Page 1

R-Series Data Center Products
User’s Guide
Rev G
Page 2

Technical Support
Please refer to our support website for technical updates, additional warranty
information and documentation, and software revisions:
Web: http://www.clearcube.com/support/
Email: support@clearcube.com
Phone: (512) 652-3400 or call toll free (866) 652-3400 (United States)
ClearCube Technology Corporate Headquarters
Mailing and Shipping Address:
ClearCube Technology, Inc.
3700 W Parmer Lane
Austin, TX 78727
Email: info@clearcube.com
Main Phone: (512) 652-3500 or call toll free (866) 652-3500 (United States)
Main Fax: (512) 652-3501
Or your local ClearCube Reseller or Authorized Service Provider
Copyrights
©2005 – 2012 by ClearCube Technology, Inc. All rights reserved. Under copyright
laws, this publication may not be reproduced or transmitted in any form, electronic or
mechanical, including photocopying, recording, storing in an information retrieval
system, or translating, in whole or in part, without the prior written consent of
ClearCube Technology, Inc.
This information is subject to change without notice and ClearCube shall not be liable
for any direct, indirect, special, incidental or consequential damages in connection
with the use of this material.
Trademarks
ClearCube™, Sentral™, Blade Switching BackPack™, PC Blade™, C/Port™, and
I/Port™, PC-over-Ethernet™, PCoE™, and the PCoE™ logo are trademarks of
ClearCube Technology Inc. Product and company names mentioned herein are
trademarks or trade names of their respective companies.
Patents
The ClearCube Architecture and its components described in this user manual are
protected by numerous granted and pending U.S. and international patents.
Granted patents include: US05926172, US05966056, US05994952, US06012101,
US06020839, US06037884, US06038616, US06119146, US06148182,
US06167241, US06385666, US06421393, US06426970, US06633934,
US06708247, US06735658, and US06886055.
Patents pending include: US S/N 09/755378, US S/N 10/279475, US S/N 10/19 871 9,
US S/N 10/198650, US S/N 10/409219, US S/N 09/728667, US S/N 09/728669, US
S/N 10/411804, US S/N 10/411908, US S/N 10/458853, US S/N 10/364584, US S/N
10/301536, US S/N 60/411066, US S/N 10/662933, US S/N 10/662889, US S/N
10/662932, US S/N 10/662968, US S/N 10/301563, US S/N 10/662936, US S/N
10/301518, US S/N 10/662955 and US S/N 10/662954.
Inquiries regarding patented technology should be directed to ClearCube Corporate
Headquarters.
Page 3

Contents
How to Use this Guide . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ix
FCC Warning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ix
California Proposition 65 Statement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ix
WEEE Information. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .x
Warning Regarding Medical and Clinical Use of ClearCube Products. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .x
Avertissement concernant l'usage médical et clinique des produits ClearCube . . . . . . . . . . . .x
Warnung zum medizinischen oder klinischen Einsatz von ClearCube-Produkten . . . . . . . . . xi
El Cuidado con Respecto al Uso Médico y Clínico de los Productos de ClearCube. . . . . . . . xi
Symbols – English . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xi
Safety Guidelines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .xiii
Symboles – Français. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xiv
Guide de sécurité . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xvi
Symbole – Deutsche. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xviii
Sicherheitsrichtlinien . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xix
Símbolos – Español . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xxi
Directrices de seguridad. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xxii
Chapter 1. ClearCube Architecture and Product Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
R-Series PC Blade . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2
R-Series Chassis. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5
C/Port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6
Multi-Video Solution . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7
Fiber Optic Extension System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7
Fiber Transceiver. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8
C7420 Fiber C/Port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8
Zero Clients and Thin Clients. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9
Chapter 2. Network Planning and Site Preparation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Rack and Cabinet Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
Space and Floor Support Requirements. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
Power and Cooling Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13
Additional Power Considerations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13
Additional Cooling and HVAC Considerations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
Cable Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
Free IP Address Requirement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .17
R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide Contents • iii
Page 4

Chapter 3. Chassis and Blade Installation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Tools for Installation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Shipment Components . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Chassis Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Unpacking the Chassis . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Installing the Chassis . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Standard Chassis Mounting Hardware. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Chassis Rapid Mount Kit. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Chassis Power Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Chassis Power Receptacles, Redundant Power, and Power Cords . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Chassis Configuration and Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
R4300 Modules . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Power Modules. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Connecting Cables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Spare Allocation Examples . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
R4300 Chassis . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Mixed-Mode Chassis Cabling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
R3040S Cabling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
NICs When Using a Traditional Video Card. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
NICs When Using a V52x0 PCoIP Host Card. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
How OS Network Connections Are Mapped to NICs on Chassis Backpack. . . . . . . . . . 41
MAC Address Label on R-Series Blades. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
R3040S Labels. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
R3080D Labels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
R1350 Labels. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
C/Port Cabling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
R3080D Cabling. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
How OS Network Connections Are Mapped to NICs on Chassis Backpack. . . . . . . . . . 44
C/Port Cabling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
RMM Firmware Update Procedures. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Updating RMM Firmware Using Telnet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Updating RMM Firmware with Sentral . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Remote Management Card Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Control Chain Auto-Negotiation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Configuring the RMM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Resetting the RMM Settings to the Factory Defaults. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Configuring the RMC. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Changing the IP Address of the RMC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Resetting the RMC IP Settings to the Factory Defaults . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
iv • Contents R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide
Page 5

R4300 Chassis Upgrade Kit Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .55
Fiber Transceiver and Cable Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .57
PC Blade Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .58
Unpacking the PC Blades . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .58
Installing PC Blades. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .58
Connecting Ethernet Cables. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .60
R3040S Blades . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .60
R3080D Video Options and Ethernet Port Behavior . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .61
R1350 Video Options and Ethernet Port Behavior . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .61
Using USB 2.0 Capability on the R3040S and R1350 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .61
R1350 Monitor Support. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .62
R3080D and R3040S Display Support and Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .62
Graphics Options and Number of Displays Supported . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .62
Configuring Multiple DVI-I Displays with V52x0 PCoIP Host Cards. . . . . . . . . . . .62
Video Resolution . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .63
Changing CMOS Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .63
Resetting an R1350 CMOS Password . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .64
Clearing All R3080D and 3040S CMOS Settings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .65
Configuring RAID on an R3040S Blade. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .66
Prerequisites and Overview of Required RAID Tasks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .66
Enable RAID in BIOS. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .67
Creating a RAID Volume Using Software RAID. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .68
Installing a Windows OS on a RAID Volume . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .69
Removing a PC Blade . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .71
Mass Storage Lockout: Disabling Access to USB Mass Storage Devices . . . . . . . . . . . .71
Re-installing System Software. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .74
Flashing the Blade BIOS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .75
Chapter 4. Hardware Upgrade and Replacement Procedures. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
Drivers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .79
Upgrading Memory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .80
Model R3040S. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .80
Model R3080D. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .82
Important Installation Considerations. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .82
Installing 2 DIMMs. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .82
Installing 3 DIMMs. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .83
Installing 4 DIMMs. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .83
Model R1350 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .83
Replacing and Upgrading Hard Disks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .84
R3040S Hard Disks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .84
R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide Contents • v
Page 6

R3040S Hard Disk Tray, Drive Layout, and SATA Headers on Motherboard. . . . . 85
Replacing an R3040S Hard Disk. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
R3080D Hard Disk. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
R1350 Hard Disk . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
Replacing CPU Fans. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
R3040S Fans. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
R3080D Fan . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
Replacing a Front LCD Panel. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
Replacing the CMOS Memory Battery. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
Replacing Blade Interposer Cards. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
R3040S Interposer Cards . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
R3080D and R1350 Interposer Card . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 104
Replacing R4300 Management, Connect and Network Modules. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
Replacing the R4300 Fan Pack. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
Replacing an R4300 Power Supply Unit (PSU) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 106
Chapter 5. Troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 107
PCoIP Issues . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 107
PCoIP Host on Different Subnet Than PCoIP Client Is Unable to Wake Up from Various
Power States. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 107
Power Issues . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108
No power to PC blade. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108
No video or link lights at desktops and no power to blades. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108
Chassis power does not come on . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108
Video Issues . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108
Digital link shows red at blade but green on C/Port. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108
Fiber Optic Troubleshooting. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109
No video and/or digital link present. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109
The monitor’s Auto-Adjust does not give a clear, sharp image. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109
Network and PXE Booting Troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109
Unable to network or PXE boot using an R3040S. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109
Appendix A. Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 111
R-Series Blades. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 111
R4300 Chassis. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 112
F6150–160 Fiber Transceiver. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 112
Appendix B. Regulatory Compliance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 115
Appendix C. Technical Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 117
Contact Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 117
Product Updates . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 117
vi • Contents R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide
Page 7

Return Merchandise Authorization (RMA) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .118
Fuse and Power Cord Replacement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .118
Appendix D. Warranty. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 121
Appendix E. Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment Directive (WEEE) . . . . 125
WEEE Information. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .125
Informations sur la DEEE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .126
Informationen über WEEE. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .126
La información de REEE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .127
R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide Contents • vii
Page 8

viii • Contents R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide
Page 9

Introduction
How to Use this Guide
Thank you for purchasing your quality ClearCube products. The ClearCube
Architecture was developed to bring you unprecedented levels of manageability,
security, reliability, and space savings. The ease of use of ClearCube’s products will
make installation straightforward.
This manual provides all the product and installation information needed to set up and
run ClearCube Technology’s R-Series architecture for managed desktop
environments. We recommend that you familiarize yourself with the ClearCube
Architecture and product descriptions and read through the entire installation and
setup procedures before beginning installation.
If you encounter any problems, please contact our Technical Support using the contact
information provided on the inside front cover of this manual and in Appendix C on
page 117.
FCC Warning
This equipment generates and uses radio frequency energy and, if not installed and
used in strict accordance with the instructions in this manual, may cause interference
to radio and television reception. Changes or modifications not expressly approved by
ClearCube Technology could void the user's authority to operate the equipment under
the FCC Rules.
California Proposition 65 Statement
WARNING: ClearCube products contain chemicals, including lead,
known to the State of California to cause cancer, birth defects, or
other reproductive harm. Wash hands after handling.
ClearCube products should be disposed of in accordance with local laws governing
computer equipment disposal.
R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide Introduction • ix
Page 10

WEEE Information
See “Appendix E.Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment Directive (WEEE)” on
page 125 for detailed information about the Waste Electrical and Electronic
Equipment Directive.
Warning Regarding Medical and Clinical Use of
ClearCube Products
ClearCube products are not designed with components and testing for a level of
reliability suitable for use in or in connection with surgical implants or as critical
components in any life support systems whose failure to perform can reasonably be
expected to cause significant injury to a human. Applications of ClearCube products
involving medical or clinical treatment can create a potential for death or bodily injury
caused by product failure, or by errors on the part of the user. Because each end-user
system environment is customized and differs from ClearCube testing platforms and
because a user may use ClearCube products in combination with other products in a
manner not evaluated or contemplated by ClearCube, the user is ultimately responsible
for verifying and validating the suitability of ClearCube products whenever ClearCube
products are incorporated in a system, including, without limitation, the appropriate
design, process and safety level of such system or application.
Avertissement concernant l'usage médical et clinique
des produits ClearCube
Les produits ClearCube ne sont pas conçus pour être utilisés avec une efficacité adéquate dans ou avec des implants chirurgicaux ou dans des appareils de maintien de vie
pour lesquels toute panne causerait de sérieux problèmes de santé ou blessures à l'être
humain. Les applications des produits de ClearCube dans des traitements médicaux ou
cliniques peuvent être dangereuses et toute panne du produit ou erreur de l'utilisateur
peuvent provoquer la mort ou des blessures. Du fait que l'environnement de chaque utilisateur final est unique et diffère de celui des plate-formes de tests de ClearCube, et que
l'utilisateur peut employer les produits ClearCube avec d'autres appareils d'une manière
qui n'a pas été évaluée ou envisagée par ClearCube, l'utilisateur est entièrement responsable de la vérification et de la confirmation de la compatibilité des produits ClearCube
lorsqu'ils sont incorporés dans un système, incluant, sans limitations, le concept approprié, le procédé et le niveau de sécurité des dits systèmes ou applications.
x • Introduction R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide
Page 11

Warnung zum medizinischen oder klinischen Einsatz
von ClearCube-Produkten
ClearCube-Produkte sind nicht für Komponenten oder zum Testen geeignet, bei denen
eine Betriebssicherheit gewährleistet sein muss, die bei der Verwendung mit oder im
Zusammenhang mit chirurgischen Implantaten oder als kritische Komponenten in jeglicher Art von Lebenserhaltungssystemen einher geht, bei denen ein Funktionsausfall
eine ernstzunehmende Verletzung eines Menschen zur Folge haben kann. Die
Anwendung von ClearCube-Produkten bei medizinischen oder klinischen Behandlungen kann potentiell zum Tode oder zu Verletzungen bei Funk t ionsausfällen des Produkts oder bei Bedienungsfehlern durch den Benutzer führen. Da jede
Endbenutzerumgebung speziell angepasst ist und sich von ClearCube-Testplattformen
unterscheidet, und da ein Benutzer ClearCube-Produkte zusammen mit anderen Produkten auf eine nicht von ClearCube in Betracht gezogene Art verwenden kann, liegt die
endgültige Verantwortung über die Prüfung und Validierung der Eignung von ClearCube-Produkten beim Benutzer, wenn ClearCube-Produkte in ein System eingebunden
sind, einschließlich und ohne Einschränkung, das geeignete Design, der Prozess und die
Sicherheitsebene eines solchen Systems oder einer solchen Anwendung.
El Cuidado con Respecto al Uso Médico y Clínico de los
Productos de ClearCube
Productos de ClearCube no son diseñados con componentes aprobados para un nivel
de certeza adecuada para el uso en o con respecto a injertos quirúrgicos o
componentes críticos en ningún sistema de apoyo de vida, cuyo fracaso para actuar, se
puede esperar razonablemente causar una herida significativa a un humano. Las
aplicaciones de productos de ClearCube, el tratamiento médico, o clínico, que
implica, puede crear un potencial para la muerte o en herida personal causada por el
fracaso del producto, o por errores por parte del usuario. Porque cada ambiente de
sistema de usuario es construido al gusto del comprador y difiere en plataformas de
prueba de ClearCube y porque un usuario puede usar los productos de ClearCube en la
combinación con otros productos en una manera no evaluada ni contemplada por
ClearCube, el usuario es últimamente responsable de verificar y validar lo apropiado
de los productos de ClearCube cuando los productos de ClearCube se incorporan en
un sistema, incluyendo, sin limitación, el diseño apropiado, el nivel del proceso, y la
seguridad de tal sistema o la aplicación.
Symbols – English
Symbols are used on the equipment to convey specific information to the operator and
service person. It is important to understand the intended meaning of these symbols.
R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide Introduction • xi
Page 12
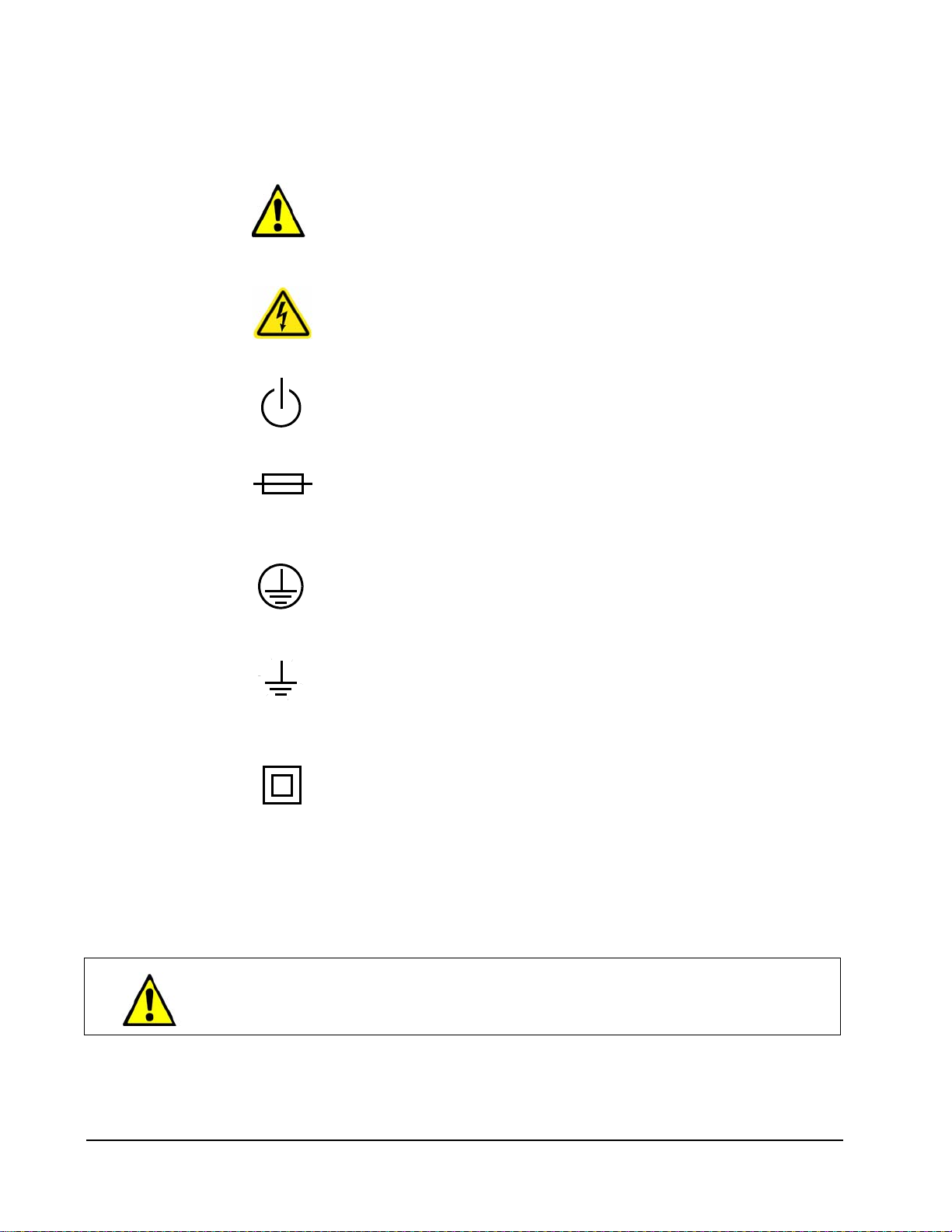
Below are the graphical symbols that are used on ClearCube Technology, Inc.
Products and their meaning.
Refer to Manual
Used on the equipment’s rating label to direct the operator or service
person to the manual for additional information.
Shock Hazard
This symbol indicates the presence of electric shock hazards. Enclosures
marked with these symbols should only be opened by qualified service
personnel. Refer to the manual for additional information.
Power
Identifies the soft-start switch located on front of the blade, used to power
the blade on and off.
Fuse
Located on equipment rating label. Symbol is accompanied with the
specifications needed for replacement. Only qualified technicians should
perform this operation.
Protective Earth Terminal
This symbol identifies the location of the protective earth terminal on the
equipment. This terminal is used to connect the protective earth conductor
of the power cord to the building's electrical distribution system's ground.
Ground Bond Terminal
This symbol identifies the location ground bond terminal. This terminal is
used to connect the ground bonding conductor, or the combination of
conductive parts to earth ground for safety purposes.
Equipment Protection Class II
May be located on the power adapter’s rating label. Indicates that
equipment is double insulated from hazardous voltages. Not to be
confused with “Class 2” that is a US National Electrical Code (NEC) circuit
classification.
These same symbols are used within this document where appropriate to indicate
situations that merit checking this or another manual, or situations that could result in
damage to equipment or physical injury.
CAUTION: A Caution notice in this manual indicates that equipment
damage or minor injury may result if proper procedures are not followed.
xii • Introduction R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide
Page 13

WARNING: A Warning notice in this manual indicates that catastrophic
equipment damage, or serious injury including death may result if
proper procedures are not followed.
Safety Guidelines
Before undertaking any troubleshooting or maintenance procedure, read carefully all
WARNING and CAUTION notices. This equipment contains voltage hazardous to
human life and is capable of inflicting personal injury.
• Installations – ClearCube equipment is required to be installed in accordance
with the local electrical codes and may be subject to inspection by the authority
having jurisdiction.
• Chassis Grounding – ClearCube’s chassis and Fiber Transceiver have been
designed with a three-conductor IEC 60320 appliance inlet that – with the proper
power cord – connects the building’s external protective earthing conductor to all
accessible metal parts of the enclosure. To minimize shock hazard, make sure
your electrical power outlet has an appropriate earth safety ground that is
connected each time you power on the equipment.
Swedish safety regulations require the following statement:
—Apparaten skall anslutas till jordat uttag när den anslutas till ett nätuerk.—
Finnish safety regulations require the following statement:
— Laite on liitettävä suojamaadoituskoskettimilla varustettuun pistorasiaan.—
• Power Cord Selection – ClearCube or ClearCube’s Distributors provides power
cords that are specifically designed for use with that particular piece of equipment
and are approved for use by the local authority having jurisdiction in the country
where the equipment is put into service. Please refer to the installation sections of
this manual for specific power cord requirements. For replacement of power
cords, refer to Appendix C – Technical Support.
• Power Adapters – ClearCube or ClearCube’s Distributors provides power
adapters that are specifically designed for use with that particular piece of
equipment and are approved for use by the local authority having jurisdiction in
the country where the equipment is put into service. Please refer to the installation
sections of this manual for specific power cord requirements. For replacement of
power cords, refer to Appendix C – Technical Support.
• IT Power Systems – ClearCube equipment has been evaluated and found to be
compatible with IT power distribution systems with a phase-to-phase voltage not
to exceed 240 V.
R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide Introduction • xiii
Page 14

•Live Circuits – Operating personnel and service personnel must not remove
protective covers when operating the ClearCube chassis. Adjustments and service
to internal components must be undertaken by qualified service technicians.
During any service of this product other than replacing a PC blade or externally
accessible modules on the chassis, the main connector to the premise wiring must
be disconnected. Dangerous voltages may be present under certain conditions.
Use extreme caution.
• Explosive Atmosphere – Do not operate the chassis in conditions where
flammable gases are present. Under such conditions this equipment is unsafe and
may ignite the gases or gas fumes.
• Part Replacement – Only service equipment with parts that are exact
replacements, both electrically and mechanically. Contact ClearCube Technology
for replacement part information. Installation of parts that are not direct
replacements will void the warranty and may cause harm to personnel operating
the chassis. Furthermore, damage or fire may occur if replacement parts are
unsuitable.
• Modification – Do not modify any part of the C/Port, chassis, or PC blade from
its original condition. Modifications may result in hazards.
• Laser Safety – The Fiber Transceiver and the Fiber C/Port have been evaluated
and certified to an EN 60825-1 – Safety of laser products. Refer to Appendix B
for more details.
CAUTION: Use of controls or adjustments or performance of procedures
other than those specified herein may result in hazardous radiation
exposure.
ClearCube Technology products that use lasers display the following graphic on the
rating label:
Marked devices comply with the FDA code of Federal 21 CFR 1040 per Notice 50
and/or the Canadian Radiation Emitting Devices Act REDR C1370.
Symboles – Français
Les symboles sur l'appareil indiquent des informations spécifiques à l'intention de
l'utilisateur ou d'un technicien de mainte nance. Il est important de bien comprendre la
xiv • Introduction R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide
Page 15

signification de ces symboles. Les symboles graphiques et leur signification,
ci-dessous, sont utilisés sur les produits de ClearCube Technology, Inc.
Se reporter au manuel
Ce symbole sur l'étiquette d'identification de l'appareil est destiné à
attirer l'attention de l'utilisateur ou du technic i en de main te na nc e su r
les renseignements supplémentaires portés sur le manuel.
Risque de choc
Ce symbole indique la présence des risques de décharge électrique.
Des clôtures identifiées par ces symboles devraient seulement être
ouvertes par le personnel de service qualifié. Se référer au manuel
pour l'information additionnelle.
Attente
Un symbole correspondant à chaque lame se trouve sur le devant du
châssis. Le bouton pour démarrage Soft Start active chaque lame
particulière.
Fusible
Voir l'étiquette d'identification de l'appareil. Le symbole est
accompagné des spécifications nécessaires au remplacement du
fusible. Seul un technicien qualifié devrait effectuer cette opé ra tio n.
Protection à la terre
Ce symbole identifie la borne utilisée pour connecter toutes les pièces
métalliques de la boîte par un conducteur externe vers la masse, afin
de protéger l'appareil contre les chocs électriques en cas de panne.
Borne en esclavage au sol
Ce symbole identifie la borne de lien d'au sol d'endroit. Cette borne
est utilisée pour relier le conducteur moulu de liaison, ou la
combinaison des pièces conductrices pour mettre à la terre la terre
pour la sûreté.
Protection d'équipement Classe II
L'information est souvent située sur l'étiquette d'identification de
l'alimentation. Elle indique que l'appareil est doublement isolé contre
les surtensions dangereuses. Ne pas confondre avec la mention
“Class 2” qui est une classification de circuit du NEC américain
(National Electrical Code).
Tous ces symboles sont utilisés dans ce document aux chapitres appropriés, afin
d'indiquer les situations qui demandent une vérification ou la consultation d'un autre
manuel, ou dans des situations qui risqueraient d'endommager l'appareil ou de
provoquer des blessures à l'utilisateur.
R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide Introduction • xv
Page 16

PRÉCAUTION : une note de précaution indique que l'appareil peut être
endommagé ou que l'utilisateur risque d'être légèrement blessé si les
procédures correctes ne sont pas suivies.
ATTENTION : ce message indique que l'appareil pourrait être sérieusement
endommagé ou que de graves blessures ou la mort peuvent résulter au cas
où les procédures correctes ne seraient pas suivies.
Guide de sécurité
Avant de dépanner ou de commencer des opérations de main tenance, veuillez lire
attentivement tous les messages sous les rubriques ATTENTION et PRÉCAUTION.
La tension de cet équipement est dangereuse pour l'être humain et peut provoquer des
blessures.
• Installations – L'équipement de ClearCube doit être installé en conformité avec
les codes électriques locaux et est sujet à une inspection par les autorités
compétentes.
• Mise à la masse du châssis – Le châssis et le transceiver fibre de ClearCube ont
été conçus avec un socle de connecteur trois conducteurs IEC 60320 qui, avec le
cordon d'alimentation adéquat, connecte la masse protectrice externe du bâtiment
à toutes les parties métalliques du châssis. Afin de réduire les risques
d'électrocution, assurez-vous que votre prise électrique est bien connectée à la
masse chaque fois que vous branchez l'appareil.
Les règlements de sûreté de la Suède exigent le rapport suivant :
—Apparaten skall anslutas till jordat uttag när den anslutas till ett nätuerk.—
Les règlements de sûreté de la Finlande exigent le rapport suivant :
— Laite on liitettävä suojamaadoituskoskettimilla varustettuun pistorasiaan.—
• Choix du câble d'alimentation – ClearCube ou ses distributeurs fournissent des
câbles d'alimentation conçus spécialement pour ce type d'équipement et qui ont
été approuvés par les autorités locales compétentes du pays de mise en service.
Veuillez vous référer au chapitre sur l'installation pour en savoir plus sur le type de
câble d'alimentation spécifique requis. Pour le remplacement des cordons
d'alimentation, consulter Annexe C – Support Technique (Appendix C – Technical
Support).
• Adaptateurs – ClearCube ou ses distributeurs fournissent des adaptateurs conçus
spécialement pour ce type d'équipement et qui ont été approuvés par les autorités
locales compétentes du pays de mise en service. Veuillez vous référer au chapitre
sur l'installation pour en savoir plus sur le type de câble d'alimentation spécifique
xvi • Introduction R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide
Page 17
requis. Pour le remplacement des cordons d'alimentation, consulter Annexe C –
Support Technique (Appendix C – Technical Support).
• Système d'alimentation IT – L'équipement ClearCube a été évalué et déclaré
compatible avec les systèmes de distribution d'alimentation IT d'une tension
composée d'un réseau triphasé ne devant pas dépasser 240 V.
• Circuits sous tension – Les agents installateurs et de maintenance ne doivent pas
enlever les caches protecteurs lorsqu'ils travaillent sur le châssis ClearCube. Les
ajustements ou réparations sur les composants internes doivent être effectués par
des techniciens qualifiés. Pour tout service sur cet appareil, à l'exception du
remplacement d'une lame PC ou du module de ventilati on, le connecteur princip al
doit être débranché. Sous certaines conditions, les tensions présentes peuvent être
dangereuses. Soyez extrêmement prudent.
• Atmosphère explosive – Ne pas faire fonctionner le châssis si des gaz
inflammables sont présents. Dans ces conditions, cet équipement est dangereux et
risque d'enflammer les gaz ou vapeurs gazeuses.
• Remplacement des pièces – Utiliser uniquement des pièces parfaitement
conformes, tant au niveau électrique que mécanique. Contacter ClearCube
Technology pour tout renseignement sur les pièces détachées. L'installation de
pièces qui ne sont pas parfaitement semblables annulera la garantie et risque de
causer des blessures au personnel travaillant sur le châssis. De plus, les pièces non
conformes peuvent provoquer des dégâts ou un incendie.
• Modification – Ne modifier aucun élément d'origine du C/Port, du châssis ou du
PC lame. Toute modification peut constituer un danger.
• Sécurité du laser – Le transceiver fibre et le C/Port ont été évalués et certifiés
conformes à la norme EN 60825-1 – Sécurité des appareils à laser. Consulter
l'Annexe B pour plus de renseignements.
PRÉCAUTION : Une utilisation de commandes, un ajustement ou
fonctionnement par des procédures différentes de celles spécifiées dans
ce document peuvent provoquer une irradiation dangereuse.
L'étiquette ci-dessous est apposée sur les appareils de ClearCube Technology qui
utilisent un affichage laser :
Les appareils ainsi identifiés sont en conformité avec le code FDA "Federal 21 CFR
1040, Notice 50" et/ou le "Canadian Radiation Emitting Devices Act REDR C1370".
R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide Introduction • xvii
Page 18

Symbole – Deutsche
Symbole auf den Geräten geben dem Benutzer und dem Wartungspersonal bestimmte
wichtige Informationen. Es ist wichtig, die beabsichtigte Bedeutung dieser Symbole
zu verstehen. Die nachstehend angezeigten Symbole verweisen auf die durch
ClearCube Technology, Inc. verwendeten Symbole und ihre Bedeutungen.
Nähere Angaben im Handbuch
Wird auf dem Gerätebewertungsetikett verwendet, um den Benutzer
oder das Wartungspersonal auf weitere Informationen im Handbuch
aufmerksam zu machen.
Schlag-Gefahr
Dieses Symbol zeigt das Vorhandensein der Gefahren des
elektrischen Schlages an. Die Einschließungen, die mit diesen
Symbolen gekennzeichnet werden, sollten von qualifiziertem
Service-Personal nur geöffnet werden. Auf das Handbuch zu
zusätzlicher Information sich beziehen.
Bereitstehen
Ein Symbol wird für jedes an der Vorderseite des Käfigs angebrachte
Blade verwendet. Der Soft Start-Schalter, der das jeweilige Blade
einschaltet.
Sicherung
Befindet sich auf dem Gerätebewertungsetikett. Das Symbol wird von
den Spezifikationen zum Austausch begleitet. Dieser Vorgang sollte
nur durch qualifiziertes Fachpersonal ausgeführt werden.
Schützender Masse Anschluß
Kennzeichnet die Klemme, die alle Metallteile des Gehäuses durch
einen externen Leiter mit der Masse verbindet, um so eine Erdung
zum Schutz gegen elektrische Stromschläge bei einer Fehlersituation
herzustellen.
Grundbondanschluß
Dieses Symbol kennzeichnet die Position des
Grundbondanschlusses. Dieser Anschluß wird benutzt, um den
Grundabbindenleiter oder die Kombination der leitenden Teile
anzuschließen, um Boden zu den Sicherheit Zwecken mit Erde zu
bedecken.
Geräteschutzklasse II
Befindet sich auf dem Gerätebewertungsetikett. Gibt an, dass das
Gerät doppelt gegen gefährliche Spannungen isoliert ist. Die ist nicht
mit der “Class 2”-Schaltkreisklassifizierung des US National Electrical
Code (NEC) zu verwechseln.
Diese Symbole werden im Dokument verwendet, um auf Situationen hinzuweisen, in
denen dieses oder ein weiteres Handbuch zu Rate gezogen werden sollten, oder falls
die Möglichkeit von Schäden oder Verletzungen besteht.
xviii • Introduction R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide
Page 19

VORSICHT: Ein Vorsichtshinweis weist darauf hin, das Geräteschäden
oder geringe Verletzungen bei unsachgemäßer Bedienung erfolgen
können.
WARNUNG: Ein Warnhinweis weist darauf hin, das vollständige
Geräteschäden oder schwere Verletzungen einschließlich des Todes bei
unsachgemäßer Bedienung erfolgen können.
Sicherheitsrichtlinien
Vor der Durchführung von Fehlerbehebungs- oder Wartungsarbeiten sollten Sie alle
WARNUNGS- und VORSICHTSHINWEISE genau durchlesen. Dieses Gerät weist
Spannungen auf, die zu Todesfällen und persönlichen Verletzungen führen können.
• Installationen – ClearCube-Geräte müssen in Übereinstimmung mit den
örtlichen elektrischen Richtlinien installiert werden und unterliegen unter
Umständen der Überwachung durch die jeweiligen Behörden.
• Gehäuseerdung – ClearCubes Chassis und Glasfaser-Transceiver wurden mit
einem Dreifachleiter-IEC 60320-Gerätesteckeingang entwickelt, welches anhand
eines geeigneten Netzkabels den externen Schutzmasseleiter des Gebäudes mit
allen zugänglichen Metallteilen des Gehäuses verbindet. Um die Gefahr eines
elektrischen Schlags zu minimieren, stellen Sie sicher, dass der Netzausgang eine
geeignete Sicherheitserdungsmasse aufweist, die bei jedem Einschalten des
Gerätes damit verbunden ist.
Sicherheit Regelungen von Schweden erfordern die folgende Aussage:
—Apparaten skall anslutas till jordat uttag när den anslutas till ett nätuerk.—
Sicherheit Regelungen von Finnland erfordern die folgende Au ssage:
— Laite on liitettävä suojamaadoituskoskettimilla varustettuun pistorasiaan.—
• Netzkabelauswahl – ClearCube oder der ClearCube Vertrieb bieten Netzkabel
an, die jeweils für das bestimmte Gerät entwickelt wurden und deren Verwendung
durch die örtlichen Behörden des jeweiligen Landes, in dem das Gerät betrieben
wird, genehmigt ist. Genaue Netzkabelanforderungen entnehmen Sie bitte den
Installationsabschnitten in diesem Handbuch. Nähere Angaben zur Auswechslung
von Netzkabeln finden Sie im Anhang C – Technischer Support (Appendix C –
Technical Support).
• Netzadapter – ClearCube oder der ClearCube Vertrieb bieten Netzadapter an, die
jeweils für das bestimmte Gerät entwickelt wurden und deren Verwendung durch
die örtlichen Behörden des jeweiligen Landes, in dem das Gerät betrieben wird,
genehmigt ist. Genaue Netzkabelanforderungen entnehmen Sie bitte den
Installationsabschnitten in diesem Handbuch. Nähere Angaben zur Auswechslung
R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide Introduction • xix
Page 20

von Netzkabeln finden Sie im Anhang C – Technischer Support (Appendix C –
Technical Support).
• IT-Leistungssysteme – ClearCube-Geräte wurden ausgewertet und kompatibel
zu IT -Leistungsv erteilungssystemen mit einer Phasenspannung von ni cht mehr als
240 V befunden.
• Angeschlossene Stromkreise – Betriebs- und Wartungspersonal sollten die
Schutzabdeckungen nicht entfernen, wenn der ClearCube Chassis in Betrieb ist.
Justierungen und Wartungsarbeiten an internen Komponenten sollten nur durch
qualifiziertes Fachpersonal vorgenommen werden. Der Hauptanschluss muss
während allen Wartungsarbeiten an diesem Produkt, außer dem Austausch eines
PC-Blades oder des Lüftereinsatzes, vom Netz getrennt werden. Unter
bestimmten Bedingungen können gefährliche Spannungen vorhanden sein.
Vorsicht ist angezeigt.
• Explosive Umgebung – Betreiben Sie den Chassis nicht in Umgebungen, in
denen entflammbare Gase vorhanden sind. Der Betrieb des Gerätes in solch en
Umgebungen ist unsicher und kann die Gase entzünden.
• Teileersatz – Geräte sollten nur mit elektrischen und mechanischen Teilen, die
exakte Ersatzteile sind, gewartet werden. Wende n Sie sich an Cle arCube
Technology, um Ersatzteilinformationen zu erhalten. Die Installation von Teilen,
die nicht direkte Ersatzteile sind, hat ein Erlöschen des Garantieanspruches zur
Folge und kann dem Benutzungspersonal des Gehäuses Schaden zufügen.
Weiterhin können ungeeignete Ersatzteile Schäden sowie Brandschäden
hervorrufen.
• Modifizierungen – Das C/Port, Chassis oder PC Blade darf in keiner Weise vom
Originalzustand geändert werden. Modifizierungen können Risiken hervorrufen.
• Lasersicherheit – Der Glasfaser-Transceiver und das Glasfaser-C/Port wurden
ausgewertet und entsprechen der Richtlinie EN 60825-1 – Sicherheit von
Laserprodukten. Nähere Angaben finden Sie im Anhang B.
VORSICHT: Die Bedienung oder das Vornehmen von Justierungen oder
Vorgängen entgegen der hier aufgeführten können eine gefährliche
Laserstrahlungsbelastung zur Folge haben.
ClearCube Technology-Produkte, die Laser verwenden, weisen das folgende Symbol
auf dem Gerätebewertungsetikett auf:
Gekennzeichnete Geräte entsprechen dem FDA Code of Federal 21 CFR 1040 per
Notice 50 und/oder dem Canadian Radiation Emitting Devices Act REDR C1370.
xx • Introduction R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide
Page 21

Símbolos – Español
Los símbolos se usan en el aparato para comunicar información específica a el
operador y a la persona de servicio. Es importante entender la intención del
significado de estos símbolos. Abajo se muestran los símbolos gráficos que se usan en
los productos ClearCube Technology, Inc., así como su significado.
Consultar el manual
Se usa en la etiqueta de especificaciones del aparato para dirigir al
operador o persona de servicio a que consulte el manual para
información adicional.
Peligro de choque
Este símbolo indica la presencia de los peligros de la descarga
eléctrica. Los recintos marcados con estos símbolos se deb en abrir
solamente por el personal de servicio cualificado. Referi r al man ual
para la información adicional.
Hacer una pausa
Un símbolo que se usa para cada blade o bandeja instalada,
localizado enfrente de el chassis. Switch de inicio suave usado para
encender cada blade en particular.
Fusible
Localizado en la etiqueta de especificaciones del aparato. El
símbolo está acompañado de las especificaciones necesarias para
su reemplazo. Solamente técnicos calificados deben de realizar
esta operación.
Terminal a tierra protectiva
Identifica a la terminal que se usa para conectar todas las partes
metálicas del gabinete a través de un conductor externo para
conectar a tierra y proteger contra descarga eléctrica en caso de
una condición de falla.
Terminal en enlace de tierra
Este símbolo identifica la localización del terminal en enlace de
tierra. Este terminal se utiliza para conectar el conductor de tierra
de la vinculación, o la combinación de piezas conductoras para
conectar a tierra la tierra para los propósitos de seguridad.
Protección del aparato Clase II
Puede estar localizado en la etiqueta de especificaciones en el
adaptador de corriente. Indica que el aparato tien e aislamiento
doble para voltajes peligrosos. No confundirlo con la "Clase 2" que
es una clasificación de circuito NEC de E.U. (National Electrical
Code).
R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide Introduction • xxi
Page 22

Estos mismos símbolos se usan en este documento cuando es apropiado para indicar
situaciones que ameritan revisar este u otro manual, o que pudieran resultar en daño al
aparato o lesión física.
PRECAUCIÓN: Un aviso de Precaución indica que puede ocurrir daño al
aparato o lesiones menores si no se siguen los procedimientos
adecuados.
ADVERTENCIA: Un aviso de Advertencia indica que puede ocurrir daño
fatal al aparato, o lesiones serias incluyendo la muerte si no se siguen
los procedimientos adecuados.
Directrices de seguridad
Antes de llevar a cabo cualquier procedimiento de diagnostico de fallas o
mantenimiento, lea cuidadosamente todas los avisos de ADVERTENCIA y
PRECAUCIÓN. Este aparato contiene voltaje peligroso para el cuerpo humanos y
tiene la capacidad de infligir lesiones personales.
• Instalaciones – Se requiere que los aparatos de ClearCube se instalen de acuerdo
con los códigos eléctricos locales y pueden estar sujetos a inspección por las
autoridades en jurisdicción.
• Conexión a tierra del chasis – El chassis de ClearCube y el Transceptor de Fibra
han sido diseñados con una entrada de aparato con tres conductores IEC 60320
que (con el cable de alimentación apropiado) conecta al conductor aterrizado
externo protectivo de construcción a todas las partes accesibles de metal del
gabinete. Para minimizar el peligro de descarga eléctrica, asegure que su toma de
corriente eléctrica tiene una conexión a tierra de seguridad apropiada cada vez que
usted enciende el aparato.
Las regulaciones de seguridad de Suecia requieren la declaración siguiente:
—Apparaten skall anslutas till jordat uttag när den anslutas till ett nätuerk.—
Las regulaciones de seguridad de Finlandia requieren la declaración siguiente:
— Laite on liitettävä suojamaadoituskoskettimilla varustettuun pistorasiaan.—
• Selección del cable de alimentación – ClearCube o distribuidores de ClearCube
proveen de cables de alimentación que están específicamente diseñados para
usarse con la pieza del aparato en particular y están aprobados para su uso por las
autoridades en jurisdicción en el país donde el aparato se pone en servicio. Por
favor consulte las secciones de instalación de este manual para los requerimientos
específicos de los cables de alimentación. Para el reemplazo de los cables de
alimentación, consulte el Apéndice C – Soporte Técnico (Appendix C – Technical
Support).
xxii • Introduction R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide
Page 23

• Adaptadores de alimentación – ClearCube o distribuidores de ClearCube
proveen de adaptadores de alimentación que están específicamente diseñados para
usarse con la pieza del aparato en particular y están aprobados para su uso por las
autoridades en jurisdicción en el país donde el aparato se pone en servicio. Por
favor consulte las secciones de instalación de este manual para los requerimientos
específicos de los cables de alimentación. Para el reemplazo de los cables de
alimentación, consulte el Apéndice C – Soporte Técnico (Appendix C – Technical
Support).
• Sistemas de alimentación eléctricos IT – El equipo ClearCube ha sido evaluado
y es compatible con sistemas de alimentación eléctricos de distribución IT con un
voltaje "fase a fase" que no exceda 240 V.
• Circuitos vivos – Personal de operación y de servicio no deben de remover las
cubiertas protectivas cuando estén operando el ClearCube chassis. Ajustes y
servicio a componentes internos deben de realizarse por técnicos de servicio
calificados. Durante cualquier servicio a los productos excluyendo el reemplazo
de la PC blade y la bandeja del ventilador, el conector principal al cableado local
se debe de desconectar. Voltajes peligrosos pueden estar presentes bajo ciertas
circunstancias. Use extrema precaución.
• Atmósfera explosiva – No opere el chassis en condiciones donde gases
inflamables estén presentes. Bajo tales condiciones este aparato no es seguro y
puede encender los gases o vapores de gases.
• Reemplazo de partes – El servicio al aparato debe de ser con partes que son de
reemplazo exacto, mecánica y eléctricamente. Comuníquese con ClearCube
T echnology para información sobre partes de reemplazo. Instalación de partes que
no son reemplazos directos cancelarán la garantía y pueden causar daño al
personal que opera el chasis. Además, puede ocurrir daño o fuego si las partes de
reemplazo son inapropiadas.
• Modificación – No modifique de su condición original ninguna parte de el
C/Port, chassis, o PC Blade. Las modificaciones pueden resultar peligrosas.
• Seguridad del láser – El Transceptor de Fibra y el C/Port han sido evaluados y
certificados a un EN 60825-1 – seguridad de productos láser. Consulte el
Apéndice B para más detalles.
PRECAUCIÓN: El uso de controles, ajustes o rendimiento de los
procedimientos, diferentes a los especificados en este documento
puede resultar en exposición a radiación peligrosa.
Productos de ClearCube Technology que usan láser muestran el siguiente gráfico en la
etiqueta de especificaciones.
R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide Introduction • xxiii
Page 24

Los dispositivos marcados cumplen con el código federal FDA 21 CFR 1040 por
notificación 50 y/o el acta canadiense REDR C1370 para dispositivos con emisión de
radiación.
xxiv • Introduction R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide
Page 25

Chapter 1. ClearCube Architecture
and Product Overview
The ClearCube architecture delivers Intel®-based PC functionality to the desktop
from a secure, centralized location. This architecture provides significant increases in
manageability and security while providing mission-critical reliability, performance,
and uptime improvements with lowered costs. Replacing a traditional PC box with a
ClearCube C/Port or client in an office or cubicle saves space, eliminates fan noise,
and simplifies cabling resulting in a clear cube. The key components of the ClearCube
Architecture are:
•PC Blade—a remotely located, Intel-based computer in a dense form factor.
•Chassis—a centralized chassis that houses multiple PC blades and accepts a
variety of plug-in module options that allow connecting all of the external cables
to the blades. Previously known as the chassis and BackPack.
• Client—a remote desktop unit (C/Port, PCoIP zero client, or thin client) to which
standard peripherals are connected.
• System Management Software—ClearCube Management Suite software and
monitoring hardware that is built into ClearCube blades, chassis, and user ports.
The ClearCube management suite software, Sentral, is an optional component.
™
• PC-over-Ethernet
ClearCube PCoE to access remote devices (such as traditional computers or
virtual machines) from your local computer, client, or thin client. PCoE provides
bidirectional audio, USB redirection, and user experience settings you can adjust
to accommodate a variety of usage and network scenarios. PCoE is an optional
component in your ClearCube environment.
This guide is one of a series of manuals that describe the ClearCube architecture.
Other manuals include:
(PCoE™) remote protocol software—You can use
• PCoIP User’s Guide
• I/Port User’s Guide
• C/Port and Multi Video Extender User’s Guide
• PCoE User’s Guide
• A-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide
R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide ClearCube Architecture and Product Overview • 1
Page 26

R-Series PC Blade
Single-Slot R3080D
Single-Slot R1350Dual-Slot R3040S
The ClearCube PC blade is a dedicated computer that delivers full PC function ality
(including USB) to the desktop from a centralized location. Each R-series PC blade
contains all the industry-standard components of a desktop PC: processor, memory,
hard disk, video support, and Ethernet. You can easily connect peripherals to the PC
blade through USB ports on the User Port that is connected to the blade over a
network. Additionally, a single USB port is located on the front of the blade. You can
load application software on to your PC blade through peripherals connected to the
USB ports, or via the Ethernet connection on each blade.
Each blade has its own systems management circuitry powered independently from
the main components. This system illuminates the front panel status indicators and
monitors blade parameters even when the blade is powered off. The front panel LCD
shows the last three digits of the blade serial number as a default. ClearCube Sentral
software can be used to program as many as 10 alphanumeric characters into the
display. Figure 1 shows several R-series PC blades.
Figure 1 R-series PC Blades: Dual-Slot R3040S, Single-Slot R3080D, and Single-Slot R1350
2 • ClearCube Architecture and Product Overview R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide
Page 27
A display area at the front of each blade provides active status indicators. The four
LEDs on the front panel of the blade are described in Table 1 on this page and shown
in Figure 2 on page 4.
Table 1 Blade LED Functions
LED Color Description
Power
C/Port
Disk
E-Net
Green
Off
Green
Red
NOTE: The C/Port LED does not provide any information about PCoIP link
Green
Off
Green
Yellow/
Amber
Blade is powered on.
Blade is powered off.
C/Port is connected, and link is good.
C/Port is not connected, or link is bad.
status. If you are using a PCoIP client, see the LED on the PCoIP client
for link status information.
If you are connecting to a blade using a PCoIP zero client and a C/Port
is not connected to the blade, the C/Port LED is not applicable and is
always red.
Flashing indicates hard disk activity.
No hard disk activity.
Model R3040S: 10/100/1000 Mb/s link — flashing indicates activity.
Model R3080D: 10/100/1000 Mb/s link — flashing indicates activity.
Model R1350: 1000 Mb/s link — flashing indicates activity.
Model R3040S: Not applicable.
Model R3080D: Not applicable.
Model R1350: 10/100 Mb/s link — flashing indicates activity.
Off
No link.
The following figure shows the blade font panel as it appears on the blade, and also as
it appears inside a chassis with the chassis door closed. Labels on the chassis door
identify the front panel LEDs, buttons, and port.
R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide ClearCube Architecture and Product Overview • 3
Page 28
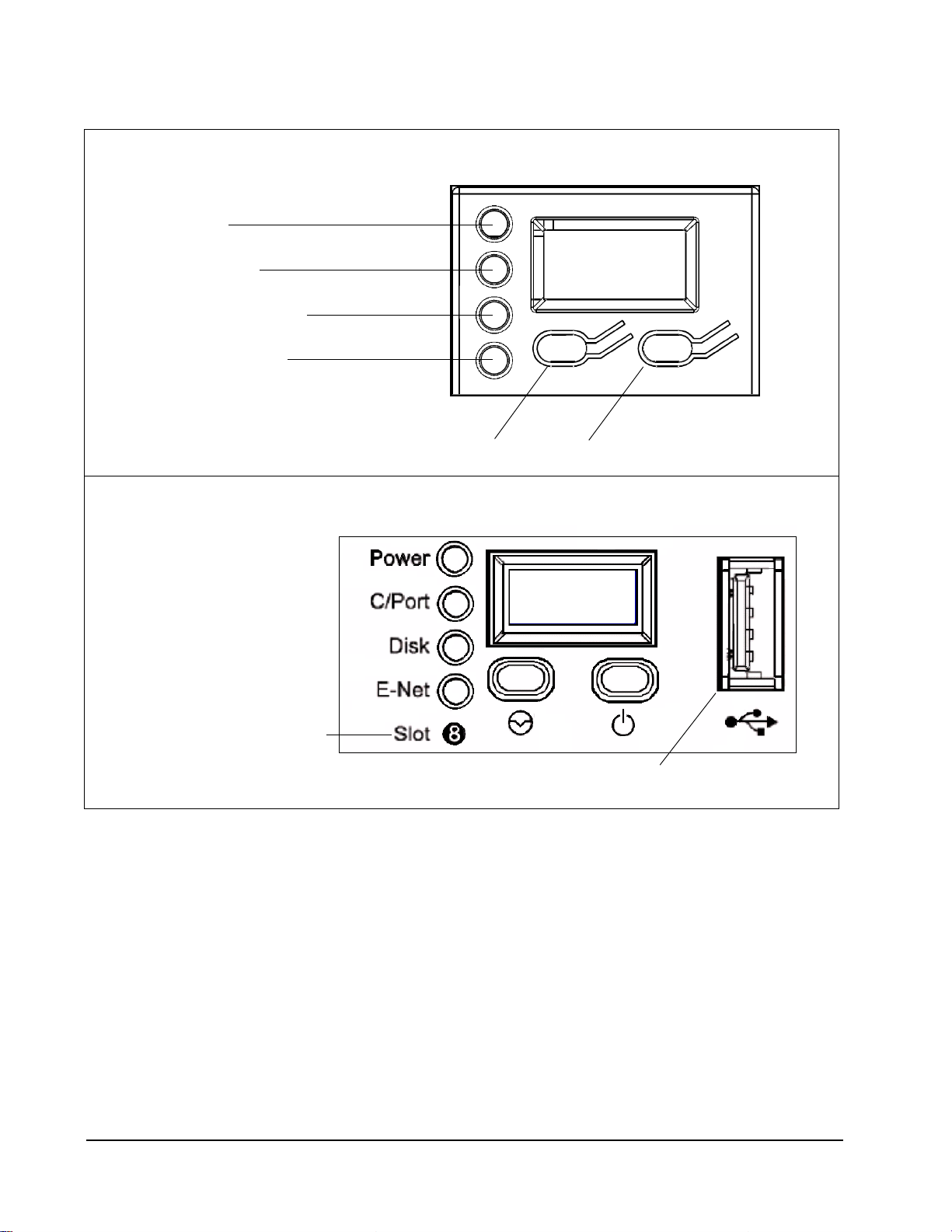
138
Chassis Slot Designation (1 to 8)
USB Port
Reset Button Power Button
Network Activity Indicator
Power Indicator
C/Port Link Indicator
‡
Hard Disk Activity Indicator
138
Front Panel Display inside Chassis (Including Labels on Chassis Door)
Front Panel Display outside of Chassis
Figure 2 ClearCube R-Series Blade Front Panel Display outside of Chassis and inside Chassis (the Chassis Door
Provides LED and Button Labels)
‡
The C/Port LED is only applicable if a C/Port is connected to a blade. If you are
using a PCoIP zero client to connect to a blade and a C/Port is not connected to the
blade, the C/Port LED is not applicable and is always red.
4 • ClearCube Architecture and Product Overview R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide
Page 29

R-Series Chassis
The ClearCube R-series chassis is a centralized chassis that houses up to eight
single-slot PC blades and up to four dual-slot PC blades. A standard 42U 19-inch rack
can hold as many as 14 chassis, for a total of 112 single-slot PC blades, 56 dual-slot
blades, or a combination of both.
Each chassis is a self-contained unit providing all of the Ethernet connections, C/Port
connections, airflow management, and power connections for PC blades. The R4300
chassis features interchangeable modules for maximum flexibility. Each chassis provides
system management connections through network and RS-485 links that you can daisy
chain from chassis to chassis. Figure 3 shows a chassis with PC blades installed.
The R4300 chassis, shown in Figure 4, provides a wide range of options for C/Port
and client connections to blades and to the ClearCube network.
The R4300 chassis provides advanced monitoring and switching functionality, with
software support for these modules provided by Sentral. The R4300 chassis and
Sentral are fully compatible with all R-series blades. The R4300 also provides full
backwards compatibility with all features implemented in Switch Manager 4.5, and is
compatible with ClearCube R4200 chassis systems utilizing Blade Switching
BackPacks (BSBPs) and Direct Connect BackPacks (DCBPs). The R4300 also
features dual redundant power supplies and dual AC power inputs.
Sentral communicates with the chassis through an Ethernet connection on the
management controller housed in each R4300. The management controller is installed
inside the R4300 and does not take up a blade slot.
Figure 3 ClearCube R-Series Chassis Front View
R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide ClearCube Architecture and Product Overview • 5
Page 30

C/Port
Figure 4 R4300 Chassis Rear View
The C/Port, shown in the following figure, is a desktop unit to which a user’s standard
peripherals are connected. The C/Port supports a 200-meter (660-foot) connection
distance from the blade and has two USB 1.1 ports, PS/2 mouse and keyboard ports,
speaker and microphone ports, and SVGA video output port. Other C/Port options
such as the Multi-Video Expander (MVX) are also available from ClearCube. For
more information, see the C/Port and Multi Video Expander User’s Guide.
Figure 5 ClearCube C/Port
6 • ClearCube Architecture and Product Overview R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide
Page 31

Multi-Video Solution
The ClearCube multi-video solution provides a revolutionary way to multi-task and
process information. While the C/Port provides all the peripheral and USB
connections, the multiplexed video signal can be passed through to the Multi-Video
Expander (MVX) via a noise-limiting VGA connector cable.
Shown in Figure 6, the MVX is physically the same size as the standard C/Port and
can be stacked on top of a C/Port. The MVX distributes the individual video frames to
the appropriate output connectors. The two video outputs on the MVX are special,
high-density connectors that can each drive two monitors.
The MVX can be used with either the standard C/Port or the Fiber C/Port for
connection over copper or fiber optic cable (the MVX does not function with other
clients). The MVX requires that the PC blade have a multi-monitor graphics card
installed. The centralized ClearCube architecture combined with multi-video
capabilities results in the ideal solution for space-constrained trading floors and other
applications requiring multiple displays. For more information, see the C/Port and
Multi Video Expander User’s Guide.
Figure 6 ClearCube MVX Back View
Fiber Optic Extension System
The Fiber Optic Extension System adds fiber optic connectivity to the ClearCube
architecture via a pair of multi-mode fiber optic cables.
The system is compatible with ClearCube R4300 chassis, backpacks, and blades. It
securely extends user desktops from centralized PC blades to a distance as great as
2000 meters (6562 feet) over a pair of 62.5 micron multi-mode fibers. The system
consists of two components, the Fiber Transceiver and the Digital Fiber C/Port.
R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide ClearCube Architecture and Product Overview • 7
Page 32

Fiber Transceiver
Front Rear
The Fiber Transceiver, shown in Figure 7, is a 1U high, rack-mounted device
designed to work specifically with the ClearCube architecture.
Figure 7 ClearCube F6150-160 Fiber Transceiver
The F6150-160 Fiber Transceiver converts signals sent between C740 Fiber C/Ports
(shown below) and ClearCube blades. A single 16-port Transceiver supports two
R4300 chassis or 16 PC blades. Each blade in a chassis is connected to the transceiver
by an Ethernet cable (≤ 10 meters).
C7420 Fiber C/Port
Figure 8 shows the C7420 Digital Fiber C/Port. In a standard installation, the Digital
Fiber C/Port resides on the user's desktop and provides standard peripheral
connections including USB, PS/2, audio, and video. The Fiber C/Port is compatible
with the Multi-Video Expander (MVX).
Figure 8 ClearCube C7420 Digital Fiber C/Port
For more information about the Fiber C/Port, see the C/Port and Multi Video
Expander User’s Guide.
8 • ClearCube Architecture and Product Overview R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide
Page 33

Zero Clients and Thin Clients
ClearCube I9424
PCoIP Zero Client
ClearCube I9440
PCoIP Zero Client
ClearCube I8520
Thin Client
ClearCube PCoIP® zero clients and thin clients connect to PC blades over a standard
Ethernet network. The Clients deliver video and peripheral signals to a local user from
a centralized PC blade, just like the C/Port. However, the key difference is that the
client connection (depending on the model) uses PCoIP protocol, Ethernet p rotocol, or
both, allowing it to work over standard switched networks. Therefore, ClearCube
clients do not require a point-to-point connection to a blade (no homerun cabling
needed).
ClearCube clients enable IT managers to use their existing IP network and cabling
infrastructure regardless of the distance between users' desktops and their centralized
PC blades.
• I9440—No operating system. Quad monitor using PCoIP technology
• I9424—No operating system. Dual monitor using PCoIP tech nology with internal
smart card reader
• I9422—No operating system. Dual monitor using PCoIP technology
• I9420—No operating system. Dual monitor using PCoIP technology
• I8520—Windows Embedded Standard with optional internal smart card reader
• I8442—Windows XP Embedded or Embedded Linux
• I8440—Windows XP Embedded or Embedded Linux
®
Figure 9 shows several ClearCube clients. For more information, see the I/Port User’s Guide.
Figure 9 Various ClearCube Clients
R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide ClearCube Architecture and Product Overview • 9
Page 34

10 • ClearCube Architecture and Product Overview R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide
Page 35

Chapter 2. Network Planning and
Site Preparation
Rack and Cabinet Requirements
Before installing the components of the ClearCube Architecture it is very important to
properly prepare the site where you will install the chassis and PC blades. This chapter
provides important information on how to plan for installation.
Figure 10 Standard 19-Inch Rack and Standard 19-Inch Cabinet
Figure 10 shows two frequently-used structures for holding ClearCube chassis. A
standard 42U rack or cabinet can hold as many as 14 chassis.
CAUTION: Equipment racks and cabinets can become highly unstable if not
adequately secured. Please read and follow the manufacturer's
specifications and recommendations for mounting instructions. Addition al
ClearCube guidelines are provided throughout this section that—with the
manufacturer's requirements—will ensure a safe installation.
R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide Network Planning and Site Preparation • 11
Page 36

Fully enclosed electrical cabinets are the preferred option for mounting your
ClearCube chassis. When using cabinets, make sure that both front and back panels
and doors are vented to provide sufficient airflow for intake and exhaust. If you plan
to use a cabinet enclosure, ensure that you have at least 34 inches (86cm) of interior
depth measured from the front of the unit, to accommodate the cabling that exits from
the back of the chassis. Provide adequate space on the back of the rack or cabinet to
allow servicing the cables and equipment. Cabinets may be fitted with casters for
easier mobility or service access.
WARNING: When installing a chassis in a cabinet enclosure, never us e only
one set of mounting brackets at the front. Select a cabinet with an
adjustable center rail or back rail in addition to the front rail. ClearCube's
adjustable mounting kit will then be required to attach the chassis to both
the front and center/back rails.
Space and Floor Support Requirements
The following table details the weight of a 42U rack or cabinet with 14 fully-loaded
chassis (not including the weight of the cabling or the rack).
Blade and chassis weights can vary depending on the
components each device contains. Blade and chassis weights
NOTE
shown in the following table are the maximum weights for each
device, where all possible components are populate d in th e
device.
Blade
R3040S
(4 per Chassis)
R3080D
(8 per Chassis)
R1350
(8 per Chassis)
Table 2. Maximum total weight and load in fully-loaded 42U rack
Blade Weight Chassis Weight
13 lbs (5.8 kg) 42 lbs (19 kg) 1316 lbs (597 kg) 219 lbs (99 kg)
5.2 lbs (2.4 kg) 42 lbs (19 kg) 1170.4 lbs (531 kg) 195 lbs (88 kg)
6 lbs (2.7 kg) 42 lbs (19 kg) 1260 lbs (572 kg) 210 lbs (95 kg)
Total Weight of 14 Fully-Loaded
Chassis
(Not Including Cables or Rack)
Load per Square Foot
(Square Meter)
Verify that the rack and floor will support this weight, even if initial installation does
not include 14 chassis units. This allows for future expansion at the location. If other
equipment is to be installed in the rack or cabinet, take this additional weight into
consideration.
WARNING: Improper structural support could cause the rack or cabinet to
lean and the floor to buckle, possibly to the point of structural damage.
12 • Network Planning and Site Preparation R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide
Page 37

Power and Cooling Requirements
The ClearCube Support site provides
Spreadsheets
ClearCube blade and chassis deployments. Documentation and tools provide:
• Tables describing chassis power requirements
• Data center branch circuit requirements for various chassis and blade deployment
scenarios
• Power requirements for uninterruptible power supply (UPS) sizing
• Maximum and minimum British thermal unit (BTU) values
• BTU calculator with features enabling you to adjust the percentage of users and
application intensity
To download
1. See the following URL: http://www.clearcube.com/support/
2. In the Product Support section, find your blade model in the PC Blades
drop-down list.
3. Click the Manuals link below the product description.
4. Click the Power & Cooling Requirements link to download an archive file. The
archive file contains spreadsheets for various product configurations. Choose the
appropriate spreadsheet and read the included instructions about how to calculate
cooling requirements.
that you can use to determine power and cooling requirements for
ClearCube Power and Cooling Requirements Spreadsheets
ClearCube Power and Cooling Requirements
:
The following sections discuss additional items to consider when planning and
designing data centers.
Additional Power Considerations
As described in the previous section, obtain
Requirements Spreadsheets
deployment.
Your ClearCube system centralizes all computing components in a single location
thereby concentrating the majority of the power needed to this one area. Although the
ClearCube solution reduces the overall power required when compared to traditional
PCs, the power demands in the data center are increased.
Ensure that your power circuits can safely handle the maximum current that a chassis
can draw (see the Mains Supply Requirement columns in the ClearCube Power &
Cooling Requirements spreadsheets). If your existing power circuit cannot handle the
maximum current, you must have additional power system capacity installed by a
qualified electrician.
to determine power requirements for your ClearCube
ClearCube Power and Cooling
R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide Network Planning and Site Preparation • 13
Page 38

If you are putting multiple chassis assemblies on a single power circuit, ensure that the
circuit can safely handle the combined maximum currents of all chassis.
CAUTION: Make sure your power strips, power grid, and circuit
breakers can safely provide the required current. Ensure that any
extension cords used meet local safety regulations and local fire
codes.
When installing uninterruptible power supplies (UPS), consult your UPS
specifications for proper sizing. ClearCube provides kVA columns in the spreadsheets
for reference. See the ClearCube Power and Cooling Requirements Spreadsheets on
the ClearCube Support site at
and cooling requirements.
http://www.clearcube.com/support/ for detailed power
Additional Cooling and HVAC Considerations
As described above, obtain
to determine cooling requirements for your ClearCube deployment.
Ensure that the air conditioning and ventilation system for the installation area can
accommodate the calculated thermal load. The rear of the chassis has air vents for four
fans. The fan openings must be at least four inches from any airflow-impeding barriers
such as walls, the back of the rack door or panel, large bundles of cables, and so on.
The availability of an air exit path from these fans is imperative to the efficient
operation of the unit. Failure to provide sufficient air venting will result in a thermal
overload of the blade. If the chassis is installed in a cabinet, use a fully-vented back
door or panel.
ClearCube Power and Cooling Requirements Spreadsheets
CAUTION: Failure to provide sufficient space and room ventilation
will result in overheating that can cause eventual unit failure not
covered as part of the unit warranty.
Cable Requirements
The chassis uses standard network cables with RJ45 connectors to connect to C/Ports
and to an Ethernet network. These can be CAT5, CAT5e, CAT6, or CAT6e cables.
C/Ports require straight-through cables with all four twisted pairs available. Network
connections follow standard Ethernet guidelines. In practice, identical copper media
can be used for C/Ports and for network connections, although ClearCube
recommends using different cable colors for C/Port and network connec tions to
simplify installation and maintenance. Throughout this guide, “C/Port cable” and
“network cable” refer interchangeably to copper-media cable such as CAT5, CAT5e,
CAT6, or CAT6e.
14 • Network Planning and Site Preparation R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide
Page 39

Each fully loaded chassis requires eight C/Port cables with RJ-45 connectors for
Homerun
C/Port Cables
Chassis
Data CenterUser Desktops
with C/Ports
Ethernet
Cables
Network
Switch
Admin C/Port
and Terminal
connections to C/Ports at the desktop and eight network cables for blade connections
to the Ethernet network hub or switch. Additionally, short color-coded C/Port cables
(Green for RS485, Red for Sparing, and Yellow for Admin Port) are provided to
configure and daisy-chain your BackPacks. You need eight network cables per chassis
to connect the blades to your network switch. If using blades with dual network ports
and a 16-port Ethernet module in an R4300, you need 16 Ethernet cables per chassis.
For installations using only PCoIP clients and thin clients, you will not need to
connect any cables to the C/Port connections. With these clients, the cables going to
the desktop are connected directly to your network switch.
The C/Port cable connections use all four-wire pairs for the
connection from the PC blade to the C/Port. If your installation
NOTE
currently splits out wire pairs for multiple uses, you mu st ensure
that a separate full connection is available for each blade to
C/Port connection.
Figure 11, Figure 12, Figure 13, and Figure 14 provide schematics of the cabling
required to connect your chassis to User Ports and your Ethernet network.
R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide Network Planning and Site Preparation • 15
Figure 11 ClearCube C/Port Architecture Cabling Diagram
Page 40

Figure 12 ClearCube Digital Fiber C/Port Architecture Cabling Diagram
Chassis
Data Center
Admin C/Port
and Terminal
User Desktops with
Fiber C/Ports
F6150
Ethernet
Cables
Fiber Transceiver
Network Switch
(Alternatively, Deployments
Can Omit the Network Switch
and Directly Connect the
Chassis to the Fiber
Transceiver)
Fiber
Cables
Chassis
Data Center
Network
Switch
Admin C/Port
and Terminal
Ethernet
Cables
User Desktops with
Zero Clients and Thin Clients
16 • Network Planning and Site Preparation R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide
Figure 13 ClearCube Client Architecture Cabling Diagram
Page 41

The following figure shows cabling between PCoIP zero clients and blades with
Chassis
Data Center & Blades with PCoIP Host CardsUser Desktops
with PCoIP Clients
Network
Switch
Admin C/Port
and Terminal
Ethernet for
PCoIP Traffic
Ethernet
Ethernet
PCoIP host cards. For more information about the cabling, shown in the following
figure, see Table 7, “R4300 Network Module Features: Models 4362 (EP2) and 4363
(EP6),” on page 32.
Free IP Address Requirement
Figure 14 Cabling Diagram Showing Optional Separation of PCoIP Traffic (Dashed Cabling)
With the R4300 chassis, the default startup configuration is DHCP (Dynamic Host
Configuration Protocol), which automatically requests an IP address from your DHCP
server. If you do not have a DHCP server, the R4300 chassis defaults to a static IP
address of 192.168.1.251. If there is no DHCP server in your environment, set the IP
Mode to Fixed IP and assign it a unique IP. This Free IP Address requirement on
R4300 in a Fixed IP mode is same as on R4200 with an installed Remote Management
Card/Controller.
The R4200 chassis with a Remote Management Controller/Card (RMC) does not
support DHCP and is always in Fixed IP mode.
R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide Network Planning and Site Preparation • 17
Page 42

18 • Network Planning and Site Preparation R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide
Page 43

Chapter 3. Chassis and Blade
Installation
The following instructions are intended for use by IT technicians familiar with
computer systems at the hardware configuration level.
Tools for Installation
All functions and operations described in the following installation procedures can be
performed with the following tools:
• #2 Phillips screwdriver
• C/Port adjustment tool (included in Chassis Accessory Kit)
A 1/4-inch nut driver with a magnetic tip is suggested for removing and replacing the
self-tapping sheet metal screws used on the chassis.
Shipment Components
Upon receipt of your shipment, carefully examine the outside of all the boxes before
opening. If you find any external damage, do not open the boxes. Contact and
notify the shipper that damage has occurred and request an inspection by them before
proceeding.
The following components are shipped in separate cartons:
•Chassis—This should be the first carton to be opened and used in the installation
process after the racks or cabinets have been installed.
• R4300 modules—Packaged separately from the chassis, these modules are
installed by the user when the chassis is installed. Each module box contains the
interconnection cables necessary to interface it to another chassis.
• PC blades – These are shipped four to a box. Do not open these boxes until your
chassis assemblies are installed and you are ready to install the PC blades.
• User ports – C/Port or other client desktop units are shipped with or without
power supplies, depending on your configuration. Do not open these boxes until
your blades are installed and you are ready to begin desktop installations.
R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide Chassis and Blade Installation • 19
Page 44

• Monitors and keyboards – Monitors are normally shipped in their own cartons.
Keyboards, if not included with user ports, may be bulk-packaged.
Shipping cartons and packing materials should be retained until your ClearCube
installation has been completed and tested.
Chassis Installation
Unpacking the Chassis
Open the chassis box, remove the packing material, and check the chassis for any
visible damage. Contact the carrier for an immediate on-site inspection if damage is
found. If there are no visible problems, remove the unit from the box and set it on a
flat working surface.
R4300 modules are packaged individually and shipped in a carton separate from the
chassis, with their appropriate patch cables in each package.
Installing the Chassis
CAUTION: To avoid equipment damage and potential personal injury,
assemble and position the chassis without blades installed.
ClearCube offers two methods to mount chassis in a rack:
• Chassis Accessory Kit, included with all chassis
• Chassis Rapid Mount (CRM) kit, available separately.
The standard Chassis Accessory Kit fits all standard 19-inch racks and provides a set
of front and back mounting brackets, with the necessary hardware. The optional CRM
kit is specially designed to fit ClearCube-supplied cabinets and racks that feature four
posts with square mounting holes for snap-in rack nuts. While this is an
industry-standard style for mounting hardware, not all third-party racks can accept the
CRM kit.
If you plan to use a cabinet enclosure, ensure that you have at least 34 inches (86 cm)
of interior depth measured from the front of the unit, to accommodate the cabling that
exits from the back of each chassis. The spacing between the front and back rails can
be no more than 30 inches (76 cm).
A chassis assembly using the Chassis Accessory Kit can be installed either from the
front or from the back of the rack. A chassis assembly using the CRM kit can be
installed only from the front of the rack.
20 • Chassis and Blade Installation R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide
Page 45

Begin installing your chassis assemblies at the bottom of the rack or cabinet. This
provides support for each chassis before it is securely mounted, and greatly simplifies
getting the chassis square and level in the rack.
Standard Chassis Mounting Hardware
To install a chassis using the standard Chassis Accessory Kit, do the following:
1. When installing into a cabinet enclosure, loosely attach the back adjustable
mounting brackets to the chassis with 5 screws on each side.
2. Position the chassis in the cabinet so that the front of the chassis lines up with the
front rail and then slide the adjustable back brackets into place. Tighten the screws
that hold the back brackets in place.
3. With the back brackets firmly attached to the chassis, slide the chassis into the
cabinet from the back. Open the front bezel of the chassis and then attach the front
brackets with three screws on each side that pass from the inside of the chassis to
tapped holes in the brackets on the outside.
NOTE
For your convenience, the front brackets can be attached from
either the inside or the outside of the chassis.
4. Using the hardware provided with your cabinet, attach the chassis mounting
brackets to the cabinet rails.
CAUTION: To avoid equipment damage and potential personal injury,
never install the chassis with only the front bracket as an attac hment.
5. If you are installing a chassis into a two-post rack with only a central mounting
point, use the front brackets attached at the center of gravity of the chassis. The
center of gravity is 14.7 inches (37 cm) back from the front faceplate. A set of
rack ear mounting holes is provided at this location (the third group of 3 holes
back). This point should line up with the rack sidebars to assure maximum
stability of the rack. Figure 15 shows a two-post open rack with one chassis
installed, properly centered in the rack.
NOTE
The CRM kit cannot be used in a two-post rack, as shown in the
following figure.
R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide Chassis and Blade Installation • 21
Page 46

Figure 15 Side View of Chassis Centered in a Two-Post Rack
6. Attach the AC power cord(s) packaged and supplied with the chassis and route it
to the back panel power connector(s) and then to a surge-protected power source
such as an uninterruptible power supply (UPS) or power strip. Use the cable
retention clamp on the chassis to avoid inadvertently disconnecting the power
If your ClearCube system installation is part of a larger office renovation or
deployment, complete the chassis hardware installation and wiring, but delay
installation of the PC blade computers until the rest of the area has been finished and
cleaned.
If installing R4300 chassis assemblies, the R4300 modules can be installed now, but
installation should be delayed until construction cleanup is completed. Modules are
required to complete cabling, but preliminary cabling for C/Ports and clients can be
completed without the modules being installed.
Chassis Rapid Mount Kit
The Chassis Rapid Mount (CRM) kit allows installing chassis in a cabinet enclosure
or other rack that provides both front and back posts.
22 • Chassis and Blade Installation R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide
Page 47

To install a chassis using the CRM kit, do the following:
Front Rack Ears Locking Latch
Main Bracket Finger Handle
Spring Slider
Flanges
Slider (Back)
Rack Ears
Back of Rack Bracket Front of Rack Bracket
Figure 16 Rack Bracket for CRM Kit
1. Unscrew the thumbscrew holding each pair of chassis and rack brackets together,
and slide the brackets apart.
2. Mount the chassis bracket to the chassis with 4 flathead screws. Repeat on the
other side.
NOTE
The chassis and rack brackets are interchangeable
side-for-side.
3. Determine the location and holes to be used to mount the rack ears on the rack
bracket. A guide is provided in the CRM packaging. Insert rack ears on
spring-loaded slider to the back side of the back rack post.
Figure 17 Rack Bracket Attachment Points
R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide Chassis and Blade Installation • 23
Page 48

4. Pull the rack bracket forward and insert the front rack ears on the back bracket
into holes on the front side of the front post. Push forward on the ears until the
latch snaps and locks into place. Ensure the front ears are placed into the
corresponding holes as the back ears, so that the rack bracket is level. To remove,
pull the finger tab inward with your finger and slide the ears forward.
5. Repeat steps 2 and 3 with the other chassis bracket on the opposite side of the
rack, in mirrored orientation. Ensure that the brackets are level with respect to
each other.
6. Slide the chassis and brackets onto the rack brackets from the front. Ensure the
“U” channels on the chassis bracket engage the flanges on the rack bracket.
7. Slide the chassis all the way onto the rack brackets until flush with the front of the rack.
8. Fully tighten the thumb screws with a Phillips head screwdriver.
9. Attach the AC power cord(s) packaged and supplied with the chassis and route it
to the back panel power connector(s) and then to a surge-protected power source
such as an uninterruptible power supply. Use the cable retention clamp on the
chassis to avoid inadvertently disconnecting the power.
The cabling and module installation notes from the previous section, “Standard
Chassis Mounting Hardware” on page 21, apply to this procedure.
Chassis Power Requirements
The
Power & Cooling Requirements Spreadsheets
tools and detailed information about chassis power and cooling requirements. See “Power
and Cooling Requirements” on page 13 for an overview of the spreadsheets and for
instructions about downloading them.
on the ClearCube Support site provide
Chassis Power Receptacles, Redundant Power, and Power Cords
The R4300 chassis has two power receptacles that provide redundant power sources.
For redundant AC inputs and increased reliability, each power receptacle must be
connected to a separate branch power circuit. If only one power cord is connected to
the R4300 chassis, it is powered only by one circuit.
Use the AC power cord packaged and s upplied with your chassis. For systems shipped
to countries that utilize a 100-130-volt power system, the included power cord is rated
at 15 amps. Systems shipped to countries with 208-240-volt power systems are
packaged with power cords rated at 10 amps.
Older model chassis (R4200 and lower) used 10-amp-rated
NOTE
24 • Chassis and Blade Installation R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide
power cords—these cords are NOT approved for use with
current model chassis on 100-130-volt power systems.
Page 49

The standard 10-amp power cords are acceptable for use with the Fiber Transceiver.
See “Safety Guidelines” on page xiii for more information.
Make sure your power strips, power grid, and circuit breakers can
safely provide the required current. Ensure that any extension cords
used meet local safety regulations and fire codes. When specifying
uninterruptible power supplies (UPS) be sure to include the Fiber
Transceiver peak current draws in your calculations to ensure the
UPS has adequate capacity.
Chassis Configuration and Operation
The R4300 chassis provides a wide range of options for zero client and C/Port
connections to blades and to networks. Chassis modules can be installed when
installing chassis or when installing blades. Because these modules provide all the
data I/O for the system, cabling cannot be completed until these modules are in place.
CAUTION: To avoid equipment damage and potential personal injury,
always install the chassis in a rack before installing any blades in it.
The three externally accessible module bays are as follows:
• Connect Bay
• Management Bay
• Network Bay
Each of these modules support hot-swap operation.
R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide Chassis and Blade Installation • 25
Page 50

The R4300 accepts the modules as shown in the positions in Figure 18.
Management Module
Connect Bay Module
Network Module
Power Supply Modules
Fan Pack
Chassis
AC Backplane
Dual A/C Input Module
Management Bay ModuleNetwork Bay Module
Connect Module
designator label
Management Module
designator label
Network Module
designator label
Figure 18 R4300 Exploded View
R4300 Modules
Install R4300 modules by sliding them into their respective bays and seating the
connector. Connect, Management, and Network modules are hot-swappable, and can
be replaced without affecting any existing switching configurations within the chassis.
A small label on each module indicates its position in the R4300, as shown below.
Figure 19 Module Designator Labels
26 • Chassis and Blade Installation R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide
Page 51

The first three characters of a module’s serial number, shown on the back apron and
Connect Bay
Management Bay
Network Bay
visible when the module is installed in its bay, are the same as the module’s
abbreviation. For example, the serial number
XCM12345 identifies a 8 x 8 Connect
Module.
Table 3 Serial Number Formats for R4300 Modules
Serial Number
Format
ACMxxxxx R4380 – Administrator Connect Module
XCMxxxxx R4387 – 8 x 8 Connect Module (C/Port Switching)
RMMxxxxx R4345 – Remote Management Module
EP2xxxxx R4363 – Ethernet Passthrough 16-Port GB Module (EP2)
EP6xxxxx R4362 – Ethernet Passthrough 16-Port Module (EP6)
FPMxxxxx
DIMxxxxx R4315 – Dual AC Input Module
PSUxxxxx R4316 – Power Supply Unit
R4320 – Fan Pack Module (contains Variable Fanspeed
Controller)
Module
To remove a Connect, Management, or Network module, press down on its green
lever (or levers) until the module is released, and pull the module out of its bay.
When hot-swapping Management, Connect, and Network
NOTE
Modules from an R4300, remove the module and wait for at
least 5 seconds before replacing it.
Figure 20 shows the back apron of the R4300, with the three module bays designated.
Figure 21 shows typical R4300 modules.
Figure 20 R4300 Module Bays
R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide Chassis and Blade Installation • 27
Page 52

Figure 21 R4300 Modules
Connect Module Management Module Network Module
USB Selected LED
Status LEDs
Selected LED
Digital Link
C/Port Connections USB Connections
Spare
Daisy Chain
Connections
Admin
Daisy Chain
Connections
The Connect Module (shown on the left in Figure 20) provides connectors for C/Ports,
USB ports, and sparing. On the right, the Network Module (either Model R4362 [EP6] or
Model R4363 [EP2]) provides Ethernet connections. In the center, the Remote
Management Module provides network and daisy-chain control connections, chassis
health indicators, and fan speed control. The Status LEDs in the blue area above the
Management Bay are shared between the sets of connectors to provide information about
each kind of connection to each blade in a manageable fashion.
Table 4 on page 28 provides details of the features of the modules, and describes their
interactions. Note that some features are color-coded to show that their functions are
inter-related. For example, features coded blue are for monitoring the status of the
various connection ports on the R4300.
Table 4 R4300 Connect Module Features
Connectors
Label Color Description
ADMIN IN Yellow
RJ45 connection that links the Admin C/Port into the Admin daisy chain, or passes the
Admin connection to another chassis by connecting to that chassis’ ADMIN OUT port.
As many as 14 chassis per Control Chain can be connected on one Admin daisy chain.
A Control Chain can have more than one Admin daisy chain.
28 • Chassis and Blade Installation R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide
Page 53

ADMIN OUT Yellow
Status LEDs
SPARE IN Red
RJ45 connection that links to the ADMIN IN connection of the next chassis in the
Admin daisy chain. On the end of the Admin daisy chain opposite the Admin C/Port,
this connector is not used.
RJ45 connection that links a Spare blade into the Spare daisy chain, or passes the
Spare connection to another chassis by connecting to that chassis’ SPARE OUT port.
As many as 14 chassis per Control Chain can be connected on one Spare daisy chain.
A Control Chain can have more than one Spare daisy chain. Not populated on ACM.
SPARE OUT Red
C/PORTS —
USB —
STATUS Blue
RJ45 connection that links to the SPARE IN connection of the next chassis
Spare daisy chain.
connector is not used. Not populated on ACM.
RJ45 connections that connect the digital and analog signals to each individual end
user’s C/Port. The numbers correspond to the blade slot numbers on the front of the
chassis. Not populated on ACM.
These connections provide USB 2.0 on blades equipped with back-panel USB
capability.
On the end of the
Spare
daisy chain opposite the Spare blade, this
in the
LEDs
These indicator LEDs work in conjunction with the Mode button on the RMM to provide
status information for three key functions: 1) blade digital link, 2) USB ports, and 3)
blade network ports. By pressing the Mode button on the RMM, administrators can
step through the three modes in sequential order. See Table 5 on page 29 for a
description of the LED functions.
Table 5 R4300 Status LEDs
These bi-color LEDs that indicate status for the connections on the module whose blue LED is lit. Status for each
set of connections can be viewed by pressing the Mode switch on the Management Bay module. The blue LED over
the connections being monitored is lit. The numbers for the LEDs correspond to the blade slot numbers on the front
of the chassis.
R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide Chassis and Blade Installation • 29
Page 54

STATUS Blue
C/PORTS Blue
• C/Port connection status
— Green = good digital link to blade
— Red = bad digital link to blade
— Off = no blade
• USB connection status
— Green = USB available
— Red = USB not available
— Off = no blade
• Network connection status
— Green = good network connection
— Off = no network connection, or no blade
Blue LED that, when lit, indicates that the Status LEDs above the Management Bay
module are displaying status for the C/Port connections. Not populated on ACM. The
Status LEDs display these conditions for C/Ports:
• Green = good digital link to blade
• Red = bad digital link to blade
• Off = no blade
USB Blue
Blue LED that
module
, when lit,
indicates that the Status LEDs
are displaying status for the USB connections. The Status LEDs display these
conditions for USB connections:
• Green = USB available
• Red = USB not available
• Off = no blade
above the Management Bay
30 • Chassis and Blade Installation R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide
Page 55

Table 6 R4300 Remote Management Module Features
RMM Reset
Control Chain
Connections
RMM Hardware
Reset SwitchDefault Switch
Ethernet
Connection
RMM StatusModule
Mode Switch
Fan Mode
Switch
LEDs
RMM MODE
DHCP
DC POWER
HEALTH
RMM Status LEDs
ACTIVITY
Ethernet LEDs
LINK
Ethernet LEDs
Label
CONTROL IN Green
Color
Code
Connectors
Description
RJ45 connection that receives control and management signals from the previous
chassis in the Control Chain via RS-485. As many as 14 chassis can be connected per
Control Chain.
CONTROL
OUT
MANAGEMENT —
MODE Blue
FAN MAX —
RST —
DFLT —
RMM MODE —
Green
RJ45 connection that
the Control Chain
RJ45 connection that passes control and management signals from the chassis to the
Sentral console via Ethernet. Has two LEDs in socket to indicate Ethernet link speed
and activity. Connection is self-adapting and does not require a crossover cable.
Push button switch that toggles through the blue Mode Selected LEDs on the Connect
and Network Modules. Press this switch to display status for the connections whose
blue LED is lit.
Push button switch that defeats the temperature sensor in the Fan Pack Module to set
fans to maximum speed.
Pinhole switch that resets the RMM power. Switching information is not affected. RMM
configuration information is not affected.
Pinhole switch that resets the RMM configuration information to the default
configuration settings, and then resets the RMM power. See Table 10 on page 49 for a
list of defaults. Switching information is not affected.
Bi-color LED indicates RMM Mode
• Green = Primary
• Yellow = Secondary
• Off = Standby
passes
via RS-485.
Switches
LEDs
control and management signals to the next chassis
in
R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide Chassis and Blade Installation • 31
Page 56

DHCP —
Primary Ethernet Secondary Ethernet
DC POWER —
HEALTH —
LINK —
Bi-color LED indicates IP address assignment mode
• Green = DHCP
• Off = fixed IP address
Bi-color LED indicates power supply status
• Green = 2 supplies good
• Red = 1 supply bad
• Off = no power or RMM not seated properly
Bi-color LED indicates system health
• Green = good
• Amber = RMM firmware update in progress
• Red = bad
• Off = no power or RMM not seated properly
See the Sentral Administrator’s Guide for more information on RMM Status indicators
Bi-color LEDs that indicate Ethernet link speed
• Green = 100 Mb/sec.
• Amber = 10 Mb/sec.
ACTIVITY —
Green LED – flashing indicates activity
Table 7 R4300 Network Module Features: Models 4362 (EP2) and 4363 (EP6)
Connectors
PRI/SEC Blue
ETHERNET —
Blue LED that
module
RJ45 connections that provide Ethernet connections for each PC blade in the chassis.
Label numbers correspond to the blade slot numbers on the front of the chassis.
• R4363 (EP2)—GB Primary ports (right side) and GB Secondary ports (left side)
• R4362 (EP6)—GB Primary ports (right side) and 10/100 Secondary ports (left side)
, when lit,
are displaying status for the Primary or Secondary Ethernet connections.
indicates that the Status LEDs
above the Management Bay
Power Modules
The R4300 contains two Power Supply Units (PSUs) and a Dual Input Module (DIM).
With the redundancy provided by two PSUs and two power inputs, the R4300 will
stay running even if one PSU fails, or a power input fails, or if a PSU and a power
input fail together.
32 • Chassis and Blade Installation R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide
Page 57

The PSUs are factory-installed, field-replaceable units. Each PSU has a green LED
Dual AC Input Module
(DIM)
Fuses
Power Supply Unit
(PSU)
visible through the fan pack that indicates its powered-on status. If one of the PSUs
fails, the DC POWER status LED on the RMM turns red to indicate a failure, and the
green LED on the failed power supply turns red.
The DIM allows providing redundant power inputs. For best reliability, attach a power
cord to both receptacles, and plug the cords into separate power sources. When using
only one power source, plug it into the receptacle labeled A for best reliability. The
DIM is not hot-swappable. Fuses on the DIM can be accessed by powering down the
chassis and removing the fan module.
CAUTION: DOUBLE POLE/NEUTRAL FUSING
The DIM employs fuses in both the neutral and hot lines. Please contact
ClearCube or a ClearCube-certified technician for assistance with
servicing or replacing these modules or replacing the fuses in them.
Connecting Cables
This section provides an overview of inter-chassis connections.
If you choose to use pre-assembled cables, be sure that the
cables for the desktop employ and terminate all four twisted
NOTE
The R4300 or R4200 link the blades within each chassis to their respective user ports
and to control signals. In addition to the user port connections, signal paths include:
• Control Chain – The RS-485-based control and management chain between
pairs. Standard Ethernet works with only two of the four pairs
connected, but the ClearCube C/Port operates only when all
four pairs of wire are used.
chassis. A Control Chain contains one Primary controller—either an RMC or an
RMM. When an RMC is present in a Control Chain, it always asserts itself as
Figure 22 R4300 Power Modules
R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide Chassis and Blade Installation • 33
Page 58

Primary, and RMMs on the chain all serve as Tertiary controllers. A Control
Chain can contain as many as 14 chassis.
• Admin Daisy Chain – The link between an Admin C/Port and the chassis served
by that Admin C/Port. An Admin Daisy Chain can connect from 1 to 14 chassis
within a single Control Chain, depending on the model of the connected C/Port.
The Admin Daisy Chain uses the same ClearCube proprietary data link that
connects blades to C/Ports.
• Spare Daisy Chain – The link between a Spare blade and the chassis served by
that Spare blade. A Spare Daisy Chain can connect from 1 to 14 chassis within a
single Control Chain, depending on the model of the connected C/Port. The Spare
Daisy Chain uses the same ClearCube proprietary data link that connects blades to
C/Ports.
Table 8 shows the distance and node limitations on the Admin and Spare Daisy
Chains for various C/Ports used with the R4300.
Table 8 R4300 Daisy-Chain Distance Limitations
C/Port Model C7100 (p/n 091024) C7110 (p/n 091052 or 091055)
Distance from R4300 10M 100M 150M 200M 10M 100M 150M 200M
Admin Daisy Chain (# of chassis) 14 14 14 14 14 14 14 14
Spare Daisy Chain (# of chassis) 14 14 14 14 14 14 14 14
C/Port Model C7120 (p/n 091056) C7100–C7120 + MVX
Distance from R4300 10M 100M 150M 200M 10M 100M 150M 200M
Admin Daisy Chain (# of chassis) 14 14 14 14 14 14 14 14
Spare Daisy Chain (# of chassis) 14 14 14 14 14 14 14 14
C/Port Model C7120W (p/n 091169) C7120W + MVX
Distance from R4300 10M 100M 150M 200M 10M 100M 150M 200M
Admin Daisy Chain (# of chassis) 14 14 14 14 14 14 11 5
Spare Daisy Chain (# of chassis) 14 14 14 14 14 14 8 0
C/Port Model
Distance from R4300 10M 100M 150M 200M 10M 100M 150M 200M
Admin Daisy Chain (# of chassis) 8 7 7 6 10 10 12 14
Spare Daisy Chain (# of chassis) 4 4 5 2 9 9 10 11
C7130 (p/n 091154) rev C02 or lower
C7130 (p/n 091 154) rev D01 or higher
Spare Allocation Examples
When using the spare switching feature of the chassis, you must consider how to
arrange your spares and how many to use. The chassis can support a ratio of one spare
for one active PC blade. A more common ratio is one spare for every seven active
blades. The lowest ratio of sparing that ClearCube recommends is one spare for 47 PC
34 • Chassis and Blade Installation R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide
Page 59

blades (configured by daisy-chaining the spare connections). Figure 23 on page 35
Spare Ratio 1:7
S
P
A
R
E
S
P
A
R
E
S
P
A
R
E
S
P
A
R
E
S
P
A
R
E
S
P
A
R
E
7654321
7654321
7654321
7654321
7654321
7654321
Chassis 1
Chassis 2
Chassis 3
Chassis 4
Chassis 5
Chassis 6
Spare Ratio 1:47
S
P
A
R
E
7654321
Chassis 1
Chassis 2
Chassis 3
Chassis 4
Chassis 5
Chassis 6
76543218
76543218
76543218
76543218
76543218
shows these sparing scenarios as examples.
Sparing is a switching function of the R4300 chassis. If no spare
NOTE
blade is connected to the Spare Daisy Chain, or if the Spare
blade is completely powered down, the spare switch action will
succeed but the user will not be connected to a usable blade.
Figure 23 Spare Allocation Examples
For a dual-slot PC blade, verify that the C/Port cable is plugged into the
even-numbered port (for example, for a PC blade installed in chassis slots 3 and 4, the
C/Port cable should be plugged into port 4).
R4300 Chassis
To connect cables to R4300-equipped chassis, do the following:
1. Label, identify, or use different color cables to discriminate between desktop and
network wiring. This color code is recommended, and matches the jumper cables
provided by ClearCube:
• Control Chain – Green
R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide Chassis and Blade Installation • 35
• Admin Daisy Chain – Yellow
• Spare Daisy Chain – Red
2. Daisy-chain the CONTROL OUT port on the top chassis in the rack to the next
lower chassis’ CONTROL IN port using the green daisy-chain cable. Continue
this daisy chain to connect all chassis in the rack.
3. Connect the MANAGEMENT port on at least one of the RMMs to your Ethernet
network hub or switch. For the best reliability, connect redundant RMMs to more
Page 60

than one switch and/or subnet to better protect against network-related failures.
As many as 14 RMMs per Control Chain (all of them) can be connected to the
network to provide failover capability. In practice, three is probably enough.
NOTE
Do not use an Ethernet port on the chassis for this connection.
4. Skip this step if installing only other clients, or if using a chassis with an ACM.
Connect eight C/Port cables from the XCM ports marked C/PORT to the patch
panel going to your desktops. If using dual-slot PC blades, plug the C/Port cable
into the even-numbered port for the two slots occupied by the blade, and leave the
odd-numbered port empty (for example, for a PC blade installed in chassis slots 3
and 4, the C/Port cable should be plugged into port 4).
5. Connect eight network cables from the EP8 ports marked ETHERNET to your
Ethernet network patch panel, hub, or switch.
6. Daisy-chain the ADMIN IN port on one chassis to the ADMIN OUT port on the
next chassis using the yellow daisy-chain cable provided . Connect the remaining
ADMIN OUT port to the Admin C/Port.
If any C/Port users also use a Multi-Video Expander (MVX) with multiple
monitors, the Admin C/Port should also be equipped with an MXV and multiple
monitors. Otherwise, video from a blade equipped with an MVX will not be
viewable at the Admin C/Port.
7. Daisy-chain the SPARE IN port on one chass is to the SPARE OUT port on the
next chassis using the red daisy-chain cable provide d. Connect the remaining
SPARE IN port to the Spare blade’s C/PORT port.
36 • Chassis and Blade Installation R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide
Page 61

We suggest routing the cables down the sides of the rack to the back panel, with
Primary Chassis
Secondary Chassis
Tertiary Chassis
with E-net Control Link
Admin
Daisy Chain
Control
Chain
with E-net Control Link
No E-net Control Link
Spare
Daisy Chain
Admin
Daisy Chain
To Network
To Network
Spare
Configuration
Cable
Admin C/Port
and Terminal
the network cables on one side and the desktop cables on the other.
Figure 24 R4300 Daisy-Chain Cabling Example
Connecting a network cable to a C/Port jack on the chassis, or a
C/Port cable to a Network jack, will not damage the unit, but the
NOTE
system will not operate correctly. This is a common installation
error and should be one of the first things checked when
troubleshooting a problem with a system’s operation.
Mixed-Mode Chassis Cabling
Mixed-mode cabling is the attachment of R4300-equipped chassis to chassis with
Blade Switching BackPacks (BSBPs) or Direct Connect BackPacks (DCBPs). The
recommended practice is to use one or more R4300s for Primary and auto-negotiated
R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide Chassis and Blade Installation • 37
Page 62

control. One or more RMMs need to be connected to Ethernet to allow
Admin C/Port
CLEARCUBE
Spare
Primary R4300
To Network
Secondary R4300
Tertiary BSBP R4200
with E-net Control Link
Admin
Daisy Chain
Control
Chain
Configuration
Cable
To Network
with E-net Control Link
No RMC
Spare
Daisy Chain
Admin
Daisy Chain
No E-net Control Link
Admin C/Port
and Terminal
auto-negotiation and control failover. Figure 25 shows an example of this.
Figure 25 Mixed-Mode Daisy-Chain Cabling Example
With an RMC-equipped BSBP as Primary, no other chassis in
NOTE
the Control Chain can serve as Secondary, because Secon dary
mode is not supported on the RMC.
38 • Chassis and Blade Installation R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide
Page 63

Spare
Daisy
Control Chain with Multiple Daisy Chains
Spare
Primary Chassis
To Network
with E-net Control Link
Configuration
Cable
Spare
Daisy
Admin
Daisy
Control
Chain
Admin C/Port
and Terminal
Control Chain with Single Daisy Chains
Admin C/Port
and Terminal
Chain
Chain
Chain #3
Spare
Daisy
Chain #2
Spare
Daisy
Chain #1
#1
Admin C/Port
and Terminal
#2
Admin
Daisy
Chain #2
Admin
Daisy
Chain #1
Spare
Configuration
Cable
Spare
Configuration
Cable
Control
Chain
Spare
Configuration
Cable
Primary Chassis
with E-net Control Link
To Network
Figure 26 Daisy-Chain Examples
R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide Chassis and Blade Installation • 39
Page 64

R3040S Cabling
R4300 Chassis Network Module
Secondary Ports Primary Ports
Because R3040S blades use two slots in a chassis, the rear of a ClearCube chassis
(shown below) provides up to four Gigabit Ethernet ports (two primary ports and two
secondary ports) for each blade, depending on video card configuration.
Figure 27 The Primary and Secondary Ports in an R3400 Chassis Network Module
NICs When Using a Traditional Video Card
When using a traditional video card in an R3040S (such as a ClearCube MGA6), the
blade provides four Gigabit Ethernet NICs. On the back of an R4300 chassis (shown
in Figure 27 above), the primary and secondary ports of both slots the blade occupies
are Gigabit Ethernet.
NICs When Using a V52x0 PCoIP Host Card
When an R4300S contains a PCoIP Host card (such as a V5220 or V5420), the blade
provides three Gigabit Ethernet NICs. The odd-numbered secondary port on the back
of the chassis (see Figure 27 above) is for PCoIP communication. The three other
ports corresponding to the slots the blade occupies are Gigabit Ethernet. Use standard
Ethernet cables in the ports you use for PCoIP traffic between ClearCube PCoIP
clients and blades containing PCoIP Host cards.
After connecting one end of an Ethernet cable to the appropriate odd-numbered
secondary port on the rear of the chassis, you have multiple options ab out how to
connect the other end of the cable:
• Direct connection to a PCoIP Client—You can use homerun cabling, or a direct
connection, between an R3040S and a ClearCube PCoIP client. Connect one end
of an Ethernet cable to the chassis port reserved for PCoIP communication (as
noted above), and then connect the other end of the cable to the Ethernet port of a
PCoIP client.
• Connect to a network—You can connect an R3040S blade to a network that
ClearCube PCoIP clients can access. Connect one end of an Ethernet cable to the
chassis port reserved for PCoIP communication (as noted above), and then
connect the other end of the cable to a network switch or router. Ensure that the
40 • Chassis and Blade Installation R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide
Page 65

blade and client are on the same subnet or, if they are on different subnets, that the
PRI
4321
PRI
4321
SEC
4321
SEC
4321
devices can communicate.
• Connect to a network that reserved for PCoIP traffic—T o isolate PCoIP traf fic
on a specific network, connect one end of an Ethernet cable to the chassis port
reserved for PCoIP communication (as noted above), and then connect the other
end of the cable to a network that you specify for PCoIP traffic.
For detailed information about setting up, configuring, and using ClearCube PCoIP
clients and hosts (blades), see ClearCube PCoIP User’s Guide.
How OS Network Connections Are Mapped to NICs on Chassis Backpack
After you insert a blade in a chassis, your Windows operating system shows 4 network
connections in the Network Connections window (click Start > Control Panel and
then double-click Network Connections to display all connections). The following
table shows how each Ethernet port on the Chassis Network Module (on the rear of
the chassis and shown above) is mapped to each network connection that your OS
displays (the following examples assume that the blade is inserted in chassis slots 3
and 4).
Table 9: Mapping of LAN Connection Names in OS, in BIOS, and in Chassis Backpack
Default LAN
Connection
Name in OS
Local Area
Connection
Local Area
Connection 2
Local Area
Connection 3
Local Area
Connection 4
Default Name in
BIOS
Lan controller #1
Lan controller #2
Lan controller #3
Lan controller #4
Ethernet Port Mapping on
Chassis Backpack
Mapped to the 2nd (higher number)
port in the pair of Primary ports
Mapped to the 1st (lower number)
port in the pair of Primary ports
Mapped to the 2nd (higher number)
port in the pair of Secondary ports
Mapped to the 1st (lower number)
port in the pair of Secondary ports
Port Location (If Blade Is in
Slots 3 & 4)
R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide Chassis and Blade Installation • 41
Page 66

MAC Address Label on R-Series Blades
Intel Inside Decal
Blade Serial Number &
Network Adapter MAC Addresses
PCoIP Video Card Configuration
(No Label if Blade Contains MGA6
1 Label if Dual Configuration
2 Labels if Quad Configuration)
Blade Part Number &
Regulatory Compliance
System Configuration
Blade System Configuration Details
(Including OS, CPU, Memory, Hard Disk, and Video Card)
Microsoft Certificate of Authenticity
Blade System Configuration Details
(Including OS, CPU, Memory, Hard Disk, and Video Card)
Intel Inside Decal
Blade Serial Number &
Network Adapter MAC Addresses
Microsoft Certificate of Authenticity
Blade Part Number &
Regulatory Compliance
Video Configuration
A label on the exterior of each R-series blade specifies the Media Access Control
address (MAC address) of each network adapter.
The following sections illustrate the location of the MAC address label and additional
labels.
R3040S Labels
The following figure shows the label on the blade exterior that specifies each network
adapter MAC address and additional labels.
R3080D Labels
The following figure shows the label on the blade exterior that specifies each network
adapter MAC address and additional labels.
42 • Chassis and Blade Installation R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide
Page 67

R1350 Labels
Blade Part Number &
Regulatory Compliance
Blade System Configuration Details
(Including OS, CPU, Memory,
Hard Disk, and Video Card)
Intel Inside Decal
Blade Serial Number &
Network Adapter MAC Addresses
Video Configuration
Microsoft Certificate of Authenticity
The following figure shows the label on the blade exterior that specifies each network
adapter MAC address and additional labels.
C/Port Cabling
When connecting a C/Port to an R3040S, only use C/Port connectors 2, 4, 6, or 8 on
the Connect Bay Module (located on the far left side of the chassis). For example, if
an R3040S is in chassis slots 3 and 4, connect your C/Port to connector 4. Connect
C/Port cables to the Connect Bay Module, as shown in Table 4 on page 28.
R3080D Cabling
The rear of a ClearCube chassis (shown Figure 27 on page 40) provides up to 2
Gigabit Ethernet ports (1 primary port and 1 secondary port) for each R3080D blade,
depending on video card configuration. The following list describes each possible
video configuration.
• ClearCube MVX (MGA6) and onboard graphics—in R3080D blades with
these video configurations, the primary and secondary ports of the slot that the
blade occupies are Gigabit Ethernet. For example, if the blade is in slot 3, primary
port 3 and secondary port 3 provide Gigabit Ethernet for the blade.
• V5x20 PCoIP Host card—in R3080D blades with this video configuration, the
primary port is Gigabit Ethernet and the secondary port is for PCoIP
communication. For example, if the blade is in slot 3, primary port 3 provides
Gigabit Ethernet and secondary port 3 provides PCoIP communication.
R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide Chassis and Blade Installation • 43
Page 68

How OS Network Connections Are Mapped to NICs on Chassis Backpack
After you insert a blade in a chassis, your Windows operating system shows 2 network
connections in the Network Connections window (click Start > Control Panel and
then double-click Network Connections to display connections). The following table
shows how each network connection that your OS displays is mapped to the Ethernet
ports (Primary & Secondary) on the rear of the chassis (shown Figure 27 on page 40).
LAN Connection Shown in OS Port on Chassis Rear
Local Area Connection Primary port
Local Area Connection 2 Secondary Port
C/Port Cabling
When connecting a C/Port to an R3080D, use the C/Port connector on the Connect
Bay Module that corresponds to the slot that the blade is in (the Connect Bay Module
is located on the rear of the chassis on the far left side, as shown in Table 4 on
page 28). For example, if an R3080D is in chassis slot 3, connect your C/Port cable to
C/Port connector 3.
RMM Firmware Update Procedures
To update RMM firmware, you need to have a TFTP server configured on your
network. The firmware can be installed using Telnet or using Sentral. You need to
first install the firmware on the Primary RMM of each Chassis Group, and then
propagate the firmware update to the rest of the RMMs in the group.
Although downgrading a firmware version is possible with the RMM architecture, it is
never recommended.
Do not remove any R4300 modules when updating the RMM
NOTE
Updating RMM Firmware Using Telnet
To install an RMM firmware update using telnet, do the following:
1. Download the firmware update package from the ClearCube Support Web site.
2. Unzip the package, and copy the files to the directory where the TFTP server is
firmware. This can cause the firmware to become corrupted.
The HEALTH LED on the RMM displays an amber signal when
firmware is being updated.
configured to get the file.
44 • Chassis and Blade Installation R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide
Page 69

3. Telnet into the Primary RMM and verify your RMM firmware version.
a. Telnet into the Primary RMM by entering the following at a command
prompt:
telnet RMMIPAddress
where RMMIPAddress is the IP address for the RMM.
b. Log in to the RMM, and enter the following command:
ver
If the RMM is version 5.x or higher, continue with this procedure. If the
RMM is version 4.x or lower, contact ClearCube Technical Support.
4. Enter the following command to update the Primary RMM:
tftp rmm52b2 TFTPServerIPAddress
where TFTPServerIPAddress is the IP address for the TFTP server.
The Primary RMM firmware will be updated along with firmware for the other
modules in this chassis. When the firmware update is completed, the RMM
restarts automatically.
5. After the RMM restarts, log into the RMM again and enter the following
command:
sfw 0
The other RMMs and modules in this Chassis Group are updated.
Updating RMM Firmware with Sentral
To update firmware using Sentral, the following pre-existing conditions must be met:
• The R4300 Chassis Group to be updated must already be discovered within
Sentral.
• A TFTP Server must be configured in Sentral's Console Configuration screen, and
running.
• The firmware update must be in a directory that is visible to the Sentral Console.
If the Sentral server is also the TFTP server, do not copy the
firmware update file to the root directory, or to the directory
NOTE
To update RMM firmware using Sentral, do the following:
1. Download the update package from the ClearCube support Web site.
where the TFTP server is configured to get the file. This will
cause the update to silently fail. For example: If the user has th e
rmm52b2 file in the directory C:\Firmware, do not configure the
TFTP server to “get” the files from this same location.
R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide Chassis and Blade Installation • 45
Page 70

2. Unzip the update package and read the enclosed Technical Bulletin (a PDF file) to
learn any special considerations for the package.
3. Copy the package to a directory visible to the Sentral Console.
4. From the Functional menu, select Management > Chassis.
5. In the Tasks menu, click Update Firmware.
6. Select the primary RMM from the Primary Execution Pane.
7. In the Tasks menu, click on Select for Update.
8. In the Serial Number column, select the serial number of the chassis containing
the RMM to be updated.
9. Click Browse and choose the firmware update file.
10. Press Update Now. The Primary RMM and the other modules in this chassis are
updated.
After the Primary RMM has been updated, do the following to update the other
RMMs in the Chassis Group:
1. From the Functional menu, select Management > Chassis.
2. In the Tasks menu, click Update Firmware.
3. In the Tasks menu, click on Update Group.
4. Select the Chassis Group that contains the RMM you just updated, and click
Select for Update.
5. Select Browse and browse for the update file.
6. Press Update Now. The other RMMs and modules in this Chassis Group are
updated.
After updating each Chassis Group, re-discover the Chassis Group. For more
information, see the Sentral Administrator’s Guide.
Remote Management Card Configuration
Control Chain Auto-Negotiation
Two types of Remote Management Cards may be present in your network:
• Remote Management Module (RMM) in R4300 chassis
• Remote Management Card (RMC) in R4200 chassis
The RMC in Blade Switching (BSBP) and Direct Connect (DCBP) BackPacks is not
capable of auto-negotiation. A BCBP or DCBP with an RMC installed is always the
Primary in the Control Chain. RMCs can be installed only in BCBPs and DCBPs.
46 • Chassis and Blade Installation R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide
Page 71

RMMs can only be installed in R4300 chassis. A BSBP without an RMC installed can
RMM (Bottom View)
JP1
– Leave JP1 jumpered on pins 2 and 3
– Jumper Pins 1 and 2 to force Primary
for auto-negotiation (Default shown)
JP1
or remove jumper entirely
perform C/Port Switching, Admin Switching, and Sparing under the control of an
RMC or an RMM.
Each RMM in an R4300 series chassis provides an Ethernet connection, allowing it to
control a chain of as many as 14 chassis. If an RMM is not connected to Ethernet, it
does not auto-negotiate, and provides control and monitoring only for the chassis in
which it is installed.
The RMM has three auto-negotiation modes:
• Primary (including jumper-strapped Primary)
• Secondary
• Standby
The model for auto-negotiation assumes that a given network contains a mix of R4300
chassis, and legacy BSBPs and DCBPs.
The R4300 Remote Management Module uses the following auto-negotiation rules:
• An RMM must be active (that is, powered up and functioning correctly) to assert
its status as Primary or other.
• If a jumper-configured RMM is present in a chain, that RMM is always Primary,
as shown in Figure 28.
• Never jumper-configure an RMM in a Control Chain that also contains an RMC.
Figure 28 RMM Jumper Location
The RMC (in a BSBP or DCBP) uses the following rules for auto-negotiating a
Primary RMC in a Control Chain:
• An RMC must be active (that is, powered up and functioning correctly) to assert
its status as Primary.
If an RMC is present in a chain, that RMC must always be the Primary.
For best results, follow these guidelines for configuring your Control Chains:
R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide Chassis and Blade Installation • 47
Page 72

• Do not use Mixed Mode (connecting a mix of R4300s, BSBPs, and/or DCBPs) for
connecting your Control Chain.
• Use an RMC to manage only BSBP- and DCBP-equipped chassis.
• Configure RMCs using Telnet.
• Use an RMM to manage new R4300 chassis, and BSBP- and DCBP-equipped
chassis that do not contain an RMC.
• Configure RMMs using Sentral.
• If your Control Chain contains a mix of R4300s, BSBPs, and/or DCBPs and you
have an RMC installed in a BSBP or DCBP, that RMC is always the Primary and
it does not provide access to all of the functions of the R4300.
• If you add BSBPs or DCBPs to a Control Chain that contains one or more RMMs,
exchange BackPacks with RMCs installed for BackPacks that do not have RMCs.
Maintain the default setting of JP1 on the RMM
NOTE
(auto-negotiation enabled). See Figure 28 on page 47. Change
this setting only at the recommendation of ClearCube Technical
Support or a ClearCube Support Engineer.
Configuring the RMM
ClearCube recommends using Sentral as the primary configuration tool for RMMs.
See the Sentral Administrator’s Guide for complete information. The RMM can also
be configured with Telnet. To configure an RMM using Telnet, do the following:
1. Open a command window and enter
telnet RMM_IPAddress
where RMM_IPAddress is the IP address of the RMM to be configured.
2. Enter the password for the RMM (no characters are echoed), and type
cfg all
48 • Chassis and Blade Installation R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide
Page 73

The following figure shows the list of configuration parameters.
Figure 29 RMM Parameters via Telnet
3. Enter the command to change a parameter in the format:
cfg ParameterName Value
where ParameterName is the parameter and Value is its desired new value.
4. When finished changing parameters, type
exit to close the Telnet window.
Resetting the RMM Settings to the Factory Defaults
In normal use, the RMM is configured using Sentral. However, it can be reset to its
factory configurations by pressing the DFLT pinhole switch on the back of the RMM.
Table 10 provides the default RMM settings. For information on configuring an RMM
with Sentral, see the Sentral Administrator’s Guide.
Table 10 R4300 RMM Default Configuration Settings
Field Name Function Setting Options Default Setting
IPMode IP Address Mode Static | DHCP DHCP
RMMIP RMM Fixed IP Address Ignored if IP Mode = DHCP 192.168.1.251
RMMNetmask RMM Netmask Ignored if IP Mode = DHCP 255.255.255.0
R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide Chassis and Blade Installation • 49
Page 74

Table 10 R4300 RMM Default Configuration Settings (Continued)
Field Name Function Setting Options Default Setting
RMMGateway RMM Gateway Ignored if IP Mode = DHCP 192.168.1.1
RMMLocation1 RMM Location 1 User-editable text string Blank
RMMEthernetSpeed RMM Ethernet Speed Auto | 10 | 100 Auto
RMMEthernetDuplex RMM Ethernet Duplex Auto | Half | Full Auto
RMMLocation2 RMM Location 2 User-editable text string Blank
SessionTimeout Session Time-out
SMIP Sentral Primary Console IP Address xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx 192.168.1.252
SMPort Sentral Management Port TCP port to the Sentral console 8080
Logging Logging Enabled | Disabled Disabled
LogServerIP Log Server IP Address Only if logging is enabled 192.168.1.253
LogServerPort Log Server Port TCP port to the Log Server 8080
LogLevel Logging Level
Alerting Alerting Enabled | Disabled Disable
AlertServerIP Alert Server IP Address Only if alerting is enabled 192.168.1.254
AlertServerPort Alert Server Port TCP port to the Alert Server 8080
AlertLevel Alert Level
CommunityString Community String Public | Private Public
SSL SSL Enabled | Disabled Disabled
Time period for which the session ID is
honored
• 2 — Errors, Warnings, and Notes
• 1 — Errors and Warnings
• 0 — Errors only
• 2 — Errors, Warnings, and Notes
• 1 — Errors and Warnings
• 0 — Errors only
120 seconds
2 (highest)
2 (highest)
Note: All RMM ALerts
are in English
SSH SSH Enabled | Disabled Disabled
Telnet Telnet (un-encrypted) Enabled | Disabled Enabled
http HTTP (un-encrypted port 80) Enabled | Disabled Enabled
AuthMode Authentication mode Domain | Local Local
AuthGroup Authentication group Group names on active directory N/A
Username Username Text string, when in local mode clearcube
Password Password Text string, when in local mode clearcube
50 • Chassis and Blade Installation R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide
Page 75

Table 10 R4300 RMM Default Configuration Settings (Continued)
Field Name Function Setting Options Default Setting
Timestamp Timestamp Seconds since Jan. 1, 1970
RMMPoll RMM Poll Time period for RMM “heartbeat” 5 minutes
SMIP2
Sentral Secondary Console IP
Address
For failover between Primary and Secondary RMMs to occur
NOTE
successfully, the RMMs must have the same password, and
Alerting and Logging must be activated. See the Sentral
Administrator’s Guide for more information.
xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx 192.168.1.252
Set from real-time
clock
Configuring the RMC
The following steps outline the process required to set up and configure your choice of
chassis control computer/server. These steps also explain the setup of the
communication link to the chassis. This description assumes that you are choosing to
control your chassis with an RMC, rather than with the recommended RMM.
• Select your chassis control computer/server: For browser-based control you
can use a PC blade or a third-party box PC, server, or a notebook computer that
has an Ethernet connection. This computer/server does not need to be dedicated
solely to this function—it can also be used for other tasks depending on the
application.
• Connect your control computer to the network: Your control computer must be
on the same LAN that connects to the Ethernet control port of the Primary chassis
with the RMC installed.
• Connect the Primary chassis and RMC to the network: An RMC can be
installed in either a BSBP or a DCBP. If an RMC is installed in a Control Chain
that contains R4300 chassis with RMMs, the Primary chassis is always the one
that has the RMC installed. The Primary chassis is indicated by a LED on the back
of the chassis next to the control in/out ports that are colored green. When the
ENET indicator is lit, this means that an RMC card is installed and this is a
Primary chassis. If the RS-485 indicator is lit, it means that this is a Slave chassis.
If you have more than one rack of chassis, you will have multiple Primary chassis,
typically one per rack.
• Daisy-chain multiple chassis: If your installation has multiple chassis, then
daisy-chain the RS-485 control connections with C/Port cables. A green cable is
provided with the chassis. Connect the RS-485 Control Output from the first
BackPack to the RS-485 Control Input on the next BackPack/chassis. Continue
daisy-chaining until all chassis are connected. You can connect all 14 chassis in a
rack together in this way. Additional chassis require an RMC for each rack of
chassis.
R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide Chassis and Blade Installation • 51
Page 76

• Configure the Blade Switching BackPack for Various Modes: Configuration
of your Blade Switching BackPack depends on that modes of operation you will
use. All modes can be used together, or individual modes can be used alone.
• Spare Switching Configuration: Multiple spare PC blades can be configured per
chassis. At the other extreme, one spare can be made available to support 14
chassis. A Spare blade is configured by connecting a short C/Port cable from its
C/Port connection to the SPARE IN connection on the chassis. For one spare to
support multiple chassis the SPARE OUT connector is daisy-chained to the
SPARE IN connector on the next chassis and so on. A short red cable for Spare
daisy-chaining is included with your chassis.
• Administrator Switching Configuration: For on-site control, the IT
administrator can connect a separate C/Port directly to the chassis’ administrator
C/Port input. This console is separate from the computer that is used to control the
chassis. For administering PC blades in more than one chassis, the Administrator
C/Port Output connection can be daisy-chained to the Administrator C/Port Input
connection on the next chassis and so on (as many as 14 chassis can be linked). A
short yellow cable for Administrator C/Port daisy-chaining is included with your
chassis.
• Supervisor Switching Configuration: This feature is configured in the same
way as the Administrator mode.
• 8 x 8 Switching: This capability lets as many as eight C/Ports switch between any
eight blades in a single chassis. This capability also lets one or more users share
multiple blades dynamically. Control over the 8 x 8 matrix of connections is
through the Sentral software. Note that 8 x 8 functionality cannot be
daisy-chained to build larger matrices. You can also use the 8 x 8 mode as a
method to provide more than one spare per chassis.
• Install and run Sentral: The Blade Switching BackPack is controlled by
ClearCube Sentral. Installation of the tools on the controlling computer is via a
CD-ROM drive.
Figure 24 on page 37, Figure 25 on page 38, and Figure 26 on page 39 show examples
of three chassis connected together to support Spare, Administrator, Supervisor, and
8 x 8 modes.
Your Chassis Accessory Kit includes snap-on ferrite cores that
NOTE
must be added to both ends of the red and yellow daisy-chain
cables in order to meet FCC and CE requirements for radiated
emissions.
The administrator's console connects to the Primary chassis through an Ethernet
connection to the RMC. The primary chassis is then daisy-chained to all other
secondary chassis in the rack via a simple cable daisy-chaining method, using the
RS-485 bus. Secondary chassis do not need an installed RMC.
Each RMC can support as many as 14 chassis (the Primary chassis plus 13 Secondary
chassis). Software components of the ClearCube Management Suite communicate
with each RMC via a unique static IP address. If your system includes more than 14
chassis or you have more than one group of chassis to manage, you need to configure
52 • Chassis and Blade Installation R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide
Page 77

each RMC with a different IP address. This allows you to log in to each group of
chassis independently.
Every primary R4200 chassis with an RMC installed is shipped
NOTE
Default RMC Settings: IP Address : 192.168.1.251
with the same default network settings. If you are using multiple
Chassis groups, you must configure new IP addresses per the
instructions below to avoid a conflict.
Gateway: 192.168.1.1
Network: 192.168.1.0
Netmask: 255.255.255.0
Changing the IP Address of the RMC
To change the IP address on an RMC, do the following:
1. From any computer on the network connected to the RMC, open a telnet session
to log into the RMC using the default RMC IP address of 192.168.1.251. If your
network settings are incompatible with the RMC’s default settings, then you need
to select one computer (notebook, blade, or other PC) that you can use to program
the RMC. Set this computer’s network settings to be compatible with the RMC
default settings and connect its network port directly to the CONTROL IN port
on the R4200 using the provided cross-over cable. To telnet into the RMC from a
DOS prompt, type:
H:\>Telnet 192.168.1.251
The result should be:
Password:
2. Type clearcube as the default pa ssword. For example:
Password: clearcube
NOTE
You will not see any letters as you type the password.
The result should be:
RMC Configuration
1. IP address: 192.168.1.251
2. Gateway: 192.168.1.1
3. Network: 192.168.1.0
4. Netmask: 255.255.255.0
5. Password: clearcube
6. Exit
3. From the list of options, select 1 to change the IP address. For example:
>1
R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide Chassis and Blade Installation • 53
Page 78

The result should be:
>1
new ip:
4. Type in the desired new IP address. For example:
>1
new ip: 192.168.1.100 (your desired IP address)
The result should be:
RMC Configuration
1. IP address: 192.168.1.100
2. Gateway: 192.168.1.1
3. Network: 192.168.1.0
4. Netmask: 255.255.255.0
5. Password: clearcube
6. Exit
NOTE
The IP address should be the new one you typed in.
5. Change the Gateway, Network, and Netmask settings, using the same procedure.
For Gateway, use your network’s default gateway setting. For Netmask, use your
network’s subnet mask setting. For Network, use the base network address,
which is typically your subnet mask ANDed with the IP address (also called the
Subnet ID). For example, if your IP address is 192.168.1.154 and your subnet
mask is 255.255.255.0, then if you AND the two addresses together you get a
Network setting of 192.168.1.0.
6. Enter
6 to exit. For example:
>6
The result should be:
>6
Save changes and reboot <y/n>?
7. Enter y for yes. For example:
>6
Save changes and reboot <y/n>? y
The result should be:
Connection to host lost.
The RMC accepts only a lowercase y as a valid positive response. If you type yes,
or an upper-case
Y, the changes are not saved. Watch for the Saving changes...
message, which confirms the configuration was saved successfully.
NOTE
You may have to close the telnet window by selecting the X in
the top right corner.
54 • Chassis and Blade Installation R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide
Page 79

Connect the CONTROL IN port to your regular network using a standard network
cable. Make sure not to use the cross-over cable you were just using. Test the
connection to the RMC by pinging its address from any other computer on the
network.
It is recommended that you change your password for security
NOTE
reasons. If you are unable to connect to the RMC card across
your network, make sure the network connection at the switch
for your RMC is able to pass 10Mbps traffic.
Resetting the RMC IP Settings to the Factory Defaults
To reset the IP address on an RMC to the factory default, do the following:
1. Shut down power on all blades in the primary R4200 chassis that houses the
RMC.
2. Remove the AC power cord from the back of the primary R4200 chassis.
3. Remove the Ethernet cable from the RS485 OUT port on the back of the primary
R4200 chassis, if one is connected.
4. Plug the Factory Default Jumper cable (provided with your R4200 chassis in the
Chassis accessory kit) into the RS485 OUT port on the back of the primary
R4200 chassis.
5. Plug the AC cable back into the R4200 chassis and wait at least 15 seconds.
6. Remove the Factory Default Jumpe r cable.
7. Reatta ch the Ethernet cable to the RS485 OUT port on the back of the primary
R4200 chassis, if one was previously connected.
8. Power the blades back up in the primary R4200 chassis (if desired).
The RMC network controller is reset to the factory default settings, with an IP address
of 192.168.1.251. Resetting the RMC to its factory defaults and connecting to it with a
laptop computer using a crossover cable is a helpful troubleshooting technique.
R4300 Chassis Upgrade Kit Installation
An R4200 chassis can be upgraded to an R4300 chassis with an available chassis
upgrade kit. To install the R4300 chassis upgrade kit, do the following:
1. Power down th e blades in the chassis.
2. Disconnect AC power from the chassis.
3. Open the front bezel of chassis and pull any installed blades out approximately
one inch to disconnect them from the BackPack connectors.
4. Remove the 5 hex head screws retaining the fan pack.
5. Use the side finger holes to pull the fan pack from the chassis.
R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide Chassis and Blade Installation • 55
Page 80

6. Remove the 2 Phillips screws retaining the BackPack.
7. Pull the BackPack by the two tabs and remove it from the chassis.
8. Unsnap and remove the black plastic shield from the AC backplane by pulling
upwards on it.
9. Remove the 9 hex head screws from the AC backplane.
10. Remove and discard the AC backplane.
Figure 30 Exploded View of Upgrade Kit Components
11. Install the new R4300 upgrade parts in the chassis.
12. Place the AC backplane module in the chassis and secure it with 4 hex head screws.
13. Insert the R4300 frame into the base of chassis. Ensure that the frame is fully
seated against the AC backplane module. Secure the R4300 frame with 2 hex head
screws in the locations indicated.
14. Insert the AC input module, and secure it with 2 hex head screws.
15. Slide the power supply modules onto the top of the frame. Ensure each unit is
captured on both sides by the guide flanges and is fully seated into the backplane
connectors.
16. Remove the cardboard shipping brace from the fan pack module and install the
fan pack into the chassis. Secure the fan pack with 5 hex head screws to complete
the base R4300 chassis assembly.
17. Connect the power cords supplied with the upgrade kit to appropriate power
source(s).
18. Install the desired modules in the Connect, Management, and Networking Bays,
as described in “Chassis Configuration and Operation” on page 25.
19. Reseat the blades and power up the chassis.
20. Power up the blades.
56 • Chassis and Blade Installation R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide
Page 81

Fiber Transceiver and Cable Requirements
Fiber Optic Cables to Fiber C/Port
(SC Connector on Transceiver End and
LC Connector on C/Port End)
Ethernet Cables to ClearCube Chassis
See ClearCube F6150 Fiber Transceiver User’s Guide for information about
installing and using the fiber transceiver and for information about transceiver power
requirements.
See http://www.clearcube.com/support/controller/home.php
Fiber Transceiver User’s Guide.
The Fiber Transceiver and Fiber C/Port are Laser Class 1 Products.
See “Safety Guidelines” on page xiii for additional information.
Make sure your power strips, power grid, and circuit breakers can
safely provide the required current. Ensure that any extension cords
used meet local safety regulations and fire codes. When specifying
uninterruptible power supplies (UPS) be sure to include the Fiber
Transceiver peak current draws in your calculations to ensure the
UPS has adequate capacity.
The F6150 Fiber transceiver contains 16 media converters. Each media converter accepts:
• An Ethernet cable to connect the transceiver to a ClearCube chassis (CAT5,
CAT5e, CAT6, or CAT6e Ethernet cable)
• A fiber cable to connect each media converter to a fiber C/Port (multi-mode,
50µm or 62.5µm fiber cable with an SC connector on the transceiver end and an
LC connector on the C/Port end)
to download the F6150
R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide Chassis and Blade Installation • 57
Figure 31 F6150 Fiber Transceiver
Page 82

The fiber optic cables from the output of the Transceiver can be home runs to the
individual fiber C/Ports, or they can be pa tch cables that run to one or more fiber patch
panels.
The following requirements apply to the ClearCube Fiber Optic Extension System:
• The power budget through all the connections between the Transceiver and the
Fiber C/Port must be 6 dB or less, including the cable itself.
• This system connects PC blades at a maximum distance of 2000 meters over a pair
of 50µm or 62.5µm multi-mode fibers.
PC Blade Installation
Unpacking the PC Blades
Once the chassis has been installed and connected to power and signal connections,
open the PC blade boxes and remove the PC blades.
Examine each PC blade for damage as a result of shipping. If you find any damage
contact the carrier to file a claim and call the ClearCube Customer Service
Department for replacement.
Do not use any PC blade that shows any sign of damage. Subsequent
damage from a defect caused by shipping could be extensive.
Installing PC Blades
Never leave a PC blade out in the open. It should either be in the chassis or in its
storage box. Dust, dirt, and other debris can cause problems so keep the boards clean
by keeping them installed or in their storage box.
Never force blades into a chassis. Mishandling blades can cause
critical hardware failure, data loss, or both.
NOTE
• 44–pin interposer—This default configuration enables you to install R-series
• 30–pin interposer—Available as a downgrade kit, this interposer enables you to
The interposer on the rear of R-series blades determines the
chassis in which you can install them.
blades in R4300 chassis
install R3080D and R1350 blades in an R4200 or in an R4300 chassis. If you use
a 30–pin interposer with the R4300 chassis, you cannot use the USB port on the
rear apron of the chassis.
58 • Chassis and Blade Installation R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide
Page 83

To install a blade, do the following:
NOTE
Never force blades into a chassis. Mishandling blades can
cause critical hardware failure, data loss, or both.
1. Lower the front bezel on the chassis by depressing the latches on each side.
2. Orient each blade right-side up (LCD panel on the bottom) and then slowly insert
the blade into the chassis by lining up the blade edges with both the top and
bottom guides in the chassis.
3. Start inserting blades with the left-most slot. There will be a slight resistance to
insertion when the back connector goes into the backplane socket.
NOTE
The R3040S (and other ClearCube dual-slot blades) can only
be inserted into chassis slots 1&2, 3&4, 5&6 and 7&8.
Always insert the PC blade slowly to avoid damage resulting from
misaligning the PC blade edges with the guides.
When properly seated, the PC blade is flush with the front edge of the bottom
guide bracket.
4. After inserting all blades, raise the chassis front bezel and snap into place.
5. In a rack installation, you can lock the chassis front bezel using a Kensington lock
on each side of the chassis. In a cabinet installation, use a locking front door to
secure the chassis and blades.
The very first time you insert the PC blade, the power does NOT
NOTE
turn on automatically. You must depress the power button on
the front of the blade to power it on.
Blades have three options for power state after AC power recovery. AC power failure
could mean either the whole chassis losing power and recovering, or just unplugging
and plugging a blade back in. The three options are:
• Power On – After power is reapplied, the blade powers up and stays on.
• Stay Off – After power is reapplied, the blade stays off
• Last State – After power is reapplied, the blade returns to the power state that it had
when the power was lost. For example, if the blade w as off when it was power was
lost, it stays off; if the blade was on when power was lost, it turns on and stays on.
The default power settings for the R-series blades are Power On.
If the user last turned the blade off by holding down the power
NOTE
button for 4 seconds, the blade will only power back on by a
subsequent power button press, rega rd le ss of the po we r
recovery state.
R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide Chassis and Blade Installation • 59
Page 84

When a blade is inserted into a chassis, it takes approximately 30 seconds for the
R4300 Chassis Network Module
Secondary Ports Primary Ports
chassis and its RMM to detect the blade and relay its information to Sentral.
Note that the blue LCD panel and the C/Port indicator remain lit, independently of
whether the blade is powered on. These indicators run off of chassis power. After the
first on/off cycle, you can power the blade back on from the shutdown state by either
pushing the power button on the blade or the Reset/Power button on the C/Port.
Connecting Ethernet Cables
The following sections describe the configuration of R-series blade Ethernet adapters.
See “R3040S Cabling” on page 40 and “How OS Network Connections Are Mapped
to NICs on Chassis Backpack” on page 41 for more information. The following figure
shows the primary and secondary ports on the rear of an R4300 chassis.
Figure 32 The Primary and Secondary Ports in an R3400 Chassis Network Module
R3040S Blades
The type of video card installed in a blade determines the number of available
Ethernet adapters:
• Traditional video card: (such as ClearCube MGA6 or off-the-shelf card)
provides four Gigabit Ethernet adapters:
– Primary ports: Gigabit Ethernet
– Secondary ports: Gigabit Ethernet
• V52x0 PCoIP Host card: provides three Gigabit Ethernet adapters:
60 • Chassis and Blade Installation R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide
– Odd-numbered secondary port: PCoIP communication to PCoIP zero
clients
– Three other ports: Gigabit Ethernet
Page 85

To connect C/Ports to a dual-slot blade, use only the even-numbered C/Port
connectors 2, 4, 6, or 8, relative to those slot pairs. The odd-numbered C/Port
connections on the chassis are not connected to dual-slot blades.
R3080D Video Options and Ethernet Port Behavior
The R3080D provide two Ethernet ports that correspond to the primary and secondary
Ethernet jacks on the rear of a chassis. Your graphics card configuration determines
the behavior of the blade’s Ethernet ports.
• Quadro4 PCI-Express card and integrated graphics (with i5-660 proce ssor):
– Primary port: Gigabit Ethernet
NOTE: Always connect cables to the primary Ethernet port first.
– Secondary port: Gigabit Ethernet
NOTE: In an R4200 chassis only the primary port is connected.
• V5220 Dual Host card:
– Primary port: Gigabit Ethernet
– Secondary port: PCoIP communication to PCoIP zero clients
R1350 Video Options and Ethernet Port Behavior
The R1350 provide two Ethernet ports that correspond to the primary and secondary
Ethernet jacks on a chassis. Your graphics card configuration determines the behavior
of the blade’s Ethernet ports.
• Quadro4 PCI-Express card and GMA 950 integrated graphics:
– Primary port: Gigabit Ethernet
NOTE: Always connect cables to the primary Ethernet port first.
– Secondary port: 10/100 Ethernet
NOTE: In an R4200 chassis only the primary port is connected.
• V5120 Dual Host card:
– Primary port: Gigabit Ethernet
– Secondary port: PCoIP communication to PCoIP zero clients
Using USB 2.0 Capability on the R3040S and R1350
The R3040S and R1350 provide two USB 2.0 port s: one on th e fron t o f the Blade and
one on the back apron of the R4300 when the blade has a 44-pin interposer installed.
The 30-pin interposer does not bring the USB 2.0 signals onto the R4300 signal
backplane.
The USB port on the R1350 connects to the corresponding USB port on the R4300.
R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide Chassis and Blade Installation • 61
Page 86

When connecting to an R3040S, use the even-numbered USB ports on the back apron
of the R4300. The odd-numbered USB ports on the chassis are not connected to the
R3040S. This is the same scheme as with connecting C/Ports to a dual-slot blade.
See “Mass Storage Lockout: Disabling Access to USB Mass Storage Devices” on
page 71 for information about enabling and disabling USB ports on user ports (zero
clients, thin clients, and so on).
R1350 Monitor Support
The following table lists each R1350 video option and the number of supported
monitors for each option.
Graphics Option
Intel® GMA 950 integrated graphics engine X
NVIDIA® Quadro®4 PCI-Express® card (MGA6) X X
V5120 Dual Host card X X
V5140 Quad Host card X X X
Single
Monitor
(with ClearCube MVX)X(with ClearCube MVX)
Dual
Monitor
Quad
Monitor
R3080D and R3040S Display Support and Configuration
This section details maximum supported displays for each R3080D and R3040S
graphics option (card), and describes how to configure display types when using
V52x0 PCoIP Host cards.
Graphics Options and Number of Displays Supported
The following table lists each video option and the number of supported displays for
each option.
Graphics Option
Single
Monitor
Dual
Monitor
Quad
Monitor
NVIDIA® Quadro®4 PCI-Express® card (MGA6) X X
(with ClearCube MVX)X(with ClearCube MVX)
V5220 Dual Host card X X
V5240 Quad Host card
X
(R3040S only)
X
(R3040S only)
X
(R3040S only)
Configuring Multiple DVI-I Displays with V52x0 PCoIP Host Cards
If your R3080D or R3040S blade contains a V52x0 PCoIP Host card, the blade
supports one DVI-I monitor and one VGA monitor by default. You can use the
included S3 Graphics
62 • Chassis and Blade Installation R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide
®
ScreenToys utility to change video settings so you can connect
Page 87

two or more DVI-I displays to your PCoIP client. Perform the following steps to
Display Devices
Area
Monitor Menu
disable the default VGA display and enable one or more additional DVI displays.
1. Connect one or more additional DVI displays to your PCoIP client.
2. Right-click an empty area on the desktop.
3. Select ScreenToys from the right-click menu to display the Device Management
dialog box.
4. From the Monitor menu, select the VGA display. The icons in the Display
Devices area refresh to reflect your selection.
5. From the Display Devices area, clear the VGA checkbox to disable the monitor
and then click Apply All.
Video Resolution
The ClearView Quadro4 video driver that comes pre-installed on ClearCube PC
blades supports video resolutions as high as 1280 x 1024. If you require video
resolutions greater than this, you need to uninstall the ClearView Quadro4 driver from
the blade and install the standard, high resolution Quadro4 video driver from the
ClearCube web site at
downloaded directly from the NVIDIA web site, as they have not been validated to
work properly with a ClearCube system.
Changing CMOS Settings
You can change CMOS and BIOS settings using the BIOS setup utility. To access the
utility, power on a blade and press the F2 key when the ClearCube splash screen
appears (the splash screen should provide prompts about additional options and
corresponding keys to press).
http://www.clearcube.com/support/. Do not use drivers
R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide Chassis and Blade Installation • 63
Page 88

From the BIOS setup utility you can configure boot sequence, hard disk settings,
power-up defaults, power management settings and more. (Note that you can select
the first boot device without entering the BIOS setup utility. Follow the on-screen
prompts as the blade boots. If you are booting from a USB CD-ROM device, select
CDROM (do not select removable device.)
ClearCube PC blades uses a lithium coin-cell battery for backing up
parameter memory. When you change this battery, remove the old battery
and wait at least 30 seconds before inserting the new battery. Otherwise,
memory corruption may occur, and may require sending the blade back to
ClearCube for repair.
You can clear existing CMOS settings and reset BIOS passwords as described in the
following sections.
Resetting an R1350 CMOS Password
To reset the CMOS password on an R1350, move the JP1 jumper on the motherboard.
You will need a set of needle-nose pliers to move the jumper. When the jumper is in
the Reset CMOS on restart position, the CMOS password is reset when the R1350
restarts. To reset the CMOS password, perform the following steps.
1. Power down the blade normally, and remove it from the chassis.
2. Move the CMOS jumper to the Reset CMOS on restart position (pins 2 and 3
jumpered).
3. Return the blade to the chassis and power it on. Wait until the operating system
starts.
4. Power off the blade, and remove it from the chassis.
5. Return the CMOS jumper to its default position (covering pins 1 and 2).
NOTE
If you do not return this jumper to its default position, th e bla de
will always reset the CMOS password when it restarts.
6. Return the blade to the chassis and power it on.
64 • Chassis and Blade Installation R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide
Page 89

Figure 33 Model R1350 MSL and CMOS Jumper Locations and Settings
JP6 JP1
USB Mass Storage
1
3
MSL Jumper
1
3
devices function
normally (default)
USB Mass Storage
devices do not
function
Reset CMOS
1
3
password on
1
3
Normal operation
CMOS Jumper
(default)
restart
Clear CMOS
Moving Jumper to This
Position Clears
CMOS Settings
Disable Clear CMOS
CMOS Settings are
Maintained
(Default Position)
MSL
R520
CMOS
JP10
JP6
1
Detail of the JP10
Clear CMOS Header
(on Bottom)
R3080D Blade
CPU 1
CPU 0
Battery
JP3
1
2
3
Disable
Enable
Base of R3040S Blade and Motherboard
Detail of the JP3
Clear CMOS Header
Clearing All R3080D and 3040S CMOS Settings
The R3080D and R3040S motherboards provide a jumper you can use to clear all
current CMOS settings. By default, the jumper is on pins 1 and 2 for normal operation.
The following figures show the location of the JP3 header and default jumper position
on the R3080D and on the R3040S.
Figure 34 Model R3080D CMOS Header and Jumper Settings
R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide Chassis and Blade Installation • 65
Figure 35 Model R3040S CMOS Header and Jumper Settings (Default Setting Shown)
Page 90

Perform the following steps to clear all CMOS settings.
1. Power down the blade and remove the blade from the chassis (if the blade is not in
an enclosure—for example, for configuration—ensure that power is
disconnected).
2. Locate header JP10 on the R3080D (see Figure 34 on page 65) or header JP3 on
the R3040S (see Figure 35 on this page).
3. Use needle-nose pliers to move the jumper from the default position (on pins 1
and 2) to the reset/clear position (on pins 2 and 3).
4. Wait five second s.
5. Using your pliers, move the jumper back to the default position (on pins 1 and 2).
6. Return the blad e in a ch ass is as d escribed in “Installing P C Blades” on page 58.
7. Power on the R3 040S.
The CMOS is cleared, including any administrator or user passwords. You can now
enter BIOS setup to make any necessary changes by pressing F2 when prompted
while starting the blade.
Configuring RAID on an R3040S Blade
R3040S blades can contain up to 4 hard disks, and supports the fo llowing RAID
configurations:
• RAID 0—implements a striped disk array. Data is broken down into blocks and
each block is written to a separate disk drive. Since no redundant information is
stored, performance is very good, but the failure of any disk in the array results in
complete data loss. RAID 0 is only used to increase disk performance.
• RAID 1—implements mirroring. This redundancy of data means that no rebuild
is necessary in case of a disk failure, only a copy to the replacement disk.
• RAID 10—implements mirroring (RAID 1) and a striped disk array (RAID 0);
RAID 10 is also called RAID 1+0. This configuration requires a minimum of four
disks: two mirrored disks to hold half of the striped data and two mirrored disks
for the remaining data.
• RAID 5—stripes both data and parity information across three or more drives.
writing data and parity blocks across all the drives in the array. RAID 5 volumes
functions if one drive fails, though performance is degraded.
Prerequisites and Overview of Required RAID Tasks
The following list provides an overview of the steps required to create a RAID volume
(perform tasks in the order listed below).
• Back up all data on your blade.
• If applicable, obtain all drivers required for your blade. After creating a RAID
volume, you will install an OS on the blade. By default, images installed on
ClearCube blades contain all necessary drivers, including the RAID drivers and
hardware drivers (NIC, chipset, and video). You can obtain drivers from the
66 • Chassis and Blade Installation R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide
Page 91

ClearCube blade image and from the ClearCube Support Web site before you
create a RAID volume, which will remove the drivers from the hard disk.
• Determine the RAID configuration to use for the volume you are creating.
• Enable RAID in R3040S BIOS and make additional BIOS configurations as
described in the following section.
• Use Intel Storage Matrix Manager to create RAID volume.
• Obtain a USB floppy drive and floppy disk to install the drivers during operating
system installation. Save the drivers to the floppy disk.
• Install an operating system on the new RAID volume, ensuring that you have the
necessary floppy drive and floppy disk containing the RAID drivers.
• Also ensure that if you are using more than two hard disks, you are using
ClearCube drive holder G0700059, with a four-disk maximum capacity.
• Ensure that each hard disk is made by the same manufacturer and is the same
model and size. (though, you shouldn't' be adding any drives because they're
FRUs in that case)
• R3040S blades support RAID 0, 1, 10, and 5. Ensure that:
– You have a thorough understanding of the RAID configura tion you are
choosing.
– Each hard disk included in the RAID volume is made by the same
manufacturer and is the same model and size.
Enable RAID in BIOS
Perform the following steps to enable RAID in the BIOS (the following steps assume
that the R3040S is in a chassis and there are two or more hard disks in the blade, as
appropriate for the RAID level you are implementing).
1. Power on the blade, and press F2 when prompted to enter the BIOS Setup Utility
(Setup). Use your ARROW keys, TAB, and ENTER to navigate through the
menu. Press ESC to exit menus.
2. From Setup, use your arrow keys to display the Advanced menu, and then select
IDE Configuration. Press Enter.
3. Ensure that SATA#1 Configuration is set to Compatible. Change the setting if
necessary.
4. Select Configure SATA#1 as and press Enter. Select RAID and press Enter.
5. Select Stable ID Support and set to Enabled.
6. Press ESC to return to the previous screen.
7. Navigate to the Boot menu, select Boot Settings Configuration, and press Enter.
8. Select Quick Boot and set to Disabled.
9. Select Quiet Boot and set to Disabled.
R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide Chassis and Blade Installation • 67
Page 92

10. Press F10 to save your changes and exit Setup.
Press CTRL+ I When This Message Is Displayed
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v8.9.1.1002 ICH10R/DO wRAIDn
Copyright(C) 2003-09 Intel Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
RAID Volumes: * = Data is Encrypted
ID Name Level Strip Size Status Bootable
0 myRAID_n RAIDnn(RAIDnn) 64KB 596.2GB Initialize Yes
Physical Disks:
Port Drive ModelSerial # Size Type/Status(Vol ID)
0 ST9320423AS5VH0R2PP 298.0GB Member Disk(0)
1 ST9320423AS5VMSEDAW 298.0GB Member Disk(0)
2 ST9320423AS5VH4T2NI 298.0GB Member Disk(0)
3 ST9320423AS5VH9D1KY 298.0GB Member Disk(0)
Press <CTRL-I> to enter Configuration Utility...
<CTRL-I>
As discussed in the first step in the following section (“Creating
NOTE
a RAID Volume Using Software RAID”), be prepared to press
CTRL+I when prompted after the blade reboots.
11. Select OK and then press Enter to reboot the blade.
You can now continue to create the RAID volume using the Intel Matrix Storage
Manager, as described in the following section.
Creating a RAID Volume Using Software RAID
This section describes how to use the Intel Matrix Storage Manager Configuration
Utility to set up and configure a RAID volume. This section assumes you are using
SATA drives and configuring software RAID.
Improper RAID configuration will result in data loss. Never change
RAID configuration without making a complete system back-up.
Perform the following steps.
1. After rebooting as described above, several post scree ns are displayed. Press
CTRL+I when the Intel Matrix Storage Manager displays
enter Configuration Utility
at the bottom of the screen (the following figure
is an example; your screen will be similar).
Press <CTRL-I> to
Figure 36 Press CTRL+I When Prompted at the Bottom of the Screen to Display the Configuration Utility
If you do not press CTRL+I in the time provided, the message Press <ESC> to
boot
is displayed. Restart the blade (it will not boot because an OS is not installed
yet) and press CTRL+I when prompted during reboot.
2. When the Intel Matrix Storage Manager Configuration Utility is displayed, ensure
68 • Chassis and Blade Installation R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide
that Create RAID Volume is selected and press Enter.
Page 93

3. From the Name field, type a name for the RAID volume you are creating (there is
a 16-character maximum and special characters are not allowed). Press Enter
after typing the name.
4. Use the arrow keys to scroll through the menu of RAID levels (R3040S supports
RAID levels 0, 1, 10, and 5). Select a level and then press Enter.
5. If you are configuring RAID 10, skip this step and continue to step 7
. Select
Disks is highlighted. Press ENTER to specify disks to add to the volume.
6. Select disks to add to the volume:
– RAID 0: Select 2 to 4 disks as described below.
– RAID 1: Select 2 disks as described below.
– RAID 5: Select 3 to 4 disks as described below.
Use the arrow keys to highlight a disk to add and then press the SPACEBAR to
select it. A green icon ( ) adjacent to the disk name indicates that the disk is
selected. After selecting disks to add to the volume, press ENTER.
7. If you are configuring RAID 1, skip this step and continue to step 8
. Use the
arrow keys to specify a strip size, and then press ENTER.
8. Specify a volume capacity and press ENTER.
9. Select Create Volume, and then press ENTER. The utility displays a warning
message indicating that you will loose all data on the disks that you add to the
volume.
10. Press the Y key to create the volume and display the Main Menu. Information
about the volume you just created and each disk in the volume is displayed in the
DISK/VOLUME INFORMATION area.
11. Press ESC to exit and then press Y. The blade will attempt to boot.
12. Power off the blade. You can now continue to install a supported OS on the blade
as described in the following section.
Installing a Windows OS on a RAID Volume
This section describes how to install an operating system from an optical disk and
include RAID drivers during installation.
These instructions assume that you are:
• REQUIRED: Installing RAID drivers from a USB 3½-inch floppy drive
• Installing a Windows operating system from an optical disc
To connect the external drives to your blade, ClearCube recommends that you connect
a USB hub to the USB port on the front of the R3040S, and then connect the floppy
drive and the optical disk drive to the USB hub.
1. Ensure that you have all required drivers (RAID drivers, chipset drivers, network
[NIC] drivers, and video drivers).
a. You can download an archive file containing all drivers for an R3040S from
the ClearCube Support site:
http://www.clearcube.com/support/
R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide Chassis and Blade Installation • 69
Page 94

From the Support site, click PC Blades > R3040S > Drivers and then click
the link for the operating system you are installing.
b. Extract the RAI D drivers in the archive file you just downloaded to a
3½-inch floppy disk (see the readme file in the archive for the location of the
RAID drivers).
c. Extract the remaining drivers to a storage device so you can install them
after installing the operating system.
2. As noted above, connect the external floppy drive and external optical drive to
the R3040S and insert the floppy disk and optical disk in the drives.
3. Place the operating system optical disk that you are installing in the optical drive.
4. Set the blade's boot priority to boot to the optical disc drive containing the OS
CD-ROM or DVD.
a. Start or restart the blade and press F2 to enter the BIOS Setup Utility.
b. Use the arrow buttons to select the Boot menu, highlight Boot Device
Priority, and then press ENTER.
c. Use the arrow keys on your keyboard to select the optical drive name.
d. Press and hold the SHIFT key and then press the + key one or more times to
move the optical drive to the top of the list, so it as listed as the 1st Boot
Device.
e. Press F10 to display a confirmation screen.
Very shortly after the Windows Setup screen is displayed in the
NOTE
following step, a message displayed on the bottom of the screen
prompts you to press F6 to install SCSI or RAID drivers. Be
prepared to press F6 very quickly after pressing ENTER, below.
Select OK and then press ENTER to save your changes and exit setup. The
blade will reboot to the optical disk and start Windows Setup.
5. Press F6 when the
or RAID driver
Press F6 if you need to install a third party SCSI
message is displayed at the bottom of the screen (almost
immediately after Windows Setup starts). After you press F6, the installer
continues installation for several minutes.
6. Windows Setup displays a screen stating that it could not determine the type of
one or more mass storage devices, and that it will load support for
<none>. This is
normal operation.
NOTE
Before continuing, ensure that a floppy disk drive and the disk
with RAID drivers is connected to the blade (as described in step
2 above).
Press S to specify drivers for the RAID disk controller.
If the drive is not connected, Windows Setup displays a message stating that it
could not find a floppy drive. If this is the case, connect th e flopp y driv e and p ress
ESC to return to the screen. You can now press S and continue installation.
70 • Chassis and Blade Installation R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide
Page 95

7. Setup displays a screen requesting that you specify the SCSI adapter. Scroll to
Intel(R) ICH8R/ICH9R/ICH10R/DO/5 Series/3400 Series SATA RAID
Controller (the third entry) and press ENTER. A message is displayed at the
bottom of the screen indicating that setup is loading files.
8. Setup displays a screen indicating that is will load support for the controller you
specified in the previous step. Press ENTER to continue. Messages are displayed
at the bottom of the screen while files are loaded.
9. Setup displays a screen in which you can configure disk partitions. Configure the
partition or partitions on the RAID volume as appropriate for your environment.
10. Windows Setup continues through additional installation and configuration steps.
Configure the operating system as appropriate for your environment. As
installation continues, the operating system typically restarts the blade; remove
the floppy disk drive from the blade as the blade restarts.
After OS installation is complete, you can deploy the R3040S in your environment.
Removing a PC Blade
To remove a blade, perform the following steps:
Always completely power down a blade using the power button or by
shutting down the OS before removing it from a chassis. Removing a
blade before completely powering down can cause critical hardware
failure, data loss, or both.
1. Lower the front bezel on the chassis by depressing the latches on each side.
2. Power down the blade and pull gently on the handle until it slides out. Be sure to
support both ends of the blade when you remove it completely from the chassis.
Never forcefully remove blades from a chassis. Mishandling blades
can cause critical hardware failure, data loss, or both.
Some surfaces on the blade may be hot, especially when the blade
has been powered on. Remove and handle the blade with care.
Never leave a PC blade unprotected when not in use. It should either be in the chassis
or in its storage box. Dust, dirt, and other debris can cause problems so keep the
boards clean by keeping them installed or in their storage box.
Mass Storage Lockout: Disabling Access to USB Mass Storage Devices
R-series PC blades offer a unique Mass Storage Lockout (MSL) security feature that
disables the use of USB mass storage devices (such as flash drives, floppy drives,
CD-ROM drives, and so on) on ClearCube C/Ports and PCoIP clients.
R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide Chassis and Blade Installation • 71
Page 96

MSL is disabled by default. To enable MSL, you must set a jumper on the MSL header:
USB Mass Storage
devices function
normally (default)
USB Mass Storage
devices do not
function
R1350 and MSL Header on V5120 Host Card (for MSL on PCoIP Client)
MSL Header J7
(Adjacent to USB Port on V5120 Card)
• To enable MSL on an R1350 blade with a V5120 Host card, use MSL header J7
located on the V5120 Host card (shown in Figure 37 on page 72). This
configuration does not support MSL through the JP6 header on the motherboard.
• For all other configurations, enable MSL using the JP6 header on the
motherboard.
Additionally, ClearCube Sentral provides software-based MSL to prevent the use of
mass storage devices. See Sentral Administrator’s Guide for more information.
NOTE
When the MSL jumper is physically set to lock out mass storage
devices, software MSL cannot override this.
Use needle-nose pliers to move the jumper, as described in the following steps.
1. Power down th e blade and remove it from the chassis (if the blade is not in an
enclosure—for example, for maintenance—ensure that power is disconnected).
2. Locate the MSL header:
– R1350 with V5120 Dual Host Card
MSL header J7 is located on the lower edge of the V5120 card, to the left of
the USB port, as shown in the following figure.
Figure 37 MSL Header on V5120 Card in R1350 Blade (MSL Header on Motherboard Is Unsupported in This
Configuration)
72 • Chassis and Blade Installation R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide
Page 97

– R1350 Using a C/Port
1
3
1
3
R1350 and MSL Header and Jumper (for MSL on C/Port)
USB Mass Storage
Devices Do Not
Function
USB Mass Storage
Devices Function
Normal (Default)
MSL Header JP6
on Motherboard
MSL Disabled
Access to
USB Device Is
Permitted
(Default Setting)
MSL Enabled
Access to
USB Device Is
Prohibited
Front of Blade
MSL
R520
CMOS
JP10
JP6
1
MSL Header (on Top)
MSL header JP6 is located to the left of the DIMM slots, above and to the left
of the SATA cable, as shown in the following figure.
Figure 38 R1350 MSL Header and Jumper Settings for Use with C/Port
– R3080D
MSL header JP6 is located below the video card and to the right of the
Ethernet port on the bottom edge of the blade, as shown in the following
figure (the CMOS header is immediately below the MSL header; ensure that
you move the jumper on the top-most header, not on the CMOS header).
Figure 39 Model R3040S MSL Header Location and Settings (Default Setting Shown on Motherboard)
R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide Chassis and Blade Installation • 73
Page 98

– R3040S
CPU 1
CPU 0
Battery
JP6
1
2
3
Enable Disable
JP6 Mass Storage Lockout Header
MSL header JP6 is located near the top edge of the motherboard, between the
upper set of memory modules and CPU1, as shown in the following figure.
Figure 40 Model R3040S MSL Header Location and Settings (Default Setting Shown on Motherboard; Top Blade Sections
Not Shown for Clarity)
3. Use needle-nose pliers to move the jumper. Perform one of the following steps:
– To enable MSL
Move the JP6 jumper to pins 1 and 2. This setting prevents access to USB
devices connected to the blade or to the client.
—OR—
– To disable MSL
Move the JP6 jumper to pins 2 and 3. This setting enables access to USB
devices connected to the blade or to the client.
4. Return the blad e to a ch ass is as d escribed in “Installing P C Blades” on page 58.
5. Power on the blade.
Depending on the MSL option you set, access to USB devices connected to the blade
or to the client is enabled or disabled.
Re-installing System Software
ClearCube blades are normally shipped with operating system facto ry-installed . Other
operating systems may be optionally available. All factory-installed operating systems
are images customized specifically for ClearCube blades, and each blade model uses an
image version that is specific to that blade model. Installing an operating system image
from one blade model onto another blade model (for example, installing the system
image from an R1350 onto an R3040S) will result in a system failure and will require
re-imaging the blade with the correct version, or reinstalling the operating system.
Standard system imaging tools are compatible with ClearCube blades and system
images. In the event that operating system re-installation is necessary, or a custom image
is desired, you may want to contact ClearCube Technical Support for assistance.
74 • Chassis and Blade Installation R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide
Page 99

Flashing the Blade BIOS
You can flash (install or re-install) the BIOS for your blade. The BIOS download
contains file the following:
• BIOS files
• BIOS flash utility
• Instructions about how to use the flash utility
From the ClearCube Support site (
http://www.clearcube.com/support/), select your
blade form the drop-down list, and then click the BIOS link, located under the blade
description. Save and then extract the archive file. Read the enclosed readme.txt file
for detailed instructions about flashing the BIOS.
R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide Chassis and Blade Installation • 75
Page 100

76 • Chassis and Blade Installation R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide
 Loading...
Loading...