Page 1

INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
DATA SH EET
84C44X; 84C64X; 84C84X
8-bit microcontrollers with
OSD and VST
Product specification
Supersedes data of October 1994
File under Integrated Circuits, IC14
1996 Nov 29
Page 2

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
8-bit microcontrollers with OSD and VST 84C44X; 84C64X; 84C84X
CONTENTS
1 FEATURES
1.1 PCF84CXXXA kernel
1.2 Derivative features PCA84C640
2 GENERAL DESCRIPTION
2.1 Important note
3 ORDERING INFORMATION
4 BLOCK DIAGRAM
5 PINNING INFORMATION
6 DIFFERENCES BETWEEN THE TYPES
7 RESET
7.1 Power-on-reset
8 ANALOG CONTROL
8.1 6-bit PWM DACs
9 VST CONTROL
9.1 14-bit PWM DAC
9.2 Coarse adjustment
9.3 Fine adjustment
10 AFC INPUT
11 INPUT/OUTPUT (I/O)
12 ON SCREEN DISPLAY
12.1 Features
12.2 Horizontal display position control
12.3 Vertical display position control
12.4 Clock generator
12.5 Display data registers
12.6 Display control registers
12.7 OSD display position
12.8 OSD character size and colour selection
12.9 Character ROM
13 EMULATION MODE
14 REGISTER MAP
15 LIMITING VALUES
16 DC CHARACTERISTICS
17 AC CHARACTERISTICS
17.1 Characteristic curves
18 PACKAGE OUTLINE
19 SOLDERING
19.1 Introduction
19.2 Soldering by dipping or by wave
19.3 Repairing soldered joints
20 DEFINITIONS
21 LIFE SUPPORT APPLICATIONS
22 PURCHASE OF PHILIPS I2C COMPONENTS
1996 Nov 29 2
Page 3
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
8-bit microcontrollers with OSD and VST 84C44X; 84C64X; 84C84X
1 FEATURES
1.1 PCF84CXXXA kernel
• 8-bit CPU, ROM, RAM, I/O in a single 42 leads shrink
DIL package
• Over 80 instructions all of 1 or 2 cycles
• 29 quasi-bidirectional standard I/O port lines
• Configuration of I/O lines individually selected by mask
• External interrupt
• 2 direct testable inputs T0 and T1
• 8-bit programmable timer/event counter
• 3 single level vectored interrupts (external,
timer/counter, I2C-bus)
• Power-on-reset and low voltage detector
• Single power supply
• 2 power reduction modes: Idle and Stop
• Operating temperature range: −20 to +70 °C
• Silicon gate CMOS fabrication process (SAC2).
1.2 Derivative features PCA84C640
Although the PCA84C640 is specifically referred to
throughout this data sheet, the information applies to all
the devices. The small differences between the 84C640
and the other devices are specified in the text and also
highlighted in Chapter 6.
The PCA84C640 comprises:
• The PCF84CXXXA processor core
• 6 kbytes mask-programmable program ROM
• 128 bytes RAM
• Multi-master I
• AFC input for Voltage Synthesized Tuning
(VST; with 3-bit DAC and comparator)
• On Screen Display (OSD) facility for two rows of
16-characters
• On Screen Display character set of 64 types
INT/T0
2
C-bus interface
• Four programmable display dot sizes
• Half dot character rounding
• Seven colours for each character
• One 14-bit PWM output for VST
• Five 6-bit PWM outputs for analog controls
• Eight port lines with 10 mA LED drive capability
• 18 general purpose bidirectional I/O lines
plus 11 function-combined I/O lines
• 2 direct testable lines
• Programmable VSYNCN and HSYNCN input polarity
• RC oscillator for OSD function.
2 GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The 84C44X; 84C64X; 84C84X denotes the types:
• PCA84C440; 84C441; 84C443; 84C444
• PCA84C640; 84C641; 84C643; 84C644
• PCA84C840; 84C841; 84C843; 84C844.
which are 8-bit microcontrollers with On Screen Display
(OSD) and Voltage Synthesized Tuning (VST) functions.
All are members of the 84CXXX microcontroller family.
There are two oscillator types for the OSD function in the
various types, i.e.,
• RC oscillator: PCA84C440; 84C443; 84C640; 84C643;
84C840; 84C843
• LC oscillator: PCA84C441; 84C444; 84C641; 84C644;
84C841; 84C844.
2.1 Important note
This data sheet details the specific properties of the
PCA84C44X, PCA84C64X and PCA84C84X.
The shared characteristics of the PCA84CXXX family of
microcontrollers are described in the PCF84CXXXA
Family single-chip 8-bit Microcontroller of
IC14”
, which should be read in conjunction with this data
sheet.
“Data Handbook
3 ORDERING INFORMATION
TYPE NUMBER
PCA84C440; 84C443; 84C640; 84C643;
84C840; 84C843
PCA84C441; 84C444; 84C641; 84C644;
84C841; 84C844
1996 Nov 29 3
NAME DESCRIPTION VERSION
SDIP42
PACKAGE
plastic shrink dual in-line
package; 42 leads (600 mil)
TEMPERATURE
RANGE (°C)
SOT270-1 −20 to +70
Page 4

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
8-bit microcontrollers with OSD and VST 84C44X; 84C64X; 84C84X
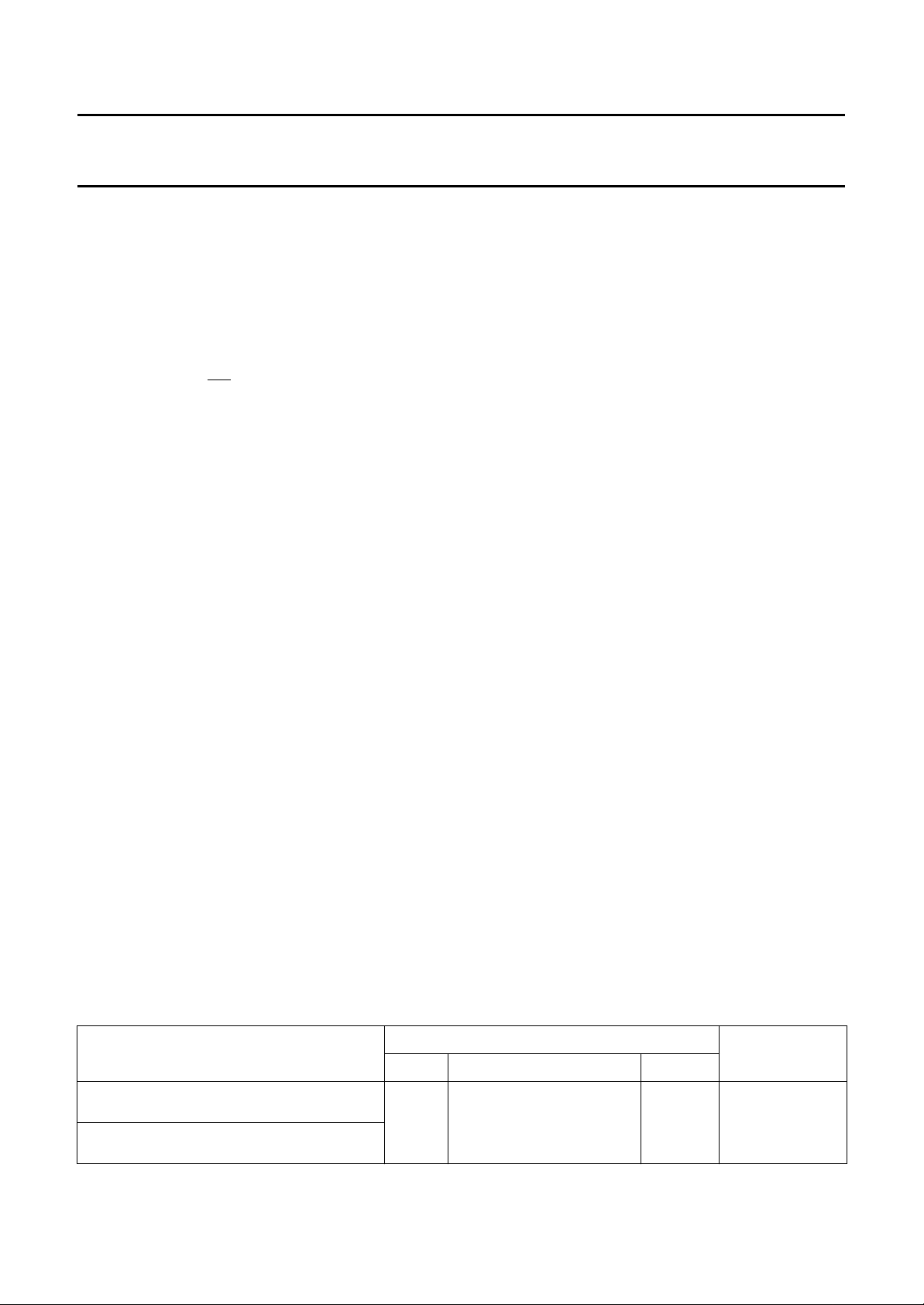
4 BLOCK DIAGRAM
handbook, full pagewidth
XTAL1 (IN)
XTAL2 (OUT)
RESET
TEST/EMU
T1
(6)
8-BIT
TIMER /
EVENT
COUNTER
PARALLEL
I/O
PORTS
5
INT/T0
CPU
84CXXX
core
excluding
ROM/RAM
ROM
8-BIT
I/O
PORTS
888
(1)
6-BIT
DAC
RAM
(2)
14-BIT
DAC
VOB
VOW2
VOW1
ON SCREEN DISPLAY
3-BIT DAC +
COMPARATOR
VOW3
DOSC1
DOSC2
8-bit internal bus
VSYNCN
HSYNCN
(3)
2
I C
INTERFACE
MCD170
P0 P1
(1) 4 kbytes for the PCA84C440; 84C441; 84C443; 84C444.
6 kbytes for the PCA84C640; 84C641; 84C643; 84C644.
8 kbytes for the PCA84C840; 84C841; 84C843; 84C844.
(2) 128 bytes for the PCA84C440; 84C441; 84C443; 84C444; 84C640; 84C641; 84C643; 84C644.
192 bytes for the PCA84C840; 84C841; 84C843; 84C844.
(3) For use with an LC oscillator, only available with the:
PCA84C441; 84C444; 84C641; 84C644; 84C841; 84C844.
2
C-bus interface not available with the:
(4) I
PCA84C443; 84C444; 84C643; 84C644; 84C843; 84C844.
(5) DP1.4 only available for PCA84C440; 84C443; 84C640; 84C643; 84C840; 84C843.
(6) T1 = pin 29 for PCA84C440; 84C443; 84C640; 84C643; 84C840; 84C843.
T1 = pin 34 for PCA84C441; 84C444; 84C641; 84C644; 84C841; 84C844.
DP0 DP1 1 2 3 4 5
(5)
PWM
Fig.1 Block diagram.
1996 Nov 29 4
TDAC AFC SDA SCL
(4)
Page 5

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
8-bit microcontrollers with OSD and VST 84C44X; 84C64X; 84C84X
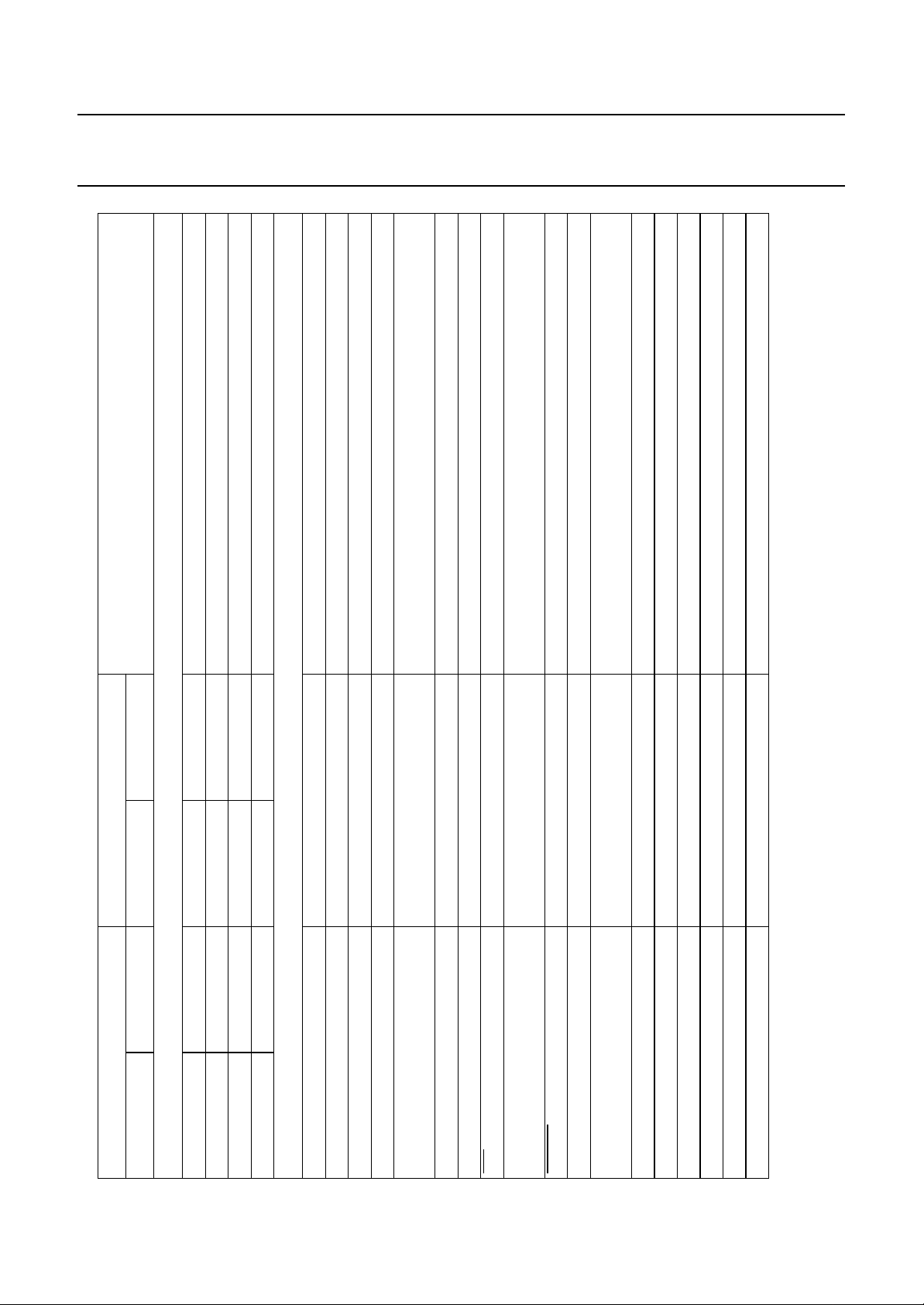
5 PINNING INFORMATION
andbook, halfpage
DP0.0/TDAC
DP0.1/PWM1
DP0.2/PWM2
DP0.3/PWM3
DP0.4/PWM4
DP0.5/PWM5
DP1.7/AFC
P1.0
P1.1
P1.2
P1.3
P1.4
P0.0
P0.1
P0.2
P0.3
P0.4
P0.5
P0.6
P0.7
V
SS
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
PCA84C440
PCA84C443
PCA84C640
PCA84C643
PCA84C840
PCA84C843
MCD172
V
42
DD
41
DP1.0
40
DP0.6/SDA
39
DP0.7/SCL
38
DP1.1
37
DP1.2
36
DP1.3
35
INT/T0
34
DP1.4
33
RESET
32
XTAL2
31
XTAL1
30
TEST/EMU
29
T1
28
DOSC1
27
VSYNCN
26
HSYNCN
25
VOB
24
VOW3
23
VOW2/DP1.5
22
VOW1/DP1.6
handbook, halfpage
DP0.0/TDAC
DP0.1/PWM1
DP0.2/PWM2
DP0.3/PWM3
DP0.4/PWM4
DP0.5/PWM5
DP1.7/AFC
P1.0
P1.1
P1.2
P1.3
P1.4
P0.0
P0.1
P0.2
P0.3
P0.4
P0.5
P0.6
P0.7
V
SS
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
PCA84C441
PCA84C444
PCA84C641
PCA84C644
PCA84C841
PCA84C844
MCD171
V
42
DD
DP1.0
41
DP0.6/SDA
40
DP0.7/SCL
39
DP1.1
38
DP1.2
37
DP1.3
36
35
INT/T0
T1
34
33
RESET
XTAL2
32
XTAL1
31
30
TEST/EMU
DOSC2
29
28
DOSC1
27
VSYNCN
26
HSYNCN
VOB
25
VOW3
24
23
VOW2/DP1.5
VOW1/DP1.6
22
Fig.2 Pinning diagram for PCA84CX40; 84CX43.
1996 Nov 29 5
Fig.3 Pinning diagram for PCA84CX41; 84CX44.
Page 6
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
8-bit microcontrollers with OSD and VST 84C44X; 84C64X; 84C84X
C-bus data line.
C- bus clock line.
2
2
DESCRIPTION
(1)
PIN
(1)
SYMBOL
quasi-bidirectional I/O line or comparator input with 3-bit DAC.
quasi-bidirectional I/O lines or character video output.
operation.
21 Ground.
42 Power supply.
84CX40; 84CX43 84CX41; 84CX44 84CX40; 84CX43 84CX41; 84CX44
Deviating pinning
DP1.0 to DP1.4 DP1.0 to DP1.3 41, 38, 37, 36, 34 41, 38, 37, 36 Derivative Port 1: quasi-bidirectional I/O lines.
T1 T1 29 34 Direct testable pin and event counter input.
DOSC1 − 28 − Connection to RC oscillator of OSD clock.
− DOSC1/DOSC2 − 28, 29 Connections to LC oscillator of OSD clock.
Mutual pinning
DP0.0/TDAC 1 Derivative Port 0: quasi-bidirectional I/O line or 14-bit DAC PWM.
DP0.1 to DP0.5/PWM1 to PWM5 2 to 6 Derivative Port 1: quasi-bidirectional I/O lines or 6-bit DAC PWM.
P1.0 to P1.4 7, 8, 10, 11 and 12 Port 1: quasi-bidirectional I/O lines.
P0.0 to P0.7 13 to 20 Port 0: quasi-bidirectional I/O port.
DP1.7/AFC 9 Derivative Port 1:
Table 1 Pin description
DP0.6/SDA 40 Derivative open drain I/O port or I
1996 Nov 29 6
DP0.7/SCL 39 Derivative open drain I/O port or I
INT/T0 35 External interrupt or direct testable line.
DP1.5 and DP1.6/VOW2 and VOW1 23, 22 Derivative Port 1:
RESET 33 Initialize input, active LOW.
XTAL2, XTAL1 32, 31 Oscillator output or input terminal for system clock.
TEST/EMU 30 Control input for testing and emulation mode. Ground for normal
VSYNCN 27 Vertical synchronous signal input.
HSYNCN 26 Horizontal synchronous signal input.
SS
VOB 25 Blanking output.
VOW3 24 Character video output of OSD.
DD
V
V
84CX41; 84CX44 denotes the types: PCA84C441, PCA84C444, PCA84C641, PCA84C644, PCA84C841 and PCA84C844.
Note
1. 84CX40; 84CX43 denotes the types: PCA84C440, PCA84C443, PCA84C640, PCA84C643, PCA84C840 and PCA84C843.
Page 7
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
8-bit microcontrollers with OSD and VST 84C44X; 84C64X; 84C84X
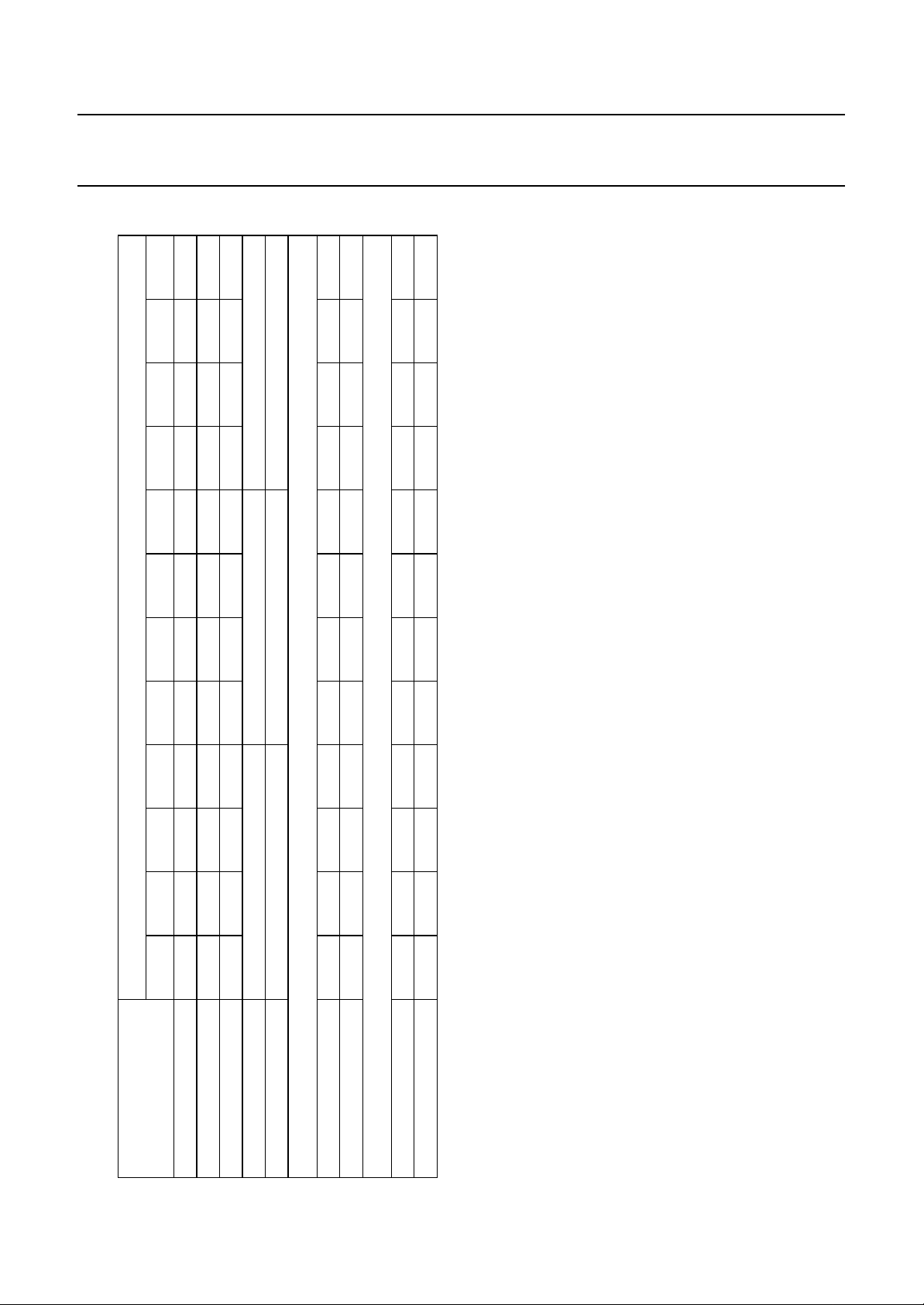
6 DIFFERENCES BETWEEN THE TYPES
PCA...
84C440 84C441 84C443 84C444 84C640 84C641 84C643 84C644 84C840 84C841 84C843 84C844
FEATURE
C-bus interface yes yes no no yes yes no no yes yes no no
2
ROM 4 kbytes 6 kbytes 8 kbytes
RAM 128 bytes 128 bytes 192 bytes
Pin assignment
Pin 29 T1 DOSC2 T1 DOSC2 T1 DOSC2 T1 DOSC2 T1 DOSC2 T1 DOSC2
Pin 34 DP1.4 T1 DP1.4 T1 DP1.4 T1 DP1.4 T1 DP1.4 T1 DP1.4 T1
Register DP1 (bit DP1.4)
Pin yes no yes no yes no yes no yes no yes no
OSD oscillator RC LC RC LC RC LC RC LC RC LC RC LC
General purpose I/O lines 18 17 18 17 18 17 18 17 18 17 18 17
Table 2 Differences between the types PCA84C44X, PCA84C64X and PCA84C84X
In this table: yes = available; no = not available.
1996 Nov 29 7
I
Latch yes no yes no yes no yes no yes no yes no
Page 8

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
8-bit microcontrollers with OSD and VST 84C44X; 84C64X; 84C84X
7 RESET
The RESET pin (active LOW input) is used to initialize the
microcontroller to a defined state. The Reset configuration
is shown in Fig.5.
V
ndbook, halfpage
R ≤ 100 kΩ
RESET
C
MCD174
DD
V
SS
Fig.4 External components for RESET pin.
7.1 Power-on-reset
The Power-on-reset circuit monitors the voltage level of
VDD. If VDD remains below the internal reference voltage
level V
When VDD rises above V
(typically 1.3 V), the oscillator is inhibited.
ref
, the oscillator is released and
ref
the internal reset is active for a period of td (typically
50 µs).
Considering the VDD rise time, the following measures for
a correct Power-on-reset can be taken:
• If the VDD rises above the minimum operation voltage
before time period t
is exceeded, no external
d
components are necessary (see Fig.6).
• If V
has a slow rise time, such that after the time
DD
period (t
Vref+td
) has elapsed the supply voltage is still
below the minimum operation voltage (V
min
),
external components are required (see Figs 4 and 7).
To guarantee a correct reset operation, ensure that the
time constant RC ≥ 8 × t
VDD
.
A definite Power-on-reset can be realized by applying an
(external)
RESET signal during power-on.
handbook, full pagewidth
V
ref
internal
reset
oscillator
inhibit
POWER-ON-RESET
Fig.5 Reset configuration.
MLA651
V
DD
RESET
V
SS
1996 Nov 29 8
Page 9

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
8-bit microcontrollers with OSD and VST 84C44X; 84C64X; 84C84X
handbook, full pagewidth
V
RESET
OSCILLATOR
handbook, full pagewidth
V
DD
RESET
without
external
component
RESET
with
external
component
DD
V
DD
V
ref
V
SS
V
DD
V
SS
t
d
oscillator start up time
MCD240
Fig.6 Reset with fast rising VDD.
V
DD
V
min
V
ref
V
SS
t
VDD
V
DD
V
SS
t
Vref
V
DD
V
SS
t
d
RC ≥ 8 × t
VDD
OSCILLATOR
Fig.7 Reset with slow VDD.
1996 Nov 29 9
oscillator start up time
MCD241
Page 10

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
8-bit microcontrollers with OSD and VST 84C44X; 84C64X; 84C84X
8 ANALOG CONTROL
8.1 6-bit PWM DACs
Five PWM outputs are available for analog control
purposes e.g. volume, balance, brightness, saturation, etc.
The block diagram of a typical 6-bit PWM DAC is shown in
Fig.8. Each PWM output can generate pulses of
programmable length that have a repetition frequency of
1
⁄64× f
8.1.1 P
, where f
PWM
IN SELECTION FOR PWM OUTPUTS
PWM
=1⁄3× f
XTAL
.
The PWM outputs PWM1 to PWM5, share the same pins
as the Derivative Port lines DP0.1 to DP0.5.
Setting the (relevant PWM enable) bit PWMnE to:
• Logic 1, selects the relevant PWMx output function
• Logic 0, selects the relevant DP0.x Port function.
8.1.2 P
OLARITY OF THE PWM OUTPUTS
The polarity of all five PWM outputs is selected by the state
of the polarity control bit P6LVL.
Setting the control bit P6LVL to:
• Logic 0, sets the PWMx outputs to the default polarity
• Logic 1, inverts all the PWMx outputs.
8.1.3 A
NALOG OUTPUT VOLTAGE
A DC voltage proportional to the PWM control setting may
be obtained by connecting an integrating network to each
of the PWM outputs (see Fig.9).
The analog value is calculated as follows:
t
HIGH
V
------------- t
r
×=
O
V
A
Where:
•
t
HIGHt0
t
•
•
t
r
0
=
t
------------- -
0
f
PWMDL× HIGH time of the PWM pulse==
64× repetition time of the PWM pulse==
3
XTAL
• PWMDL is the decimal value of the contents of the
PWM data latch.
Therefore, the analog output voltage is:
V
A
PWMDL
----------------------- 64
×=
V
O
handbook, full pagewidth
f
PWM
6-BIT PWM DATA LATCH
6-BIT DAC PWM
CONTROLLER
Q
Q
Fig.8 Block diagram of the 6-bit PWM DAC.
1996 Nov 29 10
P6LVL
DP0.x data
I/O
PWMnE
polarity control bit
DP0.x/PWMx
MCD176
Page 11
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
8-bit microcontrollers with OSD and VST 84C44X; 84C64X; 84C84X
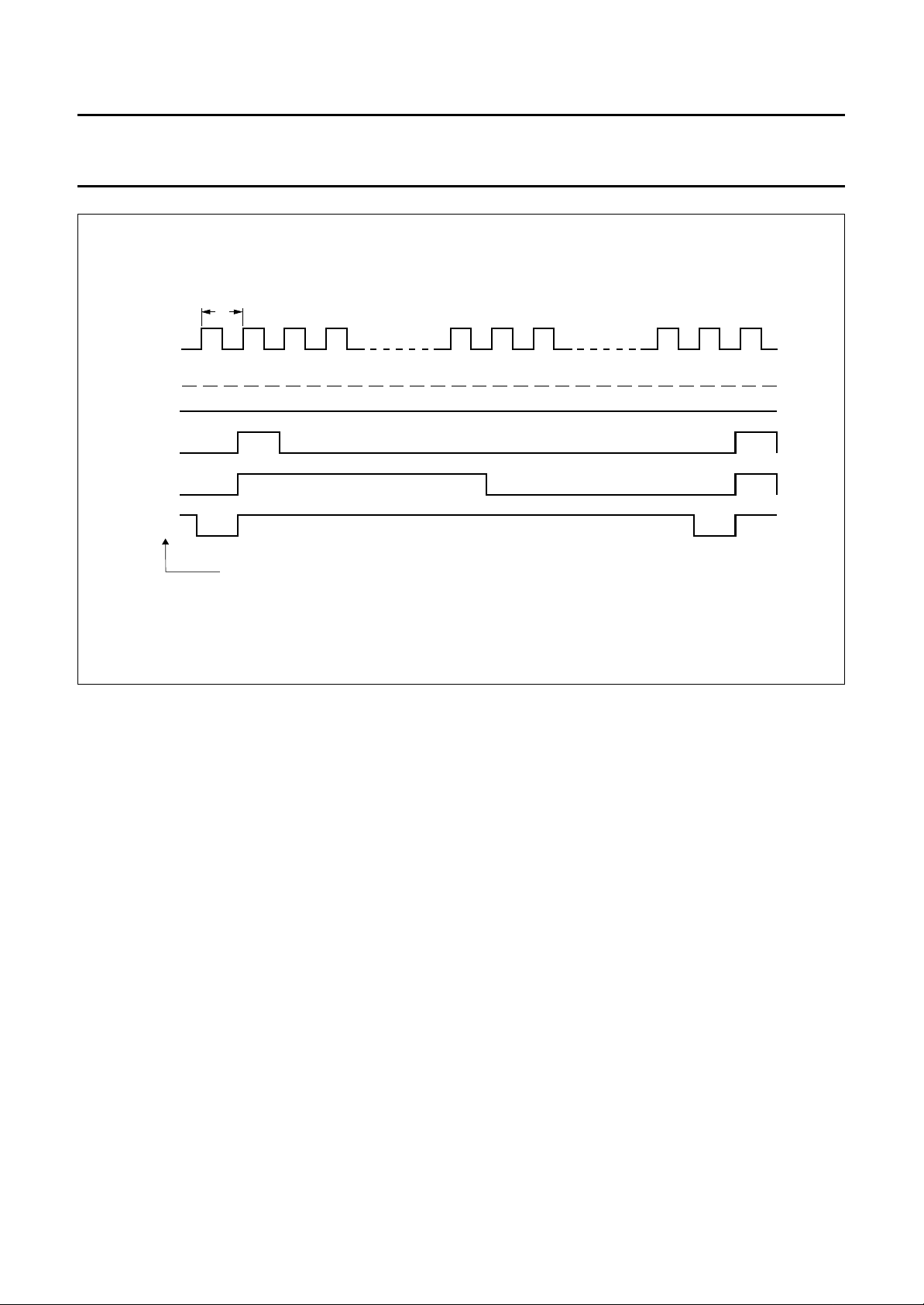
t
handbook, full pagewidth
f
PWM
00
01
m
63
0
64 1 3 m m + 1m + 263641
2
decimal value PWM data latch
Fig.9 PWM output patterns (P6LVL = 0).
MCD175
1996 Nov 29 11
Page 12

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
8-bit microcontrollers with OSD and VST 84C44X; 84C64X; 84C84X
9 VST CONTROL
9.1 14-bit PWM DAC
The PCA84C640 has one 14-bit PWM DAC output (TDAC)
with a resolution of 16384 levels for Voltage Synthesized
Tuning. The PWM DAC (see Fig.10) consists of:
• 14-bit counter
• Two 7-bit DAC interface data latches (VSTH and VSTL)
• One 14-bit DAC data latch (VSTREG)
• Pulse control.
The polarity of output TDAC is selected with bit P14LVL.
Setting the bit P14LVL to:
• Logic 1, sets the TDAC output to the default polarity
• Logic 0, inverts the TDAC output.
9.1.1 14-
BIT COUNTER
The counter is continuously running and is clocked by f0.
The period of the clock,
t
3
=
------------- -
0
f
XTAL
The repetition time for one complete cycle of the counter:
t
rt0
16384×=
The repetition time for one cycle of the lower 7-bits of the
counter is:
t
subt0
Therefore, the number of t
128×=
periods in a complete
sub
cycle tr is:
t
16384×
0
N
--------------------------t
0
9.1.2 D
128×
ATA AND INTERFACE LATCHES
128==
In order to ensure correct operation, interface data latch
VSTH is loaded first and then interface data latch VSTL.
The contents of:
• VSTH are used for coarse adjustment
• VSTL are used for fine adjustment.
9.2 Coarse adjustment
The coarse adjustment output (OUT1) is reset to LOW
(inactive) at the start of each t
It will remain LOW until the time has
period.
sub
t0VSTH 1+()×[]
elapsed and then will go HIGH and remain so until the next
t
period starts.
sub
9.3 Fine adjustment
Fine adjustment is achieved by generating additional
pulses at the start of particular sub-periods (t
subn
).
These additional pulses have a width of t0.
The sub-period in which a pulse is added is determined by
the contents of VSTL interface latch.
Table 3 gives the numbers of the t
, at the start of which
subn
an additional pulse is generated, depending on the bit in
VSTL being a logic 0. When more than one bit is a logic 0
a combination of additional pulses are generated.
For example, if VSTL = 1111010, which is a combination
of
• VSTL = 1111110: sub-period 64, and
• VSTL = 1111011: sub-periods 16, 48, 80 and 112,
then additional pulses will be given in sub-periods
16, 48, 64, 80 and 112; this is illustrated in Fig.12.
If VSTH = 0011101, VSTL = 1111010 and P14LVL = 0,
then the TDAC output is as shown in Fig.13.
Table 3 Additional pulse distribution
LOWER
7 BITS
(VSTL)
ADDITIONAL PULSE IN
SUB-PERIODS t
subn
1111110 64
1111101 32, 96
1111011 16, 48, 80, 112
1110111 8, 24, 40, 56, 72, 88, 104, 120
110 1111 4, 12, 20, 28, 36, 44, 52, 60 .... 116, 124
1011111 2, 6, 10, 14, 18, 22, 26, 30, .... 122, 126
0111111 1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13, 15, 17, .... 125, 127
At the beginning of the first t
period following the loading
sub
of VSTL, both data latches are loaded into data latch
VSTREG. After the contents of VSTH and VSTL are
latched into VSTREG, one t
period is needed to
sub
generate the appropriate pulse pattern.
To ensure correct DAC conversion, two (2) t
periods
sub
should be allowed before beginning the next sequence.
1996 Nov 29 12
Page 13

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
8-bit microcontrollers with OSD and VST 84C44X; 84C64X; 84C84X
handbook, full pagewidth
'MOV instruction'
DATA LOAD
TIMING PULSE
polarity
control bit
DATA LATCH VSTH
P14LVL
DATA LATCH VSTL
7 7
LOAD
DAC DATA LATCH VSTREG
7 7
COARSE PWM FINE
OUT2OUT1
ADD
Q
Q14 to Q8 Q7 to Q1
14-BIT COUNTER
Q
'MOV instruction'
TDAC output
f
0
Fig.10 Block diagram of the 14-bit PWM DAC.
ndbook, full pagewidth
OUT 1
t
sub0
t0 × (VSTH + 1)
t
sub1
Fig.11 Coarse adjustment output (OUT1).
1996 Nov 29 13
MCD177
t
r
t
subn
t
sub127
MCD313
Page 14

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
8-bit microcontrollers with OSD and VST 84C44X; 84C64X; 84C84X
t
handbook, full pagewidth
r
111 1110
111 1101
111 1011
111 1010
VSTL
t
sub0
t
sub16
t
sub32
t
sub48
t
sub64
t
sub80
Fig.12 Fine adjustment output (OUT2).
t
sub96
t
sub112
t
sub127
MCD314
handbook, full pagewidth
OUT 1
OUT 2
TDAC
t
sub0
t
sub16
t
sub32
t
sub48
Fig.13 TDAC output.
1996 Nov 29 14
t
t
sub64
r
t
sub80
t
sub96
t
sub112
t
sub127
MCD315
Page 15

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
8-bit microcontrollers with OSD and VST 84C44X; 84C64X; 84C84X
10 AFC INPUT
The AFC input is used to measure the level of the
Automatic Frequency Control signal. This is achieved by
comparing the AFC input signal with the output of a 3-bit
DAC as shown in Fig.14. DAC analog switches select one
of 8 resistor taps connected between VDD and VSS.
Consequently, eight different voltages may be selected
(see Table 4). The compare signal AFCC, can be tested to
determine whether the AFC input is higher or lower than
the DAC level.
The AFC input shares the same pin as the Derivative Port
line DP1.7. Setting the enable bit AFCE to:
• Logic 1, selects the AFC function
• Logic 0, selects the Derivative Port DP1.7 function.
handbook, full pagewidth
DP1.7
Table 4 Selection of V
ref
AFC2 AFC1 AFC0 V
000V
001V
010V
011V
100V
101V
110V
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
111 V
internal bus
V
ref
(for VDD= 5.0 V)
ref
× 0.125 0.625 V
× 0.250 1.250 V
× 0.375 1.875 V
× 0.500 2.500 V
× 0.625 3.125 V
× 0.750 3.750 V
× 0.875 4.375 V
DD
5.000 V
DP1.7/AFC
COMPARATOR
EN
3-BIT DAC EN
AFC2 AFC1 AFC0 AFCE
Fig.14 AFC circuit.
AFCC
inner latches
MCD178
1996 Nov 29 15
Page 16

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
8-bit microcontrollers with OSD and VST 84C44X; 84C64X; 84C84X
11 INPUT/OUTPUT (I/O)
Each parallel I/O port line may be individually configured
using one of three possible I/O mask options.
The three I/O mask options are specified below:
Option 1 Standard port with switched pull-up current
source, Fig.15.
Option 2 Open drain, Fig.16.
Option 3 Push-pull (output only), Fig.17.
handbook, full pagewidth
WRITE PULSE
OUTL/ORL/ANL/MOV
DATA BUS
D
MQ
MASTER
ORL/ANL/MOV
D
SLAVE
SQ
SQ
Table 5 specifies the possible port option list. When these
devices are used for emulation purposes, in order to match
the piggy back device provided it is recommended that the
port options listed in Table 6 are used.
V
DD
I/O PORT
LINE
IN/MOV
TR2
TR1
constant
current
TR3
V
SS
source
100 µA typ.
MLA696
handbook, full pagewidth
Fig.15 Standard output with switched pull-up current source (Option 1).
WRITE PULSE
OUTL/ORL/ANL
DATA BUS
D
MQ
MASTER
ORL/ANL
D
SLAVE
SQ
SQ
TR1
IN
V
DD
V
SS
MLA697
Fig.16 Open drain type I/O (Option 2).
I/O PORT
LINE
1996 Nov 29 16
Page 17

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
8-bit microcontrollers with OSD and VST 84C44X; 84C64X; 84C84X
handbook, full pagewidth
WRITE PULSE
OUTL/OR /ANL
DATA BUS
D
D
MQ
MASTER
ORL/ANL
SQ
SLAVE
SQ
IN
Fig.17 Push-pull type output (Option 3).
TR2
TR1
V
DD
constant
current
source
100 µA typ.
OUTPUT
LINE
V
SS
MGD864
1996 Nov 29 17
Page 18

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
8-bit microcontrollers with OSD and VST 84C44X; 84C64X; 84C84X
Table 5 User mask programmable port option list
PORT PIN OPTION
P0.0 13
P0.1 14
P0.2 15
P0.3 16
P0.4 17
P0.5 18
P0.6 19
P0.7 20
P1.0 7
P1.1 8
P1.2 10
P1.3 11
P1.4 12
DP0.0 1
DP0.1 2
DP0.2 3
DP0.3 4
DP0.4 5
DP0.5 6
DP0.6 40
DP0.7 39
DP1.0 41
DP1.1 38
DP1.2 37
DP1.3 36
DP1.4
(2)
34
DP1.5 23
DP1.6 22
DP1.7 9
VOB 25 3 R
VOW3 24 3 R
(1)
Table 6 Port options for the 84C640 in emulation mode
PORT PIN OPTION
P0.0 13 1 S
P0.1 14 1 S
P0.2 15 1 S
P0.3 16 1 S
P0.4 17 1 S
P0.5 18 1 S
P0.6 19 1 S
P0.7 20 1 S
P1.0 7 1 S
P1.1 8 1 S
P1.2 10 1 S
P1.3 11 1 S
P1.4 12 1 S
DP0.0 1
DP0.1 2
DP0.2 3
DP0.3 4
DP0.4 5
DP0.5 6
DP0.6 40 2 S
DP0.7 39 2 S
DP1.0 41
DP1.1 38
DP1.2 37
DP1.3 36
DP1.4 34
DP1.5 23
DP1.6 22
DP1.7 9
VOB 25 3 R
VOW3 24 3 R
Notes
1. Each pin can be configured to a HIGH (S) or LOW (R)
state after power-on-reset. The required state of each
pin is therefore specified by R or S.
2. DP1.4 available only with the PCA84C440,
PCA84C443, PCA84C640, PCA84C643,
PCA84C840 and PCA84C843.
1996 Nov 29 18
Page 19

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
8-bit microcontrollers with OSD and VST 84C44X; 84C64X; 84C84X
12 ON SCREEN DISPLAY
12.1 Features
• Display format: 2 rows × 16 characters
• Software controlled vertical and horizontal display
position
• 64 different (mask programmable) characters in ROM
• Black box background
• Four programmable display character sizes
• Four programmable character dot matrix sizes:
–6×9 and 6 × 13
–8×9 and 8 × 13
• Half-dot rounding for the whole screen
• 4 from 7 colours possible on screen
• Clock generator for On Screen Display function with:
– RC oscillator
– LC oscillator,
for the various types of PCA84C44X; 84C64X; 84C84X.
12.2 Horizontal display position control
The horizontal position counter is incremented every OSD
cycle after the programmed level of HSYNCN occurs at the
HSYNCN pin. The counter is reset when the opposite
polarity of the HSYNCN pulse is reached.
12.4 Clock generator
There are two types of oscillators available for the various
types. The oscillator is triggered on the trailing edge of
HSYNCN when the OSD logic is enabled and stops on the
following leading edge of HSYNCN.
The OSD oscillator must be externally adjusted to the
desired frequency (decreasing the OSD frequency gives
broader characters). Before the oscillation frequency can
be adjusted HSYNCN must be HIGH (if HLVL = 1).
Oscillation stops by setting the HSYNCN pin LOW when
HLVL = 1.
12.4.1 RC
The RC oscillator is available in the types:
PCA84C440; 84C443; 84C640; 84C643;
84C840; 84C843.
The external RC network is connected between
pin 28 and VSS (see Fig.19).
12.4.2 LC
The LC oscillator is available in the types:
PCA84C441; 84C444; 84C641; 84C644;
84C841; 84C844.
The external LC network is connected between
pins 28 and 29 (see Fig.20).
OSCILLATOR
OSCILLATOR
12.3 Vertical display position control
The vertical position counter is incremented every
HSYNCN cycle and is reset by the VSYNCN signal.
1996 Nov 29 19
Page 20

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
8-bit microcontrollers with OSD and VST 84C44X; 84C64X; 84C84X
handbook, full pagewidth
(1) See Figs 19 and 20 for connection of external components.
VSYNCN
HSYNCN
VERTICAL
DISPLAY
POSITION
CONTROL
HORIZONTAL
DISPLAY
POSITION
CONTROL
CLOCK
GENERATOR
(1)
DISPLAY
CONTROL
MEMORY
CONTROL
TIMING
GENERATOR
VOB
VOW1
VOW2
VOW3
Fig.18 OSD block diagram.
DISPLAY
CHARACTER
DATA
MEMORY
CHARACTER
ROM
DISPLAY
CONTROL
MCD179
V
MCD173
DD
V
SS
handbook, halfpage
R
DOSC1
C
Fig.19 RC oscillator. Fig.20 LC oscillator.
1996 Nov 29 20
handbook, halfpage
C1
DOSC1
L1
C2
DOSC2
MCD247
Page 21

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
8-bit microcontrollers with OSD and VST 84C44X; 84C64X; 84C84X
12.5 Display data registers
The display data registers consists of a group of 32 derivative registers located at addresses 20H to 3FH inclusive
(see Table 7). At power-up the contents of the display data registers are undefined.
The format of each display data register is shown in Table 8, and their functions described in Table 9.
Table 7 Display data registers addresses
ADDRESS DISPLAY DATA FOR BIT 7 BIT 6 BIT 5 BIT 4 BIT 3 BIT 2 BIT 1 BIT 0
20H to 2FH Row 0 = the first display row
30H to 3FH Row 1 = the second display row
Table 8 Display data register (address 20H to 3FH)
76543210
CC1 CC0 MD5 MD4 MD3 MD2 MD1 MD0
Table 9 Description of display data register bits
CC1 CC0 MD5 MD4 MD3 MD2 MD1 MD0
BIT SYMBOL DESCRIPTION
7 CC1 Colour code. The state of these two bits enable individual characters to be displayed in
6 CC0
5 MD5 Character code.
4 MD4
3 MD3
2 MD2
1 MD1
0 MD0
12.6 Display control registers
The display control registers consists of a group of 6 derivative registers located at addresses 40H to 45H inclusive
(see Table 10). Each register may be read from or written to. After a reset operation the contents of the display control
registers are zero.
Table 10 Display control registers addresses
ADDRESS REGISTER BIT 7 BIT 6 BIT 5 BIT 4 BIT 3 BIT 2 BIT 1 BIT 0
40H OSDCA CC34 CC24 CC14 RBLK ROUND STBY VLVL HLVL
41H LINE 0A SZ01 SZ00 VP05 VP04 VP03 VP02 VP01 VP00
42H LINE 0B BLK0 VB0 HP05 HP04 HP03 HP02 HP01 HP00
43H OSDCB CDTW CDTH CC33 CC23 CC32 CC12 CC21 CC11
44H LINE 1A SZ11 SZ10 VP15 VP14 VP13 VP12 VP11 VP10
45H LINE 1B BLK1 VB1 HP15 HP14 HP13 HP12 HP11 HP10
one of four colours. See Tables 24, 25 and 26.
The character set is stored in ROM and consists of 64 different characters.
The selection of each character is dependent on the state of the 6 bits, MD0 to MD5.
1996 Nov 29 21
Page 22

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
8-bit microcontrollers with OSD and VST 84C44X; 84C64X; 84C84X
12.6.1 DERIVATIVE REGISTER OSDCA
Table 11 Derivative register OSDCA (address 40H)
76543210
CC34 CC24 CC14 RBLK ROUND STBY VLVL HLVL
Table 12 Description of OSCDA bits
BIT SYMBOL DESCRIPTION
7 CC34 Character colour code bits.
6 CC24
5 CC14
4 RBLK Raster blanking control (see Fig.24). When the RBLK bit is:
3 ROUND Character rounding control (see Figs 22 and 23). The rounding function generates half dots where
2 STBY Stand-by. This bit is used to enable or disable the OSD facility. When the STBY bit is:
1VLVL Vertical synchronous signal level (see Fig.21).
0HLVL Horizontal synchronous signal level (see Fig.21).
These bits are used for colour selection purposes. See Table 24.
Logic 1, the VOB output is driven HIGH to display the OSD characters on a blank screen.
Logic 0, the VOB output returns to its normal output state on the trailing edge of VSYNCN.
the corners of two dots meet. The rounding function also works with multiple cell characters.
When the ROUND bit is:
Logic 1, the rounding function is enabled.
Logic 0, the rounding function is disabled.
Logic 1, the OSD oscillator is disabled.
Logic 0, the OSD oscillator is enabled and the OSD facility is available.
This bit selects the active level of the VSYNCN input signal. When the VLVL bit is:
Logic 1, VSYNCN is active HIGH.
Logic 0, VSYNCN is active LOW.
This bit selects the active level of the HSYNCN input signal. When the HLVL bit is:
Logic 1, HSYNCN is active HIGH.
Logic 0, HSYNCN is active LOW.
handbook, full pagewidth
HSYNCN
(VSYNCN)
HSYNCN
(VSYNCN)
characters can be displayed
Fig.21 VSYNCN and HSYNCN active level.
1996 Nov 29 22
(HLVL = VLVL = 1)
(HLVL = VLVL = 0)
MCD180
Page 23

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
8-bit microcontrollers with OSD and VST 84C44X; 84C64X; 84C84X
ROUND = 1ROUND = 0
H
H
handbook, halfpage
H
H
TTT
handbook, full pagewidth
VSYNCN
H
H
Fig.22 Rounding function.
RBLK
MCD181
TTT
MCD246
Fig.23 Rounding effect.
VOB
VOW1, 2, 3
= normal output
Fig.24 Raster blanking timing RLBK.
1996 Nov 29 23
MCD316
Page 24

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
8-bit microcontrollers with OSD and VST 84C44X; 84C64X; 84C84X
12.6.2 DERIVATIVE REGISTERS LINE 0A AND LINE 0B
REGISTER FUNCTION
LINE 0A Determine the character size and vertical position of Row 0 (the first display row).
LINE 0B Determine the horizontal position of Row 0 and the selection of background and blanking functions.
Table 13 Derivative register LINE 0A (address 41H)
76543210
SZ01 SZ00 VP05 VP04 VP03 VP02 VP01 VP00
Table 14 Description of LINE 0A bits
BIT SYMBOL DESCRIPTION
7 SZ01 Character size. The state of these two bits enable one of four possible character sizes to be
6 SZ00
5 VP05 Vertical position control.
4 VP04
3 VP03
2 VP02
1 VP01
0 VP00
selected for Row 0. Character sizes include background. See Table 23.
The vertical position of Row 0 is selected by the state of the 6 bits, VP00 to VP05.
For details see Section 12.7.1 “Vertical position”.
Table 15 Derivative register LINE 0B (address 42H)
76543210
BLK0 VB0 HP05 HP04 HP03 HP02 HP01 HP00
Table 16 Description of LINE 0B bits
BIT SYMBOL DESCRIPTION
7 BLK0 Blanking. This bit enables or disables the character display. When BLK0 is set to:
Logic 1, the outputs VOW1, VOW2, VOW3 and VOB are enabled; characters are displayed.
Logic 0, the outputs VOW1, VOW2, VOW3 and VOB are disabled; no characters are displayed.
6 VB0 Background. This bit determines whether the background display is selected or not.
The visual effect of background versus no background is shown in Fig.26. When VB0 is set to:
Logic 1, the characters in this row are displayed with background.
Logic 0, the background is disabled and only the characters are displayed.
5 HP05 Horizontal position control.
4 HP04
3 HP03
2 HP02
1 HP01
0 HP00
These 6 bits determine the start position of Row 0.
The horizontal position control is only active during OSDC clock cycles.
For details Section 12.7.2 “Horizontal position” and Fig.25.
1996 Nov 29 24
Page 25

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
8-bit microcontrollers with OSD and VST 84C44X; 84C64X; 84C84X
12.6.3 DERIVATIVE REGISTERS LINE 1A AND LINE 1B
REGISTER FUNCTION
LINE 1A Determine the character size and vertical position of Row 1 (the second display row).
LINE 1B Determine the horizontal position of Row 1 and the selection of background and blanking functions.
Table 17 Derivative register LINE 1A (address 44H)
76543210
SZ11 SZ10 VP15 VP14 VP13 VP12 VP11 VP10
Table 18 Description of LINE 1A bits
BIT SYMBOL DESCRIPTION
7 SZ11 Character size. The state of these two bits enable one of four possible character sizes to be
6 SZ10
5 VP15 Vertical position control.
4 VP14
3 VP13
2 VP12
1 VP11
0 VP10
selected for Row 1. Character sizes include background. See Table 23.
The vertical position of Row 1 is selected by the state of the 6 bits, VP10 to VP15.
For details see Section 12.7.1 “Vertical position”.
Table 19 Derivative register LINE 1B (address 45H)
76543210
BLK1 VB1 HP15 HP14 HP13 HP12 HP11 HP10
Table 20 Description of LINE 1B bits
BIT SYMBOL DESCRIPTION
7 BLK1 Blanking. This bit enables or disables the character display. When BLK1 is:
Logic 0, the outputs VOW1, VOW2, VOW3 and VOB are disabled; no characters are displayed.
Logic 1, the outputs VOW1, VOW2, VOW3 and VOB are enabled; characters are displayed.
6 VB1 Background. This bit determines whether the background display is selected or not.
The visual effect of background versus no background is shown in Fig.26. When VB1 is set to:
Logic 1, the characters in this line are displayed with background.
Logic 0, the background is disabled and only the character is displayed.
5 HP15 Horizontal position control.
4 HP14
3 HP13
2 HP12
1 HP11
0 HP10
These 6 bits determine the start position of Row 1.
The horizontal position control is only active during OSDC clock cycles.
For details Section 12.7.2 “Horizontal position” and Fig.25.
1996 Nov 29 25
Page 26

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
8-bit microcontrollers with OSD and VST 84C44X; 84C64X; 84C84X
12.6.4 DERIVATIVE REGISTER OSDCB
REGISTER FUNCTION
OSDCB Determine the selection of:
• The size of the dot matrix grid
• Four colours from a possible seven for the display.
Table 21 Derivative register OSDCB (address 43H)
76543210
CDTW CDTH CC33 CC23 CC32 CC12 CC21 CC11
Table 22 Description of OSDCB bits
BIT SYMBOL DESCRIPTION
7 CDTW Character dot width control.The state of this bit determines the dot width of the character. When
the CDTW bit is set to:
Logic 1, the character width is 6 dots.
Logic 0, the character width is 8 dots.
6 CDTH Character dot height control. The state of this bit determines the dot height of the character. When
the CDTH bit is set to:
Logic 1, the character height is 13 dots.
Logic 0, the character height is 9 dots.
5 CC33 Colour control bits.
4 CC23
3 CC32
2 CC12
1 CC21
0 CC11
In every VSYNCN cycle one screen can select any 4 colours from 7 and in addition a blank or black
screen. Combinations of CC1X, CC2X and CC3X control the character outputs VOW1, VOW2 and
VOW3 as shown in Table 24.
1996 Nov 29 26
Page 27

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
8-bit microcontrollers with OSD and VST 84C44X; 84C64X; 84C84X
12.7 OSD display position
12.7.1 V
ERTICAL POSITION
The line number of the vertical start position for:
• Row 0 is 4 × (VP00 → VP05)
• Row 1 is 4 × (VP10 → VP15).
Where:
• (VP00 → VP05) = the decimal value of VP00 → VP05
• (VP10 → VP15) = the decimal value of VP10 → VP15.
The character height in:
• Row 0 is H0 and is a function of the number of dots per
character and the state of the size control bits
SZ00 and SZ01
• Row 1 is H1 and is a function of the number of dots per
character and the state of the size control bits
SZ10 and SZ11.
Row 0 and Row 1 must not overlap each other and
therefore: VP1 ≥ (VP0 + H0); see Fig.25.
The four possible character heights are shown in Table 23.
12.7.2 H
ORIZONTAL POSITION
The horizontal start position (HP) of,
• Row 0: HP0 = 4 × (HP00 → HP05) + 5 × t
• Row 1: HP1 = 4 × (HP10 → HP15) + 5 × t
OSCD
OSCD
Where:
• (HP00 → HP05) = the decimal value of HP00 → HP05
and (HP00 → HP05) > 10
• (HP10 → HP15) = the decimal value of HP10 → HP15
and (HP10 → HP15) > 10
• t
= one OSCD clock period.
OSCD
Therefore for both Row 0 and Row 1,
HP0, HP1 ≥ 45 × t
OSCD
.
HP0
VP0
handbook, halfpage
with background without background
ROW 0 CHARACTERS
HP1
H0
ROW 1 CHARACTERS
VP1
MCD183
Fig.25 Display position. Fig.26 Background versus no background.
MCD182
1996 Nov 29 27
Page 28

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
8-bit microcontrollers with OSD and VST 84C44X; 84C64X; 84C84X
12.8 OSD character size and colour selection
12.8.1 C
HARACTER SIZE
The character sizes are selected by bits SZn1 and SZn0,
which denotes:
• SZ01 and SZ00 for Row 0
The character sizes are determined by the bits:
• SZ11 and SZ10 for Row 1.
• CDTW, for the width
• CDTH, for the height.
Table 23 Character sizes selection
H denotes one horizontal line, T denotes one OSDC clock period and D denotes dots per character width/height.
SIZE BITS CHARACTER SIZE DOT MATRIX POINT
VERTICAL HORIZONTAL
SZn1 SZn0
VERTICAL HORIZONTAL
9D 13D 6D 8D
0 0 18H 26H 12T 16T 2H 2T
0 1 36H 52H 24T 32T 4H 4T
1 0 54H 78H 36T 48T 6H 6T
1 1 72H 104H 48T 64T 8H 8T
12.8.2 COLOUR SELECTION
Colour selection is achieved using bits in the,
• OSDCA register: CC34, CC24 and CC14
• OSDCB register: CC33, CC23, CC32, CC12,
In this way every combination of four colours can be made
(black and white can not be displayed at the same time).
The user may choose one colour out of each block.
Table 24 shows the selection of the output combinations.
Tables 25 and 26 show the possible colour combinations.
CC21, and CC11
• Display data registers: CC1 and CC0.
handbook, full pagewidth
CHARACTER ROM
DISPLAY DATA
MEMORY
DISPLAY CIRCUIT
CONTROL REGISTERS
MCD184
dot
CC1
CC0
CCxx
background control
Fig.27 Colour control.
1996 Nov 29 28
OUTPUT
CONTROL
LOGIC
OR
VOW1
VOW2
VOW3
VOB
Page 29

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
8-bit microcontrollers with OSD and VST 84C44X; 84C64X; 84C84X
Table 24 Character colour control
COLOUR CODE CHARACTER OUTPUT PINS
CC1 CC0 VOW1 (Red) VOW2 (Green) VOW3 (Blue)
0 0 CC11 CC21
0 1 CC12
10
1 1 CC14 CC24 CC34
Table 25 Possible colour combinations
CC23 + CC33 CC23 CC33
(CC1, CC0) = (0, 0) (CC1, CC0) = (0, 1) (CC1, CC0) = (1, 0)
CC12 + CC32 CC32
CC11 + CC21
COLOUR
Blue 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 1
Green 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0
Red 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0
Yellow 1 1 0 −−−−−−
Magenta −− − 101−−−
Cyan −− − − − −011
Table 26 Possible colour combinations (continued)
COLOUR
Blue 0 0 1
Green 0 1 0
Red 1 0 0
Yellow 1 1 0
Magenta 1 0 1
Cyan 0 1 1
White 1 1 1
Black 0 0 0
VOW1 VOW2 VOW3 VOW1 VOW2 VOW3 VOW1 VOW2 VOW3
CC11 CC21
CC11 + CC21 CC12 CC12 + CC32 CC32 CC12 CC12 + CC32 CC32
(CC1, CC0) = (1, 1)
VOW1 VOW2 VOW3
CC14 CC24 CC34
1996 Nov 29 29
Page 30

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
8-bit microcontrollers with OSD and VST 84C44X; 84C64X; 84C84X
12.9 Character ROM
Character ROM contains the dot character fonts.
13 × 8 dots are reserved for each character, regardless of
the dot matrix size actually selected.
The dot matrix grid is shown in Fig.28.
Philips provides a software under MS DOS environment
(IBM/PC or compatible) to help customer to design the
character font on the screen and to generate the bit pattern
HEX decimal file automatically.
Contact your local Philips Sales Organization for details.
12345678
handbook, halfpage
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
MCD185
13 EMULATION MODE
The emulation mode configuration is shown in Fig.29.
In the emulation mode configuration the PCA84C640’s
CPU is disabled and only its derivative logic is active.
The device is controlled by the PCF84C00 bond-out chip.
The PCA84C640's two derivative ports act as additional
ports for the PCF84C00. The interaction between the two
devices is as follows:
1. During the first machine cycle the PCF84C00 fetches
an instruction from EPROM and then decodes that
instruction.
2. During the second machine cycle the PCF84C00
executes the decoded instruction. If the instruction is
related to the derivative ports then DXALE, DXRDN
and/or DXWRN become active and the PCA84C640
operates as a peripheral of the PCF84C00.
3. Depending on the type of instruction executed during
the second machine cycle the following data transfer
happens:
a) During TS1 data from the EPROM is available on
P0.0 to P0.7 which is then available on IB0.0 of the
PCF84C00.
b) During TS4 data from the PCA84C640 can be
transferred to the PCF84C00.
c) During TS6 data from the PCF84C00 can be
transferred to the PCA84C640.
Fig.28 Character ROM.
1996 Nov 29 30
Page 31

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
8-bit microcontrollers with OSD and VST 84C44X; 84C64X; 84C84X
handbook, full pagewidth
P0.0 to P0.7
P1.0 to P1.7
P2.0 to P2.7
PCF84C00
XTAL1
RESET
XTAL2
XTAL1
RESET
PCA84C640
DP0.0 to DP0.7
DP1.0 to DP1.7
PSEN
A0 to A12
D0 to D7
STFF
DXALE
DXRD
DXWR
P1.0
P1.1
P1.2
P1.3
P0.0 to P0.7
TEST/EMU
address bus
CE
A0 to A12
data bus
D0 to D7
EPROM
MCD317
+5 V
Fig.29 Emulation mode configuration.
1996 Nov 29 31
Page 32

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
8-bit microcontrollers with OSD and VST 84C44X; 84C64X; 84C84X
14 REGISTER MAP
The number within parentheses denotes the initial state; ‘X’ denotes don’t care.
R = Read, W = Write, R/W = Read/Write.
ADDR REG BIT 7 BIT 6 BIT 5 BIT 4 BIT 3 BIT 2 BIT 1 BIT 0 R/W
00H DP0
(pin)
01H DP1
(pin)
02H DP0R
(latch)
03H DP1R
(latch)
10H PWM1 −−PWM15
11H PWM2 −−PWM25
12H PWM3 −−PWM35
13H PWM4 −−PWM45
14H PWM5 −−PWM55
15H VSTL − VST06
16H VSTH − VST13
17H AFCO −−−−−AFC2
18H AFCC −−−−−−−AFCC
19H DP0E/
PWME
1AH DP1E/
PWMLVL
20H
to
3FH
DATA
DISPLAY
MEMORY
DP0.7
(X)
DP1.7
(X)
DP0.7
(1)
DP1.7
(1)
DP0.6
(X)
DP1.6
(X)
DP0.6
(1)
DP1.6
(1)
DP0.5
(X)
DP1.5
(X)
DP0.5
(1)
DP1.5
(1)
DP0.4
(X)
DP1.4
(X)
DP0.4
(1)
DP1.4
(1)
PWM14
(0)
(0)
PWM24
(0)
(0)
PWM34
(0)
(0)
PWM44
(0)
(0)
PWM54
SCLE
(0)
(0)
(0)
SDAE
(0)
(0)
VST05
(0)
VST12
(0)
PWM5E
(0)
(0)
VST04
(0)
VST11
(0)
PWM4E
(0)
−−−AFCE
(0)
CC1
(X)
CC0
(X)
MD5
(X)
MD4
(X)
(1)
(1)
DP0.3
(X)
DP1.3
(X)
DP0.3
(1)
DP1.3
(1)
PWM13
(0)
PWM23
(0)
PWM33
(0)
PWM43
(0)
PWM53
(0)
VST03
(0)
VST10
(0)
PWM3E
(0)
P14LVL
(0)
MD3
(X)
DP0.2
(X)
DP1.2
(X)
DP0.2
(1)
DP1.2
(1)
PWM12
(0)
PWM22
(0)
PWM32
(0)
PWM42
(0)
PWM52
(0)
VST02
(0)
VST09
(0)
(0)
PWM2E
(0)
P6LVL
(0)
MD2
(X)
DP0.1
(X)
DP1.1
(X)
DP0.1
(1)
DP1.1
(1)
PWM11
(0)
PWM21
(0)
PWM31
(0)
PWM41
(0)
PWM51
(0)
VST01
(0)
VST08
(0)
AFC1
(0)
PWM1E
(0)
VOW2E
(0)
MD1
(X)
DP0.0
(X)
DP1.0
(X)
DP0.0
(1)
DP1.0
(1)
PWM10
(0)
PWM20
(0)
PWM30
(0)
PWM40
(0)
PWM50
(0)
VST00
(0)
VST07
(0)
AFC0
(0)
(X)
TDACE
(0)
VOW1E
(0)
MD0
(X)
R
R
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
W
1996 Nov 29 32
Page 33

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
8-bit microcontrollers with OSD and VST 84C44X; 84C64X; 84C84X
ADDR REG BIT 7 BIT 6 BIT 5 BIT 4 BIT 3 BIT 2 BIT 1 BIT 0 R/W
40H OSDCA CC34
(0)
41H LINE0A SZ01
(0)
42H LINE0B BLK0
(0)
43H OSDCB CDTV
(0)
44H LINE1A SZ11
(0)
45H LINE1B BLK1
(0)
Note
1. These bits are not available in the PCA84C441, PCA84C444, PCA84C641, PCA84C644,
PCA84C841 and PCA84C844.
CC24
(0)
SZ00
(0)
VB0
(0)
CDTH
(0)
SZ10
(0)
VB1
(0)
CC14
(0)
VP05
(0)
HP05
(0)
CC33
(0)
VP15
(0)
HP15
(0)
RBLK
(0)
VP04
(0)
HP04
(0)
CC23
(0)
VP14
(0)
HP14
(0)
ROUND
(0)
VP03
(0)
HP03
(0)
CC32
(0)
VP13
(0)
HP13
(0)
STBY
(1)
VP02
(0)
HP02
(1)
CC12
(1)
VP12
(1)
HP12
(1)
VLVL
(0)
VP01
(0)
HP01
(0)
CC21
(0)
VP11
(0)
HP11
(0)
HLVL
(0)
VP00
(0)
HP00
(0)
CCV11
(0)
VP10
(0)
HP10
(0)
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
15 LIMITING VALUES
In accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System (IEC 134).
SYMBOL PARAMETER MIN. MAX. UNIT
V
V
I
I
P
T
T
DD
I
OH
OL
tot
stg
amb
supply voltage −0.3 +7.0 V
input voltage (all inputs) −0.3 VDD+ 0.3 V
maximum source current for all port lines −−10 mA
maximum sink current for all port lines −−30 mA
total power dissipation − 900 mW
storage temperature −55 +125 °C
operating ambient temperature (for all devices) −20 +70 °C
1996 Nov 29 33
Page 34

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
8-bit microcontrollers with OSD and VST 84C44X; 84C64X; 84C84X
16 DC CHARACTERISTICS
V
= 4.5 to 5.5 V; VSS=0V; T
DD
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
Supply
V
DD
I
DD
I
DD(ID)
I
DD(ST)
operating supply voltage 4.5 5.0 5.5 V
operating supply current f
supply current Idle mode VDD=5V;
supply current Stop mode VDD= 5.5 V;
= −20 to +70 °C; all voltages with respect to VSS unless otherwise specified.
amb
OSDCRC=fOSDCLC=fXTAL
;
VDD= 5 V; see note 1;
=10MHz − 510mA
f
XTAL
= 6 MHz − 3.5 8 mA
f
XTAL
f
OSDCRC=fOSDCLC
= STOP;
−
VDD= 5 V; see note 1;
= 10 MHz − 37 mA
f
XTAL
= 6 MHz − 1.5 3.5 mA
f
XTAL
= 10 MHz − 1.3 3 mA
f
XTAL
= 6 MHz; see note 1 − 0.8 1.5 mA
f
XTAL
− 510µA
see notes 1 and 2
Inputs
I
IH
HIGH level input current (pin RESET) VI= 0.5 V 20 −− µA
PORTS P0, P1, DP0, DP1, HSYNCN AND VSYNCN
V
IL
V
IH
LOW level input voltage 0 − 0.3VDDV
HIGH level input voltage 0.7VDD− V
PORTS P0, P1, DP0, DP1, INTN/T0 AND T1
I
Ll
input leakage current VSS< VI< V
DD
Ports P0, P1, DP0 and DP1 −−±10 µA
Ports INTN/T0 and T1 ±0.01 ±0.2 ±10 µA
Outputs: Ports P0, P1, DP0, DP1; VOB and VOW3 (see Figs 30, 31 and 31)
I
OL
LOW level output sink current
Port P0 V
Ports P1, DP0 and DP1 V
Ports VOB and VOW3 V
= 1.2 V 10 −− mA
O
= 0.4 V 5 10 − mA
O
= 0.4 V 1.2 3 − mA
O
PORTS P0, P1, DP0 AND DP1 (see Figs 33 and 33)
I
OH
HIGH level pull-up output source current VO=V
= 0.7V
V
O
HIGH level push-pull output source current V
O=VDD
SS
DD
− 0.4 V 3 7 − mA
OUTPUTS VOB AND VOW3 (see Fig.33)
I
OH
HIGH level push-pull output source current VO=VDD− 0.4 V 1.2 3 − mA
DD
V
− 140 400 µA
40 100 −µA
1996 Nov 29 34
Page 35

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
8-bit microcontrollers with OSD and VST 84C44X; 84C64X; 84C84X
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
AFC characteristics; Port DP1.7/AFC
V
AI
V
AE
comparator analog input voltage V
SS
conversion error range −−± 0.5 LSB
Notes
1. VIL=VSS; VIH=VDD; all outputs and sense input lines unloaded. All open drain ports connected to VSS.
2. Crystal is connected between XTAL1 and XTAL2; T1 = VSS; INT/T0 = VDD.
17 AC CHARACTERISTICS
V
=5V;T
DD
= −20 to +70 °C; all voltages with respect to VSS; unless otherwise specified.
amb
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
Oscillator
f
XTAL
f
OSC-XTAL
f
OSC-PXE
f
OSC-XTAL
f
OSC-PXE
f
OSC-XTAL
f
OSC-PXE
C
XTAL1
crystal frequency; note 1 1 − 10.0 MHz
oscillator frequency; option 1 gm= 0.4 mS (typ.)
oscillator frequency; option 2 gm= 1.6 mS (typ.)
oscillator frequency; option 3 gm= 4.5 mS (typ.)
1 − 6.0 MHz
4.0 − 10.0 MHz
1.0 − 6.0 MHz
3.0 − 10.0 MHz
external capacitance at XTAL1
with XTAL resonator not required pF
with PXE resonator − 30 100 pF
C
XTAL2
external capacitance at XTAL2
with XTAL resonator not required pF
with PXE resonator − 30 100 pF
f
DOSC
On Screen Display clock frequency 4.0 8.0 10.0 MHz
− V
DD
V
not allowed MHz
not allowed MHz
Note
1. Oscillator with three (3) options for optimum use.
1996 Nov 29 35
Page 36

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
8-bit microcontrollers with OSD and VST 84C44X; 84C64X; 84C84X
17.1 Characteristic curves
40
handbook, halfpage
I
OL
MLC004
(mA)
34
28
22
(1)
(2)
(3)
16
10
4
0246
V (V)
DD
Port P0; VO= 1.2 V.
(1) T
(2) T
(3) T
amb
amb
amb
= −20 °C.
=25°C.
=80°C.
Fig.30 Typical LOW level output sink current as a
function of the supply voltage.
10
handbook, halfpage
I
OL
MLB999
(mA)
8
(1)
6
(2)
(3)
4
2
0
0246
V (V)
DD
Ports P1, DP0 and DP1; VO= 0.4 V.
(1) T
(2) T
(3) T
amb
amb
amb
= −20 °C.
=25°C.
=80°C.
Fig.31 Typical LOW level output sink current as a
function of the supply voltage.
10
handbook, halfpage
I
OL
MLC002
(mA)
8
(1)
6
(2)
(3)
4
2
0
0246
Outputs VOW1, VOW2, VOW3 and VOB; V
(1) T
(2) T
(3) T
amb
amb
amb
= −20 °C.
=25°C.
=80°C.
= 0.4 V.
O
V (V)
DD
Fig.32 Typical LOW level output sink current as a
function of the supply voltage.
200
handbook, halfpage
I
OH
MLC001
(mA)
160
(1)
(2)
120
(3)
80
40
0
0246
V (V)
DD
Ports P0, P1, DP0 and DP1; VO=VSS.
(1) T
(2) T
(3) T
amb
amb
amb
= −20 °C.
=25°C.
=80°C.
Fig.33 Typical HIGH level pull-up output source
current as a function of the supply voltage.
1996 Nov 29 36
Page 37

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
8-bit microcontrollers with OSD and VST 84C44X; 84C64X; 84C84X
200
handbook, halfpage
I
OH
(mA)
160
120
80
40
0
0246
Ports P0, P1, DP0 and DP1; VO= 0.7VDD.
(1) T
(2) T
(3) T
amb
amb
amb
= −20 °C.
=25°C.
=80°C.
MLC005
V (V)
DD
(1)
(2)
(3)
Fig.34 Typical HIGH level pull-up output source
current as a function of the supply voltage.
V (V)
DD
MLC003
(1)
(2)
(3)
handbook, halfpage
5
I
OH
(mA)
4
3
2
1
0
0246
Outputs VOW1, VOW2, VOW3 and VOB; VO=VDD− 0.4 V.
(1) T
(2) T
(3) T
amb
amb
amb
= −20 °C.
=25°C.
=80°C.
Fig.35 Typical HIGH level pull-up output source
current as a function of the supply voltage.
1996 Nov 29 37
Page 38

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
8-bit microcontrollers with OSD and VST 84C44X; 84C64X; 84C84X
18 PACKAGE OUTLINE
SDIP42: plastic shrink dual in-line package; 42 leads (600 mil)
D
seating plane
L
Z
42
pin 1 index
e
b
SOT270-1
M
E
A
2
A
A
1
w M
b
1
22
E
c
(e )
M
1
H
1
0 5 10 mm
scale
DIMENSIONS (mm are the original dimensions)
A
A
A
UNIT b
Note
1. Plastic or metal protrusions of 0.25 mm maximum per side are not included.
max.
mm
5.08 0.51 4.0
OUTLINE
VERSION
SOT270-1
12
min.
max.
IEC JEDEC EIAJ
1.3
0.8
b
1
0.53
0.40
REFERENCES
0.32
0.23
cEe M
(1) (1)
D
38.9
38.4
1996 Nov 29 38
14.0
13.7
21
(1)
Z
1
L
M
E
3.2
15.80
2.9
15.24
EUROPEAN
PROJECTION
17.15
15.90
e
w
H
0.181.778 15.24
ISSUE DATE
90-02-13
95-02-04
max.
1.73
Page 39

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
8-bit microcontrollers with OSD and VST 84C44X; 84C64X; 84C84X
19 SOLDERING
19.1 Introduction
There is no soldering method that is ideal for all IC
packages. Wave soldering is often preferred when
through-hole and surface mounted components are mixed
on one printed-circuit board. However, wave soldering is
not always suitable for surface mounted ICs, or for
printed-circuits with high population densities. In these
situations reflow soldering is often used.
This text gives a very brief insight to a complex technology.
A more in-depth account of soldering ICs can be found in
our
“IC Package Databook”
(order code 9398 652 90011).
19.2 Soldering by dipping or by wave
The maximum permissible temperature of the solder is
The total contact time of successive solder waves must not
exceed 5 seconds.
The device may be mounted up to the seating plane, but
the temperature of the plastic body must not exceed the
specified maximum storage temperature (T
stg max
). If the
printed-circuit board has been pre-heated, forced cooling
may be necessary immediately after soldering to keep the
temperature within the permissible limit.
19.3 Repairing soldered joints
Apply a low voltage soldering iron (less than 24 V) to the
lead(s) of the package, below the seating plane or not
more than 2 mm above it. If the temperature of the
soldering iron bit is less than 300 °C it may remain in
contact for up to 10 seconds. If the bit temperature is
between 300 and 400 °C, contact may be up to 5 seconds.
260 °C; solder at this temperature must not be in contact
with the joint for more than 5 seconds.
20 DEFINITIONS
Data sheet status
Objective specification This data sheet contains target or goal specifications for product development.
Preliminary specification This data sheet contains preliminary data; supplementary data may be published later.
Product specification This data sheet contains final product specifications.
Limiting values
Limiting values given are in accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System (IEC 134). Stress above one or
more of the limiting values may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only and operation
of the device at these or at any other conditions above those given in the Characteristics sections of the specification
is not implied. Exposure to limiting values for extended periods may affect device reliability.
Application information
Where application information is given, it is advisory and does not form part of the specification.
21 LIFE SUPPORT APPLICATIONS
These products are not designed for use in life support appliances, devices, or systems where malfunction of these
products can reasonably be expected to result in personal injury. Philips customers using or selling these products for
use in such applications do so at their own risk and agree to fully indemnify Philips for any damages resulting from such
improper use or sale.
2
22 PURCHASE OF PHILIPS I
Purchase of Philips I
C COMPONENTS
2
C components conveys a license under the Philips’ I2C patent to use the
components in the I2C system provided the system conforms to the I2C specification defined by
Philips. This specification can be ordered using the code 9398 393 40011.
1996 Nov 29 39
Page 40

Philips Semiconductors – a worldwide company
Argentina: see South America
Australia: 34 Waterloo Road, NORTH RYDE, NSW 2113,
Tel. +61 2 9805 4455, Fax. +61 2 9805 4466
Austria: Computerstr. 6, A-1101 WIEN, P.O. Box 213,
Tel. +43 1 60 101, Fax. +43 1 60 101 1210
Belarus: Hotel Minsk Business Center, Bld. 3, r. 1211, Volodarski Str. 6,
220050 MINSK, Tel. +375 172 200 733, Fax. +375 172 200 773
Belgium: see The Netherlands
Brazil: see South America
Bulgaria: Philips Bulgaria Ltd., Energoproject, 15th floor,
51 James Bourchier Blvd., 1407 SOFIA,
Tel. +359 2 689 211, Fax. +359 2 689 102
Canada: PHILIPS SEMICONDUCTORS/COMPONENTS,
Tel. +1 800 234 7381
China/Hong Kong: 501 Hong Kong Industrial Technology Centre,
72 Tat Chee Avenue, Kowloon Tong, HONG KONG,
Tel. +852 2319 7888, Fax. +852 2319 7700
Colombia: see South America
Czech Republic: see Austria
Denmark: Prags Boulevard 80, PB 1919, DK-2300 COPENHAGEN S,
Tel. +45 32 88 2636, Fax. +45 31 57 1949
Finland: Sinikalliontie 3, FIN-02630 ESPOO,
Tel. +358 9 615800, Fax. +358 9 61580/xxx
France: 4 Rue du Port-aux-Vins, BP317, 92156 SURESNES Cedex,
Tel. +33 1 40 99 6161, Fax. +33 1 40 99 6427
Germany: Hammerbrookstraße 69, D-20097 HAMBURG,
Tel. +49 40 23 53 60, Fax. +49 40 23 536 300
Greece: No. 15, 25th March Street, GR 17778 TAVROS/ATHENS,
Tel. +30 1 4894 339/239, Fax. +30 1 4814 240
Hungary: see Austria
India: Philips INDIA Ltd, Shivsagar Estate, A Block, Dr. Annie Besant Rd.
Worli, MUMBAI 400 018, Tel. +91 22 4938 541, Fax. +91 22 4938 722
Indonesia: see Singapore
Ireland: Newstead, Clonskeagh, DUBLIN 14,
Tel. +353 1 7640 000, Fax. +353 1 7640 200
Israel: RAPAC Electronics, 7 Kehilat Saloniki St, TEL AVIV 61180,
Tel. +972 3 645 0444, Fax. +972 3 649 1007
Italy: PHILIPS SEMICONDUCTORS, Piazza IV Novembre 3,
20124 MILANO, Tel. +39 2 6752 2531, Fax. +39 2 6752 2557
Japan: Philips Bldg 13-37, Kohnan 2-chome, Minato-ku, TOKYO 108,
Tel. +81 3 3740 5130, Fax. +81 3 3740 5077
Korea: Philips House, 260-199 Itaewon-dong, Yongsan-ku, SEOUL,
Tel. +82 2 709 1412, Fax. +82 2 709 1415
Malaysia: No. 76 Jalan Universiti, 46200 PETALING JAYA, SELANGOR,
Tel. +60 3 750 5214, Fax. +60 3 757 4880
Mexico: 5900 Gateway East, Suite 200, EL PASO, TEXAS 79905,
Tel. +9-5 800 234 7381
Middle East: see Italy
Netherlands: Postbus 90050, 5600 PB EINDHOVEN, Bldg. VB,
Tel. +31 40 27 82785, Fax. +31 40 27 88399
New Zealand: 2 Wagener Place, C.P.O. Box 1041, AUCKLAND,
Tel. +64 9 849 4160, Fax. +64 9 849 7811
Norway: Box 1, Manglerud 0612, OSLO,
Tel. +47 22 74 8000, Fax. +47 22 74 8341
Philippines: Philips Semiconductors Philippines Inc.,
106 Valero St. Salcedo Village, P.O. Box 2108 MCC, MAKATI,
Metro MANILA, Tel. +63 2 816 6380, Fax. +63 2 817 3474
Poland: Ul. Lukiska 10, PL 04-123 WARSZAWA,
Tel. +48 22 612 2831, Fax. +48 22 612 2327
Portugal: see Spain
Romania: see Italy
Russia: Philips Russia, Ul. Usatcheva 35A, 119048 MOSCOW,
Tel. +7 095 247 9145, Fax. +7 095 247 9144
Singapore: Lorong 1, Toa Payoh, SINGAPORE 1231,
Tel. +65 350 2538, Fax. +65 251 6500
Slovakia: see Austria
Slovenia: see Italy
South Africa: S.A. PHILIPS Pty Ltd., 195-215 Main Road Martindale,
2092 JOHANNESBURG, P.O. Box 7430 Johannesburg 2000,
Tel. +27 11 470 5911, Fax. +27 11 470 5494
South America: Rua do Rocio 220, 5th floor, Suite 51,
04552-903 São Paulo, SÃO PAULO - SP, Brazil,
Tel. +55 11 821 2333, Fax. +55 11 829 1849
Spain: Balmes 22, 08007 BARCELONA,
Tel. +34 3 301 6312, Fax. +34 3 301 4107
Sweden: Kottbygatan 7, Akalla, S-16485 STOCKHOLM,
Tel. +46 8 632 2000, Fax. +46 8 632 2745
Switzerland: Allmendstrasse 140, CH-8027 ZÜRICH,
Tel. +41 1 488 2686, Fax. +41 1 481 7730
Taiwan: PHILIPS TAIWAN Ltd., 23-30F, 66,
Chung Hsiao West Road, Sec. 1, P.O. Box 22978,
TAIPEI 100, Tel. +886 2 382 4443, Fax. +886 2 382 4444
Thailand: PHILIPS ELECTRONICS (THAILAND) Ltd.,
209/2 Sanpavuth-Bangna Road Prakanong, BANGKOK 10260,
Tel. +66 2 745 4090, Fax. +66 2 398 0793
Turkey: Talatpasa Cad. No. 5, 80640 GÜLTEPE/ISTANBUL,
Tel. +90 212 279 2770, Fax. +90 212 282 6707
Ukraine: PHILIPS UKRAINE, 4 Patrice Lumumba str., Building B, Floor 7,
252042 KIEV, Tel. +380 44 264 2776, Fax. +380 44 268 0461
United Kingdom: Philips Semiconductors Ltd., 276 Bath Road, Hayes,
MIDDLESEX UB3 5BX, Tel. +44 181 730 5000, Fax. +44 181 754 8421
United States: 811 East Arques Avenue, SUNNYVALE, CA 94088-3409,
Tel. +1 800 234 7381
Uruguay: see South America
Vietnam: see Singapore
Yugoslavia: PHILIPS, Trg N. Pasica 5/v, 11000 BEOGRAD,
Tel. +381 11 625 344, Fax.+381 11 635 777
For all other countries apply to: Philips Semiconductors, Marketing & Sales Communications,
Building BE-p, P.O. Box 218, 5600 MD EINDHOVEN, The Netherlands, Fax. +31 40 27 24825
© Philips Electronics N.V. 1996 SCA52
All rights are reserved. Reproduction in whole or in part is prohibited without the prior written consent of the copyright owner.
The information presented in this document does not form part of any quotation or contract, is believed to be accurate and reliable and may be changed
without notice. No liability will be accepted by the publisher for any consequence of its use. Publication thereof does not convey nor imply any license
under patent- or other industrial or intellectual property rights.
Internet: http://www.semiconductors.philips.com
Printed in The Netherlands 457021/1200/03/pp40 Date of release: 1996 Nov 29 Document order number: 9397 750 01542
 Loading...
Loading...