Page 1

Models covered:
RTX 410-IR
RTX 610-IR
RTX 801-IR
RTX™ IR
User Manual
(Revised February 28, 2012)
Note: The contents of this user manual reflect operational instructions for RTX IR units manufactured
after 12/15/2011. RAID sets created in RTX IR units manufactured prior to this date are incompatible with
newer units.
RTX410/610/801-IR User Manual A9-468-0005 REV 1.0 - 1 -
Page 2

CRU
1: Default GUI Login Information
2: Pre-Installation Steps
3
2.1 Accessories
3
2.2 Identifying Parts
3
2.3 Warnings and Notices
4
2.4 Terminology
4
3: Introduction to RAID
5
3.1 Summary of RAID Levels
5
4: Introduction to iSCSI
6
4.1 What is iSCSI?
6
4.2 What is the benefit of iSCSI?
6
4.1 What is iSCSI Not?
6
5: Installation Steps
6
5.1 Hard Drive Installation
6
5.2 Operating RTX
6
6: Network Configuration
7
6.1 Connect RTX to your network (or computer)
7
6.2 Use the LCD to Configure the Config GUI Port
7
7: Using the GUI
10
7.1 GUI indicators
11
7.2 Overview of GUI architecture
12
7.3 Manually Creating a Usable RAID Set
12
7.4 Quick Installation
17
7.5 System Configuration
17
7.7 Volume Configuration
26
7.8 Enclosure Management
33
7.9 Maintenance
34
7.10 Online Support
36
8: iSCSI Initiator software
36
8.1 Software Installation
36
8.2 Access RTX using iSCSI Initiator Software
37
9: Usage With Mac and Windows Operating Systems
37
9.1 Usage with Mac OS X
37
9.2 Usage with Windows Operating Systems
38
10: RAID is Not A Backup
40
11: Event Notifications
40
12: Working With Volumes Over 2 TB In Size
44
13: Frequently Asked Questions
45
14: Technical Specifications
47
Table of Contents
5.3 Recovering from a Failed RAID 7
3
7.6 ISCSI Configuration 23
7.11 Logout 36
RTX410/610/801-IR User Manual A9-468-0005 REV 1.0 - 2 -
Page 3
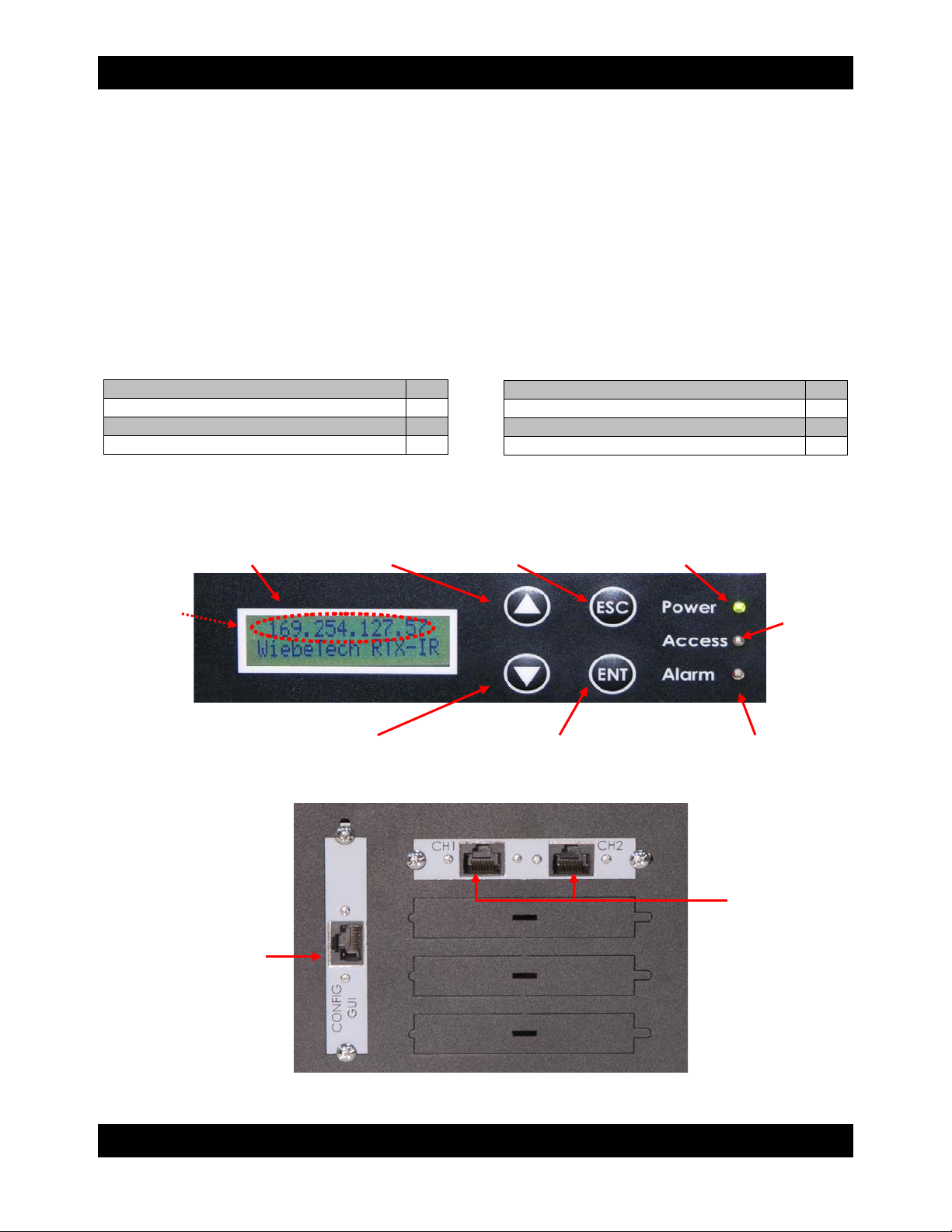
CRU
RTX Unit
1
Power Cord
1
Ethernet Cable
2
Packet of DataPort Keys
1
RTX Unit
1
Power Cord
1
Ethernet Cable
2
Packets of Lock Tools
2
LCD
Up
ESC (escape, exit)
Power LED
IP Address
Down
ENT (enter)
Alarm LED
Access
LED
RTX 801-IR
User Account
This account has read
Username: user
Password: 1234
Ethernet Configuration Port
(for GUI configuration)
iSCSI
Ports
1 Default GUI Login Information
The following login and password infor mation can be used to easily log into the GUI (See Section 7 for
instructions on how to log in to and use the GUI).
Administrator Account
This account has read and write privileges.
Username: admin
Password: 1234
-only privileges.
2 Pre-Installation Steps
2.1 RTX Accessories: Please contact CRU-DataPort if any items are missing or damaged.
RTX 410-IR and 610-IR
2.2 Identifying the Parts of RTX
LCD Panel on front of RTX
2.3 Warnings and Notices: Please read the following before be g inning installation.
General Care
Ports on rear of RTX
RTX410/610/801-IR User Manual A9-468-0005 REV 1.0 - 3 -
Page 4
CRU
Terminology
RAID
Redundant Array of Independent Disks. There are different RAID levels with
different degrees of data protection, data availability, and performance.
JBOD
“Just a Bunch Of Disks”. JBOD needs at least one hard drive.
PD
Physical Disk. Belongs to the member disk of one specific RAID group.
RG
RAID Group. A collection of removable media. One RG consists of a set of
VDs and owns one RAID level attribute.
VD
Virtual Disk. Each RG could be divided into several VDs. The VDs from one
RG have the same RAID level, but may have different volume capacity.
LUN
Logical Unit Number. A unique identifier for a SCSI device which enables
computers to differentiate among separate SCSI devices.
GUI
Graphical User Interface.
RAID cell
The number of subgroups of PDs in an RG.
DS
Dedicated Spare disk. A spare disk dedicated to one specific RG and is used
when another disk in the RG fails.
GS
Global Spare disk. A spare disk that is shared among all RGs and is used
when another disk in an RG fails.
WWN
World Wide Name. A unique identifier that identifies a particular PD.
CHAP
Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol. An optional security
mechanism to control access to RTX through its iSCSI data ports.
iSNS
Internet Storage Name Service. This protocol allows automated discovery,
management, and configuration of iSCSI devices on a TCP/IP network.
The main circuit boards of the HDD carriers are susceptible to static electricity. Proper grounding is
strongly recommended to prevent electrical damage to the enclosure or other connected devices,
including the computer host. Avoid all dramatic movement, tapping on the unit, and vibration.
Avoid placing the HDD carriers close to magnetic devices, high voltage devices, or near a heat
source. This includes any place where the product will be subject to direct sunlight. Do NOT allow
water to make contact with the carrier or receiving frame.
Before starting any type of hardware installation, ensure that all power switches have been turned off
and all power cords have been disconnected to prevent personal injury and damage to the hardware.
To avoid overheating, RTX should be operated in a well-ventilat ed ar ea and in suc h a way that
sufficient airflow is maintained across the controller chips.
RAID
Use only hard drives that are in perfect condition. Avoid using drives that have ever developed bad
sectors during previous usage. This could lead to possible device failure or loss of data.
RTX supports SATA hard drives of various specifications and different capacities. However, we
recommend using drives of the same brand and type for optimal performance. If drives of different
capacities are used in a RAID, the capacity of the smallest drive will determine how much of each
drive is used. The additional capacity on the larger drives will not be used by the RAID.
RAID level 0 will allow you to use the full combined capacity of the drives, and offers the best data
transfer speeds. However, RAID 0 offers no protection for the data. If one drive fails in a RAID 0, the
data on all of the drives is irretrievably lost. Before creating a RAID, investigate the various RAID
types and choose the one that is best for your needs.
Always back up data before switching RAID types. Switching RAID types will destroy current
data. You must reformat your drives afterwards.
2.4 Terminology
3 Introduction to RAID
RTX410/610/801-IR User Manual A9-468-0005 REV 1.0 - 4 -
Page 5

CRU
RAID
Level
Min.
Drives
Data
Redundancy
Also known as striping. Data distributed across
protection.
Also known as mirroring. All data replicated on two
Also known as Bit-Interl eav ed Par ity . Data and
disk.
Also known as Block-Interleaved Distributed
one of the drives is available for data storage.
Two parity bits are used to create double
drives is available for data storage.
Also known as a mirror of striped drives. Data and
disk.
Also known a stripe of mirrors. Data is striped
disk pair.
Also known as Striping Dedicated Parity Array.
RAID set.
RAID 50 combines the straight block-level striping
of RAID 0 with the distributed parity of RAID 5
Transfer rates are similar to
RAID 0
RAID 60 c ombines the straight block-level striping
RAID 6
Just A Bunch of Disks. This is not an actual RAID
level as each disk is treated as its own entity.
A RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) is an array of multiple hard drives that are combined in a
way that provides faster performance and/or data safety. Your RTX unit is capable of creating and
managing several different varieties of RAID. You may choose your preferred RAID level based on
factors such as disk capacity, desired data safety, and desired performance.
3.1 Summary of RAID Levels
RTX supports RAID Levels 0, 1, 3, 5, 6, 0+1, 10, 30, 50, 60, & JBOD. RAID Level 5 is most commonly
used by those seeking an optimal balance of speed and data safety.
RAID Features and Performance
0
1
3
5
6
0+1
Description
multiple drives in the array. There is no data
separate disks. This is a high availability solution,
but due to the 100% duplication, only half the total
disk capacity is available for data storage.
parity information is subdivided and distributed
across all disks. Parity must be equal to the
smalles t disk capacity in th e array. Parity
information normally stored on a dedicated parity
Parity. Data and parity information is subdiv ide d
and distributed across all disks. Can withstand the
failure of one drive. The total capacity of all but
redundancy. Can withstand the failure of two
drives. The total capacity of all but two of the
parity information is subdivided and distributed
across all disks. Parity must be equal to the
smalles t disk capacity in th e array. Parity
information normally stored on a dedicated parity
Data Transfer Rate
No data
2
protection
2 1 drive
3 1 drive Reads are similar to RAID 0
3 1 drive Reads are similar to RAID 0
4 2 drives Slightly less than RAID 5
4 1 drives*
Very high
Reads are higher than a
single disk; Writes are
similar to a single disk
Transfer rates are similar to
RAID 0
10
across two separate disks and mirrored to another
RAID 30 breaks up data into smaller blocks, and
30
then stripes the blocks of data to each RAID 3
50
60
of RAID 0 with the distributed double parity of
JBOD
*If both drives in either the RAID 0 or RAID 1 set fail, then the entire RAID will fail. If only one drive in
each of the RAID 0 and RAID 1 sets fail, then the RAID is preserved.
**One drive from each of the striped RAID sets could fail without loss of data. If two drives in the same
striped RAID set fail, then the entire RAID will fail.
RTX410/610/801-IR User Manual A9-468-0005 REV 1.0 - 5 -
4 1 drives*
6 2 drives**
6 2 drives**
8 4 drives***
1 0 drives Very high
Transfer rates are similar to
RAID 0
Transfer rates are similar to
RAID 0
Transfer rates are similar to
RAID 0
Page 6

CRU
***Two disks from each of the RAID 6 sets could fail without loss of data. The loss of three disks in the
same striped RAID 6 set fails, then the entire RAID will fail.
4 Introduction to iSCSI
4.1 What is iSCSI?
iSCSI is a technology that allows a data storage device to be accessed over a TCP/IP network using
SCSI protocols. When your computer’s OS receives a request for data access, it generates a SCSI
command and then sends an IP packet across a network or direct Ethernet connection. A software utility
known as an iSCSI initiator is used to generate the SCSI commands. Such a utility must be installed on
the computer before it can access an iSCSI storage device (See Section 8 for installation instructions).
4.2 What is the Benefit of iSCSI?
An iSCSI storage device can be placed anywhere throughout a network, so the device can reside at a
great distance from the computer which accesses it. It is also a very fast connection when used on a
gigabit network, achieving speeds of 100 megabytes (MB)/sec or more. The connection it uses (RJ45—
standard Ethernet port) is commonly found on desktop and laptop computers, so there is no need to
purchase potentially expensive host bus adapters to provide a connection.
4.3 What is iSCSI Not?
iSCSI storage devices are not Network Attached Storage (NAS) devices. They have no built-in server
capabilities and therefore cannot be accessed by more than one computer at a time. Multiple computers
can only access the data if the iSCSI device is first attached to a single computer which is then set up as
a server.
5 Installation Steps
5.1 Hard Drive Installation
a) Pull the ejection handle on the TrayFree bay to open the bay door.
b) Insert a bare SATA hard drive into the bay. Make sure it is label-side up with the SATA connection on
the drive inserted first.
c) Shut the bay door.
d) You can optionally secure each bay door. Doing so is not necessary to operate RTX.
• For RTX410 and RTX610, Insert an RTX Key into its key lock and turn it 90 degrees clockwise.
• For RTX801-IR, use the Lock Tool to slide the lock to the “locked” position.
Sticker Card
Use the stickers on the provided sticker card to label each drive. This will prevent the drives from getting
mixed up when they are removed from the bays.
5.2 Operating RTX
a) Connect RTX to a computer or network using the included Ethern et cable. Plug one cable into the “CH-
1” port. You can optionally plug a second cable into the “CH-2” port. The purpose of having multiple iSCSI
channels is to provide redundancy/failover and increased performance.
b) Connect RTX to a power outlet with the included power cord.
c) Install the hard drives into RTX (See Section 5.1).
d) Flip the power switch on the rear of the unit to turn on RTX.
e) If you have not yet configured RTX for access, refer to Sections 6, 7, and 8. Section 6 will tell you how
to connect RTX to your network or computer. Section 7 contains instructions for accessing the GUI and
RTX410/610/801-IR User Manual A9-468-0005 REV 1.0 - 6 -
Page 7

CRU
System Info
Displays the details of RAM and firmware.
Alarm Mute
Turns off the alarm sound when an error occurs.
Reset/Shutdown
Resets or shuts down the controller.
To use “Quick Install” to set up a volume by three steps. CRU-DataPort does not recommend
Smart steps to create a volume. Please refer to Section 7.7.1 for detailed operation steps in
the web GUI.
View IP Setting
Display the current IP address, subnet mask, and gatew ay .
Sets the IP address, subnet mask, and gateway. You can choose to use DHCP server (for IP
address allocation) or manually specify the IP address.
Restores factory defaults:
Default User Password: 1234
creating a usable RAID set. Section 8 contains instructions on how to access RTX through an iSCSI
initiator.
f) Format the drive. When a hard drive is first used with RTX, or when a RAID set has been created and
the user connects to RTX through an iSCSI initiator, it will show up as a blank, unallocated drive. You’ll
need to format the drive in RTX before you can use it See Section 9 for instructions on how to format the
drive with Mac or Windows operating s ystem s . Note that formatting a drive will erase all data on the
drive, so be sure to back up your data b efore installing the hard drives into this enclosure and
before beginning this operation.
5.3 Recovering from a Failed RAID
If one hard drive of a RAID set with data redundancy has failed or has been unplugged or removed, then
the status of the RAID Group will report that the RAID is degraded and RTX will automatically search for a
spare disk to rebuild the RAID. If none are found, RTX will search for a global spare disk. If neither is
found, it will wait for the user to remove the failed hard drive and insert a working replacement.
6 Network Configuration
6.1 Connecting RTX to Your Network or Computer
a) Plug an Ethernet cable into the Config GUI port on the rear of RTX.
b) Connect the other end of the Ethernet cable to your network. This usually means plugging it into a
router or hub. In an office environment, you may have a network jack built into your office wall. If a
network connection is not available, you can connect the Ethernet cable directly to an RJ45 (Ethernet)
port on your computer.
c) Connect the power cable to the rear of RTX and to a grounded electrical outlet.
d) Turn on RTX’s power using the switch on the rear panel.
6.2 Using the LCD to Configure the Config GUI Port
RTX has both an LCD interface and a GUI. The LCD interface has only basic functionality and is mainly
used to configure the IP address of the Config GUI port. Once the Config GUI has been configured, the
GUI can be used to fully configure RTX.
6.2.1 Navigating the LCD menu
Use the four function keys, ▲ (Up), ▼ (Down), ESC (Escape) and ENT (Enter) to manipulate the LCD
interface. After pressing ENT (Enter) key, you can use the ▲ (Up) and ▼ (Down) keys to select a
function. If there is an alarm or error message, the LCD will display the related information.
6.2.2 LCD Functions
Quick Install
Volume Wizard
Change IP Config
using the Quick Install option to set up your RTX. For quick set-up of a RAID, refer to Section
7.7.1.
Default Administrator Name: admin
Reset to Default
Default Administrator Password: 1234
Default User Name: user
RTX410/610/801-IR User Manual A9-468-0005 REV 1.0 - 7 -
Page 8
CRU
Default IP address: 192.168.0.1
Default gateway: 192.168.0.254
[Firmware Version
x.x.x]
[RAM Size
xxx MB]
[ENT:OK
ESC: Back]
[ENT:OK
ESC: Back]
[ENT:OK
ESC: Back]
RAID 0
xxx GB
[Local]
RAID 0+1
[IP Config]
[Static IP]
[IP Address]
[DHCP IP]
[IP Subnet Mask]
[255.255.255.0]
[IP Gateway]
[192.168.010.254]
[ENT:OK
ESC: Back]
Adjust IP
address
[IP Subnet
Mask]
Adjust Submask
IP
Adjust Gateway
IP
Default subnet mask: 255.255.255.0
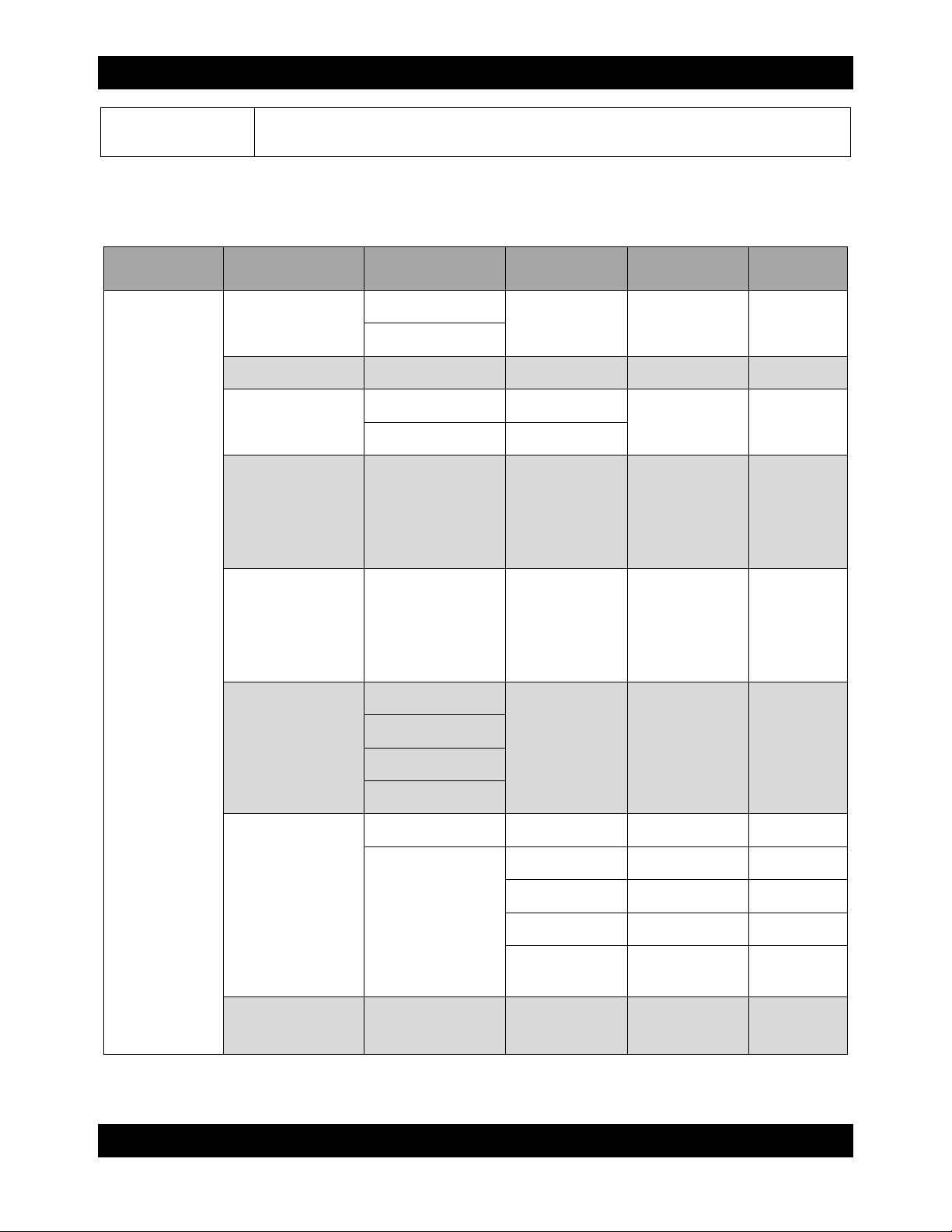
6.2.3 RTX LCD Menu Diagram
Use the following chart for reference when following the instructions in Section 6.2.4 for setting up RTX
according to your network type.
Main Menu 2nd Menu Screen 3rd Menu Screen 4th Menu Screen 5th Menu Screen
6th Menu
Screen
CRU-DataPort
RTX
[System Info.]
[Alarm Mute]
[Reset/Shutdown]
[Quick Install]
[Volume Wizard]
[View IP Setting]
[Reboot]
[Shutdown]
RAID 1
RAID 3
RAID 5
RAID 6
RAID 0+1)
RAID 0
RAID 1
RAID 3
RAID 5
RAID 6
[Apply The
Config]
[Use default
algorithm]
[ENT:OK
ESC: Back]
[Volume Size]
xxx GB
[Apply The
Config]
[ENT:OK
ESC: Back]
RTX410/610/801-IR User Manual A9-468-0005 REV 1.0 - 8 -
[Change IP Config]
[Reset to Default]
[DHCP]
[Static IP]
[ENT:OK
ESC: Back]
[IP Address]
[IP Gateway]
[Apply IP
Setting]
[ENT:OK
ESC: Back]
Page 9

CRU
6.2.4 Instructions for Differi n g Network Connection Types
DHCP-Enabled Network
On DHCP networks, a new IP address is dynamically assigned to RTX’s Config GUI port as soon
as the network detects it. You can determine this address by checking the LCD interface on the
front of RTX. It will appear in this format: xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx. Simply type this IP address into a web
browser on your computer. This will access RTX’s GUI, which you will use to configure the unit.
Static Network
a) Check your computer’s IP address, subnet mask, and gateway. Mac users can find this
information in System Preferences Network.
To do this in Windows, open Network and Sharing Center in the Control Panel (Also called “View
Network Status and Tasks” under the “Network and Internet” category). On the left pane, select
“Change adapter settings”. Right-click on your network (likely called Local Area Connection) and
select Properties. On the new window that opens, select “Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)”
and click the Properties button. Your computer’s IP address, subnet mask, and gateway will be
displayed.
b) On the RTX LCD interface, press ENT and then scroll up or down to Change IP Setting.
Press ENT.
c) Scroll up or down to find Static. Press ENT.
d) Change the IP address to closely match what your computer is using. Or, if you are on a
business network, have your IT administrator assign you an IP address. The IP address you
select must NOT be in use by another device.
For example, if your computer's IP address is 192.168.0.9, you might change the RTX’s IP to
192.168.0.7. On smaller networks, each of the first three octets must be the identical to
your computer’s IP address! When changing the IP address you'll notice that a box flashes
over the digit to be changed. While the digit is selected, press ▲ (Up) or ▼ (Down) to change it.
Press ENT to move to the next digit.
e) After the IP address is set, enter the subnet mask address exactly as it is shown on your
computer’s TCP/IP settings.
f) Next, enter the gateway address exactly as it is shown on your computer’s TCP/IP settings.
g) Confirm the settings change. To confirm, press ▲ (Up) for “yes” and then press ENT again.
h) Type the RTX’s new IP address into a web browser on your computer. This will access the
RTX’s GUI, which you will use to configure the unit.
Direct Connection to a Computer
The instructions are similar to those for a static network (see above), except that your computer
will not have an IP address assigned if it’s not a part of a network. Since RTX and your computer
must have similar IP addresses, you will assign an IP address to your computer based upon the
default IP address of RTX.
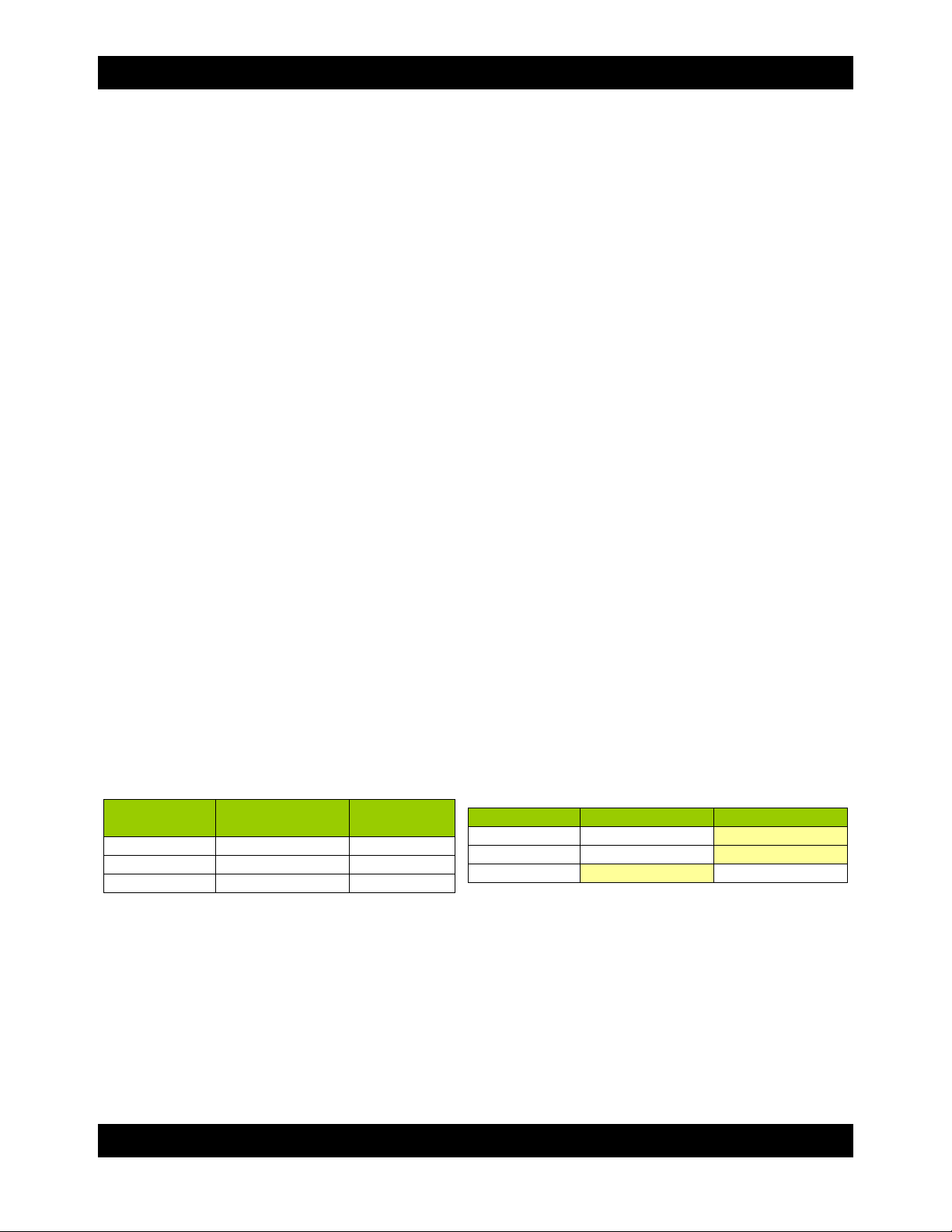
a) Check RTX’s LCD to find out the IP address of the Config GUI configuration port. It will appear
RTX410/610/801-IR User Manual A9-468-0005 REV 1.0 - 9 -
Page 10
CRU
IP Address
169.254.12.62
(blank)
Mask
255.255.000.000
(blank)
Gateway
000.000.000.000
(blank)
Before making changes
RTX
Computer
IP Address
169.254.12.62
169.254.12.63
Mask
255.255.000.000
255.255.000.000
Gateway
169.254.12.63
(blank)
After making changes
in this format: xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx.
b) Next, change your computer’s IP address so that all but the last three digits match RTX ’s
address. For example, if RTX’s IP address is 169.254.12.62, you might assign your computer the
number 169.254.12.63 (assuming no other computer on the network is already using that
number). The process of changing your computer’s IP address varies depending on its operating
system.
Mac users can go to System Preferences Network.
For modern Windows operating systems, open Network and Sharing Center in the Control Panel
(Also called “View Network Status and Tasks” under the “Network and Internet” category). On the
left pane, select “Change adapter settings”. Right-click on your network (likely called Local Area
Connection) and select Properties. On the new window that opens, select “Internet Protocol
Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)” and click the Properties button. By default, your computer is probably set
to receive a new IP address automatically. Change the setting to manual configuration and then
type in the IP address.
c) Using the same process as the previous step, change the computer’s Subnet Mask setting to
match RTX’s Subnet Mask setting.
d) Finally, use RTX’s LCD interface to change RTX ’s Gateway setting. It should match the IP
address you assigned to your computer. When changing the gateway address you'll notice that a
box flashes over the digit to be changed. While the digit is selected, press ▲ (Up) or ▼ (Down) to
change it. Press ENT to move to the next digit. After the gateway address is set, press ENT all
the way to the end and confirm the settings change. To confirm, press ▲ (Up) for “yes” and then
press ENT again.
e) Launch a web browser and type RTX’s IP address into the URL bar, as if it were a website.
This will access RTX’s GUI, which you will use to configure the unit.
The tables below show example settings. The first table shows the type of settings that will
appear by default. The next table shows how the settings might look after you’ve made changes.
RTX Computer
Connecting From Home to Office
RTX can also be used over the Internet. If you are connecting to an RTX at your office from
home, you will need to contact your IT administrator to set up a VPN client in order to log in to the
office network. Once you have logged in to the office network, you can access RTX just as if you
were actually at your office (see instructions for DHCP-enabled Network, Static Network, or Direct
Connection to a Computer, depending on how your office network is configured).
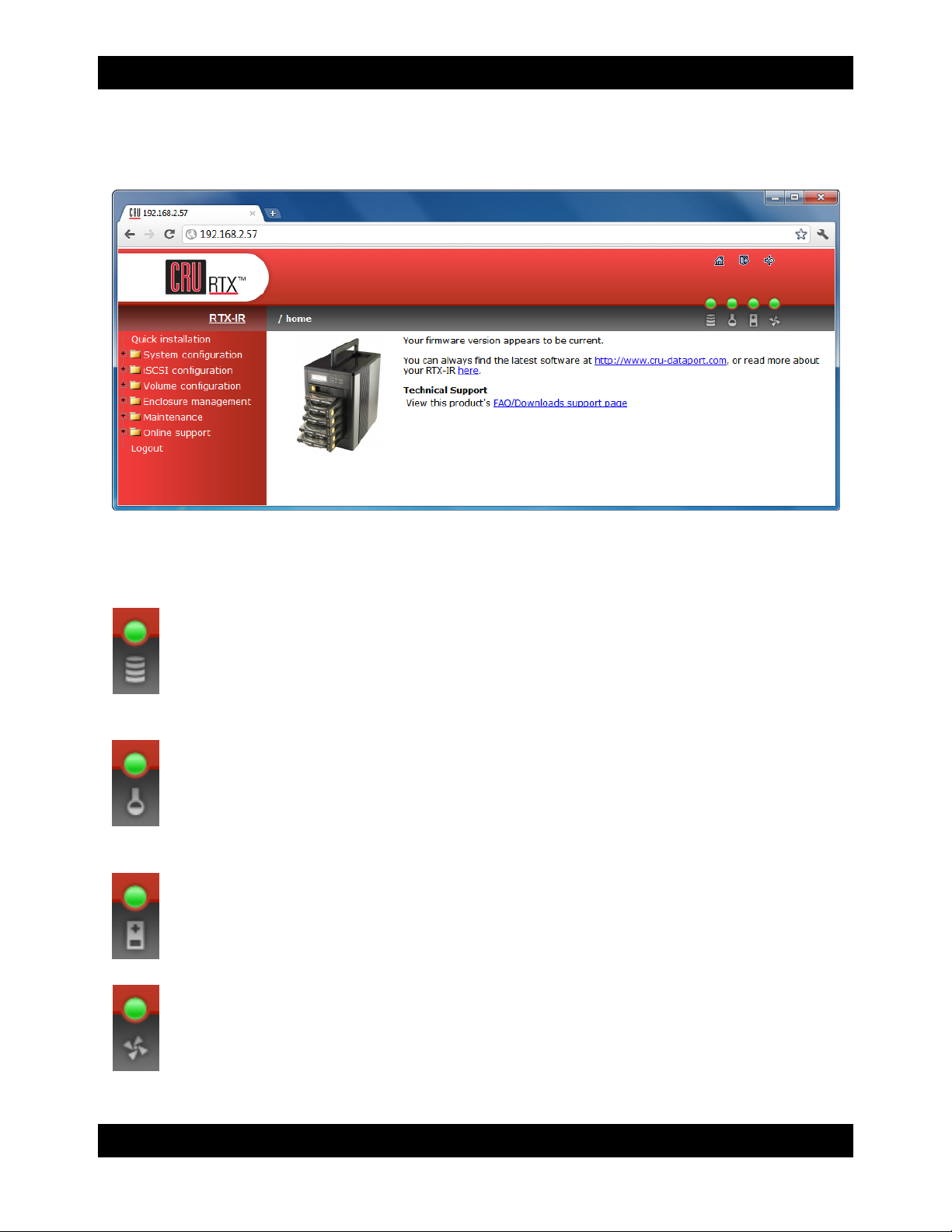
7 Using the GUI
You will use the web browser-based GUI to set up a RAID and create logical volumes on RTX. After
setting up access to the GUI and accessing it through a web browser (see Section 6.2 for instructions),
RTX410/610/801-IR User Manual A9-468-0005 REV 1.0 - 10 -
Page 11
CRU
the GUI’s main page should load, displaying a picture of RTX with several options to the left. When you
click on any option, you will be prompted for a username and password. The default administrator
username is "admin" and the default password is "1234."
7.1 GUI Indicators
The top right hand corner of the GUI window displays several indicators.
RAID light: Green indicates that the RAID is working properly. Red indicates a RAID error. If no
RAID is set up, the light will remain green.
Temperature light: Green indicates normal. Red indicates abnormal system temperature and
probable overheating.
Voltage light: Green indicates normal. Red indicates abnormal voltage status like a power surge
or a bad power supply.
Fan light: Green indicates that the fan is working properly. Red indicates a malfunctioning fan that
needs to be replaced. (only applies to RTX610-IR and 801-IR).
RTX410/610/801-IR User Manual A9-468-0005 REV 1.0 - 11 -
Page 12

CRU
7.2 Overview of GUI Architecture
• Quick installation
• System configuration
o System settings
o IP address
o Login settings
o Mail settings
o Notification settings
• iSCSI configuration
o Entity property
o NIC
o Node
o Session
o CHAP account
• Volume configuration
o Volume creation wizard
o Physical disk
o RAID group
o Virtual disk
o Logical unit
• Enclosure management
o SES configuration
o Hardware monitor
o S.M.A.R.T.
• Maintenance
o System information
o Upgrade
o Reset to factory default
o Import and export
o Event log
o Reboot and shutdown
• Online support
o Product Information and Specs
o FAQ and Downloads
• Logout
7.3 Manually Creating a Usable RAID Set
Use these sets of instructions to create a usable RAID set. To quickly create a RAID 0, 1, 3, 5, 6, or 0+1
set using the Volume Creation Wizard, see Section 7.6.1.
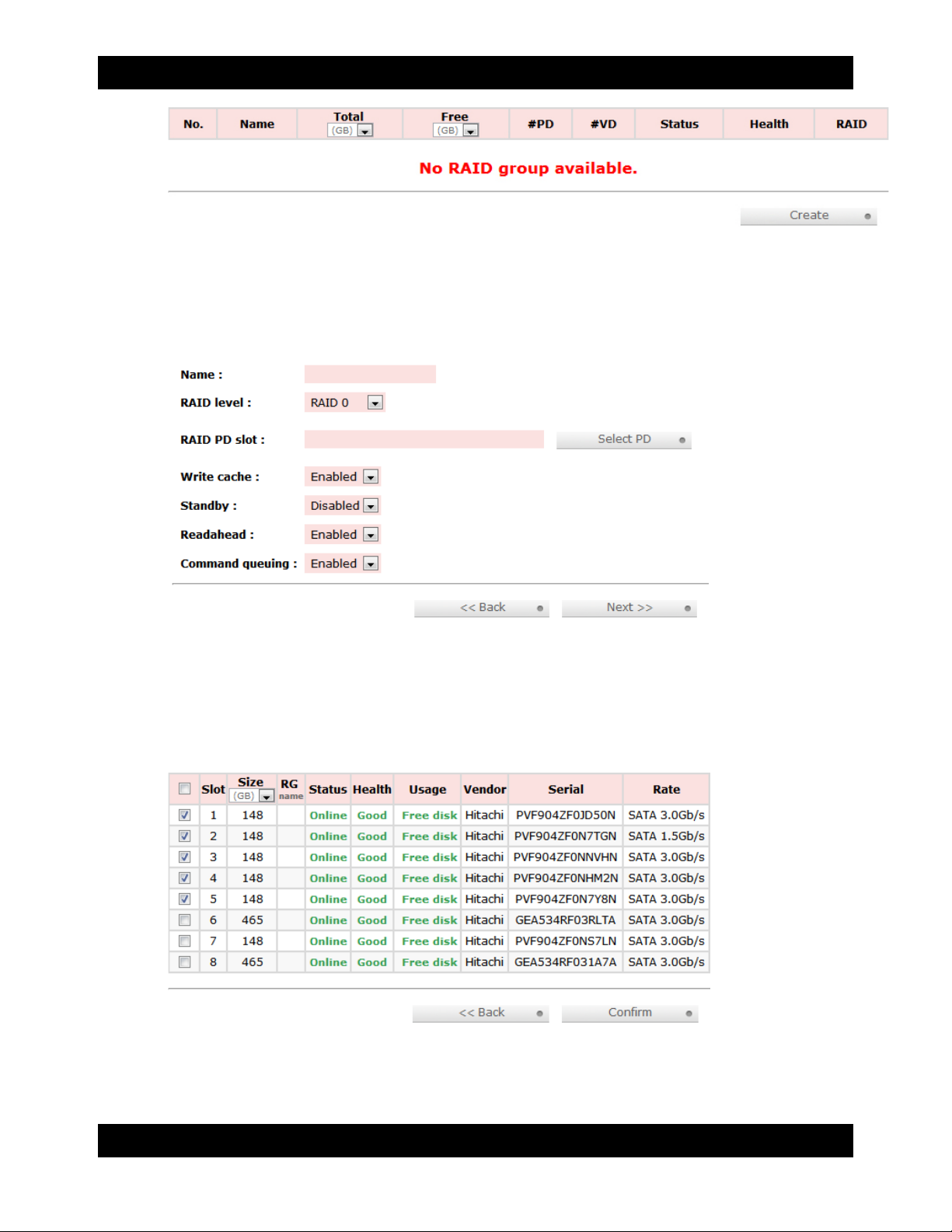
7.3.1 Manually Creating a RAID Group
To manually create a usable RAID set, you will first need to create a new RAID Group.
a) Click the “Create” button at the bottom of the page to open the RAID Group creation screen.
RTX410/610/801-IR User Manual A9-468-0005 REV 1.0 - 12 -
Page 13
CRU
b) Enter a name for the new RAID Group in the first field, and then select your desired RAID type or
JBOD from the dropdown box. CRU-DataPort recommends RAID 5 for maximum performance,
capacity, and security. For more information on RAID, see Section 3. Click “Select PD” to select
the drives that will be added to the RAID Group.
Note: Drives must be marked as Free Disks before they can be added to a RAID Group. To set
drives to Free Disks, see Section 7.7.2, subsection “Modifying Physical Disks”.
c) All available Free Disks will be displayed. Check the drives that you wish to add to the RAID
Group, then click “Confirm”.
d) The selected Physical Disks will now be displayed in the RAID Group creation screen. Enable or
Disable Write Cache, Standby, Readahead, and Command Queuing based on your needs. Most
RAID Groups will be fine with the default settings. Then click “Next” to proceed to the confirmation
screen.
RTX410/610/801-IR User Manual A9-468-0005 REV 1.0 - 13 -
Page 14

CRU
e) On the confirmation screen, verify that the RAID level is correct and all of the disks you selected
are displayed under “RAID PD slot”, then click “Confirm” to create the RAID Group.
f) The RAID Group will now display on the main RAID Group screen. To finish manually creating a
usable RAID set, a Virtual Disk still must be created and a Logical Unit must be attached. Go to
the next section, “Manually Creating a Virtual Disk”.
If you opted to create JBOD drives, skip to Section 8.3.3, “Manually Attaching a Logical Unit” as
Virtual Disks have already been created for each JBOD drive.
7.3.2 Manually Creating a Virtual Disk
After a RAID Group has been created, you can create associated Virtual Disks. You must create at least
one Virtual Disk to access the drives of RTX with a computer.
a) Click the “Create” button at the bottom of the page to open the Virtual Disk creation screen.
b) You will see the screen below. Fill in the information and then click “Confirm”. Each field is
explained below the picture.
RTX410/610/801-IR User Manual A9-468-0005 REV 1.0 - 14 -
Page 15

CRU
Name
Enter a name for the Virtual Disk.
RG Name
Choose the RAID Group to which the Virtual Disk will be added.
Capacity
Enter the capacity of the Virtual Disk. The default uses the maximum capacity of the associated
RAID Group. If you wish to create multiple Vir tual Disks on the selected RAID Group, you will
need to reduce the capacity below the maximum so that there is space left on the RAID Group for
additional Virtu al D is ks.
Stripe height (KB)
Determines how RTX organizes the RAID. Normally the default option is preferred.
Block size
Determines the minimum file size for files that will be stored on the Virtual Disk. Higher block
sizes can result in more wasted space if many small files are saved to the drive, but are
necessary to take advantage of high capacity RAIDs. If you are creating a Virtual Disk over
2TB in size for use with MacOS 10.4.x or older, or for use with Windows XP, you must
increase the block size to 4096KB to take advantage of the full capacity of the Virtual Disk.
Read/Write
Allows selection of cache type. Normally the default option is preferred.
Priority
Determines the priority that RTX will give to RAID activities (rebuild and initialization) versus
priority given to file transfers. “High prior ity” will result in slower file transfers during initialization,
but provide for faster initialization.
BG Rate
Background Task Priority. The higher the number, the more priority will be given to background
input/output.
RTX410/610/801-IR User Manual A9-468-0005 REV 1.0 - 15 -
Page 16

CRU
Readahead
Choose whether file prefetching should be enabled.
Erase
Wipes out the original data in the Virtual Disk to prevent the OS from recognizing it. The options
are “None”, “First 1GB”, and “Full D isk.”
c) After the RAID builds, the Virtual Disk will now display on the main Virtual Disk screen. If you
have enabled an Erase option, do not shut down or reboot RTX while the Virtual Disk is
initializing or the erase process will stop.
To finish manually creating a usable RAID set, at least one Logical Unit must be attached. Go to
the next section, “Manually Attaching a Logical Unit”.
7.3.3 Manually Attaching a Logical Unit
You will need to attach at least one Logical Unit to a Virtual Disk to access its RAID Group, although
multiple Logical Units can be attached to the same Virtual Disk.
a) Click the “Attach” button to attach a Logical Unit to a Virtual Disk.
b) You will see the screen below. Fill in the inf ormation. Select the Virtual Disk to which you wish to
attach a Logical Unit. The Host name can remain as an asterisk if you want any host to access
the Virtual Disk. Otherwise, change the field to limit access to specific hosts. Then select the LUN
that will be used. The default setting on this is acceptable. Finally, select the permissions that
hosts accessing this Logical Unit will have. Then click “Confirm”.
c) The main Logical Unit Screen will now display the Logical Unit you have just created. If you’ve
RTX410/610/801-IR User Manual A9-468-0005 REV 1.0 - 16 -
Page 17

CRU
been following the instructions for manually creating a usable RAID set, you have now completed
setup and can now access the RAID set through iSCSI initiator software (see Section 8 for
installation and connection instructions).
7.4 Quick Installation
CRU-DataPort does not recommend using the Quick Installation option to set up your RTX. For quickly
setting up a RAID, refer to Section 7.7.1.
Quick Install uses all physical disks in RTX and the maximum amount of space they contain to create a
RAID Group using one Virtual Disk. There will be no space set aside for spares. If some disks are used in
other RAID Groups, Quick Install cannot be run.
7.5 System Configuration
The System Configuration menu gives access to a number of options used to configure RTX system
properties. Click on “System Configuration” to access the following menu options: System Settings, IP
Address, Login Settings, Mail Settings, and Notification Settings.
7.5.1 System Settings
System Settings allows you to view and change the system name, change the date and time, and turn the
System Indication LED on or off.
RTX410/610/801-IR User Manual A9-468-0005 REV 1.0 - 17 -
Page 18

CRU
System Name
The default system name is “RTX-IR”. To change the system name, simply click in the box
displaying the system name and highlight or delete the part of the name you wish to change, then
type the new name and click the “Confirm” button at the bottom of the page.
Date and Time
The Date and Time option allows you to change the date and time settings of RTX. To change
the date or time, check the “Change date and time” check box and then click in the field that you
wish to change. Highlight or delete the information, then type in the new information and click the
“Confirm” button at the bottom of the page.
To change the time zone, click the drop down box and then scroll up or down until you reach the
correct time zone. Then choose that time zone and click the “Confirm” button at the bottom of the
page.
After confirming, a dialog box will appear verifying that changes have been made.
Alternatively, an NTP (Network Time Provider) can be used to sync RTX’s time information with
that of a standardized server. To use an NTP, click the NTP check box, then input the server
information in the server field.
Click the “Confirm” button at the bottom of the page to update the time settings. A dialog box will
appear to inform you that the changes have been made. The updated settings will reflect the time
settings of the NTP.
RTX410/610/801-IR User Manual A9-468-0005 REV 1.0 - 18 -
Page 19

CRU
System Indication
To turn the System Indication LED on or off, select the “Confirm” button in the System Indication
box. After confirming, a dialog box will appear verifying that changes have been made. To
reverse this action, press the “Confirm” button again.
7.5.2 IP Address
The IP Address option lists RTX’s MAC address and allows you to view and modify the IP information of
the Config GUI port on RTX. This option does not allow the administrator to configure the IP address of
the individual data ports. This must be done using the LCD interface on the front of RTX (Section 6.2).
An RTX configured for DHCP.
7.5.3 Login Settings
The Login Settings page allows you to configure the Auto Logout and Login Lock features, as well as
change the administrator account and user passwords.
Login Configuration
• Auto Logout will automatically log the user out of the system after a set period of 5
minutes, 30 minutes, or 1 hour of inactivity.
• Login Lock prevents multiple users from using the GUI simultaneously. Both features are
disabled by default. To enable a feature, click on the dropdown menu associated, select
the new option, and click the “Confirm” button.
RTX410/610/801-IR User Manual A9-468-0005 REV 1.0 - 19 -
Page 20

CRU
Admin Password
The Admin Password opt ion allows you to change the password for the administrator account,
which is used to access and modify the settings in the GUI. The default username is ‘admin’
and the password is ‘1234’. To change the password, click on the “Change admin password”
check box. Then enter the old password in the first field. Type the new password in the second
and third field and finally click the “Confirm” button at the bottom of the page.
A dialog box will appear asking for verification. Click “OK.” After the password has been changed,
another dialog box will appear to inform you that the password has been changed.
User Password
The User password option allows you to change the password for the user account, which is used
to view, but not modify the settings in the GUI. The default username is ‘user’ and the
password is ‘1234’. To change the password, click on the “Change user password” check box.
Then enter the old password in the first field. Type the new password in the second and third field
and finally click the “Confirm” button at the bottom of the page.
7.5.4 Mail Settings
RTX can be configured to send email to up to 3 addresses when events, warnings, and errors occur.
Contact your IT administrator to set up an email address for RTX and to input the proper SMTP settings.
RTX410/610/801-IR User Manual A9-468-0005 REV 1.0 - 20 -
Page 21

CRU
7.5.5 Notification Settings
Notification Settings allows you to configure the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP), Windows
Messenger events, the System Log server, Event Log filters, and enable or disable the internal buzzer.
SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol)
SNMP can be configured to send trap messages to up to three different addresses on the
network. To add an address, simply enter the IP address of the receiving server or computer,
then click the “Confirm” button at the bottom of the page. Note: The receiving server must be
configured to receive SNMP messages.
For more information on SNMP, you may wish to consult the third party website:
http://www.systemdisc.com/snmp
Messenger
RTX can be configured to send instant messages to up to 3 addresses when events, warnings, or
errors occur.
RTX410/610/801-IR User Manual A9-468-0005 REV 1.0 - 21 -
Page 22

CRU
Syslog Serv er (System Log Server)
The Syslog Server option allows configuration for error, warning, and information reporting via a
port on the server. Enter the server IP under Server IP/hostname and the port used in the UDP
Port line (the default port is 514). The Facility can be changed between “User”, “Kern”, and
“Local1” through “Local7” using the dropdown box. Select the check boxes for “Info”, “Error”, and
“Warning” that pertain to the information that you want to have reported.
Event Log Filter
The Event Log Filter allows you to display event messages. To configure what types of messages
are displayed, select the check boxes for “Info”, “Error”, and “Warning” that pertain to the
information that you want to have reported. The options for Pop Up Events will display those
events as a pop-up notification in your browser. The options for Show on LCM will display the
selected events in RTX IR’s LCD screen.
Buzzer
To disable the buzzer, place a checkmark next to “Always disable buzzer,” and click the “Confirm”
button at the bottom of the page.
RTX410/610/801-IR User Manual A9-468-0005 REV 1.0 - 22 -
Page 23

CRU
7.6 iSCSI Configuration
The iSCSI configuration menu options are generally used to modify the connection properties of RTX.
Click on “iSCSI configuration” to access the following menu options: Entity Property, NIC, Node, Session,
and CHAP Account.
7.6.1 Entity Property
The Entity Property option allows you to add an Internet Storage Name Service (iSNS) server IP address
to the iSNS server group, to which the iSCSI initiator can send queries. Simply enter the iSNS IP address
in the iSNS IP field and click “Confirm”. Note: Setting an iSNS is not necessary to use RTX.
7.6.2 NIC
Click on “NIC” to view the IP settings of the two gigabit Ethernet data ports. You will see the following
information:
RTX410/610/801-IR User Manual A9-468-0005 REV 1.0 - 23 -
Page 24

CRU
NIC Column Descriptions
Name
LAN1 corresponds to the port labeled CH-1 (Channel 1) on the back of RTX, while
LAN2 corresponds to the port labeled CH-2 (Channel 2).
LAG
Displays whether Link Aggregation is enabled or disabled.
LAG No
Displays the LAG number.
DHCP
Shows whether the channel has DHCP enabled.
IP Address
Displays the IP address currently in use by the channel.
Netmask
Displays the subnet mask being used by the channel.
Gateway
Displays the IP gateway. In a DHCP network, it will display the IP of the router to which
Jumbo Frame
Displays whether jumbo frames are enabled or disabled. The maximum jumbo frame
MAC Address
Displays the MAC address of each channel.
Link
Displays the status of each channel. If an Ethernet cable is connecting RTX to a
network or computer, the Link will display “Up”.
RTX is connected.
size is 3900 bytes.
Hover your mouse cursor over the appropriate button in the “Name” column to reveal a menu of
configurable options.
IP Settings for iSCSI Ports
Click on this option in order to enable DHCP or to manually set up a channel’s IP Address,
Netmask, and Gateway. Fill in the appropriate information and then click the “Confirm” button.
Set the Default Gateway
Sets the selected channel as the default gateway for RTX. To disable the default gateway, hover
your mouse cursor over the appropriate button in the “Name” column again and select the
“Disable default gateway” option. Only one channel can be the default gateway.
Enable Jumbo Frames
Enables jumbo frames for the associated channel. To disable jumbo frames, hover your mouse
cursor over the appropriate button in the “Name” column again and select the “Disable jumbo
frames” option. The maximum jumbo frame size is 3900 bytes.
Ping Host
Opens a dialog box in which the user can input the host’s IP address to initiate a ping test.
7.6.3 Node
The Node option displays RTX’s entity name, which will be seen by the iSCSI initiator, and allows you to
toggle CHAP (Challenge Handshake Authorization Protocol) on or off.
CHAP is disabled by default. To turn on CHAP, click the “Authenticate” button. This will bring up a screen
with a dropdown box. Click the dropdown box and select “CHAP”, then click the “Confirm” button.
After turning on CHAP authentication, you must set up at least one CHAP account (see Section 7.6.5).
RTX410/610/801-IR User Manual A9-468-0005 REV 1.0 - 24 -
Page 25

CRU
7.6.4 Session
The session function allows you to view information on a session initiated by an iSCSI initiator application
(see Section 8), including Initiator Name, TPGT, Error Recovery Level, and Error Recovery Count.
Hover your mouse over the button in the “No.” column and click on “List connection.” It will list all the
connections of the session.
7.6.5 CHAP Account
CHAP (Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol) is a common iSCSI authentication method. When
CHAP is enabled, RTX will require authenticatio n at login throu gh an iSCSI initiator (see Section 8).
Authentication also occurs at various times during the connection, by way of transferring the username,
initiator password (also called “initiator secret”), and target password (also called “target secret”). RTX
uses the same value for initiator secret and target secret. For added security, the authentication
information is hashed and a token is sent instead of the information itself.
a) To use CHAP, you will need to turn on CHAP authentication (see Section 7.6.3) and then follow
the steps there to set up a CHA P account.
b) After clicking on the “CHAP Account” option, you will see the following screen:
Click “Create” to create a new user. This brings up a screen with fields for User, Secret, and
Confirm. Enter a user name in the first field, and a 12-16 character password to use as the secret
in the second and third fields. Click the “Confirm” button.
c) The new CHAP account will appear on the main CHAP account screen:
RTX410/610/801-IR User Manual A9-468-0005 REV 1.0 - 25 -
Page 26

CRU
Modifying the CHAP Account
Hover your mouse cursor underneath the username to bring up a menu. Select “Modify user
information” to change the username and password, or select “Delete” to remove the user. A
confirmation box will appear. Click “OK” and the username will be deleted from RTX.
7.7 Volume Configuration
The Volume Configuration menu provides the options you will use to set up one or RAID volumes of
varying levels on RTX. Click on Volume Configuration to view the following menu options: Volume
Creation Wizard, Physical Disk, Volume Group, User Data Volume, Cache Volume, and Logical Unit.
The following diagram describes the relationship of RAID components in RTX.
Each RAID Group can be divided into several Virtual Disks. The Virtual Disks in one RAID Group share
the same RAID level, but may have different volume capacity. All Virtual Disks share the Cache Volume
to execute a data transfers. A Logical Unit Number (LUN) is a unique identifier that the computer uses to
distinguish and access SCSI devices.
7.7.1 Volume Creation Wizard
Click on the “Volume Creation Wizard” option to easily set up your RTX with a RAID 0, 1, 3, 5, 6, or 0+1
set. For using higher RAID types or configuring the drives for JBOD access, see Section 7.3.
RTX410/610/801-IR User Manual A9-468-0005 REV 1.0 - 26 -
Page 27

CRU
If any disks are not assigned to a Virtual Disk, it will walk you through a series of steps to create a usable
RAID set. If there are previous RAID Group or Virtual Disk configurations present, the wizard may limit the
choices you can select in the following steps.
a) Select your desired RAID Level from the drop-down box, then click the “Next” button. The drop-
down box displays the drive capacity next the RAID Level.
b) Choose how many disks you wish to use in the new RAID Group. The default algorithm uses all
of the disks not already assigned to a RAID Group. Or you can choose how many disks you want
the new RAID Group to use by selecting the “Customization” radio button and then using the
drop-down box to select the number of disks. The drop-down box displays the drive capacity next
the number of disks.
On the next screen, fill in the size in MB for how large you want the new RAID Group to be, then
click the “Next” button. The maximum size is filled in by the wizard automatically, so in most
cases you simply need to click the “Next” button.
Step 4 summarizes the choices you have made. If anything is incorrect, select the “Back” button
and navigate backwards through the steps to change your options. If everything looks fine, click
“Confirm.” The GUI will navigate to the Virtual Disk page which now shows a new Virtual Disk
with the name similar to “QUICK#####”. Your Virtual Disk is now initializing and may take several
hours to complete.
7.7.2 Physical Disk
Click the Physical Disk option to view and modify the status of the drives installed in RTX.
RTX410/610/801-IR User Manual A9-468-0005 REV 1.0 - 27 -
Page 28

CRU
Physical Disk Column Descriptio n s
Slot
The slot number of the hard drive. “1” corresponds to the top bay of RTX , “8” to the
configuration options for that particular hard drive, which are detailed below.
Size
The logical capacity of the drive. Can be displayed in megabytes (MB) or gigabytes
RG Name
The name of the RAID Group to which the drive is assigned, if any.
Status
Displays the operational status of the disk.
Scrubbing The hard drive is being scrubbed.
Health
Displays general operational health of the disk.
Read Errors
Usage
Displays how the disk is currently being used.
Vendor
Displays the manufacturer of the hard drive.
Serial
Displays the serial number of the hard drive.
Rate
Displays the transfer speed of the hard drive.
RTX IR does not s upport 6G speed. When a 6G drive is inserted it will only show the speed as 3G.
Write cache
The hard drive’s write cache is enabled or disabled. The default setting is Enabled.
Standby
The hard drive will automatically spin down to save power. The default setting is
The following information is displayed:
bottom bay. Hover your mouse cursor over the button below the slot number to bring up
(GB).
• Online The hard drive is online.
• Rebuilding The hard drive is being rebuil t.
• Transitioning The hard drive is being migrated or is being replaced by
another disk during rebuilding.
•
• Good The hard drive is good.
• Failed The hard drive has failed.
• Error Alert The hard drive’s S.M.A.R.T. monitoring system is reporting an
error.
•
The hard drive has unrecoverable read errors.
• RAID Disk (RD) The hard drive has been assigned to a RAID Group.
• Free Disk (FD) The hard drive is free for use.
• Dedicated Spare (DS) The hard drive has been set as a dedicated spare of
a RAID Group.
• Global Spare (GS) The hard drive has been set as a global spare of all
RAID Groups.
• SATA 1.5Gb/s SATA1 disk
• SATA 3.0Gb/s SATA2 disk
Disabled.
RTX410/610/801-IR User Manual A9-468-0005 REV 1.0 - 28 -
Page 29

CRU
Readahead
The hard drive has file prefetching enabled. The default setting is Enabled.
Command
Queuing
Newer hard drives can queue multiple commands and handle them one by one. The
default setting is Enabled.
RAID Group Column Descriptions
No.
The RAID Group number. Hover your mouse cursor over the button below the RAID
Name
The name of the RAID Group.
Total
The total capacity of the RAID Group. The drop-down box allows the user to view the
Free
The capacity of the RAID Group that hasn’t yet been assigned to a Virtual Disk. The
#PD
The number of hard drives in the RAID Group.
Modifying Physical Disks
Hover your mouse cursor over the button below the slot number to bring up a series of options for
that particular hard drive.
Set Free Disk
Frees the disk from the RAID Group it is attached to and makes it free for use. If the disk
is not currently attached to a RAID Group, this option is grayed out.
Set Global Spare
Sets the disk as a spare disk for all existing RAID Groups.
Set Dedicated Spare
Opens a page that allows the administrator to attach the disk as a spare to a specific
RAID Group.
Disk Scrub
Scrubs the disk with specific data patterns to more securely erase its data.
Upgrade
Opens a page that allows the administrator to upgrade the hard drive firmware. The
administrator may simultaneously upgrade all the hard drives in RTX that are identical to
the one selected.
Turn on Indication LED
Turns on the indication LED for the bay in which the physical disk resides.
More information
Displays more details about the hard drive.
7.7.3 RAID Group
The RAID Group screen displays information about all existing RAID Groups. For instructions on how to
create a RAID Group, see Section 7.3.1.
The RAID Group screen displays the following information:
Group number for configuration options.
capacity in either MB or GB.
drop-down box allows the user to view the capacity in either MB or GB.
RTX410/610/801-IR User Manual A9-468-0005 REV 1.0 - 29 -
Page 30

CRU
#VD
The number of Virtual Disks that have been created as part of the RAID Group.
Status
The status of the RAID Group.
Parity Checking The RAID Group’s parity is being checked.
Health
The health of the RAID Group.
RAID
The RAID level of the RAID Group.
Modifying RAID Groups
Hover your mouse cursor over the button below the RAID Group number to bring up a series of
options for that particular RAID Group.
7.7.4 Virtual Disk
The Virtual Disk screen displays any existin g Vir t u al D i sks and allows you to create and delete Virtual
Disks. For instructions on how to create a Virtual Disk, see Section 7.3.2.
RTX410/610/801-IR User Manual A9-468-0005 REV 1.0 - 30 -
• Online The RAID Group is online.
• Offline The RAID Group is offline.
• Rebuild The RAID Group is currently being rebuilt.
• Migrate The RAID Group is currently being migrated.
• Scrubbing The RAID Group is being scrubbed.
•
• Good The RAID Group is good.
• Failed The RAID Group has failed.
• Degraded The RAID Group is not healthy and incomplete, due either to a
removed hard drive or a failed drive.
Migrate
Allows the administrator to change the RAID Group’s RAID level or add disks to the RAID
without data loss. The total size of the new RAID Group must be larger or equal to the
original RAID Group or the action will trigger an “Invalid RG config” error.
Move
Allows the administrator to change which disks on which the RAID Group exists without
losing data. The total size of the new RAID Group must be larger or equal to the original
RAID Group or the action will trigger an “Invalid RG config” error.
Activate
Activate RAID Group disk roaming. This option can only be executed when the RAID
Group status is offline.
Deactivate
Deactivate the RAID Group disk roaming. This option can only be executed when the
RAID Group is online.
Confirm Parity Check
Regenerates parity for the RAID Group. Only applies to RAID sets with parity.
Delete
Deletes the RAID Group.
Set Disk Property
Enable or disable write caching, standby, readahead, and command queuing.
More Information
Displays more details about the RAID Group.
Page 31

CRU
Virtual Disk Column Descriptions
No.
The Virtual Disk number. Hover your mouse cursor over the button below the Virtual
Disk number for configuration options.
Name
The name of the Virtual Disk.
Size
The total capacity of the Virtual Disk. Can be displayed in MB or GB.
Write
The write status of the Virtual Disk.
RO
Priority
Displays the priority that RTX will give to RAID activities (rebuild, initialization) versus
BG Rate
Background Task Priority. 4 / 3 / 2 / 1 / 0 → The default value is 4. The higher the
Status
The status of the Virtual Disk.
Parity Checking
Type
Indicates that the Virtual Disk is part of a RAID Group.
Health
The health of the Virtual Disk.
R%
Shows the percentage completed of an initialization or RAID rebuild.
RAID
Displays the RAID level.
#LUN
The number of Logical Unit Numbers that are attached to the Virtual Disk.
RG Name
The name of the RAID Group to which the Virtual Disk belongs.
• WT Write Through
• WB Write Back
•
Read Only
priority given to file transfers.
• HI High Priority
• MD Medium Priority
• LO Low Priorit y
number, the more priority will be given to background input/output.
• Online The Virtual Disk is online.
• Offline The Virtual Disk is offline.
• Initiating The Virtual Disk is being initialized.
• Rebuild The Virtual Disk is being rebuilt.
• Migrate The Virtual Disk is being migrated.
• Rollback The Virtual Disk is being rolled back.
•
The Virtual Disk is undergoing a parity check.
• Optimal The Virtual Disk is working well and there is no failed physical disk
within the RAID Group.
• Degraded At least one disk from the RAID Group that the Virtual Disk
belongs to is failed or removed from RTX .
• Failed The RAID Group that the Virtual Disk belongs to has failed and
cannot recover from data loss.
• Partially Optimal The Virtual Disk has experienced recoverable read errors.
After passing a parity check, the health status will change to Optimal.
RTX410/610/801-IR User Manual A9-468-0005 REV 1.0 - 31 -
Modifying Virtual Disks
Hover your mouse cursor over the button below the Virtual Disk number to bring up a series of
options for that particular Virtual Disk.
Page 32

CRU
Logical Unit Column Descriptions
Host
The host address which can access the attached Virtual Disk. An asterisk indicates that
button below the Host for configuration options.
LUN
The Logical Unit Number (LUN).
Permission
Displays the permissions given to hosts accessing the RAID set through this Logical
VD Name
The name of the associated Virtual Disk.
#Session
The number of host sessions currently accessing the Logical Unit.
Extend
Extend the Virtual Disk capacity.
Confirm Parity Check
Regenerates parity for the RAID Group. This option allows the administrator to
regenerate parity when a parity/data inconsistency is found, or to check parity/data
consistency only.
Delete
Deletes the Virtual Disk.
Set Property
Allows the administrator to change the Virtual Disk name, change the write status,
priority, background task priority, and enable or disable Readahead.
Attach LUN
Attach a Logical Unit Number to the Virtual Disk.
Detach LUN
Detach a Logical Unit Number from the Virtual Disk.
List LUN
Lists all Logical Unit Numbers attached to the Virtual Disk.
More Information
Displays more details about the Virtual Disk, including the LUNs that have been attached
to it.
7.7.5 Logical Unit
The Logical Unit is what your computer will use to access and manage SCSI devices. For instructions on
how to attach a Logical Unit to a Virtual Disk, see Section 7.3.3.
The following information is displayed:
any host may access the attached Virtual Disk. Hover your mouse cursor over the
Unit.
• Read-Write Has permissions to read and write to the disks.
• Read-Only Has permission to read but not write to the disks.
Modifying Logical Units
Hover your mouse cursor over the button below the Host to bring up a series of options for that
particular Logical Unit.
RTX410/610/801-IR User Manual A9-468-0005 REV 1.0 - 32 -
Page 33

CRU
Detach
Detaches the Logical Unit from a Virtual Disk and deletes it.
7.8 Enclosure Management
Enclosure management gives access to the following menu options: SES Configuration, Hardware
Monitor, and S.M.A.R.T.
7.8.1 SES Configuration
SCSI Enclosure Services, or SES, is a command set that is used to manage and sense the state of the
power supplies, cooling devices, displays, indicators, and individual drives of a SCSI device. RTX is an
SES compliant enclosure. However, in order to use manage RTX using SES you must have the
appropriate software installed on your computer. An example is SMARTMon, a S.M.A.R.T. disk monitor,
offered by Santools at www.santools.com
To enable SES on RTX , you must have a Virt u al D is k set up and a Logical Unit attached. Once you have
done this, navigate to S ES Conf iguration and simply click the “Enable” button, then click “Confirm”. The
SES-enabled LUN will show up on the main SES screen.
7.8.2 Hardware Monitor
The Hardware Monitor displays information about the voltages and temperatures of RTX .
.
RTX410/610/801-IR User Manual A9-468-0005 REV 1.0 - 33 -
Page 34

CRU
Auto Shutdown
When this checkbox is enabled, RTX will automatically shut down if any of each items’ voltage or
temperature strays outside of the minimum or maximum displayed values. Auto shutd o wn is
enabled by default to protect the hardware of RTX.
7.8.3 S.M.A.R.T.
S.M.A.R.T. (Self-Monitoring Analysis and Reporting Technology) is a diagnostic tool for hard drives that
gives advanced warning in some cases of hard drive failure. S.M.A.R.T. measures various attributes of a
hard drive at all times to detect if certain values have moved outside of a certain range. The S.M.A.R.T.
option allows you to view the S.M.A.R.T. status of all of your hard drives.
RTX’s S.M.A.R.T. technology only supports SATA drives. SAS drives do not have this function and will
display “N/A” in the GUI.
7.9 Maintenance
The Maintenance screen gives access to the firmware and configuration functions: System Information,
Upgrade, Reset to Fac tor y Default, Import and Export, Event Log, and Reboot and Shutdown.
RTX410/610/801-IR User Manual A9-468-0005 REV 1.0 - 34 -
Page 35

CRU
7.9.1 System Information
Click on System Information to display RTX’s hardware profile information.
7.9.2 Upgrade
The upgrade function allows you to upgrade the firmware of RTX. DO NOT USE THIS FUNCTION
WITHOUT SPECIFIC INSTRUCTION FROM CRU-DATAPORT TECHNICAL SUPPORT. Doing so could
result in malfunction of your RTX.
7.9.3 Reset to Factory Default
The Reset to Factory Default option allows you to restore settings to the factory defaults. Click on the
“Confirm” button to verify.
7.9.4 Import & Export
The Import & Export function allows you to import or export a firmware configuration file. DO NOT USE
THIS FUNCTION WITHOUT SPECIFIC INSTRUCTION FROM CRU-DATAPORT TECHNICAL
SUPPORT. Doing so could result in malfunction of your RTX.
RTX410/610/801-IR User Manual A9-468-0005 REV 1.0 - 35 -
Page 36

CRU
7.9.5 Event Log
The Event Log allows you to view event messages. Check or uncheck the checkboxes of “Info”,
“Warning”, and “Error” filter the events displayed. Click the “Download” button to save the entire event log
as a text file. Click the “Clear” button to clear all event logs. Click the “Mute” button to stop the alarm if it is
engaged.
7.9.6 Reboot and Shutdown
The Reboot and Shutdown feature allows you to reboot or shutdown RTX’s RAID and LCD controllers.
Note: Choosing “Shutdown” will not shut down the physical components of RTX (fans, drives, power
supply). However, it will flush data from the cache to the physical drives, which is recommended to
prevent data corruption before physically shutting down using the power switch on the back of the unit.
7.10 Online Support
This screen contains helpful links to cru-dataport.com, including one for the “Product Information and
Specs” of your unit and one for “FAQs and Downloads”.
7.11 Logout
This screen allows you to log out of and exit the GUI.
8 iSCSI Initiator Software
8.1 Software Installation
This is a required step. Any computer must have initiator software installed before it can connect to an
iSCSI device such as RTX. Both freeware and commercial software utilities are available for this purpose.
Note: Initiator software is not required for additional computers that share files with the host computer
attached to RTX. In such a scenario, the host computer acts as a server to the other computers. Only the
computer directly accessing RTX needs initiator software.
8.1.1 Windows
Windows Vista and 7 alread y include the i SCSI sof twar e, no downlo ad is neces sa ry.
If necessary, users can download free Microsoft iSCSI Initiator software at the following URL:
http://www.microsoft.com/download/en/details.aspx?id=18986
8.1.2 MacOS X
Studio Network Solutions makes globalSAN iSCSI initiator, a free-to-try utility for MacOS X, available
here:
http://www.studionetworksolutions.com/support/faq.php?pi=11&fi=51
ATTO Technologies also makes a commercial iSCSI initiator for MacOS X:
http://www.attotech.com/xtend.html
8.1.3 Linux
Open-iSCSI initiator software is available for Linux users to download.
Website: http://www.open-iscsi.org/
Readme: http://www.open-iscsi.org/docs/README
RTX410/610/801-IR User Manual A9-468-0005 REV 1.0 - 36 -
Page 37

CRU
8.2 Access RTX using iSCSI Initiator Software
This software can by launched by doubl e-clicking on the iSCSI Initiator icon in the Administrative Tools
folder in the Control Panel.
8.2.1 Windows XP
After you launch the initiator you'll see a windo w with s evera l tabs , with the "Gen eral" tab opened by
default.
a) If you have set up CHAP in the RTX GUI, input the proper information by clicking on “General” tab and
then clicking on the “Secret” button.
b) Select the "Discovery" tab. Under Target Portals, click the "Add" button and enter the IP address for
the RTX’s CH-1 or CH-2 port (depending which connection link is shown as “Up” on the NIC screen).
c) Next, select the "Targets" tab. You should see a selection for the RTX in this Targets tab.
d) Select that target and click "Log on." Leave the default settings alone and click “OK”.
If the log-on is successful you'll now be able to use the RTX just like any other disk attached to your
computer.
8.2.2 Windows Vista and Windows 7
a) After you launch the initiator, input the IP address for the RTX’s CH-1 or CH-2 port (depending which
connection link is shown as “Up” on the NIC screen.
b) Click on the “Quick Connect…” button.
If the log-on is successful you'll now be able to use the RTX just like any other disk attached to your
computer.
Note: The Quick Connect feature does not support advanced connection types like CHAP. For
instructions on connecting to an iSCSI target using advanced settings, visit the following URL:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ee338480(v=ws.10).aspx#BKMK_ConnectAdvanced
8.2.3 GlobalSAN iSCSI Initiator for MacOS
This software can be launched by double-clicking on the globalSAN iSCSI icon in System Preferences.
a) After you launch the initiator you’ll see the globalSAN window pop up. Press the Add button (“+”) and
choose Portal from the dropdown menu to add a new portal.
b) On the Add Portal dialog box, enter the IP address for the RTX’s CH-1 or CH-2 port depending which
connection link is shown as “Up” on the NIC screen, and then click OK.
c) If you have set up CHAP in the RTX GUI input the proper information by clicking on the “Authentication
Settings” button.
d) Select the new target in the list to the left, then select the appropriate connection from the list that
opens up on the right side and click the “Connect” button.
If the log-on is successful you'll now be able to use the RTX just like any other disk attached to your
computer.
9 Usage with Mac and Windows Operating Systems
9.1 Usage with Mac OS X
9.1.1 Compatibility
RTX supports 3.5” SATA hard drives.
RTX410/610/801-IR User Manual A9-468-0005 REV 1.0 - 37 -
Page 38

CRU
9.1.2 Formatting a Drive
To format, use Mac OS X’s Disk Utility (found in the applications folder).
a) Click on the drive in the window to the left (see picture below).
b) Click the Erase tab in the window to the right (see picture below).
c) Select the format type. Most users prefer Mac OS Extended with Journaling (HFS+), which is required
for compatibility with Time Machine (OS 10.5 or newer). If you need to use RTX with both Mac and
Windows computers, select MS-DOS File System instead.
d) Enter a name for the new volume and then click “Erase” to start the process.
9.1.3 Mounting and Unmounting Volumes
Mounting Volumes
If the hard drives installed in RTX are already formatted with the correct Security Key inserted into the
Mini-USB Security Key Port, an icon representing RTX ’s volume will appear (mount) on the desktop. You
can begin using the volume right away. If the volume is unformatted, a message will appear on the
desktop saying that the disk is unreadable. Use OS X’s Disk Utility to easily format the drive (see section
above).
Unmounting Volumes
First, eject the data volume by dragging the volume’s icon to the trash bin, or by
selecting the icon then pressing Command-E. Next, log off the volume in your
iSCSI initiator software. If you are using the globalSAN initiator, you log off from
the “Targets” tab. Disconnecting in this way allows you to reconnect quickly later.
Another way of preventing delays is to keep your iSCSI initiator software open at
all times. You can minimize it and allow it to run in the background. Closing the
software and then reopening it can cause a lengthy delay before access to RTX
is allowed.
NOTE: It is strongly suggested that you disable automatic sleep mode on your Mac. You can still put the
Mac to sleep manually at any time as long as you follow the above procedures. This will prevent
reconnection difficulti es.
9.1.4 Creating a Boot Drive
To activate this feature, you must first install OS X on the volume in RTX. The easiest way to do this is to
clone an existing system drive using a utility such as Carbon Copy Cloner or Super Duper. Next, go to
System Preferences Startup Disk. A window will list the available bootable volumes. Select the volume
from which you wish to boot. Another method is to hold down the Option key during boot up. A screen
should appear that allows you to select the volume you wish to use. This is useful if you wish to boot from
RTX hard drive only some of the time.
9.2 Usage with Windows Operating Systems
9.2.1 Compatibility: RTX supports 3.5” hard drives.
9.2.2 Formatting a Drive: To format, use the Disk Management utility.
a) Right-click on My Computer, then select Manage. The Computer Management window will open.
b) In the left pane of this window, left-click on Disk Management.
RTX410/610/801-IR User Manual A9-468-0005 REV 1.0 - 38 -
Page 39

CRU
Drive
Properties
Device
Properties
c) The volume should appear in the list of Disks in the lower middle/right pane (see picture below). You
may need to scroll down to see it. If the volume is already formatted, you can identify it easily by its
volume name. If it’s unformatted, the Drive Properties Box will say “Unallocated” and
you’ll need to initialize the disk before formatting it. Initialize the disk by right-clicking the Device
Properties Box and selecting Initialize Disk.
d). To format the volume, right-click the Drive Properties Box and select “Format”.
e) If you are prompted to select a partition type, select MBR for volumes 2TB or smaller, or GPT for
volumes larger than 2TB. Note: Windows XP does not support GPT or volumes larger than 2TB.
f) Click through several more windows, leaving the default settings (unless you need to change them),
until you see a window that allows selection of a file system. Choose NTFS and enter a name for the new
volume. Be sure to check the box labeled “Perform a quick format” unless you want to completely erase
any data on the drive and have time to wait. A quick format should take less than a minute, while
standard formatting may take several hours.
g) Click “Next” and then “Finish” to start the format process. When the format is complete, the Drive
Properties Box will update to show the new volume name. The new volume can now be found by double
clicking on the My Computer icon on the desktop.
9.2.3 Mounting and Unmounting Volumes
Mounting Volumes
If the hard drives inside of RTX are already formatted with the correct Secur i t y Key inserted into the MiniUSB Security Key Port, you can begin using the volume right away. When RTX is properly connected
and turned on, a window may open to allow you access to the volume. If no window appears, find the
volume by double-clicking the “My Computer” icon.
Unmounting Volumes
Log off the volume using your iSCSI initiator software. In the Microsoft initiator, you can log off from the
“Targets” tab.
RTX410/610/801-IR User Manual A9-468-0005 REV 1.0 - 39 -
Page 40

CRU
Level
Type
Description
Info
PD inserted
Disk <slot> is inserted into system
Warning
Disk removed
Disk <slot> is removed from system
Error
HDD read error
Disk <slot> read block error
Error
HDD write error
Disk <slot> write block error
Error
HDD error
Disk <slot> is disabled
Error
HDD IO timeout
Disk <slot> gets no response
Info
PD upgrade started
PD [<string>] starts upgrading firmware process
Info
PD upgrade finished
PD [<string>] finished upgrading firmware process
Warning
PD upgrade failed
PD [<string>] upgrade firmware failed
Level
Type
Description
Warning
ECC single
Single-bit ECC error is detected at <address>
Error
ECC multiple
Multi-bit ECC error is detected at <address>
Info
ECC dimm
ECC Memory is installed
Info
ECC none
Non-ECC Memory is installed
Info
SCSI bus reset
Received SCSI Bus Reset event at the SCSI Bus
<number>
Error
SCSI host error
SCSI Host allocation failed
Error
SATA enable device fail
Failed to enable the SATA PCI device
Error
SATA EDMA mem fail
Failed to allocate memory for SATA EDMA
Error
SATA remap mem fail
Failed to remap SATA memory IO space
Error
SATA PRD mem fail
Failed ot initialize SATA PRD memory manager
Error
SATA revision ID fail
Failed to get SATA revision ID
Error
SATA reg fail
Failed to set SATA register
10 RAID Is Not a Backup
Because RTX features redundant RAID modes which protect against a hard drive mechanical failure, it is
an excellent part of any backup strategy. However, a RAID is not, in itself, a complete backup strategy.
Many things besides hard drive failure can damage or erase your data:
• Corruption caused by unexpected disconnection during data access (e.g. a cable is unplugged
during a data transfer, or the computer crashes or loses power while writing to the drives)
• Corruption or destruction caused by viruses or other malware
• Sabotage by a disgruntled employee or acquaintance
• Theft of your RTX
• Natural disasters such as fire, flooding, etc.
Considering these possibilities, any single copy of your important data must always be considered at risk.
That's why backing up is so important. Follow the 3-2-1 backup rule. Data should exist in three different
places on two different storage media and at least one of those copies should be maintained offsite.
Without an effective backup strategy, recovering data may be impossible, or the cost of data recovery
may be quite expensive. The CRU warranty does not cover costs associated with data loss (nor do the
warranties of other hard drive manufacturers).
Plan accordingly and backup data to minimize downtime!
11 Event Notifications
Physical Disk Events
Physical HW Events
RTX410/610/801-IR User Manual A9-468-0005 REV 1.0 - 40 -
Page 41

CRU
Error
SATA init fail
Core failed to initialize the SATA adapter
Error
SATA diag fail
SATA Adapter diagnostics failed
Error
Mode ID fail
SATA Mode ID failed
Error
SATA chip count error
SATA chip count error
Info
SAS port reply error
SAS HBA port <number> reply terminated abnormally
Info
SAS unknown port reply
error
SAS frontend reply terminated abnormally
Info
FC port reply error
FC HBA port <number> reply terminated abnormally
Info
FC unknown port reply
error
FC frontend reply terminated abnormally
Level
Type
Description
Info
Power install
Power(<string>) is installed
Error
Power absent
Power(<string>) is absent
Info
Power restore
Power(<string>) is restored to work
Error
Power fail
Power(<string>) is not functioning
Warning
Power detect
PSU signal detection(<string>)
Info
Fan restore
Fan(<string>) is restored to work
Error
Fan fail
Fan(<string>) is not functioning
Info
Fan install
Fan(<string>) is installed
Error
Fan not present
Fan(<string>) is not present
Error
Fan over speed
Fan(<string>) is over speed
Warning
Thermal level 1
System temperature(<string>) is higher
Error
Thermal level 2
System overheated(<string>)!!!
Error
Thermal level 2 shutdown
System overheated(<string>)!!! The system will autoshutdown immediately.
Error
Thermal level 2 CTR
shutdown
The controller will auto shutdown immediately, reason [
Overheated(<string>) ].
Warning
Thermal ignore value
Unable to update thermal value on <string>
Warning
Voltage level 1
System voltage(<string>) is higher/lower.
Error
Voltage level 2
System voltages(<string>) failed!!!
Error
Voltage level 2 shutdown
System voltages(<string>) failed!!! The system will autho
shutdown immediately.
Error
Voltage level 2 CTR
shutdown
The controller will auto shutdown immediately, reason [
Voltage abnormal(<string>) ].
Info
UPS OK
Successfully detect UPS
Warning
UPS fail
Failed to detect UPS
Error
UPS AC loss
AC loss for system detected
Error
UPS power low
UPS Power Low!!! The system will auto-shutdown
immediately.
Warning
SMART T.E.C.
Disk <slot> S.M.A.R.T. Threshold Exceed Condition
occurred for attribute <string>
Warning
SMART fail
Disk <slot>: Failure to get S.M.A.R.T. information
Warning
RedBoot failover
RedBoot failover event occurr ed
Warning
Watchdog shutdown
Watchdog timeout shutdown occurred
Warning
Watchdog reset
Watchdog timeout reset occurred
Info
Console Login
<username> login from <IP or serial console> via Console
UI
Info
Console Logout
<username> logout from <IP or serial console> via
Console UI
Info
Web Login
<username> login from <IP> via Web UI
EMS Events
RTX410/610/801-IR User Manual A9-468-0005 REV 1.0 - 41 -
Page 42

CRU
Info
Web Logout
<username logout from <IP> via Web UI
Info
Log clear
All event logs are cleared
Warning
Send mail fail
Failed to send event to <email>
Level
Type
Description
Info
RG create OK
RG <name> has been created
Info
RG create fail
Failed to create RG <name>
Info
RG delete
RG <name> has been deleted
Info
RG rename
RG <name> has been renamed as <name>
Info
VD create OK
VD <name> has been created.
Info
VD create fail
Failed to create VD <name>
Info
VD delete
VD <name> has been deleted
Info
VD rename
The name of VD <name> has been renamed to <name>
Info
VD read only
Cache policy of VD <name> has been set as read only
Info
VD write back
Cache policy of VD <name> has been set as write-back
Info
VD write through
Cache policy of VD <name> has been set as write-through
Info
VD extend
Size of VD <name> extends
Info
VD attach LUN OK
VD <name> has been LUN-attached
Info
VD attach LUN fail
Failed to attach LUN to VD <name>
Info
VD detach LUN OK
VD <name> has been detached
VD detach LUN fail
Failed to detach LUN from bus <number> SCSI ID
<number>, LUN <number>
Info
VD init started
VD <name> starts initialization
Info
VD init finished
VD <name> completes initialization
Warning
VD init failed
Failed to complete initialization of VD <name>
Info
VD rebuild started
VD <name> starts rebuilding
Info
VD rebuild finished
VD <name> completes rebuilding
Warning
VD rebuild failed
Failed to complete rebuild of VD <name>
Info
VD migrate started
VD <name> starts migration
Info
VD migrate finished
VD <name> completes migration
Error
VD migrate failed
Failed to complete migration of VD <name>
Info
VD scrub started
Parity checking on VD <name> starts
VD scrub finished
Parity checking on VD <name> com pletes with <ad dr ess >
parity/data inconsistency found
VD scrub aborted
Parity checking on VD <name> stops with <address>
parity/data inconsistency found
Info
RG migrate started
RG <name> starts migration
Info
RG migrate finished
RG <name> completes migration
Info
RG move started
RG <name> starts move
Info
RG move finished
RG <name> completes move
Info
VD move started
VD <name> starts move
Info
VD move finished
VD <name> completes move
Error
VD move failed
Failed to complete move of VD <name>
Info
RG activated
RG <name> has been manually activated
Info
RG deactivated
RG <name> has been manually deactivated
Info
VD rewrite started
Rewrite at LBA <address> of VD <name> starts
Info
VD rewrite finished
Rewrite at LBA <address> of VD <name> completes
Warning
VD rewrite failed
Rewrite at LBA <address> of VD <name> failed
Warning
RG degraded
RG <name> is in degraded mode
Warning
VD degraded
VD <name> is in degra ded mode
Error
RG failed
RG <name> is failed
LVM Events
Info
Info
Info
RTX410/610/801-IR User Manual A9-468-0005 REV 1.0 - 42 -
Page 43

CRU
Error
VD failed
VD <name> is failed
Error
VD IO fault
I/O failure for stripe number <address> in VD <name>
Recoverable read error
Recoverable read error occurred at LBA <address> <address> of VD <name>
Recoverable write error
Recoverable write error occur red at LBA <ad dres s > <address> of VD <name>
Unrecoverable read error
Unrecoverable read error occurred at LBA <address> <address> of VD <name>
Unrecoverable write error
Unrecoverable write error occurred at LBA <address> <address> of VD <name>
Config read rail
Config read failed at LBA <address> - <address> of PD
<slot>
Config write fail
Config write failed at LBA <address> - <address> of PD
<slot>
Error
CV boot error adjust global
Failed to change size of the global cache
Info
CV boot global
The global cache is OK
Error
CV boot error reate global
Failed to create the global cache
PD dedicated spare
Assign PD <slot> to be dedicated spare disk of RG
<name>
Info
PD global spare
Assign PD <slot> to Global Spare Disk s
PD read error
Read error occurred at LBA <address> - <address> of PD
<slot>
PD write error
Write error occurted at LBA <address> - <address> of PD
<slot>
Scrub wrong parity
The parity/data inconsisten cy is found at LBA <address> <address> when checking parity on VD <name>
Scrub data recovered
The data at LBA <address> - <address> is recovered
when checking parity on VD <name>
Info
PD freed
PD <slot> has been freed from RG <name>
Info
RG imported
Configuration of RG <name> has been imported
Info
RG restored
Configuration of RG <name> has been restored
Info
VD restored
Configuration of VD <name> has been restored
Info
PD scrub started
PD <slot> starts disk scrubbing process
Info
Disk scrub finished
PD <slot> completed disk scrubbing process
Large RG created
A large RG <name> with <number> disks included is
created
Weak RG created
A RG <name> made up disks across <number> chassis is
created
Info
RG size shrunk
The total size of RG <name> shrunk
Info
VD erase finished
VD <name> finished erasing process
Warning
VD erase failed
The erasing process of VD <name> failed
Info
VD erase started
VD <name> starts erasing process
Level
Type
Description
Info
iSCSI login accepted
iSCSI login from <IP> succeeds
Info
iSCSI login rejected
ISCSI login from <IP> was rejected, reason [<string>]
Info
iSCSI logout recvd
iSCSI logout from <IP> was received, reason [<string>]
Warning
Warning
Error
Error
Error
Error
Info
Warning
Warning
Warning
Warning
Info
Info
iSCSI Events
RTX410/610/801-IR User Manual A9-468-0005 REV 1.0 - 43 -
Page 44

CRU
Level
Type
Description
Info
System shutdown
System shutdown
Info
System reboot
System reboot
Info
System console shutdown
System shutdown from <string> via Console UI
Info
System web shutdown
System shutdown from <string> via Web UI
Info
System button shutdown
System shutdown via power button
Info
System LCM shutdown
System shutdown via LCM
Info
FW upgrade start
System firmware upgrade starts
Info
FW upgrade success
System firmware upgrade succeeds
Warning
FW upgrade failure
System firmware upgrade is failed
Error
IPC FW upgrade timeout
System firmware upgrade timeout on another controller
Info
Config imported
<string> config imported
Level
Type
Description
Info
RG owner changed
The preferred owner of RG <name> has been changed to
controller <number>
Info
Force CTR write through
Controller <number> forced to adopt write-through mode
on failover
Info
Restore CTR cache mode
Controller <number> restored to previous caching mode
on failback
Info
Failover complete
All volumes in controller <number> completed failover
process
Info
Failback complete
All volumes in controller <number> completed failback
process
Info
CTR inserted
Controller <number> is inserted into system
Error
CTR removed
Controller <number> is removed from system
Error
CTR timeout
Controller <number> gets no response
Error
CTR lockdown
Controller <number> is locked down
Error
CTR memory NG
Memory size mismatch
Error
CTR firmware NG
Firmware version mismatch
Error
CTR lowspeed NG
Low speed inter link is down
Error
CTR highspeed NG
High speed inter link is down
Error
CTR backend NG
SAS expander is down
Error
CTR frontend NG
FC IO controller is down
Info
CTR reboot FW sync
Controller reboot, reason [Firmware synchronization
completed]
System Maintenance Events
HAC Events
12 Working With Volumes Over 2TB in Size
Although RTX can create data volumes larger than 2TB, some older operating systems cannot access
such volumes. This is because they support only 32-bit LBA (Logical Block Addressing).
Newer operating systems should be able to use 2TB+ volumes without difficulty. You will simply need to
do one of the following two things while creating a Virtual Disk:
• Change the LBA to 64-bit
• Increase the block size to 4096
Windows
Neither of the options above will work for operating systems older than Windows XP. You need to make
more than one Virtual Disk, each less than 2TB in size. Each Virtual Disk also needs a different LUN.
RTX410/610/801-IR User Manual A9-468-0005 REV 1.0 - 44 -
Page 45

CRU
Mac OS
Although Mac OS 10.4.x supports only 32-bit LBA, increasing the block size to 4096 will allow you to
create a 2TB+ volume that is usable by the OS.
Linux
Versions of Linux vary, but using one of the above methods may allow you to create a 2TB+ volume that
your distribution can use.
13 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q I created one volume, but my computer sees two of them. Why?
A There may be two Logical Unit Numbers (LUN) assigned to that volume. To check this, use the GUI.
Navigate to “Volume Configuration” and then “Logical Unit”. If there are two Logical Units for the same
volume, hover your mouse over the button for one of them in the “Host” column and click on “detach.”
Note: You may still see two volumes until you restart your computer.
Q I've hooked up the Config GUI port to my DHCP-enabled network, but the LCD displays an IP address
that is not on my network and I cannot connect to the GUI control panel using that IP address in my web
browser.
A This may occur if you plugged in the Config GUI after RTX has already started up and initialized, or if
you previously configured RTX for a static network or direct connection. The solution is to use the LCD
interface to obtain a DHCP address. Press “ENT”, then use the ▲ (Up) or ▼ (Down) arrows to scroll to
the option “Change IP Config”. Press “ENT”. The screen will say “DHCP”. Press “ENT”, then press the ▲
(Up) arrow to select “Yes”. Press “ENT”. RTX will now attempt to acquire a DHCP address. This new
address will be displayed on the main screen of the LCD.
Q When I try to log on to RTX using the IP address under the iSCSI configuration menu, nothing
happens.
A Sometimes when you first set up RTX you’ll need to reattach the Logical Unit if it doesn't work the first
time.
Q How many computers can connect to one data volume on the iSCSI unit?
A The short answer is one computer to one volume. This is the safest and suggested usage of RTX. If
two people are accessing files on the same volume at the same time, there is a very high chance that
data corruption will occur. There are a few file systems that can handle different users manipulating the
same volume, but they are not supported by Mac OS or Windows. However, if the users connected to the
volume have read-only access, then corruption will not be an issue.
Q When I make more than one volume, I still see all volumes when connecting to the iSCSI IP address.
How am I supposed to allow only one person per volume if that's the case?
A When you attach a Logical Unit to a Virtual Disk you'll probably notice a "Host" field with an asterisk as
the default selection. This means that any iSCSI Initiator will be able to connect to that volume through
that Virtual Disk. All iSCSI Initiators have a unique name. You can use this name to restrict access to only
certain computers. For example, if my initiator is assigned the name
iqn.199105.com.microsoft:username01.crudataport.local, and if I put that name into the host field when
attaching a Logical Unit, then only my specific computer will be able to connect to that volume. You can
use this to give one person read access and everyone else write access by attaching two Logical Units to
one Virtual Disk.
Q If I connect one computer to RTX and then share the files from that computer, can more than one
computer access the files? Would the other computers need iSCSI initiators installed on them?
RTX410/610/801-IR User Manual A9-468-0005 REV 1.0 - 45 -
Page 46

CRU
A One computer at a time can directly access RTX, but files on RTX can be shared from that computer to
other computers. In such a scenario, the computer attached to RTX acts as a server. Only the server
computer requires an iSCSI initiator. The other computers do not need special software.
Q What is the difference between iSCSI and NAS (Network Attached Storage)?
A The difference between iSCSI and NAS is that a NAS does not need a computer to act as a server.
Q I put my computer to sleep, and now it’s having trouble reconnecting to RTX. How can I prevent this?
A To prevent difficulties such as this, follow the shutdown procedure documented in the LCD menu
diagram in Section 6.2.3. CRU-DataPort also suggests that you disable automatic sleep on your
computer so it does not go into sleep mode without preparing RTX for disconnection.
Still need help? Please contact our Technical Support team at http://www.cru-dataport.com/support
us toll free at (800) 260-9800.
or call
RTX410/610/801-IR User Manual A9-468-0005 REV 1.0 - 46 -
Page 47

CRU
Product Models:
RTX 410-IR, 610-IR and RTX 801-IR
Raid Levels Supported:
RAID 0, 1, 3, 5, 6, 0+1, 10, 30, 50, 60, & JBOD
Host Interfaces:
Dual Gigabit Ethernet
Data Interface Speeds:
Up to 200MB/s (network dependent)
Drive Types Supported:
3.5-inch SATA (Serial-ATA) hard disk drives
Online Auto-Rebuild:
Yes
•
• Access Indicator
Security:
Separate key lock for each HDD (RTX 410 and 610-IR only)
Controller Display:
LCD screen with yellow backlight/control panel
•
• Linux distributions using K ernel version 2.4 or above
•
• Output: 220 Watts (4-bay model), 350 Watts (6-bay and 8-bay models)
EMI Standard: FCC Part 15 Class A, CE
FIPS: FIPS 140-2, FIPS PUB 197
•
• RTX 801-IR: 28 pounds without drives, 42 pounds with drives
RTX410-IR: 177mm W x 270mm D x 274mm H
RTX610-IR and RTX 801-IR: 177mm W x 270mm D x 370mm H
We don’t expect anything to go wrong with your CRU product. But if it does, Tech Support
also offer phone support at (800) 260-9800 and (866) 744-8722.
Tested to comply
with FC C standards
14 Technical Specifications
Alarm Indicator
LED Indicators:
• Power Indicator
Operating System Requirements:
Power Supply:
Compliance:
Shipping Weights:
Dimensions:
Technical Support
RTX and TrayFree are trademarks of CRU Acquisitions Group, LLC. Other marks are the property of their respective owners.
© 2008, 2010 CRU Acquisitions Group, LLC.
Product Warranty
CRU-DataPort (CRU) warrants this product to be free of significant defects in material and workmanship for a period of three years
from the original date of purchase. CRU’s warranty is nontransferable and is limited to the original purchaser.
Limitation of Liability
The warranties set forth in this agreement replace all other warranties. CRU expressly disclaims all other warranties, including but
not limited to, the implied warranties of merchantability and fitness for a particular purpose and non-infringement of third-party rights
with respect to the documentation and hardware. No CRU dealer, agent, or employee is authorized to make any modification,
extension, or addition to this warranty. In no event will CRU or its suppliers be liable for any costs of procurement of substitute
products or services, lost profits, loss of information or data, computer malfunction, or any other special, indirect, consequential , or
incidental damages arising in any way out of the sale of, use of, or inability to use any CRU product or service, even if CRU has
been advised of the possibility of such damages. In no case shall CRU’s liability exceed the actual money paid for the products at
issue. CRU reserves the right to make modifications and additions to this product without notice or taking on additional liability.
FCC Compliance Statement: “This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC rules. Operation is subject to the following two
conditions: (1) This device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept any interference received, including
interference that may cause undesired operation.”
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC
Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference when the equipment is operated in a
commercial environment. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in
accordance with the instruction manual, may cause harmful interference to radio communications. Operation of this equipment in a
residential area is likely to cause harmful interference in which case the user will be required to correct the interference at this own
expense.
In the event that you experience Radio Frequency Interference, you should take the following steps to resolve the problem:
1) Ensure that the case of your attached drive is grounded.
2) Use a data cable with RFI reducing ferrites on each end.
3) Use a power supply with an RFI reducing ferrite approximately 5 inches from the DC plug.
4) Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
Windows XP, Vista, Windows 7
• Mac OS X 10.2.6 or later
Input: 100-240VAC
EMC Standard: EN55022, EN55024
RTX 410-IR: 23 pounds without drives,29 pounds with drives
• RTX 610-IR: 25 pounds without drives, 35 pounds with drives
is standing by and ready to help. Contact us at http://www.cru-dataport.com/support. We
FOR OFFICE OR COMMERCIAL
USE
RTX410/610/801-IR User Manual A9-468-0005 REV 1.0 - 47 -
 Loading...
Loading...