Daewoo DV-K84W, DV-K284W, DV-K64W, DV-K24W, DV-K8K4W Service Manual

S/M No. : KMUB1M1U01
Service Manual
Video Cassette Recorder
Model: ALL K-MECHA
MULTI MODELS
PAL/MESECAM/NTSC
(DV-K*84W Series)
(DV-K*64W Series)
(DV-K*24W Series)
(DV-K8K4W)
(DV-K#44W Series)
(DV-K#04W Series)
(DV-K#A4W Series)
(DV-K#B4W Series)
Note: 1. * : 8/4/2
2. # : 4/2
DAEWOO ELECTRONICS CO., LTD.

VVVVV
REDORDER VIDEO CASSETTE RECORDER VIDEO CASSETTE RECORDER VIDEO CASSETTE RECORDER VIDEO CASSETTE RECORDER VIDEO
VIDEO CASSETTE RECORDER VIDEO CASSETTE RECORDER VIDEO CASSETTE RECORDER VIDEO CASSETTE RECORDER VIDEO CASSETTE
RECORDER VIDEO CASSETTE RECORDER VIDEO CASSETTE RECORDER VIDEO CASSETTE RECORDER VIDEO CASSETTE RECORDER VIDEO
VIDEO CASSETTE RECORDER VIDEO CASSETTE RECORDER VIDEO CASSETTE RECORDER VIDEO CASSETTE RECORDER VIDEO CASSETTE
RECORDER VIDEO CASSETTE RECORDER VIDEO CASSETTE RECORDER VIDEO CASSETTE RECORDER VIDEO CASSETTE RECORDER VIDEO
VIDEO CASSETTE RECORDER VIDEO CASSETTE RECORDER VIDEO CASSETTE RECORDER VIDEO CASSETTE RECORDER VIDEO CASSETTE
RECORDER VIDEO CASSETTE RECORDER VIDEO CASSETTE RECORDER VIDEO CASSETTE RECORDER VIDEO CASSETTE RECORDER VIDEO
Contents
SECTION 1. CONTROLS AND FUNCTIONS...........................................................................................2
SECTION 2.
ELECTRICAL ADJUSTMENTS
2-1. SERVO CIRCUIT ADJUSTMENT METHOD...........................................................................................3
2-2. IF MODULE CIRCUIT ADJUSTMENT METHODS.................................................................................4
SECTION 3. CIRCUIT OPERA TION PRINCIPLES
3-1. POWER CIRCUIT............................................................................................................. ..........................6
3-2. KEY FEATURES OF VIDEO IC AND ITS RELATIVES..........................................................................8
3-3. RECORD AND PLAYBACK PROCESSING CIRCUIT...........................................................................8
3-4. IF CIRCUIT OPERATION........................................................................................................................12
3-5. NORMAL AUDIO SIGNAL PROCESSING(LA71501BM)....................................................................15
3-6. Hi-Fi AUDIO SIGNAL PROCESSING(BH7804K)..................................................................................16
SECTION 4.
TROUBLESHOOTING FLOW CHART
4-1. POWER CIRCUIT.....................................................................................................................................19
4-2. PIF CIRCUIT..............................................................................................................................................21
4-3. LOGIC CIRCUIT .......................................................................................................................................23
4-4. SERVO-SYSCON CIRCUIT....................................................................................................................24
4-5. AUDIO CIRCUIT (NORMAL)...................................................................................................................32
4-6. AUDIO CIRCUIT (Hi-Fi)............................................................................................................................34
4-7. VIDEO CIRCUIT .......................................................................................................................................36
SECTION 5.
WAVEFORMS ON VIDEO CIRCUIT................................................................................43
SECTION 6.
µ-COM PORT..............................................................................................................................46
SECTION 7.
VOL TAGE CHARTS................................................................................................................50
SECTION 8.
SERVICE MODE.......................................................................................................................56
SECTION 9.
CIRCUIT DIAGRAM
9-1. CONNECTION DIAGRAM.......................................................................................................................68
9-2. POWER CIRCUIT DIAGRAM..................................................................................................................69
9-3. SYSCON AND LOGIC CIRCUIT DIAGRAM..........................................................................................70
9-4. PIF CIRCUIT DIAGRAM ..........................................................................................................................71
9-5. IF/MPX MODULE CIRCUIT DIAGRAM..................................................................................................72
9-6. VIDEO/AUDIO CIRCUIT DIAGRAM.......................................................................................................73
9-7. Hi-Fi/PRE-AMP CIRCUIT DIAGRAM......................................................................................................74
SECTION 10.
COMPONENTS LOCA TION GUIDE ON PCB BOTTOM VIEW
10-1. PCB MAIN...............................................................................................................................................75
10-2. PCB IF MODULE....................................................................................................................................76
10-3. PCB LOGIC (
DV-K*84W, DV-K*64W, DV-K*24W, DV-K8K4W, DV-K#44W, DV-K#04W,DV-K#84W, DV-K#B4W
).................77
SECTION 11.
DISASSEMBL Y
11-1. PACKING ASS’Y....................................................................................................................................79
11-2. FRONT PANEL ASSEMBLY..................................................................................................... ............80
11-3. INSTRUMENT DISASSEMBLY............................................................................................................82
SECTION 12.
ELECTRICAL P ARTS LIST...............................................................................................91
SECTION 13.
OPTION T ABLE.....................................................................................................................107
SECTION 14.
SERVICE JIG CONNECTION METHODS................................................................114
VIDEO CASSETTE RECORDER
CHANNEL COVERAGE
IN/OUTPUT JACK TYPE
•••••••
SPECIFICATION
•••••••
GENERAL
Power requirement :
AC 110-240V~,50/60Hz (For M.East)
:AC 230V~, 50Hz (For Others)
Power consumption :Max. 19W (in REC mode)
Temperature :5°C~35°C (Operating)
-20°C~60°C
Operating position :Horizontal only
Dimensions (WxHxD) :360x90x288 (mm)
Weight :Approx. 4.0Kg
Format :VHS standard
Tape width :12.65mm
Tape speed :(SP): 23.39mm/sec
(LP): 11.70mm/sec
Maximum recording time
with full-size cassette :(SP): 240min. with E-240
video cassette
(LP): 480min. with E-240
video cassette
VIDEO
Signal system :PAL colour and CCIR
monochrome signals, 625
lines/50 fields
: NTSC colour and EIA
monochrome signals, 525
lines/60 fields
Recording system : Rotary two-head helical scan
with a slant double-aximuth
combination video head
Input :1.0Vp-p, 75ohms, unbalanced
Output :1.0Vp-p, 75ohms, unbalanced
Signal-to noise ratio :45dB (Rohde & Schwarz noise
meter) with NETTETE IMAGE
control at center position
Horizontal resolution :240 lines with NETTETE
IMAGE control at center position
AUDIO
Recording system : Longitudinal track
:-8 dBm, (CENELEC standard), ..
more than 47 k-ohms,
unbalanced
Output :-6dBm, (CENELEC standard),
less than 1 k-ohm, unbalanced
(100 k-ohms, load)
Frequency range :100 Hz to 8 KHz (Normal)
:20 Hz to 20 KHz (Hi-Fi)
Signal to noise ratio : 38 dB More than (Normal)
:60 dB More than (Hi-Fi)
Audio Distortion :Less than 3% SP (Normal)
:Less than 0.5% (Hi-Fi)
TUNER
Tuning system :Voltage synthesized tuner
Programmable V/S 99CH
(Hyper band)
RF Output :UHF channel 22~69
52ch: For U.K & S/Ireland
60ch: For Others
TIMER
Memory programmable : 99 CH
Back up time : Less than 1 Hour
Clock exactness :In accordance with the
exactness of power supply
frequency (50Hz)
ACCESSORIES
Provided Accessories :Remote control unit, RF Cable,
Battery
* Design and specification can be subjected to change
without notice.
MODEL Russia Middle East
JACK TYPE SCART Type
RCA JACK
(PHONE JACK)
SYSTEM PAL/SECAM-BG/DK(B/G) 2 Carrier Sound system) NTSC-M
CHANNEL
VHF 2-12, VHF 21-69, CATV S1-S41, X,Y,Z
(Hyperband)
•••••••
INFORMATION
•••••••
• Safety Check after Servicing
Examine the area surrounding the repaired location for damage or deterioration. Observe that screws, parts and wires
have been returned to original positions. Afterwards, perform the following tests and confirm the specified values in
order to verify compliance with safety standards.
1. Insulation resistance test
Confirm the specified insulation resistance or greater between power cord plug prongs and externally exposed parts
of the set (RF terminals, antenna terminals, video and audio input and output terminals, microphone jacks, earphone
jacks, etc.). See table below.
2. Dielectric strength test
Confirm specified dielectric strength or greater between power cord plug prongs and exposed accessible parts of the
set (RF terminals, antenna terminals, video and audio input and output terminals, microphone jacks, earphone jacks,
etc.) See table below.
3. Clearance distance
When replacing primary circuit components, confirm specified
clearance distance (d), (d') between soldered terminals, and
between terminals and surrounding metalic parts. See table
below.
Table 1: Rating for selected areas
* Class II model only.
Note: This table is unofficial and for reference only. Be sure to confirm the precise values for your particular country
and locality.
4. Leakage current test
Confirm specified or lower leakage current between B (earth ground, power cord plug prongs) and externally
exposed accessible parts (RF terminals, antenna terminals, video and audio input and output terminals, microphone
jacks, earphone jacks, etc.)
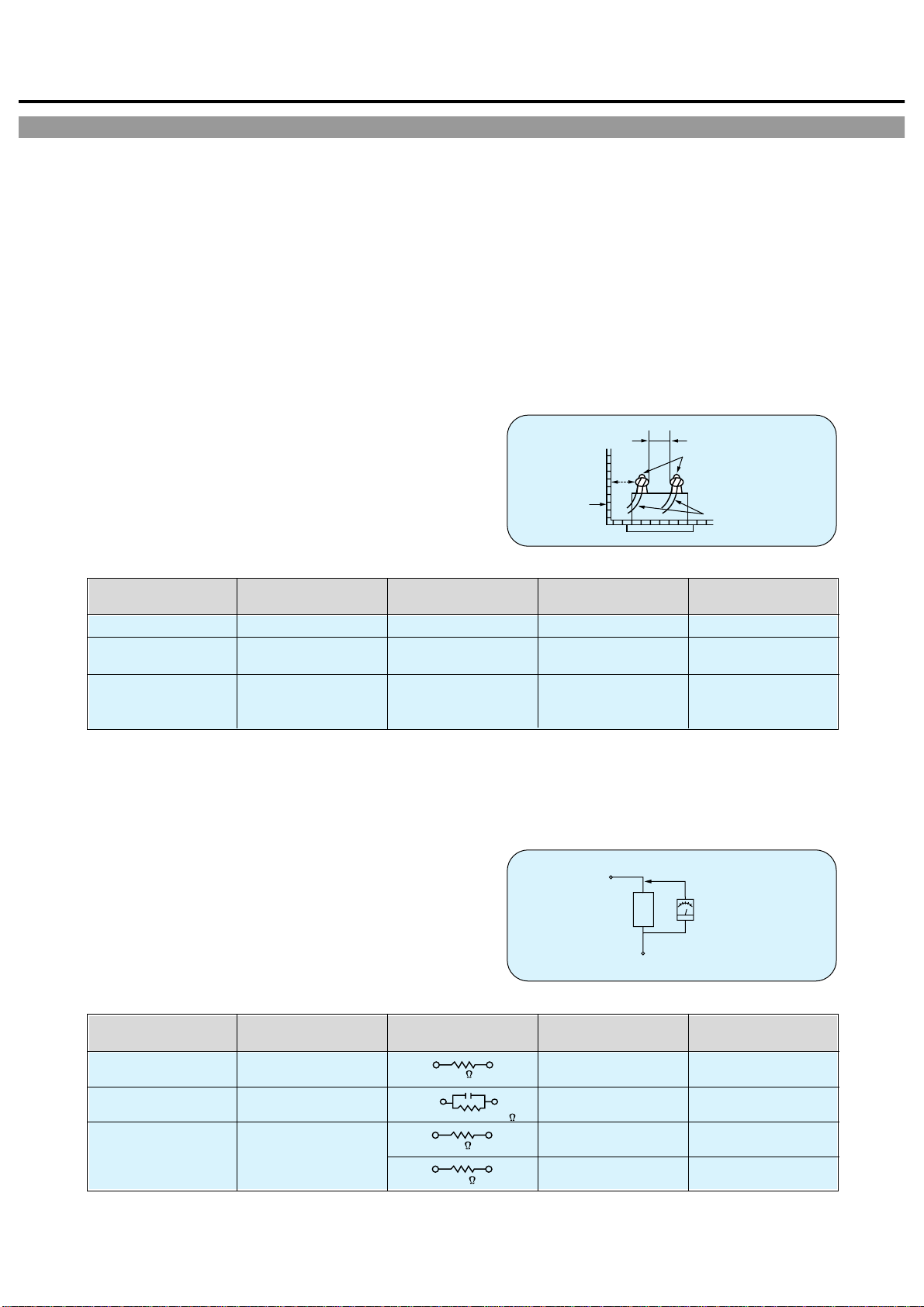
Measuring Method: (Power ON)
Insert load Z between B (earth ground, power cord plug
prongs) and exposed accessible parts. Use and AC voltmeter
to measure across both terminals of load Z. See figure and
following table.
Table 2: Leakage current ratings for selected areas
Note: This table unofficial and for reference only. Be sure to
confirm the precise values for your particular country and locality.
Z
Exposed
accessible
part
AC Voltmeter
(high impedance)
Earth Ground
power cord plug prongsB
Fig. 2
AC Line Voltage Region
Insulation Dielectric Clearance
Resistance Strength Distance (d), (d')
100V Japan ≥ 1 MΩ/500 V DC 1kV 1 minute ≥ 3 mm
110 to 130V
USA &
– – –
900V 1 minute ≥ 3.2mm
Canada
* 110 to 130 V Europe
≥ 10 MΩ/500 V DC 4 kV 1 minute
≥ 6 mm (d)
200 to 240 V Australia
≥ 8 mm (d')
(a: Power cord)
Fig. 1
d
Primary circuit terminals
Chassis
d'
a
AC Line Voltage Region
Earth Ground
Load Z Leakage Current (i)
(B) to:
100V Japan ¡ ≤ 1m A rms
Exposed accessible
parts
110 to 130 V
USA &
¡ ≤ 0.5 m A rms
Exposed accessible
Canada parts
¡ ≤ 0.7 m A peak Antenna earth
110 to 130 V Europe ¡ ≤ 2 m A dc terminals
200 to 240 V Australia ¡ ≤ 0.7 m A peak
Other terminals
¡ ≤ 2 m A dc
1k
1.5kµF
1.5k
2k
50k
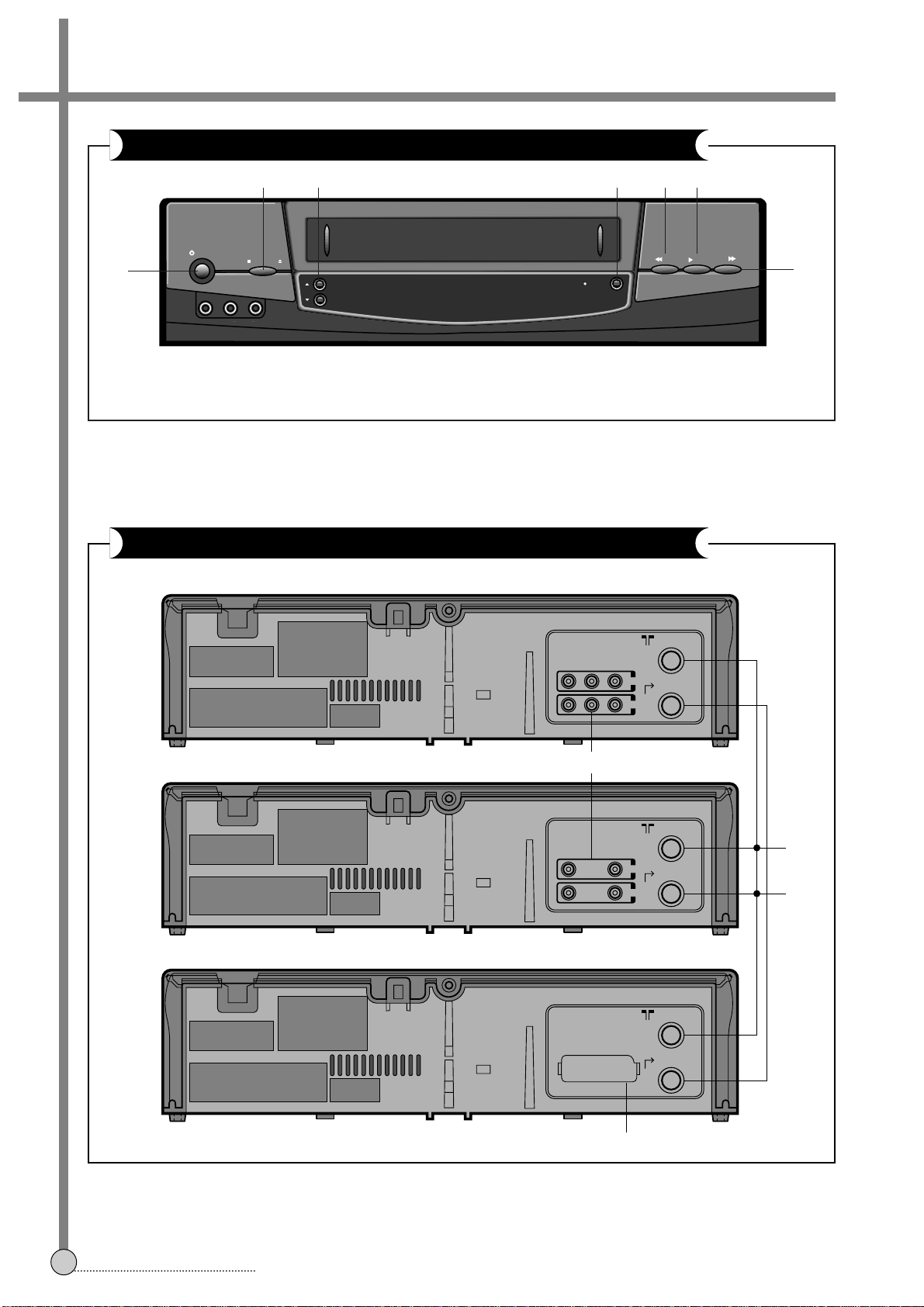
CONTROLS & FUNCTIONS
2
SECTION 1.
CONTROLS AND FUNCTIONS
CH.
STOP/ EJECT
STAND-BY
PLAY
REW
FF
VIDEO
AUDIOLR
REC/OTR
! STAND BY
@ STOP/EJECT
# CHANNEL UP/DOWN SELECTION
$ PLAY BACK
% REWIND/REVIEW
^ FAST FORWARD / CUE
& RECORD / OTR (ONE TOUCH RECORDING)
FRONT
! AV IN/OUT SOKET (PHONE)
@ EURO AV (AV IN/OUT)
# ANTENNA INPUT TERMINAL
$ ANTENNA OUTPUT TERMINAL
REAR
¡ NOTE: The above front panel to DV-K884W. for conforms the other sets (machines), refer to page 80, 81,
Front panel assembly.
!
@# &%$
^
OUT
IN
ANT IN
ANT OUT
VIDEOAUDIO
LR
!
ANT IN
VIDEOAUDIO
OUT
ANT OUT
IN
ANT IN
ANT OUT
EURO AV
@
#
$
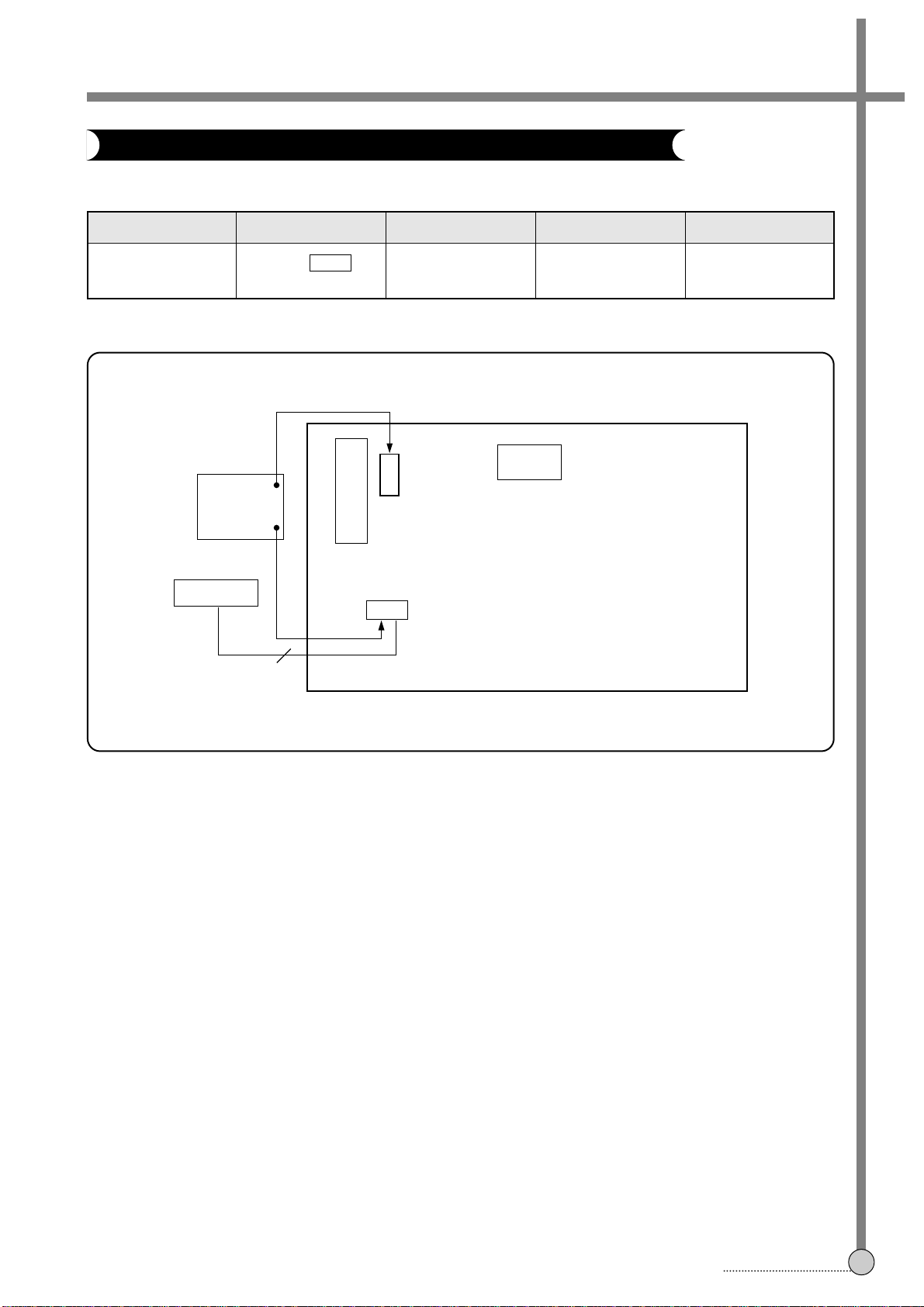
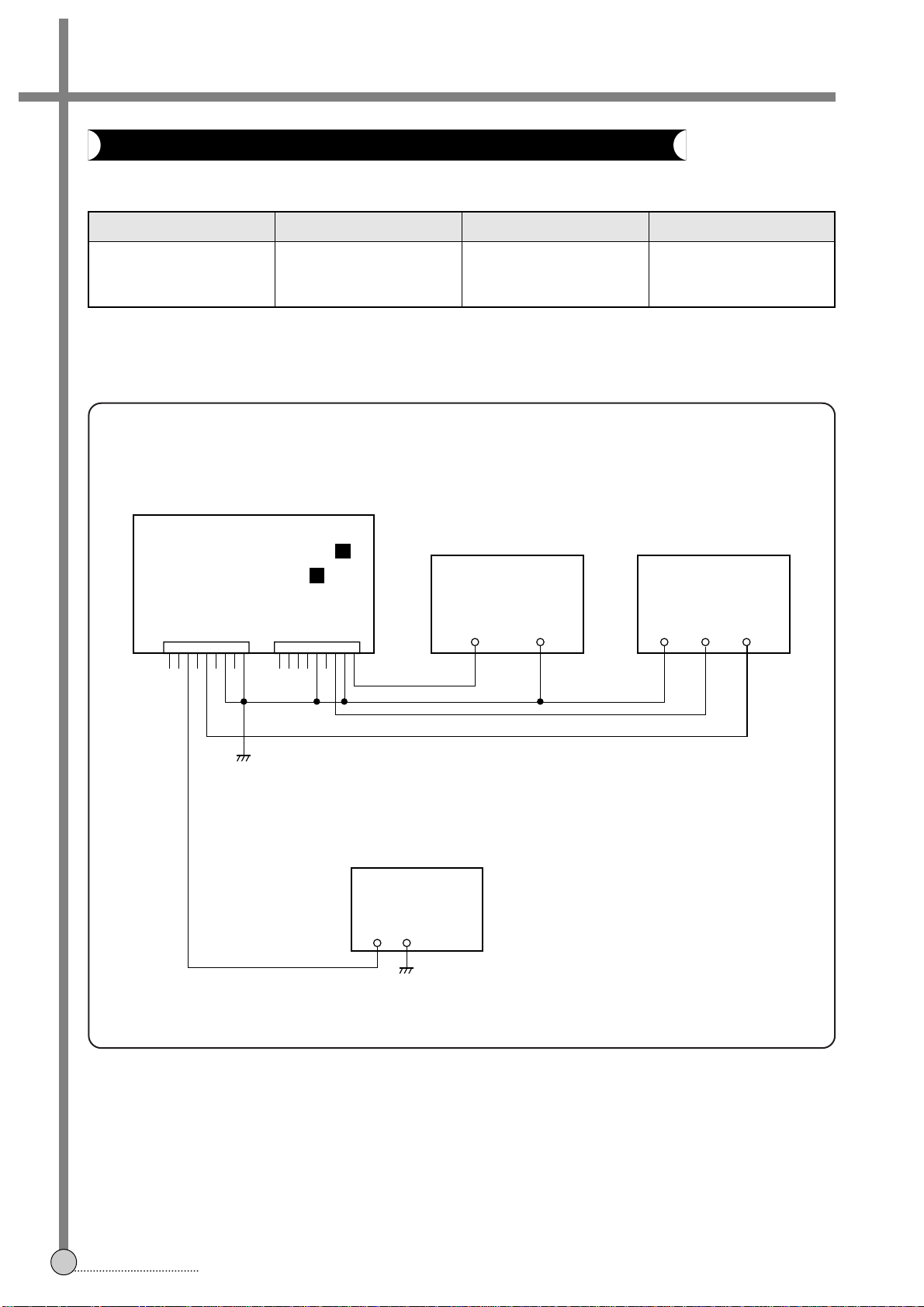
1. PLAYBACK PHASE
• CONNECTION METHOD
• ADJUSTMENT PROCEDURE
1) Play back the test tape. (DP-2)
2) Set the oscilloscope to the CHOP mode. Connect CH1 to the SW PULSE (PIN # of PT01).
3) Insert PATH JIG and Press “REC” button on the remote control.
4) Check the position of the V-sync from the rising edge of the SW pulse.
(Standard: 6.5H ± 0.5H)
ADJUSTMENT PARTS
CHECKING POINT
MEASURING EQUIPMENT
MODE TEST TAPE
Check
JP009
Oscilloscope Play DP-2
PT01 PIN $
V.OUT
ADJUSTMENTS
3
SECTION 2.
ELECTRICAL ADJUSTMENTS
2-1. SERVO CIRCUIT ADJUSTMENT METHOD
CH-2
OSCILLOSCOPE
CH-1
PATH JIG
JP009
VIDEO OUT
TOP VIEW
PRE-AMP
PT01
7
T
•
M
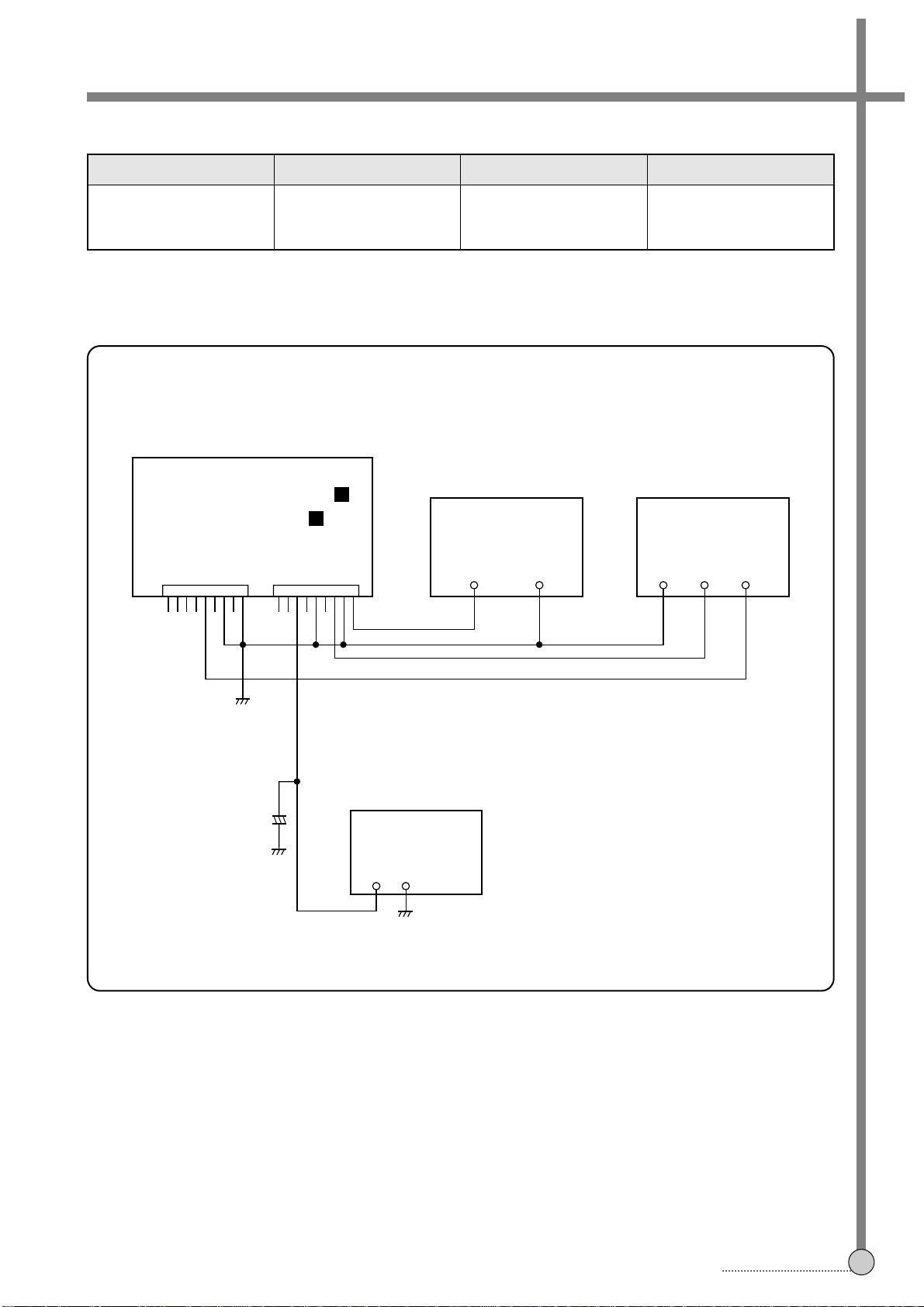
1. AFT
• AFT CONNECTION METHOD
IF MODULE PCB (TOP VIEW)
• ADJUSTMENT PROCEDURE
1) Connect the circuit as above connection diagram.
2) Set the each equipment setting as above description.
3) Adjust L101 to obtain 2.5 ± 0.15V DC Voltage at check point.
ADJUSTMENTS
4
ADJUSTMENT PARTS CHECKING POINT TEST EQUIPMENTS INPUT SIGNAL
P102
Signal Gen.
L101 Oscilloscope Refer to the following.
PIN &
Power Supply
2-2. IF MODULE CIRCUIT ADJUSTMENT METHODS
(COMPONENT SIDE)
SIGNAL
Modulation Method : 30% AM
fm : 400Hz
fc : 38.9MHz
SIGNAL LEVEL : 80dBµV
POWER SUPPLYGEN.
OUTPUT GND GND
CH1GND
0.5mS/DIV
50mV/DIV(10:1)
+9V +5V
R191
L101
9 P102 1 9 P101 1
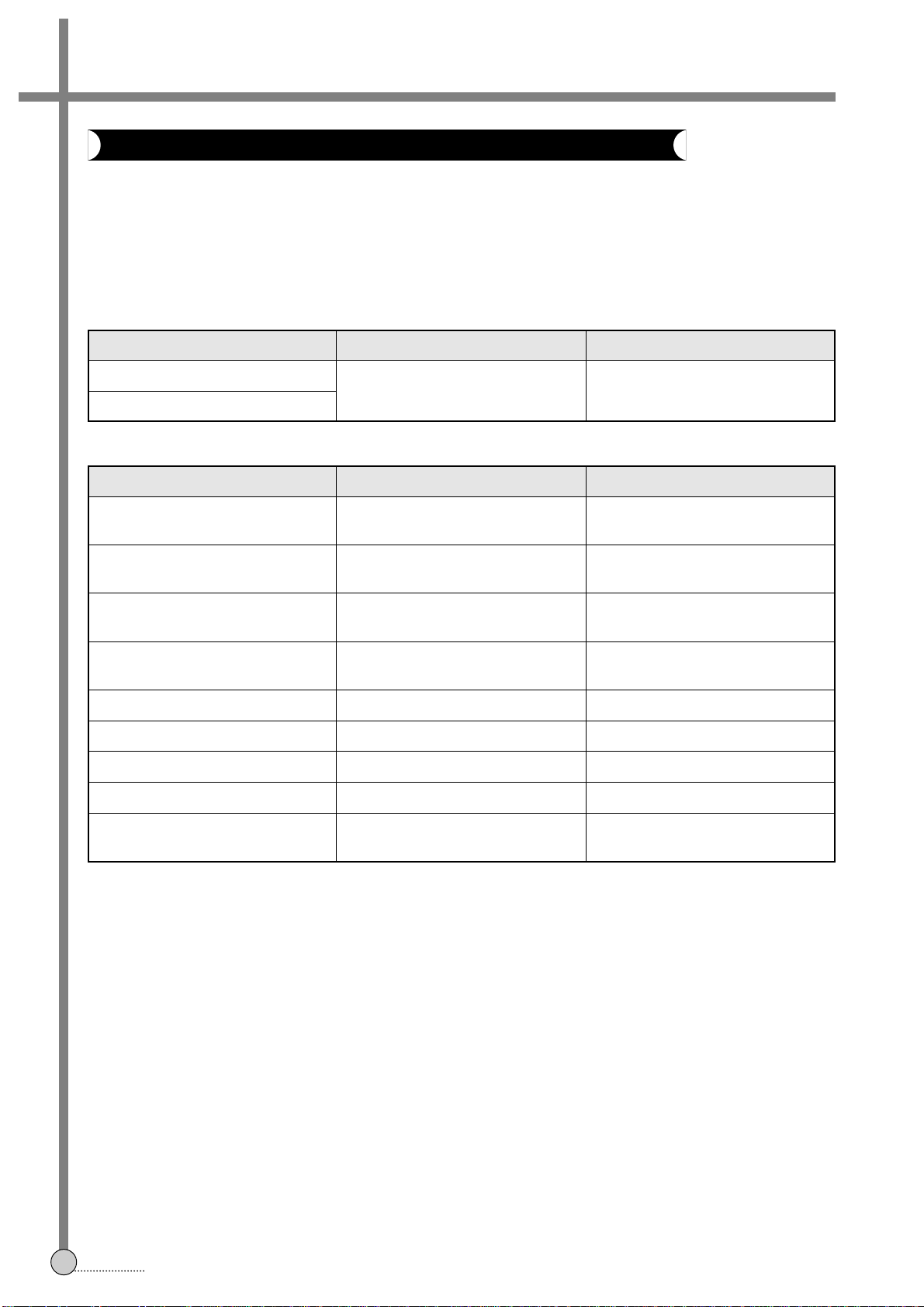
ADJUSTMENTS
5
2. RF AGC
• RF AGC CONNECTION METHOD
IF MODULE PCB (TOP VIEW)
• ADJUSTMENT PROCEDURE
1) Connect the circuit as above connection diagram.
2) Set the each equipment setting as above description.
3) Adjust R191 to obtain 6.0 ± 0.2V DC Voltage at check point.
ADJUSTMENT PARTS CHECKING POINT TEST EQUIPMENTS INPUT SIGNAL
P101
Signal Gen.
L191 Oscilloscope Refer to the following.
PIN &
Power Supply
(COMPONENT SIDE)
SIGNAL
Modulation Method : 30% AM
fm : 1KHz
fc : 38.9MHz
SIGNAL LEVEL : 95dBµV
POWER SUPPLYGEN.
OUTPUT GND GND
CH1
2.2µ/50V
+
GND
0.5mS/DIV
0.1V/DIV(10:1)
+9V +5V
R191
L101
9 P102 1 9 P101 1
CIRCUIT
6
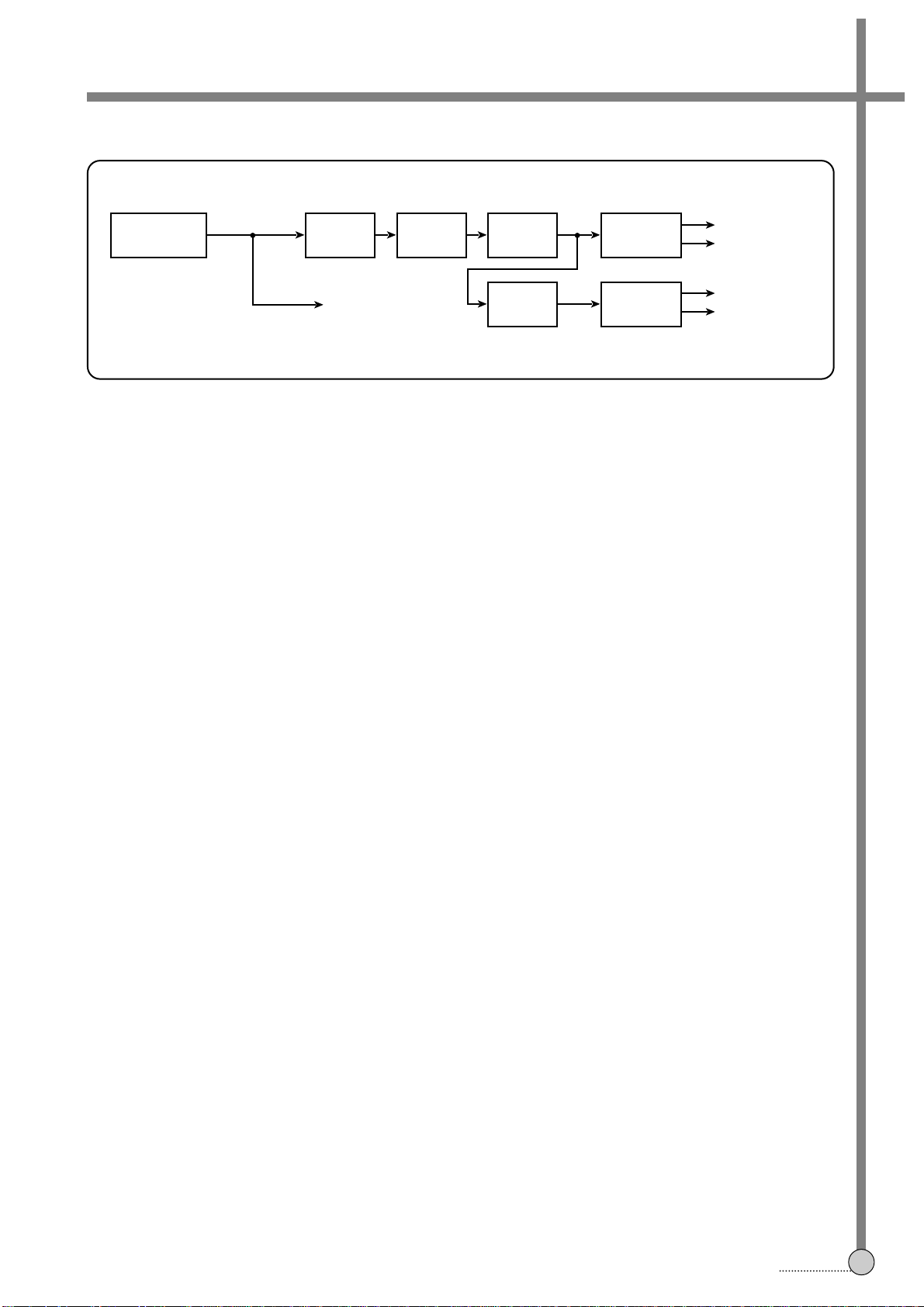
SECTION 3.
CIRCUIT OPERATION PRINCIPLES
1. OUTLINE
The part that supply DV VOLTAGE to each circuit change AC input voltage into DC voltage. It is based on
SMPS(switching mode power supply) system which is located on main PCB. SMPS module is composed of the
switching circuit and the transformer of the primary part and the recitifier circuit of the secondary part.
2. NAME AND OPERATION OF PINS ON SMPS MODULE
1) Primary Part
2) Secondary Part
3-1. POWER CIRCUIT
PIN NO NAME FUNCTION
1
AC INPUT SUPPLY AC INPUT VOLTAGE
2
PIN NO NAME FUNCTION
1 +37V
TURN VOLTAGE OF
TUNER (33V)
2 (F+4.5V)
F/L DISPLAY FILAMENT
VOLTAGE SUPPLY
3 (F-GND)
F/L DISPLAY DRIVE
VOLTAGE SUPPLY
4 –27V
F/L DISPLAY DRIVE
VOLTAGE SUPPLY
5 GND SECONDARY GND
6 GND SECONDARY GND
7 GND SECONDARY GND
8 6V EVER 5V, ON/OFF 5V
9 12.4V
CAP MOT, DRUM MOT (12V)
LOADING MOT (12V)

CIRCUIT
7
3. GENERAL CIRCUIT OPERATION
The circuit shown is a highly accurate 37V, 12.4V, 6.0V, -27V, 4.5V, 20W secondary regulated flyback power supply
that will operate from 85V to 265 VAC input voltage.
The input voltage is rectified and filtered by D801 and C1. L801, C801, C804 reduce conducted emissin current. C806,
L801, C805 reduce common mode noises. R801 is ESD path resistor.
Voltage feedback is obtained from the transformer (T11) bias winding, which eliminates the need for optocoupler and
secondary-referenced error amplifier. High-Voltage DC is applied to the primary-high-voltage DC is applied to the
primary-winding of T11.
The other side of the transformer primary is driven by the integrated high-voltage MOS FET-transistor within the
TOP225(IC11). The circuit operates at a switching frequency of 100KHz, set by the internal oscillator of the TOP
(IC11). The clamp circuit impelemented by DZ11, D11, C17 and R13 limits the leading-edge voltage spike caused by
transformer leakage inductance to a safe value.
The 37V power secondary winding is rectified by DC1, C25. The 12.4V power secondary winding is rectified and
filtered by D24, C24. The 6.0V power secondary winding is rectified and filtered by D23, L22, C23. The -27V power
secondary winding is rectified and filtered by DC2 and C22. The F(+) and F(–) power secondary winding is rectified
and filtered by DC3, C21 and C29.
A IC21(KA431) shunt regulator directly senses and accurately regulates the output voltage. The effective output
voltage can e file turned by adjusting the resistor divider formed by R24, R25 and R26. Other output voltages are
possible by adjusting the transformer turns ratio.
The IC21(KA431) regulates the output voltage by controlling optocoupling LED current (and IC11 duty cycle) to
maintain an average voltage of 2.5V at the IC21 input pin.
Divider R24, R25 and R26 determine the actual output voltage. C27, R27 rolls off the high frequency gain of the KA31
for stable operation.
R23 limits optocoupler LED current and determines high-frequency loop gain. SPFT start capacitor C26 increases
optocoupler current turn-on to limit the duty cycle and down the risting output voltage. C26 has minimal effect on the
control loop during normal operation. R22 dicharges soft start capacitor C26 when input power is removed.
The output of the T11 bias winding is rectified and filtered by D12, C11 and R11 to create a typical 12V bias voltage
R12, R13 together with the control pin dynamic impedance and capacitor ESR establish a control loop pole-zero pair.
C13, R12 also determines the auto frequency and filters internal gate drive switching current.
CIRCUIT
8
1. LA71501BM (QIP 80 PIN): NORMAL AUDIO & Y/C SIGNAL PROCESSING IC
1) Applicable to Multi system (PAL-GBI,MESECAM,3.58NTSC, 4.43NTSC and NAP-GBI)
2) Built-in NAP circuit to convert NTSC to PAL.
3) Normal audio signal processing circuit. (self-alignment for record bias)
4) Buit-in distinction SECAM signal circuit (MESECAM)
5) Built-in Record and Playback FM-EQ function (Switching the specific characteristic is possible by SERIAL CONTROL)
6) Y/C separation using comb filter
7) Built-in Input Switching circuit for 3 Video/Audio input
8) Using serial control by I
2
C-BUS
9) Complete Adjustment free
10) Crosstalk reduction by CCD IC for exclusive use (Color Comb filter is unnecessary)
2. LA70001(2CH),LA70011(4CH),LA70020(6CH): PRE-AMP IC
1) AGC circuit is built in this IC (no record current adjustment is required)
2) Built-in the playback signal ENVELOPMENT detection circuit for Auto tracking adjustment.
3. LC89978M: MULTI CCD DELAY LINE IC
1) Built-in Comb Filter for color noise reduction
2) Built-in 1H Delay Line for luminance circuit
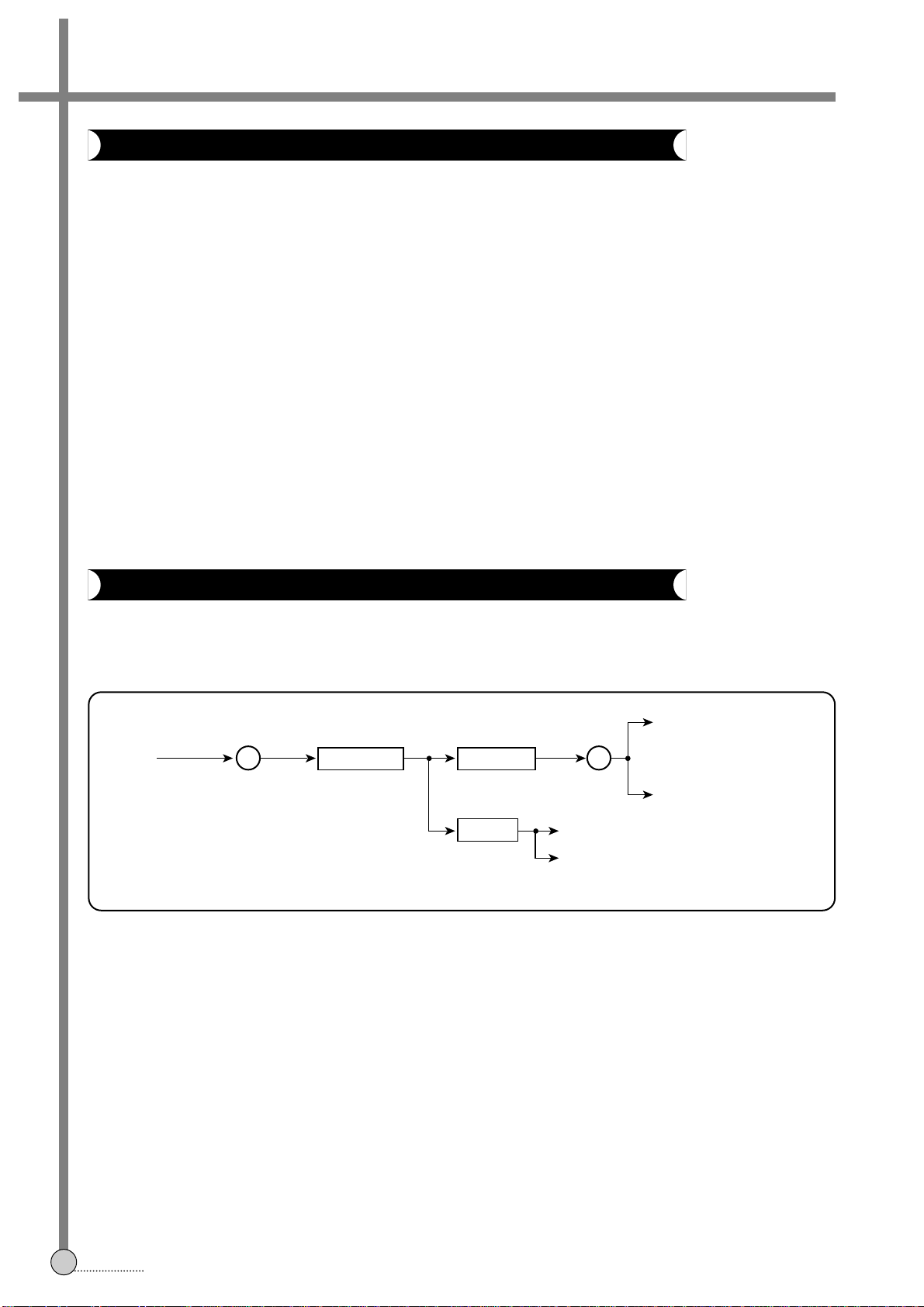
1. RECORD PROCESSING
The video input signal is selected by AV 1CHIP switching IC among EXT VIDEO INPUT(28pin), LINE VIDEO
INPUT(32pin) and IF VIDEO INPUT(30pin), is supplied to the 35th pin of AV 1CHIP IC.
The input video signal is then automatically adjusted to suitale level by the built-in VIDEO AGC circuit and supplied to
SYNC separation and FBC(feedback clamp) part respectively .
SYNC signal is obtained from the composite video signal ,is supplied to the 93rd pin of MICOM and the
11th pin of PRE-AMP IC to determine the presence of signal ,selection of PAL/NTSC and is using for SERVO control,
In PRE-AMP, is using for the HEAD-AMP switching timing and AGC circuit for self-adjustment of the record bias.
The input signal through FBC is processed in luminance signal processing part and chrominance signal processing part
independently.
3-2. KEY FEATURES OF VIDEO IC AND ITS RELATIVES
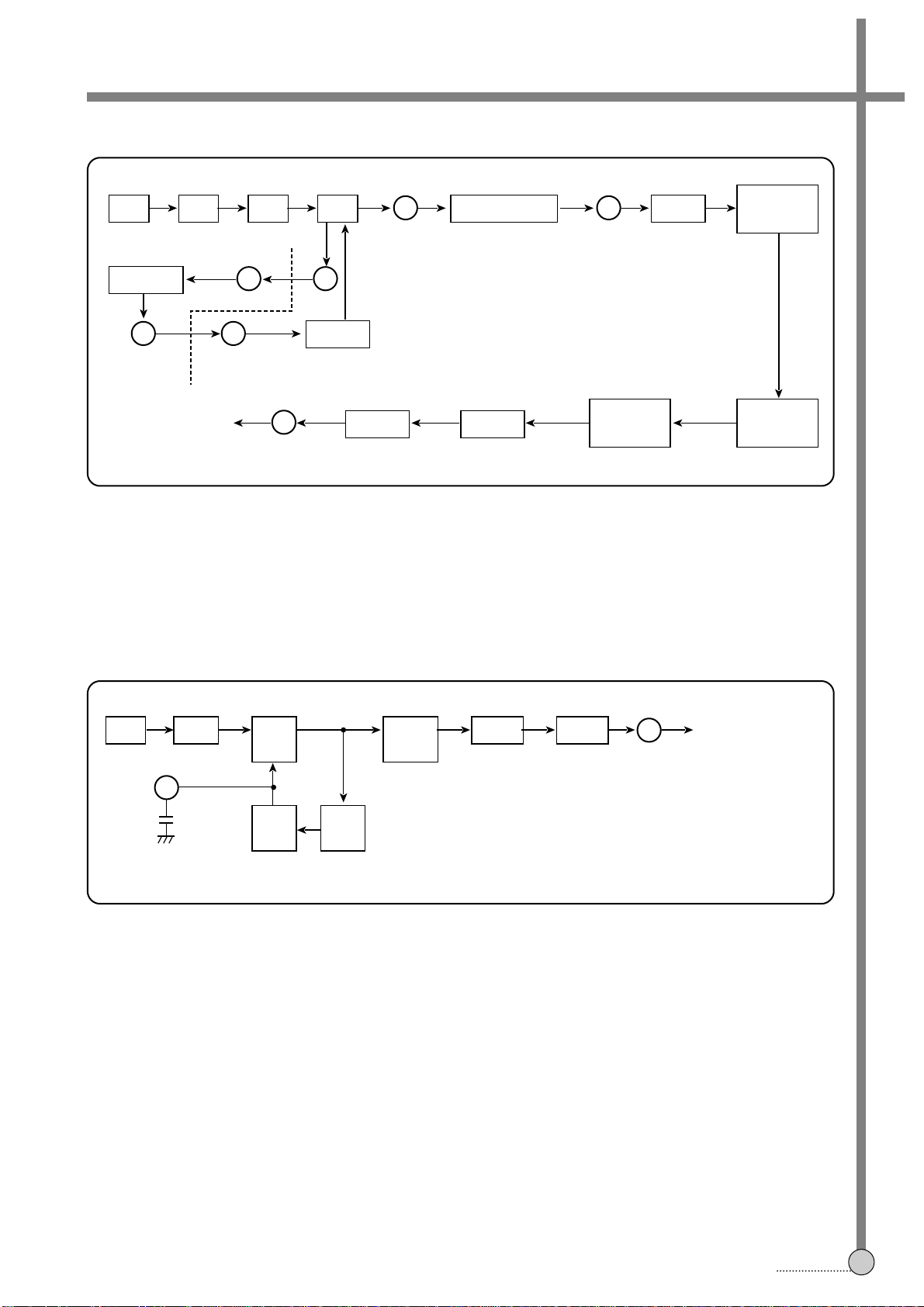
3-3. RECORD AND PLAYBACK PROCESSING CIRCUIT
35 37
VIDEO
INPUT
VIDEO AGC SYNC SEP
FBC
MICOM 93rd PIN
LUMINANCE SIGNAL PROCESSING
CHROMINANCE SIGNAL PROCESSING
PRE-AMP IC 5th PIN
FIG.1 Record Processing
¡ NOTE: Pre-Amp IC varies according to the types of machines. We conform to 4HD’s standard.
CIRCUIT
9
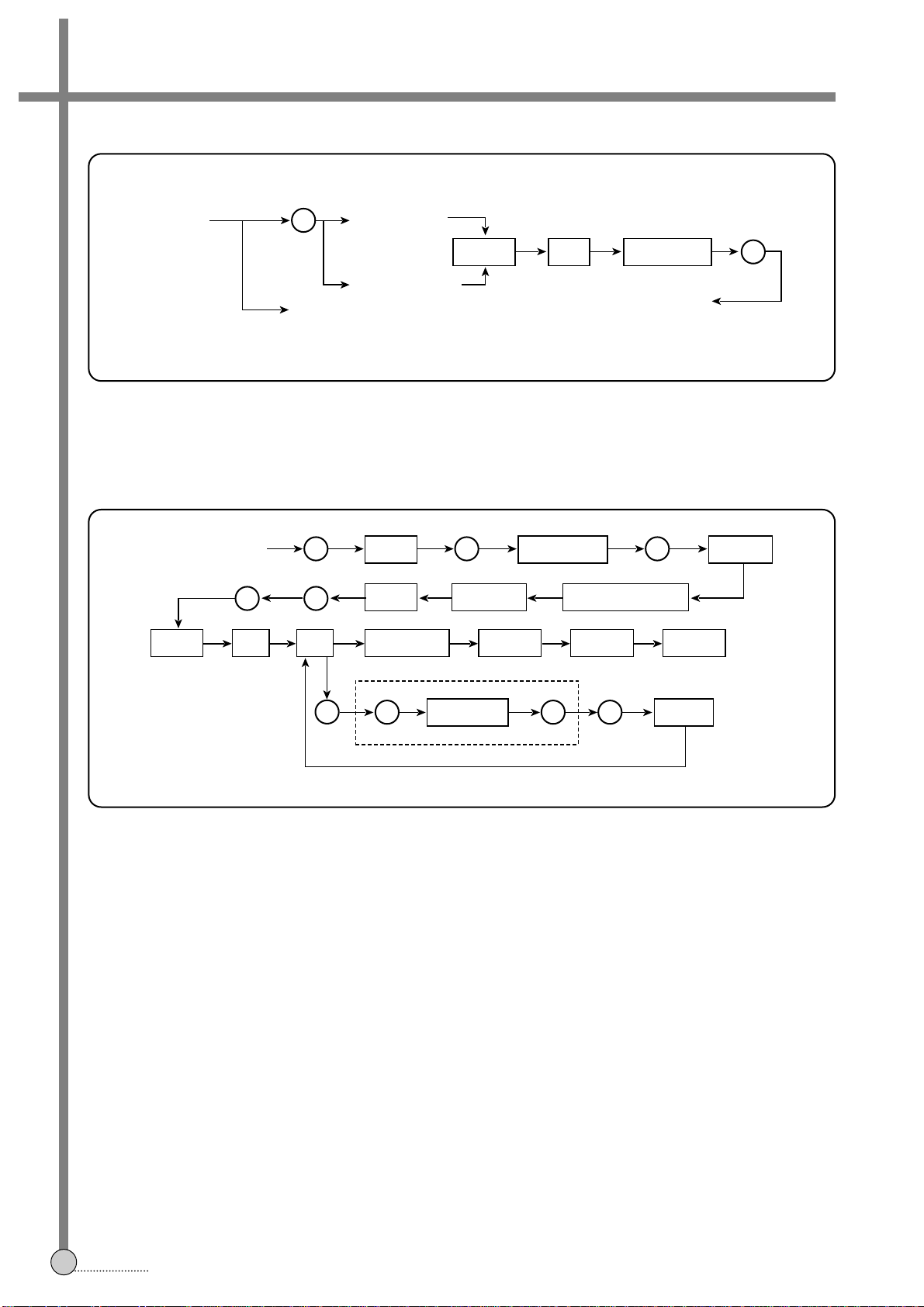
1)LUMINANCE SIGNAL PROCESSING (RECORD)
The input signal through FBC is reduced 6dB of its level and then the pure luminance signal is obtained by LOW-PASS
FILTER.
In YNR(Luminance Noise Reduction) circuit,the noise is eliminated using the original signal and 1H delayed signal.
The detail enhancer enhances overall high-frequency response, so an object with fine lines can be seen more clearly
during playback.
The nonliner Emphasis and Main Emphasis can minimize the triangular noise susceptible to frequency modulation.
The FM-modulated luminance signal is supplied to PRE-AMP through RECORD EQ for compensating the high frequency
response related to HEAD characteristic, where it RECORD EQ characteristic is determined by LSB 1-4bits of Group 4.
2)CHRONOMINANCE SIGNAL PROCESSING (RECORD)
The pure chrominance signal is obtained by BPF1(f
sc
:4.43MHz or 3.58MHz) through FBC then is supplied to ACC AMP.
The gain of ACC AMP is controlled by DC voltage at 13th pin.
The ACC AMP OUTPUT is input to MAIN CONVERTER and the main converter down-converts the chromiance signal to
627 or 629KHz.
The down-converted signal is again filtered by the COLOR LOW PASS FILTER, so the pure chrominance components is
maintained.
Meanwhile, the burst level of the ACC AMP output signal is detected by the burst gate and it determines the activation of
color killer.
The final signal through color killer is supplied to PRE-AMP IC10th pin after passing 14th pin.
18
25
407
26
FBC
1H DELAY
(LC89978M)
PRE-AMP 9th PIN
1/2 LPF YNR
BUFFER
DETAIL
ENHANCER
N.L.
EMPHASIS
MAIN
EMPHASIS
CLAMP
FM MODREC EQ
REC EQ
5 42
14
13
FBC BPF1 C-LPF KIL PRE-AMP 10th PINACC
AMP
REC
DET
REC
BGA
MAIN
CONV
FIG.2 Luminance Signal Processing (RECORD)
FIG.3 Chrominance Signal Processing (RECORD)
CIRCUIT
10
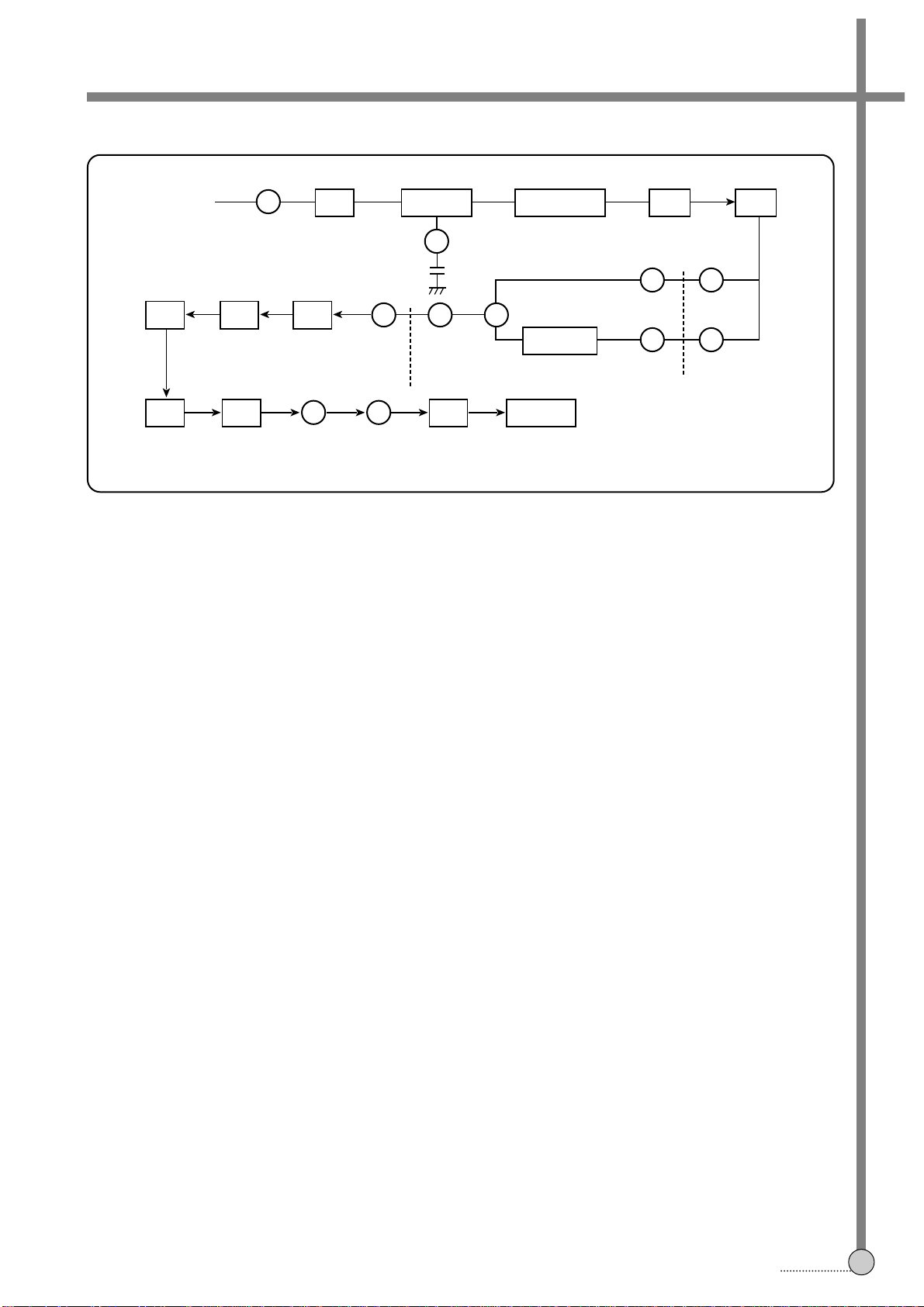
2. PLAYBACK PROCESSING
The playback ENVE signal from PRE-AMP is supplied to 15th pin of A/V IC for processing the PAL luminance and
chrominance.
The output signal through Y/C MIX after each processing of chrominance and luminace is supplied to the 18th pin of
OSC IC through 38th pin.
1)LUMINANCE SIGNAL PROCESSING (PLAYBACK)
The ENVE signal is equalized by the PB-EQ, which flatterns the whole frequency characteristic.
PB-EQ is controlled by SERIAL CONTROL and determined by the GROUP 6, 6-8bits.
The PULSE characteristic is improved by passing the phase compensation circuit.
Double Limiter restores the high frequency portion and elimiantes the SPIKE NOISE and AM components.
The FM modulated signal which is recorded is demodulated and then the RECORD NONLINER EMPHASIS characteristic
is compensated by DE-EMPAHASIS through YNR.
Double High Pass Noise Canceller eliminates the high frquency noise against playback signal.
The picture control circuit improves the picture sharpness,while picture control is determined by 1-4bits of Group 8 on
controlling the SERIAL.
38
35
Y/C MIX
PRE-AMP
7th PIN
PB ENVE
OSD IC 18th PIN
luminance signal
processing
chrominance signal
processing
VIDEO AMPFBC
15
25
42
5 7 40
17
PB-EQ
PHASE COMPPRE-AMP 7th PIN
(LC89978M)
20
26
FM AGC
DOUBLE LIMITER
CLAMP
FM DEMOD
SUB-LPF
LPF YNR N.L. DE-EM DHP NC
Y/C MIX CLAMP
PIC CTL Y/C MIX
FIG.4 Playback Processing
FIG.5 Luminance Signal Processing (PB)
2)CHROMINANCE SIGNAL PROCESSING (PB)
The down converted chrominance PAL-COLOR signal is obtained by LPF from PB ENVE.
And then the signal is up-converted to 4.43MHz or 3.58MHz by the MAIN CONVERTER.
The redundant harmonice is filtered out by the BPF, and then the signal is applyed to the CCD IC to reduce the
chrominance crosstalk.
The NTSC PLAYBACK is possible on PAL/SECAM SYSTEM by the NAP circuit, the activation of which is determined by
7-8bits of GROUP 7 on controlling the SERIAL.
The signal is mixed with the Y/C after passing the Color Noise Canceller circuit.
CIRCUIT
11
15
13
483
PRE-AMP
7th PIN
LPF
AMP
BPF2 BPF1
ACC AMP MAIN CONV
LPFKIL
NAP BPF CNC Y/C MIX
2H DELAY
(LC89978M)
501
+
1352
46 45
FIG.6 Chrominance Signal Processing (PB)
CIRCUIT
12
1. VIDEO SIGNAL FLOW
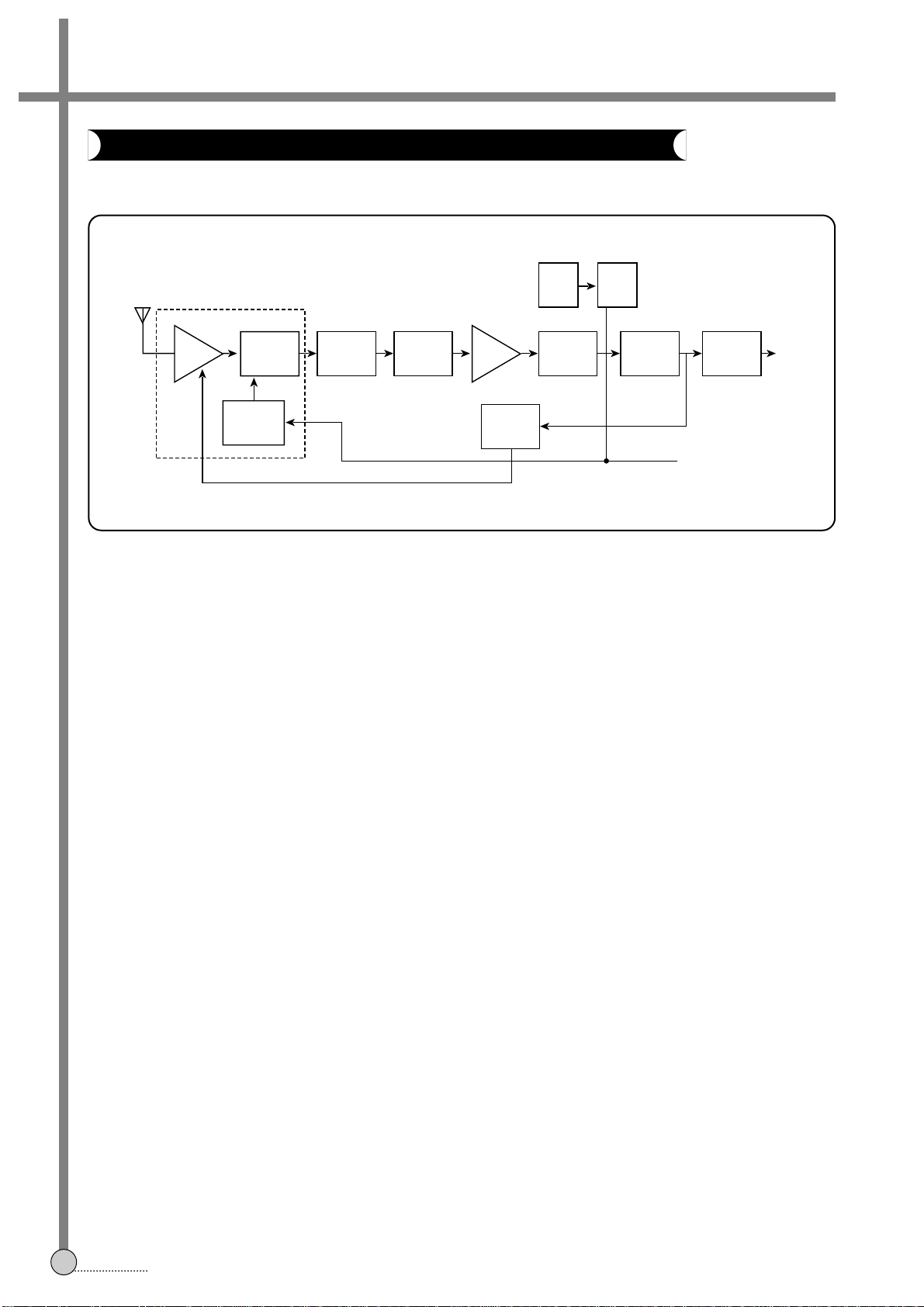
The signal from the ANT is amplified for selectivity, to decrease image interference, and increase S/N using the RF
AMP. The RF signal at the MIXER is subtracted from the LOCAL OSC frequency using the upperside band method, to
change is into the IF signal; 38.9MHz. The IF signal converted from the RF signal in the tuner block is amplified by
about 28dB to increase S/N in the pre-amp block. The reason for thesis that the SAW filter has its own insertion loss
of about-18 to -22dB. The SAW filter is a kind of BPF, used to remove the near channel harmonics and make the
desired frequency response. The IF AMP desired of about 60 to 70dB gain for receiver sensitivity and selectivity. The
vision IF AMP consists of three AC-coupled differential amplifier stages; each stage uses a controlled feedback
network called AGC. To maintain the video output signal at a constant level the automatic control voltage is generated
according to the transmission standard. For negative modulation in the PAL standard the peak-sync level is detected.
The AGC detector charges and discharges the AGC capacitor to set the IF gain and the tuner gain. We can also
adjust the tuner AGC voltage take over point. This allow the tuner and the IF SAW filter to be matched to achieve the
optimum IF input signal. The IF amplifier output signal is fed to a frequency detector and to a phase detector. The
frequency detector is operational before lock-in. A DC current is generated which is proportional to the frequency
difference between the input signal and the VCO frequency. The control voltage for the VCO is provided by the phase
detector. The demodulate output signal is fed via an integrated LPF (about 12MHz) to the video amplifier for
suppression of the carrier harmonics.
The VCO operates with a symmetrically-connected reference L-C circuit, running at the double vision carrier frequency
(77.8MHz) to decrease the frequency error. Fequency control is performed by an internal varicap diode. The voltage
used to set the VCO frequency to the actual double vision carrier frequency, is also amplified and converted to give the
AFC output current. The AFC output is fed to the µ-COM to change the LOCAL OSC frequency and for channel
searching. The VCO signal is divided by-two in a travelling wave divider, which generates two differenctial output
signals with exactly 90 degrees phase difference, independent of frequency. The video signal passing through the
5.5MHz sound trap is fed to the buffer.
3-4. IF CIRCUIT OPERATION
RF
AMP
MIXER
PRE-
AMP
LOCAL
OSC
AGC
DET
SAW
FILTER
VIDEO DET
& DEMOD
TUNER
IF
AMP
SOUND
TRAP
VCO AFC
BUFFER
VIDEO
OUT
µ-COM
2. PAL AUDIO FLOW (Two carrier) (Hi-Fi only model)
The FM sound intercarrier signal passing through the 5.5MHz/5.74MHz (DK: 6.5MHz) sound BPF is fed to a limiter
amplifier before it is demodulate. This gives high sensitivity and AM suppression. The limiter amplifier consists of
seven internal AC-coupled stages, minimizing the DC offset. The FM-PLL demodulator consists of an RC-oscillator,
loop filter and phase detector. The oscillator frequency is locked on to the FM intercarrier signal from the limiter
amplifier. As a result of this locking, the RC-oscillator is frequency modulated. The modulating signal voltage is used to
control the oscillator frequency using this technique, the FM-PLL works as a FM demodulator. The audio signal(AF1:
L+R/2, AF2:R+pilot(AM)) passing through the stereo/dual sound processor. Its identification ensures safe operation by
using internal digital PLL technique with extremely small bandwidth, synchronous detection and digital
integration(switching the maximum 2.6s; identification concerning the main functions).
The audio signal(L, R) is amplified and coming out of the stereo/digital sound processor.
CIRCUIT
13
VIDEO DET
& DEMOD
VIDEO BLOCK
intercarrier
SOUND
BPF
LIMITER
AMP
FM PLL-
DEMOD.
AF
AMP
FM PLL-
DEMOD.
DIGITAL
INTEGRATOR
AUDIO OUT (L)
AUDIO OUT (R)
STEREO(LOW)
DUAL(LOW)
CIRCUIT
14
4. TM BLOCK
The TUNER and MODULATOR which is separated to each module conventionally, is presently united to one block
(TM block)
(a) PLL METHOD AND I
2
C-BUS CONTROL
The RF OUTPUT channel can be varied from 22CH to 69CH by remote control using PLL method and I
2
C-BUS
control.
Moreover, SYSTEM(PAL, MESECAM, NTSC), SOUND CARRIER FREQUENCY, AND TPSG(TEST PATTERN
SIGNAL GENERATOR) can be changed by remote conrol as well.
The P/S ration, white clip, power saving, etc., also can be controlled only by changing a I
2
C-BUS data according to
the designer‘s intention.
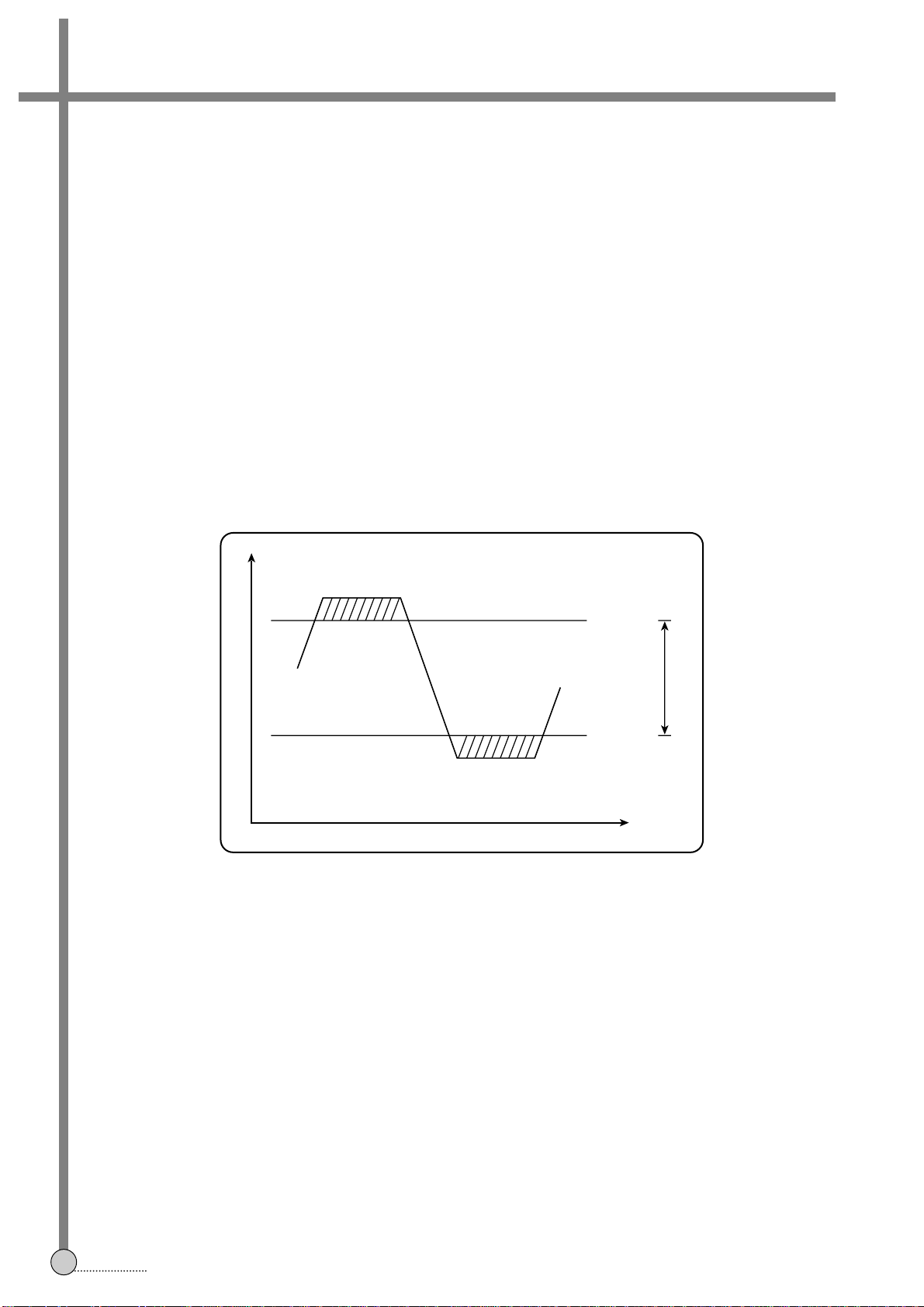
(b) DIGITAL AFT METHOD
Conventionally, when the frequency deviates, the variation of AFT output from IF circuit was compensated by
feedbacking it to TUNER AFT input.
On the other hand, if AFT, which is currently adopted to these models from IF circuit deviates the window range,
the VT value is changed to maintain the AFT voltage to be within window range by checking AFT(+) and AFT(–) on
MICOM.
VOLTAGE
AFT(+)
AFT(–)
3V
WINDOW
FREQ.
2V
CIRCUIT
15
3-5. NORMAL AUDIO SIGNAL PROCESSING(LA71501BM)
The circuitry of Normal AUDIO part is similar to that of the conventional Normal AUDIO part in case of EE and PB
mode, but in REC mode, due to the internal opeation of self-alignment, it shows a lot of differences.
1. EE MODE
LA71501BM has 3-input VIDEO/AUDIO switching circuitry internally, and its switching is controlled by the serial data
dispatched from MICOM.
In the case of Hi-Fi models, only One input is used. The Normal AUDIO signal from Hi-Fi Audio part is divided by the
resistor, R202 and R203 and then supplied to the 73rd pin of LA71501BM. Its level is automatically controlled by ALC
and then the amplified signal through LINE AMP is obtained at the 77th pin.
The signal from C208 is supplied to REC AMP after the divider circuit (R204, R205, R207) and also to the Hi-Fi IC
BH7804K.
The ALC point can be adjusted by R208 and R209, the adjustment of which is closely related to the REC level in REC
mode.
The ALC time can be adjusted by R201 and C201.
At the MONO model, 3 input VIDEO/AUDIO switching circuit (Internal IC) is fully used. IF audio signal is supplied to
pin 71, AV signal to pin 73. Additionally F/AV signal is not used. Afterwards, Mono model is the two input system.
2. PB MODE
The PB signal picked up from AUDIO HEAD is firstly processed in the frequency characteristic compensator which is
composed of R220 and C214 (EP: C214+C215) and then supplied to the 7th pin.
The input signal passes through EQ AMP, and LINE AMP, so its output signal is finally obtained from the 77th pin.
The circuitry and its operation of EQ AMP is identical to the conventional EQ AMP.
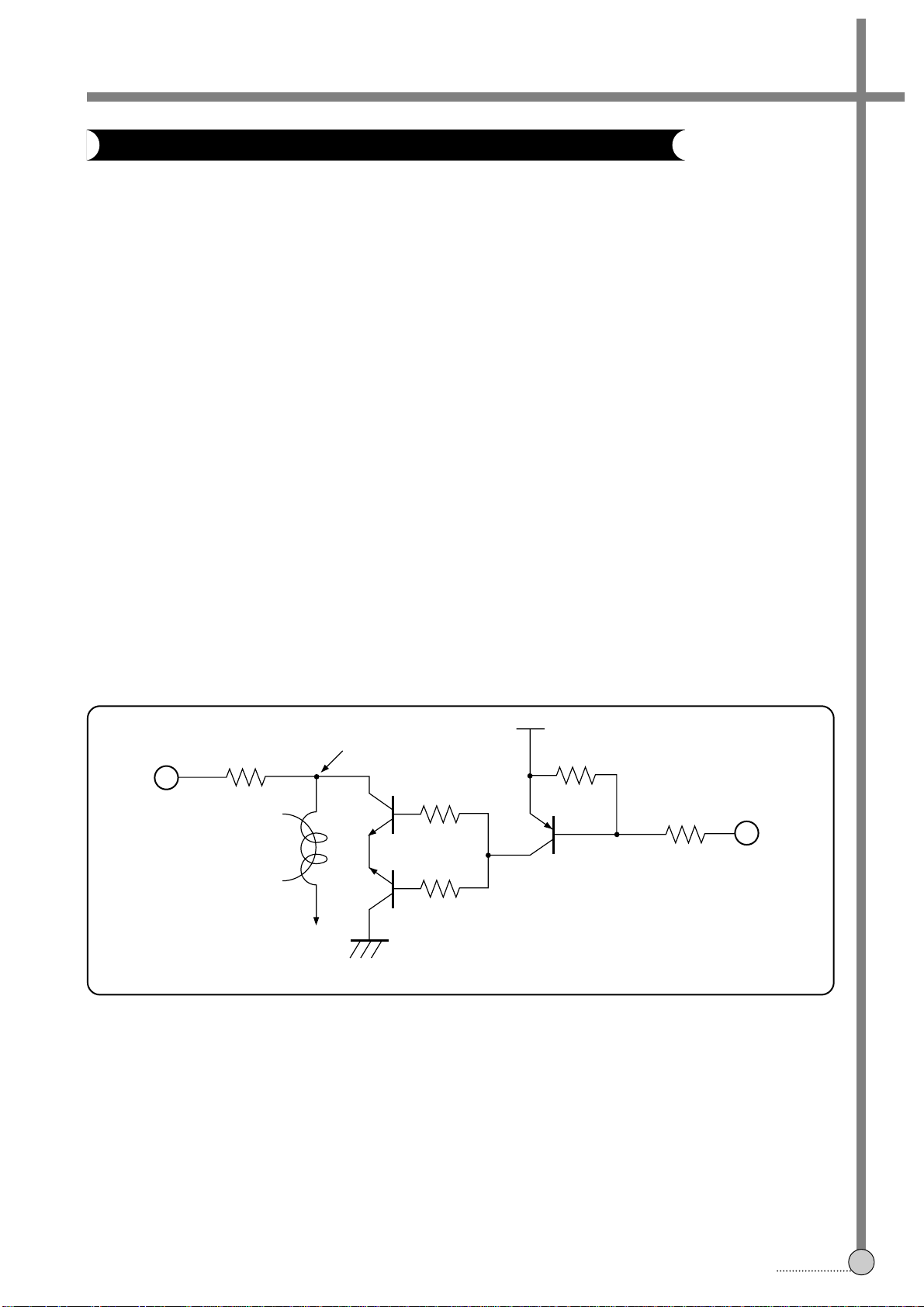
3. REC MODE
1) AUDIO SWITCHING CIRCUIT
When the AUDIO S/W signal at the 80th pin is “H”, the point at the AUDIO HEAD of the external switching circuit is
opened electrically (EE/PB=GND), so the COIL starts to oscillated.
2) As long as the voltage difference between VCC and the 5th pn is maintained at 2.0~4.3V, the COIL oscillates. In
oher words, the COUL maintains to oscillate only if the voltage at the 5th pin is 0.7~30Vp-p.
Especially, when the R/P and FE HEAD impedance is at the center, the voltage at the 5th pin should be maintained
at 1.85Vp-p, and, if not, when the HEAD impedance is MAX or MIN, the voltage at the 5th pin is liable to deviate the
ranges of 0.7~3.0Vp-p.
The higher the FE HEAD impedance is or the lower the R/P HEAD impedance is, the higher the voltage at the 5th
pin increases.
The AC signal is put on the DC voltage at the 5th pin, and it shows the internal AUTO BIASing.
The control signal at the 6th pin controls the TR(Q205) to ON/OFF, by which the AUTO BIASing is controlled.
5
80
BIAS COIL
5th PIN
R218
REC: OPEN
EE: GND
Q203
Q204
R216
VCC
R215
Q202
R214
A-H
S/W
R217
R/P
HEAD
External Switching Circuit
CIRCUIT
16
3) The output AUDIO signal at the 1st pin through REC AMP is recorded on HEAD after being mixed with the 70KHz
AC BIAS signal.
At the same time, the output AUDIO signal is supplied to the 3rd pin and then filtered by 60KHz HPF, so only the
70KHz AC BIAS signal is passed.
The pure 70KHz AC BIAS signal is then compared to the voltage of 440mV at the comparator, so the AC BIAS
signal is controlled to maintain at 440mV.
4) The recording current is determined by the 440mVrms BIAS signal and the resistance between the 1st and the 3rd
pin.
* The method to set the recording current.
BIAS=440mVrms ÷ the resistance between the 1st and the 3rd pin.
ex) 440mVrms ÷ 1.8K OHM = 244µA
where, only the low error, G type resistor should be used here.
As a rule of thumb, the resistance between the 1st and the 3rd pin should range from 1.0 ohm to 2.2K ohm.
5) The conventional AUDIO circuitry uses a peaking COIL to enhance the high frequency region, but the LA71511M
uses the resistance of R/P HEAD.
Accordingly, The resistor and the capacitor is used to fit the frequency characteristics.
4. BIAS COIL
For normal operation of AUTO BIAS, the oscillating voltage of R/P HEAD is over 40Vp-p, A/E HEAD is over 20Vp-p,
and the FE HEAD is over 40Vp-p.
Especially, the erasing current of F/E HEAD ranges from 130 to 280mA, and it should be 180mA when the HEAD
impedance is at the center.
1. SPECIAL FEATURES
BH7804K processes the conventional Hi-Fi audio and additionally, contains special parts as the below.
(1) As ± 2 power source formula is adapted, decrease of coupling capacitor is possible the REGULATOR circuit is
built in.
(2) Built in I
2
C bus control decoder circuit which has two lines formula, each mode for the inside of IC is set up by
serial data.
(3) Reverse characteristics system during recording and playback are used in both the PNR (Peak Noise Reduction)
processor and FM MODEM. And it can be simultaneous adjustment of carrier frequency and FM
deviation/playback level. And it can be independent adjustment of FM deviation/playback level. (The adjustment
of Lch and Rch is simultaneous.)
(4) Slope control FM switching noise correction circuit is built in.
(5) Auto adjust circuit of VCO and BPF making use of Fsc (3.58MHz) is built in. It is possible to adjust changelessly
without drift by board mounting stress and time.
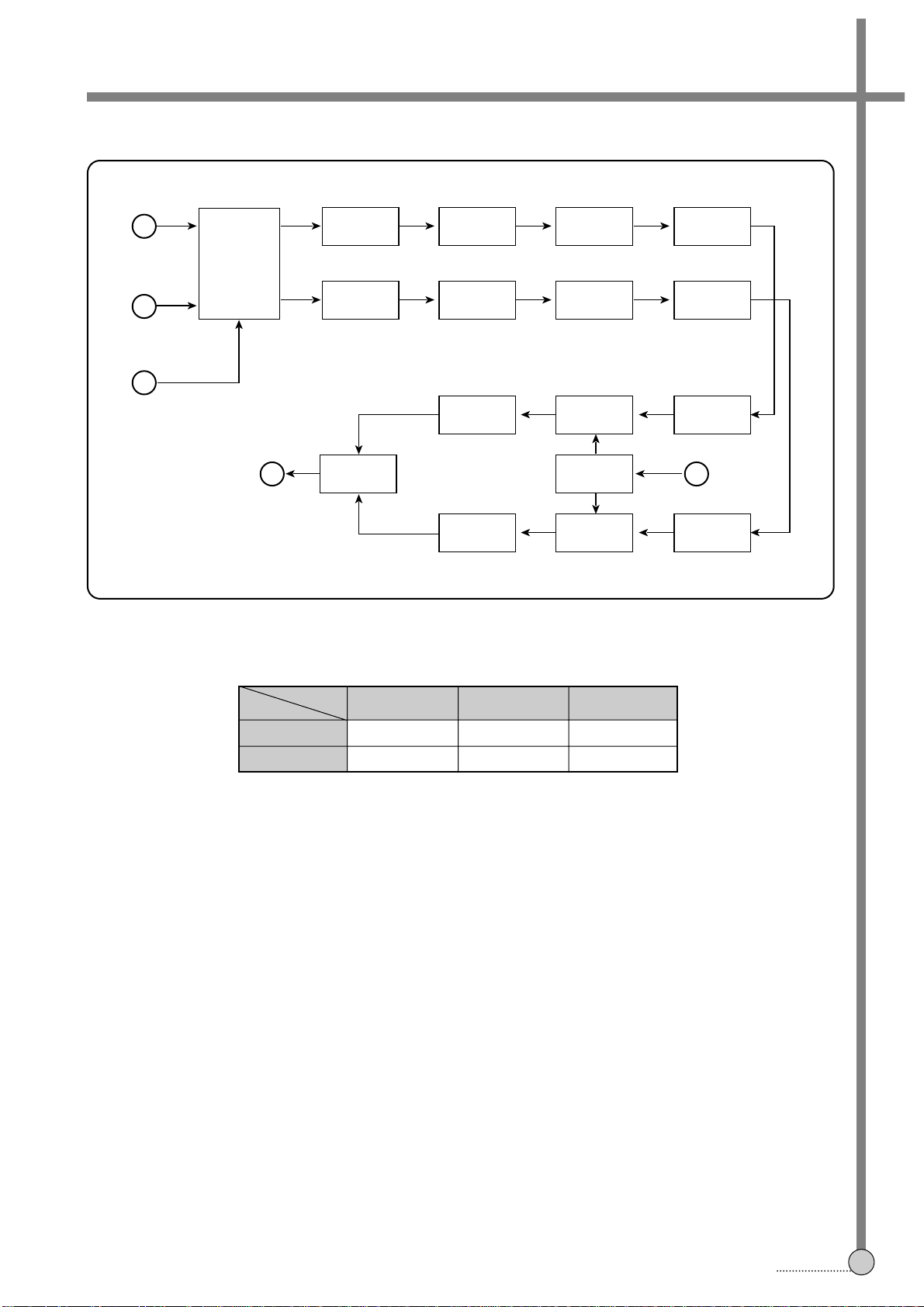
3-6. HI-FI AUDIO SIGNAL PROCESSING (BH7804K)
CIRCUIT
17
2. REC MODE
(1) Signal Flow
In this system, the input signal sources are contained with IF, AV and F.AV. each pin number’s decription is the same
as the below.
The input signals, selected by the input siwthcer, go through the LPF (at 20KHz) and PNR processor. Additionally, the
selected input signals are supplied to the Normal Audio Unit-Pin 31st. The Normal Audio cab be mixed with the L+RStereo mode, or can be selected with L only-Bilingual mode. The PNR processor compresses the audio signal in order
to reduce the audio noise and enlarge the Dynamic Range.
The FM EMPH(FM Emphasis) emphasiszes the higher band of signal. It can restrict the FM back-noise, when the
signal is demodulated. The modified audio signal is modulated by the Modulator unit. It is composed of AUDIO
LIM(Limitter), 1.4MHz & 1.8MHz (NTSC Case: 1.3MHz & 1.7MHz) modulator. The Audio limiter cuts the level of signal
to avoid the overmodulation, and then the limitted signal is modulated with two carriers-1.4MHz : Left Ch, 1.8MHz :
Right Ch. The modulated two signals are mixed by the FM MIX unit. The mix ratio of FM L and R can be adjusted with
the software-refer to the service mode. Finally, REC FM signal put out to the Pin 21st. It is supplied to the Hi-Fi
preamp.
(2) Auto Adjustment of the VCO, BPF
In this IC, the FM carrier frequency and BPF are adjusted by the synthesized PLL VCO (Phase Locked Loop Voltage
Control) unit. The Auto adjustment is executed at POWER ON, as using the Fsc-3.58MHz. The Fsc is supplied from
the OSC for Color Sub-carrier in the Video unit. If the adjustment completes successfully, IC’s pin 14th is set the
“HIGH” state-5V. Otherwise “LOW” state-0V. The adjustment of VCO, BPF occurs simultaneouslly.
L
R
821
LPF
INPUT
SW
31
PNR
FM
EMPH
LPF
LPF PNR
FM
EMPH
LPF
1.4M
MOD
AUDIO
LIM
REC FM
LPF
Fsc
AUTO
ADJ
FM
MIX
REC FM OUT
1.8M
MOD
AUDIO
LIM
REC FM
LPF
INPUT
IF AV F.AV
CH
L 24134
R 14033
CIRCUIT
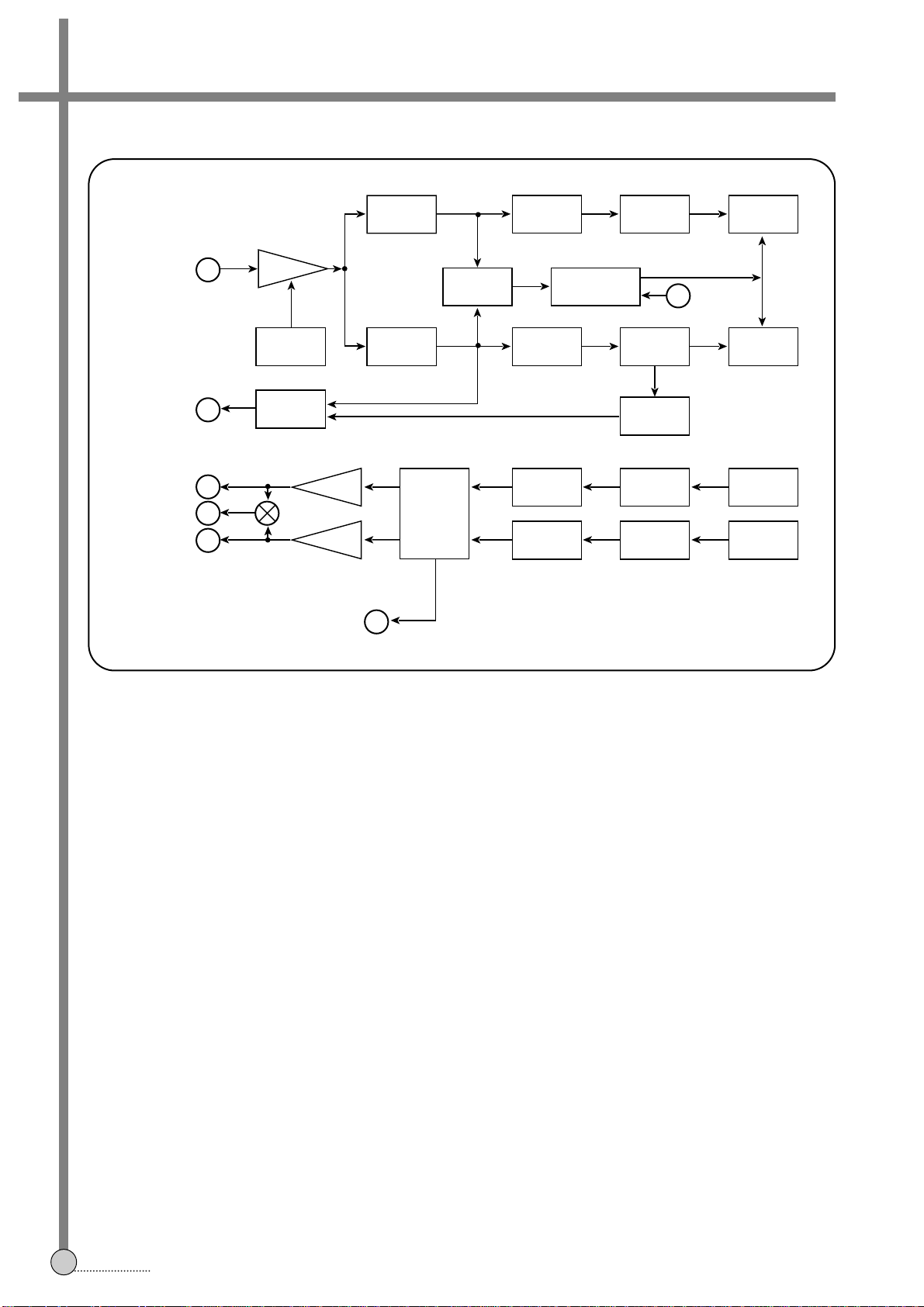
18
3. PB MODE
(1) Signal Flow
FM signal input to the Pin 13rd is amplified, and ditributed to the two BPFs-1.4MHz and 1.8MHz (NTSC Case: 1.3MHz
& 1.7MHz). The band passed FM signals are supplied to the De-Modulator unit. First, the FM LIM confines the FM to
the limitted level, and then the signals are demodulated. The converted audio signals are compensated by the SW
NOISE COMPEN. The signals are passed by the LPF, and de-emphasized by the FM DE-EMPH in order to restrict
the FM back-noise. The PNR processor expands the signals and reduces the audio noise.
The two Line AMPs amplifiy the audio level, and supply to the Audio Out Pin 30th, 29th. The Mod out Pin 27th is and
mixed audio output port for the RF-modlator. The Output SW is available to select the audio output of Left+Right
(Stereo), Left only, Right only and Normal Audio. The Pin 26th is the input port for Normal audio.
(2) Noise Compensation and Hi-Fi Detect
In the Hi-Fi audio system, the noise trouble occurs, when the FM signal is defective. The defection of FM signal is due
to the Drop Out which is scratched on the surface of tape, and the audio SW noise. If the D.O.DET detects the Drop
Out of FM signal, it requires the HOLD PULSE GEN to generate the hold pulse, and then compensate the noise. And
the HOLD PULSE GEN generates the regular pulse by the Audio SW pulses, then send the control signal to the SW
NOISE COMPEN which compensates the noise.
The ENVE/HiFi discreminates the Hi-Fi audio from the Normal audio. If the envelope of FM Hi-Fi exists,
“High”-5V-
control signal is out to the Pin 14th. Otherwise Control voltage is 0.
13
14
30
27
29
26
LPF
8
FM
LIM
DEMOD
D.O.
DET
HOLD
PULSE GEN
SW NOISE
COMPEN
LPF
LPFPNR
PNR
LPF
FM
LIM
DEMOD
SW NOISE
COMPEN
FM
ALC
AMP
FM PB IN
Hi-Fi DET
AUDIO OUT(L)
AUDIO OUT(R)
NORMAL AUDIO
A SW
PULSE
MOD OUT
AMP
AMP
ENVE/
HiFi
OUTPUT
SW
FM
DET
FM
DE-EMPH
FM
DE-EMPH
FLOW CHART
19
SECTION 4.
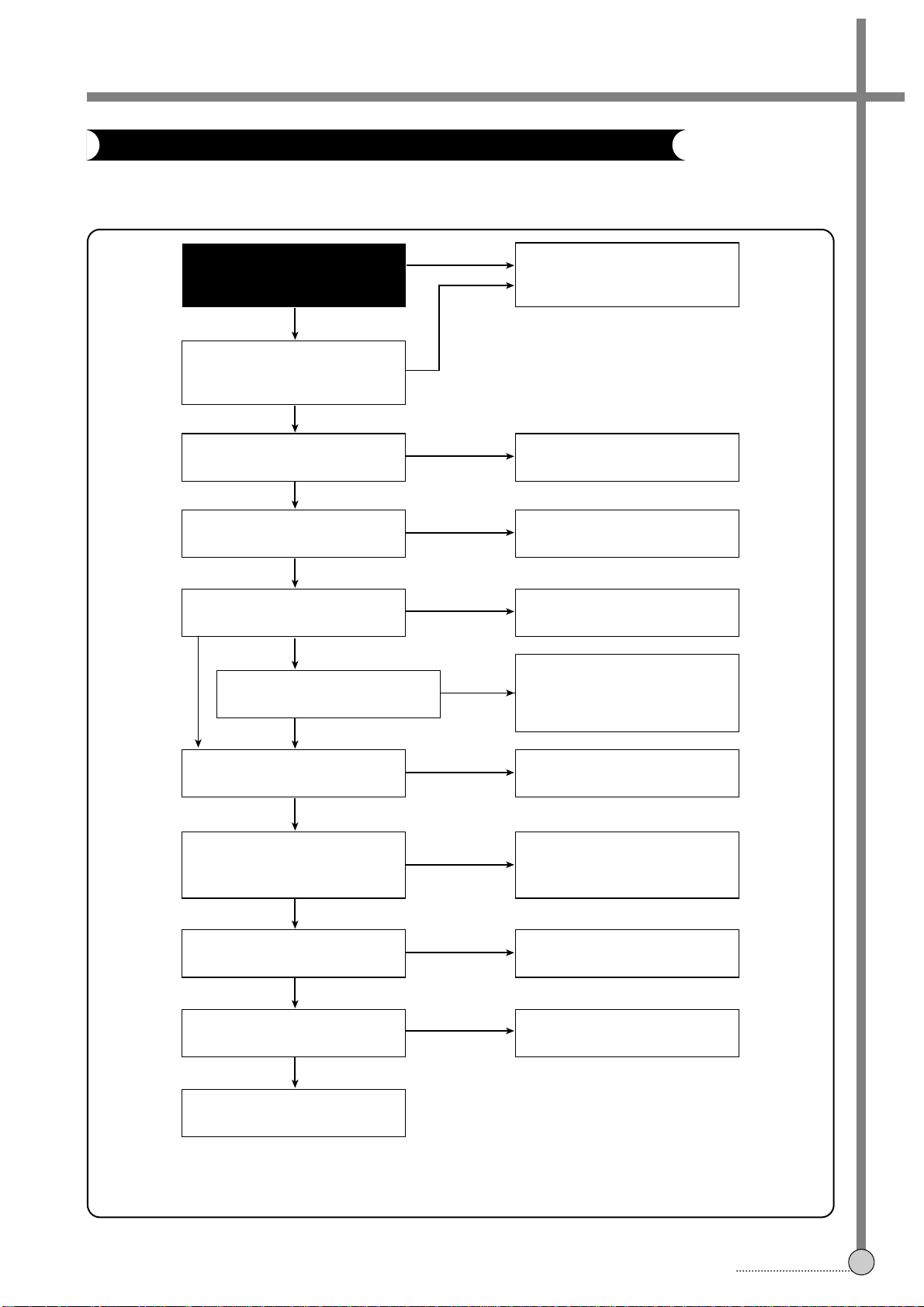
TROUBLESHOOTING FLOW CHART
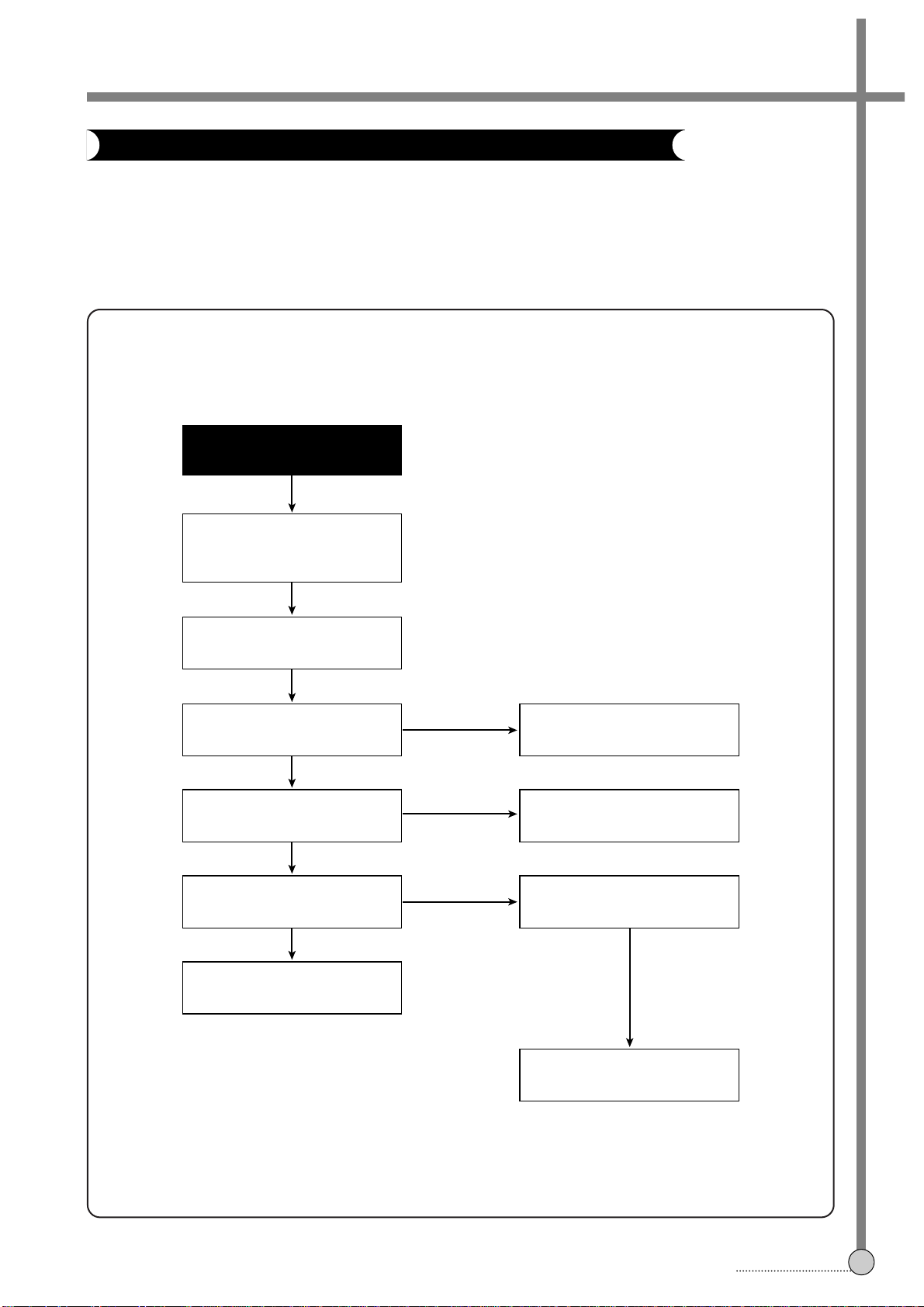
4-1. POWER CIRCUIT
When changing the parts which are broken first, remove the power plug from the socket and then discharge the
voltage across the terminals of C807 (use an external 1KΩ(2W) resistance).
When check the primary circuit, Use the oscilloscope isolated properly (Use the isolated transformer) and connect
GND to the primary GND, however it is not necessary to isolate the oscilloscope when check the secondary circuit.
A. CHECKING THE PRIMARY CIRCUIT.
Prepare the oscilloscope
connected the isolated
transformer
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
NO
NO
NO
NO
Check F801 Fuse.
Is voltage applied to D801?
Is voltage applied to the
terminals of C807?
Is 5.7 voltage applied to
IC11 control pin
Check the secondary circuit
No output Voltage.
Check T11 : #~^ pin,
L12 and IC11
Is varation between 5.7V
and 4.8V at IC11 control pin
Check L801, L802
Check R803, D801
FLOW CHART
20
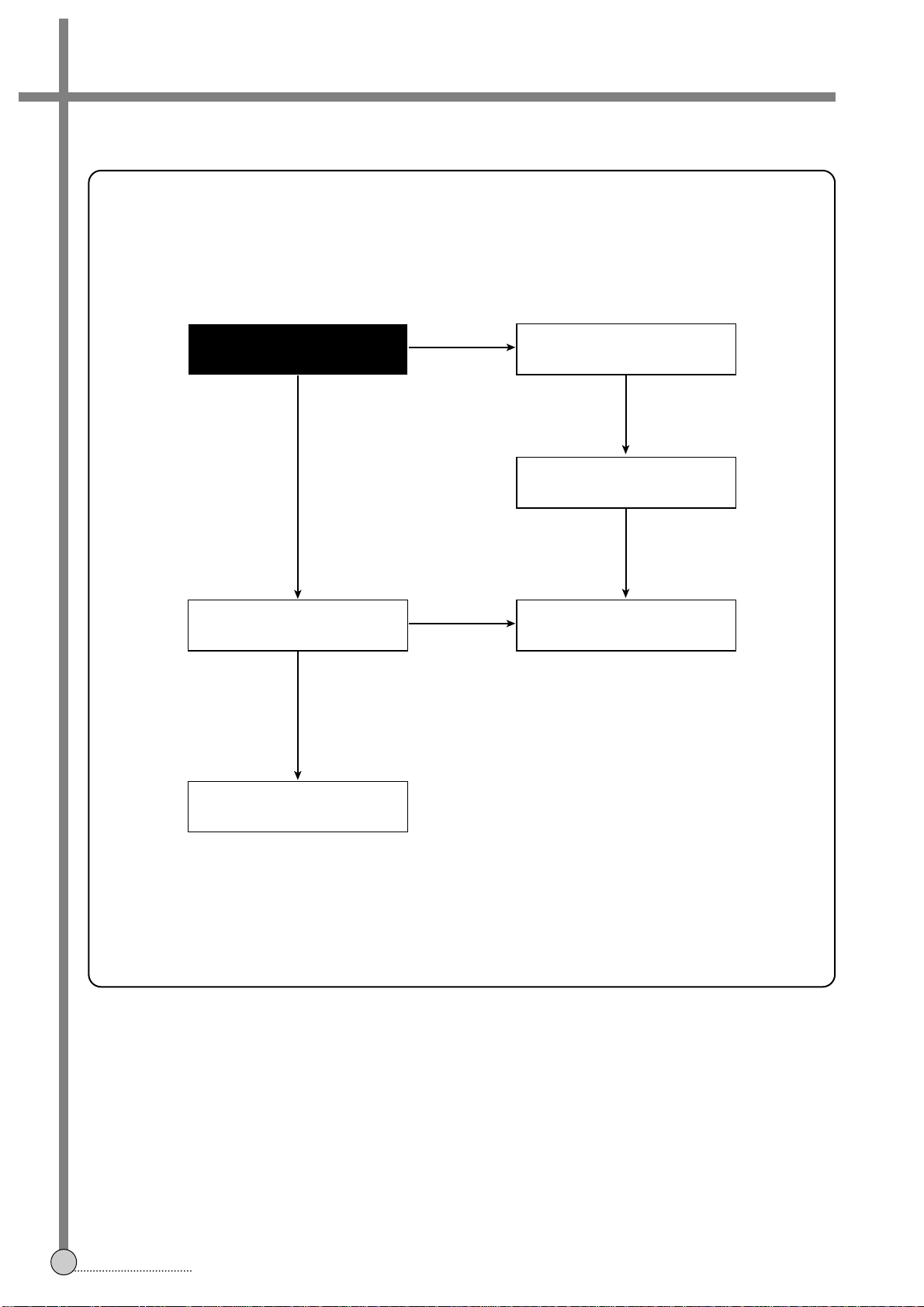
B. CHECKING THE SECONDARY CIRCUIT
YES
NO
YES
YES
YES
Check each output voltage
Check the CN21
Check transformer of NO
output stages
Check the diode of NO
output stages
Check the COIL, C of NO
output stages
END
FLOW CHART
21
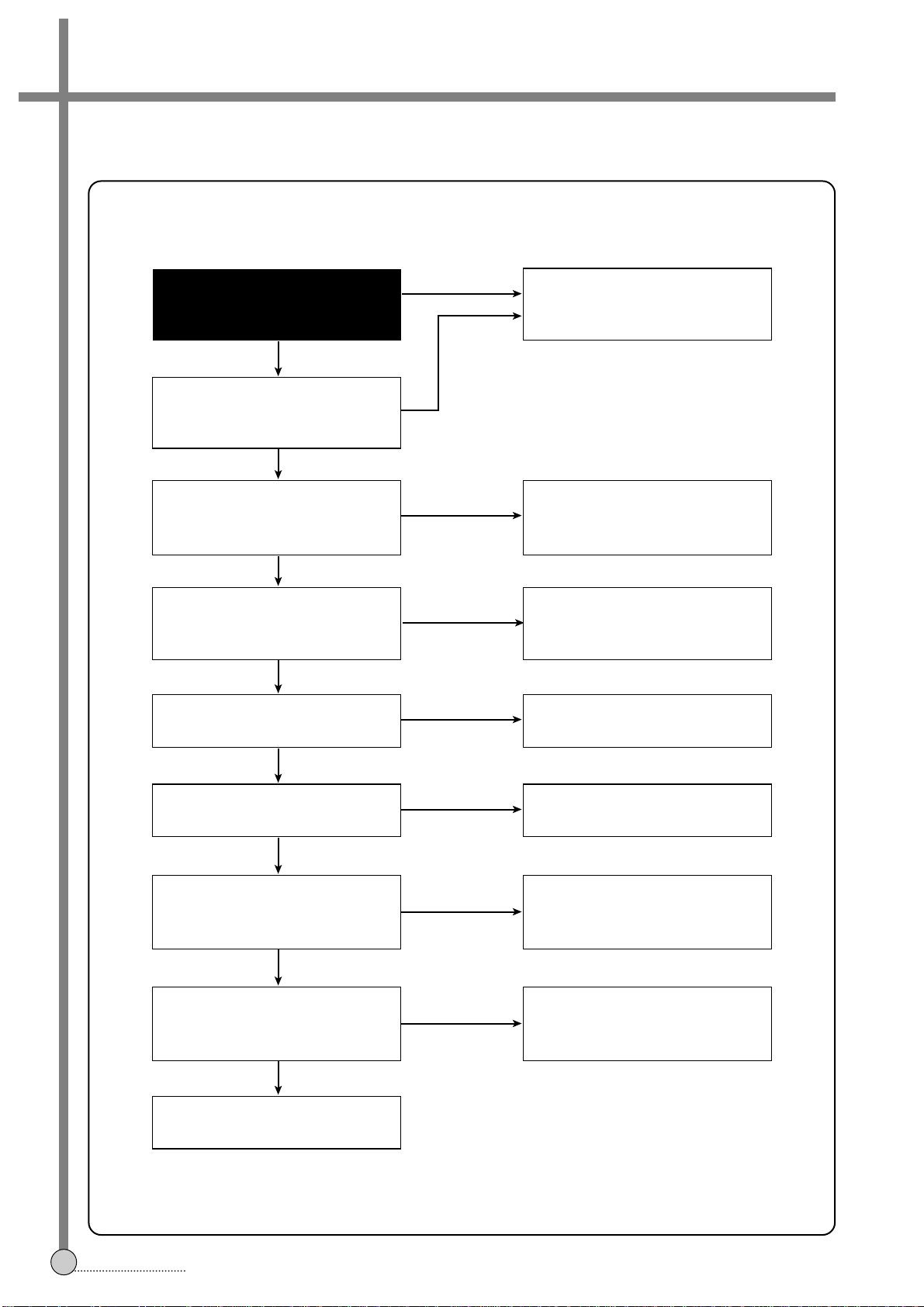
4-2. PIF CIRCUIT TROUBLESHOOTING
A. TROUBLESHOOTING OF RF RECEIVING CIRCUIT
NO
YES
YES
NO
NO
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
NO
NO
NO
NO
NO
NO
Is Video Signal Video Out point,
P101 Pin No. 4 of IF Module?
Is Audio signal at Audio Out point,
P102 Pin No.2/No. 4 of IF Module?
Check the A/V Switching and
Video Circduit.
Check Q179, Q180 and Power
Supply Circuit.
Check Q177, Q178 and Power
Supply circuit.
Check Q181 EVER 33V and then
PWM from µ-COM.
Check the transistors from Q171 to
Q176 and µ-COM ports, VL(H),
VH(H) and UHF(H)
Correct RF AGC adjustment.
Correct AFT adjustment.
Check the Power Supply Circuit.
Is +5V supplied to BB point,
Pin No. 1 of TM Block?
Is +9V supplied to IF 9V point,
P101 Pin No. 3 of IF Module?
Is +5V supplied to IF 5V point,
P102 Pin No. 5 of IF Module?
Is tunning voltage changed
when changing channels?
YES
NO
YES
Check NTSC(H) port of µ-COM
Pin No. 100 and Q103, Q104,
Q105, Q106, Q107, Q108, Q109,
Q110, Q111, Q113 of IF Module
Is NTSC(H) Supplied to p102
Pin No. 8 of IF Model?
Is +9V supplied to VL, VH or U
band point, Pin No. 15, 16 or 17 or
TM Block?
Is RF AGC adjusted well?
Is AFT adjusted well?
Change the IF Module and then
TM Block.
¡ NOTE: ƒk means when NTSC signal received.
ƒk ƒk
FLOW CHART
22
B. TROUBLESHOOTING OF RF MODULATOR OUT
NO
NO
NO
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
NO
NO
NO
NO
Is Video Signal Video In point,
Pin No. 6 of TM Block?
Is Audio signal at Audio In point,
Pin No.2 of TM Block?
Check the A/V Switching, Video
and Audio Circduit.
Correct the Option.
Check on/off 5V and Power
Supply circuit.
Check D171 and Power
Supply circuit.
Check the µ-COM port, SDA.
Are RF OUT System and RF Out
channel selected well by menu key.
Select the RIGHT System and
channel by menu key.
Is system Select Option Diode
applied well according to Option
Table?
Is +5V supplied to MB point,
Pin No. 4 of TM Block?
Is +30V supplied to TU(MD) point,
Pin No. 7 of TM Block?
YES
Change the TM Block.
Is Serial Data supplied to
SDA points, Pin No. 3 of
TM Block?
YES
NO
Check the µ-COM port, SCL.
Is Serial Clock supplied to
SCL points, Pin No. 5 of
TM Block?
FLOW CHART
23
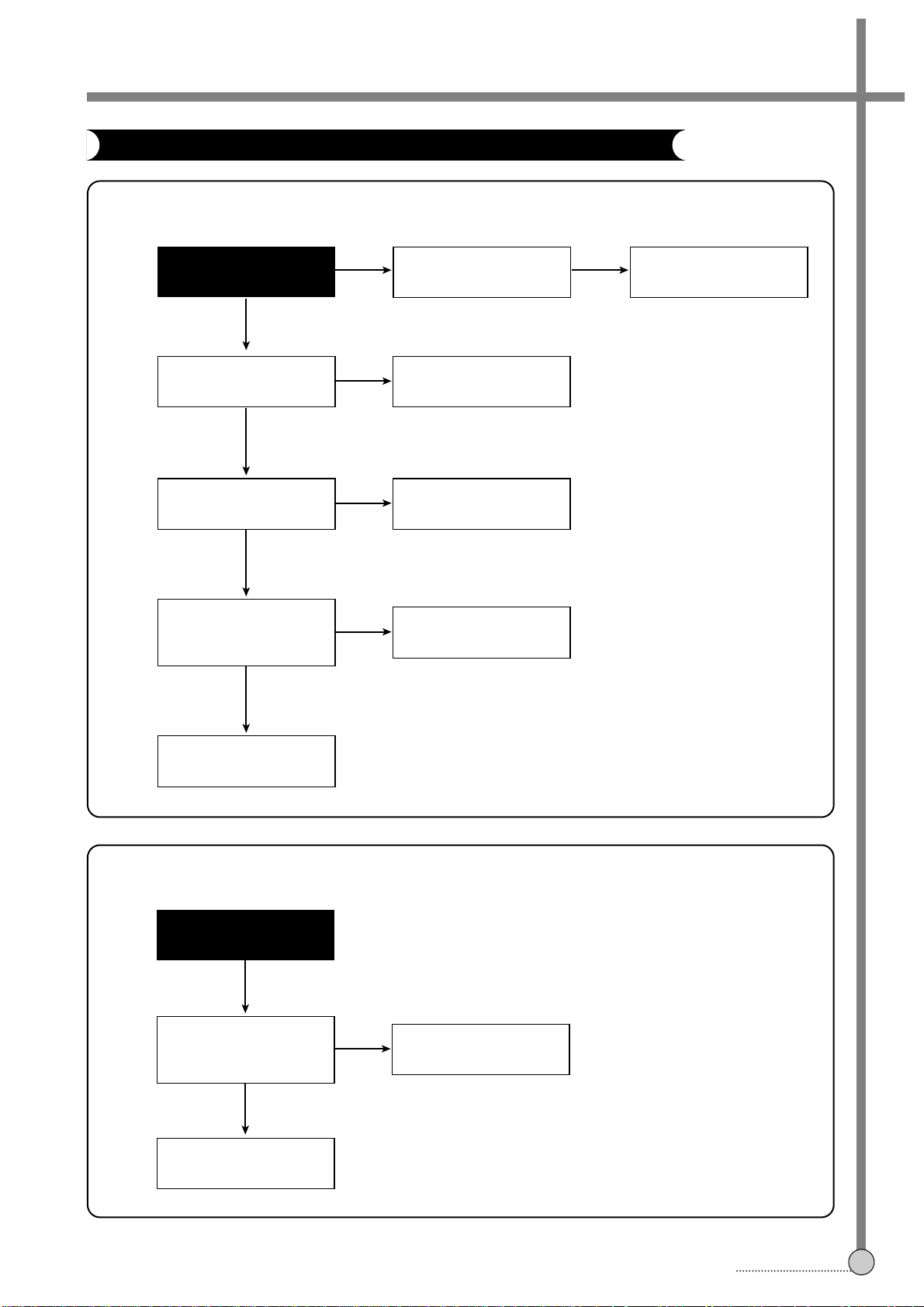
4-3. LOGIC CIRCUIT
NO
Is +5.8V supplied
fdrom D509 cathod?
Check power Module
Check power
Module
Check power
Module
Check power
Module
YES
Check IC501
and change.
YES
Digitron does
not operate.
Is +5V supplied to
pin c of IC501?
YES
Is 24V supplied to
pin C of IC501?
YES
Are -20 and -16.5V
supplied to pin e and
! of G701?
A.
Check key matrix
circuit.
Digitron is lit keys do
not operate.
Is each key pulse
applied to pin Gg
H and h of IC501?
B.
YES
Check the pin serial of
pin A,a of IC501
FLOW CHART
24
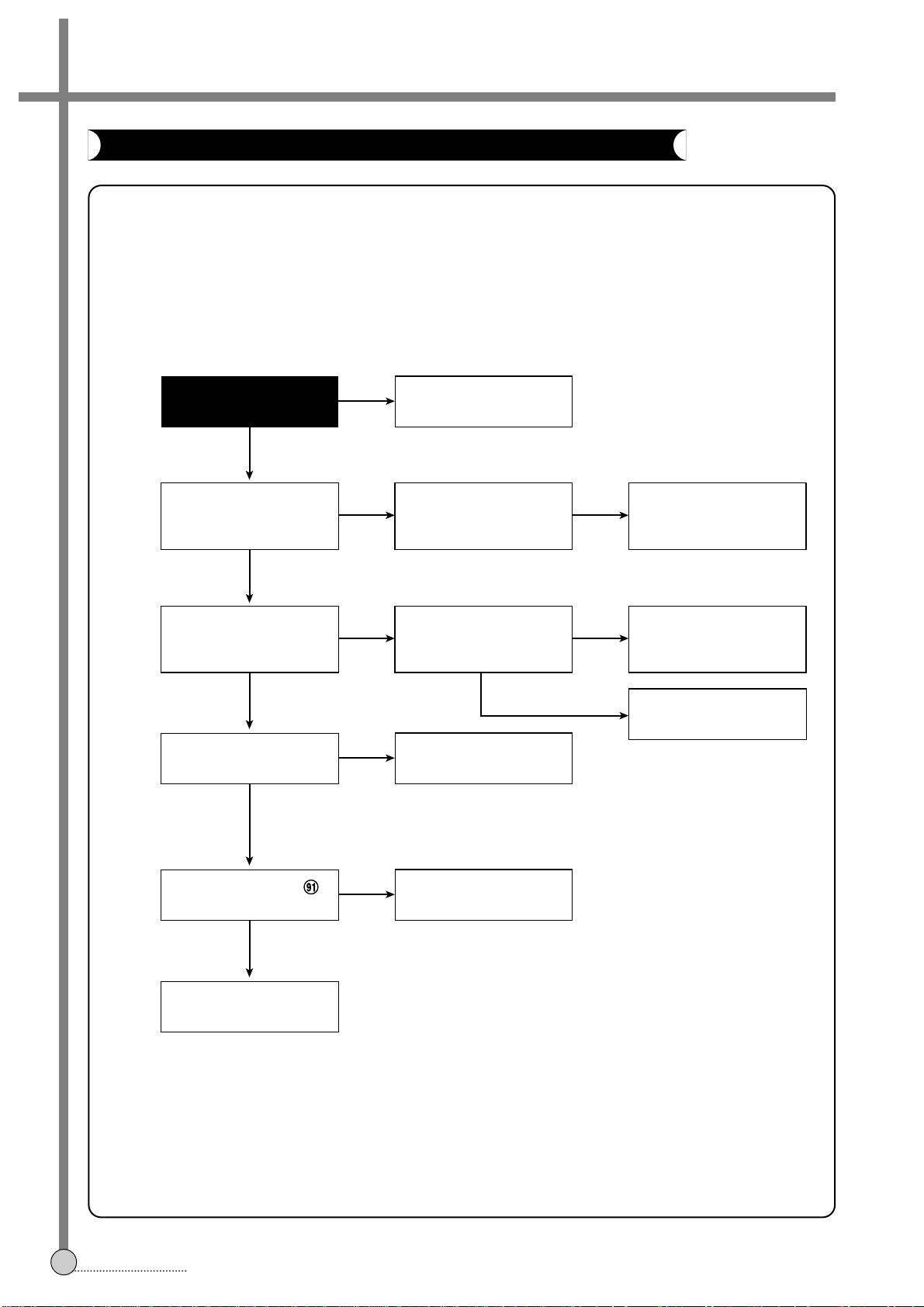
4-4. SERVO-SYSCON CIRCUIT
Playback picture
is not good
Noise appears
although
adjusting tracking.
Check and re-adjust
the path of Deck.
A.
YES
NO
NO NO
YES
YES
Adjust tracking.
Playback picture
is not good
Noise appears
although
change cassette tape.
YES
Is CTL pulse output
at pin ^ of IC505?
Is CTL pulse input
to pin Q of IC501?
Playback picture
is not good
YES
NO
NO
Check IC501
Check R528, R527,
R529, R523
YES
The voltage of pin
of IC501 not changing?
Check R551, C532
CTL HEAD height
is normal and
there is not dust?
Adjust the HEAD
height and
remove dust.
Check circuit
adjacent to IC505
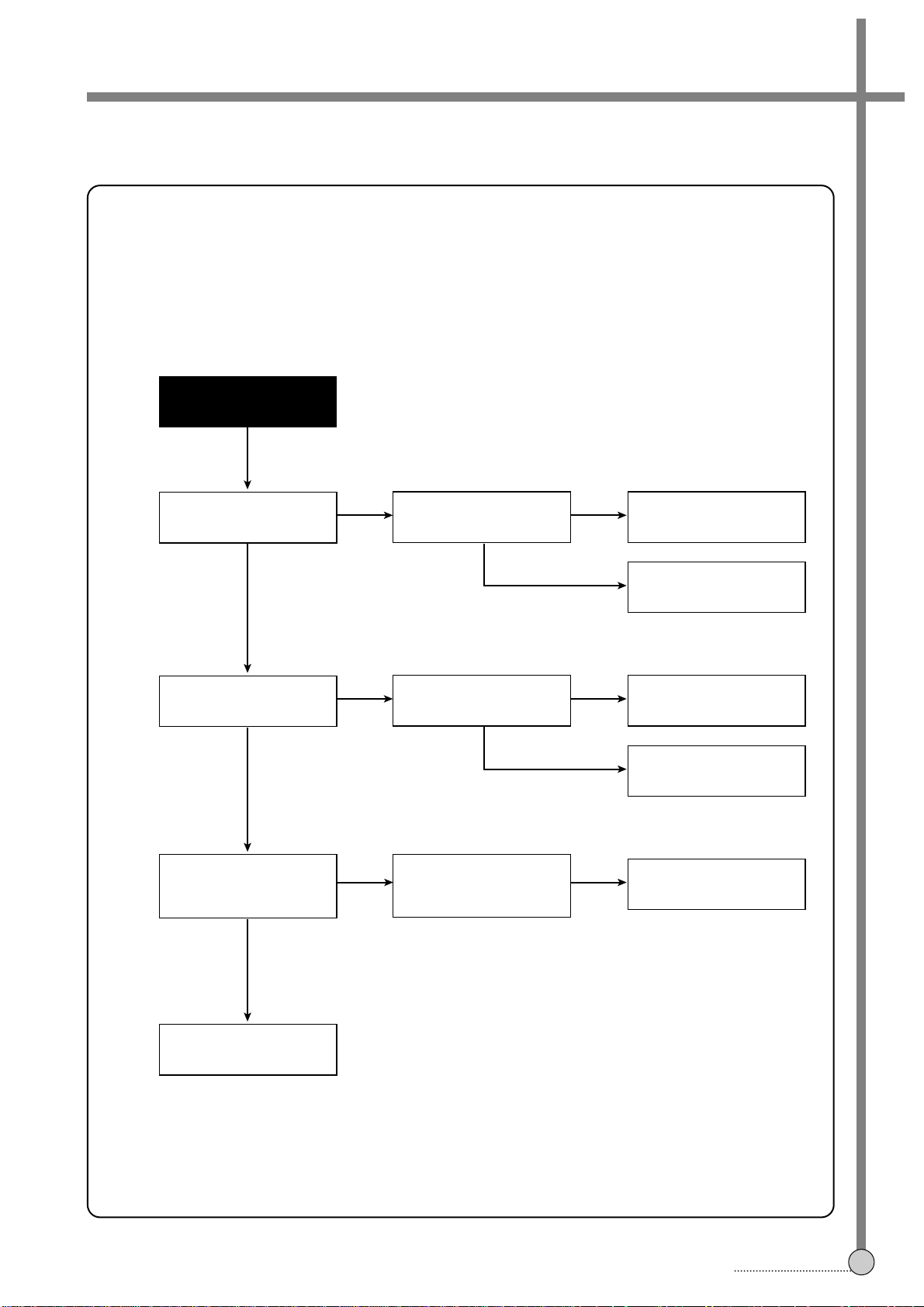
FLOW CHART
25
NO NO
Playback picture
is not good.
B.
NO NO
Check flow A.
YES
YES
YES
YES
Noise appears on the
screen on the whole.
Noise appears on the
screen at the bottom
Change Drum Ass'y
Is Enve. waveform
supplied to pin % of
PT01?
Check connector,
Head Amp
and Head dust.
NO NO
YES
Check pattern
Check video circuit.
Adjust the PG
in SVC mode.
Are SW-pulse and HA-SW
applied to preamp circuit?
Is sw pulse supplied
from pin 8 of IC501?
Check D.PG input
and connector.
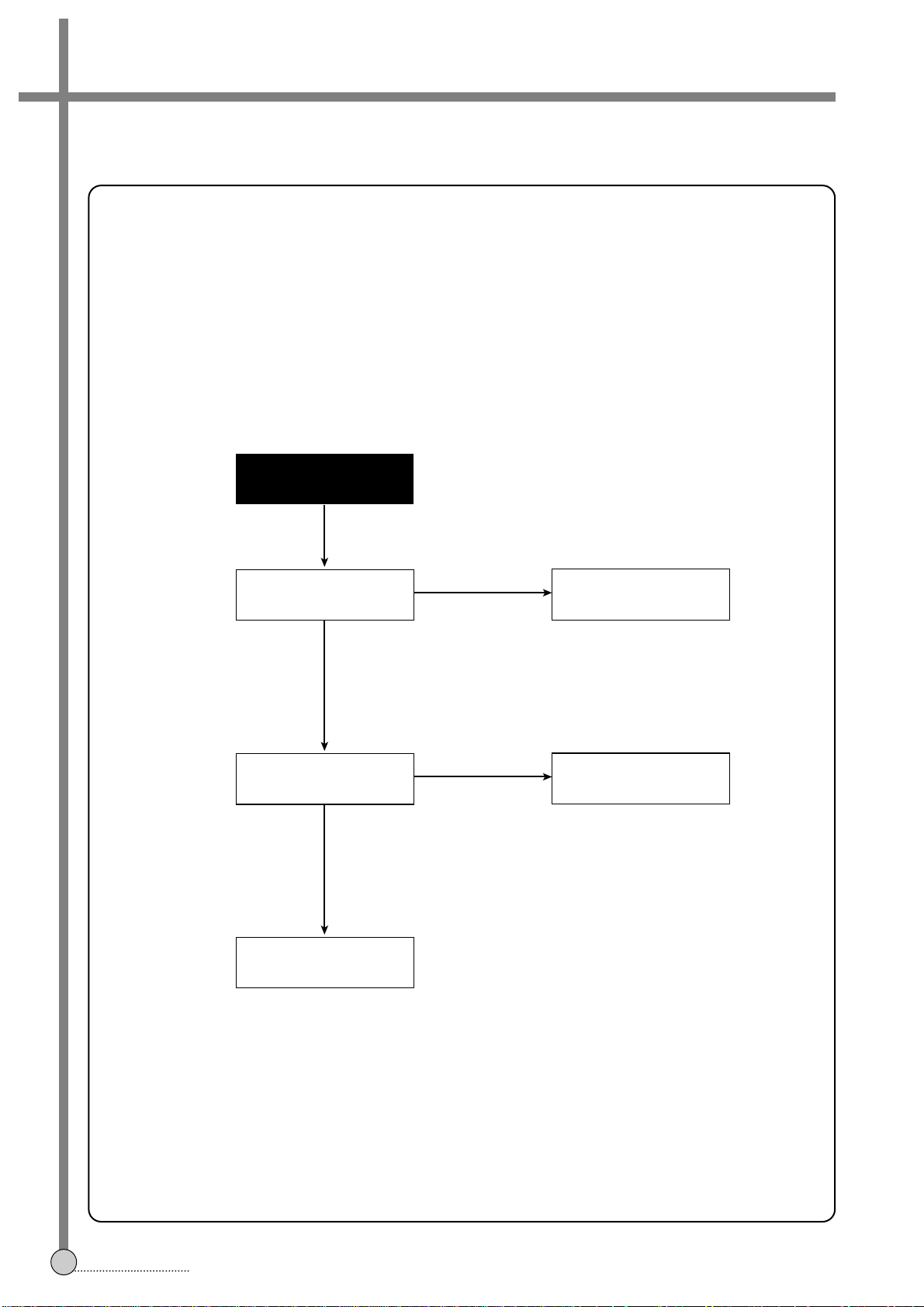
FLOW CHART
26
Auto-stop during
playback.
C.
NO
Is reel pulse applied to
pin % and ^of IC501?
Check reel sensor.
NO
YES
Is D. FG applied to
pin = of IC501?
YES
Check IC501.
Check connector and
D. FG circuits.
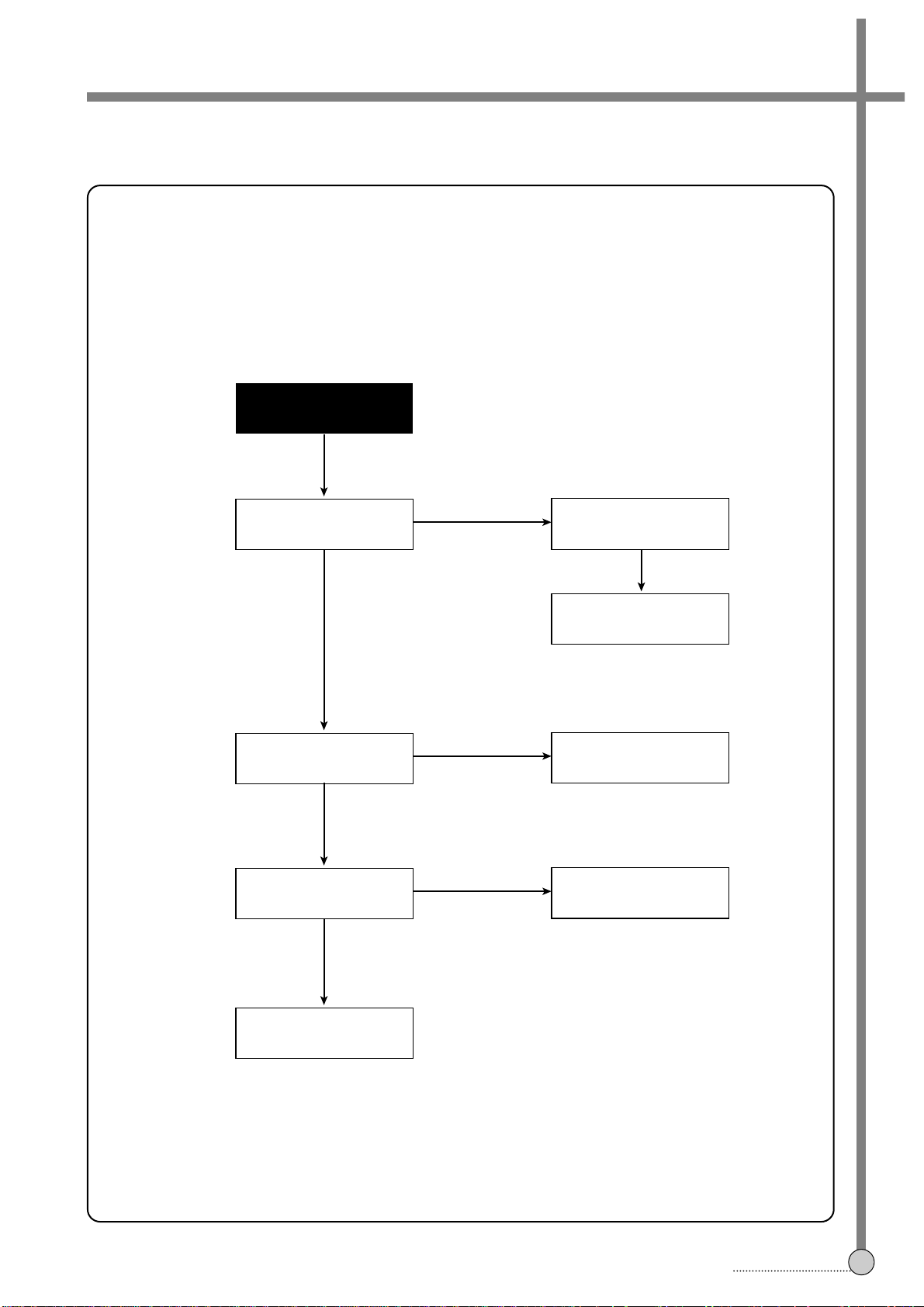
FLOW CHART
27
Drum M/T loading stops.
D.
NO
NO
Is motor 12V supplied
to IC502 & *pin 12V?
Check Q504.
Check power module.
NO
YES
YES
Is 6V supplied to
pin $ of IC502?
Check Q504.
NO
Change IC502
YES
Check connector
and motor.
Check P503 and
Loading motor
 Loading...
Loading...