Page 1

Cisco SRST SNMP MIB
Release 3.4
Guide
October 26 2005
Corporate Headquarters
Cisco Systems, Inc.
170 West Tasman Drive
San José, CA 95134-1706
USA
http://www.cisco.com
Tel: 408 526-4000
800 553-NETS (6387)
Fax: 408 526-4100
Text Part Number: OL-7959-01
Page 2

THE SPECIFICATIONS AND INFORMATION REGARDING THE PRODUCTS IN THIS MANUAL ARE SUBJECT TO CHANGE WITHOUT NOTICE. ALL
STATEMENTS, INFORMATION, AND RECOMMENDATIONS IN THIS MANUAL ARE BELIEVED TO BE ACCURATE BUT ARE PRESENTED WITHOUT
WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED. USERS MUST TAKE FULL RESPONSIBILITY FOR THEIR APPLICATION OF ANY PRODUCTS.
THE SOFTWARE LICENSE AND LIMITED WARRANTY FOR THE ACCOMPANYING PRODUCT ARE SET FORTH IN THE INFORMATION PACKET THAT
SHIPPED WITH THE PRODUCT AND ARE INCORPORATED HEREIN BY THIS REFERENCE. IF YOU ARE UNABLE TO LOCATE THE SOFTWARE LICENSE
OR LIMITED WARRANTY, CONTACT YOUR CISCO REPRESENTATIVE FOR A COPY.
The Cisco implementation of TCP header compression is an adaptation of a program developed by the University of California, Berkeley (UCB) as part of UCB’s public
domain version of the UNIX operating system. All rights reserved. Copyright © 1981, Regents of the University of California.
NOTWITHSTANDING ANY OTHER WARRANTY HEREIN, ALL DOCUMENT FILES AND SOFTWARE OF THESE SUPPLIERS ARE PROVIDED “AS IS” WITH
ALL FAULTS. CISCO AND THE ABOVE-NAMED SUPPLIERS DISCLAIM ALL WARRANTIES, EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING, WITHOUT
LIMITATION, THOSE OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT OR ARISING FROM A COURSE OF
DEALING, USAGE, OR TRADE PRACTICE.
IN NO EVENT SHALL CISCO OR ITS SUPPLIERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY INDIRECT, SPECIAL, CONSEQUENTIAL, OR INCIDENTAL DAMAGES, INCLUDING,
WITHOUT LIMITATION, LOST PROFITS OR LOSS OR DAMAGE TO DATA ARISING OUT OF THE USE OR INABILITY TO USE THIS MANUAL, EVEN IF CISCO
OR ITS SUPPLIERS HAVE BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES.
CCSP, the Cisco Square Bridge logo, Cisco Unity, Follow Me Browsing, FormShare, and StackWise are trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc.; Changing the Way We Work,
Live, Play, and Learn, and iQuick Study are service marks of Cisco Systems, Inc.; and Aironet, ASIST, BPX, Catalyst, CCDA, CCDP, CCIE, CCIP, CCNA, CCNP, Cisco,
the Cisco Certified Internetwork Expert logo, Cisco IOS, Cisco Press, Cisco Systems, Cisco Systems Capital, the Cisco Systems logo, Empowering the Internet Generation,
Enterprise/Solver, EtherChannel, EtherFast, EtherSwitch, Fast Step, GigaDrive, GigaStack, HomeLink, Internet Quotient, IOS, IP/TV, iQ Expertise, the iQ logo, iQ Net
Readiness Scorecard, LightStream, Linksys, MeetingPlace, MGX, the Networkers logo, Networking Academy, Network Registrar, Packet, PIX, Post-Routing, Pre-Routing,
ProConnect, RateMUX, Registrar, ScriptShare, SlideCast, SMARTnet, StrataView Plus, SwitchProbe, TeleRouter, The Fastest Way to Increase Your Internet Quotient,
TransPath, and VCO are registered trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. and/or its affiliates in the United States and certain other countries.
All other trademarks mentioned in this document or Website are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership relationship
between Cisco and any other company. (0406R)
Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Release 3.4 Guide
Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
All rights reserved.
Page 3

Preface v
About this Preface v
Document Objective v
Audience v
Document Organization vi
Document Conventions vi
Syntax Conventions vi
Obtaining Documentation ix
Cisco.com ix
Documentation DVD ix
Ordering Documentation ix
Documentation Feedback x
Cisco Product Security Overview x
Reporting Security Problems in Cisco Products x
Obtaining Technical Assistance xi
Cisco Technical Support Website xi
Submitting a Service Request xi
Definitions of Service Request Severity xii
CONTENTS
OL-7959-01
Obtaining Additional Publications and Information xii
Summary History of Document Changes xiii
Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Support 1-1
Overview 1-1
Design of the CISCO-SRST-MIB 1-2
Structure 1-2
CISCO-SRST-MIB Features 1-4
Common Tables 1-8
Common Notifications/Traps 1-8
Common Objects 1-8
Common Tables 1-8
Dependencies of the SRST MIB 1-11
Limitations 1-12
Performance Impact 1-12
Prerequisites 1-12
Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Release 3.4 Guide
iii
Page 4

Contents
Supported Platforms for SRST 3.4 1-13
Cisco Voice Gateways 1-13
Cisco IP Phones 1-13
Licenses 1-14
Configuration 1-14
Using SNMP and MIBs to Extract CISCO-SRST-MIB Information 1-14
How to Configure the CISCO-SRST-MIB 1-14
Enabling the SNMP Agent 1-14
Verifying the Enabling of the SNMP Agent 1-15
Configuration Examples 1-15
Complete SRST Configuration Example 1-16
Configuring SRST Mode 1-19
Enabling Traps in SRST Mode 1-21
Monitoring SCCP Phone Statistics 1-22
Retrieving SIP Phone Registrations 1-23
Receiving Notifications/Traps 1-25
Command Reference 1-26
SNMP Overview 1-27
Network Management Overview 1-27
MIB Overview 1-28
MIB Source 1-28
MIB Objects 1-28
MIB Archive 1-29
SNMP 1-29
Internet MIB Hierarchy 1-30
SNMP MIB 1-31
Compliance 1-32
Cisco Compliance 1-32
Implementation 1-32
SNMP MIB Tables 1-32
CISCO-SRST-MIB Object Groups 1-33
SRST Traps 1-43
Cisco-SRST-MIB Object Mappings 1-43
Glossary 1-47
Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Release 3.4 Guide
iv
OL-7959-01
Page 5

Preface
About this Preface
This preface describes the objectives, audience, organization, and conventions of this document, and explains
how to find additional information on related products and services. It contains the following sections:
• Document Objective, page v
• Audience, page v
• Document Organization, page vi
• Obtaining Technical Assistance, page xi
• Document Conventions, page vi
• Syntax Conventions, page vi
• Obtaining Documentation, page ix
• Cisco Product Security Overview, page x
• Obtaining Technical Assistance, page xi
• Obtaining Additional Publications and Information, page xii
• Summary History of Document Changes, page xiii
Document Objective
This document describes the information regarding the Cisco SRST Simple Network Management
Protocol (SNMP) Management Information Base (MIB). The document contains tables for you to use
when using the SNMP MIB to monitor your system.
Audience
The primary audience for this document is network operators and administrators who have experience
in the following areas:
• Telecommunications network operations
• Data network operations
• SNMP operstion
OL-7959-01
Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Release 3.4 Guide
v
Page 6
Document Organization
• MIB syntax
• Telecommunications hardware
• Data network hardware
In addition, the following audiences may find this document useful:
• Software and hardware installers
• Network designers
Document Organization
This document contains the chapters listed in Table 1.
Table 1 Document Organization
Chapter Title Description
Chapter 1 Provisioning Overview This chapter includes a description of the Cisco SRST
Preface
MIB.
Document Conventions
Caution Means reader be careful. In this situation, you might do something that could result in equipment
damage or loss of data.
Note Means reader take note. Notes contain helpful suggestions or references to materials not contained in
this manual.
Tip Means the following information might help you solve a problem.
Timesaver Means the described action saves time. You can save time by performing the action described in the
paragraph.
Syntax Conventions
Conventions used throughout this guide are shown in Table 2.
Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Release 3.4 Guide
vi
OL-7959-01
Page 7
Preface
Ta b l e 2 C o n v e n t i o n s
Convention Meaning Description / Comments
Boldface Commands and keywords
offset-list
you enter as shown.
Italics Variables for which you
supply values.
command type interface
You replace the variable with the type
of interface.
In contexts that do not allow italics,
such as online help, arguments are
enclosed in angle brackets (< >).
Square brackets ([ ]) Optional elements. command [abc]
abc is optional (not required), but you
can choose it.
Vertical bars ( | ) Separated alternative
elements.
command [ abc | def ]
You can choose either abc or def, or
neither, but not both.
Braces ({ }) Required choices. command { abc | def }
Syntax Conventions
Yo u must choose either abc or def, but
not both.
Braces and vertical bars
within square brackets
([ { | } ])
A required choice within an
optional element.
command [ abc { def | ghi } ]
You have three options:
nothing
abc def
abc ghi
Caret character (^) Control key. The key combinations ^D and Ctrl-D
are equivalent: Both mean “hold down
the Control key while you press the D
key.” Keys are indicated in capital
letters, but are not case sensitive.
A nonquoted set of
characters
A string. For example, when setting an SNMP
community string to public, do not use
quotation marks around the string;
otherwise, the string will include the
quotation marks.
System prompts
Denotes interactive
sessions, indicates that the
user enters commands at the
prompt.
Screen font Terminal sessions and
The system prompt indicates the
current command mode. For example,
the prompt
Router (config) #
indicates global configuration mode.
information the system
displays.
OL-7959-01
Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Release 3.4 Guide
vii
Page 8
Syntax Conventions
Table 2 Conventions (continued)
Convention Meaning Description / Comments
Angle brackets (< >) Nonprinting characters such
as passwords.
Exclamation point (!) at the
beginning of a line
A comment line. Comments are sometimes displayed by
the Cisco IOS software.
Conventions used in the Cisco SRST system (such as in CLI commands) are shown in Tab l e 3.
Ta b le 3 D at a Ty p e s
Data Type Definition Example
Integer A series of decimal digits from the set of 0 through 9 that
represents a positive integer. An integer may have one or
more leading zero digits (0) added to the left side to align
123
000123
4200000000
the columns. Leading zeros are always valid as long as
the number of digits is less than or equal to ten digits.
Values of this type have a range of zero through
4294967295.
Signed
integer
This data type has the same basic format as the integer
but can be either positive or negative. When negative, it
is preceded by the sign character (-). As with the integer
123
-000123
-2100000000l
data type, this data type can be as many as ten digits in
length, not including the sign character. The value of this
type has a range of 0 minus 2147483647 through
2147483647.
Hexadecimal A series of 16-based digits from the set of 0 through 9, a
through f, or A through F. The hexadecimal number may
1f3
01f3000
have one or more leading zeros (0) added to the left side.
For all hexadecimal values, the maximum size is
0xffffffff (eight hexadecimal digits).
Text A series of alphanumeric characters from the ASCII
character set, where defined. Tab, space, and double
EntityID
LineSES_Threshold999
quote (“ ”) characters cannot be used. Text can be as many
as 255 characters; however, it is recommended that you
limit the text to no more than 32 characters for
readability.
String A series of alphanumeric characters and white-space
characters. A string is surrounded by double quotes (“ ”).
“This is a descriptive
string.”
Strings can be as many as 255 characters; however, it is
recommended that you limit the strings to no more than
80 characters for readability.
Preface
Note Hexadecimal and integer fields in files may have different widths (number of characters) for column
alignment.
Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Release 3.4 Guide
viii
OL-7959-01
Page 9

Preface
Obtaining Documentation
Cisco documentation and additional literature are available on Cisco.com. Cisco also provides several
ways to obtain technical assistance and other technical resources. These sections explain how to obtain
technical information from Cisco Systems.
Cisco.com
You can access the most current Cisco documentation at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/home/home.htm
You can access the Cisco website at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com
You can access international Cisco websites at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/public/countries_languages.shtml
Obtaining Documentation
Documentation DVD
Cisco documentation and additional literature are available in a Documentation DVD package, which
may have shipped with your product. The Documentation DVD is updated regularly and may be more
current than printed documentation. The Documentation DVD package is available as a single unit.
Registered Cisco.com users (Cisco direct customers) can order a Cisco Documentation DVD (product
number DOC-DOCDVD=) from the Ordering tool or Cisco Marketplace.
Cisco Ordering tool:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/partner/ordering/
Cisco Marketplace:
http://www.cisco.com/go/marketplace/
Ordering Documentation
You can find instructions for ordering documentation at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/es_inpck/pdi.htm
You can order Cisco documentation in these ways:
• Registered Cisco.com users (Cisco direct customers) can order Cisco product documentation from
the Ordering tool:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/partner/ordering/
• Nonregistered Cisco.com users can order documentation through a local account representative by
calling Cisco Systems Corporate Headquarters (California, USA) at 408 526-7208 or, elsewhere in
North America, by calling 1 800 553-NETS (6387).
OL-7959-01
Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Release 3.4 Guide
ix
Page 10
Documentation Feedback
Documentation Feedback
You can send comments about technical documentation to bug-doc@cisco.com.
You can submit comments by using the response card (if present) behind the front cover of your
document or by writing to the following address:
Cisco Systems
Attn: Customer Document Ordering
170 West Tasman Drive
San Jose, CA 95134-9883
We appreciate your comments.
Cisco Product Security Overview
Cisco provides a free online Security Vulnerability Policy portal at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/products_security_vulnerability_policy.html
Preface
From this site, you can perform these tasks:
• Report security vulnerabilities in Cisco products.
• Obtain assistance with security incidents that involve Cisco products.
• Register to receive security information from Cisco.
A current list of security advisories and notices for Cisco products is available at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/go/psirt
If you prefer to see advisories and notices as they are updated in real time, you can access a Product
Security Incident Response Team Really Simple Syndication (PSIRT RSS) feed from this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/products_psirt_rss_feed.html
Reporting Security Problems in Cisco Products
Cisco is committed to delivering secure products. We test our products internally before we release them,
and we strive to correct all vulnerabilities quickly. If you think that you might have identified a
vulnerability in a Cisco product, contact PSIRT:
• Emergencies— security-alert@cisco.com
• Nonemergencies— psirt@cisco.com
Tip We encourage you to use Pretty Good Privacy (PGP) or a compatible product to encrypt any sensitive
information that you send to Cisco. PSIRT can work from encrypted information that is compatible with
PGP versions 2.x through 8.x.
Never use a revoked or an expired encryption key. The correct public key to use in your correspondence
with PSIRT is the one that has the most recent creation date in this public key server list:
http://pgp.mit.edu:11371/pks/lookup?search=psirt%40cisco.com&op=index&exact=on
Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Release 3.4 Guide
x
OL-7959-01
Page 11
Preface
In an emergency, you can also reach PSIRT by telephone:
• 1 877 228-7302
• 1 408 525-6532
Obtaining Technical Assistance
For all customers, partners, resellers, and distributors who hold valid Cisco service contracts, Cisco
Technical Support provides 24-hour-a-day, award-winning technical assistance. The Cisco Technical
Support Website on Cisco.com features extensive online support resources. In addition, Cisco Technical
Assistance Center (TAC) engineers provide telephone support. If you do not hold a valid Cisco service
contract, contact your reseller.
Cisco Technical Support Website
The Cisco Technical Support Website provides online documents and tools for troubleshooting and
resolving technical issues with Cisco products and technologies. The website is available 24 hours a day,
365 days a year, at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/techsupport
Obtaining Technical Assistance
Access to all tools on the Cisco Technical Support Website requires a Cisco.com user ID and password.
If you have a valid service contract but do not have a user ID or password, you can register at this URL:
http://tools.cisco.com/RPF/register/register.do
Note Use the Cisco Product Identification (CPI) tool to locate your product serial number before submitting
a web or phone request for service. You can access the CPI tool from the Cisco Technical Support
Website by clicking the Too l s & Re s ou rc e s link under Documentation & Tools. Choose Cisco Product
Identification Tool from the Alphabetical Index drop-down list, or click the Cisco Product
Identification Tool link under Alerts & RMAs. The CPI tool offers three search options: by product ID
or model name; by tree view; or for certain products, by copying and pasting show command output.
Search results show an illustration of your product with the serial number label location highlighted.
Locate the serial number label on your product and record the information before placing a service call.
Submitting a Service Request
Using the online TAC Service Request Tool is the fastest way to open S3 and S4 service requests. (S3
and S4 service requests are those in which your network is minimally impaired or for which you require
product information.) After you describe your situation, the TAC Service Request Tool provides
recommended solutions. If your issue is not resolved using the recommended resources, your service
request is assigned to a Cisco TAC engineer. The TAC Service Request Tool is located at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/techsupport/servicerequest
For S1 or S2 service requests or if you do not have Internet access, contact the Cisco TAC by telephone.
(S1 or S2 service requests are those in which your production network is down or severely degraded.)
Cisco TAC engineers are assigned immediately to S1 and S2 service requests to help keep your business
operations running smoothly.
OL-7959-01
Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Release 3.4 Guide
xi
Page 12

Obtaining Additional Publications and Information
To open a service request by telephone, use one of the following numbers:
Asia-Pacific: +61 2 8446 7411 (Australia: 1 800 805 227)
EMEA: +32 2 704 55 55
USA: 1 800 553-2447
For a complete list of Cisco TAC contacts, go to this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/techsupport/contacts
Definitions of Service Request Severity
To ensure that all service requests are reported in a standard format, Cisco has established severity
definitions.
Severity 1 (S1)—Your network is “down,” or there is a critical impact to your business operations. You
and Cisco will commit all necessary resources around the clock to resolve the situation.
Severity 2 (S2)—Operation of an existing network is severely degraded, or significant aspects of your
business operation are negatively affected by inadequate performance of Cisco products. You and Cisco
will commit full-time resources during normal business hours to resolve the situation.
Severity 3 (S3)—Operational performance of your network is impaired, but most business operations
remain functional. You and Cisco will commit resources during normal business hours to restore service
to satisfactory levels.
Severity 4 (S4)—You require information or assistance with Cisco product capabilities, installation, or
configuration. There is little or no effect on your business operations.
Preface
Obtaining Additional Publications and Information
Information about Cisco products, technologies, and network solutions is available from various online
and printed sources.
• Cisco Marketplace provides a variety of Cisco books, reference guides, and logo merchandise. Visit
Cisco Marketplace, the company store, at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/go/marketplace/
• Cisco Press publishes a wide range of general networking, training and certification titles. Both new
and experienced users will benefit from these publications. For current Cisco Press titles and other
information, go to Cisco Press at this URL:
http://www.ciscopress.com
• Pack et magazine is the Cisco Systems technical user magazine for maximizing Internet and
networking investments. Each quarter, Packet delivers coverage of the latest industry trends,
technology breakthroughs, and Cisco products and solutions, as well as network deployment and
troubleshooting tips, configuration examples, customer case studies, certification and training
information, and links to scores of in-depth online resources. You can access Packet magazine at
this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/packet
Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Release 3.4 Guide
xii
OL-7959-01
Page 13
Preface
• iQ Magazine is the quarterly publication from Cisco Systems designed to help growing companies
learn how they can use technology to increase revenue, streamline their business, and expand
services. The publication identifies the challenges facing these companies and the technologies to
help solve them, using real-world case studies and business strategies to help readers make sound
technology investment decisions. You can access iQ Magazine at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/go/iqmagazine
• Internet Protocol Journal is a quarterly journal published by Cisco Systems for engineering
professionals involved in designing, developing, and operating public and private internets and
intranets. You can access the Internet Protocol Journal at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/ipj
• World-class networking training is available from Cisco. You can view current offerings at
this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/learning/index.html
Summary History of Document Changes
Summary History of Document Changes
Table 4 describes the document changes made after the initial release of the Cisco SRST SNMP MIB
Release 3.4 Guide.
Table 4 Summary History of Document Changes
Document Number and Change
Subject
Date Change Summary
— OL-7959-01, October 26, 2005 Initial release
OL-7959-01
Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Release 3.4 Guide
xiii
Page 14

Summary History of Document Changes
Preface
Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Release 3.4 Guide
xiv
OL-7959-01
Page 15

CHA P TER
1
Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Support
Survivable Remote Site Telephony (SRST) Cisco IOS feature is used for the remote office routers that
support from 24 to 720 users in a centralized CallManager processing environment, to back up IP phone
calls and provide 911 emergency access by the public switched telephone network (PSTN). Any SRST
user can leverage SRST MIBs for better management with Simple Network Management Protocol
(SNMP) support.
Feature History of the Cisco SRST MIB Feature
Release Modification
12.4(4)T This feature was introduced on the 12.4(4)T
Finding Support Information for Platforms and Cisco IOS Software Images
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco IOS software image
support. Access Cisco Feature Navigator at http://www.cisco.com/go/fn. You must have an account on
Cisco.com. If you do not have an account or have forgotten your username or password, click Cancel at
the login dialog box and follow the instructions that appear.
Overview
OL-7959-01
The SRST 3.4 component of Cisco IOS is not capable of participating in network management using
SNMP. The SRST 3.4 effort is to make these components SNMP visible and provide necessary network
management functions. This Cisco IOS feature can be used in the deployed customer scenarios that use
SNMP managers. The Cisco IOS SNMP Agent can provide the following features for the SRST modules:
• Generate notifications/traps for various functionality failures
• Provide objects that help monitor performance/load of some of the key features
• Provide detailed configurations for help in fault isolation.
• Provide the active registrations of IP phones and Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) phones
• Publish statistics on Ephone lines and SIP phone lines
• Provide ability to mask/unmask notification
SRST 3.4 does not have product-specific network management capabilities. The SRST MIB addresses
SNMP Management Information Base (MIB) development for generating asynchronous exception
notifications/traps, displaying configurations, and monitoring performance for IP telephony
management purposes.
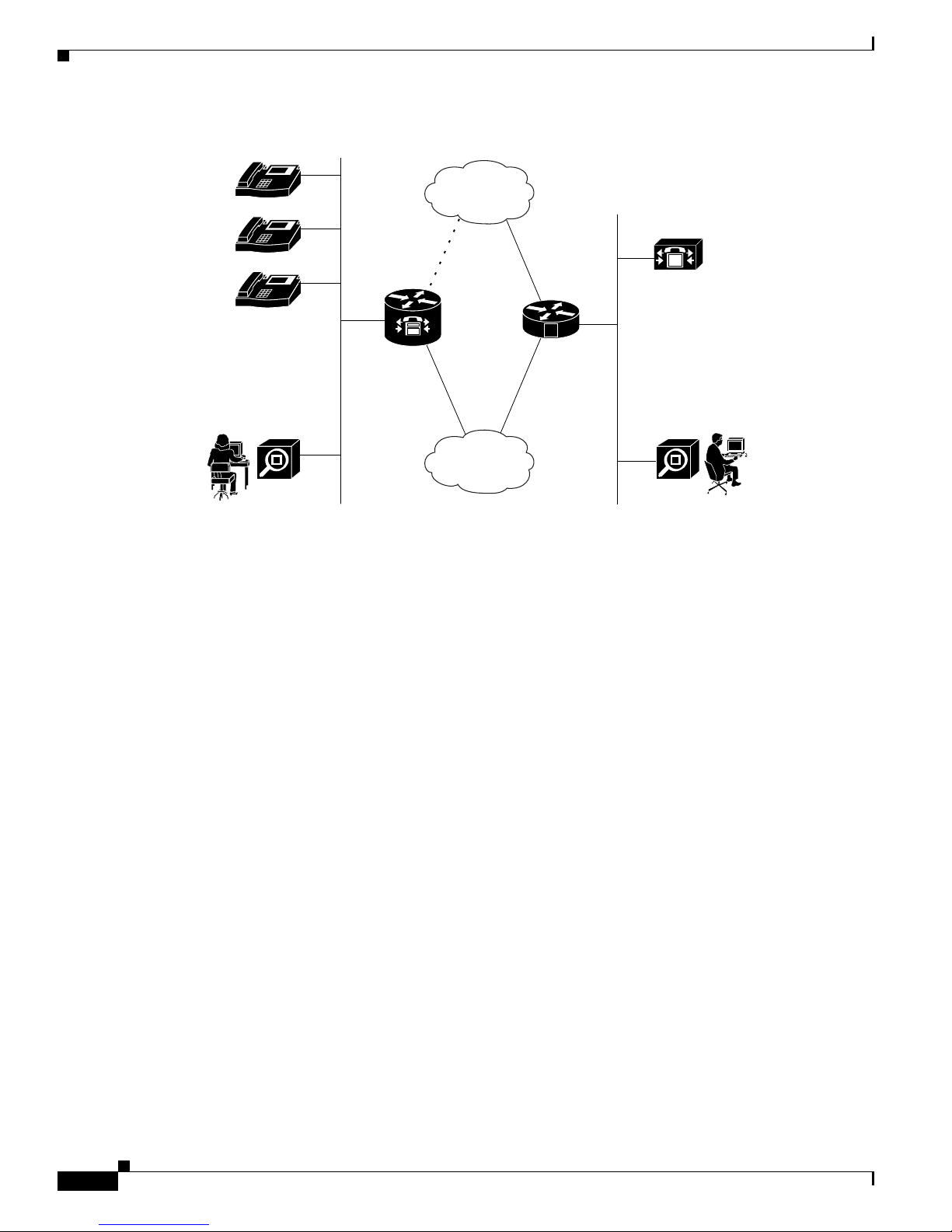
The SRST feature provides emergency back up IP phone call capabilities, as shown in Figure 1-1.
Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Release 3.4 Guide
1-1
Page 16
Overview
Chapter 1 Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Support
Figure 1-1 SRST Router Deployment with Network Management Components
IP
IP
IP
Local IP
phone cluster
SNMP
network
manager
Broken WAN
Broken WAN
Cisco
SRST
router
line
line
WAN
PSTN
V
Voice
gateway
M
Cisco
call manager
SNMP
network
manager
127128
SRST provides backup redundancy for broadband deployment of IP telephony to small branch offices.
It can be used if Cisco CallManager is no longer in service due to a loss of WAN connectivity. SRST
continues to provide basic call processing and IP telephony service to phones that fall back to SRST.
The CISCO-SRST-MIB defines managed objects that pertain to SRST, SIP Registrar, and SIP phones.
The CISCO-SRST-MIB has dependency on existing Cisco IOS MIBs, especially on the
CISCO-CCME-MIB and the CISCO-VOICE-DIAL-CONTROL-MIB.
All of these MIBs are accessible from SNMP management software running on external SNMP
managers.
Design of the CISCO-SRST-MIB
The CISCO-SRST-MIB enables you to display configurations and monitor and send traps and
asynchronous notifications to the SNMP management applications.
The CISCO-SRST-MIB approach offers the following advantages over the CLI command approach:
• A more efficient use of network bandwidth
• Greater interoperability among vendors because standard SNMP protocols are used
The following paragraphs describe the CISCO-SRST-MIB structure.
Structure
The Structure of Management Information (SMI) is represented conceptually by a tree hierarchy.
Branches along the tree have short text strings and integers to identify them. Text strings describe object
names, and integers allow computer software to encode compact representations of the names.
The CISCO-SRST-MIB is part of the Cisco management group, which is part of
private.enterprise.cisco.ciscoMgmt.
Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Release 3.4 Guide
1-2
OL-7959-01
Page 17

Chapter 1 Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Support
The CISCO-SRST-MIB structure is further divided into the following groups:
SRST MIB Groups
ciscoSrstMIBNotifications
ciscoSrstMIBObjects
ciscoSrstMIBConformance
The CISCO-SRST-MIB structure further is divided into the following subgroups:
SRST MIB object groups
csrstConf
csrstNotifInfo
csrstSipConf
csrstActiveStats
csrstMIBNotifs
Overview
CISCO-SRST-MIB, which is uniquely identified by the number 441
Therefore the ciscoSrstMIB is1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441
Objects in the CISCO-SRST-MIB can be identified by either of the following methods.
• The object identifier is 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441<SRST MIB-variable>
• The object name is iso(1).org(3).dod(6).internet(1).private(4).enterprise(1).cisco(9).ciscoMgmt(9)
.ciscoSrstMIB(441).<MIB-variable>
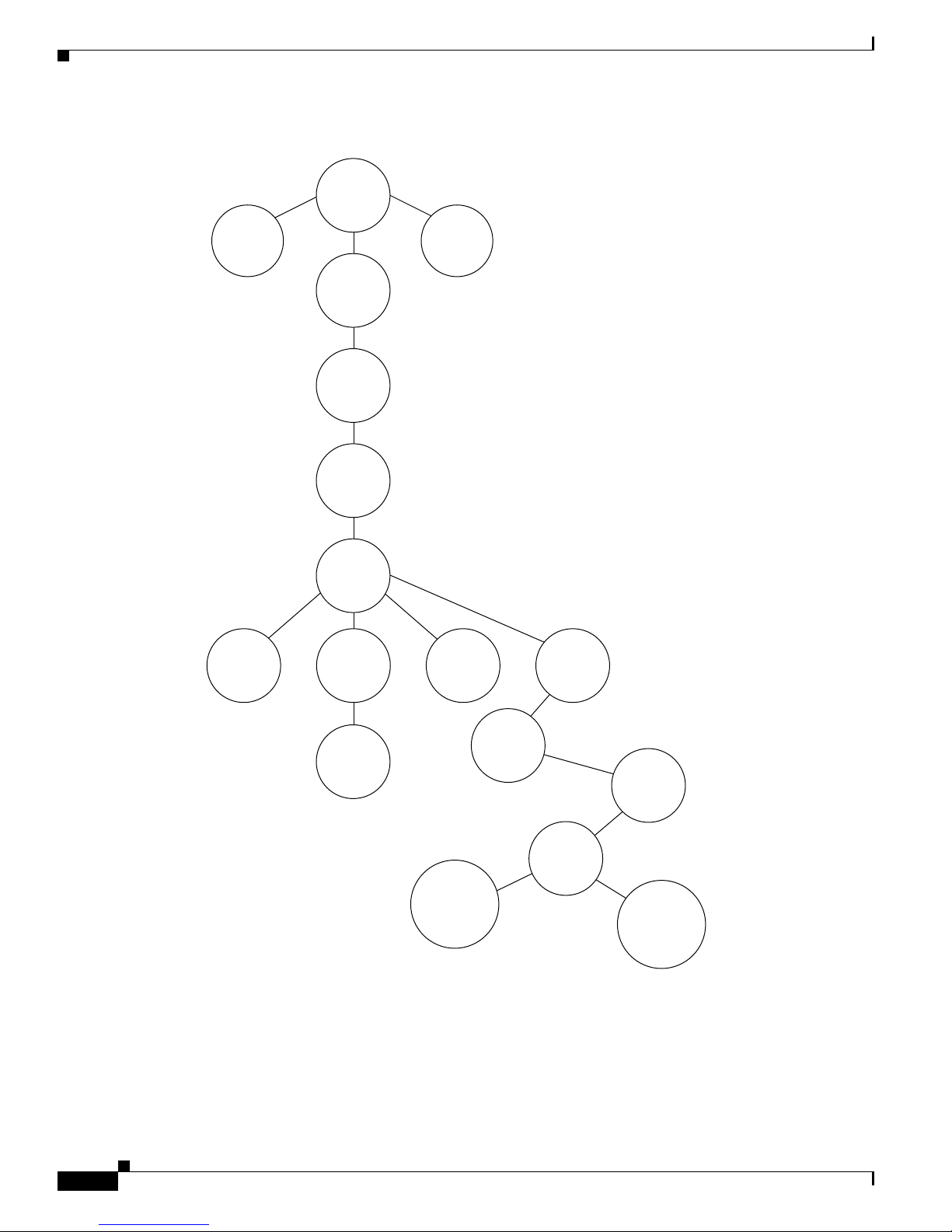
Figure 1-2 shows the position of the CISCO-SRST-MIB in the Internet MIB hierarchy.
OL-7959-01
Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Release 3.4 Guide
1-3
Page 18
Overview
Chapter 1 Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Support
Figure 1-2 CISCO-SRST-MIB Tree Structure
unnamed
CCITT
0
directory
1
ISO
1
org
3
dod
6
Internet
1
mgmt
2
joint
ISO/CCITT
2
experimental
3
private
4
CISCO-SRST-MIB Features
The SRST 3.4 features that are supported by the CISCO-SRST-MIB are:
• SRST configuration
• Ephone registrations
Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Release 3.4 Guide
1-4
mib
1
enterprise
CISCO-SRST-
MIB
441
1
ciscoMgmt
9
cisco
9
CISCO-CCME-
MIB
439
127130
OL-7959-01
Page 19
Chapter 1 Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Support
• Ephone directory number (DN) (multiple lines per phone, multiple-line appearance per phone)
• Huntstop (alias, SIP number list, between DNs)
• Class of Restriction (COR)
• Translation Rule
• Music on Hold (MoH) (flash, multicast)
• Call-forward
• Phone number alias
• Voicemail number
• Dial-plan pattern
• User-locale information
• Secondary-dial tone
• Ringing timeout
• Date format
• Dual-line mode
Overview
• Customized system message
• Consultative call transfer
• Interactive Voice Response (IVR) Application
Table 1-1 lists the objects provided in the CISCO-SRST-MIB. Tabl e 1-2 lists the notifications/traps
provided in the CISCO-SRST-MIB.
Table 1-1 Cisco-SRST-MIB Object Groups
No. Object Name Comments
csrstConf
1. csrstEnabled Indicates if SRST support is enabled or disabled
2. csrstVersion Cisco SRST version
3. csrstIPAddressType IP address type governing the address type format for objects in this MIB
4. csrstIPAddress IP address for the router to receive messages from IP phones
5. csrstPortNumber Indicates the TCP port number to use for SCCP and is range limited
6. csrstMaxConferences Maximum number of simultaneous three-party conference calls configured
7. csrstMaxEphones Maximum number of Cisco IP phones configured on the SRST router
8. csrstMaxDN Maximum number of IP phone extensions (Ephone-DNs) configured
9. csrstSipPhoneUnRegThreshold Indicates a threshold for the number of SIP phones unregistered to SRST
10. csrstCallFwdNoAnswer Cisco SRST call forwarding number when a Cisco IP phone is not answered
11. csrstCallFwdNoAnswerTo Timeout, in seconds, if a Cisco IP phone is not answered
12. csrstCallFwdBusy Cisco SRST call forwarding number when a Cisco IP phone is busy
13. csrstMohFilename Music-on-Hold is enabled or disabled
14. csrstMohMulticastAddrType Internet address type for the address type format for objects in this MIB
15. csrstMohMulticastAddr Indicates the Cisco SRST Music-On-Hold multicast IP address
OL-7959-01
Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Release 3.4 Guide
1-5
Page 20

Chapter 1 Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Support
Overview
Table 1-1 Cisco-SRST-MIB Object Groups (continued)
No. Object Name Comments
16. csrstMohMulticastPort Indicates Music-on-Hold multicast TCP port which is range limited
17. csrstVoiceMailNumber Voice mail number that is speed-dialed when the messages button is pressed
18. csrstSystemMessagePrimary System static text message displayed on Cisco IP phone during fallback
19. csrstSystemMessageSecondary System message displayed on phones not supporting static text message
20. csrstScriptName SRST session-level IVR application script
21. csrstSecondaryDialTone SRST secondary dial tone digits
22. csrstTransferSystem SRST call transfer method using the ITU-T H.450.2 standard
23. csrstUserLocaleInfo SRST language for displays on Cisco IP phone by country
24. csrstDateFormat Date display format on Cisco IP phones in the SRST system
25. csrstTimeFormat Time display format on Cisco IP phones in the SRST system
26. csrstInterdigitTo SRST interdigit timeout duration for Cisco IP phones
27. csrstBusyTo Time before disconnect when destination is busy, without call-forwarding
28. csrstAlertTo Time before disconnect when call is not answered, without call-forwarding
29. csrstXlateCalledNumber Indicates the tag used to translate a called number on the SRST router
30. csrstXlateCallingNumber Indicates the tag used to translate a calling number on the SRST router
csrstAliasTable
31. csrstAliasIndex Table index
32. csrstAliasTag A number indicating an alias pattern configured on this SRST router
33. csrstAliasNumPattern Indicates the pattern to match the incoming telephone number
34. csrstAliasAltNumber Alternate number to route incoming calls to match the number pattern
35. csrstAliasPreference Indicates the preference value of the associated dial-peer
36. csrstAliasHuntStopEnabled Hunt stops after trying the alternate number according to the alias pattern
csrstAccessCodeTable
37. csrstAccessCodeType Type of trunk line to which the access-code is applied
38. csrstAccessCode Access-code applied to the corresponding trunk line by creating dial-peers
39. csrstAccessCodeDIDEnabled Indicates the direct-inward-dial on a POTS dial-peer is enabled or disabled
csrstLimitDNTable
40. csrstLimitDNType Type of IP phone to which the limit-dn is applied
41. csrstLimitDN Maximum number of directory numbers available to each type of IP phone
42. csrstNotificationEnabled Indicates if this system produces the SRST notifications
csrstNotifInfoGroup
43. csrstSysNotifSeverity Severity of the alarm condition, for the most recent SNMP notification
44. csrstSysNotifReason Failure cause of the alarm condition for the most recent system notification
csrstActiveStats
45. csrstState Current state of Cisco SRST feature on this router
46. csrstSipPhoneCurrentRegistered Total number of SIP phones currently registered to the SRST router
Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Release 3.4 Guide
1-6
OL-7959-01
Page 21

Chapter 1 Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Support
Overview
Table 1-1 Cisco-SRST-MIB Object Groups (continued)
No. Object Name Comments
47. csrstSipCallLegs Total number of SIP call legs through the SRST router since activation
48. csrstTotalUpTime Total number of minutes that router is active in SRST mode
csrstSipConf
49. csrstSipRegSrvExpMax Max expiration time for the SIP registrar server to time out on a registration
50. csrstSipRegSrvExpMin Min. expiration time for the SIP registrar server to time out on a registration
51. csrstSipIp2IpGlobalEnabled Indicates if VoIP calls are redirected IP to IP globally
52. csrstSipSend300MultSupport Indicates if the redirect contact order is best or longest match
csrstSipVoRegPoolTable
53. csrstSipVoRegPoolTag Identifier tag configured for a voice register pool entry
54. csrstSipNetId Network identification information of the SIP voice register pool
55. csrstSipVoRegPoolIpAddrType IP address type for the address format of InetAddress objects in this MIB
56. csrstSipNetMask IP subnet configured for the SIP voice register pool
57. csrstSipProxySrvIpAddr IP address of the proxy server configured for the SIP voice register pool
58. csrstSipProxySrvPref Preference order for creating the VoIP dial-peers in the voice register pool
59. csrstSipProxySrvMonitor Configured proxy server monitoring protocol for the SIP voice register pool
60. csrstSipProxySrvAltIpAddr Alternate IP address monitored other than the proxy configured
61. csrstSipDefaultPreference Default preference of the proxy dial-peers created in the voice register pool
62. csrstSipVoRegPoolAppl Application for the SIP dial-peers configured under voice register pool
csrstSipVoRegNumberListTable
63. csrstSipVoRegNumberListIndex Table index
64. csrstSipVoRegNumberListTag Index of the number list configured for the voice register pool
65. csrstSipVoRegNumberPattern Number pattern the registrar permits to handle the register message
66. csrstSipVoRegNumberPref Number pattern preference configured for the voice register pool
67. csrstSipVoRegNumberHuntstopEnabled Huntstop for the number pattern configured for the voice register pool
csrstSipEndpointTable
68. csrstSipEndpointTag Number that indicates a SIP endpoint configured on this SRST router
69. csrstSipVoRegPoolEdptTag Voice register pool tag from which the SIP endpoint (dial-peer) is created
70. csrstSipEndpointIpAddrType IP address for the address type for InetAddress objects in this MIB
71. csrstSipEndpointIpAddress SIP endpoint IP address configured on this router
72. csrstSipEndpointDN SIP phone’s DN or line number assigned to the SIP endpoint
Table 1-2 CISCO-SRST-MIB Summary List of Notifications/Traps
No. Object Name Comments
73. csrstStateChange An SRST up or down state change notification is generated.
74. csrstFailNotif Failure notification generated for a catastrophic failure.
OL-7959-01
Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Release 3.4 Guide
1-7
Page 22

Chapter 1 Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Support
Overview
Table 1-2 CISCO-SRST-MIB Summary List of Notifications/Traps (continued)
No. Object Name Comments
75. csrstSipPhoneUnRegThresholdExceed Notification generated when the unregistration threshold is exceeded.
76. csrstSipPhoneRegFailed Notification generated when the SIP phone fails to register.
77. csrstConferenceFailed Notification generated when maximum number of conferences is exceeded.
Common Tables
The following tables are common to both the CCME and SRST MIBs:
• ccmeCorConfTable
• ccmeDialplanPatternTable
• ccmeTransferPatternTable
• ccmeEphoneBtnDNAssocConfTable
• ccmeEphoneActTable
• ccmeEphoneDnChStatsHistoryTable
• ccmeEphoneConfTable
Common Notifications/Traps
The following notifications/traps are common to both the CCME and SRST MIBs:
• ccmeEphoneUnRegistrationThresholdExceed
• ccmeEPhoneRegFailed
• ccmeEPhoneDeceased
Common Objects
The following objects are common to both the CCME and SRST MIBs:
• ccmeEphoneUnRegistrationThreshold
• ccmeEphoneTot
• ccmeEphoneTotalRegistered
• ccmeEphoneCallLegs
Common Tables
The tables listed in Table 1- 3 are common to both the CCME and SRST MIBs.
Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Release 3.4 Guide
1-8
OL-7959-01
Page 23

Chapter 1 Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Support
Table 1-3 Common Tables or Elements for the CCME and SRST MIBs
Common Table or Element Table or Element Scope of Objects
Common COR table COR table
This SRST COR feature is in the common
ccmeCorTableIndex ccme, srst-sccp, and srst-sip mode
COR table with scope set for srstSccp
ccmeCorTag ccme, srst-sccp, and srst-sip mode
ccmeCorListName ccme, srst-sccp, and srst-sip mode
ccmeCorScope ccme, srst-sccp, and srst-sip mode
ccmeCorDirection srst-sccp and srst-sip
ccmeCorStartingNumber srst-sccp and srst-sip
ccmeCorEndingNumber Srst-sccp and srst-sip
ccmeCorVoiceRegPoolNumber Applies only to srst-sip mode
ccmeCorListDefaultEnabled srst-sccp and srst-sip
Overview
Common Dial Plan table Dial Plan table
This SRST dial plan feature is in the
common Dial Plan table
ccmeDialplanPatternTag ccme and srst mode
ccmeDialplanPattern ccme and srst mode
ccmeDialplanExtLength ccme and srst mode
ccmeDialplanExtPattern ccme and srst mode
ccmeDialplanAllowRegiEnabled ccme and srst mode
Common Transfer Plan table Transfer Plan table
This SRST Transfer plan feature is in the
common Transfer Plan table
ccmeTransferPattern ccme and srst mode
ccmeTransferPatternType ccme and srst mode
Common ccmeEphoneConfTable ccmeEphoneConfTable
ccmeEphoneTag ccme and srst mode
ccmeEphoneIpAddressType ccme and srst mode
ccmeEphoneIpAddress ccme and srst mode
ccmeEphoneMacAddress ccme and srst mode
ccmeEphoneModel ccme
ccmeEphoneUsername ccme
ccmeEphoneKeepAlive ccme
ccmeEphoneAutoLineOut ccme
OL-7959-01
Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Release 3.4 Guide
1-9
Page 24

Chapter 1 Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Support
Overview
Table 1-3 Common Tables or Elements for the CCME and SRST MIBs (continued)
Common Table or Element Table or Element Scope of Objects
ccmeEphonePagingDn ccme
ccmeEphoneAddon ccme
ccmeEphoneTemplate ccme
ccmeEphonePagingPolicy ccme
ccmeEphoneKeyPhone ccme
ccmeEphoneAutoLineInEnabled ccme
ccmeEphoneAftHrsBlkExmptEnabled ccme
ccmeEphoneNightBellSvcEnabled ccme
ccmeEphoneKeepConfEnabled ccme
Common ccmeEphoneButton Association
tables
ccmeEphoneBtnDNAssocConfTable
ccmeEphoneButtonNumber ccme and srst mode
ccmeEphoneOverlayDN ccme and srst mode
Common Ephone active table
Implemented in CCME MIB—-this table is
for displaying activities of Ephones
ccmeEphoneActTable Common Ephone active table
contents apply to ccme and srst mode
ccmeEphoneDevicename
ccmeEphoneRegState
ccmeEphoneActiveDN
ccmeEphoneActivityStatus
ccmeEphoneKeepAliveCnt
ccmeEphonePendingReset
ccmeEphoneRegTime
ccmeEphoneCurrentFirmwareRev
ccmeEphonePreviousFirmwareRev
ccmeEphoneLastError
ccmeEphoneObservedType
ccmeEphoneLoginStatus
ccmeEphoneDnDStatus
ccmeEphoneDebugStatus
ccmeEphoneMediaActive
ccmeEphoneTAPIClient
ccmeEphoneMediaCapability
Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Release 3.4 Guide
1-10
OL-7959-01
Page 25

Chapter 1 Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Support
Overview
Table 1-3 Common Tables or Elements for the CCME and SRST MIBs (continued)
Common Table or Element Table or Element Scope of Objects
Ephone-DN history stats ccmeEphoneDnChStatsHistoryTable This table contents apply to ccme and
srst
ccmeEphoneDnChNum
ccmeEphoneDnChIncoming
ccmeEphoneDnChIncoming
ccmeEphoneDnChOutbound
ccmeEphoneDnChOutAnswered
ccmeEphoneDnChOutBusy
ccmeEphoneDnChDiscAtConn
ccmeEphoneDnChDiscAtAlert
ccmeEphoneDnChDiscAtHold
ccmeEphoneDnChDiscAtRing
ccmeEphoneDnChDiscAtCauseNearEnd
ccmeEphoneDnChDiscCauseFarEnd
Common Ephone statistics ccmeActiveStats
Total number of Ephones present ccmeEphoneTot ccme and srst
This refers to total number of Skinny
EphoneTotalRegistered ccme and srst
phones registered to SRST
This refers to the total number of Ephone
EphoneCallLegs ccme and srst
call legs routed through SRST
ccmeEphoneTotKeyPhConfigured ccme
ccmeEphoneTotKeyPhRegistered ccme
Trap EphoneUnRegistrationThresholdExceed ccme and srst mode
Trap EphoneFailRegistration ccme and srst mode
Trap ccmeEphoneDeceased ccme and srst mode
Read/Write object EphoneUnRegistrationThreshold ccme and srst mode
Dependencies of the SRST MIB
When using an SRST router, you can get information regarding Ephones, Ephone-dns, and related
statistics from the CCME MIB. For example:
• To retrieve the total number of SCCP phones registered (EphoneTotalRegistered) to the SRST
router, get the total number of SCCP registered from the CCME MIB.
OL-7959-01
Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Release 3.4 Guide
1-11
Page 26

Limitations
• To retrieve the total number of SCCP call legs (EphoneCallLegs) accumulated on the SRST router,
get the total number of SCCP call legs from the CCME MIB.
• To monitor the SCCP phone activities, retrieve the ccmeEphoneActTable from the CCME MIB.
Limitations
Be aware of the following design limitations when implementing the CISCO-SRST-MIB:
• Configuring objects is not provided through SNMP.
• No password or encrypted objects are provided.
• Objects that are not part of the CISCO-SRST-MIB are out of the scope of this MIB.
• SIP phone details that cannot be seen by underlying Cisco IOS SRST layers, such as the Ethernet
address, are not provided.
Performance Impact
Chapter 1 Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Support
The performance characteristics of the SRST SNMP module vary significantly depending on how often
bulk data is requested by the SNMP managers.
SNMP bulk data can consume significant CPU and DRAM resources, and even network bandwidth. We
recommend that management stations are to minimize the statistical sampling intervals as much as
possible. Even though CISCO-SRST-MIB objects are grouped to reduce the unnecessary bulk data that
can be fetched at a burst, the Cisco IOS SNMP agent does not enforce the data volume or the frequency
at which SNMP managers make requests to the SNMP agent.
To reduce performance impact, the SRST gateway managers can use the traps provided by these MIBs
by using asynchronous fault notification and traps to help isolate a fault.
There are few leaf objects, and they are light weighted and important (specified in active Group of the
MIBs). They can be sampled at relatively short intervals, which would help gather the load on the
CISCO-SRST-MIB components.
The Cisco IOS software supports SNMP versions 1, 2c, and 3 (SNMPv1, SNMPv2c, and SNMPv3). The
SRST MIB is compliant with SNMPv2c and SNMPv3.
External SNMP managers are required; they issue SNMP queries and also accept SNMP notifications
and traps. The SNMP managers include tools, such as basic Scotty command line tools, HP-OpenView,
SunNet managers, IBM Netview, Tivoli, NetIQ, and so on.
To provide complete monitoring solutions, the SNMP managers can interface with existing Cisco IOS
MIBs that address individual components and build a “schema” (or view) that helps monitor objects that
suit their configuration or needs. For SRST related scenarios, the
CISCO-VOICE-DIAL-CONTROL-MIB, various hardware interface MIBs, and the CISCO-CCM-MIB
are available.
Prerequisites
The following must be configured for the CISCO-SRST-MIB to function:
• Cisco CallManager Fallback must be configured on your system.
Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Release 3.4 Guide
1-12
OL-7959-01
Page 27

Chapter 1 Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Support
Prerequisites
• An SNMP manager must be available on the network. For more information on configuring an
SNMP server for use with a MIB, refer to the “Configuring SNMP Support” chapter of the Cisco
IOS Configuration Fundamentals and Network Management Configuration Guide, Release 12.3. at
the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/software/ios122/122cgcr/ffun_c/fcfprt3/fcf014.htm
• An SNMP Agent must be configured for the router on which the CISCO-SRST-MIB feature is to be
used. Refer to the “Enabling the SNMP Agent” section in this document for more information.
• Ensure the traps are defined in the NMS software.
• Ensure the alarm events are not put into “log only” mode and come up as an Alarm.
Supported Platforms for SRST 3.4
The SRST 3.4 feature is supported on the platforms listed in the following sections.
Cisco Voice Gateways
Cisco IP Phones
The SRST 3.4 feature is supported on the following voice gateways:
• Cisco IAD24xx
• Cisco 17xx: 1751V and 1760
• Cisco 2600XM: 261x XM, 262x XM, 265x XM, and 2691
• Cisco 3600: 3640, 3640A, and 3660
• Cisco 37xx: 3725 and 3745
• Catalyst 4500 with AGM
• Cisco 7200
The SRST 3.4 feature is supported on the following Cisco IP phones:
• Cisco IP Phone 7905 and 7905G
• Cisco IP Phone 7910G
• Cisco IP Phone 7902G
• Cisco IP Phone 7912G
• Cisco IP Expansion Module 7914
• Cisco IP Conference Station 7935
• Cisco IP Phone 7940 and 7940G
• Cisco IP Phone 7960 and 7960G
• Cisco VG248 Analog Phone Gateway Version 1.2(1) and higher
• Cisco VG224 Analog phone gateway
OL-7959-01
Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Release 3.4 Guide
1-13
Page 28

Chapter 1 Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Support
Configuration
Licenses
The following licences are required for SRST operation:
• A base SRST feature license
• A phone seat license for each phone
Depending on the platform used, the maximum number of ePhone licenses supported ranges from 24 to
240.
Configuration
To configure the SRST/CCME MIB feature, you should understanding the following concept.
Using SNMP and MIBs to Extract CISCO-SRST-MIB Information
SNMP has historically been used to collect network information. SNMP permits retrieval of critical
information from network elements such as routers, switches, and workstations. The CISCO-SRST-MIB
feature uses SNMP to gather remote site status information.
The CISCO-SRST-MIB feature allows remote site status data for the managed devices on your system
to be retrieved by SNMP. You can specify retrieval of CISCO-SRST-MIB information from a managed
device (for example, a router) either by entering commands on that managed device or by entering SNMP
commands from the NMS workstation to configure the router by the MIB. If the CISCO-SRST-MIB
information is configured from the network management system (NMS) workstation, no access to the
router is required and all configuration can be performed by SNMP. The CISCO-SRST-MIB request for
information is sent from an NMS workstation by SNMP to the router and is retrieved from the router.
This information can then be stored or viewed, thus allowing CISCO-SRST-MIB information to be easily
accessed and transported across a multivendor programming environment.
How to Configure the CISCO-SRST-MIB
This section contains the following procedures:
• Enabling the SNMP Agent, page 1-14 (required)
• Verifying the Enabling of the SNMP Agent, page 1-15 (optional)
Enabling the SNMP Agent
The SNMP Agent for the SRST/CCME MIB is disabled by default. To enable the SNMP agent for the
CISCO-SRST-MIB, perform the following steps:
Command or Action Purpose
Step 1
Step 2
Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Release 3.4 Guide
1-14
Prompt# telnet xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
Router# enable
Telnets to the router identified by the specified IP address
(represented as xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx).
Enters the enable mode.
OL-7959-01
Page 29

Chapter 1 Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Support
Command or Action Purpose
Step 3
Step 4
Step 5
Step 6
Step 7
Step 8
Router# show running-config
Router# config terminal
Router(config)# snmp-server
community xxxxxx RO
Router(config)# snmp-server
community xxxxxx RW
Router(config)# exit
Router# write memory
Verifying the Enabling of the SNMP Agent
Configuration
Displays the running configuration to determine if an SNMP agent
is already running. If no SNMP information is displayed, continue
with Step 4. If any SNMP information is displayed, you can modify
the information or change it as needed.
Enters global configuration mode.
Enables the read-only (RO) community string, where xxxxxx
represents the read-only community string
Enables the read-write (RW) community string, where xxxxxx
represents the read-write community string.
Exits global configuration mode and returns you to privileged
EXEC mode.
Writes the modified configuration to nonvolatile memory
(NVRAM), permanently saving the settings.
To verify that the SNMP agent has been enabled on a given network device, perform the following steps:
Step 1 Telnet to the target device:
Router# telnet xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
where xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx represents the IP address of the target device.
Step 2 Establish the enable mode on the device:
Router# enable
Step 3 Display the running configuration on the device and examine the output for any displayed SNMP
information:
Router# show running-config
...
...
snmp-server community public RO
snmp-server community private RW
Any “snmp-server” statement appearing in the output that takes the form shown above verifies that
SNMP has been enabled on the specified device.
Configuration Examples
Configuration examples are provided in the following sections:
• Complete SRST Configuration Example, page 1-16
• Configuring SRST Mode, page 1-19
• Enabling Traps in SRST Mode, page 1-21
• Monitoring SCCP Phone Statistics, page 1-22
• Retrieving SIP Phone Registrations, page 1-23
OL-7959-01
Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Release 3.4 Guide
1-15
Page 30

Configuration
Complete SRST Configuration Example
The following is a complete configuration example for SRST. It is provided to give you an example of
the commands used when configuring SRST.
SRST-Router#sh run
•
•
•
!
hostname SRST-Router
!
•
•
•
ip subnet-zero
ip cef
!
!
voice service voip
sip
registrar server expires max 600 min 60
!
!
voice class codec 1
codec preference 1 g711ulaw
codec preference 2 g729br8
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
voice register pool 1
id network 1.4.196.0 mask 255.255.255.0
proxy 1.4.196.1 monitor probe rtr
!
voice register pool 3
id network 1.4.4.1 mask 255.255.255.0
number 2 2020 preference 2
number 4 4040 preference 4
alias 2 2211 to 2222 preference 2
alias 4 4411 to 4444 preference 4
!
voice register pool 4
id network 1.4.199.1 mask 255.255.255.255
proxy 1.4.100.1
!
voice register pool 7
id mac 0002.0002.0002
number 3 3030 preference 3
number 10 10 preference 10
cor incoming eng 1 1000
cor incoming eng 3 3000
cor outgoing eng 4 4000
proxy 1.4.196.7 monitor probe rtr
alias 1 1012 to 1013 preference 2
alias 5 5012 to 5013 preference 4
Chapter 1 Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Support
Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Release 3.4 Guide
1-16
OL-7959-01
Page 31

Chapter 1 Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Support
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
interface FastEthernet0/0
ip address 1.4.196.1 255.255.0.0
no ip route-cache cef
no ip route-cache
no ip mroute-cache
duplex auto
speed auto
no cdp enable
!
interface FastEthernet0/1
ip address 3.0.0.1 255.255.255.0
no ip mroute-cache
duplex auto
speed auto
no keepalive
no cdp enable
!
interface Serial0/2:1
ip address 12.12.12.1 255.255.255.0
!
ip classless
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 1.4.0.1
ip route 4.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 FastEthernet0/0
ip route 223.255.254.0 255.255.255.0 1.4.0.1
ip route 223.255.254.254 255.255.255.255 FastEthernet0/0
!
no ip http server
!
snmp-server community public RW
snmp-server community test RW
snmp-server contact helloall
snmp-server host 1.4.198.78 SNMP
snmp-server host 1.4.198.78 SNMPv2c
no cdp run
arp 3.3.3.3 0000.0000.001a ARPA
!
!
tftp-server flash:P0S30202.bin
tftp-server flash:SIP000F23AD6FBC.cnf
tftp-server flash:SIPDefault.cnf
tftp-server flash:OS79XX.TXT
tftp-server flash:P0S3-04-1-00.bin
tftp-server flash:P00305000300.bin
!
control-plane
!
!
!
voice-port 0/3:2
no ignore rx-c-bit
no ignore rx-d-bit
condition tx-a-bit off
condition tx-b-bit invert
condition tx-c-bit on
!
voice-port 0/3:3
Configuration
OL-7959-01
Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Release 3.4 Guide
1-17
Page 32

Configuration
Chapter 1 Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Support
!
voice-port 4/0/0
!
voice-port 4/0/1
!
!
!
!
!
dial-peer cor custom
name test_shanmukh_member
name liz
!
!
dial-peer cor list test
!
dial-peer cor list name
!
dial-peer cor list eng
member liz
!
dial-peer cor list hr
!
!
dial-peer voice 2001 pots
destination-pattern 2001
!
dial-peer voice 9002 voip
corlist incoming eng
destination-pattern ....
session target ipv4:1.4.196.77
dtmf-relay h245-alphanumeric
ip qos dscp cs5 media
!
dial-peer voice 9003 voip
destination-pattern ....
session target ipv4:1.4.196.78
dtmf-relay h245-alphanumeric
ip qos dscp cs5 media
!
dial-peer voice 9001 voip
!
gateway
timer receive-rtp 1200
security password 1511021F0725 level endpoint
!
sip-ua
sip-server ipv4:1.4.196.1
!
!
call-manager-fallback
max-conferences 8 gain -6
limit-dn 7960 20
ip source-address 1.4.196.1 port 2000
max-ephones 10
max-dn 10
dialplan-pattern 2 2222 extension-length 2 extension-pattern 20 no-reg
dialplan-pattern 4 4444 extension-length 4 extension-pattern 4040
dialplan-pattern 5 5555 extension-length 2 extension-pattern 50
transfer-pattern 111 blind
transfer-pattern 202
transfer-pattern 301 blind
access-code bri 333 direct-inward-dial
access-code pri 44 direct-inward-dial
Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Release 3.4 Guide
1-18
OL-7959-01
Page 33

Chapter 1 Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Support
alias 1 1234 to 9988 huntstop
alias 2 2222 to 5552222
alias 4 4444 to 5554444
alias 8 8888 to 5558888
time-format 24
date-format yy-mm-dd
cor incoming eng default
cor incoming eng 1 2000
cor incoming eng 2 2000 - 2010
cor outgoing hr 1 1000
cor outgoing hr 2 2000
!
!
line con 0
exec-timeout 0 0
line aux 0
line vty 0 4
login
!
!
end
Configuring SRST Mode
Configuration
Perform the following steps to configure SRST mode.
Step 1 Have Ephones registered to CME or CallManager before enabling SRST.
Step 2 Have an Ephone-dn assigned to each Ephone.
Step 3 Have a button associated with each Ephone-dn.
Step 4 Configure and show call-manager-fallback.
Step 5 Verify the response to show call-manager-fallback is similar to the following:
SRST-Router#sh call-manager-fallback
CONFIG (Version=3.3)
=====================
Version 3.3
For on-line documentation please see:
www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/access/ip_ph/ip_ks/index.htm
ip source-address 1.4.196.1 port 2000
max-ephones 10
max-dn 10
max-conferences 8 gain -6
dspfarm units 0
dspfarm transcode sessions 0
huntstop
dialplan-pattern 2 2222 extension-length 2 extension-pattern 20 no-reg
dialplan-pattern 4 4444 extension-length 4 extension-pattern 4040
dialplan-pattern 5 5555 extension-length 2 extension-pattern 50
access-code bri 333 direct-inward-dial
access-code pri 44 direct-inward-dial
time-format 24
date-format yy-mm-dd
timezone 0 Greenwich Standard Time
transfer-pattern 111 blind
transfer-pattern 202
transfer-pattern 301 blind
cor incoming eng default
cor incoming eng 1 2000
OL-7959-01
Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Release 3.4 Guide
1-19
Page 34

Configuration
Chapter 1 Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Support
cor outgoing hr 1 1000
cor incoming eng 2 2000-2010
cor outgoing hr 2 2000
alias 1 1234 to 9988 huntstop
alias 2 2222 to 5552222
alias 4 4444 to 5554444
alias 8 8888 to 5558888
keepalive 30
timeout interdigit 10
timeout busy 10
timeout ringing 180
caller-id name-only: enable
Limit number of DNs per phone:
7910: 34
7935: 34
7936: 34
7940: 34
7960: 20
7970: 34
Log (table parameters):
max-size: 150
retain-timer: 15
local directory service: enabled.
Step 6 Simulate a link failure for Ephones to fall back to SRST mode.
Step 7 Issue the following command to check call-manager-fallback configuration:
getmany -v2c <ip addr> test csrstConf
Step 8 Verify the response to getmany is similar to the following:
moki:1929> getmany -v2c 1.4.196.1 test csrstConf
csrstEnabled.0 = true(1)
csrstVersion.0 = 3.3
csrstIPAddressType.0 = ipv4(1)
csrstIPAddress.0 = 1.4.196.1
csrstPortNumber.0 = 2000
csrstMaxConferences.0 = 8
csrstMaxEphones.0 = 10
csrstMaxDN.0 = 10
csrstSipPhoneUnRegThreshold.0 = 480
csrstCallFwdNoAnswer.0 =
csrstCallFwdNoAnswerTo.0 = 180
csrstCallFwdBusy.0 =
csrstMohFilename.0 =
csrstMohMulticastAddrType.0 = ipv4(1)
csrstMohMulticastAddr.0 = 0.0.0.0
csrstMohMulticastPort.0 = 0
csrstVoiceMailNumber.0 =
csrstSystemMessagePrimary.0 =
csrstSystemMessageSecondary.0 =
csrstScriptName.0 =
csrstSecondaryDialTone.0 =
csrstTransferSystem.0 = blind(1)
csrstUserLocaleInfo.0 = us(11)
csrstDateFormat.0 = yymmdd(4)
csrstTimeFormat.0 = twentyFourHour(2)
csrstInterdigitTo.0 = 10
csrstBusyTo.0 = 10
csrstAlertTo.0 = 180
csrstXlateCalledNumber.0 = 0
csrstXlateCallingNumber.0 = 0
csrstAliasTag.0 = 1
csrstAliasTag.1 = 2
Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Release 3.4 Guide
1-20
OL-7959-01
Page 35

Chapter 1 Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Support
csrstAliasTag.2 = 4
csrstAliasTag.3 = 8
csrstAliasTag.4 = 2
csrstAliasTag.5 = 4
csrstAliasTag.6 = 1
csrstAliasTag.7 = 5
csrstAliasNumPattern.0 = 9988
csrstAliasNumPattern.1 = 5552222
csrstAliasNumPattern.2 = 5554444
csrstAliasNumPattern.3 = 5558888
csrstAliasNumPattern.4 = 2222
csrstAliasNumPattern.5 = 4444
csrstAliasNumPattern.6 = 1013
csrstAliasNumPattern.7 = 5013
csrstAliasAltNumber.0 = 1234
csrstAliasAltNumber.1 = 2222
csrstAliasAltNumber.2 = 4444
csrstAliasAltNumber.3 = 8888
csrstAliasAltNumber.4 = 2211
csrstAliasAltNumber.5 = 4411
csrstAliasAltNumber.6 = 1012
csrstAliasAltNumber.7 = 5012
csrstAliasPreference.0 = 0
csrstAliasPreference.1 = 0
csrstAliasPreference.2 = 0
csrstAliasPreference.3 = 0
csrstAliasPreference.4 = 2
csrstAliasPreference.5 = 4
csrstAliasPreference.6 = 2
csrstAliasPreference.7 = 4
csrstAliasHuntStopEnabled.0 = true(1)
csrstAliasHuntStopEnabled.1 = false(2)
csrstAliasHuntStopEnabled.2 = false(2)
csrstAliasHuntStopEnabled.3 = false(2)
csrstAliasHuntStopEnabled.4 = false(2)
csrstAliasHuntStopEnabled.5 = false(2)
csrstAliasHuntStopEnabled.6 = false(2)
csrstAliasHuntStopEnabled.7 = false(2)
csrstAccessCodeType.3 = bri(3)
csrstAccessCodeType.4 = pri(4)
csrstAccessCode.3 = 333
csrstAccessCode.4 = 44
csrstAccessCodeDIDEnabled.3 = true(1)
csrstAccessCodeDIDEnabled.4 = true(1)
csrstLimitDNType.1 = ipPhone7910(1)
csrstLimitDNType.2 = ipPhone7935(2)
csrstLimitDNType.3 = ipPhone7940(3)
csrstLimitDNType.4 = ipPhone7960(4)
csrstLimitDN.1 = 34
csrstLimitDN.2 = 34
csrstLimitDN.3 = 34
csrstLimitDN.4 = 20
csrstNotificationEnabled.0 = false(2)
Configuration
Enabling Traps in SRST Mode
To enable traps in SRST mode, perform the following steps:
Step 1 Issue the following command:
OL-7959-01
Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Release 3.4 Guide
1-21
Page 36

Configuration
Setany -v2c <ip addr> test csrstNotificationEnabled.0 -i 1
Step 2 When the SRST has at least 1 SCCP phone with DN associated with it, an “SRST system state change
up” trap is generated.
*Mar 10 23:13:15.632: SNMP: V1 Trap, ent ciscoMgmt.441, addr 1.4.196.1, gentrap 6,
spectrap 1
ciscoMgmt.441.2.2.2.1.2.1 = 2
ciscoMgmt.441.1.3.1.2.1 = 1
ciscoMgmt.441.2.2.2.2.2.1 = SRST system state change up
Monitoring SCCP Phone Statistics
To monitor SCCP phone statistics, perform the following steps:
Step 1 Register the Ephones to the SRST router.
Step 2 Issue the following CLI command:
Show ephone summary
Chapter 1 Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Support
Step 3 Verify the response to show Ephone summary is similar to the following:
SRST-Router#sh ephone summary
ephone-1 Mac:000F.24BA.2C37 TCP socket:[1] activeLine:0 REGISTERED
mediaActive:0 offhook:0 ringing:0 reset:0 reset_sent:0 debug:0
IP:1.4.196.42 7912 keepalive 2 1:1 2:2 CM Fallback
ephone-2 Mac:0011.BBEF.7554 TCP socket:[2] activeLine:0 REGISTERED
mediaActive:0 offhook:0 ringing:0 reset:0 reset_sent:0 debug:0
IP:1.4.196.2 Telecaster 7960 keepalive 2 CM Fallback
ephone-3 Mac:000D.2808.427F TCP socket:[3] activeLine:0 REGISTERED
mediaActive:0 offhook:0 ringing:0 reset:0 reset_sent:0 debug:0
IP:1.4.196.3 Telecaster 7960 keepalive 1 CM Fallback
Max 10, Registered 3, Unregistered 0, Deceased 0, Sockets 3
ephone_send_packet process switched 0
Max Conferences 8 with 0 active (8 allowed)
Skinny Music On Hold Status
Active MOH clients 0 (max 480), Media Clients 0
No MOH file loaded
Step 4 Issue the following SNMP request:
Getmany -v2c <ip addr> test ccmeActiveStats
Step 5 Verify the response for the getmany request is similar to the following:
moki:1931> getmany -v2c 1.4.196.1 test ccmeActiveStats
ccmeEphoneCallLegs.0 = 0
ccmeEphoneTot.0 = 3
ccmeEphoneTotRegistered.0 = 3
ccmeEphoneTotKeyPhConfigured.0 = 0
ccmeEphoneTotKeyPhRegistered.0 = 0
ccmeEphoneDeviceName.1 = SEP000F24BA2C37
ccmeEphoneDeviceName.2 = SEP000D2808427F
ccmeEphoneDeviceName.3 = SEP0011BBEF7554
Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Release 3.4 Guide
1-22
OL-7959-01
Page 37

Chapter 1 Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Support
ccmeEphoneRegState.1 = registered(1)
ccmeEphoneRegState.2 = registered(1)
ccmeEphoneRegState.3 = registered(1)
ccmeEphoneActiveDN.1 = 0
ccmeEphoneActiveDN.2 = 0
ccmeEphoneActiveDN.3 = 0
ccmeEphoneActivityStatus.1 = onhook(1)
ccmeEphoneActivityStatus.2 = onhook(1)
ccmeEphoneActivityStatus.3 = onhook(1)
ccmeEphoneKeepAliveCnt.1 = 3
ccmeEphoneKeepAliveCnt.2 = 4
ccmeEphoneKeepAliveCnt.3 = 3
ccmeEphonePendingReset.1 = false(2)
ccmeEphonePendingReset.2 = false(2)
ccmeEphonePendingReset.3 = false(2)
ccmeEphoneRegTime.1 =
ccmeEphoneRegTime.2 =
ccmeEphoneRegTime.3 =
ccmeEphoneCurrentFirmwareRev.1 = CP7912010200SCCP031023
ccmeEphoneCurrentFirmwareRev.2 = 7.0(2.0)
ccmeEphoneCurrentFirmwareRev.3 = 7.0(2.0)
ccmeEphonePreviousFirmwareRev.1 =
ccmeEphonePreviousFirmwareRev.2 =
ccmeEphonePreviousFirmwareRev.3 =
ccmeEphoneLastError.1 = Initialized
ccmeEphoneLastError.2 = CM-closed-TCP
ccmeEphoneLastError.3 = CM-closed-TCP
ccmeEphoneObservedType.1 = 7912
ccmeEphoneObservedType.2 = Telecaster 7960
ccmeEphoneObservedType.3 = Telecaster 7960
ccmeEphoneLoginStatus.1 = false(2)
ccmeEphoneLoginStatus.2 = false(2)
ccmeEphoneLoginStatus.3 = false(2)
ccmeEphoneDnDStatus.1 = false(2)
ccmeEphoneDnDStatus.2 = false(2)
ccmeEphoneDnDStatus.3 = false(2)
ccmeEphoneDebugStatus.1 = false(2)
ccmeEphoneDebugStatus.2 = false(2)
ccmeEphoneDebugStatus.3 = false(2)
ccmeEphoneMediaActive.1 = false(2)
ccmeEphoneMediaActive.2 = false(2)
ccmeEphoneMediaActive.3 = false(2)
ccmeEphoneTAPIClient.1 = false(2)
ccmeEphoneTAPIClient.2 = false(2)
ccmeEphoneTAPIClient.3 = false(2)
ccmeEphoneMediaCapability.1 = audioOnly(1)
ccmeEphoneMediaCapability.2 = audioOnly(1)
ccmeEphoneMediaCapability.3 = audioOnly(1)
ccmeEphoneRemote.1 = true(1)
ccmeEphoneRemote.2 = true(1)
ccmeEphoneRemote.3 = true(1)
ccmeMohSource.0 = liveFeed(2)
ccmeNightServiceEnabled.0 = false(2)
Configuration
Retrieving SIP Phone Registrations
To retrieve SIP phone registrations, perform the following steps:
Step 1 Register the SIP phones to the SRST router.
OL-7959-01
Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Release 3.4 Guide
1-23
Page 38

Configuration
Step 2 Issue the following CLI command:
Step 3 Ver ify the show voice register response is similar to the following:
Chapter 1 Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Support
Show voice register pool <pool #>
SRST-Router#sh voice regi pool 1
Pool Tag 1
Config:
Network address is 1.4.196.0, Mask is 255.255.255.0
Proxy Ip address is 1.4.196.1
DTMF Relay is disabled
Dialpeers created:
dial-peer voice 40001 voip
destination-pattern 5001
redirect ip2ip
session target ipv4:1.4.196.41:25672
session protocol sipv2
dial-peer voice 40002 voip
destination-pattern 5001
redirect ip2ip
session target ipv4:1.4.196.1:5060
session protocol sipv2
monitor probe rtr 1.4.196.1
dial-peer voice 40003 voip
destination-pattern 5002
redirect ip2ip
session target ipv4:1.4.196.41:25672
session protocol sipv2
dial-peer voice 40004 voip
destination-pattern 5002
redirect ip2ip
session target ipv4:1.4.196.1:5060
session protocol sipv2
monitor probe rtr 1.4.196.1
Statistics:
Active registrations : 4
Total Registration Statistics
Registration requests : 4
Registration success : 4
Registration failed : 0
unRegister requests : 0
unRegister success : 0
unRegister failed : 0
Step 4 Issue the following SNMP request:
Getmany -v2c <ip addr> test csrstSipEndpointTable
Step 5 Verify the response for the getmany request is similar to the following:
moki:1919> getmany -v2c 1.4.196.1 test csrstSipEndpointTable
csrstSipVoRegPoolEdptTag.0 = 1
csrstSipVoRegPoolEdptTag.1 = 1
csrstSipVoRegPoolEdptTag.2 = 1
csrstSipVoRegPoolEdptTag.3 = 1
csrstSipEndpointIpAddrType.0 = ipv4(1)
csrstSipEndpointIpAddrType.1 = ipv4(1)
Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Release 3.4 Guide
1-24
OL-7959-01
Page 39

Chapter 1 Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Support
csrstSipEndpointIpAddrType.2 = ipv4(1)
csrstSipEndpointIpAddrType.3 = ipv4(1)
csrstSipEndpointIpAddress.0 = ipv4:1.4.196.41:26057
csrstSipEndpointIpAddress.1 = ipv4:1.4.196.1:5060
csrstSipEndpointIpAddress.2 = ipv4:1.4.196.41:26057
csrstSipEndpointIpAddress.3 = ipv4:1.4.196.1:5060
csrstSipEndpointDN.0 = 5001
csrstSipEndpointDN.1 = 5001
csrstSipEndpointDN.2 = 5002
csrstSipEndpointDN.3 = 5002
Receiving Notifications/Traps
Notifications and traps are asynchronously generated by SRST to pass information about certain device
status changes. Table 1-4 lists the SRST notifications/traps and additional information regarding each
notification or trap.
Table 1-4 SRST Notifications/Traps
Configuration
Notification/Trap Reason Severity
csrstStateChange SRST system state change up Minor
csrstStateChange SRST system state change down Minor
csrstStateChange SIP SRST system state change up Minor
csrstStateChange SIP SRST system state change down Minor
csrstFailNotif Skinny listening socket setup error Minor (when system is
running)
csrstFailNotif Maximum number of allowed sockets has been exceeded Minor (when system is
running)
csrstFailNotif Skinny server initialization failed
Major (at initialization)
Sockets initialization failed
csrstFailNotif Skinny server initialization failed
Major (at initialization)
Not enough memory
csrstFailNotif Not enough memory to create Registrar Control Block (rcb) for SIP
Minor
Voice Register DNS
csrstFailNotif Not enough memory to create Call Control Block (ccb) from SIP
Minor
registrar outgoing
There is no reason string or severity sent with the following traps:
• csrstSipPhoneUnRegThresholdExceed
• csrstSipPhoneRegFailed
• csrstConferenceFailed
The following list contains all the CISCO-SRST-MIB traps.
• csrstStatusChange - SRST status change trap (Up)
*Mar 7 20:56:23.207: SNMP: V1 Trap, ent ciscoMgmt.441, addr 1.4.196.10, gentrap
OL-7959-01
Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Release 3.4 Guide
1-25
Page 40

Configuration
Chapter 1 Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Support
6, spectrap 1
ciscoMgmt.441.2.2.2.1.2.1 = 2
ciscoMgmt.441.1.3.1.2.1 = 1
ciscoMgmt.441.2.2.2.2.2.1 = SRST system state change up
• csrstStateChange - SRST status change trap (Down)
*Mar 7 20:57:23.199: SNMP: V1 Trap, ent ciscoMgmt.441, addr 1.4.196.10, gentrap
6, spectrap 1
ciscoMgmt.441.2.2.2.1.2.1 = 2
ciscoMgmt.441.1.3.1.2.1 = 2
ciscoMgmt.441.2.2.2.2.2.1 = SRST system state change down
• csrstStateChange - SIP-SRST status change trap (Up)
*Mar 7 20:56:23.459: SNMP: V1 Trap, ent ciscoMgmt.441, addr 1.4.196.10, gentrap
6, spectrap 1
ciscoMgmt.441.2.2.2.1.2.2 = 2
ciscoMgmt.441.1.3.1.2.2 = 1
ciscoMgmt.441.2.2.2.2.2.2 = SIP SRST system state change up
• csrstStateChange - SIP-SRST status change trap (Down)
*Mar 7 20:57:23.451: SNMP: V1 Trap, ent ciscoMgmt.441, addr 1.4.196.10, gentrap
6, spectrap 1
ciscoMgmt.441.2.2.2.1.2.2 = 2
ciscoMgmt.441.1.3.1.2.2 = 2
ciscoMgmt.441.2.2.2.2.2.2 = SIP SRST system state change down
• csrstSipPhoneUnRegThresholdExceeded Trap – SIP phone unregistration threshold exceeded
*Mar 8 23:53:01.480: SNMP: V1 Trap, ent ciscoMgmt.441, addr 1.4.196.1, gentrap 6,
spectrap 3
ciscoMgmt.441.1.2.9.1.1 = 1
ciscoMgmt.441.1.3.2.1.1 = 1
• csrstFailNotif – SRST System Failure Notification
*Mar 6 01:53:58.957: SNMP: V1 Trap, ent ciscoMgmt.441, addr 1.4.196.1, gentrap 6,
spectrap 2
ciscoMgmt.441.2.2.2.1.1 = 1
ciscoMgmt.441.2.2.2.2.1 = Skinny listening socket setup error
• csrstMaxConferenceExceeded – SRST maximum number of conferences exceeded
*Mar 10 19:16:56.165: SNMP: V1 Trap, ent ciscoMgmt.441, addr 1.4.196.1, gentrap 6,
spectrap 5
ciscoMgmt.441.1.2.6.0 = 8
• csrstSipPhoneRegFailed – SIP phone failed to register
*Mar 11 19:25:00.663: SNMP: V1 Trap, ent ciscoMgmt.441, addr 1.4.196.1, gentrap 6,
spectrap 4
ciscoMgmt.441.1.4.7.1.4.0 = 1.4.196.41
Command Reference
This section documents new or modified CLI commands applicable to this Cisco IOS release. All other
CLI commands used with the CISCO-SRST-MIB feature are documented in the Cisco IOS Release 12.2
command reference publications.
Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Release 3.4 Guide
1-26
OL-7959-01
Page 41

Chapter 1 Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Support
SNMP Overview
The following sections provide an overview of the SNMP.
Network Management Overview
Network management takes place between two major types of systems: those in control (called
managing systems) and those observed and controlled (called managed systems). The most common
managing system is called a network management system (NMS). Managed systems can include hosts,
servers, or network components such as routers or intelligent repeaters.
To promote interoperability, the cooperating systems must adhere to a common framework and a
common language, called a protocol. In the Internet network management framework, that protocol is
the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP). SNMP is an application-layer protocol designed to
facilitate the exchange of network management information between network devices. The SNMP
system consists of three parts:
• SNMP manager
• SNMP agent
• MIB
The Internet network management framework is based on the idea of a managing the system interfacing
to a managed system. The managing system (called a manager) runs a network management application
(called an agent). The managed system runs an agent that answers status requests from the manager. The
manager and the managed system exchange information using SNMP.
SNMP Overview
The information exchanged between the manager and the managed system is about the Management
Information Base (MIB), which defines all the information that can be seen or changed by the manager.
The MIB may be either standard or proprietary, and a similar concept of the MIB must be shared by both
the manager and the agent.
SNMP and its MIBs are defined in a combination of system-specific language and Abstract Syntax
Notation 1 (ASN.1) Although ASN.1 is a rich definition language, SNMP uses only a subset of ASN.1,
which is defined in the SNMP Structure of Management Information (SMI). For transmission, SNMP is
encoded according to the ASN.1 basic encoding rules (BER).
SNMP may be carried over a wide choice of transport protocols. The most common combination is the
User Datagram Protocol over the Internet Protocol, UDP/IP. Other possibilities include AppleTalk,
Netware, and Ethernet.
SNMP has facilities for identifying the requester and the operational context in which a request is to be
performed by the agent, such as read-only or read-write, a MIB subset for a particular group of users, or
a subset that may be elsewhere or obtained through other mechanisms (proxy). These are the facilities
concerned with security.
SNMP has a small number of MIB management operations it can perform for observation and control of
MIB information, comprising various ways of reading (get operations), and one way of modifying (set
operations).
The following topics are included as part of the network management overview:
• MIB Overview, page 1-28
• SNMP, page 1-29
• Internet MIB Hierarchy, page 1-30
• SNMP MIB, page 1-31
OL-7959-01
Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Release 3.4 Guide
1-27
Page 42

SNMP Overview
MIB Overview
MIB Source
Chapter 1 Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Support
In a managed device, specialized low-impact software modules, called agents access information about
the device and make it available to the network management system (NMS). Managed devices maintain
values for a number of variables and report those, as required, to the NMS. For example, an agent can
report data such as the number of bytes and packets in and out of the device, or the number of broadcast
messages sent and received. In the Internet network management framework, each variable, which is a
managed object, is any information that an agent can access and report back to the NMS.
All managed objects are contained in the MIB database. The managed objects can be set or read to
provide information on network devices and interfaces. An NMS can control a managed device by
sending a message to an agent of that managed device requiring the device to change the value of one or
more of its managed objects.
MIBs come from various sources:
• Standard—On the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) standards track at Proposed, Draft, or
full standard. A Proposed Standard can change somewhat due to implementation experience. A
Draft Standard changes somewhat less, with more attention to backward compatibility. A full
Internet Standard doesn't change much. At all levels these are published as Requests for Comment
(RFCs).
MIB Objects
• Internet Draft—IETF work in progress. Sometimes the best way to instrument technology is with
an Internet Draft MIB, which is typically being worked on by an IETF working group. Such MIBs
are somewhat unstable, so it is necessary to capture the specific Internet Draft and to place the MIB
within the Cisco Enterprise MIB space (not in the Experimental branch).
• Cisco—Cisco enterprise-specific (also called proprietary or private, even though publicly
documented). Such MIBs add instrumentation not covered by standard MIBs. As of Cisco IOS
Release 10.2, Cisco has old MIBs and new MIBs. The old MIBs are from older software versions
and often have somewhat unconventional features.
• Other companies—Non-Cisco enterprise-specific. It is occasionally appropriate to implement a
MIB defined by some other company, especially for technology they originated and instrumented.
This presents problems like these associated with Internet Drafts in that a version of the MIB
definition must be captured, but the MIB itself should remain wherever in the MIB space the
originating company put it so as to easily support existing applications.
A MIB is conceptually a tree (as shown in Figure 1-4), where the leaves are the individual data objects.
An object can be, for example, a counter or a protocol status. The SNMP framework uses the term
“object” in a way different from the way OSI management uses it. An OSI object is a network entity,
such as a router or a protocol, which has attributes. These OSI attributes and SNMP objects are
essentially the same concept, that is, individual data values. A MIB object consists of the following
values:
• Object type—Identifies the type of MIB object.
• Syntax—Identifies the data type which models the object.
• Access—Identifies the maximum level of access and can have one of five values (listed from highest
to lowest level of access):
–
Read-create—Indicates that instances of the object may be read, written, and created
Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Release 3.4 Guide
1-28
OL-7959-01
Page 43

Chapter 1 Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Support
–
Read-write—Indicates that instance of the object may be read or written, but not created
–
Read-only—Indicates that instances of the object may be read but not written or created
–
Accessible-for-notify—Indicates that instances of the object may only appear in notifications
–
Not-accessible—Indicates that instances of the object may not be directly read, written, or
created
• Status—The status of a managed object can be:
–
Mandatory—Indicates that the definition is required and should be implemented
–
Current—Indicates that the definition is current
–
Deprecated—Indicates that the definition will soon be made obsolete and need no longer be
implemented
–
Obsolete—Indicates that managed nodes should not implement the object
• Description—Provides a textual description of the managed object
The following is an example of a MIB object:
tpTDMIfCollectTimeInterval OBJECT-TYPE
SYNTAX Counter32
MAX-ACCESS read-only
STATUS current
DESCRIPTION
This object shows measurement time interval seconds.
::= {tpTDMIfStatTableEntry 1}
SNMP
MIB Archive
SNMP
For descriptions of supported MIBs and how to use MIBs, see the Cisco MIB web site on CCO at
http://www.cisco.com/public/sw-center/netmgmt/cmtk/mibs.shtml.
Cisco MIBs are archived in the Cisco FTP server and are accessible by anonymous FTP at the following
location: ftp://ftpeng.cisco.com/pub/mibs
Cisco MIB variables are accessible through SNMP, which is an application-layer protocol designed to
facilitate the exchange of management information between network devices.
Instead of defining a large set of commands, SNMP places all operations in a get-request,
get-next-request, or set-request format. For example, an SNMP manager can get a value from an SNMP
agent or store a value in that SNMP agent. The SNMP manager can be part of an NMS, and the SNMP
agent can reside on a networking device such as a router. You can compile the Cisco MIB with your
network management software. If SNMP is configured on a Catalyst Switch, the SNMP agent can
respond to MIB-related queries being sent by the NMS.
An example of an NMS is the CiscoWorks network management software. CiscoWorks uses the Cisco
MIB variables to set device variables and to poll devices on the internetwork for specific information.
The results of a poll can be displayed as a graph and analyzed for the troubleshooting of internetwork
problems. Results can also be used to increase network performance, verify the configuration of devices,
monitor traffic loads, and so on.
OL-7959-01
Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Release 3.4 Guide
1-29
Page 44

Internet MIB Hierarchy
Chapter 1 Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Support
As shown in Figure 1-3, the SNMP agent gathers data from the MIB, which is the repository for
information about device parameters and network data. The agent can send traps, or notifications of
events of interest, to the manager. The Cisco trap file, mib.traps, which documents the format of the
Cisco traps, is available on the Cisco host ftp.cisco.com.
Figure 1-3 Simple Network Management Protocol Network
The SNMP manager uses information in the MIB to perform the operations described in Table 1 -5.
Table 1-5 SNMP Manager Operations
Operation Description
get-request Retrieve a value from a specific variable.
get-next-request
Retrieve the value following the named variable. Often
used to retrieve variables from within a table.
1
get-response The reply to a get-request, get-next-request,
get-bulk-request, or set-request sent by an NMS.
get-bulk-request Similar to a get-next-request, but fill the
get-response with up to max-repetition number of
get-next interactions.
set-request Store a value in a specific variable.
trap
An unsolicited message sent by an SNMP agent to an
SNMP manager indicating that some event has
occurred.
1. With this operation, an SNMP manager does not need to know the exact variable
name. A
sequential search is performed to find the needed variable from within the MIB.
Internet MIB Hierarchy
The MIB structure is logically represented by a tree hierarchy (see Figure 1-4). The structure uses
branches and the branches that fall below each category have short text strings and integers to identify
them. Text strings describe object names, and integers allow computer software to create compact,
encoded representations of the names. For example, the Cisco MIB variable authAddr is an object name
and is denoted by number 5, which is listed at the end of its object identifier number 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.2.1.5.
The object identifier in the Internet MIB hierarchy is the sequence of numeric labels on the nodes along
a path from the root to the object. The Internet standard MIB is represented by the object identifier
1.3.6.1.2.1. It also can be expressed as iso.org.dod.internet.mgmt.mib. (See Figure 1-4.)
Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Release 3.4 Guide
1-30
OL-7959-01
Page 45

Chapter 1 Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Support
Internet MIB Hierarchy
Figure 1-4 Internet MIB Hierarchy
unnamed
CCITT
0
iso
1
org
3
dod
6
internet
1
joint
ISO/CCITT
2
SNMP MIB
directory
1
mgmt
2
mib
1
experi-
mental
3
private
4
S1202a
An SNMP MIB is an abstract database, that is, a conceptual specification for information that a
management application may read and modify in a certain form. This does not imply that the information
is kept in the managed system in that same form. The SNMP agent translates between the internal data
structures and formats of the managed system and the external data structures and formats defined for
the MIB.
The SNMP MIB is conceptually a tree structure with conceptual tables, described in more detail in the
following sections. Relative to this tree structure, the term “MIB” is used in two ways. In one way, it is
actually a MIB branch, usually containing information for a single aspect of technology, such as a
transmission medium or a routing protocol. A MIB used in this way is more accurately called a MIB
module, and is usually defined in a single document.
In the other way, a MIB is a collection of such branches. Such a collection of MIB branches might
comprise, for example, all of the MIB modules implemented by a given agent, or the entire collection of
MIB modules defined for SNMP.
OL-7959-01
Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Release 3.4 Guide
1-31
Page 46

Compliance
Compliance
Chapter 1 Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Support
MIBs can be standard or enterprise. Internet standard MIBs are defined by working groups of the IETF
and published as RFCs. Enterprise MIBs are defined by other organizations, which are usually individual
companies. Done properly, enterprise MIBs instrument technology not covered by standard MIBs, either
completely or as an extension to a standard MIB.
The prototypical standard MIB is MIB-II, the second revision of the original SNMP MIB. MIB-II
contains branches for the basic areas of instrumentation, such as the system, its network interfaces, IP,
and TCP. All of these started out in a single MIB module, but as SNMPv2 evolves, they are being split
into separate modules.
Cisco MIBs are a set of variables that are private extensions to the Internet standard MIB-II. The MIB-II
is documented in RFC 1213 (Management Information Base for Network Management of TCP/IP-based
Internets: MIB-II). This RFC includes information on the benefits of the new feature, supported
platforms, related documents, troubleshooting tips, configuration examples, and a detailed command
reference.
Cisco Compliance
At present, Cisco implementations of standard MIBs are often read-only or have some objects or object
groups missing because of security concerns or time requirements for implementation. Since
Cisco IOS Release 10.2, developers must document such specifics with AGENT-CAPABILITIES from
RFC 1904.
Implementation
To find what MIBs Cisco implements, start at ftp-eng.cisco.com with
ftp://ftp-eng.cisco.com/pub/mibs/README.
This contains a list of MIBs available for various software versions. The MIB list cannot account for
MIBs not included in a particular software subset or because a feature is turned off. Whether or not the
MIB is included is the function of AGENT-CAPABILITIES descriptions and the snmpORTable (RFC
1907) in later software versions.
SNMP MIB Tables
Tables are a powerful and often confusing aspect of SNMP MIBs. Architectural purists say SNMP has
conceptual tables, not real tables. This is because every object, whether in a table or not, is a leaf of the
tree, identified by an object identifier (OID) that includes an instance. So, in an abstract sense, all objects
are alike. But practically speaking, SNMP has tables, and using or implementing them gets somewhat
more complex than implementing scalars, which are single object instances.
Tables have a rigid structure, defined in the SMI. Tables can contain only simple objects, not other tables,
although multiple indexes can represent the concept of tables in tables. An entry, or row, in a table is
uniquely identified by one or more table indexes, also called auxiliary objects. The OID of an object from
a table is the OID for that object's position in the MIB tree concatenated with a representation of all the
table indexes for an entry in the table.
Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Release 3.4 Guide
1-32
OL-7959-01
Page 47

Chapter 1 Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Support
For example, the Interface MIB (RFC 1573) has a key table called the ifTable. Its index object is ifIndex,
an integer. Minus the instance, the OID for a counter from that table is:
iso.internet.mgmt.mib-2.interfaces.ifTable.ifEntry.ifInOctets
Or, numerically:
1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.10
For the interface with ifIndex 7, the full OID is:
iso.internet.mgmt.mib-2.interfaces.ifTable.ifEntry.ifInOctets.7
1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.10.7
Observe that row selection (instance) comes after column selection. This can be particularly confusing
when you are applying the principle of lexical order to a table. Using the GetNext protocol operation to
walk a table, you can proceed by column, that is, all instances for a column are returned before the next
column is started.
Table indexes can be much more complex than tables. Here is an example from the Cisco VINES MIB.
The INDEX clause from the ASN.1 definition is:
INDEX { cvForwNeighborHost,
ifIndex,
CISCO-SRST-MIB Object Groups
cvForwNeighborPhysAddress }
The first two indexes are simple integers, with ifIndex being imported from the standard ifTable. The
final index is a variable length octet string. Including the integers is simple and obvious. The
variable-length index object gets more complex. RFC 1212 includes rules for encoding variable length
index objects as instances. The general rule is that the value is preceded by a length, and the length and
each part of the value are separate subidentifiers.
So, for example, if we have neighbor host number 9, ifIndex 3, and an Ethernet neighbor physical address
0000.0c03.1ef0, the instance portion of an object for that row is 9.3.6.0.0.12.3.30.240.
In RFC 1902, SNMPv2 extends the instance encoding rules to include an “IMPLIED” keyword that can
be used on the final instance object if it is variable length. When “IMPLIED” is present, the string
instance cannot have a zero length in front of it.
Because lexical ordering for variable length instance objects effectively sorts them by length, your
ASCII text index will not come out naturally in alphabetical order.
CISCO-SRST-MIB Object Groups
Table 1 -6 lists the CISCO-SRST-MIB objects, which are presented according to their group.
The CISCO-SRST-MIB is organized by the following groups listed in Tabl e 1-6
• csrstConf
• csrstNotifInfo
• csrstActiveStats
• csrstSipConf
• CiscoSrstMIBNotifs
OL-7959-01
Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Release 3.4 Guide
1-33
Page 48

CISCO-SRST-MIB Object Groups
Table 1-6 SRST MIB Object Groups and Descriptions
Max
MIB Group MIB Object
Access Description
csrstConfGroup
csrstEnabled read-only Cisco SRST support is enabled or disabled. When
csrstVersion read-only Cisco SRST version.
csrstIPAddressType read-only Internet address type governing the address type
csrstIPAddress read-only Cisco SRST IP address for the router to receive
csrstPortNumber read-only This object indicates the TCP port number to use for
csrstMaxConferences read-only Maximum number of simultaneous three-party
Chapter 1 Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Support
enabled, the router is in fallback mode to provide
call-handling support to IP phones. If disabled, all of
the objects in this group have no significance.
format for one or more InetAddress objects in this
MIB. The associated InetAddress objects' description
will refer back to this type object as appropriate.
messages from IP phones, typically one of the
addresses of an Ethernet port of the router. The type of
IP address used here is indicated by the
csrstSysIPAddressType object.
Skinny Client Control Protocol (SCCP) and is range
limited. This port also indicates through which IP
phones communicate with SRST.
conference calls configured on the router. Range is
IOS version and platform dependent. With SRST
Version 3.0 onwards, the following are the maximum
values for each platform -
Cisco 1751, Cisco 1760, Cisco 2600, Cisco 3640
1-34
- 8 conferences.
Cisco 3660, Cisco 3725, Cisco 3745
- 16 conferences.
Default is half the maximum number of simultaneous
three-party conferences for each platform.
csrstMaxEphones read-only Maximum number of Cisco IP phones configured on
the SRST router. Range is IOS version and platform
dependent.
csrstMaxDN read-only Maximum number of IP phones extensions
(Ephone-dns) or directory number configured on this
SRST router. Range is IOS version and platform
dependent. Default is 0."
-- This object is changeable by NMS to set a threshold
-- for a trap to be reported. This refers to SIP phones -only.
Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Release 3.4 Guide
OL-7959-01
Page 49

Chapter 1 Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Support
Table 1-6 SRST MIB Object Groups and Descriptions (continued)
Max
MIB Group MIB Object
Access Description
csrstSipPhoneUnRegThresholdread-write This object indicates a threshold for the number of SIP
phones unregistered to SRST. This threshold is
changeable by the NMS user.
csrstCallFwdNoAnswer read-only Cisco SRST call forwarding number when a Cisco IP
phone is not answered. This directory number is a fully
qualified E.164 number.
csrstCallFwdNoAnswerTo read-only Timeout in seconds if a Cisco IP phone is not
answered, Cisco SRST will call forward to another
directory number.
csrstCallFwdBusy read-only Cisco SRST call forwarding number when a Cisco IP
phone is busy. This directory number is a fully
qualified E.164 number.
csrstMohFilename read-only Cisco SRST Music-On-Hold is enabled with file on
flash, or disabled without a file on flash. MOH is
enabled by default.
csrstMohMulticastAddrType read-only Internet address type governing the address type
format for one or more InetAddress objects in this
MIB. The associated InetAddress objects' description
will refer back to this type object as appropriate.
csrstMohMulticastAddr read-only This object indicates Cisco SRST Music-On-Hold
Multicast IP address. When configured, this feature
enables continuous IP multicast output of MOH from
a Flash MOH file. This object has no significance if
MOH is not configured. Default is the csrstIPAddress
object for Cisco SRST. The type of IP address used
here is indicated by the csrstMohMulticastAddrType
object.
csrstMohMulticastPort read-only This object indicates Cisco SRST Music-On-Hold
Multicast TCP port which is range limited When
configured, this feature enables
csrstVoiceMailNumber read-only Cisco SRST voice mail number that is speed-dialed
when the messages button on a Cisco IP phone is
pressed. This voice mail number is a fully qualified
E.164 number. If voice-mail number is not configured,
this object will have a string length of 2 with the value
'**'.
csrstSystemMessagePrimary read-only Cisco SRST system static text message that is
displayed on Cisco IP phone during fallback. Length
of text string is less than 32 characters. Default
message is 'CM Fallback Service Operating'.
csrstSystemMessageSecondaryread-only Cisco SRST system message that is displayed on Cisco
IP phone that does not support static text message and
have a limited display space during fallback. Length of
text string is less than 20 characters. Default messages
is 'CM Fallback Service'.
CISCO-SRST-MIB Object Groups
OL-7959-01
Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Release 3.4 Guide
1-35
Page 50

CISCO-SRST-MIB Object Groups
Table 1-6 SRST MIB Object Groups and Descriptions (continued)
Max
MIB Group MIB Object
Access Description
csrstScriptName read-only Cisco SRST session-level IVR application script. This
application can be written in Tool Command Language
(TCL) and is applied to all Cisco IP phone lines served
by the SRST router. If no application script name is
configured, the default built-in IOS application will be
applied to all phone lines served by the SRST router
and this object will be a zero-length string.
csrstSecondaryDialTone read-only Cisco SRST secondary dial tone digits. When a Cisco
IP phone user dials a PSTN access prefix, defined by
the secondary dial tone digits, the secondary dial tone
is enabled.
csrstTransferSystem read-only Cisco SRST call transfer method using the ITU-T
H.450.2 standard. Default setting is blind.
blind (1),
fullBlind (2),
fullConsult (3),
Chapter 1 Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Support
localConsult (4)
blind - Calls are transferred without consultation using
a single phone line and the Cisco proprietary method.
fullBlind - Calls are transferred without consultation
using H.450.2 standard methods.
fullConsult - Calls are transferred using H.450.2 with
consultation using the second phone line if available,
or the calls fall back to full-blind if the second line is
unavailable.
localConsult - Calls are transferred with local
consultation using the second phone line if available,
or the calls fall back to blind for non- local
consultation or transfer target. This mode is intended
for use primarily in Voice over Frame Relay (VoFR)
networks.
Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Release 3.4 Guide
1-36
OL-7959-01
Page 51

Chapter 1 Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Support
Table 1-6 SRST MIB Object Groups and Descriptions (continued)
Max
MIB Group MIB Object
Access Description
csrstUserLocaleInfo read-only Cisco SRST language for displays on Cisco IP phone
by country.
denmark (1),
france (2),
germany (3),
italy (4),
netherlands (5),
norway (6),
portugal (7),
russian (8),
spain (9),
CISCO-SRST-MIB Object Groups
sweden (10),
us (11) - default
csrstDateFormat read-only Date display format on Cisco IP phones in the Cisco
SRST system.
mmddyy (1) - default,
ddmmyy (2),
yyddmm (3)
yymmdd (4)
csrstTimeFormat read-only Time display format on Cisco IP phones in the Cisco
SRST system.
twelveHour (1) - default,
twentyFourHour (2)
csrstInterdigitTo read-only Cisco SRST interdigit timeout duration in seconds for
Cisco IP phones.
csrstBusyTo read-only Cisco SRST time in seconds before disconnect when
destination is busy, without call-forwarding.
csrstAlertTo read-only Cisco SRST time in seconds before disconnect when
call is not answered, without call-forwarding.
csrstXlateCalledNumber read-only This object indicates the tag of a corresponding
translation rule, which utilizes the number-translation
mechanism of the IOS to translate a called number on
the Cisco SRST router.
csrstXlateCallingNumber read-only This object indicates the tag of a corresponding
translation rule, which utilizes the number-translation
mechanism of the IOS to translate a calling number on
the Cisco SRST router.
OL-7959-01
Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Release 3.4 Guide
1-37
Page 52

CISCO-SRST-MIB Object Groups
Table 1-6 SRST MIB Object Groups and Descriptions (continued)
Max
MIB Group MIB Object
Access Description
csrstAliasTag read-only A unique sequence number that indicates a particular
alias pattern configured on this SRST router.
csrstAliasNumPattern read-only This object indicates the pattern to match the incoming
telephone number. It may include wildcards.
csrstAliasAltNumber read-only This object indicates the alternate telephone phone
number to route incoming calls to match the number
pattern. This has to be a valid extension for an IP phone
actively registered on the SRST router.
csrstAliasPreference read-only This object indicates the preference value of the
associated dial-peer. A value of 0 has the highest
preference.
csrstAliasHuntStopEnabled read-only This object specifies that if hunt stop is enabled, after
the caller tried the alternate number according to the
alias pattern, it will stop call hunting. If hunt stop is
disabled, it will rollover to another directory number if
available.
csrstAccessCodeType read-only This object indicates the type of trunk line to which the
access-code is applied to.
Chapter 1 Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Support
fxo (1),
em (2),
bri (3),
pri (4)
The type of trunk lines can be fxo, e&m, bri, and pri.
fxo - Enables a foreign exchange office (FXO)
interface.
em - Enables an analog ear and mouth (E&M)
interface.
bri - Enables a BRI interface.
pri - Enables a PRI interface.
csrstAccessCode read-only This object indicates the access-code to be applied to
the corresponding trunk line by creating dial-peers.
csrstAccessCodeDIDEnabledread-only This object indicates the direct-inward- dial on a POTS
dial-peer is enabled or disabled.
Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Release 3.4 Guide
1-38
OL-7959-01
Page 53

Chapter 1 Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Support
Table 1-6 SRST MIB Object Groups and Descriptions (continued)
Max
MIB Group MIB Object
Access Description
csrstLimitDNType read-only This object indicates the type of IP phone to which the
limit-dn is applied to.
ipPhone7910 (1),
ipPhone7935 (2),
ipPhone7940 (3),
ipPhone7960 (4),
ipPhone7970 (5),
ipPhone7936 (6)
csrstLimitDN read-only This object indicates the maximum number of
directory numbers available to each type of IP phone.
The current range of maximum lines setting is from 1
to 34. The default is 6.
csrstNotificationEnabled read-write This variable indicates whether this system produces
the SRST notifications. A false value will prevent
SRST notifications from being generated by this
system.
csrstNotifInfoGroup
csrstSysNotifSeverity accessible-
for-notify
The internally-defined severity of the particular alarm
condition, associated with the most recent SNMP
notification. A subsequent event in which the alarm
condition changes from its failed state back to a
'normal' state has a severity of 'clear'. This
severity-level value is supplied with each SRST
specific notification.
csrstSysNotifReason accessible-
for-notify
The internally-defined failure cause of the particular
alarm condition, associated with the most recent
system notification.
csrstActiveStatsGroup
csrstState read-only This object indicates the current state of Cisco SRST
feature on this router.
Active - At least one IP or SIP phone is registered
Inactive - Cisco SRST has no IP or SIP phones
registered
CISCO-SRST-MIB Object Groups
csrstSipPhoneCurrentRegiste
red
csrstSipCallLegs read-only Total number of SIP call legs routed through the SRST
OL-7959-01
This object has no significance if csrstEnabled object
is disabled.
read-only Total number of SIP phones currently registered to the
SRST router.
router since going active. This includes incoming and
outgoing calls.
Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Release 3.4 Guide
1-39
Page 54

CISCO-SRST-MIB Object Groups
Table 1-6 SRST MIB Object Groups and Descriptions (continued)
Max
MIB Group MIB Object
Access Description
csrstTotalUpTime read-only Accumulated total number of minutes that router is
active in SRST mode.
csrstSipConfGroup
csrstSipRegSrvExpMax read-only This object indicates the maximum expiration time for
the SIP Registrar Server to timeout on a registration.
csrstSipRegSrvExpMin read-only This object indicates the minimum expiration time for
the SIP Registrar Server to timeout on a registration.
csrstSipIp2IpGlobalEnabled read-only This object indicates whether voip calls are re-directed
IP to IP globally.
csrstSipSend300MultSupportread-only This object indicates whether the redirect contact order
is best or longest match. This applies globally for SIP.
bestMatch (1),
longestMatch (2)
bestMatch - Uses the current system configuration to
set the order of contacts.
longestMatch - Sets the contact order by using the
destination pattern longest match first, and then the
second longest match, the third longest match, etc.
csrstSipVoRegPoolTag not-accessi
ble
A unique identifier tag configured for a voice register
pool entry.
csrstSipNetId read-only This object indicates the network identification
information of the SIP voice register pool configured
on this router. This object can be the network Id, IP
address, or MAC address.
csrstSipVoRegPoolIpAddrTyperead-only Internet address type governing the address type
format for one or more InetAddress objects in this
MIB. The associated InetAddress objects' description
will refer back to this type object as appropriate.
csrstSipNetMask read-only This object indicates the IP subnet configured for the
SIP voice register pool. The type of IP subnet used here
is indicated by the csrstSipVoRegPoolIpAddrType
object.
csrstSipProxySrvIpAddr read-only This object indicates the IP address of the proxy server
configured for the SIP voice register pool. The type of
IP address used here is indicated by the
csrstSipVoRegPoolIpAddrType object.
csrstSipProxySrvPref read-only This object indicates the preference order for creating
the VoIP dial peers in the voice register pool. Setting
the preference enables the desired dial peer to be
selected when multiple dial peers within a hunt group
are matched for a dial string. A value of 0 has the
highest preference.
Chapter 1 Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Support
Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Release 3.4 Guide
1-40
OL-7959-01
Page 55

Chapter 1 Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Support
Table 1-6 SRST MIB Object Groups and Descriptions (continued)
Max
MIB Group MIB Object
Access Description
csrstSipProxySrvMonitor read-only Cisco SIP SRST monitoring protocol of the proxy
server configured for the SIP voice register pool. This
monitoring protocol can be ICMP ping or RTR probes.
icmp (1),
rtr (2)
csrstSipProxySrvAltIpAddr read-only Cisco SIP SRST monitoring of an alternate IP address
other than the proxy configured for the SIP voice
register pool. The type of IP address used here is
indicated by the csrstSipVoRegPoolIpAddrType
object.
csrstSipDefaultPreference read-only This object indicates the default preference of the
proxy dial-peers created in the voice register pool If
csrstSipProxySrvPref object is not set, the default
preference is applied to the dial-peers created. A value
of 0 has the highest preference.
csrstSipVoRegPoolAppl read-only Application for the SIP dial-peers configured under
voice register pool.
csrstSipVoRegNumberListTagread-only This object indicates the particular index of the
number list configured for the corresponding voice
register pool.
csrstSipVoRegNumberPatternread-only This object indicates the number pattern that the
registrar permits to handle the register message from
the SIP phone. This number pattern is a fully qualified
E.164 number.
csrstSipVoRegNumberPref read-only This object indicates the preference of the number
pattern configured for the corresponding voice register
pool.
csrstSipVoRegNumberHunts
topEnabled
read-only This object indicates huntstop is enabled (true) or
disabled (false) for the number pattern configured for
the corresponding voice register pool. If enabled, the
incoming call will stop hunting if the dial-peer is busy.
If disabled, the incoming call will hunt further for
dial-peers.
csrstSipEndpointTag not-accessi
ble
This object is a number that indicates a SIP endpoint
configured on this SRST router
csrstSipVoRegPoolEdptTag read-only This object indicates the voice register pool tag from
which the corresponding SIP endpoint (dial-peer) is
created.
csrstSipEndpointIpAddrType read-only Internet address type governing the address type
format for one or more InetAddress objects in this
MIB. The associated InetAddress objects' description
will refer back to this type object as appropriate.
CISCO-SRST-MIB Object Groups
OL-7959-01
Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Release 3.4 Guide
1-41
Page 56

Chapter 1 Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Support
CISCO-SRST-MIB Object Groups
Table 1-6 SRST MIB Object Groups and Descriptions (continued)
Max
MIB Group MIB Object
Access Description
csrstSipEndpointIpAddress read-only This object indicates the SIP endpoint IP address
configured on this router. The type of IP address used
here is indicated by the csrstSipEndpointIpAddrType
object.
csrstSipEndpointDN read-only This object indicates the SIP phone's DN or line
number assigned to the SIP endpoint.
csrstActiveStatsGroup
csrstSipVoRegNumberListTagread-only This object indicates the particular index of the
number list configured for the corresponding voice
register pool.
csrstState read-only This object indicates the current state of Cisco SRST
feature on this router.
Active - At least one IP or SIP phone is registered
Inactive - Cisco SRST has no IP or SIP phones
registered
csrstSipPhoneCurrentRegiste
red
read-only Total number of SIP phones currently registered to the
SRST router.
csrstSipCallLegs read-only Total number of SIP call legs routed through the SRST
router since going active. This includes incoming and
outgoing calls.
csrstTotalUpTime read-only Accumulated total number of minutes that router is
active in SRST mode.
csrstMIBNotifsGroup
csrstStateChange notificationAn SRST up or down state change notification is
generated. This indicates one or more phones is
registered to the SRST router or none is registered.
csrstFailNotif notificationA failure notification is generated when the SRST
Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Release 3.4 Guide
1-42
csrstSysNotifSeverity
csrstState
csrstSysNotifReason
router encounters a catastrophic failure.
OL-7959-01
Page 57

Chapter 1 Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Support
Table 1-6 SRST MIB Object Groups and Descriptions (continued)
Max
MIB Group MIB Object
csrstSipPhoneUnRegThresho
ldExceed
csrstSipPhoneRegFailed notificationA SIP phone fail registration notification is generated
csrstConferenceFailed notificationA conference failure notification is generated when the
Access Description
notificationA SIP phone unregistration notification is generated
when the number of SIP phone unregistrations have
exceeded the threshold. The number of currently
registered SIP phones is provided here by
csrstSipPhoneCurrentRegistered object as a reference
such that if csrstSipPhoneCurrentRegistered falls
below csrstSipPhoneUnRegThreshold, a notification
will be generated to indicate that the number of
unregistered SIP phones has crossed the threshold.
csrstSipPhoneUnRegThreshold
csrstSipPhoneCurrentRegistered
when the SIP phone fails to register.
csrstSipEndpointIpAddress
maximum number of conferences are exceeded.
SRST Traps
SRST Traps
SRST traps are SNMP traps, which are unsolicited notifications of an unusual or a catastrophic system
event sent to the system administrator.
SRST traps or alerts are sent for the following:
• Notification (alarm/trap): SRST SCCP port is down.
• Threshold (trap and event correlation) on phones registering back and forth between CM and SRST
router due to flapping WAN link.
• Threshold (trap and event correlation) on phones registering back and forth between SIP
server/proxy and SIP SRST router due to flapping WAN link.
Note Send traps by modem or ISDN dial backup links to a secondary NMS when the primary NMS is down.
(Do this through the configuration in the SRST router.)
Cisco-SRST-MIB Object Mappings
csrstMaxConferences
Table 1 -7 lists the CISCO-SRST-MIB OID mappings.
OL-7959-01
Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Release 3.4 Guide
1-43
Page 58

Cisco-SRST-MIB Object Mappings
Table 1-7 Cisco-SRST-MIB OID Mappings
Object Name Object ID
ciscoMgmt 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9
ciscoSrstMIB 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441
ciscoSrstMIBNotifications 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.0
csrstStateChange 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.0.1
csrstFailNotif 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.0.2
csrstSipPhoneUnRegThresholdExceed 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.0.3
csrstSipPhoneRegFailed 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.0.4
csrstConferenceFailed 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.0.5
ciscoSrstMIBObjects 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.1
csrstGlobal 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.1.1
csrstConf 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.1.2
csrstEnabled 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.1.2.1
csrstVersion 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.1.2.2
csrstIPAddressType 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.1.2.3
csrstIPAddress 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.1.2.4
csrstPortNumber 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.1.2.5
csrstMaxConferences 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.1.2.6
csrstMaxEphones 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.1.2.7
csrstMaxDN 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.1.2.8
csrstSipPhoneUnRegThreshold 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.1.2.9
csrstCallFwdNoAnswer 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.1.2.10
csrstCallFwdNoAnswerTo 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.1.2.11
csrstCallFwdBusy 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.1.2.12
csrstMohFilename 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.1.2.13
csrstMohMulticastAddrType 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.1.2.14
csrstMohMulticastAddr 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.1.2.15
csrstMohMulticastPort 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.1.2.16
csrstVoiceMailNumber 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.1.2.17
csrstSystemMessagePrimary 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.1.2.18
csrstSystemMessageSecondary 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.1.2.19
csrstScriptName 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.1.2.20
csrstSecondaryDialTone 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.1.2.21
csrstTransferSystem 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.1.2.22
csrstUserLocaleInfo 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.1.2.23
csrstDateFormat 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.1.2.24
csrstTimeFormat 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.1.2.25
Chapter 1 Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Support
Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Release 3.4 Guide
1-44
OL-7959-01
Page 59

Chapter 1 Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Support
Table 1-7 Cisco-SRST-MIB OID Mappings (continued)
Object Name Object ID
csrstInterdigitTo 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.1.2.26
csrstBusyTo 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.1.2.27
csrstAlertTo 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.1.2.28
csrstXlateCalledNumber 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.1.2.29
csrstXlateCallingNumber 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.1.2.30
csrstAliasTa ble 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.1.2.31
csrstAliasEntry 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.1.2.31.1
csrstAliasIndex 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.1.2.31.1.1
csrstAliasTag 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.1.2.31.1.2
csrstAliasNumPattern 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.1.2.31.1.3
csrstAliasAltNumber 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.1.2.31.1.4
csrstAliasPreference 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.1.2.31.1.5
csrstAliasHuntStopEnabled 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.1.2.31.1.6
csrstAccessCodeTa bl e 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.1.2.32
csrstAccessCodeEntry 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.1.2.32.1
csrstAccessCodeType 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.1.2.32.1.1
csrstAccessCode 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.1.2.32.1.2
csrstAccessCodeDIDEnabled 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.1.2.32.1.3
csrstLimitDNTabl e 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.1.2.33
csrstLimitDNEntry 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.1.2.33.1
csrstLimitDNType 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.1.2.33.1.1
csrstLimitDN 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.1.2.33.1.2
csrstNotificationEnabled 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.1.2.34
csrstActiveStats 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.1.3
csrstState 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.1.3.1
csrstSipPhoneCurrentRegistered 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.1.3.2
csrstSipCallLegs 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.1.3.3
csrstTotalUpTime 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.1.3.4
csrstSipConf 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.1.4
csrstSipRegSrvExpMax 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.1.4.1
csrstSipRegSrvExpMin 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.1.4.2
csrstSipIp2IpGlobalEnabled 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.1.4.3
csrstSipSend300MultSupport 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.1.4.4
csrstSipVoRegPoolTab le 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.1.4.5
csrstSipVoRegPoolEntry 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.1.4.5.1
csrstSipVoRegPoolTag 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.1.4.5.1.1
Cisco-SRST-MIB Object Mappings
OL-7959-01
Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Release 3.4 Guide
1-45
Page 60

Cisco-SRST-MIB Object Mappings
Table 1-7 Cisco-SRST-MIB OID Mappings (continued)
Object Name Object ID
csrstSipNetId 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.1.4.5.1.2
csrstSipVoRegPoolIpAddrType 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.1.4.5.1.3
csrstSipNetMask 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.1.4.5.1.4
csrstSipProxySrvIpAddr 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.1.4.5.1.5
csrstSipProxySrvPref 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.1.4.5.1.6
csrstSipProxySrvMonitor 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.1.4.5.1.7
csrstSipProxySrvAltIpAddr 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.1.4.5.1.8
csrstSipDefaultPreference 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.1.4.5.1.9
csrstSipVoRegPoolAppl 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.1.4.5.1.10
csrstSipVoRegNumberListTab le 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.1.4.6
csrstSipVoRegNumberListEntry 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.1.4.6.1
csrstSipVoRegNumberListIndex 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.1.4.6.1.1
csrstSipVoRegNumberListTag 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.1.4.6.1.2
csrstSipVoRegNumberPattern 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.1.4.6.1.3
csrstSipVoRegNumberPref 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.1.4.6.1.4
csrstSipVoRegNumberHuntstopEnabled 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.1.4.6.1.5
csrstSipEndpointTab le 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.1.4.7
csrstSipEndpointEntry 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.1.4.7.1
csrstSipEndpointTag 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.1.4.7.1.1
csrstSipVoRegPoolEdptTag 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.1.4.7.1.2
csrstSipEndpointIpAddrType 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.1.4.7.1.3
csrstSipEndpointIpAddress 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.1.4.7.1.4
csrstSipEndpointDN 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.1.4.7.1.5
ciscoSrstMIBConformance 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.2
ciscoSrstMIBCompliances 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.2.1
ciscoSrstMIBCompliance 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.2.1.1
ciscoSrstMIBGroups 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.2.2
csrstConfGroup 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.2.2.1
csrstNotifInfoGroup 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.2.2.2
csrstSysNotifSeverity 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.2.2.2.1
csrstSysNotifReason 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.2.2.2.2
csrstActiveStatsGroup 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.2.2.3
csrstSipConfGroup 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.2.2.4
csrstMIBNotifsGroup 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.441.2.2.5
Chapter 1 Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Support
Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Release 3.4 Guide
1-46
OL-7959-01
Page 61

Chapter 1 Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Support
Glossary
The following terms are used in this document.
ATA — Analog Telephone Adaptor
BRI — Basic Rate Interface
ccb — Call Control Block
CCME — Cisco CallManager Express
COR — Class of Restriction
CTI — Computer Telephony Integration
CUE — Cisco Unity Express
DN — directory number
DnD — do-not-disturb
E&M — ear and mouth (also recEive and transMit)
Ephone — Ethernet phone
Glossary
FXO — foreign exchange office
GUI — Graphical User Interface
IETF — Internet Engineering Task Force
IVR — Interactive Voice Response
MIB — Management Information Base
MoH — Music on hold
MWI — message-waiting indicator
OID — Object Identifier
PLAR — private line, automatic ringdown
PRI — Primary Rate Interface
rcb — Registrar Control Block
RFC — Requests for Comment
SCCP — Skinny Client Control Protocol
SIP — Session Initiated Protocol
SNMP — Simple Network Management Protocol
SRST — Survivable Remote Site Telephony
TCL — Tool Command Language
VoFR — Voice over Frame Relay
OL-7959-01
Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Release 3.4 Guide
1-47
Page 62

Glossary
Chapter 1 Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Support
Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Release 3.4 Guide
1-48
OL-7959-01
 Loading...
Loading...