Page 1

Service Manual
D1 High Power Open Circuit Pumps
Size 65/130/145/193/260
www.danfoss.com
Page 2
Service Manual
D1 High Power Open Circuit Pumps Size 65/130/145/193/260
Revision history Table of revisions
Date Changed Rev
July 2019 Added 65cc size 0201
October 2018 Added Shaft Replacement 0106
July 2018 Fixed layout 0105
June 2018 Major Update 0104
October 2017 Added Size 130 0103
June 2016 Added Size 260 0102
April 2016 Converted to Danfoss layout - DITA CMS 0101
July 2015 Added 145 cc information AB
January 2014 First edition AA
2 | © Danfoss | July 2019 L1527453 | AX00000292en-CN0201
Page 3

Service Manual
D1 High Power Open Circuit Pumps Size 65/130/145/193/260
Contents
Introduction
Overview..............................................................................................................................................................................................5
General instructions........................................................................................................................................................................ 5
Remove the unit.......................................................................................................................................................................... 5
Keep it clean..................................................................................................................................................................................5
Replace all O-rings and gaskets............................................................................................................................................. 5
Secure the unit.............................................................................................................................................................................5
Safety precautions............................................................................................................................................................................5
Unintended Machine Movement..........................................................................................................................................5
Flammable Cleaning Solvents................................................................................................................................................6
Fluid Under Pressure..................................................................................................................................................................6
Personal Safety.............................................................................................................................................................................6
Symbols used in Danfoss literature............................................................................................................................................6
Design...................................................................................................................................................................................................6
Cross-section view........................................................................................................................................................................... 8
Operation
NPNN (Pressure Compensated Control).................................................................................................................................. 9
NPSN (Pressure Compensated Control + Load Sensing Control).................................................................................11
NPNR (Pressure Compensated Control + Remote Pressure Compensated Control)............................................ 13
TPSN (Power Control + Pressure Compensated Control + Load Sensing Control)................................................15
NNES (Electric Displacement Control + Load Sensing Control)....................................................................................17
Solenoid Specification............................................................................................................................................................ 19
Standard EDC Valve................................................................................................................................................................. 20
NNES Priority.............................................................................................................................................................................. 20
TPE2/TPE5 (Power Control + Pressure Compensated Control + Electric Displacement Control).................... 21
TPE2/TPE5 Priority....................................................................................................................................................................21
NPE2/NPE0 (Pressure Compensated Control + Electric Displacement Control).....................................................22
Operating parameters
Pressure............................................................................................................................................................................................. 23
Speed..................................................................................................................................................................................................23
Fluid.................................................................................................................................................................................................... 23
Viscosity........................................................................................................................................................................................24
Temperature...............................................................................................................................................................................24
Fluid velocity.............................................................................................................................................................................. 24
Technical specifications
D1 pump specifications...............................................................................................................................................................25
D1P fluid specifications................................................................................................................................................................26
Fluid and filter maintenance
Recommendations of fluid and filter maintenance...........................................................................................................27
Pressure measurements
Port Locations and Gauge Installation (65).......................................................................................................................... 28
Port Locations and Gauge Installation (130/145)...............................................................................................................29
Port Locations and Gauge Instalation (193/260)................................................................................................................30
Initial start-up procedures
General...............................................................................................................................................................................................31
Start-up Procedure........................................................................................................................................................................ 31
Troubleshooting
Excessive Noise and /or Vibration............................................................................................................................................32
Low Pump Output Flow...............................................................................................................................................................32
No or Low System Pressure........................................................................................................................................................32
Actuator Response is Sluggish..................................................................................................................................................33
Pressure or Flow Instability.........................................................................................................................................................33
System Operating Hot..................................................................................................................................................................34
High Inlet Vacuum.........................................................................................................................................................................34
Adjustments
©
Danfoss | July 2019 L1527453 | AX00000292en-CN0201 | 3
Page 4

Service Manual
D1 High Power Open Circuit Pumps Size 65/130/145/193/260
Contents
Calculate Power Control Start Point Pressure and Corresponding Flow in Advance........................................... 35
Electric Displacement Control Adjustment .........................................................................................................................36
Pressure Compensated Control Adjustment.......................................................................................................................38
Power Control Adjustment.........................................................................................................................................................38
Load Sensing Control Adjustment...........................................................................................................................................38
Displacement Limiters Adjustment.........................................................................................................................................42
Adjust Displacement Limiters..............................................................................................................................................42
Minor repairs
Shaft replacement......................................................................................................................................................................... 43
Shaft removal.............................................................................................................................................................................43
Shaft installation....................................................................................................................................................................... 44
Shaft Seal Replacement...............................................................................................................................................................45
Removal........................................................................................................................................................................................45
Installation...................................................................................................................................................................................45
Auxiliary Flange and Charge Pump Replacement............................................................................................................. 46
Auxiliary flange removal........................................................................................................................................................ 46
Auxiliary flange installation...................................................................................................................................................46
130/145........................................................................................................................................................................................ 47
193/260........................................................................................................................................................................................ 48
Control (193/260)...........................................................................................................................................................................49
Removal........................................................................................................................................................................................49
Installation...................................................................................................................................................................................49
Control (130/145)...........................................................................................................................................................................51
Shuttle Valve or Plug.....................................................................................................................................................................52
Shuttle valve or plug removal..............................................................................................................................................52
Shuttle valve or plug installation........................................................................................................................................52
Edge Filter (260)..............................................................................................................................................................................52
Edge filter removal...................................................................................................................................................................52
Edge filter installation.............................................................................................................................................................52
Displacement Limiters................................................................................................................................................................. 54
Displacement limiter screw removals...............................................................................................................................54
Displacement limiter screws installation......................................................................................................................... 54
Plug and fitting installation........................................................................................................................................................56
193 TPE2 control....................................................................................................................................................................... 56
260 TPE2 control....................................................................................................................................................................... 57
130/145 TPSN control............................................................................................................................................................. 58
Plugs and fasteners....................................................................................................................................................................... 59
Fastener and torque chart.....................................................................................................................................................59
Plug size and torque chart.....................................................................................................................................................60
4 | © Danfoss | July 2019 L1527453 | AX00000292en-CN0201
Page 5

Service Manual
D1 High Power Open Circuit Pumps Size 65/130/145/193/260
Introduction
Pump service overview
This manual includes information on maintenance, troubleshooting, and minor repair of D1P pumps.
Performing minor repairs may require removal from the vehicle/machine. Thoroughly clean the unit
before beginning maintenance or repair activities. Since dirt and contamination are the greatest enemies
of any type of hydraulic equipment, follow cleanliness requirements strictly. This is especially important
when changing the system filter and when removing hoses or plumbing.
A worldwide Global Service Partner Network is available for major repairs. Major repairs require the
removal of the unit’s endcap, which voids the warranty unless done by a Global Service Partner. Danfoss
Global Service Partners are trained by the factory and certified on a regular basis. You can locate your
nearest Global Service Partner using the distributor locator at www.danfoss.com.
For detailed technical information, refer to the Technical Information manual.
General instructions
Remove the unit
If necessary, remove the unit from the vehicle/machine. Chock the wheels on the vehicle or lock the
mechanism to inhibit movement. Be aware that hydraulic fluid may be under high pressure and/or hot.
Inspect the outside of the pump and fittings for damage. Cap hoses after removal to prevent
contamination.
Safety precautions
Keep it clean
Cleanliness is a primary means of assuring satisfactory pump life on either new or repaired units.
Clean the outside of the pump thoroughly before disassembly. Take care to avoid contamination of the
system ports. Cleaning parts by using a clean solvent wash and air drying is usually adequate.
As with any precision equipment, you must keep all parts free of foreign material and chemicals. Protect
all exposed sealing surfaces and open cavities from damage and foreign material. If left unattended,
cover the pump with a protective layer of plastic.
Replace all O-rings and gaskets
Danfoss recommends that you replace all O-rings, seals and gaskets. Lightly lubricate all O-rings with
clean petroleum jelly prior to assembly.
Secure the unit
If removed from machine, place the unit in a stable position with the shaft pointing downward. It
will be necessary to secure the pump while removing and torquing fasteners and components.
Unintended Machine Movement
Unintended movement of the machine or mechanism may cause injury to the technician or bystanders.
Secure the machine or disable/disconnect the mechanism while servicing to protect against unintended
movement.
©
Danfoss | July 2019 L1527453 | AX00000292en-CN0201 | 5
Page 6
Service Manual
D1 High Power Open Circuit Pumps Size 65/130/145/193/260
Introduction
Flammable Cleaning Solvents
Some cleaning solvents are flammable.
Do not use cleaning solvents in an area where a source of ignition may be present to avoid possible fire.
Fluid Under Pressure
Escaping hydraulic fluid under pressure can have sufficient force to penetrate your skin causing serious
injury and/or infection. This fluid may also be hot enough to cause burns.
Relieve pressure in the system before removing hoses, fittings, gauges, or components. Never use your
hand or any other body part to check for leaks in a pressurized line. Use caution when dealing with
hydraulic fluid under pressure. Seek medical attention immediately if you are cut by hydraulic fluid.
Personal Safety
Protect yourself from injury whenever servicing a hydraulic system.
Use proper safety equipment, including safety glasses, at all times.
Symbols used in Danfoss literature
WARNING may result in injury Tip, helpful suggestion
CAUTION may result in damage to product or
property
Reusable part Apply grease / petroleum jelly
Non-reusable part, use a new part Apply locking compound
Non-removable item Inspect for wear or damage
Option - either part may exist Clean area or part
Superseded - parts are not interchangeable Be careful not to scratch or damage
Measurement required Note correct orientation
Flatness specification Mark orientation for reinstallation
Parallelism specification Torque specification
External hex head Press in - press fit
Internal hex head Pull out with tool – press fit
Torx head Cover splines with installation sleeve
O-ring boss port Pressure measurement/gauge location or
Lubricate with hydraulic fluid
specification
The symbols above appear in the illustrations and text of this manual. They are intended to communicate
helpful information at the point where it is most useful to the reader. In most instances, the appearance
of the symbol itself denotes its meaning. The legend above defines each symbol and explains its purpose.
D1 pumps design
Danfoss D1 high power open circuit piston pumps convert input torque into hydraulic power. Rotational
force is transmitted through the input shaft to the cylinder block. The input shaft is supported by roller
6 | © Danfoss | July 2019 L1527453 | AX00000292en-CN0201
Page 7

Service Manual
D1 High Power Open Circuit Pumps Size 65/130/145/193/260
Introduction
bearings at the front and rear of the pump and is splined into the cylinder block . A lip-seal at the front
end of the pump prevents leakage where the shaft exits the pump housing. The spinning cylinder block
contains nine reciprocating pistons. Each piston has a brass slipper connected at one end by a ball joint.
The slippers are held to the swashplate by the retainer. The block spring holds the cylinder block to the
valve plate. The reciprocating movement of the pistons occurs as the slippers slide against the inclined
swashplate during rotation. Via the valve plate, one half of the cylinder block is connected to pump inlet
and the other half to pump outlet. As each piston cycles in and out of its bore, fluid is drawn from the
inlet and displaced to the outlet thereby imparting power into the system circuit. A small amount of fluid
is allowed to “leak” from the cylinder block / valve plate and slipper / swashplate interfaces for lubrication
and cooling. Case drain ports are provided to return this fluid to the reservoir.
The volume of fluid displaced into the system circuit is controlled by the angle of the swashplate. The
swashplate is forced into an inclined position (into stroke) by the bias piston and spring. The servo piston
opposes the action of the bias piston and spring forcing the swashplate out of stroke.
The pump control, by varying the pressure at the servo piston, controls the displacement of fluid in the
system circuit.
©
Danfoss | July 2019 L1527453 | AX00000292en-CN0201 | 7
Page 8
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
Service Manual
D1 High Power Open Circuit Pumps Size 65/130/145/193/260
Introduction
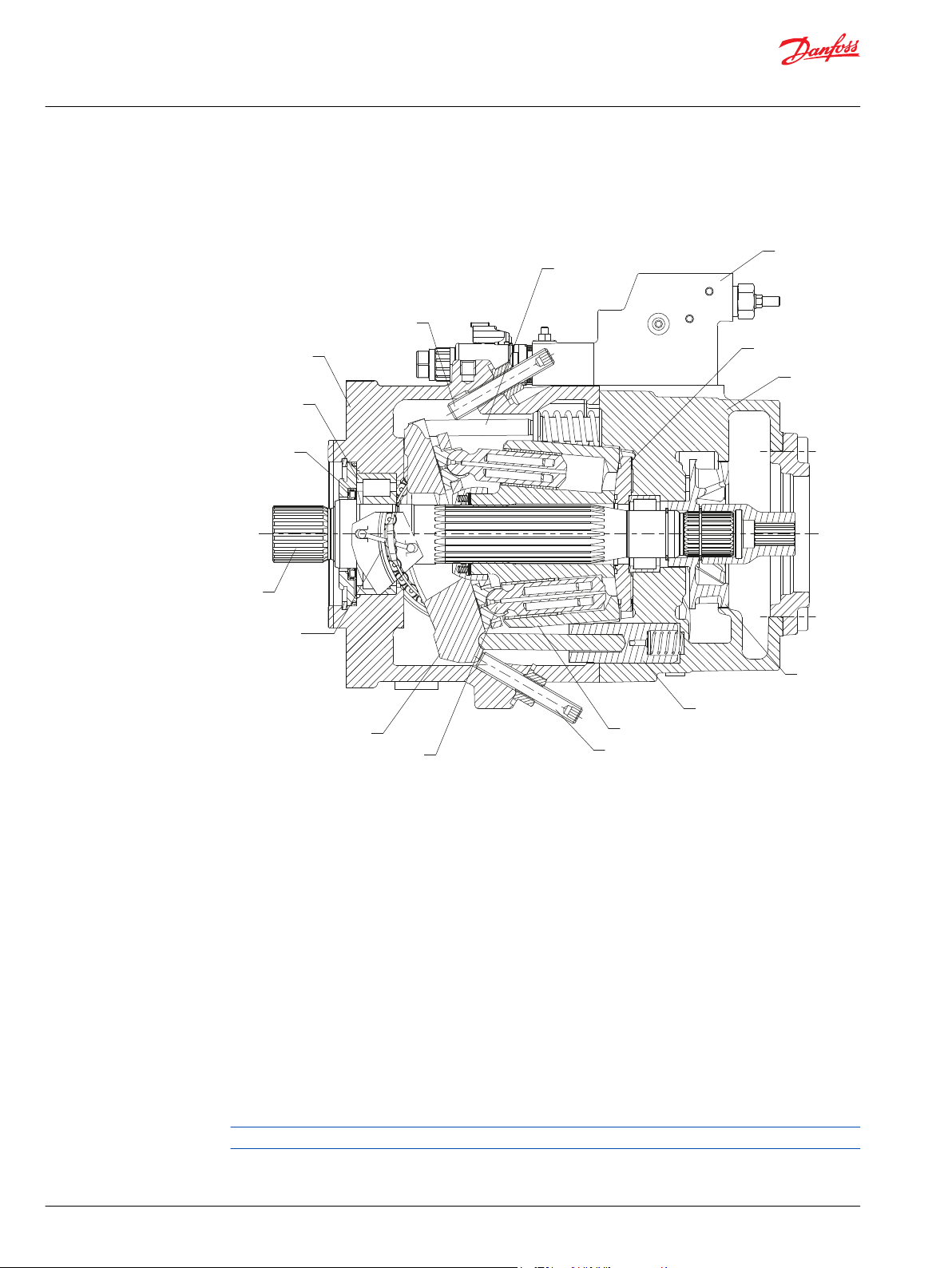
D1 pump cross-section view
D1 pump
1. Shaft seal
2. Roller bearing
3. Housing
4. Minimum displacement limiter
5. Bias piston
6. Control
7. Valve plate
8. Endcap
9. Charge pump
10. Servo piston
11. Cylinder block
12. Maximum displacement limiter
13. Piston
14. Swashplate
15. Swashplate Bearing
16. Input shaft
Some internal parts may be different depending on the pump size.
8 | © Danfoss | July 2019 L1527453 | AX00000292en-CN0201
Page 9
0
0
Q max
Flow
Pressure
Service Manual
D1 High Power Open Circuit Pumps Size 65/130/145/193/260
Operation
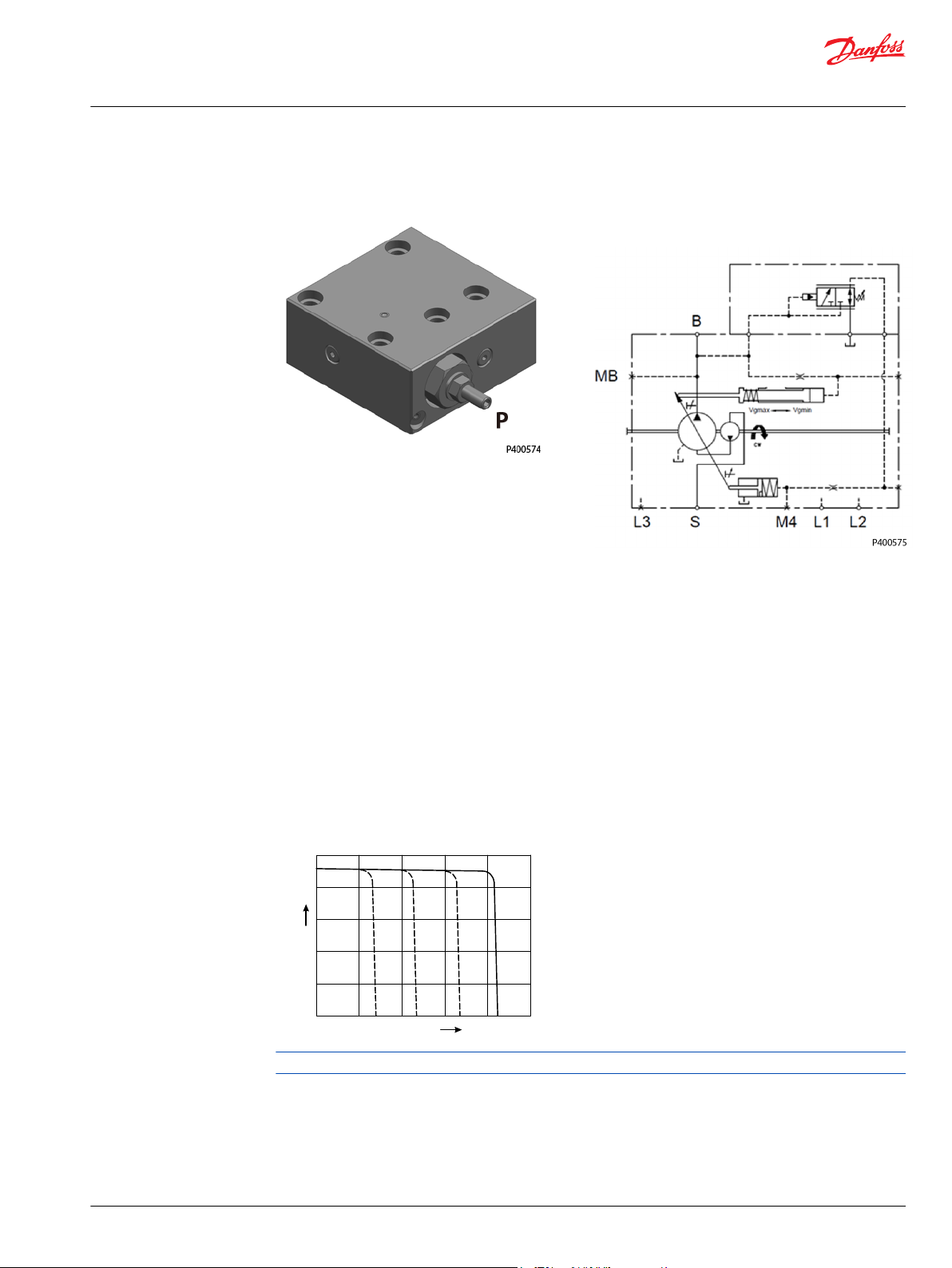
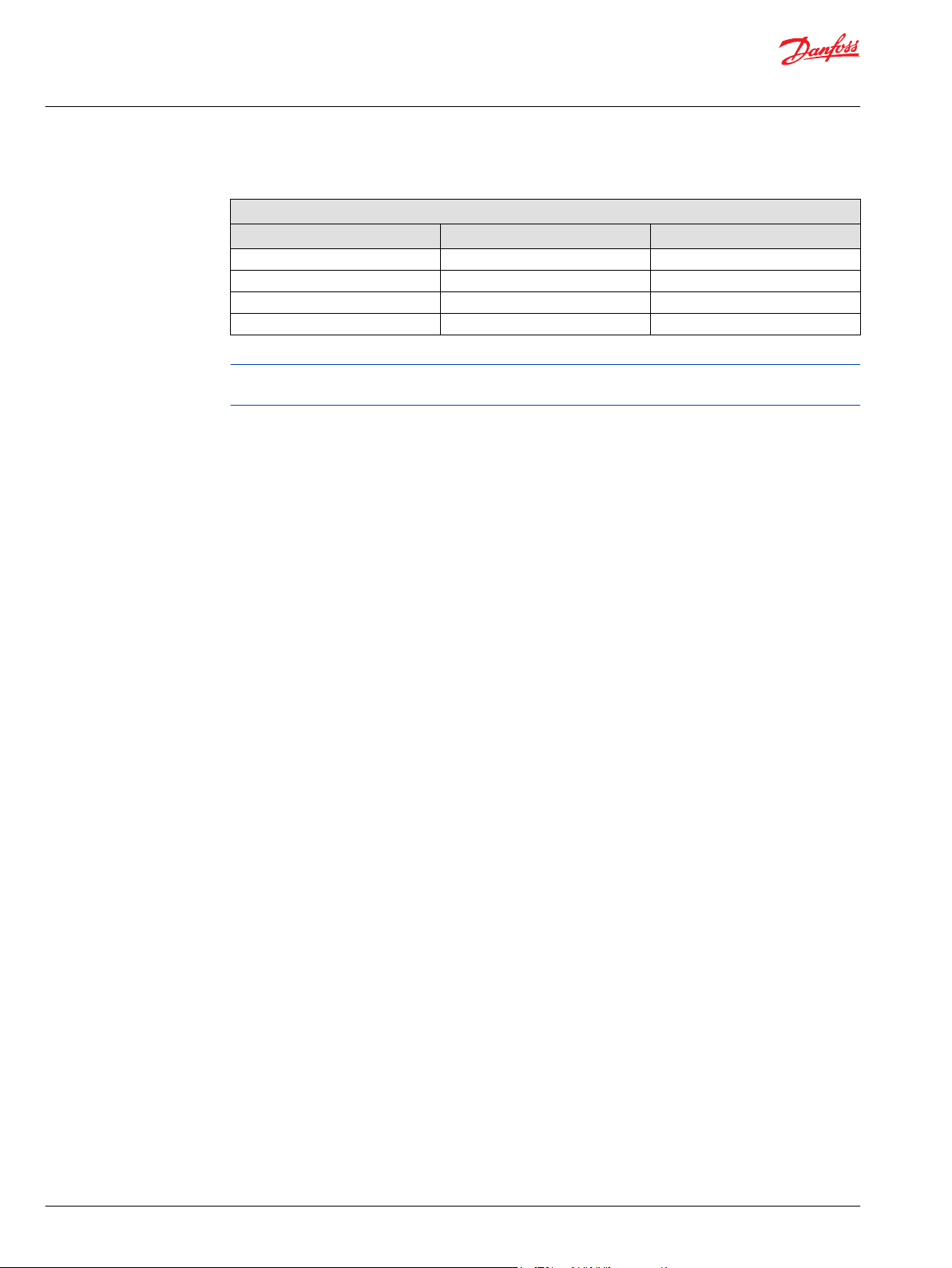
NPNN (Pressure Compensated Control)
D1P 130/145/193/260+NPNN
Pressure Compensated Control (P) Principle
The P control design maintains a constant pressure in the hydraulic circuit as flow varies. The P control
modulates pump flow accordingly to maintain system pressure at the P setting as the P adjusting screw
and spring defines.
Pressure Compensated Control (P) Operation
When system pressure, acting on the non-spring end of the P spool, overcomes the force of the P spring,
the spool shifts porting system pressure to the servo piston and the swashplate angle decreases. When
system pressure drops below the P setting, the P spring shifts the spool in the opposite direction
connecting the servo piston to pump case and the swashplate angle increases. The swashplate is
maintained at whatever angle is required to keep system pressure at the P setting.
P characteristic
It is recommended that a relief valve be installed in the pump outlet for additional system protection.
©
Danfoss | July 2019 L1527453 | AX00000292en-CN0201 | 9
Page 10
Service Manual
D1 High Power Open Circuit Pumps Size 65/130/145/193/260
Operation
Response/Recovery
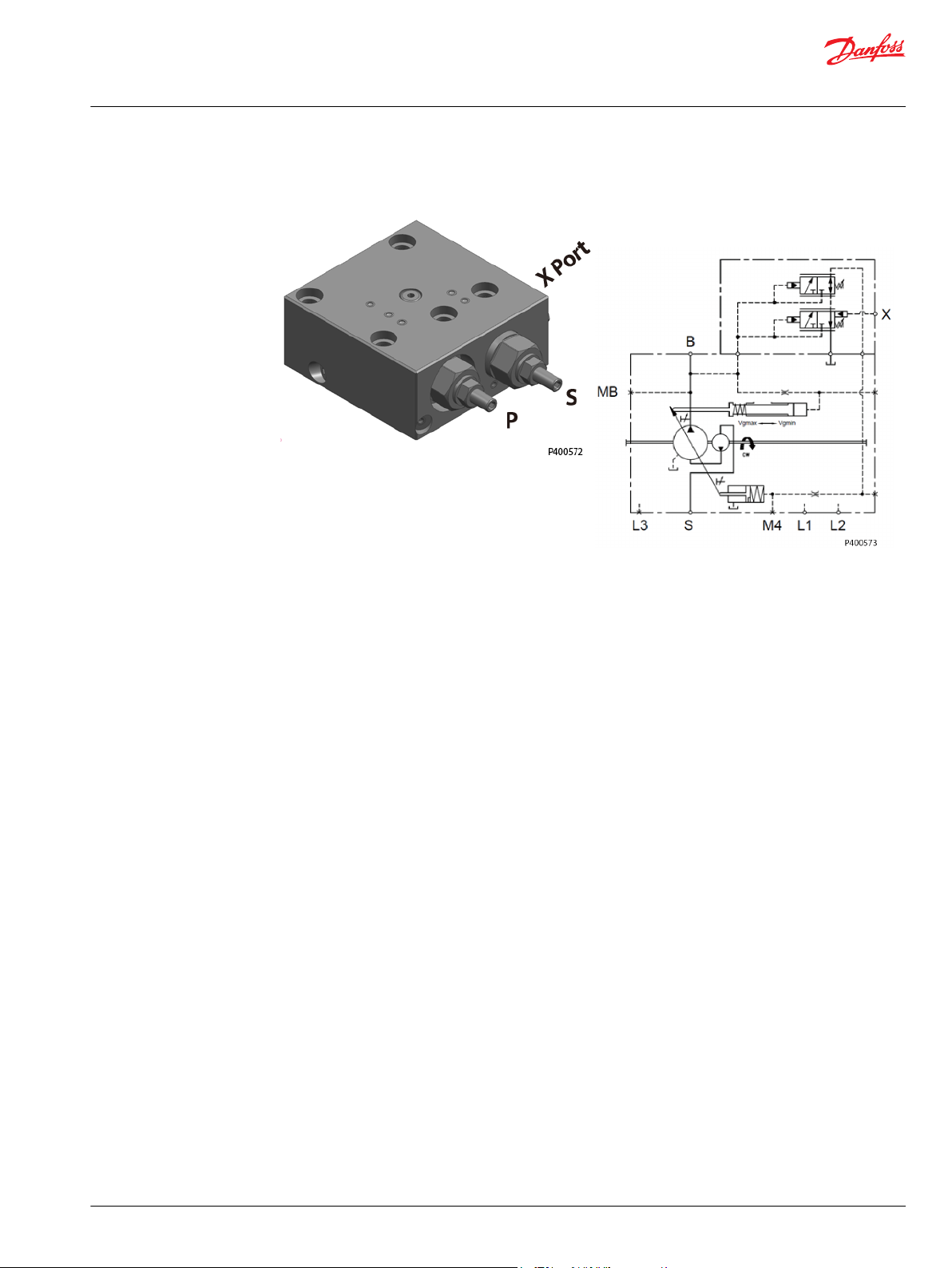
Pressure Compensated (PC) Control Response/Recovery Times* @80°C, 350 bar, 1500rpm
Frame Size Response (msec) Recovery (msec)
130cc 150 270
145cc 150 270
1
193cc
260cc 154 327
1
Tested at 1800rpm
Values may vary depending on application conditions. For more information, please contact Danfoss
Power Solutions.
280 500
10 | © Danfoss | July 2019 L1527453 | AX00000292en-CN0201
Page 11
Service Manual
D1 High Power Open Circuit Pumps Size 65/130/145/193/260
Operation
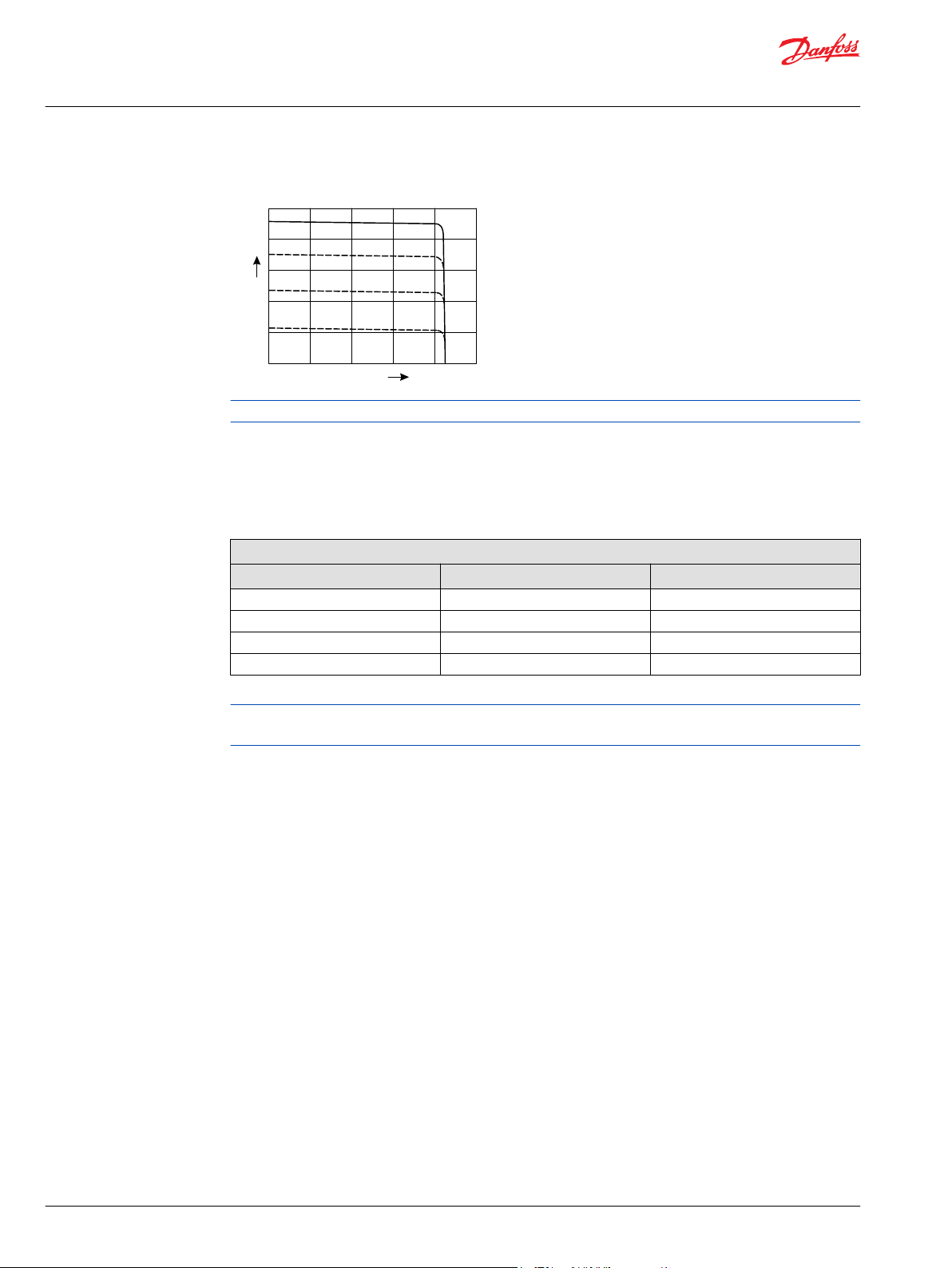
NPSN (Pressure Compensated Control + Load Sensing Control)
D1P 130/145/193/260+NPSN
Pressure Compensated Control (P) Principle and Operation
Please refer to NPNN (Pressure Compensated Control) on page 9
Load Sensing Control (S) Principle
The S control design matches pump flow with system demand. The S control senses the flow demand of
the system as a pressure drop across the external control valve (1).
As (1) opens and closes, the pressure difference (delta) across the valve changes. When opening, the delta
decreases. When closing, the delta increases. The S control then increases or decreases pump flow to the
system until the pressure delta becomes equal to the S setting as defined by the S adjusting screw and
spring.
Load Sensing Control (S) Operation
Through internal porting, system pressure [upstream of (1)] is applied to the non-spring end of the S
spool, and through hydraulic line connected at port X, load pressure [downstream of (1)] is applied to the
spring end. This arrangement allows the S spool to act on the delta between system pressure and load
pressure. The S spring sets the threshold of operation (S setting).
Because the swashplate is biased to maximum angle, the pump attempts to deliver full flow to the
hydraulic system. When the flow being delivered exceeds demand, the pressure delta across the (1) is
great enough to overcome spring force and shift the S spool porting system pressure to the servo piston.
The pump de-strokes reducing flow until the delta across the (1) becomes equal to the S setting.
When flow being delivered is less than demand, the delta across the (1) drops below the S setting and the
S spring shifts the spool connecting the servo piston to pump case. The pump strokes increasing flow
until the delta across the (1) becomes equal to the S setting.
When the external control valve (1) is placed in neutral, it connects the LS signal line to drain. With no LS
pressure acting on the non-spring end of the LS spool, the pump adjusts stroke to whatever position
necessary to maintain system pressure at the LS setting. The pump is now in low pressure standby mode.
(1) is not in the scope of supply.
©
Danfoss | July 2019 L1527453 | AX00000292en-CN0201 | 11
Page 12
0
0
Q max
Flow
Pressure
P setting
Service Manual
D1 High Power Open Circuit Pumps Size 65/130/145/193/260
Operation
S characteristic
For additional system protection, install a relief valve in the pump outlet line.
NPSN Priority
The Pressure Compensated Control (P) has priority over the Load Sensing Control (S).
Response/Recovery
Load Sensing (LS) Response/Recovery Times @80°C, 1500rpm, LS Setting at 25 bar
Frame Size Response (msec) Recovery (msec)
130cc 260 360
145cc 260 360
1
193cc
260cc 309 327
1
Tested with a LS setting of 20bar
233 264
Values may vary depending on application conditions. For more information, please contact Danfoss
Power Solutions
12 | © Danfoss | July 2019 L1527453 | AX00000292en-CN0201
Page 13
0
0
Q max
Flow
Pressure
RP setting
PC setting
Service Manual
D1 High Power Open Circuit Pumps Size 65/130/145/193/260
Operation
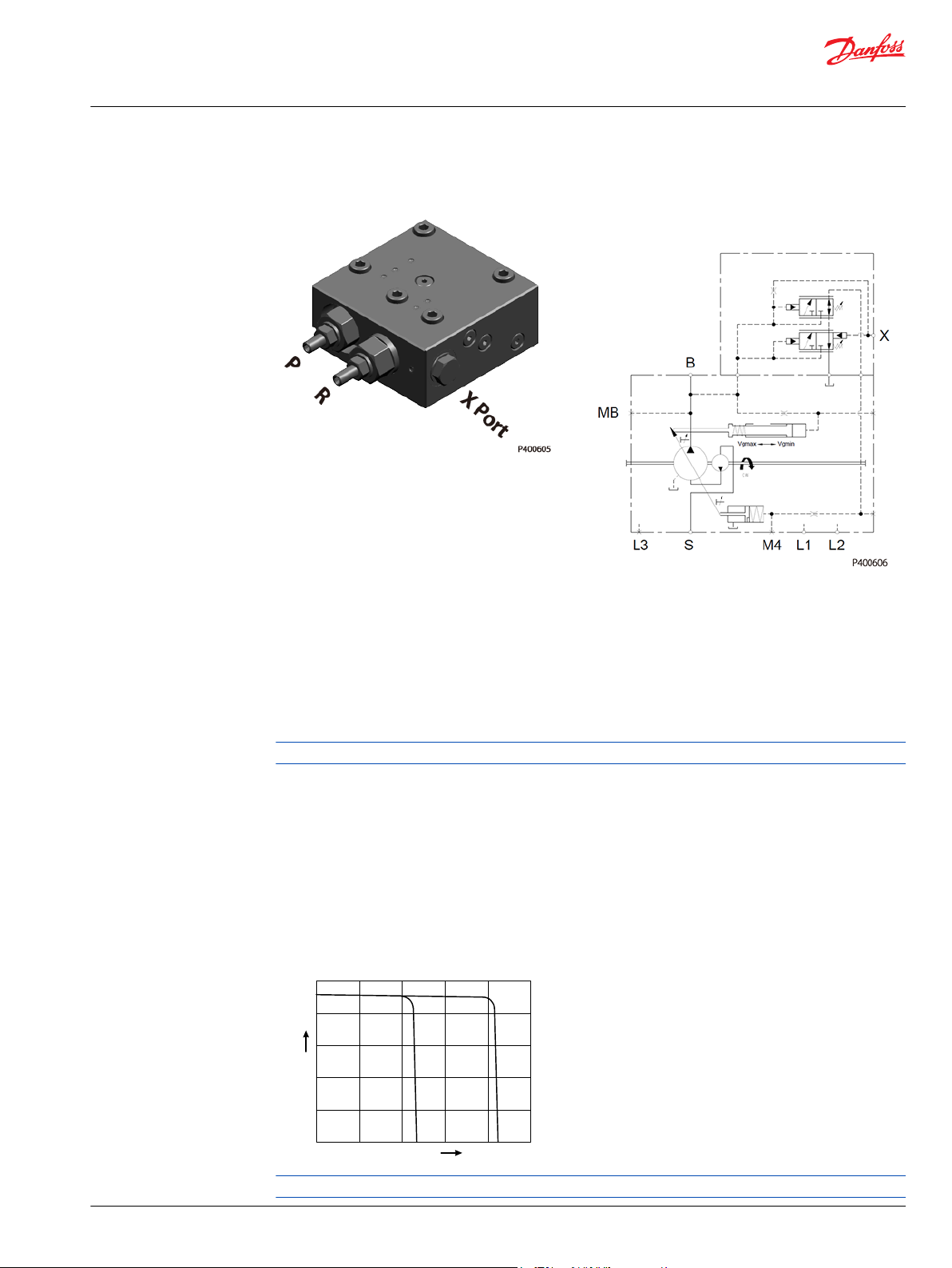
NPNR (Pressure Compensated Control + Remote Pressure Compensated Control)
D1P 130/145/193/260+NPNR
Pressure Compensated Control (P) Principle and Operation
Please refer to NPNN (Pressure Compensated Control) on page 9.
Remote Pressure Compensated Control (R) Principle
The remote PC control is a two-stage control that allows multiple PC settings. Remote PC controls are
commonly used in applications requiring low and high pressure PC operation.
For this control, Danfoss recommends a load sense setting of 20bar.
Remote Pressure Compensated Control (R) Operation
The remote PC control uses a pilot line connected to an external hydraulic valve. The external valve
changes pressure in the pilot line, causing the PC control to operate at a lower pressure. When the pilot
line is vented to reservoir, the pump maintains pressure at the load sense setting. When pilot flow is
blocked, the pump maintains pressure at the PC setting. An on-off solenoid valve can be used in the pilot
line to create a low-pressure standby mode. A proportional solenoid valve, coupled with a
microprocessor control, can produce an infinite range of operating pressures between the low pressure
standby setting and the PC setting.
R characteristic
©
Danfoss | July 2019 L1527453 | AX00000292en-CN0201 | 13
For additional system protection, install a relief valve in the pump outlet line.
Page 14

Service Manual
D1 High Power Open Circuit Pumps Size 65/130/145/193/260
Operation
NPNR Priority
When the pump’s X-port is vented to tank, or limited to some pressure setting via a remote valve, the
remote pressure compensator function will control the maximum outlet pressure of the pump. If the
pump’s outlet pressure reaches the pressure setting of the pressure compensator (PC) function, the PC
function will take priority and limit the pump’s maximum pressure.
14 | © Danfoss | July 2019 L1527453 | AX00000292en-CN0201
Page 15
X
MB
B
(1)
P400251
Vg min
Vg max
L3
S M4 L1 L2
P400080
X
Vg min
CW
Vg max
MB
B
L3
S M4 L1 L2
(1)
Service Manual
D1 High Power Open Circuit Pumps Size 65/130/145/193/260
Operation
TPSN (Power Control + Pressure Compensated Control + Load Sensing Control)
D1P 130/145+TPSN
D1P 193/260+TPSN
*Control oil filter is optional
Power Control (T) Principle
The power control regulates the displacement of the pump depending on the working pressure so that a
given drive power is not exceeded at constant drive speed, this function can prevent engine stall or
protect electric generator.
©
PB = working pressure
PB • Vg = C Vg = displacement
C = constant
The precise control with a hyperbolic control characteristic, provides an optimum utilization of available
power.
Danfoss | July 2019 L1527453 | AX00000292en-CN0201 | 15
Page 16
Q max
0
0
Flow
Pressure
Service Manual
D1 High Power Open Circuit Pumps Size 65/130/145/193/260
Operation
Power Control (T) Operation
The working pressure acts on a rack-pivot via a roller jack which produces a rotating torque, an externally
adjustable spring force counteracts this which determines the power setting.
If the moment generated by working pressure exceeds the moment generated by spring force, the
control valve is actuated by the rack-pivot, and pump reduces displacement. The lever length at the rackpivot is shortened and the working pressure can increase at the same rate as the displacement decreases
without the drive powers being exceeded.
(PB • Vg = C).
The hydraulic output power (characteristic T) is influenced by the efficiency of the pump.
T characteristic
Pressure Compensated Control (P) Principle and Operation
Please refer to NPNN (Pressure Compensated Control) on page 9
Load Sensing Control (S) Principle and Operation
Please refer to NPSN (Pressure Compensated Control + Load Sensing Control) on page 11
TPSN Priority
The Pressure Compensated Control (P) has priority over the Power Control (T), Power Control has priority
over Load Sensing Control (S).
16 | © Danfoss | July 2019 L1527453 | AX00000292en-CN0201
Page 17
W
X
E
B
Vgmax Vgmin
B
MB
S
M4
L3
L1 L2
Service Manual
D1 High Power Open Circuit Pumps Size 65/130/145/193/260
Operation
NNES (Electric Displacement Control + Load Sensing Control)
Warning
(1) Adjustment is not permissible
D1P 130/145/193/260 NNES
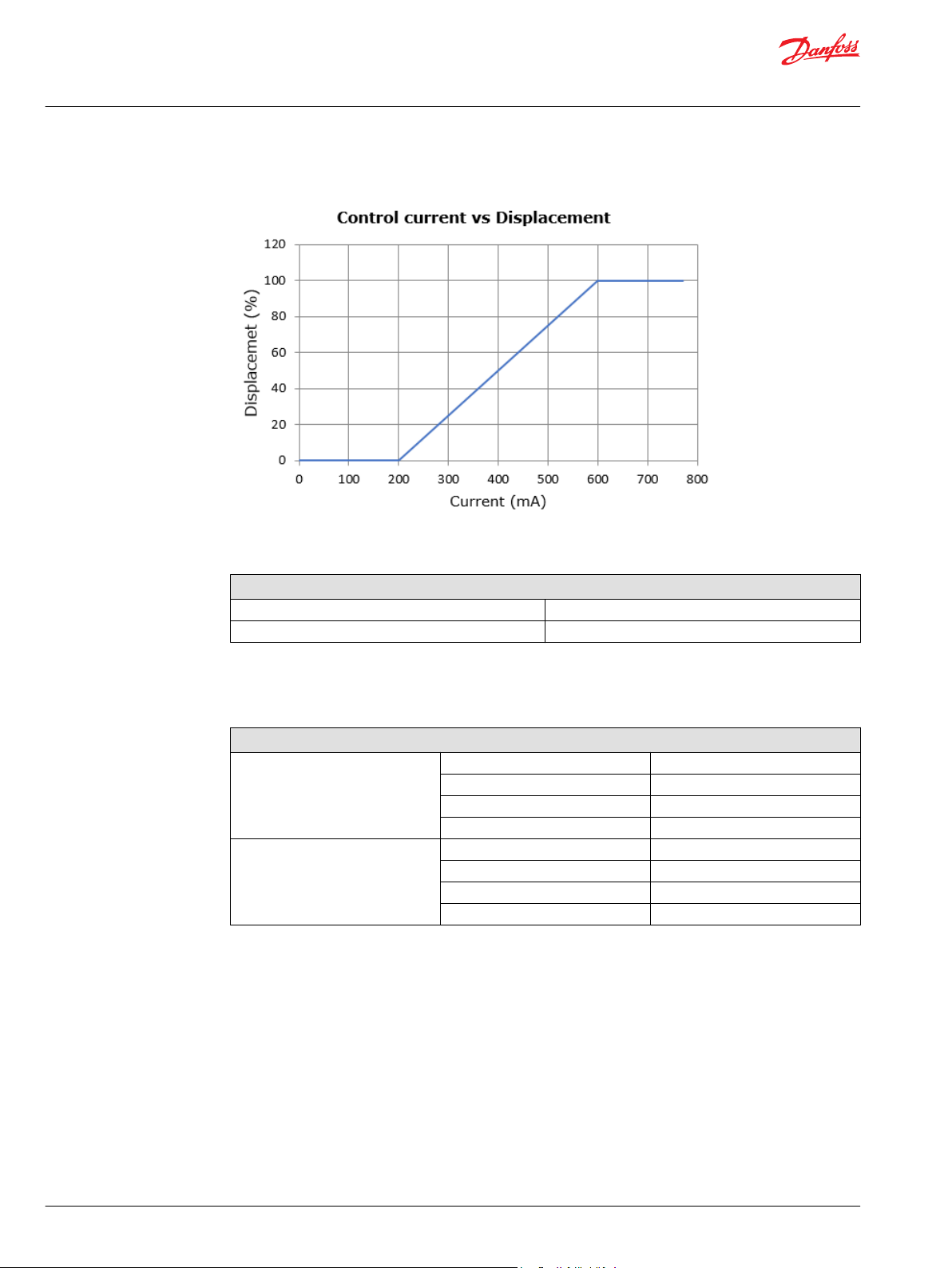
Electric Displacement Control (E) Principle
The electric displacement control uses an electric proportional solenoid valve to vary the pump’s
displacement from minimum displacement to maximum displacement or from maximum displacement
to minimum displacement. The swashplate angle (pump displacement) is proportional to the electrical
input signal (control current).
Electric Displacement Control (E) Operation
This control is current driven, requiring a Pulse Width Modulated (PWM) signal. Pulse width modulation
allows more precise control of current to the solenoid. The PWM signal causes the solenoid pin to push
against the E spool, which depressurizes the end of servo piston, the swashplate angle increases under
the force of the bias piston
A swashplate feedback link provides swashplate position force to the solenoid through the E spool’s
linear spring. The control reaches equilibrium when the position of the swashplate spring feedback force
exactly balances the input command solenoid force from the operator. As working pressure changes with
load, the control and servo/swashplate system work constantly to maintain the commanded position of
the swashplate.
Electric Displacement Control (E) Operating Instruction
To make sure the electric displacement control works properly, a minimum control pressure of 30 bar
[435 psi] is required. The required control pressure is taken either from the working pressure, or from the
externally applied control pressure at the E port.
If you can’t make sure that the working pressure is above 30 bar all the time, then a minimum of 30bar
[435 psi] pressure supply at the E port is mandatory in order to control the displacement of the pump at
all times. This pressure supply can be provided from different sources, such as an additional small gear or
piston pump and a relief valve, or an accumulator.
If E port is not connected, remove the shuttle valve
©
Danfoss | July 2019 L1527453 | AX00000292en-CN0201 | 17
Page 18
Service Manual
D1 High Power Open Circuit Pumps Size 65/130/145/193/260
Operation
Typical operating curve
Hysteresis
EDC Hysteresis
Input hysteresis <4.5%
Output hysteresis @50% displacement <4.0%
1
Values may vary depending on application conditions. For more information, please contact Danfoss Power
Solutions
1
Response/Recovery
Response/Recovery Times @ 1500rpm (50°C)
Response 0%-100% 130cc (263 bar) 260 msec
Response 100%-0% 130cc (263 bar) 390 msec
1
145cc (263 bar) 260 msec
193cc (160 bar) 272 msec
260cc (200 bar) 370 msec
145cc (263 bar) 390 msec
193cc (160 bar) 186 msec
260cc (200 bar) 390 msec
MOR
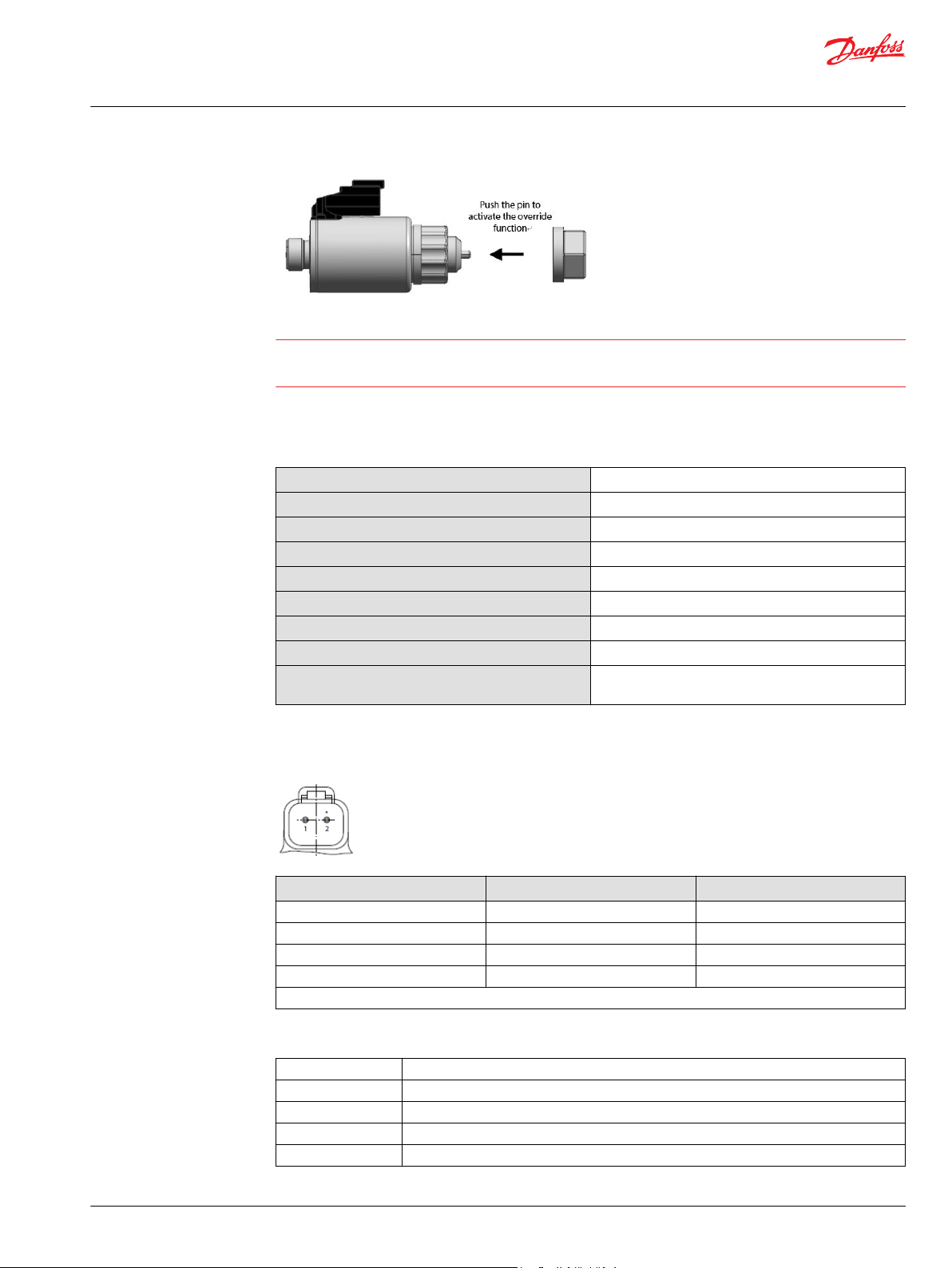
Each Electric Displacement Control (EDC) is equipped with a Manual Over Ride (MOR) function for
temporary actuation of the control to aid in diagnostics, even if insufficient or no current is supplied to
the solenoid actuator. Initial activation of the MOR function will require a higher force to overcome the
sticking effect between the pin and O-ring seal. Repeated activation of this functionality should provide
better controllability.
18 | © Danfoss | July 2019 L1527453 | AX00000292en-CN0201
Page 19
W
Service Manual
D1 High Power Open Circuit Pumps Size 65/130/145/193/260
Operation
Warning
Do not actuate the MOR unless the machine is in a “SAFE” mode. Unintended MOR operation will cause
the pump to go into stroke, use only for diagnosis purposes.
Solenoid Specification
Technical data - Solenoid
Voltage
Start current at Vg min.
End Current at Vg max.
Maximum current
Coil Resistance @ 20 °C [70 °F]
PWM Range
PWM Frequency (preferred)
IP Rating (IEC 60 529) + DIN 40 050, part 9
IP Rating (IEC 60 529) + DIN 40 050, part 9 with
mating connector
*
PWM signal required for optimum control performance
*
24V (±20%)
200 mA
600 mA
770 mA
22.7 Ω
70~200 Hz
100 Hz
IP 67
IP 69K
Mating connector for Solenoid
Description Ordering Number Quantity
Mating Connector DEUTSCH DT06-2S 1
Wedge Lock DEUTSCH W2S 1
Socket contact (16 and 18 AWG) DEUTSCH 0462-201-16141 2
Danfoss mating connector kit K29657 1
The mating connector is not included in the delivery contents, this can be delivered by Danfoss on request.
Compatible PLUS+1® controllers(see below):
MC012 L1301095
MC024 L1315302
MC038 11051653
MC050 L1301752
MC088 11006645
For further information: please visit: http://www.danfoss.com/Products/MobileElectronics/index.htm
©
Danfoss | July 2019 L1527453 | AX00000292en-CN0201 | 19
Page 20

DEUTSCH DT04-2P
74.5 4.5
(3)
A
(2)
(1)
45°
Ø37.1
36.7
Ø4
Ø13
M18x1.5
Service Manual
D1 High Power Open Circuit Pumps Size 65/130/145/193/260
Operation
Standard EDC Valve
The position of the connector can be changed by turning the solenoid body. Proceed as follows:
1. Loosen protection cap (1).
2. Loosen lock nut (2).
3. Turn the solenoid body (3) to the desired position.
4. Tighten the lock nut (2).
5. Tighten the protection cap (1).
Tightening Torque of lock nut: 5 ± 1 N•m [44.25 ± 8.85 lbf•in]
Standard EDC Valve
A - Actuation Forces
Breakaway Force (First actuation) 45 N [10.12 lbf] max.
Repeat of Actuation 25 N [5.62 lbf] max.
NNES Priority
Both the Electric Displacement Control (EDC) and the Load Sensing Control (LS) are used to control the
pump’s displacement. The pump will output the smallest displacement when both control functions are
given control instruct.
20 | © Danfoss | July 2019 L1527453 | AX00000292en-CN0201
Page 21

W
MB
E B
L3
S M4 L1 L2
Vg min
Vg max
P400074
*
Service Manual
D1 High Power Open Circuit Pumps Size 65/130/145/193/260
Operation
TPE2/TPE5 (Power Control + Pressure Compensated Control + Electric Displacement Control)
D1P 130/145+TPE5
D1P 193/260+TPE2
*Control oil filter is optional
Warning
(1) Adjustment is not permissible
Power Control (T) Principle and Operation
Please refer to TPSN (Power Control + Pressure Compensated Control + Load Sensing Control) on page 15
Pressure Compensated Control (P) Principle and Operation
Please refer to NPNN (Pressure Compensated Control) on page 9
Electric Displacement Control (E2/E5) Principle and Operation
Please refer to NNES (Electric Displacement Control + Load Sensing Control) on page 17
TPE2/TPE5 Priority
The Pressure Compensated Control (P) has priority over the Power Control (T), and the Power Control (T)
has priority over Electric Displacement Control (EDC).
©
Danfoss | July 2019 L1527453 | AX00000292en-CN0201 | 21
Page 22

B
MB
S
M4
L3
L1 L2
Vgmax Vgmin
E
Vgmax Vgmin
B
MB
S
M4L3L1 L2
Service Manual
D1 High Power Open Circuit Pumps Size 65/130/145/193/260
Operation
NPE2/NPE0 (Pressure Compensated Control + Electric Displacement Control)
D1P 260 with NPE2 (left); D1P 260 with NPE0 (right)
Pressure Compensated Control (P) Principle and Operation
Please refer to NPNN (Pressure Compensated Control) on page 9.
Electric Displacement Control (E2/E0) Principle and Operation
Please refer to NNES (Electric Displacement Control + Load Sensing Control) on page 17.
Shuttle Valve/Pilot Supply
Please refer to Electric Displacement Control (E) Operating Instruction section at NNES (Electric
Displacement Control + Load Sensing Control) on page 17.
To determine if an external control pilot supply is needed, please consult your Danfoss Power Solutions
representative.
D1P pumps configured with an NPE2 control will come with a shuttle valve installed at the E port. D1P
pumps with an NPE0 control will not include the shuttle valve.
22 | © Danfoss | July 2019 L1527453 | AX00000292en-CN0201
Page 23

0.8
0.9
Speed
n
max
/
n
max1
0.9
1.0
Displacement Vg/Vgmax
1.0
1.1
1.2
Pabs=1 bar [14.5 psi]
Pabs=1.5 bar [21.8 psi]
P400076
Service Manual
D1 High Power Open Circuit Pumps Size 65/130/145/193/260
Operating parameters
D1P pressure overview
D1P speed overview
Maximum
working
pressure
The highest recommended outlet (application). Operating at or below this pressure
should yield satisfactory product life. For all applications, the load should move below
this pressure. This corresponds to the maximum allowable pressure compensated
control setting.
Maximum
(peak) pressure
The highest intermittent (t<1s) outlet pressure allowed. Maximum machine load
should never exceed this pressure, and pressure overshoots should not exceed this
pressure.
Inlet pressure The absolute pressure in the pump suction port, it is related to pump speed. Make
sure it is in the allowable range, see D1 pump specifications on page 25.
Case pressure The case pressure at the ports L1 and L2 may be a maximum of 1.2 bar [17.4 psi]
higher than the inlet pressure at the port S but not higher than 2 bar. Size drain
plumbing accordingly and connect it to tank directly. The housing must always be
filled with hydraulic fluid.
Rated
speed
The fastest recommended operating speed at full displacement and at least 0.6 bar [8.7
psi] abs with charge pump (0.8 bar [11.6 psi] abs without charge pump) inlet pressure.
Operating at or below this speed should yield satisfactory product life.
Maximum
speed
The highest recommended operating speed at full power conditions. Operating at or
beyond maximum speed requires positive inlet pressure and/or a reduction of pump
outlet flow. Refer to Inlet pressure vs. speed on page 23, chart below.
Inlet pressure vs. speed
Minimum
speed
The lowest operating speed allowed. Operating below this speed will not yield
satisfactory performance.
Caution! Threat to pump life!
Working outside of the pump's operating parameters may result in shortened life expectancy of the
pump.
Always work within the operating conditions of the pump application.
With accurate duty cycle information, your Danfoss Power Solutions representative can assist you in
calculating expected pump life.
D1P fluid overview
Ratings and performance data for D1 pumps are based on operating with premium hydraulic fluids
containing oxidation, rust, and foam inhibitors. These include premium turbine oils, API CD engine oils
©
Danfoss | July 2019 L1527453 | AX00000292en-CN0201 | 23
Page 24

Service Manual
D1 High Power Open Circuit Pumps Size 65/130/145/193/260
Operating parameters
per SAE J183, M2C33F or G automatic transmission fluids (ATF), Dexron II (ATF) meeting Allison C-3 or
Caterpillar T0‑2 requirements, and certain specialty agricultural tractor fluids. For more information on
hydraulic fluid selection, see Danfoss Power Solutions publications 520L0463 Hydraulic Fluids and
Lubricants, Technical Information, and 520L0465 Experience with Biodegradable Hydraulic Fluids,
Technical Information.
D1P viscosity
Minimum Viscosity This should only occur during brief occasions of maximum ambient temperature
and severe duty cycle operation.
Maximum
Viscosity
This should only occur at cold start. Pump performance will be reduced. Limit
speeds until the system warms up.
Maintain fluid viscosity within the recommended range for maximum efficiency and pump life.
D1P temperature overview
Minimum
Temperature
Relates to the physical properties of the component materials. Cold oil will not
affect the durability of the pump components. However, it may affect the ability of
the pump to provide flow and transmit power
Maximum
Temperature
Relates to material properties. Don’t exceed it. Measure maximum temperature at
the hottest point in the system. This is usually the case drain.
D1P fluid velocity
Choose piping sizes and configurations sufficient to maintain optimum fluid velocity, and minimize
pressure drops. This reduces noise, pressure drops, overheating and maximizes system life and
performance.
Recommended fluid velocities
System lines
Suction line
Case drain
6 to 9 m/sec
1 to 2 m/sec
3 to 5 m/sec
Typical guidelines; obey all pressure ratings.
Velocity equations
SI units
Q = flow (l/min)
A = area (mm²)
Velocity = (16.67•Q)/A (m/sec)
24 | © Danfoss | July 2019 L1527453 | AX00000292en-CN0201
Page 25

Service Manual
D1 High Power Open Circuit Pumps Size 65/130/145/193/260
Technical specifications
D1 pump specifications
(Theoretical values, without efficiency and tolerances; values rounded)
65 130 145 193 260
Features Unit
W/O
Charge
Pump
Displacement
Maximum
Minimum 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Available Rotation
Min.
Rated at max.
Input Speed
displacement (Vg
max.)
Maximum at Vg <
3
Vg max.
Flow at max. speed & displacement (n
max. & Vg max.)
cm3 [in3]
CCW [L]
CW [R]
rpm
l/min
[US gal/
65 [3.84] 130 [7.93] 130 [7.93] 145 [8.85] 145 [8.85] 193 [11.78] 260 [15.87]
500 500 500 500 500 500 500
2550 2200
3000 2500 2500 2200 2500 2500 2300
165 [44] 286 [76] 325 [86] 319 [84] 363 [96] 483 [128] 598 [158]
min]
System (Working)
4
Pressure
Inlet Pressure
(Absolute)
Case Pressure
(Absolute)
Max. Working
Pressure
bar [psi]
Max. Pressure 400 [5802]
Minimum
Maximum 30 [435] 30 [435]
bar [psi]
0.8 [11.6] 0.8 [11.6] 0.6 [8.7] 0.8 [11.6] 0.6 [8.7] 0.6 [8.7] 0.6 [8.7]
Maximum above
inlet
bar [psi]
Maximum 2 [29]
Filling Capacity L [US gal] 2.1 [0.55] 2.9 [0.77] 2.9 [0.77] 3.8 [1] 4.6 [1.3]
Torque at Vg max. & Δp = 350 bar N•m
362 [3204] 724 [6408] 808 [7151] 1075 [9515] 1448
[lbf•in]
Power at Q max. (max. flow) & Δp = 350
kW [hp] 97 [130] 159 [213] 190 [255] 186 [249] 211 [283] 281 [377] 349 [468]
bar
Mass Moment of Inertia of internal
rotating components
2
kg•m
[slug•ft2]
0.0151
[0.0111]
Mass kg [lb] 47 [104] 68 [150] 74 [163] 68 [150] 74 [163] 106 [234] 141 [311]
External Shaft
Loads
Mounting Flange
Load Moments
External Moment
M
e
Vibratory
(continuous)
Shock (maximum) 4506
N•m
[lbf•in]
N•m
[lbf•in]
250 [2216] 476 [4213] 476 [4213] 822 [7275] 1081 [9568]
2360
[20888]
[39881]
1
The values apply at absolute pressure (Pabs) of at least 0.8 bar [11.6psi] at the suction port S and mineral hydraulic fluid.
2
The values apply at absolute pressure (Pabs) of at least 0.6 bar [8.7psi] at the suction port S and mineral hydraulic fluid.
3
The values apply at Vg ≤ Vg max or in case of an increase in the inlet pressure (Pabs) at the suction port S. Please refer to Inlet Pressure vs Speed Graph
at D1P speed overview on page 23
4
Applied pressures above maximum working pressure requires Danfoss application approval. Maximum (peak) pressure is the highest intermittent
(t<1s) outlet pressure allowed.
5
If the application requires the higher inlet pressure than 5 bar [72.5psi] (up to 30 bar [435psi]), please contact.Danfoss Power Solutions.
W/O
Charge
Pump
1
W/ Charge
Pump
2
2500
Charge
2200
W/O
Pump
2
W/ Charge
Pump
3
2500
W/Charge
Pump
2500
350 [5076]
5
2 [29] 30 [435] 2 [29] 2 [29] 2 [29]
1.2 [17.4]
0.0299
[0.0221]
0.0306
[0.0226]
0.0299
[0.0221]
0.0306
[0.0226]
0.0576
[0.0426]
4553 [40297] 4553 [40297] 6286
[55636]
8692 [76930] 8692 [76930] 13782
[121980]
W/Charge
Pump
3
2300
3
[12816]
0.2080
[0.1537]
8477
[75027]
16338
[144603]
Counterclockwise (CCW) & Clockwise (CW) directions as viewed from the shaft end of the pump.
©
Danfoss | July 2019 L1527453 | AX00000292en-CN0201 | 25
Page 26

Service Manual
D1 High Power Open Circuit Pumps Size 65/130/145/193/260
Technical specifications
Exceeding the permissible values could cause a loss of function, reduced life or the destruction of the
pump.
Do not exceed the values shown in the table above.
D1P fluid specifications
Features Units Value
Intermittent
Viscosity
Minimum 7 [49]
Recommended range 16 - 36 [81 - 168]
Maximum (cold start)
Temperature range
Minimum (cold start)
Maximum intermittent
Temperature Range: -40 - 90 °C
Filtration (minimum)
Cleanliness per ISO 4406
[-40 - 194°F]
Temperature Range: 90 - 115 °C
[194 - 239°F]
1)
Intermittent = Short term t < 3min per incident.
2)
Cold start = Short term t < 3min, p ≤ 30 bar [435 psi], n ≤ 1000 min-1(rpm) , please contact Danfoss Power Solutions
especially when the temperature is below -25 °C [-13 °F].
3)
Must not be exceeded locally either (e.g. in the bearing area) . The temperature in the bearing area is (depending
on pressure and speed ) up to 5 °C [41 °F] higher than the average case drain temperature.
1)
5 [42]
mm2/sec
[SUS]
2)
2)
1)
°C [°F]
1600 [xxxxx]
-40 [-40 °F]
115 [239 °F]
3)
20/18/15
19/17/14
26 | © Danfoss | July 2019 L1527453 | AX00000292en-CN0201
Page 27

Service Manual
D1 High Power Open Circuit Pumps Size 65/130/145/193/260
Fluid and filter maintenance
Recommendations of fluid and filter maintenance
To ensure optimum life of D1 pumps, perform regular maintenance of the fluid and filter. Contaminated
fluid is the main cause of unit failure. Take care to maintain fluid cleanliness when servicing.
Check the reservoir daily for proper fluid level, the presence of water, and rancid fluid odor. Water in the
fluid may be noted by a cloudy or milky appearance or free water in the bottom of the reservoir. Rancid
odor indicates the fluid has been exposed to excessive heat. Change the fluid immediately if these
conditions occur. Correct the problem immediately.
Change the fluid and filter per the vehicle / machine manufacturer’s recommendations or at these
intervals: Change the fluid more frequently if it becomes contaminated with foreign matter (dirt, water,
grease, etc.) or if the fluid is subjected to temperature levels greater that the recommended maximum.
Fluid and filter change interval
Reservoir type Maximum change interval
Sealed 2000 hours
Breather 500 hours
Dispose of used hydraulic fluid properly. Never reuse hydraulic fluid.
Change filters whenever the fluid is changed or when the filter indicator shows that it is necessary to
change the filter. Replace all fluid lost during filter change.
©
Danfoss | July 2019 L1527453 | AX00000292en-CN0201 | 27
Page 28

Inlet port S
L1
MB
Load sensing signal
port X
Outlet port B
L2
L3
M4
M5
Service Manual
D1 High Power Open Circuit Pumps Size 65/130/145/193/260
Pressure measurements
Port Locations and Gauge Installation (65)
The following table and drawing show the port locations and gauge sizes needed. When testing system
pressures, calibrate pressure gauges frequently to ensure accuracy. Use snubbers to protect gauges.
Port Purpose Port size Wrench size Range of gauge
L1, L2, L3 Case drain M18x1.5 8mm 0-60 bar [0-870.23 psi]
M
B
M
4
M
5
D1P 65 port locations with TPSN control
Outlet pressure gauge port M12x1.5 6mm 0-600 bar [0-8702.26 psi]
Servo piston chamber pressure
gauge port
Suction pressure gauge port M12x1.5 6mm 0-600 bar [0-8702.26 psi]
M12x1.5 6mm 0-600 bar [0-8702.26 psi]
28 | © Danfoss | July 2019 L1527453 | AX00000292en-CN0201
Page 29

P400254
MB
L1
B : Outlet port
X : Load sensing
signal port
S : Inlet port
M4
L3
L2
Service Manual
D1 High Power Open Circuit Pumps Size 65/130/145/193/260
Pressure measurements
Port Locations and Gauge Installation (130/145)
The following table and drawing show the port locations and gauge sizes needed. When testing system
pressures, calibrate pressure gauges frequently to ensure accuracy. Use snubbers to protect gauges.
Port Purpose Port size Wrench size Range of gauge
L1, L2, L3 Case drain M26x1.5 12 mm 0-60 bar [0-870.23
M
B
M
4
130/145 Port locations, Control type: TPSN
Outlet M12x1.5 6 mm 0-600 bar [0-8702.26
Servo piston chamber M12x1.5 6 mm 0-600 bar [0-8702.26
psi]
psi]
psi]
©
Danfoss | July 2019 L1527453 | AX00000292en-CN0201 | 29
Page 30

MB
E : External Control
Port
L1
S : Inlet Port
B : Outlet Port
M4
L3
L2
MB
L1
X : Load Sensing
Signal Port
M4
L3
L2
B : Outlet Port
S : Inlet Port
P400092
Service Manual
D1 High Power Open Circuit Pumps Size 65/130/145/193/260
Pressure measurements
Port Locations and Gauge Instalation (193/260)
Port Purpose Port size Wrench size Range of gauge
L1, L2, L3 Case drain M33x2 17 mm 0-60 bar [0-870.23
M
B
M
4
193/260 Port location, Control type: TPE2
Outlet M12x1.5 6 mm 0-600 bar [0-870.23
Servo piston chamber M12x1.5 6 mm 0-600 bar [0-870.23
psi]
psi]
psi]
193/260 Port location, Control type: TPSN
30 | © Danfoss | July 2019 L1527453 | AX00000292en-CN0201
Page 31

C
Service Manual
D1 High Power Open Circuit Pumps Size 65/130/145/193/260
Initial start-up procedures
General
Follow this procedure when starting-up a new D1 installation or when restarting an installation in which
the pump has been removed.
Prior to installing the pump, inspect for damage incurred during shipping. Make sure all system
components (reservoir, hoses, valves, fittings, heat exchanger, etc.) are clean prior to filling with fluid.
Start-up Procedure
1. Connect the pump to the prime mover.
Ensure that the pump shaft is properly aligned with the shaft of the prime mover. Alignment should
be within 0.25 mm and the angle must not exceed 0.2°.
Caution
Incorrect shaft alignment may result in damage to drive shaft, bearings, or seal which can cause
external oil leakage.
2. Fill the reservoir with a recommended hydraulic fluid.
Always filter fluid through a 10 micron filter while pouring into the reservoir. Never reuse hydraulic
fluid.
3. Fill the main pump housing with clean hydraulic fluid. Pour filtered oil directly into the upper most
case drain port.
4. Fill the inlet line leading from the pump to the reservoir. Check the inlet line for properly tightened
fittings and be certain it is free of restrictions and air leaks.
5. To ensure the pump stays filled with oil, install the case drain line in the upper most case drain port.
6. Install a gauge at port MB to monitor system pressure during start up.
Follow recommendations in the vehicle / machine operator’s manual for prime mover start up
procedures.
7. Switch system to free circulation or to lowest pressure, jog the prime mover or run at the lowest
possible speed until pump and all pipes are filled and free from air bubbles. Raise pressure setting
only when all air is removed.
Let the pump work at reduced pressure for 5 - 10 min, check if all pipes and connections are leak-free
and tight.
8. Check the suction pressure at port S of the axial piston pump at nominal speed and maximum flow,
make sure it is in allowable range.
9. Check the case drain pressure at the connected port L1 or L2 at maximum pressure, make sure it is in
allowable range.
10. Shut down the prime mover and remove the pressure gauge. Replace plug at port MB.
11. Check the fluid level in the reservoir; add clean filtered fluid if necessary.
The pump is now ready for operation.
©
Danfoss | July 2019 L1527453 | AX00000292en-CN0201 | 31
Page 32

Service Manual
D1 High Power Open Circuit Pumps Size 65/130/145/193/260
Troubleshooting
Excessive Noise and /or Vibration
Item Description Action
Check fluid level in reservoir. Insufficient hydraulic fluid causes
Check for air in system. Air in system causes noisy, erratic
Check pump inlet pressure / vacuum. Improper inlet conditions cause
Inspect shaft couplings. A loose or incorrect shaft coupling
Check shaft alignment. Misaligned shafts create excessive
Hydraulic fluid viscosity above
acceptable limits.
Low Pump Output Flow
cavitation.
control.
erratic behavior and low output flow.
causes excessive noise and / or
vibration.
noise and / or vibration.
Hydraulic fluid viscosity above
acceptable limits or low fluid
temperature will not allow the pump
to fill or control to operate properly.
Fill the reservoir to proper level.
Purge air and tighten fittings. Check
inlet for leaks.
Correct pump inlet pressure /
vacuum conditions.
Repair or replace coupling and
ensure that correct coupling is used.
Correct shaft misalignment.
Allow system to warm up before
operating, or use fluid with the
appropriate viscosity grade for
expected operating temperatures.
Item Description Action
Check fluid level in reservoir. Insufficient hydraulic fluid will limit
Hydraulic fluid viscosity above
acceptable limits.
Check external system relief valve
setting.
Check pressure compensate (PC),
load sensing (LS) and power (T)
control setting.
Check LS control signal pressures. Incorrect LS signal will not allow
Check Pilot pressure for hydraulics
displacement control and input
current for electric displacement
control.
Check pump inlet pressure / vacuum. High inlet vacuum causes low output
Check input speed. Low input speeds decrease flow. Adjust input speed.
Check pump rotation. Incorrect rotational configuration
output flow and cause internal
damage to pump.
Fluid viscosity above acceptable
limits or low fluid temperature will
not allow the pump to fill or control
to operate properly.
External relief valve set below PC
setting causes low output flow.
Low PC setting prevents the pump
from achieving full stroke. Low LS
setting limits output flow. Low T
setting limits output flow.
pump to operate correctly.
Incorrect input signal causes low
output flow.
flow.
causes low flow.
Fill the reservoir to proper level.
Allow system to warm up before
operating, or use fluid with the
appropriate viscosity grade for
expected operating temperatures.
Adjust external relief valve following
manufacturer’s recommendation.
External relief valve setting must be
above PC setting to operate properly.
Contact Danfoss Service.
Inspect system to ensure that proper
LS signal transmit to pump.
Adjust input hydraulic or electric
signal to right value.
Correct inlet pressure conditions.
Use pump with appropriate
rotational configuration.
No or Low System Pressure
Item Description Action
Check pressure compensate (PC) and
power (T) control setting.
Check external relief valve. External relief valve setting below PC
Low PC and T setting leads to low
system pressure.
setting.
Contact Danfoss Service.
Adjust external relief valve according
to manufacturer’s recommendations.
External relief valve must be set
above PC setting to operate properly.
32 | © Danfoss | July 2019 L1527453 | AX00000292en-CN0201
Page 33

Service Manual
D1 High Power Open Circuit Pumps Size 65/130/145/193/260
Troubleshooting
Item Description Action
Check pilot pressure or control
pressure.
Internal system leaks. Worn internal parts don’t allow the
Actuator Response is Sluggish
Item Description Action
Check external system relief valve
setting.
Check pressure compensate (PC),
load sensing (LS) and power (T)
control setting.
Check LS control signal pressures. Incorrect LS signal will not allow
Check Pilot pressure for hydraulics
displacement control and input
current for electric displacement
control.
Internal system leaks. Worn internal parts don’t allow the
Hydraulic fluid viscosity above
acceptable limits.
Check external system valving. Malfunctioning valving may not allow
Check pump case pressure. High case pressure causes the system
Check pump inlet pressure / vacuum. High inlet vacuum causes low output
Insufficient pilot pressure or control
pressure.
pump to operate properly.
Low external relief valve setting slows
down system.
Low PC setting prevents the pump
from achieving full stroke. Low LS
setting limits output flow. Low T
setting limits output Torque.
pump to operate correctly.
Incorrect input signal causes low
output flow.
pump to operate properly.
Hydraulic fluid viscosity above
acceptable limits or low fluid
temperature will not allow the pump
to fill or control to operate properly.
system to respond properly.
to be sluggish.
flow.
Increase them to appropriate value.
Refer to Authorized Service Center for
required repair.
Adjust external relief valve setting
following manufacturer’s
recommendations. External relief
setting must be above PC setting to
operate properly.
Contact Danfoss Service.
Inspect system to ensure that proper
LS signal transmit to pump.
Adjust input hydraulic or electric
signal to right value.
Refer to Authorized Service Center for
required repair.
Allow system to warm up before
operation or sue fluid with the
appropriate viscosity grade for
expected operating temperatures.
Repair or replace system valving as
required.
Correct case drain line restrictions.
Correct inlet pressure conditions.
Pressure or Flow Instability
Item Description Action
Check for air in system. Air in system causes erratic operation. Activate PC allowing system to bleed
Check LS setting. Low LS setting may cause instability. Contact Danfoss Service.
Check LS signal line. Blocked LS signal line interferes with
Check external relief valve and PC
setting.
Check external relief valve. Chattering external relief valve may
©
Danfoss | July 2019 L1527453 | AX00000292en-CN0201 | 33
proper LS operation.
Insufficient pressure differential
between PC setting and external
relief valve.
cause unstable feedback to pump
control.
air. Check inlet line for leaks and
eliminate source of air ingression.
Remove blockage.
Adjust external relief valve or PC
control settings to appropriate level.
Relief valve setting must be above PC
setting to operate properly.
Adjust or replace relief valve.
Page 34

C
Service Manual
D1 High Power Open Circuit Pumps Size 65/130/145/193/260
Troubleshooting
System Operating Hot
Item Descriptin Action
Check fluid level in reservoir. Insufficient volume of hydraulic fluid
Inspect heat exchanger. Check air
flow and input air temperature for
the heat exchanger.
Check external system relief valve
setting.
Check pump inlet pressure / vacuum. High inlet vacuum adds heat to
High Inlet Vacuum
Item Description Action
Check fluid temperature. Low temperature increases viscosity.
Inspect inlet screen. Blocked or restricted inlet screen
Check inlet piping. Too many fittings, bends, or long
Hydraulic fluid viscosity above
acceptable limits.
will not meet cooling demands of
system.
Insufficient air flow, high input air
temperature, or undersized heat
exchanges will not meet cooling
demands of the system.
Fluid passing through relief valve
adds heat to system.
system.
High fluid viscosity causes high inlet
vacuum.
causes high inlet vacuum.
piping causes high inlet vacuum.
High fluid viscosity causes high inlet
vacuum.
Fill reservoir to proper level. Verify
proper size of reservoir.
Clean, repair, or replace heat
exchanger as required. Verify proper
size of heat exchanger.
Adjust external system relief valve
setting following manufacturer’s
recommendations. External relief
valve setting must be above PC
setting for proper operation.
Correct inlet pressure / vacuum
conditions.
Allow system to warm up before
operating.
Clean screen / remove blockage.
Eliminate fittings to make path more
direct.
Select fluid with appropriate viscosity
for expected operating temperature.
Caution
High inlet vacuum causes cavitation which can damage internal pump components.
34 | © Danfoss | July 2019 L1527453 | AX00000292en-CN0201
Page 35

Power = P • n • Vg •
10
-3
600
• η
90 = P • 1500 • 193 •
10
-3
600
• (.912)
Power [kW] =
P • Q
600
• η
90 =
245 • Q
600
• (.912)
Service Manual
D1 High Power Open Circuit Pumps Size 65/130/145/193/260
Adjustments
Calculate Power Control Start Point Pressure and Corresponding Flow in Advance
If Power/Torque control is used:
1. Calculate the power control start point pressure according to the formula:
P Power control start point pressure [bar]
n Pump input speed [rpm]
Vg Pump theoretical displacement [cc]
η Total efficiency, set at 91.2%
The start point pressure is the point in the Pressure vs Flow performance curve in which the Torque
control becomes active. The PC setting must be higher than this value, otherwise the PC function will
take priority before the MTC function becomes active. If the desired power setting is 90kW, the pump
input speed is 1500 rpm and the pump’s theoretical displacement is 193cc, then solve for start point
Pressure:
Start point Pressure is calculated to be 170bar.
2. Use the average value between the start point Pressure and the Pressure Compensated Control
setting as a reference value; this value must be inside the "TC active" region. For example: Power
control start point Pressure is 170 bar, and the Pressure compensated control setting desired is 320
bar. Use the average value (170+320)/2=245 bar.
©
Danfoss | July 2019 L1527453 | AX00000292en-CN0201 | 35
3. Calculate corresponding flow by using the following formula:
Q=201 l/min
Page 36

W
C
Service Manual
D1 High Power Open Circuit Pumps Size 65/130/145/193/260
Adjustments
Adjustments
Control 65 130/145 193 260
NPNN If the desired
power setting is
90kW, the pump
input speed PC
[bar per turn]
NPSN & NPNR PC [bar per turn] N/A 163.2 163.2 163.2
LS [bar per turn] N/A 26.4 26.4 26.4
TPSN PC [bar per turn] 163.2 271 163.2 163.2
LS [bar per turn] 26.4 50 26.4 26.4
MTC [kW per
turn]@1500rpm
NNES LS [bar per turn] N/A 26.4 26.4 26.4
EDC [mA offset
per turn]
TPE5 PC [bar per turn] N/A 163.2 N/A N/A
MTC [kW per
turn]@1500rpm
EDC [mA offset
per turn]
TPE2 PC [bar per turn] N/A N/A 163.2 163.2
MTC [kW per
turn]@1500rpm
EDC [mA offset
per turn]
N/A 163.2 163.2 163.2
31 39 73.5 99
N/A 263 263 263
N/A 50.8 N/A N/A
N/A 263 N/A N/A
N/A N/A 73.5 99
N/A N/A 263 263
Electric Displacement Control Adjustment
1. Install a pressure gauge in port MB to measure outlet pressure. Install a flow meter in outlet line to
measure pump flow.
Warning
Escaping hydraulic fluid under pressure can have sufficient force to penetrate your skin causing
serious injury and/or infection. Relieve pressure in the system before removing hoses, fittings,
gauges, or components.
Unintended movement of the machine or mechanism may cause injury to the technician or
bystanders. To protect against unintended movement, secure the machine or disable / disconnect
the mechanism while servicing.
Caution
Contamination can damage internal components and void the manufacturer’s warranty. Take
precautions to ensure system cleanliness when removing and reinstalling system lines.
2. Start the prime mover and input 700 mA to electric displacement control solenoid valve, then allow
fluid to reach normal operating temperature. The pump must be at full displacement at this point.
Danfoss recommends a prime mover speed of 1500rpm (unless specified otherwise).
The testing setup must be plumbed in a way so the EDC function works properly. Please refer to
Electric Displacement Control (E) Operating Instruction.
3. Totally lock the LS control (if used) to avoid interference with EDC adjustment.
a) Loosen the LS control lock nut and turn the LS control adjusting screw clockwise all the way to the
end, while holding the LS control adjusting screw.
b) Torque the control lock nut to 21.6~24.6 N•m [191-218 lbf•in].
36 | © Danfoss | July 2019 L1527453 | AX00000292en-CN0201
Page 37

Service Manual
D1 High Power Open Circuit Pumps Size 65/130/145/193/260
Adjustments
4. Load the pump's outlet pressure to 50 bar and input 400mA to electric displacement control, then
loosen the electric displacement control lock nut and turn its adjusting screw until the pump
displacement achieves (see Displacement table below), which can calculated by monitoring pump
outlet flow and pump speed. Clockwise turning adjusting screw decrease pump displacement,
counterclockwise turning increase pump displacement. The displacement - current curve will offset
(see Adjustments table) per turn.
5. While holding the position of the electric displacement control adjusting screw, torque the lock nut
to 9.5 N•m [84 lbf•in].
6. Test another current value. Input 500 mA to electric displacement control, check if the displacement
is within the range specified in the below table at this moment. If it is, the electric displacement
control adjustment complete, if it is not, please re-adjust.
7. Stop the prime mover, remove the pressure gauge and flow meter, and return the system to its
normal operating configuration.
Displacement
Input Current Size 130 Size 145 Size 193 Size 260
400mA+/-8 mA 67.5cc+/-5cc 67.5cc+/-5cc 92.5 cc+/-5cc 140.5 cc+/-5cc
500mA+/-8 mA 101cc+/-5cc 101cc+/-5cc 115.5 cc+/-5cc 172.5 cc+/-5cc
©
Danfoss | July 2019 L1527453 | AX00000292en-CN0201 | 37
Page 38

Service Manual
D1 High Power Open Circuit Pumps Size 65/130/145/193/260
Adjustments
Pressure Compensated Control Adjustment
1. Install a pressure gauge in port MB to measure outlet pressure.
2. Ensure the pump is operating at maximum displacement. If the control has Electric Displacement
Control, input 700mA to obtain maximum displacement.
3. Load the pump outlet pressure to at least 30 bar higher than the expected pressure compensated
control setting. This may be achieved by operating a hydraulic function to its full extension, putting
the pump in a dead-head condition.
4. Loosen the Pressure compensated control lock nut and turn the Pressure compensated control
adjusting screw until the desired setting is indicated on the pressure gauge at port MB. Clockwise
rotation increases pressure, counterclockwise rotation decreases; approximate gain per turn (see
Adjustments table). Once the PC adjustment is complete, hold the position of the adjustment screw
and torque the PC control lock nut to 21.6-24.6 N·m [lbf·in].
5. Stop the prime mover, remove the pressure gauge, and return the system to its normal operating
configuration.
If the pressure does not increase, an external system relief valve may require adjustment. External
system relief valve must be set above the Pressure compensated control setting for proper operation.
Power Control Adjustment
1. Install a pressure gauge in port MB to measure outlet pressure. Install a flow meter in outlet line to
2. Start the prime mover and make sure the pump is operating at maximum displacement. If the control
3. Load the pump outlet pressure to the reference pressure value previously obtained in the calculation,
4. Stop the prime mover, remove the pressure gauge and flow meter, and return the system to its
Load Sensing Control Adjustment
1. Install a pressure gauge in port MB to measure outlet pressure, Tee-in a pressure gauge to the LS
2. Start Prime mover and allow fluid to reach normal operating temperature.
3. Totally lock the LS control; to do this first loosen the LS control lock nut and turn the LS control
4. Adjust Power control and pressure compensated control (if used).
measure pump flow.
has Electric Displacement Control, input 700mA to obtain maximum displacement. By doing this, the
functions will not interfere with each other, if maximum displacement is commanded by the EDC at
all times, the MTC function will take priority once the start point pressure is reached.
loosen the power control lock nut and turn the power control adjusting screw and monitor the flow
meter, when the flow meter shows the flow corresponding to the previous calculation, stop turning,
while holding the position of power control adjusting screw, torque the power control lock nut to
21.6~24.6 N•m [191-218 lbf•in]. Clockwise rotation increases power, counterclockwise rotation
decreases, approximate gain per turn (See Adjustments table.)
normal operating configuration.
signal line (port X) to measure LS signal pressure. Install a flow meter in outlet line to measure pump
flow.
adjusting screw clockwise all the way to the end, while holding the LS control adjusting screw, torque
the control lock nut to 21.6~24.6 N•m [191-218 lbf•in].
38 | © Danfoss | July 2019 L1527453 | AX00000292en-CN0201
Page 39

W
C
Measurement Point,
Outlet Pressure Port MB
M12x1.5
0-600 bar
6 mm
22.5 - 27.5 N·m
Power Control
Adjusting Screw
4 mm
Pressure Compensated
Control Adjusting Screw
4 mm
Power Control
Lock Nut
13 mm
21.6 - 24.6 N·m
Pressure Compensated
Control Lock Nut
13 mm
21.6 - 24.6 N·m
Electric Displacement
Control Adjusting Screw
3 mm
Electric Displacement
Control Lock Nut
10 mm
9.1 - 10.1 N·m
P400094
Service Manual
D1 High Power Open Circuit Pumps Size 65/130/145/193/260
Adjustments
5. After Step 4, slowly operate a hydraulic function that will demand approximately half flow from the
pump, but keep outlet pressure below the power control pressure starting point (if Power control is
used). Danfoss recommends loading the outlet pressure to 50bar.
Warning
Escaping hydraulic fluid under pressure can have sufficient force to penetrate your skin causing
serious injury and/or infection. Relieve pressure in the system before removing hoses, fittings,
gauges, or components.
Unintended movement of the machine or mechanism may cause injury to the technician or
bystanders. To protect against unintended movement, secure the machine or disable / disconnect
the mechanism while servicing.
Caution
Contamination can damage internal components and void the manufacturer’s warranty. Take
precautions to ensure system cleanliness when removing and reinstalling system lines.
6. Loosen the LS control lock nut. While watching the pressure gauges, turn the LS control adjusting
screw counterclockwise until the desired pressure differential between port MB and port X is
achieved (LS setting). Clockwise rotation increases the setting, counterclockwise rotation will
decrease it; approximate gain (see Table 1) per turn. While holding the position of the LS adjusting
screw, torque the LS lock nut to 21.6~24.6 N•m [191-218 lbf•in].
7. Stop the prime mover, remove the pressure gauge and flow meter, and return the system to its
normal operating configuration.
TPE5/TPE2 (130/145/193/260)
©
Danfoss | July 2019 L1527453 | AX00000292en-CN0201 | 39
Page 40

Measurement point
Outlet pressure port MB
Power control adjustment screw
Power control lock nut
Pressure compensated
control adjustment screw
Pressure compensated
control lock nut
Load sensing
adjustment screw
Load sensing
lock nut
M12x1.5
0-600 bar
6 mm
22.5 - 27.5 N·m
4 mm
13 mm
21.6 - 24.6 N·m
4 mm
13 mm
21.6 - 24.6 N·m
4 mm
13 mm
21.6 - 24.6 N·m
Service Manual
D1 High Power Open Circuit Pumps Size 65/130/145/193/260
Adjustments
TPSN (65)
40 | © Danfoss | July 2019 L1527453 | AX00000292en-CN0201
Page 41

Measurement Point,
Outlet Pressure Port MB
M12x1.5
0-600 bar
6 mm
22.5 - 27.5 N·m
Power Control Adjusting Screw
4 mm
Load Sensing Adjusting Screw
4 mm
Pressure Compensated
Control Adjusting Screw
4 mm
Power Control Lock Nut
13 mm
21.6 - 24.6 N·m
Pressure Compensated
Control Lock Nut
13 mm
21.6 - 24.6 N·m
Load Sensing Lock Nut
13 mm
21.6 - 24.6 N·m
P400095
P400255
Measurement Point,
Outlet Pressure Port MB
M12x1.5
0-600 bar
6 mm
22.5 - 27.5 N·m
Power Control
Adjusting Screw
4 mm
Power Control
Lock Nut
13 mm
21.6 - 24.6 N·m
Pressure Compensated
Control Lock Nut
13 mm
21.6 - 24.6 N·m
Pressure Compensated
Control Adjusting Screw
4 mm
Load Sensing
Adjusting Screw
4 mm
Load Sensing Lock Nut
13 mm
21.6 - 24.6 N·m
Service Manual
D1 High Power Open Circuit Pumps Size 65/130/145/193/260
Adjustments
TPSN (130/145)
©
Danfoss | July 2019 L1527453 | AX00000292en-CN0201 | 41
TPSN (193/260)
Please refer to Operation for information about the other control options.
Page 42

W
C
Service Manual
D1 High Power Open Circuit Pumps Size 65/130/145/193/260
Adjustments
Displacement Limiters Adjustment
Adjust Displacement Limiters
Warning
Escaping hydraulic fluid under pressure can have sufficient force to penetrate your skin causing serious
injury and/or infection. Relieve pressure in the system before removing hoses, fittings, gauges, or
components.
Unintended movement of the machine or mechanism may cause injury to the technician or bystanders.
To protect against unintended movement, secure the machine or disable / disconnect the mechanism
while servicing.
Caution
Contamination can damage internal components and void the manufacturer’s warranty. Take
precautions to ensure system cleanliness when removing and reinstalling system lines.
1. Install a flow meter in outlet line to measure pump flow.
2. Start the prime mover and allow fluid to reach normal operating temperature.
3. Adjust the control properly to make sure the pump at maximum displacement.
4. Loosen the maximum or minimum displacement limiter lock nut with an external hex wrench and
turn the adjusting screw with an internal hex wrench until the desired flow is achieved.
Option Description
Maximum displacement
•
Clockwise turn decreases displacement
•
Counter-clockwise turn increases displacement
Minimum displacement
•
Clockwise turn increases displacement
•
Counter-clockwise turn decreases displacement
Displacement change per turn
Displacement 65 130/145 193 260
Max. displacement
change per turn
Min. displacement
change per turn
4.7cm3/rev 11 cm3/rev 15 cm3/rev 19 cm3/rev
6cm3/rev 9 cm3/rev 14 cm3/rev 18 cm3/rev
5. While holding the position of the adjusting screw, torque the lock nut to required torque.
Wrench sizes and Torque
65 130/145 193 260
Screws
Nuts
5 mm 5 mm 8 mm 8 mm
17 mm 17 mm 24 mm 24 mm
43~48 N·m
[380.58~424.84 lbf·in]
43~48 N·m
[380.58~424.84 lbf·in]
180~206 N·m
[1593.13~1823.25 lbf·in]
[1593.13~1823.25 lbf·in]
180~206 N·m
42 | © Danfoss | July 2019 L1527453 | AX00000292en-CN0201
Page 43

P400369
D901
D902
D900
D900
D920
D910
G110
G620
G600
G610
22mm
6mm
Service Manual
D1 High Power Open Circuit Pumps Size 65/130/145/193/260
Minor repairs
D1P shaft replacement
Replacing the shaft requires removing the pump from the machine. If a second pump is used, you must
first remove it before working on the D1 pump. The shaft assembly is serviceable without dissembling
the pump.
D1P shaft removal
Remove any auxiliary pad or running cover and the impeller (if used) using the following steps:
1. Set the pump on a working surface with the shaft facing down.
2. Remove the snap ring (G610) with snap-ring pliers, remove the impeller (G600) and another snap ring
(G620) with snap-ring pliers.
3. Turn the housing 180 degrees, mounting flange side up, remove the snap ring (F210) using snap-ring
pliers.
4. Remove the shaft seal seal group (F220), remove and discard the O-ring (F230).
Shaft seal (F222) and carrier (F221) are set as one group. remove and discard group.
5. Danfoss recommends screwing in the max displacement limiter enough so to prevent internal
component movement during the shaft removal. Remove shaft and front bearing assembly (E000T)
after shaft seal group has been removed.
The shaft and front bearing sub-assembly are light pressed to the housing. For ease of removal, use a
lift ring and a lifting device.
©
Danfoss | July 2019 L1527453 | AX00000292en-CN0201 | 43
6. If front bearing removal is required, press it out of the shaft toward the rear end of the shaft.
Page 44

C
C
C
P400617
F210
F220
F221
F222
F230
E000T
Service Manual
D1 High Power Open Circuit Pumps Size 65/130/145/193/260
Minor repairs
D1P shaft installation
1. Before reinstalling the shaft, press the shaft bearing onto shaft (if bearing was removed), using
external snap ring pliers to install retainer ring (not shown, see Repair Instructions manual) in shaft.
Caution
The washer from the bearing must be on the shaft shoulder side and the retainer ring must be facing
the bearing with the small corner side.
2. With the pump’s mounting flange side up, coat bearing hole with hydraulic fluid, install shaft and
front bearing group to housing, knocking the bearing cup side lightly with a copper hammer if there
is considerable resistance until the shaft and bearing assembly is properly set in place.
Caution
Do not hit the shaft, using a protective sleeve is recommended. Be careful with contaminants during
the process.
3. Coat with assembly grease to hold the O-ring (F230) in bearing hole.
Caution
Be careful when touching shaft splines; The retainer ring must be facing the bearing with small corner
side.
4. Lubricate the lip of the shaft seal (F222) with clean hydraulic grease. Install the carrier and seal
assembly (F220) and make sure it is set properly by applying uniform force around the carrier. Once
the seal carrier is properly set, use internal snap ring pliers to install retainer ring (F210) in housing.
5. If the pump has an impeller, reinstall it after the shaft installation is complete.
44 | © Danfoss | July 2019 L1527453 | AX00000292en-CN0201
Page 45

F230
F220
F210
P400096
Service Manual
D1 High Power Open Circuit Pumps Size 65/130/145/193/260
Minor repairs
Shaft Seal Replacement
D1 pump uses a lip-type shaft seal. You can replace this seal without major disassembly of the unit.
Replacing the shaft seal requires removing the pump from the machine.
Removal
1. Using the appropriate snap-ring pliers, remove the retaining ring (F210) from the housing.
2. Remove the shaft seal and its carrier (F220) with appropriate tool (such as a flat-head screwdriver)
from the bore in the pump housing and discard.
3. Remove the O-ring (F230) and discard.
Installation
1. Inspect the pump housing and new seals for damage. Inspect the sealing area on the shaft for rust,
wear, or contamination. Polish the sealing area on the shaft if necessary.
2. Lubricate new O-ring (F230) with petroleum jelly and fit in the housing groove.
3. Lubricate the lip of the new shaft seal with clean hydraulic fluid. Place a protective sleeve over the
shaft end to prevent damage to the seal during installation.
4. Keeping the new seal and its carrier perpendicular to the shaft, press them into the housing just far
enough to clear the retaining ring groove. Install seal with the cupped side toward the shaft bearing.
Do not damage the seal during installation.
5. Using the appropriate snap ring pliers, install the seal retaining ring.
6. Remove the installation sleeve.
©
Danfoss | July 2019 L1527453 | AX00000292en-CN0201 | 45
Page 46

Service Manual
D1 High Power Open Circuit Pumps Size 65/130/145/193/260
Minor repairs
Auxiliary Flange and Charge Pump Replacement
Follow these steps to either remove, replace, or exchange auxiliary mounting pads and charge pump
(impeller).
D1P auxiliary flange removal
1. Remove the screws (H140), retaining the cover plate (H150). Remove the seal (H130).
2. Remove the drive coupling (H200) if present.
3. Remove the 4 screws (H120), retaining the pad adapter (H100) to the end cap. Discard the pad
adapter O-ring (H110).
4. Use the appropriate snap-ring pliers, remove the retaining ring (G610) from the shaft.
5. Pull out the charge pump, discard it if it is damaged.
D1P auxiliary flange installation
1. Push in the new charge pump far enough to clear the retaining ring groove (if impeller was replaced).
2. Use the appropriate snap-ring pliers to install retaining ring (G610) onto the shaft.
3. Lubricate new O-ring (H110) with petroleum jelly. Install the pad adapter to the end cap.
4. Install the 4 screws (H120) and torque to required torques.
5. Install the drive coupling (H200) if present.
6. Install the cover (H150) with seal (H130), lubricate the seal with petroleum jelly.
7. Install the screws (H140) and torque to required torques.
46 | © Danfoss | July 2019 L1527453 | AX00000292en-CN0201
Page 47

H140
H140
H140
H140
H110
H100
H120
H150
H150
H150
H130
H130
H120
H120
H130
H130
H125
H120
H120
H100
H100
H100
H100
H110
H110
H110
H110
H200
H200
H200
H200
NN
D5
C5
B1
A1
Service Manual
D1 High Power Open Circuit Pumps Size 65/130/145/193/260
Minor repairs
130/145
All torques tolerance ±10%
©
Danfoss | July 2019 L1527453 | AX00000292en-CN0201 | 47
Page 48

A1/A3
NN
D2/D5
C5/C9
B1
E2 (E3)*
H200
H200
H200
H200
H110
H110
H110
H110
H100
H100
H100
H100
H120
H120
H120
H120
H200
H110
H110
H100
H100
H120
H120
H108
H105
H107
H130
H130
H130
H130
H140
H140
H140
H140
H140
H150
H150
H150
H150
H130
H150
Service Manual
D1 High Power Open Circuit Pumps Size 65/130/145/193/260
Minor repairs
193/260
All torques tolerance ±10%
* E3 option is only for 260.
48 | © Danfoss | July 2019 L1527453 | AX00000292en-CN0201
Page 49

Service Manual
D1 High Power Open Circuit Pumps Size 65/130/145/193/260
Minor repairs
Control (193/260)
Removal
1. Remove the control from the endcap by removing the mounting bolts (See Control seal type and
mounting bolts). If the control has the TC/DC feedback link (D640), ensure that it does not stay in the
hole of the bias piston in the endcap, remove it and place it with the control.
2. Remove and discard the seals (See Control seal type and mounting bolts) .
Installation
1. Install new seals (See table Control seal type and mounting bolts). Proper gasket alignment is dictated
by alignment pins in the control housing. For O-rings, lightly lubricate them prior to assembly.
2. If the control uses a TC/DC feedback link, make sure that it is set in the bias piston hole, then install
the control housing assembly onto the endcap using the mounting bolts.
Control seal type and mounting bolts
Control Seal type Mounting bolts TC/DC feedback link
NPNN (130-260) Gasket (D145) 5 short bolts (D175) No
NPSN (130-260) Gasket (D145) 5 short bolts (D175) No
TPSN (193/260) Gasket (D145) 5 short bolts (D175) Yes
TPSN (130/145) 1 O-ring (D140) & 3 O-
rings (D150)
NNES (130-260) Gasket (D145) 5 short bolts (D175) Yes
TPE2/TPE5 (130-260) Gasket (D145) 3 long bolts (D170) & 2
NPNR (130-260) Gasket (D145) 5 short bolts (D175) No
5 short bolts (D175) Yes
Yes
short bolts (D180)
Torque requirements
Bolt Torque
D175 22.5-27.5 N·m [199-243 lbf·in]
D170 22.5-27.5 N·m [199-243 lbf·in]
D180 22.5-27.5 N·m [199-243 lbf·in]
©
Danfoss | July 2019 L1527453 | AX00000292en-CN0201 | 49
Page 50

6mm
D170
D145
22.5-27.5 N
·m
6mm
D180
22.5-27.5 N
·m
P400293
P400294
6mm
D175
22.5-27.5 N.·m
D145
Service Manual
D1 High Power Open Circuit Pumps Size 65/130/145/193/260
Minor repairs
193/260 TPE2 Control
193/260 TPSN Control
50 | © Danfoss | July 2019 L1527453 | AX00000292en-CN0201
Page 51

D150
D140
D175
P400259
6mm
22.5-27.5 N·m
Service Manual
D1 High Power Open Circuit Pumps Size 65/130/145/193/260
Minor repairs
Control (130/145)
130/145 TPSN Control
©
Danfoss | July 2019 L1527453 | AX00000292en-CN0201 | 51
Page 52

D901
D902
D900
D900
D920
D910
G110
22mm
6mm
Service Manual
D1 High Power Open Circuit Pumps Size 65/130/145/193/260
Minor repairs
Shuttle Valve or Plug
D1P shuttle valve or plug removal
Follow the steps below to remove the shuttle valve (if an EDC control is used) or plug.
1. For Electronic Displacement Control (EDC) function, first remove the plug assembly-HEX(D900).
2. Pull out shuttle valve seat (D920) with a M6 screw.
3. Remove the spool (D910) with an appropriate tool.
4. For controls without EDC function, there is only a plug which normally does not need to be removed.
D1P shuttle valve or plug installation
1. For controls with EDC, coat the shuttle valve spool (D910) with cleaning hydraulic oil and install to E
port in the endcap.
2. Install shuttle valve seat (D920) according to the direction showing in the picture.
3. Install E port plug assembly (D900).
4. If the shuttle valve is not used, replace it with the plug (D900).
The shuttle valve must also be installed in NNES and TPE2/TPE5 controls if the application requires
this feature. To determine if a shuttle valve is needed, please consult with your Danfoss
representative.
Edge Filter (260)
D1P edge filter removal
1. Remove the plug G255.
2. Remove the filter G254.
D1P edge filter installation
1. Install the filter G254 and torque to the required specification.
52 | © Danfoss | July 2019 L1527453 | AX00000292en-CN0201
Page 53

D900
D900
D920
D901
D902
D910
G255
G254
Service Manual
D1 High Power Open Circuit Pumps Size 65/130/145/193/260
Minor repairs
2. Install the plug G255 and torque to the required specification.
Wrench size and torque
Item Wrench size Torque
G254 6mm hex 9.9-12.1 Nm
G255 6mm hex 30.6-37.4 Nm
D900 6mm hex 30.6-37.4 Nm
D901 22mm hex 30.6-37.4 Nm
©
Danfoss | July 2019 L1527453 | AX00000292en-CN0201 | 53
Page 54

Service Manual
D1 High Power Open Circuit Pumps Size 65/130/145/193/260
Minor repairs
Displacement Limiters
D1P displacement limiter screws removal
The removal steps of the maximum (bottom of the pump) and minimum (top of the pump, control side)
are the same.
1. Loosen the lock nut (F120) with an external hex wrench.
2. Counter clockwise turn the adjusting screw (F110) with an 8mm internal hex wrench until it
completely out.
3. Inspect the lock nut seal and adjusting screw, if they are damaged , discard them.
D1P displacement limiter screws installation
The installation steps of the maximum (bottom of the pump) and minimum (top of the pump) are the
same.
1. Clockwise turn the adjusting screw (F110) with the appropriate internal hex wrench until you feel it
start against the swashplate.
2. Install the lock nut (F120), while holding the adjusting screw position, torque the lock nut to required
torque.
Wrench size and torque
Frame size Wrench size Torque
65cc 5 mm (screws), 17 mm
(nuts)
130/145cc 5 mm (screws) 17 mm
(nuts)
193cc 8 mm (screws), 24 mm
(nuts)
260cc 8 mm (screws), 24 mm
(nuts)
43~48 N·m [380.58~424.84 lbf·in]
43~48 N·m [380.58~424.84 lbf·in]
180~206 N·m [1593.13~1823.25 lbf·in]
180~206 N·m [1593.13~1823.25 lbf·in]
54 | © Danfoss | July 2019 L1527453 | AX00000292en-CN0201
Page 55

F110
F120
F110
F120
P400265
Service Manual
D1 High Power Open Circuit Pumps Size 65/130/145/193/260
Minor repairs
©
Danfoss | July 2019 L1527453 | AX00000292en-CN0201 | 55
Page 56

G235
G250
F140
F150
G225
F160
G240
G130
G140
Service Manual
D1 High Power Open Circuit Pumps Size 65/130/145/193/260
Minor repairs
Plug and fitting installation
If any plugs or fittings are removed from the unit during service, install and torque as indicated. The
following drawings are in generic configurations to show item number for wrench size and torque
reference.
D1P 193 TPE2 control plug fittings
Plug fitting reference
Item Description Wrench size Torque
F160 Drain port L1 (M33 x 2) 17 mm hex 68.4-83.6 Nm
56 | © Danfoss | July 2019 L1527453 | AX00000292en-CN0201
G225 Outlet pressure test port MB (M12 x 1.5) 6 mm hex 22.5-27.5 Nm
G230 Bias orifice 3 mm hex 3.6-4.4 Nm
G240 Bias orifice plug (M8 x 1) 4 mm hex 9.9-12.1 Nm
G235 Servo pressure test port M4 (M12 x 1.5) 6 mm hex 22.5-27.5 Nm
G140 Servo orifice 4 mm 3.6-4.4 Nm
F140 Drain port L3 (M33 x 2) 17 mm hex 68.4-83.6 Nm
F150 Drain port L2 (M33 x 2) 17 mm hex 68.4-83.6 Nm
G250 Servo orifice plug (M12 x 1.5) 6 mm hex 22.5-27.5 Nm
Page 57

G235
G250
G253
F140
F150
G255
G254
G130
G140
G225
F160
Service Manual
D1 High Power Open Circuit Pumps Size 65/130/145/193/260
Minor repairs
D1P 260 TPE2 control plug fittings
Plug fitting reference
Item Description Wrench size Torque
G130 Bias orifice 3 mm hex 3.6-4.4 Nm
G140 Servo orifice 4 mm 3.6-4.4 Nm
G225 Outlet pressure test port MB (M12 x 1.5) 6 mm hex 22.5-27.5 Nm
G235 Servo pressure test port M4 (M12 x 1.5) 6 mm hex 22.5-27.5 Nm
G250 Servo orifice plug (M12 x 1.5) 6 mm hex 22.5-27.5 Nm
G253 Bias orifice plug (5/16 - 24 UNF-2A) 1/8 in 9.9-12.1 Nm
G254 Edge filter 6 mm hex 9.9-12.1 Nm
G255 Edge filter plug (M14 x 1.5) 6 mm hex 30.6-37.4 Nm
F140 Drain port L3 (M33 x 2) 17 mm hex 68.4-83.6 Nm
F150 Drain port L2 (M33 x 2) 17 mm hex 68.4-83.6 Nm
F160 Drain port L1 (M33 x 2) 17 mm hex 68.4-83.6 Nm
©
Danfoss | July 2019 L1527453 | AX00000292en-CN0201 | 57
Page 58

G225
F160
G240
G130
G235
G250
F140
F150
G140
Service Manual
D1 High Power Open Circuit Pumps Size 65/130/145/193/260
Minor repairs
D1P 130/145 TPSN control plug fittings
58 | © Danfoss | July 2019 L1527453 | AX00000292en-CN0201
Plug fitting reference
Item Description Wrench size Torque
G130 Bias orifice 3 mm hex 3.6-4.4 Nm
G140 Servo orifice 4 mm 3.6-4.4 Nm
G225 Outlet pressure test port MB (M12 x 1.5) 6 mm hex 22.5-27.5 Nm
G235 Servo pressure test port M4 (M12 x 1.5) 6 mm hex 22.5-27.5 Nm
G250 Servo orifice plug (M14 x 1.5) 6 mm hex 30.6-37.4 Nm
F140 Drain port L3 (M26 x 1.5) 12 mm hex 68.4-83.6 Nm
F150 Drain port L2 (M26 x 1.5) 12 mm hex 68.4-83.6 Nm
F160 Drain port L1 (M26 x 1.5) 12 mm hex 68.4-83.6 Nm
Page 59

F120
F140
F110
G235
H120
H120
H120 H120
F120
D180
D170
G225
D480
D380
D175
D480
D470
D370
D380
D870
D880
D370
D470
F110
D110
D120
F160
P400267
F120
F140
F120 F110
F110
F160
D175
G225
D870
D880
D370
D380
H120
D470
D480
H120
H120
G235
H120
P400261
Service Manual
D1 High Power Open Circuit Pumps Size 65/130/145/193/260
Minor repairs
D1P plugs and fasteners
Size 193/260
Size 130/145
D1P fastener size and torque chart
All torques tolerance (except already given range) : ±10%
Item Fastener
D170
D180
D175 Control
H120 Adapter
F110 Displacemen
D370 P adjusting
D470 T adjusting
©
Danfoss | July 2019 L1527453 | AX00000292en-CN0201 | 59
Control
assembly
screws
assembly
screws
screws
t limiter
screws
screw
screw
Wrench size Torque Wrench size Torque Wrench size Torque Wrench size Torque
N/A N/A 6 mm
6 mm
internal hex
5 mm
internal hex
4 mm
internal hex
4 mm
internal hex
65 130/145 193 260
internal hex
25 N·m
[221.27 lbf·in]
N/A 10 mm
6 mm
internal hex
internal hex
N/A 5 mm
internal hex
N/A 4 mm
internal hex
N/A 4 mm
internal hex
25 N·m
[221.27 lbf·in]
25 N·m
[221.27 lbf·in]
130 N·m
[1150.6 lbf·in]
N/A 8 mm
N/A 4 mm
N/A 4 mm
6 mm
internal hex
6 mm
internal hex
14 mm
internal hex
internal hex
internal hex
internal hex
25 N·m
[221.27 lbf·in]
25 N·m
[221.27 lbf·in]
215 N·m
[1902.91
lbf·in]
N/A 8 mm
N/A 4 mm
N/A 4 mm
6 mm
internal hex
6 mm
internal hex
14 mm
internal hex
internal hex
internal hex
internal hex
25 N·m
[221.27 lbf·in]
25 N·m
[221.27 lbf·in]
215 N·m
[1902.91
lbf·in]
N/A
N/A
N/A
Page 60

Service Manual
D1 High Power Open Circuit Pumps Size 65/130/145/193/260
Minor repairs
All torques tolerance (except already given range) : ±10% (continued)
Item Fastener
D870 S adjusting
screw
D110 E2 adjusting
screw
F120 Displacemen
t limiter lock
nuts
D380 P locknut 13 mm
D480 T locknut 13 mm
D880 S locknut 13 mm
D120 E2/E5
locknut
Wrench size Torque Wrench size Torque Wrench size Torque Wrench size Torque
4 mm
internal hex
17 mm
external hex
external hex
external hex
external hex
N/A N/A 10 mm
65 130/145 193 260
N/A 4 mm
N/A N/A N/A 3 mm
43 -48 N·m
[380.58-424.8
4 lbf·in]
21.6-24.6
N·m
[191.18-217.7
3 lbf·in]
21.6-24.6
N·m
[191.18-217.7
3 lbf·in]
21.6-24.6
N·m
[191.18-217.7
3 lbf·in]
internal hex
17 mm
external hex
13 mm
external hex
13 mm
external hex
13 mm
external hex
external hex
N/A 4 mm
43 -48 N·m
[380.58-424.8
4 lbf·in]
21.6-24.6
N·m
[191.18-217.7
3 lbf·in]
21.6-24.6
N·m
[191.18-217.7
3 lbf·in]
21.6-24.6
N·m
[191.18-217.7
3 lbf·in]
9.1-10.1 N·m
[80.54-89.39
lbf·in]
internal hex
internal hex
24 mm
external hex
13 mm
external hex
13 mm
external hex
13mm
external hex
10 mm
external hex
N/A 4 mm
N/A 3 mm
180 - 206
N·m
[1593.13-182
3.25 lbf·in]
21.6-24.6
N·m
[191.18-217.7
3 lbf·in]
21.6-24.6
N·m
[191.18-217.7
3 lbf·in]
21.6-24.6
N·m
[191.18-217.7
3 lbf·in]
9.1-10.1 N·m
[80.54-89.39
lbf·in]
internal hex
internal hex
24 mm
external hex
13 mm
external hex
13 mm
external hex
13mm
external hex
10 mm
external hex
N/A
N/A
180 - 206
N·m
[1593.13-182
3.25 lbf·in]
21.6-24.6
N·m
[191.18-217.7
3 lbf·in]
21.6-24.6
N·m
[191.18-217.7
3 lbf·in]
21.6-24.6
N·m
[191.18-217.7
3 lbf·in]
9.1-10.1 N·m
[80.54-89.39
lbf·in]
D1P plug size and torque chart
All torques tolerance (except already given range) : ±10%
65 130/145 193 260
Item
F140
F150
G225
G235
ED-ring
plug
N/A N/A N/A M26X1.5 12 mm
M12X1.5 6 mm
Wrench
size
internal
hex
Torque ED-ring
25 N·m
[221.27
lbf·in]
plug
M12X1.5 6 mm
Wrench
size
internal
hex
internal
hex
Torque ED-ring
76 N·m
[672.66
lbf·in]
25 N·m
[221.27
lbf·in]
plug
M33X2 17 mm
M12X1.5 6 mm
Wrench
size
internal
hex
internal
hex
Torque ED-ring
225 N·m
[1991.42
lbf·in]
25 N·m
[221.27
lbf·in]
plug
M33X2 17 mm
M12X1.5 6 mm
Wrench
size
internal
hex
internal
hex
Torque
225 N·m
[1991.42
lbf·in]
25 N·m
[221.27
lbf·in]
60 | © Danfoss | July 2019 L1527453 | AX00000292en-CN0201
Page 61

Danfoss
Power Solutions GmbH & Co. OHG
Krokamp 35
D-24539 Neumünster, Germany
Phone: +49 4321 871 0
Danfoss
Power Solutions ApS
Nordborgvej 81
DK-6430 Nordborg, Denmark
Phone: +45 7488 2222
Danfoss
Power Solutions (US) Company
2800 East 13th Street
Ames, IA 50010, USA
Phone: +1 515 239 6000
Danfoss
Power Solutions Trading
(Shanghai) Co., Ltd.
Building #22, No. 1000 Jin Hai Rd
Jin Qiao, Pudong New District
Shanghai, China 201206
Phone: +86 21 3418 5200
Products we offer:
Hydro-Gear
www.hydro-gear.com
Daikin-Sauer-Danfoss
www.daikin-sauer-danfoss.com
DCV directional control
•
valves
Electric converters
•
Electric machines
•
Electric motors
•
Hydrostatic motors
•
Hydrostatic pumps
•
Orbital motors
•
PLUS+1® controllers
•
PLUS+1® displays
•
PLUS+1® joysticks and
•
pedals
PLUS+1® operator
•
interfaces
PLUS+1® sensors
•
PLUS+1® software
•
PLUS+1® software services,
•
support and training
Position controls and
•
sensors
PVG proportional valves
•
Steering components and
•
systems
Telematics
•
Danfoss Power Solutions is a global manufacturer and supplier of high-quality hydraulic and
electric components. We specialize in providing state-of-the-art technology and solutions
that excel in the harsh operating conditions of the mobile off-highway market as well as the
marine sector. Building on our extensive applications expertise, we work closely with you to
ensure exceptional performance for a broad range of applications. We help you and other
customers around the world speed up system development, reduce costs and bring vehicles
and vessels to market faster.
Danfoss Power Solutions – your strongest partner in mobile hydraulics and mobile
electrification.
Go to www.danfoss.com for further product information.
We offer you expert worldwide support for ensuring the best possible solutions for
outstanding performance. And with an extensive network of Global Service Partners, we also
provide you with comprehensive global service for all of our components.
Local address:
Danfoss can accept no responsibility for possible errors in catalogues, brochures and other printed material. Danfoss reserves the right to alter its products without notice. This also applies to products
already on order provided that such alterations can be made without subsequent changes being necessary in specifications already agreed.
All trademarks in this material are property of the respective companies. Danfoss and the Danfoss logotype are trademarks of Danfoss A/S. All rights reserved.
©
Danfoss | July 2019 L1527453 | AX00000292en-CN0201
 Loading...
Loading...