time
Clr fall time
Clr pulse width
Clr fall to Hst rise time
Vst rise time
Vst fall time
Vst data set-up time
Vst data hold time
Vckn∗2rise time
Vckn∗2fall time
Vck1 fall to Vck2 rise time
Vck1 rise to Vck2 fall time
En rise time
En fall time
Vck2 rise to En fall time
tfHckn
to1Hck
to2Hck
trClr
tfClr
twClr
toHst
trVst
tfVst
tdVst
thVst
trVckn
tfVckn
to1Vck
to2Vck
trEn
tfEn
tdVck2
–15
–15
3400
1850
–50
–50
–20
–20
–20
0
0
3500
1950
32
–32
0
0
0
30
15
15
100
100
3600
2050
100
100
50
–20
100
100
20
20
100
100
20
ns
µs
ns
Vck1 rise to En rise time
∗2
Hckn and Vckn mean Hck1, Hck2 and Vck1, Vck2. (fHckn = 2.75MHz, fVckn = 7.81kHz)
tdVck1
–20
– 6 –
0
20
Page 7
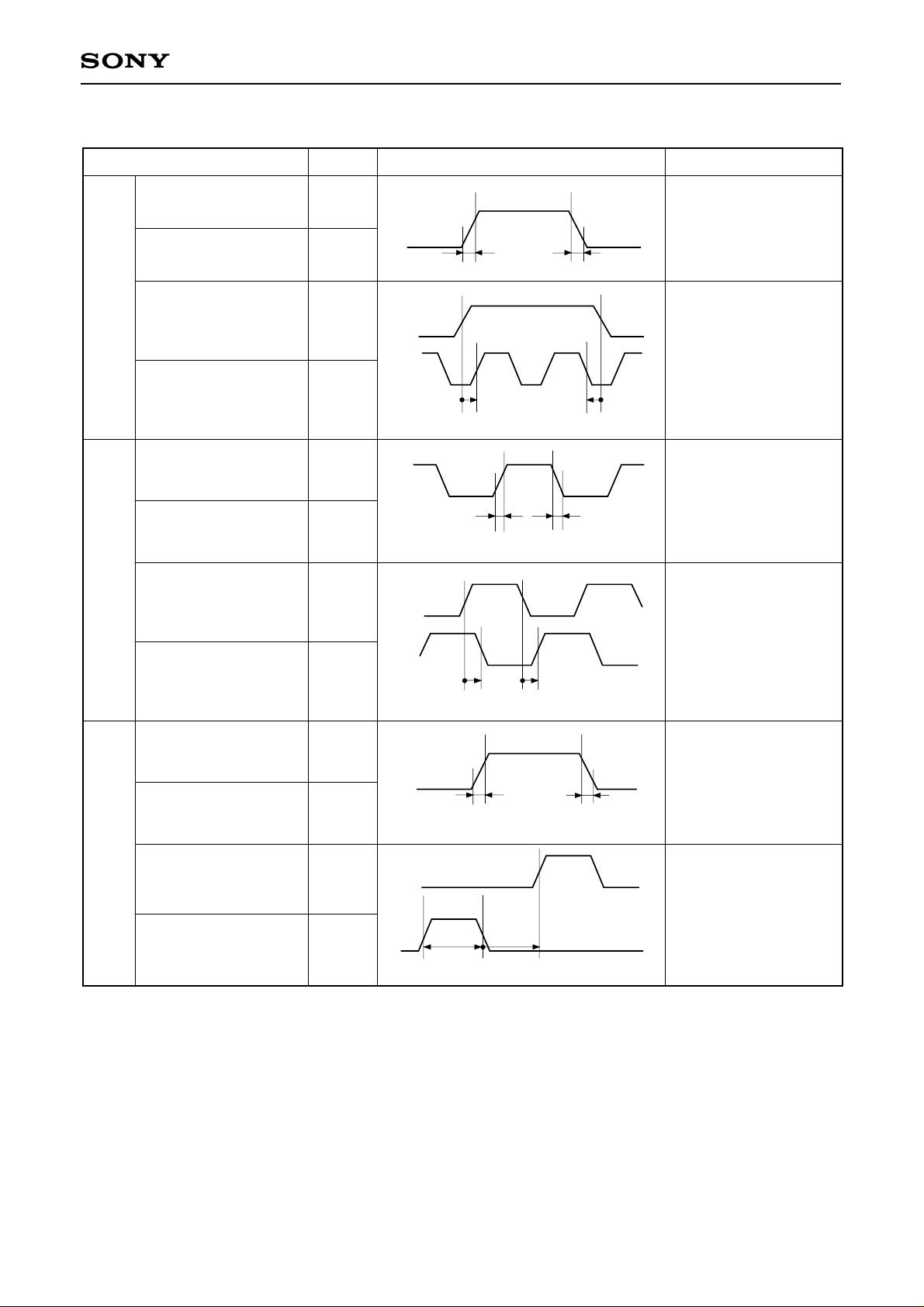
<Horizontal Shift Register Driving Waveform>
Item Symbol Waveform Conditions
LCX009AKB
HST
HCK
Hst rise time
Hst fall time
Hst data set-up time
Hst data hold time
Hckn∗2rise time
Hckn∗2fall time
Hck1 fall to
Hck2 rise time
Hck1 rise to
Hck2 fall time
trHst
tfHst
tdHst
thHst
trHckn
tfHckn
to1Hck
to2Hck
Hst
∗3
Hst
Hck1
Hckn
∗3
Hck1
Hck2
90%
10%
trHst tfHst
50%
50%
tdHst thHst
90%
∗2
10%
trHckn tfHckn
50%
50%
to2Hck to1Hck
90%
50%
50%
50%
90%
10%
10%
50%
∗2
• Hckn
duty cycle 50%
to1Hck = 0ns
to2Hck = 0ns
∗2
• Hckn
duty cycle 50%
to1Hck = 0ns
to2Hck = 0ns
• Hckn
∗2
duty cycle 50%
to1Hck = 0ns
to2Hck = 0ns
tdHst = 60ns
thHst = –120ns
• tdHst = 60ns
thHst = –120ns
CLR
Clr rise time
Clr fall time
Clr pulse width
Clr fall to
Hst rise time
trClr
tfClr
twClr
toHst
Clr
Hst
Clr
90%
10%
trClr tfClr
50%
50% 50%
twClr toHst
90%
10%
∗2
• Hckn
duty cycle 50%
to1Hck = 0ns
to2Hck = 0ns
∗2
• Hckn
duty cycle 50%
to1Hck = 0ns
to2Hck = 0ns
– 7 –
Page 8

<Vertical Shift Register Driving Waveform>
Item Symbol Waveform Conditions
LCX009AKB
VST
VCK
Vst rise time
Vst fall time
Vst data set-up time
Vst data hold time
Vckn∗2rise time
Vckn∗2fall time
Vck1 fall to
Vck2 rise time
Vck1 rise to
Vck2 fall time
trVst
tfVst
tdVst
thVst
trVckn
tfVckn
to1Vck
to2Vck
Vst
∗3
Vst
Vck1
Vckn
∗3
Vck1
Vck2
90%
10%
trVst tfVst
50%
50%
tdVst thVst
90%
10%
trVckn tfVckn
50%
50%
to2Vck to1Vck
90%
50%
50%
50%
90%
10%
10%
50%
∗2
• Vckn
duty cycle 50%
to1Vck = 0ns
to2Vck = 0ns
∗2
• Vckn
duty cycle 50%
to1Vck = 0ns
to2Vck = 0ns
∗2
• Vckn
duty cycle 50%
to1Vck = 0ns
to2Vck = 0ns
tdVst = 32µs
thVst = –32µs
• tdVst = 32µs
thVst = –32µs
En rise time
En fall time
EN
Vck2 rise to
En fall time
Vck1 rise to
En rise time
∗3
Definitions: The right-pointing arrow ( ) means +.
trEn
tfEn
tdVck2
tdVck1
∗3
Vck2
En
The left-pointing arrow ( ) means –.
The black dot at an arrow ( ) indicates the start of measurement.
90%
En
tfEn trEn
50%
50%
tdVck2 tdVck1
10%
10%
50%
50%
90%
∗2
• Vckn
duty cycle 50%
to1Vck = 0ns
to2Vck = 0ns
∗2
• Vckn
duty cycle 50%
to1Vck = 0ns
to2Vck = 0ns
– 8 –
Page 9

Electrical Characteristics (Ta = 25°C, HVDD = 13.5V, VVDD = 13.5V)
1. Horizontal drivers
LCX009AKB
Item
Input pin capacitance Hckn
Hst
Input pin current Hck1
Hck2
Hst
Rgt
Video signal input pin capacitance
Current consumption
2. Vertical drivers
Item
Input pin capacitance Vckn
Vst
Input pin current Vck1
Vck2
Symbol Min. Typ. Max. Unit Condition
CHckn
CHst
IHck1
IHck2
IHst
IRgt
Csig
IH
–200
–500
–300
–100
5
5
–60
–260
–100
–15
45
3
10
10
60
4
pF
pF
µA
µA
µA
µA
pF
mA
Hck1 = GND
Hck2 = GND
Hst = GND
Rgt = GND
Hckn: Hck1, Hck2 (2.75MHz)
Symbol Min. Typ. Max. Unit Condition
CVckn
CVst
IVck1
IVck2
–100
–400
5
5
–30
–200
10
10
pF
pF
µA
µA
Vck1 = GND
Vck2 = GND
Vst
En
Clr
Current consumption
IVst,
IEn,
IClr
IV
–100
–15
400
1000
µA
Vst, En, Clr = GND
µA
Vckn: V ck1 , V ck2 (7.87kHz)
3. Total power consumption of the panel
Item
Total power consumption of the panel (NTSC)
Symbol Min. Typ. Max. Unit
PWR 45 70 mW
4. COM input resistance
Item
Symbol Min. Typ. Max. Unit
COM – Vss input resistance Rcom 0.5 1 MΩ
– 9 –
Page 10

LCX009AKB
Electro-optical Characteristics (Ta = 25°C, NTSC mode)
Item
Contrast ratio
Optical transmittance
Chromaticity
V90
V – T
characteristics
V50
V10
Half tone color
reproduction range
ON time
Response time
OFF time
Flicker
Image retention time
Optimum Vcom voltage
Symbol
25°C
60°C
CR25
CR60
T
R
X
Y
G
X
Y
B
X
Y
25°C
60°C
25°C
60°C
25°C
60°C
R vs. G
B vs. G
0°C
25°C
0°C
25°C
60°C
60min.
Rx
Ry
Gx
Gy
Bx
By
V90-25
V90-60
V50-25
V50-60
V10-25
V10-60
V50RG
V50BG
ton0
ton25
toff0
toff25
F
YT60
Vcomopt
Measurement
method
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
Min. Typ.
80
80
2.7
0.560
0.300
0.275
0.541
0.120
0.040
1.1
1.0
1.5
1.4
2.2
2.1
—
—
—
200
200
3.5
0.630
0.345
0.310
0.595
0.148
0.088
1.6
1.3
2.0
1.8
2.7
2.5
–0.10
0.10
25
—
—
—
—
—
5.45
65
20
—
—
5.60
8
Max. Unit
—
—
—
—
%
0.670
0.390
0.347
0.650
CIE
standards
0.187
0.122
2.2
2.1
2.5
V
2.4
3.2
3.1
–0.25
V
0.45
100
40
ms
150
60
–40
20
5.75
dB
s
V
– 10 –
Page 11

<Electro-optical Characteristics Measurement>
Basic measurement conditions
(1) Driving voltage
HVDD = 13.5V, VVDD = 13.5V
VVC = 6.0V, Vcom = 5.6V
(2) Measurement temperature
25°C unless otherwise specified.
(3) Measurement point
One point in the center of screen unless otherwise specified.
(4) Measurement systems
Two types of measurement system are used as shown below.
(5) RGB input signal voltage (Vsig)
Vsig = 6 ± VAC [V] (VAC: signal amplitude)
∗ Measurement system I
LCX009AKB
Back Light
3.5mm
LCD panel
Luminance
Meter
∗ Measurement system II
Optical fiber
Light receptor lens
Drive Circuit
Light
Source
LCD panel
1. Contrast Ratio
Contrast Ratio (CR) is given by the following formula (1).
Measurement
Equipment
Back light: color temperature 6500K, +0.004uV (25°C)
∗
Back light spectrum (reference) is listed on another page.
Light Detector
Measurement
Equipment
L (White)
CR=
L (Black)
... (1)
L (White): Surface luminance of the TFT-LCD panel at the RGB signal amplitude VAC = 0.5V.
L (Black): Surface luminance of the panel at VAC = 4.5V
Both luminosities are measured by System I.
– 11 –
Page 12

2. Optical Transmittance
Optical Transmittance (T) is given by the following formula (2).
LCX009AKB
T = × 100 [%] ... (2)
Luminance of Back Light
L (White)
L (White) is the same expression as defined in the "Contrast Ratio" section.
3. Chromaticity
Chromaticity of the panels are measured by System I. Raster modes of each color are defined by the
representations at the input signal amplitude conditions shown in the table below. System I uses
Chromaticity of x and y on the CIE standards here.
Signal amplitudes (VAC) supplied to each input
R input G input B input
R
G
0.5
4.5
4.5
0.5
4.5
4.5
Raster
B
4.5
4.5
0.5
(Unit: V)
4. V-T Characteristics
V-T characteristics, the relationship between signal
amplitude and the transmittance of the panels, are
measured by System II. V90, V50 and V10 correspond
90
to the each voltage which defines 90%, 50% and 10%
of transmittance respectively.
50
5. Half Tone Color Reproduction Range
Half tone color reproduction range of the LCD panels is
characterized by the differences between the V-T
characteristics of R, G and B. The differences of these
V-T characteristics are measured by System II. System
II defines signal voltages of each R, G, B raster modes
which correspond to 50% of transmittance, V50R, V50G
and V50B respectively. V50RG and V50BG, the voltage
differences between V50R and V50G, V50B and V50G, are
simply given by the following formula (3) and (4)
respectively.
V50RG = V50R – V50G ... (3)
V50BG = V50B – V50G ... (4)
Transmittance [%]
10
100
50
R raster
Transmittance [%]
0
V90 V50 V10
VAC – Signal amplitude [V]
V50RG
V50BG
G raster
50R V50B
V
V50G
VAC – Signal amplitude [V]
B raster
– 12 –
Page 13

LCX009AKB
6. Response Time
Input signal
Response time ton and toff are defined by
the formula (5) and (6) respectively.
ton = t1 – tON ... (5)
toff = t2 – tOFF ... (6)
4.5V
6V
0.5V
t1: time which gives 10% transmittance of
the panel.
t2: time which gives 90% transmittance of
the panel.
The relationships between t1, t2, tON and
tOFF are shown in the right figure.
0V
Light transmission
output waveform
100%
90%
10%
0%
tON t1
ton
tOFF t2
toff
7. Flicker
Flicker (F) is given by the formula (7). DC and AC (NTSC: 30Hz, rms, PAL: 25Hz, rms) components of the
panel output signal for gray raster∗mode are measured by a DC voltmeter and a spectrum analyzer in
System II.
component
AC
F [dB] = 20 log
{}
DC component
(7)
...
∗
R, G, B input signal condition for gray raster mode is given by
Vsig = 6 ± V50 [V]
where: V50 is the signal amplitude which gives 50% of
transmittance in V-T curve.
8. Image Retention Time
Image retention time is given by the following procedures:
Apply monoscope signal to the LCD panel for 60 minutes and then change monoscope signal∗to gray scale
signal (Vsig = 6 ± VAC (V); VAC = 3 to 4V) so as to give the maximum image retention. Hold input signal VAC.
The time of the residual image to disappear gives the image retention time.
∗
Monoscope signal conditions:
Black level
Vsig = 6 ± 4.5 or 6 ±2.0 [V]
(shown in the right figure)
Vcom = 5.6V
4.5V
2.0V
6V
White level
2.0V
4.5V
0V
– 13 –
Vsig waveform
Page 14

9. Method of Measuring the Optimum Vcom
There are two methods of measuring the optimum Vcom using the photoelectric element.
9-1. Method of Measuring Flicker
In the field invert drive mode, adjust the flicker level of the half tone (Vsig = 1.5 to 2.5V) using the
photoelectric element and oscilloscope so that its 30Hz component becomes minimum. The Vcom value
at this time is taken to be the optimum Vcom.
9-2. Method of Measuring Contrast
In the normal 1H invert drive mode, adjust the optical output voltage of the half tone (Vsig = 1.5 to 2.5V) so
that it becomes minimum. The Vcom value at this time is taken to be the optimum Vcom.
Example of Back Light Spectrum (Reference)
LCX009AKB
0.4
0.3
0.2
0.1
0
400 500 600 700
Wavelength 380 – 780 [nm]
– 14 –
Page 15

Description of Operation
1. Color Coding
Color filters are coded in a delta arrangement.
The shaded area is used for the dark border around the display.
LCX009AKB
Gate SW
dummy 1 to 4
B R G B R G B R G B R G B R G B R
B R G B R G B R G B R G B R G B R
B R G B R G B R G B R G B R G B R
B R G B R G B R G B R G B R G B R
Gate SW Gate SW Gate SW Gate SW
Active area
Gate SW
dummy 5 to 8
2
GRBGRBGRBGRBGRBGR
GRBGRBGRBGRBGRBGR
GRBGRBGRBGRBGRBGR
GRBGRBGRBGRBGRBGR
225
228
Photo-shielding
B R G B R G B R G B R G B R G B R
RBGRBGRBGRBGRBGR
827
14 800 13
G
1
– 15 –
Page 16

LCX009AKB
2. LCD Panel Operations
• A vertical driver, which consists of vertical shift registers, enable-gates and buffers, applies a selected pulse
to every 225 gate lines sequentially in every single horizontal scanning period. A vertical shift register scans
the gate lines from the top to bottom of the panel.
• The selected pulse is delivered when the enable pin turns to High level. PAL mode images are displayed by
controlling the enable and VCK1, VCK2 pins. The enable pin should be High when not in use.
• A horizontal driver, which consists of horizontal shift registers, gates and CMOS sample-and-hold circuit,
applies selected pulses to every 800 signal electrodes sequentially in a single horizontal scanning period.
• Scanning direction of horizontal shift register can be switched with RGT pin.Scanning direction is left to right
for RGT pin at High level; and right to left for RGT pin at Low level.(These scanning directions are from a
front view.) Normally, set to High level.
• Vertical and horizontal drivers address one pixel, and then dot Thin Film Transistors (TFTs; two TFTs for one
dot) turn on to apply a video signal to the dot. The same procedures lead to the entire 225 × 800 dots to
display a picture in a single vertical scanning period.
• Pixels are arranged in a delta pattern, where sets of RGB pixels are positioned with 1.5-dot offset against
juxtaposed horizontal line. For this reason, 1.5-dot offset of a horizontal driver output pulse against horizontal
synchronized pulse is required to apply a video signal to each dot properly. 1 H reversed displaying mode is
required to apply video signal to the panel.
• The CLR pin is provided to eliminate the shading effect caused by the coupling of selected pulses. While
maintaining the CLR at High level, the VVDD potential drops to approximately 8.5V. This pin should be
grounded when not in use.
• The video signal must be input with polarity-inverted system in every horizontal cycle.
• Timing diagrams of the vertical and the horizontal right-direction scanning (RGT = High level) display cycle
are shown below.
Hck1 and Hck2 should be exchanged to display the left-direction horizontal scanning (RGT = Low level). This
exchange enables the center of the image to be fixed by eliminating offsets.
(1) Vertical display cycle
VD
Vst
Vck1
1 2 224 225
Vck2
(2) Horizontal display cycle (right-direction scanning)
BLK
Hst
Hck1
Hck2
The horizontal display cycle consists of 800/3 = 267 clock pulses because of RGB simultaneous sampling∗.
∗
Refer to Description of Operation "3. RGB Simultaneous Sampling''
123456
Vertical display 225H (14.3ms)
270
271
Horizontal display cycle (48.4µs)
– 16 –
Page 17

LCX009AKB
3. RGB Simultaneous Sampling
Horizontal driver performs R, G and B signal sampling simultaneously, which requires the phase matching
between R, G, B signals to prevent horizontal resolution from deteriorating. The phase matching by an
external signal delaying circuit is needed before applying video signal to the LCD panel.
Two methods are applied for the delaying procedure: Sample-and-hold and Delay circuit. These two block
diagrams are as follows.
The LCX009AKB has a right/left inverse function. The following phase relationship diagram indicates the
phase setting for the right-direction scanning (RGT = High level). For the left-direction scanning (RGT = Low
level), the phase setting should be inverted for B and G signals.
(1) Sample-and-hold (right-direction scanning)
B
R
G
S/H S/H AC Amp
CKB
S/H
CKR
CKG
S/H AC Amp
CKG
S/H AC Amp
CKG
4
3
2
<Phase relationship of delaying sample-and-hold pulses> (right-direction scanning)
HCKn
CKB
CKR
BLUE
RED
LCX009AKB
GREEN
CKG
(2) Delay circuit (right-direction scanning)
B
R
G
Delay Delay AC Amp
Delay AC Amp
AC Amp
– 17 –
4
3
2
BLUE
RED
LCX009AKB
GREEN
Page 18

Example of Color Filter Spectrum (Reference)
100
80
LCX009AKB
Color Filter Spectrum
R
G
60
Transmittance [%]
40
20
B
0
400 500 600 700
Wavelength [nm]
– 18 –
Page 19

Color Display System Block Diagram (1)
An example of single-chip display system is shown below.
+12V +5V +13.5V
LCX009AKB
Composite video
Y/C
Y/color difference
CXA1854R
RED
GREEN
BLUE
HST
HCK1
HCK2
VST
VCK1
VCK2
EN
VCOM
LCD panel
NTSC/PAL
LCX009AKB
(Refer to CXD1845R data sheet.)
CLR
RGT
– 19 –
Page 20

Color Display System Block Diagram (2)
An example of dual-chip display system is shown below.
+12V +5V +13.5V
LCX009AKB
Composite video
Y/C
Y/color difference
Decoder/Driver
CXA1785AR
FRPSYNC
TG
CXD2411R
+5V
RED
GREEN
BLUE
Hst
Hck1
Hck2
Vst
Vck1
Vck2
En
Clr
Vcom
LCD Panel
NTSC/PAL
LCX009AKB
(Refer to CXD2411R data sheet.)
RGT
– 20 –
Page 21

Notes on Handling
(1) Static charge prevention
Be sure to take following protective measures. TFT-LCD panels are easily damaged by static charge.
a) Use non-chargeable gloves, or simply use bare hands.
b) Use an earth-band when handling.
c) Do not touch any electrodes of a panel.
d) Wear non-chargeable clothes and conductive shoes.
e) Install conductive mat on the working floor and working table.
f) Keep panels away from any charged materials.
g) Use ionized air to discharge the panels.
(2) Protection from dust and dirt
a) Operate in clean environment.
b) When delivered, a surface of a panel (Polarizer) is covered by a protective sheet. Peel off the protective
sheet carefully not to damage the panel.
c) Do not touch the surface of a panel. The surface is easily scratched. When cleaning, use a clean-room
wiper with isopropyl alcohol. Be careful not to leave stain on the surface.
d) Use ionized air to blow off dust at a panel.
LCX009AKB
(3) Other handling precautions
a) Do not twist or bend the flexible PC board especially at the connecting region because the board is easily
deformed.
b) Do not drop a panel.
c) Do not twist or bend a panel or a panel frame.
d) Keep a panel away from heat source.
e) Do not dampen a panel with water or other solvents.
f) Avoid to store or to use a panel in high temperature or in high humidity, which results in panel damages.
– 21 –
Page 22

Package Outline Unit: mm
LCX009AKB
18.4 ± 0.3
sc
Active Area
CK1
Thickness of the connector 0.3 ± 0.05
8.5 ± 0.05
1.3 ± 0.3
4
(29.0)
(40.2)
1
61.2 ± 0.9
2
4-R1.0
21.0 ± 0.15
32.2 ± 0.8
Incident
4.0 ± 0.5
3
Reinforcing board
5
6
light
6
Active Area
22.0 ± 0.15
P 0.5 ± 0.02 × 15 = 7.5 ± 0.03
electrode (enlarged)
(10.7)
9.5 ± 0.25
(14.4)
11.0 ± 0.25
0.35
0.5 ± 0.1
PIN16PIN1
2.9 ± 0.15
+ 0.04
– 0.03
0.5 ± 0.15
3.0 ± 0.3
No
1
2
3
4
5
6
Description
F P C
Molding material
Outside frame
Reinforcing board
Reinforcing material
Polarizing film
weight 2g
– 22 –
 Loading...
Loading...