Page 1
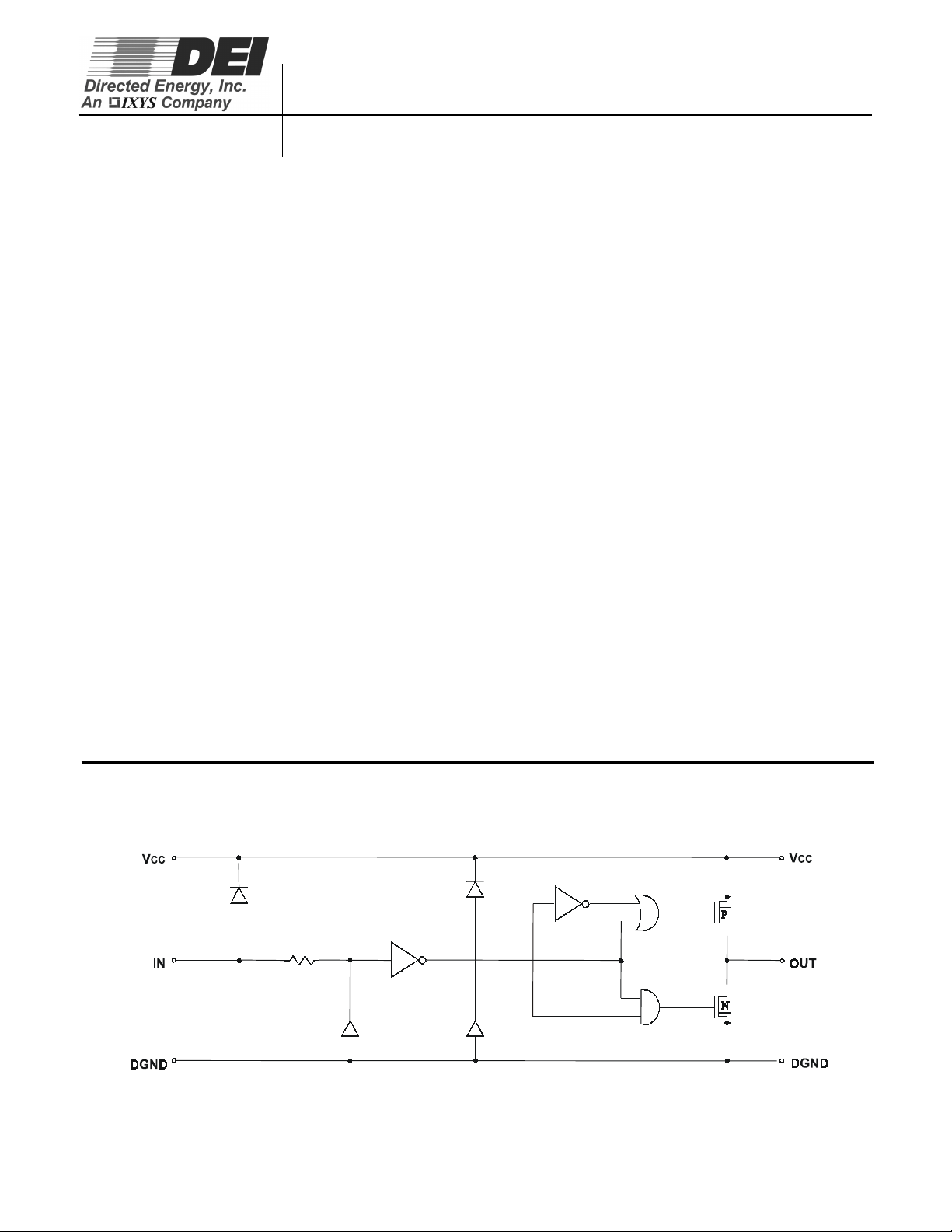
DEIC420
20 Ampere Low-Side Ultrafast RF MOSFET Driver
Features
• Built using the advantages and compatibility
of CMOS and IXYS HDMOSTM processes
• Latch-Up Protected
• High Peak Output Current: 20A Peak
• Wide Operating Range: 8V to 30V
• Rise And Fall Times of <4ns
• Minimum Pulse Width Of 8ns
• High Capacitive Load
Drive Capability: 4nF in <4ns
• Matched Rise And Fall Times
• 32ns Input To Output Delay Time
• Low Output Impedance
• Low Quiescent Supply Currentt
Applications
• Driving RF MOSFETs
• Class D or E Switching Amplifier Drivers
• Multi MHz Switch Mode Power Supplies (SMPS)
• Pulse Generators
• Acoustic Transducer Drivers
• Pulsed Laser Diode Drivers
• DC to DC Converters
• Pulse Transformer Driver
Description
TheDEIC420 is a CMOS high speed high current gate
driver specifically designed to drive MOSFETs in Class D
and E HF RF applications at up to 45MHz, as well as
other applications requiring ultrafast rise and fall times or
short minimum pulse widths. The DEIC420 can source
and sink 20A of peak current while producing voltage rise
and fall times of less than 4ns, and minimum pulse
widths of 8ns. The input of the driver is compatible with
TTL or CMOS and is fully immune to latch up over the
entire operating range. Designed with small internal
delays, cross conduction/current shoot-through is
virtually eliminated in the DEIC420. Its features and wide
safety margin in operating voltage and power make the
DEIC420 unmatched in performance and value.
The DEIC420 is packaged in DEI's low inductance RF
package incorporating DEI's patented
techniques to minimize stray lead inductances for
optimum switching performance. For applications that do
not require the power dissipation of the DEIC420, the
driver is also available in a 28 pin SOIC package. See
the IXDD415SI data sheet for additional information. The
DEIC420 is a surface-mount device, and incorporates
patented RF layout techniques to minimize stray lead
inductances for optimum switching performance.
(1)
DEI U.S. Patent #4,891,686
(1)
RF layout
Figure 1 - DEIC420 Functional Diagram
Copyright © DIRECTED ENERGY, INC. 2001
First Release
Page 2

DEIC420
Absolute Maximum Ratings
Parameter Value
Supply Voltage 30V
All Other Pins
Power Dissipation
T
T
Storage Temperat ure
Soldering L ead Temperature
(10 seconds maximum)
AMBIENT
≤25 oC
CASE
≤25 oC
-0.3V to VCC + 0.3V
2W
100W
-65oC to 150oC
300oC
Electrical Characteristics
Unless otherwise noted, TA = 25 oC, 8V ≤ V
All voltage measurements with respect to DGND. DEIC420 configured as described in Test Conditions.
Symbol Parameter Test Conditions Min Typ Max Units
V
IH
High input voltage 3.5 V
VIL Low input voltage 0.8 V
VIN Input voltage range -5 V
IIN Input current
VOH High output voltage V
VOL Low output voltage 0.025 V
ROH Output resistance
@ Output high
ROL Output resistance
@ Output Low
I
Peak output current VCC = 15V
PEAK
I
Continuous output
DC
current
f
Maximum frequency CL=4nF Vcc=15V 45 MHz
MAX
tR Rise time
tF Fall time
t
On-time propagation
ONDLY
delay
t
Off-time propagation
OFFDLY
delay
P
Minimum pulse width FWHM CL=1nF Vcc=15V
Wmin
(1)
C
(1)
C
(1)
(1)
VCC Power supply voltage 8 15 30 V
ICC Power supply current V
(1)
Refer to Figures 3a and 3b
Specifications Subject To Change Without Notice
≤ 30V .
CC
0V ≤ V
IN
V
≤
I
= 10mA, V
OUT
I
= 10mA, V
OUT
4 A
=1nF Vcc=15V VOH=2V to 12V
L
=4nF Vcc=15V VOH=2V to 12V
C
L
=1nF Vcc=15V VOH=12V to 2V
L
=4nF Vcc=15V VOH=12V to 2V
C
L
C
=4nF Vcc=15V 32 38 ns
L
C
=4nF Vcc=15V 29 35 ns
L
+3V to +3V C
= 3.5V
IN
= 0V
V
IN
= + VCC
V
IN
Parameter Value
Maximum Junction Temperature
Operating Temperature Range
Thermal Impedance (Junction To Case)
θ
JC
CC
= 15V
CC
= 15V 0.4 0.6
CC
-10 10
- .025 V
CC
0.4 0.6
150oC
-40oC to 85oC
0.13oC/W
+ 0.3 V
CC
20 A
3
ns
4
3
ns
3.5
=1nF Vcc=15V
L
8
9
ns
1 0 3
10
10
A
µ
Ω
Ω
ns
ns
ns
mA
A
µ
A
µ
2
Page 3
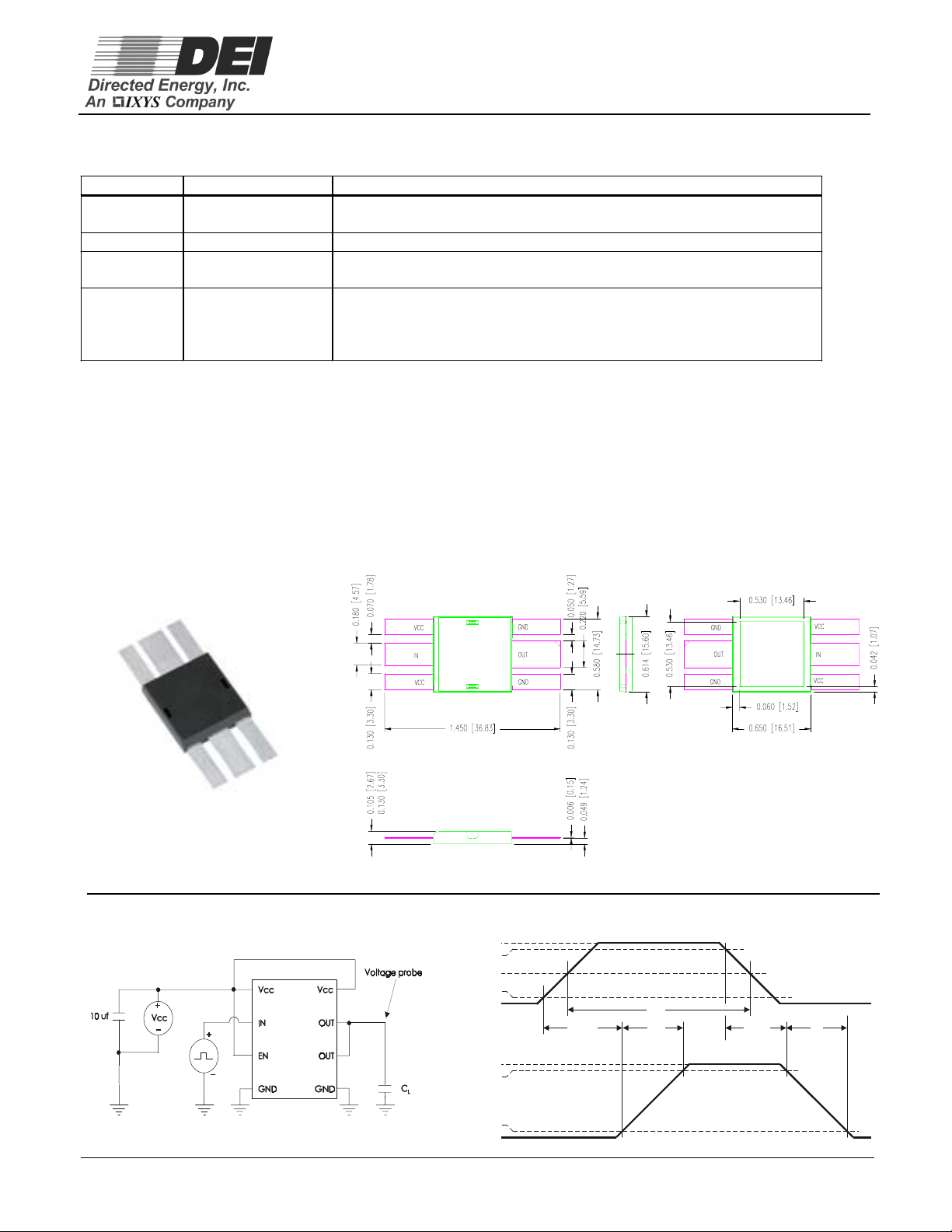
DEIC420
Lead Description - DEIC420
SYMBOL FUNCTION DESCRIPTION
VCC Supply Voltage
IN Input Input signal-TTL or CM OS compatible.
OUT Output
GND Power Ground
Note 1: Operating the device beyond parameters with listed “absolute maximum ratings” may cause permanent
damage to the device. Typical values indicate conditions for which the device is intended to be functional, but do not
guarantee specific performance limits. The guaranteed specifications apply only for the test conditions listed.
Exposure to absolute maximum rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
CAUTION: These devices are sensitive to electrostatic discharge; follow proper ESD procedures
when handling and assembling this component.
Figure 2 - DEIC420 Package Photo And Outline
Positiv e power-supply vol tage input. These leads provide power to
the entire c hip. The range for this voltage is from 8V t o 30V .
Driver Output. For application purposes, this lead is connected,
directly to the Gate of a MOSFET
The system ground l eads. Internal ly c onnected to all circuit ry, these
leads provide ground reference for the entire chip. These leads
should be connected to a low noise analog ground plane for
optim um perf ormance.
Figure 3a - Characteristics Test Diagram
V
IN
Figure 3b - Timing Diagram
5V
90%
INPUT
2.5V
10%
0V
t
ONDLY
Vcc
90%
OUTPUT
10%
0V
3
PW
MIN
t
R
t
OFFDLY
F
t
Page 4

Typical Performance Characteristics
)
DEIC420
Fig. 4
Rise Time (ns)
Fig. 6
Rise Time vs. Load C apacitance
V
= 15V, VOH = 2V To 12V
CC
5
4
3
2
Fig. 5
5
4
3
2
Fall Tim e vs. Load Capacitance
= 15V, VOH = 12V T o 2V
V
CC
Fall Time (ns)
Fig. 7
1
0
1k 2k 3k 4k0
Load Capa citance (pF)
Supply Current vs. Load Capa citance
10
40 MHz
30 MHz
20 MHz
Vcc=15V
1
0
1k 2k 3k 4k0
Load Capacitance (pF)
S up p ly C u rre n t vs . F re q u en c y
6
5
4
Vcc=15V
C
4 nF
2 nF
1 nF
L
= 0
3
2
Supply Current (A)
1
0
10 20 30 40
Frequency (MHz)
Fig. 8
50
40
30
20
Propagation Delay (ns)
10
Propagation Delay Times vs. Input Voltage
=4nF VCC=15V
C
L
t
ONDLY
t
OFFDLY
0
24681012
Input Voltage (V)
1
10 MHz
5 MHz
Supply Current (A)
1 MHz
0.1
0k 1k 2k 3k 4k
Load Capa citance (pF)
Fig. 9
Propagation Delay Times vs. Junction Temperature
= 4nF, VCC = 15V
C
50
45
40
35
30
Time (ns)
25
20
15
10
-40-200 20406080100120
L
Temperature (°C
t
ONDLY
t
OFFDLY
4
Page 5

DEIC420
Fig. 10
50
40
30
20
Propagation Delay (ns)
10
0
8 1012141618
Propagation Delay vs. Supply Voltage
=4nF VIN=5V@ 100kH z
C
L
t
ONDLY
t
OFFDLY
Supply Voltage (V)
Typical Output Waveforms
Unless otherwise noted, all waveforms are taken driving a 1nF load, 1MHz repetition frequency, VCC=15V, Case Temperature = 25°C
Figure 11 3ns Rise Time
Figure 12 3ns Fall Time
Figure 13 <8ns Minimum Pulse Width
Figure 14 1MHz CW Repetition Frequency
5
Page 6

DEIC420
Figure 15 13.56MHz CW Repetition Frequency
Figure 17 - High Frequency Gate Drive Circuit
Figure 16 50MHz Burst Repetition Frequency
6
Page 7

APPLICATIONS INFORMATION
High Frequency Gate Drive Circuit
DEIC420
The circuit diagram in figure 17 is a circuit diagram for a
very high switching speed, high frequency gate driver
circuit using the DEIC420. This is the circuit used in the
EVIC420 Evaluation Board,and is capable of driving a
MOSFET at up to the maximum operating limits of the
DEIC420. The circuit's very high switching speed and
high frequency operation dictates the close attention to
several important issues with respect to circuit design.
The three key elements are circuit loop inductance, Vcc
bypassing and grounding.
Circuit Loop Inductance
Referring to Figure 17, the Vcc to Vcc ground current
path defines the loop which will generate the inductive
term. This loop must be kept as short as possible. The
output lead must be no further than 0.375 inches
(9.5mm) from the gate of the MOSFET. Furthermore the
output ground leads must provide a balanced symmetric
coplanar ground return for optimum operation.
Vcc Bypassing
In order for the circuit to turn the MOSFET on properly,
the DEIC420 must be able to draw up to 20A of current
from the Vcc power supply in 2-6ns (depending upon the
input capacitance of the MOSFET being driven). This
means that there must be very low impedance between
the driver and the power supply. The most common
method of achieving this low impedance is to bypass the
power supply at the driver with a capacitance value that
is at least two orders of magnitude larger than the load
capacitance. Usually, this is achieved by placing two or
three different types of bypassing capacitors, with
complementary impedance curves, very close to the
driver itself. (These capacitors should be carefully
selected, low inductance, low resistance, high-pulse
current-service capacitors). Care should be taken to
keep the lengths of the leads between these bypass
capacitors and the DEIC420 to an absolute minimum.
the DEIC420 and whatever logic is driving it. All three of
these paths should be as low in resistance and
inductance as possible, and thus as short as practical.
Output Lead Inductance
Of equal importance to supply bypassing and grounding
are issues related to the output lead inductance. Every
effort should be made to keep the leads between the
driver and its load as short and wide as possible, and
treated as coplanar transmission lines.
In configurations where the optimum configuration of
circuit layout and bypassing cannot be used, a series
resistance of a few Ohms in the gate lead may be
necessary to prevent ringing.
Heat Sinking
For high power operation, the bottom side metalized
substrate should be placed in compression against an
appropriate heat sink. The substrate is metalized for
improved heat dissipation, and is not electrically
connected to the device or to ground.
See the DEI technical note "DE-Series MOSFET and IC
Mounting Instructions" on the DEI web site at
www.directedenergy.com/apptech.htm for detailed
mounting instructions. The package dimensions of the
DEIC420 are identical to those of the DE-275 MOSFET.
The bypassing should be comprised of several values of
chip capacitors symmetrically placed on ether side of
the IC. Recommended values are .01uF, .47uF chips
and at least two 4.7uF tantalums.
Grounding
In order for the design to turn the load off properly, the
DEIC420 must be able to drain this 20A of current into
an adequate grounding system. There are three paths for
returning current that need to be considered: Path #1 is
between the DEIC420 and its load. Path #2 is between
the DEIC420 and its power supply. Path #3 is between
Directed Energy, Inc.
An IXYS Company
2401 Research Blvd. Ste. 108, Ft. Collins, CO 80526
Tel: 970-493-1901; Fax: 970-493-1903
e-mail: deiinfo@directedenergy.com
www.directedenergy.com
7
Doc #9200-0230 Rev 2
 Loading...
Loading...