Page 1

Caution
: In this Manual, some parts can be changed for improving. their
performance without notice in the parts list. So, if you need the
latest parts information, please refer to PPL(Parts Price List)in
Service Information Center.
Service Manual
COLOR Television
CHASSIS :
Model :
CP-520V
DTX-21G2/21B4/21U7
P/N:TCP520VEF0
Dec. 2006
Page 2

CP-520V Service Manual
1
CONTENTS
DOCUMENT HISTORY 3
1 MAIN FEATURES 4
1.1 SPECIFICATIONS 4
1.1.1 GENERAL 4
1.1.2 EURO-SCART 1 (21 Pin) 4
1.1.3 EURO-SCART 2 (21 Pin) 5
1.2 CHANNEL/FREQUENCY TABLE 6
2 SAFETY INSTRUCTION 9
3 ALIGNMENT INSTRUCTIONS 10
3.1 MICROCONTROLLER CONFIGURATION : SERVICE MODE 10
3.2 SERVICE MODE NAVIGATION 10
3.3 MICROCONTROLLER CONFIGURATION : OPTION BITS 10
3.4 OPTION 1 11
3.5 OPTION 2 11
3.6 NVM DEFAULT SETTING 12
3.7 TV SET ALIGNMENT 14
3.7.1 G2 ALIGNMENT 14
3.7.2 WHITE BALANCE 14
3.7.3 FOCUS 14
3.7.4 VERTICAL GEOMETRY 14
3.7.5 HORIZONTAL PICTURE CENTRING 14
3.7.6 AGC 14
4 IC DESCRIPTION 15
4.1 UOC III SERIES 15
4.1.1 IC MARKING AND VERSION 15
4.1.2 BLOCK DIAGRAM 16
4.1.3 PINNING 17
4.1.4 FEATURES 20
4.2 LA42032 STEREO AUDIO AMPLI FIER 23
4.2.1 FEATURES 24
4.3 LA78040 VERTICAL AMPLIFIER 26
4.3.1 FEATURES 26
4.4 24WC16 - 16 KB EEPROM 28
4.5 STR - W6754 29
4.5.1 GENERAL DESCRIPTION 29
4.5.2 FEATURES 29
4.5.3 BLOCK DIAGRAM 29
4.5.4 PIN DESCRIPTION 30
4.5.5 CONTROL PART - ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS 30
Page 3

CP-520V Service Manual
2
5 CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION 32
5.1 BLOCK DIAGRAM 32
5.2 FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION OF VIDEO PROCESSOR 33
5.2.1 Vision IF amplifier 33
5.2.2 QSS sound circuit 33
5.2.3 FM demodulator 33
5.2.4 Audio input selector and volume contro 34
5.2.4.1 STEREO AND AV STEREO VERSIONS 34
5.2.4.2 MONO VERSIONS 34
5.2.5 CVBS and Y/C input signal selection 34
5.2.5.1 ALL VERSIONS 34
5.2.6 Synchronisation circuit 35
5.2.7 Horizontal and vertical drive 36
5.2.8 Chroma, luminance and feature processing 36
5.2.9 Colour decoder 37
5.2.10 RGB output circuit 38
5.2.11 I2C-BUS USER INTERFACE DESCRIPTION 40
5.3 GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF THE TV SOUND OF SOUND PROCESSOR 40
5.3.1 Supported standards 41
5.4 FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION SOUND PROCESSOR 42
5.4.1 The UOC III TV Sound Concept 42
5.4.2 Functional Overview Of the digital controller sound part 43
5.4.3 Demodulator and decoder 44
6 SERVICE PARTS LIST 47
6.1 DTX-21G2FZP-SB 47
7 EXPLODED VIEW 52
7.1 DTX-21G2 52
7.2 DTX-21B4 53
7.3 DTX-21U7 54
8 PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD 55
8.1 4859813693(OLD PCB) 55
8.2 4859816393(NEW PCB) 56
9 SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM 57
9.1 CP-520V 57
Page 4

CP-520V Service Manual
DOCUMENT HISTORY
VERSION DATE COMMENTS
V1.46 07/07/06 Creation of document (Author JS KIM) for project CP520 50Hz TV.
3
Page 5
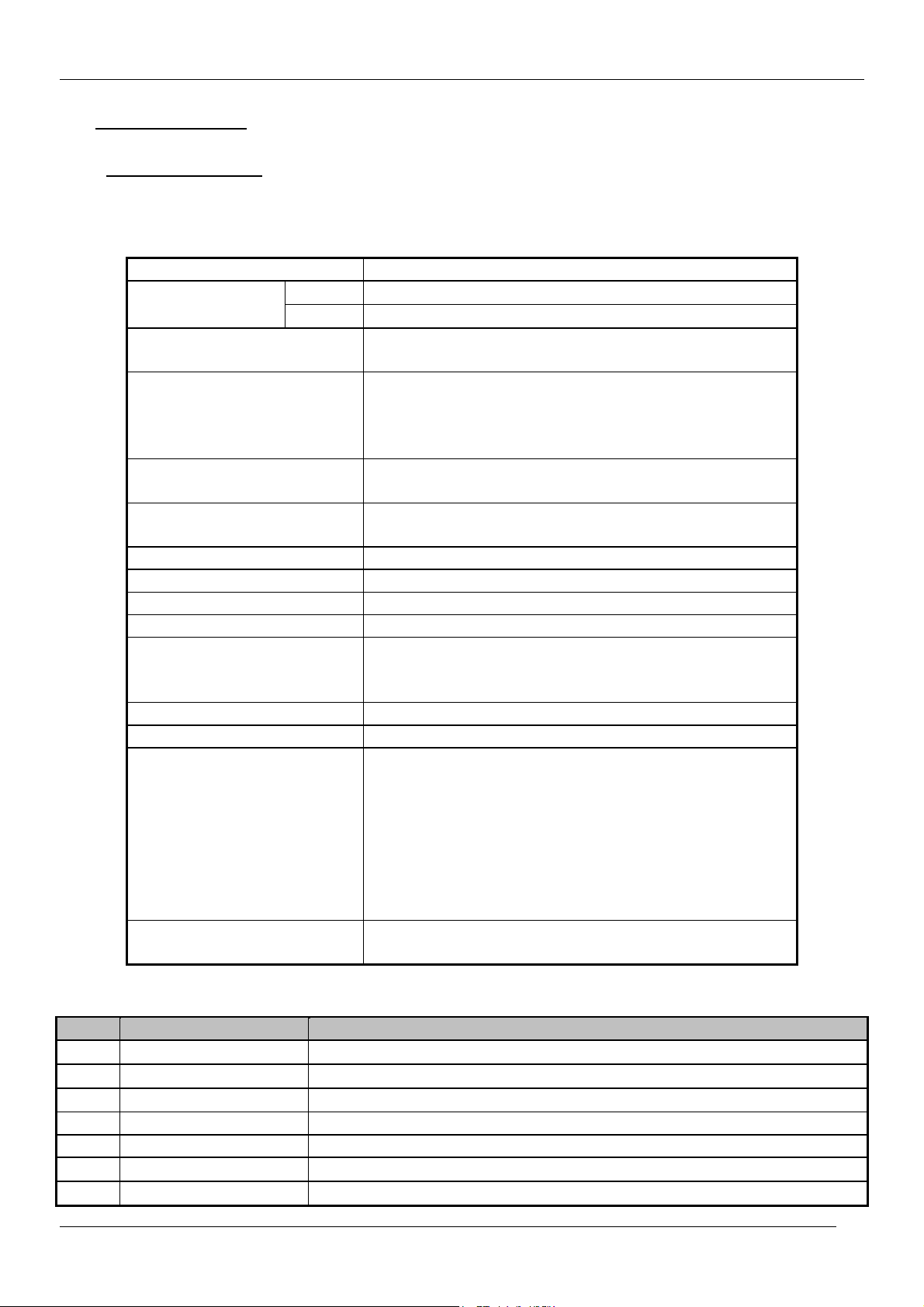
1 MAIN FEATURES
1.1 SPECIFICATIONS
1.1.1 GENERAL
TV standard PAL - SECAM B/G D/K, PAL I/I, SECAM L/L’
Sound system NICAM B/G, I, D/K, L,
Power
consumption
CP-520V Service Manual
Tuner PAL, SECAM Colour system
AV PAL, SECAM, PAL 60, NTSC M, NTSC 4.43
FM 2Carrier B/G, D/K
59W
Sound Output
Power
Speaker 12W 8 ohm x2
Teletext system 10 pages memory FASTEXT (FLOF or TOP)
Aerial input 75 ohm unbalanced
Channel coverage Off-air channels, S-cable channels and hyperband
Tuning system frequency synthesiser tuning system
Visual screen size 51cm
Channel indication On Screen Display
Program Selection 100 programmes
Aux. terminal EURO-SCART 1 : Audio / Video In and Out, R/G/B
Remote Control
Unit
4.5W x 2 (at 60% mod, 10% THD)
In, Slow and Fast switching.
EURO-SCART 2 : Audio / Video In and Out, SVHS
In.
AV3 : Audio-Video Jack on front of cabinet.
Headphone jack (3.5 mm) on front of cabinet
SVHS3 (option) : Jack on front of cabinet – sound
input common with AV3.
R-49C10
1.1.2 EURO-SCART 1 (21 Pin)
Pin Signal Description Matching value
1 Audio Output Right
2 Audio Input Right
3 Audio Output Left
4 Audio Earth
5 Blue Earth
6 Audio Input Left
7 Blue Input
0.5 Vrms, Impedance < 1 kΩ, ( RF 54% Mod )
0.5 Vrms, Impedance > 10 kΩ
0.5 Vrms, Impedance < 1 kΩ, ( RF 54% Mod )
0.5 Vrms, Impedance > 10 kΩ
0.7 Vpp ±0.1V, Impedance 75Ω
4
Page 6
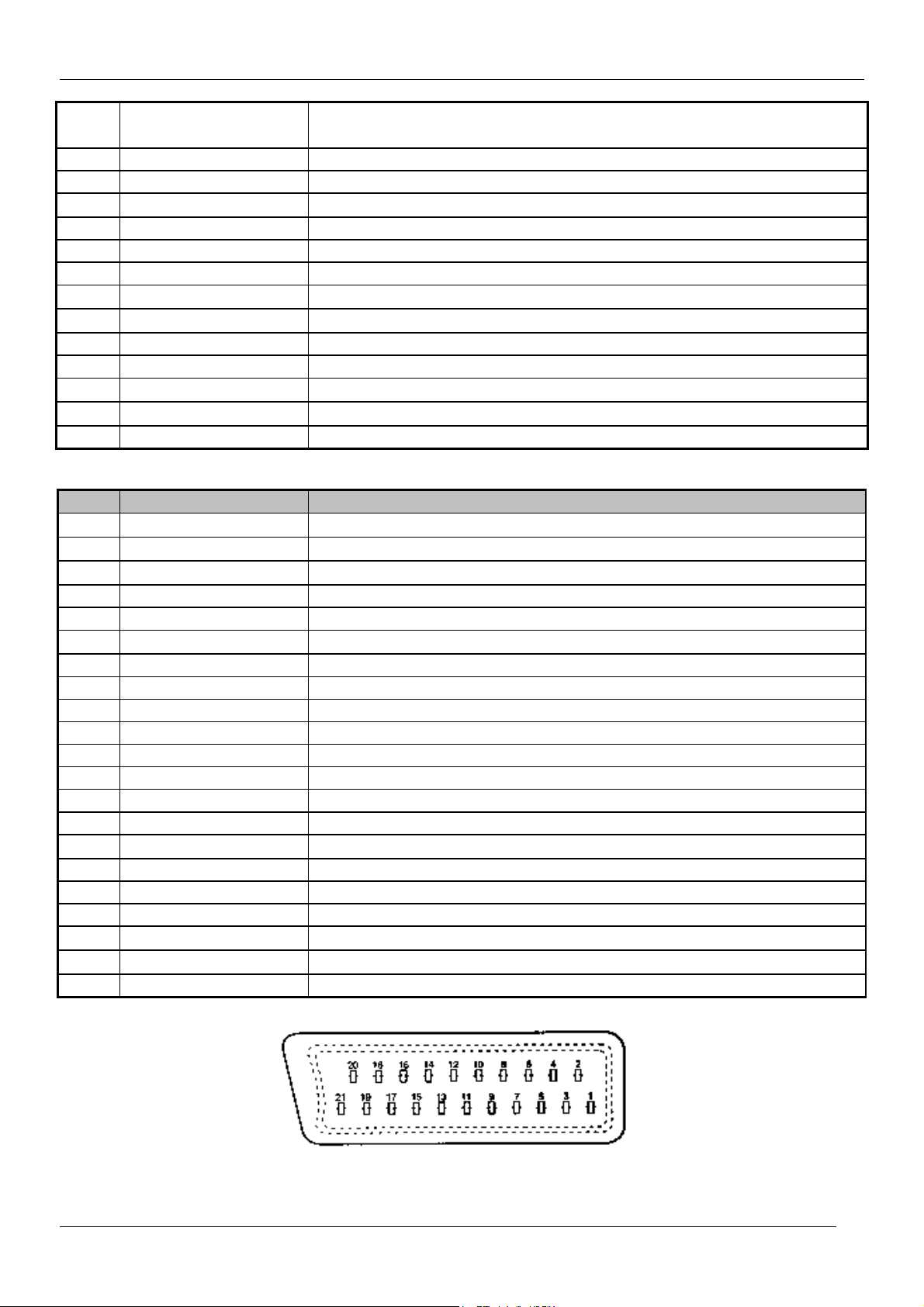
CP-520V Service Manual
8 Slow Switching TV : 0 to 2V, AV 16/9 : 4.5 to 7V, AV 4/3 : 9.5 to 12V , Impedance
> 10 kΩ
9 Green Earth
10 N.C.
11 Green Input
12 N.C.
13 Red Earth
14 Blanking Earth
15 Red Input
16 Fast Switching
17 Video Out Earth
18 Video In Earth
19 Video Output
20 Video Input
21 Common Earth
1.1.3 EURO-SCART 2 (21 Pin)
Pin Signal Description Matching value
1 Audio Output Right
2 Audio Input Right
3 Audio Output Left
4 Audio Earth
5 Earth
6 Audio Input Left
7 N.C.
8 N.C.
9 N.C.
10 N.C.
11 N.C.
12 N.C.
13 Earth
14 Earth
15 Chroma Input
16 N.C.
17 Earth
18 Video In Earth
19 Video Output
20 Video Input, Y In.
21 Common Earth
0.7 Vpp ± 0.1V, Impedance 75Ω
0.7 Vpp ± 0.1V, Impedance 75Ω
0 to 0.4V : Logic “0”, 1 to 3V : Logic “1”, Impedance 75Ω
1 Vpp ± 3dB, Impedance 75Ω
1 Vpp ± 3dB, Impedance 75Ω
0.5 Vrms, Impedance < 1 kΩ, ( RF 54% Mod )
0.5 Vrms, Impedance > 10 kΩ
0.5 Vrms, Impedance < 1 kΩ, ( RF 54% Mod )
0.5 Vrms, Impedance > 10 kΩ
± 3dB for a luminance signal of 1 Vpp
1 Vpp ± 3dB, Impedance 75Ω ( Monitor output )
1 Vpp ± 3dB, Impedance 75Ω
5
Page 7
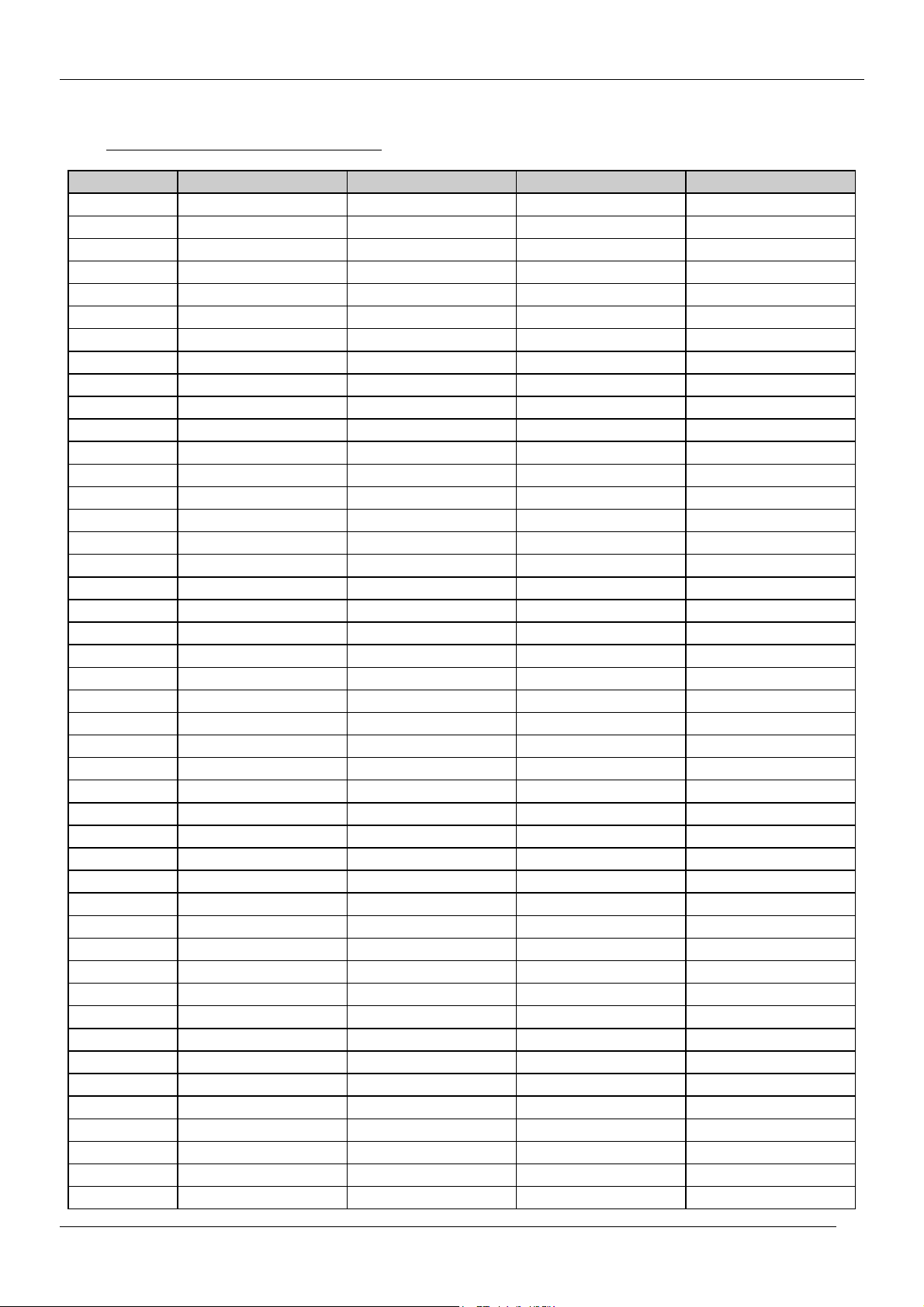
CP-520V Service Manual
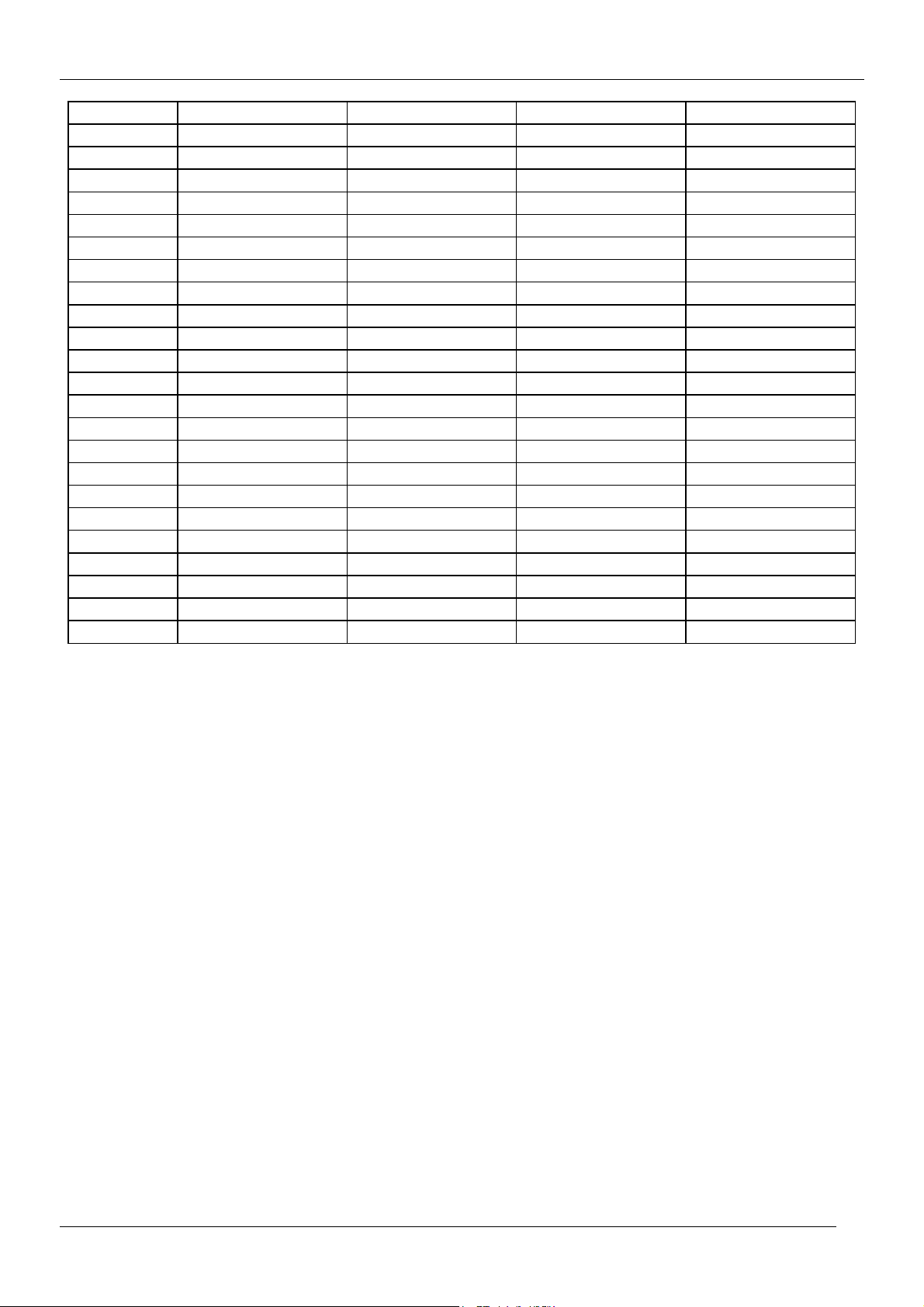
1.2 CHANNEL/FREQUENCY TABLE
CHANNEL EUROPE CCIR FRANCE GB(IRELAND) EAST OIRT
C01 46.25 - 45.75 49.75
C02 48.25 55.75 (L') 53.75 59.25
C03 55.25 60.5 (L') 61.75 77.25
C04 62.25 63.75 (L') 175.25 85.25
C05 175.25 176.00 183.25 93.25
C06 182.25 184.00 191.25 175.25
C07 189.25 192.00 199.25 183.25
C08 196.25 200.00 207.25 191.25
C09 203.25 208.00 215.25 199.25
C10 210.25 216.00 223.25 207.25
C11 217.25 189.25 (LUX) 231.25 215.25
C12 224.25 69.25 (L') 239.25 223.25
C13 53.75 76.25 (L') 247.25 C14 - 83.25 (L') 49.75 C15 82.25 90.25 57.75 C16 - 97.25 65.75 C17 183.75 - 77.75 C18 192.25 - 85.75 C19 201.25 - - C20 - - - C21 471.25 471.25 471.25 471.25
C22 479.25 479.25 479.25 479.25
C23 487.25 487.25 487.25 487.25
C24 495.25 495.25 495.25 495.25
C25 503.25 503.25 503.25 503.25
C26 511.25 511.25 511.25 511.25
C27 519.25 519.25 519.25 519.25
C28 527.25 527.25 527.25 527.25
C29 535.25 535.25 535.25 535.25
C30 543.25 543.25 543.25 543.25
C31 551.25 551.25 551.25 551.25
C32 559.25 559.25 559.25 559.25
C33 567.25 567.25 567.25 567.25
C34 575.25 575.25 575.25 575.25
C35 583.25 583.25 583.25 583.25
C36 591.25 591.25 591.25 591.25
C37 599.25 599.25 599.25 599.25
C38 607.25 607.25 607.25 607.25
C39 615.25 615.25 615.25 615.25
C40 623.25 623.25 623.25 623.25
C41 631.25 631.25 631.25 631.25
C42 639.25 639.25 639.25 639.25
C43 647.25 647.25 647.25 647.25
C44 655.25 655.25 655.25 655.25
C45 663.25 663.25 663.25 663.25
6
Page 8
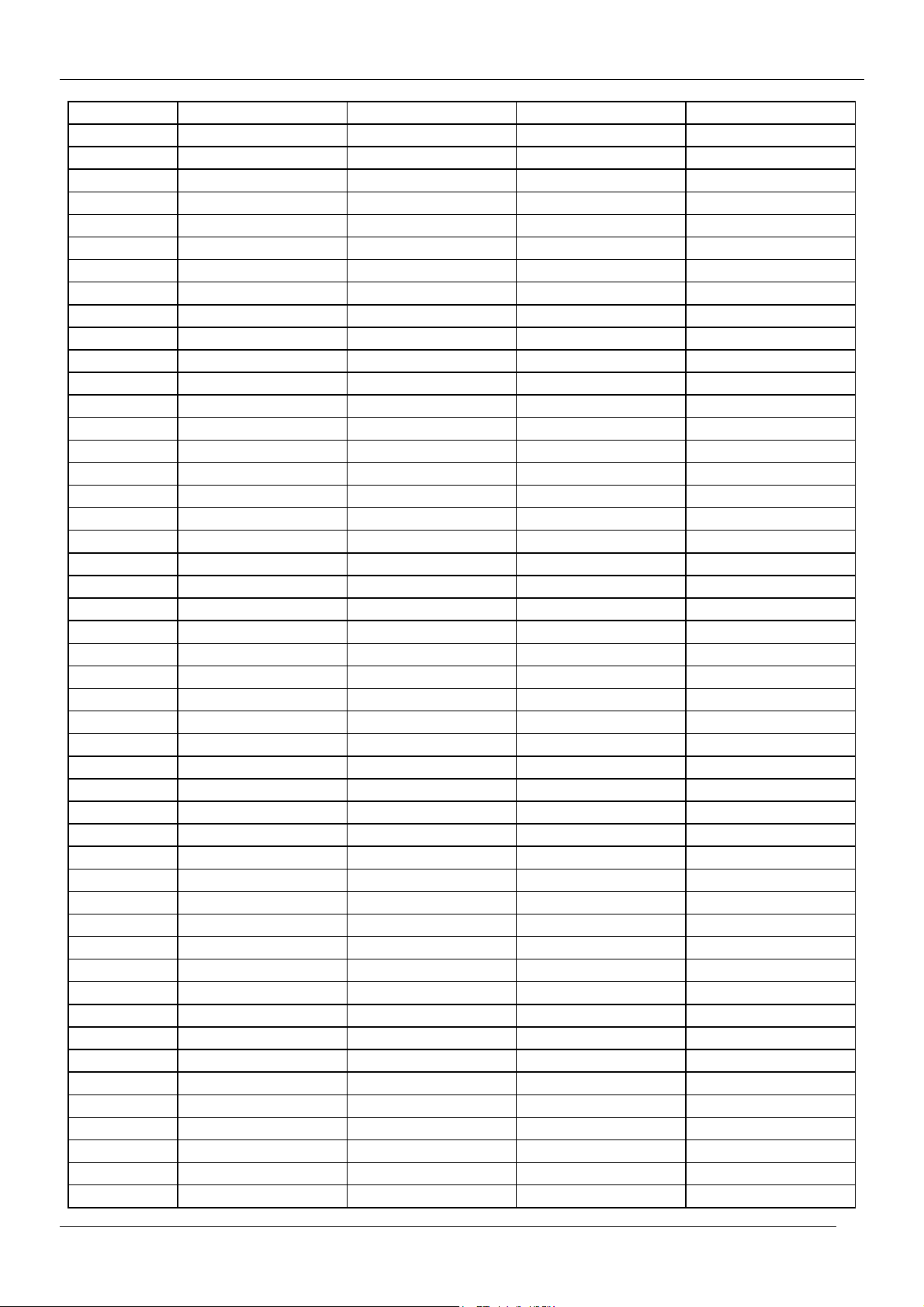
CP-520V Service Manual
C46 671.25 671.25 671.25 671.25
C47 679.25 679.25 679.25 679.25
C48 687.25 687.25 687.25 687.25
C49 695.25 695.25 695.25 695.25
C50 703.25 703.25 703.25 703.25
C51 711.25 711.25 711.25 711.25
C52 719.25 719.25 719.25 719.25
C53 727.25 727.25 727.25 727.25
C54 735.25 735.25 735.25 735.25
C55 743.25 743.25 743.25 743.25
C56 751.25 751.25 751.25 751.25
C57 759.25 759.25 759.25 759.25
C58 767.25 767.25 767.25 767.25
C59 775.25 775.25 775.25 775.25
C60 783.25 783.25 783.25 783.25
C61 791.25 791.25 791.25 791.25
C62 799.25 799.25 799.25 799.25
C63 807.25 807.25 807.25 807.25
C64 815.25 815.25 815.25 815.25
C65 823.25 823.25 823.25 823.25
C66 831.25 831.25 831.25 831.25
C67 839.25 839.25 839.25 839.25
C68 847.25 847.25 847.25 847.25
C69 855.25 855.25 855.25 855.25
C70 863.25 863.25 863.25 863.25
C71 69.25 - - -
C72 76.25 - - -
C73 83.25 - - -
C74 90.25 - - -
C75 97.25 - - -
C76 59.25 - - -
C77 93.25 - - -
S01 105.25 104.75 103.25 105.25
S02 112.25 116.75 111.25 112.25
S03 119.25 128.75 119.25 119.25
S04 126.25 140.75 127.25 126.25
S05 133.25 152.75 135.25 133.25
S06 140.25 164.75 143.25 140.25
S07 147.25 176.75 151.25 147.25
S08 154.25 188.75 159.25 154.25
S09 161.25 200.75 167.25 161.25
S10 168.25 212.75 - 168.25
S11 231.25 224.75 - 231.25
S12 238.25 236.75 - 238.25
S13 245.25 248.75 255.25 245.25
S14 252.25 260.75 263.25 252.25
S15 259.25 272.75 271.25 259.25
S16 266.25 284.75 279.25 266.25
S17 273.25 296.75 287.25 273.25
7
Page 9
CP-520V Service Manual
S18 280.25 136.00 295.25 280.25
S19 287.25 160.00 303.25 287.25
S20 294.25 - - 294.25
S21 303.25 303.25 - 303.25
S22 311.25 311.25 311.25 311.25
S23 319.25 319.25 319.25 319.25
S24 327.25 327.25 327.25 327.25
S25 335.25 335.25 335.25 335.25
S26 343.25 343.25 343.25 343.25
S27 351.25 351.25 351.25 351.25
S28 359.25 359.25 359.25 359.25
S29 367.25 367.25 367.25 367.25
S30 375.25 375.25 375.25 375.25
S31 383.25 383.25 383.25 383.25
S32 391.25 391.25 391.25 391.25
S33 399.25 399.25 399.25 399.25
S34 407.25 407.25 407.25 407.25
S35 415.25 415.25 415.25 415.25
S36 423.25 423.25 423.25 423.25
S37 431.25 431.25 431.25 431.25
S38 439.25 439.25 439.25 439.25
S39 447.25 447.25 447.25 447.25
S40 455.25 455.25 455.25 455.25
S41 463.25 463.25 463.25 463.25
8
Page 10

CP-520V Service Manual
2 SAFETY INSTRUCTION
WARNING: Only competent service personnel may carry out work involving the testing or repair
of this equipment.
X-RAY RADIATION PRECAUTION
1. Excessive high voltage can produce potentially hazardous X-RAY RADIATION. To avoid
such hazards, the high voltage must not exceed the specified limit. The nominal value of the high
voltage of this receiver is 25KV at max beam current.
The high voltage must not, under any circumstances, exceed 29KV.
Each time a receiver requires servicing, the high voltage should be checked. It is important to
use an accurate and reliable high voltage meter.
2. The only source of X-RAY Radiation in this TV receiver is the picture tube. For continued
X-RAY RADIATION protection, the replacement tube must be exactly the same type tube as
specified in the parts list.
SAFETY PRECAUTION
Potentials of high voltage are present when this receiver is operating. Operation of the receiver
outside the cabinet or with the back board removed involves a shock hazard from the receiver.
Servicing should not be attempted by anyone who is not thoroughly familiar with the precautions
necessary when working on high voltage equipment.
Discharge the high potential of the picture tube before handling the tube. The picture tube is
highly evacuated and if broken, glass fragments will be violently expelled.
If any Fuse in this TV receiver is blown, replace it with the FUSE specified in the Replacement
Parts List.
When replacing a high wattage resistor (metal oxide film resistor) in the circuit board, keep the
resistor 10 mm away from circuit board.
Keep wires away from high voltage or high temperature components.
This receiver must operate under AC 230 volts, 50 Hz. NEVER connect to a DC supply or any
other voltage or frequency.
PRODUCT SAFETY NOTICE
Many electrical and mechanical parts in this equipment have special safety-related
characteristics. These characteristics are often passed unnoticed by a visual inspection and the
X-RAY RADIATION protection afforded by them cannot necessarily be obtained by using
replacement components rated for higher voltage, wattage, etc. Replacement parts which have
these special safety characteristics are identified in this manual and its supplements, electrical
components having such features are identified by designated symbol on the parts list. Before
replacing any of these components, read the parts list in this manual carefully. The use of
substitutes replacement parts which do not have the same safety characteristics as specified in
the parts list may create X-RAY Radiation.
9
Page 11
CP-520V Service Manual
10
3 ALIGNMENT INSTRUCTIONS
3.1 MICROCONTROLLER CONFIGURATION : SERVICE MODE
To switch the TV set into service mode please see instruction below.
1 - Select PR. number 91
2 - Adjust sharpness to minimum and exit all menus.
3 – Within 2 seconds press the key sequence : RED - GREEN - menu
The software version is displayed beside the word Service, e.g. “SERVICE VER 1.46”.
To exit SERVICE menu press menu key or Std By key.
3.2 SERVICE MODE NAVIGATION
Pr Up/Down remote keys : cycle through the service items available.
Vol -/+ remote keys : Dec./Increment the values within range – Cycle trough option bits.
OK key : Toggle bits in option byte
Order Item Default setting
1 HOR CEN
2 RED GAIN
3 GRN GAIN
4 BLUE GAIN
5 RED BIAS
6 GRN BIAS
7 AGC LEVEL
8 G2 – SCREEN
9 OPTION1
10 OPTION2
11 AVL
12 PARABOLA
13 HOR WIDTH
14 CORNER T
15 CORNER B
16 HOR. PARAL
17 V. LINEAR
18 V. SLOPE
19 EW TRAPEZ
20 S CORRECT
21 VERT CENT
22 VERT SIZE
3.3 MICROCONTROLLER CONFIGURATION : OPTION BITS
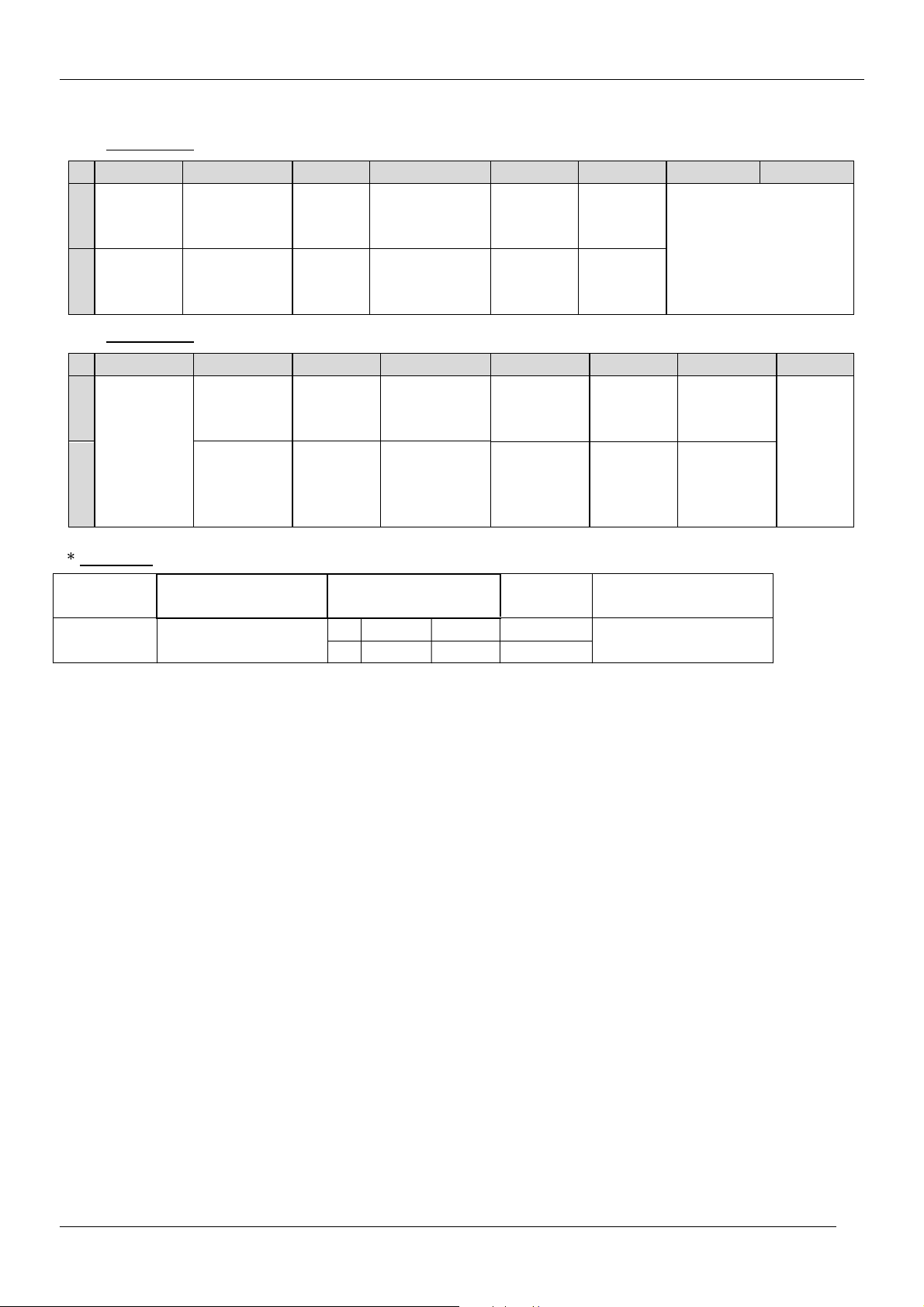
There are two option bytes available (16 bits in all). These option bits are available from Service
mode. First find the OPTION1 or OPTION2 control, and then use the Volume PLUS/MINUS
buttons on the remote control keypad to locate the bits, and OK key to toggle them. The table
below shows the two option bytes available;
Page 12
11
3.4 OPTION 1
OPTION
B7 B6 B5 B4 B3 B2 B1 B0
TOP
1
Teletext
OFF
TOP
0
Teletext
ON
3.5 OPTION 2
B7 B6 B5 B4 B3 B2 B1 B0
1
Fixed to
‘ 0’
0
FASTEXT
(FLOF)
OFF
FASTEXT
(FLOF) ON
JVC
remote
control
Daewoo
Remote
control
TUBE
4:3
TUBE
16:9
AVL
control
OFF
AVL
control
ON
VAI bit set
to 1 in
SECAM L
VAI bit set
to 0 in
SECAM L
PICTURE
TILT ON
PICTURE
TILT OFF
Dolby
Virtual
OFF
Dolby
Virtual
ON
5 keys
local
keyboard
7 keys
lacal
keyboard
SVHS3
disable
SVHS3
enable
Full
ATSS
Basic
ATSS
CP-520V Service Manual
TUNER OPTIONS
00 = Philips
01 = Not used
10 = Alps, LG
11 = Parstnic, SS
Double
Window
Enabled
Double
Window
Disabled
n.u.
Must
be set
to 1 for
future
compa
tibility
CHASSIS MODEL
CP-520V
OPTION
BIT[b7…b0]
I 0011 1110 3EDTX-21G2/B4/U7
II 0000 1111 0F
DW[hex] REMARKS
OPTION1 “ b1,b0” depends on Tuner
Page 13

CP-520V Service Manual
12
3.6 NVM default setting
The purpose of this message, when you change a virgin EEPROM, is to allow to modify
the NVM DATA to desired values.
1 - Introduction :
The NVM default valus are fixed for the user, but for flexibility in service, these data are stored in
NVM and can be changed when the TV set is in a special mode call "NVM EDITOR". This mode
can only be access from "FACTORY" mode.
2 - Entering into "FACTORY" mode.
To switch the TV set into FACTORY mode, use the factory remote control, and press on “SVC”
key. The factory menu will appear on the screen, showing “FACTORY” , plus other relevant
information like software version and date.
WARNING : When in "FACTORY" mode you should not press any key other than the keys
described in the procedure below. Unwanted key stroke could misadjust the TV set.
3 - Entering into "NVM EDITOR" mode.
To switch the TV set into NVM EDITOR mode, use the user remote control, and press on
“PICTURE/OK” key. The NVM EDITOR window will appear on the screen. This mode allow you
to access all data stored in NVM. The current NVM address is given in column "ADDR." in both
DECimal and HEXadecimal format. The column DATA gives the value contained at selected
address in both DECimal and HEXadecimal format.
4 - Navigation in "NVM EDITOR" mode.
Use Program Up/Dwn keys to select the desired address. Use Volume Up/Dwn keys to change
the data at selected address. You must press "PICTURE/OK" key to store value after
modification.
The data can be adjusted between 0 and 63.
5 - Exit "NVM EDITOR" mode.
To switch the TV set back into FACTORY mode, use the user remote control, and press on
“MENU” key.
The factory menu will appear on the screen, showing “FACTORY”.
6 - Exit "FACTORY" mode.
To exit "FACTORY" mode, use the factory remote control, and press on “SVC” key.
The factory menu will disappear from the screen.
Page 14
CP-520V Service Manual
13
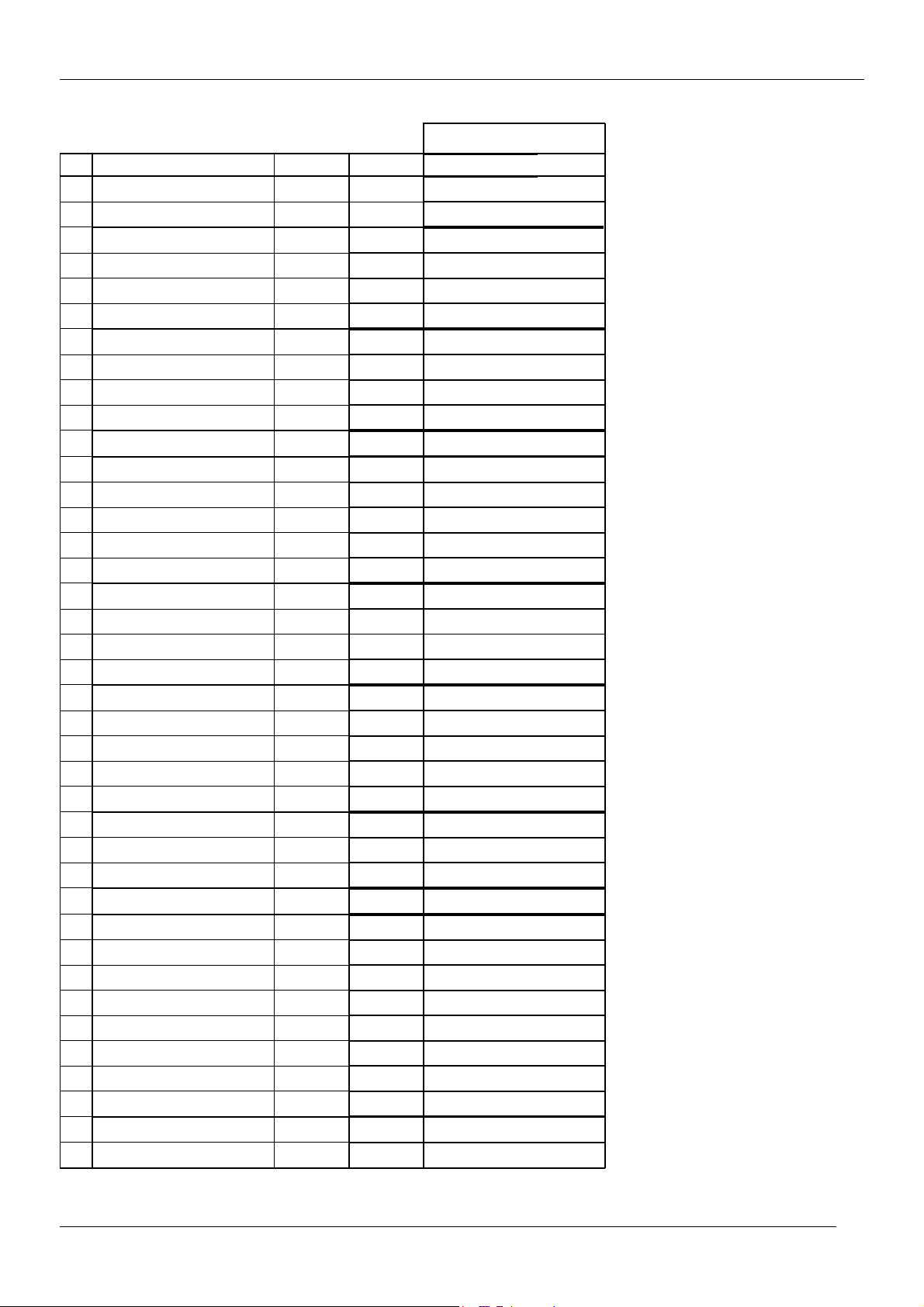
NVM DATA CHANGE LIST
No Register Name Address Default
1 OCP_THRESHOLD 0x58F 0x91
2 DCXO 0x590 0x4E
3 AGC_PHILIPS 0x5C1 0xAB
4 AGC_NC 0x5C2 0xAB
5 AGC_ALPS, LG 0x5C3 0xB6
6 AGC_PARTSNIC 0x5C4 0xB6
7 AGC_PHILIPS_START 0x5C5 0x16 O x OF
8 AGC_NC_START 0x5C6 0x16
9 AGC_ALPS, LG_START 0x5C7 0x16
10 AGC_PARTSNIC_START 0x5C8 0x16
11 AVLLEV 0x621 0x5
12 Nor1_Bright 0x64A 0x23
13 Nor1_contrast 0x64B 0x2E
14 Nor1_Colour 0x64C 0x1C
15 Nor1_Sharpness 0x64D 0x23
16 Nor1_Tint 0x64E 0x20
17 Nor1_JVC_Bri 0x64F 0x2D
18 Nor1_JVC_Cont 0x650 0x2A
19 Nor1_JVC_Colour 0x651 0x1B
20 Nor1_JVC_Sharp 0x652 0x23
21 Nor2_Bright 0x653 0x28
22 Nor2_Contrast 0x654 0x13
23 Nor2_Colour 0x655 0x19
24 Nor2_Sharpness 0x656 0x1B
25 Nor2_Tint 0x657 0x20
26 PresetGainRGB 0x673 0x2A
27 PresetGainRGB 0x674 0x2A
28 PresetGainRGB 0x675 0x2A
29 Cathode_Drive 0x67B 0x1
30 Y_delay_PAL_BG 0x686 0x5
31 Y_delay_SECAM_BG 0x687 0x8
32 Y_delay_PAL_DK 0x688 0x5
33 Y_delay_SCM_DK 0x689 0x5
34 Y_delay_PAL_I 0x68A 0x7
35 Y_delay_SECAM 0x68B 0x5
36 Y_delay_SECAM-L 0x68C 0x8
37 Y_delay_AV 0x68D 0xA
38 G2_Bright 0x68E 0x1A
39 G2_Contrast 0x68F 0x42
(hex) CP-520V
21G2/B4/U7
<
<
<
<
<
<
O x OF
O x OF
O x OF
<
<
<
<
<
<
<
<
<
<
<
<
<
<
O x 10
O x 10
O x 10
<
O x 02
O x 0B
O x 0
O x 08
O x 0B
O x 07
O x 07
O x 05
0x28
-
-
-
-
-
-
-<
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-<
Page 15
CP-520V Service Manual
14
3.7 TV SET ALIGNMENT
3.7.1 G2 ALIGNMENT
- Tune a colour bar pattern.
- Find the “G2 – SCREEN” item in service mode.
- Adjust screen volume (on FBT) to bring the cursor to central position(Green).
3.7.2 WHITE BALANCE
- Select a dark picture and adjust RED BIAS and GRN BIAS to the desired colour temperature.
- Select a bright picture and adjust RED, GRN and BLUE GAIN to the desired colour temperature.
3.7.3 FOCUS
Adjust the Focus volume (on FBT) to have the best resolution on screen.
3.7.4 VERTICAL GEOMETRY
Adjust V. LINEAR (linearity), S CORRECT (S. Correction), VERT SIZE (Vertical amplitude),
VERT CENT (vertical centring) to compensate for vertical distortion.
3.7.5 HORIZONTAL PICTURE CENTRING
Adjust HOR CEN (Horizontal centre) to have the picture in the centre of the screen.
3.7.6 AGC
- Make sure option bits are correct for the tuner fitted on the chassis (See above how to change
option bits).
- Adjust the antenna signal level at 62 dBµV
- Tune a colour bar pattern.
- Find the “AGC” item in service mode.
- Press the key “OK” on the remote keypad and wait until AGC level stabilise to the optimum
value.
- Alternatively, use “Vol Up/Dwn” keys to adjust manually to the desired Tuner Take Over Point
(TOP).
Page 16
15
4 IC DESCRIPTION
CP-520V Service Manual
4.1 UOC
III
Series
The UOC
III
series combines the functions of a Video Signal Processor (VSP) together with a
FLASH embedded TEXT/Control/Graphics µ-Controller (TCG µ-Controller) and US Closed
Caption decoder. In addition the following functions can be added:
• Adaptive digital (4H/2H) PAL/NTSC combfilter
• Teletext decoder with 10 page text memory
• Multi-standard stereo decoder
• BTSC stereo decoder
• Digital sound processing circuit
• Digital video processing circuit
4.1.1 IC MARKING AND VERSION
Chassis IC marking OSD languages ATSS countries Text
BULGARIAN,
Austria, Belgium,
Switzerland, Czech
Republic, Germany,
Denmark, Spain,
France, Finland, GB,
Greece, Hungary, Italy,
Ireland, Norway,
Netherlands, Portugal,
Poland, Sweden,
Slovak Republic,
Others
PAN-EUROPEAN
LATIN, CYRILLIC,
GREEK.
CP-520V
CZECH, GERMAN,
DANISH, SPANISH,
FRENCH, FINNISH,
ENGLISH, GREEK,
HUNGARIAN,
ITALIAN,
NORWEGIAN,
DUTCH, POLISH,
ROMANIAN,
RUSSIAN,
SWEDISH,
SLOVAKIAN.
Page 17
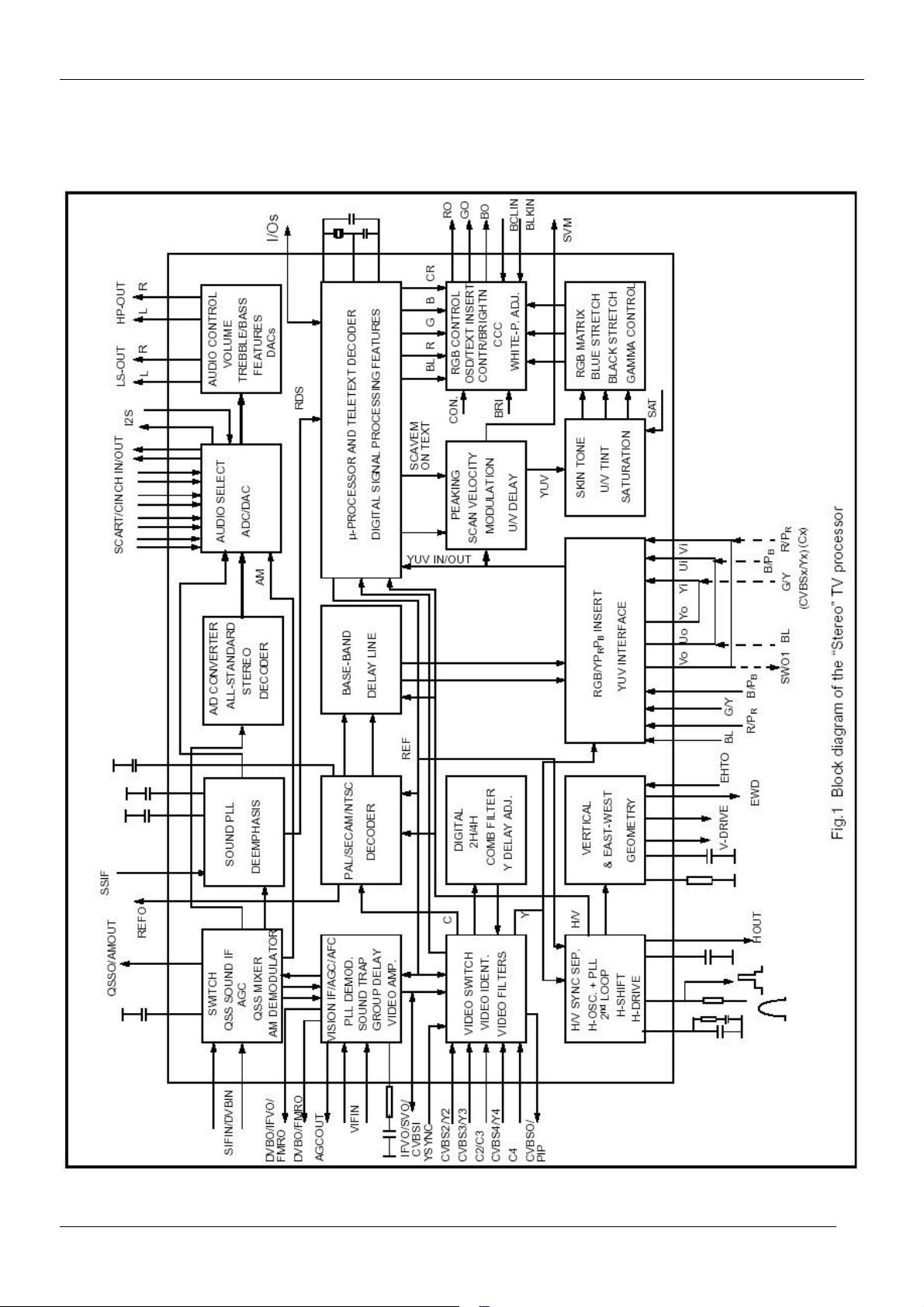
16
4.1.2. BLOCK DIAGRAM
CP-520V Service Manual
Page 18
CP-520V Service Manual
17
4.1.3. PINNING
QFP 128pin Symbol Short Description
1 P1.5/TX Port 1.5 or UART bus
2 P1.4/RX port 1.4 or UART bus
3 P1.2/INT2 port 1.2 or external interrupt 2
4 VSSC3 Ground
5 VDDC3 digital supply to core (1.8V)
6 P2.5/PWM4 port 2.5 or PWM4 output
7 P2.4/PWM3 port 2.4 or PWM3 output
8 VSSC/P digital ground for m-Controller core and periphery
9 P3.3/ADC3 port 3.3 or ADC3 input
10 P3.2/ADC2 port 3.2 or ADC2 input
11 DECV1V8 decoupling 1.8 V supply
12 VDDC1 digital supply to core (+1.8 V)
13 P3.1/ADC1 port 3.1 or ADC1 input
14 P3.0/ADC0 port 3.0 or ADC0 input
15 P2.3/PWM2 port 2.3 or PWM2 output
16 P2.2/PWM1 port 2.2 or PWM1 output
17 P2.1/PWM0 port 2.1 or PWM0 output
18 P2.0/TPWM port 2.0 or Tuning PWM output
19 VDDP(3.3V)
20 P1.7/SDA port 1.7 or I2C-bus data line
21 P1.6/SCL port 1.6 or I2C-bus clock line
22 P1.3/T1 port 1.3 or Counter/Timer 1 input
23 P0.0/I2SDI1/O port 0.0 or I2S digital input 1 or I2S digital output
24 P0.1/I2SDO1 port 0.1 or I2S digital output 1
25 P0.2/I2SDO2 port 0.2 or I2S digital output 2
26 P0.3/I2SCLK port 0.3 or I2S clock
27 P0.4/I2SWS port 0.4 or I2S word select
28 VSSC2 Ground
29 VDDC2 digital supply to core (1.8 V)
30 P1.1/T0 port 1.1 or Counter/Timer 0 input
31 P1.0/INT1 port 1.0 or external interrupt 1
32 INT0/P0.5
33 VDDadc(1.8) supply voltage video ADC
34 VSSadc ground for on-chip temperature sensor
35 VDDA2(3.3) supply voltage SDAC (3.3 V)
36 VDDA(1.8) analogue supply for audio ADCs (1.8 V)
37 GNDA Ground
38 VREFAD reference voltage for audio ADCs (3.3/2 V)
39 VREFAD_POS positive reference voltage (3.3 V)
40 VREFAD_NEG negative reference voltage (0 V)
41 VDDA1
42 BO Blue output
supply to periphery and on-chip voltage regulator (3.3
V)
external interrupt 0 or port 0.5 (4 mA current sinking
capability for direct drive of LEDs)
analog supply for TCG m-Controller and digital supply
for
TV-processor (+3.3 V)
Page 19

CP-520V Service Manual
18
43 GO Green output
44 RO Red output
45 BLKIN black current input
46 BCLIN beam current limiter input
47 VP3 3rd supply for TV processor
48 GND3 ground 3 for TV-processor
49 B/PBIN3 3rd B input / PB input
50 G/YIN3 3rd G input / Y input
51 R/PRIN3 3rd R input / PR input
52 INSSW3 3rd RGB / YPBPR insertion input
53 VOUT(SWO1)
54 UOUT(INSSW2)
55 YOUT Y-output (for YUV interface)
56 YSYNC Y-input for sync separator
57 YIN (G/YIN2/CVBS-Yx)
58 UIN (B/PBIN2) U-input for YUV interface (2nd B input / PB input)
59 VIN (R/PRIN2/CX)
60 VDDcomb supply voltage for comb filter (5 V)
61 VSScomb ground connection for comb filter
62 HOUT horizontal output
63 FBISO/CSY
64 SVM scan velocity modulation output
65 CVBSO/PIP CVBS / PIP output
66 AUDOUTHPR audio output for headphone channel (right signal)
67 AUDOUTHPL audio output for headphone channel (left signal)
68 AUDOUTLSR audio output for audio power amplifier (right signal)
69 AUDOUTLSL audio output for audio power amplifier (left signal)
70 C2/C3 chroma-2/3 input
71 CVBS3/Y3 CVBS3/Y3 input
72 AUDIOIN3R audio 3 input (right signal)
73 AUDIOIN3L audio 3 input (left signal)
74 CVBS2/Y2 CVBS2/Y2 input
75 AUDIOIN2R audio 2 input (right signal)
76 AUDIOIN2L audio 2 input (left signal)
77 C4 chroma-4 input
78 CVBS4/Y4 CVBS4/Y4 input
79 AUDIOIN4R audio-4 input (right signal)
80 AUDIOIN4L audio-4 input (left signal)
81 IFVO/SVO/CVBSI (2) IF video output / selected CVBS output / CVBS input
82 VP2 2nd supply voltage TV processor (+5 V)
83 AGC2SIF AGC capacitor second sound IF
84 VCC8V 8 Volt supply for audio switches
85 DVBO/FMRO (2) Digital Video Broadcast output / FM radio output
86 DVBO/IFVO/FMRO (2)
V-output for YUV interface (general purpose switch
output)
U-output for YUV interface (2nd RGB / YPBPR
insertion input)
Y-input for YUV interface (2nd G input / Y input or
CVBS/YX input))
V-input for YUV interface (2nd R input / PR input or CX
input)
flyback input/sandcastle output or composite H/V
timing output
Digital Video Broadcast output / IF video output / FM
radio output
Page 20

19
87 SIFAGC/DVBAGC (2)
88 PLLIF IF-PLL loop filter
89 GND2 ground 2 for TV processor
90
91 DECSDEM decoupling sound demodulator
92 AUDOUTSR audio output for SCART/CINCH (right signal)
93 AUDOUTSL audio output for SCART/CINCH (left signal)
94 AUDIOIN5R audio-5 input (right signal)
95 AUDIOIN5L audio-5 input (left signal)
96
97 EHTO EHT/overvoltage protection input
98 AGCOUT tuner AGC output
99 SIFIN2/DVBIN2 (2) SIF input 2 / DVB input 2
100 SIFIN1/DVBIN1 (2) SIF input 1 / DVB input 1
101 GNDIF ground connection for IF amplifier
102 IREF reference current input
103 VSC vertical sawtooth capacitor
104 VIFIN2 IF input 2
105 VIFIN1 IF input 1
106 VDRA vertical drive A output
107 VDRB vertical drive B output
108 EWD/AVL (1) East-West drive output or AVL capacitor
109 DECBG bandgap decoupling
110 SECPLL SECAM PLL decoupling
111 GND1 ground 1 for TV-processor
112 PH1LF phase-1 filter
113 PH2LF phase-2 filter
114 VP1 1st supply voltage TV-processor (+5 V)
115 DECDIG decoupling digital supply
116 VGUARD/SWIO
117 VSSA1 Ground
118 XTALOUT crystal oscillator output
119 XTALIN crystal oscillator input
120 VREF_POS_HPR positive reference voltage SDAC (3.3 V)
121 VREF_NEG_HPL+HPR negative reference voltage SDAC (0 V)
122 VREF_POS_LSR+HPR positive reference voltage SDAC (3.3 V)
123 VREF_NEG_LSL+HPL negative reference voltage SDAC (0 V)
124 VREF_POS_LSL positive reference voltage SDAC (3.3 V)
125 VDDA3(3.3V) supply (3.3 V)
126 VDDC4 digital supply to SDACs (1.8V)
127 VSSC4 Ground
128 VSSP2 Ground
QSSO/AMOUT/AUDEE
M (2)
AVL/SWO/SSIF/
REFO/REFIN (2)
AGC sound IF / internal-external AGC for DVB
applications
QSS intercarrier output / AM output / deemphasis
(front-end audio
out)
Automatic Volume Levelling / switch output / sound IF
input /
subcarrier reference output / external reference signal
input for I
signal mixer for DVB operation
V-guard input / I/O switch (e.g. 4 mA current sinking
capability for
direct drive of LEDs)
CP-520V Service Manual
Page 21

CP-520V Service Manual
20
4.1.4 FEATURES
Analogue Video Processing (all versions)
· Multi-standard vision IF circuit with alignment-free PLL demodulator
· Internal (switchable) time-constant for the IF-AGC circuit
· Switchable group delay correction and sound trap (with switchable centre frequency) for the
demodulated CVBS signal
· DVB/VSB IF circuit for preprocessing of digital TV signals.
· Video switch with 3 external CVBS inputs and a CVBS output. All CVBS inputs can be used as
Y-input for Y/C signals. However, only 2 Y/C sources can be selected because the circuit has 2
chroma inputs. It is possible to add an additional CVBS(Y)/C input (CVBS/YX and CX) when the
YUV interface and the RGB/YPRPB input are not needed.
· Automatic Y/C signal detector
· Adaptive digital (4H/2H) PAL/NTSC comb filter for optimum separation of the luminance and the
chrominance signal.
· Integrated luminance delay line with adjustable delay time
· Picture improvement features with peaking (with switchable centre frequency, depeaking,
variable positive/negative peak ratio, variable pre-/overshoot ratio and video dependent coring),
dynamic skin tone control, gamma control and blue- and black stretching. All features are
available for CVBS, Y/C and RGB/YPBPR signals.
· Switchable DC transfer ratio for the luminance signal
· Only one reference (24.576 MHz) crystal required for the TCG m-Controller, digital sound
processor, Teletext and the colour decoder
· Multi-standard colour decoder with automatic search system and various “forced mode”
possibilities
· Internal base-band delay line
· Indication of the Signal-to-Noise ratio of the incoming CVBS signal
· Linear RGB/YPBPR input with fast insertion.
· YUV interface. When this feature is not required some pins can be used as additional
RGB/YPBPR input. It is also possible to use these pins for additional CVBS (or Y/C) input
(CVBS/YX and CX).
· Tint control for external RGB/YPBPR signals
· Scan Velocity Modulation output. The SVM circuit is active for all the incoming CVBS, Y/C and
RGB/YPBPR signals. The SVM function can also be used during the display of teletext pages.
· RGB control circuit with ‘Continuous Cathode Calibration’, white point and black level off-set
adjustment so that the colour temperature of the dark and the light parts of the screen can be
chosen independently.
· Contrast reduction possibility during mixed-mode of OSD and Text signals
· Adjustable ‘wide blanking’ of the RGB outputs
· Horizontal synchronization with two control loops and alignment-free horizontal oscillator
· Vertical count-down circuit
· Vertical driver optimized for DC-coupled vertical output stages
· Horizontal and vertical geometry processing with horizontal parallelogram and bow correction
and horizontal and vertical zoom
· Low-power start-up of the horizontal drive circuit
Analogue video processing (stereo versions)
· The low-pass filtered ‘mixed down’ I signal is available via a single ended or balanced output
stage.
Analogue video processing (mono versions)
· The low-pass filtered ‘mixed down’ I signal is available via a single ended output stage
Digital Video Processing (some versions)
· Double Window mode applications. It is possible to display a video and a text window or 2 text
Page 22

CP-520V Service Manual
21
windows in parallel.
· Linear and non-linear horizontal scaling of the video signal to be displayed.
Sound Demodulation (all versions)
· Separate SIF (Sound IF) input for single reference QSS (Quasi Split Sound) demodulation.
· AM demodulator without extra reference circuit
· The mono intercarrier sound circuit has a selective FM-PLL demodulator which can be switched
to the different FM sound frequencies (4.5/5.5/6.0/6.5 MHz). The quality of this system is such
that the external band-pass filters can be omitted. In the stereo versions of UOCIII the use of this
demodulator is optional for special applications. Normally the FM demodulators of the stereo
demodulator/decoder part are used (see below).
· The FM-PLL demodulator can be set to centre frequencies of 4.72/5.74 MHz so that a second
sound channel can be demodulated. In such an application it is necessary that an external
bandpass filter is inserted.
· The vision IF and mono intercarrier sound circuit can be used for the demodulation of FM radio
signals. With an external FM tuner also signals with an IF frequency of 10.7 MHz can be
demodulated.
· Switch to select between 2nd SIF from QSS demodulation or external FM (SSIF)
Audio Interfaces and switching (stereo versions with Audio DSP)
· Audio switch circuit with 4 stereo inputs, a stereo output for SCART/CINCH, 1 stereo output for
HEADPHONE. The headphone channel has an analogue volume control circuit for the L and R
channel. Finally 1 stereo SPEAKER output with digital controls.
· AVL (Automatic Volume Levelling) circuit for the headphone channel.
· Digital input crossbar switch for all digital signal sources and destinations
· Digital output crossbar for exchange of channel processing functionality
· Digital audio input interface (stereo I2S input interface)
· Digital audio output interface (stereo I2S output interface)
Audio interfaces and switching (AV stereo versions without Audio DSP)
· Audio switch circuit with 4 stereo inputs, a stereo output for SCART/CINCH and a stereo
SPEAKER output with analogue volume control.
· Analogue mono AVL circuit at left audio channel
Audio interfaces and switching (mono versions)
· Audio switch circuit with 4 external audio (mono) inputs and a volume controlled output
· AVL circuit
Stereo Demodulator and Decoder (full stereo versions)
· Demodulator and Decoder Easy Programming (DDEP)
· Auto standard detection (ASD)
· Static Standard Selection (SSS)
· DQPSK demodulation for different standards, simultaneously with 1-channel FM demodulation
· NICAM decoding (B/G, I, D/K and L standard)
· Two-carrier multistandard FM demodulation (B/G, D/K and M standard)
· Decoding for three analog multi-channel systems (A2, A2+ and A2*) and satellite sound
· Adaptive de-emphasis for satellite FM
· Optional AM demodulation for system L, simultaneously with NICAM
· Identification A2 systems (B/G, D/K and M standard) with different identification time constants
· FM pilot carrier present detector
· Monitor selection for FM/AM DC values and signals, with peak and quasi peak detection option
· BTSC MPX decoder
· SAP decoder
· dbx® noise reduction (4)
· Japan (EIAJ) decoder
· FM radio decoder
· Soft-mute for DEMDEC outputs DEC, MONO and SAP
Page 23

CP-520V Service Manual
22
· FM overmodulation adaptation option to avoid clipping and distortion
Audio Multi Channel Decoder (stereo versions with Audio DSP)
· Dolby® Pro Logic® (DPL) (1)
· Five channel processing for Main Left and Right, Subwoofer, Centre and Surround. To exploit
this feature an external DAC is required.
Volume and tone control for loudspeakers (stereo versions with Audio DSP)
· Automatic Volume Level (AVL) control
· Smooth volume control
· Master volume control
· Soft-mute
· Loudness
· Bass, Treble
· Dynamic Bass Boost (DBB) (2)
· Dynamic Virtual Bass (DVB) (3)
· BBE® Sound processing (4)
· Graphic equalizer
· Processed or non processed subwoofer
· Programmable beeper
Reflection and delay for loudspeaker channels (stereo versions with Audio DSP)
· Dolby® Pro Logic® Delay (1)
· Pseudo hall/matrix function
Psycho acoustic spatial algorithms, downmix and split in loudspeaker channels (stereo
versions with Audio DSP)
· Extended Pseudo Stereo (EPS) (5)
· Extended Spatial Stereo (ESS) (6)
· Virtual Dolby® Surround (VDS 422,423) (1)
· SRS 3D and SRS TruSurround® (4)
RDS/RBDS
· Demodulation of the European Radio Data system (RDS) or the USA Radio Broadcast Data
System (RBDS) signal
· RDS and RBDS block detection
· Error detection and correction
· Fast block synchronisation
· Synchronisation control (flywheel)
· Mode control for RDS/RBDS processing
· Different RDS/RBDS block information output modes
m-Controller
· 80C51 m-controller core standard instruction set and timing
· 0.4883 ms machine cycle
· maximum of 256k x 8-bit flash programmable ROM
· maximum of 8k x 8-bit Auxiliary RAM
· 12-level Interrupt controller for individual enable/disable with two level priority
· Two 16-bit Timer/Counter registers
· One 24-bit Timer (16-bit timer with 8-bit Pre-scaler)
· WatchDog timer
· Auxiliary RAM page pointer
· 16-bit Data pointer
· Stand-by, Idle and Power Down modes
· 24 general I/O
· 14 bits PWM for Voltage Synthesis Tuning
· 8-bit A/D converter with 4 multiplexed inputs
Page 24

CP-520V Service Manual
23
· 5 PWM (6-bits) outputs for analogue control functions
· Remote Control Pre-processor (RCP)
· Universal Asynchronous Receiver Transmitter (UART)
Data Capture
· Text memory up to 10 pages
· Inventory of transmitted Teletext pages stored in the Transmitted Page Table (TPT) and Subtitle
Page Table (SPT)
· Data Capture for US Closed Caption
· Data Capture for 525/625 line WST, VPS (PDC system A) and Wide Screen Signalling (WSS)
bit decoding
· Automatic selection between 525 WST/625 WST
· Automatic selection between 625 WST/VPS on line 16 of VBI
· Real-time capture and decoding for WST Teletext in Hardware, to enable optimized mprocessor throughput
· Automatic detection of FASTEXT transmission
· Real-time packet 26 engine in Hardware for processing accented, G2 and G3 characters
· Signal quality detector for video and WST/VPS data types
· Comprehensive teletext language coverage
· Vertical Blanking Interval (VBI) data capture of WST data
Display
· Teletext and Enhanced OSD modes
· Features of level 1.5 WST and US Close Caption
· 50Hz/60Hz display timing modes
· Two page operation for 16:9 screens
· Serial and Parallel Display Attributes
· Single/Double/Quadruple Width and Height for characters
· Smoothing capability of both Double Size, Double Width & Double Height characters
· Scrolling of display region
· Variable flash rate controlled by software
· Soft colours using CLUT with 4096 colour palette
· Globally selectable scan lines per row (9/10/13/16/) and character matrix [12x9, 12x10, 12x13,
12x16, 16x18, (VxH)]
· Fringing (Shadow) selectable from N-S-E-W direction
· Fringe colour selectable
· Contrast reduction of defined area
· Cursor
· Special Graphics Characters with two planes, allowing four colours per character
· 64 software redefinable On-Screen display characters
· 4 WST Character sets (G0/G2) in single device (e.g. Latin, Cyrillic, Greek, Arabic)
· G1 Mosaic graphics, Limited G3 Line drawing characters
· WST Character sets and Closed Caption Character set in single device
· SVM for Text
4.2 LA42032 STEREO AUDIO AMPLIFIER
The LA42032 is a dual-channel audio power amplifier with an output power of 2 x 5 W at an 8
Ω load and a 9 V supply.
Page 25

24
4.2.1 FEATURES
LA42032
CP-520V Service Manual
5W x 2 Channel(Vcc=9V, R
Standby function
•
Mute function
•
Thermal protection circuit
•
L=8Ω)•
Pin description
Pin Symbol Description
1 R.F.
2 Right input
3 Ground
4 Left Input
5 Standby
6 Mute
7 Supply Voltage
8 Positive Left output
9 Negative Left Output
10 Ground
11 Negative Right Output
12
13
Rin
GND
Lin
STB
Mute
Vcc
Lo(+)
Lo(-)
GND
Ro(-)
Ro(+)
N.C.
Ripple Filter
Positive Right Output
Not Connected
R.F.
Rin
GND
Lin
STB
Mute
Vcc
Lo(+)
Lo(-)
GND
Ro(-)
Ro(+)
N.C.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
MBK932
Page 26

CP-520V Service Manual
25
Block diagram LA42032
Page 27

CP-520V Service Manual
4.3 LA78040 VERTICAL AMPLIFIER
The LA78040 are power circuit for use in 90° and 110° colour deflection systems for field
frequencies of 25 to 200Hz field frequencies, and for 4:3 and 16/9 picture tubes. The IC contains
a vertical deflection output circuit, operating as a high efficiency class G system. The full bridge
output circuit allows DC coupling of the deflection coil in combination with single positive supply
voltages.
4.3.1 FEATURES
§ Built-in pump-up circuti for low power dissipation
§ Vertical output circuit
§ Thermal protection circuit
1
Vin(-)
2
Vcc
-14V
Vout
Vcc
Vin(+)
3
4
5
6
7
LA78040
MGL867
Pump Up Out
26
Page 28

27
Pinning
Pin Symbol Description
1 Vin(-) Inverting Input
2 Vcc Supply voltage
3 Pump Up Out Pump Up Out
4 -14V -14V
5 Vout Ver. Output
6 Vcc Output Stage Vcc
7 Vin(+) Non Inv. Input
CP-520V Service Manual
Block diagram LA78040
Page 29

CP-520V Service Manual
28
4.4 24WC16 - 16 KB EEPROM
Features :
§ 16 Kbit serial I2C bus EEPROM
§ 400KHz I2C Bus Compatible
§ supply voltage : 1.8 V to 6.0 V
§ Low Power CMOS Technology
§ 1 Million Erase/Write cycles (minimum)
§ 100 year data retention (minimum)
Pin description
Pin No. Name Description
1, 2, 3 A0, A1, A2 Device address – not used
5 SDA Serial Data/Address Input/Output
6 SCL Serial clock
7 WP Write control
8 Vcc Supply voltage
4 Vss Ground
The memory device is compatible with the I2C memory standard. This is a two wire serial
interface that uses a bi-directional data bus and serial clock. The memory carries a built-in 4-bit
unique device type identifier code (1010) in accordance with the I2C bus definition.
Serial Clock (SCL)
The SCL input is used to strobe all data in and out of the memory.
Serial Data (SDA)
The SDA pin is bi-directional, and is used to transfer data in or out of the memory.
Page 30

29
The STR-W6754 is a quasi-resonant regulator specifically designed
to satisfy the requirements for increased integration and reliability in
switch-mode power supplies. It incorporates a primary control and drive
circuit with an avalanche-rated power MOSFET.
• Auto-Bias Function Stable Burst Operation Without Generating Interference
• Internal Off-Timer Circuit
• Built-In Constant-Voltage Drive
• Multiple Protections: Pulse-by-Pulse Overcurrent Protection
Overload Protection with Auto Recovery
Latching Overvoltage Protection
Undervoltage Lockout with Hysteresis
• RoHS Compliant
4.5 STR - W6754
4.5.1 GENERAL DESCRIPTION
CP-520V Service Manual
4.5.2 FEATURES
4.5.3 BLOCK DIAGRAM
Page 31

CP-520V Service Manual
30
4.5.4 PIN DESCRIPTION
PIN NAME SYMBOL DESCRIPTION
1 Drain D MOSFET drain
3 Source/Ground S/GND Ground
4 Supply Vcc Power Supply
5 Overload Protection SS/OLP Overload Protection and Soft Start Operation Time set up
6 Feedback FB
7 Overcurrent Protection OCP/BD
Constant Voltage Control Signal Input,
Burst mode Oscillation Control
Overcurrent Protection Signal Input/
Bottom Detection Signal Input
4.5.5 CONTROL PART - ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Limits
Characteristic Symbol Test Conditions Min. Typ. Max. Units
Start-Up Operation
Operation Start Voltage V
Soft-Start Operation Stop Voltage V
Soft-Start Oper. Charging Current I
Operation Stop Voltage V
Circuit Current in Non-Operation I
Normal Operation
Drain-Source Breakdown Voltage V
Drain Leakage Current I
On-State Resistance r
ItnerruC tiucriC
Oscillation Frequency f
Bottom-Skip Oper. Threshold Volt. V
Quasi-Resonant Oper. Threshold V
OCPBD(BS1)
V
OCPBD(BS2)
OCPBD(TH1)
V
OCPBD(TH2)
Feedback-Pin Threshold Voltage V
Feedback-Pin Current I
Standby Operation
CC(ON)
SS/OLP
SS/OLP
CC(OFF)
CC(OFF)
(BR)DSS
DSS
DS(on)
temiT gnihctiwS
f
CC(ON)
osc
FB(OFF)
FB(ON)
Turn-on, VCC = 0 19.9 V 16.3 18.2 19.9 V
1.1 1.2 1.4 V
-390 -550 -710 µA
Turn-off, VCC = 19.9 8.8 V 8.8 9.7 10.6 V
V
CC
I
D
V
DS
ID = 1.9 A, TJ = +25°C – – 0.96 Ω
– – 400 ns
– – 6.0 mA
19 22 25 kHz
-605 -665 -720 mV
-385 -435 -485 mV
280 400 520 mV
670 800 930 mV
1.32 1.45 1.58 V
600 1000 1400 µA
Aµ001––V 51 =
V––056Aµ 003 =
Aµ003––V 056 =
Standby Operation Start Voltage V
Standby Oper. Start Volt. Interval V
Standby Non-Operation Current I
Feedback-Pin Current I
FB(ON)
Feedback-Pin Threshold Voltage V
Minimum ON Time t
on(min)
CC(S)
CC
CC(S)
FB(S)
VCC = 0 12.2 V 10.3 11.1 12.1 V
1.10 1.35 1.65 V
V
CC
V
CC
VCC = 12.2 V 0.55 1.10 1.50 V
0.5 0.8 1.2 µs
Aµ6502–V 2.01 =
Aµ410.4–V 2.01 =
Page 32

CP-520V Service Manual
31
Limits
Characteristic Symbol Test Conditions Min. Typ. Max. Units
Protection Operation
OVP Operation Voltage V
Maximum ON Time t
OLP Operation Voltage V
OLP Operation Current I
Overcurrent Detect. Threshold Volt. V
OCPBD(LIM)
OCP/BD-Pin Current I
Latch Holding Current I
Latch Release Voltage V
Other
Thermal Resistance R
CC(OVP)
on(max)
SSOLP
SSOLP
OCPBD
CC(H)
CC(L)
θJF
Turn-off, VCC = 0 29.9 V 25.5 27.7 29.9 V
27.5 32.5 39.0 µs
4.0 4.9 5.8 V
-6.0 -11 -16 µA
-0.895 -0.940 -0.995 V
-40 -100 -250 µA
VCC = 29.9 V
– 0.3 V – 45 140 mA
CC(OF F)
VCC = 29.9 6 V 6.0 7.2 8.5 V
Output junction-to-frame – – 1.6 °C/W
Page 33

32
5 CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
5.1 BLOCK DIAGRAM
CP-520V Service Manual
Page 34

CP-520V Service Manual
33
5.2 FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION OF VIDEO PROCESSOR
5.2.1 Vision IF amplifier
The vision IF amplifier can demodulate signals with positive and megative modulation. The PLL
demodulator is completely alignment-free.
The VCO of the PLL circuit is internal and the grequency is fixed to the required value by using
the clock ftequency of the TCG u-Controller as a reference. The setting of the various
frequencies (e.g. 38, 38.9, 45.75 and 58.75MHz) can be made via the control bits IFA-IFC in
subaddress 2FH. Because of the internal VCO the IF circuit has a high immunity to EMC
interferences.
The output of the AFC detector can be read from output byte o4H and has a resolution of
7bit(25kHz per step). By means of this information a fast tuning algorithm can be designed.
The IC contains a group delay correction circuit which can be switched between the BG and a
uncompensated group delay response characteristic. This hasthe advantage that in multistandard receivers no compromise has to be made for the choice of the SAW filter. This group
delay corection is realised for the demodulated CVBS output signal. The IC contains in addition a
sound trap circuit with a switchable centre frequency.
5.2.2 QSS sound circuit
The sound IF amplifier is similar to the vision IF amplifier and has an external AGC decoupling
capacitor.
ThesinglereferenceQSSmixerisrealisedbyamultiplier. In this multiplier the SIF signal is converted
to the intercarrier frequency by mixing it with the regenerated picture carrier from the VCO. The
mixer output signal is suppliedtotheoutputviaahigh-passfilterforattenuation of the residual video
signals. With this system a high performance hi-fi stereo sound processing can be achieved.
TheAMsounddemodulatorisrealisedbyamultiplier.The modulated sound IF signal is multiplied in
phase with the limited SIF signal. The demodulator output signal is supplied to the output via a
low-pass filter for attenuation of the carrier harmonics.
SwitchingbetweentheQSSoutputandAMoutputismade by means of the AM bit in subaddress 33H.
5.2.3 FM demodulator
TheFMdemodulatorisrealisedasnarrow-bandPLL with internal loop filter, which provides the
necessary selectivity without using an external band-pass filter. To obtain a good selectivity a
linear phase detector and a constant input signal amplitude are required. For this reason the
intercarrier signal is internally supplied to the demodulator via a gain controlled amplifier and
AGC circuit. To improve the selectivity an internal bandpass filter is connected in front of the PLL
circuit.
The nominal frequency of the demodulator is tuned to the required frequency (4.5/5.5/6.0/6.5
MHz) by means of a calibration circuit which uses the clock frequency of the TCG(1)-Controller
as a reference. It is also possible to frequencies of 4.72 and 5.74Mhz so that a second sound
channel can be demodulated. In the latter application an external bandpass filter has to be
Page 35

CP-520V Service Manual
34
applied to obtain sufficient selectivity (the sound input can be activated by means of the setting of
CMB2-CMB0 bits in subaddress 4AH). The setting to the wanted frequency is realised by means
of the control bits FMA, FMB and FMC in the control bit 33H.
From the output status bytes it can be read whether the PL Lfrequency is inside or outside the
window and whether thePLL is in lock or not. With this information it is possible to make an
automatic search system for the incoming sound frequency. This can be realised by means of a
software loop which switches the demodulator to the various frequencies and then select the
frequency on which a lock condition has been found.
The amplitude deemphasis output signal changed with 6dB by means of the AGN bit. In this way
output signal differences between the 4.5 MHz standard (frequency deviation25 kHz) and the
other standards (frequency deviation50 kHz) can be compensated.
5.2.4 Audio input selector and volume control
5.2.4.1 STEREO AND AV STEREO VERSIONS
The audio input selector circuit has 4 external stereo inputs, a stereo output for SCART/CINCH
and stereo outputs for headphone and audio power amplifiers. The selection is made with the
bits SAS2/0, SO2/0 and HPO2/0. AV stereo versions without Audio DSP have no headphone
output. The input signal selection for the volumecontrolledaudiooutputsisrealisedbytheHPO2/0
bits.
The gain from an external audio input to each of the (non-controlled) analog output is 0 or
+6dB(controlled by the DSG bit). A supply voltage of 5V allows input and output amplitude of
1VRMS full scale, as required to comply with the SCART specification, the audio supply voltage
must be 8V. In that case the gain of the audio amplifier must be doubled. This can be realised
with the DSG bit in subaddress 32H.
The circuit contains an analogue stereo volume control circuit with a control range of about 70dB.
This volume control circuit is used for the headphone channel (stereo versions with Audio DSP)
or for the main channel (AV stereo versions without Audio DSP). The analogue control circuit
also contains an Automatic Volume Levelling(AVL) function. When this function is activated it
stabilises the audio output signal to a certainl evel so that big fluctuations of the output power are
prevented.
5.2.4.2 MONO VERSIONS
The audio input selector circuit has 4 inputs for mono signals. The selection is made with the
HPO2/0 bits.
The circuit contains an analogue volume control circuit with a control range of about 70dB and an
AVL circuit.
5.2.5 CVBS and Y/C input signal selection
5.2.5.1 ALL VERSIONS
Page 36

CP-520V Service Manual
35
The Ics have 3 inputs for external CVBS signals. All CVBS inputs can be used as Y input for the
insertion of Y/C signals.However, the CVBS(Y)2 input has to be combined with the C3 input. It is
possible to add and extra CVBS(Y/C) input via the pins which are intended to be used for YUV
interface (or RGB/YPrPb input). The selection of this additional CVBS(Y/C) input is made via the
YC bit.
The function of the IFVO/SVO/CVBSI pin is determined by the SVO1/SVO0 bits. When used as
output a selection can be made between the IF video output signal or the selected CVBS signal
(monitor out). This pin can also be used as additional CVBS input. This signal is inserted in front
of the group delay / sound trap circuit. It is also possible to use the group delay and sound trap
circuit for the CVBS2 signal (via the CV2 bit).
For the CVBS(Y/C) inputs the circuit can detect whether a CVBS or Y/C signal is present on the
input. The result can be read from the status register (YCD bit in subaddress 03H) and this
information can be used to put the input switch in the right position (by means of the INA-IND bits
in subaddress 38H). The Y/C detector is only active for the CVBS(Y)3/C3, CVBS(Y)4/C4 and
CVBS(Y)x/Cx inputs. It is not active for the CVBS(Y)2/C3 input.
The video ident circuit can be connected to all video input signals. This ident circuit is
independent of the synchronisation and can be used to switch the synchronisation and can be
used to switch the presence of a video signal (via the VID bit). In this way a very stable OSD can
be realised. The result of the video ident circuit can be read from the output bit SID (subaddress
00).
5.2.6 Synchronisation circuit
The IC contains separator circuits for the horizontal and vertical sync pulses. To obtain an
accurate timing of the displayed picture the input signal of the sync separator is not derived from
the various CVBS/Y or RGB/YPrPb inputs but from the YOUT pin. For this reason the YOUT pin
must be capacitively coupled to the YSYNC pin. The delay between the various inputs and the
YOUT signal can have rather large differences (e.g. comb filter active or not). By choosing the
YOUT signal as input signal for the sync separator these delays have no effect on the picture
position. Only for RGB signals without sync on green the input of the sync separator has to be
connected to one of the CVBS inputs. This selection is made by means of the SYS bit.
The horizontal drive signal is obtained from an internal VCO which is running at a frequency of
25 MHz. This oscillator is stabilised to this frequency by using the clock signal coming from the
reference oscillator of the TCG -Controller.
To obtain a stable On-Screen-Display (OSD) under all conditions it is important that the first
control loop is switched off or set to low gain when no signal is available at the input. The input
signal condition is detected by the video identification circuit. The video identification circuit can
automatically switch first control loop to a low gain when no input signal is available. This mode is
obtained when the VID bit is set to “0”. When the VID bit is “1” the mode of the first control loop
can be switched by means of the FOA/FOB or POC bits.
For a good performance during normal TV reception (display of the front-end signal) various
connections are active between the vision IF amplifier and the synchronisation circuit (e.g. gating
pulses for the AGC detector and noise gating of the sync separator). These connections are not
allowed when external video signals are displayed. The switching of these connections can be
coupled to the input signal selection bits (INA-IND). This mode is obtained when the VDXEN bit
is “0”. Due to the input signal selector configuration it is possible that the internal CVBS signal is
Page 37

CP-520V Service Manual
36
available on one of the other CVBS inputs.In this condition the connections between the vision IF
amplifier and the synchronisation circuit can be switched on and off by means of the VDX bit.
The VDXEN bit must be set to “1” for this mode.
The vertical synchronisation is realised by means of a divider circuit.
5.2.7 Horizontal and vertical drive
The horizontal drive is switched on and off via the soft start/stop procedure. The soft start
function is realised by means of variation of the TON of the horizontal drive pulses. During the
soft-stop period the horizontal output frequency is doubled resulting in a reduction of the EHT so
that the picture tube capacitance can easily be discharged. In addition the horizontal drive circuit
has a ‘low-power start-up’ function.
The vertical ramp generator needs an external resistor and capacitor. For the vertical drive a
differential output current is available. The outputs must be DC coupled to the vertical output
stage.
The IC has the following geometry control functions:
n Vertical amplitude
n Vertical slope
n S-correction
n Vertical shift
n Vertical zoom
n Vertical scroll
n Vertical linearity correction. When required the linearity setting for the upper and lower part
of the screen can have a different setting.
n Horizontal shift
n EW width
n EW parabola width
n EW upper and lower corner parabola correction
n EW trapezium correction
n Horizontal parallelogram and bow correction.
When the East-West geometry function is not required (e.g. for 90 picture tubes) the EW output
pin can be used for the connection of the AVL capacitor. This function is chosen by means of the
AVLE bit.
5.2.8 Chroma, luminance and feature processing
Someversionscontaina4H/2H(2D)adaptivePAL/NTSC comb filter. The comb filter is
automatically activated when standard CVBS signals are received.A signal is considered as
“standard signal” when a PAL or NTSC signal is identified and when the vertical divider is in the
modes ‘standard narrow window’ or ‘standard TV norm’.For non-standard signals and for
SECAM signals the comb filter is bypassed and the signal is filtered by means of bandpass and
trap filters.
The chroma band-pass and trap circuits (including the SECAM cloche filter) are realised by
means of internal filters and are tuned to the right frequency by comparing the tuning frequency
with the reference frequency of the colour decoder.
Page 38

CP-520V Service Manual
37
The circuit contains the following picture improvement features:
n Peaking control circuit. The peaking function can be activated for all incoming CVBS, Y/C
and RGB/YPrPb signals. Various parameters of the peaking circuit can be adapted by means
of the I2C-bus. The main parameters are:
- Peaking centre frequency (via the PF1/PF0 bits in subaddress 19H).
- Ratio of positive and negative peaks (via the RPO1/RPO0 bits in subaddress 47H). The
peaks in the direction “white” are the positive peaks.
- Ratio of pre- and aftershoots (via the RPA1/RPA0 bits in subaddress 47H).
n Video dependent coring in the peaking circuit. The coring can be activated only in the low-
light parts of the screen. This effectively reduces noise while having maximum peaking in the
bright parts of the picture.
n Black stretch. This function corrects the black level for incoming signals which have a
difference between the black level and the blanking level. The amount of stretching (A-A in
Fig. 72) and the minimum required back ground to activate the stretching can be set by
means of the I2C-bus (BSD/AAS in subaddress 45H).
n Gamma control. When this function is active the transfer characteristic of the luminance
amplifier is made non-linear.Thecontrolcurvecanbeadaptedbymeans of I2C-bus settings (see
Fig. 74). It is possible to make the gamma control function dependent on the picture content
(Average Picture Level, APL). The effect is illustrated in Fig. 75. Previously this function was
mentioned under the name “white stretch function”.
n Blue-stretch. This circuit is intended to shift colour near ‘white’ with sufficient contrast values
towards more blue to obtain a brighter impression of the picture.
n Dynamic skin tone (flesh) control. This function is realised in the YUV domain by detecting
the colours near to the skin tone.
n Scan-Velocity modulation output. Also the SVM function can be activated for all incoming
CVBS, Y/C and RGB/YPrPb signals. The delay between the RGB output signals and the
SVM output signal can be adjusted (by means of the SVM2-SVM0 bits in subaddress 48H)
so that an optimum picture performance can be obtained. Furthermore a coring function can
be activated. It is possible to generate Scan Velocity Modulation drive signals during the
display of ‘full screen’ teletext (not in mixed mode). Another feature is that the SVM output
signal can be made dependent on the horizontal position on the screen (parabola on the
SVM output).
5.2.9 Colour decoder
The ICs decode PAL, NTSC and SECAM signals. The PAL/NTSC decoder does not need
external reference crystals but has an internal clock generator which is stabilised to the required
frequency by using the clock signal from the reference oscillator of the TCG u -Controller.
Under bad-signal conditions (e.g. VCR-playback n feature mode), it may occur that the colour
killer is activated although the colour PLL is still in lock. When this killing action is not wanted it is
possible to overrule the colour killer by forcing the colour decoder to the required standard and to
activate the FCO-bit (Forced Colour On) in subaddress3CH. The sensitivity of the colour decoder
for PAL and NTSC can be increased by means of the setting of the CHSE1/CHSE0 bits in
subaddress 3CH.
The Automatic Colour Limiting (ACL) circuit (switchable via the ACL bit in subaddress 3BH)
prevents that oversaturation occurs when signals with a high chroma-to-burst ratio are received.
The ACL circuit is designed such that it only reduces the chroma signal and not the burst signal.
This has the advantage that the colour sensitivity is not affected by this function.
Page 39

CP-520V Service Manual
38
The SECAM decoder contains an auto-calibrating PLL demodulator which has two references,
viz: the divided reference frequency (obtained from the-Controller) which is used to tune the PLL
to the desired free-running frequency and the bandgap reference to obtain the correct absolute
value of the output signal. The VCO of the PLL is calibrated during each vertical blanking period,
when the IC is in search or SECAM mode. The frequency offset of the B-Y demodulator can be
reduced by means of the SBO1/SBO0 bits in subaddress 3CH.
The base-band delay line is integrated. In devices without CVBS comb filter this delay line is also
active during NTSC to obtain a good suppression of cross colour effects. The demodulated
colour difference signals are internally supplied to the delay line. The baseband comb filter can
be switched off by means of the BPS bit (subaddress 3CH).
The subcarrier output is combined with a 3-level output switch (0 V, 2.1 V and 4.5 V). The output
level and the availability of the subcarrier signal is controlled by the CMB2-CMB0 bits.
5.2.10 RGB output circuit
In the RGB control circuit the signal is controlled on contrast, brightness and saturation. The IC
has a YUV interface so that additional picture improvement ICs can be applied. To compensate
signal delays in the external YUV path the clamp pulse in the control circuit can be shifted by
means of the CLD bit in subaddress 44H. When the YUV interface is not required some of the
pins can be used for the insertion of RGB/YPrPb signals or as additional CVBS(Y)/C input. When
the YUV interface is not used one of the pins (VOUT) is transferred to general purpose output
switch (SWO1). The IC has also a YUV interface to th edigita ldie. Via this loop digital features
like “double window” are added.
A tint control is available for the base-band U/V signals. For this reason this tint control can be
activated for all colour standards. The signals for OSD and text are internally supplied to the
control circuit. The output signal has an amplitude of about 1.2V black-to-white at nominal input
signals and nominal settings of the various controls.
To obtain an accurate biasing of the picture tube the ‘Continuous Cathode Calibration’ system
has been included in these ICs. The system is slightly adapted compared with the previous
circuits. In the new configuration the cut-off level of the picture tube is controlled with a
continuous loop whereas the correction of the amplitude of the output signals is realised by
means of a digital loop. As a consequence the current measurement can be controlled from theProcessor. The value of the “highcurrent”intheCCCloopcanbechosenviatheSLG0 and SLG1 bits
(subaddresses 42H and 46H). The gain control in the 3 RGB channels is realised by means of 7bit DACs. The total gain control range is6 dB. The change in amplitude at the cathodes of the
picture tube for one LSB is about 1.1 Vp-p. The setting of the control DAC is determined by the
following registers:
n The white point setting of the R, G and B channel in subaddress 20H to 22H. This register
has a resolution of 6 bits and the control range in output signal amplitude is +/-3 dB.
n The cathode drive setting (CL3-CL0 in subaddress 42H). This setting is valid for all channels,
there solution is 4 bits and the control range is +/-3 dB.
n The gain setting of the R, G and B channel. During switch on this register is loaded with the
preset gain setting of subaddress 23H to 25H and when necessary it will be adapted by the
CCC control loop. These registers have a resolution of 7 bits. The control of the gain setting
is illustrated in table below.
Page 40

CP-520V Service Manual
39
WPR(GB) ‘0’ B5 B4 B3 B2 B1 B0 Max 64
CL ‘0’ B3 B2 B1 B0 ‘0’ ‘0’ Max 60
CCC-gain B6 B5 B4 B3 B2 B1 B0 Max 126
R(GB)-gain B6 B5 B4 B3 B2 B1 B0 Max 126
The setting of the gain registers of the 3 channels can be stored during switch off and can be
loaded again during switch-on so that the drive conditions are maintained.
When required the operation of the CCC system can be changed into a one-point black current
system. The switching between the 2 possibilities is realised by means of the EGL bit (EGL = 0)
in subaddress 42H. When used asone-point control loop the system will control the black level of
the RGB output signals to the ‘low’ reference current and not on the cut off point of the cathode.
In this way spreads in the picture tube characteristics will not be taken into account. In this
condition the settings of the “white point control registers”(subaddress 20H-22H) and the
“cathode drive level bits” (CL3 - CL0 in subaddress 42H) are added to the settings of the RGB
preset gain registers (subaddress 23H - 25H).
A black level off-set can be made with respect to the level which is generated by the black
current stabilization system. In this way different colour temperatures can be
obtainedforthebrightandthedarkpartofthepicture.The black level control is active on the Red and
the Green output signal. It is also possible to control the black level of the Blue and the Green
output signal (OFB bit = 1).
In the Vg2 adjustment mode (AVG=1) the black current stabilization system checks the output
level of the 3 channels and indicates whether the black level of the highest output is in a certain
window(WBC-bit) or below or above this window (HBC-bit). This indication can be read from the
status byte 01 and can be used for automatic adjustment of the Vg2 voltage during the
production of the TV receiver. During this test the vertical scan remains active so that the
indication of the 2 bits can be made visible on the TV screen.
The control circuit contains a beam current limiting circuit and a peak white limiting circuit. The
control is realised by means of a reduction of the contrast and brightness control settings. The
way of control (first contrast and then brightness or contrast and brightness in parallel) can be
chosen by means of the CBS bit (subaddress 44H). The peak white level is adjustable via the
I2C-bus.
To prevent that the peak white limiting circuit reacts on the high frequency content of the video
signal a low-passfilter is inserted in front of the peak detector. The circuit also contains a softclipper which prevents that the high frequency peaks in the output signal become too high. The
difference between the peak white limiting level and the soft clipping level is adjustable via the
I2C-bus in a few steps.
During switch-off of the TV receiver a fixed beam current is generated by the black current
control circuit. This current ensures that the picture tube capacitance is discharged. During the
switch-off period the vertical deflection can be placed in an overscan position so that the
discharge is not visible on the screen.
A wide blanking pulse can be activated in the RGB outputs by means of the HBL bit in
subaddress 43H. The timing of this blanking can be adjusted by means of the bits WBF/R bits in
subaddress 26H.
Page 41

CP-520V Service Manual
40
5.2.11 I2C-BUS USER INTERFACE DESCRIPTION
The UOC III series is fully controlled via the I2C-bus. Control is exercised by writing data to one
or more internal registers. Status information can be read from a set of info registers to enable
the controlling microcontroller determine whether any action is required. The device has an I2Cbus slave transceiver, in accordance with the fast-mode specification, with a maximum speed of
400 kbits/s. Information concerning the I2C-bus can be found in brochure “I2C-bus and how to
use it” (order number 939839340011). To avoid conflicts in a real application with other ICs
providing similar or complementary functions, there are two possible slave addresses available
which can be selected by the SVM pin(pin 65).
Possible slave address
SVM PIN SLAVE ADDRESS A6 TO A0
Scavem application 1 0 0 0 1 0 1
Tied 5 volts 1 0 0 0 1 1 1
The device will not respond to a ‘generalcall’ on the I2C-bus, i.e. when a slave address of
0000000 is sent by a master.
Write registers
Each address of the address space (see below) can only be written.
Correct operation is not guaranteed if registers in the range $FB to $FF will be addressed!
Read registers
The output registers of the TV processor are only available via auto-increment mode, no address
can be used and all registers must be read.
5.3 GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF THE TV SOUND OF SOUND PROCESSOR
The TV Sound Processor is a digital TV sound processor for analog multi-channel sound
systems in TV sets. It is based on a 24 bit DSP and designed to support several applications.
A new easy-to-use control concept was implemented for easiest configuration programming of
the very complex functionality of the TV Sound Processor. Pre-defined setups are available for
all implemented sound processing modes. Aloud speaker switching concept allows it to adapt the
pre-defined setups to the specific loudspeaker application.The built-in intelligence for pre-defined
standards and Auto Standard Detection (ASD) allows an easy setup of the demodulator and
decoder part.
The control concept for the audio processor is based on the following new features:
n Pre-defined setups for the sound processing modes like Dolby® Pro Logic® and Virtual
Dolby® Surround (422, 423)
n Flexible configuration of audio outputs to the loudspeaker configuration with an additional
output crossbar
n Master volume function
The control concept for the demodulator and decoder (DEMDEC) is based on the following new
features:
n Easy demodulator setup for all implemented standards with Demodulator and Decoder Easy
Programming (DDEP) for a pre-selected standard or combined with Auto Standard Detection
(ASD) for automatic detection of a transmitted standard
Page 42

CP-520V Service Manual
41
n Automatic decoder configuration and signal routing depending on the selected or detected
standard
n FM overmodulation adaptation option to avoid clipping and distortion
5.3.1 Supported standards
The multistandard capability of the TV Sound Processor covers all terrestrial TV sound standards,
FM Radio and satellite FM.
The AM sound of L/L' standard is normally demodulated in the 1st sound IF. The resulting AF
signal has to been tered into the mono audio input of the TV Sound Processor. A second
possibility is to use the AMdemodulator in the DEMDEC part, however this may result in limited
performance.
Korea has a stereo sound system similar to Europe. It is supported by the TV Sound Processor.
Differences include deviation, modulation contents and identification. It is based on M standard.
Other features of the DEMDEC are:
n M/BTSC and N standards supported
n M/Japan (EIAJ) supported
n FM Radio stereo decoding
n Alignment-free, fully digital system
n For BTSC full dbx® performance
n SAP demodulation (without dbx®) simultaneously with stereo decoding, or mono plus SAP
with dbx®
n Line/pilot frequency selectable from 15.734 kHz and 15.625 kHz (or automatic detection /
auto search)
n High selectivity for pilot detection, high robustness against high-frequent audio components
n Pilot lock indicator
n SAP detector
n Separate noise detectors for stereo and SAP with adjustable threshold levels, hysteresis, and
automute function
An overview of the supported standards and sound systems and their key parameters is given in
the following tables.
The analog multi-channel sound systems (A2, A2+ and A2*) are sometimes also named 2CS (2
carrier systems).
ANALOG 2-CARRIER SYSTEMS
[Table] Frequency modulation
STANDARD
M Mono 4.5 15/25/50 Mono - 15/75
M A2+ 4.5/4.724 15/25/50 1/2(L+R) 1/2(L+R) 15/75(Korea)
B/G A2 5.5/5.742 27/50/80 1/2(L+R) R 15/50
I Mono 6.0 27/50/80 mono - 15/50
D/K(1) A2* 6.5/6.258 27/50/80 1/2(L+R) R 15/50
D/K(2) A2* 6.5/6.742 27/50/80 1/2(L+R) R 15/50
D/K(3) A2* 6.5/5.742 27/50/80 1/2(L+R) R 15/50
SOUND
SYSTEM
CARRIER
FREQUENCY
(MHz)
FM DEVIATION(kHz)
NOM./MAX./OVER
MODULATION
SC1 SC2
BANDWIDTH/
DE-EMPHASIS
(kHz/us)
[Table] Identification for A2 systems
Page 43

CP-520V Service Manual
42
PARAMETER A2/A2* A2+ (KOREA)
Pilot frequency 54.6875kHz = 3.5 x line freq. 55.0699 kHz = 3.5 x line freq.
Stereo identification frequency 117.5 Hz = line freq / 133 149.9 Hz = line freq / 105
Dual indetification frequency 274.1 Hz = line freq / 57 276.0 Hz = line freq / 57
AM modulation depth 50% 50%
2-CARRIERSYSTEMSWITHNICAM
[Table] NICAM standards
SC1
MODULATION
STANDARD
B/G 5.5 FM - 27/50/80 5.85 J17 40 Note1
I 6.0 FM - 27/50/80 6.552 J17 100 Note1
D/K 6.5 FM - 27/50/80 5.85 J17 40 Note1
L 6.5 AM 54/100 - 5.85 J17 40 Note1
FREQUENCY
(MHz)
TYPE
INDEX(%)
NOM./MAX.
DEVIATION
(kHz)
NAM./MAX.
/OVER
SC2
(MHz)
NICA
M
DE-
EMPAHSIS
ROLL-
OFF (%)
NICAM
CODING
Note 1. See ‘EBU specification’ or equivalent specification.
5.4 FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION SOUND PROCESSOR
5.4.1 The UOC III TV Sound Concept
The UOCIII sound concept is implemented over the video processor and TCG-microcontroller.
Only relevant blocks, functions and signal flows for sound are given.
The tuner receives a RF signal and converts it to IF. Via appropriate SAW filters the SIF signal is
delivered to the QSS stage of the video processor and if channels according to standard L/L’ are
received also to the AM demodulator. The Quasi Split Sound demodulation generates the SSIF
or intercarrier signal. By the SSIF switch it is possible to choose between the internally derived
Page 44

CP-520V Service Manual
43
intercarrier and an external second SIF(2NDSIFEXT), e.g. an intercarrier coming from a PIP
frontend. In other applications a 10.7MHz radio IF or satellite FM may be connected to this input.
The selected SSIF passes some anti alias filtering, is amplified in an AGC amplifier (SSIF AGC)
and is then converted from analogue to digital (SSIF ADC).
The audio signal out of the AM demodulator is connected to the analogue crossbar at the video
processor. All other inputs to this multiplexer/audio switch come from external, either from a PIP
frontend or SCART/CINCH(AUDINx) or the DAC output signals from the digital controller. The
audio AD converters are digitising the audio signals foreseen for further digital processing. One
stereo output (AUDOUTS) is available for connections to SCART/CINCH sockets.
The sound part on the digital controller consists of the demodulator/decoder(DEMDEC), a digital
input crossbar, the digital audio processing for the loudspeaker and DAC channels, the I2S
processing and interfacing, a digital output crossbar as well as the DA conversion.
An auxiliary audio control (volume control, AUX audio contr.) is available on the video processor.
Here it is applied to the headphone channel.
The part of the concept located in the digital controller will be described in the next chapters.
5.4.2 Functional Overview Of the digital controller sound part
The digital controller sound part consists of the SSIFADC, audio ADCs, DEMDEC HW, the sound
DSP core, audio DACs and I2S interface hardware as shown in fig below. The DEMDEC part of
the Sound DSP is used for the decoder and partly demodulator tasks. The AUDIO part provides
the sound features, from the level adjust unit up to the output crossbar. Audio DACs and I2S
hardware are converting the processed signals to analogue or digital audio.
The SSIF signal is applied to the SSIF ADC for conversion and is then fed to the DEMDEC
hardware processing mainly for demodulation but also some decoding tasks. Remaining
Page 45

CP-520V Service Manual
44
decoding is done in the DEMDEC block of the Sound DSP. The DEMDEC processing will be
described in the next chapter.
The audio signals (AUD ADC IN) from the analogue crossbar pass the audio ADC and are fed
directly into the AUDIO part of the Sound DSP like the I2S signals, which is coming from I2S
processing hardware. After level adjust all signals from the DEMDEC and the I2S input are
available at the digital input crossbar. A special input is provided for the Noise/Silence Generator
needed for olby® Pro Logic® processing.
In standard TV applications the main channel signal(L,R) will be connected to the DAC2 for
reproduction at the speakers. With multichannel signals centre, surround or subwoofer channels
may be passed to the I2S outputs where external DACs may be applied. By this it is possible to
build Dolby Normal/Wide, Dolby Phantom Centre or Dolby 3 Stereo set-ups and also a VDS423
application.
5.4.3 Demodulator and decoder
INTRODUCTION
The TV sound processor provides an easy-to-use programming interface and built-in intelligence
for the demodulator and decoder part.
The sound demodulator is able to search for sound carriers and react to transmission mode
changes autonomously, without interaction of the micro controller software.
It is possible for a typical terrestrial TV application to setup the entire demodulator with
transmission of few control words.
The control interface still allows access to every detail, called demodulator expert mode, for
special applications such as satellite TV, more elaborated search algorithms etc.
The new TV Sound ProcessorDemodulator and
DecoderEasyProgramming(DDEP)interfaceprovides three possible approaches to setup the
demodulator and decoder parts:
n Auto Standard Detection (ASD)
n Static Standard Selection (SSS)
n Demodulator and Decoder Expert Mode (DDXM)
MIXER
The digitized 2nd SIF input signal is fed to the mixers, which mix one or both input sound carriers
down to zero IF. The mixer frequency is derived by the standard setting (Easy Programming) or
in the Demodulator and Decoder Expert Mode (DDXM) by a 24-bit control word for each carrier.
For NICAM demodulation, a feedback signal is added to the control word of the second carrier
mixer to establish a carrier-frequency loop.
FMANDAMDEMODULATION
An FM or AM input signal is fed via a band-limiting filter to a one of two demodulators that can be
used for either FM or AM demodulation. Four filters with different bandwidth are available. The
Page 46

CP-520V Service Manual
45
output signal of the first demodulator can be used for further demodulation of multiplex signals
used in the BTSC, EIAJ and FM Radio standards.
FMIDENTIFICATION
The identification of the FM sound mode is performed by AM synchronous demodulation of the
pilot signal and narrow-band detection of the identification frequencies. The result is available via
the control bus interface. A selection can be made for three different modes that represent
different trade-offs between speed and reliability of identification. The mode is set by DDEP (for
FM two-carrier standards) or via expert mode. DDEP also performs automatic FM de-matrix
control in dependence on the identification.
FM/AMDECODING
A high-pass filter suppresses DC offsets from the FM/AM demodulators due to carrier frequency
offsets and supplies the monitor/peak function with DC values and an un-filtered signal, e.g. for
the purpose of carrier detection.
The audio bandwidth is approx. 15 kHz.
The de-emphasis function offers fixed settings for the supported standards (50s, 60s, 75s and
J17).
A matrix performs the de-matrixing of the A2 stereo, dual and mono signals to obtain the left (L)
and right (R) or language A and B signals.
FMPILOTCARRIERPRESENTDETECTOR
The TV Sound Processor provides FM A2 standard pilot carrier detection.
NICAMDEMODULATION
The NICAM signal is transmitted via DQPSK modulation at a bit rate of 728kBit/s. The NICAM
demodulator performs DQPSK demodulation and feeds the resulting bit stream and clock signal
to the NICAM decoder.
A timing loop controls the sample rate conversion circuitry to lock the sampling rate to the symbol
timing of the NICAM data.
NICAM DECODER
The NICAM decoder performs all decoding functions in accordance with theEBU NICAM 728
specification. After locking to the frame alignment word, the data is de scrambled by applying the
defined pseudo-random binary sequence; the NICAM decoder will then synchronize to the
periodic frame flag bitC0.
The status of the NICAM decoder can be read out from the NICAM status register by the user
(see the control-bus register description). The OSB bit indicates that the decoder has locked to
the NICAM data. The VDSP bit indicates that the decoder has locked to the NICAM data and that
the data is valid sound data. The C4 bit indicates that the sound conveyed by the FM mono
channel is identical to the sound conveyed by the NICAM channel. The error byte contains the
Page 47

CP-520V Service Manual
46
number of sound sample errors, resulting from parity checking, that occurred in the past 128ms
period. The Bit Error Rate (BER) can be calculated using the following equation;
During NICAM mode a switchable J17 de-emphasis is supplied.
NICAM AUTO-MUTE
If the Auto Standard Detection (ASD) or the Static Standard Detection (SSS) feature is activated
the following auto mute function is in effect.
If NICAM B/G, I, D/K is received, the auto-mute is enabled and the signal quality becomes poor,
the built-in control automatically switches the output signal (DEC output) to FM channel 1. The
automatic switching depends on the NICAM bit error rate. The auto-mute function can be
disabled via the control bus.
This function is enabled by setting bit NIC_AMUTE to 0. Upper and lower error limits may be
defined by writing appropriate values to the corresponding control bits (NICLOERRLIM and
NICUPERRLIM). When the number of errors in a 128 ms period exceeds the upper error limit the
auto-mute function will switch the output sound from
NICAMtowhateversoundisonthefirstsoundcarrier(FM or AM). When the error count is smaller than
the lower error limit the NICAM sound is restored.
The auto-mute function can be disabled by setting bit NIC_AMUTE to 1. In this condition clicks
become audible when the error count increases; the user will hear a signal of degrading quality.
For NICAM L applications, it is recommended to demodulate AM sound in the first sound IF. The
demodulated AM is provided by the internal IF processor. For applications with external IF
processing the external demodulated AM signal can be connected to the SCART/Mono input of
the TV Sound Processor. By setting the EXTAM bit, the auto-mute function will switch to the
audio ADC input signal named EXTAM instead of switching to the first sound carrier. The ADC
source selector should be set to internal AM mono signal or to the external SCART/mono input,
where the AM sound signal should be connected.
Page 48

47
CP-520V Service Manual
6. SERVICE PARTS LIST
6.1 DTX-21G2FZP-SB
z_loc z_parts_code parts_name parts_descr remark
z_loc z_parts_code parts_name parts_descr remark
ZZ100 PTACPWE519 ACCESSORY AS DTX-21G2FZS-SB
12000 48B5849C1001 TRANSMITTER REMOCON R-49C10
13000 4850Q00910 BATTERY AAA R03 SUPERGARD/ROCKET
14000 4858213801 BAG INSTRUCTION L. D. P. E. T0. 05X250X400
ZZ120 PTBCSHE519 COVER BACK AS DTX-21G2FZS-SB
M211 4852172311G COVER BACK 21G2 HIPS GY8301A
M541 4855415800 S/PLATE 150ART P/E FILM (C/TV)
M542 4855800022P1 LABEL SERIAL ART 90 55X34
ZZ130 PTCACAE524 CABINET AS DTX-21G2FZP-SB
20 2193110002 SOLDER WIRE SN-3.0AG-0.5CU (DHB-RMA3)
40 4856812001 TIE CABLE NYLON66 DA100
M191 4851954300 DOOR AS 21G2 GY340A+SV128BP/PC
M201A 4856017703 SCREW CRT FIX 5X30 L80 BK 3CR
M201B 4856215402 WASHER RUBBER 20’’
M201C 4856017710 SCREW CRT FIX 5X30 L190 BK 3CR
M211A 7172401652 SCREW TAPPTITE TT2 TRS 4X16 MFZN BK 3CR
M211B 7178301052 SCREW TAPPTITE TT2 WAS 3X10 MFZN BK 3CR
M231A 7172401252 SCREW TAPPTITE TT2 TRS 4X12 MFZN BK 3CR
M481 4854869711 BUTTON POWER 21G2 ABS GY340A+SV128BP
M481A 4856715600 SPRING 14A5 SWPA
M501 485506202001 DECO CTRL 21G2 PC T0.25
M561 48556192SD02 MARK BRAND “DAEWOO 68MM (20””21””)”
M781 4857817610 CLOTH BLACK “300 MM 20”””
M791 4857923300 DOOR LOCK LA701 (KIFCO)
PWC1 4859903110 CORD POWER W/F 6-LO (LOMAX)
SP01A 7172401252 SCREW TAPPTITE TT2 TRS 4X12 MFZN BK 3CR
SP02A 7172401252 SCREW TAPPTITE TT2 TRS 4X12 MFZN BK 3CR
V901 4859640060 “CRT (THOMSON 21””)” A51ELD032X001
ZZ131 58G0000177 COIL DEGAUSSING DC-21SF AL
ZZ132 48519A7610 CRT GROUND AS 2103S-1015-1P
ZZ200 PTFMSJY21G2S MASK FRONT AS DTY-21G2 SV128BP
M231 4852330711 PANEL FRONT 21G2 HIPS BK+GY8204BP
M801 4852090511S MASK FRONT 21G2 GY340A
ZZ210 PTSPPWE519 SPEAKER AS DTX-21G2FZS-SB
P601A 4850704S28 CONN AS YH025-04+35089+ULW=600
SP01 4858317410 SPEAKER SP-58126FC
SP02 4858317410 SPEAKER SP-58126FC
ZZ290 PTMPMSE524 PCB MAIN MANUAL AS DTX-21G2FZP-SB
10 2193110001 SOLDER WIRE SN-3.0AG (NP303T) 3.0
20 2193110002 SOLDER WIRE SN-3.0AG-0.5CU (DHB-RMA3)
30 2291050617P FLUX SOLDER CF-329D
40 2291050314 FLUX SOLVENT IM-1000
C403 CMYH3C662H C MYLAR 1.6KV BUP 6600PF H
C407 CMXF2E224J C MYLAR 250V MPU 0.22MF J
C408 CEXF2E100V C ELECTRO 250V RSS 10MF (10X20) TP
C626 CEXF1C102V C ELECTRO 16V RSS 1000MF (10X20) TP
C801 CL1UC3474M C LINE ACROSS 0.47MF 1J(UCVSNDF/SV
C804 CEYD2G181D C ELECTRO 400V FHS 180MF
C805 CCXR3D681K C CERA 2KV R 680PF K 125C
C811 CH1BFE222M C CERA AC U/C/V AC400V 2200PF
C812 CCXB3D471K C CERA 2KV B 470PF K (TAPPING)
C813 CEXF2C101V C ELECTRO 160V RSS 100MF (16X25) TP
C814 CEXF2C470V C ELECTRO 160V RSS 47MF (13X25) TP
C816 CEXF1C102V C ELECTRO 16V RSS 1000MF (10X20) TP
C818 CEXF1C222V C ELECTRO 16V RSS 2200MF(13X25)TP
C827 CCXB3D471K C CERA 2KV B 470PF K (TAPPING)
D707 DLH3PRG03- LED BLOCK LH-3P-RG-03
F801 5FSCB4022R FUSE CERA SEMKO F4AH 4A 250V MF51
HP01 4859102130 JACK EARPHONE YSC-1537
I301 1LA78040— IC VERTICAL LA78040
I301A 4857027100 HEAT SINK SPCC T1.0+SN
I301B 7174300851 SCREW TAPPTITE TT2 RND 3X8 MFZN 3CR
I502 124LC16B1B IC MEMORY 24LC16B1B
I601 1LA42032E- IC AUDIO AMP LA42032-E
I601A 4857024401 HEAT SINK AL EX (NO ANODIZING)
I601B 7174300851 SCREW TAPPTITE TT2 RND 3X8 MFZN 3CR
I801 1STRW6754- IC POWER STR-W6754
I801A 4857024600 HEAT SINK AL EX B/K
I801B 7174300851 SCREW TAPPTITE TT2 RND 3X8 MFZN 3CR
I802 1LTV817C— IC PHOTO COUPLER LTV-817C
I804 1LE33CZ—- IC REGULATOR LE33CZ
IF01 1441VF6—- IC PREAMP 441VF6
JPA01 4859200401 SOCKET RGB SR-21A1 (ANGLE TYPE)
JPA02 4859200401 SOCKET RGB SR-21A1 (ANGLE TYPE)
JPA03 4859108450 JACK PIN BOARD YSC03P-4120-14A
L401 58H0000020 COIL H-LINEARITY L-76(76.5UH)
LF801 5PLF24A1— FILTER LINE LF-24A1
P401 4850705N14 CONNECTOR BIC-05T-25T+ULW=500
P402 4859242420 CONN WAFER YFW800-04
P501 4850705N14 CONNECTOR BIC-05T-25T+ULW=500
P601 4859231720 CONN WAFER YW025-04
P701 4859231720 CONN WAFER YW025-04
P801 4859242220 CONN WAFER YFW800-02
P802 4859242220 CONN WAFER YFW800-02
Q402 TST1803DFH TR HORI ST1803DFH
Q402A 4857027201 HEAT SINK AL T1.0
Q402B 7174301051 SCREW TAPPTITE TT2 RND 3X10 MFZN 3CR
R311 RS02Y229JS R M-OXIDE FILM 2W 2.2 OHM J SMALL
R406 RS02Y103JS R M-OXIDE FILM 2W 10K OHM J SMALL
R407 RS02Y102JS R M-OXIDE FILM 2W 1K OHM J SMALL
R411 RS02Y109JS R M-OXIDE FILM 2W 1 OHM J SMALL
R800 RX07B229JP R CEMENT 7W 2.2 OHM J BEN 15MM 4P
R801 DTC7R0M270 POSISTOR PDC7R0MP6B7Z81C
R805 RS02Y228JS R M-OXIDE FILM 2W 0.22 OHM J SMALL
SCT01 4859304130 SOCKET CRT ISHG93S
SW801 5S40101143 SW PUSH PS3-22SP (P.C.B)
T401 50D10A3—- TRANS DRIVE TD-10A3
T402 50H0000310 FBT LTC-565
T801 50M3541C4- TRANS SMPS TSM-3541C4
U100 4859730330 TUNER VARACTOR TAEM-G010D
X501 5XJ24R576E CRYSTAL QUARTZ HC-49/S 24.576MHZ 30PPM
Z101 5PK3953M— FILTER SAW K3953M
Z102 5PK9650M— FILTER SAW K9650M
ZZ200 PTMPJBE520 PCB MAIN EYE LET AS DTX-21U7FZS
E01 4856310600 EYE LET BSR 2.3(R2.3) BIG
E02 4856310600 EYE LET BSR 2.3(R2.3) BIG
E03 4856310600 EYE LET BSR 2.3(R2.3) BIG
E05 4856310600 EYE LET BSR 2.3(R2.3) BIG
E06 4856310300 EYE LET BSR T0.2 (R1.6) SMALL
E08 4856310300 EYE LET BSR T0.2 (R1.6) SMALL
E09 4856310300 EYE LET BSR T0.2 (R1.6) SMALL
E10 4856310300 EYE LET BSR T0.2 (R1.6) SMALL
E11 4856310300 EYE LET BSR T0.2 (R1.6) SMALL
E12 4856310300 EYE LET BSR T0.2 (R1.6) SMALL
E13 4856310300 EYE LET BSR T0.2 (R1.6) SMALL
E14 4856310300 EYE LET BSR T0.2 (R1.6) SMALL
E15 4856310300 EYE LET BSR T0.2 (R1.6) SMALL
E16 4856310300 EYE LET BSR T0.2 (R1.6) SMALL
E17 4856310300 EYE LET BSR T0.2 (R1.6) SMALL
E18 4856310300 EYE LET BSR T0.2 (R1.6) SMALL
E19 4856310300 EYE LET BSR T0.2 (R1.6) SMALL
E20 4856310300 EYE LET BSR T0.2 (R1.6) SMALL
E21 4856310600 EYE LET BSR 2.3(R2.3) BIG
E22 4856310600 EYE LET BSR 2.3(R2.3) BIG
E23 4856310600 EYE LET BSR 2.3(R2.3) BIG
E24 4856310600 EYE LET BSR 2.3(R2.3) BIG
E25 4856310600 EYE LET BSR 2.3(R2.3) BIG
ZZ200 PTMPJ2E520 PCB CHIP MOUNT B AS DTX-21U7FZS
I501 1TDA20HF01 IC MICOM FLASH TDA12020H1/N1/F01
ZZ200 PTMPJRE520 PCB MAIN RADIAL AS DTX-21U7FZS
C101 CEXF1H100V C ELECTRO 50V RSS 10MF (5X11) TP
C102 CEXF1C101V C ELECTRO 16V RSS 100MF (6.3X11) TP
C105 CEXF1H100V C ELECTRO 50V RSS 10MF (5X11) TP
C106 CEXF1E470V C ELECTRO 25V RSS 47MF (5X11) TP
C302 CEXF1H101V C ELECTRO 50V RSS 100MF (8*11.5) TP
C305 CEXF1C331V C ELECTRO 16V RSS 330MF (8X11.5) TP
C306 CEXF1C331V C ELECTRO 16V RSS 330MF (8X11.5) TP
C307 CMXM2A104J C MYLAR 100V 0.1MF J TP
C401 CMXM2A104J C MYLAR 100V 0.1MF J TP
C402 CCXB2H102K C CERA 500V B 1000PF K (TAPPING)
Caution : In this Service Manual, some parts can be changed for improving, their performance
without notice in the parts list. So, if you need the latest parts information, please refer to PPL(Parts
Price List) in Service Information Center(http://svc.dwe.co.kr)
Page 49

48
CP-520V Service Manual
z_loc z_parts_code parts_name parts_descr remark
z_loc z_parts_code parts_name parts_descr remark
C405 CCXB2H561K C CERA 500V B 560PF K (TAPPING)
C406 CEXF2C109V C ELECTRO 160V RSS 1MF (6.3*11) TP
C409 CXSL2H470J C CERA 500V SL 47PF J (TAPPING)
C410 CMXM2A104J C MYLAR 100V 0.1MF J TP
C501 CEXF1E470V C ELECTRO 25V RSS 47MF (5X11) TP
C502 CEXF1E470V C ELECTRO 25V RSS 47MF (5X11) TP
C505 CBXF1H104Z C CERA SEMI 50V F 0.1MF Z (TAPPING)
C507 CBXF1H104Z C CERA SEMI 50V F 0.1MF Z (TAPPING)
C508 CEXF1E470V C ELECTRO 25V RSS 47MF (5X11) TP
C509 CBXF1H104Z C CERA SEMI 50V F 0.1MF Z (TAPPING)
C510 CEXF1E101V C ELECTRO 25V RSS 100MF (6.3X11) TP
C511 CCXB1H102K C CERA 50V B 1000PF K (TAPPING)
C513 CBXF1H104Z C CERA SEMI 50V F 0.1MF Z (TAPPING)
C514 CCXB1H102K C CERA 50V B 1000PF K (TAPPING)
C515 CBXF1H104Z C CERA SEMI 50V F 0.1MF Z (TAPPING)
C516 CBXF1H104Z C CERA SEMI 50V F 0.1MF Z (TAPPING)
C517 CEXF1C101V C ELECTRO 16V RSS 100MF (6.3X11) TP
C518 CBXF1H104Z C CERA SEMI 50V F 0.1MF Z (TAPPING)
C519 CBXF1H104Z C CERA SEMI 50V F 0.1MF Z (TAPPING)
C520 CEXF1H229V C ELECTRO 50V RSS 2.2MF (5X11) TP
C521 CMXM2A222J C MYLAR 100V 2200PF J TP
C522 CBXF1H104Z C CERA SEMI 50V F 0.1MF Z (TAPPING)
C524 CMXM2A682J C MYLAR 100V 6800PF J TP
C525 CEXF1H109V C ELECTRO 50V RSS 1MF (5X11) TP
C526 CMXL1J224J C MYLAR 63V MEU 0.22MF J TP
C527 CEXF1H100V C ELECTRO 50V RSS 10MF (5X11) TP
C528 CCXF1H223Z C CERA 50V F 0.022MF Z (TAPPING)
C529 CMXL1J154J C MYLAR 63V MEU 0.15MF J
C534 CEXF1H229V C ELECTRO 50V RSS 2.2MF (5X11) TP
C535 CMXL1J474J C MYLAR 63V 0.47MF MKT
C536 CMXL1J474J C MYLAR 63V 0.47MF MKT
C537 CEXF1H229V C ELECTRO 50V RSS 2.2MF (5X11) TP
C538 CEXF1H229V C ELECTRO 50V RSS 2.2MF (5X11) TP
C539 CMXM2A332J C MYLAR 100V 3300PF J TP
C540 CMXM2A473J C MYLAR 100V 0.047MF J TP
C542 CEXF1H100V C ELECTRO 50V RSS 10MF (5X11) TP
C543 CEXF1H229V C ELECTRO 50V RSS 2.2MF (5X11) TP
C545 CEXF1H229V C ELECTRO 50V RSS 2.2MF (5X11) TP
C547 CEXF1H100V C ELECTRO 50V RSS 10MF (5X11) TP
C548 CEXF1H100V C ELECTRO 50V RSS 10MF (5X11) TP
C549 CMXL1J474J C MYLAR 63V 0.47MF MKT
C552 CMXL1J474J C MYLAR 63V 0.47MF MKT
C553 CMXL1J474J C MYLAR 63V 0.47MF MKT
C554 CMXL1J474J C MYLAR 63V 0.47MF MKT
C556 CCXB1H102K C CERA 50V B 1000PF K (TAPPING)
C558 CBXF1H104Z C CERA SEMI 50V F 0.1MF Z (TAPPING)
C560 CEXF1H229V C ELECTRO 50V RSS 2.2MF (5X11) TP
C561 CEXF1H229V C ELECTRO 50V RSS 2.2MF (5X11) TP
C562 CMXM2A104J C MYLAR 100V 0.1MF J TP
C563 CEXF1H100V C ELECTRO 50V RSS 10MF (5X11) TP
C567 CEXF1H100V C ELECTRO 50V RSS 10MF (5X11) TP
C568 CBXF1H104Z C CERA SEMI 50V F 0.1MF Z (TAPPING)
C569 CEXF1E470V C ELECTRO 25V RSS 47MF (5X11) TP
C574 CBXF1H104Z C CERA SEMI 50V F 0.1MF Z (TAPPING)
C576 CBXF1H104Z C CERA SEMI 50V F 0.1MF Z (TAPPING)
C577 CEXF1E470V C ELECTRO 25V RSS 47MF (5X11) TP
C579 CCXB1H102K C CERA 50V B 1000PF K (TAPPING)
C581 CBXF1H104Z C CERA SEMI 50V F 0.1MF Z (TAPPING)
C601 CEXF1E470V C ELECTRO 25V RSS 47MF (5X11) TP
C602 CEXF1H479V C ELECTRO 50V RSS 4.7MF (5*11) TP
C603 CEXF1H479V C ELECTRO 50V RSS 4.7MF (5*11) TP
C609 CEXF1E470V C ELECTRO 25V RSS 47MF (5X11) TP
C610 CEXF1H100V C ELECTRO 50V RSS 10MF (5X11) TP
C611 CEXF1H100V C ELECTRO 50V RSS 10MF (5X11) TP
C625 CEXF1H479V C ELECTRO 50V RSS 4.7MF (5*11) TP
C802 CCXF3A472Z C CERA 1KV F 4700PF Z (T)
C803 CCXF3A472Z C CERA 1KV F 4700PF Z (T)
C806 CEXF1H100V C ELECTRO 50V RSS 10MF (5X11) TP
C807 CEXF1H109V C ELECTRO 50V RSS 1MF (5X11) TP
C815 CEXF2A100V C ELECTRO 100V RSS 10MF (6.3X11) TP
C817 CEXF1A471V C ELECTRO 10V RSS 470MF(TAPPING)
C819 CEXF2C109V C ELECTRO 160V RSS 1MF (6.3*11) TP
C820 CMXM2A104J C MYLAR 100V 0.1MF J TP
C821 CEXF1C101V C ELECTRO 16V RSS 100MF (6.3X11) TP
C824 CEXF1A471V C ELECTRO 10V RSS 470MF(TAPPING)
C833 CEXF1C101V C ELECTRO 16V RSS 100MF (6.3X11) TP
C834 CEXF1C101V C ELECTRO 16V RSS 100MF (6.3X11) TP
C835 CEXF1C471V C ELECTRO 16V RSS 470MF (10X12.5)TP
C904 CCXB3A271K C CERA 1KV B 270PF K (TAPPING)
CA10 CCXB1H102K C CERA 50V B 1000PF K (TAPPING)
F801A 4857415001 CLIP FUSE PFC5000-0702
F801B 4857415001 CLIP FUSE PFC5000-0702
I803 1K1A431B— IC REGULATOR(SHUNT) KIA431B 2.495V 0.5% TO-92
I805 1K1A431B— IC REGULATOR(SHUNT) KIA431B 2.495V 0.5% TO-92
L517 5CPX479K— COIL PEAKING 4.7UH K RADIAL
L518 5CPX479K— COIL PEAKING 4.7UH K RADIAL
L519 5CPX479K— COIL PEAKING 4.7UH K RADIAL
L802 58CX430599 COIL CHOKE AZ-9004Y 940K TP
Q101 T2SC5343Y- TR 2SC5343Y
Q401 TKTC3207— TR KTC3207
Q501 T2SC5343Y- TR 2SC5343Y
Q502 T2SA1980Y- TR 2SA1980Y
Q503 T2SC5343Y- TR 2SC5343Y
Q504 T2SA1980Y- TR 2SA1980Y
Q506 T2SC5343Y- TR 2SC5343Y
Q507 T2SA1980Y- TR 2SA1980Y
Q508 T2SC5343Y- TR 2SC5343Y
Q513 T2SA1980Y- TR 2SA1980Y
Q514 TH2N7000— TR H2N7000
Q515 TH2N7000— TR H2N7000
Q601 T2SA1980Y- TR 2SA1980Y
Q602 T2SC5343Y- TR 2SC5343Y
Q801 T2SC5343Y- TR 2SC5343Y
Q802 T2SC5343Y- TR 2SC5343Y
Q803 T2SC5343Y- TR 2SC5343Y
Q804 TKTA1270Y- TR KTA1270Y
Q805 TKTA1270Y- TR KTA1270Y
Q806 T2SC5343Y- TR 2SC5343Y
Q807 TKTA1270Y- TR KTA1270Y
Q808 T2SC5343Y- TR 2SC5343Y
Q809 TKTC3202Y- TR KTC3202Y
Q901 TKTC3207— TR KTC3207
Q902 TKTC3207— TR KTC3207
Q903 TKTC3207— TR KTC3207
Q904 TBF420—— TR BF420
Q905 TBF420—— TR BF420
Q906 TBF420—— TR BF420
Q907 TBF421—— TR BF421
Q908 TBF421—— TR BF421
Q909 TBF421—— TR BF421
R823 RN02B390JS R METAL FILM 2W 39 OHM J SMALL
R836 RN02B390JS R METAL FILM 2W 39 OHM J SMALL
R837 RN02B100JS R METAL FILM 2W 10 OHM J SMALL
R838 RN02B240JS R METAL FILM 2W 24 OHM J SMALL
R904 RN02B123JS R METAL FILM 2W 12K OHM J SMALL
R905 RN02B123JS R METAL FILM 2W 12K OHM J SMALL
R906 RN02B123JS R METAL FILM 2W 12K OHM J SMALL
R910 RN01B680JS R METAL FILM 1W 68 OHM J SMALL
SW700 5S50101090 SW TACT SKHV17910A
SW701 5S50101090 SW TACT SKHV17910A
SW702 5S50101090 SW TACT SKHV17910A
SW703 5S50101090 SW TACT SKHV17910A
SW704 5S50101090 SW TACT SKHV17910A
Z603 5PXF1B471M FILTER EMI CFI 06 B 1H 470PF
Z604 5PXF1B471M FILTER EMI CFI 06 B 1H 470PF
Z605 5PXF1B471M FILTER EMI CFI 06 B 1H 470PF
Z606 5PXF1B471M FILTER EMI CFI 06 B 1H 470PF
Z607 5PXF1B471M FILTER EMI CFI 06 B 1H 470PF
Z608 5PXF1B471M FILTER EMI CFI 06 B 1H 470PF
Z609 5PXF1B471M FILTER EMI CFI 06 B 1H 470PF
Z610 5PXF1B471M FILTER EMI CFI 06 B 1H 470PF
Z611 5PXF1B471M FILTER EMI CFI 06 B 1H 470PF
Z612 5PXF1B471M FILTER EMI CFI 06 B 1H 470PF
ZZ200 PTMPJAE520 PCB MAIN AXIAL AS DTX-21U7FZS
10 2TM14006LB TAPE MASKING 3M #232 6.0X2000M (WITH GLUE)
20 2TM10006LB TAPE MASKING 3M #232-MAP-C 6.2X2000M (W/O GLUE)
A001 4859813693 PCB MAIN CP-520V (DTX) 330X246(1X1)T1.6
C107 CCZB1H102K C CERA 50V B 1000PF K (AXIAL)
C123 CCZL1H472K C CERA 50V B 4700PF K AXL (1608)
C301 CCZJ1H103Z C CERA 50V F 0.01MF Z AXL (1608)
C310 CCZJ1H473Z C CERA 50V F 0.047MF Z AXL (1608)
C412 CCZJ1H473Z C CERA 50V F 0.047MF Z AXL (1608)
C503 CCZB1H102K C CERA 50V B 1000PF K (AXIAL)
C504 CCZB1H102K C CERA 50V B 1000PF K (AXIAL)
C512 CCZJ1H104Z C CERA 50V F 0.1MF Z AXL (1608)
C523 CCZB1H102K C CERA 50V B 1000PF K (AXIAL)
C530 CCZB1H101K C CERA 50V B 100PF K (AXIAL)
C531 CCZJ1H103Z C CERA 50V F 0.01MF Z AXL (1608)
C532 CCZJ1H103Z C CERA 50V F 0.01MF Z AXL (1608)
C533 CCZB1H102K C CERA 50V B 1000PF K (AXIAL)
C541 CCZJ1H104Z C CERA 50V F 0.1MF Z AXL (1608)
C544 CCZJ1H104Z C CERA 50V F 0.1MF Z AXL (1608)
Page 50

49
CP-520V Service Manual
z_loc z_parts_code parts_name parts_descr remark
z_loc z_parts_code parts_name parts_descr remark
C546 CCZJ1H104Z C CERA 50V F 0.1MF Z AXL (1608)
C550 CCZJ1H103Z C CERA 50V F 0.01MF Z AXL (1608)
C551 CCZJ1H104Z C CERA 50V F 0.1MF Z AXL (1608)
C555 CCZB1H102K C CERA 50V B 1000PF K (AXIAL)
C557 CCZJ1H104Z C CERA 50V F 0.1MF Z AXL (1608)
C564 CCZJ1H104Z C CERA 50V F 0.1MF Z AXL (1608)
C565 CCZJ1H104Z C CERA 50V F 0.1MF Z AXL (1608)
C566 CCZJ1H104Z C CERA 50V F 0.1MF Z AXL (1608)
C575 CCZB1H102K C CERA 50V B 1000PF K (AXIAL)
C578 CCZJ1H104Z C CERA 50V F 0.1MF Z AXL (1608)
C589 CCZL1H472K C CERA 50V B 4700PF K AXL (1608)
C590 CCZJ1H104Z C CERA 50V F 0.1MF Z AXL (1608)
C591 CCZJ1H104Z C CERA 50V F 0.1MF Z AXL (1608)
C592 CCZJ1H103Z C CERA 50V F 0.01MF Z AXL (1608)
C605 CBZR1C472M C CERA Y5R 16V 4700PF M AXIAL
C606 CBZR1C472M C CERA Y5R 16V 4700PF M AXIAL
C612 CCZJ1H104Z C CERA 50V F 0.1MF Z AXL (1608)
C613 CCZJ1H104Z C CERA 50V F 0.1MF Z AXL (1608)
C614 CCZJ1H104Z C CERA 50V F 0.1MF Z AXL (1608)
C615 CCZJ1H104Z C CERA 50V F 0.1MF Z AXL (1608)
C616 CCZB1H102K C CERA 50V B 1000PF K (AXIAL)
C617 CCZB1H102K C CERA 50V B 1000PF K (AXIAL)
C618 CCZB1H102K C CERA 50V B 1000PF K (AXIAL)
C619 CCZB1H102K C CERA 50V B 1000PF K (AXIAL)
C701 CCZJ1H103Z C CERA 50V F 0.01MF Z AXL (1608)
C808 CCZB1H471K C CERA 50V B 470PF K (AXIAL)
C809 CCZJ1H473Z C CERA 50V F 0.047MF Z AXL (1608)
C810 CCZB1H821K C CERA 50V B 820PF K (AXIAL)
C828 CCZB1H561K C CERA 50V B 560PF K (AXIAL)
C901 CCZB1H331K C CERA 50V B 330PF K (AXIAL)
C902 CCZB1H331K C CERA 50V B 330PF K (AXIAL)
C903 CCZB1H331K C CERA 50V B 330PF K (AXIAL)
CA01 CCZB1H101K C CERA 50V B 100PF K (AXIAL)
CA02 CCZB1H101K C CERA 50V B 100PF K (AXIAL)
CA03 CCZB1H101K C CERA 50V B 100PF K (AXIAL)
CA04 CCZB1H101K C CERA 50V B 100PF K (AXIAL)
CA05 CCZB1H101K C CERA 50V B 100PF K (AXIAL)
CA06 CCZB1H101K C CERA 50V B 100PF K (AXIAL)
CA28 CCZB1H102K C CERA 50V B 1000PF K (AXIAL)
D101 DUZ33B—— DIODE ZENER UZ-33B
D102 DBA282—— DIODE BA282
D103 D1N4148—- DIODE 1N4148 (TAPPING)
D104 DTZX3V9B— DIODE ZENER TZX3V9B (TAPPING)
D301 D1N4004S— DIODE 1N4004S
D302 D1N4937G— DIODE 1N4937G
D303 D1N4937G— DIODE 1N4937G
D401 D1N4937G— DIODE 1N4937G
D402 D1N4148—- DIODE 1N4148 (TAPPING)
D403 D1N4148—- DIODE 1N4148 (TAPPING)
D404 D1N4937G— DIODE 1N4937G
D501 D1N4148—- DIODE 1N4148 (TAPPING)
D502 DTZX3V9B— DIODE ZENER TZX3V9B (TAPPING)
D503 DTZX3V9B— DIODE ZENER TZX3V9B (TAPPING)
D522 DTZX3V9B— DIODE ZENER TZX3V9B (TAPPING)
D523 DTZX3V9B— DIODE ZENER TZX3V9B (TAPPING)
D524 DTZX5V6B— DIODE ZENER TZX5V6B (TAPPING)
D525 DTZX6V2—- DIODE ZENER TZX6V2B (TAPPING)
D526 DTZX6V2—- DIODE ZENER TZX6V2B (TAPPING)
D527 DTZX6V2—- DIODE ZENER TZX6V2B (TAPPING)
D601 D1N4148—- DIODE 1N4148 (TAPPING)
D602 D1N4148—- DIODE 1N4148 (TAPPING)
D801 DLT2A05G— DIODE LT2A05G
D802 DLT2A05G— DIODE LT2A05G
D803 DLT2A05G— DIODE LT2A05G
D804 DLT2A05G— DIODE LT2A05G
D805 D1N4937G— DIODE 1N4937G
D806 D1N4937G— DIODE 1N4937G
D807 D1N4148—- DIODE 1N4148 (TAPPING)
D808 DTZX6V2—- DIODE ZENER TZX6V2B (TAPPING)
D809 DRGP15J—- DIODE RGP15J
D811 D1N4937G— DIODE 1N4937G
D812 DRGP15J—- DIODE RGP15J
D817 DRGP15J—- DIODE RGP15J
D817B DRGP15J—- DIODE RGP15J
D818 DTZX4V3B— DIODE ZENER TZX4V3B (TAPPING)
D819 DRGP15J—- DIODE RGP15J
D820 DTZX2V4A— DIODE ZENER TZX2V4A (TAPPING)
D821 DTZX2V4A— DIODE ZENER TZX2V4A (TAPPING)
D902 D1N4148—- DIODE 1N4148 (TAPPING)
DA01 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
DA02 DTZX5V6B— DIODE ZENER TZX5V6B (TAPPING)
DA03 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
DA04 DTZX5V6B— DIODE ZENER TZX5V6B (TAPPING)
DA06 DTZX5V6B— DIODE ZENER TZX5V6B (TAPPING)
DA08 DTZX5V6B— DIODE ZENER TZX5V6B (TAPPING)
DA09 DTZX5V6B— DIODE ZENER TZX5V6B (TAPPING)
DA10 DTZX5V6B— DIODE ZENER TZX5V6B (TAPPING)
DA11 DTZX5V6B— DIODE ZENER TZX5V6B (TAPPING)
DA13 DTZX5V6B— DIODE ZENER TZX5V6B (TAPPING)
DA14 DTZX5V6B— DIODE ZENER TZX5V6B (TAPPING)
DA15 DTZX5V6B— DIODE ZENER TZX5V6B (TAPPING)
DA16 DTZX5V6B— DIODE ZENER TZX5V6B (TAPPING)
DA20 DTZX5V6B— DIODE ZENER TZX5V6B (TAPPING)
DA21 DTZX5V6B— DIODE ZENER TZX5V6B (TAPPING)
DA22 DTZX5V6B— DIODE ZENER TZX5V6B (TAPPING)
DF01 DTZX3V9B— DIODE ZENER TZX3V9B (TAPPING)
J001 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J002 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J003 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J004 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J005 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J006 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J007 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J008 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J009 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J010 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J011 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J012 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J013 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J014 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J015 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J016 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J017 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J018 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J019 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J020 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J021 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J022 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J023 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J024 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J025 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J026 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J027 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J028 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J029 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J030 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J031 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J032 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J034 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J035 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J037 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J038 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J039 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J040 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J041 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J043 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J044 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J045 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J046 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J047 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J048 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J049 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J050 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J051 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J052 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J053 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J054 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J055 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J056 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J057 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J058 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J059 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J061 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J062 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J063 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J065 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J066 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J067 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J068 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J069 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J070 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
Page 51

50
CP-520V Service Manual
z_loc z_parts_code parts_name parts_descr remark
z_loc z_parts_code parts_name parts_descr remark
J071 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J072 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J073 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J074 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J075 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J076 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J078 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J079 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J080 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J081 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J083 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J084 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J085 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J086 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J088 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J089 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J091 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J094 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J095 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J096 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J097 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J098 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J099 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J100 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J101 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J102 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J103 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J104 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J105 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J106 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J107 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J108 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J109 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J110 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J111 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J112 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J113 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J114 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J115 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J116 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J117 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J118 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J119 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J120 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J121 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J122 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J123 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J124 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J125 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J126 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J127 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J128 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J129 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J131 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J132 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J133 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J134 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J136 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J137 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J204 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J205 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J206 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J500 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
J900 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
L101 5CPZ100K02 COIL PEAKING 10UH 3.5MM K (LAL02TB)
L301 5MC0000100 COIL BEAD MD-5 (HC-3550)
L505 5CPZ479K02 COIL PEAKING 4.7UH 3.5MM K (LAL02TB)
L506 5CPZ479K02 COIL PEAKING 4.7UH 3.5MM K (LAL02TB)
L507 5CPZ479K02 COIL PEAKING 4.7UH 3.5MM K (LAL02TB)
L508 5CPZ479K02 COIL PEAKING 4.7UH 3.5MM K (LAL02TB)
L509 5CPZ479K02 COIL PEAKING 4.7UH 3.5MM K (LAL02TB)
L510 5CPZ479K02 COIL PEAKING 4.7UH 3.5MM K (LAL02TB)
L512 5CPZ479K02 COIL PEAKING 4.7UH 3.5MM K (LAL02TB)
L513 5CPZ479K02 COIL PEAKING 4.7UH 3.5MM K (LAL02TB)
L514 5CPZ100K04 COIL PEAKING 10UH 10.5MM K (LAL04TB)
L515 5CPZ100K02 COIL PEAKING 10UH 3.5MM K (LAL02TB)
L516 5CPZ479K02 COIL PEAKING 4.7UH 3.5MM K (LAL02TB)
L523 5CPZ479K02 COIL PEAKING 4.7UH 3.5MM K (LAL02TB)
L601 5CPZ100K02 COIL PEAKING 10UH 3.5MM K (LAL02TB)
L602 5CPZ100K02 COIL PEAKING 10UH 3.5MM K (LAL02TB)
L801 5MC0000100 COIL BEAD MD-5 (HC-3550)
R101 RD-2Z332J- R CARBON FILM 1/2 3.3K OHM J
R104 RD-AZ101J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 100 OHM J
R105 RD-AZ101J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 100 OHM J
R106 RD-AZ101J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 100 OHM J
R107 RD-AZ472J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 4.7K OHM J
R108 RD-AZ473J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 47K OHM J
R109 RD-AZ123J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 12K OHM J
R110 RD-AZ683J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 68K OHM J
R115 RD-AZ103J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 10K OHM J
R116 RD-AZ101J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 100 OHM J
R301 RD-AZ202J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 2K OHM J
R302 RD-AZ202J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 2K OHM J
R303 RD-AZ471J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 470 OHM J
R304 RD-AZ152J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 1.5K OHM J
R305 RD-4Z279J- R CARBON FILM 1/4 2.7 OHM J
R306 RD-4Z279J- R CARBON FILM 1/4 2.7 OHM J
R308 RN-4Z1501F R METAL FILM 1/4 1.5K OHM F
R310 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
R312 RD-2Z561J- R CARBON FILM 1/2 560 OHM J
R401 RD-AZ102J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 1K OHM J
R402 RD-AZ102J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 1K OHM J
R403 RD-2Z102J- R CARBON FILM 1/2 1K OHM J
R404 RD-AZ472J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 4.7K OHM J
R408 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
R409 RD-4Z103J- R CARBON FILM 1/4 10K OHM J
R410 RD-4Z103J- R CARBON FILM 1/4 10K OHM J
R412 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
R413 RD-4Z102J- R CARBON FILM 1/4 1K OHM J
R421 RD-4Z182J- R CARBON FILM 1/4 1.8K OHM J
R501 RD-AZ332J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 3.3K OHM J
R502 RD-AZ332J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 3.3K OHM J
R503 RD-AZ102J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 1K OHM J
R504 RD-AZ472J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 4.7K OHM J
R505 RD-AZ101J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 100 OHM J
R506 RD-AZ103J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 10K OHM J
R507 RD-AZ332J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 3.3K OHM J
R508 RD-AZ332J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 3.3K OHM J
R510 RD-AZ103J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 10K OHM J
R511 RD-AZ103J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 10K OHM J
R512 RD-AZ101J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 100 OHM J
R514 RD-AZ101J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 100 OHM J
R515 RD-AZ101J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 100 OHM J
R516 RD-AZ153J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 15K OHM J
R517 RD-AZ101J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 100 OHM J
R518 RD-AZ101J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 100 OHM J
R519 RD-AZ102J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 1K OHM J
R520 RD-AZ202J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 2K OHM J
R527 RD-AZ101J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 100 OHM J
R528 RD-AZ101J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 100 OHM J
R529 RD-AZ101J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 100 OHM J
R530 RD-AZ101J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 100 OHM J
R531 RD-AZ181J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 180 OHM J
R532 RD-AZ102J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 1K OHM J
R533 RD-AZ102J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 1K OHM J
R534 RD-AZ472J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 4.7K OHM J
R537 RD-AZ183J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 18K OHM J
R539 RD-AZ471J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 470 OHM J
R540 RD-AZ471J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 470 OHM J
R541 RN-AZ3902F R METAL FILM 1/6 39K OHM F
R542 RD-AZ682J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 6.8K OHM J
R543 RD-AZ222J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 2.2K OHM J
R544 RD-AZ222J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 2.2K OHM J
R545 RD-AZ473J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 47K OHM J
R546 RD-AZ181J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 180 OHM J
R547 RD-AZ563J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 56K OHM J
R550 RD-4Z562J- R CARBON FILM 1/4 5.6K OHM J
R551 RD-AZ823J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 82K OHM J
R552 RD-AZ103J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 10K OHM J
R553 RD-AZ103J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 10K OHM J
R554 RD-AZ103J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 10K OHM J
R555 RD-AZ103J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 10K OHM J
R556 RD-AZ101J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 100 OHM J
R557 RD-AZ101J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 100 OHM J
R558 RD-AZ391J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 390 OHM J
R559 RD-AZ222J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 2.2K OHM J
R560 RD-AZ222J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 2.2K OHM J
R561 RD-AZ101J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 100 OHM J
R562 RD-AZ101J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 100 OHM J
R563 RD-AZ101J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 100 OHM J
R564 RD-AZ101J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 100 OHM J
Page 52

51
CP-520V Service Manual
z_loc z_parts_code parts_name parts_descr remark
z_loc z_parts_code parts_name parts_descr remark
R565 RD-AZ154J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 150K OHM J
R566 RD-AZ103J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 10K OHM J
R567 RD-AZ103J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 10K OHM J
R568 RD-AZ103J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 10K OHM J
R569 RD-AZ103J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 10K OHM J
R571 RD-AZ102J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 1K OHM J
R572 RD-AZ103J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 10K OHM J
R573 RD-AZ103J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 10K OHM J
R574 RD-AZ103J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 10K OHM J
R575 RD-AZ103J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 10K OHM J
R576 RD-AZ102J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 1K OHM J
R577 RD-AZ102J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 1K OHM J
R578 RD-AZ102J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 1K OHM J
R579 RD-AZ101J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 100 OHM J
R580 RD-AZ123J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 12K OHM J
R582 RD-AZ101J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 100 OHM J
R583 RD-AZ101J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 100 OHM J
R584 RD-AZ101J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 100 OHM J
R585 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
R586 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
R587 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
R588 RD-AZ102J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 1K OHM J
R589 RD-AZ102J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 1K OHM J
R590 RD-AZ334J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 330K OHM J
R598 RD-AZ182J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 1.8K OHM J
R599 RD-AZ224J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 220K OHM J
R605 RD-AZ132J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 1.3K OHM J
R606 RD-AZ132J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 1.3K OHM J
R607 RD-AZ512J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 5.1K OHM J
R608 RD-AZ202J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 2K OHM J
R609 RD-AZ223J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 22K OHM J
R610 RD-AZ103J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 10K OHM J
R611 RD-4Z301J- R CARBON FILM 1/4 300 OHM J
R612 RD-4Z301J- R CARBON FILM 1/4 300 OHM J
R613 RD-AZ829J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 8.2 OHM J
R614 RD-AZ829J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 8.2 OHM J
R615 RD-AZ829J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 8.2 OHM J
R616 RD-AZ474J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 470K OHM J
R617 RD-AZ829J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 8.2 OHM J
R618 RD-AZ474J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 470K OHM J
R619 RD-AZ153J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 15K OHM J
R620 RD-AZ153J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 15K OHM J
R701 RN-AZ1002F R METAL FILM 1/6 10K OHM F
R702 RN-AZ1502F R METAL FILM 1/6 15K OHM F
R703 RD-AZ101J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 100 OHM J
R704 RD-AZ101J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 100 OHM J
R713 RD-AZ472J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 4.7K OHM J
R720 RD-AZ122J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 1.2K OHM J
R721 RD-AZ181J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 180 OHM J
R722 RD-AZ221J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 220 OHM J
R723 RD-AZ331J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 330 OHM J
R724 RD-AZ471J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 470 OHM J
R804 RD-2Z104J- R CARBON FILM 1/2 100K OHM J
R806 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
R807 RD-AZ152J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 1.5K OHM J
R808 RD-4Z221J- R CARBON FILM 1/4 220 OHM J
R809 RD-AZ102J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 1K OHM J
R810 RC-2Z565KP R CARBON COMP 1/2 5.6M OHM K
R811 RN-4Z9102F R METAL FILM 1/4 91.0K OHM F
R812 RN-4Z1502F R METAL FILM 1/4 15K OHM F
R813 RN-4Z2201F R METAL FILM 1/4 2.2K OHM F
R814 RD-AZ103J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 10K OHM J
R815 RD-AZ102J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 1K OHM J
R816 RD-4Z399J- R CARBON FILM 1/4 3.9 OHM J
R817 RD-AZ101J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 100 OHM J
R818 RD-AZ103J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 10K OHM J
R819 RD-AZ103J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 10K OHM J
R820 RD-AZ273J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 27K OHM J
R824 RN-AZ3301F R METAL FILM 1/6 3.3K OHM F
R825 RN-AZ3301F R METAL FILM 1/6 3.3K OHM F
R827 RD-AZ473J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 47K OHM J
R828 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
R829 RD-AZ472J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 4.7K OHM J
R830 RD-AZ471J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 470 OHM J
R831 RD-AZ203J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 20K OHM J
R832 RD-AZ472J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 4.7K OHM J
R834 RD-AZ181J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 180 OHM J
R835 RD-AZ473J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 47K OHM J
R850 RD-AZ102J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 1K OHM J
R901 RD-AZ101J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 100 OHM J
R902 RD-AZ101J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 100 OHM J
R903 RD-AZ101J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 100 OHM J
R907 RD-AZ271J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 270 OHM J
R908 RD-AZ271J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 270 OHM J
R909 RD-AZ271J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 270 OHM J
R911 RD-4Z102J- R CARBON FILM 1/4 1K OHM J
R912 RD-2Z202J- R CARBON FILM 1/2 2K OHM J
R913 RD-2Z202J- R CARBON FILM 1/2 2K OHM J
R914 RD-2Z202J- R CARBON FILM 1/2 2K OHM J
R920 85801060GY WIRE COPPER 1/0.6 TIN COATING
RA01 RD-AZ101J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 100 OHM J
RA02 RD-AZ101J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 100 OHM J
RA03 RD-AZ101J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 100 OHM J
RA04 RD-AZ101J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 100 OHM J
RA05 RD-AZ103J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 10K OHM J
RA06 RD-AZ750J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 75 OHM J
RA07 RD-AZ332J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 3.3K OHM J
RA08 RD-AZ750J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 75 OHM J
RA09 RD-AZ750J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 75 OHM J
RA10 RD-AZ470J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 47 OHM J
RA11 RD-AZ680J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 68 OHM J
RA12 RD-AZ102J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 1K OHM J
RA13 RD-AZ222J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 2.2K OHM J
RA14 RD-AZ220J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 22 OHM J
RA15 RD-AZ750J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 75 OHM J
RA16 RD-AZ750J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 75 OHM J
RA17 RD-AZ103J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 10K OHM J
RA18 RD-AZ332J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 3.3K OHM J
RA19 RD-AZ750J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 75 OHM J
RA20 RD-AZ101J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 100 OHM J
RA21 RD-AZ101J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 100 OHM J
RA23 RD-AZ220J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 22 OHM J
RA24 RD-AZ222J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 2.2K OHM J
RA25 RD-AZ102J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 1K OHM J
RA29 RD-AZ101J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 100 OHM J
RA32 RD-AZ470J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 47 OHM J
RA35 RD-AZ750J- R CARBON FILM 1/6 75 OHM J
ZZ140 PTPKCPE519 PACKING AS DTX-21G2FZS-SB
M681 6520010200 STAPLE PIN #3417 ALL
M801 DMP5019100 BOX DTY-21G2 (NEW)
M811 485819BQ00 PAD 21G2 EPS
M822 4858219101 BAG P.E. 1300X1150 (U.K) LAMINATED
Page 53

CP-520V Service Manual
7. Exploded View
52
7-1 DTX-21G2
Page 54

CP-520V Service Manual
Exploded View
53
7-2 DTX-21B4
Page 55

CP-520V Service Manual
Exploded View
54
7-3 DTX-21U7
Page 56

CP-520V Service Manual
8. Printed Circuit Board
55
8.1 4859813693 (OLD PCB)
Page 57

CP-520V Service Manual
Printed Circuit Board
56
8.2 4859816393 (NEW PCB)
Page 58

CP-520V Service Manual
9. Schematic Diagram
57
Page 59

DAEWOO ELECTRONICS CORP.
PRINTED DATE : Dec. 2006
686, AHYEON-DONG, MAPO-GU,
SEOUL, KOREA.
C.P.O. BOX 8003 SEOUL KOREA
 Loading...
Loading...