Page 1

ADMINISTRATION
GUIDE
Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG
Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x
Page 2
Contents
Chapter 1: Getting Started 10
Starting the Web-based Configuration Utility 10
Out-Of-Band Port 13
USB Port 15
Basic or Advanced Display Mode 16
Quick Start Device Configuration 17
Interface Naming Conventions 18
Window Navigation 19
Search Facility 22
Chapter 2: Dashboard 23
Grid Management 23
System Health 24
Resource Utilization 25
Identification 26
Port Utilization 27
PoE Utilization 27
Latest Logs 28
Suspended Interfaces 28
Stack Topology 29
Traffic Errors 30
Chapter 3: Configuration Wizards 31
Getting Started Wizard 31
VLAN Configuration Wizard 33
ACL Wizard 34
Chapter 4: Status and Statistics 37
System Summary 38
CPU Utilization 40
Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x 1
Page 3
Contents
Interface 40
Etherlike 42
Port Utilization 43
GVRP 43
802.1X EAP 44
ACL 45
TCAM Utilization 46
Health and Power 48
Switched Port Analyzer (SPAN and RSPAN) 54
Diagnostics 57
RMON 61
sFlow 69
View Logs 72
Chapter 5: Administration 74
Device Models 74
System Settings 77
Console Settings (Autobaud Rate Support) 77
User Accounts 78
Idle Session Timeout 79
System Log 80
Reboot 84
Routing Resources 85
Ping 89
Traceroute 91
Chapter 6: Administration: File Management 92
System Files 92
Firmware Operations 94
File Operations 98
Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x 2
Page 4
Contents
File Directory 105
DHCP Auto Configuration/Image Update 106
Chapter 7: Administration: Stack Management 116
Overview 116
Types of Units in Stack 117
Stack Topology 118
Unit ID Assignment 119
Master Selection Process 120
Stack Changes 120
Unit Failure in Stack 121
Stack Ports 123
Software Auto Synchronization in Stack 126
Stack Management 130
Chapter 8: Administration: Time Settings 132
System Time Configuration 133
SNTP Modes 134
System Time 135
SNTP Unicast 137
SNTP Multicast/Anycast 139
SNTP Authentication 140
Time Range 141
Recurring Time Range 143
Chapter 9: Administration: Discovery 144
Bonjour 144
LLDP and CDP 145
Discover - LLDP 147
Discovery - CDP 167
Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x 3
Page 5
Contents
Chapter 10: Port Management 178
Workflow 178
Port Settings 179
Error Recovery Settings 183
Loopback Detection Settings 184
Link Aggregation 186
UDLD 193
PoE 201
Green Ethernet 212
Chapter 11: Smartport 219
Overview 219
How the Smartport Feature Works 224
Auto Smartport 225
Error Handling 228
Default Configuration 228
Relationships with Other Features 229
Common Smartport Tasks 229
Configuring Smartport Using The Web-based Interface 231
Built-in Smartport Macros 236
Chapter 12: VLAN Management 247
Overview 247
Regular VLANs 254
Private VLAN Settings 262
GVRP Settings 262
VLAN Groups 263
Voice VLAN 269
Access Port Multicast TV VLAN 282
Customer Port Multicast TV VLAN 285
Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x 4
Page 6
Contents
Chapter 13: Spanning Tree 289
STP Flavors 289
STP Status and Global Settings 290
STP Interface Settings 292
RSTP Interface Settings 295
Multiple Spanning Tree Overview 297
MSTP Properties 297
VLANs to a MSTP Instance 298
MSTP Instance Settings 299
MSTP Interface Settings 300
Chapter 14: Managing MAC Address Tables 303
Static Addresses 304
Dynamic Addresses 305
Reserved MAC Addresses 306
Chapter 15: Multicast 308
Multicast Forwarding Overview 308
Properties 314
MAC Group Address 315
IP Multicast Group Address 316
IPv4 Multicast Configuration 318
IPv6 Multicast Configuration 324
IGMP/MLD Snooping IP Multicast Group 330
Multicast Router Port 331
Forward All 331
Unregistered Multicast 332
Chapter 16: IP Configuration 334
Overview 334
Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x 5
Page 7
Contents
IPv4 Management and Interfaces 337
IPv6 Management and Interfaces 364
Policy-Based Routing 388
Domain Name System 391
Chapter 17: IP Configuration: RIPv2 396
Overview 396
How Rip Operates on the Device 397
Configuring RIP 400
Access Lists 405
Chapter 18: IP Configuration: VRRP 408
Overview 408
VRRP Topology 409
Configurable Elements of VRRP 410
Configuring VRRP 413
Chapter 19: IP Configuration: SLA 417
Overview 417
Using SLA 419
Chapter 20: Security 424
Configuring TACACS+ 425
RADIUS 429
Password Strength 440
Key Management 442
Management Access Method 445
Management Access Authentication 450
SSL Server 451
TCP/UDP Services 454
Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x 6
Page 8
Contents
Storm Control 455
Port Security 458
IP Source Guard 460
ARP Inspection 464
Denial of Service Prevention 469
Chapter 21: Security: 802.1X Authentication 480
Overview 480
Properties 493
Port Authentication 495
Host and Session Authentication 498
Authenticated Hosts 499
Locked Clients 499
Web Authentication Customization 500
Chapter 22: Security: Secure Sensitive Data Management 504
Introduction 504
SSD Management 505
SSD Rules 505
SSD Properties 510
Configuration Files 513
SSD Management Channels 517
Menu CLI and Password Recovery 518
Configuring SSD 518
Chapter 23: Security: SSH Server 522
Overview 522
Common Tasks 523
SSH User Authentication 524
SSH Server Authentication 525
Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x 7
Page 9
Contents
Chapter 24: Security: SSH Client 527
Overview 527
SSH User Authentication 533
SSH Server Authentication 534
Change User Password on the SSH Server 536
Chapter 25: Security: IPv6 First Hop Security 537
IPv6 First Hop Security Overview 537
Router Advertisement Guard 540
Neighbor Discovery Inspection 541
DHCPv6 Guard 541
Neighbor Binding Integrity 542
IPv6 Source Guard 544
Attack Protection 545
Policies, Global Parameters and System Defaults 547
Common Tasks 549
Default Settings and Configuration 551
Configuring IPv6 First Hop Security through Web GUI 552
Chapter 26: Access Control 571
Overview 571
MAC-Based ACLs Creation 575
IPv4-based ACL Creation 577
IPv6-Based ACL Creation 582
ACL Binding 585
Chapter 27: Quality of Service 588
QoS Features and Components 589
General 591
QoS Basic Mode 603
Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x 8
Page 10
Contents
QoS Advanced Mode 605
QoS Statistics 618
Chapter 28: SNMP 622
Overview 622
Engine ID 627
Views 629
Groups 630
Users 631
Communities 633
Trap Settings 635
Notification Recipients 636
Notification Filter 640
Chapter 29: Smart Network Application (SNA) 642
SNA Sessions 643
SNA Graphics 644
Top Right-Hand Menu 646
Topology View 647
Right-Hand Information Panel 654
Operations 667
Overlays 672
Tags 676
Search 680
Notifications 682
Device Authorization Control (DAC) 685
DAC Workflow 685
Services 693
Saving SNA Settings 709
Technical Details 710
Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x 9
Page 11

Getting Started
This section provides an introduction to the web-based configuration utility, and covers the
following topics:
1
• Starting the Web-based Configuration Utility
• Out-Of-Band Port
• USB Port
• Basic or Advanced Display Mode
• Quick Start Device Configuration
• Interface Naming Conventions
• Window Navigation
• Search Facility
Starting the Web-based Configuration Utility
This section describes how to navigate the web-based switch configuration utility.
If you are using a pop-up blocker, make sure it is disabled.
Browser Restrictions
If you are using IPv6 interfaces on your management station, use the IPv6 global address and
not the IPv6 link local address to access the device from your browser.
Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x 8
Page 12
1
Getting Started
Starting the Web-based Configuration Utility
Launching the Configuration Utility
To open the web-based configuration utility:
STEP 1 Open a Web browser.
STEP 2 Enter the IP address of the device you are configuring in the address bar on the browser, and
then press Enter.
NOTE When the device is using the factory default IP address of 192.168.1.254, its system LED
flashes continuously. When the device is using a DHCP-assigned IP address or an
administrator-configured static IP address, the system LED is on solid.
On the SG350XG and the SG550XG, the default IP address 192.168.1.254 is configured to the
OOB port of the device, while on the other devices it is configured on the default VLAN (Vlan
1). To access the device with the IP address configured on the OOB port, make sure the OOB
port is connected to your network or PC.
Logging In
The default username/password is cisco/cisco. The first time that you log in with the default
username and password, you are required to enter a new password.
NOTE If you have not previously selected a language for the GUI, the language of the Login page is
determined by the language(s) requested by your browser and the lang uages configured on your
device. If your browser requests Chinese, for example, and Chinese has been loaded into your
device, the Login page is automatically displayed in Chinese. If Chinese has not been loaded
into your device, the Login page appears in English.
The languages loaded into the device have a language and country code (en-US, en-GB and so
on). For the Login page to be automatically displayed in a particular language, based on the
browser request, both the language and country code of the browser request must match those
of the language loaded on the device. If the browser request contains only the language code
without a country code (for example: fr). The first embedded language with a matching
language code is taken (without matching the country code, for example: fr_CA).
Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x 9
Page 13
Getting Started
Starting the Web-based Configuration Utility
To log in to the device configuration utility:
STEP 1 Enter the username/password. The password can contain up to 64 ASCII characters.
Password-complexity rules are described in Password Strength.
STEP 2 If you are not using English, select the desired language fr om the Lan guage dro p-down menu.
To add a new language to the device or update a current one, see the description of the
Language Menu described in Application Header.
STEP 3 If this is the first time that you logged on with the default user ID (cisco) and the default
password (cisco) or your password has expired, the Change Password Page appears. See
Password Expiration for additional information.
STEP 4 Choose whether to select Password Complexity Settings in the Password Strength page.
STEP 5 Enter the new password and click Apply.
When the login attempt is successful, the Getting Started page appears.
1
If you entered an incorrect username or password, an error message appears and the Login
page remains displayed on the window.
Select Don't show this page on startup to prevent the Getting Started page from being
displayed each time that you log on to the system. If you select this option, the System
Summary page is opened instead of the Getting Started page.
HTTP/HTTPS
You can either open an HTTP session (not secured) by clicking Log In, or you can open an
HTTPS (secured) session, by clicking Secure Browsing (HTTPS). You are asked to approve
the logon with a default RSA key, and an HTTPS session is opened.
NOTE There is no need to input the username/password prior to clicking the Secure Browsing
(HTTPS) button.
For information on how to configure HTTPS, see SSL Server.
Password Expiration
The New Password page is displayed in the following cases:
• The first time that you access the device with the default username cisco and password
cisco. This page forces you to replace the factory default password.
Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x 10
Page 14
1
Getting Started
Out-Of-Band Port
• When the password expires, this page forces you to select a new password.
Logging Out
By default, the application logs out after ten minutes of inactivity. You can change this default
value as described in the Defining Idle Session Timeout section.
!
CAUTION Unless the Running Configuration is copied to the Startup Configuration, rebooting the device
removes all changes made since the last time the file was saved. Save the Running
Configuration to the Startup Configuration before log ging off to preserve any changes you
made during this session.
A flashing red X icon to the left of the Save application link indicates that Running
Configuration changes have not yet been saved to the Startup Configuration file. The flashing
can be disabled by clicking on the Disable Save Icon Blinking button on the Copy/Save
Configuration page
Out-Of-Band Port
When the device auto-discovers a connected device, such as an IP phone (see What is a
Smartport), and it configures the port appropriately for the device. These configuration
commands are written to the Running Configuration file. This causes the Save icon to begin
blinking when the you log on, even though you did not make any configuration changes.
When you click Save, the Copy/Save Configuration page appears. Save the Running
Configuration file by copying it to the Startup Configuration file. After this save, the red X icon
and the Save application link are no longer displayed.
To logout, click Logout in the top right corner of any page. The system logs out of the device.
When a timeout occurs or you intentionally log out of the system, a message is displayed and
the Login page appears, with a message indicating the logged-out state. After you log in, the
application returns to the initial page.
The initial page displayed depends on the “Do not show this page on startup” option in the
Getting Started page. If you did not select this option, the initial page is the Getting Started
page. If you did select this option, the initial page is the System Summary page.
NOTE OOB is only supported on SG350XG and SG550XG devices.
Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x 11
Page 15
Getting Started
Out-Of-Band Port
1
The switch supports an Out-of-Band (OOB) port. This port is used for the management
network. The out-of-band and the in-band ports share the same IP routing table, therefore you
cannot use the same subnet on both in-band and out-of-band interfaces.
The OOB port is assigned an MAC address which is different from the base MAC
address and the addresses of the in-band ports. This MAC address is used as the
source MAC address in all frames (including IP frames) sent by the switch on the
OOB port.
The IP address assigned to this port cannot be assigned to the in-band ports at the same time.
In addition, the IP address assigned to the OOB port must not belong to any IP subnet
configured at the in-band interfaces of the devices.
By default, the OOB port is configured with the default IP address 192.168.1.254. This default
IP address is used when no other address was assigned (dynamically or statically). This sub net
is a reserved one and cannot be assigned on the in-band interfaces.
Bridging
Bridging between the OOB port and the in-band Layer 2 interfaces is not
supported. The OOB port cannot be a member of VLAN or LAG, and the bridge’s
protocols (for example, STP, GVRP, etc.) cannot be enabled on the OOB port.
Only untagged traffic is supported on the OOB port.
Port Configuration
The following Ethernet configuration is supported for the OOB port:
• Speed (10/100/1000)
• Duplex
• Auto-negotiation
DHCP Client
DHCP client (IPv4 and IPv6) is en abled by default on th e OOB port and on the default VLAN.
Static route on OOB port
Static routes are supported on the OOB port.
Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x 12
Page 16
1
Getting Started
USB Port
IPv4 Address on OOB port
Only one IPv4 address can be defined on the OOB port.
The default static IP address is set only on the OOB.
IP Applications
All IP applications, such as telnet, SSH, except for the following ones are supported on the
OOB port:
• ARP Proxy
• Routing protocols
• Relay applications (DHCP, DHCPv6 and UDP)
USB Port
QoS & ACL
QoS and ACL are not supported on the OOB port (so all TCAM-based features like DOS
Attack Prevention are also not supported).
Only Management ACLs are supported.
Stack Support
The OOB port name is always mapped to the physical OOB port of master unit. The physical
OOB ports of slaves are not functional and will not establish a link when connected to a
neighbor device or PC.
The USB port can be used for connecting external storage (disk-on-key) devices. It can hold
configuration, SYSLOG and image files. In a stack, only the master’s USB port is active. The
USB port fully supports the F AT32 file system, and provides partial support (read only) for the
NTFS file system.
Both relative path or fully qualified paths can be used.
The system supports the following user actions on the USB port through the GUI:
• Display the USB contents
Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x 13
Page 17
Getting Started
Basic or Advanced Display Mode
• Copy files to/from USB (the same as with TFTP)
• Delete, rename and display the contents of USB files
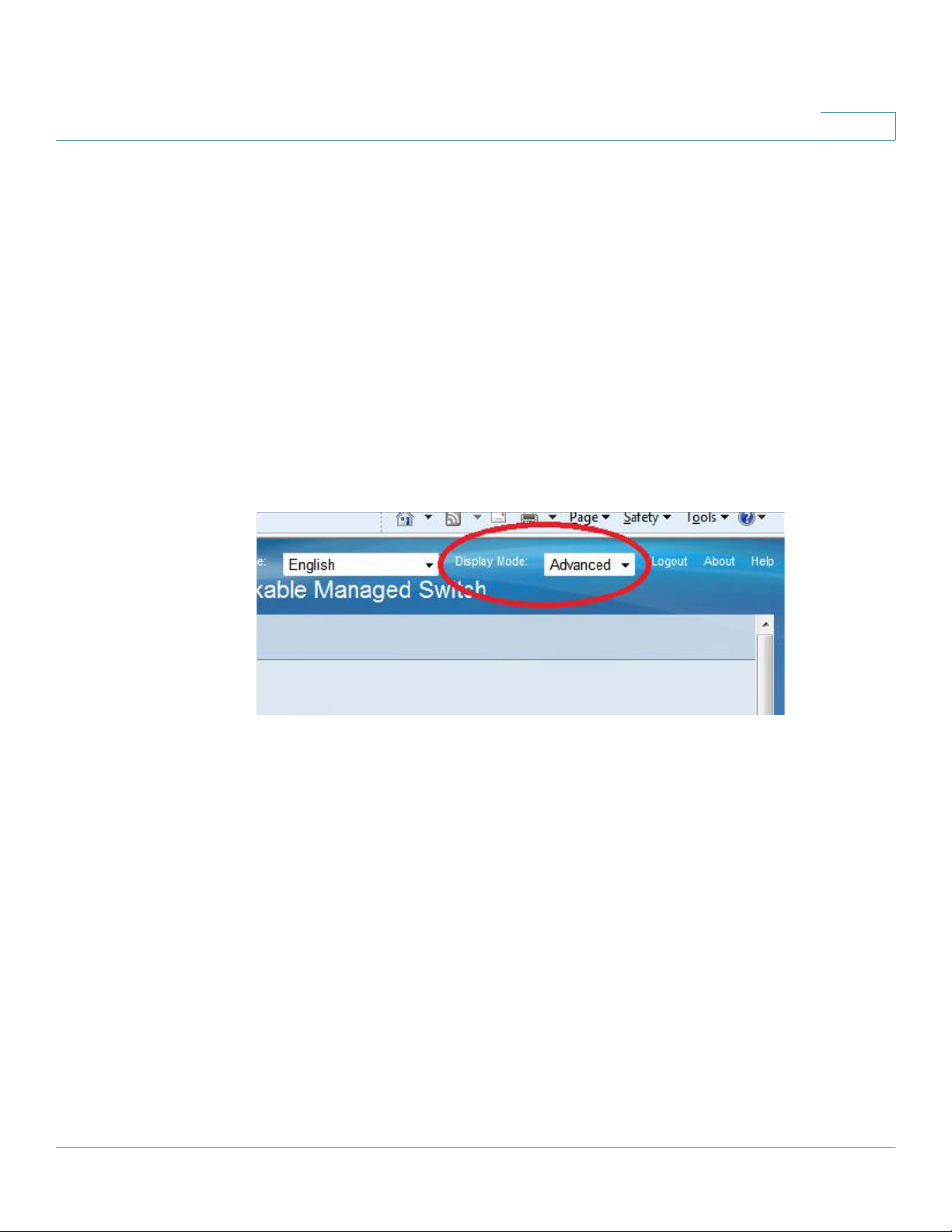
Basic or Advanced Display Mode
The product supports many features, and therefore the WEB GUI includes hundreds of
configuration and display pages. These pages are divided into the following display modes:
• Basic—Basic subset of configuration options are available. If you are missing some
configuration option, select the Advanced mode in the device header.
• Advanced—Full set of configuration options are available.
Navigate from one mode to another, as shown below:
1
When the user switches from basic to advanced, the browser reloads the page. However, after
reload, the user stays on the same page.
When the user switches from advanced to basic, the browser reloads the page. If the page
exists also on the basic mode, the user stays on the same page. If the page does not exist in the
basic mode, the browser will load the first page of the folder which was used by the user . If the
folder does not exist, the Getting Started page will be displayed.
If there is advanced configuration, and the page is loaded in basic mode, a page-level message
will be displayed to the user (e.g. there are 2 radius server configured but in basic mode only a
single server can be displayed, or there is 802.1X port authentication with time range
configured but time range is not visible in basic mode).
When switching from one mode to another, any configuration which was made on the page
(without Apply) is deleted.
Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x 14
Page 18
1
Quick Start Device Configuration
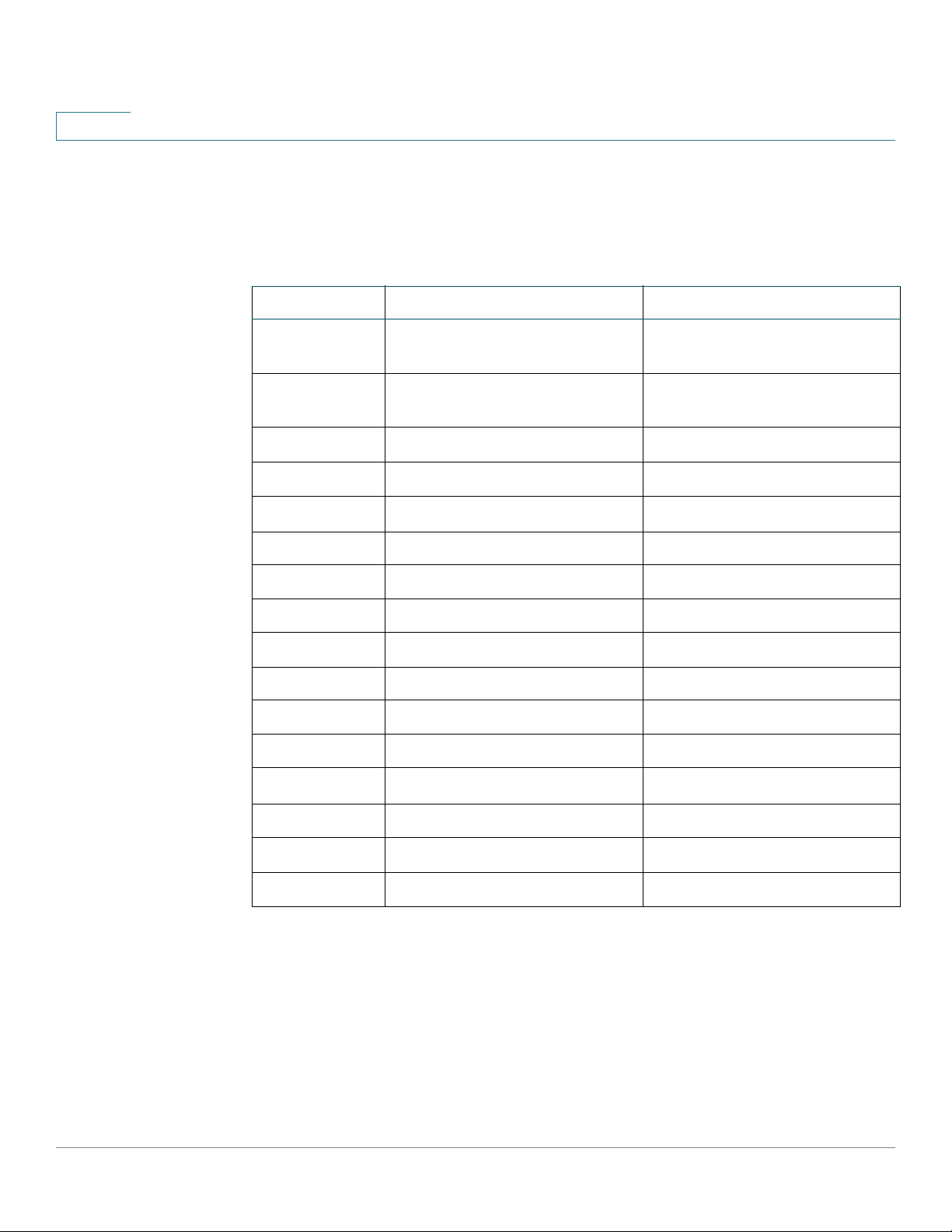
For quick initial setup, you can use the configuration wizards described in VLAN
Configuration Wizard or use the links on the Getting Started page, as described below:
Category Link Name (on the Page) Linked Page
Getting Started
Quick Start Device Configuration
Initial Setup
Device Status System Summary System Summary
Quick Access Change Device Password User Accounts
Manage Stack Administration: Stack
Management
Change Management Application s
and Services
Change Device IP Address IPv4 Interface
Create VLAN VLAN Settings
Configure Port Settings Port Settings
Port Statistics Interface
RMON Statistics Statistics
Vi ew Log RAM Memory
Upgrade Device Software Firmware Operations
Backup Device Configuration File Operations
Create MAC-Based ACL MAC-Based ACLs Creation
TCP/UDP Services
Create IP-Based ACL IPv4-based ACL Creation
Configure QoS QoS Properties
Configure SPAN Switched Port Analyzer (SPAN)
There are two hot links on the Getting Started page that take you to Cisco web pages for more
information. Clicking on the Support link takes you to the device product support page, and
clicking on the Forums link takes you to the Support Community page.
Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x 15
Page 19
Getting Started
Interface Naming Conventions
Interface Naming Conventions
Within the GUI, interfaces are denoted by concatenating the following elements:
• Type of interface: The following types of interfaces are found on the various types of
devices:
- Fast Ethernet (10/100 bits)—These are displayed as FE. Supported only on the
350 family.
- Gigabit Ethernet ports (10/100/1000 bits)—These are displayed as GE.
Supported only on the 350 family
- Ten Gigabit Ethernet ports (1000/10,000 Mbps)—These are displayed as XG.
- Out-of-Band Port—This is displayed as OOB.
1
- LAG (Port Channel)—These are displayed as LAG.
- VLAN—These are displayed as VLAN.
- Tunnel —These are displayed as Tunnel.
• Unit Number—Number of the unit in the stack. The unit number together with the
interface number completely identifies the port. For example, GE1/0/4 is port number
4 on the first unit of the stack.
• Slot Number—The slot number is always 0.
• Interface Number: Port, LAG, Tunnel, or VLAN ID.
Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x 16
Page 20
1
Window Navigation
This section describes the features of the web-based switch configuration utility.
Application Header
The Application Header appears on every page. It provides the following application links:
Getting Started
Window Navigation
Application Link
Name
Username Displays the name of the user logged on to the device. The default
Description
A flashing red X icon displayed to the left of the Save application
link indicates that Running Configuration changes have been made
that have not yet been saved to the Startup Configuration file. The
flashing of the red X can be disabled on the Copy/Save
Configuration page.
Click Save to display the Copy/Save Configuration page. Save the
Running Configuration file by copying it to the Startup
Configuration file type on the device. After this save, the red X
icon and the Save application link are no longer displayed. When
the device is rebooted, it copies the Startup Configuration file type
to the Running Configuration and sets the device parameters
according to the data in the Running Configuration.
username is cisco. (The default password is cisco).
Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x 17
Page 21
Getting Started
Window Navigation
1
Application Link
Name
Language Menu This menu provides the following options:
Logout Click to log out of the web-based switch configuration utility.
Description
• Select a language: Select one of the languages that appear
in the menu. This language will be the web-based
configuration utility language.
• Download Language: Add a new language to the device.
• Delete Language: Deletes the second language on the
device. The first language (English) cannot be deleted.
• Debug: Used for translation purposes. If you select this
option, all web-based configuration utility labels disappear
and in their place are the IDs of the strings that correspond
to the IDs in the language file.
NOTE T o upgrade a language file, use the Upgrade/Backup
Firmware/Language page.
About Click to display the device name and device version number.
Help Click to display the online help.
The SYSLOG Alert Status icon appears when a SYSLOG message,
above the critical severity level, is logged. Click the icon to open
the RAM Memory page. After you access this page, the SYSLOG
Alert Status icon is no longer displayed. To display the page when
there is not an active SYSLOG message, Click Status and
Statistics > View Log > RAM Memory.
Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x 18
Page 22

1
Getting Started
Window Navigation
Management Buttons
The following table describes the commonly-used buttons that appear on various pages in the
system.
Button Name Description
Use the pull-down menu to configure the number of entries per
page.
Indicates a mandatory field.
Add Click to display the related Add page and add an entry to a table.
Enter the information and click Apply to save it to the Running
Configuration. Click Close to return to the main page. Click Save
to display the Copy/Save Configuration page and save the Running
Configuration to the Startup Configuration file type on the device.
Apply Click to apply changes to the Running Configuration on the device.
If the device is rebooted, the Running Configuration is lost, unless
it is saved to the Startup Configuration file type or another file
type. Click Save to display the Copy/Save Configuration page and
save the Running Configuration to the Startup Configuration file
type on the device.
Cancel Click to reset changes made on the page.
Clear Filter Click to clear filter to select information displayed.
Clear All Interfaces
Counters
Clear Interface
Counters
Clear Logs Clears log files.
Clear Table Clears table entries.
Close Returns to main page. If any changes were not applied to the
Click to clear the statistic counters for all interfaces.
Click to clear the statistic counters for the selected interface.
Running Configuration, a message appears.
Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x 19
Page 23
Getting Started
Search Facility
1
Button Name Description
Copy Settings A table typically contains one or more entries containing
configuration settings. Instead of modifying each entry
individually, it is possible to modify one entry and then copy the
selected entry to multiple entries, as described below:
1. Select the entry to be copied. Click Copy Settings to display the
popup.
2. Enter the destination entry numbers in the to field.
3. Click Apply to save the changes and click Close to return to the
main page.
Delete After selecting an entry in the table, click Delete to remove.
Details Click to display the details associated with the entry selected.
Search Facility
Edit Select the entry and click Edit. The Edit page appears, and the
entry can be modified.
1. Click Apply to save the changes to the Running Configuration.
2. Click Close to return to the main page.
Go Enter the query filtering criteria and click Go. The results are
displayed on the page.
Refresh Click Refresh to refresh the counter values.
Test Click Test to perform the related tests.
Restore Defaults Click Restore Defaults to restore factory defaults.
The search function helps the user to locate relevant GUI pages.
The search result for a keyword includes links to the relevant pages, and also links to the
relevant help pages.
Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x 20
Page 24
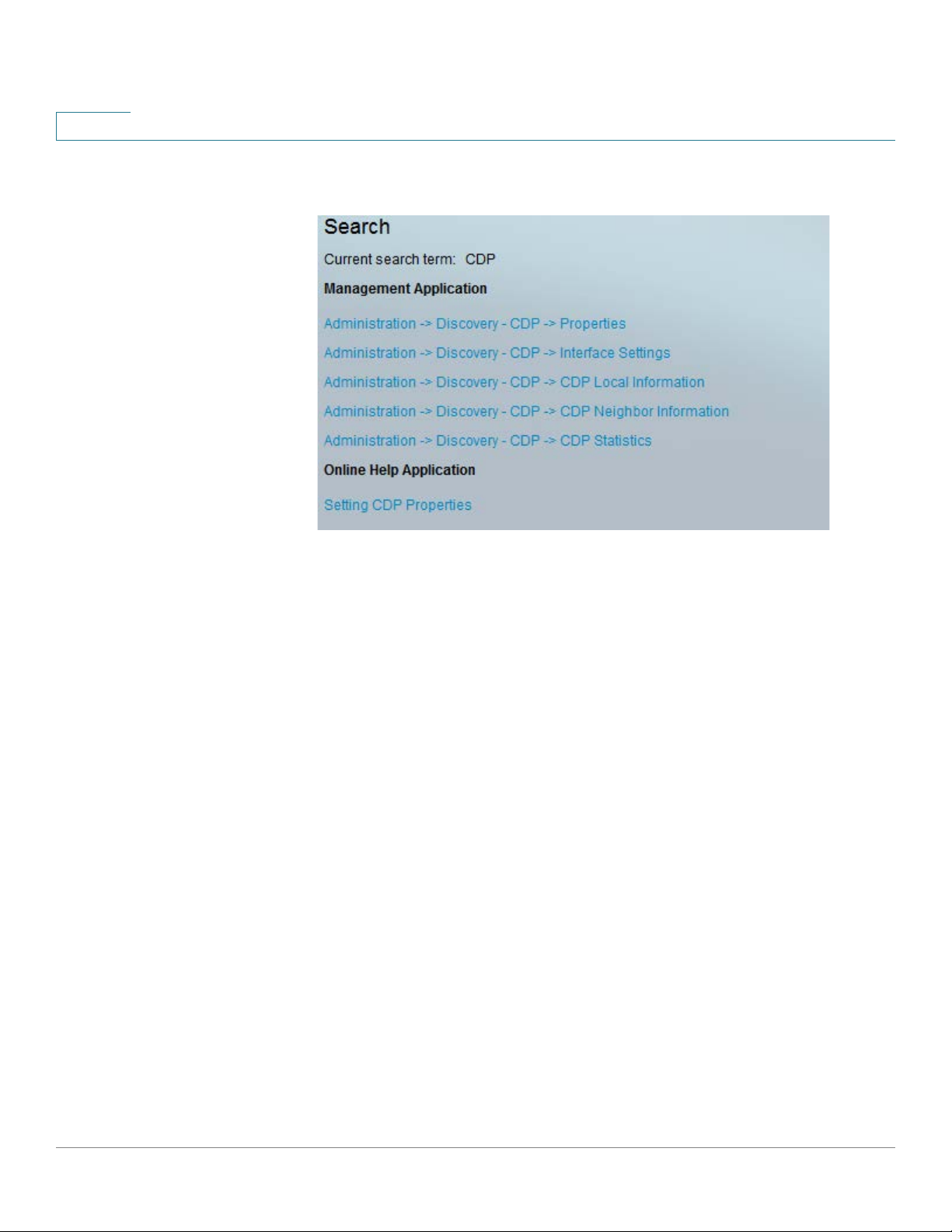
1
Getting Started
Search Facility
To access the search function, enter a key word and click on the magnifying glass icon. The
following is an example of the results when searching for the keyword: CDP:
If you are in Basic mode, links to pages in Advanced mode are displayed but not available.
Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x 21
Page 25

Dashboard
2
The dashboard is a collection of 8 squares, initially empty, that can be populated by various
types of information
You can select a number of modules from the available modules and place them in this grid.
You can also customize settings of the currently-displayed modules.
When the dashboard loads, the modules you selected for the dashboard are loaded in their
locations in the grid. The data in the modules is updated periodically , in intervals depending on
the module type. These intervals are configurable for some modules.
This following topics are covered in this chapter:
• Grid Management
Grid Management
• System Health
• Resource Utilization
• Identification
• Port Utilization
• PoE Utilization
• Latest Logs
• Suspended Interfaces
• Stack T opology
• Traffic Errors
The dashboard consists of multiple modules, but only a subset of the modules can be viewed at
the same time.
Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x 20
Page 26

2
Dashboard
Grid Management
When you open the dashboard, a wire frame view of the grid is displayed, as shown below
(only 2 squares are shown in the following screen capture):
To display modules that are not currently being displayed, click on Customize on the upper-
right of the dashboard, as shown below:
Add modules to the grid by selecting a module from the list of modules on the right and
dragging and dropping it to any space in the grid.
The modules are divided into the following groups:
• Small Modules are modules that take up a single square
• Large Modules take up two squares.
If you drag a module into a space currently occupied, the new module replaces the previous
one.
You can re-arrange the placement of the modules in the grid by dragging a module from one
occupied grid position to another position. The module can be dropped in an unoccupied spot,
or in a spot occupied by a module of the same size. If the selected spot is occupied, the
modules switch places.
21 Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x
Page 27
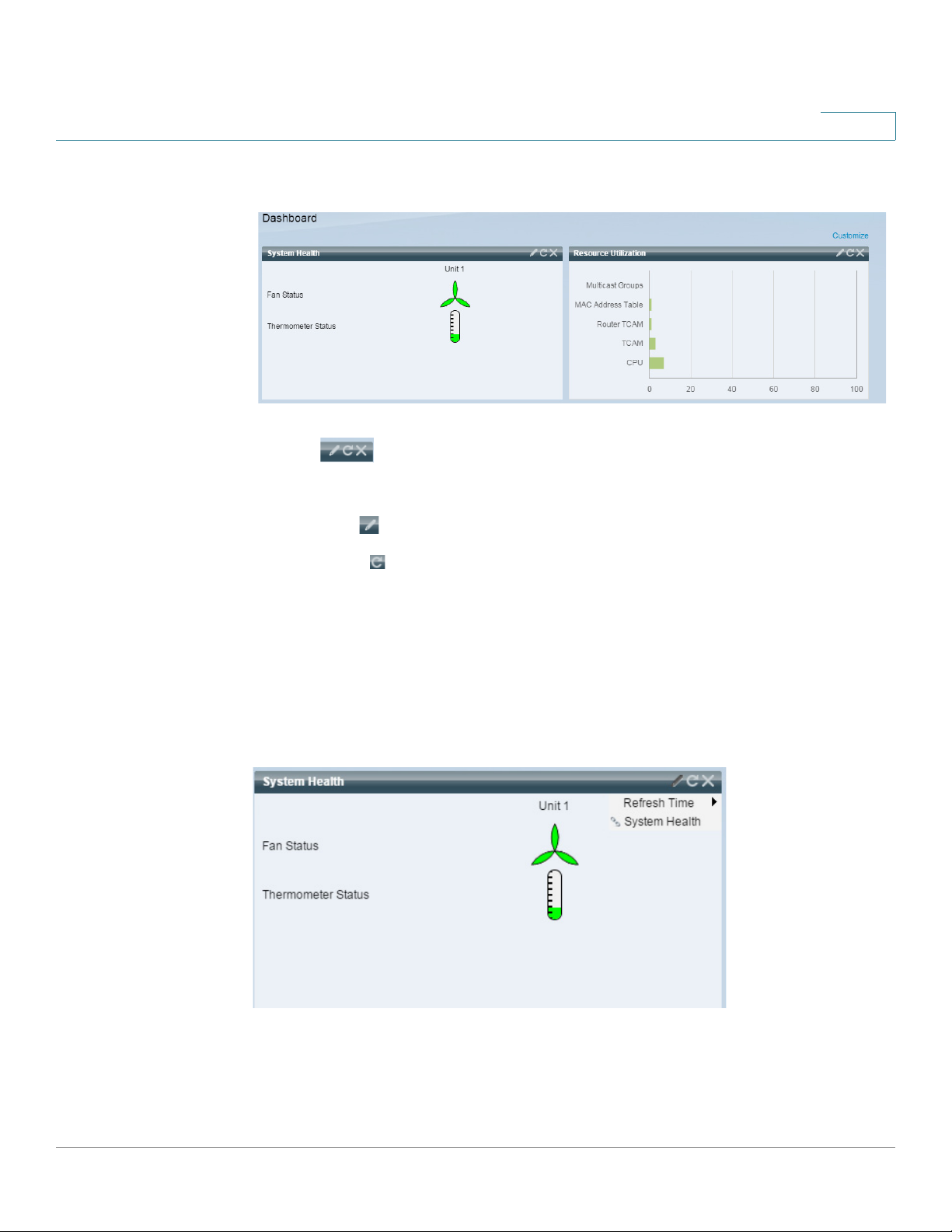
Dashboard
System Health
2
Only when you click Done (in the right-hand corner), are the modules populated by the
relevant information, as shown below:
The title bar of each module in the dashboard displays the title of the module and three
buttons:
These button perform the following:
System Health
• Pencil — Opens configuration options (depending on the module).
• Refresh — Refreshes the information.
• X — Removes the module from the dashboard.
This module displays information about device temperature (when such information is
available) for a standalone device or for each device in the stack, as shown below:
The following icons are shown:
• Fan Status—Yellow if one fan failed and is backed up by the redundant fan; Green if
the fan is operational; Red if the fan is faulty.
Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x 22
Page 28
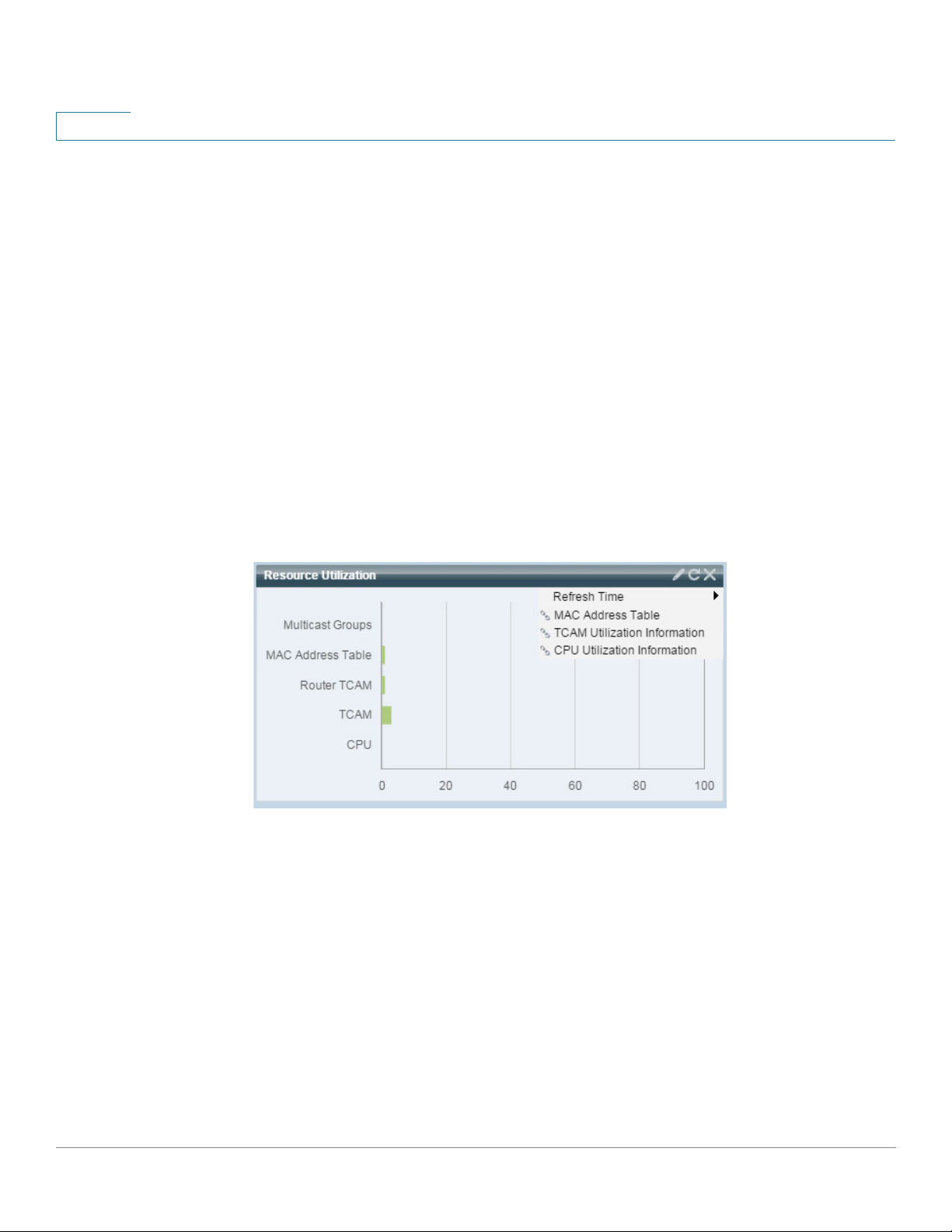
2
The following configuration options (pencil icon in upper right-hand corner) are available:
Resource Utilization
Dashboard
Resource Utilization
• Thermometer Status
- Temperature is OK—Green with a nearly empty thermometer.
- Temperature generates a warning—Yellow with a half full thermometer.
- Temperature is critical—Red with a full thermometer.
• Refresh Time—Select one of the options displayed.
• System Health—Click to open the Health and Power page.
This module displays the utilization status in terms of a percentage of the various system
resources as a bar chart, as shown below:
The resources monitored are:
• Multicast Groups—Percentage of Multicast groups that exist out of the maximum
possible number that are permitted to be defined.
• MAC Address T able—Percentage of MAC Address table in use.
• Router TCAM—Usage in percentage of router TCAM.
• TCAM—Usage in percentage of all non-IP TCAM entries.
• CPU—Percentage of CPU being used.
Each bar becomes red if the resource utilization is higher than 80 percent.
23 Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x
Page 29
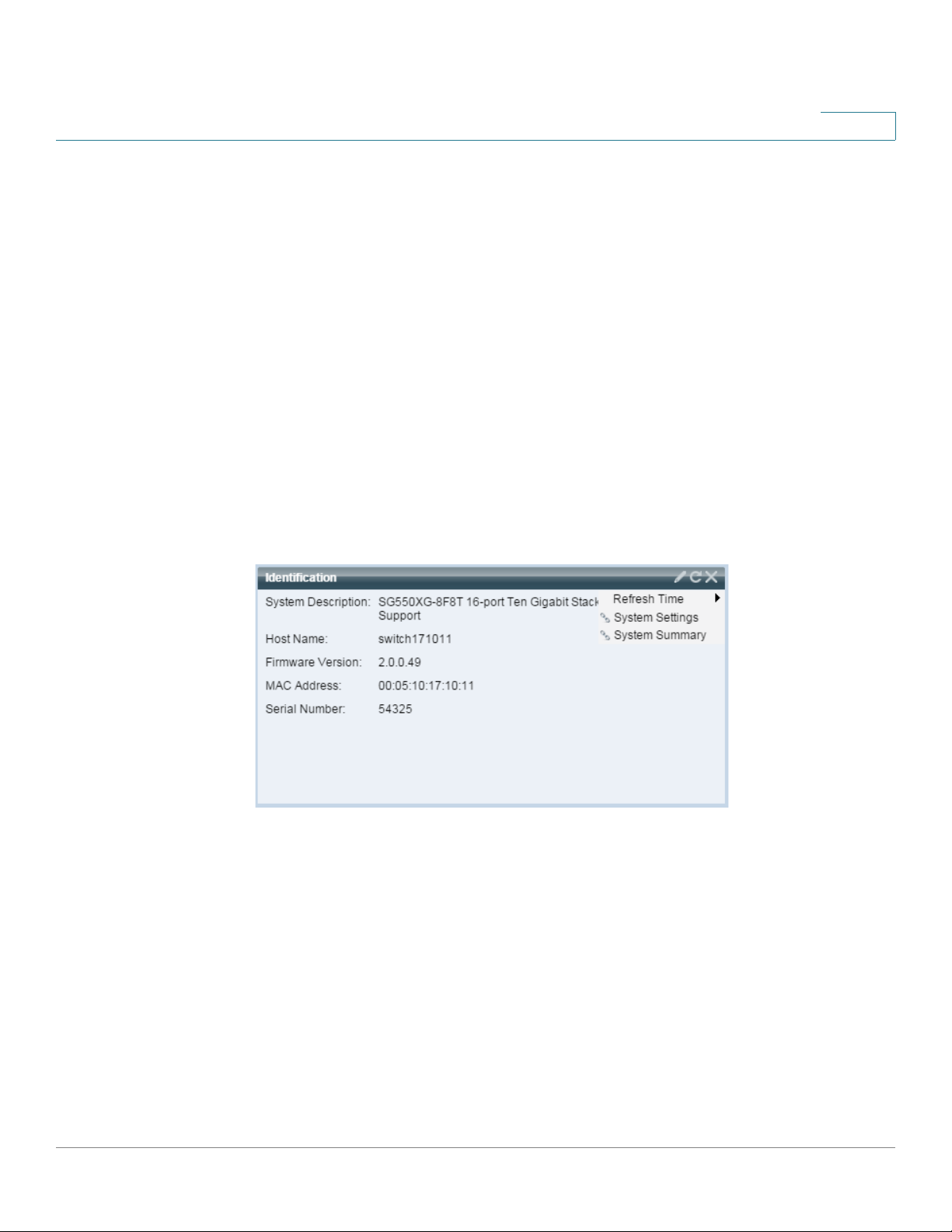
Dashboard
Identification
Identification
2
Hovering over a bar displays a tooltip displaying the numeric utilization information (used
resources/max available).
The following configuration options (right-hand corner) are available:
• Refresh Time—Select one of the options displayed.
• Multicast Groups—Click to open MAC Group Address
• MAC Address T able—Click to open Dynamic Addresses.
• TCAM Utilization Information—Click to open TCAM Utilization.
• CPU Utilization Information—Click to open CPU Utilization.
This module displays basic information regarding the device and stack, as shown below:
It displays the following fields:
• System Description—Displays description of the device.
• Host Name—Entered in the System Settings page or default is used. Also can be
added in the Getting Started Wizard.
• Firmware Version—Current firmware version running on device.
• MAC Address (master unit)—MAC address of the unit.
• Serial Number (master unit)—Serial number of the unit.
• System Location—Enter the physical location of the device.
Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x 24
Page 30

2
Port Utilization
Dashboard
Port Utilization
• System Contact—Enter the name of a contact person.
• T otal Available Power—Amount of power available to the device.
• Current Power Consumption—Amount of power consumed by the device.
The following configuration options (right-hand corner) are available:
• Refresh Time—Select one of the options displayed.
• System Settings—Click to open System Settings.
• System Summary—Click to open System Summary.
This modules displays the ports on the device in either device or chart view. The view is
selected in the configuration options (pencil icon in upper-right corner).
• Display Mode—Device View
Displays the device. Hovering over a port displays information about it.
25 Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x
Page 31

Dashboard
Port Utilization
2
• Display Mode—Chart View
A list of ports is displayed. The port utilization is displayed in bar format:
For each port, the following port utilization information is displayed:
Tx—% (green)
Rx—% (blue)
• Refresh Time—Select one of the displayed options.
• Interface Statistics—Lick to link to the Status and Statistics -> Interface page.
Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x 26
Page 32

2
PoE Utilization
Dashboard
PoE Utilization
This module displays a graphic representation of the PoE utilization status., as shown below:
Latest Logs
For a standalone unit, this module displays a gauge with a dial of values from 0-100. The
section of the dial from the traps threshold to 100 is red. In the middle of the gauge, the actual
PoE utilization value is shown in watts.
Each bar represents the PoE utilization percentage value of the device on a scale of 0 to 100. If
the PoE utilization is higher than the traps threshold, the bar is red. Otherwise the bar is green.
When hovering on a bar, a tooltip appears showing the actual PoE utilization of the unit in
watts.
This module contains information about the five latest events logged by the system as
SYSLOGs, as shown below:
27 Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x
Page 33

Dashboard
Suspended Interfaces
The following configuration options (right-hand corner) are available:
• Severity Threshold—Described in Log Settings.
• Refresh Time—Select one of the options displayed.
• View Logs—Click to open RAM Memory.
NOTE See View Logs for more information.
Suspended Interfaces
This module displays interfaces that have been suspended in either device or table view. The
view is selected in the configuration options (pencil icon in upper-right corner).
• Device View
2
In this view, the device is displayed This is shown below:
When units are connected in a stack, a drop-down selector enables the user to select the
device to be viewed. All suspended ports in the device are shown as red.
Hovering over a suspended port displays a tooltip with the following information:
- Port name.
- If the port is a member of a LAG, the LAG identity of the port.
- The suspension reason if it is suspended.
• Table V iew
Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x 28
Page 34

2
Dashboard
Stack Topology
In table view , there is no need to select a specific stack unit. Information is displayed in
table form, as shown below:
The following fields are displayed:
- Interface—Port or LAG that was suspended
- Suspension Reason—Reason interface was suspended
- Auto-recovery current status—Has auto recovery been enable for the featu re that
caused the suspension.
Stack Topology
NOTE Stacking is only supported on the SG350 (excep t fo r the Sx350) and SG550 family of devices.
The following configuration options (right-hand corner) are available:
• Display Mode—Select either Device View or Table View.
• Refresh Time—Select one of the options displayed.
• Error Recovery Settings—Click to open Error Recovery Settings.
This module is a graphic representation of the stack topology and is identical in behavior to the
Stack T opology View section in the Stack Management screen, as shown below:
The following fields are displayed:
• Stack Topology—Either Chain or Ring (see Types of Stack Topology).
• Stack Master—Number of unit functioning as the master unit of the stack.
Hovering over a unit in the module displays a tooltip identifying the unit and providing basic
information on its stacking ports.
29 Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x
Page 35

Dashboard
Traffic Errors
Traffic Errors
2
Hovering over a stack connection in the module displays a tooltip detailing the connected units
and the stacking ports generating the connection.
The following configuration options (right-hand corner) are available:
• Refresh Time—Select one of the options displayed.
• Stack Management—Click to open Stack Management.
This modules displays the number of error packets of various types that are counted on the
RMON statistics. The view is selected in the configuration options (pencil icon in upper-right
corner).
The following can be selected in from the pencil icon:
• Display Mode - Device View
The device module mode displays a diagram of the device, as shown below:
In stacking mode, a drop-down selector enables you to select the device to be viewed.
All suspended ports in the device are shown as red.
Hovering over a suspended port displays a tooltip with the following information:
- Port name.
- If the port is a member of a LAG, the LAG identity of the port.
- Details of the last error logged on the port.
• Display Mode - Table View
- Interface—Name of port
Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x 30
Page 36

2
Dashboard
Traffic Errors
- Last traffic error—Traffic error that occurred on a port and the last time the error
occurred.
• Refresh Time—Select one of the refresh rates.
• Traffic Error Information—Click to link to the Statistics page.
31 Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x
Page 37

Configuration Wizards
This section describes the following configuration wizards:
It covers the following topics:
• Getting Started Wizard
• VLAN Configuration Wizard
•ACL Wizard
3
Getting Started Wizard
This wizard assists in the initial configuration of the device.
STEP 1 Click Configuration Wizards > Getting Started W izard.
STEP 2 Click Launch Wizard and Next.
STEP 3 Enter the fields:
• System Location—Enter the physical location of the device.
• System Contact—Enter the name of a contact person.
• Host Name—Select the host name of this device. This is used in the prompt of CLI
commands:
- Use Default—The default hostname (System Name) of these switches is:
switch123456, where 123456 represents the last three bytes of the device MAC
address in hex format.
- User Defined—Enter the hostname. Use only letters, digits, and hyphens. Host
names cannot begin or end with a hyphen. No other symbols, punctuation
characters, or blank spaces are permitted (as specified in RFC1033, 1034, 1035).
STEP 4 Click Next.
Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x 30
Page 38

3
Configuration Wizards
Getting Started Wizard
STEP 5 Enter the fields:
• Interface—Select the IP interface for the system.
• IP Interface Source—Select one of the following options:
- DHCP—Select for the device to receive its IP address from a DHCP server.
- Static—Select to enter the IP address of the device manually.
If you selected Static as the IP address type, enter the following fields:
• IP Addr ess—IP address of the interface.
• Network Mask—IP mask for this address.
• Administrative Default Gateway—Enter the default gateway IP address.
• DNS Server—Enter the IP address of the DNS server.
STEP 6 Click Next
STEP 7 Enter the fields:
• Username—Enter a new user name between 0 and 20 characters. UTF-8 characters are
not permitted.
• Password—Enter a password (UTF-8 characters are not permitted). If the password
strength and complexity is defined, the user password must comply with the policy
configured in Password Strength.
• Confirm Password—Enter the password again.
• Password Strength—Displays the strength of password. The policy for password
strength and complexity are configured in the Password Strength page.
• Keep current username and password—Select to keep current username and
password.
STEP 8 Click Next
STEP 9 Enter the fields:
• Clock Source—Select one of the following:
- Manual Settings—Select to enter the device system time. If this is selected, enter the
Date and Time.
- Default SNTP Servers—Select to use the default SNTP servers.
31 Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x
Page 39

Configuration Wizards
VLAN Configuration Wizard
NOTE The default SNTP servers are defined by name, thus DNS must be configured
and operational (DNS server configured and reachable). This is done in DNS Settings.
- Manual SNTP Server—Select and enter the IP address of an SNTP server.
STEP 10 Click Next to view a summary of configuration that you entered.
STEP 11 Click Apply to save the configuration data.
VLAN Configuration Wizard
This wizard assists in configuring VLANs. Each time you run this wizard, you can configure
ports membership in a single VLAN. The first steps are for Trunk port mode (where you
configure trunk ports tagged and untagged ports), and then you configure Access port mode.
3
STEP 1 Click Configuration Wizards > VLAN Configuration Wizard.
STEP 2 Click Launch Wizard and Next.
STEP 3 Select the ports that are to be configured as trunk port (by clicking with mouse on the required
ports in the graphical display). Ports that are already configured as Trunk ports are preselected.
STEP 4 Click Next.
STEP 5 Enter the fields:
• VLAN ID—Select the VLAN you want to configure. You can select either an existing
VLAN or New VLAN.
• New VLAN ID—Enter the VLAN ID of a new VLAN.
• VLAN Name—Optionally, enter VLAN name.
STEP 6 Select the trunk ports that are to be configured as untagged members of the VLAN (by
clicking with mouse on the required ports in the graphical display). T he trunk ports that are no t
selected in this step becomes tagged members of the VLAN.
STEP 7 Click Next.
STEP 8 Select the ports are that to be the access ports of the VLAN. Access ports of a VLAN is
untagged member of the VLAN. (by clicking with mouse on the required ports in the graphical
display).
Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x 32
Page 40

3
STEP 9 Click Next to see the summary of the information that you entered.
STEP 10 Click Apply.
ACL Wizard
STEP 1 Click Configuration Wizards > ACL Wizard.
STEP 2 Click Next.
STEP 3 Enter the fields:
Configuration Wizards
ACL W izard
To create a new ACL.
• ACL Name—Enter the name of a new ACL.
• ACL Type—Select the type of ACL: IPv4 or MAC.
STEP 4 Click Next.
STEP 5 Enter the fields:
• Action on match—Select one of the options:
- Permit Traffic—Forward packets that meet the ACL criteria.
- Deny Traffic—Drop packets that meet the ACL criteria.
- Shutdown Interface—Drop packets that meet the ACL criteria, and disable the port
from where the packets received. Such ports can be reactivated from the Error
Recovery Settings page.
STEP 6 For a MAC-based ACL, enter the fields:
• Source MAC Address—Select Any if all source address are acceptable or User defined
to enter a source address or range of source addresses.
• Source MAC Value—Enter the MAC address to which the source MAC address is to
be matched and its mask (if relevant).
• Source MAC Wildcard Mask—Enter the mask to define a range of MAC addresses.
• Destination MAC Address—Select Any if all destination addresses are acceptable or
User defined to enter a destination address or a range of destination addresses.
• Destination MAC Value—Enter the MAC address to which the destination MAC
address is to be matched and its mask (if relevant).
33 Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x
Page 41

Configuration Wizards
ACL W izard
STEP 7 For a IPv4-based ACL, enter the fields:
3
• Destination MAC Wildcard Mask—Enter the mask to define a range of MAC
addresses. Note that this mask is different than in other uses, such as subnet mask. Here,
setting a bit as 1 indicates don't care and 0 indicates to mask that value.
NOTE Given a mask of 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 1 1 11 1 1 1 1 (which means that
you match on the bits where there is 0 and don't match on the bits where there are 1's).
You need to translate the 1's to a decimal integer and you write 0 for each four zeros. In
this examp le since 1111 1111 = 255, the mask would be written: as 0.0.0.255.
• Time Range Name—If Time Range is selected, select the time range to be used. Time
ranges are defined in the System Time Configuration section. This field is only
displayed if a Time Range was previously created.
• Protocol—Select one of the following options to create an ACL based on a specific
protocol:
- Any (IP)—Accept all IP protocols packets
- TCP—Accept Transmission Control Protocols packets
- UDP—Accept User Datagram Protocols packets
- ICMP—Accept ICMP Protocols packets
- IGMP—Accept IGMP Protocols packets
• Source Port for TCP/UDP—Select a port from the drop-down list.
• Destination Port for TCP/UDP—Select a port from the drop-down list.
• Source IP Addr ess—Select Any if all source address are acceptable or User defined to
enter a source address or range of source addresses.
• Source IP Value—Enter the IP address to which the source IP address is to be matched.
• Source IP Wildcard Mask—Enter the mask to define a range of IP addresses. Note that
this mask is different than in other uses, such as subnet mask. Here, setting a bit as 1
indicates don't care and 0 indicates to mask that value.
• Destination IP Address—Select Any if all source address are acceptable or User
defined to enter a source address or range of source addresses.
• Destination IP Value—Enter the IP address to which the source IP address is to be
matched.
• Destination IP Wildcard Mask—Enter the mask to define a range of IP addresses.
Note that this mask is different than in other uses, such as subnet mask. Here, setting a
bit as 1 indicates don't care and 0 indicates to mask that value.
Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x 34
Page 42

3
Configuration Wizards
ACL W izard
• Time Range Name—If Time Range is selected, select the time range to be used. Time
ranges are defined in the System Time Configuration section. This field is only
displayed if a Time Range was previously created.
STEP 8 Click Next.
STEP 9 Confirm that you want the ACL and ACE to be created.
The details of the ACL rule are displayed. You can click Add another rule to this ACL to
add another rule.
STEP 10 Click Next and enter the ACL Binding information:
• Binding Type—Select one of the following options to bind the ACL:
- Physical interfaces only—Bind the ACL to a port. In this case, click a port or ports
on which to bind the ACL.
- VLANs only—Bind the ACL to a VLAN. Enter the list of VLANs in the Enter the
list of VLANs you want to bind the ACL to field.
- No binding—Do not bind the ACL.
Click Apply.
35 Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x
Page 43

Status and Statistics
This section describes how to view device statistics.
It covers the following topics:
•System Summary
• CPU Utilization
• Interface
4
•Etherlike
• Port Utilization
• GVRP
• 802.1X EAP
•ACL
• TCAM Utilization
• Health and Power
• Switched Port Analyzer (SPAN)
• Diagnostics
•RMON
•sFlow
•View Logs
Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x 34
Page 44

4
System Summary
Status and Statistics
System Summary
The System Summary page provides a graphic view of the device, and displays device status,
hardware information, firmware version information, general PoE status, and other items.
To view system information, click Status and Statistics > System Summary.
System Information:
• System Description—A description of the system.
• System Location—Physical location of the device. Click Edit to go the System
Settings page to enter this value.
• System Contact—Name of a contact person. Click Edit to go the System Settings
page to enter this value.
• Host Name—Name of the device. Click Edit to go the System Settings page to enter
this value. By default, the device host name is composed of the word switch
concatenated with the three least significant bytes of the device MAC address (the six
furthest right hexadecimal digits).
• System Object ID—Unique vendor identification of the network management
subsystem contained in the entity (used in SNMP).
• System Uptime—Time that has elapsed since the last reboot.
• Current Time—Current system time.
• Base MAC Addr ess—Device MAC address. If there are several units in the stack, the
base MAC address of the master unit is displayed.
• Jumbo Frames—Jumbo frame support status. This support can be enabled or disabled
by using the Port Settings page.
NOTE Jumbo frames support takes effect only after it is enabled, and after the device is
rebooted.
Software Information:
• Firmware Version (Active Image)—Firmware version number of the active image.
NOTE In a stack, the Firmware Version number shown is based on the version of the
master.
• Firmware MD5 Checksum (Active Image)—MD5 checksum of the active image.
35 Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x
Page 45

Status and Statistics
System Summary
4
• Firmware Version (Non-active)—Firmware version number of the non-active image.
If the system is in a stack, the version of the master unit is displayed.
• Firmware MD5 Checksum (Non-active)—MD5 checksum of the non-active image.
• Locale—Locale of the first language. (This is always English.)
• Language Version—Language package version of the first or English language.
• Language MD5 Checksum—MD5 checksum of the language file.
TCP/UDP Services Status:
To reset the following fields, click Edit to open the TCP/UDP Services page.
• HTTP Service—Whether HTTP is enabled/disabled.
• HTTPS Service—Whether HTTPS is enabled/disabled.
• SNMP Service—Whether SNMP is enabled/disabled.
• Telnet Service—Whether Telnet is enabled/disabled.
• SSH Service—Whether SSH is enabled/disabled.
PoE Power Information on Master Unit: (on devices supporting PoE)
• PoE Power Information on Master Unit—Click on Detail to link you directly to the
Overview page. This page shows the PoE power information on a per-unit basis.
• Maximum Available PoE Power (W)—Maximum available power that can be
delivered by the switch.
• Total PoE Power Consumption (W)—Total PoE power delivered to connected PoE
devices.
• PoE Power Mode—Port Limit or Class Limit.
The master unit is displayed graphically., as shown below:
Hovering on a port displays its name.
The following information is displayed for each unit:
Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x 36
Page 46

4
CPU Utilization
Status and Statistics
CPU Utilization
• Unit ID
• Serial Number—Serial number.
• PID VID—Part number and version ID.
The device CPU handles the following types of traffic, in addition to end-user traf fic handling
the management interface:
• Management traffic
• Protocol traffic
• Snooping traffic
Excessive traffic burdens the CPU, and might prevent normal device operation. The device
uses the Secure Core Technology (SCT) feature to ensure that the device receives and
processes management and protocol traf fic, n o matter how much total traffic is received
is enabled by default on the device and cannot be disabled.
There are no interactions with other features.
To display CPU utilization:
STEP 1 Click Status and Statistics > CPU Utilization.
The CPU Input Rate field displays the rate of input frames to the CPU per second.
The window contains a graph displaying CPU utilization on the device. The Y axis is
percentage of usage, and the X axis is the sample number.
STEP 2 Ensure that the CPU Utilization check box is enabled.
STEP 3 Select the Refresh Rate (time period in seconds) that passes before the statistics are refreshed.
A new sample is created for each time period.
The window containing a graph displaying CPU utilization on the device is displayed.
. SCT
37 Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x
Page 47

Status and Statistics
Interface
Interface
STEP 1 Click Status and Statistics > Interface.
STEP 2 Enter the parameters.
4
The Interface page displays traffic statistics per port. The refresh rate of the information can be
selected.
This page is useful for analyzing the amount of traffic that is both sent and received and its
dispersion (Unicast, Multicast, and Broadcast).
To display Ethernet statistics and/or set the refresh rate:
• Interface—Select the interface for which Ethernet statistics are to be displayed.
• Refresh Rate—Select the time period that passes before the interface Ethernet statistics
are refreshed.
The Receive Statistics area displays information about incoming packets.
• Total Bytes (Octets)—Octets received, including bad packets and FCS octets, but
excluding framing bits.
• Unicast Packets—Good Unicast packets received.
• Multicast Packets—Good Multicast packets received.
• Broadcast Packets—Good Broadcast packets received.
• Packets with Errors—Packets with errors received.
The Transmit Statistics area displays information about outgoing packets.
• Total Bytes (Octets)—Octets transmitted, including bad packets and FCS octets, but
excluding framing bits.
• Unicast Packets—Good Unicast packets transmitted.
• Multicast Packets—Good Multicast packets transmitted.
• Broadcast Packets—Good Broadcast packets transmitted.
STEP 3 To view statistics counters in table view or graphic view:
• Click View All Interfaces Statistics to see all ports in table view.
Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x 38
Page 48

4
Etherlike
Status and Statistics
Etherlike
• Click View Interface History Graph to display these results in graphic form. In this
view , you can select the Time Span for which the results will be displayed and the type
of statistic to be displayed. For example, if you select Last 5 Minutes and Unicast
Packets, you will see how many Unicast packets received in the last 5 minutes.
The Etherlike page displays statistics per port according to the Etherlike MIB standard
definition. The refresh rate of the information can be selected. This page provides more
detailed information regarding errors in the physical layer (Layer 1) that might disrupt traffic.
To view Etherlike Statistics and/or set the refresh rate:
STEP 1 Click Status and Statistics > Etherlike.
STEP 2 Enter the parameters.
• Interface—Select the specific interface for which Ethernet statistics are to be
displayed.
• Refresh Rate—Select the amount of time that passes before the Etherlike statistics are
refreshed.
The fields are displayed for the selected interface.
NOTE If one of the following fields shows a number of errors (not 0), a Last Update time is displayed.
• Frame Check Sequence (FCS) Errors—Received frames that failed the CRC (cyclic
redundancy checks).
• Single Collision Frames—Frames that involved in a single collision, but successfully
transmitted.
• Late Collisions—Collisions that have been detected after the first 512 bits of data.
• Excessive Collisions—Transmissions rejected due to excessive collisions.
• Oversize Packets—Packets greater than 2000 octets received.
• Internal MAC Receive Errors—Frames rejected because of receiver errors.
• Pause Frames Received—Received flow control pause frames. This field is only
supported for XG ports. When the port speed is 1G, the received pause frames counte r
is not operational.
39 Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x
Page 49

Status and Statistics
Port Utilization
STEP 3 To view statistics counters in table view:
Port Utilization
4
• Pause Frames T ransmitted—Flow control pause frames transmitted from the selected
interface.
• Click View All Interfaces Statistics to see all ports in table view.
The Port Utilization page displays utilization of broadband (both incoming and outgoing) per
port.
To display port utilization:
GVRP
STEP 1 Click Status and Statistics > Port Utilization.
STEP 2 Enter the Refresh Rate, which is the time period that passes before the interface Ethernet
statistics are refreshed.
The following fields are displayed for each port:
• Interface—Name of port.
• Tx Utilization—Amount of bandwidth used by outgoing packets.
• Rx Utilization—Amount of bandwidth used by incoming packets.
To view a graph of historical utilization over time on the port, select a port and click the click
View Interface History Graph. In addition to the above, the following field is displayed:
• Time Span—Select a unit of time. The graph displays the port utilization over this unit
of time.
The GVRP page displays information regarding GARP VLAN Registration Protocol (GVRP)
frames that sent or received from a port. GVRP is a standards-based Layer 2 network
protocol, for automatic configuration of VLAN information on switches. It is defined in the
802.1ak amendment to 802.1Q-2005.
Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x 40
Page 50

4
Status and Statistics
GVRP
GVRP statistics for a port are only displayed if GVRP is enabled globally and on the port. See
the GVRP Settings page.
To view GVRP statistics and/or set the refresh rate:
STEP 1 Click Status and Statistics > GVRP.
STEP 2 Enter the parameters.
• Interface—Select the specific interface for which GVRP statistics are to be displayed.
• Refresh Rate—Select the time period that passes before the GVRP page is refreshed.
The Attribute Counter block displays the counters for various types of packets per interface.
These are displayed for Received and Transmitted packets.
• Join Empty—GVRP Join Empty packets received/transmitted.
• Empty—GVRP empty packets received/transmitted.
• Leave Empty—GVRP Leave Empty packets received/t ransmitted.
• Join In—GVRP Join In packets received/transmitted.
• Leave In—GVRP Leave In packets received/transmitted.
• Leave All—GVRP Leave All packets received/transmitted.
The GVRP Error Statistics section displays the GVRP error counters.
• Invalid Protocol ID—Invalid protocol ID errors.
• Invalid Attribute Type—Invalid attribute ID errors.
• Invalid Attribute Value—Invalid attribute value errors.
• Invalid Attribute Length—Invalid attribute length errors.
• Invalid Event—Invalid events.
STEP 3 To clear statistics counters:
• Click View All Interfaces Statistics to see all ports on a single page.
41 Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x
Page 51

Status and Statistics
802.1X EAP
802.1X EAP
STEP 1 Click Status and Statistics > 802.1x EAP.
STEP 2 Select the Interface that is polled for statistics.
STEP 3 Select the Refresh Rate (time period) that passes before the EAP statistics are refreshed.
4
The 802.1x EAP page displays detailed information regarding the EAP (Extensible
Authentication Protocol) frames that sent or received. To configure the 802.1X feature, see
the Properties page.
To view the EAP Statistics and/or set the refresh rate:
The values are displayed for the selected interface.
• EAPOL Frames Received—Valid EAPOL frames received on the port.
• EAPOL Frames Transmitted—Valid EAPOL frames transmitted by the port.
• EAPOL Start Frames Received—EAPOL Start frames received on the port.
• EAPOL Logoff Frames Received—EAPOL Logoff frames received on the port.
• EAP Response/ID Frames Received—EAP Resp/ID frames received on the port.
• EAP Response Frames Received—EAP Response frames received by the port (other
than Resp/ID frames).
• EAP Request/ID Frames Transmitted—EAP Req/ID frames transmitted by the port.
• EAP Request Frames Transmitted—EAP Request frames transmitted by the port.
• Invalid EAPOL Frames Received—Unrecognized EAPOL frames received on this
port.
• EAP Length Error Frames Received—EAPOL frames with an invalid Packet Body
Length received on this port.
• Last EAPOL Frame Version—Protocol version number attached to the most recently
received EAPOL frame.
• Last EAPOL Frame Source—Source MAC address attached to the most recently
received EAPOL frame.
STEP 4 To clear statistics counters:
• Click View All Interfaces Statistics to view the counters of all interfaces.
Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x 42
Page 52

4
ACL
Status and Statistics
ACL
• Click Clear Interface Counters to clear the counters of all interfaces.
When the ACL logging feature is enabled, an informational SYSLOG message is generated
for packets that match ACL rules.
To view the interfaces on which packets forward or rejected based on ACLs:
STEP 1 Click Status and Statistics > ACL.
STEP 2 Select the Refresh Rate (time period in seconds) that passes before the page is refreshed. A
new group of interfaces is created for each time period.
The following information is displayed:
STEP 3 To manage statistics counters:
TCAM Utilization
TCAM holds the rules produced by applications, such as ACLs (Access Control Lists),
Quality of Service (QoS), while Router TCAM holds the rules for IP Routing and user-created
rules.
• Global T rapped Packet Counter—Number of packets trapped globally due to lack of
resources.
• T rapped Packets—Port/LAG Based—The interfaces on which packets forwarded or
rejected based on ACL rules.
• Trapped Packets—VLAN Based—The VLANs on which packets forwarded or
rejected based on ACL rules.
• Click Clear Counters to clear the counters of all interfaces.
Some applications allocate rules upon their initiation. Additionally , processes that initialize
during system boot use some of their rules during the startup process.
To view TCAM utilization, click Status and Statistics > TCAM Utilization.
43 Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x
Page 53

Status and Statistics
TCAM Utilization
4
The TCAM Utilization page shows the following fields:
• Unit No—Unit in stack for which TCAM utilization appears. This is not displayed
when the device is in not part of a stack.
• Maximum TCAM Entries for Routing and Multicast Routing—M ax imu m router
TCAM entries available for routing and Multicast Routing.
• IPv4 Routing
- In Use—Number of router TCAM entries used for IPv4 routing.
- Maximum—Number of available router TCAM entries that can be used for IPv4
routing.
• IPv4 Multicast Routing
- In Use—Number of router TCAM entries used for IPv4 Multicast routing.
- Maximum—Number of available router TCAM entries that can be used for IPv4
Multicast routing.
• IPv4 Policy Based Routing
- In Use—Number of router TCAM entries used for IPv4 Policy-based routing.
- Maximum—Number of available router TCAM entries that can be used for IPv4
Policy-based routing.
• IPv6 Routing
- In Use—Number of router TCAM entries used for IPv6 Multicast routing.
- Maximum—Number of available router TCAM entries that can be used for IPv6
Multicast routing.
• IPv6 Multicast Routing—Number of router TCAM entries used for IPv6 routing.
- In Use—Number of Router TCAM entries used for IPv6 routing.
- Maximum—Number of available Router TCAM entries that can be used for IPv6
routing.
• IPv6 Policy Based Routing
- In Use—Number of router TCAM entries used for IPv6 Policy-based routing.
- Maximum—Number of available router TCAM entries that can be used for IPv6
Policy-based routing.
Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x 44
Page 54

4
Health and Power
Status and Statistics
Health and Power
• Maximum TCAM Entries for Non-IP Rules—Maximum number of available router
TCAM entries that can be used for non-IP rules.
• Non-IP Rules
- In Use—Number of TCAM entries used for non-IP rules.
- Maximum—Number of available TCAM entries that can be used for non-IP rules.
To view how the allocation among various processes can be changed, see the Routing
Resources section.
The Health and Power page monitors the temperature status, power supply status and fan
status on all relevant devices. Depending on the model, there are one or more fans on a device.
Some models have no fans at all.
Redundant Power
This feature is only supported on the SG550 series.
The RPS 2300 is a backup for AC power. It is used for supplying power to the device if the AC
power supply stops working. It is only supported on the 550 family.
If it becomes necessary to switch to the backup power, the device changes between the power
sources without reboot and without any disruption to the device operation. The device polls
the RPS status every 1 sec, if RPS is providing power, the RPS LED is set, and if the RPS is
active, a SYSLOG is generated.
When main power supply is again operational, the devices notifies the RPS to stop providing
power. A SYSLOG is generated.
The RPS LED (on the device front panel) displays the current RPS status:
• Off – RPS is not connected
• Green (solid) – RPS is ready
• Amber (blinking) – RPS is currently supplying power to the device
• Amber (solid) – RPS is connected but providing power to two o ther devices. In this
case, the RPS will not be able to provide power to the current device, while providing
power to the two other devices.
45 Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x
Page 55

Status and Statistics
Health and Power
4
Fans
In some devices the fans are mandatory for the device operation since without them the device
becomes too hot and automatically shut-down. Since a fan is a moving part, it is subject to
failures. A redundant fan is installed on the system. This fan is not operational unless one or
more of the system fans fails. In this case, the redundant fan becomes part of the environment
monitoring of the device.
It is recommended to let the redundant fan work for at least 1 minute once a day.
Some devices have a temperature sensor to protect its hardware from overheating. In this case,
the following actions are performed by the device if it overheats and during the cool down
period after overheating:
Event Action
At least one temperature
sensor exceeds the Warning
threshold
At least one temperature
sensor exceeds the Critical
threshold
The following are generated:
• SYSLOG message
• SNMP trap
The following are generated:
• SYSLOG message
• SNMP trap
The following actions are performed:
• System LED is set to solid amber (if hardware
supports this).
• Disable Ports — When the Critical temperature
has been exceeded for two minutes, all ports will
be shut down.
• (On devices that support PoE) Disable the PoE
circuitry so that less power is consumed and less
heat is emitted.
Cool down period after the
Critical threshold was
exceeded (all sensors are
lower than the Warning
threshold - 2 °C).
Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x 46
After all the sensors cool down to Warning Threshold
minus 2 degree C, the PHY will be re-enabled, and all
ports brought back up.
If fan status is OK, the ports are enabled.
(On devices that support PoE) the PoE circuitry is
enabled.
Page 56

4
Status and Statistics
Health and Power
To view the device health parameters, click Status and Statistics > Health.
NOTE Only fields that are relevant to the device are displayed.
This section displays the power saved by the device due to the Green Ethernet and Led Disable
features, as well as due to ports being down (physically or due to time range settings).
The PoE savings displays the total power saved by using the PoE time range feature that shuts
down PoE to ports at specific times (usually when the PoE network element is not in use).
The following information is displayed (the order of the fields may be different depending on
the device):
Power Savings
• Current Green Ethernet and Port Power Savings—Current amount of the power
savings on all the ports.
• Cumulative Green Ethernet and Port Power Savings—Accumulative amount of the
power savings on all the ports since the device was powered up.
• Projected Annual Green Ethernet and Port Power Savings—Projection of the
amount of the power that will be saved on the device during one week. This value is
calculated based on the savings that occurred during the previous week.
• Current PoE Power Savings—Current amount of the PoE power saved on ports that
have PDs connected to them and on which PoE is not operational due to the Time
Range feature.
• Cumulative PoE Power Savings—Cumulative amount of the PoE power, since the
device was powered up, saved on ports which have PDs connected to them and to
which PoE is not operational due to the Time Range feature.
• Projected Annual PoE Power Savings—Yearly projected amount of PoE power,
since device was powered up, saved on ports that have PDs connected to them and to
which PoE is not operational due to the Time Range feature. The projection is based on
the savings during the previous week.
To schedule power operations for a specific time range, click the blue links in the following
sentence on the page: “Power Savings can be increased by using a Time Ra nge to schedule
data and PoE operations.” The following pages are displayed:
• Time Range—The Administration > Time Settings > Time Range page is
displayed. Set the time range for the power operations.
• Data—The Port Management > Port Settings page is displayed. Connect the time
range to one or more ports.
47 Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x
Page 57

Status and Statistics
Health and Power
4
• PoE—The Port Management > PoE > Settings page is displayed. Connect the time
range to the PoE operations on one or more ports.
If the device is not part of a stack, the Health and Power page displays the following
fields:
Health Table
• Fan Status—The following values are possible:
- OK—Fan is operating normally.
- Failure—More than one fan is not operating correctly.
- N/A—Fan is not applicable for the specific model.
• Redundant Fan Status—The following values are possible:
- Ready—Redundant fan is operational but not required.
- Active—One of the main fans is not working and this fan is replacing it.
• Temperature—The options are:
- OK—The temperature is below the warning threshold.
- Warning—The temperature is between the warning threshold to the critical
threshold.
- Critical—Temperature is above the critical threshold.
- N/A—Not relevant.
Main Power Status (these fields are found on device that are PD devices and in
devices that support RPS)
- Main Power Supply Status—Displays one of the following for the main power
supply:
Active—Power supply is being used.
Failure—Main power has failed.
- Main Power Supply Budget—Amount of power that can be can be allocated for
device PSE operation by the main power supply.
Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x 48
Page 58

4
Status and Statistics
Health and Power
- Redundant Power Supply Status—Displays one of the following for the backup
power supply:
Active—Power supply is being used.
Available—Redundant power source is connected, but not used.
Not Available—Redun dant power so urce is co nn ected, bu t is already pro vid ing
power to other devices.
Not Connected—Redundant power source is not connected.
- Redundant Power Supply Budget—Amount of power that can be can be
allocated for device PSE operation by the backup power supply.
Power Supply Over Ethernet Status (there can be up to 2 PDs)
- PD Port 1 ID—Port number of PD port1
- PD Port 1 Status—Connected or not connected
- PD Port 1 Type—T yp e of PD
- PD Port 1 Budget—Maximum amount of power that can be can be allocated for
device PSE operation
- PD Port 2 ID—Port number of PD port1
- PD Port 2 Status—Connected or not connected
- PD Port 2 Type—T yp e of PD
- PD Port 2 Budget—Maximum amount of power that can be can be allocated for
device PSE operation
If the device is part of a stack, the Health and Power page displays the following fields:
• Unit No.—Displays the unit number in the stack.
• Fan Status—The following values are possible:
- OK—Fan is operating normally.
- Failure—Fan is not operating correctly.
- N/A—Fan ID is not applicable for the specific model.
• Redundant Fan Status—The following values are possible:
- Ready—Redundant fan is operational but not required.
- Active—One of the main fans is not working and this fan is replacing it.
49 Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x
Page 59

Status and Statistics
Health and Power
4
- Failure—Regular fans failed and redundant fan is not operating correctly.
• Temperature—The options are:
- OK—The temperature is below the warning threshold.
- Warning—The temperature is between the warning threshold to the critical
threshold.
- Critical—Temperature is above the critical threshold.
- N/A—Not relevant.
Power Supply Status (these fields are found on device that are PD devices and in devices that
support RPS)
• Power Supply Status—The options are:
- Main—Displays one of the following:
Active—Power supply is being used.
Failure—Main power has failed.
- Redundant—Provides the status of the redundant power supply. Displays one of
the following:
Active—Redundant Power Supply (RPS) supply is being used.
Available—RPS is connected but is not being used.
Not Available—RPS is connected but is already providing power to other
devices.
Not Connected—The RPS is not connected.
Present—The RPS is connected.
Ethernet Power Supply Table (displayed only if one of the units in the stack supports PD
ports). The following fields are displayed:
• Port Name—Number of port.
• PD Status—Displays one of the following values:
- Connected—The PD port is connected to a PSE device that is providing power.
- Not Connected—The PD port is not connected to a PSE device.
• Negotiation Mode—One of the following values.
- Auto—CDP or LLDP negotiation is used to determine power level.
Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x 50
Page 60

4
- Force 802.3AF—Both sides use the AF power standard.
- Force 802.3AT—Both sides use the AT power standard.
- Force 60W—Both sides use the 60W power.
• Power Budget—Amount of power actually allocated to the port.
Switched Port Analyzer (SPAN and RSPAN)
The SPAN feature, which is sometimes called port mirroring or port monitoring, selects
network traffic for analysis by a network analyzer. The network analyzer can be a Cisco
SwitchProbe device or other Remote Monitoring (RMON) probes.
Status and Statistics
Switched Port Analyzer (SPAN and RSPAN)
Port mirroring is used on a network device to send a copy of network packets, seen on a single
device port, multiple device ports, or an entire VLAN, to a network monitoring connection on
another port on the device. This is commonly used when monitoring of network traffic, such
as for an intrusion-detection system, is required. A network analyzer, connected to the
monitoring port, processes the data packets.
The device can mirror up to eight interfaces per session.
A packet, which is received on a network port and assigned to a VLAN that is subject to
mirroring, is mirrored to the analyzer port even if the packet was eventually trapped or
discarded. Packets sent by the device are mirrored when Transmit (Tx) mirroring is activated.
Mirroring does not guarantee that all traffic from the source port(s) is received on the analyzer
(destination) port. If more data is sent to the analyzer port than it can support, some data might
be lost.
VLAN mirroring cannot be active on a VLAN that was not manually created. For example, if
VLAN 23 was created by GVRP, port mirroring will not work on it.
Remote SPAN
RSPAN extends SPAN by enabling monitoring of multiple switches across your network and
allowing the analyzer port to be defined on a remote switch. In addition to the start (source)
and final (destination) switches, you can define intermediate switches over which the traffic
flows, as shown in Figure 1.
51 Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x
Page 61

Status and Statistics
Start Switch
Intermediate
Switch(es)
231 4 Final Switch 87
Define RSPAN VLAN
(ex. 10)
Define RSPAN VLAN
10 with port 2 and 3 as
members
Define RSPAN VLAN
10, with port 7 as
member but not port 8
Source
Port
Reflector
Port
Source
Port
Analyzer
Port
Switched Port Analyzer (SPAN and RSPAN)
Figure 1 RSPAN Switch Deployment:
The traffic for each RSPAN session is carried over a user-specified RSPAN VLAN that is
dedicated for that RSPAN session in all participating switches. The traffic from the source
interfaces on the start device is copied to the RSPAN VLAN through a reflector port and then
forwarded over trunk ports on the intermediate devices to the destination session on the final
switch, which is monitoring the RSPAN VLAN.
4
The reflector port is the mechanism that copies packets to an RSPAN VLAN. It is a network
port that handles various types of traffic.
The RSPAN VLAN must be configured on all the intermediate switches.
NOTE RSPAN does not always successfully copy all the packets when they are arrive from multiple
sources simultaneously. If accurate monitoring is required, the TCAM-based mirror policy can
be used.
RSPAN Workflow
The following workflow describes how to configure the start, intermediate and final switches:
• Start Switch
• Intermediate Switch(es)
• Final Switch
Start Switch
1. Define the RSPAN VLAN. This RSPAN VLAN must be the same in all switches.
2. Define one or more source interfaces, which can be ports or a VLAN, and ensure that it is
Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x 52
not a member of the RSPAN VLAN.
Page 62

4
Status and Statistics
Switched Port Analyzer (SPAN and RSPAN)
3. Define a reflector port (destination, egress port) and ensure that it is not a member of the
RSPAN VLAN.
4. Define the Destination Type as Remote VLAN.
5. Set Network Traffic to Enable.
Intermediate Switch(es)
1. Define the RSPAN VLAN. This RSPAN VLAN must be the same in the start, intermediate
and final switches.
2. Ensure that there are at least two ports that are members of the RSPAN VLAN. Traf fic will
pass through the switch via the RSPAN VLAN.
Final Switch
1. Define the RSPAN VLAN. This RSPAN VLAN must be the same in the start, intermediate
and final switches.
2. Ensure that the source port, which is connected to the intermediate switch, is a member of
the RSPAN VLAN.
3. Define the Source Interface as Remote VLAN.
4. Define a destination port and make sure it is not in the RSPAN VLAN.
5. Define the Destination Type as Local Interface.
RSPAN VLANs
An RSPAN VLAN must be defined on the start, intermediate and final devices.
To configure a VLAN as an RSPAN VLAN:
STEP 1 Click Status and Statistics > SPAN & RSPAN > RSPAN VLANs.
The previously-defined RSPAN VLAN is displayed.
STEP 2 To configure a VLAN as an RSPAN VLAN, select it from the RSPAN VLAN dropdown list
of VLANs.
STEP 3 Click Apply.
53 Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x
Page 63

Status and Statistics
Switched Port Analyzer (SPAN and RSPAN)
SPAN Session Destinations
A destinatio n port must be configured on the st art and final devices. On the start device, this is
the reflector port. On the final device, it is the analyzer port.
To add a destination port:
STEP 1 Click Status and Statistics > SPAN & RSPAN > SPAN Session Destinations.
The previously-defined destinations are displayed.
STEP 2 Click Add.
STEP 3 Enter the following fields:
• Session ID—Select a session ID. This must match the session IDs of the source ports.
• Destination T ype—Select one of the following options:
4
- Local Interface—Is the destination port on the same device as the source ports
(relevant to SPAN).
- Remote VLAN—Is the destination port on a different device than the source port
(relevant to RSPAN).
If the Destination Type is Remote VLAN, configure the following field:
- Reflector Port—Select a unit/port that functions as a target port on the first device.
If the Destination Type is Local Interface, configure the following field:
- Port—Select a unit/port that functions as the analyzer port on the device.
• Network T raffic—Select to enable that traffic other than monitored traffic is possible
on the port.
STEP 4 Click Apply.
SPAN Session Sources
One or more SPAN or RSPAN sources must be configured on the start and final devices.
To configure the source ports to be mirrored:
STEP 1 Click Status and Statistics > SPAN & RSPAN > SPAN Session Sources.
STEP 2 Click Add.
Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x 54
Page 64

4
Status and Statistics
Diagnostics
STEP 3 Select the session number from Session ID. This must be the same for all source ports and the
destination port.
STEP 4 For SPAN or for RSPAN on the start switch, select the unit and port or VLAN from which
traffic is monitored (Source Interface). On the final switch, for RSPAN, select Remote
VLAN.
STEP 5 In the Monitor Type field, select whether incoming, outgoing, or both types of traffic are
mirrored.
- Rx and Tx—Port mirroring on both incoming and outgoing packets.
- Rx—Port mirroring on incoming packets.
- Tx—Port mirroring on outgoing packets.
STEP 6 Click Apply. The source interface for the mirroring is configured.
Diagnostics
This section contains information for configuring port mirroring, running cab le tests, and
viewing device operational information.
It covers the following topics:
• Copper Ports Tests
• Optical Module Status
• Tech-Support Information
Copper Ports Tests
The Copper Test page displays the results of integrated cable tests performed on copper cables
by the Virtual Cable Tester (VCT).
VCT performs two types of tests:
• Time Domain Reflectometry (TDR) technology tests the quality and characteristics of
a copper cable attached to a port. Cables of up to 140 meters long can be tested. These
results are displayed in the Test Results block of the Copper Test page.
55 Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x
Page 65

Status and Statistics
Diagnostics
CAUTION When a port is tested, it is set to the Down state and communications are interrupted. After the
4
• DSP-based tests are performed on active XG links to measure cable length. These
results are displayed in the Advanced Information block of the Copper Test page. This
test can run only when the link speed is 10G.
Preconditions to Running the Copper Port Test
Before running the test, do the following:
• (Mandatory) Disable Short Reach mode (see the Properties page)
• (Optional) Disable EEE (see the Properties page)
Use a CAT6a data cable when testing cables using (VCT).
The test results have an accuracy within an error range of +/- 10 for advanced Testing and +/-
2 for basic testing.
test, the port returns to the Up state. It is not recommended that you run the copper port test on
a port you are using to run the web-based switch configuration utility, because communications
with that device are disrupted.
To test copper cables attached to ports:
STEP 1 Click Status and Statistics > Diagnostics > Copper Test.
STEP 2 Select the unit and port on which to run the test.
STEP 3 Click Copper Test.
STEP 4 When the message appears, click OK to confirm that the link can go down or Cancel to abort
the test.
The following fields are displayed in the Test Results block:
• Last Update—Time of the last test conducted on the port.
• Test Results—Cable test results. Possible values are:
- OK—Cable passed the test.
- No Cable—Cable is not connected to the port.
- Open Cable—Cable is connected on only one side.
- Short Cable—Short circuit has occurred in the cable.
- Unknown Test Result—Error has occurred.
Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x 56
Page 66

4
Status and Statistics
Diagnostics
• Distance to Fault—Distance from the port to the location on the cable where the fault
was discovered.
• Operational Port Status—Displays whether port is up or down.
The Advanced Information block contains the following information, which is refreshed
each time you enter the page:
• Cable Length: Provides an estimate for the length.
• Pair—Cable wire pair being tested.
• Status—Wire pair status. Red indicates fault and Green indicates status OK.
• Channel—Cable channel indicating whether the wires are straight or cross-over.
• Polarity—Indicates if automatic polarity detection and correction has been activated
for the wire pair.
• Pair Skew—Difference in delay between wire pairs.
Optical Module Status
The Optical Module Status page displays the operating conditions reported by the SFP (Small
Form-factor Pluggable) transceiver.
The following GE SFP (1000Mbps) transceivers are supported:
• MGBBX1: 1000BASE-BX-20U SFP transceiver, for single-mode fiber, 1310 nm
wavelength, supports up to 40 km.
• MGBLH1: 1000BASE-LH SFP transceiver, for single-mode fiber, 1310 nm
wavelength, supports up to 40 km.
• MGBLX1: 1000BASE-LX SFP transceiver, for single-mode fiber, 1310 nm
wavelength, supports up to 10 km.
• MGBSX1:1000BASE-SX SFP transceiver, for multimode fiber, 850 nm wavelength,
supports up to 550 m.
• MGBT1: 1000BASE-T SFP transceiver for category 5 copper wire, supports up to
100 m.
The following XG SFP+ (10,000Mbps) transceivers are supported:
• Cisco SFP-10GSR
57 Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x
Page 67

Status and Statistics
Diagnostics
4
• Cisco SFP-10GLRM
• Cisco SFP-10GLR
The following XG passive cables (Twinax/DAC) are supported:
• Cisco SFP-H10GCU1m
• Cisco SFP-H10GCU3m
• Cisco SFP-H10GCU5m
To view the results of optical tests, click Status and Statistics > Diagnostics > Optical
Module Status.
This page displays the following fields:
• Port—Port number on which the SFP is connected.
• Description—Description of optical transceiver.
• Serial Number—Serial number of optical transceiver.
• PID—VLAN ID.
• VID—ID of optical transceiver.
• Temperature—Temperature (Celsius) at which the SFP is operating.
• Voltage—SFPs operating voltage.
• Current—SFPs current consumption.
• Output Power—Transmitted optical power.
• Input Power—Received optical power.
• Transmitter Fault—Remote SFP reports signal loss. Values are True, False, and No
Signal (N/S).
• Loss of Signal—Local SFP reports signal loss. Values are True and False.
• Data Ready—SFP is operational. Values are True and False.
Tech-Support Information
This page provides a detailed log of the device status. This is valuable when the technical
support are trying to help a user with a problem, since it gives the output of many show
commands (including debug command) in a single command.
Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x 58
Page 68

4
RMON
Status and Statistics
RMON
To view technical support information useful for debugging purposes:
STEP 1 Click Status and Statistics > Diagnostics > Tech-Support Information.
STEP 2 Click Generate.
Information from a variety of show CLI commands is displayed.
NOTE Generation of output from this command may take some time. When the information is
generated, you can copy it from the text box in the screen.
RMON (Remote Networking Monitoring) enables an SNMP agent in the device to proactively
monitor traffic statistics over a given period and send traps to an SNMP manager. The local
SNMP agent compares actual, real-time counters against predefined thresholds and generates
alarms, without the need for polling by a central SNMP management platform. This is an
effective mechanism for proactive management, provided that you have set the correct
thresholds relative to your network’s base line.
RMON decreases the traffic between the manager and the device since the SNMP manager
does not have to poll the device frequently for information, and enables the manager to get
timely status reports, since the device reports events as they occur.
With this feature, you can perform the following actions:
• V iew the current statistics (from the time that the counter values cleared). You can also
collect the values of these counters over a period of time, and then view the table of
collected data, where each collected set is a single line of the History tab.
• Define interesting changes in counter values, such as “reached a certain number of late
collisions” (defines the alarm), and then specify what action to perform when this
event occurs (log, trap, or log and trap).
Statistics
The Statistics page displays detailed information regarding packet sizes and information
regarding physical layer errors. The information is displayed according to the RMON
standard. An oversized packet is defined as an Ethernet frame with the following criteria:
• Packet length is greater than MRU byte size.
59 Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x
Page 69

Status and Statistics
RMON
STEP 1 Click Status and Statistics > RMON > Statistics.
STEP 2 Select the Interface for which Ethernet statistics are to be displayed.
STEP 3 Select the Refresh Rate, which is the time period that passes before the interface statistics are
4
• Collision event has not been detected.
• Late collision event has not been detected.
• Received (Rx) error event has not been detected.
• Packet has a valid CRC.
To view RMON statistics and/or set the refresh rate:
refreshed.
The following statistics are displayed for the selected interface.
NOTE If one of the following fiel ds shows a number of errors (not 0), a Last Update time is displayed.
• Bytes Received—Octets received, including bad packets and FCS octets, but excluding
framing bits.
• Drop Events—Packets dropped.
• Packets Received—Good packets received, including Multicast and Broadcast
packets.
• Broadcast Packets Received—Good Broadcast packets received. This number does
not include Multicast packets.
• Multicast Packets Received—Good Multicast packets received.
• CRC & Align Errors—CRC and Align errors that have occurred.
• Undersize Packets—Undersized packets (less than 64 octets) received.
• Oversize Packets—Oversized packets (over 2000 octets) received.
• Fragments—Fragments (packets with less than 64 octets, excluding framing bits, but
including FCS octets) received.
• Jabbers—Received packets that longer than 1632 octets. This number excludes frame
bits, but includes FCS octets that had either a bad FCS (Frame Check Sequence) with
an integral number of octets (FCS Error) or a bad FCS with a non-integral octet
(Alignment Error) number. A Jabber packet is defined as an Ethernet frame that satisfies
the following criteria:
- Packet data length is greater than MRU.
Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x 60
Page 70

4
Status and Statistics
RMON
- Packet has an invalid CRC.
- Received (Rx) Error Event has not been detected.
• Collisions—Collisions received. If Jumbo frames are enabled, the threshold of Jabber
frames is raised to the maximum size of Jumbo frames.
• Frames of 64 Bytes—Frames, containing 64 bytes that were sent or received.
• Frames of 65 to 127 Bytes—Frames, containing 65-127 bytes that were sent or
received.
• Frames of 128 to 255 Bytes—Frames, containing 128-255 bytes that were sent or
received.
• Frames of 256 to 511 Bytes—Frames, containing 256-511 bytes that were sent or
received.
• Frames of 512 to 1023 Bytes—Frames, containing 512-1023 bytes that were sent or
received.
• Frames of 1024 Bytes or More—Frames, containing 1024-2000 bytes, and Jumbo
Frames, that were sent or received.
STEP 4 To view counters in table view or graphic view:
• Click View All Interfaces Statistics to see all ports in table view.
• Click Graphic View to display these results in graphic form. In this view, you can select
the Time Span for which the results will be displayed and the type of statistic to be
displayed.
RMON History
The RMON feature enables monitoring statistics per interface.
The History page defines the sampling frequency, amount of samples to store and the port
from which to gather the data.
After the data is sampled and stored, it appears in the History Table page that can be viewed by
clicking History Table.
61 Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x
Page 71

Status and Statistics
RMON
STEP 1 Click Status and Statistics > RMON > History. The fields disp layed on this page are defined
STEP 2 Click Add.
STEP 3 Enter the parameters.
4
To enter RMON control information:
in the Ad d RMON History page, below. The only field is that is on this page and not defined in
the Add page is:
• Current Number of Samples—RMON is allowed by the standard to not grant all
requested samples, but rather to limit the number of samples per request. Therefore, this
field represents the sample number actually granted to the request that is equal or less
than the requested value.
• New History Entry—Displays the number of the new History table entry.
• Source Interface—Select the type of interface from which the history samples are to
be taken.
• Max No. of Samples to Keep—Enter the number of samples to store.
• Sampling Interval—Enter the time in seconds that samples are collected from the
ports. The field range is 1-3600.
• Owner—Enter the RMON station or user that requested the RMON information.
STEP 4 Click Apply. The entry is added to the History Control Table page, and the Running
Configuration file is updated.
STEP 5 Click History Table (described below) to view the actual statistics.
RMON History Table
The History page displays interface-specific statistical network samplings. The samples
configured in the History Control table described above.
To view RMON history statistics:
STEP 1 Click Status and Statistics > RMON > History.
STEP 2 Click History Table.
STEP 3 From the History Entry No. drop down menu, optionally select the entry number of the
sample to display.
Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x 62
Page 72

4
Status and Statistics
RMON
The fields are displayed for the selected sample.
• Owner—History table entry owner.
• Sample No.—Statistics taken from this sample.
• Drop Events—Dropped packets due to lack of network resources during the sampling
interval. This may not represent the exact number of dropped packets, but rathe r the
number of times dropped packets detected.
• Bytes Received—Octets received including bad packets and FCS octets, but excluding
framing bits.
• Packets Received—Packets received, including bad packets, Multicast, and Broadcast
packets.
• Broadcast Packets—Good Broadcast packets excluding Multicast packets.
• Multicast Packets—Good Multicast packets received.
• CRC Align Errors—CRC and Align errors that have occurred.
• Undersize Packets—Undersized packets (less than 64 octets) received.
• Oversize Packets—Oversized packets (over 2000 octets) received.
• Fragments—Fragments (packets with less than 64 octets) received, excluding framing
bits, but including FCS octets.
• Jabbers—T otal number of received packets that longer than 2000 octets. This number
excludes frame bits, but includes FCS octets that had either a bad FCS (Frame Check
Sequence) with an integral number of octets (FCS Error) or a bad FCS with a nonintegral octet (Alignment Error) number.
• Collisions—Collisions received.
• Utilization—Percentage of current interface traffic compared to maximum traffic that
the interface can handle.
RMON Events Control
You can control the occurrences that trigger an alarm and the type of notification that occurs.
This is performed as follows:
• Events Page—Configures what happens when an alarm is triggered. This can be any
combination of logs and traps.
63 Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x
Page 73

Status and Statistics
RMON
STEP 1 Click Status and Statistics > RMON > Events.
STEP 2 Click Add.
STEP 3 Enter the parameters.
4
• Alarms Page—Configures the occurrences that trigger an alarm.
To define RMON events:
This page displays previously defined events.
The fields on this page are defined by the Add RMON Events dialog box except for the Time
field.
• Time—Displays the time of the event. (This is a read-only table in the parent window
and cannot be defined).
• Event Entry—Displays the event entry index number for the new entry.
• Community—Enter the SNMP community string to be included when traps are sent
(optional). Note that the community must be defined using the Notification Recipients
pages for the trap to reach the Network Management Station.
• Description—Enter a name for the event. This name is used in the Add RMON Alarm
page to attach an alarm to an event.
• Notification Type—Select the type of action that results from this event. Values are:
- None—No action occurs when the alarm goes off.
- Log (Event Log Table)—Add a log entry to the Event Log table when the alarm is
triggered.
- Trap (SNMP Manager and Syslog Server)—Send a trap to the remote log server
when the alarm goes off.
- Log and Trap—Add a log entry to the Event Log table and send a trap to the remote
log server when the alarm goes off.
• Owner—Enter the device or user that defined the event.
STEP 4 Click Apply. The RMON event is saved to the Running Configuration file.
STEP 5 Click Event Log Table to display the log of alarms that have occurred and that have been
logged (see description below).
Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x 64
Page 74

4
Status and Statistics
RMON
RMON Events Logs
The Events page displays the log of events (actions) that occurred. Two types of events can be
logged: Log or Log and Trap. The action in the event is performed when the event is bound to
an alarm (see the RMON Alarms page) and the conditions of the alarm have occurred.
STEP 1 Click Status and Statistics > RMON > Events.
STEP 2 Click Event Log Table.
This page displays the following fields:
• Event Entry No.—Event’s log entry number.
• Log No.—Log number (within the event).
• Log Time—Time that the log entry was entered.
• Description—Description of event that triggered the alarm.
RMON Alarms
RMON alarms provide a mechanism for setting thresholds and sampling intervals to generate
exception events on counters or any other SNMP object count er maintained by the agent. Both
the rising and falling thresholds must be configured in the alarm. After a rising threshold is
crossed, no rising events are generated until the companion falling threshold is crossed. After a
falling alarm is issued, the next alarm is issued when a rising threshold is crossed.
One or more alarms are bound to an event, which indicates the action to be taken when the
alarm occurs.
Alarm counters can be monitored by either absolute values or changes (delta) in the counter
values.
To enter RMON alarms:
STEP 1 Click Status and Statistics > RMON > Alarms.
All previously-defined alarms are displayed. The fields are described in the Add RMON
Alarm page below. In addition to those fields, the following field appears:
• Counter Value—Displays the value of the statistic during the last sampling period.
STEP 2 Click Add.
65 Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x
Page 75

Status and Statistics
RMON
STEP 3 Enter the parameters.
4
• Alarm Entry—Displays the alarm entry number.
• Interface—Select the type of interface for which RMON statistics are displayed.
• Counter Name—Select the MIB variable that indicates the type of occurrence
measured.
• Sample Type—Select the sampling method to generate an alarm. The options are:
- Absolute—If the threshold is crossed, an alarm is generated.
- Delta—Subtracts the last sampled value from the current value. The difference in
the values is compared to the threshold. If the threshold was crossed, an alarm is
generated.
• Rising Threshold—Enter the value that triggers the rising threshold alarm.
• Rising Event—Select an event to be performed when a rising ev ent is triggered. Events
are configured in the RMON Events Control page.
• Falling Threshold—Enter the value that triggers the falling threshold alarm.
• Falling Event—Select an event to be performed when a falling event is triggered.
• Startup Alarm—Select the first event from which to start generation of alarms. Rising
is defined by crossing the threshold from a low-value threshold to a highe r-value
threshold.
- Rising Alarm—A rising value triggers the rising threshold alarm.
- Falling Alarm—A falling value triggers the falling threshold alarm.
- Rising and Falling—Both rising and falling values trigger the alarm.
• Interval—Enter the alarm interval time in seconds.
• Owner—Enter the name of the user or network management system that receives the
alarm.
STEP 4 Click Apply. The RMON alarm is saved to the Running Configuration file.
Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x 66
Page 76

4
sFlow
Status and Statistics
sFlow
The sFlow feature enables co lle cting statistics using the sFlow sampling technology, based on
sFlow V5.
This sampling technology is embedded within switches and routers. It provides the ability to
continuously monitor traffic flows on some or all the interfaces, simultaneously.
The sFlow monitoring system consists of an sFlow agent (embedded in a switch or router or in
a stand alone probe) and a central data collector, known as the sFlow collector.
The sFlow agent uses sampling technology to capture traffic and statistics from the device it is
monitoring. sFlow datagrams are used to forward the sampled traffic and statistics to an sFlow
collector for analysis.
sFlow V5 defines:
• How traffic is monitored.
• The sFlow MIB that controls the sFlow agent.
• The format of the sample data used by the sFlow agent when forwarding data to a
central data collector. The device provides support for two types of sFlow sampling:
flow sampling and counters sampling. The following counters sampling is performed
according to sFlow V5 (if supported by the interface):
- Generic interface counters (RFC 2233)
- Ethernet interface counters (RFC 2358)
Workflow
By default, flow and counter sampling are disabled.
To enable sFlow sampling:
1. Set the IP address of a receiver (also known as a collector) for sFlow statistics. Use the
sFlow Receiver Settings page for this.
2. Enable flow and/or co unter sampling, direct the samples to a receiving index, and configure
the average sampling rate. Use the sFlow Interface Settings pages for this.
3. View and clear the sFlow statistics counters. Use the sFlow Statistics page for this.
sFlow Receiver Settings
To set the sFlow receiver parameters:
67 Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x
Page 77

Status and Statistics
sFlow
STEP 1 Click Status and Statistics > sFlow > sFlow Receivers.
STEP 2 Enter the following fields:
STEP 3 To add a receiver (sflow analyzer), click Add and select one of the pre-defined sampling
STEP 4 Enter the receiver’s address fields:
4
• IPv4 Source Interface— Select the IPv4 source interface.
NOTE If the Auto option is selected, the system takes the source IP address from the IP
address defined on the outgoing interface.
• IPv6 Source Interface— Select the IPv6 source interface
The sflow parameters are displayed in the Sflow Receiver Table.
definition indices in Receiver Index.
• Receiver Definition—Select whether to specify the sflow receiver By IP address or
By name.
If Receiver Definition is By IP Address:
• IP Version—Select whether an IPv4 or an IPv6 address for the server is used.
• IPv6 Address Type—Select the IPv6 address type (if IPv6 is used). The options are:
- Link Local—The IPv6 address uniquely identifies hosts on a single network link.
A link local address has a prefix of FE80, is not routable, and can be used for
communication only on the local network. Only one link local address is supported.
If a link local address exists on the interface, this entry replaces the address in the
configuration.
- Global—The IPv6 address is a global Unicast IPV6 type that is visible and
reachable from other networks.
• Link Local Interface—Select the link local interface (if IPv6 is used) from the list.
STEP 5 Enter the fields:
• Server IP Addr ess/Name—Enter the IP address or the name of the receiver , whichever
is relevant.
• Port—Port to which SYSLOG message are sent.
• Maximum Datagram Size—Maximum number of bytes that can be sent to the receiver
in a single sample datagram (frame).
STEP 6 Click Apply.
Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x 68
Page 78

4
Status and Statistics
sFlow
sFlow Interface Settings
To sample datagrams or counters from a port, the port must be associated with a receiver.
sFlow port settings can be configured only after a receiver has been defined in the sFlow
Receiver Settings pages.
To enable sampling and configure the port from which to collect the sFlow information:
STEP 1 Click Status and Statistics > sFlow > sFlow Interface Settings.
The sflow interface settings are displayed.
STEP 2 To associate an sFlow receiver with a port, select a port, click Edit, and enter the fields:
- Interface—Select the unit/port from which information is collected.
- (Flow Sampling) State—Enable/disable flow sampling.
- Sampling Rate—If x is entered, a flow sample will be taken for each x frames.
- Maximum Header Size—Maximum number of bytes that should be copied from a
sampled packet.
- Receiver Index—Select one of the indices that was defined in the sFlow Receiver
Settings pages.
- (Counter Sampling) State—Enable/disable counters sampling.
- Sampling Interval—If x is entered, this specifies that a counter sample will be
taken for each x seconds.
- Receiver Index—Select one of the indices that was defined in these sFlow
Receiver Settings pages.
STEP 3 Click Apply.
sFlow Statistics
To view sFlow statistics:
• Click Status and Statistics > sFlow > sFlow Statistics.
The following sflow statistics per interface are displayed:
- Interface — Port for which sample was collected.
- Packets Sampled — Number of packets sampled.
- Datagrams Sent to Receiver — Number of sFlow sampling packets sent.
69 Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x
Page 79

Status and Statistics
View Logs
View Logs
4
The device can write to the following logs:
• Log in RAM (cleared during reboot).
• Log in Flash memory (cleared only upon user command).
You can configure the messages that are written to each log by severity , and a message can go
to more than one log, including logs that reside on external SYSLOG servers.
RAM Memory
The RAM Memory page displays all messages that saved in the RAM (cache) in
chronological order. Entries are stored in the RAM log according to the configuration in the
Log Settings page.
Pop-Up SYSLOG Notifications
When a new SYSLOG message is written to the RAM log file, a notification is displayed in
the web GUI showing its contents.
The web GUI will poll the RAM log every 10 seconds. Notifications pop-ups for all
SYSLOGs created in the last 10 seconds will appear at the bottom right of the screen.
The notification pop-up displays as follows:
To view log entries, click Status and Statistics > View Log > RAM Memory.
The following are displayed at the top of the page:
• Alert Icon Blinking—Toggles between disable and enable.
• Log Pop-Up—Enables receiving pop-up SYSLOGs as described above.
Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x 70
Page 80

4
Status and Statistics
View Logs
• Current Logging Threshold—Specifies the levels of logging that are generated. This
can be changed by clicking Edit by the field’s name.
This page contains the following fields for every log file:
• Log Index—Log entry number.
• Log Time—Time when message was generated.
• Severity—Event severity.
• Description—Message text describing the event.
To clear the log messages, click Clear Logs. The messages are cleared.
Flash Memory
The Flash Memory page displays the messages that stored in the Flash memory, in
chronological order . The minimum sev erity for logging is configured in the Log Settings page.
Flash logs remain when the device is rebooted. You can clear the logs manually.
To view the Flash logs, click Status and Statistics > View Log > Flash Memory.
The Current Logging Threshold specifies the levels of logging that are generated. This can
be changed by clicking Edit by the field’s name.
This page contains the following fields for each log file:
• Log Index—Log entry number.
• Log Time—Time when message was generated.
• Severity—Event severity.
• Description—Message text describing the event.
To clear the messages, click Clear Logs. The messages are cleared.
71 Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x
Page 81

Administration
This section describes how to view system information and configure various options on the
device.
It covers the following topics:
5
• Device Models
• System Settings
• Console Settings (Autobaud Rate Support)
• Stack Management
• User Accounts
• Idle Session Timeout
• Time Settings
•System Log
• File Management
•Reboot
• Routing Resources
• Discovery - Bonjour
• Discovery - LLDP
• Discovery - CDP
•Ping
• Traceroute
Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x 61
Page 82

Administration
Device Models
Device Models
NOTE See Interface Naming Conventions for port naming conventions.
5
All models can be fully managed through the web-based switch configuration utility.
The following table describes the various models, the number and type of ports on them and
their PoE information.
The following are the supported device models.
SKU Name Description Number of
Fans
SG350-10 SG350-10 10-port Gigabit Managed
Switch
SG350-10P SG350-10P 10-port Gigabit POE
Managed Switch
SG355-10P SG355-10P 10-port Gigabit POE
Managed Switch (Internal Power
Supply)
SG350-10MP SG350-10MP 10-port Gigabit Max-
POE Managed Switch
SG350-28 SG350-28 28-port Gigabit Managed
Switch
SG350-28P SG350-28P 28-port Gigabit POE
Managed Switch
SG350-28MP SG350-28MP 28-port Gigabit Max-
PoE Managed Switch
0
0
0
1
0
2
3
Redundant Fans
Quantity
Temperature
Sensor
SG350X-24 24-Port Gigabit Stackable Managed
Switch
SG350X-24P 24-Port Gigabit PoE Stackable
Managed Switch
SG350X-24MP 24-Port Gigabit PoE Stackable
Managed Switch
SG350X-48 48-Port Gigabit Stackable Managed
Switch
Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x 62
1
2
3
2
Page 83

5
Administration
Device Models
SKU Name Description Number of
Fans
SG350X-48P 48-Port Gigabit PoE Stackable
Managed Switch
SG350X-48MP 48-Port Gigabit PoE Stackable
Managed Switch
SG350XG-24F SG350XG-24F 24-Port 10G SFP+
Stackable Managed Switch
SG350XG-24T SG350XG-24T 24-Port 10GBase-T
Stackable Managed Switch
SG350XG-48T SG350XG-48T 48-Port 10GBase-T
Stackable Managed Switch
SG350XG-2F10 SG350XG-2F10 12-Port 10G Stackable
Managed Switch
SF550X-24 24-Port 10/100 Stackable Managed
Switch
SF550X-24P 24-Port 10/100 PoE Stackable Managed
Switch
4
4
40 2
40 4
40 5
30 4
2
4
Redundant Fans
Quantity
Temperature
Sensor
SF550X-24MP 24-Port 10/100 PoE Stackable Managed
Switch
SF550X-48 48-Port 10/100 Stackable Managed
Switch
SF550X-48P 48-Port 10/100 PoE Stackable Managed
Switch
SF550X-48MP 48-Port 10/100 PoE Stackable Managed
Switch
SG550XG-8F8T 16-port Ten Gigabit Stackable Switch
with RPS Support
SG550XG-24T 24-port 10GBase-T Stackable Switch(2
combo) with RPS support
SG550XG-48T 48-port 10GBase-T Stackable Switch (2
combo) with RPS support
SG550XG-24F 24-port SFP+ Ten Gigabit Stackable
Switch (2 combo) with RPS support
5
2
5
5
31 4
41 4
51 5
41 4
63 Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x
Page 84

Administration
System Settings
System Settings
STEP 1 Click Administration > System Settings.
STEP 2 View or modify the system settings.
5
To enter system settings:
• System Description—Displays a description of the device.
• System Location—Enter the physical location of the device.
• System Contact—Enter the name of a contact person.
• Host Name—Select the host name of this device. This is used in the prompt of CLI
commands:
- Use Default—The default hostname (System Name) of these switches is:
switch123456, where 123456 represents the last three bytes of the device MAC
address in hex format.
- User Defined—Enter the hostname. Use only letters, digits, and hyphens. Host
names cannot begin or end with a hyphen. No other symbols, punctuation
characters, or blank spaces are permitted (as specified in RFC1033, 1034, 1035).
• Custom Banner Settings—The following banners can be set:
- Login Banner—Enter text to display on the Login page be fore login. Click Preview
to view the results.
- Welcome Banner—Enter text to display on the Login page after login. Click
Preview to view the results.
NOTE When you define a login banner from the web-based configuration utility , it also
activates the banner for the CLI interfaces (Console, Telnet, and SSH).
STEP 3 Click Apply to save the values in the Running Configuration file.
Console Settings (Autobaud Rate Support)
The console port speed can be set to one of the following speeds: 4800, 9600, 19200, 38400,
57600, and 115200 or to Auto Detection.
Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x 64
Page 85

5
Administration
Stack Management
If Auto Detection is selected, the device detec t s co ns o l e sp ee d automatically.
When Auto Detection is not enabled, the console port speed is automatically set to the last
speed that was set manually at (115,200 by default).
When Auto Detection is enabled but the console baud-rate has not yet been discovered, the
system uses speed 115,200 for displaying text (for example, the boot-up information).
After Auto Detection is enabled in the Console Settings page, it can be activated by connecting
the console to the device and pressing the Enter key twice. The device detects the baud rate
automatically.
To enable Auto Detection or to manually set the baud rate of the console:
STEP 1 Click Administration > Console Settings.
STEP 2 Select one of the following options in the Console Port Baud Rate field:
STEP 3 Click Apply.
Stack Management
See Administration: Stack Management.
User Accounts
The User Accounts page enables entering additional users that are permitted to access to the
device (read-only or read-write) or changing the passwords of existing users.
After adding a level 15 user (as described below), the default user is removed from the system.
• Auto Detection—The console baud rate is detected automatically.
• Static—Select one of the available speeds.
NOTE It is not permitted to delete all users. If all users are selected, the Delete button is disabled.
65 Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x
Page 86

Administration
User Accounts
5
To add a new user:
STEP 1 Click Administration > User Accounts.
This page displays the users defined in the system and their user privilege level.
STEP 2 Select Password Recovery Service to enable this feature. When this is enabled, an end user,
with physical access to the console port of the device, can enter the boot menu and trigger the
password recovery process. When the boot system process ends, you are allowed to login to
the device without password authentication. Entering the device is allowed only via the
console and only when the console is connected to the device with physical access.
When password recovery mechanism is disabled, accessing the boot menu is still allowed and
you can trigger the password recovery process. The difference is that in this case, all
configuration and user files are removed during the system boot process, and a suitable log
message is generated to the terminal.
STEP 3 Click Add to add a new user or click Edit to modify a user.
STEP 4 Enter the parameters.
• User Name—Enter a new username between 0 and 20 characters. UTF-8 characters are
not permitted.
• Password—Enter a password (UTF-8 characters are not permitted). If the password
strength and complexity is defined, the user password must comply with the policy
configured in Password Strength.
• Confirm Password—Enter the password again.
• Password Strength Meter—Displays the strength of password. The policy for
password strength and complexity are configured in the Password Strength page.
• User Level—Select the privilege level of the user being added/edited.
- Read-Only CLI Access (1)—User cannot access the GUI, and can only access CLI
commands that do not change the device configuration.
- Read/Limited Write CLI Access (7)—User cannot access the GUI, and can onl y
access some CLI commands that change the device configuration. See the CLI
Reference Guide for more information.
- Read/Write Management Access (15)—User can access the GUI, and can configure
the device.
STEP 5 Click Apply. The user is added to the Running Configuration file of the device.
Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x 66
Page 87

5
Idle Session Timeout
The Idle Session Timeout configures the time intervals that the management sessions can
remain idle before they timeout and you must log in again to reestablish one of the following
sessions:
• HTTP Session Timeout
• HTTPS Session Timeout
• Console Session Timeout
• Telnet Session Timeout
• SSH Session Timeout
To set the idle session timeout for various types of sessions:
Administration
Idle Session Timeout
STEP 1 Click Administration > Idle Session Timeout.
STEP 2 Select the timeout for the each type of session from the corresponding list. The default timeout
STEP 3 Click Apply to set the configuration settings on the device.
Time Settings
System Log
value is 10 minutes.
See Administration: Time Settings.
This section describes the system logging, which enables the device to generate multiple
independent logs. Each log is a set of messages describing system events.
The device generates the following local logs:
• Log sent to the console interface.
• Log written into a cyclical list of logged events in the RAM and erased when the
device reboots.
67 Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x
Page 88

Administration
System Log
5
• Log written to a cyclical log-file saved to the Flash memory and persists across
reboots.
In addition, you can send messages to remote SYSLOG servers in the form of SNMP traps and
SYSLOG messages.
This section covers the following sections:
• Log Settings
• Remote Logging Settings
Log Settings
You can select the events to be logged by severity level. Each log message has a severity level
marked with the first letter of the severity level concatenated with a dash (-) on each side
(except for Emergency that is indicated by the letter F). For example, the log message "%INITI-InitCompleted: … " has a severity level of I, meaning Informational.
The event severity levels are listed from the highest severity to the lowest severity, as follows:
• Emergency—System is not usable.
• Alert—Action is needed.
• Critical—System is in a critical condition.
• Error—System is in error condition.
• Warning—System warning has occurred.
• Notice—System is functioning properly, but a system notice has occurred.
• Informational—Device information.
• Debug—Detailed information about an event.
You can select different severity levels for RAM and Flash logs. These logs are displayed in
the RAM Memory page and Flash Memory page, respectively.
Selecting a severity level to be stored in a log causes all of the higher severity events to be
automatically stored in the log. Lower severity events are not stored in the log.
For example, if Warning is selected, all severity levels that are Warning and higher are stored
in the log (Emergency, Alert, Critical, Error, and Warning). No events with severity level
below Warning are stored (Notice, Informational, and Debug).
Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x 68
Page 89

5
Administration
System Log
To set global log parameters:
STEP 1 Click Administration > System Log > Log Settings.
STEP 2 Enter the parameters.
• Logging—Select to enable message logging.
• Syslog Aggregator—Select to enable the aggregation of SYSLOG messages and traps.
If enabled, identical and contiguous SYSLOG messages and traps are aggregated over
the specified Max. Aggregation Time and sent in a single message. The aggregated
messages are sent in the order of their arrival. Each message states the number of times
it was aggregated.
• Max. Aggregation Time—Enter the interval of time that SYSLOG messages are
aggregated.
• Originator Identifier—Enables adding an origin identifier to SYSLOG messages. The
options are:
- None—Do not include the origin identifier in SYSLOG messages.
- Hostname—Include the system host name in SYSLOG messages.
- IPv4 Address—Include the IPv4 address of the sending interface in SYSLOG
messages.
- IPv6 Address—Include the IPv6 address of the sending interface in SYSLOG
messages.
- User Defined—Enter a description to be included in SYSLOG messages.
• RAM Memory Logging—Select the severity levels of the messages to be logged to the
RAM.
• Flash Memory Logging—Select the severity levels of the messages to be logged to the
Flash memory.
• Click Apply. The Running Configuration file is updated.
Remote Logging Settings
The Remote Log Servers page enables defining remote SYSLOG servers to which log
messages are sent. For each server, you can configure the severity of the messages that it
receives.
69 Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x
Page 90

Administration
System Log
5
To define SYSLOG servers:
STEP 1 Click Administration > System Log > Remote Log Servers.
STEP 2 Enter the following fields:
• IPv4 Source Interface—Select the source interface whose IPv4 address will be used as
the source IPv4 address of SYSLOG messages sent to SYSLOG servers.
• IPv6 Source Interface—Select the source interface whose IPv6 address will be used as
the source IPv6 address of SYSLOG messages sent to SYSLOG servers.
NOTE If the Auto option is selected, the system takes the source IP address from the IP
address defined on the outgoing interface.
Information is described for each previously-configured log server. The fields are described
below in the Add page.
STEP 3 Click Add.
STEP 4 Enter the parameters.
• Server Definition—Select whether to identify the remote log server by IP address or
name.
• IP Version—Select the supported IP format.
• IPv6 Address Type—Select the IPv6 address type (if IPv6 is used). The options are:
- Link Local—The IPv6 address uniquely identifies hosts on a single network link. A
link local address has a prefix of FE80::/10, is not routable, and can be used for
communication only on the local network. Only one link local address is supported.
If a link local address exists on the interface, this entry replaces the address in the
configuration.
- Global—The IPv6 address is a global Unicast IPV6 type that is visible and
reachable from other networks.
• Link Local Interface—Select the link local interface (if IPv6 Address T ype Link Local
is selected) from the list.
• Log Server IP Addr ess/Name—Enter the IP address or domain name of the log server .
• UDP Port—Enter the UDP port to which the log messages are sent.
• Facility—Select a facility value from which system logs are sent to the remote server.
Only one facility value can be assigned to a server. If a second facility code is assigned,
the first facility value is overridden.
Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x 70
Page 91

5
STEP 5 Click Apply. The Add Remote Log Server page closes, the SYSLOG server is added, and the
File Management
Administration
File Management
• Description—Enter a server description.
• Minimum Severity—Select the minimum level of system log messages to be sent to
the server.
Running Configuration file is updated.
See Administration: File Management.
Reboot
Some configuration changes, such as enabling jumbo frame support, require the system to be
rebooted before they take effect. However, rebooting the device deletes the Running
Configuration, so it is critical that the Running Configuration is saved to the Startup
Configuration before the device is rebooted. Clicking Apply does not save the configuration to
the Startup Configuration. For more information on files and file types, see the System Files
section.
You can back up the device configuration by using the File Operations page or clicking Save
at the top of the window. Yo u can also upload the configuration from a remote device in the
same page.
You might want to set the time of the reboot for some time in the future. This could happen, for
example, in one of the following cases:
• You are performing actions on a remote device, and a mistake in these actions might
create loss of connectivity to the remote device. Pre-scheduling a reboot restores the
working configuration and enables restoring the connectivity to the remote device after
the specified time expires. If these actions are successful, the delayed reboot can be
manually cancelled.
• Reloading the device cause loss of connectivity in the network, thus by using delayed
reboot, you can schedule the reboot to a time that is more convenient for the users (e.g.
late night).
71 Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x
Page 92

Administration
Routing Resources
5
To reboot the device:
STEP 1 Click Administration > Reboot.
STEP 2 Click the Reboot button to reboot the device.
• Reboot—Reboots the device. Since any unsaved informatio n in the Running
Configuration is discarded when the device is rebooted, you must click Save in the
upper-right corner of any window to preserve current configuration across the boot
process. If the Save option is not displayed, the Running Configuration matches the
Startup Configuration and no action is necessary.
The following options are available:
- Immediate—Reboot immediately.
- Date—Enter the date (month/day) and time (hour and minutes) of the schedule
reboot. This schedules a reload of the software to take place at the specified time
(using a 24-hour clock). If you specify the month and day, the reload is scheduled
to take place at the specified time and date. If you do not specify the month and day,
the reload takes place at the specified time on the current day (if the specified time
is later than the current time) or on the next day (if the specified time is earlier than
the current time). Specifying 00:00 schedules the reload for midnight. The reload
must take place within 24 days.
Routing Resources
TCAM entries are divided into the following groups:
NOTE This option can only be used if the system time has either been set manually or
by SNTP.
- In—Reboot within the specified number of hours and minutes. The maximum
amount of time that can pass is 24 days.
• Restore to Factory Defaults—Reboots the device by using the factory default
configuration. This process erases all except the Active Image, Inactive Image, Mirror
configuration and Localization files
The stack unit ID is set to auto.
• Clear Startup Configuration File—Check to clear the startup configuration on the
device for the next time it boots up.
Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x 72
Page 93

5
Administration
Routing Resources
• IP Entries—Router TCAM entries reserved for IP static routes, IP interfaces, and IP
hosts.
• Non-IP Entries—TCAM entries reserved for other applications, such as ACL rules,
CoS policers, and VLAN rate limits.
The following table describes the number of TCAM entries used by the various features:
Logical Entity IPv4 IPv6 (PCL
TCAM)
IP Neighbor 1 entry 1 entry 4 Entries
IP Address on an interface 2 entries 2 entries 8 entries
IP Remote Route 1 entry 1 entry 4 Entries
On-Link-Prefix 1 Entry 4 Entries
The Routing Resources page enables you to adjust the Router TCAM allocation.
If you change the router TCAM allocation incorrectly, an error message is displayed. If your
router TCAM allocation is feasible, a message is displayed that an automatic reboot will be
performed with the new settings. Routing resources can be modified incorrectly, in one of the
following ways:
• The number of router TCAM entries you allocate is less than the number currently in
use.
• The number of router TCAM entries that you allocate is greater than the maximum
available for that category (maximum values are displayed on the page).
IPv6 (Router
TCAM)
To view and modify routing resources:
STEP 1 Click Administration > Routing Resources.
The following fields are displayed:
IPv4 Routing Resources
• Neighbors (x TCAM entry per neighbor)—Count is the number of neighbors
recorded on the device and TCAM Entries is the number of router TCAM entries being
used for the neighbors. There are 4 TCAM entries per neighbor for the SG550XG
family and 1 for the SG350XG family.
73 Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x
Page 94

Administration
Routing Resources
5
• Interfaces (2 TCAM entries per interface)—Count is the number of IP addresses on
interfaces on the device and TCAM Entries is the number of router TCAM entries
being used for the IP addresses.
• Routes (1 TCAM entry per route)—Count is the number of routes recorded on the
device and TCAM Entries is the number of router TCAM entries being used for the
routes.
• Total—Displays the number of router TCAM entries which are currently being used.
• Maximum Entries—Select one of the following options:
- Use Default—Use default values.
- User Defined—Enter a value.
IPv4 Multicast Routing Resources
• IPv4 Multicast Routes (2 TCAM entries per route)—Count is the number of
Multicast routes recorded on the device and TCAM Entries is the number of TCAM
entries being used for the Multicast routes.
• Maximum Entries—Select one of the following options:
- Use Default—Use default values.
- User Defined—Enter a value.
IPv4 Policy Based Routing Resources
• IPv4 Policy Based Routes (4 TCAM entries per route)—Count is the number of
Multicast routes recorded on the device and TCAM Entries is the number of TCAM
entries being used for the Multicast routes.
• Maximum Entries—Select one of the following options:
- Use Default—Use default values.
- User Defined—Enter a value.
IPv6 Routing Resources
• Neighbors (x TCAM entries per neighbor)—Count is the number of neighbors
recorded on the device and TCAM Entries is the number of TCAM entries being used
for neighbors.
• Interfaces (x TCAM entries per interface)—Count is the number of interfaces on the
device and TCAM Entries is the number of TCAM entries being used for the
interfaces.
Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x 74
Page 95

5
Administration
Routing Resources
• On Link Prefixes (x TCAM entries per prefix)—Count is the number of on link
prefixes recorded on the device and TCAM Entries is the number of TCAM entries
being used for them.
• Routes (x TCAM entries per route)—Count is the number of on link prefixes
recorded on the device and TCAM Entries is the number of TCAM entries being used
for them.
• Total—Total number of TCAM entries being used.
• Maximum Entries—Select one of the following options:
- Use Default—Use default values.
- User Defined—Enter a value.
IPv6 Multicast Routing Resources
• IPv6 Multicast Routes (8 TCAM entries per route)—Count is the number of
Multicast routes recorded on the device and TCAM Entries is the number of TCAM
entries being used for the Multicast routes.
• Maximum Entries—Select one of the following options:
- Use Default—Use default values.
- User Defined—Enter a value.
IPv6 Policy Based Routing Resources
• IPv6 Policy Based Routes (4 TCAM entries per route)—Count is the number of
Multicast routes recorded on the device and TCAM Entries is the number of TCAM
entries being used for the Multicast routes.
• Maximum Entries—Select one of the following options:
- Use Default—Use default values.
- User Defined—Enter a value.
STEP 2 Save the new settings by clicking Apply. This checks the feasibility of the routing resources
settings. If it is incorrect, an error message is displayed. If it is correct, the settings are copied
to the Running Configuration file.
TCAM Resources Table—Displays the number of TCAM entries actually in use and
available.
• Maximum TCAM Entries for Routing and Multicast Routing—Number of TCAM
entries available for routing and Multicast routing.
75 Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x
Page 96

Administration
Routing Resources
5
• IPv4 Routing
- In Use—Number of TCAM entries utilized for IPv4 routing.
- Maximum—Maximum number of TCAM entries available for IPv4 Routing.
• IPv4 Multicast Routing
- In Use—Number of TCAM entries utilized for IPv4 Multicast routing.
- Maximum—Maximum number of TCAM entries available for IPv4 Multicast
routing.
• IPv4 Policy Based Routing
- In Use—Number of router TCAM entries used for IPv4 Policy-based routing.
- Maximum—Number of available router TCAM entries that can be used for IPv4
Policy-based routing.
• IPv6 Routing
- In Use—Number of TCAM entries utilized for IPv6 routing.
- Maximum—Maximum number of TCAM entries available for IPv6 Routing.
• IPv6 Multicast Routing
- In Use—Number of TCAM entries utilized for IPv6 Multicast routing.
- Maximum—Maximum number of TCAM entries available for IPv6 Multicast
routing.
• IPv6 Policy Based Routing
- In Use—Number of router TCAM entries used for IPv6 Policy-based routing.
- Maximum—Number of available router TCAM entries that can be used for IPv6
Policy-based routing.
• Maximum TCAM Entries for Non-IP Rules—Number of TCAM entries available
for non-IP rules.
• Non-IP Rules
- In Use—Number of TCAM entries utilized for non-IP rules.
- Maximum—Maximum number of TCAM entries available for non-IP rules.
Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x 76
Page 97

5
Discovery - Bonjour
See Bonjour.
Discovery - LLDP
See Discover - LLDP.
Discovery - CDP
See Discovery - CDP.
Administration
Discovery - Bonjour
Ping
The Ping utility tests if a remote host can be reached and measures the round-trip time for
packets sent from the device to a destination device.
Ping operates by sending Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) echo request packets to
the target host and waiting for an ICMP response, sometimes called a pong. It measures the
round-trip time and records any packet loss.
To ping a host:
STEP 1 Click Administration > Ping.
STEP 2 Configure ping by entering the fields:
• Host Definition—Select whether to specify the source interface by its IP address or
name. This field influences the interfaces that are displayed in the Source IP field, as
described below.
• IP Version—If the source interface is identified by its IP address, select either IPv4 or
IPv6 to indicate that it will be entered in the selected format.
77 Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x
Page 98

Administration
Ping
5
• Source IP—Select the source interface whose IPv4 address will be used as the source
IPv4 address for communication with the destination. If the Host Definition field was
By Name, all IPv4 and IPv6 addresses will be displayed in this drop-down field. If the
Host Definition field was By IP Address, only the existing IP addresses of the type
specified in the IP Version field will be displayed.
NOTE If the Auto option is selected, the system computes the source address based on
the destination address.
• Destination IPv6 Address Type—Select one of the following options:.
- Link Local—The IPv6 address uniquely identifies hosts on a single network link. A
link local address has a prefix of FE80, is not routable, and can be used for
communication only on the local network. Only one link local address is supported.
If a link local address exists on the interface, this entry replaces the address in the
configuration.
- Global—The IPv6 address is a global Unicast IPV6 type that is visible and
reachable from other networks.
• Link Local Interface—If the IPv6 address type is Link Local, select from where it is
received.
• Destination IP Address/Name—Address or host name of the device to be pinged.
Whether this is an IP address or host name depends on the Host Definition.
• Ping Interval—Length of time the system waits between ping packets. Ping is repeated
the number of times configured in the Number of Pings field, whether the ping
succeeds or not. Select to use the default interval or specify your own value.
• Number of Pings—The number of times the ping operation is performed. Select to use
the default or specify your own value.
• Status—Displays whether the ping succeeded or failed.
STEP 3 Click Activate Ping to ping the host. The ping status appears and a message is added to the list
of messages, indicating the result of the ping operation.
STEP 4 View the results of ping in the Ping Counters and Status section of the page:
• Number of Sent Packets—Number of packets sent by ping
• Number of Received Packets—Number of packets received by ping
• Packets Lost—Percentage of packets lost in ping process
• Minimum Round Trip Time—Shortest time for packet to return
• Maximum Round Trip Time—Longest time for packet to return
Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x 78
Page 99

5
Traceroute
Administration
Traceroute
• A verage Round Trip Time—Average time for packet to return
• Status—Fail or succeed
Traceroute discovers the IP routes along which packets forwarded by sending an IP packet to
the target host and back to the device. The T raceroute page shows each hop between the device
and a target host, and the round-trip time to each such hop.
STEP 1 Click Administration > Traceroute.
STEP 2 Configure Traceroute by entering information into the following fields:
• Host Definition—Select whether hosts are identified by their IP address or name.
• IP Version—If the host is identified by its IP address, select either IPv4 or IPv6 to
indicate that it will be entered in the selected format.
• Source IP—Select the source interface whose IPv4 address will be used as the source
IPv4 address for communication messages. If the Host Definition field was By Name,
all IPv4 and IPv6 addresses will be displayed in this drop-down field. If the Host
Definition field was By IP Address, only the existing IP addresses of the type specified
in the IP Version field will be displayed.
• Host IP Address/Name—Enter the host address or name.
• TTL—Enter the maximum number of hops that Traceroute permits. This is used to
prevent a case where the sent frame gets into an endless loop. The Traceroute command
terminates when the destination is reached or when this value is reached. To use the
default value (30), select Use Default.
• Timeout—Enter the length of time that the system waits for a frame to return before
declaring it lost, or select Use Default.
STEP 3 Click Activate Traceroute. The operation is performed.
A page appears showing the Round Trip Time (RTT) and status for each trip in the fields:
• Index—Displays the number of the hop.
• Host—Displays a stop along the route to the destination.
Round Trip Time (1-3)—Displays the round trip Time in (ms) for the first through third
frame and the Status of the first through third operation.
79 Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x
Page 100

Administration: File Management
This section describes how system files are managed.
The following topics are covered:
• System Files
• Firmware Operations
• File Operations
6
System Files
• File Directory
• DHCP Auto Configuration/Image Update
System files are files that contain information, such as: configuration information or firmware
images.
Generally, every file under the flash://system/ folder is a system file.
Various actions can be performed with these files, such as: selecting the firmware file from
which the device boots, copying various types of configuration files internally on the device,
or copying files to or from an external device, such as an external server.
Configuration files on the device are defined by their type, and contain the settings and
parameter values for the device.
Other files on the device include firmware and log files, and are referred to as operational
files.
The configuration files are text files and can be edited in a text editor, such as Notepad after
they are copied to an external device, such as a PC.
Cisco Sx350, SG350X, SG350XG, Sx550X & SG550XG Series Managed Switches, Firmware Release 2.2.5.x 73
 Loading...
Loading...