Page 1

M
-
3
p
SD
300L
Satellite Modem
Installation and O
IMPORTANT NOTE: The information contained in this document supersedes all previously
published information regarding this product. Product specifications are subject to change
without prior notice.
Part Number MN/SDM300L3.IOM Revision 1
eration Manual
Page 2

Page 3

SDM-300L3
Comtech EF Data is an ISO 9001
Registered Company.
Satellite Modem
Installation and Operation Manual
Part Number MN/SDM300L3.IOM
Revision 1
July 25, 2004
Copyright © Comtech EF Data, 2000. All rights reserved. Printed in the USA.
Comtech EF Data, 2114 West 7th Street, Tempe, Arizona 85281 USA, 480.333.2200, FAX: 480.333.2161.
Page 4

Customer Support
Contact the Comtech EF Data Customer Support Department for:
• Product support or training
• Information on upgrading or returning a product
• Reporting comments or suggestions concerning manuals
A Customer Support representative may be reached at:
Comtech EF Data
Attention: Customer Support Department
2114 West 7th Street
Tempe, Arizona 85281 USA
480.333.2200 (Main Comtech EF Data Number)
480.333.4357 (Customer Support Desk)
480.333.2161 FAX
or, E-Mail can be sent to the Customer Support Department at:
service@comtechefdata.com
Contact us via the web at www.comtechefdata.com
1. To return a Comtech EF Data product (in-warranty and out-of-warranty) for
repair or replacement:
2. Request a Return Material Authorization (RMA) number from the Comtech EF
Data Customer Support Department.
3. Be prepared to supply the Customer Support representative with the model
number, serial number, and a description of the problem.
4. To ensure that the product is not damaged during shipping, pack the product in
its original shipping carton/packaging.
5. Ship the product back to Comtech EF Data. (Shipping charges should be
prepaid.)
For more information regarding the warranty policies, see, p. xviii.
.
ii
Page 5

Table of Contents
CHAPTER 1. INTRODUCTION............................................................................................. 1–1
1.1 Overview....................................................................................................................... 1–3
1.2 Options Summary........................................................................................................ 1–3
1.3 Comtech EF Data Part Numbers ................................................................................ 1–4
1.4 FAST Accessible Options........................................................................................... 1–5
1.5 Compatibility................................................................................................................ 1–6
1.6 Description of the Modulator...................................................................................... 1–6
1.6.1 Overview................................................................................................................................1–6
1.6.2 Description.............................................................................................................................1–6
1.6.3 Description of Modulation Types ...........................................................................................1–7
1.6.4 BPSK Encoding .....................................................................................................................1–8
1.6.5 QPSK Encoding.....................................................................................................................1–8
1.6.6 OQPSK Encoding..................................................................................................................1–9
1.6.7 8-PSK Encoding ....................................................................................................................1–9
1.7 Description of the Demodulator............................................................................... 1–10
1.7.1 Overview..............................................................................................................................1–10
1.7.2 Functional Description .........................................................................................................1–11
1.8 Description of Monitor & Control............................................................................. 1–12
1.8.1 Overview..............................................................................................................................1–12
1.8.2 Functional Description .........................................................................................................1–13
1.9 Dimensional Envelope .............................................................................................. 1–15
iii
Page 6

SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
Preface MN/SDM300L3.IOM
CHAPTER 2. INSTALLATION/ UPGRADES ....................................................................... 2–1
2.1 Unpacking .................................................................................................................... 2–1
2.2 Installation.................................................................................................................... 2–2
2.3 Software and Hardware Installation/Upgrades ......................................................... 2–4
2.3.1 Overhead Interface PCB Installation .....................................................................................2–4
2.3.2 Reed-Solomon PCB ..............................................................................................................2–6
2.3.3 Turbo Codec Installation........................................................................................................2–8
2.4 Data I/O Interface Connector (J8) Removal/Installation......................................... 2–11
2.5 Hardware Upgrades................................................................................................... 2–14
2.5.1 Main PCB Firmware Chips .................................................................................................2–14
2.5.2 Overhead Interface PCB Firmware Chips ..........................................................................2–14
2.6 Flash Upgrading ........................................................................................................ 2–16
CHAPTER 3. CONNECTOR PINOUTS ................................................................................ 3–1
3.1 Connector Overview.................................................................................................... 3–1
3.2 Connector Description................................................................................................ 3–3
3.2.1 Remote Connector and Pinouts (J6) .....................................................................................3–3
3.2.2 Fault Connector and Pinouts (J7)..........................................................................................3–4
3.2.3 Data I/O Interface Connector (J8) .........................................................................................3–5
3.2.4 G.703 T1, E1/ASYNC Interface Adapter .............................................................................3–11
3.2.5 Auxiliary 1 Connector and Pinouts (J9) ...............................................................................3–12
3.2.6 Alarms Connector and Pinouts (J10) ..................................................................................3–13
3.2.7 RF Output Connector (CP1)................................................................................................3–13
3.2.8 External Reference (CP2) ...................................................................................................3–13
3.2.9 RF Input Connector (CP3)...................................................................................................3–13
3.2.10 AC Power Connector...........................................................................................................3–14
3.2.11 Ground Connector (GND)....................................................................................................3–14
CHAPTER 4. FRONT PANEL OPERATION ....................................................................... 4–1
4.1 Front Panel................................................................................................................... 4–1
4.2 LED Indicators ............................................................................................................. 4–2
4.3 Front Panel Keypad..................................................................................................... 4–3
4.4 Menu System ............................................................................................................... 4–4
4.5 Menu Tree..................................................................................................................... 4–6
iv
Page 7

SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
Preface MN/SDM300L3.IOM
4.6 Opening Screen ........................................................................................................... 4–7
4.6.1 FUNCTION SELECT: CONFIGURATION.............................................................................4–7
4.6.2 FUNCTION SELECT: MONITOR........................................................................................4–61
4.6.3 FUNCTION SELECT: FAULTS/ALARMS ...........................................................................4–68
4.6.4 FUNCTION SELECT: STORED FLTS/ALMS .....................................................................4–74
4.6.5 FUNCTION SELECT: REMOTE AUPC (Conditional).........................................................4–79
4.6.6 FUNCTION SELECT: UTILITY............................................................................................4–83
4.7 SDM-300L Custom Modem Defaults ...................................................................... 4–129
CHAPTER 5. MODEM TYPE ............................................................................................... 5–1
5.1 Modem Type................................................................................................................. 5–1
5.2 IDR Operation ............................................................................................................. 5–2
5.3 IBS Operation............................................................................................................... 5–3
5.3.1 309 IBS Operation .................................................................................................................5–3
5.3.2 VSAT IBS Operation..............................................................................................................5–3
5.4 D&I Operation .............................................................................................................. 5–4
5.5 ASYNC/AUPC Operation............................................................................................. 5–5
5.6 Closed Network Operation (Comtech EF Data) ........................................................ 5–6
5.7 Custom Operation ....................................................................................................... 5–8
5.8 Reed-Solomon Modes................................................................................................. 5–9
CHAPTER 6. CLOCKING AND RX BUFFERING SETTINGS ............................................ 6–1
6.1 Clocking Options......................................................................................................... 6–1
6.1.1 EIA-232, EIA-422, or V.35 Master/Master.............................................................................6–1
6.1.2 EIA-232, EIA-422, or V.35 Master/Slave...............................................................................6–1
6.2 IDR/IBS G.703 Master/Master ..................................................................................... 6–2
6.2.1 IDR/IBS G.703 Master/Slave.................................................................................................6–2
6.2.2 D&I G.703 Master/Master......................................................................................................6–3
6.3 Buffering....................................................................................................................... 6–9
6.4 Doppler ....................................................................................................................... 6–12
6.5 Plesiochronous.......................................................................................................... 6–13
6.6 ASymmetrical Loop Timing ...................................................................................... 6–14
v
Page 8

SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
Preface MN/SDM300L3.IOM
6.7 Frame/Multiframe Length.......................................................................................... 6–17
6.7.1 Multiples of the Frame Length.............................................................................................6–17
6.7.2 Total Buffer Length ..............................................................................................................6–17
6.7.3 Converting Between Bits and Seconds ...............................................................................6–17
CHAPTER 7. FEC AND TURBO .......................................................................................... 7–1
7.1 Introduction.................................................................................................................. 7–1
7.2 Coding .......................................................................................................................... 7–2
7.3 Turbo Product Codec (Hardware Option) ................................................................. 7–2
7.3.1 Introduction ............................................................................................................................7–2
7.3.2 Mod/Demod Processing Delay..............................................................................................7–3
7.3.3 Comparison of all TPC Modes...............................................................................................7–4
7.4 Uncoded Operation (No FEC)..................................................................................... 7–5
CHAPTER 8. SYSTEM CHECKOUT .................................................................................... 8–1
8.1 System Checkout ........................................................................................................ 8–1
8.1.1 Interface Checkout ................................................................................................................8–2
8.1.2 Modulator Checkout ..............................................................................................................8–3
8.1.3 Demodulator Checkout..........................................................................................................8–5
CHAPTER 9. FAULT ISOLATION........................................................................................ 9–1
9.1 Fault Isolation .............................................................................................................. 9–1
9.1.1 System Faults/Alarms............................................................................................................9–2
9.1.2 Faults/Alarms Display............................................................................................................9–2
9.1.3 Faults/Alarms Analysis ..........................................................................................................9–2
CHAPTER 10. OPEN NETWORK OPERATIONS............................................................. 10–1
10.1 Introduction................................................................................................................ 10–1
10.2 IBS............................................................................................................................... 10–1
10.3 IDR .............................................................................................................................. 10–5
10.4 Drop & Insert (D&I) .................................................................................................... 10–9
10.4.1 Description of D&I Operation.............................................................................................10–11
10.4.2 D&I Framing Formats ........................................................................................................10–14
10.4.3 D&I Modem Defaults .........................................................................................................10–17
10.5 2xADPCM Voice in 64 kbps IBS ............................................................................. 10–18
vi
Page 9

SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
Preface MN/SDM300L3.IOM
CHAPTER 11. ASYNCHRONOUS INTERFACE/AUPC ...................................................... 11–1
11.1 Asynchronous Interface/AUPC ................................................................................ 11–1
11.2 AUPC .......................................................................................................................... 11–4
11.2.1 AUPC – Between Two Modems..........................................................................................11–5
11.2.2 Self-Monitoring Local Modem AUPC Control ......................................................................11–6
11.3 ASYNC........................................................................................................................ 11–7
11.3.1 Terrestrial Data Interfaces ...................................................................................................11–7
11.3.2 ASYNC Data Interfaces.......................................................................................................11–7
11.3.3 MUX Operation....................................................................................................................11–8
11.3.4 DEMUX Operation...............................................................................................................11–8
11.3.5 Buffer Operation ..................................................................................................................11–8
11.3.6 Loop Timing Operation ........................................................................................................11–9
11.3.7 Baseband Loopback Operation...........................................................................................11–9
11.3.8 Non-ASYNC Operation......................................................................................................11–10
11.4 ASYNC Channel EIA-485 2- and 4-Wire Operation ............................................... 11–10
11.4.1 Valid ASYNC Baud Rates .................................................................................................11–11
11.4.2 Front Panel Operation .......................................................................................................11–11
11.4.3 ASYNC Remote Operation................................................................................................11–12
11.4.4 ASYNC/AUPC Modem Defaults........................................................................................11–24
CHAPTER 12. G.703 ............................................................................................................ 12–1
CHAPTER 13. FULLY ACCESSIBLE SYSTEM TOPOLOGY (FAST)................................ 13–1
CHAPTER 14. SPECIFICATIONS..................................................................................... 14–1
14.1 Specifications ............................................................................................................ 14–1
14.2 Specification Summary............................................................................................. 14–3
14.3 L-Band Modulator Specification Summary ............................................................. 14–4
14.4 Demodulator Specification Summary...................................................................... 14–5
vii
Page 10

SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
Preface MN/SDM300L3.IOM
14.5 L-Band Modulator Specifications ............................................................................ 14–6
14.5.1 Digital Data Rate .................................................................................................................14–6
14.5.2 Modulation and Encoding Types .........................................................................................14–8
14.5.3 Scrambling Types................................................................................................................14–9
14.5.4 Modulator Frequency Reference.........................................................................................14–9
14.5.5 Modulator Spurious Emissions..........................................................................................14–10
14.5.6 Modulator Phase Noise .....................................................................................................14–10
14.5.7 Modulator IF Output Spectrum Shape...............................................................................14–10
14.5.8 L-Band INMARSAT Spurious Emissions...........................................................................14–10
14.5.9 Differential Encoder ...........................................................................................................14–11
14.5.10 BPSK Bit Ordering.........................................................................................................14–11
14.5.11 Interleaver (Reed-Solomon Codec)...............................................................................14–11
14.5.12 Modulator Transmit Frequency (IF) ...............................................................................14–11
14.5.13 Transmit Frequency Change Time ................................................................................14–11
14.5.14 Modulator Transmit IF Output Switch............................................................................14–11
14.5.15 Modulator Transmit IF Power ........................................................................................14–11
14.5.16 Modulator Power Offset.................................................................................................14–12
14.5.17 Modulator I / Q Imbalance .............................................................................................14–12
14.5.18 Modulator Output Noise Floor .......................................................................................14–12
14.5.19 Modulator Spectrum Rotation........................................................................................14–12
14.5.20 Modulator Output Return Loss ......................................................................................14–12
14.5.21 L-Band ODU Reference Signal .....................................................................................14–12
14.5.22 L-Band ODU Control and Monitor .................................................................................14–12
14.5.23 Modulator Transmit IF Test Modes................................................................................14–12
14.5.24 L-Band ODU Supply Voltage.........................................................................................14–13
14.5.25 ODU DC Current Sense ................................................................................................14–13
14.6 Encoding .................................................................................................................. 14–13
14.6.1 BPSK Encoding .................................................................................................................14–13
14.6.2 OQPSK Encoding..............................................................................................................14–14
14.6.3 8PSK Encoding .................................................................................................................14–14
14.7 L-Band Demodulator Specifications...................................................................... 14–15
14.7.1 Digital Data Rate ...............................................................................................................14–15
14.7.2 Demodulation and FEC Decoding Types ..........................................................................14–17
14.7.3 Descrambling Types..........................................................................................................14–18
14.7.4 Differential Decoder...........................................................................................................14–18
14.7.5 BPSK Bit Ordering.............................................................................................................14–18
14.7.6 Deinterleaver (Reed-Solomon Codec) ..............................................................................14–18
14.7.7 Demodulator Spectrum Rotation .......................................................................................14–19
14.7.8 Receive Frequency............................................................................................................14–19
14.7.9 Input Overload ...................................................................................................................14–19
14.7.10 Demodulator Input Return Loss.....................................................................................14–19
14.7.11 LNB Prime Power ..........................................................................................................14–19
14.7.12 LNB Band Control..........................................................................................................14–19
14.7.13 LNB Reference Signal ...................................................................................................14–19
14.7.14 Receive Input Power (Composite).................................................................................14–20
14.7.15 Demodulator Input Shape..............................................................................................14–20
14.7.16 Receive Input Power (Desired Carrier) .........................................................................14–21
14.7.17 Demodulator Channel Spacing/Adjacent Carrier Performance.....................................14–21
viii
Page 11

SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
Preface MN/SDM300L3.IOM
14.8 Bit Error Rate Performance .................................................................................... 14–22
14.8.1 Performance With Noise, Viterbi Decoder, and Closed Network ......................................14–22
14.8.2 Performance With Noise, Viterbi Decoder, and Reed-Solomon (Optional) ......................14–22
14.8.3 Performance With BPSK and {O}QPSK BER Performance..............................................14–22
14.8.4 Performance with Noise Turbo Product Codec (Optional) ................................................14–23
14.8.5 Performance With Noise, 1544 kbps Sequential Decoder and Reed .......................................
Solomon(Optional)..............................................................................................................14–23
14.8.6 Performance With Noise, 56 kbps Sequential Decoder (Optional) ...................................14–23
14.8.7 Performance With Noise, 1544 kbps Sequential Decoder (Optional) ...............................14–24
14.8.8 BER Threshold ..................................................................................................................14–24
14.9 Acquisition Time...................................................................................................... 14–25
14.9.1 Receive Carrier Acquisition Range....................................................................................14–26
14.9.2 Receive Carrier Reacquisition ...........................................................................................14–26
14.9.3 AGC Output .......................................................................................................................14–26
14.9.4 Doppler Tracking Performance..........................................................................................14–26
14.10 Interface Specifications .......................................................................................... 14–27
14.10.1 TX Clock Switching Due to Failure of Selected Clock...................................................14–27
14.10.2 TX Clock Phase Adjustment..........................................................................................14–27
14.10.3 TX Data Phase Adjustment ...........................................................................................14–27
14.10.4 Transmit Clock Source ..................................................................................................14–27
14.10.5 Send Clock Timing Source ............................................................................................14–27
14.10.6 Doppler/Plesiochronous Buffer Clock Source ...............................................................14–28
14.10.7 RX Clock Switching Due to Failure of Selected Clock ..................................................14–28
14.10.8 RX Clock Phase Adjustment .........................................................................................14–28
14.10.9 RX Clock Jitter ...............................................................................................................14–28
14.10.10 RX Data Phase Adjustment...........................................................................................14–28
14.10.11 Buffer Centering.............................................................................................................14–28
14.10.12 Receive Doppler/Plesiochronous Buffer Size................................................................14–29
14.10.13 Switch Faults .................................................................................................................14–29
14.11 Decoding .................................................................................................................. 14–29
14.11.1 BPSK Decoding .............................................................................................................14–29
14.11.2 QPSK Decoding.............................................................................................................14–29
14.11.3 OQPSK Decoding (Optional).........................................................................................14–30
14.11.4 8PSK Decoding .............................................................................................................14–30
14.12 Terrestrial Interface Types...................................................................................... 14–31
14.12.1 EIA-232 Specification ....................................................................................................14–31
14.12.2 V.35 Specification V.10, V.11 Specification, Circuit Supported ....................................14–32
14.12.3 EIA-449/EIA-422 Mil-188-114A Specification................................................................14–33
14.12.4 Optional G.703 with ASYNC (Requires optional Overhead Card) ................................14–33
14.13 Asynchronous Overhead Specification (Optional) .............................................. 14–34
14.13.1 Asynchronous Baud Rates ............................................................................................14–35
14.13.2 Asynchronous Overhead Data Format..........................................................................14–35
14.13.3 Asynchronous Overhead Parameters ...........................................................................14–35
14.13.4 AUPC with Reed-Solomon Option.................................................................................14–35
14.13.5 Turbo AUPC ..................................................................................................................14–36
ix
Page 12

SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
Preface MN/SDM300L3.IOM
14.14 IBS (Optional with Overhead Card)........................................................................ 14–36
14.14.1 IBS Primary Data Interfaces ..........................................................................................14–36
14.14.2 IBS Clock and Dejitter ...................................................................................................14–36
14.14.3 IBS Framing...................................................................................................................14–36
14.14.4 IBS Engineering Service Channel .................................................................................14–37
14.14.5 IBS Scrambling ..............................................................................................................14–37
14.15 Drop and Insert (Optional with Overhead Card)................................................... 14–37
14.14.1 D&I Primary Data Interfaces..........................................................................................14–38
14.14.2 D&I Framing...................................................................................................................14–38
14.16 IDR (Optional with Overhead Card) ....................................................................... 14–38
14.16.1 IDR Primary Data Interfaces..........................................................................................14–39
14.16.2 IDR Framing ..................................................................................................................14–39
14.16.3 IDR Engineering Service Channel.................................................................................14–39
14.16.4 Optional: Dual 32 Kpps ADPCM (2XASPCM Audio).....................................................14–39
14.17 System Specifications ............................................................................................ 14–40
14.17.1 Loopback Modes ...........................................................................................................14–40
14.17.2 Test Modes ....................................................................................................................14–40
14.17.3 Remote Control..............................................................................................................14–41
14.17.4 Modem Remote Address...............................................................................................14–41
14.17.5 Monitored Signals..........................................................................................................14–41
14.18 Stored Faults............................................................................................................ 14–42
14.19 Stored Configurations............................................................................................. 14–42
14.20 Interoperability Modes ............................................................................................ 14–42
CHAPTER 15. BUC FSK COMMUNICATIONS ................................................................... 15–1
15.1 Introduction................................................................................................................ 15–1
15.2 Message Structure .................................................................................................... 15–2
15.2.1 Command Message Structure (IDU to ODU)......................................................................15–2
15.2.2 Response Message Structure (BUC to IDU).......................................................................15–3
15.3 Power Class ............................................................................................................... 16–3
APPENDIX A. Remote Control Operation ........................................................................... A–1
APPENDIX B. Burst Mode Modulator Operation ..............................................................B-1
GLOSSARY .............................................................................................................................. g-1
INDEX ........................................................................................................................................ i-1
x
Page 13

SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
Preface MN/SDM300L3.IOM
Figures
Figure 1-1. Block Diagram........................................................................................................................1–2
Figure 1-2. Demodulator Block Diagram................................................................................................1–10
Figure 1-3. M&C Block Diagram.............................................................................................................1–13
Figure 1-4. Dimensional Envelope Drawing...........................................................................................1–15
Figure 2-1. Installation of the Optional Mounting Bracket KT/6228-1 ......................................................2–3
Figure 2-2. Overhead Interface PCB Installation .....................................................................................2–5
Figure 2-3. Reed-Solomon Codec Installation .........................................................................................2–7
Figure 2-4. Turbo Codec Installation ......................................................................................................2–10
Figure 2-5. Data I/O Connector (J8) Removal/Installation .....................................................................2–13
Figure 2-6. Overhead Board with Field-Changeable Chips ...................................................................2–15
Figure 2-7. Main Board Field-Changeable Chips (Shown with Overhead Card Removed)...................2–15
Figure 3-1. SDM-300L3 Rear Panel.........................................................................................................3–2
Figure 4-1. Front Panel View....................................................................................................................4–1
Figure 4-2. Keypad ...................................................................................................................................4–3
Figure 4-3. Menu Tree..............................................................................................................................4–6
Figure 4-4. RF Loopback........................................................................................................................4–21
Figure 4-5. IF Loopback .........................................................................................................................4–22
Figure 4-6. Baseband Loopback ............................................................................................................4–30
Figure 4-7. Interface Loopback ..............................................................................................................4–31
Figure 6-1. EIA-422, EIA-232, or V.35 Master/Master Clocking Diagram................................................6–4
Figure 6-2. EIA-422, EIA-232, or V.35 Master/Slave Clocking Diagram..................................................6–5
Figure 6-3. IDR/IBS G.703 Master/Master Clocking Diagram..................................................................6–6
Figure 6-4. IDR/IBS G.703 Master/Slave Clocking Diagram....................................................................6–7
Figure 6-5. D&I G.703 Master/Master Clocking Diagram.........................................................................6–8
Figure 6-6. Clock Slip .............................................................................................................................6–10
Figure 6-7. Doppler Shift ........................................................................................................................6–11
Figure 6-8. Transmit Section of the Asymmetrical Loop Timing Block Diagram....................................6–15
Figure 6-9. Receive Section of the Asymmetrical Loop Timing Block Diagram.....................................6–16
Figure 7-1. Viterbi Decoder ......................................................................................................................7–7
Figure 7-2. Viterbi Decoder and Reed-Solomon ......................................................................................7–8
Figure 7-3. BPSK and (O)QPSK BER Performance ................................................................................7–9
Figure 7-4. Turbo Product Codec...........................................................................................................7–10
Figure 7-5. Sequential Decoder, Reed-Solomon, and 1544 kbps .........................................................7–11
Figure 7-6. Sequential Decoder and 56 kbps.........................................................................................7–12
Figure 7-7. Sequential Decoder and 1544 kbps.....................................................................................7–13
Figure 8-1. Fault Isolation Test Setup ......................................................................................................8–2
Figure 8-2. Typical Output Spectrum .......................................................................................................8–5
Figure 8-3. Typical Eye Constellations.....................................................................................................8–6
Figure 9-1. SDM-300L Fault Tree ............................................................................................................9–3
Figure 10-1. IBS Interface Block Diagram..............................................................................................10–3
Figure 10-2. IDR Interface Block Diagram .............................................................................................10–7
Figure 10-3. D&I with Asynchronous Overhead Data Flow..................................................................10–10
Figure 10-4. E1 Framing Formats ........................................................................................................10–15
Figure 10-5. T1 Framing Formats ........................................................................................................10–16
Figure 11-1. ASYNC/AUPC Block Diagram ...........................................................................................11–3
Figure 11-2. Remote ASYNC Connection Diagram for Y-Cable..........................................................11–13
Figure 11-3. Remote ASYNC Connection Diagram for Breakout Panel ..............................................11–13
Figure 14-1. Block Diagram....................................................................................................................14–2
Figure 14-2. Carrier Level vs Symbol Rate ..........................................................................................14–21
xi
Page 14

SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
Preface MN/SDM300L3.IOM
Tables
Table 1-1. FAST Options and Required Configurations...........................................................................1–5
Table 2-1. Connector (J8) Matrix............................................................................................................2–11
Table 3-1. Modem Rear Panel Connectors..............................................................................................3–2
Table 3-2. Remote Connector and Pinouts (J6).......................................................................................3–3
Table 3-3. Fault Connector and Pinouts (J7) ...........................................................................................3–4
Table 3-4. 25-Pin D Connector Pinouts....................................................................................................3–6
Table 3-5. 34-Pin Winchester Connector Pinouts (V.35) .........................................................................3–7
Table 3-6. 37-Pin Connector Pinouts (Optional) ......................................................................................3–8
Table 3-7. 50-Pin Connector Pinouts .......................................................................................................3–9
Table 3-8. AUX 1 Connector and Pinouts (J9).......................................................................................3–12
Table 3-9. Alarms Connector and Pinouts (J10) ....................................................................................3–13
Table 4-1. LED Indicators.........................................................................................................................4–2
Table 4-2. SDM-300L Custom Modem Defaults ..................................................................................4–129
Table 4-2. SDM-300L Custom Modem Defaults (Continued) ..............................................................4–130
Table 5-1. Modem Type Selection ...........................................................................................................5–1
Table 5-2. IDR Parameter Settings ..........................................................................................................5–2
Table 5-3. IBS Parameter Settings...........................................................................................................5–3
Table 5-4. D&I Parameter Settings ..........................................................................................................5–4
Table 5-5. N x 64 Chart ............................................................................................................................5–4
Table 5-6. Asynchronous Parameter Settings .........................................................................................5–5
Table 5-7. EFD Closed Network Parameter Settings...............................................................................5–7
Table 5-8. Reed-Solomon Modes ............................................................................................................5–9
Table 7-1. Available TPC Modes..............................................................................................................7–2
Table 7-2. Turbo Product Coding processing delay comparison ..............................................................7–3
Table 8-1. Conversion to S/N and Eb/N0 Chart .......................................................................................8–4
Table 10-1. IBS Modem Defaults ...........................................................................................................10–4
Table 10-2. IDR Modem Defaults...........................................................................................................10–8
Table 10-3. D&I Modem Faults ............................................................................................................10–17
Table 11-1. Setting AUPC Parameters ..................................................................................................11–4
Table 11-2. ASYNC Remote Operation ...............................................................................................11–12
Table 11-3. Local EIA-232 to Remote EIA-232....................................................................................11–14
Table 11-4. Local EIA-232 to Remote EIA-485 (4-Wire)......................................................................11–15
Table 11-5. Local EIA-232 to Remote EIA-485 (2-Wire)......................................................................11–16
Table 11-6. Local EIA-485 (4-Wire) to Remote EIA-232......................................................................11–17
Table 11-7. Local EIA-485 (4-Wire) to Remote EIA-485 (4-Wire)........................................................11–18
Table 11-8. Local EIA-485 (4-Wire) to Remote EIA-485 (2-Wire)........................................................11–19
Table 11-9. Local EIA-485 (2-Wire) to Remote EIA-232......................................................................11–20
Table 11-10. Local EIA-485 (2-Wire) to Remote EIA-485 (4-Wire)......................................................11–22
Table 11-11. ASYNC/AUPC Modem Defaults......................................................................................11–24
Table 12-1. G.703 Specifications ...........................................................................................................12–1
Table 13-1. System Specification Summary ..........................................................................................13–3
Table 13-2. L-Band Modulator................................................................................................................13–4
Table 13-3. Demodulator Specification ..................................................................................................13–5
Table 13-4. Modulator Digital Data Rates ..............................................................................................13–6
Table 13-5. Modulation and Encoding Types.........................................................................................13–8
Table 13-6. Scrambling Types ...............................................................................................................13–9
Table 13-7. Demodulator Digital Data Rate .........................................................................................13–15
Table 13-8. L-Band Demodulation and FEC Decoding Types.............................................................13–17
Table 13-9. Descrambling Types .........................................................................................................13–18
Table 13-10. ASYNC Overhead Parameters .......................................................................................13–35
xii
Page 15

SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
Preface MN/SDM300L3.IOM
About this Manual
This manual provides installation and operation information for the Comtech EF Data
SDM-300L3 satellite modem. This is a technical document intended for earth station
engineers, technicians, and operators responsible for the operation and maintenance of
the SDM-300L3.
Related Documents
The following documents are referenced in this manual:
• Comtech EF Data UB-530 Universal Breakout Panel Installation and Operation
Manual
Conventions and References
Cautions and Warnings
CAUTION indicates a hazardous situation that, if not avoided, may result in
minor or moderate injury. CAUTION may also be used to indicate other
CAUTION
WARN ING
IMPORTANT
unsafe practices or risks of property damage.
WARNING indicates a potentially hazardous situation that, if not avoided,
could result in death or serious injury.
IMPORTANT indicates a statement that is associated with the task
being performed. .
xiii
Page 16

SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
Preface MN/SDM300L3.IOM
Metric Conversion
Metric conversion information is located on the inside back cover of this manual. This
information is provided to assist the operator in cross-referencing non-metric to metric
conversions.
Recommended Standard Designations
Recommended Standard (RS) Designations are equivalent toElectronic Industries
Association (EIA) designations. Reference to either designation is permissible, however,
Comtech EF Data has determined to use only one designator thru-out the manual.
Trademarks
Windows is a trademark of the Microsoft Corporation.
Other product names mentioned in this manual may be trademarks or registered
trademarks of their respective companies and are hereby acknowledged.
Reporting Comments or Suggestions Concerning this Manual
Comments and suggestions regarding the content and design of this manual will be
appreciated. To submit comments, please contact the Comtech EF Data Technical
Publications department: techpub@comtechefdata.com
Overview of Changes to Revision 0
Incorporated Erratas A through N
Incorporated Addendum A
Incorporated engineering updates.
Updated Front Panel Operation menus to SW Version 2.2.1
Updated Remote Control Commands to FW/8460-1AD
xiv
Page 17
SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
Preface MN/SDM300L3.IOM
Electrical Safety
The SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem has been shown to comply with the following safety standard:
• EN 60950: Safety of Information Technology Equipment, including electrical business
machines.
The equipment is rated for operation over the range 85 to 264 volts AC. It has a maximum
power consumption of 55 watts without BUC power supply. Input power increases to 175W
with 100W, 24V BUC power supply at maximum load. Input power increases to 230W with
150W, 48V BUC power supply at maximum load.
FUSES
The SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem is fitted with two fuses, one each for line and neutral
connections. These are contained within the body of the IEC power connector, behind a small
plastic flap.
• Use T3.15A, 20mm fuses.
IMPORTANT
Environmental
The SDM-300L3 must not be operated in an environment where the unit is exposed to
extremes of temperature outside the ambient range 0 to 50°C (32 to 122°F), precipitation,
condensation, or humid atmospheres above 95% RH, altitudes (un-pressurised) greater
than 2000 metres, excessive dust or vibration, flammable gases, corrosive or explosive
atmospheres.
Operation in vehicles or other transportable installations that are equipped to provide a
stable environment is permitted. If such vehicles do not provide a stable environment,
safety of the equipment to EN60950 may not be guaranteed.
For continued operator safety, always replace the fuses with the
correct type and rating.
xv
Page 18
SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
Preface MN/SDM300L3.IOM
Installation
The installation and connection to the line supply must be made in compliance to local or
national wiring codes and regulations.
The SDM-300L3 is designed for connection to a power system that has separate ground,
line and neutral conductors. The equipment is not designed for connection to power
system that has no direct connection to ground.
The SDM-300L3 is shipped with a line inlet cable suitable for use in the country of
operation. If it is necessary to replace this cable, ensure the replacement has an equivalent
specification. Examples of acceptable ratings for the cable include HAR, BASEC and
HOXXX-X. Examples of acceptable connector ratings include VDE, NF-USE, UL, CSA,
OVE, CEBEC, NEMKO, DEMKO, BS1636A, BSI, SETI, IMQ, KEMA-KEUR and
SEV.
International Symbols:
Symbol Definition Symbol Definition
~
Alternating Current
Fuse
Telecommunications Terminal Equipment Directive
In accordance with the Telecommunications Terminal Equipment Directive 91/263/EEC,
this equipment should not be directly connected to the Public Telecommunications
Network.
Protective Earth
Chassis Ground
xvi
Page 19

SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
Preface MN/SDM300L3.IOM
EMC (Electromagnetic Compatibility)
In accordance with European Directive 89/336/EEC, the SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem
has been shown, by independent testing, to comply with the following standards:
Emissions: EN 55022 Class B - Limits and methods of measurement of radio
interference characteristics of Information Technology Equipment.
(Also tested to FCC Part 15 Class B)
Immunity: EN 50082 Part 1 - Generic immunity standard, Part 1: Domestic,
commercial and light industrial environment.
Additionally, the SDM-300L3 has been shown to comply with the following standards:
EN 61000-3-2 Harmonic Currents Emission
EN 61000-3-3 Voltage Fluctuations and Flicker
EN 61000-4-2 ESD Immunity
EN 61000-4-4 EFT Burst Immunity
EN 61000-4-5 Surge Immunity
EN 61000-4-6 RF Conducted Immunity
EN 61000-4-8 Power frequency Magnetic Field Immunity
EN 61000-4-9 Pulse Magnetic Field Immunity
EN 61000-4-11 Voltage Dips, Interruptions, and Variations Immunity
EN 61000-4-13 Immunity to Harmonics
In order that the Modem continues to comply with these standards,
observe the following instructions:
IMPORTANT
• Connections to the transmit and receive IF ports (Type N and Type F, female,
connectors) should be made using a good quality coaxial cable - for example
RG58/U (50Ω or RG59/U (75Ω).
• All 'D' type connectors attached to the rear panel must have back-shells that
provide continuous metallic shielding. Cable with a continuous outer shield
(either foil or braid, or both) must be used, and the shield must be bonded to the
back-shell.
• The equipment must be operated with its cover on at all times. If it becomes
necessary to remove the cover, the user should ensure that the cover is correctly
re-fitted before normal operation commences.
xvii
Page 20

SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
Preface MN/SDM300L3.IOM
Warranty Policy
This Comtech EF Data product is warranted against defects in material and workmanship
for a period of two years from the date of shipment. During the warranty period, Comtech
EF Data will, at its option, repair or replace products that prove to be defective.
For equipment under warranty, the customer is responsible for freight to Comtech EF
Data and all related custom, taxes, tariffs, insurance, etc. Comtech EF Data is responsible
for the freight charges only for return of the equipment from the factory to the customer.
Comtech EF Data will return the equipment by the same method (i.e., Air, Express,
Surface) as the equipment was sent to Comtech EF Data.
Limitations of Warranty
The foregoing warranty shall not apply to defects resulting from improper installation or
maintenance, abuse, unauthorized modification, or operation outside of environmental
specifications for the product, or, for damages that occur due to improper repackaging of
equipment for return to Comtech EF Data.
No other warranty is expressed or implied. Comtech EF Data specifically disclaims the
implied warranties of merchantability and fitness for particular purpose.
Exclusive Remedies
The remedies provided herein are the buyer's sole and exclusive remedies. Comtech EF
Data shall not be liable for any direct, indirect, special, incidental, or consequential
damages, whether based on contract, tort, or any other legal theory.
Disclaimer
Comtech EF Data has reviewed this manual thoroughly in order that it will be an easy-touse guide to your equipment. All statements, technical information, and
recommendations in this manual and in any guides or related documents are believed
reliable, but the accuracy and completeness thereof are not guaranteed or warranted, and
they are not intended to be, nor should they be understood to be, representations or
warranties concerning the products described. Further, Comtech EF Data reserves the
right to make changes in the specifications of the products described in this manual at any
time without notice and without obligation to notify any person of such changes.
If you have any questions regarding your equipment or the information in this manual,
please contact the Comtech EF Data Customer Support Department.
xviii
Page 21

Chapter 1. INTRODUCTION
The SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem is designed to meet the requirements of the Satellite
Digital Communications industry. The modem is a high performance, full duplex modem
compliant with IESS-308/309/310/315, FDC, and V.35 specifications, but also adds
significant other features in Closed Network modes. It offers variable data rates from 2.4
kbps to 5.0 Mbps, in BPSK, QPSK, Offset QPSK, and 8-PSK. Viterbi, Sequential,
concatenated Reed-Solomon (R-S), Trellis Coded Modulation (TCM), and Turbo Product
Coding (TPC) are provided as Forward Error Correction (FEC) options. EIA-232, EIA422, G.703, and V.35 (25-pin) interface types are available. The range of IF frequency
simultaneously covers 950 to 1750 MHz.
Burst Modulator Operation: 19.2 kbps and/or 57.6 kbps 1/2 rate QPSK
SDM-300L3
Satellite Modem
1–1
Page 22
SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
Introduction MN/SDM300L3.IOM
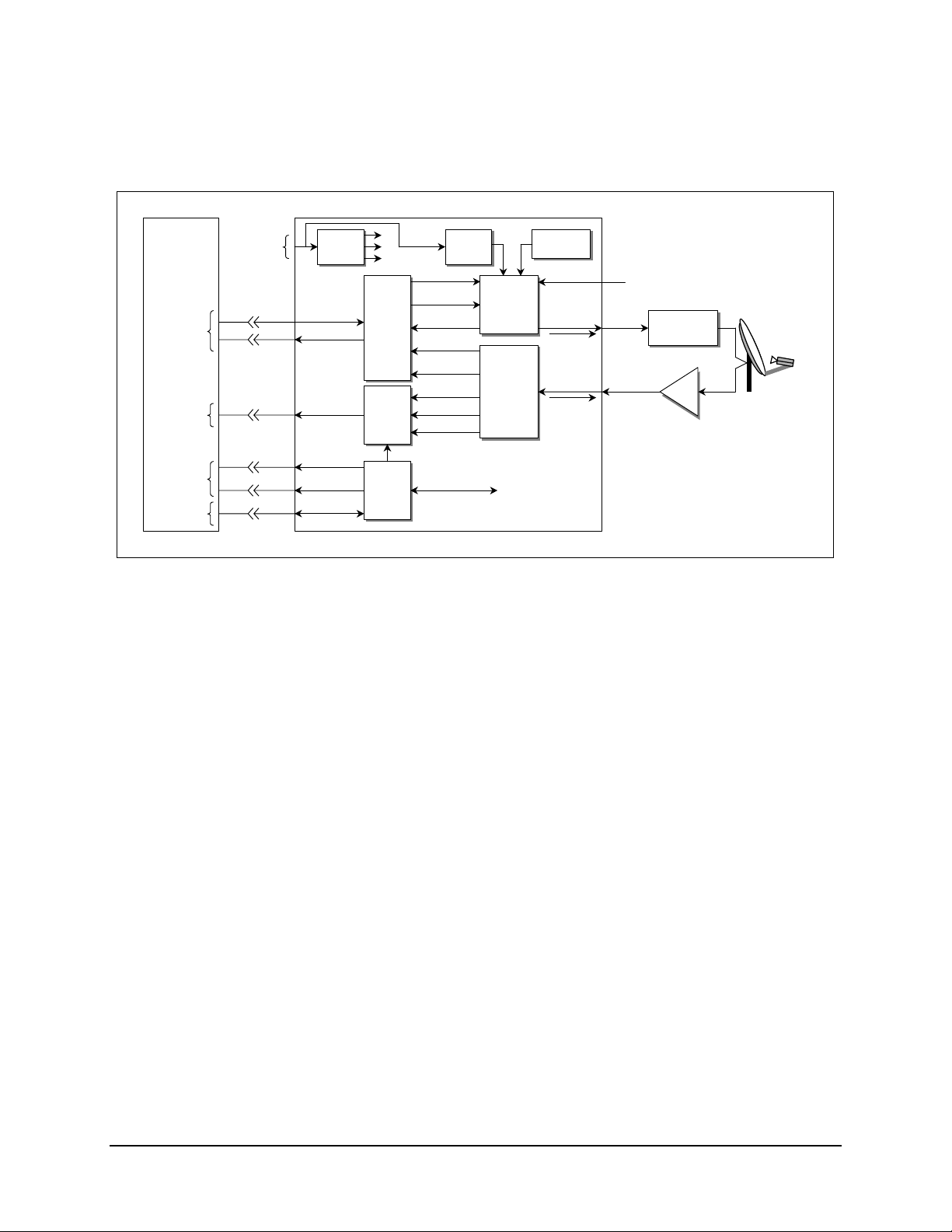
Refer to Figure 1-1 for a system block diagram.
(Optional)
Breakout Panel
UB-530
User
Data
AUX 1
OC-TTL
Faults
Form C
Contacts
Remote
Port
Notes:
1. The UB-530 universal breakout panel (BOP) is an option for V.35, G703, EIA-232, and
2. When the modem is equipped with a 50-pin data I/O connector, the use of the BOP is
3. Contact Comtech EF Data for information concerning universal breakout panels.
AC Or
Optional
DC
Prime
Power
J8
J9
J7
J10
J6
Power
Power
Supply
Supply
AUX 1
Fault Relays
Alarm Relays
Remote Port
Data
Data
Interface
Interface
AUX 1
AUX 1
M&C
M&C
AC Only
Tx Data
Tx Clock
ST Clock
Rx Data
Rx Clock
I/Q
Sat Clock
AGC
Control / Status
Opt ODU
Opt ODU
Supply
Supply
Encoder /
Encoder /
Modulator
Modulator
Demodulator
Demodulator
/ Decoder
/ Decoder
Ref Osc
Ref Osc
Ext Ref
Tx IF
Note 1
Rx IF
Note 2
CP2
CP1
CP3
RF Equipment
Notes:
1) Tx IF (L-Band only) Outputs a 10 MHz
Reference and Optional ODU Voltage.
2) Rx IF Outputs LNB Voltage and 10 MHz
Reference.
SDM-300L Satellite Modem
Figure 1-1. Block Diagram
EIA-422.
required to interface the customer data connector to the modem.
Transmit
Transmit
RF Equipment
LNB
LNB
1–2
Page 23
SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
Introduction MN/SDM300L3.IOM
1.1 Overview
The SDM-300L3 utilizes advanced technology and digital signal processing techniques.
This design eliminates circuitry to perform modem signal processing, resulting in higher
reliability. The following lists the unit's features:
• 2.4 kbps to 5.0 Mbps
• Fully Accessible System Topology (FAST)
• Closed Network Capability
• Automatic Uplink Power Control (AUPC)
• Asynchronous (ASYNC) Channel Unit Overhead
• Reed-Solomon
• Turbo Product Coding
• FAST Acquisition
• Built-In Test
• BPSK, QPSK, OQPSK, and 8-PSK
• BUC FSK Communications
1.2 Options Summary
A summary of the available options for the unit is provided. Contact Comtech EF Data
Customer Support for upgrade information.
Option
Single Data/Code Rate Yes FAST
Low Rate Variable
Full Rate Variable
OQPSK Yes FAST
8-PSK Requires Viterbi, Reed-Solomon
TX/RX L-Band ± 0.02 ppm
TX only, L-Band ± 0.02 ppm
RX only, L-Band ± 1.0 ppm
TX/RX L-Band ± 1.0 ppm
Sequential or Viterbi Codec Modem can be supplied with either:
TX Reed-Solomon Codec Concatenates with Viterbi Yes User
RX Reed-Solomon Codec Concatenates with Viterbi Yes User
Turbo Codec Yes User
Asymmetrical Loop Timing (SCT) Yes FAST
Asynchronous (Async/AUPC) Interface
with 50 pin D Connector
AUPC (No ASYNC) Requires Reed-Solomon cards Yes User or FAST
2xADPCM Voice (included with IBS or
IDR)
Description & Comments
≤ 512 kbps
≤ 5.0 Mbps
Codec. Overhead card required for
Open Network.
L-Band Modem with high stability
reference.
Hardware limited with high stability
reference.
Hardware limited with 1 ppm reference Yes Factory
L-Band modem with 1 ppm reference Yes Factory
Viterbi, Sequential
Requires Overhead Card. Includes
automatic uplink power control (AUPC)
Two voice channels in a 64 kbps IBS
channel. Requiring Overhead card
Availability
Yes FAST
Yes FAST
Yes User
Standard Factory
Yes Factory
Yes FAST
Yes User
Yes
Install
Option
User
1–3
Page 24
SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
Introduction MN/SDM300L3.IOM
Option
G.703 Interface. Note, For BNC or 15 pin
D interface see UB-530 breakout panels.
G.703/ASYNC, Closed Network only BNC-F connectors and ASYNC.
37-Pin Female D Connector EIA-422/EIA-449 Interface and
25-Pin Female D Connector EIA-530 (RS-422), EIA-232 and V.35 Yes User
34-Pin Female V.35 “Winchester” Connector with V.35 Yes User
50-Pin Female D Connector for use
Overhead card.
Without
IBS Interface Requires Overhead Card Yes User
IDR Interface Requires Overhead Card Yes User
Drop & Insert Interface Requires Overhead Card Yes User
Primary Power: Auto-ranging AC 85 to 264
VAC
Primary Power: 48 VDC (Modem only, No
BUC)
ODU DC Power: 24V or 48V. Primary
input = AC Only
Description & Comments
Requires Overhead Card with 50 pin D
Connector
Requires Overhead card
Mil-188-114
Includes EIA-422, EIA-232, and V.35
Use with redundancy switches
Yes Factory
Yes Factory
100W @ 24V
150W @ 48V
Availability
Yes User
Yes User
Yes User
Yes User
Yes Factory
1.3 Comtech EF Data Part Numbers
Part No. Description Remarks
PL/9066-3 RX only IF 1.0 ppm Use with internal reference LNBs.
PL/9066-2 TX only IF 0.02 ppm Hardware limited version
PL/9066-1 TX/RX IF 0.02 ppm Full Duplex
PL/9066-5 TX/RX IF 1.0 ppm Full Duplex (No BUCs)
PL/5727-1 25-pin EIA-530 Interface
PL/6031-1 37-pin EIA-449 Interface
PL/5305-2
PL/5509-2
PL/6167-1 50-pin Interface No Overhead
PL/6032-1 34-pin Interface V.35
PL/5305-2
PL/7838-1
PL/6284 TX Reed-Solomon
PL/6285 RX Reed-Solomon
PL/9394-1 TX/RX Turbo
PL/9658-1 Duplex Reed-Solomon
PS/AC65W01P01 90-264 VAC Modem PS Modem only
PS/DC-DC5V65W -48 VDC Modem PS Modem only
KT/9567-2 90 – 264 VAC, 100W
KT/9567-3 90 – 264 VAC, 150 W
50-pin Interface With Overhead
G.703/ASYNC Interface with Overhead
BUC P/S, 24V, CE Mark
BUC P/S, 48 VDC
Hardware limited version.
Closed Network
24 VDC, 100W
AC BUC Power Supply
48 VDC 150 W
AC BUC Power Supply
Install
Option
1–4
Page 25
SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
Hi
h
V
i
bl
D
t
M/bits)
XXXXXXX
X
Introduction MN/SDM300L3.IOM
1.4 FAST Accessible Options
Comtech EF Data FAST system allows immediate implementation of different options
through the user interface keypad. Some FAST options are available through the basic
platform unit, while others require that the unit be equipped with optional hardware or
that the hardware be installed in the field. Refer to Table 1-1 for a listing of possible
configurations.
The options available through the FAST architecture include:
ASYNC/AUPC*
•
Viterbi Decoder
•
Sequential Decoder
•
8-PSK
•
IDR *
•
Reed-Solomon*
•
2xADPCM Voice*
•
* Optional hardware required.
Asymmetrical loop timing
•
G.703 operation*
•
Variable data rates
•
IBS*
•
D&I
•
OQPSK
•
HARDWARE
Basic Platform SDM-300L3
FAST Option
FAST Option with Reed-
Solomon hardware
FAST Option with Overhead
hardware
Option withTurbo hardware
Notes:
1. The basic modem is shipped with either Sequential or Viterbi decoder.
2. Requires G.703 Interface module and Overhead card.
3. Either IBS Option or IDR option includes 2xADPCM voice in 64 kbps IBS.
4. Duplex Reed-Solomon and Turbo can be installed together, however, only one at a time can
be selected.
Table 1-1. FAST Options and Required Configurations
a
a
e
a
ar
g
Single Data Rate
X
rate (up to 4.375
Low Variable Data
rate(up to 512 k/bits)
X
(Note 1)
Sequential Decoder
X
Viterbi Decoder
(Note
1)
Asymetrical Loop
Timing
X
BUC FSK; DISEQ
OQPSK
8 PSK
Reed-Solomon
CODEC (Note 4)
ASYNC/AUPC
Overhead
X
X X X
Open Network
(IDR/IBS)
Drop and Insert
Turbo CODEC
(Note 4)
G.703 Interface
X
(Note
2)
2 x ADPCM Voice in
X (Note
3)
64 kbps
1–5
Page 26

SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
Introduction MN/SDM300L3.IOM
1.5 Compatibility
The SDM-300L3 is functionally compatible with many Comtech EF Data modems.
When properly configured, the unit will interoperate with the following Comtech EF
Data modems:
• CDM-550/550T • SDM-650B
• CDM-600/600L
(Open Network and Turbo only)
• SDM-100/100A • SDM-8000
• SDM-300/300A
• SDM-6000
1.6 Description of the Modulator
1.6.1 Overview
The modulator provides PSK modulated carriers within the 950 to 1750 MHz range. The
types of modulation that encode the transmitted baseband data from the interface PCB
are:
• BPSK
• QPSK
• OQPSK
• 8-PSK
1.6.2 Description
The modulator is composed of eight basic subsections. These subsections are divided into
the baseband processing section and the RF section of the modulator. The modulator
controls all programmable functions on this module. Fault information from the
modulator is sent to the M&C. Refer to Chapter 9 for a list of reported faults.
The major modulator subsections are:
• Scrambler/Differential Encoder
• Convolutional Encoder
• Programmable Vector Rotation
• I/Q Nyquist Filters
• Modulator
• RF Synthesizer
• Output Amplifier
• Output Level Control
1–6
Page 27

SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
Introduction MN/SDM300L3.IOM
If the modem is so equipped, the optional overhead or Reed-Solomon PCB first processes
the data. The data is then sent to the scrambler for energy dispersal, and then to the
differential encoder. The differential encoder is a 2-bit encoder, which allows for
resolution of two of the four ambiguity states of the QPSK or OQPSK demodulator.
The data is sent to the convolutional encoder for encoding the baseband data. The code
rates 1/2, 3/4, 7/8, and 2/3 are based on the symbol rate range of 2.4 kbps to 2.5 Mbps.
For Viterbi codes, the convolutional encoder encodes the data at 1/2 rate. If the selected
code rate is 3/4, then 2 of every 6 symbols are punctured. For 3 bits in, there are 4
symbols out.
• For Sequential codes, the convolutional encoder generates the parity bits from the
input data stream, which allows for error correction at the far end of the link. The
rate of the encoder may be 1/2, 3/4, and 7/8.
For example, the 7/8 rate puts out 8 symbols for every 7 bits in. In {O}QPSK
mode, the data is split into two separate data streams to drive the I and Q channels
of the modulator.
The baseband processing for the SDM-300L3 is the same as for the SDM-300L1 and
SDM-300A modulator except that the digital modulation is not used. Instead, the
baseband Nyquist filtered I and Q signals pass through D/A converters to drive an analog
vector modulator.
The local oscillator input to the vector modulator is a single loop synthesizer
incorporating a Direct Digital Synthesis (DDS) chip to accommodate 100 Hz steps over
the range of 950 to 1750 MHz. The modulator output then passes through amplifiers and
AGC incorporating programmable output level control and switched low pass filters for
harmonic attenuation.
1.6.3 Description of Modulation Types
The modulation types for the modem include BPSK, QPSK, OQPSK, or 8-PSK.
The PSK data transmission encoding method uses the phase modulation technique. This
method varies the phase angle of the carrier wave to represent a different bit value for the
receiver. The higher levels of modulation are required for an operating range that has a
limited bandwidth.
The order of modulation is represented by mPSK, where “m” relates to the number of
discrete phase angles. Refer to the following list for a brief description of the modulation
types.
• BPSK: 2 discrete phase angles represent the 2 possible states of a symbol.
1–7
Page 28

SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
Introduction MN/SDM300L3.IOM
• QPSK (OQPSK): 4 discrete phase angles represent the 4 possible states of a
symbol.
• 8-PSK: 8 discrete phase angles represent the 8 possible states of a symbol.
Note: The code rate determines the number of symbols per bit.
1.6.4 BPSK Encoding
The modulator converts transmitted baseband data into a modulated BPSK carrier at
2.4 kbps to 1.25 Mbps (1/2 rate). Using vector analysis of the constellation pattern, BPSK
represents one symbol with the carrier phase either at 0° or 180°. The 1/2 rate encoding at
the convolutional encoder provides two symbols output for every bit input.
Uncoded (1/1 rate) BPSK operation also is allowed from 4.8 kbps to 2.5 Mbps.
Code Rate Symbols/Bit Bits/Hz
1/2 2 0.5
1/1 1 1
1.6.5 QPSK Encoding
The modulator converts transmitted baseband data into a modulated QPSK carrier at the
following parameters:
• 4.6 kbps to 5.0 Mbps (1/1 rate, uncoded)
• 4.8 kbps to 2.5 Mbps (1/2 rate)
• 7.2 kbps to 3.75 Mbps (3/4 rate)
• 8.4 kbps to 4.375 Mbps (7/8 rate)
Using vector analysis of the constellation pattern, QPSK represents a symbol with the
carrier phase angle at 45°, 135°, 225°, or 315°. The 1/1, 1/2, 3/4, and 7/8 rates encoded at
the convolutional encoder provide the desired input/output bit rates.
Code Rate Symbols/Bit Bits/Hz
1/1 1 2
1/2 2 1
3/4 1.33 1.5
7/8 1.143 1.75
1–8
Page 29
SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
Introduction MN/SDM300L3.IOM
1.6.6 OQPSK Encoding
The modulator PCB converts the transmitted baseband data into a modulated OQPSK
carrier within the same parameters as QPSK.
The OQPSK modulation is mainly different from QPSK by offsetting the I and Q channel
modulation signals. This offset prevents the RF envelope from going through zero. Under
certain conditions, this may allow less back-off in the High Power Amplifier (HPA)
system. The 1/1, 1/2, 3/4, and 7/8 rates encoded at the convolutional encoder provide the
desired input/output bit rates.
Code Rate Symbols/Bit Bits/Hz
1/1 1 2
1/2 2 1
3/4 1.333 1.5
7/8 1.143 1.75
1.6.7 8-PSK Encoding
The modulator converts transmitted baseband data into modulated 8-PSK carrier at the
following parameters:
• 64 kbps to 5.000 Mbps (2/3 rate)
Using vector analysis of the constellation pattern, 8-PSK represents a symbol with carrier
phase angles at 22.5°, 67.5°, 112.5°, 157.5°, 202.5°, 247.5°, 292.5°, and 337.5°. The 2/3
rate encoding provides the desired input/output bit rates.
Code Rate Symbol/Bit Bit/s Hz
2/3 1.5 2
1–9
Page 30
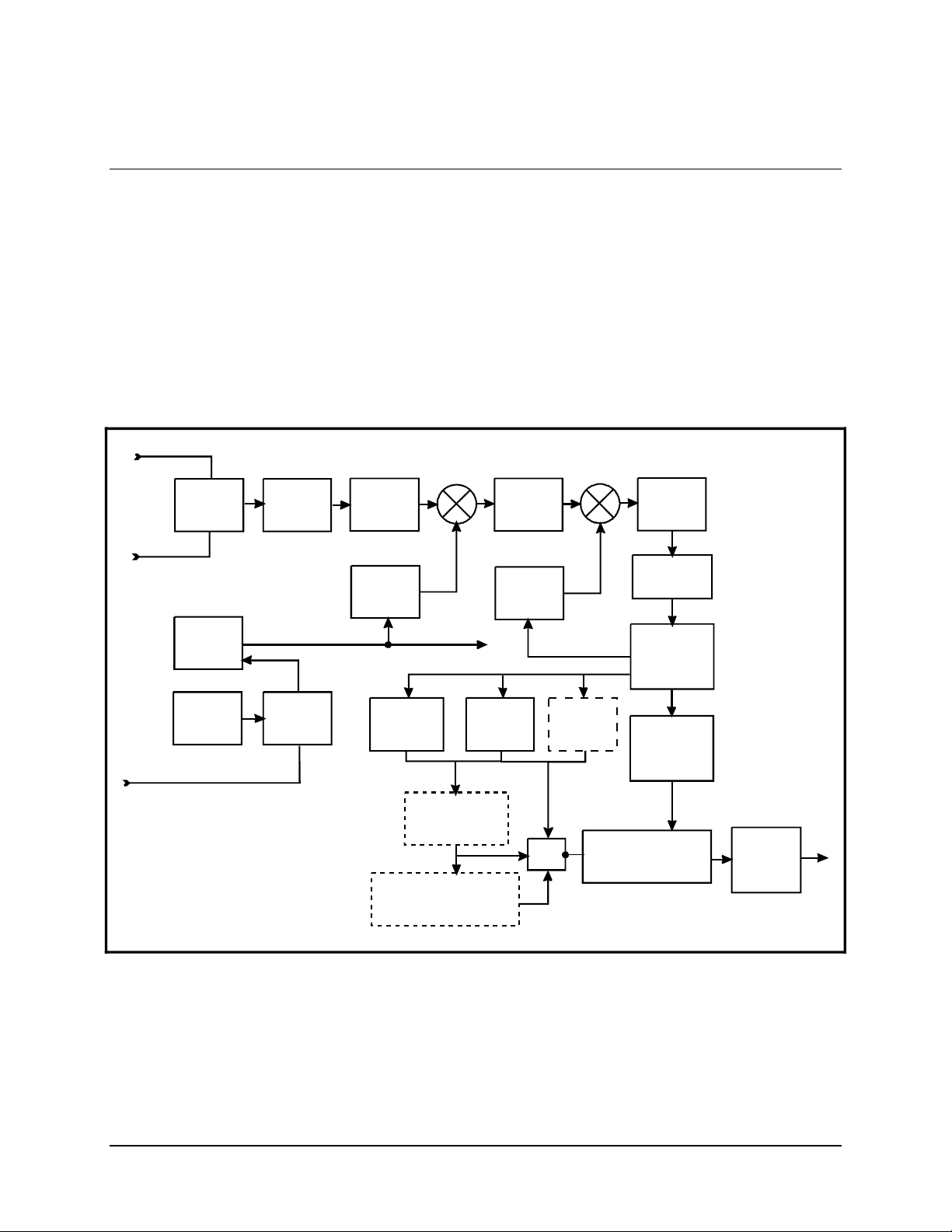
SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
Introduction MN/SDM300L3.IOM
1.7 Description of the Demodulator
A block diagram of the demodulator is shown in Figure 1-2.
1.7.1 Overview
The demodulator converts PSK modulated carriers within the 950 to 1750 MHz range to
a demodulated baseband data stream. The converted modulation types are BPSK, QPSK,
OQPSK, and 8-PSK. The demodulator then performs FEC decoding on the data stream to
produce the error corrected data output to the data interface.
LOOPBACK
L-BAND INPUT
SWITCH
L-BAND INPUT
REF
VCXO
OC XO
OPT
HIGH
STABILITY
EXT REFERENCE
AGC
REF
PLL
LPF BPF
LO #1
REFERENCE
SEQUENTIAL
DECODER
OPTIONAL
REED-SOLOMON
CODEC
OPTIONAL
OVERHEAD DEFRAMING
IBS/IDR, ASYNC/AUPC
DROP & INSERT
LO #2
VITERBI
DECODER
MUX
OPTIONAL
TURBO
CODEC
PLESIOC HRONOUS
BPF
A TO D
CONVERTER
DIGITAL
SIGNAL
PROCESSING
DIGITAL
CLOCK
RECOVERY-
LOOP
DOPPLER/
BUFFER
INTERFACE
Figure 1-2
. Demodulator Block Diagram
1–10
Page 31

SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
Introduction MN/SDM300L3.IOM
1.7.2 Functional Description
The demodulator functions as an advanced, digital, coherent-phase-lock receiver and
decoder. Demodulator faults also are reported to the front panel. The demodulator
consists of the following basic subsections.
• Digital Costas Loop
• RF Section
• Automatic Gain Control
• Analog-to-Digital (A/D) Converter
• Soft Decision Mapping
• Programmable Vector Rotation
• Digital Nyquist Filters
• FEC Decoder
• Digital Clock Recovery Loop
• Decoder
The modulated IF signal at 950 to 1750 MHz enters the RF module for conversion to an
IF frequency. The IF is then sampled by an A to D converter and digitally demodulated.
The I and Q data is then sent to the digital Nyquist filters, resulting in a filtered, digital
representation of the received signal. The digital data is then sent to four separate circuits:
• Automatic Gain Control
• Carrier Recovery (Costas) Loop
• Clock Recovery Loop
• Soft Decision Mapping
The AGC provides a gain feedback signal to the RF section. This closed loop control
ensures that the digital representation of the I and Q channels is optimized for the Costas
and Clock loops, as well as the soft-decision mapping circuitry.
When the active decoder determines that the modem is locked, the M&C stops the sweep
and begins the de-stress process. This involves fine tuning the DDS based on the phase
error in the Costas loop. The de-stress process continues as long as the modem is locked.
If the carrier is interrupted, the M&C resumes the sweep process.
The digital Costas loop, in conjunction with a Direct Digital Synthesizer (DDS), performs
the carrier recovery function. The Costas loop consists of a Costas phase detector, loop
filter, and DDS, all implemented digitally. The DDS performs the function of a
Voltage-Controlled Oscillator (VCO) in an analog implementation, but can be easily
programmed to the desired center frequency via the M&C. The output of the DDS is sent
to the RF module and provides the reference to which the local oscillator is locked. The
M&C sweeps the local oscillator (via DDS programming) through the user-specified
sweep range.
The digital clock loop, in conjunction with another DDS, performs the clock recovery
function. The clock loop consists of a phase detector, loop filter, and DDS, all
1–11
Page 32

SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
Introduction MN/SDM300L3.IOM
implemented digitally. The DDS performs the function of a VCO in an analog
implementation. The recovered data and symbol clocks are then used throughout the
demodulator.
The soft decision mapper converts the digital I and Q data to 3-bit soft decision values.
These values are then fed to the programmable vector rotation circuit, providing
compatibility with spectrum reversal of the I and Q channels.
The output of the vector rotation circuit is then sent to the Viterbi decoder and optional
Sequential decoder. The output is then sent to the optional Reed-Solomon or Overhead
PCB. With the Turbo coding hardware option, the vector rotation circuit output is sent to
the optional Turbo Codec for decoding.
1.8 Description of Monitor & Control
1.8.1 Overview
The Monitor & Control (M&C) monitors the modem and provides configuration updates
to other modems within the modem when necessary. The modem configuration
parameters are maintained in battery-backed RAM, which provides total recovery after
power-down situation. The M&C functions include extensive fault and status reporting.
All modem functions are accessible through a local front panel interface and a remote
communications interface.
A block diagram of the M&C is shown in Figure 1-3.
1–12
Page 33

SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
Introduction MN/SDM300L3.IOM
1.8.2 Functional Description
The M&C card is composed of the following subsections:
• Microcontroller with Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter (UART)
• Digital-to-Analog Converter (DAC)
• Read Only Memory (ROM)
• Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC)
• Read Access Memory (RAM)
• Universal ASYNC
• User Interface
• Fault and Alarm Relays
FAULT
MODEM
AND ALARM
RELAYS
11 M Hz
CLOCK
DAC
ADC
2
IC BUS
CONTROLLER
EIA-232
OR
EIA-485
Figure 1-3
ROM
(M&C,
BULK,
BOOT)
MICRO-
RAM AND
REAL
TIME
CLOCK
9-PIN
REMOTE
. M&C Block Diagram
1–13
Page 34

SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
Introduction MN/SDM300L3.IOM
The heart of the M&C card is the Dallas 80C310 microcontroller operating at 11 MHz.
This microcontroller contains 256 Kbytes of internal RAM. The ROM at U8 is 29F040
(512 Kbytes).
ROM access times must be equal to or greater than 150 ns. The RAM size can be 8 or
32 Kbytes. This RAM chip is internally battery-backed and contains a real time clock
used by the M&C.
The non-volatile RAM on the M&C module allows the module to retain configuration
information without prime power for 1 year (approximately). If the modem is powered
down, the following sequence is carried out by the M&C microcontroller.
1. When power is applied to the M&C, the microcontroller checks the non-volatile
memory to see if valid data has been retained. If valid data has been retained, the
modem is reconfigured to the parameters maintained by the RAM.
2. If the non-volatile memory fails the valid data test, a default configuration from
ROM is loaded into the system.
The UART supports serial ASYNC communications channels (remote port) with a
maximum data rate of 19200 bit/s. The UART is a built-in peripheral of the
microcontroller. The communications type can be EIA-232, EIA-485 (2-wire),
EIA-485 (4-wire), and software selectable.
The DAC supplies a voltage that controls the contrast of the display. The ADC monitors
all the voltages from the power supply. The DAC and ADC are mapped to the
microcontroller with an Integrated Circuit (IC) bus.
The user interface includes the following parts:
• Front panel
• Status LEDs
• Keyboard
• Sounder (beeper)
All functions are memory-mapped to the microcontroller.
1–14
Page 35

SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
Introduction MN/SDM300L3.IOM
1.9 Dimensional Envelope
Refer to Figure 1-2 for the unit’s dimensional envelope drawing.
Note: Dimensions are listed in inches and centimeters are in parentheses.
Figure 1-4. Dimensional Envelope Drawing
1–15
Page 36

SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
Introduction MN/SDM300L3.IOM
This page is intentionally left blank.
1–16
Page 37

Chapter 2. INSTALLATION/
2.1 Unpacking
The modem and manual are packaged in pre-formed, reusable, cardboard cartons
containing foam spacing for maximum shipping protection.
Do not use any cutting tool that will extend more than 1 inch into
the container and cause damage to the modem.
CAUTION
Unpack the modem:
1. Cut the tape at the top of the carton indicated by OPEN THIS END.
2. Remove the cardboard/foam space covering the modem and caddypacks.
3. Remove the modem, caddypacks, manual, and power cord from the carton.
4. Save the packing material for storage or reshipment purposes.
5. Inspect the equipment for any possible damage incurred during shipment.
6. Check the equipment against the packing list to ensure the shipment is correct.
7. Refer to Section 2.2 for installation instructions.
UPGRADES
2–1
Page 38

SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
Installation/Upgrades MN/SDM300L3.IOM
2.2 Installation
The modem arrives fully assembled from the factory. After unpacking the modem, install
the modem as follows:
2.2.1 Modem Installation (Optional)
Refer to Figure 2-1. Use the following mounting kit KT/6228-1.
OPTIONAL: MOUNTING KIT, KT/6228-1 (MODEM TO EQUIPMENT RACK)
QTY Part Number Description
2 FP/6138-1 Bracket, Rear Support
4 HW/10-32x1/2RK Bolt, #10 Rack
2 HW/10-32X1/4 SHC Screw, Socket 10-32 x 1/4inch
Tools Required:
Screw Driver
5/32-inch
Phillips
SAE Allen Wrench
1. Install the IDU rear support brackets as follows:
a. Install provided rear support bracket onto the mounting rail of the rack.
Fasten with provided bracket bolts.
b. Fasten the provided #10 socket head screws to the rear-side mounting
holes on either side of the chassis modem. Mount the modem into the
equipment rack ensuring that the socket heads engage into the slots of the
rear support brackets.
Note: It may be necessary to adjust the location of the rear mounting rails of the rack.
2–2
Page 39

SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
U
Installation/Upgrades MN/SDM300L3.IOM
Equipment
Rack
Mounting
Rail
#10 Socket head
*
screw
BRACKET
*
BOLTS
Support
*
Bracket
* Note: Components of mounting kit KT/6228-1
ID
Figure 2-1. Installation of the Optional Mounting Bracket KT/6228-1
2–3
Page 40

SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
Installation/Upgrades MN/SDM300L3.IOM
2.3 Software and Hardware Installation/Upgrades
2.3.1 Overhead Interface PCB Installation
The overhead interface PCB can be installed at the factory or in the field. The overhead
interface PCB is required to access certain options and functionality of the modem.
Observe the following:
• If the overhead interface PCB is installed at the factory, then the 50-pin interface
relay card will be pre-installed or the G.703/ASYNC card.
• If the overhead interface PCB is installed in the field, then one of four
connector/card combinations will have been shipped with the overhead interface
PCB.
2.3.1.1 Installation
This equipment contains parts and assemblies sensitive to damage by ESD.
Use ESD precautionary procedures when touching, removing, or inserting
CAUTION
The following tool is required to install the overhead interface PCB:
Use the following information to install the overhead interface PCB as a daughter card on
the main PCB. Refer to Figure 2-2 for the installation location of the overhead interface
daughter card.
CAUTION
PCBs.
Description Application
Phillips Screwdriver
Turn the power off before installation. High current VDC is present. Failure
to do so could result in damage to the modem components.
1. Turn off the modem and unplug the power supply.
2. Remove the rear panel retaining screws. Slide the modem assembly out from the
top cover assembly.
3. Install the overhead interface PCB, face down, onto the main PCB by mating the
male header connectors with the female header connectors in the position shown
in Figure 2-2.
4. Align the overhead interface PCB standoffs with the main PCB mounting holes.
Install the four mounting screws and washers.
To remove and replace cross-point screws.
2–4
Page 41

SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
Installation/Upgrades MN/SDM300L3.IOM
The mounting hardware must be installed to provide proper
grounding between the overhead interface PCB and the main PCB.
CAUTION
5. After completing the installation procedure turn on the modem. Select the desired
modem option to use the overhead card.
Overhead
Card
Figure 2-2. Overhead Interface PCB Installation
2–5
Page 42

SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
Installation/Upgrades MN/SDM300L3.IOM
2.3.2 Reed-Solomon PCB
The Simplex TX/RX Reed-Solomon and Duplex Reed-Solomon PCBs are installed in the
same slots as the Turbo module.
Do not mix the Simplex Reed-Solomon PCBs with Turbo PCB or the Duplex
Reed-Solomon PCBs. Damage to the equipment may be the result.
CAUTION
2.3.2.1 Unpacking
This equipment contains parts and assemblies sensitive to damage by ESD.
Use ESD precautionary procedures when touching, removing, or inserting
CAUTION
PCBs.
1. Remove the Reed-Solomon PCB and mounting hardware from the cardboard
caddypack and anti-static material.
2. Check the packing list to ensure the shipment is complete.
3. Inspect the Reed-Solomon PCB for any shipping damage.
2.3.2.2 Installation
The following tool is required to install the overhead interface PCB:
Description Application
Phillips Screwdriver
Use the following information to install the Reed-Solomon Codec PCB as a daughter
card on the main PCB.
Refer Figure 2-3 for installation location of the Reed-Solomon daughter card.
Turn the power off before installation. High current VDC is present. Failure
to do so could result in damage to modem components.
CAUTION
1. Turn off the modem and unplug the power supply.
2. Remove the rear panel retaining screws. Slide the modem assembly out from the
top cover assembly.
2. Install the Reed-Solomon PCB to the main PCB by mating the male SIMM
connectors with the female SIMM connectors in the position shown in
Figure 2-3
To remove and replace cross-point screws.
2–6
Page 43

SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
Installation/Upgrades MN/SDM300L3.IOM
4. After completing the above installation procedure turn on the modem. If the
Reed-Solomon PCB was installed properly, the Utility: Modem Type: Card #2
Type or Card #3 Type. Menu will show “Reed-Solomon 02 or 03, or ReedSolomon. Duplex Reed-Solomon depending on board installed.
Reed-Solomon Cards (TX,
RX, or Duplex in Either
Slot)
Figure 2-3. Reed-Solomon Codec Installation
2–7
Page 44

SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
Installation/Upgrades MN/SDM300L3.IOM
2.3.3 Turbo Codec Installation
The Turbo Card is installed in the same slots as the Reed-Solomon PCBs. While the
Reed-Solomon uses two cards (TX and RX), the Turbo Codec uses only a single card.
Duplex Reed-Solomon can be installed with Turbo Codec.
DO not mix Simplex Reed-Solomon PCBs with Turbo PCs. Damage to the
equipment may be the result.
CAUTION
2.3.3.1 Unpacking
This equipment contains parts and assemblies sensitive to damage by ESD.
Use ESD precautionary procedures when touching, removing, or inserting
CAUTION
PCBs.
1. Remove the Turbo Codec PCB and mounting hardware from the cardboard
caddypack and anti-static material.
2. Check the packing list to ensure the shipment is complete.
3. Inspect the Turbo PCBs for any shipping damage.
2.3.3.2 Installation
The following tool is required to install the overhead interface PCB:
Description Application
Phillips Screwdriver
Use the following information to install the Turbo Codec PCB as a daughter card on the
main PCB.
Refer Figure 2-4 for installation location of the Turbo Codec PCB.
Turn the power off before installation. High current VDC is present. Failure
to do so could result in damage to modem components.
CAUTION
1. Turn off the modem and unplug the power supply.
2. Remove the rear panel retaining screws. Slide the main modem assembly out
from the rear of the modem chassis.
3. If required: Card 1 Overhead Board Removal – Remove the four rear panel
screws around the 50-pin I/O switch module. Unplug the I/O module, then
remove the seven mounting screws holding the Overhead board and carefully lift
the board out.
To remove and replace cross-point screws.
2–8
Page 45

SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
Installation/Upgrades MN/SDM300L3.IOM
4. If required: Reed-Solomon Removal – Remove the Reed-Solomon boards from
the SIMM sockets by pushing the spring clips outward while rocking the board
vertically, then lift the board out.
5. Turbo Codec Installation - Align the Turbo board with either of the SIMM
sockets while holding it vertically with components toward Rear panel. Seat the
connector into the socket and tilt the board toward the Front Panel until the
spring clips lock the board into place.
6. Replace the top cover and reinstall the two side screws.
7. Turn on the AC power. Modem will reinitialize.
Notes:
1. In this configuration, the Modem allows only Data Rates and Formats valid for
Turbo.
2. Open-network modem types cannot be selected.
2–9
Page 46

SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
(
)
Installation/Upgrades MN/SDM300L3.IOM
Figure 2-4. Turbo Codec Installation
Turbo Codec
Installed
Either Slot
2–10
Page 47

SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
Installation/Upgrades MN/SDM300L3.IOM
2.4 Data I/O Interface Connector (J8) Removal/Installation
Note: The following procedures outline the removal and installation of the Data I/O
connector (J8). These procedures are written with the assumption that the same
configured connector will be reinstalled. However, the operator does have an option to
install a different configured connector. Refer to Table 2-1 for a matrix explaining
connector options.
Table 2-1. Connector (J8) Matrix
Modem Configuration EIA-232 EIA-422/EIA449 V.35 Overhead
25-pin Connector X X X
34-pin Connector X
37-pin Connector X
50-pin Connector X X X X
To remove Data I/O Connector (J8), as follows:
1. (For Ribbon-Configured Connector PL/6031.) Remove Data I/O connector (J8)
(Figure 2-5) as follows:
a. Remove four screws securing the rear panel to the chassis.
b. Pull out rear panel to gain access to disconnect connector (J8).
c. Disconnect connector (J8) from the PCB.
d. Remove the four screws securing connector (J8) to the rear panel.
e. Remove the connector (J8).
2. Remove 50-pin Data I/O connector (J8) as follows:
a. Remove the four screws securing the connector (J8) to the rear panel.
b. Establish a grip on connector (J8) and pull backwards until separation of the
connectors is obtained.
c. Remove connector (J8).
2–11
Page 48

SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
Installation/Upgrades MN/SDM300L3.IOM
To install Data I/O Connector (J8), as follows:
1. (For Ribbon-Configured Connector PL/6031.) Install Data I/O connector (J8)
(Figure 2-5) as follows:
a. Position connector (J8) in rear panel.
Use care when connecting the data I/O connector (J8) to the PCB.
Damage to the connector pins may render the data I/O connector
CAUTION
(J8) unserviceable. Misalignment can be the result.
b. Connect connector (J8) to the PCB.
c. Secure connector (J8) to the rear panel with four screws.
d. Position the rear panel to mate with the chassis and secure with four screws.
2. Install 50-pin Data I/O connector (J8) as follows:
Use care when connecting the Data I/O connector (J8) to the PCB.
Damage to the connector pins may render the data I/O connector
CAUTION
(J8) unserviceable. Misalignment can be the result.
a. Connect connector (J8) to the PCB.
b. Secure connector (J8) using four screws.
2.4.1 G.703/ASYNC Module
This module installs as the previous modules. Use the same installation steps. The
G.703/ASYNC card requires the Overhead card.
2–12
Page 49

SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
Installation/Upgrades MN/SDM300L3.IOM
For Ribbon-Configured Connector
For 50-Pin Connector with Overhead Interface Board
Figure 2-5. Data I/O Connector (J8) Removal/Installation
2–13
Page 50

SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
Installation/Upgrades MN/SDM300L3.IOM
2.5 Hardware Upgrades
2.5.1 Main PCB Firmware Chips
The main PCB has one field-changeable flash memory chip for the M&C firmware. If
necessary, this chip can be removed and a new chip added to allow for additional options,
enhancements, or repairs. See Figure 2-6 for the locations of the field-changeable chips.
The bulk firmware for the FPGA downloads is stored in a non-replaceable flash memory
device. Bulk firmware can be upgraded by reflashing the device through the remote
control port as described in paragraph 2.7. The M&C firmware also can be upgraded by
reflashing through the host por
2.5.2 Overhead Interface PCB Firmware Chips
The overhead interface PCB has four field-changeable firmware chips. If necessary, these
chips can be removed and new chips added to allow for additional options,
enhancements, or repairs. See Figure 2-7 for the locations of the field-changeable chips.
2–14
Page 51

SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
Installation/Upgrades MN/SDM300L3.IOM
U26
U25
U7
U3
Figure 2-6. Overhead Board with Field-Changeable Chips
U68
Figure 2-7. Main Board Field-Changeable Chips (Shown with Overhead Card Removed)
2–15
Page 52

SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
Installation/Upgrades MN/SDM300L3.IOM
2.6 Flash Upgrading
The SDM-300L3 eliminates the need for physically replacing EPROMs to update
firmware. Instead, the SDM-300L3 modem uses ‘flash memory’ technology internally,
and new firmware can be uploaded to the unit from an external PC.
Performing a flash upgrade erases the non-volatile RAM, which is
where the modem's configuration is stored. Users shall re-enter the
IMPORTANT
The SDM-300L3 provides for flash upgrading the M&C firmware or the BULK
firmware.
Note: While the M&C and BULK firmware downloads are independent processes, the
modem may have to be upgraded to the latest releases of both the M&C and BULK for
proper function.
Flash updating firmware is a simple process, and users can obtain updates by any of the
following means:
The upgrade is performed without opening the unit, by connecting the modem to the
serial port of a computer and executing a flash uploader utility program.
The cable to connect the PC to the modem is the same as is used for normal EIA-232
remote control, and comprises three wires connected between two 9-pin ‘D’ type female
connectors. Ensure this cable is connected and working properly before proceeding with
a flash update.
WARN ING
desired configuration parameters.
• Download from the Comtech EF Data website:
(http://www.comtechefdata.com
)
• Request as E-mail attachments
• Request shipment on diskettes or cd-rom.
The Remote Control port EIA-232 lines used for Flash upgrading also are
connected to the Primary 25-pin data connector (P3B), and are used when
1:N Redundancy Switch is connected. Ensure that NOTHING is connected
to P3B pins 4, 21 and 22 – if these pins are used, the EIA-232 remote
control port will not function, and Flash upgrading is impossible.
2–16
Page 53

SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
Installation/Upgrades MN/SDM300L3.IOM
2.6.1 Downloading Flash Updates from the Web
The latest firmware releases and a free software utility are available on the Comtech EF
Data web site (http://www.comtechefdata.com
Windows 95/98 or Windows NT/2000/XP and provides all of the support required to
perform a Comtech EF Data firmware reflash. If web downloading is not available or
practical, contact the Customer Support department to obtain the firmware via an
alternate method.
The downloadable firmware files are provided in both .zip or self extracting .exe formats.
If your firewall does not permit downloading an .exe file, try the .zip file instead. The
downloadable file contents are identical, usually comprising an uploader program, a help
file, and a flashable data file.
). This utility is designed to run under
2.6.1.1 How to Download Flash Upgrade Files
1 Create a new folder on the PC. This folder will be the destination folder for any flash
upgrade files downloaded.
2 On the Comtech EF Data web site (http://www.comtechefdata.com/
“downloads” link.
3
Click the “flash upgrades” link for detailed downloading instructions.
4
Click the “flash firmware data files” link (located at the bottom of the instruction
page). The flash firmware data files are organized by product.
5
Click the "SDM300L3" link.
6 Identify and download the latest M&C firmware file to the destination folder on the
PC.
7 Repeat Step 6 for the BULK firmware file.
), click the
2.6.1.2 How to Perform a Flash Upgrade
Full on-line help is provided with the uploader program. If you experience a problem, or
have a question, contact Comtech EF Data Customer Support for assistance.
1 On the PC, double-click the .exe or .zip flash upgrade file to uncompress its contents.
2 Identify and execute the uploader program.
3 Follow the instructions presented on the screen to select a firmware file and initiate
the upload.
Following a successful upload process, the modem will automatically restart, running the
new version of firmware.
2–17
Page 54

SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
Installation/Upgrades MN/SDM300L3.IOM
This page is intentionally left blank.
2–18
Page 55

Chapter 3. CONNECTOR PINOUTS
3.1 Connector Overview
When a breakout panel, such as the UB-530, is not required, the rear panel connectors
provide all necessary external connections between the modem and other equipment.
Table 3-1 lists these connectors and Figure 3-1 show their locations.
Notes:
1. Refer to the Comtech EF Data UB-530 Universal Breakout Panel Installation
and Operation Manual for connecting the UB-300 breakout panel.
2. Refer to the Comtech EF Data UB-54 Breakout Panel Installation and Operation
Manual for connecting the UB-54 breakout panel in a MUX option
configuration.
3–1
Page 56

SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
Connector Pinouts MN/SDM300L3.IOM
J8
J6
J9
CP3
J7
J10 CP2
J2 J3 J4 J5
G.703/ASYNC
INTERFACE
OPTIONAL
Figure 3-1. SDM-300L3 Rear Panel
Table 3-1. Modem Rear Panel Connectors
Name
TX/IF OUTPUT CP1 Type N , Female RF Output
EXT REF CP2 BNC, Female EXT REF IN
RF IF INPUT CP3 Type F or N Female
Data/I/O (Optional) J2
REMOTE J6 9-pin D, Female Remote Interface
FAULT J7 9-pin D, Female FORM C Fault Relay Contacts
DATA I/O
(Customer-select)
AUX 1 J9 9-pin D, Female (TTL) Faults
ALARMS J10 9-pin D, Female FORM C Alarm
AC INPUT NONE IEC
GROUND NONE 10-32 Stud
Desig.
J3
J4
J5
J8
Ref.
Connector Type
BNC, Female
BNC, Female
BNC, Female
15-pin D Female
25-pin D, Female
34-pin, Female
37-pin D, Female
50-pin D, Female
RF Input 75Ω
G.703/ASYNC Closed Network
Data Input/Output (standard modem)
V.35
EIA-449
Data Input/Output
(modem with
ASYNC/AUPC/IDR/IBS/G.703 option)
Satellite Clock
Demod I/Q
Automatic Gain Control (AGC) Out
Relay Contacts
CP1
Function
3–2
Page 57

SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
Connector Pinouts MN/SDM300L3.IOM
Note: The European EMC Directive (EN55022, EN50082-1) requires using properly shielded
cables for DATA I/O. These cables must be double-shielded from end-to-end, ensuring a
continuous ground shield.
3.2 Connector Description
3.2.1 Remote Connector and Pinouts (J6)
The remote connector is a 9-pin subminiature female D connector (J6) located on the rear
panel of the modem. Screw locks are provided for mechanical security of the mating
connector.
The remote connector interfaces the M&C functions to a remote location. The remote
location can be an M&C computer located away from the modem, but attached via cable to
the remote connector. This DCE interface is user selectable for either EIA-232 or EIA-484.
Refer to Table 3-2 for pinout information.
Table 3-2. Remote Connector and Pinouts (J6
EIA-232 EIA-485
Pin #
1 1 GND
2 RD (RX) 2
3 TD (TX) 3
4 4* +RX/TX +TX
5 GND 5* -RX/TX -TX
6 DSR 6
7 RTS 7
8 CTS 8* +RX/TX +RX
9 9* -RX/TX -RX
*For 2-Wire Operation:
• Only two wires are required.
• Tie pins 4 and 8 together (both +).
• Tie pins 5 and 9 together (both -).
Name
Pinout
Pin #
Name
(2-Wire)
)
Name
(4-Wire)
3–3
Page 58

SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
Connector Pinouts MN/SDM300L3.IOM
3.2.2 Fault Connector and Pinouts (J7)
The fault connector provides Form C contact closures for fault reporting. The three Form C
summary fault contacts, ratings 1A maximum at 24 VDC, 0.5A at 120 VAC, are
Modulator, Demodulator, and Common Equipment.
The fault interface connection is a 9-pin subminiature female D connector (J7) located on
the rear panel of the modem. Screw locks are provided for mechanical security on the
mating connector. Refer to Table 3-3 for pinout information.
Table 3-3. Fault Connector and Pinouts (J7)
Pin # Signal Function Name
1 Common equipment is not faulted NO
2 COM
3 Common equipment is faulted NC
4 Modulator is not faulted NO
5 COM
6 Modulator is faulted NC
7 Demodulator is not faulted NO
8 COM
9 Demodulator is faulted NC
Note: A connection between the common (COM) and normally open (NO)
contacts indicates no fault.
3–4
Page 59

SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
Connector Pinouts MN/SDM300L3.IOM
3.2.3 Data I/O Interface Connector (J8)
The Data I/O interface connector conducts data input and output signals to and from the
modem, and connects to the customer’s terrestrial equipment, breakout panel, or protection
switch. The modem is currently available with a choice of four Data I/O connectors, as
follows:
• 25-pin D connector is the standard connector shipped with a base platform
modem.
• 50-pin D connector is the standard connector when the modem is ordered with
the optional overhead PCB or if the overhead PCB has been installed in the field.
• 50-pin D that can be ordered with the basic modem, but it does not include the
Overhead Card. This is used with breakout panels and switches.
• 37-pin D is an alternate connector available upon special request for the base
platform modem.
• 34-pin Winchester is an alternate connector available upon special request for the
base platform modem.
• G.703 T1, E1/ASYNC Interface Adapter is an alternate connector available
upon special request for the basic platform modem.
• Eurocom Interface – Refer to Chapter XXXX.
The Data I/O pinout is different for each of the interface configurations. For pinout
information, refer to the appropriate table as follows:
Standard: 25-pin D connector
Optional: 34-pin Winchester connector
Optional: 37-pin D connector
Optional: 50-pin D connector
Table 3-4
Table 3-5
Table 3-6
Table 3-7
3–5
Page 60

SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
Connector Pinouts MN/SDM300L3.IOM
Table 3-4. 25-Pin D Connector Pinouts
25-Pin D Connector
Pin # EIA-422 EIA-232 V.35
1 SHLD SHLD SHLD
2 SD-A TXD SD-A
3 RD-A RXD RD-A
4 RS-A RTS RTS
5 CS-A CTS CTS
6 DM-A DSR DSR
7 SIGGND SIGGND SIGGND
8 RR-A DCD RLSD
9 RT+B SCR+B
10 RR-B
11 TT+B SCTE+B
12 ST+B SCT+B
13 CS+B
14 SD+B SD+B
15 ST-A ST SCT-A
16 RD+B RD+B
17 RT-A RXC SCR-A
18 LL LL LL
19 RS+B
20* MC-A MC MC-A
21 DF DF DF
22 DM+B
23* MC+B MC-B
24 TT-A TXC SCTE-A
25 MF MF MF
*Note: Use the MASTER clock for EXTERNAL clock input. This clock input
should equal the data rate unless the Asymmetrical Loop Timing Option (ASLT)
is available. The ASLT option allows selection of different clock rates that vary
from the digital data rate. Refer to the Utility/Modem Type/Modem Options menu
for the ASLT option information.
3–6
Page 61

SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
Connector Pinouts MN/SDM300L3.IOM
Table 3-5. 34-Pin Winchester Connector Pinouts (V.35)
Pin # Name
A SIGGND
B SHLD
C Request to Send (RTS)
D Clear to Send (CTS)
E Data Set Ready (DSR)
F Receive Line Signal Detect (RLSD)
P Send Data A (SD-A)
R Receive Data A (RD-A)
S Send Data B (SD+B)
T Receive Data B (RD+B)
U Serial Clock Transmit External A (SCTE-A)
V Serial Clock Receive A (SCR-A)
W Serial Clock Transmit External B (SCTE+B)
X Serial Clock Receive B (SCR+B)
Y Serial Clock Transmit A (SCT-A)
c (CC) MC-A
d (DD) MC-B
m (MM) Modulator Fault (MF)
n (NN) Demodulator Fault (DF)
a(AA) Serial Clock Transmit B (SCT+B)
Note: Pins H, J, K, L, M, N, Z, a (AA), b (BB), e (EE), f (FF), h (HH), j (JJ),
k (KK), l (LL) have no connection.
The modem is available with a Winchester V.35 as the data I/O connector (PL/6032).
There is a jumper on the unit that either opens or closes the CC line. The interface is
shipped with jumpers in positions 2 and 3, because:
1. Comtech EF Data has determined that several locations use Fireberd test
equipment and a conflict will occur if CC is connected between the modem and
the Fireberd.
2. Placing the jumper in positions 2 and 3 opens up the CC line, because the
TTC/Fireberd test equipment interfaces use the line for DTE/DCE control.
3. Grounding pin CC at the Fireberd interface will change the Fireberd to a
DCE device.
4. Comtech EF Data uses the CC and DD for the input master clock (same as the
external clock input to the modem). To input an external clock, change the jumper
to positions 1 and 2 (the pin closest to the Winchester connector).
3–7
Page 62

SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
Connector Pinouts MN/SDM300L3.IOM
Table 3-6. 37-Pin Connector Pinouts (Optional)
Pin # EIA-422/MIL-188-144
1, 19 Shield
3 MF
4 SD-A
5 ST-A
6 RD-A
7 RS-A
8 RT-A
9 CS-A
11 DM-A
13 RR-A
16 MC-A
17 TT-A
20, 37 SIGGND
21 DF
22 SD+B
23 ST+B
24 RD+B
25 RS+B
26 RT+B
27 CS+B
29 DM+B
31 RR+B
34 MC+B
35 TT+B
There are jumpers on the PL/6031 EIA-422 interface. Place the jumpers on the center pin
and the pin towards the Master Clock (MC) to allow an external clock input on pins 16
and 34.
If desired, place the jumpers on the TR side to allow an external clock input on pins 12
and 30. Place the jumpers on the TR side for Demand Assigned Multiple Access
(DAMA) applications.
3–8
Page 63

SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
Connector Pinouts MN/SDM300L3.IOM
Table 3-7. 50-Pin Connector Pinouts
50-Pin D Connector
Pin # IDR IBS Async D&I
1 GND GND GND GND
2 GND GND GND GND
3 AGC Out AGC Out AGC Out AGC Out
4 EIA-422 TXOctA In ESC TXDB In (EIA-485 only)
5 EIA-422 TXOctB In ESC TXDA In
(EIA-232 only)
6 EIA-422 RXOctA Out ESC RXDB Out
7 EIA-422 RXOctB Out ESC RXDA Out
(EIA-232 only)
8 BWO1_C EIA-422 RX Oct A
9 BWO2_C EIA-422 RX Oct B
10 BWO3_C PRIMARY_C PRIMARY_C
11 BWO4_C SECONDARY_C SECONDARY_C
12 BWAI 1 V.35/EIA-422 SCTE/TT-A V.35/EIA-422 SCTE/TT A
13 BWAI 2 V.35/EIA-422 SCTE/TT-B V.35/EIA-422 SCTE/TT B
14 BWAI 3 EIA-422 TX Oct A
15 BWAI 4 EIA-422 TX Oct B
16 Demod Fault C
17 Def Maint Alrm
18 G.703 SDB In G.703 SDB In G.703 SDB In G.703 SDB In
19 EIA-422 ExtClkB In V.35/EIA-422 EXCB In V.35/EIA-422 EXCB In EIA-422 EXCB In
20 G.703 RDB Out G.703 RDB Out G.703 RDB Out G.703 RDB Out
21 EIA-422 8k TClkA Out V.35/EIA-422 ST-A Out V.35/EIA-422 ST-A Out
22 EIA-422 8k TClkB Out V.35/EIA-422 ST-B Out V.35/EIA-422 ST-B Out
23 EIA-422 8k RClkA Out V.35/EIA-422 RT-A Out V.35/EIA-422 RT-A Out
24 EIA-422 8k RClkB Out V.35/EIA-422 RT-B Out V.35/EIA-422 RT-B Out
25 BWO1_NC ESC TCLK Out (EIA-232)
26 BWO2_NC ESC RCLK Out (EIA-232)
27 BWO3_NC PRIMARY_NC PRIMARY_NC
28 BWO4_NC SECONDARY_NC SECONDARY_NC
29 Aud1-B In (or 64SDB) V.35/EIA-422 RTS-B V.35/EIA-422 RTS-B
30 Aud1-B Out (or 64RTB) V.35 RLSD/EIA-422 RR-B V.35 RLSD/EIA-422 RR-B
31 Aud2-B In (or 64STB) V.35/EIA-422 CTS-B V.35/EIA-422 CTS-B
32 Aud2-B Out (or 64RDB) V.35 DSR/EIA-422 DM-B V.35 DSR/EIA-422 DM-B
33 DF
34 G.703 SDA In G.703 SDA In G.703 SDA In G.703 SDA In
35 EIA-422 ExtClkA In V.35/EIA-422 EXCA In V.35/EIA-422 EXCA In EIA-422 EXCA In
36 G.703 RDA Out G.703 RDA Out G.703 RDA Out G.703 RDA Out
37 EIA-422 8k TXDA In V.35/EIA-422 SD-A In V.35/EIA-422 SD-A In G.703 DDO-A Out
38 EIA-422 8k TXDB In V.35/EIA-422 SD-B In V.35/EIA-422 SD-B In G.703 DDO-B Out
39 EIA-422 8k RXDA Out V.35/EIA-422 RD-A Out V.35/EIA-422 RD-A Out G.703 IDI-A In
40 EIA-422 8k RXDB Out V.35/EIA-422 RD-B Out V.35/EIA-422 RD-B Out G.703 IDI-B In
41 BWO1_NO ESC DSR (EIA-232)
42 BWO2_NO
43 BWO3_NO PRIMARY_NO PRIMARY_NO
44 BWO4_NO SECONDARY_NO SECONDARY_NO
45 Aud1-A In (or 64SDA) V.35/EIA-422 RTS-A V.35/EIA-422 RTS-A
46 Aud1-A Out (or 64RTA) V.35 RLSD/EIA-422 RR-A V.35 RLSD/EIA-422 RR-A
47 Aud2-A In (or 64STA) V.35/EIA-422 CTS-A V.35/EIA-422 CTS-A
48 Aud2-A Out (or 64RDA) V.35 DSR/EIA-422 DM-A V.35 DSR/EIA-422 DM-A ESC DSR (EIA-232 only)
49 MF
50 Demod Fault NO
ESC TXDA In
(EIA-485 and EIA-232)
(EIA-485 only)
ESC RXDA Out
(EIA-485 and EIA-232)
ESC TXD In
(EIA-232 only)
ESC RXD Out
(EIA-232 only)
3–9
Page 64

SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
Connector Pinouts MN/SDM300L3.IOM
Notes:
1. IDR configuration connector pinouts:
a. Backward alarm relay contacts are named for normal no fault conditions (BWOx-C
connected to BWOx-NC if no fault).
b. Backward alarm inputs should be grounded or pulled logic low to clear the alarm.
c. Signals MF, DF, and DMA are open-collector, high-impedance (if faulted). A
backup protection switch uses MF and DF if the modem is used in a redundant
system.
d. Relay contacts DF-C and DF-NO are named for faulted condition (DF-C connected
to DF-NO, unless demodulator [Demod] fault).
2. D&I/ASYNC interface connector pinouts:
a. With regard to alarm relay contacts, COMM is connected to NO when there is no
fault. COMM is connected to NC in a faulted condition.
b. Signals MF, DF, and DMA are open-collector, high-impedance (if faulted). A
backup protection switch uses MF and DF if the modem is used in a redundant
system.
3. The breakout panel provides the external connections between the modem and the
terrestrial equipment when the modem has a 50-pin connection.
3–10
Page 65

SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
Connector Pinouts MN/SDM300L3.IOM
3.2.4 G.703 T1, E1/ASYNC Interface Adapter
The G.703 T1, E1/ASYNC Interface Adapter has three BNC connectors and a 15-pin
subminiature D connector.
BNC connectors (SD (J2) and RD (J3) support the G.703 unbalanced 75Ω TX and RX
data interfaces. BNC connector MC (J4) supports the 75Ω unbalanced Master Clock
interface.
The 15-pin D connector (J5) supports the G.703 balanced TX and RX data, balanced
Master Clock, Open Collector mod and demod fault, and ASYNC overhead data
interfaces.
The following table shows the pinouts for the15-pin D connector.
This interface supports access to IBS or IDR overhead signals. However,
this interface does not support D&I functions.
IMPORTANT
Pin # Signal
1 SD 2 GND
3 RD4 GND
5 ETXB
6 ERXB
7 MC8 MC+
9 SD+
10 N.C.
11 RD+
12 ETXA
13 ERXA
14 MODFL
T
15 DMDFL
T
3–11
Page 66

SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
Connector Pinouts MN/SDM300L3.IOM
3.2.5 Auxiliary 1 Connector and Pinouts (J9)
The auxiliary 1 (AUX 1) connector provides:
• MOD and DEMOD (TTL) faults
• Satellite clock
• Satellite I&Q
• Automatic Gain Control (AGC) output voltage
The faults are open collector levels that indicate a modulator or demodulator failure. A logic
“1” indicates the faulted condition.
AGC_OUT is a programmable voltage, 0 to 10V, for a receive signal level between
-25 and -60 dBm.
AUX 1 connection is a 9-pin female D connector (J9) located on the rear panel of the
modem. Screw locks are provided for mechanical security on the mating connector. Refer
to Table 3-8 for pinout information.
Table 3-8. AUX 1 Connector and Pinouts (J9)
Pin # Signal Function Name
1 Satellite Clock - SAT_CLK2 External TX Enabled EXT_TX_EN
3 Satellite Clock + SAT_CLK+
4 MODULATOR TTL Fault MDFLTTTL
5 Ground GRN
6 RX_Q RX Q Channel Eye
7 DEMODULATOR TTL Fault DMDFLTTL
8 RX 1 Channel Eye RX_1
9 AGC Output AGC
3–12
Page 67

SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
Connector Pinouts MN/SDM300L3.IOM
3.2.6 Alarms Connector and Pinouts (J10)
The alarm connector provides Form C contact closures for alarm reporting. The two Form C
summary fault contacts are Modulator and Demodulator.
The alarm connection is a 9-pin female D connector (J10) located on the rear panel of the
modem. Screw locks are provided for mechanical security on the mating connector. Refer to
Table 3-9 for pinout information.
Table 3-9. Alarms Connector and Pinouts (J10)
Pin # Signal Function Name
1 Alarm 1 is faulted NO
2 COM
3 Alarm 1 is not faulted NC
4 Alarm 2 is faulted NO
5 COM
6 Alarm 2 is not faulted NC
7 Alarm 3 is faulted NO
8 COM
9 Alarm 3 is not faulted NC
• Alarm 1 = Not used
• Alarm 2 = TX
• Alarm 3 = RX
3.2.7 RF Output Connector (CP1)
CP1 is a 50Ω Type N connector for the TX IF signal. It operates between 950 to 1750 MHz,
in 100 Hz steps at power levels between 0 and –40 dBm in 0.1 dBm steps.
3.2.8 External Reference (CP2)
CP2 is a BNC connector for an EXT REF. The input impedance is 75Ω. For normal
operation, the desired carrier signal level is ≥ 0 dB. EXT REF frequencies are EXT 1,
EXT 5, EXT 10, and EXT 20 MHz.
3.2.9 RF Input Connector (CP3)
CP3 is a 75Ω, Type F Female connector for an RX IF signal.
Optional: Type N Female connector for an RX IF signal.
3–13
Page 68

SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
Connector Pinouts MN/SDM300L3.IOM
3.2.10 AC Power Connector
A standard, detachable, non-locking, 3-prong power cord (IEC plug) supplies the
Alternating Current (AC) power to the modem. Observe the following:
Input Power
Input Voltage
Connector Type
Fuse Protection
55W maximum, 40W typical
without BUC power supply
90 to 132 or 175 to 264 VAC
Unit switches ranges automatically
I.E.C
T3.15A 20mm type fuses
Line and neutral fusing
3.2.11 Ground Connector (GND)
A #10-32 stud on the rear panel of the modem is used for connecting a common chassis
ground among all equipment.
Note: The AC power connector provides the safety ground.
3–14
Page 69

Chapter 4. FRONT PANEL
4.1 Front Panel
The modem front panel (Figure 4-1) enables control of modem configuration parameters
and displays the modem status.
Figure 4-1. Front Panel View
OPERATION
The front panel features include:
• 32-character, 2-line LCD display
• 6-button keypad for local control
• 10 LEDs to provide overall status at a glance
All functions are accessible at the front panel by entering one of six pre-defined Function
Select categories or levels:
• Configuration
• Monitor
• Faults/Alarms
• Stored Faults/Alarms
• Remote AUPC (ASYNC mode only)
• Utility
4–1
Page 70

SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
Front Panel Operation MN/SDM300L3.IOM
4.2 LED Indicators
The 10 LEDs on the front panel indicate:
• General modem summary faults
• Status
• Alarms
The indicators are defined in Table 4-1 as follows:
Table 4-1. LED Indicators
Name LED Meaning
Faults
Transmit Red A fault condition exists in the transmit chain.
Receive Red A fault condition exists in the receive chain.
Common Red A common equipment fault condition exists.
Stored Yellow A fault has been logged and stored.
The fault may or may not be active.
Status
Power On Green Power is applied to the modem.
Transmitter On Green Transmitter is currently on.
This indicator reflects the actual condition of the transmitter, as
opposed to the programmed condition.
Carrier Detect Green Decoder is locked.
Test Mode Yellow Flashes when the modem is in a test configuration.
Alarms
Transmit Yellow A transmit function is in an alarm condition.
Receive Yellow A receive function is in an alarm condition.
4–2
Page 71

SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
Front Panel Operation MN/SDM300L3.IOM
4.3 Front Panel Keypad
The front panel keypad permits local operation of the modem. The keypad consists of six
keys (Figure 4-2).
ENTER
CLEAR
Figure 4-2. Keypad
Each key provides one or more logical functions. These functions are defined in the
following table.
ENTER This key is used to select a displayed function or to execute a modem
CLEAR This key is used to back out of a selection or to cancel a configuration change,
Left and Right
Diamond Keys
Top and Bottom
Diamond Keys
configuration change.
which has not been executed using [ENTER]. Pressing [CLEAR] generally returns
the display to the previous selection.
These keys are used to move to the next selection or to move the cursor for
certain functions.
Note: Throughout this chapter, [←] and [→] are used to indicate left and right
diamond keys.
These keys are used primarily to change configuration data (numbers). At times,
they are also used to move from one section to another.
Note: Throughout this chapter, [↑] and [↓] are used to indicate top and bottom
diamond keys.
The modem responds by beeping whenever a key is pressed:
• A single beep indicates a valid entry and the appropriate action was taken.
• A double beep indicates an invalid entry or a parameter is not available for
operation.
4–3
Page 72

SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
Front Panel Operation MN/SDM300L3.IOM
4.4 Menu System
Note: The menus show features and options that are not available. However, they are
shown to preserve the menu structure and reserve the structure for the future. This does
not imply an intent or obligation to add these features or options in the future.
Use the Main menu in Figure 4-3 as a quick reference for accessing the modem functions.
When the modem power is applied, the base level of the menu system displays the
sign-on message:
• Line 1 of the sign-on message is the modem model number and type.
• Line 2 is the version number of the firmware.
The main level of the menu system is Function Select. To access this level from the
sign-on message, press the [←] or [→] keys. From the Function Select menu; select one
of the functional categories:
• Configuration
• Monitor
• Faults/Alarms
• Stored Faults/Alarms
• Remote AUPC (ASYNC mode only)
• Utility
Press [←] or [→] to move from one selection to another. When line 2 displays the desired
function, select that level by pressing [ENTER]. After entering the appropriate functional
level, press [←] or [→] to move to the desired function.
To view or change the modem’s configuration, enter the Configuration level from the
Function Select menu. Once in the Configuration menu, press [←] or [→] to scroll
through the Configuration menu selection:
• Modulator
• Demodulator
• Interface
• Local AUPC (ASYNC Mode or Local Modem AUPC only)
• MUX (Optional)
• Save
• Recall
Press [ENTER] to select the desired Configuration menu option. To view the options for
the selected configuration parameters, press [←] or [→]. To change a configuration
parameter, press [ENTER] to begin the change process.
4–4
Page 73

SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
Front Panel Operation MN/SDM300L3.IOM
Press [↑] or [↓] to change the parameters. After the display represents the correct
parameters, press [ENTER] to execute the change. This action initiates the necessary
programming by the modem.
To undo a parameter change prior to execution
, press [CLEAR].
Notes:
1. Figure 4-3 list the front panel menu window selections.
2. Comtech EF Data recommends that selection of the desired Modem Type be
made prior to making any other setting. This procedure is located in the Utility
Modem Type menu.
3. Menus or commands that are specific to certain modem configurations are only
accessible after selecting the appropriate modem configuration. This prevents
incompatible parameters from accidentally being selected.
4. All of the windows are accessible in the Custom mode. Take caution not to select
incompatible parameters, as the modem does not shut out incompatible command
choices in the Custom mode.
4.4.5 REVISION EMULATION
To program an emulation mode from Version X.X.X through the current version, use the
revision emulation feature in the Utility: Modem Type menu.
Software Version # Firmware # Rev. Description of Change
2.1.12 FW/8460-1 M Original issue
2.1.22 FW/8460-1 AA Incorporated engineering changes
2.2.1 FW/8460-1 AD Incorporated Duplex Reed-Solomon
4–5
Page 74

SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
Front Panel Operation MN/SDM300L3.IOM
4.5 Menu Tree
SELECT (4.6)
CONFIGURATION
MONITOR
FAULTS/ALARMS
STORED FLTS/ALMS
REMOTE AUPC
UTILITY
CONFIGURATION (4.6.1)
MODULATOR
DEMODULATOR
INTERFAC E
LOCAL AUPC
SAVE
RECALL
MONITOR (4.6.2)
RAW BER
CORRECTED BER
Eb/No
RECEIVE SIGNAL
SWEEP FREQUENCY
BUFFER FILL
FRAME ERRORS
LNB CURRENT
LNB VOLTAGE
ODU CURRENT
ODU VOLTAGE
ODU OUTPUT LEVEL
ODU TEMPERATURE
ODU PLL LOCK
ODU SOFTWARE
ODU POWER CLASS
TX L-BAND FREQ
RX L-BAND FREQ
FAULTS/ALARMS (4.6.3)
MODULATOR
DEMODULATOR
TX INTERFACE
RX INTERFACE
COMMON
BACKWARD ALARMS
OUTDOOR UNIT
STORED FLTS/ALMS (4.6.4)
MODULATO R
DEMODULATOR
TX INTERF ACE
RX INTERFACE
COMMON
BACKWARD ALARMS
OUTDOOR UNIT
UNAVIL SECONDS
CLEAR
REMOTE AUPC (4.6.5)
UTILITY (4.6.6)
MODULATOR
DEMODULATOR
INTERFAC E
OUTDOOR UNIT
SYSTEM
MODEM TYPE
FACTORY SETUP
TX-X CODE/DATA RATE
TX-IF FREQUENCY
TX TERMINAL FREQ
TX-IF OUTPUT
TX POWER LEVEL
SCRAMBLER
DIFF. ENCODER
CARRIER MODE
MODEM REFERENCE
FSK OUTPUT
ODU POWER SUPPLY
ODU OUTPUT DELAY
ODU 10 MHz REF
RS ENCODER
RX-X CODE/DATA RATE
RX-IF FREQUENCY
RX TERMINAL FREQ
DESCRAMBLER
DIFF. DECODER
RF LOOP BACK
IF LOOP BACK
BER THRESHOLD
SWEEP CENTER
LNB POWER
LNB VOLTAGE
LNB 10 MHz REF
SWEEP RANGE
REACQUIS ITION
RS DECODER
ASSIGNED TX FILTERS
TX TERMINAL LO
MOD POWER OFFSET
MODULATOR TYPE
ENCODER TYPE
SCRAMBLER TYPE
TX BPSK ORDERING
MOD SPECTRUM
TX-RS N/K DEEP
TX IESS-310
TX IESS-315
TX MODE
ODU ALARM - LO W
ODU ALARM - HIGH
RF MODE CONTROL
TX SYMBOL RATE
ASSIGNED RX FILTERS
RX TERMINAL LO
DEMODULATOR TYPE
DECODER TYPE
DESCRAMBLER TYPE
RX BPSK ORDERING
DEMOD SPECTRUM
RX-RS N/K DEEP
RX IESS-310 MODE
RX IESS-315 MODE
LNB ALARM - LO W
LNB ALARM - HIG H
RX SYMBOL RATE
TX CLOCK SOURCE
TX CLOCK PHASE
EXT-CLK FREQ
BUFFER CLOCK
RX CLOCK PHASE
B-BAND LOOP BACK
INTRFC LOOP BACK
BUFFER SIZE
BUFFER CENTER
LOOP TIMING
TX DATA FAUL T
RX DATA FAULT
TX 2047 PATTERN
RX 2047 PATTERN
TX CODING FORMAT
RX CODING FORMAT
SERVICE CHANNEL ADJUST
DROP FORMAT
INSERT FORMAT
DROP CHANNEL ASSIGNMENTS
INSERT CHANNELS
ASYNC TX/RX BAUD
ASYNC TX/RX LENG TH
ASYNC TX/RX STOP
ASYNC TX/RX PARITY
LOCAL AUPC
AUPC ENABLE
NOMINAL POWER
MINIMUM POW ER
MAXIMUM POWER
TARGET EB/NO
TRACKING RATE
LOCAL CL ACTION
REMOTE CL ACTION
TX OVERHEAD TYPE
RX OVERHEAD TYPE
TX TERR IN TERFACE
RX TERR INTERFACE
BUFFER PROGRAM
FRAMING STRUCTURE
RTS TX-IF CNTRL
TX DATA PHASE
RX DATA PHASE
E1 INSERT CRC
IDR BW ALAR M CONTROL
ASYNC TX TYPE
ASYNC RX TYPE
IDR TX ESC TYPE
IDR RX ESC TYPE
IBS TX ESC TYPE
IBS RX ESC TYPE
CTS DELAY
ODU FSK ADDRESS
ODU OUTPUT POWER
ODU PWR LEVELING
TIME/DATE
REMOTE BAUD RATE
REMOTE ADDRESS
REMOTE TYPE
OPERATION DUPLEX
YEAR DISPLAY
TEST MODE STATUS
LAMP TEST
SELF TEST
DISPLAY CONTRAST
M&C FIRMWARE
BOOT FIRMWARE
FPGA FIRMWARE
TURBO FIRMWARE
DEMO MODE
EXT AGC: MIN/MAX PW R
MASTER RESET
MODEM TYPE
MODEM OP TIONS
CARD #X TYPE
CARD #X OPTIONS
LOCAL MODEM AUPC
MODEM SE RIAL #
CARD #X SERIAL
CONFIG CODE - MODEM
CONFIG CODE - CARD #X
Figure 4-3. Menu Tree
4–6
Page 75

SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
Front Panel Operation MN/SDM300L3.IOM
4.6 OPENING SCREEN
This screen is displayed whenever power is first applied to the unit.
SDM-300L3 CUSTOM
VER: X.X.X
Press [→] key to go to the any of the following FUNCTIONAL SELECT menu screens
• CONFIGURATION
• MONITOR
• FAULTS/ALARMS
• STORED FLTS/ALMS
• UTILITY
Note: At any time, pressing CLEAR will return to a main heading.
4.6.1 FUNCTION SELECT: CONFIGURATION
FUNCTIONAL SELECT
CONFIGURATION
Press [→] key to go to any of the following sub-menus. Press <ENTER> to review or
edit the menu.
CONFIGURATION MODULATOR Permits the user to configure the modulator portion of
CONFIGURATION DEMODULATOR Permits the user to configure the demodulator portion of
CONFIGURATION INTERFACE Permits the user to configure the interface portion of the
CONFIGURATION LOCAL AUPC Permits the user to configure the AUPC parameters of
CONFIGURATION SAVE Permits the user to save the configuration of the modem
CONFIGURATION RECALL Permits the user to configure the modem with a
the modem.
the modem.
modem.
the modem.
to non-volatile memory.
previously saved configuration.
4–7
Page 76

SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
Front Panel Operation MN/SDM300L3.IOM
4.6.1.1 FUNCTION SELECT: CONFIGURATION: MODULATOR
CONFIGURATION
MODULATOR
Press <ENTER > to review or edit the following sub-menus.
FUNCTION SELECT: CONFIGURATION: MODULATOR: TX-X CODE/DATA RATE
TX-A QPSK 1/2
64.000 Kbps
TX-B QPSK 1/2
128.000 Kbps
Upon entry, the current transmitter rate is displayed with the flashing cursor on the first
character of the code rate on line 1. Line 2 displays the data rate. Press [←] or [→] to
make the selection. To select the currently defined variable data rate, select TX-V, and
press <ENTER> twice.
TX-C QPSK 1/2
256.000 Kbps
TX-D QPSK 1/2
512.000 Kbps
TX-V QPSK 1/2
38.400 Kbps
4–8
Page 77

SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
Front Panel Operation MN/SDM300L3.IOM
To change the rate using the variable rate selection, press <ENTER> when TX-V is
displayed. A flashing cursor is displayed on the first character of the coding type on line
1. Press [←] or [→] to move the flashing cursor, and [↑] or [↓] to increment or
decrement the digit at the flashing cursor. Press <ENTER> to execute the change.
Notes:
1. When the TX rate has been programmed, the transmitter is automatically turned
off to prevent swamping of other channels. To turn the transmitter on, use the
TX-IF Output function.
2. Code Rate 3/4 not compatible with a combination of a CSC Closed Modulator
Type and Sequential Encoder.
Code Rate Data Rate Range
Non-Turbo Requirements
BPSK 1/2 2.4 to 1250 kbps
{O}QPSK 1/2 4.8 to 2500 kbps
{O}QPSK 3/4 7.2 to 3750 kbps
QPSK 7/8 8.4 to 4375 kbps
8-PSK 2/3 64.0 to 5000 kbps
BPSK 1/1 4.8 to 2500 kbps
{O}QPSK 1/1 9.6 to 5000 kbps
Turbo Requirements
BPSK 21/44 2.4 to 1193.181 kbps
BPSK 5/16 2.4 to 781.25 kbps
{O}QPSK 1/2 4.8 to 2386.363 kbps
8-PSK 3/4 384 to 5000 kbps
Burst Mode Data Range
BPSK 5/16 2.4 to 781.25 kbps
{O} QPSK 1/2 4.8 to 2386.363 kbps
8-PSK 3/4 384 to 5000 kbps
Burst Mode Data Range
BPSK 5/16 2.4 to 781.25 kbps
{O} QPSK 1/2 4.8 to 2386.363 kbps
8-PSK 3/4 384 to 5000 kbps
Notes:
1. Max Symbol Rate = 2500 ksps
2. Max Data Rate for Low Var. Rate: 512 kbps.
3. OQPSK Option only: OQPSK 1/2, 3/4, and 7/8
4–9
Page 78

SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
Front Panel Operation MN/SDM300L3.IOM
FUNCTION SELECT: CONFIGURATION: MODULATOR:
TX-IF FREQUENCY (CONDITIONAL)
TX-IF FREQUENCY
1200.0000 MHz
Conditional: This menu is displayed when LO is programmed to 0
IMPORTANT
Programs the modulator transmit frequency between 950 and 1750 MHz, in 100 Hz steps.
Upon entry, the current transmitter frequency is displayed with the flashing cursor on the
first character. Press [←] or [→] to move the flashing cursor, and [↑] or [↓] to increment
or decrement the digit at the flashing cursor. Press <ENTER> to execute the change.
Note: When the transmitter frequency is changed, the transmitter is automatically turned
off to prevent the possible swamping of other channels. To turn the transmitter on, use
the TX-IF Output function.
under Utility: Modulator: TX Terminal LO menu.
FUNCTION SELECT: CONFIGURATION: MODULATOR:
TX TERMINAL FREQUENCY (CONDITIONAL)
TX TERMINAL FREQUENCY
5845.0000 MHz
Conditional: This menu is available only when TX Terminal LO and Mix
IMPORTANT
The remainder of the functions are the same as TX-IF Frequency.
Note: This menu permits programming the TX frequency of the satellite terminal,
including the modem and ODU/BUC. When properly setup, it indicates the frequency
radiated toward the satellite.
are programmed under Utility: Modulator menu.
4–10
Page 79

SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
Front Panel Operation MN/SDM300L3.IOM
FUNCTION SELECT: CONFIGURATION: MODULATOR:
TX-IF OUTPUT
TX-IF OUTPUT
OFF
Programs the modulator output On or Off. Upon entry, the current status of the output is
displayed. Press [↑] or [↓] to make the selection. Press <ENTER> to execute the change.
FUNCTION SELECT: CONFIGURATION: MODULATOR: TX POWER LEVEL
TX POWER LEVEL
- 10.0 dBm
Programs the modulator output power level from 0 to -40 dBm
Upon entry, the current transmitter power level is displayed with the flashing cursor on
the first character. Press [↑] or [↓] to increase or decrease the output power level in 0.1
dBm steps. Press <ENTER> to execute the change.
TX POWER LEVEL
-10.0 dBm (ADJ)
This menu appears when:
1. ODU Power Leveling is On (Utility: Outdoor Unit), or
2. The MOD Power Offset (Utility: Modulator) is ≠ 0 dB.
3. (ADJ) appears after the power level in the TX Power Level screen when this
menu is active.
Notes:
1. When Power Leveling is Enabled, manual changes to the output level are
inhibited, and the menu indicates the TX Power Level TX by the modulator.
2. When MOD power offset is active the output power is adjusted [↑] and [↓] with
arrow keys. However, the value indicated in the display is:
Modulator Power Level + Offset
4–11
Page 80

SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
Front Panel Operation MN/SDM300L3.IOM
FUNCTION SELECT: CONFIGURATION: MODULATOR: SCRAMBLER
SCRAMBLER
ON
Programs the scrambler On or Off.
Upon entry, the current status of the scrambler is displayed. Press [↑] or [↓] to make the
selection. Press <ENTER> to execute the change.
FUNCTION SELECT: CONFIGURATION: MODULATOR: DIFF. ENCODER
DIFF. ENCODER
ON
Programs the differential encoder On or Off.
Upon entry, the current status of the scrambler is displayed. Press [↑] or [↓] to make the
selection. Press <ENTER> to execute the change.
4–12
Page 81

SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
Front Panel Operation MN/SDM300L3.IOM
FUNCTION SELECT: CONFIGURATION: MODULATOR:
CARRIER MODE
CARRIER MODE
NORMAL-MODULATED
Programs the modem for alternate carrier modes. All modes, except Normal-Modulated
are Test Modes. Four modes of operation are available:
NORMAL-MODULATED
CENTER-CW
DUAL-CW
OFFSET-CW
Upon entry, the Center mode is displayed. To activate this test mode, press <ENTER>.
Press [↑] or [↓] to select the desired mode. To return to the Configuration menu, press
[CLEAR].
This mode is normally selected.
Generates a CW-carrier at the current modulator frequency. This can be used to
measure the output frequency.
Generates a dual side-band suppressed carrier signal. Side-bands are at one-half of
the symbol rate from the carrier. This is used to check the channel balance and
carrier null.
Generates a single, upper, side-band-suppressed carrier signal. The upper sideband is at one-quarter of the symbol rate from the carrier. When inverted spectrum
is selected, this generates a single, lower, side-band-suppressed carrier.
FUNCTION SELECT: CONFIGURATION: MODULATOR: MODEM REFERENCE
MODEM REFERENCE
INTERNAL
Select either: Internal, EXT1 MHz, EXT5 MHz, EXT 10MHz, EXT 20MHz, or
Output 10 MHz.
Use only Internal or EXT 10 MHz with a Block Up Converter (BUC) or
IMPORTANT
Upon entry, the current status of the scrambler is displayed. Press [↑] or [↓] to make the
selection. Press <ENTER> to execute the change.
Note: If any EXT REF is selected for the modem reference and is disconnected or not
present at CP3, an alarm is generated, and the modem switches to its Internal Clock.
Outdoor Unit (ODU).
4–13
Page 82

SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
Front Panel Operation MN/SDM300L3.IOM
FUNCTION SELECT: CONFIGURATION: MODULATOR:
FSK OUTPUT
FSK OUTPUT
OFF
Note: FSK is operational only with a BUC or ODU that incorporates FSK capabilities.
Programs the FSK Output On or Off. Upon entry, the current status of the FSK Output is
displayed. Press [↑] or [↓] to make the selection. Press <ENTER> to execute the change.
The modem will attempt to communiate with the ODU/BUC when the FSK is tuned On.
When the communicateions are successful the Monitor menu willl indicate the ODU
Output Level, ODU Temperature, ODU, PLL Lock, ODU Software, and ODU Power Class
( for BUCs that support these parameters). If communications are not established then all of
the following are indicated as faults under the Faults/Alarms: Outdoor Unit menu:
Temperature, PLL Lock, and Checksum.
Every 10 seconds the modem will try to re-establish FSK communications. It is possible the
address the modem is using to contast the ODU/BUC differs from the address in the
ODU/BUC. Usually the default address = 1. Check this at the ODU FSK Address menu
located under the Utility: Outdoor Unit menu.
FUNCTION SELECT: CONFIGURATION: MODULATOR: ODU POWER SUPPLY
ODU POWER SUPPLY
OFF
Programs the ODU Power Supply On or Off. DC power is transmitted up the center
conductor of the TX-IF connector. Upon entry, the current status of the ODU Power is
displayed. Press [↑] or [↓] to make the selection. Press <ENTER> to execute the change.
4–14
Page 83

SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
Front Panel Operation MN/SDM300L3.IOM
FUNCTION SELECT: CONFIGURATION: MODULATOR: ODU OUTPUT DELAY
ODU OUTPUT DELAY
00.00 MIN SEC
Programs the ODU Output delay with 0.0 to 20.00 minutes. At power up, the M&C delays
carrier turn On by the programmed time. During output delay timeout, the front panel
carrier On LED flashes and the ODU output delay screen shows the remaining delay time.
Normally, when using this feature, the ODU 10MHz reference is On and the ODU Power
Supply is On. This allows the ODU or BUC time to warm-up before the carrier is
transmitted. Upon entry, the current status of the ODU Output Delay is displayed. Press [↑]
or [↓] to make the selection. Press <ENTER> to execute the change.
FUNCTION SELECT: CONFIGURATION: MODULATOR: ODU 10 MHZ REF
ODU 10 MHz REF
OFF
Programs the ODU 10 MHz REF On or Off. The reference is transmitted up the center
conductor of the TX-IF connector.
Upon entry, the current status of the ODU 10 MHz REF is displayed. Press [↑] or [↓] to
make the selection. Press <ENTER> to execute the change.
4–15
Page 84

SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
Front Panel Operation MN/SDM300L3.IOM
FUNCTION SELECT: CONFIGURATION: MODULATOR: RS ENCODER (CONDITIONAL)
RS ENCODER
OFF
Conditional: Reed-Solomon option only.
IMPORTANT
Programs the Reed-Solomon Encoder On or Off.
Upon entry, the current status of the Reed-Solomon encoder is displayed. Press [↑] or [↓]
to make the selection. Press <ENTER> to execute the change.
4.6.1.2 FUNCTION SELECT: CONFIGURATION: DEMODULATOR
CONFIGURATION
DEMODULATOR
Press <ENTER> to review or edit the following sub-menus.
FUNCTION SELECT: CONFIGURATION: DEMODULATOR: RX-X CODE/DATA RATE
RX-A QPSK 1/2
64.000 Kbps
RX-B QPSK 1/2
128.000 Kbps
4–16
Page 85

SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
Front Panel Operation MN/SDM300L3.IOM
RX-C QPSK 1/2
256.000 Kbps
RX-D QPSK 1/2
512.000 Kbps
RX-V QPSK 1/2
38.400 Kbps
Upon entry, the current transmitter rate is displayed with the flashing cursor on the first
character of the code rate on line 1. Line 2 displays the data rate. Press [←] or [→] to
make the selection. To select the currently defined variable data rate, select RX-V, and
press [ENTER] twice.
To change the rate using the variable rate selection, press [ENTER] when RX-V is
displayed. A flashing cursor is displayed on the first character of the coding type on line
1. Press [←] or [→] to move the flashing cursor, and [↑] or [↓] to increment or
decrement the digit at the flashing cursor. Press [ENTER] to execute the change.
Notes:
1. When the RX rate has been programmed, the transmitter is automatically turned
off to prevent swamping of other channels. To turn the transmitter on, use the
RX-IF Output function.
2. Code Rate 3/4 not compatible with a combination of a CSC Closed Modulator
Type and Sequential Encoder.
4–17
Page 86

SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
Front Panel Operation MN/SDM300L3.IOM
Code Rate Data Rate Range
Non-Turbo Requirements
BPSK 1/2 2.4 to 1250 kbps
{O}QPSK 1/2 4.8 to 2500 kbps
{O}QPSK 3/4 7.2 to 3750 kbps
QPSK 7/8 8.4 to 4375 kbps
8-PSK 2/3 64.0 to 5000 kbps
BPSK 1/1 4.8 to 2500 kbps
{O}QPSK 1/1 9.6 to 5000 kbps
Turbo Requirements
BPSK 21/44 2.4 to 1193.181 kbps
BPSK 5/16 2.4 to 781.25 kbps
{O}QPSK 1/2 4.8 to 2386.363 kbps
8-PSK 3/4 384 to 5000 kbps
Burst Mode Data Range
BPSK 5/16 2.4 to 781.25 kbps
(O)QPSK 1/2 4.8 to 2386.363 kbps
8-PSK 3/4 384 to 5000 kbps
Notes:
1. Max Symbol Rate = 2500 ksps
2. Max Data Rate for Low Var. Rate: 512 kbps.
3. OQPSK Option only: OQPSK 1/2, 3/4, and 7/8
FUNCTION SELECT: CONFIGURATION: DEMODULATOR: RX-IF FREQUENCY (CONDITIONAL)
RX-IF FREQUENCY
1200.0000 MHz
Conditional: This menu is displayed when LO is programmed to 0
IMPORTANT
Programs the demodulator receive frequency between 950 and 1750 MHz,
in 100 Hz steps.
Upon entry, the current receive frequency is displayed with the flashing cursor on the
first character. Press [←] or [→] to move the flashing cursor, and [↑] or [↓] to increment
or decrement the digit at the flashing cursor. Press <ENTER> to execute the change.
under Utility: Demodulator: RX Terminal LO menu.
4–18
Page 87

SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
Front Panel Operation MN/SDM300L3.IOM
FUNCTION SELECT: CONFIGURATION: DEMODULATOR:
RX TERMINAL FREQUENCY (CONDITIONAL)
RX TERMINAL FREQUENCY
4200.0000 MHz
Conditional: This menu is available only when RX Terminal LO and Mix
IMPORTANT
The reminder of the functions is the same as RX-IF Frequency.
Note: This permits programming of the RX frequency of the satellite terminal, including
the modem and LNB. When properly setup it indicates the satellite frequency of the
desired RX carrier received from the satellite.
are programmed under Utility: Demodulator menu.
FUNCTION SELECT:CONFIGURATION:DEMODULATOR:
DESCRAMBLER
Programs the descrambler On or Off.
Upon entry, the current status of the descrambler is displayed. Press [↑] or [↓] to make
the selection. Press <ENTER> to execute the change.
DESCRAMBLER
ON
4–19
Page 88

SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
Front Panel Operation MN/SDM300L3.IOM
FUNCTION SELECT:CONFIGURATION:DEMODULATOR:
DIFF. DECODER
DIFF. DECODER
ON
Programs the differential decoder On or Off.
Upon entry, the current status of the differential decoder is displayed. Press [↑] or [↓] to
make the selection. Press <ENTER> to execute the change.
4–20
Page 89

SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
/
Front Panel Operation MN/SDM300L3.IOM
FUNCTION SELECT: CONFIGURATION: DEMODULATOR: RF LOOP BACK
RF LOOP BACK
OFF
This is a Test Mode.
IMPORTANT
Programs the modem for RF loopback operation. When RF loopback is turned on, the
demodulator is programmed to the same frequency as the modulator. When RF loopback
is turned off, the demodulator is tuned to the previous frequency. Refer to (Figure 4-4)
for a block diagram of RF loopback operation.
Note: RF loopback nullifies IF loopback.
Upon entry, the current status of the RF loopback is displayed. Press [↑] or [↓] to make
the selection. Press [ENTER] to execute the change.
CUSTOMER
DATA
REMOTE SE RIAL
INTERFACE
FAULT IND ICATORS
DATA
INTERFA CE
SATELLITE MODEM
ENCODER/
MODULATOR
MICRO-
COMPUTER
DEMODULATOR
DECODER
TX = 1200 MHz
SUPPLY
POWER
RX = 1225 MHz
RF LBK = 1200 MHz
LOOPBACK CHANGES DEMOD
RECEI VE FREQUENC Y TO
70 MHz W ITHOUT LOSING
ORIGINAL PROGRAMMING
INFORMATION.
TRANSMIT RF
EQUIPMENT
AC P OWER
RECEIVE RF
EQUIPMENT
ANTENNA
Figure 4-4. RF Loopback
Note: When RF loopback is turned on, the demodulator receive frequency is programmed to be the same frequency as the
modulator transmit frequency. This test mode will verify the satellite link without changing the programmed frequency of the
demodulator. When RF loopback is turned off, the demodulator is programmed back to the previous frequency.
4–21
Page 90

SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
Front Panel Operation MN/SDM300L3.IOM
FUNCTION SELECT: CONFIGURATION: DEMODULATOR: IF LOOP BACK
IF LOOP BACK
OFF
This is a Test Mode.
IMPORTANT
Programs the modem for IF loopback operation. When IF loopback is turned on, the
demodulator input is connected to the modulator output through an internal attenuator
and the modulator continues to TX a signal. The demodulator is programmed to the same
frequency as the modulator. When IF loopback is turned off, the demodulator is tuned to
the previous frequency and is reconnected to the IF input. Refer to Figure 4-5 for a block
diagram of IF loopback operation.
Note: IF loopback nullifies RF loopback.
CUSTOMER
DATA
REMOTE SERIAL
INTERFACE
FAULT INDICATORS
IBS, IDR or 308-2
INTERFACE
SATELLITE MODEM
ENCODER/
MODULATOR
MICRO-
COMPUTER
DEMODULATOR/
DECODER
POWER SUPPLY
TRANSMIT RF
EQUIPMENT
AC POWER
RECEIVE RF
EQUIPMENT
ANTENNA
Figure 4-5. IF Loopback
Note: When IF loopback is turned on, the demodulator is looped back to the modulator inside the modem and the demodulator is
programmed to the same frequency as the modulator. This test mode will verify the operation of the modem. When IF loopback is
turned off, the demodulator is programmed back to the previous frequency and is reconnected to the IF input.
4–22
Page 91

SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
Front Panel Operation MN/SDM300L3.IOM
FUNCTION SELECT: CONFIGURATION: DEMODULATOR: BER THRESHOLD
BER THRESHOLD
NONE
Sets the BER threshold. If the BER threshold set is exceeded, a receive fault will be
indicated by the modem status indicators. BER threshold may be set from 1.0 E-3 to 1.0
E-8, or may be disabled by specifying NONE.
Upon entry, the current setting of the BER threshold is displayed. Press [↑] or [↓] to
select the desired setting. Press <ENTER> to execute the change.
FUNCTION SELECT: CONFIGURATION: DEMODULATOR: SWEEP CENTER
SWEEP CENTER
+0Hz
Programs the sweep center frequency for the directed sweep function. When in directed
sweep, the value from the sweep monitor screen (when the modem was last locked)
should be entered for the sweep center frequency. The sweep center frequency can be set
in the range from -75000 to +75000 Hz.
4–23
Page 92

SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
Front Panel Operation MN/SDM300L3.IOM
FUNCTION SELECT: CONFIGURATION: DEMODULATOR:
SWEEP RANGE
SWEEP RANGE
60000 Hz
Programs the overall travel of the sweep width range during acquisition in the directed
sweep mode. The sweep width may be set from 0 to 1,000,000 Hz. When set at 60000
Hz, the modem is in the default acquisition mode. The smaller the range, the faster the
modem will lock, provided the receive carrier center frequency is within the RX IF
frequency sweep range.
Upon entry, the current programmed setting is displayed. Press [←] or [→] to move the
flashing cursor. Press [↑] or [↓] to increment or decrement the digit at the flashing cursor.
Press <ENTER> to execute the change.
FUNCTION SELECT: CONFIGURATION: DEMODULATOR: REACQUISITION
REACQUISITION
0 SECONDS
Programs the sweep reacquisition mode time duration. This is the time that the modem
will remain in a narrow sweep after loss of acquisition. After this timer runs out, the
modem will return to the normal acquisition sweep. The reacquisition time is 0 to 999
seconds.
Upon entry, the current programmed setting is displayed with a flashing cursor on the
first character. Press [←] or [→] to move the flashing cursor. Press [↑] or [↓] to
increment or decrement the digit at the flashing cursor. Select the number of seconds
desired for the reacquisition mode. Press <ENTER> to execute the change.
4–24
Page 93

SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
Front Panel Operation MN/SDM300L3.IOM
FUNCTION SELECT: CONFIGURATION: DEMODULATOR: LNB POWER
LNB POWER
OFF
Programs the LNB Power On or Off. The LNB voltage is transmitted up the center
conductor of the RF-IF connector.
Upon entry, the current status of the descrambler is displayed. Press [↑] or [↓] to make
the selection. Press <ENTER> to execute the change.
FUNCTION SELECT: CONFIGURATION: DEMODULATOR: LNB VOLTAGE
LNB VOLTAGE
13 VDC
Programs the LNB Power at 13, 18, or 24 VDC.
Upon entry, the current status of the descrambler is displayed. Press [↑] or [↓] to make
the selection. Press <ENTER> to execute the change.
FUNCTION SELECT: CONFIGURATION: DEMODULATOR: LNB 10 MHZ REF
LNB 10 MHz REF
OFF
Programs the LNB 10 MHz REF to On or OFF. The LNB 10 MHz reference is
transmitted out the center conductor of the RF-IF connector.
Upon entry, the current status of the descrambler is displayed. Press [↑] or [↓] to make
the selection. Press <ENTER> to execute the change.
4–25
Page 94

SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
Front Panel Operation MN/SDM300L3.IOM
FUNCTION SELECT: CONFIGURATION: DEMODULATOR: RS DECODER
RS DECODER
OFF
Programs the Reed-Solomon decoder On, Off, or Correction_Off.
Upon entry, the current status of the Reed-Solomon decoder is displayed. Use [↑] or [↓]
to select one of the following modes:
ON
CORRECTION_OFF
OFF
Press [ENTER] to execute the change.
If none of the proper overhead types or data rates apply, the ReedSolomon decoder in the On state will be rejected (double beep). With
the Reed-Solomon decoder turned On (not off or Correction_ Off), the
IMPORTANT
corrected BER will be reported from the outer decoder (Reed-Solomon
decoder).
Enables the Reed-Solomon decoder to provide data error corrections.
This is the Normal operating Mode.
Turns off the Reed-Solomon decoder data error correction circuitry. Data
flow is then routed through normal data paths without error corrections.
This is a Test Mode.
The RS decoder is normally disabled (off position). To execute any of
the Reed-Solomon decoder modes, enter the desired Reed-Solomon
decoder and select the desired mode. This is a Test Mode.
4–26
Page 95

SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
Front Panel Operation MN/SDM300L3.IOM
4.6.1.3 FUNCTION SELECT: CONFIGURATION: INTERFACE
CONFIGURATION
INTERFACE
Press <ENTER > to review or edit the following sub-menus.
FUNCTION SELECT: CONFIGURATION: INTERFACE: TX CLOCK SOURCE
TX CLOCK SOURCE
TX TERRESTRIAL
Programs the clock source for the modem transmitter clock to the following
configurations:
TX TERRESTRIAL
SCT (INTERNAL)
Note: When loop timing is enabled, SCT (LOOP) is
EXT. CLOCK/DATA CLOCK
Upon entry, the current transmit clock setting is displayed. Press [↑] or [↓] to make the
selection. Press <ENTER> to execute the change.
Sets the TX clock to recover timing from the incoming
clock/data.
Sets the TX clock to operate from the modem internal clock
(this is also the fallback clock).
displayed instead of SCT (INTERNAL).
Sets the TX clock to operate from the external reference
clock (Ext Clock).
TX Data Rate and Ext Clock frequency shall match or unless
the ASLT option is installed. The correct frequency must be
programmed into EXT-CLK FREQ.
4–27
Page 96

SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
Front Panel Operation MN/SDM300L3.IOM
FUNCTION SELECT: CONFIGURATION: INTERFACE: TX CLOCK PHASE
TX CLOCK PHASE
AUTO
Programs the TX clock phase to AUTO, NORMAL, or INVERT.
Note: AUTO is the default.
Upon entry, the current setting of the TX clock phase is displayed. Press [↑] or [↓] to
make the selection. When AUTO is selected, the modem will automatically select
NORMAL or INVERT to properly phase the TX clock with the TX data. Press
<ENTER> to execute the change.
FUNCTION SELECT: CONFIGURATION: INTERFACE: EXT-CLK FREQ
EXT-CLK FREQ
1544.000 KHz
Programs the EXT REF clock input frequency between 8.000 kHz and 10000.000 kHz.
Notes:
1. When an ODU or BUC is operated with an EXT REF, 10 MHz is required.
2. The clock rate shall be equal to the data rate unless the asymmetrical loop timing
option is present.
This clock frequency can be any multiple of 600 Hz from 2.4 to 64 kHz, and can be any
multiple of 8 kHz from 64 kHz to 4.376 MHz. This can be used for the Doppler/
Plesiochronous buffer reference. It can be a reference to SCT. Use the master clock input
on J8 for the external master reference. The EXT REF on CP3 only allows for 1, 5, 10,
and 20 MHz EXT REF input.
Upon entry, the current setting for the EXT REF is displayed. Press [←] or [→] to
increment or decrement the digit at the flashing cursor. Press <ENTER> to execute the
change.
4–28
Page 97

SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
Front Panel Operation MN/SDM300L3.IOM
FUNCTION SELECT: CONFIGURATION: INTERFACE: BUFFER CLOCK
BUFFER CLOCK
RX (SATELLITE)
Programs the interface buffer output clock to one of the following modes:
RX (SATELLITE)
SCT (INTERNAL)
EXT. CLOCK
TX TERRESTRIAL
INSERT CLOCK
Upon entry, the current setting of the plesiochronous buffer clock is displayed. Press [↑]
or [↓] to make the selection. Press <ENTER> to execute the change.
Sets the output buffer clock to the satellite clock.
(Bypasses the buffer.)
Sets the buffer clock to operate from the modem internal clock. This is
also the fallback clock
Sets this clock source to the external clock.
Sets the buffer output clock to recover timing from the incoming TX
data clock.
Selects the recovered clock from the insert send data input received
from the terrestrial equipment.
FUNCTION SELECT: CONFIGURATION: INTERFACE: RX CLOCK PHASE
RX CLOCK PHASE
NORMAL
Programs the RX clock phase to Normal or Inverted.
Upon entry, the current status of the RX Clock is displayed. Press [↑] or [↓] to make the
selection. Press <ENTER> to execute the change.
4–29
Page 98

SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
Front Panel Operation MN/SDM300L3.IOM
FUNCTION SELECT: CONFIGURATION: INTERFACE: B-BAND LOOP BACK
B-BAND LOOP BACK
OFF
This is a Test Mode.
IMPORTANT
Programs the modem for baseband loopback operation. When baseband loopback is
turned on, the data and timing signals are switched from the demodulator to the
modulator on the modem side of the interface. The DTE baseband signals are also looped
back from the transmitter data and clock to receiver data and clock on the customer side
of the interface. This is a bi-directional loopback of the baseband data. Refer to Figure
4-6 for a block diagram of baseband loopback operation.
CUSTOMER
DATA
REMOTE SERIAL
INTERFACE
FAULT IN DIC ATORS
IBS OR IDR
INTERFACE
SATELLITE MODEM
ENCODER/
MODULATOR
MICRO-
COMPUT ER
DEMODULATOR/
DECODER
POWER SUPPLY
TRANSMIT RF
EQUIPMENT
AC POWER
RECEIVE RF
EQUIPMENT
ANTENNA
Figure 4-6. Baseband Loopback
Note: When baseband loopback is turned on, data is looped back on the customer side of the interface. This is a bi-directional
loopback of the baseband data. This test mode will verify the customer equipment and cabling between the modem and the
customer equipment. The baseband loopback is not bi-directional in D&I.
4–30
Page 99

SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
/
Front Panel Operation MN/SDM300L3.IOM
FUNCTION SELECT: CONFIGURATION: INTERFACE: INTRFC LOOP BACK (CONDITIONAL)
INTRFC LOOP BACK
OFF
This is a Test Mode. Conditional: This menu is only available when the
IMPORTANT
Programs the modem for Interface Loopback operation. When INTERFACE
LOOPBACK is turned on, data is looped back at the modem side of the interface. This is
a bi-directional loop back of the data after the base band data has had the overhead added.
Refer to Figure 4-7 for the interface loopback block diagram.
Upon entry, the current status is displayed. [↑] or [↓] to make the selection. Press
[ENTER] to execute the change.
overhead interface PCB or Reed-Solomon PCB is installed.
CUSTOMER
DATA
REMOTE SERIAL
INTERFACE
FAULT IN DIC ATORS
IBS or IDR
INTERFACE
SATELLITE MODEM
ENCODER/
MODULATOR
MICRO-
COMP UTE R
DEMODULATOR
DECODER
POWER SUPPLY
TRANSMIT RF
EQUIPMENT
AC POWER
RECEIVE RF
EQUIPMENT
ANTENNA
Figure 4-7. Interface Loopback
Note: When interface loopback is turned on, data is looped back on the modem side of the interface. This test mode will verify the
internal channel unit interface operation.
4–31
Page 100

SDM-300L3 Satellite Modem Revision 1
Front Panel Operation MN/SDM300L3.IOM
FUNCTION SELECT: CONFIGURATION: INTERFACE: BUFFER SIZE (CONDITIONAL)
Conditional: The Bits or Milliseconds menu is displayed depending
upon whether Bits or Milliseconds is selected under the Utility:
IMPORTANT
Interface Buffer Program menu.
BUFFER SIZE
384 BITS
BUFFER SIZE
6 MILLI SECONDS
Sets the size of the buffer in either Bits or Milliseconds..
Upon entry, the current buffer length is displayed. Press [↑] or [↓] to select the desired
buffer size. The buffer size is displayed in seconds or bits. Enter the Utility Interface
menu to change the buffer units to seconds or bits.
• If selecting seconds, choose from 1 to 99 ms, in increments of 1 ms ≤ 2.6 Mbps
or 0 (Bypass).
• If selecting bits, choose from 32 to 262144 bits, in increments of 16 bits.
• Press [ENTER] to execute the change.
When D&I is selected for modem type, the buffer units are automatically set to ms. The
user may select as follows:
• nn = 7.5, 15, or 30 ms for E1CAS format.
• nn = 6, 12, 24, or 30 ms for T1IBS/T1S/T1ESFS format.
• nn = 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, or 32 ms for all other D&I formats.
Note: To have the modem calculate the plesiochronous shift, set the buffer units to ms.
When a specific buffer depth is desired, set the buffer units to bits. Select bits or ms from
the Utility: Interface menu.
4–32
 Loading...
Loading...