Conexant M4640-19, M4641-20, M4641-19 Datasheet

Data Sheet
Conexant
Doc. No. 100779C
Proprietary Information and Specifications are Subject to Change June 14, 2000
M46
Baseband Processor for GSM Applications
Conexant’s M46 Baseband Processor (BP) is a highly integrated, dual core
processor optimized for use in Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM)
cellular handset applications. With its companion devices, the 20420 Integrated
Analog (IA) device (refer to Conexant document number 100773) and the 20436
Power Management Integrated Circuit (PMIC) device (refer to Conexant document
number 100772), the BP forms Conexant’s baseband device set for GSM singleband or multi-band handsets.
The BP integrates the industry standard ARM 7 THUMB core, Conexant’s high
performance Digital Signal Processor (DSP) core, a Viterbi co-processor, and
auxiliary digital support circuitry. Both the DSP core and the ARM7 THUMB
Reduced Instruction Set Computer (RISC) architecture are well suited to meet the
needs of low power, high performance embedded systems such as cellular phones.
The BP operates over a range of 2.7 V to 3.6 V making it ideal for low power
applications.
The baseband processing tasks are divided between the two processor cores. The
DSP core executes the physical layer processing functions and the microcontroller
core executes the Layer 2 and Layer 3 protocol software and the Man-Machine
Interface (MMI) functions. The two cores communicate through a dedicated block
of dual port memory. Each of the functional blocks in the device can be individually
powered down to ensure minimum current consumption in the idle or standby
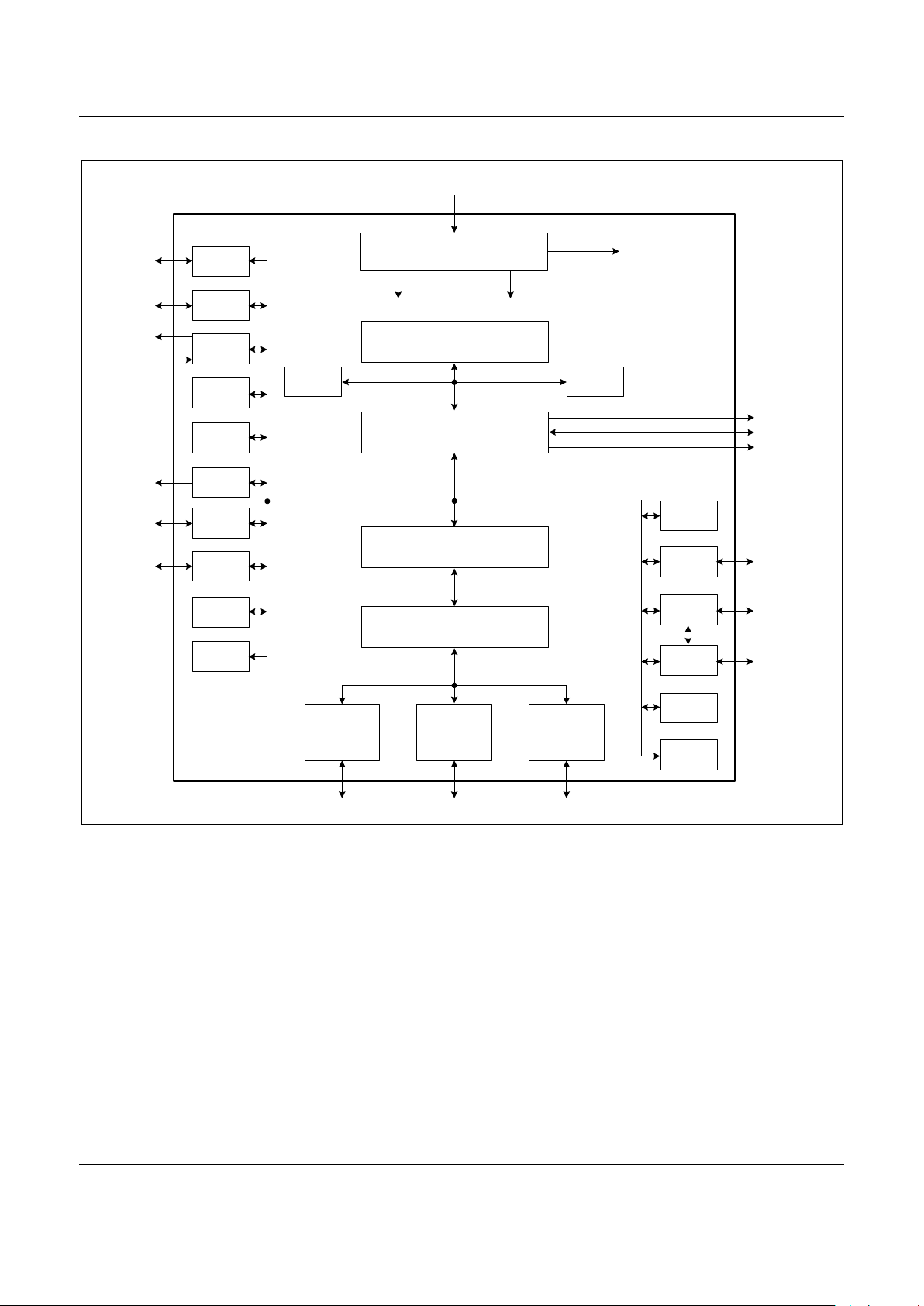
mode. A block diagram of the device is provided in Figure 1.
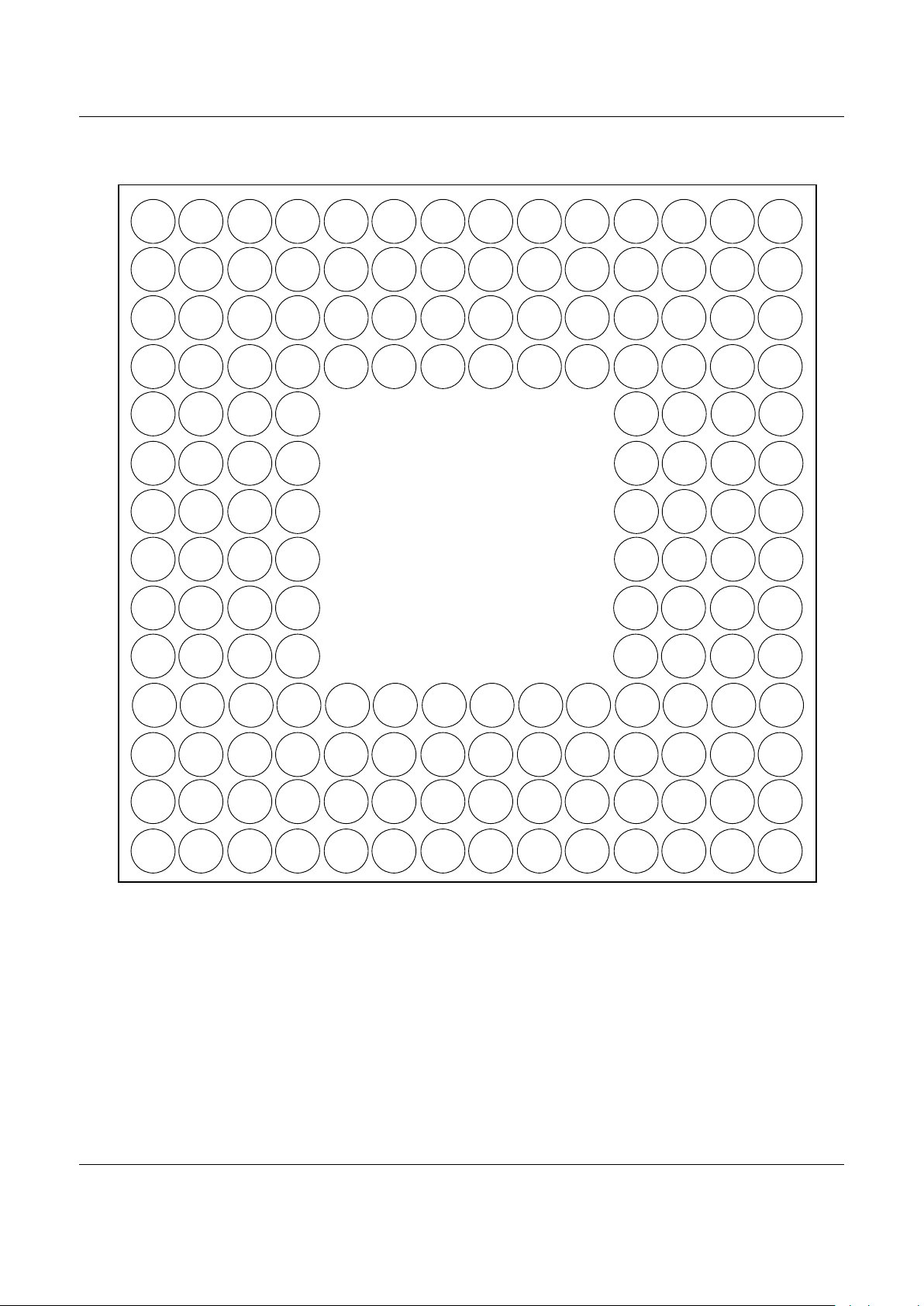
The BP is packaged in a 160-pin micro Ball Grid Array (µBGA) with a 16-bit data
bus and a 22-bit address bus. The package and pin configuration of the BP are
shown in Figure 2. The signal pin assignments and functional pin descriptions are
provided in Table 1.
Features
• Execution of GSM protocol stack software (Layers
1, 2, and 3)
• Execution of MMI software
• Interface to handset MMI peripherals (e.g., keypad,
LCD, buzzer, etc.)
• Interface to data terminals
• Functional interface to a Subscriber Identity
Module (SIM)
• Interface to handset memory components (Flash,
SRAM, etc.)
• Integrated Real-Time Clock (RTC)
• Supports full rate and enhanced full rate speech
coders
• Encryption/decryption
• Automatic Frequency Control (AFC)
• Automatic Gain Control (AGC)
• Digital Audio Interface (DAI)
• Interfaces to Conexant IA and PMIC devices
• Low power operation (2.7 V to 3.6 V)
• Optional voice features: voice recognition, voice
prompts, conversation record, and voice memo
• Optional 14.4 kbps data/fax support
Applications
• GSM 900/1800/1900 handsets or modules
M46 Baseband Processor
2
Conexant
100779C
June 14, 2000 Proprietary Information and Specifications are Subject to Change
Clock Generation and PLL
DSP Clock
ARM Clock
ARM Core
IROM
IRAM
System Integration Unit
Dual Port RAM
DSP Core
SIM
Interface
Debug
Serial Port
Pulse Width
Modulator
Serial Data
Services Serial
Port
IrDA Pulse
Shaper
Conexant
Serial Bus
Keypad
Interface
GPIO Ports
ARM
Interrupt
Controller
Clock
Enables
Real-Time
Clock
Timers
DMA
Controller
Cyclic
Redundancy
Check
Autobaud
Control Port
Receive Port
Codec Port
System
Reference Clock
SIM Interface
Debug Port
Annunciator
SDS Port
IrDA Compatible
SDS Port
Conexant Serial
Bus
Keypad
GPIO
RTC Alarm
RTC Supply
System Address Bus
System Data Bus
System Chip Selects
DSP Control Port
DSP Receive Port
DSP Codec Port
External
Expansion Bus
Internal
Peripheral Bus
ARM Bus
Clock for Internal
Peripherals
Escape
Sequence/
Flow Control
C854
Figure 1. BP Block Diagram
Baseband Processor M46
100779C
Conexant
3
Proprietary Information and Specifications are Subject to Change June 14, 2000
C808
A
1234 567891011121314
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
J
K
L
M
N
P
CVDDTDI BS[0]TCLKSIM_DATAGPIO_C[1]
TDOSIM_CLKD[10] A[10]A[13]A[15]A[16]A[19]A[21]READIROMEN
DSPVSS
CVDD
CVSSCS[1]
CVSS
IOVDDIOVSS IOVSSGPIO_C[0] A[7]D[0] D[1]
IOVSSDSPVDDCNTRLCLK RX_CLOCK DSPVSS DSPVSS
DSPVSS KPDSTB[0]KPDSTB[3]
KPDSTB[4]
KPDSTB[1]KPDSTB[5]
KPDSTB[6]
KPDSTB[7]
KPDSTB[2]
VRTC
DSPVDD
SDS_RX
SRLCLKENCDRDAT CDCRATE
SRLDATASDS_TXCNTRLDATRSPNSDATCDCCLKCNTRLRT
DSPVDD PLLVDDXTLOKPDRTN[2]
KPDRTN[3]
ALARM
DSPVDD A[0]
A[3]A[6]D[12] D[14] D[13] A[4]
A[2]D[15]DCDRDAT A[1] A[5]DSPVSS
DSPVDDA[11]D[9]D[11]GPIO_C[2] GPIO_C[3] BS[1] D[2] D[3] D[4]A[17]
A[18]
IOVSS
IOVSS
GPIO_A[0]
GPIO_B[5]
GPIO_B[0]
GPIO_B[2]
GPIO_C[5]
GPIO_A[6]
GPIO_A[7]
GPIO_B[7]
GPIO_A[1]
GPIO_B[3]
GPIO_C[4]
GPIO_B[4]
GPIO_A[2]GPIO_B[6]
GPIO_C[7]
GPIO_A[3] GPIO_C[6]
GPIO_A[4]
GPIO_A[5]
GPIO_D[0]
GPIO_B[1]
GPIO_D[2] GPIO_D[1]
CLK_REQRX_DATARX_RATE PLLVSS
IOVSS A[9] D[7]A[12]A[14]A[20]CS[0]WRITETESTPTMSTRES
IOVDD A[8]D[8] D[5]D[6]
IOVDD
IOVDDKPDRTN[0]
KPDRTN[1]
XTLIIOVDDRESETDSPTEST STROBE
IOVDDSYS_CLK YCLK
N/C N/C N/C N/C N/C
N/C
N/C
N/C
N/C
N/C
N/C
N/C
N/C
N/C
N/C
Figure 2. BP Device 160-Pin µµµµBGA Pinout (Top View)
M46 Baseband Processor
4
Conexant
100779C
June 14, 2000 Proprietary Information and Specifications are Subject to Change
Table 1. BP Pinout Assignments (1 of 2)
Pin # Pin Name Description Pin# Pin Name Description
Power Supply
M7, D13 CVDD Microcontroll er supply E4, H3, M13, E12,A7DSPVSS DSP ground
L7, D10 CVSS Microcontroller ground C12 PLLVDD PLL supply
K3, M9, J14, B12,
B7, C6
IOVDD I/O pins supply D12 PLLVSS PLL ground
K2, P10, K13, E14,
B14, D7
IOVSS I/O pins ground A14 VRTC Supply pin for Real-Tim e Clock circuitry
E2, H4, L11, E13,C7DSPVDD DSP supply
Test/JTAG
P4 TESTP Test M4 TCLK JTAG clock
M5 TDI JTAG data In P2 TRES JTAG reset
N4 TDO JTAG data Out N5 IROMEN Enable Internal ROM
P3 TMS JTAG mode select
System
B2 RESET Power-on reset B3 STROBE Test
D4 CLK_REQ Clock request signal C13 ALARM RTC alarm
C3 SYS_CLK System clock B13 XTLI 32 kHz cryst al input
C4 YCLK Test C11 XTLO 32 kHz crystal output
B1 DSPTST Test
External Bus
H12 A[0] K11 D[0]
H13 A[1] K14 D[1]
H11 A[2] L12 D[2]
J12 A[3] L13 D[3]
J13 A[4] L14 D[4]
H14 A[5] M14 D[5]
J11 A[6] M12 D[6]
K12 A[7] P14 D[7] Data bus 0 to 15
M11 A[8] M10 D[8]
P13 A[9] L9 D[9]
N12 A[10] Address bus 0 to 21 N2 D[10]
L10 A[11] L4 D[11]
P12 A[12] J2 D[12]
N11 A[13] J4 D[13]
P11 A[14] J3 D[14]
N10 A[15] H2 D[15]
N9 A[16] N6 READ Read strobe
L8 A[17] P5 WRITE Write strobe
M8 A[18] P7 CS[0] Flash select, chip select 0
N8 A[19] L6 CS[1] RAM select, chip select 1
P8 A[20] M6 BS[0] Byte select for 16-bit SRAM ( lower byte)
N7 A[21] L5 BS[1] Byte select for 16-bit SRAM (upper byte)
Baseband Processor M46
100779C
Conexant
5
Proprietary Information and Specifications are Subject to Change June 14, 2000
Table 1. BP Pinout Assignments (2 of 2)
Pin # Pin Name Description Pin# Pin Name Description
Keypad Control
A10 KPDSTB[0] B8 KPDSTB[6] Keypad strobe lines 0 t o 7
D9 KPDSTB[1] C8 KPDSTB[7]
C9 KPDSTB[2] Keypad strobe lines 0 to 7 B11 KPDRTN[0]
A9 KPDSTB[3] A11 KPDRTN[1] Keypad return lines 0 to 3
B9 KPDSTB[4] C10 KPDRTN[2]
D8 KPDSTB[5] B10 KPDRTN[3]
GPIO
D6 GPIO_A[0] GPIO signal port A[0] (I/O select bit = 0)
Keyboard return 4 (I/ O select bit = 1)
B5 GPIO_B[6] GPIO signal port B[0] to B[7]
A6 GPIO_A[1] C2 GPIO_B[7]
B6 GPIO_A[2] A2 GPIO_C[4] GPIO signal port C[4] (I/O select bit = 0)
G11 GPIO_A[3] F11 GPIO_C[5] GPIO si gnal port C[5] (I/O select bit = 0)
DEBUG_TX (I/O select bit = 1)
G2 GPIO_A[4] GPIO signal port A[1] to A[7] G12 GPIO_C[6] GPIO signal port C[6] (I/O select bit = 0)
DEBUG_RX (I/O select bit = 1)
P1 GPIO_A[5] B4 GPIO_C[7] GPIO signal port C[7]
C14 GPIO_A[6] P6 GPIO_D[0] GPIO signal port D[0] (I/O select bit = 0)
CS[2] (I/O select bit = 1)
C5 GPIO_A[7] N14 GPIO_D[1] GPIO signal port D [1] (I/O select bit = 0)
CS[3] (I/O select bit = 1)
D11 GPIO_B[0] N13 GPIO_D[2] GPIO signal port D[2] (I/O select bit = 0)
CS[4] (I/O select bit = 1)
N1 GPIO_B[1] K4 GPIO_C[0] GPIO port C[0] (I/O select bit = 0)
SIM_5V_3V (I/O select bit = 1)
E11 GPIO_B[2] GPIO signal port B[0] to B[7] M2 GPIO_C[1] GPIO port C[1] ( I/O select bit = 0)
SIM_ENABLE (I/O select bit = 1)
A3 GPIO_B[3] L2 GPIO_C[2] GPIO port C[2] (I/O select bit = 0)
SIM_RW (I/O select bit = 1)
A4 GPIO_B[4] L3 GPIO_C[3] GPIO port C[3] (I/O select bit = 0)
SIM_RESET (I/O select bit = 1)
D5 GPIO_B[5]
Serial Data Port
F13 SDS_RX SDS port data in F14 SRLDATA Conexant serial bus data I/O
F12 SDS_TX SDS port data out G13 SRLCLK Conexant serial bus clock
IA Serial Ports
D3 RX_DATA Receive port data F1 CNTRLRT Control port rate
E3 RX_CLOCK Receive port clock H1 DCDRDAT Codec port data to IA
D2 RX_RATE Receive port rate G3 ENCDRDAT Codec port data from IA
F4 CNTRLDAT Control port data to IA F2 CDCCLK Codec port clock
F3 RSPNSDAT Control port data from IA G4 CDCRATE Codec port data
E1 CNTRLCLK Control port clock
SIM
N3 SIM_CLK Clock si gnal for SIM interface M3 SIM_DATA Bi-directional SIM data s ignal

M46 Baseband Processor
6
Conexant
100779C
June 14, 2000 Proprietary Information and Specifications are Subject to Change
Technical Description
The BP is a dual-core device consisting of an ARM7 THUMB
microcontroller core, a Conexant proprietary DSP core, and all
the digital control circuitry required in a GSM handset. The
following sections describe the operation and programming of
each of the functional blocks in the BP. Table 2 specifies the
address and default value for each of the registers in the device.
Note that the table specifies the value of each register before
the BP IROM code is executed.
ARM7 THUMB Core
The ARM7 THUMB core is a member of the Advanced RISC
Machines (ARM) family of general purpose 32-bit
microcontrollers that offer high performance with very low power
consumption. The ARM architecture is based on RISC principles
with a simple yet powerful instruction set. This simplicity enables
high instruction throughput and rapid real-time interrupt
response.
Pipelining is used extensively to ensure that all parts of the
processing and memory systems can operate continuously.
While one instruction is being executed, the next instruction is
being decoded and a third is being fetched from memory.
For further information on ARM7 THUMB please refer to the
ARM7TDMI data sheet published by ARM.
Internal Memory
The BP is supported by 12 kB of Internal RAM (IRAM) and 16
kB of Internal ROM (IROM). Both the IRAM and the IROM
directly interface to the 32-bit data and address buses from the
microcontroller core.
The IROM contains the embedded firmware which is executed
on power up. The IRAM is used for data storage during run time.
System Integration Unit (SIU)
The SIU is used to interface the 32-bit ARM bus to 8, 16, or 32bit memory and peripherals connected to the External
Expansion Bus (EXB) and Internal Peripheral Bus (IPB). Since
the ARM only interfaces to 32-bit devices, the SIU formats the
address and data to and from the ARM to allow 8, 16, or 32-bit
data transfers.
The SIU also performs address decoding to generate internal
and external chip select signals. These peripherals can be
internal to the BP or external. Internal peripherals (such as the
pulse width modulator) interface to the IPB while external
peripherals (such as system Flash memory) interface to the
EXB. The SIU performs the following main functions:
•
Generates the required internal or external chip selects
•
Formats the address bus and data bus for 8, 16 or 32-bit
transfers
Separating the buses minimizes power dissipation since only the
required bus lines are driven at any one time.
Internal Peripheral Bus (IPB)
The IPB interfaces to internal peripherals on the BP. The bus
supports both 8-bit and 16-bit peripherals. The bus is only active
when one of the internal peripherals is being accessed; if a
device on the EXB is being accessed, the re is no activity on the
IPB.
External Expansion Bus (EXB)
The EXB allows external memory devices such as flash and
SRAM to be connected to the BP. Internal to the BP, the EXB is
connected to the SIU. The device features a 16-bit data bus
D[15:0] and a 22-bit address bus A[21:0].
Besides the address and data buses, the EXB also consists of
the following control signals:
•
READ – active low read strobe that is asserted while data
is read from the external peripheral.
•
WRITE – active low write strobe that is asserted while data
is being written to the external peripheral.
•
CS[4:0] – configurable chip select signals.
•
BS[1:0] – active low upper byte/lower byte select signals.
These are used when the BP is transferring byte wide data
to/from 16-bit peripherals. The polarity of these signals is
programmable.
Note that the BP always produces a byte address. When word
data (32-bit data) is transferred, A[1:0] bits are always low (set
to “0”), and when half word data (16-bit data) is transferred, the
A[0] bit is always low (set to “0”).
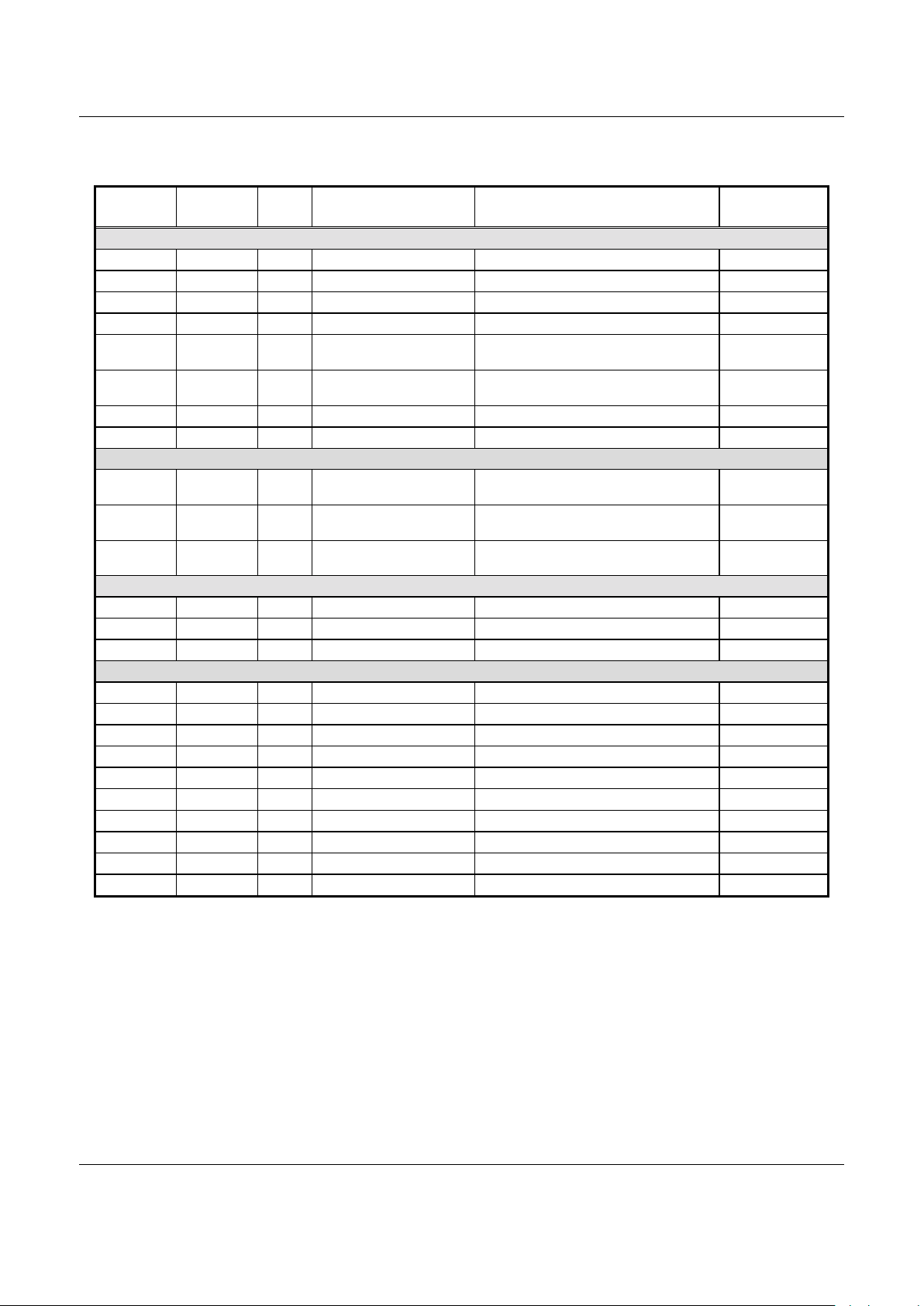
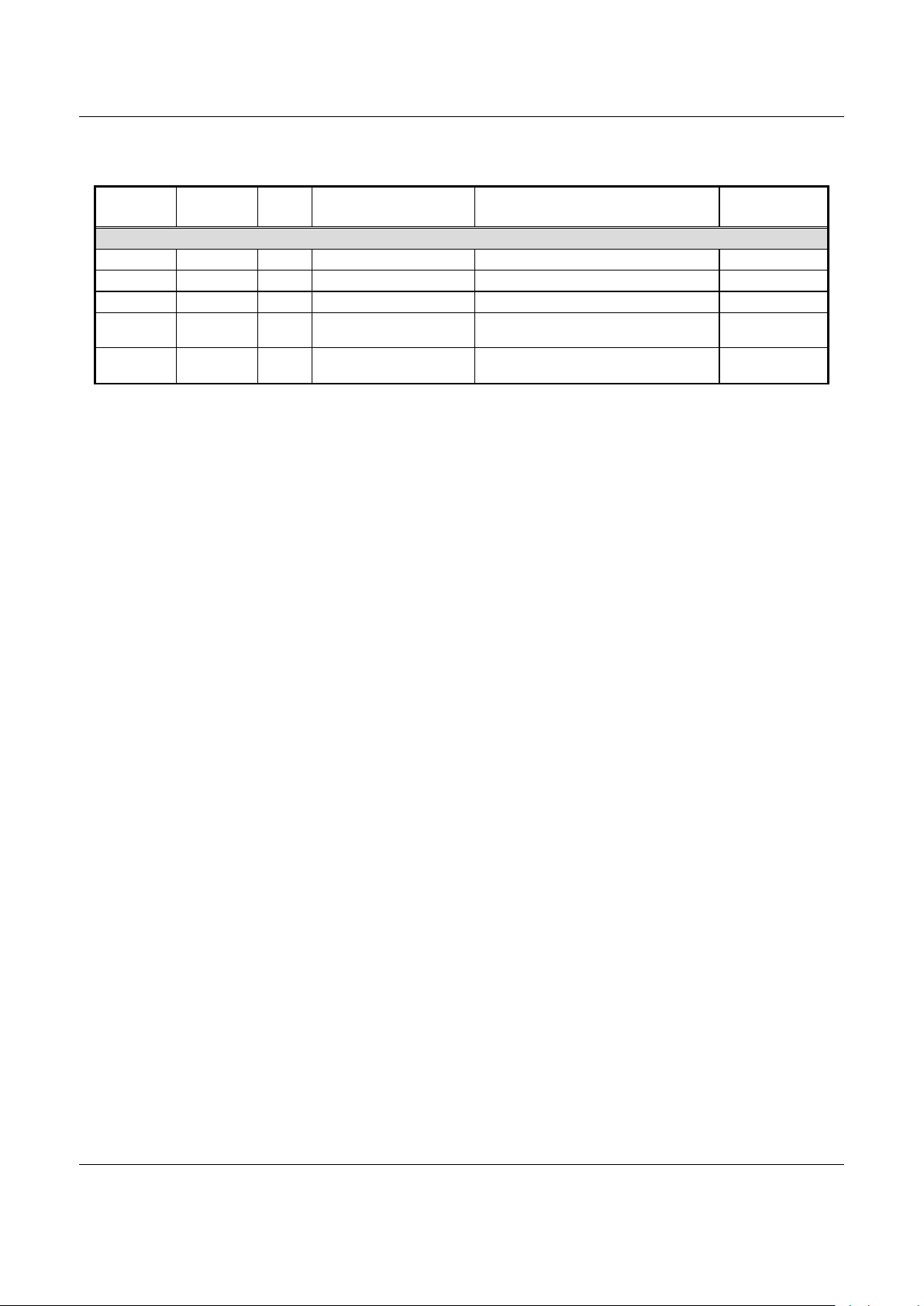
The timing diagrams for read and write accesses over the EXB
are shown in Figures 3 and 4, respectively. Figure 3 shows a
read from a 16-bit external device that requires two wait states.
Figure 4 shows a write to a 16-bit external device that requires
two wait states.
Note that the ARM clock signal is internal to the device and is
not output on any of the device pins.
Table 3 provides the values for all of the timing parameters.
Chip Select Signals__________________________________
The BP has five chip select signals. Two of these ,CS0 and
CS1, are on dedicated pins while the other three are multiplexed
with General Purpose Input Output (GPIO) signals.
Each of the chip select signals has a configuration register.
Each register is 16 bits wide but only the least significant 9 bits
are used. The function of each register bit is shown in Table 4.
The address and default values for the Chip Select Signal
Registers are specified in Table 2.
Baseband Processor M46
100779C
Conexant
7
Proprietary Information and Specifications are Subject to Change June 14, 2000
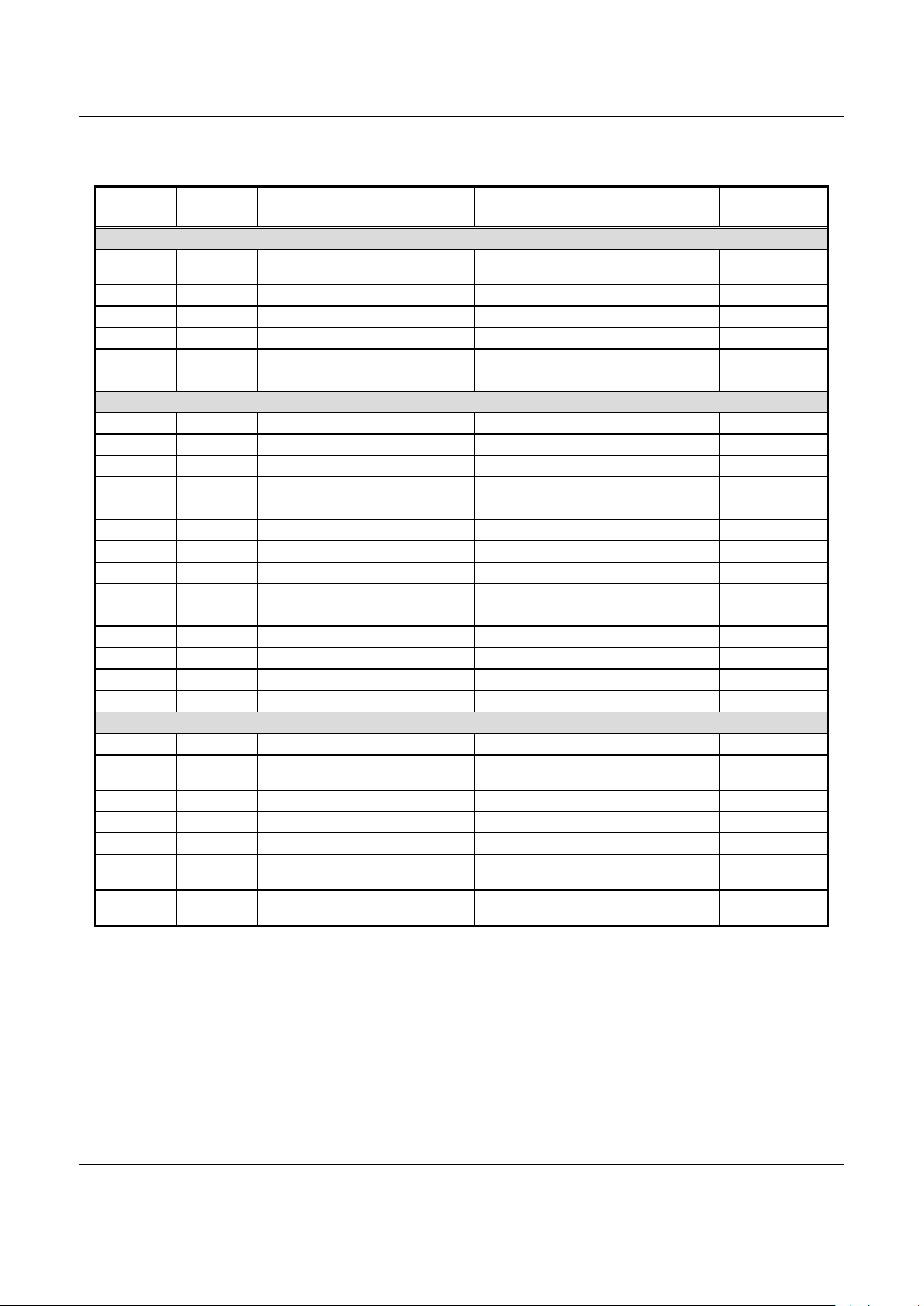
Table 2. BP Register Addresses (1 of 6)
Address
(Hex)
Block Size
(bytes)
Type Name Function Default Value
(Hex)
Chip Select Configurati on Registers
0040000 2 R/W SIU Configuration Bit [15] control s the polarity of t he byte select
signals
0002
0040002 2 R/W CS0 Configuration Control register for configuration of CS0 signal 0005
0040004 2 R/W CS1 Configuration Control register for configuration of CS1 signal 000E
0040006 2 R/W CS2 Configuration Control register for configuration of CS2 signal 000E
0040008 2 R/W CS3 Configuration Control register for configuration of CS3 signal 000E
004000A 2 R/W CS4 Configuration Control register for configuration of CS4 signal 000E
Real-Time Clock
0040080 2 R/W RTC Seconds Real-Time Clock seconds Undefined
0040082 2 R/W RTC Minutes Real-Time Clock minut es Undefined
0040084 2 R/W RTC Hour s Real-Time Clock hours Undefined
0040086 2 R/W RTC Days Real-Time Clock days Undefined
0040088 2 R/W RTC Mont hs Real-Time Clock months Undefined
004008A 2 R/W RTC Years Real-Time Clock years Undefined
004008C 2 R/W RTC Control Control of the Real-Time Clock operation Undefined
004008E 2 Reserved
0040090 2 Reserved
0040092 2 R/W Alarm Minutes Alarm minutes Undefined
0040094 2 R/W Alarm Hours Alarm hours Undefined
0040096 2 R/W Alarm Days Alarm days Undefined
0040098 2 R/W Alarm Months Alarm months Undefined
004009A 2 R/W Alarm Years Alarm years Undefined
Interrupt Control ler
0040110 4 R/W I nterrupt Pending Reading gives interrupts that are pending. 0000 0000
0040114 4 R/W I nterrupt Select Directs a given i nterrupt to the IRQ or the FIQ input
to the ARM.
0000 0000
0040118 4 R/W I nterrupt Enable Enables the corresponding interrupt source. 0000 0000
004011C 4 R/W External Interrupt Polar ity Set the polarity of external interrupts. 0000 0000
0040120 4 Reserved
0040124 4 R FIQ Interrupt Determine if a part icular interrupt is generating an
FIQ interrupt to the ARM.
0000 0000
0040128 4 R IRQ Interrupt Determine if a partic ular interrupt is generating an
IRQ interrupt to the ARM.
0000 0000
M46 Baseband Processor
8
Conexant
100779C
June 14, 2000 Proprietary Information and Specifications are Subject to Change
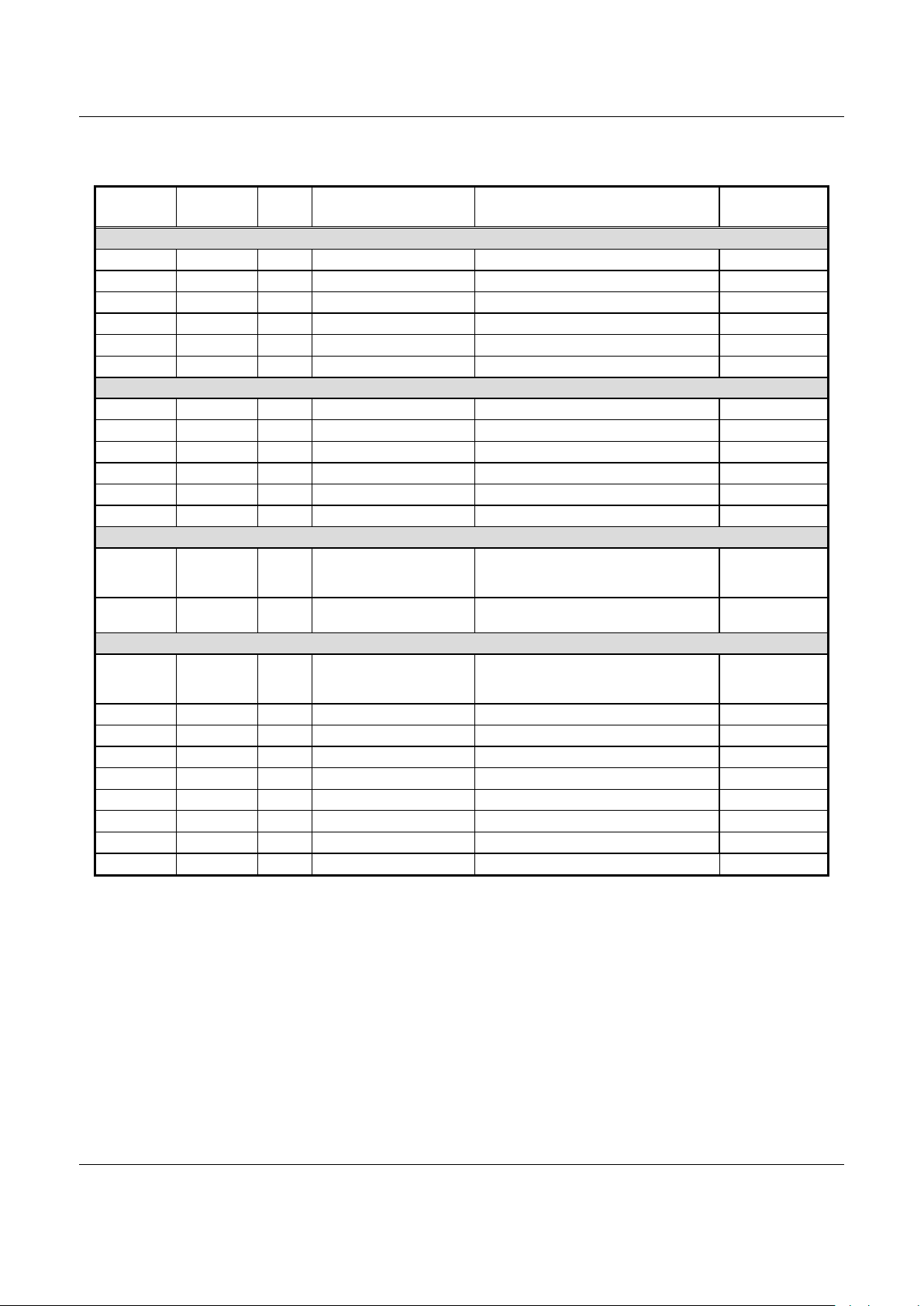
Table 2. BP Register Addresses (2 of 6)
Address
(Hex)
Block Size
(bytes)
Type Name Function Default Value
(Hex)
Timers
0040180 2 R/W Timer A Mode Timer A confi guration 0808
0040182 2 R/W Ti mer A Latch Timer A latch contents 0000
0040184 2 R/W Timer A Counter Timer A FFFF
0040190 2 R/W Timer B Mode Timer B confi guration 0808
0040192 2 R/W Ti mer B Latch Timer B latch contents 0000
0040194 2 R/W Timer B Counter Timer B FFFF
Precision Timing Generators (PTGs)
00401C0 2 R/W PTG A Mode PTG A configuration 0000
00401C2 2 R/W PTG A Latch PTG A latch contents 0000
00401C4 2 R/W PTG A Counter FFFF
00401C8 2 R/W PTG B Mode PTG B configuration 0000
00401CA 2 R/W PTG B Latch PTG B latch contents 0000
00401CC 2 R/W PTG B Counter FFFF
Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC)
00401D0 2 R/W CRC Data Writing will input 8-bit data to the Shift Register.
Reading will read 16-bit results from the Poly nomial
Register.
FFFF
00401D2 2 W CRC Reset Writing to this address will reset polynomial Shift
Register to 0xFFFF.
0000
Serial Data Services (SDS) Serial Port
0040200 2 R/W SDS Seri al Buffer In /Out Buffer Reading from this address will read the contents of
the Serial In buffer. Writing to this address will write
to the Serial Out buffer.
0000
0040202 2 R/W SDS Ser ial Port Mode SDS port configuration. 0000
0040204 2 R/W SDS Ser ial Port Interrupt Interrupt enable and f lags. 0000
0040206 2 R/W SDS Ser ial Port Line Word length, parity and formatting. 0000
0040208 2 R/W SDS Ser ial Port Status SDS port status. 6060
004020A 2 R/W SDS Serial Port Form Vary duration of stop bits. 0000
004020C 2 W SDS Serial Out Divider Latch Controls serial out baud rate. 0000
004020E 2 W SDS Serial In Divider Latch Controls serial in baud rate. 0000
0040210 2 Reserved
Baseband Processor M46
100779C
Conexant
9
Proprietary Information and Specifications are Subject to Change June 14, 2000
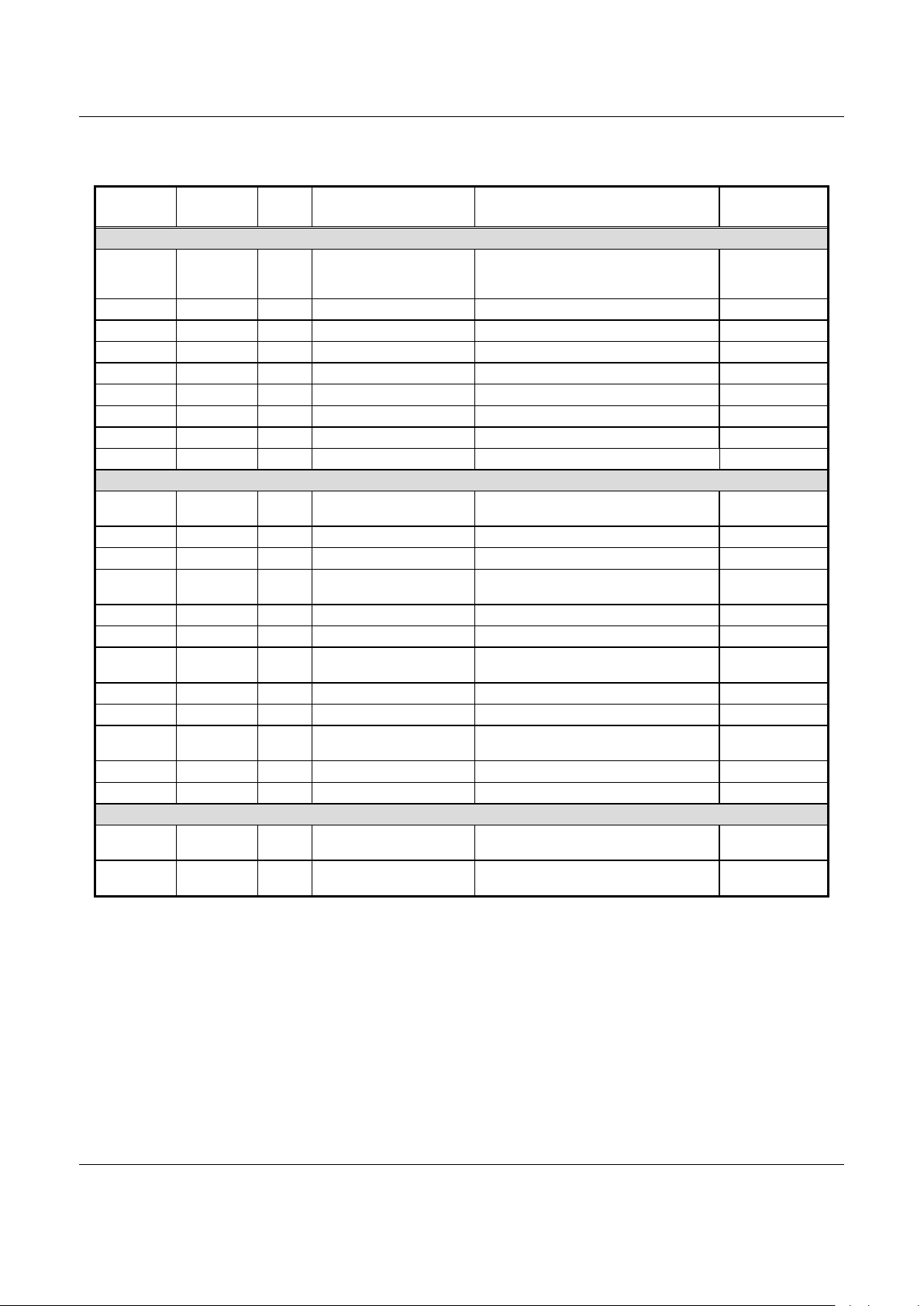
Table 2. BP Register Addresses (3 of 6)
Address
(Hex)
Block Size
(bytes)
Type Name Function Default Value
(Hex)
Debug Serial Port
0040220 2 R/W Debug Seri al In / Out Buffer Reading from this address will read the contents of
the Serial In buffer. Writing to this address will write
to the Serial Out buffer.
0000
0040222 2 R/W Debug Ser ial Port Mode Debug port configuration. 0000
0040224 2 R/W Debug Ser ial Port Interrupt Interrupt enable and flags. 0000
0040226 2 R/W Debug Ser ial Port Line Word length, parity and formatting. 0000
0040228 2 R/W Debug Ser ial Port Status Debug port status. 6060
004022A 2 R/W Debug Serial Port Form Vary duration of stop bits. 0000
004022C 2 W Debug Serial Out Divider Latch Controls serial out baud rate. 0000
004022E 2 W Debug Serial In Divider Latch Controls serial in baud rate. 0000
0040230 2 Reserved
GPIO Ports
0040280 2 R/W Por t A I/O Select Selec t special functi on associated with GPIO
signal.
0000
0040282 2 R/W Por t A Data I/O Port A read/write data. Undefined
0040284 2 R/W Por t A I/O Configuration Select port A GPIO signals as inputs or outputs. 00FF
0040288 2 R/W Por t B I/O Select Selec t special functi on associated with GPIO
signal.
00FF
004028A 2 R/W Port B Data I/O Port B read/write data. Undefined
004028C 2 R/W Port B I/O Configuration Select port B GPIO signals as inputs or outputs. FFFF
0040290 2 R/W Por t C I/O Select Select special f unction associated with GPIO
signal.
00FF
0040292 2 R/W Por t C Data I/O Port C read/writ e data. 00C0
0040294 2 R/W Por t C I/O Configuration Select port C GPIO signals as inputs or outputs . 00FF
0040298 2 R/W Por t D I/O Select Select special f unction associated with GPIO
signal.
0007
004029A 2 R/W Port D Data I/O Port D read/write data. 0007
004029C 2 R/W Port D I/O Configuration Select port D GPIO signals as inputs or outputs. 00FF
Conexant Serial Bus
0040300 2 R/W Ser ial Bus Data I/O B it [0] at this address is connected t o the serial data
signal.
0003
0040302 2 R/W Ser ial Bus Clock Bit [0] at this address is connected to the serial
clock signal.
0003
M46 Baseband Processor
10
Conexant
100779C
June 14, 2000 Proprietary Information and Specifications are Subject to Change
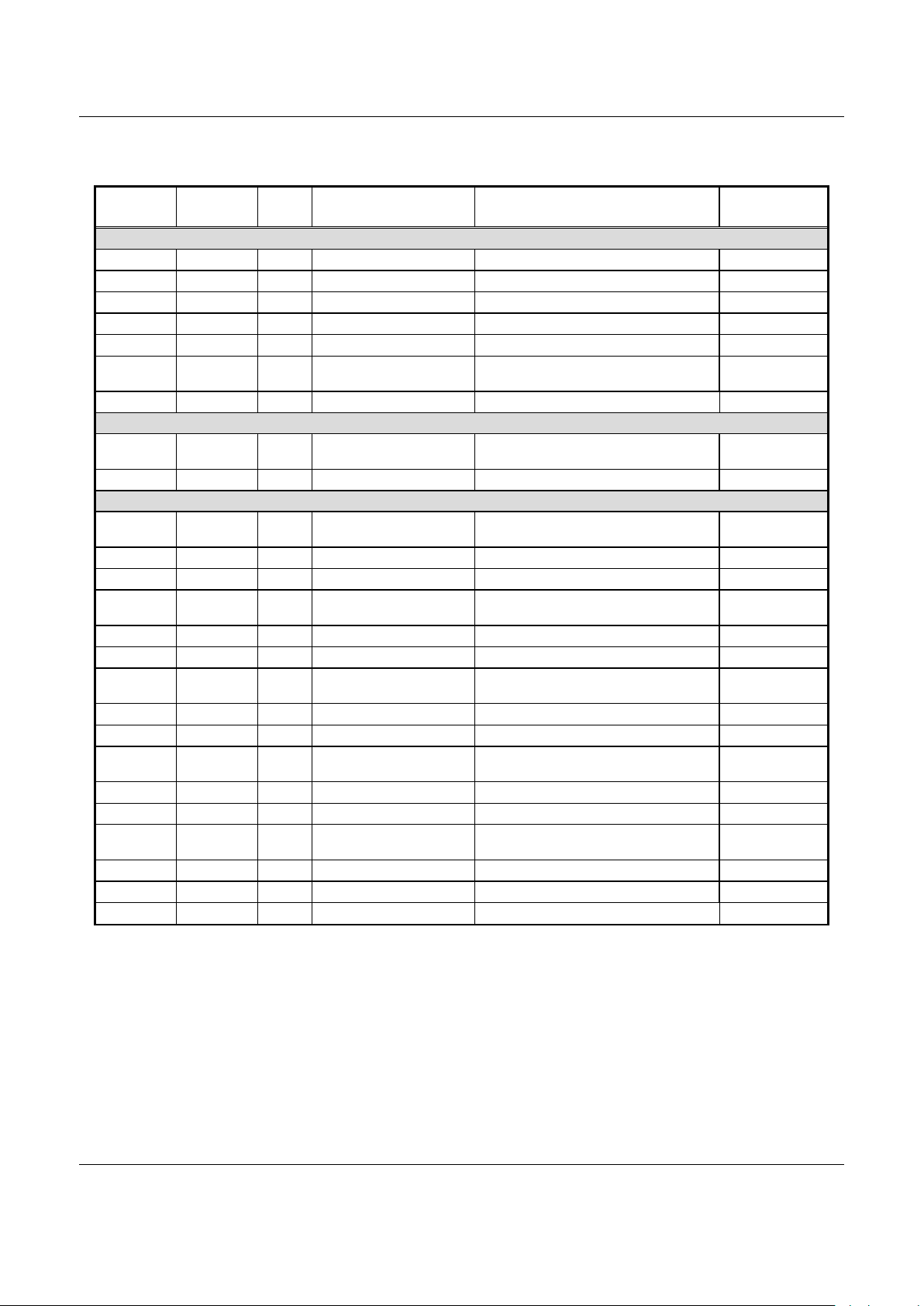
Table 2. BP Register Addresses (4 of 6)
Address
(Hex)
Block Size
(bytes)
Type Name Function Default Value
(Hex)
Escape Sequence/Flow Control Detection
0040320 2 R/W Cont rol Sets mode of detection circuitry. 0000
0040322 2 R/W St atus Stores the status of the detection bloc k. 0000
0040324 2 R/W Escape Sequence Character Character to detect as escape sequence. 002B
0040326 2 R/W XON Char acter Character to detect as XON. 0011
0040328 2 R/W XOFF Char acter Character to detect as XOFF. 0013
004032A 2 R/W Escape Sequence Timeout Number of 20 ms counts for timeout of escape
sequence detection.
0000
004032C 2 R/W Reserved
IrDA Pulse Shaper
0040340 2 R/W Pul se Length Sets transmit pulse duration and expect ed receive
pulse duration.
0000
0040342 2 R/W Divider Ratio Sets number of PTG A pulses per bit period. 000F
DMA Controller
0040500 4 R/W DMA0 Addr ess Address of DMA channel 0 transfers (c hannel 0 is
used for SDS_RX transfer s).
0000 0000
0040504 4 R/W DMA0 Thr eshold Threshold address of DMA channel 0. 0000 0000
0040508 2 R/W DMA0 Cont rol DMA channel 0 control. 0000
0040510 4 R/W DMA1 Addr ess Address of DMA channel 1 transfers (c hannel 1 is
used for DEBUG_RX transfer s).
0000 0000
0040514 4 R/W DMA1 Thr eshold Threshold address of DMA channel 1. 0000 0000
0040518 2 R/W DMA1 Cont rol DMA channel 1 control. 0000
0040520 4 R/W DMA2 Addr ess Address of DMA channel 2 transfers (c hannel 2 is
used for SDS_TX transfer s).
0000 0000
0040524 4 R/W DMA2 Thr eshold Threshold address of DMA channel 2. 0000 0000
0040528 2 R/W DMA2 Cont rol DMA channel 2 control. 0000
0040530 4 R/W DMA3 Addr ess Address of DMA channel 3 transfers (c hannel 3 is
used for DEBUG_TX transfer s).
0000 0000
0040534 4 R/W DMA3 Thr eshold Threshold address of DMA channel 3. 0000 0000
0040538 2 R/W DMA3 Cont rol DMA channel 3 control. 0000
0040540 4 R/W DMA4 Addr ess Address of DMA channel 4 transfers (c hannel 4 is
used for SIM transf ers)
0000 0000
0040544 4 R/W DMA4 Thr eshold Threshold address of DMA channel 4. 0000 0000
0040548 2 R/W DMA4 Cont rol DMA channel 4 control. 0000
0040550 2 Reserved
Baseband Processor M46
100779C
Conexant
11
Proprietary Information and Specifications are Subject to Change June 14, 2000
Table 2. BP Register Addresses (5 of 6)
Address
(Hex)
Block Size
(bytes)
Type Name Function Default Value
(Hex)
Autobaud
0040740 16 R/W Decision Values Thresholds for baudrate decision. Undefined
0040750 16 R/W Timer Values Values to load into PTG B. Undefined
0040760 2 R/W Cont rol Configures operation of Autobaud block. 0000
0040762 2 R Status Stores status of Autobaud block. 0000
0040764 2 R Status Failure If Autobaud detection fails, this regi ster indicates
the cause of the failure.
0000
0040766 2 R First/Second Character Stores the first and s econd characters r eceived
during the last autobaud at tempt.
0000
0040768 2 R Autobaud Count Count value for start bit. 0000
004076A 2 R Temporary Character Temporary character value. 0000
Keypad
0040800 2 R/W Keypad I/O Configuration Configure the keypad strobe lines as inputs or
outputs (as the strobe lines as GPIO type signals).
0000
0040802 2 R/W Keypad St robe Data written to this register will appear on the
keypad strobe lines.
0000
0040804 2 R/W Keypad Return Lines Status of keypad return lines are stored in this
register.
001F
Clock Generation and Phase Locked Loop
0040902 2 R/W Cl ock Enables Turn on / off the clock to each block. 4003
0040B00 2 R/W Reserved
0040B02 2 R/W Reserved
Annunciator
0040A00 2 R/W PWM 1 Control PWM 1 configuration. 0000
0040A02 2 R/W PWM 1 Duty Cycle PWM 1 duty cycle. 0000
0040A04 2 R/W PWM 1 Divider Ratio PWM 1 divider ratio. 0000
0040A06 2 R/W PWM 1 Counter Register PWM 1 counter register. 0064
0040A08 4 R/W PWM 1 Data Pattern PWM 1 data pattern. 0000
0040A10 2 R/W PWM 2 Control PWM 2 configuration. 0000
0040A12 2 R/W PWM 2 Duty Cycle PWM 2 duty cycle. 0000
0040A14 2 R/W PWM 2 Divider Ratio PWM 2 divider ratio. 0000
0040A16 4 R/W PWM 2 Counter Register PWM 2 counter register. 0064
0040A18 4 R/W PWM 2 Data Pattern PWM 2 data pattern. 0000
M46 Baseband Processor
12
Conexant
100779C
June 14, 2000 Proprietary Information and Specifications are Subject to Change
Table 2. BP Register Addresses (6 of 6)
Address
(Hex)
Block Size
(bytes)
Type Name Function Default Value
(Hex)
SIM Interface
0040A80 4 R/W SIM Control SIM configuration 20D1 7420
0040A84 2 R/W SIM Status Stores the current status of the SI M Interface. 0000
0040A86 2 R/W SIM Interrupt Enable Enable/disable SIM Interrupt sources. 0000
0040A88 2 R/W SIM Output Buffer Data to be transmitted over the SIM interface is
written to this buffer.
0000
0040A8A 2 R/W SIM Input Buf fer Data received over the SIM interface is stored in
this buffer.
0000
Byte Select Signals __________________________________
The byte select signals, BS[1:0], are used to transfer byte wide
data to and from 16-bit peripherals. When BS[0] is asserted, it
indicates that data is on bits D[7:0]; if BS[1] is asserted, data is
on bits D[15:8]. Both of these signals are active low.
During write operations to 16-bit peripherals, the byte select
signals must be connected to the corresponding pins on the
peripheral. These signals allow each 8-bit half of the 16-bit
peripheral register to be written to independently. This is
required since the ARM compiler may generate two byte
transactions when accessing a 16-bit peripheral instead of a
single half word (16-bit) transfer.
The polarity of the byte select signals is programmable. Bit [15]
of the SIU Configuration Register controls the polarity of these
signals. If this bit is set to “0,” the signals are active low. If this
bit is set to “1,” the bits are active high.
Clock Generation and Phase Locked Loop
The BP clock generation circuitry takes a 3.9 MHz square wave
system clock input, buffers it, and routes it to the internal
peripherals. Each of the peripherals has a dedicated clock
enable signal so that the clock signal can be turned off when the
peripheral is not in use.
The 3.9 MHz signal is also routed to the Phase Locked Loop
(PLL) circuitry which generates both the ARM and DSP clock
signals.
Clock Enables ______________________________________
Each of the device circuitry blocks has a dedicated clock enable
signal. This allows the clock signal to the circuitry block to be
turned off when it is not in use. The clock enable signals are
controlled by the contents of the Clock Control Register. If a
particular bit is set to “1,” the clock to the associated block is
turned on; if the bit is set to “0,” the clock is turned off. Table 5
describes the function of each bit in this register.
If a “0” is written to a specific bit, the associated clock will go low
at the next high-to-low transition of the system clock and stay
low until it is enabled again.
If a “1” is written to a specific bit, the associated clock will be
turned on at the next low-to-high transition of the system clock.
The address and default settings for the Clock Control Register
are specified in Table 2.
PLL Operation ______________________________________
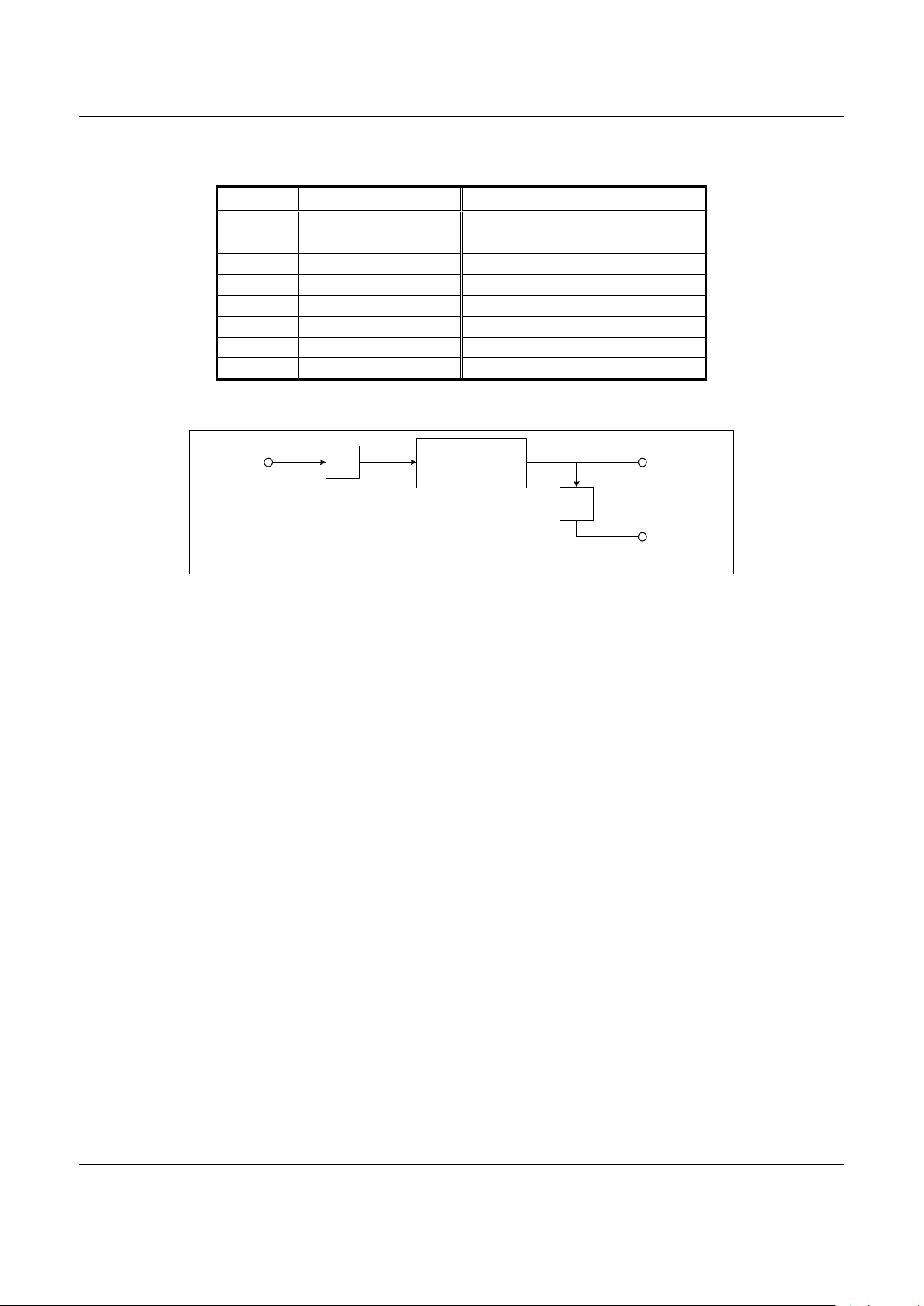
A functional block diagram of the PLL is shown in Figure 5.
The system clock input (3.9 MHz) is divided down by the division
factor, P. This factor is a 2-bit number with a value of 2. The
output from this divider is input to the PLL block, which
generates an output at N times the input frequency, where N is
the multiplying factor (the value of N is 20). The PLL output is
input to the DSP core. The PLL output is also divided down by a
factor, M, to generate the ARM clock. The value of M is 2.
ARM Interrupt Controller
The ARM core can handle two interrupts:
•
Fast Interrupt Request (FIQ)
•
Interrupt Request (IRQ)
The FIQ has a higher priority than the IRQ. The IRQ is masked
when an FIQ sequence is entered. In the case of an FIQ
interrupt, fewer registers are required to be saved to memory.
Therefore, switching into the interrupt handler is slightly faster.
All possible interrupt sources (internal and external) are routed
to the Interrupt Controller, which generates either the FIQ or
IRQ interrupt.
Interrupt Controller Registers _________________________
The address and default settings for the Interrupt Controller
Registers are specified in Table 2.
Baseband Processor M46
100779C
Conexant
13
Proprietary Information and Specifications are Subject to Change June 14, 2000
ARM CLOCK
(internal)
A[21:0]
D[15:0]
CHIP SELECT
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
Valid Data
Valid Data
READ
X
X
X
X
T_addr_hold
T_cs_hold
T_access
T_oen
X
X
T_data_hold
C509
Figure 3. EXB Read Timing Diagram
ARM
CLOCK
(internal)
A[21:0]
D[15:0]
CHIP SELECT
X
X
X
X
Valid Data
Valid Data
W
RITE
X
X
X
X
T_addr_hold
T_cs_hold
T_access
T_wen
T_data_hold
X
C510
Figure 4. EXB Write Timing Diagram
M46 Baseband Processor
14
Conexant
100779C
June 14, 2000 Proprietary Information and Specifications are Subject to Change
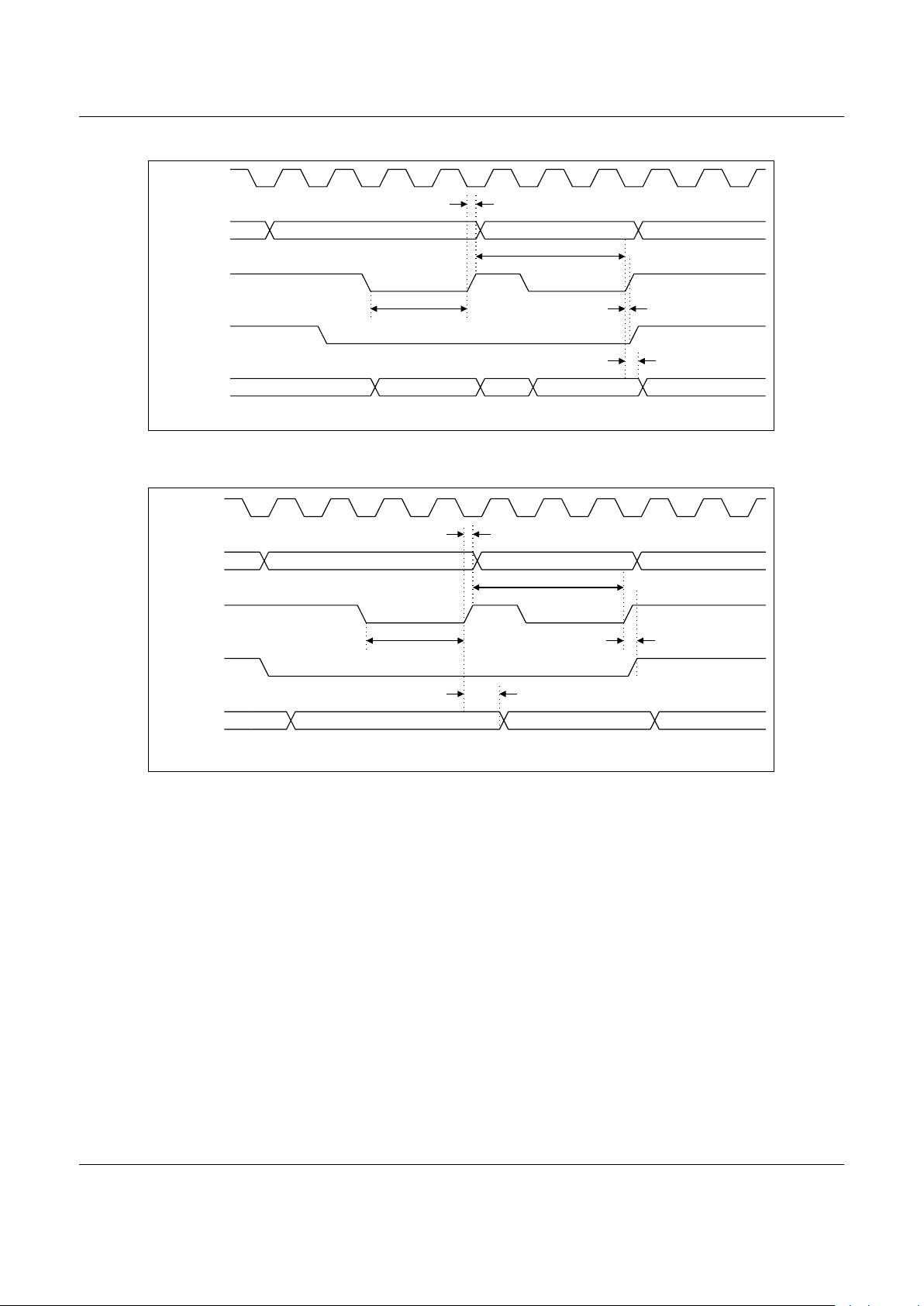
Table 3. EXB Timing Specifications
Parameter Symbol Min Max (Note 1) Units
Read Timing for 0 Wait States
Access time T_access 45 ns
Address bus hold time after read strobe T_addr_hold 6 ns
Chip select hold time after read strobe T_cs_hold 6 ns
Duration of read str obe T_oen 20 ns
Data bus hold time after write strobe T_data_hold 0 ns
Write Timing for 0 Wait States
Access time T_access 43 ns
Address bus hold time after read strobe T_addr_hold 4 ns
Chip select hold time after read strobe T_cs_hold 5 ns
Duration of write strobe T_wen 20 ns
Data bus hold time after write strobe T_data_hold 34 ns
Read Timing for 1 or More Wait States
Access time T_access
WS × 51 + 25
ns
Address bus hold time after read strobe T_addr_hold 24 ns
Chip select hold time after read strobe T_cs_hold 2 ns
Duration of read str obe T_oen
WS × 51
ns
Data bus hold time after write strobe T_data_hold 0 ns
Write Timing for 1 or More Wait States
Access time T_access
WS × 51 + 25
ns
Address bus hold time after read strobe T_addr_hold 4 ns
Chip select hold time after read strobe T_cs_hold 1 ns
Duration of write strobe T_wen
WS × 51 – 1
ns
Data bus hold time after write strobe T_data_hold 30 ns
Note 1: WS is the number of wait states.
Table 4. Chip Select Configuration Register
Bit Name Function
15:9 Reserved N/A
8:7 DELAY Assertion of the chip select will be asserted this many cycles after the
address is st able. This allows for peripherals that require extra
address bus sett ling time.
6 POLARITY Chip select polarity:
1 = active high
0 = active low
5:4 SIZE[1:0] Data bus width:
00 = byte
01 = half word
10 = word
11 = undefined
3:1 WAIT[2:0] Number of wait states. Maximum is seven.
0 ENABLE Chip select enable:
0 = disabled
1 = enabled
Baseband Processor M46
100779C
Conexant
15
Proprietary Information and Specifications are Subject to Change June 14, 2000
Table 5. Clock Control Register Functions
Bit Block Controlled Bit Block Controlled
15 IrDA / Escape Sequence 7 PTGA
14 DSP 6 CRC
13 Reserved 5 Timer B
12 DMA Controlled 4 PWM
11 Autobaud 3 SIM
10 SDS Port 2 Reserved
9 Debug Port 1 SIU
8PTGB 0ARM Core
PLL
÷P
÷M
System Clock
DSP Clock
(Input Clock x N)
ARM Clock
Input
Clock
C855
Figure 5. PLL Functional Block Diagram
Interrupt Pending Register. All interrupt sources are latched
into the Interrupt Pending Register. When an interrupt is latched
into this register the bit will remain set to “1” until the interrupt
source has disappeared and the bit is cleared by the ARM. The
source of each of the bits in the register is specified in Table 6.
Interrupt Select Register. Every enabled interrupt source can
generate either an FIQ or IRQ interrupt to the ARM core. The
Interrupt Select Register contains a bit for each possible
interrupt source. If the associated bit is set to “1,” an FIQ
interrupt is generated when an interrupt occurs and the interrupt
is enabled. Conversely, if the bit is set to “0,” an IRQ interrupt is
generated when an interrupt occurs and the interrupt is enabled.
The Interrupt Select Register bits have the same mapping to the
interrupt sources as the Interrupt Pending Register (see
Table 6).
Interrupt Enable Register. The Interrupt Enable Register
contains a corresponding bit for each possible interrupt source.
If the bit is set to “1,” and an interrupt occurs, an interrupt is sent
to the ARM. Either an FIQ or IRQ interrupt is generated
depending on the status of the associated interrupt bit in the
Interrupt Select Register. If the bit is set to “0,” the interrupt is
disabled.
The Interrupt Enable Register bits have the same mapping to
the interrupt sources as the Interrupt Pending Register (see
Table 6).
External Interrupt Polarity Register. The polarity of all external
interrupts is selected by writing to the appropriate bit in the
Interrupt Polarity Register. If the bit is set to “1,” an interrupt is
generated on the falling edge of the signal. If the bit is set to “0,”
the rising edge of the signal is the interrupting edge.
Care must be taken since the act of altering the bit could result
in the generation of an interrupt edge. This potential hazard can
be avoided by using software to disable the interrupt source
when the polarity bit is changed.
The External Interrupt Polarity Register bits have the same
mapping to the interrupt sources as the Interrupt Pending
Register (see Table 6). For internally generated interrupts, the
associated bits in this register are unused.
FIQ Interrupt Register. The FIQ Interrupt Register contains bits
for all the possible interrupt sources. The FIQ Interrupt Register
bits have the same mapping to the interrupt sources as the
Interrupt Pending Register (see Table 6). If a bit for a particular
interrupt is set to 1, the following conditions apply to that
interrupt:
•
The interrupt has occurred
•
The interrupt is enabled
•
The interrupt is set to generate an FIQ interrupt
If the bit is set to 0, at least one of the conditions listed above is
not met.
 Loading...
Loading...