Page 1

Cisco Unified Web and E-Mail Interaction
Manager Installation Guide
For Unified Contact Center Express
Release 4.2(1)
June 2009
Americas Headquarters
Cisco Systems, Inc.
170 West Tasman Drive
San Jose, CA 95134-1706
USA
http://www.cisco.com
Tel: 408 526-4000
800 553-NETS (6387)
Fax: 408 527-0883
Page 2

THE SPECIFICATIONS AND INFORMATION REGARDING THE PRODUCTS IN THIS MANUAL ARE SUBJECT TO CHANGE WITHOUT NOTICE. ALL
STATEMENTS, INFORMATION, AND RECOMMENDATIONS IN THIS MANUAL ARE BELIEVED TO BE ACCURATE BUT ARE PRESENTED WITHOUT
WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED. USERS MUST TAKE FULL RESPONSIBILITY FOR THEIR APPLICATION OF ANY PRODUCTS.
THE SOFTWARE LICENSE AND LIMITED WARRANTY FOR THE ACCOMPANYING PRODUCT ARE SET FORTH IN THE INFORMATION PACKET THAT
SHIPPED WITH THE PRODUCT AND ARE INCORPORATED HEREIN BY THIS REFERENCE. IF YOU ARE UNABLE TO LOCATE THE SOFTWARE LICENSE
OR LIMITED WARRANTY, CONTACT YOUR CISCO REPRESENTATIVE FOR A COPY.
The Cisco implementation of TCP header compression is an adaptation of a program developed by the University of California, Berkeley (UCB) as part of UCB’s public
domain version of the UNIX operating system. All rights reserved. Copyright © 1981, Regents of the University of California.
NOTWITHSTANDING ANY OTHER WARRANTY HEREIN, ALL DOCUMENT FILES AND SOFTWARE OF THESE SUPPLIERS ARE PROVIDED “AS IS” WITH
ALL FAULTS. CISCO AND THE ABOVE-NAMED SUPPLIERS DISCLAIM ALL WARRANTIES, EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING, WITHOUT
LIMITATION, THOSE OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT OR ARISING FROM A COURSE OF
DEALING, USAGE, OR TRADE PRACTICE.
IN NO EVENT SHALL CISCO OR ITS SUPPLIERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY INDIRECT, SPECIAL, CONSEQUENTIAL, OR INCIDENTAL DAMAGES, INCLUDING,
WITHOUT LIMITATION, LOST PROFITS OR LOSS OR DAMAGE TO DATA ARISING OUT OF THE USE OR INABILITY TO USE THIS MANUAL, EVEN IF CISCO
OR ITS SUPPLIERS HAVE BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES.
CCDE, CCENT, Cisco Eos, Cisco Lumin, Cisco Nexus, Cisco StadiumVision, Cisco TelePresence, the Cisco logo, DCE, and Welcome to the Human Network are
trademarks; Changing the Way We Work, Live, Play, and Learn and Cisco Store are service marks; and Access Registrar, Aironet, AsyncOS, Bringing the Meeting To You,
Catalyst, CCDA, CCDP, CCIE, CCIP, CCNA, CCNP, CCSP, CCVP, Cisco, the Cisco Certified Internetwork Expert logo, Cisco IOS, Cisco Press, Cisco Systems,
Cisco Systems Capital, the Cisco Systems logo, Cisco Unity, Collaboration Without Limitation, EtherFast, EtherSwitch, Event Center, Fast Step, Follow Me Browsing,
FormShare, GigaDrive, HomeLink, Internet Quotient, IOS, iPhone, iQ Expertise, the iQ logo, iQ Net Readiness Scorecard, iQuick Study, IronPort, the IronPort logo,
LightStream, Linksys, MediaTone, MeetingPlace, MeetingPlace Chime Sound, MGX, Networkers, Networking Academy, Network Registrar, PCNow, PIX, PowerPanels,
ProConnect, ScriptShare, SenderBase, SMARTnet, Spectrum Expert, StackWise, The Fastest Way to Increase Your Internet Quotient, TransPath, WebEx, and the
WebEx logo are registered trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. and/or its affiliates in the United States and certain other countries.
All other trademarks mentioned in this document or Website are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership relationship
between Cisco and any other company. (0807R)
Any Internet Protocol (IP) addresses used in this document are not intended to be actual addresses. Any examples, command display output, and figures included in the
document are shown for illustrative purposes only. Any use of actual IP addresses in illustrative content is unintentional and coincidental.
Cisco Unified Web and E-Mail Interaction Manager Installation Guide: For Unified Contact Center Express
© 2009 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Page 3

Contents
Preface .................................................................................................................................................7
About this guide . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Document conventions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Other learning resources . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Online help . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Document set. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Chapter 1: Planning..........................................................................................................................10
Configuration options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Additional partitions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Chapter 2: Pre-installation tasks...................................................................................................13
Verifying system requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Bandwidth and hardware requirements. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Software requirements. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Collecting required information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Configuring environment variables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Verifying SQL Server authentication settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Verifying state of Microsoft Search service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Setting up user accounts and permissions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Verifying directory names . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Creating WebLogic domains . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Creating a WebLogic domain for the primary application server. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Creating WebLogic domains for secondary application servers. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Verifying WebLogic domains. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Configuring virus scanner. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Verifying Network Configuration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Verifying Unified CCX installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Page 4

Chapter 3: Installation process...................................................................................................... 27
Installing a single-server or collocated configuration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Additional steps for collocated configurations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Installing a split-server or collocated configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Additional steps for collocated configurations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Installing a distributed-server configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Installing the database . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Installing the primary application server and file server. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Installing secondary application servers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Installing the web server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
Installing the services server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Chapter 4: Post-installation tasks .................................................................................................54
Setting up archives for partition databases . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Applying updates . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Changing web server settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Configuring Internet Information Services . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Configuring pool thread limit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Configuring content expiration settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
Removing extension mapping. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
Changing authentication settings for web site. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
Changing security credentials for network directory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
Changing logon parameters for Cisco service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
Configuring permissions for installation directory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
Configuring a web site for the messaging applet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
Creating a new web site . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
Verifying messaging applet web site . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
Configuring web site properties . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
Creating virtual directories . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Configuring the Applet host setting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
Setting up secure socket layer. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
Separating the web server from the application server. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
Starting and stopping Cisco Interaction Manager. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
Logging in to the business partition . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
Logging in from Internet Explorer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
4 Cisco Unified Web and E-Mail Interaction Manager Installation Guide
Page 5

Logging in from Cisco Agent Desktop Embedded Browser. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
Configuring some important settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
Mandatory settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
Optional settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Uninstalling Cisco Interaction Manager . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Chapter 5: Additional partitions.....................................................................................................76
About partitions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .77
Installing business partitions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
Chapter 6: Archives..........................................................................................................................81
About archives . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .82
Setting up the archive for a partition. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
Enabling network DTC access . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
Setting up the archive . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
Chapter 7: SSL for secure connections ........................................................................................87
Installing a security certificate . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
Generating a security certificate request . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
Submitting the certificate request . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
Installing the certificate on the web server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92
Configuring SSL access . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
Configuring the viewing of attachments . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95
Testing SSL access . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95
Appendix A: Reference sheet ........................................................................................................97
Configuration details. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
File server details . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .97
Database details. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .97
Application server details . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
Unified CCX Data Integration Wizard details . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
Web server details. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
Services server details. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
Contents 5
Page 6

Archive details . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
Additional partition details . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
Appendix B: Path to Maintenance Release 4.2(5)....................................................................104
6 Cisco Unified Web and E-Mail Interaction Manager Installation Guide
Page 7

Preface
About this guide
Document conventions
Other learning resources
Page 8
Welcome to Cisco® Interaction Manager™, multichannel interaction software used by businesses all over the
world to build and sustain customer relationships. A unified suite of the industry’s best applications for web and
email interaction management, it is the backbone of many innovative contact center and customer service
helpdesk organizations.
Cisco Interaction Manager includes a common platform and one or both of the following applications:
Cisco Unified Web Interaction Manager (Unified WIM)
Cisco Unified E-Mail Interaction Manager (Unified EIM)
About this guide
Cisco Unified Web and E-Mail Interaction Manager Installation Guide is intended for installation engineers,
system administrators, database administrators, and others who are responsible for installing and maintaining
your Cisco Interaction Manager installation.
This guide is for installations that are integrated with Cisco Unified Contact Center Express (Unified CCX).
Important: In this release, Unified WIM is not integrated with Unified CCX.
Document conventions
This guide uses the following typographical conventions.
Convention Indicates
Italic Emphasis.
Or the title of a published document.
Bold Labels of items on the user interface, such as buttons, boxes, and lists.
Or text that must be typed by the user.
Monospace
Variable User-specific text; varies from one user or installation to another.
Document conventions
The name of a file or folder, a database table column or value, or a command.
8 Cisco Unified Web and E-Mail Interaction Manager Installation Guide
Page 9
Other learning resources
Various learning tools are available within the product, as well as on the product CD and our web site. You can
also request formal end-user or technical training.
Online help
The product includes topic-based as well as context-sensitive help.
Use To view
Help button
F1 keypad button Context-sensitive information about the item selected on the screen.
Online help options
Document set
Unified WIM and Unified EIM documentation is available in the
includes the following documents:
Cisco Unified Web and E-Mail Interaction Manager System Requirements
Cisco Unified Web and E-Mail Interaction Manager Browser Settings Guide
Cisco Unified Web and E-Mail Interaction Manager Administration Console User’s Guide
Cisco Unified Web and E-Mail Interaction Manager Agent Console User’s Guide
Cisco Unified Web and E-Mail Interaction Manager Knowledge Base Console User’s Guide
Cisco Unified Web and E-Mail Interaction Manager Reports Console User’s Guide
Cisco Unified Web and E-Mail Interaction Manager Supervision Console User’s Guide
Cisco Unified Web and E-Mail Interaction Manager System Console User’s Guide
Topic s i n Cisco Unified Web and E-Mail Interaction Manager Help; the Help
button appears in the console toolbar on every screen.
Documents
folder on the product CD. It
Cisco Unified Web and E-Mail Interaction Manager Tools Console User’s Guide
The latest versions of all Cisco documentation can be found online at http://www.cisco.com
All Unified EIM documentation can be found online at
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps7236/tsd_products_support_series_home.html
All Unified WIM documentation can be found online at
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps7233/tsd_products_support_series_home.html
In particular, Release Notes for these products can be found at
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps7236/prod_release_notes_list.html
For general access to Cisco Voice and Unified Communications documentation, go to
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/sw/voicesw/tsd_products_support_category_home.html
Preface 9
Page 10

Planning
Configuration options
Additional partitions
Page 11

Designing the right configuration for your business is the first step toward setting up a robust and scalable
system. Configuration options for Cisco Interaction Manager are many—ranging from a simple single-server
installation to many flavors of distributed installations. This chapter describes available configuration options,
best practices for distributed-server installations, and considerations that will help you determine how many
partitions to install. See Cisco Unified Web and E-Mail Interaction Manager Solutions Reference Network
Design Guide for deployment recommendations for various scenarios.
A reference sheet is provided on page 97 to help you record your configuration choices and related details. You
will need to refer to this sheet often during the installation process.
If this installation is the first step towards installing Maintenance Release (MR) 4.2(5), refer to “Appendix B:
Path to Maintenance Release 4.2(5)” on page 104 for a flowchart depicting the various tasks that must be
completed to get to MR 4.2(5).
Configuration options
A Cisco Interaction Manager installation has five components. They are:
1. File server, which is always installed on the same machine as the primary application server
2. Database
3. Application server
4. Web server, which in the case of Unified WIM is installed on a separate machine outside the firewall for
security reasons
5. Services server
You can install these components in any of the following three types of configuration:
1. Single server or collocated: All components are on a single server. This is the simplest type of
configuration. A true single-server deployment is possible only for Unified EIM installations. If the
installation includes Unified WIM, it becomes a collocated deployment, where the web server is installed on
a separate machine outside the firewall.
2. Split server or collocated:
other components are on the other server. A true split-server deployment is possible only for Unified EIM
installations. If the installation includes Unified WIM, it becomes a collocated deployment, where the web
server is installed on a separate machine outside the firewall.
3. Distributed server: Components are distributed over three or more servers. A wide range of options is
available for distributed-server configurations (See Cisco Unified Web and E-Mail Interaction Manager
Solutions Reference Network Design Guide and Cisco Unified Contact Center Express (CCX) Configuration
& Ordering Tool for deployment recommendations). The database is usually installed on a dedicated server,
and the other components are spread over two or more servers. If the installation includes Unified WIM, the
web server is installed on a separate machine outside the firewall.
Components are split across two servers. The database is on one server, while all
11
Page 12

Additional partitions
Meant for enterprise-wide deployments, a single installation of Unified WIM and Unified EIM can be used by
independent business units in an organization with the help of separate business partitions. While the hardware
and software is common for all partitions, system resources and business objects are stored and managed
separately for each partition. Create additional partitions if you want to:
Segregate data between business units in your enterprise.
Serve multiple customers from a single installation.
Additional business partitions are ideal for organizations where business units (or clients, in the case of an
outsourced services provider) do not need to share customer, interaction, or product information. For example, a
bank that serves individual retail consumers as well as corporations might want two partitions as the product
offerings and customer service needs for these segments are different. Partitions can also be used for different
geographies. The same bank, to continue with our example, might choose to use separate partitions for their US
and China businesses because of legal and regulatory needs.
The installation program, by default, sets up two partitions:
1. The System partition, which is shared by all business partitions
2. A business partition with one department
You can create additional business partitions by using the installation program (see “Additional partitions” on
page 76).
Each partition is created with one department.
departments within a partition share system resources and can also share specific business resources. Additional
departments are created in the Administration Console. See Cisco Unified Web and E-Mail Interaction Manager
Administration Console User’s Guide for more information.
While partitions do not share system resources or business objects,
12 Cisco Unified Web and E-Mail Interaction Manager Installation Guide
Page 13

Pre-installation
tasks
Verifying system requirements
Collecting required information
Configuring environment variables
Verifying SQL Server authentication settings
Verifying state of Microsoft Search service
Setting up user accounts and permissions
Verifying directory names
Creating WebLogic domains
Configuring virus scanner
Verifying Network Configuration
Verifying Unified CCX installation
Page 14

This chapter describes pre-installation procedures. It is important to perform these procedures carefully. As you
need to prepare the installation environment in advance, read this installation guide and the following documents
before planning and implementing the installation:
Cisco Unified Web and E-Mail Interaction Manager Release Notes
Cisco Unified Web and E-Mail Interaction Manager System Requirements
Cisco Unified Web and E-Mail Interaction Manager Solutions Reference Network Design Guide
Verifying system requirements
Bandwidth and hardware requirements
To verify bandwidth and hardware requirements:
Confirm that the bandwidth and servers required for the configuration of your choice is available. The
following resources will help you determine these requirements:
Cisco Unified Web and E-Mail Interaction Manager System Requirements
Cisco Unified Web and E-Mail Interaction Manager Solutions Reference Network Design Guide
Cisco Unified Contact Center Express (CCX) Configuration & Ordering Tool
Cisco Customer Response Solutions (CRS) Software and Hardware Compatibility Guide
Software requirements
Cisco Unified Web and E-Mail Interaction Manager System Requirements lists the software environment that
must be set up on the various server-class machines. Create the environment in the following order.
To set up the required software environment:
1. On the web and application server machines:
a. Install BEA® WebLogic Server™ 8.1 SP 6 (included on the Cisco product CD).
b. Create WebLogic domains (see “Creating WebLogic domains” on page 17 for the procedure); make
sure you choose Sun JDK.
2. On the services server machines in distributed-server configurations:
Install JDK 1.4.2_11 (included on the Cisco product CD with BEA® WebLogic Server).
3. On the database server machine:
a. Make sure that the following three services are running: NT LM Security Support Provider service,
Remote Procedure Call (RPC) service, and the Remote Procedure Call (RPC) Locator service.
b. Install Microsoft® SQL Server® 2000 SP 4. Select the default SQL instance while installing SQL
Server.
c. Verify that the SQL collation setting is:
14 Cisco Unified Web and E-Mail Interaction Manager Installation Guide
SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS
Page 15
d. Enable mixed-mode authentication.
e. In SQL Enterprise Manager, ensure that the Full-text Search service is running.
4. Ensure that an accessible POP3 server is running.
Collecting required information
To collect required information:
Use the reference sheet provided in Appendix A (page 97) to gather the information that you will need
during the installation process.
Configuring environment variables
To configure environment variables on all application and services server machines:
1. Ensure that the JDK path is added to the
BEA_Home
2. Set the
\JDK142_11\bin.
TEMP
environment variable to point to some physical location on the system. For example,
path
environment variable. For example,
Verifying SQL Server authentication settings
To verify the authentication mode of SQL Server:
1. Go to Start > Programs > Microsoft SQL Server > Enterprise Manager.
2. Browse to Microsoft SQL Servers > SQL Server Group > Server_Name.
3. Right-click Server_Name and click Properties.
4. In the SQL Server Properties window, go to the Security tab.
C:\temp
.
Pre-installation tasks 15
Page 16
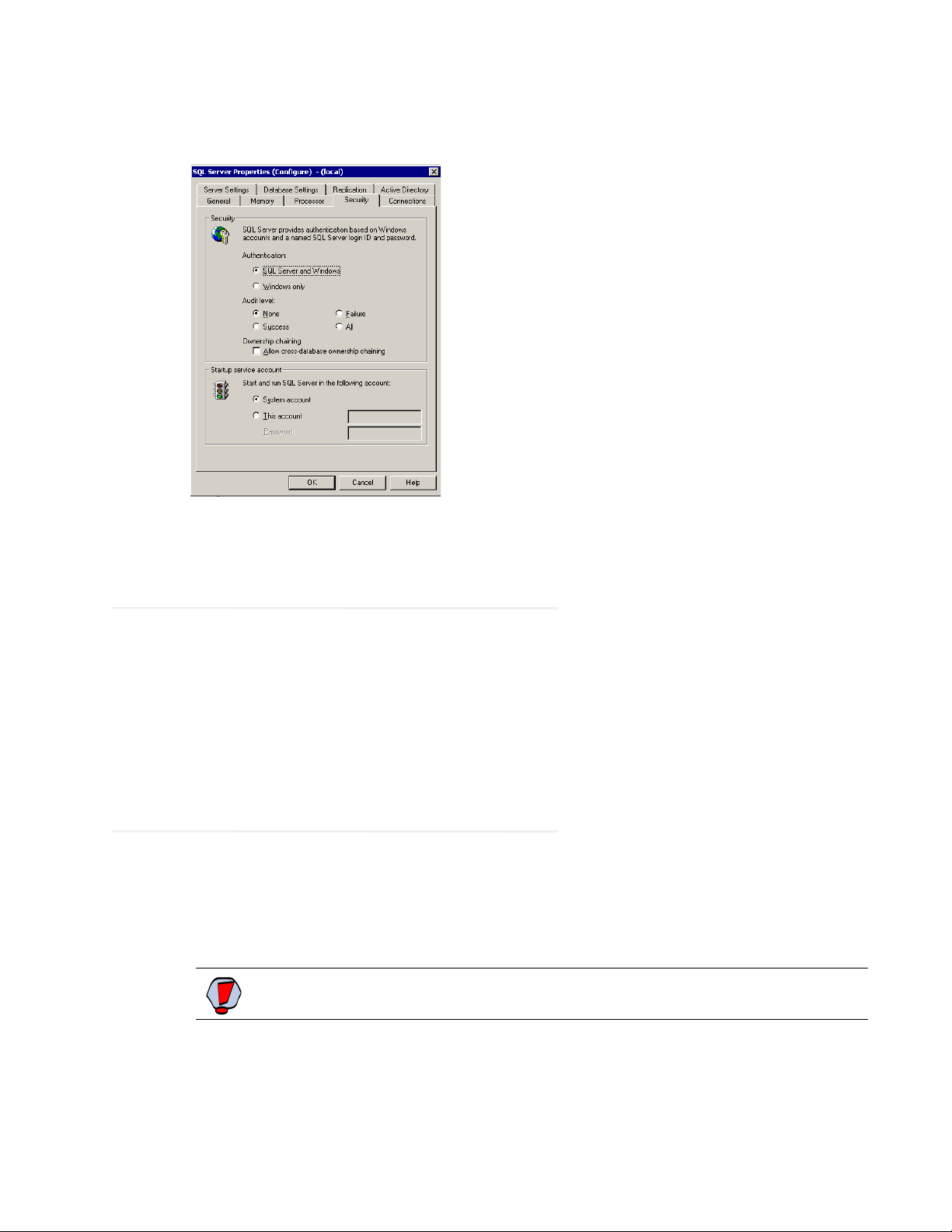
5. Verify that the SQL Server authentication mode is set to SQL Server and Windows. If authentication is set to
Windows only, then the application won’t be able to connect to the database.
Verify SQL Server authentication
Verifying state of Microsoft Search service
To verify the state of the Microsoft Search service:
1. Go to Start > Programs > Administrative Tools > Services.
2. Ensure that the Microsoft Search service is running.
This service is required for text searches.
Setting up user accounts and permissions
You will need administrator privileges on the local system to perform the installation.
To set up user accounts and permissions:
1. Create a domain user account for exclusive use by Cisco Interaction Manager.
Caution: Do not change the password of the domain account after Cisco Interaction Manager is
installed. The system becomes inaccessible if the password is changed later.
2. Add this account to your local administrator group. Use this account to install and configure the system.
16 Cisco Unified Web and E-Mail Interaction Manager Installation Guide
Page 17

3. Verify that the IIS service is running. In a single-server or split-server configuration, you can run the system
using the local system account. In a collocated or distributed-server configuration, a domain account must be
used.
Verifying directory names
To verify directory names:
Ensure that the names of your BEA, WebLogic, and JDK home directories do not contain any spaces.
Creating WebLogic domains
You need to create WebLogic domains for each application server in your configuration before starting the
installation program. The procedures for creating the WebLogic domain for the primary application server and
that for secondary application servers is different.
Creating a WebLogic domain for the primary application server
To create the WebLogic domain for the primary application server:
1. Go to Start > Programs > BEA WebLogic Platform 8.1 > Configuration Wizard.
2. In the Create or Extend a Configuration window, select Create a new WebLogic configuration.
Choose to create a new WebLogic configuration
Pre-installation tasks 17
Page 18
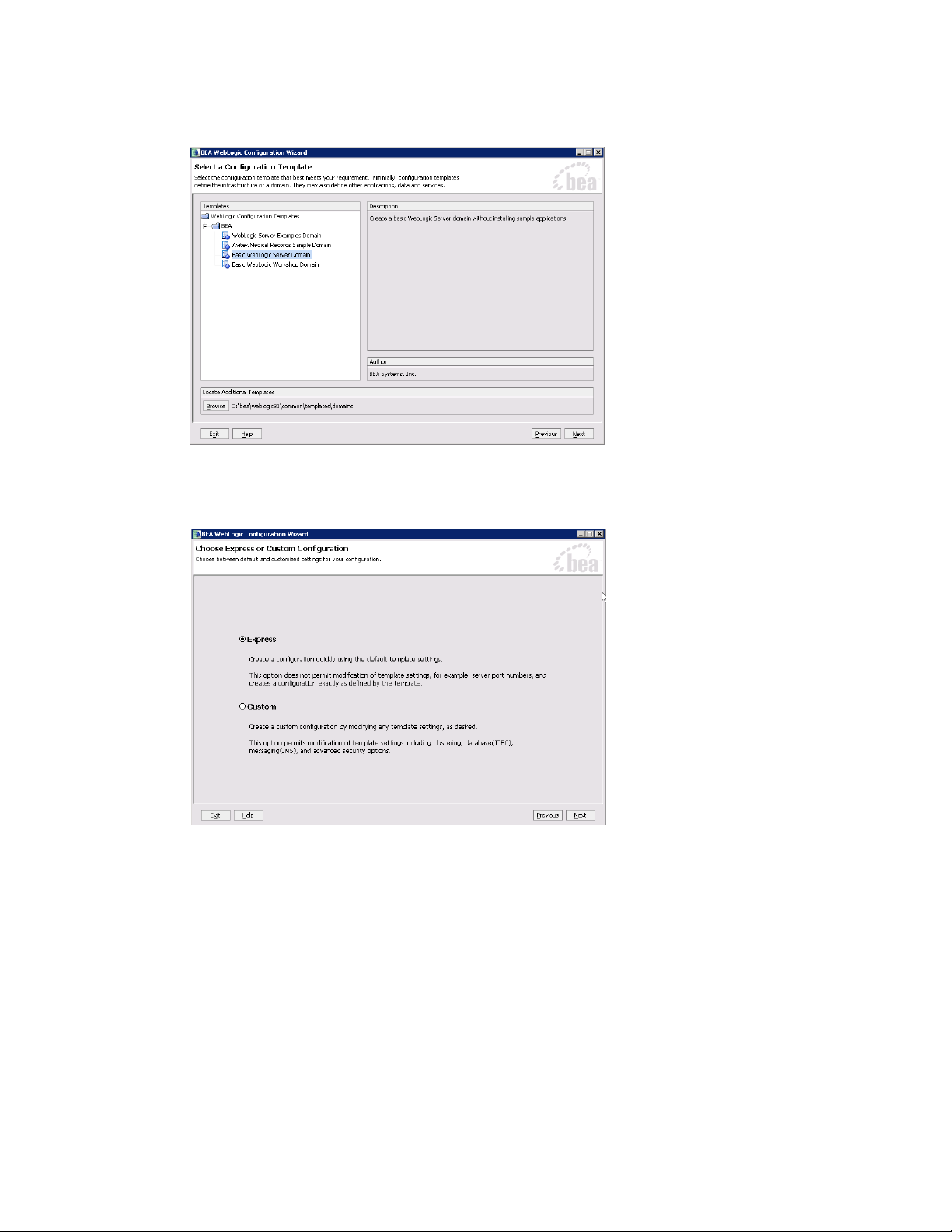
3. In the Select a Configuration Template window, select Basic WebLogic Server Domain.
Choose configuration template
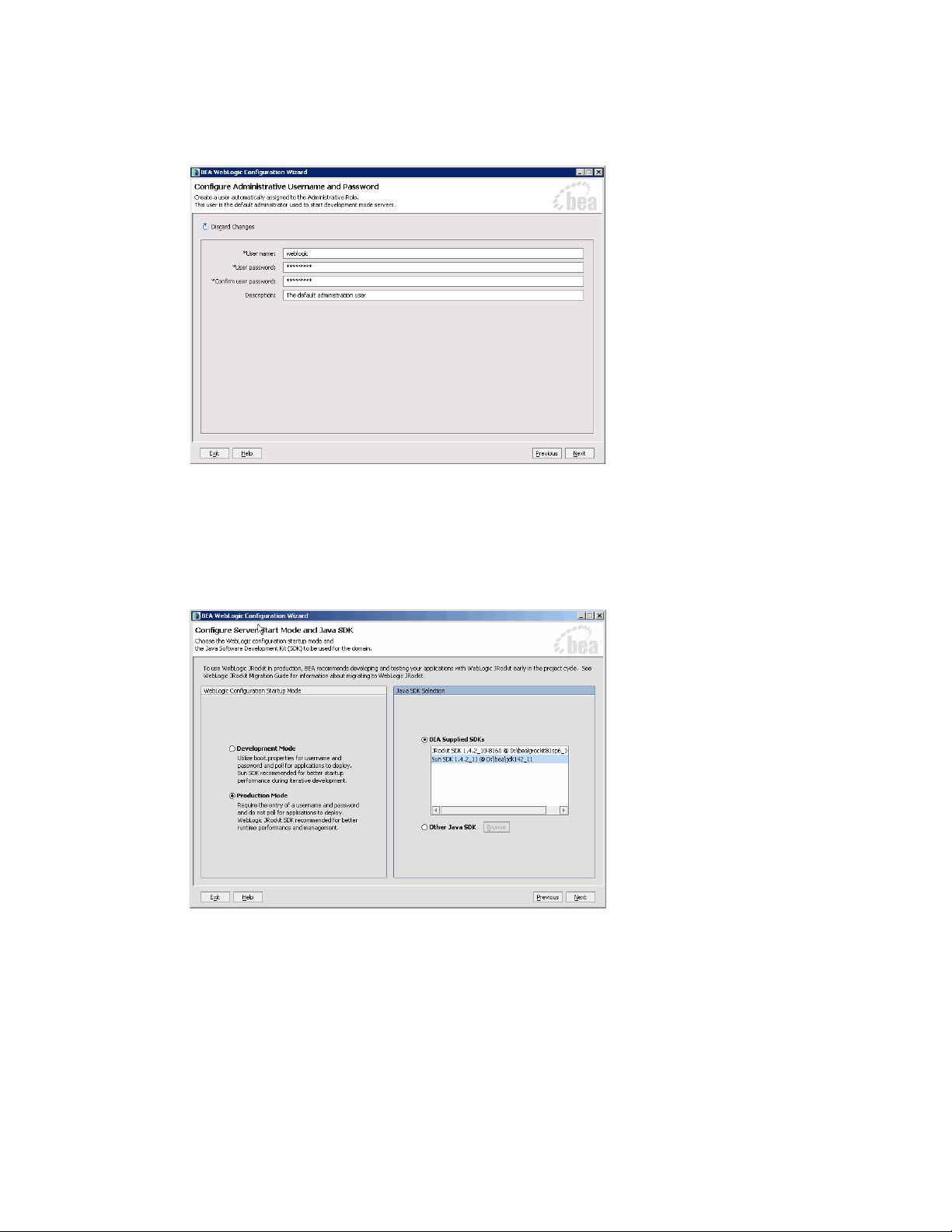
4. In the Choose Express or Custom Configuration window, select the Express configuration option.
Choose express configuration
18 Cisco Unified Web and E-Mail Interaction Manager Installation Guide
Page 19
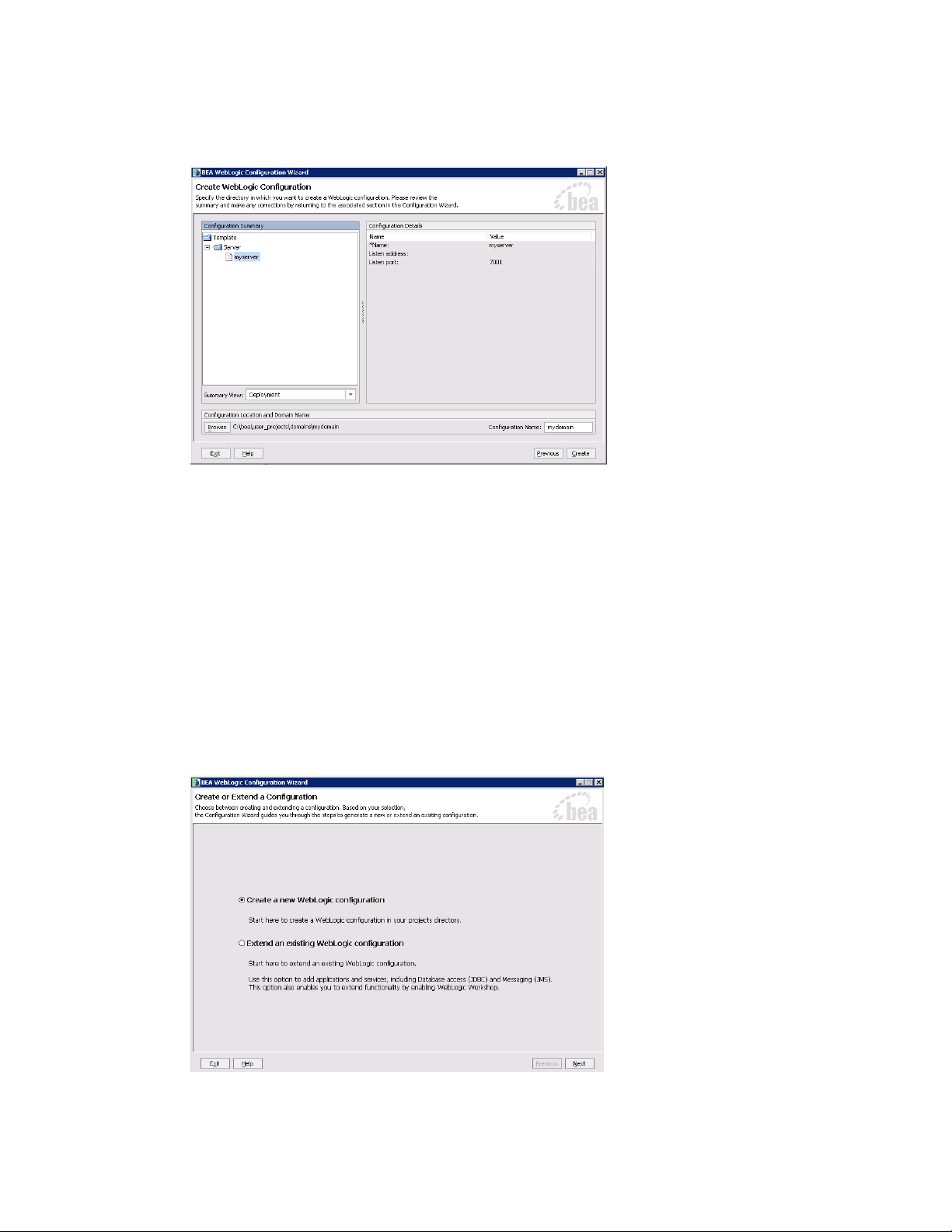
5. In the Configure Administrative Username and Password window, configure the user name and password of
the WebLogic administrator.
Create administrative user
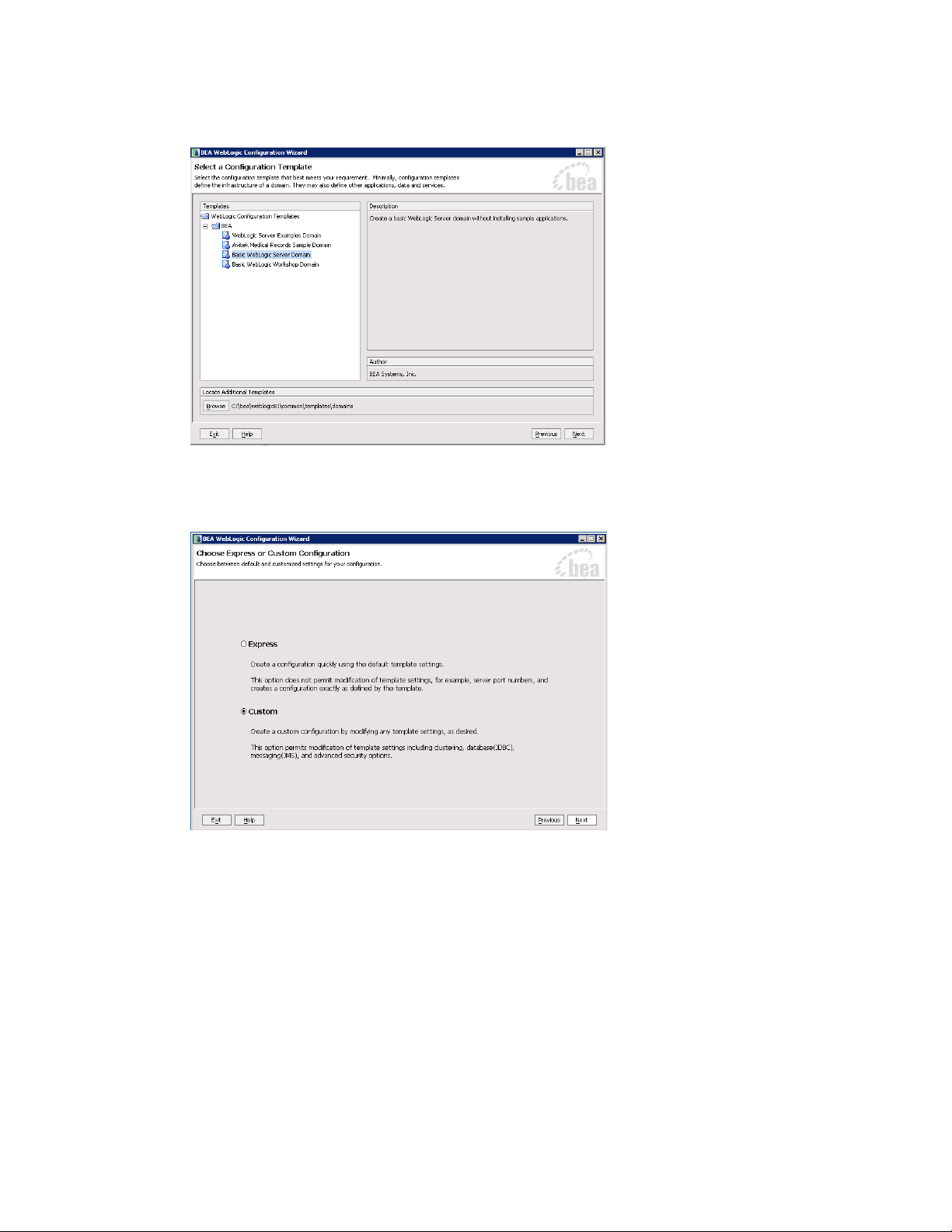
6. In the Configure Server Start Mode and Java SDK window, select the following options:
In the WebLogic Configuration Startup Mode section, select the start mode to be Production Mode.
In the Java SDK Selection section, in the BEA Supplied SDKs list select Sun SDK 1.4.2_11.
Configure server start mode and Java SDK
Pre-installation tasks 19
Page 20
7. In the Create WebLogic Configuration window, select myserver and click Create to complete the process of
creating the domain.
Create WebLogic configuration
After creating the WebLogic domain, you can verify that it has been created successfully. For details see
“Verifying WebLogic domains” on page 26.
Creating WebLogic domains for secondary application servers
Skip this procedure, if you have only one application server.
To create the WebLogic domain for a secondary application server:
1. Go to Start > Programs > BEA WebLogic Platform 8.1 > Configuration Wizard.
2. In the Create or Extend a Configuration window, select Create a new WebLogic configuration.
Choose to create a new WebLogic configuration
20 Cisco Unified Web and E-Mail Interaction Manager Installation Guide
Page 21
3. In the Select a Configuration Template window, select Basic WebLogic Server Domain.
Choose configuration template
In the Choose Express or Custom Configuration window, select the Custom configuration option.
4.
Choose custom configuration
Pre-installation tasks 21
Page 22
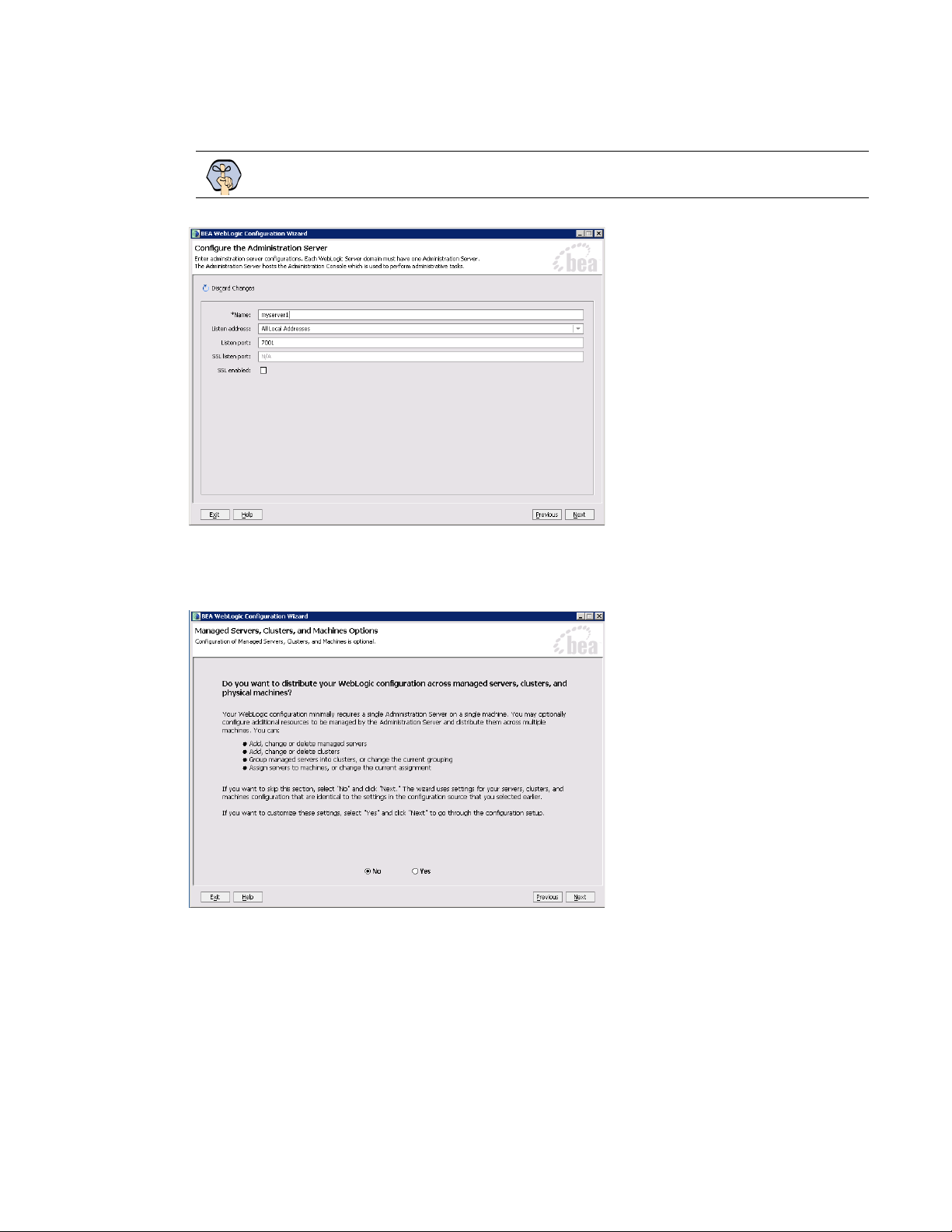
5. In the Configure the Administration Server window, provide the name of the server you want to create.
Important: The server name should be different than that of the primary application server.
Configure the administration server
6. In the Manage Servers, Clusters, and Machines Options window, select No.
Select No to skip the configuration of Managed Servers, Clusters, and Machines
22 Cisco Unified Web and E-Mail Interaction Manager Installation Guide
Page 23
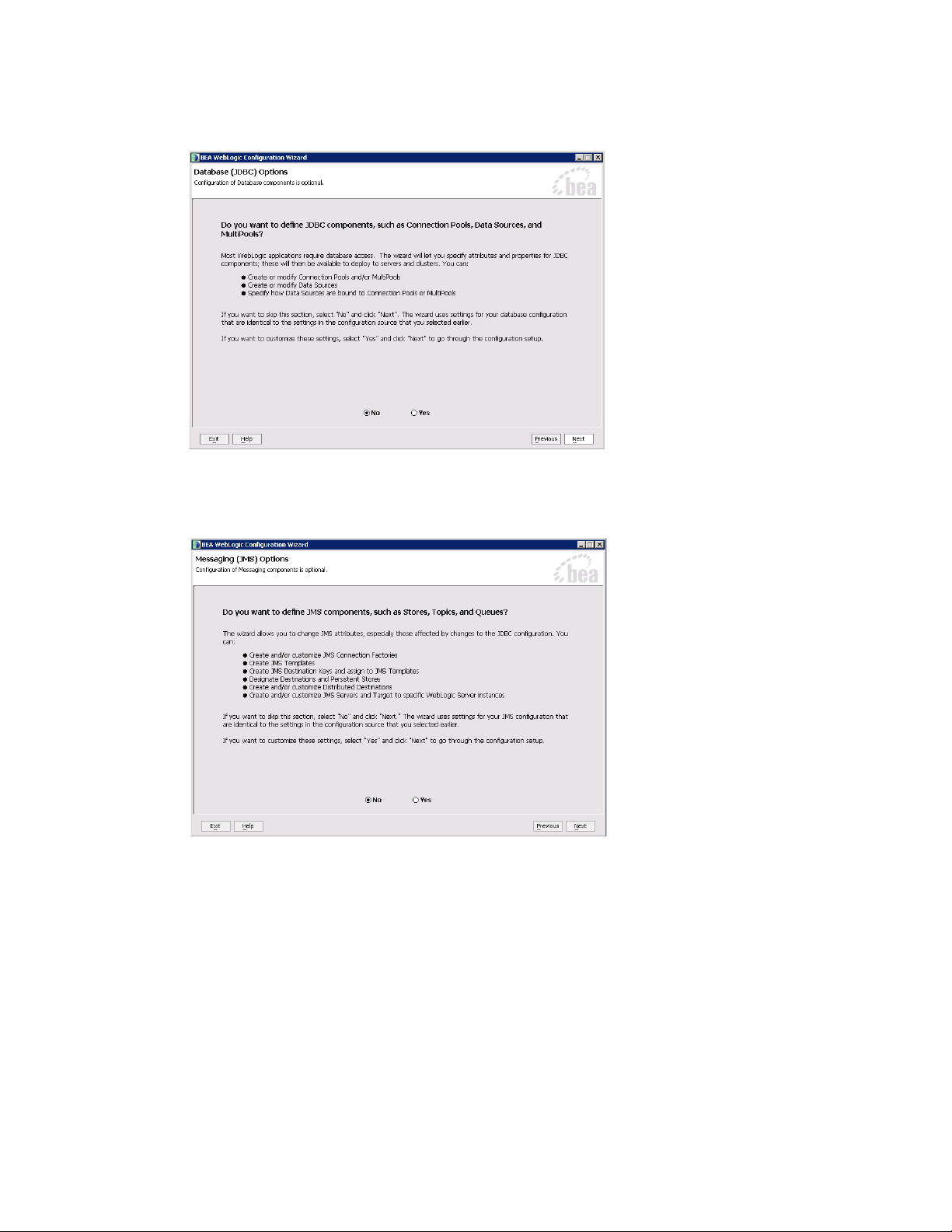
7. In the Database (JDBC) Options window, select No.
Select No to skip the configuration of Database (JDBC) components
8. In the Messaging (JMS) Options window, select No.
Select No to skip the configuration of Messaging components
Pre-installation tasks 23
Page 24
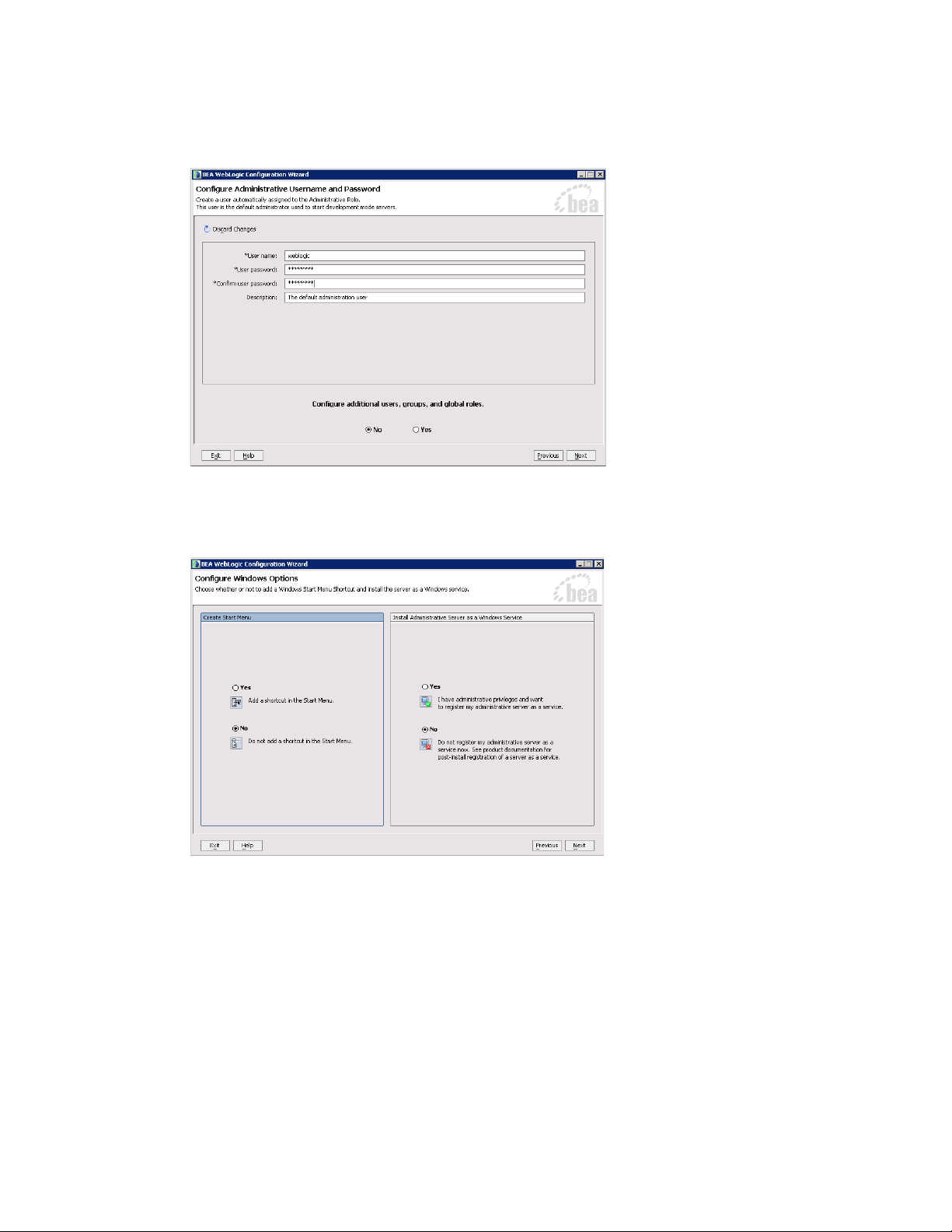
9. In the Configure Administrative Username and Password window, configure the user name and password of
the WebLogic administrator.
Create administrative user
10. In the Configure Windows Options window, select No for both options.
Configure Windows options
11. In the Configure Server Start Mode and Java SDK window, select the following options:
In the WebLogic Configuration Startup Mode section, select the start mode to be Production Mode.
24 Cisco Unified Web and E-Mail Interaction Manager Installation Guide
Page 25
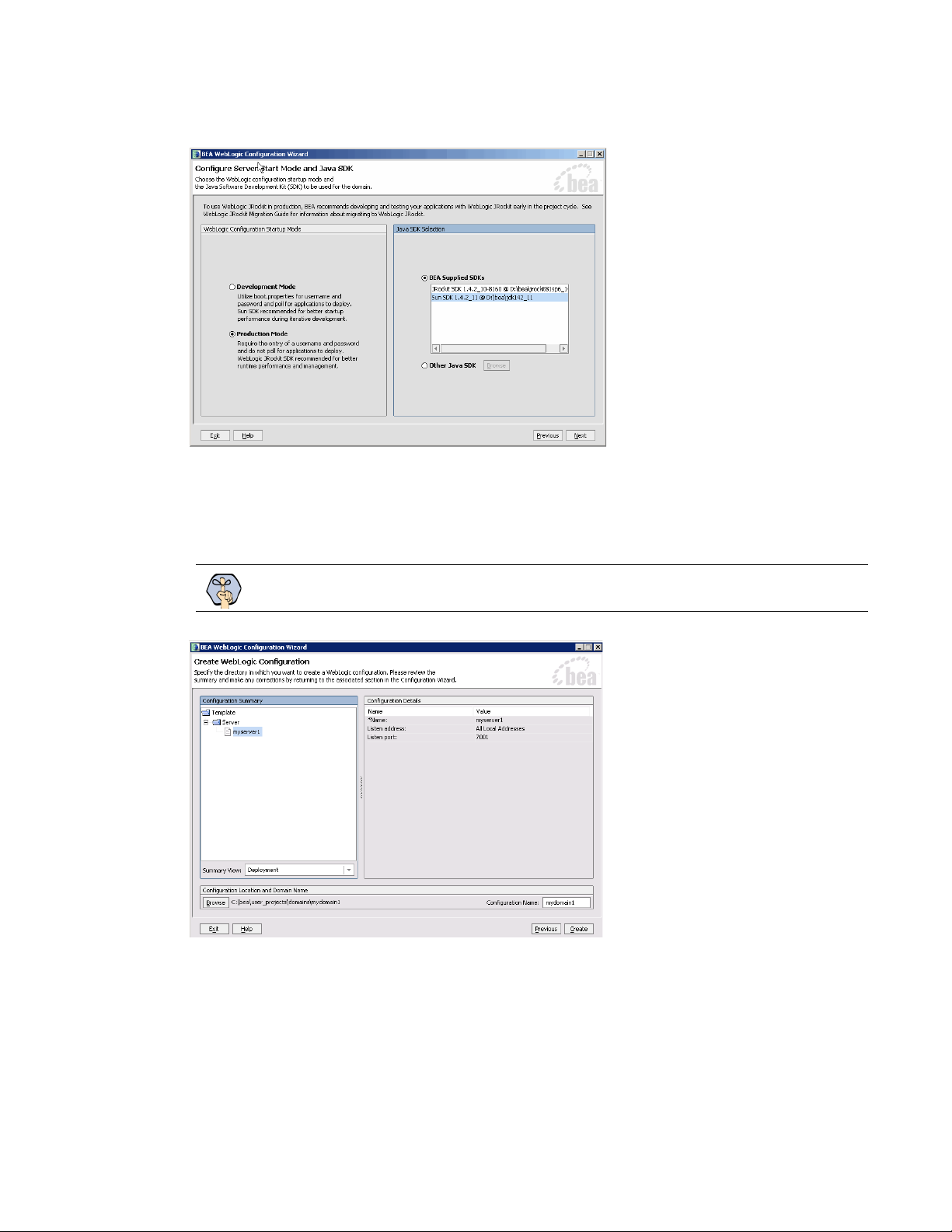
In the Java SDK Selection section, in the BEA Supplied SDKs list select Sun SDK 1.4.2_11.
Configure server start mode and Java SDK
12. In the Create WebLogic Configuration window, select the administration server you created in Step 5
(page 22) and click
Create to complete the process of creating the domain.
Important: The domain name should be different than that of the primary application server.
Create WebLogic configuration
After creating the WebLogic domain, you can verify that it has been created successfully. For details see
“Verifying WebLogic domains” on page 26.
Pre-installation tasks 25
Page 26
Verifying WebLogic domains
After creating a WebLogic domain, you can verify that it has been created successfully.
To verify a WebLogic domain:
1. Go to BEA_Home \
2. Verify that there is a folder with the same name that you provided while creating the WebLogic domain.
user_projects\domains.
Configuring virus scanner
Ensure that the virus scanner is configured to allow sending emails through the SMTP port (Port 25). In a
distributed installation, configure this setting on the services server.
Verifying Network Configuration
These tasks must be completed in all collocated, split-server, and distributed-server configurations.
To verify network configuration:
1. Ensure that all machines in the configuration are in the same network domain. Note that the application
cannot be installed in a workgroup.
2. Ensure that all the machines are in the same LAN.
3. Ensure that the system clocks of all the machines are synchronized.
Verifying Unified CCX installation
Verify that Unified CCX has been installed and configured on one or more MCS servers. Refer to the Unified
CCX documentation for details. Also, verify that these servers are in the same local area network as the Cisco
Interaction Manager servers and are accessible from the Cisco Interaction Manager servers.
26 Cisco Unified Web and E-Mail Interaction Manager Installation Guide
Page 27

Installation
process
Installing a single-server or collocated configuration
Installing a split-server or collocated configuration
Installing a distributed-server configuration
Page 28
This chapter helps you install the product in the configuration you have chosen (see “Configuration options” on
page 11). It describes the process of installing single-server, split-server, and distributed-server configurations.
Before beginning the installation, ensure that you have complied with all the prerequisites listed in “Pre-
installation tasks” on page 13.
Installing a single-server or collocated configuration
A true single-server deployment is possible only for Unified EIM installations. If the installation includes
Unified WIM, it becomes a collocated deployment, where the web server is installed on a separate machine
outside the firewall.
To install a single-server or collocated configuration:
1. Run
Setup.exe
from the product CD.
2. When the Introduction window appears, read the installation instructions.
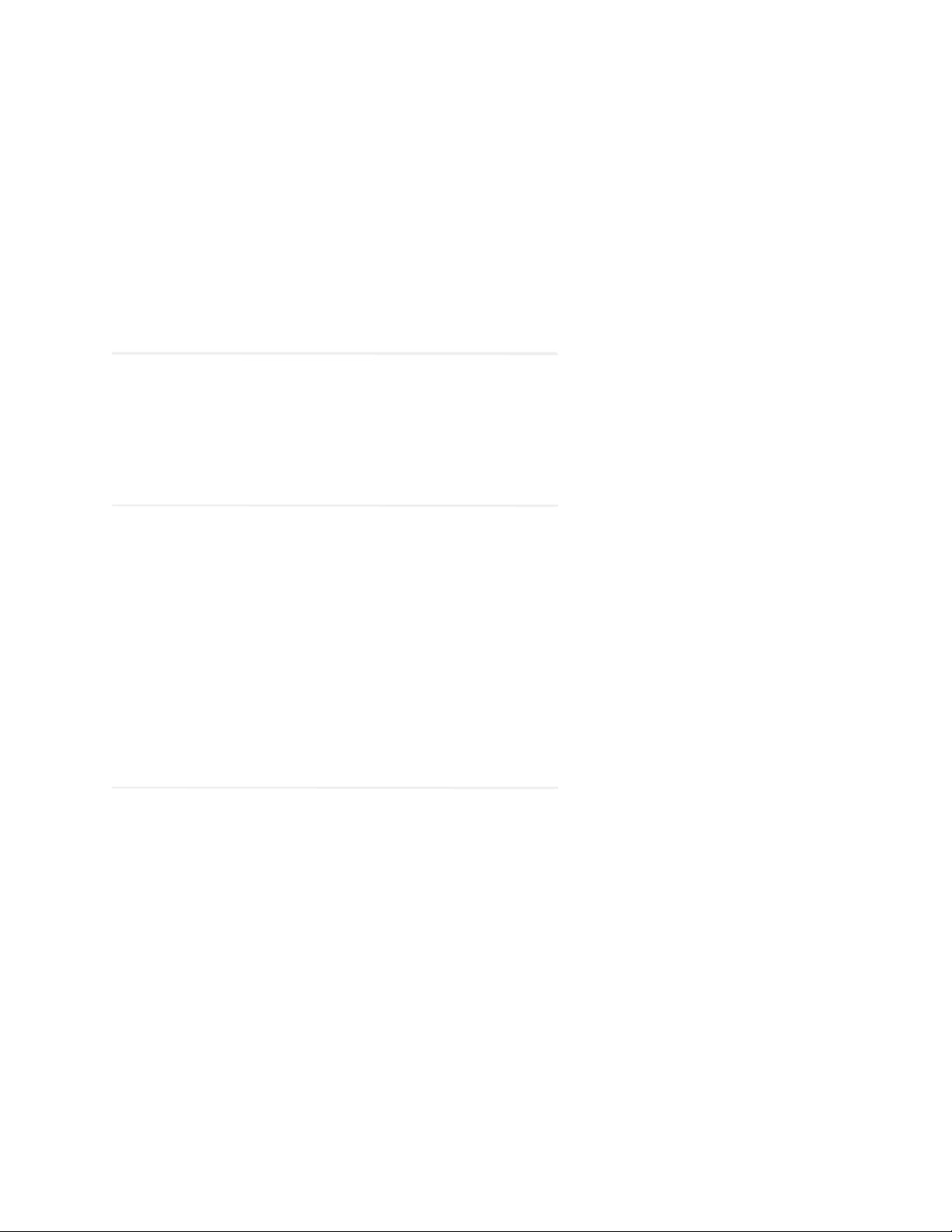
3. In the License Agreement window, review the licensing terms and select the I accept the terms of the
License Agreement option.
Read and accept the terms of the License Agreement
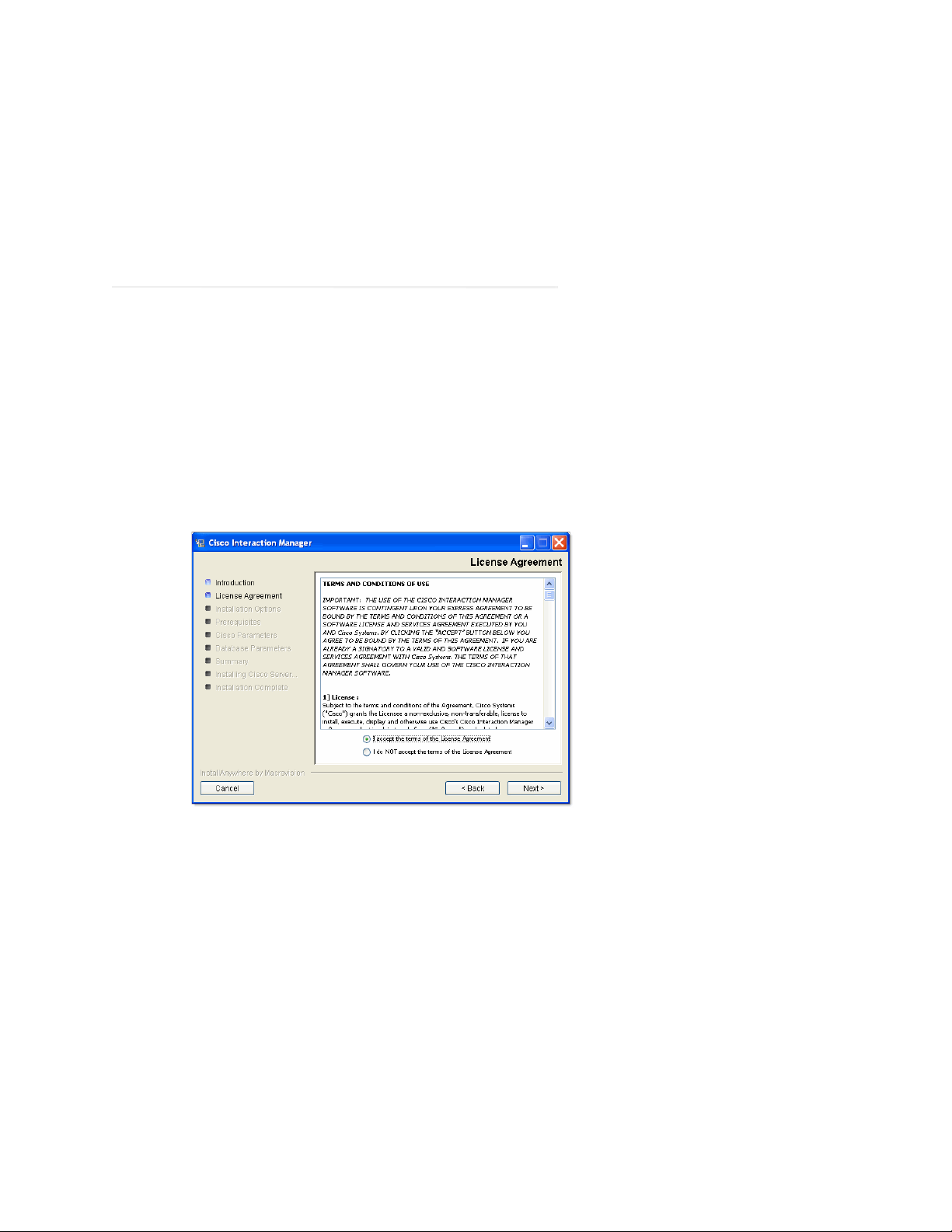
4. In the Installation Options window, select the components to install.
If it you are installing only Unified EIM, you can set up a pure single-server configuration. In this case,
select the following options:
File Server
Application Server
Web S erver
Services Server
Database
28 Cisco Unified Web and E-Mail Interaction Manager Installation Guide
Page 29
Select installation options for a single-server Unified EIM installation
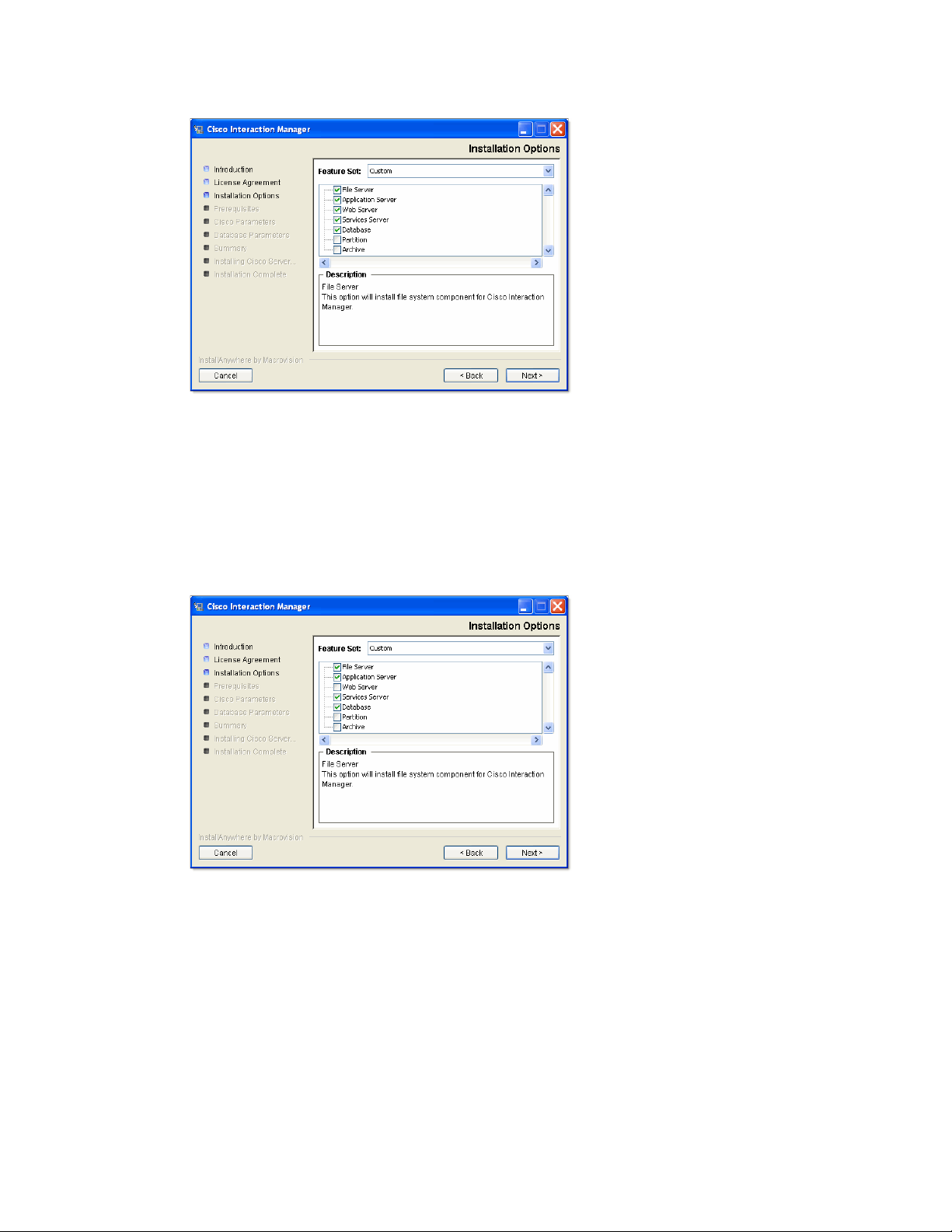
If it you are installing both applications or only Unified WIM, use a collocated configuration, where the web
server is installed on a separate machine outside the firewall. In this case, select the following options:
File Server
Application Server
Services Server
Database
Select installation options for a collocated installation that includes Unified WIM
Installation process 29
Page 30
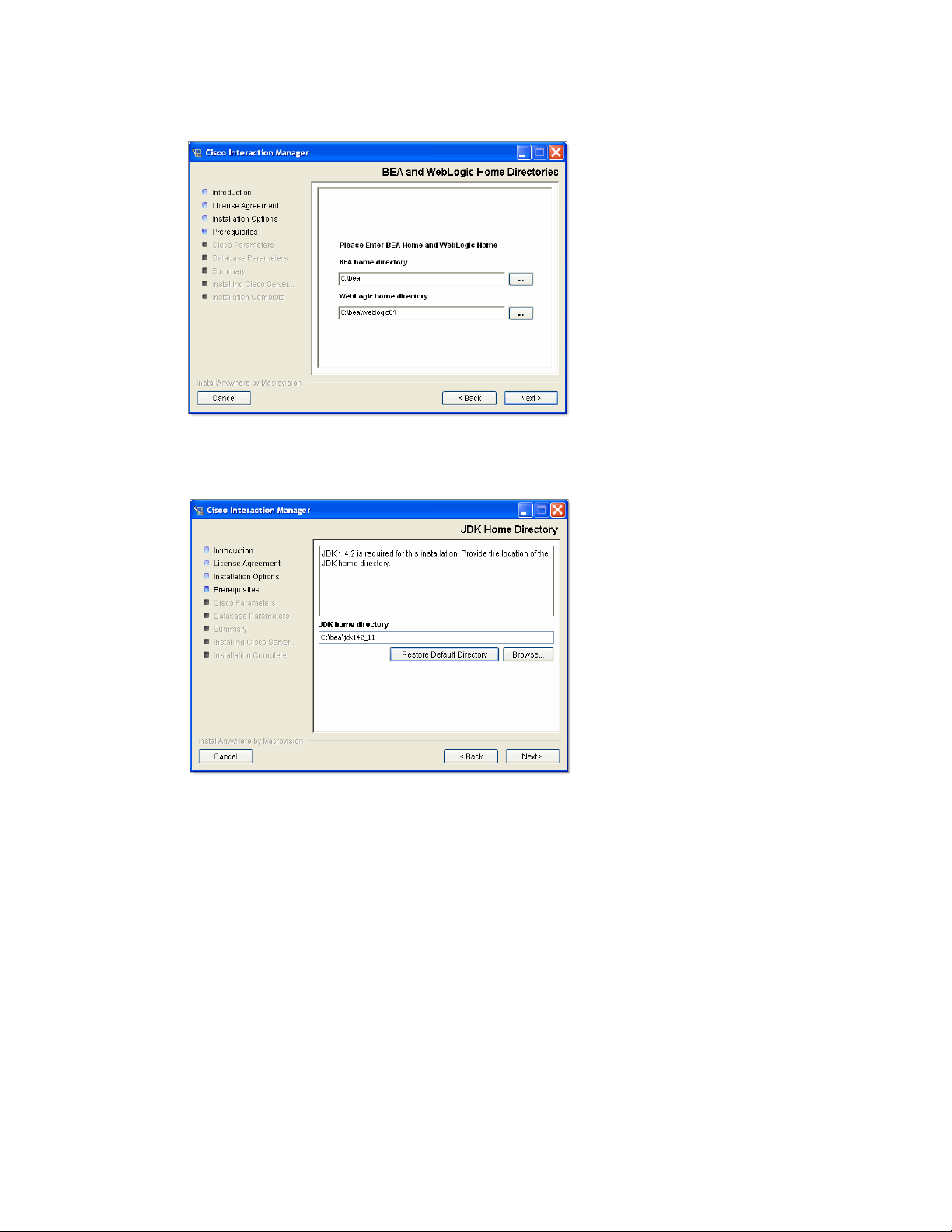
5. Type the path or browse to the BEA and WebLogic home directories.
Provide the path to the BEA and WebLogic home directories
6. Type the path or browse to the JDK home directory.
Provide the path to the JDK home directory
30 Cisco Unified Web and E-Mail Interaction Manager Installation Guide
Page 31

7. Type the path or browse to the folder where you would like to install Cisco Interaction Manager.
Provide a location for the Cisco Interaction Manager home directory
8. In the WebLogic Server and RMI Parameters window, provide the following details:
Important: WebLogic domain parameters information should match the information provided
while configuring the WebLogic domain.
Domain Location: Location of the WebLogic domain you configured on page 17. For example,
BEA_Home
Server name: Name of your WebLogic server (page 17). The default name is
User name: User name of the WebLogic system user (page 17), required to access the WebLogic
\user_projects\domains\
Domain_Name.
myserver
.
Server Administration Console.
Password: Password for the WebLogic system user (page 17).
Listen port: Port number of the WebLogic server.
SSL listen port: Secure Socket Layer Listen port number used by WebLogic.
RMI registry port: Port number used by the Remote Method Invocation (RMI) registry naming
service.
RMI activation port: Port number used by the RMI Daemon Process.
Installation process 31
Page 32

Provide WebLogic server and RMI parameters
Cisco Interaction Manager has two distinct areas: the system area and the partition (or business) area. An
administrator type user is created for each area during the installation. In the next two windows, you will be
asked for user names and passwords for these two users:
System Administrator
Partition Administrator
9. In the Cisco System Administrator Account window, create the first system administrator user account.
Provide the following:
User name: User name for the system administrator.
Password: Password for the system administrator.
Verify password: Verify the password.
Create the first system administrator user account
10. In the Cisco Partition Administrator Account and Partition window, create the first partition administrator
user account and the partition. Provide the following:
User name: User name for the partition administrator.
Password: Password for the partition administrator.
32 Cisco Unified Web and E-Mail Interaction Manager Installation Guide
Page 33

Verify password: Verify the password.
Partition name: Name for the partition.
Description of partition: Description for the partition.
Create the first partition administrator user account and the partition
11. In the Master Database Parameters window, provide the following details:
Server name: Name of the local server on which the MSSQL database is to be installed.
Important: Make sure you provide the DNS host name and not the IP address of the server. If you
don't provide the host name, the installation will fail.
Database name: Name of the master database. The installation program creates the master database
with the name you provide here.
Database listen port: Port number of the MSSQL Server.
Datafile path: Path of the folder on the database server, where you want to create the data file. For
example:
Datafile initial size: Minimum size of the data file for the database.
Datafile maximum size: Maximum size of the data file for the database.
Datafile increment size: Additional file size limit that will be allocated to a database object after the
initial size is full.
Logfile initial size: Minimum size of the log file.
Logfile maximum size: Maximum size of the log file.
Database administrator user name: User name of the database administrator for MSSQL Server.
Database administrator password: Password of the database administrator.
Cisco Database user name: User name required to connect to the Cisco Interaction Manager master
database. The installation program creates the database and its user.
Cisco Database password: Password for Cisco Interaction Manager master database user.
MSSQL_Home
\MSSQL\Data
.
Installation process 33
Page 34

Provide master database parameters
12. In the Partition Database Parameters window, provide the following details:
Important: Partition database should be created on the same database server as master
database.
Server name: Name of the local server on which your MSSQL database is installed.
Database name: Name of the partition database. The installation program creates a database with the
name you type here.
Important: Make sure you provide the DNS host name and not the IP address of the server. If you
don't provide the host name, the installation will fail.
Database listen port: Port number of the MSSQL Server.
Datafile path: Path of the folder on the database server, where you want to create the data file. For
example:
Datafile initial size: Minimum size of the data file for the database.
Datafile maximum size: Maximum size of the data file for the database.
Datafile increment size: Additional file size limit that will be allocated to a database object after the
initial size is full.
Logfile initial size: Minimum size of the log file.
MSSQL_Home
\MSSQL\Data
.
Logfile maximum size: Maximum size of the log file.
Database administrator user name: User name of the database administrator for MSSQL Server.
Database administrator password: Password of the database administrator.
Cisco Database user name: User name required to connect to the Cisco Interaction Manager database.
The installation program creates the database and its user.
Cisco Database password: Password for Cisco Interaction Manager database user.
34 Cisco Unified Web and E-Mail Interaction Manager Installation Guide
Page 35

Provide partition database parameters
13. Review the information displayed in the Summary window, and click Install.
14. In the Installation Complete window, click Finish to complete the installation process for Cisco Unified
Web and E-Mail Interaction Manager. The next few screens will help you set up the integration with Unified
CCX.
15. In the next window, click the Finish button to launch the Cisco Unified CCX Data Integration Wizard.
Click the Finish button
Installation process 35
Page 36

16. In the Welcome window, read the introduction and click Next.
Click the Next button
17. In the next window, provide the following details to configure a socket connection to the Unified CCX
server.
Cisco Unified CCX Main Server: Provide the host name or IP address of the primary Unified CCX
server.
Cisco Unified CCX HA Server: Provide the host name or IP address of the secondary Unified CCX
server, which serves as the “high availability” server. This is an optional field. If you provide the
secondary Unified CCX server details, Unified WIM and Unified EIM attempts to connect to the
secondary Unified CCX server when the connection to the primary Unified CCX server fails.
Cisco Unified CCX Master Listener TCP Port: Provide the port number of the licensing port in
Unified CCX, which is used to connect to Unified CCX to download license information. This port
corresponds to the Master Listener TCP Port configured in the System Parameters section of Unified
CCX Administration. The default value is 994.
Cisco Unified CCX RmCm TCP Port: Provide the port number to be used to connect to Unified CCX
to download configuration data for agents, teams, supervisors, and CSQs (queues). This port
corresponds to the RmCm TCP Port configured in the System Parameters section of Unified CCX
Administration. The default value is 42027.
Select Ye s to download voice contact service queues (CSQ) from Unified CCX during the configuration
of the system. Clear this option if you don’t want voice queues in your Unified WIM and Unified EIM
system.
Click Save.
36 Cisco Unified Web and E-Mail Interaction Manager Installation Guide
Page 37
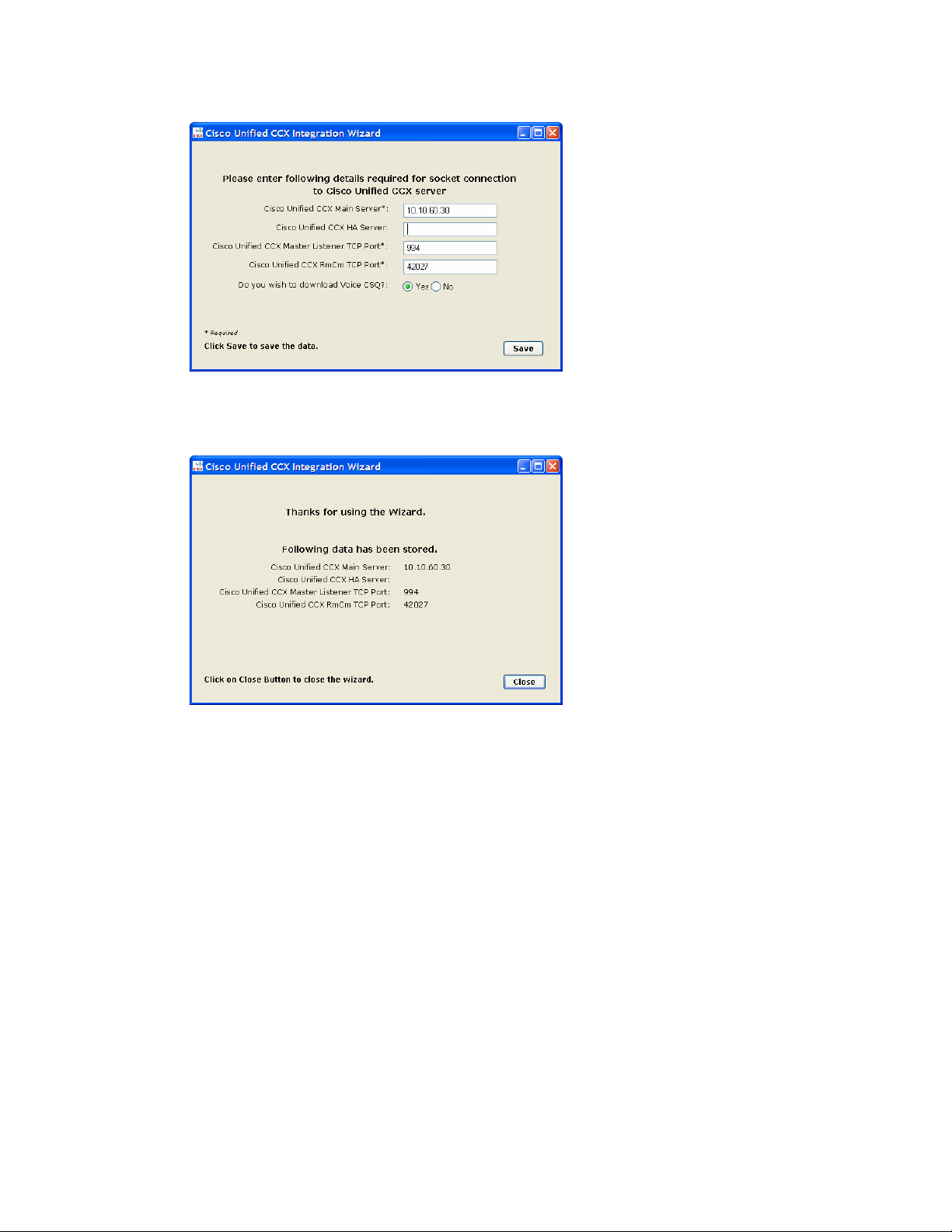
Provide Unified CCX server details
18. Review integration details and click Close to complete the process.
Close the wizard
Additional steps for collocated configurations
If the installation includes Unified WIM, it becomes a collocated deployment, where the web server is installed
on a separate machine outside the firewall. For a collocated configuration, now install the web server.
To install the web server:
Follow all the steps in the section “To install the web server:” on page 50.
Installation process 37
Page 38

Installing a split-server or collocated configuration
A true split-server deployment is possible only for Unified EIM installations. If the installation includes Unified
WIM, it becomes a collocated deployment, where the web server is installed on a separate machine outside the
firewall.
To install a split-server or collocated configuration:
Follow all the steps in the section “To install a single-server or collocated configuration:” on page 28. In
Steps 11 and 12 make sure to give the following values:
Server name: Give the name of the remote server on which you want to install the Partition and Master
Databases.
Important: Make sure you provide the DNS host name and not the IP address of the server. If you
don't provide the host name, the installation will fail.
Additional steps for collocated configurations
If the installation includes Unified WIM, it becomes a collocated deployment, where the web server is installed
on a separate machine outside the firewall. For a collocated configuration, now install the web server.
To install the web server:
Follow all the steps in the section “To install the web server:” on page 50.
Installing a distributed-server configuration
In the procedure described here, each component is installed separately on a dedicated machine.
Important: Refer to the sheet on page 97 for details that you are asked to provide during the
installation.
Make sure you install the components in the following order:
1. Database
2. Application server and file server
3. Web server
4. Services server
38 Cisco Unified Web and E-Mail Interaction Manager Installation Guide
Page 39

Installing the database
Important: Ensure that MSSQL Server, MS Search Service, and MSSQL Server Agent Service are
running. In a distributed installation, verify that all machines are in the same domain and LAN, and
their clocks are synchronized.
This section describes the process of installing Cisco Interaction Manager master database and the default
partition database.
To install the database:
1. Follow Steps 1–3 in “To install a single-server or collocated configuration:” on page 28.
2. In the Installation Options window, select the Database option.
Select the Database option
Cisco Interaction Manager has two distinct areas: the system area and the partition (or business) area. An
administrator type user is created for each area during the installation. In the next two windows, you will be
asked for user names and passwords for these two users:
System Administrator
Partition Administrator
3. In the Cisco System Administrator Account window, create the first system administrator user account.
Provide the following:
User name: User name for the system administrator.
Password: Password for the system administrator.
Verify password: Verify the password.
Installation process 39
Page 40

Create the first system administrator user account
4. In the Cisco Partition Administrator Account and Partition window, create the first partition administrator
user account and the partition. Provide the following:
User name: User name for the partition administrator.
Password: Password for the partition administrator.
Verify password: Verify the password.
Partition name: Name for the partition. This name will be part of the URL that users will use to log in
to Cisco Interaction Manager: http://
Cisco_Home/Partition_Name. Make sure that the name does not
contain any spaces.
Description of partition: Description for the partition.
Create the first partition administrator user account and the partition
5. In the Master Database Parameters window provide the following details:
Server name: Name of the local or remote server on which you want to install MSSQL database.
Database name: Name of the master database. The installation program creates a database with the
name you type here.
40 Cisco Unified Web and E-Mail Interaction Manager Installation Guide
Page 41

Important: Make sure you provide the DNS host name and not the IP address of the server. If you
don't provide the host name, the installation will fail.
Database listener port: Port number of the MSSQL Server.
Datafile path: Path of the folder on the database server, where you want to create the data file. For
example,
Datafile initial size (MB): Minimum size of the data file for the database.
Datafile maximum size (MB): Minimum size of the data file for the database.
Datafile increment size (MB): Additional file size limit that will be allocated to a database object after
the initial size is full.
Logfile initial size (MB): Minimum size of the log file.
Logfile maximum size (MB): Maximum size of the log file.
Database administrator user name: User name of the database administrator for MSSQL Server.
Database administrator password: Password of the database administrator.
Cisco Database user name: User name required for connecting to the Unified WIM and Unified EIM
master database. The installation program creates the database and its user.
Cisco Database password: Password for the Unified WIM and Unified EIM master database user.
MSSQL_Home
\MSSQL\Data
.
Provide master database parameters
6. In the Partition Database Parameters window, provide the following details:
Important: Partition database should be created on the same database server as the master
database.
Server name: Name of the local or remote server on which your MSSQL database is installed.
Database name: Name of the partition database. The installation program creates a database with the
name you type here.
Installation process 41
Page 42

Important: Make sure you provide the DNS host name and not the IP address of the server. If you
don't provide the host name, the installation will fail.
Database listener port: Port number of the MSSQL Server.
Datafile path: Path of the folder on the database server, where you want to create the data file. For
example,
Datafile initial size (MB): Minimum size of the data file for the database.
Datafile maximum size (MB): Maximum size of the data file for the database.
Datafile increment size (MB): Additional file size limit that will be allocated to a database object after
the initial size is full.
Logfile initial size (MB): Minimum size of the log file.
Logfile maximum size (MB): Maximum size of the log file.
Database administrator user name: User name of the database administrator for MSSQL Server.
Database administrator password: Password of the database administrator.
Cisco Database user name: User name required for connecting to the Unified WIM and Unified EIM
database. The installation program creates the database and its user.
Cisco Database password: Password for the Unified WIM and Unified EIM database user.
MSSQL_Home
\MSSQL\Data
.
Provide partition database parameters
7. Review the information displayed in the Summary window, and click Install.
8. In the Install Complete window, click the Finish button to complete the installation process.
Installing the primary application server and file server
In this section, we describe the process of creating the primary application server and file server.
To install the primary application server and file server:
1. Follow Steps 1–3 in “To install a single-server or collocated configuration:” on page 28.
42 Cisco Unified Web and E-Mail Interaction Manager Installation Guide
Page 43

2. In the Installation Options window, select the following options:
File Server
Application Server
Select the Application Server and File Server option
3. Type the path or browse to the BEA and WebLogic home directories.
Provide the path to the BEA and WebLogic home directories
Installation process 43
Page 44

4. Type the path to or browse to the JDK home directory.
Provide the path to the JDK home directory
5. Type the path to or browse to the folder where you would like to install the components.
Provide a location of the Unified WIM and Unified EIM home directory
6. In the WebLogic Server and RMI Parameters window, provide the following details:
Important: WebLogic domain parameters information should match the information provided
while configuring the WebLogic domain.
Domain location: Location of the WebLogic domain you configured on page 17. For example,
BEA_Home
Server name: Name of your WebLogic server (page 17). The default name is myserver.
User name: User name of the WebLogic system user (page 17), required to access the WebLogic
Server Administration Console.
Password: Password for the WebLogic system user (page 17).
44 Cisco Unified Web and E-Mail Interaction Manager Installation Guide
\user_projects\domains\
Domain_Name.
Page 45

Listen port: Port number of the WebLogic server.
SSL listen port: Secure Socket Layer Listen port number of WebLogic.
RMI registry port: Port number used by the Remote Method Invocation (RMI) registry naming
service.
RMI activation port: Port number used by the RMI Daemon Process.
Provide WebLogic server and RMI parameters
7. In the Web Server and Services Server Parameters window, type the names of the web server and the
services server.
Important: Make sure you provide the DNS host names and not the IP addresses of the servers. If
you don't provide the host names, the installation will fail.
Provide the names of the web server and services server
8. In the Master Database Parameters window, provide the following details:
Server name: Name of the local or remote server on which your MSSQL database is installed.
Database name: Name of the master database.
Installation process 45
Page 46

Important: Make sure you provide the DNS host name and not the IP address of the server. If you
don't provide the host name, the installation will fail.
Database listen port: MSSQL server port number.
Cisco Database user name: User name for the Unified WIM and Unified EIM master database.
Cisco Database password: Password for the Unified WIM and Unified EIM master database user.
Provide master database parameters
9. In the Partition Database Parameters window, provide the following details:
Important: Partition database should be created on the same database server as the master
database.
Server name: Name of the local or remote server on which your MSSQL database is installed.
Important: Make sure you provide the DNS host name and not the IP address of the server. If you
don't provide the host name, the installation will fail.
Database name: Name of the partition database.
Database listen port: Port number of the MSSQL Server.
Cisco Database user name: User name of the Unified WIM and Unified EIM database.
Cisco Database password: Password for the Unified WIM and Unified EIM database user.
46 Cisco Unified Web and E-Mail Interaction Manager Installation Guide
Page 47

Provide partition database parameters
10. Review the information displayed in the Summary window, and click Install.
11. In the Installation Complete window, click Finish to complete the installation process for Unified WIM and
Unified EIM. The next few screens will help you set up the integration with Unified CCX.
12. In the next window, click the Finish button to launch the Cisco Unified CCX Data Integration Wizard.
Click the Finish button
Installation process 47
Page 48
13. In the Welcome window, read the introduction and click Next.
Click the Next button
14. In the next window, provide the following details to configure a socket connection to the Unified CCX
server.
Cisco Unified CCX Main Server: Provide the host name or IP address of the primary Unified CCX
server.
Cisco Unified CCX HA Server: Provide the host name or IP address of the secondary Unified CCX
server, which serves as the “high availability” server. This is an optional field. If you provide the
secondary Unified CCX server details, Unified WIM and Unified EIM attempts to connect to the
secondary Unified CCX server when the connection to the primary Unified CCX server fails.
Cisco Unified CCX Master Listener TCP Port: Provide the port number of the licensing port in
Unified CCX, which is used to connect to Unified CCX to download license information. This port
corresponds to the Master Listener TCP Port configured in the System Parameters section of Unified
CCX Administration. The default value is 994.
Cisco Unified CCX RmCm TCP Port: Provide the port number to be used to connect to Unified CCX
to download configuration data for agents, teams, supervisors, and CSQs (queues). This port
corresponds to the RmCm TCP Port configured in the System Parameters section of Unified CCX
Administration. The default value is 42027.
Select Ye s to download voice contact service queues (CSQ) from Unified CCX during the configuration
of the system. Clear this option if you don’t want voice queues in your Unified WIM and Unified EIM
system.
Click Save.
48 Cisco Unified Web and E-Mail Interaction Manager Installation Guide
Page 49

Provide Unified CCX server details
15. Review integration details and click Close to complete the process.
Close the wizard
Installing secondary application servers
Install secondary application servers, following the steps detailed in this section. You will need to create a new
WebLogic domain on a different server because the secondary server cannot share the WebLogic domain or
server of the primary application and web servers.
To install a secondary application server:
1. First, create a WebLogic domain. For details see “Creating WebLogic domains for secondary application
servers” on page 20.
Important: The WebLogic domain name and server name should be different than those of the
primary application server.
2. Then, follow the steps from page 42. In step 7 on page 44 make sure you give the following values:
Domain location: The domain location should be different than the one given for the primary Unified
WIM and Unified EIM application server.
Installation process 49
Page 50

Server name: The server name should be different than the one given for the primary Unified WIM and
Unified EIM application server.
Listen port: The port number should be the same as the one given for the primary Unified WIM and
Unified EIM application server.
Installing the web server
In this section, we describe the process of creating the web server.
To install the web server:
1. Follow Steps 1–3 in “To install a single-server or collocated configuration:” on page 28.
2. In the Installation Options window, select the Web Server option.
Select the Web Se r ve r option
3. In the File Server Parameters window, provide the following details:
File Server name: Name of the file server.
Important: Make sure you provide the DNS host name and not the IP address of the server. If you
don't provide the host name, the installation will fail.
User name to connect to File server share: Type the user name to connect to the file server share. The
user name is the domain name of the user account created exclusively for Unified WIM and Unified
EIM.
Password to connect to File server share: Password for the user.
50 Cisco Unified Web and E-Mail Interaction Manager Installation Guide
Page 51

Provide file server parameters
4. In the Application Server Parameters window, type the name of the Unified WIM and Unified EIM
application server name for which you want to configure the web server.
Important: Make sure you provide the DNS host name and not the IP address of the server. If you
don't provide the host name, the installation will fail.
Provide the application server name
5. Review the information displayed in the Summary window, and click Install.
6. In the Installation Complete window, click Finish to complete the installation process.
Installation process 51
Page 52

Installing the services server
In this section, we describe the process of creating the services server.
To install the services server:
1. Follow Steps 1–3 in “To install a single-server or collocated configuration:” on page 28.
2. In the Installation Options window, select the Services Server option.
Select the Services Server option
3. Type the path or browse to the JDK home directory.
Provide the path to the JDK home directory
52 Cisco Unified Web and E-Mail Interaction Manager Installation Guide
Page 53

4. Type the path to or browse to the folder where you would like to install the services server.
Provide a location for the Unified WIM and Unified EIM home directory
5. Type the name of the file server.
Important: Make sure you provide the DNS host name and not the IP address of the server. If you
don't provide the host name, the installation will fail.
Provide the name of the file server
6. Review the information displayed in the Summary window, and click Install.
7. In the Installation Complete window, click Finish to complete the installation process.
Go to “Post-installation tasks” on page 54, and perform the post-installation procedures described there. If you
need to install an additional partition before that, go to “Additional partitions” on page 76.
Installation process 53
Page 54

Post-installation
tasks
Setting up archives for partition databases
Applying updates
Changing web server settings
Changing logon parameters for Cisco service
Configuring permissions for installation directory
Configuring a web site for the messaging applet
Setting up secure socket layer
Separating the web server from the application server
Starting and stopping Cisco Interaction Manager
Logging in to the business partition
Configuring some important settings
Uninstalling Cisco Interaction Manager
Page 55

This chapter guides you through the tasks to be performed after installing the system. It also describe the process
of uninstalling Unified WIM and Unified EIM.
Setting up archives for partition databases
It is important to set up an archive for each partition database to keep the size of the database manageable and to
avoid performance issues that could appear later.
See “Setting up the archive for a partition” on page 82 for details of the installation procedure for the archive.
Applying updates
To apply updates:
1. Verify that Unified WIM and Unified EIM is stopped.
2. Open the
3. Apply all updates with the help of instructions in the accompanying readme files.
Updates
folder in the Application CD.
Changing web server settings
Configuring Internet Information Services
This procedure helps eliminate 503 errors on the web server. Perfom these tasks on all web servers.
To configure Internet Information Services (IIS) on the web server:
1. On the web server, go to Start menu > Administrative Tools > Internet Information Services (IIS)
Manager.
Post-installation tasks 55
Page 56

2. In the navigation tree, go to
Application Pools
>
DefaultAppPool
. Right-click the node and select
Properties.
Open the DefaultAppPool node
3. In the DefaultAppPool Properties window, on the Recycle tab, clear the following options:
Recycle worker process (in minutes)
Recycle worker process (number of requests)
Clear the Recycle worker process options
4. On the Performance tab, clear the following options:
Shutdown worker process after being idle for
56 Cisco Unified Web and E-Mail Interaction Manager Installation Guide
Page 57

Limit the kernel request queue
Clear the Shutdown worker process and Limit kernel request queue options
5. On the Health tab, clear the following options:
Enable pinging
Enable rapid fail protection
Click Apply
Clear the Enable pinging and Enable rapid fail protection options
. Then click OK to close the window.
Configuring pool thread limit
This procedure increases the capacity of IIS to handle concurrent requests. Perfom these tasks on all web servers.
To configure pool thread limit:
1. On the machine where the web server associated with the primary application server is installed, go to Start
menu > Run.
Post-installation tasks 57
Page 58

2. Type:
Regedit
Press the Enter key.
3. In the Registry Editor window, navigate to
Services> InetInfo
Navigate to InetInfor parameters
>
Parameter.
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE
>
System
>
4. Go to Edit menu > New > DWORD Value.
5. Change the name of the new registry value that gets created to PoolThreadLimit.
6. Right-click PoolThreadLimit and select Modify.
7. In the Edit DWORD Value window, set properties as following:
Value data: ffffffff
CurrentControlSet
>
Important: Make sure you have typed “f” eight times.
Base: Hexadecimal
Configure the registry value
Configuring content expiration settings
As part of the post-install procedure, you can configure the content expiration of cache pages in your web server.
By doing so, the browser compares the current date with the expiration date that you have set to determine
58 Cisco Unified Web and E-Mail Interaction Manager Installation Guide
Page 59

whether to display a cached page, or request an updated page from the server. We recommend you set the
expiration to 365 days for optimum performance.
Important: You must set this option for all partitions, including the System partition.
To configure content expiration:
1. Go to Start > Programs > Administrative Tools > Internet Services Manager.
2. Browse to Web Site > Default Web Site > system.
3. Right-click system and click Properties.
4. In the system Properties window, go to the HTTP Headers tab, and perform the following steps:
Select the Enable content expiration option.
Set the web site content to expire after 365 days. Click OK.
Enable content expiration
Removing extension mapping
Remove extension mapping for the temp virtual directory created by the installation program.
To remove extension mapping:
1. Go to Start > Settings > Control Panel > Administrative Tools > Internet Information Services.
2. Browse to Web Sites > Default web Site > temp.
3. Right-click the temp virtual directory and click Properties.
Post-installation tasks 59
Page 60

4. In the temp Properties window, on the Virtual Directory tab, click the Create button, and then click the
Configuration button.
Click the Create button and the Configuration button
5. In the Application Configuration window, on the Mappings tab, look for
exist, select them, and click the Remove button. Click OK.
Remove mapping for .jsp and .asp extensions
6. Restart IIS.
.jsp
and
.asp
extensions. If they
Changing authentication settings for web site
You need to change the authentication settings for the web site only when the application server and web server
are configured on two different machines.
To change authentication settings for the web site:
1. Go to Start > All Programs > Administration Tools > Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
60 Cisco Unified Web and E-Mail Interaction Manager Installation Guide
Page 61

2. Browse to Web Sites > Default Web Site.
3. Right-click Default Web Site and click Properties.
4. In the Default Web Site Properties window, go to the Directory Security tab.
5. In the Authentication and access control section, click the Edit button.
Click the Edit button
6. In the Authentication Details window, change the authentication details from internet user account to
domain user account. Perform this step only for distributed-server installations. Click OK.
Change the authentication settings
Post-installation tasks 61
Page 62

Changing security credentials for network directory
Important: This procedure is required only in collocated or distributed-server deployments.
This section describes the procedure for configuring network directory security credentials for each Unified
WIM and Unified EIM virtual directory. These steps are required when the web server and the file server are
installed on different machines. Repeat the procedure for each partition.
To change the network directory security settings:
1. Go to Start > All Programs > Administration Tools > Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
2. Browse to Web Sites > Default Web Site.
3. Right-click the Cisco virtual directory and click Properties.
4. In the virtual directory properties window, go to Virtual Directories tab and select the following options:
In the The content for this resource should Come from: section, select the A share located on another
computer option.
Provide the Network directory name and click the Connect As button.
Click the Connect As button
5. In the Network Directory Security Credentials window, change the following configurations and click OK.
Provide the user name and password of the domain user.
Clear the Always use the authenticated user’s credentials when validating access to the network
directory option.
62 Cisco Unified Web and E-Mail Interaction Manager Installation Guide
Page 63
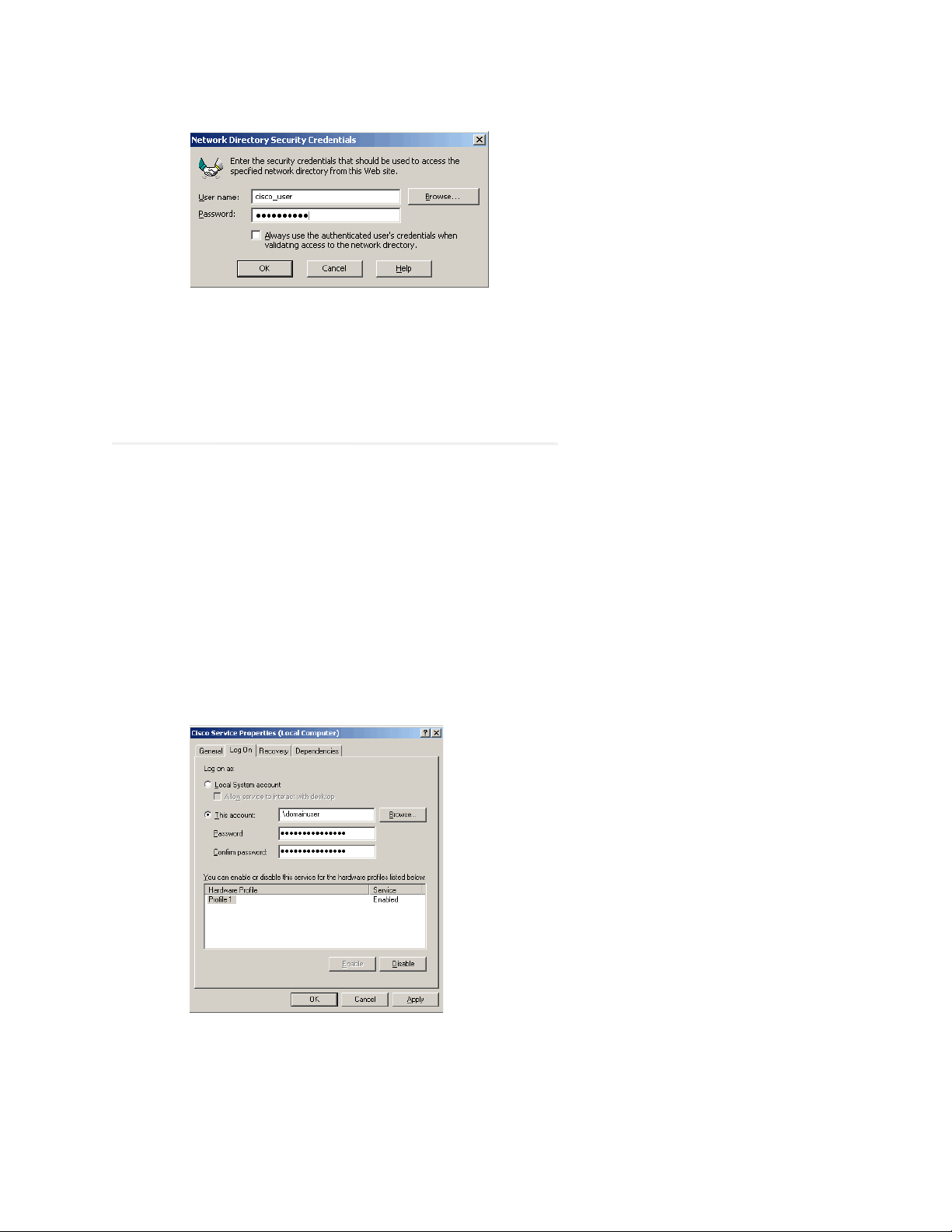
Configure the security credentials for network directory
Repeat these steps for all the Unified WIM and Unified EIM virtual directories.
Changing logon parameters for Cisco service
You need to change logon parameters for the domain user. In a distributed installation, do it on both application
and services servers.
To change the logon parameters:
1. Go to Start > All Programs > Administrative Tools > Services.
2. In the Services window, locate the Cisco Service and double-click it.
3. In the Cisco Service Properties window, on the Log On tab change the following setting and click Apply.
In the Log on as section select the This account option.
Provide the user name and password of the domain user you had created earlier for Unified WIM and
Unified EIM services (page 16).
Change the logon parameters
4. Start the services using the domain user account.
Post-installation tasks 63
Page 64

Configuring permissions for installation directory
For security reasons, change the permissions for the installation directory. In a distributed installation, carry out
these tasks on the file server.
To configure permissions:
1. Remove permissions to everyone from the
2. Give full control to the domain user account that you had created earlier for Cisco Interaction Manager
services (page 16).
cisco
share.
Configuring a web site for the messaging applet
When the application is accessed, a messaging applet is launched in the browser. This applet gets messages for
the user from the database.
Important: You need to perform these tasks only if you are using a load balancer in your
installation and your installation includes Unified WIM.
This section explains the procedures that you must perform to configure a new web site for the messaging applet.
These include:
Creating a new web site
Verifying messaging applet web site
Configuring the properties of the new web site
Creating virtual directories
Configuring the Applet host setting
Creating a new web site
You need to create a new web site for the messaging applet. From here on in the document, the new web site is
referred to as Messaging Applet web site.
Important: Before you start, get another IP address assigned to the web server. Make sure that
both the IP addresses map to the same LAN card. Also, get a fully qualified domain name for the
new IP address.
To configure a new web site:
1. Go to Start > Settings > Control Panel > Administrative Tools > Internet Information Services.
2. Browse to Web Sites.
3. Right-click Web Sites and click New > Web Site.
64 Cisco Unified Web and E-Mail Interaction Manager Installation Guide
Page 65

The Web Site Creation Wizard is launched.
4. When the Welcome window appears, read the installation instructions. Click Next.
5. In the Web Site Description window, provide a description of the web site. This would be the name of the
new web site. Click Next.
Provide a name for the web site
6. In the IP Address and Port Settings window, provide the following details:
From the dropdown list, select the new IP address you got for the web server.
Provide the TCP port this web site should use. The default value is 80.
Don’t provide any host header for the web site.
Click Next.
Configure the IP address and port settings
Post-installation tasks 65
Page 66

7. In the Web Site Home Directory window, type the path or browse to the default directory for the web site. It
should be the same as configured for the Default Web Site. For example,
Next.
Provide the location of the default directory for the web site
8. In the Web Site Access Permissions window, set the read access permission for the web site. Click Next.
c:\Inetpub\wwwroot
. Click
Configure the access permissions
9. In the next window, click the Finish button to complete the configuration process.
Verifying messaging applet web site
To verify the messaging applet web site:
1. Open Internet Explorer.
2. Type the URL
http:/
your browser, where
applet web site is created.
If you see an HTML page, it means that the messaging applet web site has been configured successfully.
Note that the links on the HTML page are accessible only when the application is running.
66 Cisco Unified Web and E-Mail Interaction Manager Installation Guide
Web_Server_FQDN
Web_Server_FQDN is the fully qualified domain name of the server where the messaging
/system/system/web/view/platform/debug/debugmessaging.html
in
Page 67

Configuring web site properties
To configure the properties:
1. Go to Start > Settings > Control Panel > Administrative Tools > Internet Information Services.
2. Browse to Web Sites, and select the Messaging Applet web site.
3. Right-click Messaging Applet web site and click Properties.
4. In the Messaging Applet web site properties window, go to the Home Directories tab.
5. In the Application Settings section, in the Execute Permissions field, select the Script only option.
Configure the execute permission
6. In the same section, click the Configurations button.
The Application Configuration window opens, where you need to add mappings for
.egain
7. In the Mappings tab, click the Add button.
Click the Add button
extensions.
.controller
and
Post-installation tasks 67
Page 68

8. In the Add/Edit Application Extension Mapping window that opens, provide the following details:
Executable: Provide the path to the file containing the WebLogic plugin for IIS. For example,
Drive_Name\
Extension: Provide the extension as
Verbs: Select the Limit to option. As values provide: Get, Head, Post, and Trace.
Script engine: Select the option.
Verify that files exists: Clear the option.
Inetpub\wwwroot\cisco\iisproxy.dll
.egain
.
Click OK.
Configure the properties for the .egain extension
9. In the Mappings tab, click the Add button again. Then, repeat step 8 (page 68) to add the
extension. Make sure that in the Extension field you specify the
Configure the properties for the .controller extension
Creating virtual directories
For the Messaging Applet web site create virtual directories corresponding to the business partition and the
system partition. If you have installed more than one business partition, then create a virtual directory for each
additional partition. The names of the virtual directories should be the same as configured in the default web site.
To create a virtual directory:
1. Go to Start > Settings > Control Panel > Administrative Tools > Internet Information Services.
2. Browse to Web Sites.
.controller
extension.
.controller
3. Right-click the Messaging Applet web site. Click New > Virtual Directory.
The Virtual Directory Creation Wizard is launched.
4. When the Welcome window appears, read the installation instructions. Click Next.
68 Cisco Unified Web and E-Mail Interaction Manager Installation Guide
Page 69

5. In the Virtual Directory Alias window, provide the name of the virtual directory. The name should be the
same as configured in the default web site. Click Next.
Provide the name for the virtual directory
6. In the Web Site Content Directory window, browse to the eService folder in the Cisco home directory. For
example,
Cisco_Home
\eService
. In a distributed installation, you have to provide the path to the Unified
WIM and Unified EIM home directory of the File Server. For example,
\\
File_Server_Name\Cisco_Home
\eService
. Click Next.
Browse to the Cisco home directory
7. In the Virtual Directory Permissions window, select the following options:
Read
Run scripts (such as ASP)
Post-installation tasks 69
Page 70

Click Next.
Configure the access permissions
8. In the next window, click the Finish button to complete the configuration process.
9. Make sure that the permissions configured for this virtual directory are the same as configured for the
corresponding virtual directory of the default web site. Follow all the steps in “Changing security credentials
for network directory” on page 62. In step 2, make sure you select the Messaging Applet web site.
Repeat the process for creating additional virtual directories.
Configuring the Applet host setting
After configuring the new web site, and acquiring the security certificate for the web site, do the final step of
configuring the Applet host setting in the master and active databases.
To configure the Applet host setting:
On the master and active databases, run the following query:
Update egpl_pref_globalsettings
set setting_act_val = ‘
where setting_name = ‘Common.messaging.applethost’
Where, Web_Server_FQDN is:
The fully qualified domain name of the web server where the messaging applet web site is created, if the
installation includes a load balancer.
The fully qualified domain name of the primary, if the installation does not include a load balancer.
Web_Server_FQDN
’
70 Cisco Unified Web and E-Mail Interaction Manager Installation Guide
Page 71

Setting up secure socket layer
Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) is widely used to create a secure communication channel between web browsers and
servers. Set up SSL for more secure connections to your Cisco Interaction Manager installation. This is an
optional step.
See Chapter 7, “SSL for secure connections” for details of the set up procedure.
Separating the web server from the application server
Perform these tasks only if you installed the web server and the application server on the same machine and now
you want to separate the two servers. The procedure for separating the web server from the application server
involves installing web server components on a separate server and then changing the value of the
Common.messaging.applehost
To separate the web server from the application server:
1. First, install the web server. For details, see “Installing the web server” on page 50.
On the master and active databases, run the following query:
setting in the master and active databases.
Update egpl_pref_globalsettings
set setting_act_val = ‘
where setting_name = ‘Common.messaging.applethost’
Where, Web_Server_FQDN is:
The fully qualified domain name of the web server where the messaging applet web site is created, if the
installation includes a load balancer.
The fully qualified domain name of the primary, if the installation does not include a load balancer.
Web_Server_FQDN
’
Starting and stopping Cisco Interaction Manager
To start Cisco Interaction Manager:
In the NT Services panel, start Cisco Service to start all Cisco Interaction Manager services. If it is a
distributed-server installation, first start the Cisco Service on the services server and then on each
application server. After starting Cisco Service, wait for five minutes before you attempt to log in to the
product.
Post-installation tasks 71
Page 72

To stop Cisco Interaction Manager:
In the NT Services panel, stop the Cisco Service to stop all Cisco Interaction Manager services. If it is a
distributed-server installation, stop the Cisco Service on the services server and on each application server.
After stopping the service, ensure that all associated java, javaw, cmd, and rmid processes are terminated.
Then wait for five minutes before you start the service again.
Logging in to the business partition
The common system partition as well as the first business partition are created during the installation.
Logging in from Internet Explorer
To log in to the business partition:
1. Type the URL
web server and
installation, you are prompted to provide the virtual site name in the Partition Administrator Account and
Partition window. If you have configured the web server to use SSL, then the URL is
https://
2. In the Login window, type the user name and password you had set up for the partition administrator in the
Partition Administrator Login Parameters window during the installation. Click the Log In button.
http://
Web_Server/Partition_Virtual_Directory in your browser, where Web_Server is your
Partition_Virtual_Directory is the virtual directory created for this partition. During the
Web_Server/Partition_Virtual_Directory.
Logging in from Cisco Agent Desktop Embedded Browser
This release of Unified WIM and Unified EIM can also be used with the embedded browser in Cisco Agent
Desktop (CAD).
See CAD documentation for details about configuring a new task button in CAD to launch Unified WIM and
Unified EIM using a URL. The URL is
the web server to use SSL, then the URL is
Make sure that Unified WIM and Unified EIM is configured to run in its own browser tab, uninterrupted by
other browser applications.
http://
https://
Web_Server/Partition_Virtual_Directory. If you have configured
Web_Server/Partition_Virtual_Directory.
72 Cisco Unified Web and E-Mail Interaction Manager Installation Guide
Page 73

Configuring some important settings
Settings allow you to configure various aspects of Unified WIM and Unified EIM. Some settings are configured
at the partition level, while others have to be set up for each department.
In this section, we describe certain settings that should be configured soon after installation. These settings are of
two types:
1. Mandatory settings: These settings must be configured before using Unified WIM and Unified EIM. These
include the settings related to ESMTP protocol, which must be configured if you are using ESMTP protocol
for exception and spam emails and notifications.
2. Optional settings: Although it is not mandatory to change these settings, you are likely to feel the need to
configure them for your business.
Mandatory settings
At the partition level
Make sure you configure the following settings for each partition.
Default SMTP server
Notifications mail SMTP Server
Notifications mail redirection from address
Notifications mail redirection to address
Configure the following partition-level settings only if you use ESMTP protocol for exception and spam emails
and notifications.
Exception mails SMTP user name
Exception mails SMTP password
SPAM mails SMTP user name
SPAM mails SMTP password
Notification mails SMTP user name
Notification mails SMTP password
At the department level
Configure the following setting for each department.
Default From address for alarm
Post-installation tasks 73
Page 74

Optional settings
Although it is not mandatory to change these settings, you are likely to feel the need to configure them for your
business.
At the partition level
Customer departmentalization
Deletion time out
Exception email SMTP
Exception mail redirection to address
Exception mail redirection from address
Expiry time for auto pushback
Inactive time out
SPAM mail SMTP Server
SPAM mail redirection from address
SPAM mail redirection to address
At the department level
Business calendar time zone
Uninstalling Cisco Interaction Manager
To ensure that critical data is not lost, the program does not uninstall the following components:
The database
The
To uninstall Cisco Interaction Manager:
1. Go to Start > Settings > Control Panel.
2. Double-click Add/Remove Programs.
3. From the list of currently installed programs, select Cisco Unified Web and E-Mail Interaction Manager
Storage
and click Remove.
folder on the file system.
74 Cisco Unified Web and E-Mail Interaction Manager Installation Guide
Page 75

4. In the Uninstall Cisco Interaction Manager window, click the Uninstall button.
Click the Uninstall button
5. On the database server, go to the SQL Enterprise Manager and delete the database manually, if required.
Post-installation tasks 75
Page 76

Additional
partitions
About partitions
Installing business partitions
Page 77

The System partition and the first business partition are installed by default. You can create additional business
partitions with the installation program. This chapter describes the procedure for installing and configuring a new
business partition.
About partitions
As Unified WIM and Unified EIM is designed for enterprise-wide deployments, a single installation can be used
by various independent or semi-independent business units in an organization. You can easily set up Unified
WIM and Unified EIM to mirror the structure of your business.
A Unified WIM and Unified EIM installation can have one or more business partitions, which are meant to be
used as independent units. While the hardware and software is common for all partitions, system resources and
business objects are stored and managed separately for each partition. Partitions are ideal for organizations where
business units (or clients, in the case of an outsourced services provider) do not need to share customer,
interaction, or product information.
The installation program creates the System partition and a single-department business partition. You can create
additional business partitions by using the installation program. Create additional partitions if you:
Want complete segregation of data between business units in your enterprise.
Are an outsourcing or application service provider, and want to serve multiple customers from a single
installation.
Installing business partitions
Important: Before installing the new partition ensure that Unified WIM and Unified EIM is installed
and it is running.
To create a new business partition:
1. On the file server, run
2. When the Introduction window appears, read the installation instructions.
Setup.exe
from the Application CD.
Additional partitions 77
Page 78

3. In the License Agreement window, review the licensing terms agreement select the I accept the terms of
the License Agreement option.
Read and accept the terms of the License Agreement
4. In the Installation Options window, select the Partition option.
Select the Partition option
5. In the Web Server Parameters window, provide the following details:
User name to connect to File server share: Type the user name to connect to file server share. The
user name is the domain name of the user account created exclusively for Unified WIM and Unified
EIM. For details, see “Setting up user accounts and permissions” on page 16.
Password to connect to File server share: Type the password to connect to file server share.
78 Cisco Unified Web and E-Mail Interaction Manager Installation Guide
Page 79

Provide web server parameters
6. In the Cisco Partition Administrator Account and Partition window, create the partition administrator user
account and the partition. Provide the following:
User name: User name for the partition administrator.
Password: Password for the partition administrator.
Verify password: Verify the password.
Partition name: Name for the partition. This name will be part of the URL that users will use to log in
to Cisco Interaction Manager:
http://
Host_Name/Partition_Name. Make sure that the name does not
contain any spaces.
Description of partition: Description for the partition.
Create the partition administrator user account and the partition
7. In the Partition Database Parameters window provide the following details:
Important: Partition database should be created on the same database server as the master
database.
Additional partitions 79
Page 80

Server name: Name of the local or remote server on which your MSSQL database is installed.
Database name: Name of the master database. The installation program creates a database with the
name you type here.
Important: Make sure you provide the DNS host name and not the IP address of the server. If you
don't provide the host name, the installation will fail.
Database listener port: Port number of the MSSQL Server.
Datafile path: Path of the folder on the database server, where you want to create the data file. For
example,
Datafile initial size (MB): Minimum size of the data file for the database.
Datafile maximum size (MB): Maximum size of the data file for the database.
Datafile increment size (MB): Additional file size limit that will be allocated to a database object after
the initial size is full.
Logfile initial size (MB): Minimum size of the log file.
Logfile maximum size (MB): Maximum size of the log file.
Database administrator user name: User name of the database administrator for MSSQL Server.
Database administrator password: Password of the database administrator.
Cisco Database user name: User name required for connecting to the Unified WIM and Unified EIM
database. The installation program creates the database and its user.
Cisco Database password: Password for the Unified WIM and Unified EIM database user.
MSSQL_Home
\MSSQL\Data
.
Provide partition database parameters
8. Review the information displayed in the Summary window, and click Install.
9. In the Install Complete window, click Finish to complete the installation process.
Important: If SSL is configured for the application, then for each new partition, you need to create
a virtual directory in the Applet Messaging web site. For details see “Creating virtual directories” on
page 68.
80 Cisco Unified Web and E-Mail Interaction Manager Installation Guide
Page 81

Archives
About archives
Setting up the archive for a partition
Page 82

About archives
Data is stored in the active database. With time, the size of the data usually increases to a point where it begins
to affect the performance of the system. Hence, it is important that data that is not in use anymore is stored
somewhere other than the active database.
Archiving is a systematic process which moves the data from the active database to the archive database.
Periodic archiving helps to keep the size of the active database within prescribed levels, thereby improving the
performance of the system.
Archives can be set up for all partitions except the system partition. The application’s installation program helps
you install archives. You can install them while installing the application or creating a new partition. You can
also choose them later—in that case, make sure that the file server is properly installed.
Setting up the archive for a partition
Enabling network DTC access
If you are installing the archive database on a server other than the partition database server, you need to first
enable network DTC access on the partition database server and the archive database server.
To enable network DTC access:
1. Go to Start > Settings > Control Panel.
2. Double-click Add/Remove Programs.
3. In the Add/Remove Programs window, click the Add/Remove Windows Components button.
Click the Add/Remove Windows Component button
82 Cisco Unified Web and E-Mail Interaction Manager Installation Guide
Page 83

4. In the Windows Components window, select the Application Server option and click the Details button.
Select the Application Server option
5. In the Application Server window, select Enable network DTC access and click OK.
Select the Enable network DTC access option
6. In the Windows Components Wizard, click Next and then click Finish.
Setting up the archive
To set up the archive:
1. On the file server, run
2. When the Introduction window appears, read the installation instructions.
Setup.exe
from the Application CD.
Archives 83
Page 84

3. In the License Agreement window, review the licensing terms agreement select the I accept the terms of
the License Agreement option.
Read and accept the terms of the Licence Agreement
4. In the Installation Options window, select the Archive option.
Select the Archive option
5. In the Partition Name Parameter window provide the following details:
Partition name: Name of the partition for which you want to create the archive database.
Database administrator user name: User name of the partition database administrator for MSSQL
server.
Database administrator password: Password of the partition database administrator.
84 Cisco Unified Web and E-Mail Interaction Manager Installation Guide
Page 85

Provide partition parameters
6. In the Archive Database Parameters window provide the following details:
Server name: Name of the local or remote MSSQL database server on which your archive database
will be installed.
Important: Make sure you provide the DNS host name and not the IP address of the server. If you
don't provide the host name, the installation will fail.
Database name: Name of the archive database. The installation program creates a database with the
name you type here.
Database listener port: Port number of the MSSQL Server.
Datafile path: Path of the folder on the database server, where you want to create the data file. For
example,
Datafile initial size (MB): Minimum size of the data file for the database.
Datafile maximum size (MB): Maximum size of the data file for the database.
Datafile increment size (MB): Additional file size limit that will be allocated to a database object after
the initial size is full.
Logfile initial size (MB): Minimum size of the log file.
Logfile maximum size (MB): Maximum size of the log file.
MSSQL_Home
\MSSQL\Data
.
Administrator user name: User name of the archive database administrator for MSSQL Server.
Administrator password: Password of the archive database administrator.
Cisco Database user name: User name required for connecting to the archive database.
Cisco Database password: Password for the archive database user.
Archives 85
Page 86

Provide archive database parameters
7. Review the information displayed in the Summary window, and click Install.
8. In the Install Complete window, click Finish to complete the installation process.
86 Cisco Unified Web and E-Mail Interaction Manager Installation Guide
Page 87

SSL for secure
connections
Installing a security certificate
Configuring SSL access
Configuring the viewing of attachments
Testing SSL access
Page 88

Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) is widely used to create a secure communication channel between web browsers and
servers. Set up SSL for more secure connections to your Unified WIM and Unified EIM installation by following
the procedures described in this chapter.
Installing a security certificate
This section explains the procedures that you must perform to acquire a certificate request. These include:
Generating a security certificate request
Submitting the certificate request
Installing the certificate on the Web Server
Generating a security certificate request
This procedure creates a new certificate request, which is then sent to a Certificate Authority (CA) for
processing. If successful, the CA will send back a file containing a validated certificate.
Important: You need to generate the security certificate request for the Default web site and the
Messaging Applet web site.
To generate a certificate request:
1. Go to Start > Settings > Control Panel > Administrative Tools > Internet Information Services.
2. Browse to Web Sites >
3. Right-click Web_Site_Name and click Properties.
4. In the Default Web Site Properties window, go to the Directory Security tab.
5. In the Secure communications section, click the Server Certificate button to launch the Web Server
Certificate Wizard.
Web_Site_Name.
Click the Server Certificate button
88 Cisco Unified Web and E-Mail Interaction Manager Installation Guide
Page 89

6. In the Welcome to the Web Server Certificate Wizard window, click the Next button.
7. In the Server Certificate window, select the Create a New Certificate option. Click Next.
Select the Create a new certificate option
8. In the Delayed or Immediate Request window, select the Prepare the request now, but send it later option
and click Next.
Select to prepare the certificate request now and send it later
9. In the Name and Security Settings window, provide the following details:
Type a descriptive name for the certificate. The wizard uses the name of the current web site by default.
Type a bit length for the key.
Click Next.
SSL for secure connections 89
Page 90

Provide the name for the certificate and configure the security settings
10. In the Organization Information window, type the organization name (such as Cisco) and unit (such as
Service department). Click Next. As this information will be placed in the certificate request, make sure it is
accurate.
Provide information about your organization
11. In the Your Site’s Common Name window, in the Common name field, type the DNS name of the web
server. Click Next.
Provide the fully qualified domain name of your web site
90 Cisco Unified Web and E-Mail Interaction Manager Installation Guide
Page 91

12. In the Geographical Information window, provide the location information, and click Next.
Provide the geographical information
13. In the Certificate Request File Name window, type the file name for the certificate request. The default name
and location is
c:\certreq.txt
. Click Next.
Provide a file name for the certificate request
14. In the Request File Summary window, review the summary and click Next to generate the certificate.
Submitting the certificate request
Go to the companies web site, which issues SSL certificates (such as VeriSign), and submit your certificate
request. Make sure you provide the same information as you provided while generating the certificate request. To
submit the request, you will need the certificate request file that was generated earlier (page 88).
On completion of the process, the vendor will generate the certificate and send it to you.
Important: You need to submit the certificate request for the Default web site and the Messaging
Applet web site.
SSL for secure connections 91
Page 92

Installing the certificate on the web server
Once you receive the certificate from your vendor, install it on your web server.
Important: You need to install the certificate for the Default web site and the Messaging Applet
web site.
To install the certificate on the web server:
1. Save a copy of the certificate you received from your vendor on the local machine.
2. Go to Start > Settings > Control Panel > Administrative Tools > Internet Information Services.
3. Browse to Web Sites >
4. Right-click Web_Site_Name and click Properties.
5. In the web site properties window, go to the Directory Security tab.
6. In the Secure communications section, click the Server Certificate button to launch the Web Server
Certificate Wizard.
Click the Server Certificate button
Web_Site_Name.
7. In the Welcome to the Web Server Certificate Wizard window, click the Next button.
92 Cisco Unified Web and E-Mail Interaction Manager Installation Guide
Page 93

8. In the Pending Certificate Request window, select the Process the pending request and install the
certificate option. Click Next.
Select to process the pending request and install the certificate
9. In the Process a Pending Request window, type the path and file name of the local copy of the certificate.
Click Next.
Provide the path and file name of the certificate
10. In the SSL Port window, specify the SSL port for the web site.
Specify the SSL port
11. In the Certificate Summary window, review the certificate summary and click Next. Click Finish.
SSL for secure connections 93
Page 94

The certificate is now installed on the web server.
Configuring SSL access
This procedure uses Internet Services Manager to configure the virtual directory to require SSL for access.
Important: You need to configure the SSL access for the Default web site and the Messaging
Applet web site.
To configure SSL access:
1. Go to Start > Settings > Control Panel > Administrative Tools > Internet Information Services.
2. Browse to Web Sites >
3. Right-click Web_Site_Name and click Properties.
4. In the web site properties window, go to the Directory Security tab.
5. In the Secure communications section, click the Edit button.
Click the Edit button
Web_Site_Name.
94 Cisco Unified Web and E-Mail Interaction Manager Installation Guide
Page 95

6. In the Secure Communications window, select the Require secure channel (SSL) and Require 128-Bit
encryption options. Click OK, and then click OK again to close the Properties window.
Configure the secure communications options
7. Restart the IIS Service. Make sure that both web sites have started.
Clients browsing to this virtual directory must now use HTTPS.
Configuring the viewing of attachments
To enable users to view attachments:
1. In Cisco_Home
a. Change the value of
https://
provided.
b. Change the value of
https://
provided.
c. Change the value of
https://
provided.
2. In
Cisco_Home
from
http://
domain name of the web server is provided.
\config\egpl_master.properties
webtemp.webdir
Web_Server
Web_Server
Web_Server
\config\egml_mailconfig.properties
Web_Server
/temp.
Task.Attachment.WebTemp
/temp.
Live.Attachment.WebTemp
/temp
/temp
Also, verify that the fully qualified domain name of the web server is
Also, verify that the fully qualified domain name of the web server is
. Also, verify that the fully qualified domain name of the web server is
to
https://
from
Web_Server
:
http://
from
from
/temp.
Testing SSL access
Web_Server
http://
http://
change the value of
/temp to
Web_Server
Web_Server
Also, verify that the fully qualified
/temp
/temp
Attachment.WebTemp
to
to
To test SSL access to Unified WIM and Unified EIM:
1. Open your web browser.
SSL for secure connections 95
Page 96

2. Use HTTP in the URL for Unified WIM and Unified EIM. For example,
You should see a message asking you to view the page over a secure channel.
3. Now use HTTPS in the URL for Unified WIM and Unified EIM. For example,
https://
4. In the security message that appears, click the View certificate button.
5. After verifying the certificate information, click OK. And then click Ye s to proceed to the URL.
The Unified WIM and Unified EIM login window appears.
Web_Server/Partition.
http://
Web_Server/Partition.
96 Cisco Unified Web and E-Mail Interaction Manager Installation Guide
Page 97

Appendix A: Reference sheet
Configuration details
Additional partition
Yes
No
Configuration type and option
Single server
Split server
Distributed server
File server details
# Item Value
1. Location of Unified WIM and Unified EIM home
directory
Database details
# Item Value Notes
1. System Administrator user name
2. System Administrator password
3. Partition Administrator user name
Page 98

# Item Value Notes
4. Partition Administrator password
5. Partition name
6. Partition description
Master database parameters
7. Server name Make sure you provide the DNS host
name and not the IP address of the
server. If you don't provide the host
name, the installation will fail.
8. Database name
9. Database listener port
10. Datafile path
11. Datafile initial size
12. Datafile maximum size
13. Datafile increment size
14. Logfile initial size
15. Logfile maximum size
16. Database administrator user name
17. Database administrator password
18. Unified WIM and Unified EIM Database user
name
19. Unified WIM and Unified EIM Database
password
Partition Database parameters
20. Server name Make sure you provide the DNS host
name and not the IP address of the
server. If you don't provide the host
name, the installation will fail.
21. Database name
22. Database listener port
23. Datafile path
24. Datafile initial size
25. Datafile maximum size
26. Datafile increment size
27. Logfile initial size
98 Cisco Unified Web and E-Mail Interaction Manager Installation Guide
Page 99

# Item Value Notes
28. Logfile maximum size
29. Database administrator user name
30. Database administrator password
31. Unified WIM and Unified EIM Database user
name
32. Unified WIM and Unified EIM Database
password
Application server details
# Item Value Notes
1. Location of BEA home directory
2. Location of WebLogic home directory
3. Location of JDK home directory
4. Location of file server
5. Location of Unified WIM and Unified EIM home
directory
6. Web server name Make sure you provide the DNS host
name and not the IP address of the server.
If you don't provide the host name, the
installation will fail.
7. Services server name Make sure you provide the DNS host
name and not the IP address of the server.
If you don't provide the host name, the
installation will fail.
WebLogic server parameters
8. Domain location
9. Server name
10. User name
11. Password
12. Listen port
13. SSL listen port
RMI parameters
Appendix A: Reference sheet 99
Page 100

# Item Value Notes
14. RMI registry port
15. RMI activation port
Master database parameters
16. Server name Make sure you provide the DNS host
17. Database name
18. Database listen port
19. Unified WIM and Unified EIM Database user
name
20. Unified WIM and Unified EIM Database password
Partition database parameters
21. Server name Make sure you provide the DNS host
22. Database name
23. Database listen port
24. Unified WIM and Unified EIM Database user
name
name and not the IP address of the server.
If you don't provide the host name, the
installation will fail.
name and not the IP address of the server.
If you don't provide the host name, the
installation will fail.
25. Unified WIM and Unified EIM Database password
Unified CCX Data Integration Wizard details
# Item Value Notes
1. Unified CCX Main Server
2. Unified CCX HA Server
3. Unified CCX Master Listener TCP Port 994 (default)
4. Unified CCX RmCm TCP Port 42027 (default)
100 Cisco Unified Web and E-Mail Interaction Manager Installation Guide
 Loading...
Loading...