Page 1

Customer Assistance
A1
Our Thanks to You
Introduction
Thank you for purchasing the Cobra CPI 1575
inverter. Properly used, this Cobra product
will give you many years of reliable service.
How Your Cobra Power Inverter Works
The Cobra power inverter is an electronic product that has
been designed and built to take low voltage DC (Direct
Current) power from your automobile or other low voltage
power supplies and convert it to standard 115 volt AC
(Alternating Current) power like the current you have in
your home. This conversion process thereby allows you
to use many of your household appliances and electronic
products in automobiles, RVs, boats, tractors, trucks and
virtually anywhere else.
Customer Assistance
Should you encounter any problems with this product,
or not understand its many features, please refer to this
owner’s manual. If you require further assistance after
reading this manual, Cobra Electronics offers the
following customer assistance services:
For Assistance in the U.S.A.
Automated Help Desk English only.
24 hours a day, 7 days a week 773-889-3087 (phone).
Customer Assistance Operators English and Spanish.
8:00 a.m. to 6:00 p.m. CT, Monday through Friday
(except holidays) 773-889-3087 (phone).
Questions English and Spanish.
Faxes can be received at 773-622-2269 (fax).
Technical Assistance English only.
www.cobra.com (on-line: Frequently Asked Questions).
English and Spanish. productinfo@cobra.com (e-mail).
For Assistance Outside the U.S.A.
Contact Your Local Dealer
©2008 Cobra Electronics Corporation
6500 West Cortland Street
Chicago, Illinois 60707 USA
www.cobra.com
Operating Instructions
Nothing Comes Close To A Cobra
™
1500 WATT POWER INVERTER
CPI 1575
Printed in China
Part No. 480-400-P
Version A
Nothing Comes Close to a Cobra
®
For more information or to
order any of our products,
please visit our website:
www.cobra.com
The Cobra line of quality
products includes:
CB Radios
microTALK®Radios
Radar/Laser Detectors
Safety Alert®Traffic Warning Systems
Mobile GPS Navigation Systems
HighGear®Accessories
CobraMarine®VHF Radios
CobraMarine®Chartplotters
Power Inverters
Accessories
10275_CPI1575_PH3 8/14/07 8:37 AM Page 1
Page 2
25
Nothing Comes Close to a Cobra
™
A3A2
Product Features
Introduction
Introduction
Assistance
Warranty
Contents
Introduction
Our Thanks to You . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A1
Customer Assistance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A1
Product Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A2
Important Safety Information . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Quick Evaluation Before Installation . . . . . . .4
Installation
Installation Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Mounting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Connecting Cables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Power Consumption . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Ground Wiring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Operation
Turning Your Inverter On or Off . . . . . . . . 14
Remote On/Off Switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Operating Indicators . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Operating Limits . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Troubleshooting Guide . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Warranty
Warranty . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Customer Assistance
Maintenance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .23
Product Service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Accessories and Order Form . . . . . . . . . . 24
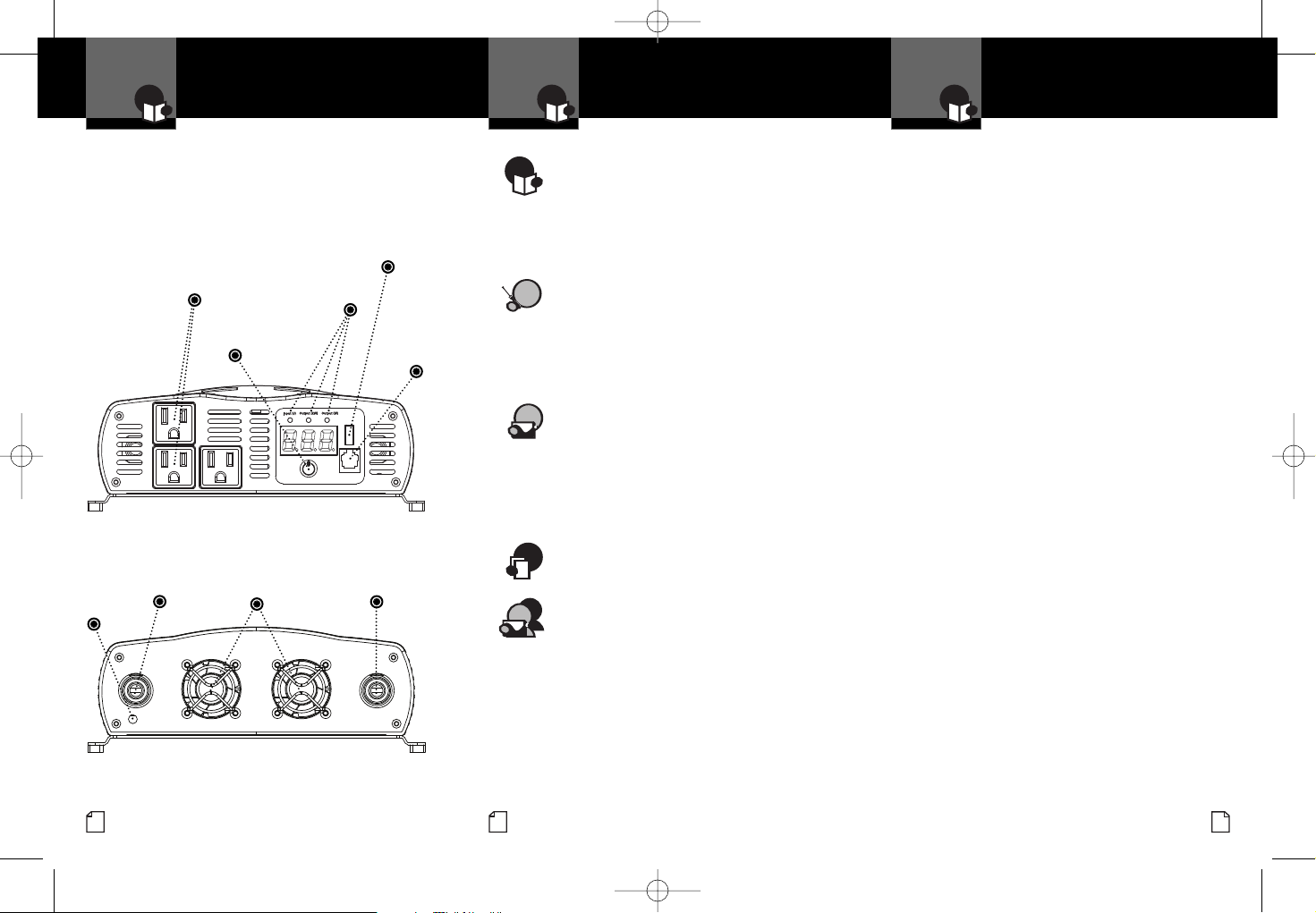
Remote On/Off
U
SB
Power
On/Off Power
Switch
Remote
On/Off
Switch
Jack
AC Outlets
Positive Battery
Cable Terminal
(Red)
Negative Battery
Cable Terminal
(Black)
Cooling Fans
Features
• Three AC Receptacles
• Voltage & Power Meter
• Remote On/Off Capable
• Automatic Thermal
Protection/Shutdown
• Reverse Polarity
Protection
• Low Battery Alarm
• Low Battery Shutdown
Voltage Input &
Power Output
Indicators
USB Outlet
Chassis
Ground
Terminal
Output End
Input End
Notes
Notes
10275_CPI1575_PH3 8/14/07 8:37 AM Page 4
Page 3

Warranty
Notes
W
arranty
Notes
Assistance
Warranty
Notes
1
Nothing Comes Close to a Cobra
™
Introduction
Important Safety Information
Important Safety Information
•
Before installing and using your Cobra power inverter,
please read these general precautions and warnings.
Caution and Warning Statements
To make the most of this inverter, it must be installed
and used properly. Please read the installation and
operating instructions carefully before installing and
using it. Special attention must be paid to the CAUTION
and WARNING statements in the manual.
CAUTION Statements specify conditions which
could cause damage to the unit or other equipment.
WARNING Statements identify conditions that
could result in personal injury or loss of life.
General Precautions
1. Never install the inverter in a boat’s engine compartment
where gas and battery fumes are present.
2. Do not operate the inverter if it has been dropped
or damaged in any way.
3. Do not open the inverter; it contains no userserviceable parts. Attempting to service unit
could cause electrical shock.
NOTE Internal components remain
charged after all power is disconnected.
4. Do not expose the inverter to rain, snow,
bilge water or spray.
5. Do not obstruct the ventilation openings.
6. Do not install the inverter in zero-clearance
compartment.
CAUTION This inverter should be used in
negative ground applications only.
Assistance
Warranty
Notes
Installation
10275_CPI1575_PH3 8/14/07 8:37 AM Page 1
Page 4
Assistance
W
arranty
N
otes
3
Nothing Comes Close to a Cobra
™
2
Important Safety Information
Introduction
WARNING Power inverters contain components
that tend to produce arcs or sparks. To prevent
fire or explosion, do not install the inverter in
areas or compartments containing batteries or
flammable materials or in locations that require
ignition-protected equipment.
WARNING To reduce the risk of fire, do not cover
or obstruct the ventilation openings. Do not install
inverter in zero-clearance compartment.
Caution: Rechargeable Appliances
Certain chargers for small nickel cadmium batteries
can be damaged if connected to the Cobra 1500 watt
inverter. Two particular types of equipment are
prone to this problem:
1. Small battery-operated appliances
such as flashlights, razors, and
night lights that can be plugged
directly into an AC receptacle to
recharge.
2. Certain battery chargers for
battery packs used in hand
power tools. These chargers have
a WARNING label stating that
dangerous voltages are present
at the battery terminals.
This problem does not occur with the vast majority of
battery operated equipment. Most use a separate charger
or transformer that is plugged into the AC receptacle and
produces a low voltage output. If the label on the AC
adapter or charger states that it produces a low voltage
AC or DC output (less than 30 volts), the inverter will
have no problem powering the adapter safely.
Cobra 1500 Watt Output Waveform
Some very sensitive electronic equipment may not operate
satisfactory on “square wave” or “modified sine wave.”
The output waveform is referred to as “square wave” or
“modified sine wave.” It is a stepped waveform designed
to have characteristics similar to the sine wave shape of
utility power.
A waveform of this nature is suitable for most AC loads
(including linear and switching power suppliers used in
electronic equipment, transformers and motors).
Important Safety Information
Introduction
Plug In Directly
Dangerous Voltages
10275_CPI1575_PH3 8/14/07 8:37 AM Page 2
Page 5
5
Nothing Comes Close to a Cobra
™
4
Quick Evaluation
Before Installation
Introduction
Quick Evaluation
Before Installation
Introduction
Quick Evaluation Before Installation
•
This section provides you with basic information about the
inverter and how to check its performance before installation.
Be sure to have on hand:
£ A 12 volt DC power source (such as a vehicle battery).
The power source must provide
between 11 and 15 volts DC and
be able to supply enough current to
run the test load. As a rough guide,
divide the wattage of the test load by
10 to get the current (in amperes)
the power source must deliver.
£ Cables to connect the power source to the inverter
(not included).
The cables must be as short and thick as possible in
order to reduce the voltage drop between the power
source and the inverter when it is drawing current
from the power source.
If the cable suffers an excessive voltage drop, the inverter
may shut down when drawing higher currents because
the voltage at the inverter dropped below 10 volts.
#4 AWG stranded copper cable is recommended.
It should be no longer than four feet (one and one-half
meters).
The end of the cable that connects to the inverter
must have its insulation stripped off for about
one-half inch (one and one-half cm) back from
the end, exposing the bare copper.
The other end of the cable, which connects to the power
source, must be terminated with a lug or other connector
that provides a secure, low resistance connection.
For example, if the power source is a battery, the cable
must be terminated with a battery terminal that clamps
to the post on the battery.
P
ower Source
£ A test load that can be plugged into the AC receptacle on
the inverter for short term testing at a low power level.
The following cables are recommended for testing low
power level test loads only.
Test Load Minimum
Power Cable Size
100W # 16 AWG copper
250W # 12 AWG copper
500W # 8 AWG copper
To check your inverter’s performance before installation:
1.
Turn the inverter off (see page 14
for details). If the power source is
a DC power supply, switch it off
as well.
2. Connect cables to power input
terminals (see page 8 for details).
3. Connect cables to power source
(see page 8 for details).
4. Check to make sure all
connections are secure.
5. Turn the inverter on. If the power
source is a DC power supply,
switch it on first.
6. Plug in the test load.
The inverter should supply power
to the load. If the inverter is not
working properly, refer to the
troubleshooting guide on page 20
or power and protection indicators
section on page 16.
NOTE A USB device can be
used to check the output
of the USB Outlet.
Assistance
Warranty
Notes
Installation
Test Load
Power Button
Connect Terminals
P
o
wer Button
Connect
T
est Load
USB Outlet
Connect Power Source
Intro Operation Customer
Assistance
Warranty
N
otes
Main Icons
Secondary Icons
Installation
Intro Operation Customer
Assistance
Warranty
Notes
Main Icons
Secondary Icons
Installation
Intro Operation Customer
Assistance
Warranty
Notes
Main Icons
Secondary Icons
Installation
Intro Operation Customer
Assistance
Warranty
Notes
Main Icons
Secondary Icons
Installation
10275_CPI1575_PH3 8/14/07 8:38 AM Page 4
Page 6

Assistance
W
arranty
Notes
Warranty
Notes
7
Nothing Comes Close to a Cobra
™
6
Mounting
Installation Requirements
•
The inverter must be installed in an area that meets all
of the following requirements:
A. Dry
Do not place in an area where water can drip
or splash on the inverter.
B. Cool
Ambient air temperature should be between 30°F
and 105°F (0°C and 40°C). The cooler the better.
C. Ventilate
Allow at least one inch (three cm) of clearance around
the inverter for proper airflow. Make sure that ventilation
openings on the ends of the unit are not obstructed.
D. Safe
Do not install the inverter in the same compartment
as a battery or in any compartment that contains
flammable liquids such as gasoline.
E. Close to Battery
Install unit as close to battery as possible (without
being in the same compartment) to minimize the
length of cable required to connect the inverter to
the battery. It is better and cheaper to run longer
AC wires than longer DC wires (cables).
CAUTION To avoid fire, do not cover or
obstruct ventilation openings. Do not install
inverter in a zero-clearance compartment.
Overheating may result.
CAUTION The inverter must only be connected to
batteries with a nominal output voltage of 12 volts.
It will not work with a 6 volt battery, and will be
damaged if it is connected to a 16 volt battery.
WARNING This unit contains components
which can produce arcs or sparks. To prevent
fire or explosion, do not install in compartments
containing a battery or flammable materials,
or in a location which requires ignition
protected equipment.
WARNING This unit is suitable for installation
in negative ground applications only. Do not
attempt to install to a positive ground application.
Mounting
•
To mount your inverter:
1. Place the inverter on a flat surface with the
mounting bracket against the mounting surface.
2. Mount to secure surface using mounting hardware
that is corrosion resistant (not included).
The inverter can be mounted horizontally or vertically.
If mounted vertically, neither end of the unit should be at
the top (to avoid foreign material from falling or settling
into the unit).
Assistance
Warranty
Installation
Installation
Requirements
Assistance
Warranty
Installation
Mounting Hardware
DC TO AC INVERTER
DC TO AC INVERTER
•1500 watts continuous • 3000 wattspeak
•
5V usb output
CPI 1575
Mounting Brackets
10275_CPI1575_PH3 8/14/07 8:38 AM Page 6
Page 7

9
Nothing Comes Close to a Cobra
™
8
Connecting Cables (not included)
•
Power wire and wiring are very important to the
performance of the inverter. Because the inverter has a
low voltage, high current input, low resistance wiring is
essential between the battery and inverter. This is so it
can deliver the maximum amount of energy to the load.
Use only copper wire. Aluminum wire has about one-third
more resistance than copper wire of the same size, plus it
is difficult to make good, low-resistance connections to
aluminum wire.
We recommend #4 AWG copper cable (90°C insulation
rating) as the minimum size for connections between
the battery and inverter.
Keep the cable length as short as possible, no more
than four feet (one and a half meters). This will keep the
voltage drop to a minimum.
If the cable has too much voltage drop, the inverter may
shut down when drawing higher currents because voltage
at the inverter may drop below 10 volts. If you must use
longer cables, choose thicker cables, such as #2 AWG,
and trim the ends of the cable to fit the terminals.
To connect the cables between the
inverter and the battery:
1. Press the Power Button on the inverter to the off
position. If the power source is a DC power supply,
switch it off as well.
2. On the end of the cable that connects to the inverter,
strip back the insulation about one-half inch (one and
one-half cm), exposing the bare copper conductor.
3. Connect cable to the Power Input Terminals on input
end of the inverter. The red terminal is positive (+) and
the black terminal is negative (-). Insert the bare ends
of the cables into the terminals and tighten the screws
to clamp the wires securely.
It is a good idea to check and tighten these screws
from time to time. They can become loose by
vibrations or thermal cycling.
4. Connect cables to the power source:
a. Connect the cable from the Negative (Black)
Terminal of inverter to the Negative Terminal
of the power source. Make a secure connection.
Connecting Cables Connecting Cables
Assistance
Warranty
Installation
Assistance
Warranty
Installation
Insert Bare Cables
Power Button
Intro Operation Customer
Assistance
Warranty
Notes
ain Icons
Installation
Strip the Insulation
10275_CPI1575_PH3 8/14/07 8:38 AM Page 8
Page 8

Assistance
Warranty
Notes
W
arranty
N
otes
Warranty
N
otes
CAUTION We recommend a main fuse in the
battery’s positive cable to protect against DC
wiring short circuits (external to the inverter).
The fuse should be as close to the battery as
possible. We recommend a Buss Fuse ANL-250
or equivalent. The specific fuse ampere rating
should be sized to allow operation of all your
DC powered equipment.
CAUTION Remove any jewelry (watch, ring, etc.).
Be careful not to short circuit the battery with any
metallic object (wrench, etc.).
WARNING If you are making a permanent AC
connection to the inverter, make sure that the AC
wiring steps are performed before any DC wiring is
done. (DC hook-up energizes internal components,
regardless of the position of the On/Off Switch).
Working on AC connections in such a circumstance
may result in an electric shock.
WARNING 115 volt AC power is potentially lethal.
Do not work on AC wiring when it is connected to
the inverter (even if it is switched off) unless the
DC power source is physically disconnected from
the inverter. Also, do not work on AC wiring if it
is connected to another AC power source such
as a generator or the utility line.
WARNING You may observe a spark when
making the connection because current can
flow to charge the capacitors in the inverter.
Do not make this connection in the presence
of flammable fumes. Explosion or fire may
result. Thoroughly ventilate the battery
compartment before making this connection.
b. Connect the cable from the Positive (Red) Terminal
of the inverter to the Positive Terminal of the power
source (the battery’s main fuse or the battery selector
switch, if you are using one). Make a secure connection.
You might observe a spark when you make this connection
since current can flow to charge capacitors in the inverter.
All power connections to your Cobra inverter must
be Positive to Positive and Negative to Negative.
CAUTION Electrical installations must meet
local and national wiring codes, and should be
performed by a qualified electrician.
CAUTION Do not connect the inverter and another
AC source (such as a generator or utility power)
to the AC wiring at the same time. The inverter
will be damaged if its output is connected to AC
voltage from another source. Damage can even
occur if the inverter is switched off.
CAUTION Do not connect the inverter to an AC
branch circuit that has high-power consumption
loads. It will not operate electric heaters, air
conditioners, stoves, and other electrical
appliances that consume more than 1500 watts.
CAUTION Loose connectors result in excessive
voltage drop and may cause over heated wires
and melted insulation.
CAUTION Reverse polarity connections (positive
to negative) will blow internal fuses in the inverter
and may permanently damage the unit. Such damage
is not covered by the warranty.
11
Nothing Comes Close to a Cobra
™
10
Connect Cables
Connecting Cables Connecting Cables
Assistance
Warranty
Installation
Assistance
Warranty
Installation
10275_CPI1575_PH3 8/14/07 8:38 AM Page 10
Page 9

13
Nothing Comes Close to a Cobra
™
12
Power Consumption
•
For each piece of equipment you will be operating from
the inverter, you must determine the battery’s reserve
capacity (how long the battery can deliver a specific amount
of current – in automotive batteries, usually 25 ampere) or
ampere-hour capacity (a measure of how many amperes a
battery can deliver for a specified length of time).
Example – Reserve capacity: a battery with a reserve
capacity of 180 minutes can deliver 25 ampere for 180
minutes before it is completely discharged.
Example – Ampere-hour capacity: a battery with an
ampere-hour capacity of 100 ampere-hours can deliver
5 ampere for 20 hours before it is completely discharged.
To determine the battery ampere-hour
capacity you require:
1. Determine how many watts each piece of equipment
consumes. This can normally be found on the product
label. If only the current draw is given, multiply the
current draw by 115 to get the watt consumption.
2. Estimate the time (in hours) that each piece of equipment
will be running between battery charging cycles.
3. Calculate the total watt-hours of energy consumption
(power x operating time) using the average power
consumption and the total estimated running time
(in hours). Power x Operating Time = Watt-Hours.
4. Divide the watt-hours by 10 to determine how many
battery (12 volt) ampere-hours will be consumed.
Ground Wiring
•
There is a screw on the rear panel for Chassis Ground.
This is to connect the chassis of the inverter to ground.
The Chassis Ground Screw must be connected to a
grounding point, which will vary depending on where
the unit is installed. Use a #8 AWG copper wire
(preferably with green/yellow insulation) to connect
the chassis ground screw to the grounding point.
In a vehicle: Connect the Chassis Ground to the chassis
of the vehicle.
In a boat: Connect to the Boat Grounding System.
In a fixed location: Connect the Chassis Ground Screw
to earth ground by connecting to a ground rod (a metal
rod pounded into the earth) or other proper service
entrance ground.
Power Consumption Ground Wiring
Assistance
Warranty
Installation
Assistance
Warranty
Installation
Chassis Ground
Laptop
100 watts x 2 hours
= 200 watt-hours
TV/VCR (up to 25
")
115 watts x 3 hours
= 345 watt-hours
Blender
300 watts x 15 minutes
= 75 watt-hours
10275_CPI1575_PH3 8/14/07 8:38 AM Page 12
Page 10

15
Nothing Comes Close to a Cobra
™
14
Turning Your Inverter On or Off
•
Be sure to have your power inverter properly installed
before attempting to turn the unit on (see installation
page 6).
To turn the power inverter on:
1. If a DC power supply is being used as the power
source, switch it on.
2. On the Output End, press the Power Button to on.
The inverter is now ready to deliver AC power to your loads.
If several loads are to be operated by the inverter, turn
them on separately, after the inverter has been turned on.
This will ensure that the inverter does not have to deliver
the starting currents required for all the loads at once.
NOTE The Power Button turns the control circuit
in the inverter on and off. It does not disconnect
power from the inverter.
When the button is in the
off position, the inverter
draws no current from the battery. When it’s in the
on position, but no power is being supplied to a
load, the inverter draws less than 600 milliamperes
from the battery. This is low current draw. It would
take more than a week to discharge a 100 amperehour battery at this rate depending on the age of
the battery.
Remote On/Off Switch
•
An optional Remote On/Off Switch (see page 24 to order
accessories) can be connected to the Remote Jack
allowing you to turn the Cobra power inverter on or off
from a convenient location when the inverter is installed
in an out of reach location.
Power On and Off
Operation
Remote On/Off Switch
Operation
Power Button
Remote Switch
Remote Jack
Intro Operation Customer
A
ssistance
Warranty
N
otes
Installation
Assistance
Warranty
Notes
Installation
Intro Operation Customer
A
ssistance
Warranty
N
otes
Installation
10275_CPI1575_PH3 8/14/07 8:38 AM Page 14
Page 11

17
Nothing Comes Close to a Cobra
™
16
Operating Indicators
Operation
Operating Indicators
Operation
Operating Indicators
•
Indicators at the Output End of the unit show the unit’s
power status and alarms for conditions that could cause
it to shut down.
Power on – The Voltage Input
and Power Output indicators
automatically toggle between input
and output values at three-second
intervals. The three LEDs indicate
the mode the meter is in and the
three digits indicate the voltage
or power value.
Current Overload Protection –
If the inverter is overloaded,
it will shut down to protect itself.
The meter will flash as shown to
indicate Overload Protect.
To restore normal operation,
disconnect the excessive load
and turn the unit Off and On
again using the Power Button.
Short Circuit Protection – If the
AC output of the inverter is shortcircuited for one second or more,
it will shut down to protect itself.
The meter will flash as shown to
indicate Short Circuit Protect and
an alarm will sound.
To restore normal operation,
disconnect the short circuit and
turn the unit Off and On again
using the Power Button.
Low Voltage Protection – If the
DC input voltage drops below
the alarm threshold of 10.5V the
meter will flash as shown to
indicate Low Voltage Protection,
but the unit will continue to
operate. If the input voltage drops
to 10.0V or less, the inverter will
shut down to protect itself, the
meter will continue to flash as
shown, and an alarm will sound.
To restore normal operation, return
the DC input voltage to at least
12V. The inverter will automatically
return to normal operation.
High Voltage Protection – If the
DC input voltage rises above 15.0V,
the inverter will shut down to protect
itself, the meter will flash as shown
to indicate Over Voltage Protection,
and an alarm will sound.
To restore normal operation, return
the DC input voltage to less than
15V. The inverter will automatically
return to normal operation.
High Voltage
Over Current
Short Circuit
L
ow Voltage
Output Watts
10275_CPI1575_PH3 8/14/07 8:38 AM Page 16
Page 12

18
19
Nothing Comes Close to a Cobra
™
Operating Limits
Operation
Operating Limits
•
Power Output
The inverter can deliver 1500 watts for about 60 minutes.
The inverter must cool for 15 minutes before it can
resume operation at 1500 watts. Note: The wattage
rating applies to resistive loads.
The inverter will operate most AC loads within its power
rating. Some induction motors used in freezers, pumps,
and other motor-operated equipment require very high
surge currents to start. The inverter may not be able
to start some of these motors even though their rated
current draw is within the inverter’s limits. The inverter
will normally start single phase induction motors rated
at one-half HP or less.
Input Voltage
The inverter will operate from input voltage ranging
from 10 volts to 15 volts. Optimum performance will
occur when the voltage is between 12 volts and 14 volts.
If the voltage drops below 10.5V+/-0.3V, an audible low
battery warning will sound. The inverter will shut down if
the input voltage drops below 9.5V+/-0.3V. This protects
the battery from being over-discharged. It will restart
when the input voltage exceeds 12V+/-0.3V.
The inverter will also shut down if the input voltage
exceeds 15.5V+/-0.5V. This protects the inverter
against excessive input voltage. Although the inverter
has protection against over-voltage, it may still be
damaged if the input voltage were to exceed 16 volts.
H
igh Temperature
Over Temperature Protection –
If the internal inverter temperature
rises above the alarm threshold,
the meter will flash as shown, an
alarm will sound to indicate Over
Temperature Protect, and the unit
will continue to operate. If the
internal temperature rises to 40ºC
(104ºF), the inverter will shut down
to protect itself, the meter will
flash as shown and the alarm will
continue to sound.
NOTE Internal inverter temperature
can rise due to being operated in a
high heat environment or due to the
fan or vents being blocked during
operation (even in relatively cool
outside air).
To restore normal operation, turn
the unit Off and allow it to cool.
The inverter will automatically
return to normal operation after
it has cooled.
Assistance
Warranty
N
otes
Installation
Operating Indicators
Operation
10275_CPI1575_PH3 8/14/07 8:38 AM Page 18
Page 13

21
Nothing Comes Close to a Cobra
®
20
Specifications
Operation
Specifications
•
Continuous output power (1 hour) . . . . . . . . . . . 1500W
Surge rating (0.1 second) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3000W
Peak efficiency (12V – 1⁄2 load) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . > 88%
Efficiency (full load, 12V) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . > 83%
No load current draw . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . < 0.6A (12.6V)
Output waveform (resistive load) . . . Modified sine wave
Output frequency . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58HZ – 62HZ
Output voltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109V – 120V
USB output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5V
Input voltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10.4VDC – 14.4VDC
Alarm voltage (unload) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10.2V – 10.8V
Shutdown voltage (unload) . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9.2V – 9.8V
Operating temperature range . . . . . . . . . . . . 0°C – 40°C
(32°F – 104°F)
Storage temperature range . . . . . . . . . . . . -40°C – 85°C
(-40°F – 185°F)
Protection . . . . . . . . . .Overload, short-circuit, overtemp,
reverse polarity, under/over voltage
Notes
All protection is automatically recovered.
To protect the battery, if the unit needs to be restarted
after low voltage protection, the voltage of DC input
should be above 12V.
To extend the life of the fan, it will stop when there is no
load. The speed of the fan increases as the load increases.
The unit is completely insulated in input and output for
added safety.
Troubleshooting Guide
Operation
Problem/Symptom
Low output voltage
No output voltage
No output voltage
after prolonged use
No output voltage,
“Protect” indicator
lighted
No output voltage
No output voltage
Low battery alarm
on all the time
Possible Causes
Overload
Low input
voltage
Thermal
shutdown
High input
voltage
Short circuit
Inverter
switched off
No power
to inverter
Reverse
DC polarity
Poor DC wiring
Poor battery
condition
Solution
Reduce the load.
Recharge battery.
Check connections
and cable.
Allow inverter
to cool off.
Reduce load,
continuous
operation input
current required.
Improve ventilation;
Make sure ventilation
openings in the
inverter are not
obstructed.
Reduce ambient
temperature.
Make sure
the inverter is
connected to
12V battery.
Check regulation
of charging system.
Check load for
proper operation.
Turn inverter on.
Check wiring
to inverter.
Observe
correct polarity.
Check connections.
Make sure battery
is fully charged.
Troubleshooting Guide
•
10275_CPI1575_PH3 8/14/07 8:38 AM Page 20
Page 14

23
Nothing Comes Close to a Cobra
™
22
Maintenance
•
Very little maintenance is required to keep the inverter operating
properly. The exterior of the unit should be cleaned periodically
with a damp cloth to prevent accumulation of dust and dirt. At the
same time, tighten the screws on the DC input terminals. Be sure
vents and fans are free of dust or debris.
Product Service
•
For any questions about operating or installing this new Cobra
product, or if parts are missing…
PLEASE CALL COBRA
FIRST
…do not return this product to the store. See customer
assistance on page A1.
If your product should require factory service, please call Cobra
first before sending your power inverter. This will ensure the
fastest turn-around time on your repair. You may be asked
to send your power inverter to the Cobra factory.
It will be necessary to furnish the following to have the product
serviced and returned.
1. For warranty repair include some form of proof-of-purchase,
such as a mechanical reproduction or carbon copy of a sales
receipt. If you send the original receipt, it cannot be returned.
2. Send the entire product.
3. Enclose a description of what is happening with the power
inverter. Include a typed or clearly printed name and address
of where the power inverter is to be returned.
4. Pack power inverter securely to prevent damage in transit.
If possible, use the original packing material.
5. Ship prepaid and insured by way of a traceable carrier
such as United Parcel Service (UPS) or Priority Mail to
avoid loss in transit to:
Cobra Factory Service
Cobra Electronics Corporation
6500 West Cortland Street
Chicago, Illinois 60707 USA.
6.
If the power inverter is in warranty, upon receipt of your power
inverter, it will either be repaired or exchanged depending on the
model. Please allow approximately three to four weeks before
contacting Cobra for status. If the power inverter is out of
warranty, a letter will automatically be sent informing you
of the repair charge or replacement charge.
If you have any questions, please call 773-889-3087 for assistance.
Maintenance and
Product Service
Customer Assistance
Limited Two-Year Warranty
•
For Products Purchased in the U.S.A.
Cobra Electronics Corporation warrants that its Cobra power
inverter, and the component parts thereof, will be free of defects in
workmanship and materials for a period of two years from the date
of first consumer purchase. This warranty may be enforced by the
first consumer purchaser, provided that the product is utilized
within the U.S.A.
Cobra will, without charge, repair or replace, at its option, defective
power inverters, products or component parts upon delivery to the
Cobra Factory Service department, accompanied by proof of the
date of first consumer purchase, such as a duplicated copy of a
sales receipt.
You must pay any initial shipping charges required to ship the
product for warranty service, but the return charges will be at
Cobra’s expense, if the product is repaired or replaced under
warranty. This warranty gives you specific legal rights, and you
may also have other rights which may vary from state to state.
Exclusions: This limited warranty does not apply:
1. To any product damaged by accident.
2. In the event of misuse or abuse of the product or
as a result of unauthorized alterations or repairs.
3. If the serial number has been altered, defaced, or removed.
4. If the owner of the product resides outside the U.S.A.
All implied warranties, including warranties of merchantability
and fitness for a particular purpose are limited in duration to the
length of this warranty. Cobra shall not be liable for any incidental,
consequential or other damages; including, without limitation, to
damages resulting from loss of use or cost of installation.
Some states do not allow limitations on how long an implied warranty
lasts and/or do not allow the exclusion or limitation of incidental or
consequential damages, so the above limitations may not apply to you.
For Products Purchased Outside the U.S.A.
Please contact your local dealer for warranty information.
Trademark Acknowledgement
•
Cobra®, Nothing Comes Close to a Cobra®and the snake
design are registered trademarks of Cobra Electronics
Corporation, USA. Cobra Electronics Corporation™ is a
trademark of Cobra Electronics Corporation, USA.
Warranty and Trademark
Acknowledgement
Warranty
10275_CPI1575_PH3 8/14/07 8:38 AM Page 22
Page 15

Name
Address (No P.O. Boxes)
City State/Province Zip Country
Telephone
Credit Card Number Type: ❒ Visa ❒ Mastercard ❒ Discover E xp.Da te
Customer Signature
Optional Accessories
You can find quality Cobra products and accessories at your
local Cobra dealer, or in the U.S.A., you can order directly
from Cobra.
Ordering from U.S.A.
Call 773-889-3087 for pricing or visit www.cobra.com.
For credit card orders, complete and return this order
form to fax number 773-622-2269. Or call 773-889-3087
(Press 1 from the main menu) 8:00 a.m. to 6:00 p.m. CT,
Monday through Friday.
Make check or money order payable to:
Cobra Electronics, Attn: Accessories Dept.
6500 West Cortland Street, Chicago, IL 60707 USA
To order online, please visit our website: www.cobra.com
•
An optional Remote On/Off Switch can be
connected to the Remote Jack allowing you to
turn the Cobra CPI 1575 inverter on or off
from a convenient location when the inverter
is installed in an out of reach location.
R
emote On/Off
Switch (CPI A20)
Accessories and
Order Form
Customer Assistance
24
10275_CPI1575_PH3 8/14/07 8:38 AM Page 24
 Loading...
Loading...