Datamax-ONeil A-Class, E-Class Mark II, E-Class Mark III, EX2, H-Class Programmer's Manual
...Page 1

Class Series II
Programmer’s Manual
Covers the following models:
E-Class Mark II
E-Class Mark III Basic and Advanced (Serial# 3xxxxxxx or earlier)
A-Class / A-Class Mark II
MP Compact4 Mark II
M-Class Mark II
H-Class
I-Class
Ex2
Page 2

Page 3

Page 4

CG Times (based upon Times New Roman), CG Triumvirate, MicroType, and TrueType are
trademarks of the AGFA Monotype Corporation.
PCL, Intellifont, and HP Laser JetII are trademarks of the Hewlett Packard Corporation.
Macintosh is a trademark of the Apple Corporation.
Windows is a trademark of the Microsoft Corporation.
All other brand and product names are trademarks, service marks, registered trademarks,
or registered service marks of their respective companies.
Information in this manual is subject to change without notice and does not represent a
commitment on the part of Datamax-O’Neil Corporation. No part of this manual may be
reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, for any purpose other than the
purchaser’s personal use, without the expressed written permission of Datamax-O’Neil
Corporation.
All rights reserved
Copyright © 2013, Datamax-O’Neil
Part Number 88-2341-01
Revision L
Page 5

Page 6

Page 7

Contents
1 Overview ................................................................................................. 1
Who Should Use this Manual ............................................................................... 1
The Scope of this Manual ..................................................................................... 1
General Conventions ............................................................................................ 3
Computer Entry and Display Conventions ............................................................ 3
Important Safety Instructions ................................................................................ 3
Special Instructions .............................................................................................. 4
Typical Data Flow Sequence ................................................................................ 4
2 Control Code Command Functions ........................................................... 9
Introduction ............................................................................................ 9
Attention-Getters .................................................................................................. 9
Alternate Control Code Modes ........................................................................... 10
3 Immediate Command Functions ............................................................ 11
Introduction .......................................................................................... 11
SOH # Reset ................................................................................................... 11
SOH * Reset ................................................................................................... 11
SOH A Send ASCII Status String ..................................................................... 12
SOH a Send ASCII Extended Status String .................................................... 12
SOH B Toggle Pause ....................................................................................... 13
SOH C Stop/Cancel ......................................................................................... 14
SOH D SOH Shutdown .................................................................................... 14
SOH E Send Batch Remaining Quantity .......................................................... 14
SOH e Send Batch Printed Quantity ................................................................ 15
SOH F Send Status Byte ................................................................................. 15
i
Page 8

4 System-Level Command Functions ........................................................ 17
Introduction .......................................................................................... 17
STX A Set Time and Date ............................................................................... 17
STX a Enable Feedback Characters .............................................................. 18
STX B Get Printer Time and Date Information ................................................ 18
STX c Set Continuous Paper Length .............................................................. 19
STX E Set Quantity for Stored Label ............................................................... 19
STX e Select Edge Sensor ............................................................................. 20
STX F Form Feed ........................................................................................... 20
STX f Set Form Stop Position (Backfeed) ...................................................... 20
STX G Print Last Label Format........................................................................ 21
STX I Input Image Data ................................................................................. 21
STX i Scalable Font Downloading ................................................................. 22
STX J Set Pause for Each Label .................................................................... 23
STX K Extended System-Level Commands .................................................... 23
STX k Test RS-232 Port ................................................................................. 23
STX L Enter Label Formatting Command Mode ............................................. 23
STX M Set Maximum Label Length ................................................................. 24
STX m Set Printer to Metric Mode ................................................................... 24
STX n Set Printer to Imperial Mode ................................................................ 24
STX O Set Start of Print Position ..................................................................... 25
STX o Cycle Cutter ......................................................................................... 26
STX P Set Hex Dump Mode ........................................................................... 26
STX p Controlled Pause ................................................................................. 26
STX Q Clear All Modules ................................................................................. 27
STX q Clear Module ....................................................................................... 27
STX R Ribbon Saver Control .......................................................................... 27
STX r Select Reflective Sensor ...................................................................... 28
STX S Set Feed Speed ................................................................................... 28
STX T Print Quality Label ............................................................................... 28
STX t Test DRAM Memory Module ................................................................ 29
STX U Label Format String Replacement Field............................................... 29
STX V Software Switch Settings ..................................................................... 31
STX v Request Firmware Version .................................................................. 32
STX W Request Memory Module Information .................................................. 32
ii
Page 9

STX w Test Flash Memory Module ................................................................. 33
STX X Set Default Module .............................................................................. 33
STX x Delete File from Module ....................................................................... 34
STX Y Output Sensor Values .......................................................................... 35
STX y Select Font Symbol Set ....................................................................... 35
STX Z Print Configuration Label ..................................................................... 36
STX z Pack Module ........................................................................................ 36
5 Extended System-Level Command Functions ........................................ 37
Introduction .......................................................................................... 37
STX K Memory Configuration ......................................................................... 37
STX K}E Empty Sensor Calibration .................................................................... 38
STX K}M Manual Media Calibration ................................................................... 39
STX K}Q Quick Media Calibration ...................................................................... 39
STX KaR Read Data from RFID Tag .................................................................. 40
STX KaW Write Data to RFID Tag ..................................................................... 41
STX Kb Backfeed Time Delay ........................................................................... 41
STX KC Get Configuration ................................................................................. 42
STX Kc Configuration Set ................................................................................. 43
STX KD Database Configuration ..................................................................... 102
STX Kd Set File as Factory Default................................................................. 103
STX KE Character Encoding ........................................................................... 103
STX KF Select Factory Defaults ...................................................................... 105
STX Kf Set Present Distance ......................................................................... 105
STX KH Dot Check .......................................................................................... 106
STX KJ Assign Communication Port (MCL) .................................................... 107
STX KI GPIO Input ......................................................................................... 108
STX Kn NIC Reset .......................................................................................... 108
STX KO GPIO Output ...................................................................................... 109
STX Kp Module Protection .............................................................................. 110
STX KQ Query Memory Configuration ........................................................... 111
STX Kq Query Memory Configuration ............................................................. 113
STX KR Reset Memory Configuration ............................................................. 114
STX Kr Resettable Counter Reset .................................................................. 114
STX KS Memory Configuration, Scalable Font Cache .................................... 114
iii
Page 10

STX KtA Write Application Family Identifier (AFI) to Tag .................................. 115
STX KtD Write Data Storage Format Identifier (DSFID) to Tag ........................ 115
STX KtE Write Electronic Article Surveillance (EAS) Bit ................................... 116
STX KtH Read and Feedback Tag Information to Host .................................... 116
STX KtR Read Data from RFID Tag ................................................................. 117
STX KtW Write Data to RFID Tag .................................................................... 119
STX KuB Read Data from Gen2 Tag Section ................................................... 120
STX KuF Send RFID Device Firmware Version ............................................... 120
STX KuJ Write Data to Gen 2 Tag Section ....................................................... 120
STX KuR Read Data from RFID Tag ................................................................ 121
STX KuW Write Data to RFID Tag ................................................................... 122
STX KV Verifier Enable/Disable ...................................................................... 122
STX KW Memory Configuration, Printable Label Width .................................... 122
STX Kx Delete Configuration File ................................................................... 123
STX KZ Immediately Set Parameter ............................................................... 123
6 Label Formatting Command Functions ................................................ 125
Introduction ......................................................................................... 125
: Set Cut by Amount ............................................................................. 125
A Set Format Attribute ........................................................................... 126
B Bar Code Magnification ...................................................................... 127
C Set Column Offset Amount ................................................................ 127
c Set Cut by Amount ............................................................................. 128
D Set Dot Size Width and Height .......................................................... 128
E Terminate Label Formatting Mode and Print Label ............................ 129
e Recall Printer Configuration ............................................................... 129
F Advanced Format Attributes .............................................................. 129
f Set Present Speed ............................................................................. 130
G Place Data in Global Register ............................................................ 130
H Enter Heat Setting ............................................................................. 131
J Justification ........................................................................................ 131
M Select Mirror Mode ............................................................................ 132
m Set Metric Mode ................................................................................. 132
n Set Inch (Imperial) Mode .................................................................... 132
P Set Print Speed .................................................................................. 133
iv
Page 11

p Set Backfeed Speed .......................................................................... 133
Q Set Quantity of Labels to Print ........................................................... 134
R Set Row Offset Amount ..................................................................... 134
r Recall Stored Label Format ............................................................... 135
S Set Feed Speed ................................................................................. 136
s Store Label Format in Module ............................................................ 136
T Set Field Data Line Terminator .......................................................... 137
t Add or subtract date time from the printer date .................................. 137
U Mark Previous Field as a String Replacement Field .......................... 137
X Terminate Label Formatting Mode ..................................................... 139
y Select Font Symbol Set ..................................................................... 139
z Zero (Ø) Conversion to “0” ................................................................. 140
+ (>)(() Make Last Field Entered Increment ................................................. 140
– (<)()) Make Last Field Entered Decrement ............................................... 141
^ Set Count by Amount ......................................................................... 142
Special Label Formatting Command Functions ........................................... 143
STX D Print adjusted date ............................................................................. 143
STX S Recall Global Data and Place in Field ............................................... 144
STX T Print Time and Date ........................................................................... 144
7 Font Loading Command Functions ....................................................... 147
Introduction ......................................................................................... 147
*c###D Assign Font ID Number ..................................................................... 147
)s###W Font Descriptor .................................................................................. 148
*c###E Character Code ................................................................................. 148
(s#W Character Download Data ................................................................. 148
8 Generating Label Formats ................................................................... 149
Introduction ......................................................................................... 149
Format Record Commands .............................................................................. 149
Generating Records ......................................................................................... 150
The Structure of a Record ................................................................................ 150
Record Structure Types .................................................................................... 154
Advanced Format Attributes ............................................................................. 163
v
Page 12

Appendix A .............................................................................................. 167
ASCII Control Chart ............................................................................... 167
Appendix B .............................................................................................. 169
Sample Programs .................................................................................. 169
Appendix C .............................................................................................. 179
Available Fonts – Sizes, References, and Samples ...................................... 179
Appendix D ............................................................................................. 185
Reset Codes ......................................................................................... 185
Appendix E .............................................................................................. 187
Single Byte Symbol Sets ........................................................................ 187
Appendix F .............................................................................................. 199
Bar Code Summary Data ........................................................................ 199
Bar Code Default Widths and Heights ....................................................... 202
Appendix G.............................................................................................. 205
Bar Code Details ................................................................................... 205
Appendix H ............................................................................................. 251
Single and Double Byte Character Font Mapping ........................................ 251
vi
Page 13

Appendix I .............................................................................................. 253
Symbol Sets and Character Maps ............................................................ 253
Double-Byte Symbols, Chinese, Kanji, and Korean ..................................... 256
Appendix J .............................................................................................. 257
General Purpose Input Output (GPIO) Port Applications .............................. 257
Appendix K .............................................................................................. 271
Maximum Field & Character Values .......................................................... 271
Print Resolutions and Maximum Width & Record Column Values ................... 272
Column, Present, & Row Adjust Fine Tune Range ....................................... 273
Memory Module Identifiers and Allocations ................................................ 274
Appendix L .............................................................................................. 275
Speed Ranges ....................................................................................... 275
Appendix M ............................................................................................. 277
Commands by Function .......................................................................... 277
Appendix N ............................................................................................. 279
Image Loading ...................................................................................... 279
Appendix O ............................................................................................. 281
UPC-A and EAN-13: Variable Price/Weight Bar Codes ................................. 281
Appendix P .............................................................................................. 283
International Language Print Capability (ILPC) Programming Examples ......... 283
vii
Page 14

Appendix Q ............................................................................................. 293
Plug and Play IDs .................................................................................. 293
Appendix R .............................................................................................. 295
Line Mode 295
Appendix S .............................................................................................. 299
RFID Overview ...................................................................................... 299
Appendix T .............................................................................................. 305
WiFi Region Country Codes ..................................................................... 305
Appendix U ............................................................................................. 311
Graphics Display Icon Key ...................................................................... 311
Control Panel Button Sequences .............................................................. 312
Appendix V .............................................................................................. 315
Bar Code Symbology Information Resources ............................................. 315
Glossary .................................................................................................. 317
viii
Page 15

1
Who Should Use this Manual
This manual is intended for programmers who wish to create their own label production
software.
The Scope of this Manual
This manual, arranged alphabetically by command, explains Datamax-O’Neil Programming
Language (DPL) and its related uses in the writing, loading and storing of programs for the
control and production of label formats (designs) for the following printers at, or above, the
listed firmware version below:
Model distinctions, including configurations (i.e., Display or Non-Display) and equipment
types (e.g., GPIO-1, graphics display, RFID, etc.), will be indicated in this text to
differentiate command compatibility. The appendices of this manual also contain details that
cannot be ignored; the use of any command will require checking for possible exclusionary
conditions.
Overview
Printer Firmware Version
A-Class 11.08
A-Class Mark II 12.07
E-Class Mark II 12.01
E-Class Mark III Basic and Advanced Models
EX2 11.08
H-Class 12.071
I-Class 11.08
M-Class Mark II 12.071
MP Compact4 Mark II 14.02
Serial# 3xxxxxxx or earlier; Firmware Version
14.07 or greater
•
See the <STX>KC command for information regarding attainment of the printer’s firmware
version; and then, if necessary, upgrade that firmware. Upgrades are available at
http://www.datamax-oneil.com.
• Programming information for Class Series printers (or firmware versions for Class Series
printers) not found in this manual can be found in the Class Series Programmer’s Manual
(part number 88-2316-01), except the S-Class printer and the legacy model printers which
can be found in the DPL Programmer’s Manual (part number 88-2051-01); and, for the E-
3202 see the E-3202 Programmer’s Manual (part number 88-2257-01). All manuals can be
downloaded from our web site at http://www.datamax-oneil.com.
• References to “Menu Settings” refer either to the set-up menu or to the system menu of
the printer; consult to the appropriate Operator’s Manual for details.
• Where applicable, printer responses to a host device will depend upon the communication
port, port settings, and cabling.
Class Series 2 Programmer’s Manual 1
Page 16

Overview
This manual contains the following sections and appendices:
OVERVIEW on page 1
Contents, organization, and conventions used in this manual; also includes a
typical data flow sequence for the printer.
CONTROL CODE COMMAND FUNCTIONS on page 9
Description of the attention-getter characters necessary for the printer to receive a
command sequence, and available alternate characters and line terminators.
IMMEDIATE COMMAND FUNCTIONS on page 11
Description of the commands, listed alphabetically, that perform status queries and
printer control commands.
SYSTEM-LEVEL COMMAND FUNCTIONS on page 17
Description of the commands, listed alphabetically, that control the printer and
allow scalable font and image downloads.
EXTENDED SYSTEM-LEVEL COMMAND FUNCTIONS on page 37
Description of the commands (listed alphabetically) that control the printer.
LABEL FORMATTING COMMAND FUNCTIONS on page 125
Description of commands, listed alphabetically, that control the position of text and
images on the media, print or store, and end the formatting process.
FONT LOADING COMMAND FUNCTIONS on page 145
Description of commands, listed alphabetically, used when downloading font data
in PCL-4 compatible bitmaps.
GENERATING LABEL FORMATS on page 147
Description of the structure of records, the different types, and their use in
generating label formats.
APPENDICES on pages 165 – 313
These contain details that cannot be ignored including various tables, programming
examples, printer default values, and bar code symbology details. See the Table of
Contents for specific content information.
GLOSSARY on page 315
Definitions of words, abbreviations, and acronyms used in this manual.
2 Class Series 2 Programmer’s Manual
Page 17

Overview
General Conventions
These are some of the conventions followed in this manual:
On the header of each page, the name of the section.
On the footer of each page, the page number and the title of the manual.
Names of other manuals referenced are in Italics.
Notes are added to bring your attention to important considerations, tips or helpful
suggestions.
Boldface is also used to bring your attention to important information.
This manual refers to IBM-PC based keyboard command characters for access to the
ASCII character set. Systems based on different formats (e.g., Apple’s Macintosh )
should use the appropriate keyboard command to access the desired ASCII
character. See Appendix A for the ASCII character set.
Computer Entry and Display Conventions
Command syntax and samples are formatted as follows:
The Courier font in boldface indicates the DPL command syntax, and Italics are
used to indicate the command syntax parameters.
Regular Courier font indicates sample commands, files and printer responses.
Square brackets ([ ]) indicate that the item is optional.
<CR> is used to identify the line termination character. Other strings placed
between < > in this manual represent the character of the same ASCII name, and
are single-byte hexadecimal values (e.g., <STX>, <CR>, and <0x0D> equal 02, 0D,
and 0D, respectively).
Hexadecimal values are often displayed in “C” programming language conventions
(e.g., 0x02 = 02 hex, 0x41 = 41 hex, etc.)
Important Safety Instructions
The exclamation point within an equilateral triangle is intended to alert the
user to the presence of important operating and maintenance instructions.
Class Series 2 Programmer’s Manual 3
Page 18

Overview
Special Instructions
The green check box is intended to alert the user to conventions used within this
text or to notable operating details of the printer.
Typical Data Flow Sequence
The typical data flow sequence is summarized in the following bullets and detailed in the
table below. Printer Commands data is transmitted to the printer as shown in the table from
left to right, top to bottom.
Status commands
Configuration commands
Download commands
Label format
Status commands
Label reprint commands
Memory cleanup
Printer Commands Description Notes
<SOH>A
<STX>WG
<STX>O220
<STX>n
<STX>V0
<SOH>D
<STX>IApImagename<CR>image data...data
<CR>
<STX>L
D11
131100000500050Typical text field 01
Q0001
“Status” commands: Get
Status, Request Memory
Module Storage
Information…
“Configuration”
commands, download
image…
“Download” commands,
image, fonts…
Begin label
Label Header record
Label Formatting Data
record –
Object type, orientation,
position, data
Label Quantity
Optional,
bidirectional
communication
required for these
commands.
See <STX>Kc to
reduce configuration
commands
transferred
RAM (temporary) or
Flash (semipermanent)
memory.
Existing label
formats may be
recalled. Label
header records are
not required.
E
4 Class Series 2 Programmer’s Manual
Label Terminate record
Page 19
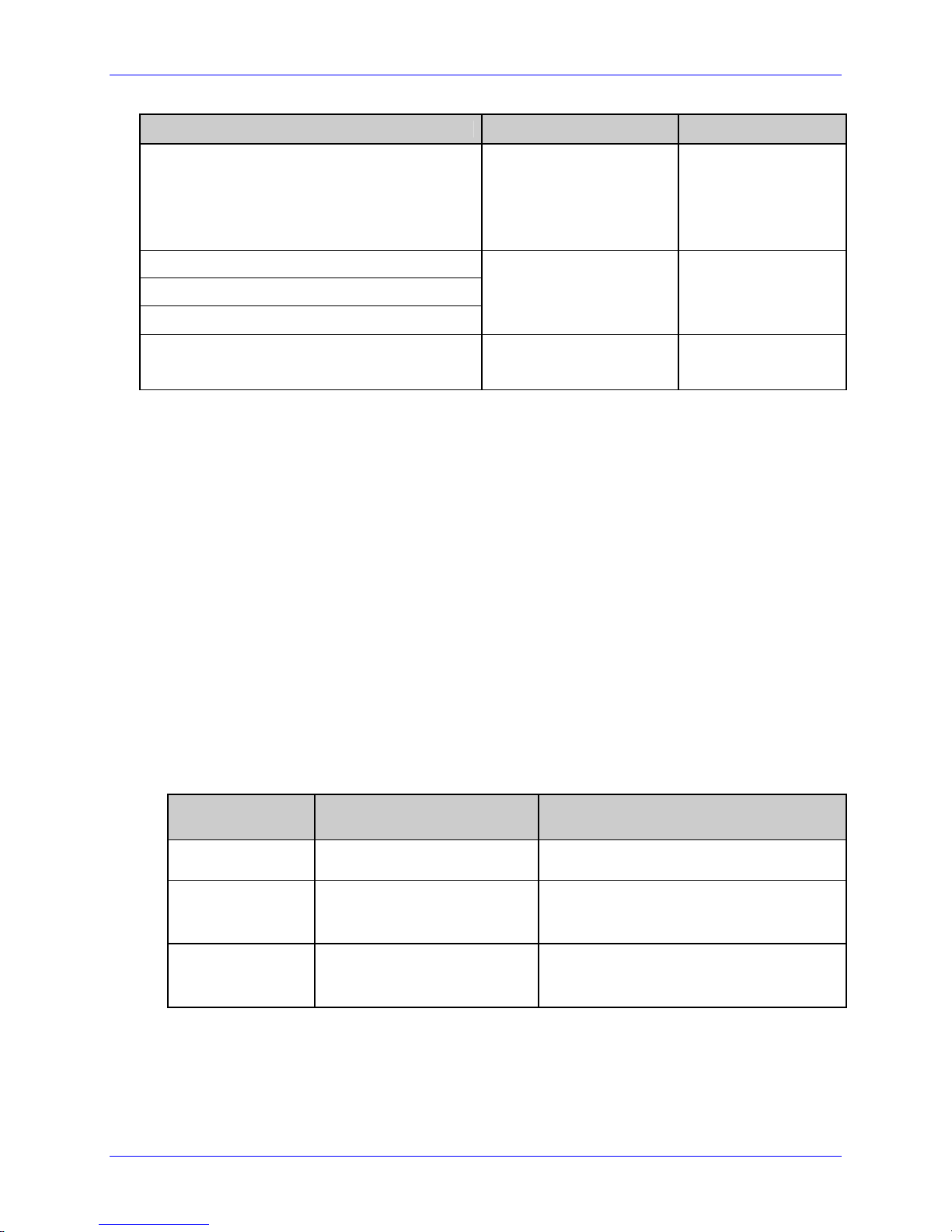
Printer Commands Description Notes
<SOH>A
<STX>U01new data for field 01
<STX>E0005
<STX>G
Overview
Status command
Reprint with New Data
Records
Optional,
bidirectional
communication
required for these
commands.
Used for fast
reprints.
<STX>xImagename<CR>
<STX>zA
Memory cleanup
Typically used for
temporary storage.
Commands are available for retrieving stored label formats, updating data, and adding new
data. These techniques are used for increasing throughput; see <STX>G, Label Recall
Command “r”, and Label Save Command “s”.
Typical commands used in the various stages shown above are listed in the tables that
follow.
Configuration Commands
The following table lists some commands useful in controlling printer configuration.
These commands are generally effective only for the current power-up session; toggling
power restores the default configuration. See <STX>Kc for changes to the default powerup configuration. Changing the default power-up configuration and saving objects in
printer Flash memory can reduce the data transmitted for each label and therefore
improve throughput.
Configuration
Command
Name Function
<STX>A
<STX>c
<STX>e
Class Series 2 Programmer’s Manual 5
Set Date and Time Sets Date and Time.
Set Continuous Paper Length
Set Edge Sensor
Must be 0000 for gap media; not used
for reflective media.
Sets sensing for gap or registration hole
type stock.
Page 20

Overview
Configuration
Command
<STX>Kf
Set Present Distance
Name Function
Determines label stop position, head
relative. <STX>f edge sensor relative
equivalent command, older models.
<STX>Kc
<STX>F
<STX>M
<STX>m
<STX>n
<STX>O
Configuration Set
Send Form Feed
Set Maximum Label Length
Set to Metric Mode
Set to Inch Mode
Set Start of Print Position
Determines default power-up
configuration.
Sets the stop position of the printed
label.
Length to search for next gap or
reflective mark; not used with
continuous media.
Subsequent measurements interpreted
in metric (most units, mm/10). Label
equivalent command can be used.
Subsequent measurements interpreted
in inches (most units in/100) label
equivalent command can be used.
Effect is not on the label immediately
following command since media position
is at Start of Print between labels;
<STX>K default position relative 64
in/100 maximum deviation.
<STX>S
<STX>V
6 Class Series 2 Programmer’s Manual
Set Feed Rate Sets blank label movement speed.
Software Switch
Enables optional hardware, cutter, and
present sensor.
Page 21

Download Commands
Download
Command
Overview
Name Function
<STX>I
<STX>i
<ESC>
Download Image
Download Scalable Font
Download Bitmapped Font
Downloads Image to selected memory
module.
Downloads Scalable Font to selected
memory module.
Downloads Bitmapped Font to selected
memory module.
Label Header Commands
These commands determine how the label formatting occurs, the print quality and
quantity. They are typically issued immediately following the <STX>L start of the label
format. The Format Attribute (A) and the Offset (C, R) commands can be changed at
any point between format records to achieve desired effects.
Label Header Command Name
A
C
D
H
M
P
P
Q
R
S
Set Format Attribute
Column Offset
Set Width and Dot Size
Set Heat Setting
Set Mirror Mode
Set Print Speed
Set Backup Speed
Set Quantity
Set Row Offset
Set Feed Speed
Class Series 2 Programmer’s Manual 7
Page 22

Overview
8 Class Series 2 Programmer’s Manual
Page 23

2
Control Code Command Functions
Introduction
The printer requires a special “attention-getter” character in order to receive a command
sequence, informing the printer that it is about to receive a command and the type of
command it will be. Control Commands, System-Level Commands, and Font Loading
Commands have their own unique attention-getter, followed by a command character that
directs printer action.
Attention-Getters
The attention-getters (e.g., “SOH”) are standard ASCII control labels that represent a one
character control code (i.e., ^A or Ctrl A). Appendix A contains the entire ASCII Control
Code Chart.
Attention-Getter ASCII Character Decimal Value HEX Value
Immediate Commands
System-Level Commands
Font Loading Commands
Table 2-1: Attention Getter Listings
Easy Control Codes
DPL has been enhanced to accept a 3-character SOH and STX sequence. Easy Control Codes
are always enabled, whether in Standard, Alternate, Alternate 2, or Custom Control Code
Mode. Two types of sequences have been created to meet any application’s requirements.
Use these sequences where you normally would use a single SOH or STX character.
Control Character
SOH %01 ^01
STX %02 ^02
3 “%” Character
Table 2-2: Easy Control Code Listings
SOH 1 01
STX 2 02
ESC 27 1B
Sequence
3 “^”Character
Sequence
Command Type
Control
System
Class Series 2 Programmer’s Manual 9
Page 24
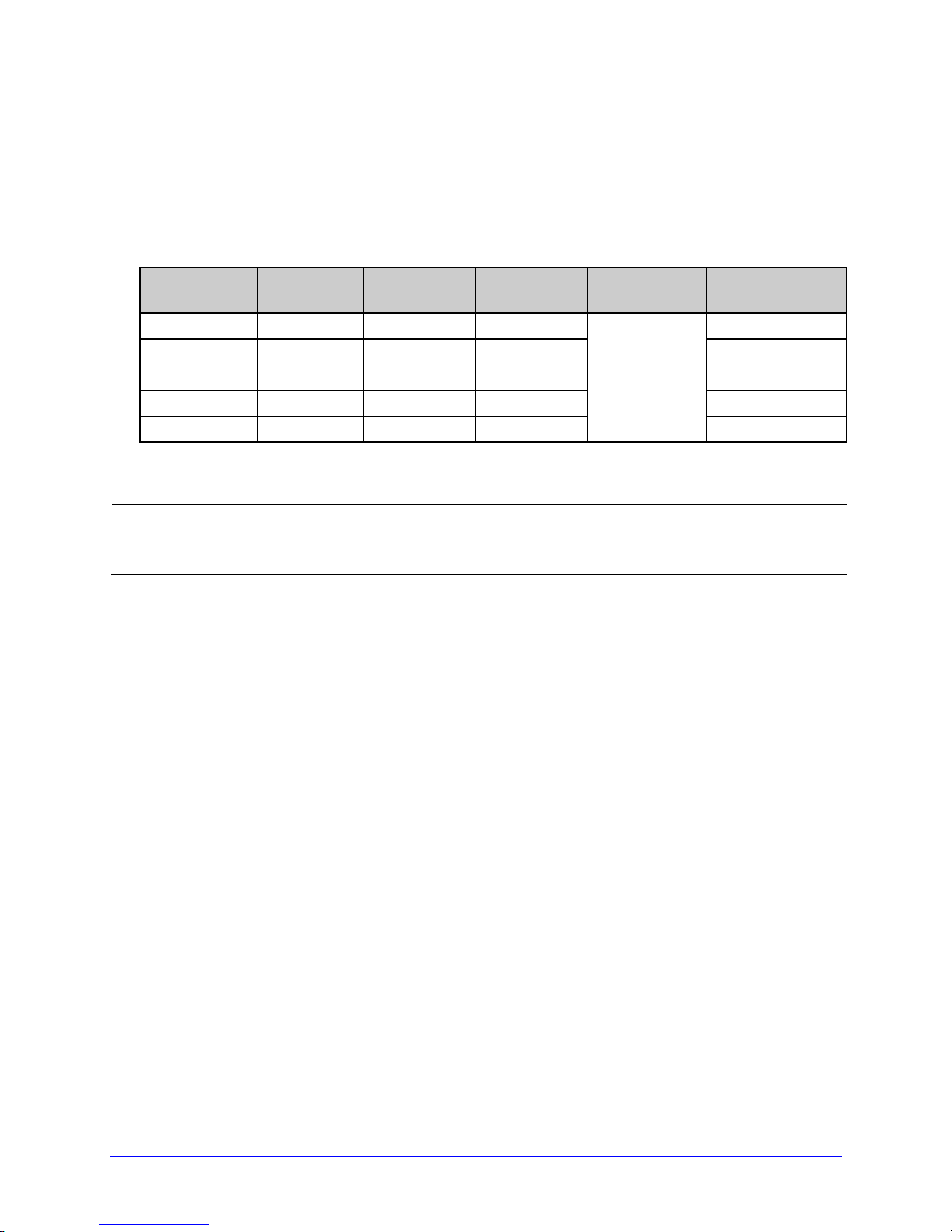
Control Code Command Functions
Alternate Control Code Modes
For systems unable to transmit certain control codes, Alternate Control Code Modes are
available. Configuring the printer to operate in an Alternate Control Code Mode (selected via
the Setup Menu, the <STX>Kc command or, where applicable, the <STX>KD command)
requires the substitution of Standard Control Characters with Alternate Control Characters in
what is otherwise a normal data stream.
Control
Character
SOH 0x01 0x5E 0x5E
STX 0x02 0x7E 0x7E
CR 0x0D 0x0D 0x7C
ESC 0x1B 0x1B 0x1B
“Count By”
[1]
See Label Formatting Commands, ^ set count by amount.
Throughout this manual <SOH>, <STX>, <CR>, <ESC>, and ^ will be used to indicate control
codes. The actual values will depend on whether standard or alternate control codes are
enabled for the particular application.
Standard Alternate Alternate 2 Custom
[1]
0x5E 0x40 0x40
Table 2-3: Alternate Control Code Listings
User Defined
Command
Type
Control
System
Line Termination
Font Loading
Label Formatting
Alternate Line Terminator Example: Alternate Control Codes provide for substitution of
the line terminator, as well as the control characters listed above. For example using
Alternate 2, the line terminator <CR> (0x0D) is replaced by | (0x7C). The following is a
sample label format data stream for a printer configured for Alternate-2 Control Codes:
~L|1911A10001000101234560|X|~UT01ABCDE|~G|
10 Class Series 2 Programmer’s Manual
Page 25

<
<
3
Immediate Command Functions
Introduction
When the printer receives an Immediate Command, its current operation will be
momentarily interrupted to respond to the command. Immediate Commands may be issued
before or after System-Level commands; however, they may not be issued among Label
Formatting Commands or during font or image downloading. Immediate Commands consist
of:
1. Attention-Getter, 0x01 or 0x5E; see Control Code Command Functions.
2. Command Character
SOH # Reset
This command resets the printer. Resetting the printer returns all settings to default and
clears both the communications and printing buffers. The command also clears DRAM
memory.
Syntax:
Printer Response: The printer will reset.
SOH>#
<XON> T
(The T may come before the <XON>)
SOH * Reset (Display-Equipped Models only)
This command forces a soft reset of the microprocessor, resetting the printer, returning
all factory default values, and clearing the communication and print buffers.
Syntax:
Printer Response: The printer will reset.
Class Series 2 Programmer’s Manual 11
SOH>*
<XON> R
(The R may come before the <XON>)
Page 26

Immediate Command Functions
<
<
SOH A Send ASCII Status String
This command allows the host computer to check the current printer status. The printer
returns a string of eight characters, followed by a carriage return. Each character (see
below) indicates an associated condition, either true (Y) or false (N). Byte 1 is
transmitted first. See <SOH>F.
Syntax:
Sample:
Printer Response:
Where:
SOH a Send ASCII Extended Status String
This command allows the host computer to check an extended current printer status.
The printer returns a string of seventeen characters, followed by a carriage return. Most
characters (see below) indicate an associated condition, either true (Y) or false (N). Byte
1 is transmitted first. See <SOH>F.
Syntax:
Sample:
Printer Response:
SOH>A
<SOH>A
abcdefgh<CR>
Possible
Values
-
a
b
c
d
e
f
g
h
Y/N Y = Interpreter busy (imaging) 1
-
Y/N Y = Paper out or fault 2
-
Y/N Y = Ribbon out or fault 3
-
Y/N Y = Printing batch 4
-
Y/N Y = Busy printing 5
-
Y/N Y = Printer paused 6
-
Y/N Y = Label presented 7
-
Y/N Y = (Internal) Rewinder out or fault 8
Table 3-1: ASCII Status Bytes
SOH>a
<SOH>a
abcdefgh:ijklmnop<CR>
Interpretation
Transmit
Sequence
12 Class Series 2 Programmer’s Manual
Page 27
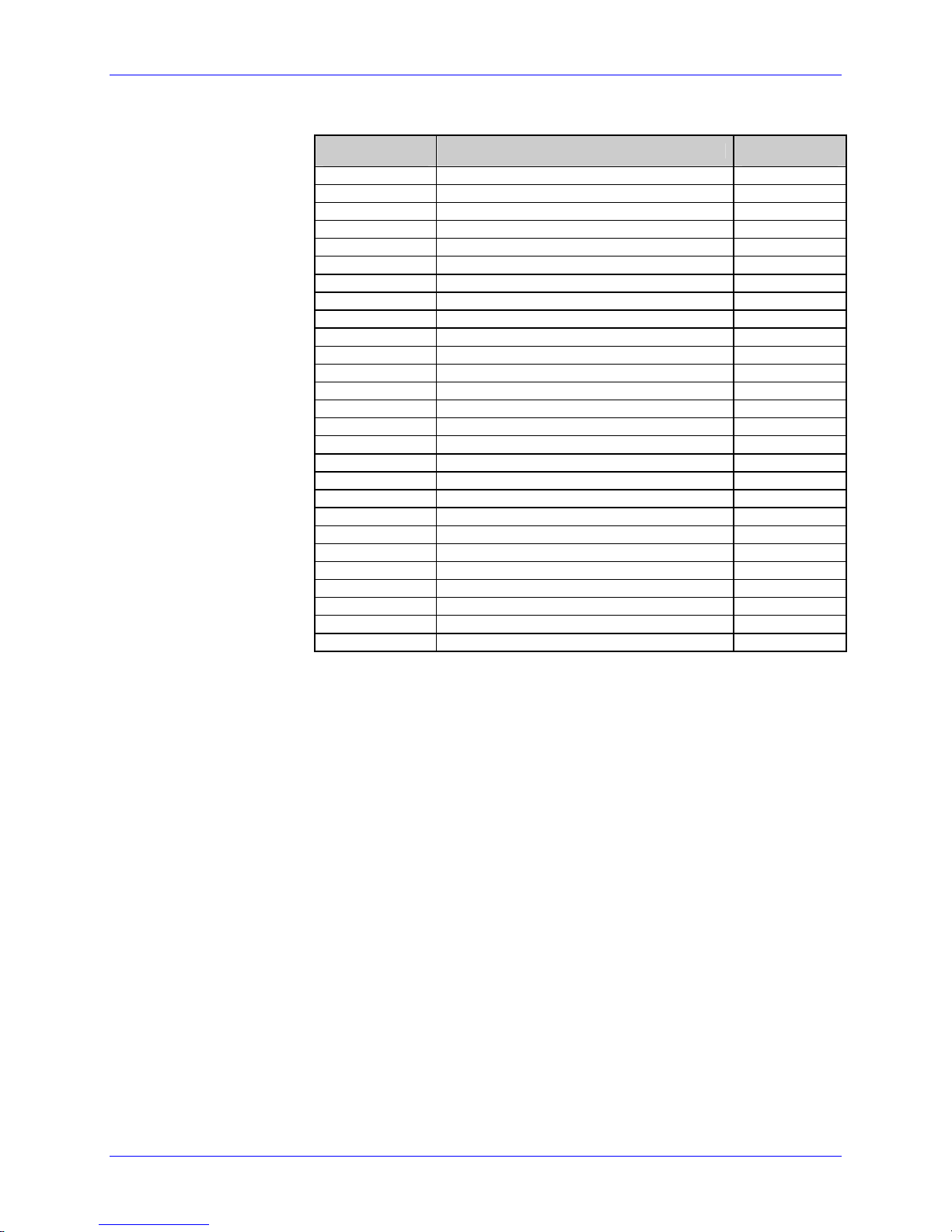
Immediate Command Functions
<
Where:
SOH B Toggle Pause
This command toggles the printer’s paused state between “On” and “Off.” (This is the
same function achieved by pressing the PAUSE Key.)
Syntax:
Sample:
Printer Response: This command will illuminate the Paused/Stop Indicator and/or
Possible
Values
a
b
c
d
e
f
g
h
i
j
k
l
m
n
o
p
q
r
s
t
u
v
w
x
-
Y/N Y = Interpreter busy (imaging) 1
-
Y/N Y = Paper out or fault 2
-
Y/N Y = Ribbon out or fault 3
-
Y/N Y = Printing batch 4
-
Y/N Y = Busy printing 5
-
Y/N Y = Printer paused 6
-
Y/N Y = Label presented 7
-
Y/N Y = Rewinder out or fault 8
-
: : = Always : 9
-
Y/N Y = Cutter Fault 10
-
Y/N Y = Paper Out 11
-
Y/N Y = Ribbon Saver Fault 12
-
Y/N Y = Print Head Up 13
-
Y/N Y = Top of Form Fault 14
-
Y/N Y = Ribbon Low 15
-
Y/N Y = N (reserved for future) 16
-
Y/N Y = N (reserved for future) 17
-
: : = Always : 18
-
Y/N Y = Ready (no data or signal) 19
-
Y/N Y = Waitng for Signal 20
-
Y/N Y = Waitng for Data 21
-
Y/N Y = Com1 has data not parsed 22
-
Y/N Y = N (reserved for future) 23
-
Y/N Y = N (reserved for future) 24
-
Y/N Y = N (reserved for future) 25
-
Y/N Y = N (reserved for future) 26
<CR> 27
Interpretation
Table 3-1: ASCII Status Bytes
SOH>B
<SOH>B
indicate PAUSED on the LCD or graphics display panel, suspend
printing, and wait until one of the following occurs:
• The <SOH>B command is sent to the printer.
• The PAUSE Key is pressed.
Upon which the printer will turn the Paused/Stop Indicator “Off”
and/or remove PAUSED from the LCD or graphics display, then
resume operation from the point of interruption. (If the Receive
Buffer is not full, an <XON> character will be transmitted from
the printer.)
Transmit
Sequence
Class Series 2 Programmer’s Manual 13
Page 28

Immediate Command Functions
<
<
SOH C Stop/Cancel
This command performs the same function as pressing the STOP/CANCEL Key (i.e., it
clears the current format from the print buffer, pauses the printer, and illuminates the
Paused/Stop Indicator). (The pause condition is terminated as described under <SOH>B.)
Syntax:
Sample:
Printer Response: The print buffer is cleared and the Paused/Stop Indicator is
SOH D SOH Shutdown
This command is ignored by the printer.
SOH E Send Batch Remaining Quantity
This command causes the printer to return a four-digit number indicating the quantity of
labels that remain to be printed in the current batch, followed by a carriage return.
Communications latency may cause this value to be higher than actual on some printers.
Syntax:
Printer response:
Where:
SOH>C
<SOH>C
illuminated (and/or PAUSED is displayed on the LCD or graphics
display) as operations are suspended, until one of the following
occurs:
• The <SOH>B command is sent to the printer; or
• The PAUSE Key is pressed.
Upon which the printer will turn the Paused/Stop Indicator
“Off” and/or remove PAUSED from the LCD or graphics
display. (If the Receive Buffer is not full, an <XON> character
will be transmitted from the printer.)
SOH>E
nnnn<CR>
nnnn -
Are four decimal digits, 0-9999.
14 Class Series 2 Programmer’s Manual
Page 29

Immediate Command Functions
<
<
“
SOH e Send Batch Printed Quantity
This command causes the printer to return a four-digit number indicating the quantity of
labels that have been printed in the current batch, followed by a carriage return.
Communications latency may cause this value to be lower than actual on some printers.
Syntax:
Printer response:
Where:
SOH F Send Status Byte
This command instructs the printer to send a single status byte where each bit (1 or 0)
represents one of the printer’s status flags, followed by a carriage return (see below). If
an option is unavailable for the printer, the single bit will always be zero. See <SOH>A.
Syntax:
Response format:
Where:
SOH>e
nnnn<CR>
nnnn -
Are four decimal digits, 0-9999.
SOH>F
X<CR>
X” is 0 through 0xef with bits as indicated in the “Condition”
column below:
Bit* Value Condition
8 1 or 0 (Internal) Rewinder out or fault
7 1 or 0 Label presented
6 1 or 0 Printer paused
5 1 or 0 Busy printing
4 1 or 0 Printing batch
3 1 or 0 Ribbon out or Fault
2 1 or 0 Paper out or Fault
1 1 or 0 Command interpreter busy (imaging)
*
One is the least significant bit.
Class Series 2 Programmer’s Manual 15
Page 30

Immediate Command Functions
16 Class Series 2 Programmer’s Manual
Page 31

<
4
System-Level Command Functions
Introduction
The most commonly used commands are the System-Level Commands. These are used to
load and store graphics information, in addition to printer control. System-Level Commands
are used to override default parameter values (fixed and selectable) and may be used
before or after Immediate Commands but cannot be issued among Label Formatting
Commands. System-Level Commands consist of:
1. Attention-Getter, 0x02 or 0x7E; see Control Code Command Functions.
2. Command Character
3. Parameters (if any).
STX A Set Time and Date
This command sets the time and date. The initial setting of the date will be stored in the
printer’s internal inch counter. This date can be verified by printing a Configuration
Label.
Syntax:
Where:
Sample:
Printed response:
•
• Printers without the Real Time Clock option lose the set time/date when power is
• Response format is variable; see the Special Label Formatting Command <STX>T.
When set to 000, the Julian date is automatically calculated; otherwise, the Julian
date will print as entered, without daily increments. If factory defaults are restored
the actual Julian date will also be restored.
removed.
STX>AwmmddyyyyhhMMjjj
w
mm
dd
yyyy
hh
MM
jjj
<STX>A1020319960855034
Mon. Feb 3, 1996, 8:55AM, 034
1 digit for day of week; 1 = Monday; 7 = Sunday
2 digits for month
2 digits for day
4 digits for year
2 digits for hour in 24 hour format
2 digits for minutes
3 digits for Julian date / constant; see notes below.
Class Series 2 Programmer’s Manual 17
Page 32

System-Level Command Functions
<
<
STX a Enable Feedback Characters
This command enables the feedback ASCII hex characters to be returned from the
printer following specific events after each completed batch of labels when using serial
communications. The default value is ”OFF”.
Syntax:
Printer response: Event dependent. (Also see Appendix D for error codes.)
Where:
STX B Get Printer Time and Date Information
This command instructs the printer to retrieve its internal time and date information.
Syntax:
Sample:
Response format:
Where:
Response sample:
STX>a
Event Return Characters
Invalid character
Label printed
End of batch
STX>B
<STX>B
wmmddyyyyhhMMjjj<CR>
w
mm
dd
yyyy
hh
MM
jjj
* See <STX>A for details and restrictions.
1 digit for day of week; 1 = Monday
2 digits for month
2 digits for day
4 digits for year
2 digits for hour in 24 hour format
2 digits for minutes
3 digits for Julian date / constant*
1020319960855034<CR>
0x07 ( BEL )
0x1E ( RS )
0x1F ( US )
18 Class Series 2 Programmer’s Manual
Page 33

System-Level Command Functions
<
<
>
STX c Set Continuous Paper Length
This command sets the label size for applications using continuous media. It disables the
top-of-form function performed by the Media Sensor. The sensor, however, continues to
monitor paper-out conditions. See <STX>M.
Syntax:
Where:
Sample:
This command must be reset to zero for edge or reflective sensing operation.
STX E Set Quantity for Stored Label
This command sets the number of labels for printing using the format currently in the
print buffer. (The printer automatically stores the most recent format received in the
buffer until the printer is reset or power is removed.) When used in conjunction with the
<STX>G command, this will print the format.
Syntax:
Where:
Sample:
Printer response: 25 labels of the current format in memory will be printed.
If no <CR> terminates the command, a four-digit quantity (nnnn) can be entered; and,
specifying 9999 will cause continuous printing.
STX>cnnnn
nnnn -
<STX>c0100
Specifies the length of the media feed for each label
format, in inches/100 or millimeters/10 (see <STX>m).
The sample above sets a label length of 100, which equals 1.00
inch (assuming Imperial Mode is selected).
STX>Ennnnn<CR
nnnnn -
<CR> -
<STX>E00025<CR>
<STX>G
A five-digit quantity, including leading zeros.
0x0d terminates the name.
Class Series 2 Programmer’s Manual 19
Page 34

System-Level Command Functions
<
<
<
STX e Select Edge Sensor
This command enables transmissive (see-through) sensing for top-of-form detection of
die-cut and holed (notched) media. This sensor will detect a minimum gap of 0.1 inches
(2.5 mm) between labels (see the Operator’s Manual for media requirements). This is
the default setting.
Syntax:
This command is ignored when <STX>cnnnn is issued with a non-zero value for nnnn.
STX F Form Feed
This commands the printer to form feed to the next start of print.
Syntax:
Printer response: The printer will form feed.
STX f Set Form Stop Position (Backfeed Command)
This sets the stop position of the printed label, allowing the label to stop at a point past
the start-of-print position. When the next label format is sent, the printer motor
reverses direction to retract the media to the start-of-print position. If quantities of more
than one label are requested, the printer will operate without backfeeding. Backfeed will
then only occur when printing has stopped for a few seconds.
Non-Display Models: Option Control must be set via the printer menu to “Host” for this
command to have effect.
Display-Equipped Models: This command is not honored; see
Syntax:
Where:
Sample:
STX>e
STX>F
<STX>Kf and <STX>Kc.
STX>fnnn
nnn -
Is a three-digit distance from the Media Sensor, in
inches/100 or mm/10. This distance is independent of
the start-of-print position (<STX>O), yet it must be
greater than the start-of-print position to take effect.
<STX>f230
The sample above sets a stop position distance of 230 (2.3 inches
from the Media Sensor’s eye).
20 Class Series 2 Programmer’s Manual
Page 35

System-Level Command Functions
<
<
>
d
STX G Print Last Label Format
This command prints a previously formatted label and restarts a canceled batch job
following the last processed label. This is used when there is a label format in the buffer.
The <STX>E command is used to enter the quantity. (Without the <STX>E command, one
label will print.)
Syntax:
STX>G
STX I Input Image Data
This command must precede image downloading from the host to the printer. The data
that immediately follows the command string will be image data. If any of the 8-bit
input formats are to be used, it is necessary to disable the Immediate Command
interpreter by executing an <SOH>D command before issuing the <STX>I command. See
Appendix N for more information. To print an image, refer to Generating Label Formats.
A-Class (and large display H–Class models): A “ready mode” logo image can be
input using this command. The image must be stored on a Flash module. The image
name must be “logolab” (lowercase only) in the following DPL command. Also, printer
power must be cycled for the new image to appear. The available display area is 312
pixels wide by 94 pixels high. Images larger than this specified width or height will be
clipped along the right and/or bottom edges.
The native format for storing downloaded PCX and BMP images is RLE-2, which results
in a better compression ratio for less module space usage when downloading gray-scale
Syntax:
Where:
images and images with large black or white areas.
STX>Iabfnn…n<CR
ata
a -
b -
f -
Memory Module Bank Select (see Appendix K).
Data Type (optional), A or omit:
b Value: Image Data Value Range:
A ASCII Characters 0-9, A-F, (7 bit)
omit 00-FF, (8 bit)
Format Designator:
f Designator: Format Type:
F
B
b
I
i
P
p
7-bit D-O image load file
.BMP 8-bit format, flipped, black
and white (B&W)
.BMP 8-bit format, B&W
.IMG 8-bit format, flipped, B&W
.IMG 8-bit format, B&W
.PCX 8-bit format, flipped, B&W
.PCX 8-bit format, B&W
Class Series 2 Programmer’s Manual 21
Page 36

System-Level Command Functions
<
e
<CR>
x
…
Sample:
STX i Scalable Font Downloading
The command structure for downloading TrueType (.TTF) scalable fonts (files may be
single-byte or double-byte character systems) is as follows:
Syntax:
Where:
Sample:
nn…n -
Up to 16 characters used as an image name.
<CR> -
0x0d terminates the name.
data -
Image data
<SOH>D
<STX>IDpTest <CR>
data...data <CR>
The sample above instructs the printer to (1) receive an 8-bit PCX
image sent by the host in an 8-bit data format, (2) name the
image “Test”, and (3) store it in Module D (with a .dim file
extension).
STX>imtnnNam
x…xdata
m -
t -
nn -
Name -
<CR> -
xx…x -
data -
<STX>iDT52Tree Frog<CR>000087C2data...
The designator of the module where the font is to be
saved; see Appendix K.
Type of scalable font being downloaded:
T = TrueType
Two-digit font reference ID. Valid range is 50-99,
9A-9Z, 9a-9z (base 62 numbers).
The title, up to 16 characters, for this font.
0x0d terminates the Name.
Eight-digit size of the font data, number of bytes,
hexadecimal, padded with leading zeros.
The scalable font data.
The sample above downloads a TrueType font to Module D, and
assigns it the Font ID of 52 with the name “Tree Frog” and file
extension .dtt. The size of the font data is 0x87C2 bytes long.
22 Class Series 2 Programmer’s Manual
Page 37

System-Level Command Functions
<
<
<
STX J Set Pause for Each Label
This command causes the printer to pause after printing each label. It is intended for
use with the peel mechanism or tear bar when the Present Sensor option is not installed.
After removing the printed label, the PAUSE Key must be pushed in order to print the
next label. (The printer must be reset to clear the <STX>J command.)
Syntax:
STX K Extended System-Level Commands
This is an expansion of the System-Level Command structure; see Extended SystemLevel Commands for more information.
STX k Test RS-232 Port
This command instructs the printer to transmit the Y character from the printer’s RS-232
port. (Failure to receive Y could indicate an interfacing problem.)
Syntax:
Printer response:
STX L Enter Label Formatting Command Mode
This command switches the printer to the Label Formatting Command Mode, where the
printer expects to receive only Record Structures and Label Formatting Commands.
Immediate, System-Level, and Font Loading commands will be ignored until the label
formatting mode is terminated with E, s, or X, (see Label Formatting Commands for
additional information).
Syntax:
STX>J
STX>k
Y
STX>L
Class Series 2 Programmer’s Manual 23
Page 38

System-Level Command Functions
<
<
<
STX M Set Maximum Label Length
This command instructs the printer move media this distance in search of the top-ofform (label edge, notch, black mark, etc.) before declaring a paper fault. A paper fault
condition can occur if this setting is too close (within 0.1 inch [2.54 mm]) to the physical
length of the label. Therefore, it is a good practice to set this command to 2.5 to 3 times
the actual label length used. The minimum value should be at least 5” (127 mm).
Syntax:
Where:
Sample:
STX m Set Printer to Metric Mode
This command sets the printer to interpret measurements as metric values (e.g.,
<STX>c0100 will equal 10.0 mm). The default is Imperial (see <STX>n).
Syntax:
STX n Set Printer to Imperial Mode
This command sets the printer to interpret measurements as inch values (e.g.,
<STX>c0100 will equal 1.00 inch), and is the default mode.
Syntax:
STX>Mnnnn
nnnn -
Is a four-digit length, 0000-9999, in/100 or mm/10.
Maximum setting is 9999 (99.99 inches or 2540
mm). The default setting is 16 inches/ 406.4 mm.
<STX>M0500
The sample above sets a maximum travel distance of 5 inches
(unless the printer is in metric mode; see <STX>m).
STX>m
STX>n
24 Class Series 2 Programmer’s Manual
Page 39

System-Level Command Functions
<
STX O Set Start of Print (SOP) Position
This command sets the point to begin printing relative to the top-of-form (the label’s
edge as detected by the Media Sensor). The printer will feed from the top-of-form to the
value specified in this command to begin printing.
This value operates independently of the <STX>f command.
Non-Display Models: The printer Options Control must be set (via the menu) to “Host”
for this command to have effect.
Display-Equipped Models: If SOP Emulation is set to “enabled” (via the menu), this
command sets the point where printing starts, emulating the selected legacy printer’s
distance, as measured between the media sensor and the print head burn line. In
addition, regardless of the SOP Emulation setting, the start of print position can be finetuned via the menu: Menu Mode / Print Control / Custom Adjustments / Row Adjust.
Syntax:
Where:
Sample
(Non-Display
models):
Sample
(Display-Equipped
models):
STX>Onnnn
nnnn -
Is a four-digit offset value in inches/100 or mm/10.
The “zero” setting is the default value, and settings
below 50 are adjusted back to the default value.
Non-Display: The default setting is 0220 in Imperial
Mode (0559 in Metric Mode).
Display-Equipped: The default setting is “Off” and the
printer assumes the natural SOP position.
<STX>O0300
The sample above sets a start of print position of 3.0 inches
(unless in Metric Mode; see <STX>m).
<STX>O0210
The sample above will begin printing 0.1 inch closer to the leading
edge of the label if the 220 (Allegro) SOP Emulation was selected,
or 1.0 inch farther away from the leading edge if 110 (ProdPlus)
SOP Emulation was selected.
Class Series 2 Programmer’s Manual 25
Page 40

System-Level Command Functions
<
<
<
STX o Cycle Cutter
This command will cause the optional cutter mechanism to immediately perform a cut
after all previously received commands are executed. The cutter must be installed,
enabled and the interlock(s) closed for operation.
Syntax:
STX P Set Hex Dump Mode
This command instructs the printer to assume Hex Dump Mode. Instead of a formatted
product, data sent following this command will be printed in its raw ASCII format. To
capture all data, labels should be at least four inches (102 mm) long and as wide as the
maximum print width. This command has the same effect as turning “On” the printer
while depressing the FEED Key (return normal operation by manual reset).
Syntax:
Printer response is
data dependent
(layout may vary):
STX>o
STX>P
STX p Controlled Pause
This command will cause the printer to pause only after all previously received
commands are executed, often useful between label batches. (This command will not
clear the pause condition; see <SOH>B).
Syntax:
26 Class Series 2 Programmer’s Manual
STX>p
Page 41

System-Level Command Functions
<
<
<
STX Q Clear All Modules
This command instructs the printer to clear all Flash and DRAM modules (except as
noted); see the corresponding Operator’s Manual for applicable module options. All
stored data will be destroyed.
Syntax:
Will not affect Module Y or the ILPC Font module.
STX q Clear Module
This command clears the selected Flash or DRAM module. During normal operations if a
module becomes corrupted (identifiable when the printer responds with a “No Modules
Available” message to a <STX>W command) it must be cleared. All stored data will be
destroyed.
Syntax:
Where:
Sample:
STX>Q
STX>qa
a -
<STX>qA
Memory module designator; see Appendix K.
The sample above clears memory Module A.
Will not affect Module Y or the ILPC Font module.
STX R Ribbon Saver Control
This command enables the operation of the optional Ribbon Saver. It is the only
command used to control the Ribbon Saver. Its operation is continuous when enabled.
The printer must be set to thermal transfer (ribbon) printing mode then, during
operation, the Ribbon Saver engages automatically, lifting when the minimum amount of
label white space is exceeded.
Syntax:
Where:
Sample:
This command is ignored on non-equipped printers.
STX>Rx
x -
Y - Enabled (Default = Menu selection.)
N - Disabled
<STX>RY
The sample above will turn the ribbon saver on.
Class Series 2 Programmer’s Manual 27
Page 42

System-Level Command Functions
<
<
<
STX r Select Reflective Sensor
This command enables reflective (black mark) sensing for top-of-form detection of rolled
butt-cut, and fan-fold or tag stocks with reflective marks on the underside. This Media
Sensor will detect a minimum mark of 0.1 inches (2.54 mm) between labels (see the
Operator’s Manual for media requirements). The end of the black mark determines the
top of form. Use the <STX>O command to adjust the print position.
Syntax:
Default setting: Edge sensing
STX S Set Feed Speed
This command controls the output rate of the media when the FEED Key is pressed.
Syntax:
Where:
STX T Print Quality Label
This command instructs the printer to produce a Print Quality label, a format comprised
of different patterns and bar codes useful in printer setup. To capture all printed
information, use the labels as wide as the maximum print width (see Appendix K) and at
least four inches (102 mm) long.
Syntax:
Printer response
(dot patterns may
vary):
STX>r
STX>Sn
n -
STX>T
Is a letter value (see Appendix L).
28 Class Series 2 Programmer’s Manual
Page 43

System-Level Command Functions
<
<
>
STX t Test DRAM Memory Module
This command tests the DRAM module. The printer returns a one-line message stating
the module condition (no message is returned if a module is unavailable). The printer
must have Feedback Characters enabled for this command to function. Feedback
Characters can be enabled via the menu (see the Operator’s Manual for additional
information).
Syntax:
3
Response format:
STX>t
Module D: xxxxK RAM Tested results <CR>
Where:
xxxx
Module size in Kbytes.
-
results
Test results given as “Good” or “Bad”.
-
STX U Label Format String Replacement Field
This command places new label data into format fields to build a label. Two options are
available: Exact Length and Truncated Length.
To easily keep track of fields, place all of the fields to be updated with the command at
the beginning of the label format. A maximum of 99 format fields can be updated. Fields
are numbered consecutively 01 to 99 in the order received.
Exact Length Replacement Field Functions – The new data string must equal the
original string length and contain valid data. When the dynamic data is shorter than the
length of the originally defined data field, then field will be padded with blanks (or zero
when the Format Record header specifies a numeric bar code).
Syntax:
Where:
Exact Length
Sample:
STX>Unnss…s<CR
nn
ss…s
- Is the format field number, 2 digits.
Is the new string data, followed by a <CR>
-
<STX>L
1A1100001000100data field 1<CR>
161100001100110data field 2<CR>
161100001200120data field 3<CR>
Q0001
E
<STX>U01123<CR>
<STX>U02New data F2<CR>
<STX>E0002
<STX>G
Class Series 2 Programmer’s Manual 29
Page 44

System-Level Command Functions
<
>
The sample above produces three labels. The first is formatted
with the commands between <STX>L and E. The next two labels
print with the replacement data contained in the <STX>U
commands (see <STX>E and <STX>G). The bar code is the same
length: 3 digits and nine spaces.
Truncated Length Replacement Field Functions – A variant of the <STX>U command
includes the truncate option “T”, where dynamic data shorter than the originally defined
field length will not be padded and the original maximum field length is maintained for
subsequent replacements.
Syntax:
Where:
Truncated Sample:
STX>UTnnss…s<CR
nn
T
ss…s
<STX>L
1A1100001000100data field 1<CR>
161100001100110data field 2<CR>
161100001200120data field 3<CR>
Q0001
E
<STX>UT01123<CR>
<STX>U02New data F2<CR>
<STX>E0002
<STX>G
- Is the format field number, 2 digits.
-
Truncate option
-
Is the new string data, followed by a <CR>.
The sample above produces three labels. The first is formatted
with the commands between <STX>L and E. The next two labels
print with the replacement data contained in the <STX>U
commands (see <STX>E and <STX>G). The bar code is shortened;
it only has three digits (and no spaces).
30 Class Series 2 Programmer’s Manual
Page 45

System-Level Command Functions
<
STX V Software Switch Settings
This command controls the printer options, where the appropriate value allows the
option(s) to be “On” or “Off.” Each option has a corresponding bit whose value is “1”
when enabled. The tables below indicate the bit assignments and corresponding
command value needed to enable the desired option(s). Printer options are set by
entering selections through the menu. The software setting command allows two of
these option settings to be modified without returning to the menu.
Syntax:
Where:
Sample:
Bit Assignment Printer Option
STX>Vn
n
<STX>V5
- Is a single digit ASCII numeric value from 0-F. The
value of n is used to override the power-up option
settings. Reset or power-up returns the printer to the
original settings.
The sample above corresponds to setting Bits 0 and 2, creating a
command value of 5. When applied, this enables the Present
Sensor and Cutter options.
0 Cutter
1 N/A
2 Present Sensor
3 N/A
Table 4-1: Software Switch Bit Assignment
Use the bit assignment table above to determine the command value n in the binary
table below (e.g., the command value 5 sets the bits 0 and 2 to “1”).
Command Values for Bits Assigned
n Value
0 0 0 0 0
1 0 0 0 1
4 0 1 0 0
5 0 1 0 1
3 2 1 0
Table 4-2: Software Switch Binary
Bit
Class Series 2 Programmer’s Manual 31
Page 46

System-Level Command Functions
<
<
STX v Request Firmware Version
This command causes the printer to send its version string (same as printed on the
configuration label). The version may be different from printer to printer.
Syntax:
Printer Response:
STX W Request Memory Module Information
This command requests a memory module directory listing. Results may vary depending
on printer class, model, or firmware version.
Syntax:
Where:
Sample:
Printer response
(using an H-Class):
STX>v
VER: H-4212–11.04 01/01/2008<CR>
STX>W[b][c]a
b s
c e
a -
<STX>WF
MODULE: D<CR>
S50 92244ttf50<CR>
AVAILABLE BYTES: 945152<CR>
MODULE: G<CR>
AVAILABLE BYTES: 852480<CR>
MODULE: X<CR>
AVAILABLE BYTES: 852480<CR>
MODULE: Y<CR>
AVAILABLE BYTES: 852480<CR>
optional – list file size also
optional – list file extension also
Data type:
F
=
G
L
C
X
N
M
f
p
*
Downloaded fonts
=
Graphics (Image)
=
Label formats
=
Configuration files
=
Menu language files
=
Plug-ins
=
Miscellaneous type files
=
Resident fonts
=
Entire module contents
=
All types
32 Class Series 2 Programmer’s Manual
Page 47

System-Level Command Functions
<
<
STX w Test Flash Memory Module
This command tests the Flash module. The time for each test will vary from 20 to 120
seconds, depending upon the size of the module. All stored data will be destroyed. If
no module is present, there will be no printer response.
Syntax:
Where:
Response format:
Where:
STX X Set Default Module
This command, typically used prior to the loading of PCL-4 bitmapped fonts (see Font
Loading Commands), is designed to allow the user to select between modules when
downloading information. The default module is one of the following:
1. The first alpha designator of the existing modules if item 2 has not occurred.
2. The module selected by this command.
Syntax:
Where:
Sample:
The sample above sets “B” as the default module.
STX>wa
a
Module A: xxxxK results
A
xxxx
results - Test results given as “Good” or “Bad”.
STX>Xa
-
Module designator; see Appendix K.
Module tested.
-
-
Module size in Kbytes.
a
<STX>XB
- Module designator; See Appendix K.
Class Series 2 Programmer’s Manual 33
Page 48

System-Level Command Functions
<
>
G
L F
S C X N M u
STX x Delete File from Module
This command removes a specific file from the specified module. The file name is
removed from the module directory and thus the file cannot be accessed. The actual
storage space occupied by the file is not released. To reclaim deleted file storage space
use <STX>z to pack the module.
Syntax:
Where:
Sample:
STX>xmtnn…n<CR
m
t
nn…n -
- Module designator; see Appendix K.
The file type identification code:
-
=
Image file
=
Label format file
=
Downloaded bitmapped font file
=
Downloaded scalable font file
=
Configuration file
=
Language file
=
Plug-in file
=
Miscellaneous file type
=
The file to delete, where:
Unknown type – must use extension if
applicable
• Font (bitmapped), three character font identifier;
• Font (scalable), two character font identifier;
• Graphic name, up to sixteen alphanumeric
characters; or,
• Label format name, up to sixteen alphanumeric
characters.
<STX>xDS50<CR>
The sample above deletes a downloaded scalable font with ID 50
from Module D.
34 Class Series 2 Programmer’s Manual
Page 49

System-Level Command Functions
<
<
STX Y Output Sensor Values
This command causes a sensor value response. When <STX>Y is received, the printer will
respond with the digitally converted values of the internal analog sensors (see below).
To repeat the display of values, send the printer a “SPACE” character (20 hexadecimal);
or, send <ESC> to terminate this function.
The printer must have Feedback Characters enabled for this command to function.
(Feedback Mode [Characters] can be enabled via command or menu setting; see the
<STX>KcFM command or the Operator’s Manual for additional information).
Syntax:
Printer response:
Where:
•
• Some readings require printer-controlled paper movement to produce a meaningful
• Media Sensor readings require the appropriate sensor selection, transmissive
Equipped sensors vary with printer, model, and options;
value; and,
(<STX>e) or reflective (<STX>r), and label stock placed in the sensor.
STX>Y
Thermistor ADC: 0048 Reflective ADC: 0000
Transmissive ADC: 0204 Paperout ADC: 0000 24 Volt ADC:
0217 Contrast ADC: 0093 TOF Adjust ADC: 0170 Ribbon
ADC: 0125 Battery Level: Good <CR>
Paperout ADC: 0225 indicates paper is present;
0000 indicates paper is not present.
Battery level: Good indicates a sufficient battery charge;
Low indicates an insufficient charge.
STX y Select Font Symbol Set
This command selects the scalable font symbol set. The selected symbol set remains
active until another symbol set is selected. See the <STX>KS command and Appendices
E, I, and H for more information. Option dependent and not all symbol sets can be used
with all fonts.
Syntax:
Where:
Sample:
STX>ySxx
S
-
Byte-size designation; see Appendix H:
S = Single byte symbol sets.
U = Double byte symbol sets.
xx
-
Symbol set selection.
<STX>ySPM
The sample above selects the PC-850 multilingual set.
Class Series 2 Programmer’s Manual 35
Page 50

System-Level Command Functions
<
<
STX Z Print Configuration Label
This command causes the printer to produce a Database Configuration Label. To capture
all printed information, use the labels as wide as the maximum print width (see
Appendix K) and at least four inches (102 mm) long.
Syntax:
Printer response:
STX>Z
CONFIGURATION
TUE 09:09 AM 10FEB2009
PRINTER KEY:
4212-HE25-060224-090
APPLICATION VERSION:
83-2541-11H3 11.083 12/22/2008
MCL Version: 1.00.06-072
BOOT LOADER:
83-2539-11A 11.01 10/02/2007
UNLOCKED:
CG TIMES
FPGA:
HP10
iPH:
5x-00289 #163
MACM:
00-0d-70-03-8b-b9
MACO:
NOT SET
MACR:
00-90-c9-01-D0-64
SYSTEM INFORMATION
PRINT BUFFER SIZE:
100 in.
FLASH SIZE:
8 MB
RAM TEST:
PASS
MODE:
DISABLED
BACKUP DELAY (1/50s):
0
FONT EMULATION:
STANDARD FONTS
LABEL STORE:
STATE & FIELDS
MENU LANGUAGE:
ENGLISH
FAULT HANDLING:
LEVEL:
STANDARD
VOID DISTANCE:
0.50 in.
RETRY COUNT:
1
BACKFEED ON CLEAR:
DISABLED
COMMUNICATIONS
SERIAL PORT A:
BAUD RATE:
9600 BPS
PROTOCOL:
BOTH
PAR ITY:
NONE
DATA BITS:
8
Printed information will vary according to printer, model, firmware version, and options.
STX z Pack Module
This command causes the printer to reclaim all storage space associated with all deleted
files on the specified module (see <STX>X and <STX>x).
STX>zm
m
- The module identification character; see Appendix K.
Syntax:
Where:
Valid for I-Class and A-Class only, ignored by all others.
36 Class Series 2 Programmer’s Manual
Page 51

<
kz
]
>
5
Extended System-Level Command Functions
Introduction
Issued in the same context as System-Level Commands, the Extended System-Level
Commands expand certain System-Level Commands to provide an extra degree of printer
control.
STX K Memory Configuration
This command configures the available DRAM (including any installed optional DRAM) as
a method for managing printer memory. Memory can be assigned to specific entities or
functions in units of 4KB blocks. The allocation(s) set by this command, draw from the
same memory pool, affecting maximum print length and label throughput (see note
below). The printer executes the memory configuration specified by the command during
the next idle period following its receipt, and is stored in Flash memory then reinstated
upon a power-up or reset. If the total requested memory allocation exceeds the
configurable memory available, contains no fields, or for configurations not specified, the
command will be rejected and the printer will assume its previous configuration. Any of
the three fields are optional, and are separated by the colon. Brackets indicate optional
fields.
Syntax:
Sample:
Where,
i, j, k are M, S, or W; x, y, z are four-digit maximum numbers of 4K byte blocks or
inches/100 or (mm/10) as described below.
M Represents the start of a sequence (up to five characters) that assigns memory to
an Internal Module. If this field does not appear, then the Internal Module is not
affected. If no Internal Module exists, it will be created and formatted. Existing
Internal Modules will be erased, re-sized and formatted. The number that follows
the M is a decimal number (up to four digits) that specifies the size in 4KB blocks of
memory to assign to the Internal Module. A value of “0000” will delete the Internal
Module (see Appendix J for additional information).
S Represents the start of a sequence (up to five characters) that assigns the amount
of internal memory allocated to the smooth scalable font processor. This field is
optional; if it does not appear, the current amount of memory assigned to the
STX>Kix[:jy][:
<STX>KM0020:S0015<CR>
The sample above allocates 20*4*1024 bytes for module space and
15*4*1024 bytes for the scalable cache.
<CR
Class Series 2 Programmer’s Manual 37
Page 52

Extended System-Level Command Functions
smooth scalable font processor will remain unchanged. The allocation must be at
least 15 (60KB) to print scalable fonts, and at least 30 for double-byte fonts. The
number that follows the S is a decimal number (up to four digits) that specifies the
size in 4 KB blocks to assign to the smooth scalable font processor. Any value less
than the minimum requirement results in the amount assigned to be zero (0),
thereby disabling the printing of smooth scalable fonts. The recommended value is
0025 (100KB).
W Represents the start of a sequence (up to five characters) that sets the printable
label width. Setting a width smaller than the natural (maximum) width of the printer
effectively extends printable label length. This field is optional; if it does not appear,
the current printable label width is left unchanged. The number that follows the W is
a decimal number (up to four digits) that specifies the printable label width in either
ths
of an inch or in millimeters, depending on the current units setting of the
100
printer (imperial or metric). If the value specified exceeds the printable width of the
printer, the printable label width is set to the maximum. If the value specified is less
than the minimum value allowed (200) then the printable label width is set to the
minimum allowed value.
•
Label printing requirements may be computed as bytes (label print length times
STX K}E Empty Sensor Calibration (Non-Display Models only)
This command causes the printer to determine and save the calibration value for an
empty media sensor condition. This calibration function should be performed when no
material is installed in the media sensor. Depending upon the printer model, different
front panel LED flash sequences and printer responses (below) will indicate calibration
progress and outcome; see the corresponding printer operator manual for LED flash
sequences details.
width allocation times print head resolution divided by 8). For maximum throughput,
the memory allocated should allow for a minimum of three times the computed
requirement, or the available label length (as determined by <STX>KQ command)
should be three times the label print length; and,
• These commands will result in a system reset for the EX2.
Printer Response Alternate
REMOVE STOCK[CR] N/A
ENTER TO CONTINUE[CR] N/A
PASSED CALIBRATION[CR] FAILED CALIBRATION[CR]
38 Class Series 2 Programmer’s Manual
Page 53

Extended System-Level Command Functions
STX K}M Manual Media Calibration (Non-Display Models only)
This command causes the printer to save the sampled calibration values as an operator
places different portions of label stock within the media sensor. Depending upon the
printer model, different front panel LED flash sequences and printer responses (below)
will indicate calibration progress and outcome; see the corresponding printer operator
manual for LED flash sequences details. Sending <ESC> to the printer instead of <CR>
will terminate the process and leave the TOF Sensor values unchanged.
Printer Response Alternate
LOAD STOCK[CR]
ENTER TO CONTINUE[CR]
LOAD MARK[CR]
ENTER TO CONTINUE[CR]
REMOVE STOCK[CR]
ENTER TO CONTINUE[CR]
N/A
LOAD GAP[CR]
N/A
PASSED CALIBRATION[CR] FAILED CALIBRATION[CR]
STX K}Q Quick Media Calibration (Non-Display Models only)
This command causes the printer to move media, sample, and then save sensor samples
as calibration values. This calibration function should be performed with media installed
in the printer. Depending upon the printer model, different front panel LED flash
sequences and printer responses (below) will indicate calibration progress and outcome;
see the corresponding printer operator manual for LED flash sequences details.
Printer Response Alternate
FAILED CALIBRATION[CR]
ADJUST GAIN SETTING[CR]
PASSED CALIBRATION[CR] FAILED CALIBRATION[CR]
Class Series 2 Programmer’s Manual 39
N/A
Page 54

Extended System-Level Command Functions
<
e
<CR>
STX KaR Read Data from RFID Tag
(Direct Mode – Generic Read/Write Interface)
This command instructs the RFID device to read data from the tag and then place that
data into a replaceable field. It is expected that the tag transponder will be within the
read / write distance of the RFID programming device; otherwise, “Void” will be printed
in the text or bar code label field.
Syntax:
Where:
Sample:
STX>KaRAaaabbbcde
A
aaa
bbb
c
d
ee
<STX>L
1911A1802000010TEXT
U
X
<STX>KaR0000010001
<STX>G
- Optional – for data in the ASCII format.
The number of bytes to read.
-
HF - Starting block number (000 maximum block
number, which is dependent upon the
transponder manufacturer).
UHF – Should be 000.
Command 1. Reserved. Should be 0.
-
Command 2. Reserved. Should be 0.
-
-
Field number in which to place the data (must be 01,
02, 03, etc.) matching the order of Label Formatting
command U.
The 00 value will send read data to the host with no
printing.
The sample above creates a replaceable text field (01), recalls data
from the RFID tag block zero (reading only one block), and prints
the data in the location specified by the replaceable field. Since
there are two digits per each hex value, replaceable fields should be
twice as long than if using ASCII data (e.g., the character “A” would
be returned as “41”).
40 Class Series 2 Programmer’s Manual
Page 55

Extended System-Level Command Functions
<
e
<CR>
<
>
STX KaW Write Data to RFID Tag
(Direct Mode – Generic Read/Write Interface)
This command instructs the RFID device to write data to the tag. It is expected that the
tag transponder will be within the read / write distance of the RFID programming device;
otherwise, a warning will occur and a warning message (Read / Write Fail) will be
displayed.
Syntax:
STX>KaWAaaabbbcdee…
Where:
Aaaa
-
Optional – for data in the ASCII format, followed by
the byte count (000-999).
bbb
HF – Starting block number (000 maximum block
-
number, which is dependent upon the
transponder manufacturer).
UHF – Should be 000.
c
Command 1. Reserved for Future (should be 0)
-
d
Command 2. Reserved for Future (should be 0)
-
ee…e
Data to be encoded on RFID tag (HF – the last used
-
block will be null-padded, if necessary).
UHF ASCII formats must be 8 or 12 characters; and,
UHF Hexadecimal formats must be 16 or 24
character pairs.
Sample:
<STX>KaW0000054455354[CR]
The sample above writes the data “TEST” at block zero.
STX Kb Backfeed Time Delay
This command controls the time a printed label is allowed to remain “presented” before
being retracted to the start of print position.
Syntax:
Where:
STX>Kbnnn<CR
nnn
-
Seconds/10
Class Series 2 Programmer’s Manual 41
Page 56

Extended System-Level Command Functions
<
>
STX KC Get Configuration
This command returns the configuration of the printer. The form of the returned data is
similar to that of a printed Configuration Label. This command should be parsed by
KEYWORDS, not character positions. Each line is terminated by a CR (0x0d) & LF
(0x0a).
Syntax:
Printer response:
CONFIGURATION
TUE 02:01PM 01AUG2005
PRINTER KEY:
4308-TB10-010327-494
APPLICATION VERSION:
83-2284-06E
06.06 07/09/2001
BOOT LOADER:
83-2269-03D 03.04 10/30/2000
SYSTEM INFORMATION
PRINT BUFFER SIZE:
280 in.
FLASH SIZE:
4 MB
RAM TEST:
PASS
OPTIONAL LANGUAGES:
FRANCAIS
ITALIANO
DEUTSCH
ESPAÑOL
CONFIGURATION FILE:
NONE
MEDIA SETTINGS
MEDIA TYPE
THERMAL TRANSFER
SENSOR TYPE
GAP
LABEL LENGTH
04.00 in.
MAXIMUM LABEL LENGTH
•30.00 in.
PAPER OUT DISTANCE
00.25 in.
LABEL WIDTH
4.16 in.
SENSOR CALIBRATION
PAPER SENSOR LEVEL
144
GAP SENSOR LEVEL
30
EMPTY SENSOR LEVEL
0
STX>KC<CR
SENSOR GAIN
10
PRINT CONTROL
HEAT
10
PRINT SPEED
6.0in/sec
FEED SPEED
6.0in/sec
REVERSE SPEED
4.0in/sec
ROW OFFSET
00.00 in.
COLUMN OFFSET
00.00 in.
PRESENT DISTANCE
0.00 in.
CUSTOM ADJUSTMENTS:
DARKNESS
32
ROW ADJUST
64 DOTS
COLUMN ADJUST
0 DOTS
PRESENT ADJUST
64 DOTS
PRINTER OPTIONS
MODULES
A: NOT INSTALLED
B: NOT INSTALLED
D: FORMATTED
F: NOT INSTALLED
G: FORMATTED
X: FORMATTED
Y: 83-2296-01C
Z: NOT INSTALLED
PRESENT SENSOR
NOT INSTALLED
CUTTER
NOT INSTALLED
GPIO PORT:
NOT INSTALLED
SYSTEM SETTINGS
FACTORY SETTING FILE
NONE
INTERNAL MODULE
1024 KB
DEFAULT MODULE
D
SCALEABLE FONT CACHE
312 KB
SINGLE BYTE SYMBOLS
PC-850 MULTILINGUAL
DOUBLE BYTE SYMBOLS
UNICODE
ABSOLUTE COUNTER
3782 in.
27MAR2001
RESETTABLE COUNTER
205 in.
27MAR2001
FORMAT ATTRIBUTES
XOR
IMAGING MODE
MULTIPLE LABEL
PAUSE MODE
DISABLED
SELECT SECURITY
DISABLED
PEEL MODE
DISABLED
UNITS OF MEASURE
IMPERIAL
SOP EMULATION
DISABLED
BACK AFTER PRINT
DISABLED
MENU LANGUAGE
ENGLISH
COMMUNICATIONS
SERIAL PORT A:
BAUD RATE
9600 BPS
PROTOCOL
BOTH
PARITY
NONE
DATA BITS
8
STOP BITS
1
SERIAL PORT B:
NOT INSTALLED
PARALLEL PORT A:
PORT DIRECTION
UNI-DIRECTIONAL
PORT STATUS
DISABLED
PARALLEL PORT B:
PORT DIRECTION
BI-DIRECTIONAL
PORT STATUS
DISABLED
NIC ADAPTER:
DMXNET INACTIVE
HOST SETTINGS:
HOST TIMEOUT
10 SEC
CONTROL CODES
STANDARD CODES
FEEDBACK
CHARACTERS
DISABLED
ESC SEQUENCES
ENABLED
HEAT COMMAND
ENABLED
SPEED COMMANDS
ENABLED
DIAGNOSTICS
HEX DUMP MODE
DISABLED
PRINT TEST
RATE(min)
0
SENSOR READINGS
THR TRAN RIBM 24V
132 141 159 178
PS HD RANK
000 254 000
RIBBON SENSOR
LIMITS
RIBBON ADC LOW
105
RIBBON ADC HIGH
182
END OF LIST
The format of the displayed information will vary with printer, model, firmware version,
and equipped options.
42 Class Series 2 Programmer’s Manual
Page 57

Extended System-Level Command Functions
<
v
[
v
]
v
]
<CR>
STX Kc Configuration Set
This command specifies the Power-up Configuration parameter values for the printer and
is equivalent to using other system commands followed by the <SOH>U. This command
is intended for easily configuring a custom setup, but NOT for dynamic
configuration changes. Configuration commands are examined for differences
relative to the current configuration, and have no impact when no differences exist.
Display-equipped models will reset upon completion of a command stream containing
parameter value changes, while non-display models reset only for certain functions,
such as memory allocation. In any case, no commands should be sent to the printer
until this reset is complete. Other command highlights include the following:
• These parameter values are equivalent to changing the respective menu settings and
do not affect the factory default settings of the printer.
• If separated by a semi-colon (;), multiple parameter values may be sent in a single
command stream; see sample below.
• All values are stored in Flash memory and remain in effect until new values are
received or until factory defaults are restored.
• If system commands are sent that override the Power-up Configuration value(s), the
Power-up Configuration value(s) will be restored the next time the printer is powered
“On” or is reset.
• These parameters are the same as those found in the Setup Menu (non-display
models), or as those found in the Menu System (display-equipped models). The
respective functions are documented in the appropriate Operator’s or Maintenance
Manual. Not all commands are effective on all Class printers.
Illegal or out of range parameter values may have unpredictable results. In addition,
media sensing scaling values, TOF Bias, etc. may not be effective on other same-type
printers due to hardware tolerances.
Syntax:
STX>Kcaa
al
;aa
al
1
1
I
I
[;aa
al
n
n
Where:
aa
1,
-
Are two letter parameter names.
aaI, aan
val
val
1,
I,
valn
-
Are parameter values, with ranges
appropriate for the associated parameter.
Sample:
<STX>KcPA120;CL600;STC<CR>
The sample above sets the Present Adjust to 120 dots, and the
Sensor Type to Continuous with a label length of six inches.
The following table summarizes (alphabetically by name) different Configuration Set
command parameters, value ranges, command equivalents and applicability. If no
command equivalent is given, or where clarification is required, descriptions immediately
follow the table.
Class Series 2 Programmer’s Manual 43
Page 58

Extended System-Level Command Functions
44 Class Series 2 Programmer’s Manual
Configuration Set Commands
<STX>Kc
Parameter Name
Parameter
Pneumonic
Value /
Range
Units /
Interpretation
Menu Item (or Number)
(if available)
Command
Equivalent
Alignment Length
AL
0 – 999 1/100 inch (18) N/A
Backup After Print
BA
Y, N
Y = Enabled,
N = Disabled
System Settings N/A
Backup Delay
BD
0 – 255 1/50 second System Settings N/A
Backup Label
BL
0, 3, 4
0 = Disabled,
3 = Active Low,
4 = Active High
Printer Options N/A
Backup (Reverse) Speed
BS or bS
alpha character
Model specific
ranges; see
Appendix L.
Print Control
pa
British Pound
BP
Y, N
Y = Enabled,
N = Disabled
N/A N/A
Buzzer Enable
BZ
Y, N
Y = Enabled,
N = Disabled
System Settings N/A
(continued)
Page 59

Extended System-Level Command Functions
Class Series 2 Programmer’s Manual 45
<STX>Kc
Parameter Name
Parameter
Pneumonic
Value /
Range
Units /
Interpretation
Menu Item (or Number)
(if available)
Command
Equivalent
Column Adjust
[1]
CA
xxx dots
Resolution specific;
see Appendix K,
and Column Adjust
Fine Tune
Print Control (7) N/A
Column Adjust Fine
Tune
CF
+ / – dots
Resolution specific;
see Appendix K.
Print Control N/A
Column Offset
CO
0 – 9999 1/100 in.
Print Control
Cnnnn
Comm Heat Commands
CH
Y, N
1, 0
Y = Enabled,
N = Disabled
1 = Enabled,
0 = Disabled
Communications (25)
(E-Class - 24)
N/A
Comm Speed Commands
CS
Y, N
1, 0
Y = Enabled,
N = Disabled
1 = Enabled,
0 = Disabled
Communications (26)
(E-Class - 24)
N/A
(continued)
Page 60

Extended System-Level Command Functions
46 Class Series 2 Programmer’s Manual
<STX>Kc
Parameter Name
Parameter
Pneumonic
Value /
Range
Units /
Interpretation
Menu Item (or Number)
(if available)
Command
Equivalent
Comm TOF Commands
CT
Y, N
Y = Enabled,
N = Disabled
Communications N/A
Continuous Label Length
CL
0 – 9999 1/100 in. Media Settings (12)
<STX>c
Control Codes
CC
S, 1, 2
S = Standard,
1 = Alternate,
2 = Alternate-2
Communications (11)
N/A
Cut Behind
CB
0 – 9 Queued label count Printer Options N/A
Cutter Equipped
CE
A/Y, E, N/D
A, E/Y, N
A or Y = Auto,
E = Enabled,
N or D = Disabled
A = Auto,
E or Y = Enabled,
N = Disabled
Printer Options
<STX>V
(continued)
Page 61

Extended System-Level Command Functions
Class Series 2 Programmer’s Manual 47
<STX>Kc
Parameter Name
Parameter
Pneumonic
Value /
Range
Units /
Interpretation
Menu Item (or Number)
(if available)
Command
Equivalent
Darkness
DK
1 – 64 N/A Print Control N/A
Default Module
DM
D, G
A, B
Module Letter System Settings
<STX>X
Delay Rate
(Test Labels)
DR
0 – 120 Seconds Diagnostics N/A
Disable Symbol Set
Selection
NS
Y, N
Y = Enabled,
N = Disabled
N/A N/A
Display Mode
GD
S, E
S = Standard,
E = Enhanced
System Settings N/A
Double Byte Symbol Set
DS
2-Byte alpha
character
AA – ZZ, printer
resident symbol set
System Settings
<STX>y,
ySxx
DPI Emulation
DE
200, 300,
400, 600
Dots per inch System Settings N/A
Empty Sensor Level
EV
0 – 255 N/A Media Settings N/A
(continued)
Page 62

Extended System-Level Command Functions
48 Class Series 2 Programmer’s Manual
<STX>Kc
Parameter Name
Parameter
Pneumonic
Value /
Range
Units /
Interpretation
Menu Item (or Number)
(if available)
Command
Equivalent
End Character
EN
D N/A N/A N/A
End Of Print
EP
1, 2, 3, 4
1 = Low Pulse,
2 = High Pulse,
3 = Active Low,
4 = Active High
Printer Options N/A
ESC Sequences
ES
Y, N
Y = Enabled,
N = Disabled
Communications N/A
Fault Handling
FH
L, D, R, B See Table 5-2.
System Settings (24)
N/A
Feed Speed
SS or sS
Alpha character
Model specific
ranges;
see Appendix L.
Print Control
Sa
(continued)
Page 63

Extended System-Level Command Functions
Class Series 2 Programmer’s Manual 49
<STX>Kc
Parameter Name
Parameter
Pneumonic
Value /
Range
Units /
Interpretation
Menu Item (or Number)
(if available)
Command
Equivalent
Feedback Mode
FM
Y, N
Y = Enabled,
N = Disabled
Communications
<STX>a
Font Emulation
FE
0, 1, 2
0 = No Substitution
1 = Sub CG Times
SA0
2 = Sub User S50
N/A N/A
Format Attributes
FA
X, O, T
X = XOR,
O = Opaque,
T = Transparent
System Settings An
Gain Reflective Value
GR
0 – 31 N/A Media Settings N/A
Gap / Mark Value
GM
0 – 255 N/A Media Settings N/A
Gap Sensor Location
(MP Comapct4 Mark II only)
GL
0 or 1
0 = Outer sensor,
default
1 = Inner sensor
N/A <STX>KcGL
GPIO Equipped
GE
A, V, N, 2
A = Applicator,
V = Verifier,
N = Disabled,
A = Applicator2
Printer Options (23)
N/A
(continued)
Page 64

Extended System-Level Command Functions
50 Class Series 2 Programmer’s Manual
<STX>Kc
Parameter Name
Parameter
Pneumonic
Value /
Range
Units /
Interpretation
Menu Item (or Number)
(if available)
Command
Equivalent
GPIO Error Pause
GP
E, D
E = Enabled,
D = Disabled
Printer Options N/A
GPIO Slew
GS
0 – 4
0 = Standard,
1 = Low Pulse,
2 = High Pulse,
3 = Active Low,
4 = Active High
Printer Options N/A
Head Bias
HB
L, R
L = Leftmost dot is
zero,
R = Rightmost dot is
zero
System Settings N/A
Head Cleaning
HC
0 – 9999
Inches (or
centimeters)
multiplied by 1000
Media Settings N/A
Heat
HE
0 – 30 N/A
Print Control (21)
Hnn
Host Timeout
HT
1 – 60 Seconds Communications N/A
(continued)
Page 65

Extended System-Level Command Functions
Class Series 2 Programmer’s Manual 51
<STX>Kc
Parameter Name
Parameter
Pneumonic
Value /
Range
Units /
Interpretation
Menu Item (or Number)
(if available)
Command
Equivalent
Ignore Control Codes
IC
Y, N
1, 0
Y = Enabled,
N = Disabled
1 = Enabled,
0 = Disabled
Communications
N/A
Ignore Distances
IE
1, 0
1 = Enabled,
0 = Disabled
N/A N/A
Imaging Mode
IL
M, S
M = Multiple label,
S = Single label
System Settings (22)
N/A
Input Mode
EM
0, 1, 3, 7, 9
0 = DPL,
1 = Line,
3 = PL-Z,
7 = PL-B,
9 = Auto
System Settings (19)
N/A
Internal Module
IM
100 – up to max.
available; see
Appendix K
Kbytes System Settings (15) N/A
(continued)
Page 66

Extended System-Level Command Functions
52 Class Series 2 Programmer’s Manual
<STX>Kc
Parameter Name
Parameter
Pneumonic
Value /
Range
Units /
Interpretation
Menu Item (or Number)
(if available)
Command
Equivalent
Label Alignment
LA
N, A, Y See Table 5-3. 17 N/A
Label Rotation
LR
Y, N
Y = Rotate 180
N = None
System Settings N/A
Label Store
LM
F, S
F = Fields,
S = States & Fields
System Settings N/A
Label Width
LW
0075 – head width;
see Appendix K
1/100 inch Media Settings (13)
<STX>KW
Language Select
LS
String Language Name System Settings N/A
Legacy Emulation
LE
N, A, P, L
N, A, P, L, M
N = None,
A = Allegro,
P = Prodigy,
L = Prodigy Plus,
M = Prodigy Max
X = XL
System Settings (20)
N/A
Mark Value
MV
0 – 255 N/A Media Settings N/A
(continued)
Page 67

Extended System-Level Command Functions
Class Series 2 Programmer’s Manual 53
<STX>Kc
Parameter Name
Parameter
Pneumonic
Value /
Range
Units /
Interpretation
Menu Item (or Number)
(if available)
Command
Equivalent
Maximum Length Ignore
SM
0, 1
0 =
Normal processing,
1 = Ignore
Communications N/A
Maximum Length
ML
0 – 9999 1/100 inch Media Settings
<STX>M
Media Type
MT
D, T
D = Direct,
T = Thermal Transfer
Media Settings (1) N/A
Menu Mode
MM
U, A
U = User,
A = Advanced
System Settings N/A
Module Command
MCC
Z, G
B
See Table 5-4. N/A N/A
Network Configuration
(for firmware versions
14.00 and later)
NE
G, WE, WIFI, DV1,
DV2, SV1
See command
(NE) Network
Configuration
N/A N/A
Network Setup
(for firmware versions
13.99 and earlier)
NT
A, B, C, D, E, F, G,
I, m, N, P, S, T, U,
W, w, X, Y, Z, $
See Table 5-5. N/A N/A
No Reprint
NR
Y, N
Y = Enabled,
N = Disabled
N/A N/A
Option Feedback
OF
D, Rx, S See Table 5-6. Communications N/A
(continued)
Page 68

Extended System-Level Command Functions
54 Class Series 2 Programmer’s Manual
<STX>Kc
Parameter Name
Parameter
Pneumonic
Value /
Range
Units /
Interpretation
Menu Item (or Number)
(if available)
Command
Equivalent
Paper Empty
PO
0 – 9999 1/100 inch Media Settings N/A
Paper Value
PV
0 – 255 N/A Media Settings N/A
Parallel Direction
PP
xz See Table 5-7. Communications N/A
Password Set
PW
A – Z,
0 – 9
Four characters
(or, if security is
enabled then eight
characters).
System Settings N/A
Pause Mode
PM
Y, N
Y = Enabled,
N = Disabled
System Settings
<STX>J
Peel Mode
PE
Y, N
Y = Enabled,
N = Disabled
System Settings N/A
(continued)
Page 69

Extended System-Level Command Functions
Class Series 2 Programmer’s Manual 55
<STX>Kc
Parameter Name
Parameter
Pneumonic
Value /
Range
Units /
Interpretation
Menu Item (or Number)
(if available)
Command
Equivalent
Present Adjust
[1]
PA
xxx dots
Model specific;
see Appendix K,
and Present Adjust
Fine Tune.
Print Control (8) N/A
Present Adjust Fine
Tune
PJ
+ / – dots
Dots (model
specific),
see Appendix K.
Print Control N/A
Present Distance
PD
0 – 400 1/100 inch Print Control
<STX>Kf
Present Sensor
Equipped
PS
A/Y, E, N/D
A or Y = Auto,
E = Enabled,
N or D = Disabled
Printer Options (3)
<STX>V
Print Contrast
PC
0 – 64 N/A Print Control N/A
Printer Level
PL
000000 – FFFFFF Hex Codes System Settings N/A
(continued)
Page 70

Extended System-Level Command Functions
56 Class Series 2 Programmer’s Manual
<STX>Kc
Parameter Name
Parameter
Pneumonic
Value /
Range
Units /
Interpretation
Menu Item (or Number)
(if available)
Command
Equivalent
Print Speed
pS
Alpha character
Model specific
ranges; see
Appendix L.
Print Control
Pa
Query Configuration
QQ
Q, K N/A Configuration Label N/A
Reflective Paper Value
RV
0 – 255 N/A Media Settings N/A
Retract Delay
RW
1 – 255
Specified value times
ten milliseconds
Printer Options N/A
Rewinder Adjust
RR
-xx, +yy
Applied torque,
where -30 to +15 is
the valid range.
Printer Options N/A
Rewinder Equipped
RM
A/Y, E, N/D
A or Y = Auto,
E = Enabled,
N or D = Disabled
Printer Options N/A
RFID Configuration
RI
A, B, D, E, L, M, N,
P, R, S, T, U, V, W
See Table 5-8. Printer Options N/A
Ribbon Low Diameter
RL
100 – 200 1/100 in. Media Settings N/A
(continued)
Page 71

Extended System-Level Command Functions
Class Series 2 Programmer’s Manual 57
<STX>Kc
Parameter Name
Parameter
Pneumonic
Value /
Range
Units /
Interpretation
Menu Item (or Number)
(if available)
Command
Equivalent
Ribbon Low Pause
RP
Y, N
Y = Enabled,
N = Disabled
Media Settings N/A
Ribbon Low Signal
RS
3, 4
3 = Active Low,
4 = Active High
Print Options N/A
Ribbon Saver Enable
RE
A/Y, E, N/D
A or Y = Auto,
E = Enabled,
N or D = Disabled
Printer Options
<STX>R
Row Adjust
[1]
RA
xxxx dots
Model specific; see
Appendix K,
and Row Adjust Fine
Tune
Print Control (6) N/A
Row Adjust Fine Tune
RF
+ / – dots
Resolution specific;
see Appendix K.
Printer Control N/A
Row Offset
RO
0 – 9999 1/100 in. Print Control
Rnnnn
SOP Adjust
[1]
SA
0 – 255
(128 nominal)
N/A,
see Row Adjust Fine
Tune
N/A
<STX>O
SOP Emulation
SE
A, L, P, D
A = Allegro,
L = Prodigy Plus,
P = Prodigy,
D = Disable
System Settings N/A
(continued)
Page 72

Extended System-Level Command Functions
58 Class Series 2 Programmer’s Manual
<STX>Kc
Parameter Name
Parameter
Pneumonic
Value /
Range
Units /
Interpretation
Menu Item (or Number)
(if available)
Command
Equivalent
Save As Filename
SF
Alphanumeric
string
Up to 16 characters System Settings N/A
Scalable Font Bolding
FB
1 – 36 N/A System Settings N/A
Scalable Font Cache
SC
100 – 8192 Kbytes System Settings (14) N/A
Scalable Heap
SH
0 – 9999 Kbytes N/A N/A
Scanner Configuration
SN
C, H, M,
D, B, V
See Table 5-11. Printer Options N/A
Security Lock
Sl
N, Y, T See Table 5-9. System Settings N/A
Sensor Gain Value
SG
0 – 32 N/A Media Settings N/A
(continued)
Page 73

Extended System-Level Command Functions
Class Series 2 Programmer’s Manual 59
<STX>Kc
Parameter Name
Parameter
Pneumonic
Value /
Range
Units /
Interpretation
Menu Item (or Number)
(if available)
Command
Equivalent
Sensor Type
ST
G, C, R
G = Gap (edge),
C = Continuous,
R = Reflective
Media Settings (2)
<STX>e,
<STX>r,
<STX>c
Serial Port
SP
xyz See Table 5-12.
Communications
9 & 10
N/A
Single Byte Symbol Set
AS
2-Byte alpha
character
AA – ZZ, printer
resident symbol set
System Settings
<STX>y,
ySxx
Slew Speed
FS
Alpha character
Model specific
ranges; see
Appendix L.
Print Control
<STX>KZSx
Software Switch
SV
Y, N
Y = Processed
N = Ignored
Communications N/A
(continued)
Page 74

Extended System-Level Command Functions
60 Class Series 2 Programmer’s Manual
<STX>Kc
Parameter Name
Parameter
Pneumonic
Value /
Range
Units /
Interpretation
Menu Item (or Number)
(if available)
Command
Equivalent
Start of Print
EQ
3, 4
3 = Active Low,
4 = Active High
Printer Options N/A
Stop Location
SL
A, H, P,
C, T, N
See Table 5-10. 16 N/A
TOF Precedence
TP
Y, N
Y = Enabled,
N = Disabled
N/A N/A
User Label Mode
UD
Y, N
Y = Enabled,
N = Disabled
System Settings N/A
Unit of Measure
UM
M, I
M = Metric,
I = Imperial
System Settings (5)
<STX>m,
<STX>n
User Terminator
UT
ON N/A N/A N/A
(continued)
Page 75

Extended System-Level Command Functions
Class Series 2 Programmer’s Manual 61
<STX>Kc
Parameter Name
Parameter
Pneumonic
Value /
Range
Units /
Interpretation
Menu Item (or Number)
(if available)
Command
Equivalent
Verifier Equipped
VE
A/Y, E, N/D
A or Y = Auto,
E = Enabled,
N or D = Disabled
Printer Options
<STX>KV
Verifier Type
VT
A, B, C, D
Reserved for future
use
N/A N/A
WiFi Security
(for firmware versions
13.99 and earlier. For
firmware versions 14.00
and later see Network
Setup parameter NE)
WS
A, K, S,
L, P, U
See Table 5-14. N/A N/A
WiFi Setup
(for firmware versions
13.99 and earlier. For
firmware versions 14.00
and later see Network
Setup parameter NE)
WE
A, C, F, I, L, M, N,
P, R, T, V, X
See Table 5-13. N/A N/A
1. Commands are provided for backward compatibility on EX2. The KcQQQ command will respond with the new command equivalent; see
associated new commands.
2. The EX2 will accept display-equipped module IDs (D & G) as command parameters for upward compatibility; query commands will result in
printer responses with module IDs that are non-display compatible, providing backward compatibility.
3. Present distance changes for EX2 will only be accepted if the Stop Location (SL) is set to “Host.”
Table 5-1: Configuration Set Commands
Page 76

Extended System-Level Command Functions
<STX>Kc Parameter Overviews
(AL) Alignment Length – This command, critical for small labels when Label
Alignment is set to YES, allows a length (measured from leading edge to leading
edge of two successive labels) to be entered. The measured length must be provided
to the nearest hundredth of an inch. For very small labels, errors of 0.01” can result
in noticeable print variations on the labels between the media sensor and the print
head. The number of labels that can be fit between the Media Sensor and the print
head will magnify any error in label alignment length. Errors in measurement are
more favorable on the low side rather than the high side.
Non-Display models: The printer will verify the label position using the provided
Alignment Length before printing the first label after power-up.
(AS) Single Byte Symbol Set – This command allows for a default single-byte
symbol set. See <STX>y or ySxx for command details.
(BA) Backup After Print – This command determines the timing of the label back
up positioning when the present distance is set and the GPIO option or Present
Sensor option (including Peel and Present) is enabled. When enabled, the printer
immediately backs up the label after the applicator-issued start of print signal is
received or the label is removed, resulting in faster throughput. If disabled, the
printer will not initiate repositioning until the next label is ready to print (may help
prevent the curling of the label edge).
(BD) Backup Delay – This command sets a time delay for the retraction of a
presented label in one-fiftieth (1/50) of a second increments.
(BL) Backup Label – This command determines the timing of reverse label motion
when the GPIO option is installed and enabled; see Appendix J for details.
(BP) British Pound – This command, when enabled, will automatically switch from
the Number symbol (#) found at 0x23 (default PC-850 Multilingual Symbol Set) to
the British Pound symbol (£) at 0x9C.
(BS or bS) Backup Speed – This command controls the rate of label movement
during backup positioning for start of print, cutting or present distance; see Appendix
C for available speed ranges.
62 Class Series 2 Programmer’s Manual
Page 77

Extended System-Level Command Functions
(BZ) Buzzer Enable – This command controls the audible signaling device that
acknowledges User Interface entries and, if enabled, sounds printer warning and
fault conditions.
(CA) Column Adjust – This command fine-tunes the Column Offset setting by
shifting both the horizontal start of print position and the Label Width termination
point to the right in dots (see Appendix K) to compensate for slight mechanical
differences sometimes evident when multiple printers share label formats. Note that
the EX2 accepts this command for backward compatibility only, limited in range (28-
228). The <STX>KcQQQ response will show the Column Adjust Fine Tune (CF)
equivalent value.
(CB) Cut Behind – This command allows the printer to queue a specified number of
small labels before a cut is performed to increase throughput.
(CC) Control Codes – This command, depending upon printer type, allows a
change to the prefix of the software commands interpreted by the printer:
Value
S Standard Codes
Units /
Interpretation
Control Code Definition
Hex 01 = SOH command; Hex 02 = STX command; countby = ^; Hex 1B = ESC; Hex 0x0D = Carriage Return
1 Alternate Codes
2 Alternate Codes 2
Hex 5E = SOH command; Hex 7E = STX command; countby = @; Hex 1B = ESC; Hex 0x0D = Carriage Return
Hex 5E = SOH command; Hex 7E = STX command; countby = @; Hex 1B = ESC; Hex 0x7C = Carriage Return
(CE) Cutter Equipped – This command allows the printer to sense the cutter option.
“A” - automatically senses device presence; if undetected, no error is generated. “E” enables the device, where its presence must be detected; otherwise, a fault is
generated. “N” - disables device detection. One of these values is returned in
response to <STX>KcQQQ. Note that alternate values are accepted for backward
compatibility as follows: For display-equipped models “Y” is equivalent to “A”; and,
for non-display models “Y” is equivalent to “E”.
(CF) Column Adjust Fine Tune – This command fine-tunes the Column Offset
setting by shifting both the horizontal start of print position and the Label Width
termination point to the right in dots (see Appendix K) to compensate for slight
mechanical differences sometimes evident when multiple printers share label
formats.
Class Series 2 Programmer’s Manual 63
Page 78

Extended System-Level Command Functions
(CH) Communicated Heat Commands – This command causes the printer to
ignore DPL Heat commands; instead, the Heat value is controlled via the menu
setting.
(CL) Continuous Label Length – See <STX>c for command details.
(CO) Column Offset – See Cnnnn for command details.
(CS) Communicated Speed Commands – This command causes the printer to
ignore DPL speed commands; instead, speed values are controlled via the menu
setting.
(CT) Communicated TOF Commands – This command causes the printer to
ignore DPL TOF (Gap, Continuous, and Reflective) commands; instead, the sensor
type is controlled via the menu setting.
(DE) DPI Emulation – This command allows printers with higher resolutions to
emulate lower print resolutions, as follows:
• 600 DPI can emulate 300 and 203 DPI resolutions; and,
• 400 DPI can emulate a 203 DPI resolution.
(DK) Darkness – This command adjusts the length of the print head strobe to finetune the HEAT setting.
(DM) Default Module – See <STX>X for command details.
64 Class Series 2 Programmer’s Manual
Page 79

Extended System-Level Command Functions
(DR) Delay Rate – This command sets the number of minutes to delay between
multiple batch printings of Quick Test Labels.
(DS) Double Byte Symbol Set – See <STX>y or ySxx for command details.
(EM) Input Mode – This command determines the data processing mode:
Value Interpretation
0 DPL Character strings are parsed for standard DPL processing.
No parsing occurs; instead, each carriage return (<CR>)
1 Line
terminated data line is printed according to a stored template
(see Appendix S).
Input Mode Interpretation
Character strings are parsed for PL-Z processing, applicable
only if the appropriate firmware is installed, as indicated by a
“Z” in the version string (except for H-Class and M-Class
Mark II, which is standard).
3 PL-Z
For RFID, the hardware option, tag type and size
should be preselected, and a tag calibration performed.
Also, if possible, driver / software options to use
“Printer Defaults” should be chosen to minimize
potential conflicts.
Character strings are parsed for PL-B processing, applicable
7 PL-B
only if the appropriate firmware is installed, as indicated by a
“B” in the version string.
Character strings are automatically parsed and processed
according to the identified language.
9 Auto
A clean file is required, where extra leading characters
may cause the language to be unrecognizable;
otherwise, the appropriate Input Mode must be
selected.
(EN) End Character – This command terminates a <STX>Kc string.
Class Series 2 Programmer’s Manual 65
Page 80

Extended System-Level Command Functions
(EP) End of Print – This command defines the signal output used to signify the End
of Print (EOP) process:
Value Units End of Print Interpretation
1 Low Pulse
2 High Pulse
Outputs a low pulse (approximately 30 milliseconds long)
following printing.
Outputs a high pulse (approximately 30 milliseconds long)
following printing.
3 Active Low Outputs a logic low (zero) following printing.
4 Active High Outputs a logic high (one) following printing.
(EQ) Start of Print – This command defines the type of signal input required to
control the Start of Print (SOP) process:
Value Units Start of Print Interpretation
3 Active Low
4 Active High
SOP signal must go low for at least 50 milliseconds to initiate
printing.
SOP signal must go high for at least 50 milliseconds to
initiate printing.
(ES) ESC Sequences – This command allows data containing invalid ESC control
code sequences to be processed (helpful because some systems send a “banner” to
the printer). When set to “Disabled,” ESC sequences are ignored and the data is
processed. Bitmapped font downloads are disabled in this mode.
(EV) Empty Sensor Level – This command sets threshold value for the “Empty”
media sensor parameter.
(FA) Format Attribute – See the “An” command for details (Label Formatting
Command Functions).
(FB) Scalable Font Bolding – This command sets a bolding factor to fine tune
scalable fonts, where one causes the least amount of bolding and thirty-six the most
(default value is 8).
66 Class Series 2 Programmer’s Manual
Page 81

Extended System-Level Command Functions
(FE) Font Emulation –This command allows font substitution for all internal fonts,
allowing a new default font to be defined without changing the host DPL data
streams. Selecting a default font that supports a desired character set could match
with third party software to print native characters without modifying the PC drivers.
In other words, match the PC font with the Printer Font then no interpretation would
be required by driver or printer. Depending on host drivers, the user may have to
disable Symbol Set commands and modify the Default Symbol set.
(FH) Fault Handling – This command determines the level of user intervention and
the disposition of the label being printed when a fault condition (ribbon out, media
out, etc.) occurs.
Value
Units /
Interpretation
0 = No Reprint
1 = Standard
Selection / Definition
Printing stops and a fault message is displayed. After the
problem is corrected, the FEED Key must be pressed to
clear the fault. The label in process is not reprinted.
Printing stops and a fault message is displayed. After the
problem is corrected, the FEED Key must be pressed to
clear the fault. The label in process is reprinted.
L
(continued)
2 = Void and
Retry
Depending upon the RETRY COUNT, one of the following
actions when faulted:
• If the Retry Count has not been exceeded, “VOID” is
printed on the label in process and reprinting occurs
automatically;
• If the Retry Count has been exceeded, printing stops and
a fault message is displayed. After the problem is
corrected, the FEED Key must be pressed to clear the
fault. The label in process is reprinted; or,
• If the CANCEL Key is pressed, the operator now has the
option of canceling the reprint. To allow reprinting, press
the ESCAPE Key; or, to cancel reprinting, press the
ENTER Key (and, the entire label batch will be cancelled
by pressing the ENTER Key again).
VOID will not be printed when insufficient text space
exists (see VOID DISTANCE, below) or if the fault
occurs after the label reaches its Present Distance
at, or above, the TOF.
Class Series 2 Programmer’s Manual 67
Page 82

Extended System-Level Command Functions
Value
Units /
Interpretation
Selection / Definition
Increases throughput when bar codes reside near the
trailing edge of the label (in the direction of FEED).
• If unreadable, the fault will occur after the next
3 = Delayed
Scan Fault
L
label prints.
• The label immediately following a faulted label is
not scanned for errors.
• VOID AND RETRY and REPRINT are automatically
disabled; the job can only be cancelled.
4 = Void Retry
& Cont.
VOID is printed on a faulted label, with reprint attempts
occurring automatically, until the RETRY COUNT has been
exceeded and then that label will be skipped (discarded)
and printing will continue to the next label in queue.
Sets the distance (.10 - 2.00) to backup the faulted label to
print “VOID” on its trailing edge, which also indirectly
establishes the font size of the void message.
D
Void Distance
(.10 - 2.00)
Establishes the number of times a reprint will be attempted
R
Retry Count
(0 – 3)
when using the RFID or Scanner option; if the last label
printed in this count has been voided, a fault will be
declared.
B
Example: <STX>KcFHD112<CR>
Enable / Disable
Y, N
Retract from presented distance prior to feed-clear motion.
This option is intended for use with applicator equipment
that may require certain GPIO signals for proper operation.
Table 5-2: Fault Handling Command
The example above configures the printer to back up and print a one-inch tall “VOID”
message on a faulted label; if two successive faults occur during the printing of that
label, then the FEED Key must be pressed to clear the fault.
(FM) Feedback Mode – See <STX>a for command details.
(FS) Slew Speed – This command controls the rate of label movement between
printing areas when the GPIO port is used; see Appendix L for ranges.
(GD) Display Mode – This command controls the size of displayed menu
characters, where Enhanced makes them larger.
68 Class Series 2 Programmer’s Manual
Page 83

Extended System-Level Command Functions
(GE) GPIO Equipped – This command is used to interface the printer to external
controlling devices (see Appendix J):
Value
Units /
Interpretation
GPIO Enable Definition
Enables the standard applicator mode, de-asserting DRDY
A Applicator
as soon as last label starts printing, allowing FEED any
time, and not de-asserting DRDY when PAUSED.
N Disabled Disables the GPIO Port.
V Verifier Enables the GPIO Port for a bar code verifier.
Enables the alternate applicator mode, where Data Ready
(DRDY) is extended to overlap the End Of Print (EOP) signal
2 Applicator2
by about 1 msec when printing the last label; and, where
PAUSE or FAULT de-asserts the DRDY signal and inhibits
the FEED operation.
(GL) Gap Sensor Location (MP Compact4 Mark II only) – This command will tell the
printer which sensor to use when GAP mode is selected either by the <STX>KcSTG;
or by <STX>e. Outer Gap sensor is defined as the sensor 6.3mm from the edge of
the media, (Outer is default). Inner Gap sensor is defined as the sensor 17.2mm
from the edge of the media
(GM) Gap / Mark Value – This command sets threshold value for the media
sensor’s “gap” or “mark” parameter.
(GP) GPIO Error Pause – This command enables or disables the printer from
sending a service required fault to the GPIO output (Applicator Interface CCA, Type 2
only).
(GR) Gain Reflective Value – This command sets the sensitivity of the reflective
media sensor.
(GS) GPIO Slew – This command sets the GPIO slew function and control:
Value Slew Interpretation
0 Standard (Active Low)
1 Low Pulse *
2 High Pulse *
3 Slews while low (Active Low)
4 Slews while high (Active High)
* Pulse must be at least 60 milliseconds in length; functions as if pressing the Feed Key,
clearing alarms and advancing media.
Class Series 2 Programmer’s Manual 69
Page 84

Extended System-Level Command Functions
(HB) Head Bias – This command instructs the printer to switch the dot zero
position, as viewed from the label exit. When dot zero occupies the left-most location
on the print head then printing is left justified; and, when dot zero occupies the
right-most location, printing is right justified.
(HC) Head Cleaning – This command controls the print head cleaning routine. The
entered value specifies the inch (or centimeter) count to reach before prompting a
print head cleaning. If the number specified is exceeded three times, the printer will
fault until cleaning is initiated.
The number specified is multiplied by one thousand, and zero disables this function.
(HE) Heat – See Hnn for command details.
(HT) Host Timeout – This command controls the number of seconds a
communications port must be idle before the printer will process data from a
different port or use a different parsing method. The value is also used to “timeout”
an image / label format download (i.e., if, at any time, data flow stops before a
complete label format is received, the data will be ignored).
(IC) Ignore Control Codes – This command allows the user to remove control
codes (< 20 Hex) in the data field. The selected line terminator is processed. When
enabled, DPL Control Code (SOH, STX, CR, ESC, and ^) characters are removed
from the data string. (Note that some fonts do have printable characters in this
range and they will not be printed when enabled.)
(IE) Ignore Distances – This command, when enabled, prevents <STX>O
processing that will change the start of print position.
70 Class Series 2 Programmer’s Manual
Page 85

Extended System-Level Command Functions
(IL) Imaging Mode – This command instructs the printer whether to pre-image the
label format:
Value
M Multiple Label
S Single Label
Units /
Interpretation
Imaging Mode Definition
The printer images multiple labels as memory
permits, achieving the fastest throughput; however,
if time-stamping, the time will reflect the moment
the label is imaged rather than when actually
printed.
The printer images the next label only after the
previous label has been successfully printed. Single
processing provides time-stamps that are more
accurate, but it slows label throughput time.
(IM) Internal Module – This command sets the number of 1K blocks (or 4K blocks
for Non-Display models; see the <STX>KM command) allocated for Module D.
(LA) Label Alignment – This command prevents labels with lengths that are less
than the distance between the print head and the Media Sensor from being wasted at
power-up. See the appropriate Operator’s Manual for specific information. Unless
otherwise noted, the following information pertains to all Non-Display models:
Value &
Mode
Media Type Description / Operation
When disabled, Non-Display models begin printing
at the current location, unless equipped with RTC
(Real Time Clock); see note below. The EX2
assumes the label position has not moved while
power was “Off” and that no system changes have
occurred.
N =
Disabled
6.5-inch and greater
(≥ 16.51 cm) die-cut,
notched, reflective,
continuous, and
multiple form lengths.
In auto mode, the printer will verify the label
position using the provided Alignment Length
A =
Auto
6.5-inch or less
(≤16.51 cm)
die-cut, notched, and
reflective
Y =
Enabled
before printing the first label after power-up. Press
and hold the FEED Key four seconds so the printer
will measure the length of the label. The EX2 will
only measure the label length when new label stock
is loaded.
When enabled, the printer will verify the label
position using the provided Alignment Length
before printing the first label after power-up.
Specify the Label Alignment Length using the
<STX>KcAL command, or the Setup Menu.
Table 5-3: Label Alignment Command
The Real Time Clock (RTC) option allows the position-state of the label to be stored,
thus eliminating the need for an alignment prior to first label printing (assuming the
label has not moved during power off). If the stock has been changed then a Forced
Alignment (press and hold FEED 4 seconds) is recommended.
Class Series 2 Programmer’s Manual 71
Page 86

Extended System-Level Command Functions
(LE) Legacy Emulation – This command enables the <STX>O and <STX>f print
positioning commands to allow backward compatibility with label formats that were
designed for the Allegro
Equipped, also Prodigy Max
®
Prodigy®, and Prodigy Plus® (If the printer is Display-
®
emulation).
Use causes the printer to ignore Label commands A, M, n, and T.
(LR) Label Rotation – This command sets label rotation, allowing formats to be
flipped 180 degrees.
(LS) Language Select – This command selects the language for the menu system
messages and configuration label. Only languages that are resident will be available.
Language name limited to a twenty character maximum.
(LM) Label Store – This command selects the level of stored format recall to
include the label-formatting command fields, or the label-formatting command fields
and the printer state.
(LW) Label Width – This command sets the maximum limit for the printable width.
Objects extending beyond this limit will NOT print; see Appendix K. (For Non-Display
models also see the <STX>KW command.)
The EX2 requires this command prior to the start of the label format command
(<STX>L).
72 Class Series 2 Programmer’s Manual
Page 87

Extended System-Level Command Functions
(MCC) Module Command – This command adjusts the size of Flash module on the
optional Expansion Card according to the table below (see Appendix K for
appropriate module details):
Value Module Command Units / Interpretation
Zxx
Where xx =
Size: 1 – 7 Mbytes. This is the amount to be allocated to
Module Z; any remaining memory will be allocated to Module F.
Size: 1 – 56, in 128 Kbytes blocks. This is the amount to be
Gxx
Where xx =
allocated to Module G; any remaining memory will be allocated
to Module X.
Table 5-4: Module Command
(ML) Maximum (Label) Length – See <STX>M for command details.
(MM) Menu Mode – This command sets the menu access level of the printer –
where User is a basic listing of menu settings and controls, and Advanced is a full
menu listing.
(MT) Media Type – This command selects the printing method: Direct Thermal for
use with heat sensitive media or Thermal Transfer for use with media requiring a
ribbon to create an image. (For Non-Display models also see the <STX>KD
command.)
(MV) Mark Value – This command sets threshold value for the reflective media
sensor’s “mark” parameter.
Class Series 2 Programmer’s Manual 73
Page 88

Extended System-Level Command Functions
(NE) Network Configuration – (for firmware version 14.00 and later) This
command configures the printer for an wired or wireless Ethernet connection.
Syntax is:
[nnn1,vvvv1:nnn2,vvvv2:…,nnnn,vvvvn:XX[…]YY[…] ];
aa
i
where:
Configuration Group Identifier
aa
i
[ ] Group Scope Delimiters
, Item – Value Delimiter
: Item – Value Pair Delimiter
,vvvvi: Configuration Item – Value pairs
nnn
i
nnn
Decimal Item Numbers from 1 to 9999
i
, Decimal Item Number Delimiter
vvvv
Item Value (syntax defined later)
i
: Item Value Delimiter
XX[…] Nested Configuration Sub-Group data stream
XX Sub-Group Identifier (1 – N alpha characters)
[ ] Sub-Group Scope Delimiters
; Configuration Group Terminator
The value fields can be represented as one of the following types:
Decimal Value
A decimal value string consisting of an optional leading ‘+-‘ character and followed by
decimal numeric characters 0 – 9.
Scientific Notation Value
A numeric value in scientific notation: (+-)nnnn.mmmmE+-XXX.
Hexadecimal Value
A hexadecimal value expressed like ‘0xb9E23c’.
Binary Bit Value
A binary bit value expressed like ‘0b011011’
Boolean Value
A single character from the following set: ‘Y, N, T, F, 0, 1’
String Value
A string of characters delimited by quotes, ‘…’. The ‘\’ acts as the escape character
permitting the following escaped character sequences:
o \nnewline (0x0a)
o \rcarriage return (0x0d)
o \bbackspace
o \ttab
o \fform feed
o \\backslash
o \’quote
o \dddddd consists of 3 OCTAL DIGITS
74 Class Series 2 Programmer’s Manual
Page 89

Extended System-Level Command Functions
Example:
<STX>KcNE[G[1,0:2,’sysadm’:]WE[1,N:2,’192.168.10.26’:]WIFI[1,Y::DV1[1,0:]]]; <CR>
<STX>Kc This is the beginning of command
NE Network Ethernet group
G General Network sub-group
1,0 1 = Primary Interface Item, 0 = Wired Ethernet Value
2,’sysadm’ 2 = Network Password, followed by string password value
WE Wired Ethernet (802.3) sub-group
1,N 1 = DHCP Enabled, N = Boolean Value for Not Enabled
2,’192.168.10.26’ 2 = Static IP Address, followed by IP address string
WIFI Wireless Ethernet (802.11) sub-group
1,Y 1 = DHCP Enabled, Y = Boolean Value for Enabled
DV1 DPAC Version 1 sub-group defined for WLS sub-group
1,0 1 = DPAC Version 1 Network Type, 0 = Value for Infrastructure
Network Configuration Parameters
The two character identifier for the Network Configuration Parameters is ‘NE’. No
Item-Value pairs are defined for ‘NE’ but there is the following sub-groups:
General Network Configuration Parameters – Identifier ‘G’
802.3 Wired Ethernet Configuration Parameters – Identifier ‘WE’
802.11 Wireless Ethernet (WIFI) Configuration Parameters – Identifier
‘WIFI’. This sub group consits of 4 addtional sub-groups:
General WIFI Configuration Parameters - Identifier ‘G’
DPAC Version 1 - Identifier ‘DV1’
DPAC Version 2 - Identifier ‘DV2’
Silex Version 1 - Identifier ‘SV1’
The configuration data stream for the network configuration parameters has the
following structure:
NE[G[…]WE[…]WIFI[..]];
Class Series 2 Programmer’s Manual 75
Page 90

Extended System-Level Command Functions
General Configuration Parameters – Identifier ‘G’
The ‘G’ sub-group contains network configuration parameters that apply ‘globally’ or
‘generally’ to any ethernet interface used. No sub-groups are currently defined for
the ‘G’ sub-group of configuration parameters, only item-value pairs. The ‘ItemValue’ pairs within the ‘G’ sub-group are defined by the following table:
Item
Number
1 Primary Interface Y Decimal Indicates the primary or used
2 Network Password Y String Provides the network password used
3 SNMP Enable Y Boolean Enables or Disables the SNMP
4 Telnet Enable Y Boolean Enables or Disables the TELNET
5 FTP Enable Y Boolean Enables or Disables the FTP Server.
6 HTTP Enable Y Boolean Enables or Disables the HTTP (WEB
7 LPD Enable Y Boolean Enables or Disables the LPD (Line
8 NetBIOS Enable Y Boolean Enables or Disables the NetBIOS
9 Netcenter Enable Y Boolean Enables or Disables the Netcenter
10 Gratuitous ARP
11 Printer TCP Port Y Decimal Value of the TCP Port for Print
12 Default MTU N Decimal Provides a Default MTU Size (used
13 Static Primary WINS
14 Static Secondary
15 Static Primary DNS
16 Static Secondary
17 SNMP TRAP IP
18 SNMP Server
19 NetBIOS Name Y String NetBIOS Name for the Printer.
20 Domain Name N String Domain Name – Not currently used.
21 Email Address N String Email Address – Not currently used.
Name Available
to User
(Y/N)
Y Decimal Value of the Gratuitous ARP Period in
Period
Y String Static Primary WINS Server IP
Server IP Address
Y String Static Secondary WINS Server IP
WINS Server IP
Address
Y String Static Primary DNS Server IP Address
Server IP Address
Y String Static Secondary DNS Server IP
DNS Server IP
Address
Y String SNMP TRAP IP Address in dotted
Address
Y String SNMP Server IP Address in dotted
Address
Value Type Description
ethernet interface type. Interface
types are Wired Ethernet (802.3) and
Wireless Ethernet (802.11). It is
called ‘Primary’ since, in the future if
multiple ethernet interfaces would be
supported, it would be the PRIMARY
interface used.
for WEB and TELNET sessions.
services.
services.
Pages) Server.
Printer Daemon) services.
services.
services.
seconds. 0 = Disabled.
Services.
internally).
Address in dotted decimal notation.
Address in dotted decimal notation.
in dotted decimal notation.
Address in dotted decimal notation.
decimal notation.
decimal notation.
76 Class Series 2 Programmer’s Manual
Page 91

Extended System-Level Command Functions
802.3 – Wired Ethernet Configuration Parameters – Identifier ‘WE’
The ‘WE’ sub-group contains network configuration parameters that apply only to the
Wired Ethernet (802.3 Specification) ethernet interface. No sub-groups are currently
defined for the ‘WE’ sub-group of configuration parameters, only item-value pairs.
The ‘Item-Value’ pairs within the ‘WE’ sub-group are defined by the following table:
Item
Number
1 DHCP Enable Y Boolean Indicates if the DHCP Protocol is to
2 Static Printer IP
3 Static Printer
4 Static Printer
5 PHY Mode Y Decimal Defines the ethernet PHY Mode
6 PHY Advertise Mode Y Decimal Defines the ethernet PHY Advertise
7 PHY Capabilities to
8 MTU Y Decimal Defines the Maximum Transmission
Name Available
to User
(Y/N)
Address
Subnet Mask
Default Gateway or
Router
Advertise
Value Type Description
be used to automatically obtain all
required network addresses.
Formally known as IP Discovery.
Y String Static IP Address for the Printer in
dotted decimal notation.
Y String Static Subnet Mask for the Printer in
dotted decimal notation.
Y String Static Default Gateway (Router) IP
Address in dotted decimal notation.
(Auto, 10BaseT HD, etc.)
Auto-Negotiate = 0
10BaseT Half Duplex = 1
10BaseT Full Duplex = 2
100BaseT Half Duplex = 3
100BaseT Full Duplex = 4
mode.
Auto = 0
All Capabilities = 1
Y Decimal Defines the ethernet PHY capabilities
to advertise.
Always = 0
Unit size for the wired interface.
Defaults to the DEFAULT MTU from
the ‘G’ sub-group.
802.11 – Wireless Ethernet - WIFI Configuration Parameters – Identifier ‘WIFI’
The ‘WIFI’ sub-group contains network configuration parameters that apply only to the Wireless Ethernet
(802.11 Specification) ethernet interface. Four (4) sub-groups are currently defined for the ‘WIFI’ subgroup of configuration parameters and are as follows:
General WIFI Configuration Parameters – Identifier ‘G’
DPAC Version 1 – Identifier ‘DV1’
DPAC Version 2 (Veyron) – Identifier ‘DV2’
SILEX Version 1 – Identifier ‘SV1’
Class Series 2 Programmer’s Manual 77
Page 92
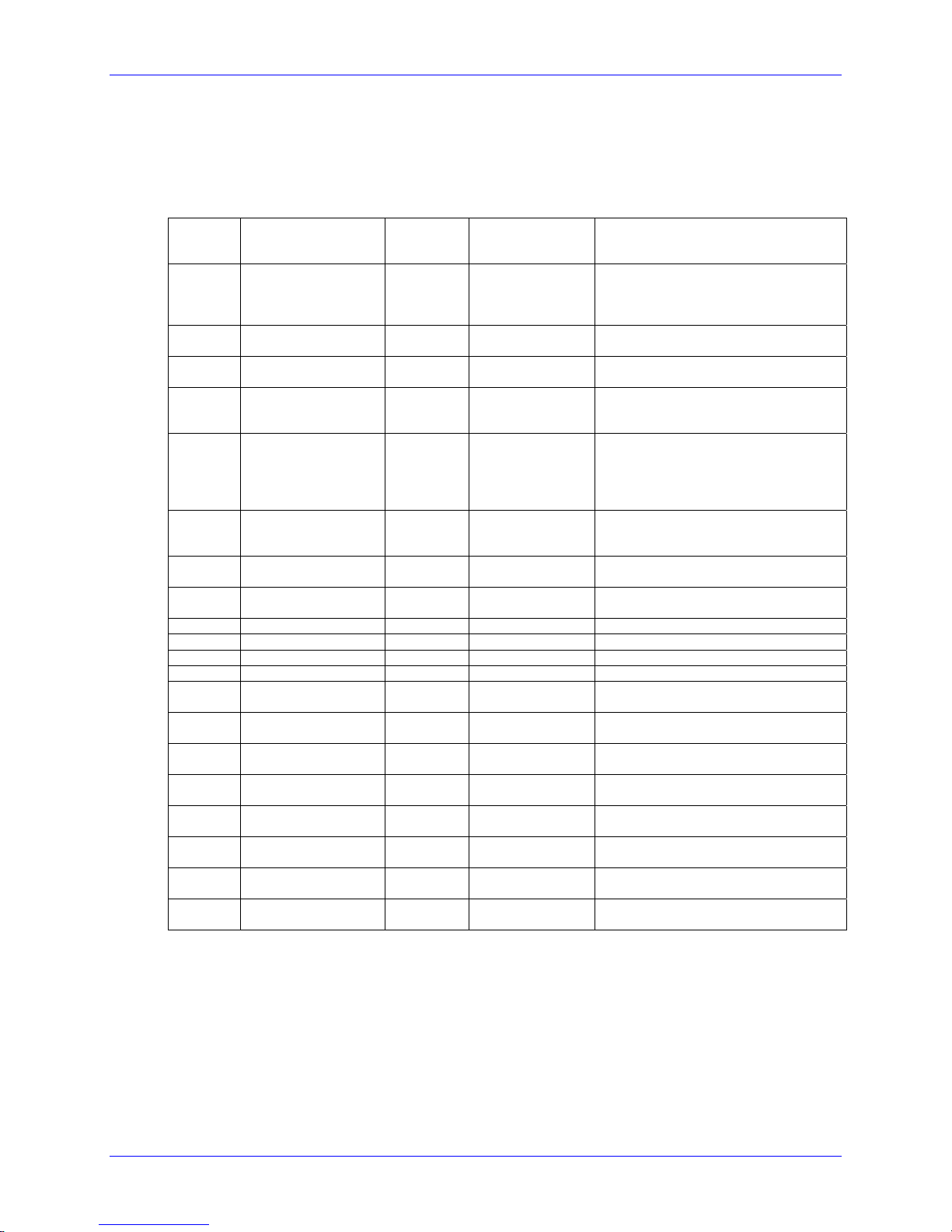
Extended System-Level Command Functions
General WIFI Configuration Parameters – Identifier ‘G’
The ‘G’ WIFI sub-group contains the configuration parameters that are generally common to ALL WIFI
radio modules used by Datamax-O’Neil. These configuration parameters are universally standard within
the WIFI realm and are interpreted commonly by the various WIFI radio modules. The ‘Item-Value’ pairs
within the ‘G’ sub-group of the ‘WIFI’ sub-group are defined by the following table:
Item
Number
Name Available
to User
Value Type Description
(Y/N)
1 DHCP Enable Y Boolean Indicates if the DHCP Protocol is to
be used to automatically obtain all
required network addresses.
Formally known as IP Discovery.
2 Static Printer IP
Address
3 Static Printer
Subnet Mask
4 Static Printer
Default Gateway or
Y String Static IP Address for the Printer in
dotted decimal notation.
Y String Static Subnet Mask for the Printer in
dotted decimal notation.
Y String Static Default Gateway (Router) IP
Address in dotted decimal notation.
Router
5 MTU Y Decimal Defines the Maximum Transmission
Unit size for the wired interface.
Defaults to the DEFAULT MTU from
the ‘G’ sub-group. Cannot exceed
the maximum ethernet packet size!!!
6 Ad-Hoc Channel Y Decimal WIFI Channel Number used when
operating in Peer-Peer (Ad-Hoc)
mode.
7 Region Code Y String Two (2) character zero terminate
Region Code string, such as “US”.
8 WEP Key Used Y Decimal A decimal number from 1 to 4 that
designates the WEP key used.
9 WEP Key 1 Y String 10 or 26 digit WEP Key 1
10 WEP Key 2 Y String 10 or 26 digit WEP Key 2
11 WEP Key 3 Y String 10 or 26 digit WEP Key 3
12 WEP Key 4 Y String 10 or 26 digit WEP Key 4
13 Pre-Shared Key or
PSK
Y String 8 to 64 character Pre-Shared Key
used by WPA-PSK or WPA2-PSK
14 LEAP Used ID Y String User ID String for LEAP (Cisco) EAP
Protocol.
15 LEAP Password Y String Password String for LEAP (Cisco) EAP
Protocol.
16 EAP User ID Y String User ID String for other EAP
Protocols.
17 EAP Password Y String Password String for other EAP
Protocols
18 EAP Realm Y String Realm String for EAP Protocols that
utilize a Realm.
19 SSID Y String String that represents the SSID if in
Infrastructure mode.
20 WIFI Type Y Decimal WIFI Module type (DPAC1=1,
SILEX=2, DPAC2=3)
78 Class Series 2 Programmer’s Manual
Page 93

Extended System-Level Command Functions
DPAC Version 1 WIFI Configuration Parameters – Identifier ‘DV1’
The ‘DV1’ WIFI sub-group contains the configuration parameters that are specific to
the DPAC Version 1 WIFI radio module used by Datamax-O’Neil. The ‘Item-Value’
pairs within the ‘DV1’ sub-group of the ‘WIFI’ sub-group are defined by the following
table:
Item
Number
1 Network Type Y Decimal Value that represents a Valid
2 WIFI Security Type Y Decimal Value that represents the DPAC
3 WIFI Authentication
4 Static Radio IP
5 Static Radio Subnet
Name Available
to User
(Y/N)
Type
Address
Mask
Value Type Description
Network Type for the DPAC Version 1
module.
AD-HOC = 0
Infrastructure = 1
Version 1 Security Codes supported.
Security Disabled = 0
WEP, 64 Bit Key = 1
WEP, 128 Bit Key = 2
WPA-PSK = 3
WPA CISCO LEAP = 4
TKIP+40Bit WEP using EAP (LEAP) = 5
TKIP+128Bit WEP using EAP (LEAP) = 6
TKIP+40Bit WEP using WPA-PSK = 7
TKIP+128Bit WEP using WPA-PSK = 8
Y Decimal Value that represents the DPAC
Version 1 Authentication Types
supported (Auto, Open, Shared Key).
Automatic = 0
Open = 1
Shared Key = 2
Y String Static IP Address for the DPAC
Version 1 radio module in dotted
decimal notation.
Y String Static Subnet Mask for the DPAC
Version 1 radio module in dotted
decimal notation.
Class Series 2 Programmer’s Manual 79
Page 94

Extended System-Level Command Functions
DPAC Version 2 WIFI Configuration Parameters – Identifier ‘DV2’
The ‘DV2’ WIFI sub-group contains the configuration parameters that are specific to
the DPAC Version 2 (Veyron) WIFI radio module used by Datamax-O’Neil. The ‘ItemValue’ pairs within the ‘DV2’ sub-group of the ‘WIFI’ sub-group are defined by the
following table:
Item
Number
1 Network Type Y Decimal Value that represents a Valid
2 WIFI Security Type Y Decimal Value that represents the DPAC
3 WIFI Authentication
Name Available
to User
(Y/N)
Type
Value Type Description
Network Type for the DPAC Version 2
module.
AD-HOC = 0
Infrastructure = 1
Version 2 Security Codes supported.
Security Disabled = 0
WEP, 64 Bit Key = 1
WEP, 128 Bit Key = 2
WPA-PSK = 3
WPA CISCO LEAP = 4
TKIP+40Bit WEP using EAP (LEAP) = 5
TKIP+128Bit WEP using EAP (LEAP) = 6
TKIP+40Bit WEP using WPA-PSK = 7
TKIP+128Bit WEP using WPA-PSK = 8
WPA2-PSK = 9
WPA/WPA2 TLS = 10
WPA/WPA2 PEAP = 11
WPA/WPA2 TTLS = 12
Y Decimal Value that represents the DPAC
Version 2 Authentication Types
supported (Auto, Open, Shared
Key, EAP, etc.).
Automatic = 0
Open = 1
Shared Key = 2
80 Class Series 2 Programmer’s Manual
Page 95

Extended System-Level Command Functions
SILEX Version 1 WIFI Configuration Parameters – Identifier ‘SV1’
The ‘SV1’ WIFI sub-group contains the configuration parameters that are specific to
the SILEX Version 1 WIFI radio module used by Datamax-O’Neil. The ‘Item-Value’
pairs within the ‘SV1’ sub-group of the ‘WIFI’ sub-group are defined by the following
table:
Item
Number
1 Network Type Y Decimal Value that represents a Valid Network
2 Encryption Type Y Decimal Value that represents the SILEX Version
3 Authentication Type Y Decimal Value that represents the SILEX Version
4 Inner
5 Use WPA Group Key Y Boolean Enables or Disables use of the WPA
Name Available
to User
(Y/N)
Authentication Type
Value Type Description
Type for the SILEX Version 1 module.
AD-HOC = 0
Infrastructure = 1
1 Encryption Types supported.
Security disabled = 0
WEP64 = 1
WEP128 = 2
WPA = 3
WPA2 = 4
1 Authentication Types supported (Auto,
Open, Pre-Shared Key, EAP, etc.).
Open System = 0
Shared Key = 1
Pre-Shared Key = 2
TTLS = 3
LEAP = 4
PEAP = 5
EAP-FAST = 6
TLS = 7
Y Decimal Value that represents the Inner
Authentication Type used if a Tunneled
EAP method is specified.
None = 0
PAP = 1
MSCHAP_V2 = 2
Group Key.
Class Series 2 Programmer’s Manual 81
Page 96

Extended System-Level Command Functions
(NT) Network Setup – (for firmware version 13.99 and earlier) This command
configures the printer for an Ethernet connection.
Value Parameter Interpretation Default Value*
Is the transmission interval for
A x
Gratuitous ARP, where:
x = The interval, 0 – 2048, in minutes
0
Is Network Bios Name, where:
B y
y = Up to 16 alphanumeric characters,
no spaces
Transmits the printer’s Wired network
communication capability, where x:
C x
0 = Advertises the DUPLEX CAPABILITY
set value.
1 = Advertises all possibilities for
DUPLEX CAPABILITY.
Is Discovery (DHCP or Bootp), where a:
D a
Y = Enable
N = Disable
Is the communication capability for the
Wired network, where x:
E x
0 = Auto-Negotiate
1 = 10Base-T, Half Duplex
2 = 10Base-T, Full Duplex
3 = 100Base-T, Half Duplex
4 = 100Base-T, Full Duplex
DMX_[and the last
3 octets (in
hexadecimal) of
the MACM (or
MACO) Address]
0
Y
0
F a
G xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
(continued)
82 Class Series 2 Programmer’s Manual
Is FTP enable, where a:
Y = Enable
N = Disable
Is the Gateway Address, where:
x = 0 to 9
N
000.000.000.000
Page 97

Extended System-Level Command Functions
Value Parameter Interpretation Default Value*
Is the IP Address, where:
I xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
192.168.010.026
x = 0 to 9
Is MTU packet size, where:
m x
1500
x = a range, 512 – 65515, in bytes
Is the SNMP Trap Address, where:
N xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
000.000.000.000
x = 0 to 9
Is the destination Port Number, where:
P xxxx
9100
x = 0 to 9
Is the Subnet Mask, where:
S xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
255.255.255.000
x = 0 to 9
Is SNMP enable, where a:
T a
Y = Enable
N = Disable
Is the WINS2 Address, where:
U xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
x = 0 to 9
Is WiFi enable, where a:
w a
Y = Enable
N = Disable
Is the WINS1 Address, where:
W xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
x = 0 to 9
Is Telnet enable, where a:
X a
Y = Enable
N = Disable
Is the DNS1 Address, where:
Y xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
x = 0 to 9
Y
000.000.000.000
N
000.000.000.000
N
000.000.000.000
K a
(continued)
Class Series 2 Programmer’s Manual 83
Is TCP Keep Alive enable, where a:
Y = Enable
N = Disable
N
Page 98

Extended System-Level Command Functions
Value Parameter Interpretation Default Value*
Is the DNS2 Address, where:
Z xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
000.000.000.000
x = 0 to 9
Sets the webpage password, where:
$ xxxxxx
sysadm
x = alphanumeric characters
* Prior to the introduction of WiFi, 192.0.0.192 was the IP default value and the Subnet
Mask was 0.0.0.0.
Table 5-5: Network Setup
Each octet must be zero-filled to be properly interpreted (e.g., an IP Address of
Example:
<STX>KcNTI010.012.000.243;NTS255.255.000.000;NTG010.012.254.254;NTDN;<CR>
The command string above is typical of a network setup string (where the values
meanings are shown in the following table). This configuration setup command string
may be included with any other Kc sub-commands.
10.12.0.243 must be sent to the printer as 010.012.000.243).
Sub-commands and Values Interpretation
NTI010.012.000.243
NTS255.255.000.000
NTG010.012.254.254
NTDN
IP Address: 10.12.0.243
Subnet Mask: 255.255.0.0
Gateway Address: 10.12.254.254
DHCP is disabled
(NR) No Reprint – This command controls the label reprint function following the
correction of a fault condition. Upon detection of a fault (ribbon out, paper out, etc.),
printing stops and a fault indicator is illuminated. After the problem is corrected, the
FEED Key must be pressed to clear the fault and resume normal operation. When
enabled, the label in process is not reprinted.
84 Class Series 2 Programmer’s Manual
Page 99

Extended System-Level Command Functions
(NS) Disable Symbol Set Selection – This command prevents the <STX>y and y
commands from changing the default single-byte symbol set. When enabled, DPL
Symbol Set commands are ignored.
When enabled, the only way to change the current symbol set is with the <STX>KcAS
command.
(OF) Option Feedback Mode – This command configures the printer to output the
status of the RFID or Scanner option to the active port, as follows.
Value Option Feedback Mode Units / Interpretation
D
= Disable
=
D, Rx, S
Rx
S
RFID Enable, where x is the response format:
A = ASCII
H = Hexadecimal
= Scanner Enable
Table 5-6: Option Feedback Command
Not supported on the I-4208 printer.
Once enabled, the printer will report information about the results of the last label
printed. One response per label is returned to the host (this includes each voided and
retried label). The format and contents of the returned information is as follows:
Class Series 2 Programmer’s Manual 85
Page 100

Extended System-Level Command Functions
Response format:
Where:
<A;B;C;D;E;F>[CR]
A
- Device type:
R = RFID
S = Scanner
B
- Resulting status:
C = entire label complete
F = faulted (failed) label
U = unknown
C
- The number of expected reads for bar codes or tags,
given in two characters.
D
- The number of good reads for bar codes or tags, given in
two characters.
E
- The printer’s internal Job Identifier and Sub Job
Identifier, given in four characters each.
F
- The data read, delimited with semicolons (;) if multiple
reads.
RFID response sample differences: Since RFID commands vary in operation, the
data returned also differs. Write commands return entire tag data; Write/Verify
commands return the data written; and, Read commands return data and length
requested in the specified format. (See Appendix S for a listing of commands.)
Write response example:
<R;C;00;00;0013:0001>[CR]
Write/Verify hexadecimal response example:
<R;C;01;01;0012:0001;446174616D61782077726974657320524649442062657374>
[CR]
Read hexadecimal response example:
<R;C;01;01;0013:0001;446174616D61782077726974657320524649442062657374>
[CR]
Write/Verify ASCII response example:
<R;C;01;01;0012:0001; Datamax writes RFID best >[CR]
Read ASCII response example:
<R;C;01;01;0013:0001; Datamax writes RFID best >[CR]
Scanner response samples:
A successfully read label example:
<S;C;03;03;0002:0001;DATA1;DATA2;DATA3>[CR]
A failed label, successfully retried:
<S;F;02;01;0002:0001;DATA1>[CR]
<S;C;02;02;0002:0001;DATA1;DATA2>[CR]
86 Class Series 2 Programmer’s Manual
 Loading...
Loading...