Conexant Bt8110, Bt8110B User Manual
查询BT8110供应商
Bt8110/8110B
High-Capacity ADPCM Processor
This specification describes the Bt8110 and Bt8110B multichannel ADPCM processor
CMOS integrated circuits that implement Adaptive Differential Pulse-Code Modulation
(ADPCM) encoding and decoding. The fixed-rate coding algorithms include those
specified in ANSI Standard T1.303-1989. These algorithms are identical to those in
ITU-T Recommendations G.726 and G.727. These circuits also implement the
variable-rate or embedded codes specified in ANSI Standard T1.310-1991 and ITU-T
Recommendation G.727.
A single ADPCM processor integrated circuit can provide 24 or 32 full-duplex
channels of ADPCM processing (encoding and decoding). In some applications, two
circuits can be combined to provide 48 or 64 full-duplex channels. Both A-law and µ-law
PCM translations are provided.
Interface options such as serial and parallel inputs and outputs, along with hardware
and microprocessor control modes, are provided by the integrated circuits. Up to 14
separate ADPCM algorithms are available in any given configuration on a per-channel
basis.
The Bt8110 requires an external lookup table ROM. The Bt8110B has an internal
lookup table ROM, or can use an external lookup table ROM. When in direct framer
interface mode, transparent channels in the Bt8110 will operate at 56 kbit/s; the
Bt8110B operates at 64 kbit/s. A hardware control, direct framer interface mode has
been added to the Bt8110B. For more details on the Bt8110B mode controls, refer to
Table 1-1 and Tab le 1- 4.
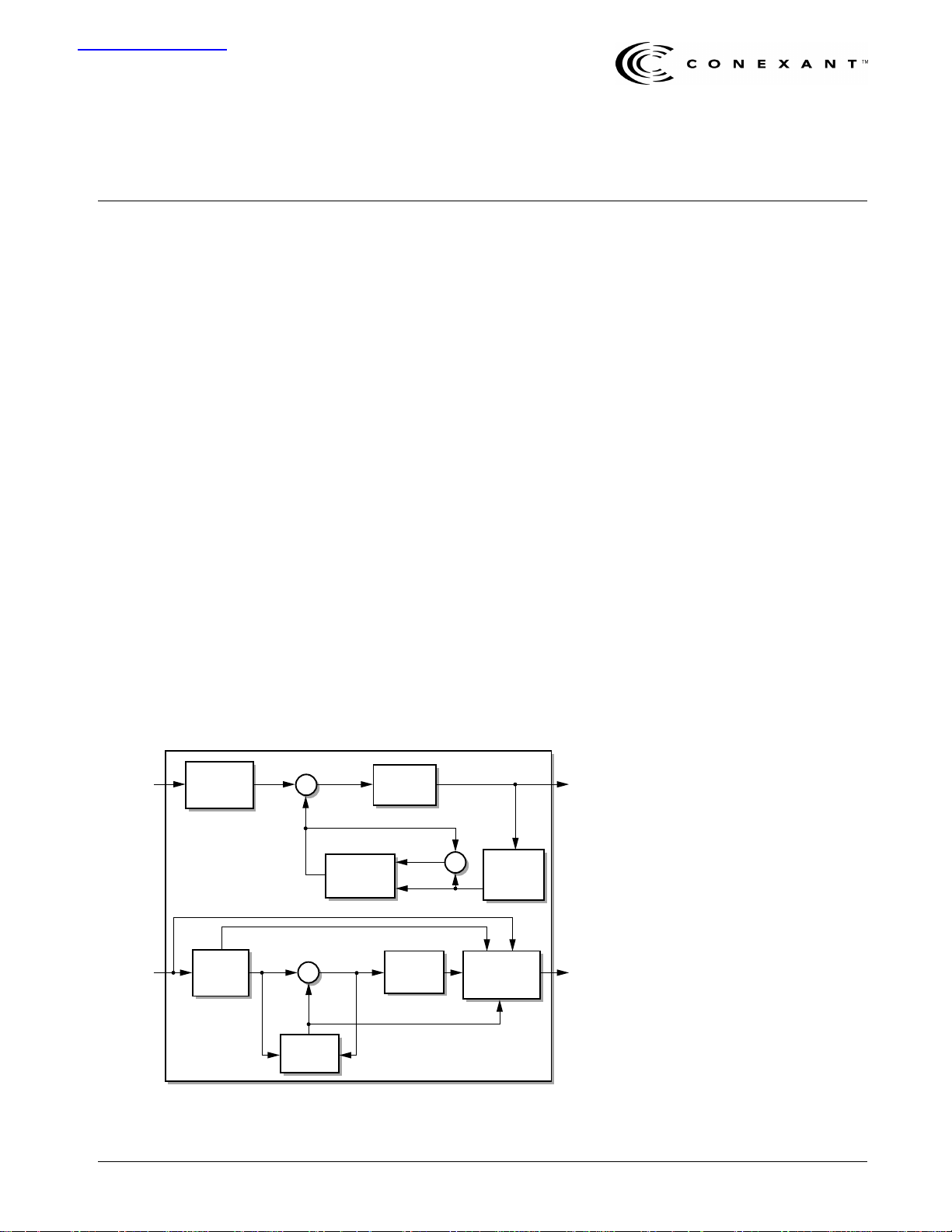
Functional Block Diagram
64 Kbit/s
PCM
Input
32 Kbit/s
ADPCM
Input
Convert to
Uniform
PCM
ENCODER
Inverse
Adaptive
Quantizer
DECODER
Input
Signal
Quantized
Difference
Signal
Difference
+
+
–
Signal
Estimate
Reconstructed
+
+
–
Signal
Estimate
Adaptive
Predictor
Signal
Adaptive
Predictor
Signal
Adaptive
Quantizer
Reconstructed
Signal
Quantized
Difference Signal
Convert to
PCM
+
Quantizer
Synchronous
Coding
Adjustment
32 Kbit/s
ADPCM
Output
Inverse
Adaptive
64 Kbit/s
PCM
Output
Distinguishing Features
• Bt8110B offers internal ROM
• 24 or 32 full-duplex channel capacity
(48 or 64 channels with two
processors)
• 2-, 3-, 4- and 5-bit quantization
dynamically selectable on a
channel-by-channel, frame-by-frame
basis
• Transparent channel operation
• Two control modes available:
microprocessor and hardware.
• Direct framer interface for both T1
and E1 signal formats
• Supports the optimal RESET function
described in the algorithm standards
• Supports even-bit inversion of A-law
inputs and outputs (required by
ITU-T Recommendations G.726, and
G.727)
• Minimum throughput delay
• Pin compatible with Bt8110
• 8 mw per-channel, low-power CMOS
Applicable Standards
• ANSI T1.302-1987
• ANSI T1.303-1989
• ANSI T1.310-1991
• ITU-T G.726, G.727
• ANSI T1.501-1994
• ANSI T1Y1 Technical Reports #3 and
#10
Applications
• T1/E1 Transcoders
• T1/E1 Multiplexers
• Personal Communications Systems:
Digital European Cordless
Telecommunications (DECT),
Personal Access Communications
System (PACS)
• Wireless Local Loop
• Voice PairGain
• DCME Systems
• Speech Processing/Recording
• Voice Mail/Packetization
• Voice over ATM/Frame Relay
Data Sheet 100060C
January 2000
Ordering Information
Model Number Package Ambient Temperature Range
Bt8110EPJ 68-Pin Plastic Leaded Chip Carrier (PLCC) –40 °C to +85 °C
Bt8110EPJB 68-Pin Plastic Leaded Chip Carrier (PLCC) –40 °C to +85 °C
Revision History
Revision Level Date Description
A Advanced Created
B December 1996
C January 2000 The timing diagrams for the following figures have been
updated: Figure 2-3, Figure 2-5, Figure 2-6, Figure 2-7,
Figure 2-8, Figure A-2, Figure A-3, Figure A-4.
© 1996, 2000 Conexant Systems, Inc.
All Rights Reserved.
Information in this document is provided in connection with Conexant Systems, Inc. ("Conexant") products. These
materials are provided by Conexant as a service to its customers and may be used for informational purposes only.
Conexant assumes no responsibility for errors or omissions in these materials. Conexant may make changes to
specifications and product descriptions at any time, without notice. Conexant makes no commitment to update the
information contained herein. Conexant shall have no responsibility whatsoever for conflicts or incompatibilities arising
from future changes to its specifications and product descriptions.
No license, express or implied, by estoppel or otherwise, to any intellectual property rights is granted by this document.
Except as provided in Conexant’s Terms and Conditions of Sale for such products, Conexant assumes no liability
whatsoever.
THESE MATERIALS ARE PROVIDED "AS IS" WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EITHER EXPRESS OR
IMPLIED, RELATING TO SALE AND/OR USE OF CONEXANT PRODUCTS INCLUDING LIABILITY OR WARRANTIES RELATING TO FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE, MERCHANTABILITY, OR INFRINGEMENT OF ANY
PATENT, COPYRIGHT OR OTHER INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHT. Conexant further does not warrant the accuracy or completeness of the information, text, graphics or other items contained within these materials. Conexant shall
not be liable for any special, indirect, incidental, or consequential damages, including without limitation, lost revenues
or lost profits, which may result from the use of these materials.
Conexant products are not intended for use in medical, life saving or life sustaining applications. Conexant customers
using or selling Conexant products for use in such applications do so at their own risk and agree to fully indemnify
Conexant for any damages resulting from such improper use or sale.
The following are trademarks of Conexant Systems, Inc.: Conexant, the Conexant C symbol, and “What’s Next in
Communications Technologies”. Product names or services listed in this publication are for identification purposes
only, and may be trademarks of third parties. Third-party brands and names are the property of their respective
owners.
Reader Response: Conexant strives to produce quality documentation and welcomes your feedback. Please send
comments and suggestions to conexant.tech.pubs@conexant.com. For technical questions, contact your local
Conexant sales office or field applications engineer.
100060C Conexant

Table of Contents
List of Figures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . v
List of Tables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . vii
1.0 Product Description. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-1
1.1 Channel Capacity and Configuration Modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-2
1.1.1 Signal Inputs and Outputs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-2
1.1.2 Embedded Coding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-3
1.1.3 Control Mode. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-3
1.2 Pin Descriptions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-4
2.0 Functional Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-1
2.1 Overview. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-1
2.1.1 Clocking and Synchronization. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-3
2.1.2 Microprocessor Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-3
2.1.3 Address Map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-4
2.2 Modes of Operation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-5
2.2.1 24- or 32-Channel Full-Duplex Interleaved Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-5
2.2.1.1 Signal Inputs and Outputs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-6
2.2.1.2 Reset Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-8
2.2.2 48- or 64-Channel Encoder-Only Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-8
2.2.3 48- or 64-Channel Decoder-Only Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-9
2.3 Direct Framer Interface Operation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-11
2.3.1 T1 Framer Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-11
2.3.2 E1 Framer Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-12
2.4 Hardware Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-13
2.4.1 Mode Pins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-14
2.4.2 Control Pins. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-14
3.0 Registers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-1
3.1 0x00–0x3F—Per-Channel Control Registers (per_chan_ctrl). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-1
3.2 0x40—Mode Control Register (mode). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-3
100060C Conexant iii

Bt8110/8110B
High-Capacity ADPCM Processor
4.0 Electrical and Mechanical Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-1
4.1 Microprocessor Interface Timing. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-1
4.1.1 Bt8110 Timing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-2
4.1.2 ROM Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-4
4.2 Absolute Maximum Ratings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-5
4.3 DC Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-6
4.4 Mechanical Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-7
Appendix A. Hardware Mode Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-1
A.1 48- or 64-Channel Full-Duplex Hardware Mode Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-1
A.1.1 Introduction. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-1
A.1.2 Configuration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-1
A.1.3 Functional Timing. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-3
Appendix B. T1 Speech Compression. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . B-1
B.1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . B-1
B.1.1 Configuration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . B-1
B.1.2 Functional Timing Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . B-3
B.1.3 Microprocessor Interface And Per-Channel Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . B-5
Appendix C. E1 Speech Compression. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-1
C.1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-1
C.1.1 Configuration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-1
C.1.2 Functional Timing Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-3
C.1.3 Microprocessor Interface and Per-Channel Configuration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-5
Appendix D. T1 ADPCM Transcoder . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . D-1
D.1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . D-1
D.1.1 Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . D-1
D.1.2 Summary. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . D-3
D.1.3 ADPCM Transcoder System Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . D-4
Appendix E. E1 ADPCM Transcoder . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . E-1
E.1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . E-1
E.1.1 Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . E-1
E.1.2 Summary. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . E-3
E.1.3 ADPCM Transcoder System Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . E-3
iv Conexant 100060C

Bt8110/8110B List of Figures
High-Capacity ADPCM Processor
List of Figures
Figure 1-1. Bt8110 Pinout Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-4
Figure 1-2. Bt8110 Logic Diagram. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-6
Figure 1-3. Bt8110B Pinout Diagram. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-7
Figure 1-4. Bt8110B Logic Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-9
Figure 2-1. Bt8110 Block Diagram. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-2
Figure 2-2. Bt8110B Block Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-2
Figure 2-3. Input and Output Timing for 24- or 32-Channel Full-Duplex
Interleaved Operation (Microprocessor Control) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-6
Figure 2-4. Input and Output Timing for 48- or 64-Channel Half-Duplex
Encoder-Only Operation (Microprocessor Control) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-9
Figure 2-5. Input and Output Timing for 48- or 64-Channel Half-Duplex
Decoder-Only Operation (Microprocessor Control). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-10
Figure 2-6. Hardware Control Interleaved Timing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-15
Figure 2-7. Hardware Control Encoder-Only Timing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-16
Figure 2-8. Hardware Control Decoder-Only Timing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-17
Figure 4-1. Microprocessor Interface Timing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-2
Figure 4-2. Input and Output Signal Timing. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-3
Figure 4-3. 68-Pin Plastic Leaded Chip Carrier (J-Bend). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-7
Figure A-1. 48- or 64-Channel Configuration of the Bt8110/8110B. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-2
Figure A-2. 48- or 64-Channel Full-Duplex Interleaved Mode Functional Timing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-3
Figure A-3. 96- or 128-Channel Half-Duplex Encoder-Only Functional Timing. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-4
Figure A-4. 96- or 128-Channel Half-Duplex Decoder-Only Functional Timing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-5
Figure B-1. T1 Speech Compression Interface Block Diagram. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . B-2
Figure B-2. T1 Speech Compression Functional Timing Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . B-4
Figure C-1. E1 Speech Compression Interface Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-2
Figure C-2. E1 Speech Compression Functional Timing Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-4
Figure D-1. Single-Board Transcoder Assembly. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .D-2
Figure D-2. Single-Board Transcoder Application . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .D-3
Figure E-1. Single-Board Transcoder Assembly. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .E-2
Figure E-2. Single-Board Transcoder Application . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .E-3
100060C Conexant v

List of Figures Bt8110/8110B
High-Capacity ADPCM Processor
vi Conexant 100060C

Bt8110/8110B List of Tables
High-Capacity ADPCM Processor
List of Tables
Table 1-1. ADPCM Operational Modes. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-2
Table 1-2. Bt8110 Pin Descriptions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-5
Table 1-3. Bt8110B Pin Descriptions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-8
Table 1-4. Bt8110/8110B Hardware Signal Definitions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-10
Table 2-1. Signal Connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-4
Table 2-2. Parallel Signal Input Bus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-7
Table 2-3. Parallel Signal Output Bus. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-8
Table 2-4. Bt8110/8110B Connection for Hardware Mode. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-13
Table 2-5. Mode Pins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-14
Table 3-1. Bt8110 or Bt8110B with External Lookup Table ROM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-2
Table 3-2. Bt8110B Internal Lookup Table ROM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-2
Table 3-3. Interleaved Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-5
Table 3-4. Encoder/Decoder–Only Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-6
Table 4-1. Microprocessor Interface Timing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-1
Table 4-2. Bt8110/8110B Hardware Mode Timing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-3
Table 4-3. Input and Output Signal Timing. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-3
Table 4-4. System Clock Frequencies . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-4
Table 4-5. Absolute Maximum Ratings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-5
Table 4-6. DC Characteristics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-6
Table A-1. Mode Settings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-2
Table B-1. Bt8110/8110B Microprocessor Connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . B-5
Table B-2. Microcontroller Memory Map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . B-6
Table B-3. Bt8110/8110B Processor Per-Channel Control Locations. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . B-7
Table C-1. Bt8110/8110B Microprocessor Connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-5
Table C-2. Bt8110/8110B Microprocessor Memory Map. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-6
Table C-3. Bt8110/B Per-Channel Control Locations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-7
Table D-1. ADPCM Transcoder System Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . D-4
Table E-1. ADPCM Transcoder System Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . E-3
100060C Conexant vii

List of Tables Bt8110/8110B
High-Capacity ADPCM Processor
viii Conexant 100060C

1
1.0 Product Description
The Adaptive Differential Pulse Code Modulation (ADPCM) algorithm is a
transcoding operation which consists of encoding 64 kbit/s Pulse Code
Modulation (PCM) to 16, 24, 32, or 40 kbit/s ADPCM and decoding from
ADPCM to 64 kbit/s PCM. The multichannel processor provides transcoding for
both A-law and
channel-by-channel basis.
The Bt8110/8110B has a maximum capacity of 64 channels of ADPCM
operations. It can be configured to provide 24 or 32 full-duplex channels
providing both encoding and decoding. It can also be configured to provide 48 or
64 half-duplex channels providing either encoding or decoding. The
Bt8110/8110B consists of a VLSI CMOS integrated circuit and a ROM.
NOTE: In the Bt8110, the ROM is external. Additionally, for the Bt8110, a 64 K
ROM will provide six different ADPCM codes, while a 128 K ROM will
provide 14 different ADPCM codes. (See Table 3-1.). The Bt8110B has an
internal ROM or can be used with the external ROM. The Bt8110B’s
internal ROM contains 14 different ADPCM codes (see Tabl e 3- 2),
µ-law PCM codes. The PCM coding rate is selectable on a
Two Bt8110/8110Bs and a single ROM can be configured to provide 48 or 64
full-duplex channels for operation in transcoding applications. There are two
control modes for the Bt8110/8110B: Hardware and Microprocessor. The
hardware mode provides for input of code selection, transparency selection,
algorithm reset, and PCM coding law on a per-channel basis. The microprocessor
mode is provided via an integral interface to a microprocessor consisting of a
microprocessor, program and data memory, and desired status indicators.
100060C Conexant 1-1
1.0 Product Description Bt8110/8110B
1.1 Channel Capacity and Configuration Modes High-Capacity ADPCM Processor
1.1 Channel Capacity and Configuration Modes
There are four configurations for the operational mode of the Bt8110/8110B (see
Table 1 -1 ). These configurations are established by setting the three mode control
bits ([MODE[2:0]) and the enable framer bit [EN_FRMR] in the Mode Control
Register [mode; 0x40], in the microprocessor mode or on signal pins in the
hardware mode (AD[2:0] and CTRL[0]). Table 1-1 summarizes the
configurations and the input code applied to each.
Table 1-1. ADPCM Operational Modes
CTRL
[1]
NOTE(S):
(1)
2. CTRL[1] and CTRL[0] are available only in the Bt8110B.
CTRL
[0]
x0100
x 0 101 Encoder Only 6.144 48
x 0 110 Decoder Only 6.144 48
0 1 100 Direct Framer Interface 12.352 24
Interleaved operation means that the Bt8110/8110B alternates between encoder and decoder operation on consecutive
inputs. This requires that the inputs and outputs be interleaved (PCM/ADPCM/PCM, etc.) as well.
Mode
Control
Function
Encoder/Decoder Interleaved
In T1 and E1 direct framer interface modes the Bt8110/8110B can connect
directly to a T1 or E1 framer providing 24 or 32 full-duplex channels of encoding.
These configurations are described in detail in Appendix B and C.
(1)
Clock
Rate
(MHz)
6.144 24
Channel
Capacity
Full-duplex
Half-duplex
Half-duplex
Full-duplex
Clock
Rate
(MHz)
8.192 32 Full-duplex
8.192 64 Half-duplex
8.192 64 Half-duplex
8.192 32 Full-duplex
1.1.1 Signal Inputs and Outputs
Channel
Capacity
The Bt8110/8110B provides both parallel and serial inputs and outputs. The 8-bit
parallel inputs are selected by setting the input PSIGEN high. The serial input is a
multiplexed encoder/decoder input to provide interleaved signals. The transfer
rate of the serial input and output is one-half the input clock rate (CLOCK). The
serial output is also multiplexed in interleaved encoder/decoder operation.
ADPCM inputs and outputs appear on the most significant bits.
The serial signal input and output words are 8 bits, with the most signif icant
bit (sign bit for PCM) appearing first. When transparent operation is selected for
a given channel for either an encoder or a decoder, all 8 bits are transferred
without modification from the input to both the serial and parallel outputs.
NOTE: The exception is with the Bt8110 when the parallel interface is selected in
the direct T1/E1 framer interface mode; then the decoder path PSIG[0]
must held at a logic low level.
1-2 Conexant 100060C

Bt8110/8110B 1.0 Product Description
High-Capacity ADPCM Processor
1.1.2 Embedded Coding
The Bt8110/8110B has the capability to provide embedded coding according to
ANSI Standard T1.310-1991 and ITU-T Recommendation G.727. This coding
technique allows the encoding to be performed with 5 bits of encoding
information, and the decoding to be done with anywhere from 2 to 5 input bits.
The coding algorithm is defined so that although the coding distortion increases
as the number of bits at the decoder decreases, the encoder and the decoder will
remain synchronized.
ROM code selected. Along with four different standard (non-embedded) ADPCM
codes, two embedded codes can be provided with a 64 K ROM and up to six
different embedded codes, with eight different standard (non-embedded) codes,
can be provided with a 128 K ROM. The encoder always provides the maximum
number of bits (up to 5) defined by the code selected. The decoder requires up to
5 ADPCM bits and a 2-bit encoded input that indicates how many bits are present
at the decoder input. This input signal is applied to bits 1 and 2 of the parallel
input bus. If embedded coding is not in use, bits 1 and 2 should be connected to
ground.
1.1.3 Control Mode
1.1 Channel Capacity and Configuration Modes
The Bt8110/8110B is designed so that embedded coding is enabled by the
Each channel has four sets of per-channel control inputs. These are for selecting
the PCM coding law (A-law or
the RESET function of the ADPCM coding algorithm, and selecting which of 14
codes (six codes for a 64 K ROM) is used for encoding or decoding.
The microprocessor mode is selected by setting input MICREN high. The
microprocessor can address 65 different registers. There is a control register for
each of the encoder and decoder channel operations and a mode control register
that sets the operating mode of the Bt8110/8110B.
µ-law), selecting transparent operation, selecting
100060C Conexant 1-3
1.0 Product Description Bt8110/8110B
1.2 Pin Descriptions High-Capacity ADPCM Processor
1.2 Pin Descriptions
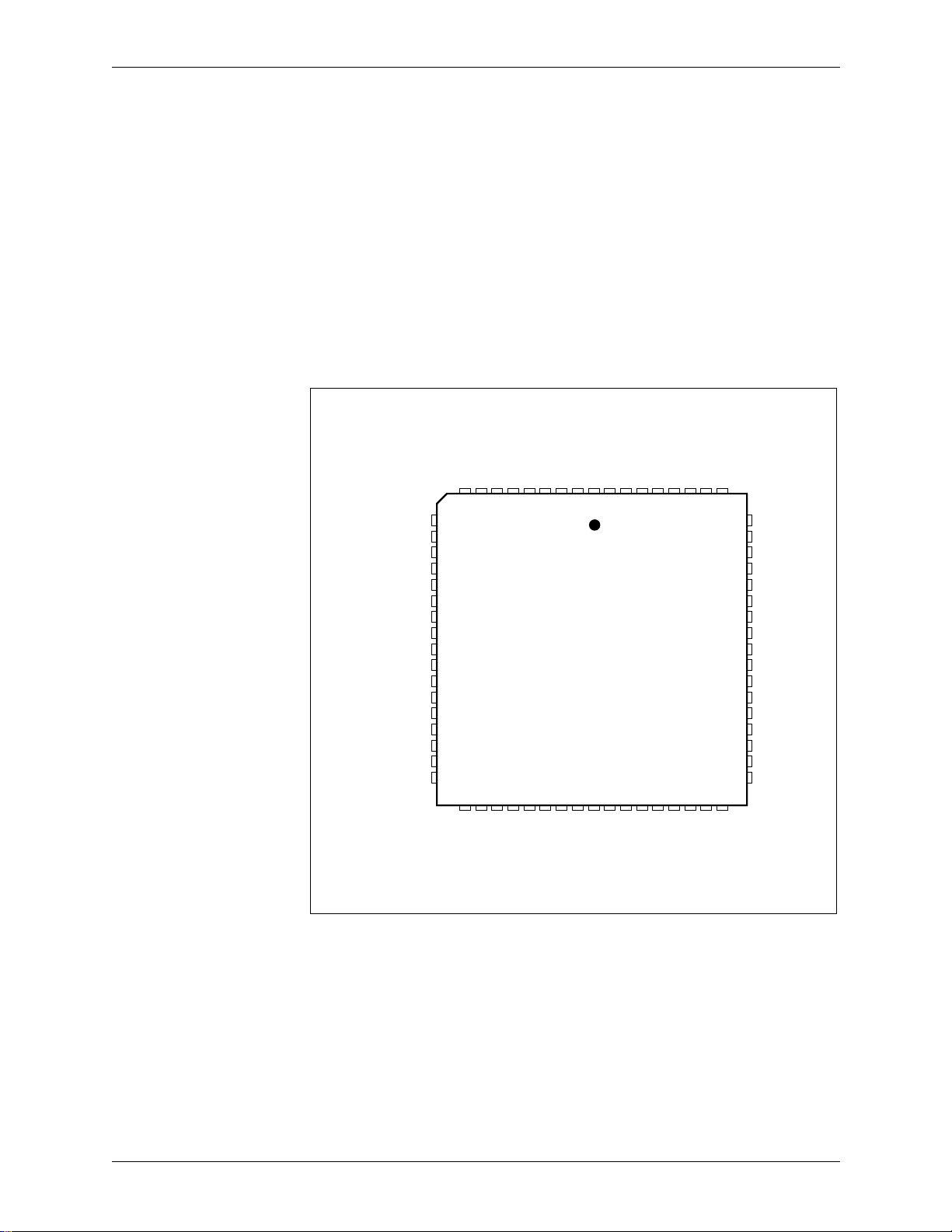
The Bt8110 and Bt8110B are packaged as 68-pin Plastic Leaded Chip Carriers
(PLCCs). Figures 1-1 and 1-2 illustrate the pinouts for the Bt8110 and Bt8110B,
respectively. Pin assignments are listed in numerical order in Table 1 -2 for
Bt8110, and in Tab le 1 -3 for Bt8110B. Figures 1-2 and 1-4 show the functionally
partitioned logic diagrams for Bt8110 and Bt8110B. Pin descriptions, names, and
I/O assignments are detailed in Table 1-2.
Figure 1-1. Bt8110 Pinout Diagram
VCC
PSIGEN
PSIG[7]
PSIG[6]
PSIG[5]
PSIG[4]
WR*
PSIG[3]
GND
VCC
PSIG[2]
PSIG[1]
PSIG[0]
GND
A[0]
A[1]
A[2]
GND
AD[0]
AD[1]
AD[2]
SERIAL_IN
CLOCK
SERIAL_OUT
VCC
GND
AD[3]
RESET
SYNC
CS
MICREN
AD[4]
AD[5]
VCC
987654321
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
2728293031323334353637383940414243
GND
ALE
AD[6]
Processor
Y
TDP
PCM_STB
ADPCM_STB
68676665646362
Bt8110
ADPCM
SE
VCC
GND
A[13]
AD[12]
VCC
GND
AD[11]
AD[10]
61
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
51
50
49
48
47
46
45
44
A[9]
A[3]
A[4]
A[5]
D[0]
D[1]
D[2]
D[3]
VCC
GND
D[4]
D[5]
D[6]
D[7]
A[6]
A[7]
A[8]
GND
100060_002
1-4 Conexant 100060C

Bt8110/8110B 1.0 Product Description
High-Capacity ADPCM Processor
Table 1-2. Bt8110 Pin Descriptions
1.2 Pin Descriptions
Pin Pin Label I/O Pin Pin Label I/O
1 GND I 35 GND I
2 PSIG[3] I 36 VCC I
3WR*I37A[13]O
4 PSIG[4] I 38 A[12] O
5 PSIG[5] I 39 VCC I
6 PSIG[6] I 40 GND I
7 PSIG[7] (MSB) I 41 A[11] O
8 PSIGEN I 42 A[10] O
9VCCI43A[9]O
10 GND I 44 GND I
11 AD[0] I 45 A[8] O
12 AD[1] I 46 A[7] O
13 AD[2] I 47 A[6] O
14 SERIAL_IN I 48 D[7] I
15 CLOCK I 49 D[6] I
16 SERIAL_OUT O 50 D[5] I
17 VCC I 51 D[4] I
18 GND I 52 GND I
19 AD[3] I 53 VCC I
20 RESET I 54 D[3] I
21 SYNC I 55 D[2] I
22 CS I 56 D[1] I
23 MICREN I 57 D[0] I
24 AD[4] I 58 A[5] 0
25 AD[5] I 59 A[4] O
26 VCC I 60 A[3] O
27 GND I 61 A[2] O
28 AD[6] I 62 A[1] O
29 ALE I 63 A[0] O
30 PCM_STB O 64 GND I
31 ADPCM_STB O 65 PSIG[0] I
32 Y O 66 PSIG[1] I
33 TDP O 67 PSIG[2] I
34 SE O 68 VCC I
100060C Conexant 1-5
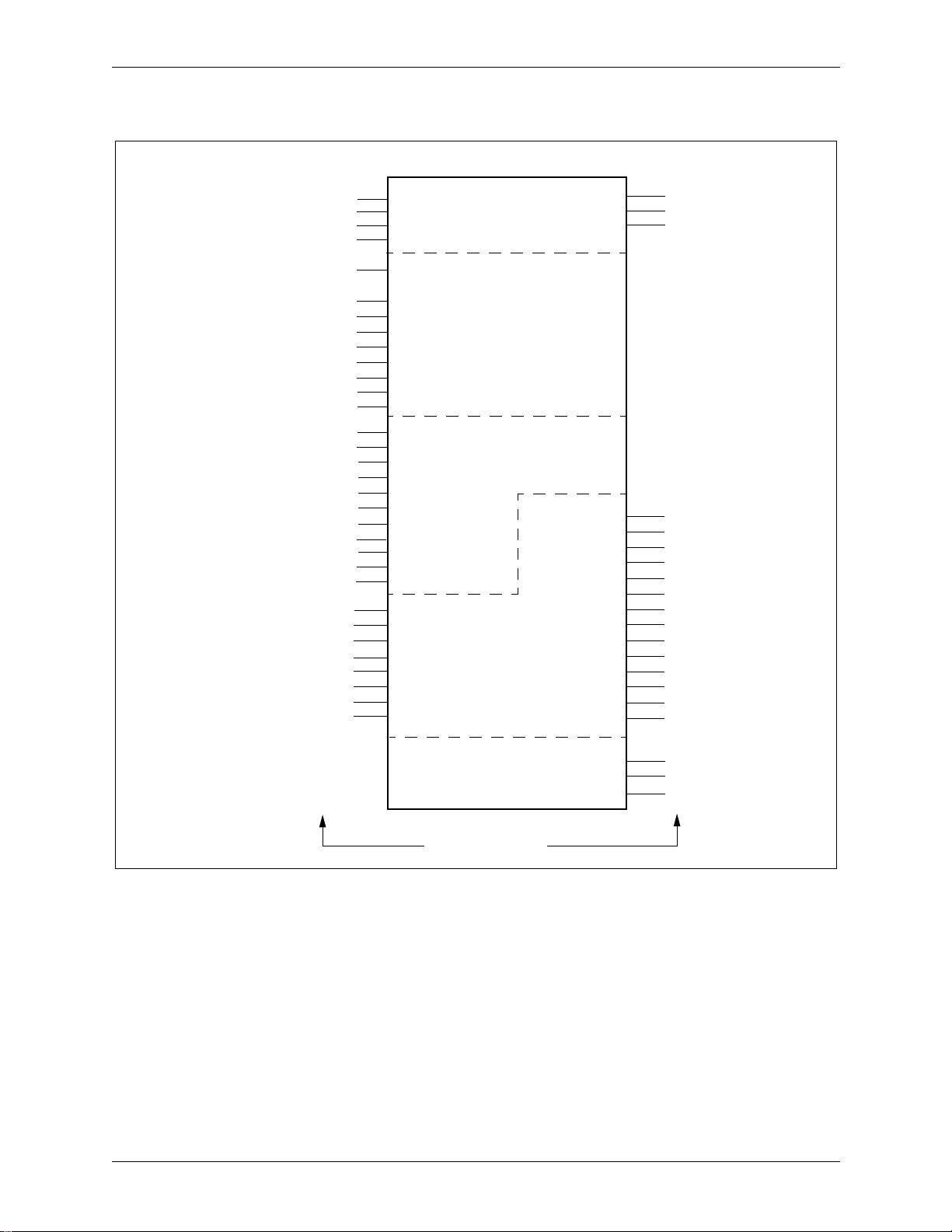
1.0 Product Description Bt8110/8110B
1.2 Pin Descriptions High-Capacity ADPCM Processor
Figure 1-2. Bt8110 Logic Diagram
Clock In
Sync In
Serial Input
Parallel Signal Enable
(MSB) Parallel Signal In 7
Parallel Signal In 6
Parallel Signal In 5
Parallel Signal In 4
Parallel Signal In 3
Parallel Signal In 2 I PSIG[2]
Parallel Signal In 1
Parallel Signal In 0
Microcontroller Enable
Address Latch Enable
Chip Select
µP Address/Data 6
µP Address/Data 5
µP Address/Data 4
µP Address/Data 1 I AD[1]
µP Address/Data 0
ROM Data 7
ROM Data 6
ROM Data 5
ROM Data 4
ROM Data 3
ROM Data 2
ROM Data 1
ROM Data 0 I
Reset
Write*
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
IµP Address/Data 3
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
15
21
14
20
8
7
6
5
4
2
67
66
65
23
29
22
3
28
25
24
19
13
12
11
48
49
50
51
54
55
56
57
CLOCK
SYNC
SERIAL_IN
RESET
PSIGEN
PSIG[7]
PSIG[6]
PSIG[5]
PSIG[4]
PSIG[3]
PSIG[1]
PSIG[0]
MICREN
ALE
CS
WR*
AD[6]
AD[5]
AD[4]
AD[3]
AD[2]IµP Address/Data 2
AD[0]
D[7]
D[6]
D[5]
D[4]
D[3]
D[2]
D[1]
D[0]
Clock and
Serial
Interface
Parallel Input Interface
Microprocessor
SERIAL_OUT
Interface
ROM
Interface
ADPCM_STB
PCM_STB
A[13]
A[12]
A[11]
A[10]
A[9]
A[8]
A[7]
A[6]
A[5]
A[4]
A[3]
A[2]
A[1]
A[0]
31
30
16
37
38
41
42
43
45
46
47
58
59
60
61
62
63
ADPCM Strobe
O
PCM Strobe
O
Serial Output
O
ROM Address 13
O
ROM Address 12
O
ROM Address 11
O
ROM Address 10
O
ROM Address 9
O
ROM Address 8
O
ROM Address 7
O
ROM Address 6
O
ROM Address 5
O
ROM Address 4
O
ROM Address 3
O
ROM Address 2
O
ROM Address 1
O
ROM Address 0
O
Test
Interface
I = Input, O = Output
34
33
TDP TDP ParameterO
Y O Y Parameter
32
SE Parameter
O
100060_003
SE
1-6 Conexant 100060C
Bt8110/8110B 1.0 Product Description
High-Capacity ADPCM Processor
Figure 1-3. Bt8110B Pinout Diagram
GND
AD[0]
AD[1]
AD[2]
SERIAL_IN
CLOCK
SERIAL_OUT
VCC
GND
AD[3]
RESET
SYNC
CS
MICREN
AD[4]
AD[5]
VCC
VCC
PSIGEN
PSIG[7]
PSIG[6]
PSIG[5]
PSIG[4]
WR*
PSIG[3]
GND
VCC
PSIG[2]
PSIG[1]
PSIG[0]
GND
987654321
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
2728293031323334353637383940414243
ALE
GND
AD[6]
Processor
Y
TDP
PCM_STB
ADPCM_STB
68676665646362
Bt8110B
ADPCM
SE
VCC
GND
A[13]
A[12]
CTRL[1]
CTRL[0]
1.2 Pin Descriptions
A[0]
A[1]
A[2]
61
A[3]
60
A[4]
59
A[5]
58
D[0]
57
D[1]
56
D[2]
55
D[3]
54
VCC
53
GND
52
D[4]
51
D[5]
50
D[6]
49
D[7]
48
A[6]
47
A[7]
46
A[8]
45
44
GND
A[9]
A[11]
A[10]
100060_004
100060C Conexant 1-7
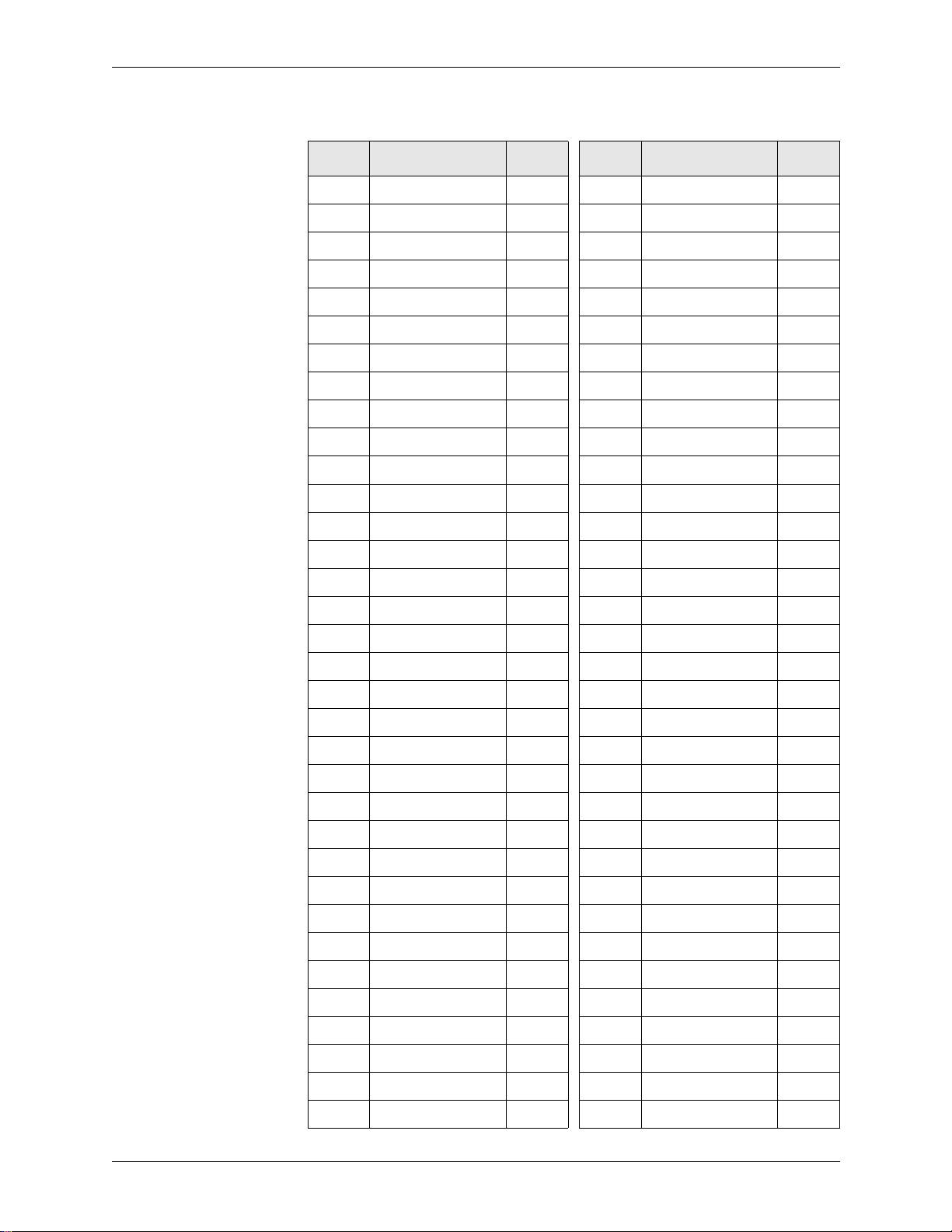
1.0 Product Description Bt8110/8110B
1.2 Pin Descriptions High-Capacity ADPCM Processor
Table 1-3. Bt8110B Pin Descriptions
Pin Pin Label I/O Pin Pin Label I/O
1 GND I 35 GND I
2 PSIG[3] I 36 VCC I
3WR*I37A[13]O
4 PSIG[4] I 38 A[12] O
5 PSIG[5] I 39 CTRL[1] I
6 PSIG[6] I 40 CTRL[0] I
7 PSIG[7] (MSB) I 41 A[11] O
8PSIGEN I42 A[10] O
9VCCI43A[9]O
10 GND I 44 GND I
11 AD[0] I 45 A[8] O
12 AD[1] I 46 A[7] I/O
13 AD[2] I 47 A[6] I/O
14 SERIAL_IN I 48 D[7] I
15 CLOCK I 49 D[6] I
16 SERIAL_OUT O 50 D[5] I
17 VCC I 51 D[4] I
18 GND I 52 GND I
19 AD[3] I 53 VCC I
20 RESET I 54 D[3] I
21 SYNC I 55 D[2] I
22 CS I 56 D[1] I
23 MICREN I 57 D[0] I
24 AD[4] I 58 A[5] I/0
25 AD[5] I 59 A[4] I/O
26 VCC I 60 A[3] I/O
27 GND I 61 A[2] I/O
28 AD[6] I 62 A[1] I/O
29 ALE I 63 A[0] I/O
30 PCM_STB O 64 GND I
31 ADPCM_STB O 65 PSIG[0] I
32 Y O 66 PSIG[1] I
33 TDP O 67 PSIG[2] I
34 SE O 68 VCC I
1-8 Conexant 100060C
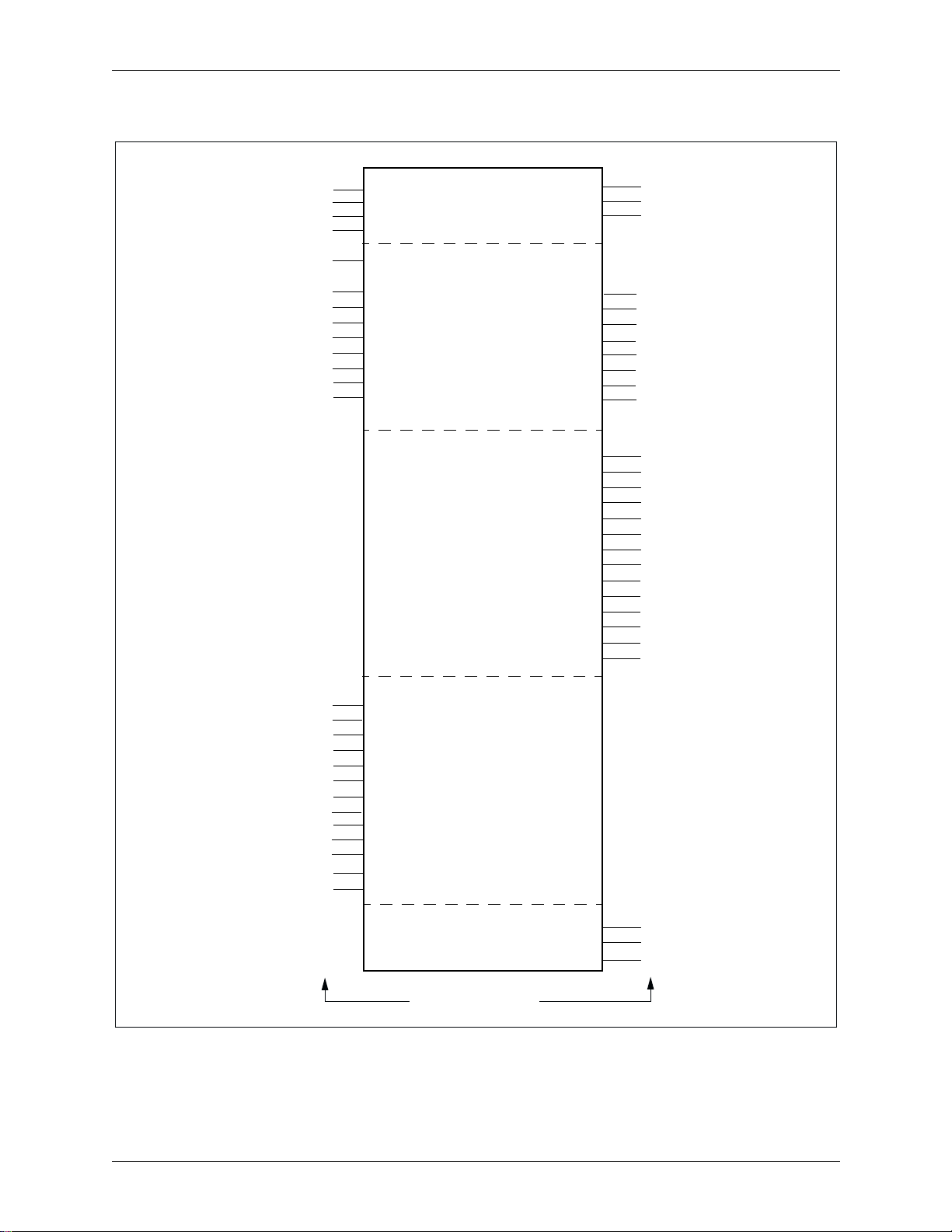
Bt8110/8110B 1.0 Product Description
High-Capacity ADPCM Processor
Figure 1-4. Bt8110B Logic Diagram
Clock In
Sync In
Serial Input
Reset
Parallel Signal Enable
(MSB) Parallel Signal In 7
Parallel Signal In 6
Parallel Signal In 5
Parallel Signal In 4
Parallel Signal In 3
Parallel Signal In 2 I PSIG[2]
Parallel Signal In 1
Parallel Signal In 0
1.2 Pin Descriptions
D[7]
D[6]
D[5]
D[4]
D[3]
D[2]
D[1]
D[0]
A[13]
A[12]
A[11]
A[10]
A[9]
A[8]
A[7]
A[6]
A[5]
A[4]
A[3]
A[2]
A[1]
A[0]
31
30
16
48
49
50
51
54
55
56
57
37
38
41
42
43
45
46
47
58
59
60
61
62
63
ADPCM Strobe
O
PCM Strobe
O
Serial Output
O
ROM Data In/PData Out
I/O
ROM Data In/PData Out
I/O
ROM Data In/PData Out
I/O
ROM Data In/PData Out
I/O
ROM Data In/PData Out
I/O
ROM Data In/PData Out
I/O
ROM Data In/PData Out
I/O
ROM Data In/PData Out
I/O
ROM Address 13
O
ROM Address 12
O
ROM Address 11
O
ROM Address 10
O
ROM Address 9
O
ROM Address 8
O
ROM Address 7
I/O
ROM Address 6
I/O
ROM Address 5
I/O
ROM Address 4
I/O
ROM Address 3
I/O
ROM Address 2
I/O
ROM Address 1
I/O
ROM Address 0
I/O
15
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
21
14
20
8
7
6
5
4
2
67
66
65
CLOCK
SYNC
SERIAL_IN
RESET
PSIGEN
PSIG[7]
PSIG[6]
PSIG[5]
PSIG[4]
PSIG[3]
PSIG[1]
PSIG[0]
Clock and
Serial
Interface
Parallel
Interface
(ROM Interface)
ROM
Interface
ADPCM_STB
SERIAL_OUT
PCM_STB
Microcontroller Enable
Address Latch Enable
Chip Select
Write*
µP Address/Data 6
µP Address/Data 5
µP Address/Data 4
µP Address/Data 1 I AD[1]
µP Address/Data 0
Control Inputs
Control Inputs
23
I
29
I
22
I
3
I
28
I
25
I
24
I
19
IµP Address/Data 3
13
12
11
I
I
39
40
I
MICREN
ALE
CS
WR*
AD[6]
AD[5]
AD[4]
AD[3]
AD[2]IµP Address/Data 2
AD[0]
CTRL[1]
CTRL[0]
I = Input, O = Output
Microprocessor and
Hardware Control
Interface
Test
Interface
SE
34
33
TDP TDP ParameterO
Y O Y Parameter
32
SE Parameter
O
100060_005
100060C Conexant 1-9
1.0 Product Description Bt8110/8110B
1.2 Pin Descriptions High-Capacity ADPCM Processor
Table 1-4. Bt8110/8110B Hardware Signal Definitions (1 of 2)
Pin Label Signal Name I/O Definition
CLOCK Clock I The system clock provided to the Bt8110/8110B. Maximum clock
frequency is 16.5 MHz, and it must have minimum high and low
periods of 27 ns (duty cycle of 45% to 55% at 16.5 MHz, or 22%
to 78% at 8.192 MHz).
SYNC Synchronization I Provides input and output synchronization.
(1)
RESET
ADPCM_STB ADPCM Strobe O Active when the parallel ADPCM inputs and outputs are enabled in
PCM_STB PCM Strobe O Active when the parallel PCM inputs and outputs are enabled in
Clock I and Serial Interface
SERIAL_IN Serial Data Input I This pin has multiplexed PCM and ADPCM signals in interleaved
Reset I Selects the algorithm reset function per ANSI T1.303-1989 and
ITU-T G.726.
interleaved mode, and is active for both PCM inputs and ADPCM
outputs in encoder mode. This pin is disabled in decoder mode.
interleaved mode, and is active for both ADPCM inputs and PCM
outputs in decoder mode. This pin is disabled in encoder mode.
mode; PCM signals for encoder mode, and ADPCM signals for
decoder mode.
SERIAL_OUT Serial Data Output O This pin has multiplexed PCM and ADPCM signals in interleaved
mode; ADPCM signals for encoder mode, and PCM signals for
decoder mode.
PSIGEN Parallel Signal Enable I A control signal that enables parallel inputs. Does not affect parallel
outputs (D[7:0]), which are always available. On the Bt8110B, this
signal has extra functionality (see note in Section 2.2.1.1).
PSIG[7:0] Parallel Signal Input I The parallel input data bus. The most significant bit (sign bit for
PCM, I1 for ADPCM) appears on PSIG[7]. This input bus is also
used to indicate ADPCM word length when embedded decoding is
performed. When serial inputs are used, these inputs should be left
unconnected (internal pull-down resistors included) except as
required for embedded decoding.
Parallel Interface
D[7:0] Parallel Signal Output/
ROM Data Input
Microprocessor Interface
MICREN
(1)
CS
(1)
WR*
(1)
ALE
(1)
Microprocessor Enable I Active high input that selects per-channel control via a
Chip Select I Active high input that enables write operations to the
Write* I Active low input that performs the write operation to the
µP Address Latch
Enable.
I/O On the Bt8110, these signals are inputs, accepting data from the
external lookup table ROM. The data on these pins also provides
parallel PCM and ADPCM output functionality for the Bt8110. On
the Bt8110B, these signals are outputs when internal ROM is used.
D[7] is the most significant bit of the PCM and ADPCM data.
microprocessor interface.
Bt8110/8110B. In hardware mode this pin enables transparent
operation.
Bt8110/8110B. In hardware mode this pin enables A-law PCM
coding (low for µ-law).
I ALE is a microprocessor-generated signal that causes the
Bt8110/8110B to latch in the address on the address/data bus. ALE
is active high with the address being latched on the falling edge of
the signal. In hardware mode this pin becomes an optional code
input.
AD[6:0] µP Address/Data Bus I Microprocessor 7-bit address and data bus.
1-10 Conexant 100060C
Bt8110/8110B 1.0 Product Description
High-Capacity ADPCM Processor
Table 1-4. Bt8110/8110B Hardware Signal Definitions (2 of 2)
Pin Label Signal Name I/O Definition
A[13:0] ROM Address Bus I/O On the Bt8110, these signals are ouputs driving the address lines
on the external lookup table ROM. On the Bt8110B, A[7:0] are
inputs when internal lookup table ROM is used. A[13:8] must be
left open when using the Bt8110B with internal lookup table ROM
enabled.
using Bt8110B with internal lookup table ROM enabled.
enabled, A[0] and A[3] have the following functions:
• A[0] Disable G.726 TR predictor reset. This function forces the
• A[3] Disable even-bit inversion in A-law. This function disables
• A[2:0], A[5:4] are used to allow the Bt8110B to be compatible
• A[7:6] are factory test pins on the Bt8110B that must always
ROM Interface
CTRL[1,0] Control Inputs I On the Bt8110B two new control inputs are provided in place of
Vcc and GND. CTRL[1] (pin 39) is Vcc in the Bt8110, and CTRL[0]
is GND in Bt8110.
1.2 Pin Descriptions
A[7:0] may be left open or held low for normal operation when
When using the Bt8110B with internal lookup table ROM
output TD of block TONE to a value of 0.
even-bit inversion per G.711.
Signal A[0] will be sampled at the same input times as the
code select inputs, and so “disable predict or reset” can be
controlled on a channel-by-channel bases. A[3] is not timed
and so it affects every channel.
with pre-Bt8110 designs.
be open or held at logic low level.
The modes that these new control inputs implement are:
CTRL[1] CTRL[0] Mode
low low Internal ROM only, interleaved,
encode only & decode only modes
low high Internal ROM only, direct framer
interface. This option provides a
hardware-mode direct framer
interface.
high low Bt8110–compatible mode, external
ROM required
high high Not used (production test only)
In Bt8110-compatible mode, existing ROMS will work.
V
CC
GND Ground I Nine pins are provided for ground on the Bt8110. Eight pins are
Supply Voltage
SE SE Parameter O The serial output pin for the SE parameter. Used only for factory
TDP TDP Parameter O The serial output pin for the TDP parameter. Used only for factory
Test Signals
Y Y Parameter O The serial output pin for the Y parameter. Used only for factory test
Supply I Seven pins are provided for supply voltage on the Bt8110. Six pins
are provided on the Bt8110B.
provided on the Bt8110B.
test purposes and should be left unconnected.
test purposes and should be left unconnected.
purposes and should be left unconnected.
NOTE(S):
(1)
All inputs are active high except WR* which adapts to the type of microprocessor being used. See Section 2.1.2.
100060C Conexant 1-11

1.0 Product Description Bt8110/8110B
1.2 Pin Descriptions High-Capacity ADPCM Processor
1-12 Conexant 100060C

2
2.0 Functional Description
2.1 Overview
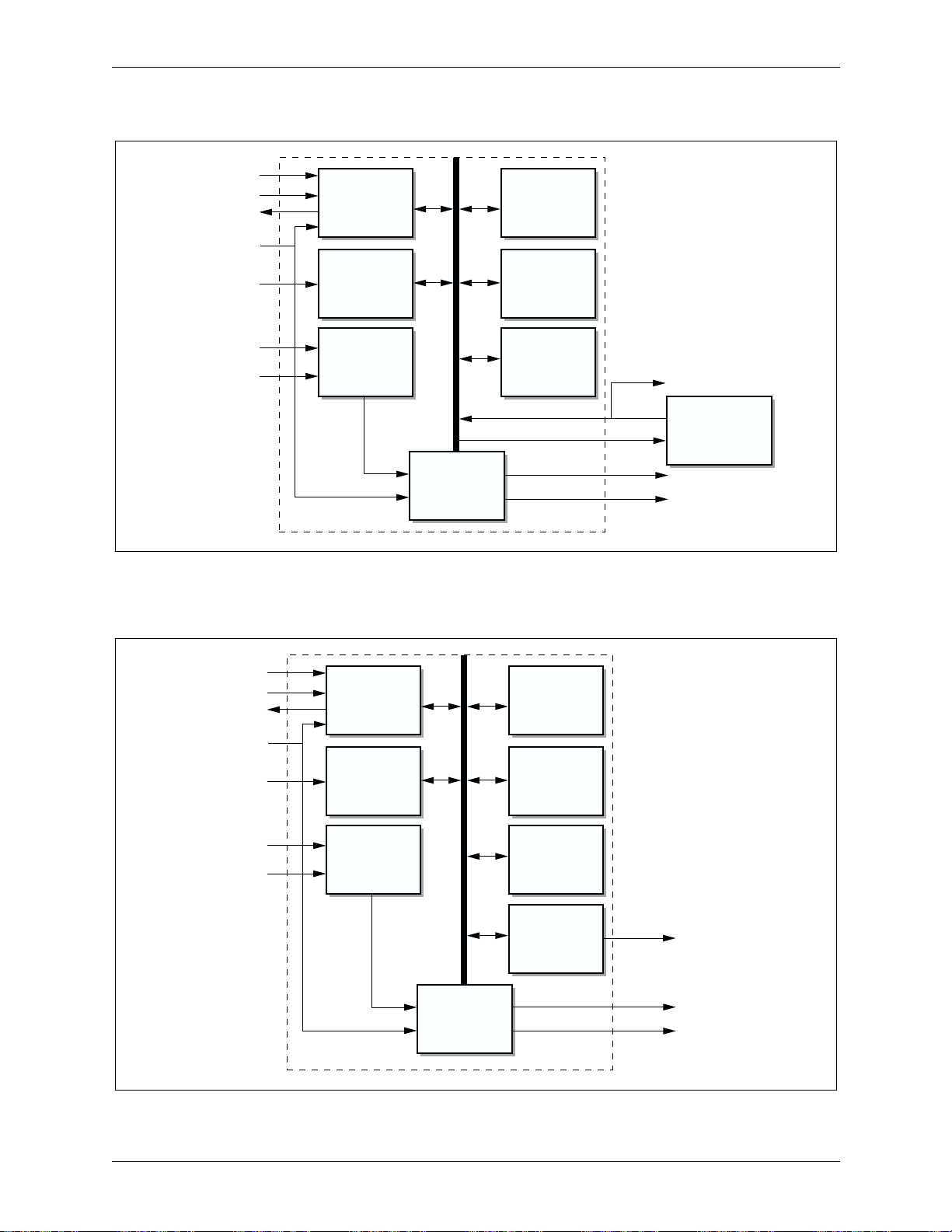
Figure 2-1 and Figure 2-2 illustrate block diagrams for Bt8110 and Bt8110B,
respectively. The quantizer and reconstruction tables are stored in the external
(Bt8110) or internal (Bt8110B) ROM that holds the fixed parameter values and
lookup tables specified in the ADPCM algorithms. Both the encoder and decoder
paths through the ADPCM processor provide the conversion of a 64-kbps µ-law
or A-law PCM channel to and from a 16-, 24-, 32-, or 40-kbit/s ADPCM channel.
The logic is arranged in a serial architecture to take full advantage of time
sharing of common circuitry. In the encoder path, prior to the conversion of the
PCM input to uniform PCM, a difference signal is obtained by subtracting an
estimate of the input signal from the input signal itself. An adaptive 3-, 7-, 15-, or
31-level quantizer (or 4-, 8-, or 16-level for embedded codes) is used to assign
two, three, four, or five binary digits, respectively, to the value of the difference
signal for transmission. An inverse quantizer produces a quantized difference
signal from the corresponding binary digits. The signal estimate is added to this
quantized difference signal to produce the reconstructed version of the input
signal. Both the reconstructed signal and the quantized difference signal are
operated upon by an adaptive predictor that produces the estimate of the input
signal, thereby completing the feedback loop.
The decoder path includes a structure identical to the feedback portion of the
encoder, together with a uniform PCM to µ-law or A-law conversion and
synchronous coding adjustment. The synchronous coding adjustment prevents
cumulative distortion occurring on synchronous tandem codings
(ADPCM-PCM-ADPCM... digital connections) under certain conditions. The
synchronous coding adjustment is achieved by adjusting the PCM output codes in
a manner that eliminates quantizing distortion in the next ADPCM encoding
stage.
100060C Conexant 2-1
2.0 Functional Description Bt8110/8110B
2.1 Overview High-Capacity ADPCM Processor
Figure 2-1. Bt8110 Block Diagram
SYNC
SERIAL_IN
SERIAL_OUT
CLOCK
PSIG[7:0]
ALE, CS,
MICREN
AD[6:0]
Figure 2-2. Bt8110B Block Diagram
Serial
Processor
Parallel
Processor
Microprocessor
Interface
Memory
Control
Quantizer
Adjustment
Memory
Quantizer
Signal
Memory
Predictor
Weight
Memory
Parallel Signal Output
D[7:0]
A[13:0]
Reconstruction
and Quantizer
Table Memory
ADPCM_STB
PCM_STB
100060_006
SYNC
SERIAL_IN
SERIAL_OUT
CLOCK
PSIG[7:0]
ALE, CS,
MICREN
AD[6:0]
Serial
Processor
Parallel
Processor
Microprocessor
Interface
Memory
Control
Quantizer
Adjustment
Memory
Quantizer
Signal
Memory
Predictor
Weight
Memory
Reconstruction
and Quantizer
Table Memory
D[7:0]
Parallel Signal
Output
ADPCM_STB
PCM_STB
100060_007
2-2 Conexant 100060C

Bt8110/8110B 2.0 Functional Description
High-Capacity ADPCM Processor
2.1.1 Clocking and Synchronization
Each operating mode of the Bt8110/8110B requires clock and synchronization
inputs to allow proper operation. If the microprocessor mode is used, then the
synchronization signal frequency can be any submultiple of a PCM frame
(8 kHz). If the hardware mode is used, then the synchronization frequency can be
any submultiple of 1/32 of the clock frequency; in this case the synchronization
signal is used to identify consecutive inputs and outputs.
The CLOCK signal must operate at a frequency of 8.192 MHz to obtain the
8 kHz frame rate for PCM signals. This clock can be gapped and may have a peak
rate of 16.5 MHz (maximum rate of 16.384 MHz is used in the E1 transcoder
application).
The SYNC signal must operate at a submultiple of the 8 kHz frame rate. The
SYNC signal is active on the falling edge; the rising edge can occur anywhere in
the frame. (In direct framer interface mode, the SYNC signal is active on the
rising edge.) The SYNC signal synchronizes internal modulo-32 counters and an
internal word counter. Its falling edge synchronizes the counters, and this can
occur at any submultiple of 8 kHz.
ADPCM_STB and PCM_STB are output timing signals that can be used to
enable three-state inputs to the parallel input bus and to clock the parallel output
bus signals. They are each low for two clock cycles. The rising edge of each
signal can be used to clock the parallel output data into an octal register.
2.1 Overview
2.1.2 Microprocessor Interface
An integral control interface to an Intel 8051-family microprocessor, Motorola
68HC11-family, or equivalent is provided. This microprocessor interface allows
the operation mode and the per-channel configuration of the Bt8110/8110B to be
selected directly from a software-based system. The use of this interface is
optional; it is enabled by setting the MICREN control input high. When MICREN
is set high, all mode and per-channel configuration is done through the
microprocessor. The microprocessor being used should be connected as shown in
Table 2 -1 .
The microprocessor interface to the Bt8110/8110B consists of 11 pins: µP
enable (MICREN) address latch enable (ALE), write enable (WR*), chip select
(CS), and seven multiplexed address/data bits (AD[6:0]). These signals are
connected as shown in Tabl e 2-1 .
The microprocessor interface is designed to allow the direct connection of an
Intel 8051-family or Motorola 68HC11 microprocessor. The chip select input can
be taken from one of the address inputs or from an address decoding circuit to
locate the Bt8110/8110B within any desired memory address range. The chip
select input to the Bt8110/8110B allows the control of multiple circuits from a
single microprocessor.
The microprocessor interface is write-only. Data read from the address space
of the Bt8110/8110B will be invalid.
100060C Conexant 2-3
2.0 Functional Description Bt8110/8110B
2.1 Overview High-Capacity ADPCM Processor
Table 2-1. Signal Connections
Bt8110/8110B
Pin
MICREN
ALE Address Latch Enable ALE AS
WR* Write Enable WR* E
CS Chip Select A[n] A[n]
AD[0] Address/Data AD[0] AD[0]
AD[1] Address/Data AD[1] AD[1]
AD[2] Address/Data AD[2] AD[2]
AD[3] Address/Data AD[3] AD[3]
AD[4] Address/Data AD[4] AD[4]
AD[5] Address/Data AD[5] AD[5]
AD[6] Address/Data AD[6] AD[6]
The interface for the Intel 8051 or Motorola 68HC11 microprocessors
comprises the latch enable signal, the write enable (8051) or enable signal
(68HC11), the chip select signal (one pin from port P2 of the 8051) and the seven
low bits of the 8-bit address/data bus (port P0 of the 8051). For the 68HC11
microprocessor, the enable signal E is connected to the write enable pin. The
setup and hold times required for the latch enable and write enable signals are
10 ns. Other (much faster) processors can be used as long as the multiplexed
address/data bus feature of the 8051 is supported.
Detailed timing requirements for the microprocessor interface are given in
Section 4.1.
Function Intel 8051 Motorola 68HC11
µP Enable
V
CC
V
CC
2.1.3 Address Map
The address map for the controller is given in the Register Summary, Tabl e 3-3
and Tab le 3 -4 , where both interleaved and encoder/decoder operations are shown.
The internal control registers for the 32 encoders and the 32 decoders for
interleaved operation are located at addresses 0x00–0x3F. A write to address 0x40
will load the Mode Control Register [mode; 0x40].
2-4 Conexant 100060C

Bt8110/8110B 2.0 Functional Description
High-Capacity ADPCM Processor
2.2 Modes of Operation
This section details the functional timing of the clock, synchronization, and signal
interfaces. The data and control interfaces include the clock and synchronization
inputs, the PCM and ADPCM inputs and outputs, and the control inputs to select
algorithm reset, transparent operation, PCM code type, and the selected coding
algorithm when the microprocessor interface is not selected. The 24- or
32-channel full-duplex interleaved encoder and decoder operation is presented
first, followed by 48- or 64-channel encoder-only operation, and 48- or
64-channel decoder-only operation.
2.2.1 24- or 32-Channel Full-Duplex Interleaved Operation
Figure 2-3 illustrates the operation of the Bt8110/8110B in 24- or 32-channel
full-duplex interleaved mode with microprocessor control. The channel numbers
in parentheses are for the 24-channel full-duplex mode. In this diagram, inputs
are shown changing on negative edges of the input clock, and outputs are shown
changing on positive edges. This is the recommended method for operating the
Bt8110/8110B to avoid any timing problems. Detailed timing parameters are
given in Chapter 4.0.
To operate the Bt8110/8110B in the 24- or 32-channel full-duplex interleaved
mode, the Mode Control Register located at address 0x40 should be set to a value
of 0x0C for 32 channels, 0x04 for 24 channels.
In many 24-channel configurations, a gapped clock will be used to account for
the frame bit of the T1 signal; this operates correctly as long as there are exactly
32 clock cycles per channel processed.
2.2 Modes of Operation
100060C Conexant 2-5

2.0 Functional Description Bt8110/8110B
2.2 Modes of Operation High-Capacity ADPCM Processor
Figure 2-3. Input and Output Timing for 24- or 32-Channel Full-Duplex Interleaved Operation (Microprocessor Control)
Ref. Cycle
8.192
(6.144) MHz
Clock
SYNC
ADPCM_STB
PCM_STB
4.096
(3.072) Mbit/s
SERIAL_IN
PSIG[7:0]
RESET
SERIAL_OUT
D[7:0]
D[7:0] Int
NOTE(S):
(1) Bt8110B only.
(1)
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31
I1 I2 I3 I4 I5 I1 I2 I3 I4 I5S 234 5678
ADPCM-31 (23)
ADPCM-31 (23) ADPCM-0PCM-0
ADPCM-0PCM-0
I1 I2 I3 I4 I55678
ADPCM-30 (22)
PCM-29 (21)
ADPCM-30 (22)
PCM-29 (21)
PCM-29 (21)
ADPCM-0PCM-0
I1 I2S23 4 56 78
ADPCM-31 (23)ADPCM-30 (22)
ADPCM-31 (23)
100060_008
2.2.1.1 Signal Inputs
and
Outputs
Either serial or parallel signal inputs can be used in all modes. When the PSIGEN
input is tied high, the parallel signal inputs for both PCM and ADPCM are
enabled.
The SERIAL_IN signal contains the serial PCM encoder input, sign bit first,
and the serial ADPCM input. (The ADPCM values are preceded by I with I1
being the most significant bit.) The input is applied at a rate of 4.096 Mbit/s
(3.072 Mbit/s for 24-channel). The timing is arranged as shown so that the middle
of bit 3 of the ADPCM is coincident with falling edges of SYNC. For codes of
less than 5 bits, the unused serial input ADPCM bits must be set to zero.
The PSIG[7:0] signal is used for the signal input when PSIGEN is high. It is
also used for the ADPCM word length indication when embedded decoding is
performed. Table 2 -2 is the arrangement of the input bits on the bus.
NOTE: On the Bt8110B only, a latch has been added to the parallel input signal
enable, PSIGEN. This signal now has the same input timing as the parallel
input itself. This allows different inputs for the encoder and decoder,
respectively, in interleaved mode, and using the serial input for idle code
insertion under control of PSIGEN when the normal input is parallel
mode, or vice versa.
2-6 Conexant 100060C
 Loading...
Loading...