Page 1

FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the
CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
Release 2.13
Corporate Headquarters
Cisco Systems, Inc.
170 West Tasman Drive
San Jose, CA 95134-1706
USA
http://www.cisco.com
Tel: 408 526-4000
800 553-NETS (6387)
Fax: 408 526-4100
Customer Order Number: OL-8376-01
Page 2

r
THE SPECIFICATIONS AND INFORMATION REGARDING THE PRODUCTS IN THIS MANUAL ARE SUBJECT TO CHANGE WITHOUT NOTICE. ALL
STATEMENTS, INFORMATION, AND RECOMMENDATIONS IN THIS MANUAL ARE BELIEVED TO BE ACCURATE BUT ARE PRESENTED WITHOUT
WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED. USERS MUST TAKE FULL RESPONSIBILITY FOR THEIR APPLICATION OF ANY PRODUCTS.
THE SOFTWARE LICENSE AND LIMITED WARRANTY FOR THE ACCOMPANYING PRODUCT ARE SET FORTH IN THE INFORMATION PACKET THAT
SHIPPED WITH THE PRODUCT AND ARE INCORPORATED HEREIN BY THIS REFERENCE. IF YOU ARE UNABLE TO LOCATE THE SOFTWARE LICENSE
OR LIMITED WARRANTY, CONTACT YOUR CISCO REPRESENTATIVE FOR A COPY.
The Cisco implementation of TCP header compression is an adaptation of a program developed by the University of California, Berkeley (UCB) as part of UCB’s public
domain version of the UNIX operating system. All rights reserved. Copyright © 1981, Regents of the University of California.
NOTWITHSTANDING ANY OTHER WARRANTY HEREIN, ALL DOCUMENT FILES AND SOFTWARE OF THESE SUPPLIERS ARE PROVIDED “AS IS” WITH
ALL FAULTS. CISCO AND THE ABOVE-NAMED SUPPLIERS DISCLAIM ALL WARRANTIES, EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING, WITHOUT
LIMITATION, THOSE OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT OR ARISING FROM A COURSE OF
DEALING, USAGE, OR TRADE PRACTICE.
IN NO EVENT SHALL CISCO OR ITS SUPPLIERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY INDIRECT, SPECIAL, CONSEQUENTIAL, OR INCIDENTAL DAMAGES, INCLUDING,
WITHOUT LIMITATION, LOST PROFITS OR LOSS OR DAMAGE TO DATA ARISING OUT OF THE USE OR INABILITY TO USE THIS MANUAL, EVEN IF CISCO
OR ITS SUPPLIERS HAVE BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES.
CSP, CCVP, the Cisco Square Bridge logo, Follow Me Browsing, and StackWise are trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc.; Changing the Way We Work,
ive, Play, and Learn, and iQuick Study are service marks of Cisco Systems, Inc.; and Access Registrar, Aironet, ASIST, BPX, Catalyst, CCDA, CCDP,
CIE, CCIP, CCNA, CCNP, Cisco, the Cisco Certified Internetwork Expert logo, Cisco IOS, Cisco Press, Cisco Systems, Cisco Systems Capital, the
isco Systems logo, Cisco Unity, Empowering the Internet Generation, Enterprise/Solver, EtherChannel, EtherFast, EtherSwitch, Fast Step, FormShare,
igaDrive, GigaStack, HomeLink, Internet Quotient, IOS, IP/TV, iQ Expertise, the iQ logo, iQ Net Readiness Scorecard, LightStream, Linksys,
eetingPlace, MGX, the Networkers logo, Networking Academy, Network Registrar, Pac ke t , PIX, Post-Routing, Pre-Routing, ProConnect, RateMUX,
criptShare, SlideCast, SMARTnet, StrataView Plus, TeleRouter, The Fastest Way to Increase Your Internet Quotient, and TransPath are registered
ademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. and/or its affiliates in the United States and certain other countries.
ll other trademarks mentioned in this document or Website are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a
artnership relationship between Cisco and any other company. (0502R)
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
Copyright © 2006 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Page 3

Preface v
Audience v
Conventions v
Product Documentation vi
Obtaining Documentation vii
Documentation Feedback ix
Cisco Product Security Overview ix
Obtaining Technical Assistance x
Obtaining Additional Publications and Information xi
CONTENTS
CHAPTER
OL-8376-01
1 FAQs and Troubleshooting 1-1
General FAQs and Troubleshooting 1-1
Deployment Wizard Troubleshooting 1-10
Faults FAQs and Troubleshooting 1-11
Devices FAQs and Troubleshooting 1-15
Configuration FAQs and Troubleshooting 1-21
Firmware FAQs and Troubleshooting 1-27
Reports FAQs and Troubleshooting 1-31
Radio Manager FAQs and Troubleshooting 1-35
Sites FAQs and Troubleshooting 1-41
Intrusion Detection System FAQs and Troubleshooting 1-49
Admin FAQs and Troubleshooting 1-54
Internal AAA Server (WLSE Express Only) FAQs and Troubleshooting 1-62
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
iii
Page 4

Contents
CHAPTER
I
NDEX
2 Fault Descriptions 2-1
Access Point /Bridge Faults 2-2
Radio Interface Faults 2-8
IDS (Intrusion Detection System) Faults 2-14
Voice Faults 2-24
WLSE Faults 2-24
AAA Server Faults 2-26
Switch Faults 2-31
Router Fault 2-33
WLSM Faults 2-33
iv
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
OL-8376-01
Page 5

Audience
Preface
This guide provides troubleshooting hints, FAQs, and information on faults for the CiscoWorks Wireless
LAN Solution Engine and Wireless LAN Engine Express. This guide consists of the following chapters:
• FAQs and Troubleshooting
• Fault Descriptions
This guide is frequently updated on Cisco.com.
This document is for system administrators and network administrators who are responsible for
managing a wireless network and are familiar with the concepts and terminology of Ethernet and
wireless local area networking.
Conventions
This document uses the following conventions:
Item Convention
Commands and keywords boldface font
Variables for which you supply values italic font
Displayed session and system information
Information you enter
Variables you enter
Menu items and button names boldface font
Selecting a menu item in paragraphs Option > Network Preferences
Selecting a menu item in tables Option > Network Preferences
screen font
boldface screen font
italic screen
font
OL-8376-01
Note Means reader take note. Notes contain helpful suggestions or references to material not covered in the
publication.
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
v
Page 6

Product Documentation
Caution Means reader be careful. In this situation, you might do something that could result in equipment
damage or loss of data.
Product Documentation
Note We sometimes update the documentation after original publication. Therefore, you should also review
the documentation on Cisco.com for any updates.
Table 1 describes the product documentation for WLSE 2.12. Unless otherwise indicated, these
documents apply to both the WLSE and WLSE Express.
Table 1 Product Documentation
Document Title Available Formats
Release Notes for the
CiscoWorks Wireless LAN
Solution Engine
Configuring Devices for
Management by the
CiscoWorks Wireless LAN
Solution Engine
Installation and
Configuration Guide for the
1130-19 CiscoWorks
Wireless LAN Solution
Engine
Installation and
Configuration Guide for the
1030CiscoWorks Wireless
LAN Solution Engine
Express
Installation and
Configuration Guide for the
1133 CiscoWorks Wireless
LAN Solution Engine
On Cisco.com:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/rtrmgmt/cwparent/c
w_1105/wlse/2_13/index.htm
On Cisco.com:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/rtrmgmt/cwparent/c
w_1105/wlse/2_13/index.htm
• Printed document included with the product.
• PDF on the WLSE Recovery CD-ROM.
• On Cisco.com:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/rtrmgmt/cwpare
nt/cw_1105/wlse/2_13/index.htm
• Printed document included with the product.
• PDF on the WLSE Recovery CD-ROM.
• On Cisco.com:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/rtrmgmt/cwpare
nt/cw_1105/wlse/2_13/index.htm
• Printed document included with the product.
• PDF on the WLSE Recovery CD-ROM.
• Online:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/rtrmgmt/cwpare
nt/cw_1105/wlse/2_13/index.htm
Preface
vi
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
OL-8376-01
Page 7

Preface
Table 1 Product Documentation (continued)
Document Title Available Formats
Regulatory Compliance and
Safety Information for the
1130-19 CiscoWorks
Wireless LAN Solution
Engine
• Printed document included with the product.
• PDF on the WLSE Recovery CD-ROM.
• On Cisco.com:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/rtrmgmt/cwpare
nt/cw_1105/wlse/2_13/index.htm
Regulatory Compliance and
Safety Information for the
1030 CiscoWorks Wireless
LAN Solution Engine
Express
• Printed document included with the product.
• PDF on the WLSE Recovery CD-ROM.
• On Cisco.com:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/rtrmgmt/cwpare
nt/cw_1105/wlse/2_13/index.htm
Regulatory Compliance and
Safety Information for the
CiscoWorks 1133 Wireless
LAN Solution Engine
• Printed document included with the product.
• PDF on the WLSE Recovery CD-ROM.
• Online:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/rtrmgmt/cwpare
nt/cw_1105/wlse/2_13/index.htm
User Guide for the
CiscoWorks Wireless LAN
Solution Engine
• From the WLSE online help.
• PDF on the WLSE Recovery CD-ROM.
• On Cisco.com:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/rtrmgmt/cwpare
nt/cw_1105/wlse/2_13/index.htm
Upgrading CiscoWorks
Wireless LAN Solution
Engine Software
• From the WLSE online help.
• On Cisco.com:
www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/rtrmgmt/cwparent/cw_
1105/wlse/2_13/index.htm.
Supported Devices Table for
the CiscoWorks Wireless
LAN Solution Engine
Context-sensitive online
On Cisco.com:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/rtrmgmt/cwparent/cw_1
105/wlse/2_13/index.htm
Select an option from the WLSE navigation tree, then click Help.
help
Developer Guide for the
CiscoWorks Wireless LAN
Solution Engine
On Cisco.com in the Software Center:
http://www.cisco.com/cgi-bin/tablebuild.pl/wlan-sol-eng
Obtaining Documentation
Obtaining Documentation
Cisco documentation and additional literature are available on Cisco.com. Cisco also provides several
ways to obtain technical assistance and other technical resources. These sections explain how to obtain
technical information from Cisco Systems.
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
OL-8376-01
vii
Page 8

Obtaining Documentation
Cisco.com
You can access the most current Cisco documentation at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/techsupport
You can access the Cisco website at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com
You can access international Cisco websites at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/public/countries_languages.shtml
Product Documentation DVD
Cisco documentation and additional literature are available in the Product Documentation DVD package,
which may have shipped with your product. The Product Documentation DVD is updated regularly and
may be more current than printed documentation.
The Product Documentation DVD is a comprehensive library of technical product documentation on
portable media. The DVD enables you to access multiple versions of hardware and software installation,
configuration, and command guides for Cisco products and to view technical documentation in HTML.
With the DVD, you have access to the same documentation that is found on the Cisco website without
being connected to the Internet. Certain products also have .pdf versions of the documentation available.
Preface
The Product Documentation DVD is available as a single unit or as a subscription. Registered Cisco.com
users (Cisco direct customers) can order a Product Documentation DVD (product number
DOC-DOCDVD=) from the Ordering tool or Cisco Marketplace.
Cisco Ordering tool:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/partner/ordering/
Cisco Marketplace:
http://www.cisco.com/go/marketplace/
Ordering Documentation
Beginning June 30, 2005, registered Cisco.com users may order Cisco documentation at the Product
Documentation Store in the Cisco Marketplace at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/go/marketplace/
Cisco will continue to support documentation orders using the Ordering tool:
• Registered Cisco.com users (Cisco direct customers) can order documentation from the
Ordering tool:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/partner/ordering/
• Instructions for ordering documentation using the Ordering tool are at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/es_inpck/pdi.htm
• Nonregistered Cisco.com users can order documentation through a local account representative by
calling Cisco Systems Corporate Headquarters (California, USA) at 408 526-7208 or, elsewhere in
North America, by calling 1 800 553-NETS (6387).
viii
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
OL-8376-01
Page 9

Preface
Documentation Feedback
You can rate and provide feedback about Cisco technical documents by completing the online feedback
form that appears with the technical documents on Cisco.com.
You can send comments about Cisco documentation to bug-doc@cisco.com.
You can submit comments by using the response card (if present) behind the front cover of your
document or by writing to the following address:
Cisco Systems
Attn: Customer Document Ordering
170 West Tasman Drive
San Jose, CA 95134-9883
We appreciate your comments.
Cisco Product Security Overview
Cisco provides a free online Security Vulnerability Policy portal at this URL:
Documentation Feedback
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/products_security_vulnerability_policy.html
From this site, you can perform these tasks:
• Report security vulnerabilities in Cisco products.
• Obtain assistance with security incidents that involve Cisco products.
• Register to receive security information from Cisco.
A current list of security advisories and notices for Cisco products is available at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/go/psirt
If you prefer to see advisories and notices as they are updated in real time, you can access a Product
Security Incident Response Team Really Simple Syndication (PSIRT RSS) feed from this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/products_psirt_rss_feed.html
Reporting Security Problems in Cisco Products
Cisco is committed to delivering secure products. We test our products internally before we release them,
and we strive to correct all vulnerabilities quickly. If you think that you might have identified a
vulnerability in a Cisco product, contact PSIRT:
• Emergencies— security-alert@cisco.com
An emergency is either a condition in which a system is under active attack or a condition for which
a severe and urgent security vulnerability should be reported. All other conditions are considered
nonemergencies.
• Nonemergencies — psirt@cisco.com
OL-8376-01
In an emergency, you can also reach PSIRT by telephone:
• 1 877 228-7302
• 1 408 525-6532
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
ix
Page 10
Obtaining Technical Assistance
Tip We encourage you to use Pretty Good Privacy (PGP) or a compatible product to encrypt any sensitive
information that you send to Cisco. PSIRT can work from encrypted information that is compatible with
PGP versions 2.x through 8.x.
Never use a revoked or an expired encryption key. The correct public key to use in your correspondence
with PSIRT is the one linked in the Contact Summary section of the Security Vulnerability Policy page
at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/products_security_vulnerability_policy.htm
The link on this page has the current PGP key ID in use.
Obtaining Technical Assistance
Cisco Technical Support provides 24-hour-a-day award-winning technical assistance. The Cisco
Technical Support & Documentation website on Cisco.com features extensive online support resources.
In addition, if you have a valid Cisco service contract, Cisco Technical Assistance Center (TAC)
engineers provide telephone support. If you do not have a valid Cisco service contract, contact your
reseller.
Preface
Cisco Technical Support & Documentation Website
The Cisco Technical Support & Documentation website provides online documents and tools for
troubleshooting and resolving technical issues with Cisco products and technologies. The website is
available 24 hours a day, at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/techsupport
Access to all tools on the Cisco Technical Support & Documentation website requires a Cisco.com user
ID and password. If you have a valid service contract but do not have a user ID or password, you can
register at this URL:
http://tools.cisco.com/RPF/register/register.do
Note Use the Cisco Product Identification (CPI) tool to locate your product serial number before submitting
a web or phone request for service. You can access the CPI tool from the Cisco Technical Support &
Documentation website by clicking the Tools & Resources link under Documentation & Tools. Choose
Cisco Product Identification Tool from the Alphabetical Index drop-down list, or click the Cisco
Product Identification Tool link under Alerts & RMAs. The CPI tool offers three search options: by
product ID or model name; by tree view; or for certain products, by copying and pasting show command
output. Search results show an illustration of your product with the serial number label location
highlighted. Locate the serial number label on your product and record the information before placing a
service call.
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
x
OL-8376-01
Page 11

Preface
Submitting a Service Request
Using the online TAC Service Request Tool is the fastest way to open S3 and S4 service requests. (S3
and S4 service requests are those in which your network is minimally impaired or for which you require
product information.) After you describe your situation, the TAC Service Request Tool provides
recommended solutions. If your issue is not resolved using the recommended resources, your service
request is assigned to a Cisco engineer. The TAC Service Request Tool is located at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/techsupport/servicerequest
For S1 or S2 service requests or if you do not have Internet access, contact the Cisco TAC by telephone.
(S1 or S2 service requests are those in which your production network is down or severely degraded.)
Cisco engineers are assigned immediately to S1 and S2 service requests to help keep your business
operations running smoothly.
To open a service request by telephone, use one of the following numbers:
Asia-Pacific: +61 2 8446 7411 (Australia: 1 800 805 227)
EMEA: +32 2 704 55 55
USA: 1 800 553-2447
For a complete list of Cisco TAC contacts, go to this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/techsupport/contacts
Obtaining Additional Publications and Information
Definitions of Service Request Severity
To ensure that all service requests are reported in a standard format, Cisco has established severity
definitions.
Severity 1 (S1)—Your network is “down,” or there is a critical impact to your business operations. You
and Cisco will commit all necessary resources around the clock to resolve the situation.
Severity 2 (S2)—Operation of an existing network is severely degraded, or significant aspects of your
business operation are negatively affected by inadequate performance of Cisco products. You and Cisco
will commit full-time resources during normal business hours to resolve the situation.
Severity 3 (S3)—Operational performance of your network is impaired, but most business operations
remain functional. You and Cisco will commit resources during normal business hours to restore service
to satisfactory levels.
Severity 4 (S4)—You require information or assistance with Cisco product capabilities, installation, or
configuration. There is little or no effect on your business operations.
Obtaining Additional Publications and Information
Information about Cisco products, technologies, and network solutions is available from various online
and printed sources.
• Cisco Marketplace provides a variety of Cisco books, reference guides, documentation, and logo
merchandise. Visit Cisco Marketplace, the company store, at this URL:
OL-8376-01
http://www.cisco.com/go/marketplace/
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
xi
Page 12

Obtaining Additional Publications and Information
• Cisco Press publishes a wide range of general networking, training and certification titles. Both new
and experienced users will benefit from these publications. For current Cisco Press titles and other
information, go to Cisco Press at this URL:
http://www.ciscopress.com
• Packet magazine is the Cisco Systems technical user magazine for maximizing Internet and
networking investments. Each quarter, Packet delivers coverage of the latest industry trends,
technology breakthroughs, and Cisco products and solutions, as well as network deployment and
troubleshooting tips, configuration examples, customer case studies, certification and training
information, and links to scores of in-depth online resources. You can access Packet magazine at
this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/packet
• iQ Magazine is the quarterly publication from Cisco Systems designed to help growing companies
learn how they can use technology to increase revenue, streamline their business, and expand
services. The publication identifies the challenges facing these companies and the technologies to
help solve them, using real-world case studies and business strategies to help readers make sound
technology investment decisions. You can access iQ Magazine at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/go/iqmagazine
Preface
or view the digital edition at this URL:
http://ciscoiq.texterity.com/ciscoiq/sample/
• Internet Protocol Journal is a quarterly journal published by Cisco Systems for engineering
professionals involved in designing, developing, and operating public and private internets and
intranets. You can access the Internet Protocol Journal at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/ipj
• Networking products offered by Cisco Systems, as well as customer support services, can be
obtained at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/index.html
• Networking Professionals Connection is an interactive website for networking professionals to share
questions, suggestions, and information about networking products and technologies with Cisco
experts and other networking professionals. Join a discussion at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/discuss/networking
• World-class networking training is available from Cisco. You can view current offerings at
this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/learning/index.html
xii
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
OL-8376-01
Page 13

CHAPTER
1
FAQs and Troubleshooting
Revised: June 20, 2006, OL-8376-01
This chapter provides FAQs and troubleshooting hints for all WLSE functions.
This chapter is organized as follows:
• General Questions—Information that is general in nature and not directly related to one of the
following categories—See General FAQs and Troubleshooting, page 1-1
• Deployment Wizard—Deployment Wizard Troubleshooting, page 1-10
• Faults—Faults FAQs and Troubleshooting, page 1-11
• Devices—Devices FAQs and Troubleshooting, page 1-15
• Configuration—Configuration FAQs and Troubleshooting, page 1-21
• Firmware—Firmware FAQs and Troubleshooting, page 1-27
• Reports—Reports FAQs and Troubleshooting, page 1-31
• Radio Manager—Radio Manager FAQs and Troubleshooting, page 1-35
• Sites—Sites FAQs and Troubleshooting, page 1-41
• Intrusion Detection System (IDS)—Intrusion Detection System FAQs and Troubleshooting, page
1-49
• Admin (troubleshooting the WLSE appliance)—Admin FAQs and Troubleshooting, page 1-54
• Internal AAA Server (WLSE Express Only)—Internal AAA Server (WLSE Express Only) FAQs
and Troubleshooting, page 1-62
General FAQs and Troubleshooting
• General FAQs, page 1-1
• General Troubleshooting, page 1-4
General FAQs
• Q.Can several users be logged on and managing the same access point at once?
• Q.Does the WLSE support Network Address Translation (NAT)?
• Q.Is Telnet enabled or disabled by default on the WLSE?
OL-8376-01
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
1-1
Page 14

General FAQs and Troubleshooting
• Q.Which ports and protocols does the WLSE use?
• Q.Which transport protocols and authentication methods does WLSE use?
• Q.Can I use a different HTTP port to manage the access point?
• Q.Can SSH be disabled?
• Q.Devices are being displayed by IP address instead of hostname. Can I change this?
• Q.How can I get information about the WLSE’s operating system and hardware?
• Q.Can I install WLSE 2.13 software on a CiscoWorks 1105 appliance?
• Q.How many access points can a WLSE manage?
• Q.What MIBs does WLSE 2.13 support?
• Q.Why doesn't my WLSE session automatically time out when there has been no input for the
configured time-out period?
• Q.Will access point connectivity be disrupted during and upgrade?
Q.
Can several users be logged on and managing the same access point at once?
A.
Yes, several users can view data and reports on the same access point. More than one user can create
configuration and firmware update jobs for the same access point and these will be run in the order
they are scheduled. Configuration templates may be modified by more than one user at the same time
and the last write will overwrite the others.
Chapter 1 FAQs and Troubleshooting
Q.
Does the WLSE support Network Address Translation (NAT)?
A.
No.
Q.
Is Telnet enabled or disabled by default on the WLSE?
A.
Telnet is disabled by default for security reasons. SSH is enabled by default.
Q.
Which ports and protocols does the WLSE use?
A.
For information about the TCP and UDP ports and protocols used by and hosted by the WLSE, see
Appendix C, “Ports and Protocols”, in the online help or in the User Guide for the CiscoWorks
Wireless LAN Solution Engine, Release 2.13 on Cisco.com at
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/rtrmgmt/cwparent/cw_1105/wlse/2_13/index.ht
m.
Q.
Which transport protocols and authentication methods does WLSE use?
A.
See Appendix C, “Ports and Protocols”, in the online help or the User Guide for the CiscoWorks
Wireless LAN Solution Engine, Release 2.13 on Cisco.com at
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/rtrmgmt/cwparent/cw_1105/wlse/2_13/index.ht
m.
Q.
Can I use a different HTTP port to manage the access point?
A.
Yes, the HTTP port can be changed on the access point. The change will be reflected in WLSE after
the next inventory cycle, or if you choose to run inventory now for the devices on which HTTP port
was changed. This is assuming the inventory is done by SNMP and not HTTP.
1-2
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
OL-8376-01
Page 15

Chapter 1 FAQs and Troubleshooting
Q.
Can SSH be disabled?
A.
It cannot be disabled on the WLSE itself, but you can use the firewall command to deny all SSH
connections. For example, the following CLI command will cause the WLSE to reject all incoming
SSH connections on the Ethernet 0 interface but allows connections through other protocols and
other ports:
firewall ethernet0 private ssh
Q.
Devices are being displayed by IP address instead of hostname. Can I change this?
A.
Select Devices > Discover > DISCOVER > Advanced Options. In the Name Format field, enter
%hostname% as the name format.
Q.
How can I get information about the WLSE’s operating system and hardware?
A.
For information about the operating system, WLSE model name, CPU and disk capacity, run the
show version CLI command. For other information about the hardware, see the Technical
Specifications appendix in the Installation and Configuration Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless
LAN Solution Engine.
Q.
Can I install WLSE 2.13 software on a CiscoWorks 1105 appliance?
A.
No. WLSE 2.13 software can be installed on a CiscoWorks 1130 series or 1030 Express only.
General FAQs and Troubleshooting
Q.
How many access points can a WLSE manage?
A.
A WLSE Express (1030) can manage 50 access points (100 radios). A WLSE 1130 series can
manage up to 2500 access points (5000 radios). You can purchase a CD to upgrade the WLSE
Express to managing 100 access points.
Q.
What MIBs does WLSE 2.13 support?
A.
WLSE 2.13 supports the following MIBs:
MIB Name Description
MIB-II This MIB is used to manage TCP/IP-based Internets.
CISCO-CDP-MIB This MIB is used to manage the Cisco Discovery Protocol in Cisco
devices.
CISCO-DEVICE-EXCEPTION
-REPORTING-MIB
CISCO-APPLIANCE-REDUN
DANCY-MIB
This MIB defines the SNMP objects for devices that use SNMP
notification as an exception reporting mechanism.
This MIB defines the SNMP objects that report the status of High
Availability (HA) functionality in Cisco network management
appliance devices.
HOST-RESOURCES-MIB This MIB is used to manage host systems.
Q.
Why doesn't my WLSE session automatically time out when there has been no input for the
configured time-out period?
A.
This is a known problem that does not occur on all UI screens. However, note that after the
configured time elapses, even if the session has not timed out, when you click on any other WLSE
tab in the UI, a new login prompt appears.
OL-8376-01
Q.
Will access point connectivity be disrupted during and upgrade?
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
1-3
Page 16

General FAQs and Troubleshooting
A.
Upgrading your WLSE will not disrupt service on your access points. The APs connectivity will
remain intact and the WLAN will function normally.
General Troubleshooting
This section provides the following troubleshooting information:
• Symptom After the WLSE reboots, the Internal Server Error message appears in the UI.
• Symptom When I try to access an access point web page through the WLSE, the following error
message appears: Action Cancelled.
• Symptom Cannot recover after incorrect setup program entry.
• Symptom Cannot log into the system.
• Symptom Cannot log in as a system administrator.
• Symptom After the WLSE 1130 series starts up, the setup login prompt appears. After you use the
setup program, the WLSE cannot connect to the network.
• Symptom Cannot connect to the WLSE using a Web browser.
Chapter 1 FAQs and Troubleshooting
• Symptom The system time or date is incorrect.
• Symptom The system cannot boot from the hard drive during a reboot.
• Symptom Cannot connect to system with Telnet or Telnet interaction is slow.
• Symptom Cannot boot from the recovery CD.
• Symptom Cannot successfully connect to the WLSE by using a console.
• Symptom Pop-up windows are blocked and screens are not refreshed.
• Symptom After performing certain operations on the WLSE, such as clicking Apply in the Display
Faults page, then clicking the client browser Refresh button, a pop-up message is generated
indicating that the page cannot be refreshed.
• Symptom The Web interface of the WLSE is not available, but you can log in to the CLI.
Symptom After the WLSE reboots, the Internal Server Error message appears in the UI.
Possible Cause The servlet engine in the WLSE is starting up. In a redundant WLSE pair, the active
WLSE has lost contact with the standby WLSE. The standby WLSE is not up yet and returns this
error when the active WLSE makes a request of it. This message will disappear when the standby
WLSE has started up.
Recommended Action Wait for 20 to 30 seconds, then log in again.
1-4
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
OL-8376-01
Page 17

Chapter 1 FAQs and Troubleshooting
Symptom When I try to access an access point web page through the WLSE, the following error message
appears: Action Cancelled.
Possible Cause The SNMP user on the access point does not have enough rights.
Recommended Action Log in to the access point web interface, select Setup > Security > User
Information, and make sure that the user corresponding to the SNMP community (which is set up
in the WLSE under Discovery > Device Credentials) has been granted rights for the following:
firmware, admin, and SNMP.
Symptom Cannot recover after incorrect setup program entry.
Possible Cause You entered incorrect text during the initial setup and want to fix the entry.
Recommended Action Exit setup by pressing Ctrl-c. Then run erase config to remove the incorrect
installation information and rerun the setup program. If you use the erase config command to erase
the previous WLSE configuration, and run the setup program again, you will be required to get a
new certificate. Use the mkcert command or Admin > Appliance > Security > SSL (HTTPS).
General FAQs and Troubleshooting
Symptom Cannot log into the system.
Possible Cause You did not run the setup program to create an initial system configuration or you
lost all the user account passwords.
Recommended Action
1.
Did you run the setup program after booting the system for the first time?
If no, run the setup program.
If yes, continue to the next step.
2. Do you know the password for any system user accounts?
If no, see Symptom Cannot log in as a system administrator., page 1-5.
If yes, continue to the next step.
3. If you are certain you entered a valid username and password, contact Cisco’s Technical
Assistance Center for assistance.
Symptom Cannot log in as a system administrator.
Possible Cause All administrator passwords have been lost.
Recommended Action Perform the procedure from the “Managing the WLSE System via the CLI”
chapter of the User Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine, Release 2.13 on
Cisco.com at
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/rtrmgmt/cwparent/cw_1105/wlse/2_13/index.ht
m.
OL-8376-01
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
1-5
Page 18

General FAQs and Troubleshooting
Symptom After the WLSE 1130 series starts up, the setup login prompt appears. After you use the setup
program, the WLSE cannot connect to the network.
Possible Cause
–
–
–
–
Recommended Action
1. Verify that the network cable is connected to the Ethernet 0 port and the Ethernet indicator is lit.
–
–
Chapter 1 FAQs and Troubleshooting
The network cable is not connected to the Ethernet 0 port.
The Ethernet 0 interface is disabled or misconfigured.
The system is configured correctly, but the network is down or misconfigured.
DNS is misconfigured. Ping commands will result in a 50-70% failure rate in Pings from the
WLSE (Web interface and CLI).
If the network cable is not connected, connect it.
If the network cable is connected but the Ethernet indicator is not lit, these are the probable
causes:
The network cable is faulty.
The network cable is the wrong type (for example, a cross-over type, rather than the required
straight-through type).
The port on the default gateway to which the system connects is down.
–
If the network cable is connected and the Ethernet indicator is on but the system cannot connect
to the network, continue to the next step.
2. Use the ping command to perform the following tests:
–
Try to ping a well-known host on the network. A DNS server is a good target host.
If the ping command gets a response, the system is connected to the network. If the system
cannot connect to a particular host, the problem is either with the network configuration or that
host. Contact your network administrator for assistance.
If the ping command does not get a response, continue.
–
Attempt to connect to another host on the same subnet as the system.
If the ping command can connect to a host on the same subnet, but cannot connect to a host on
a different subnet, the default gateway is probably down.
If the ping command cannot connect to any hosts, continue to the next step.
3. Use the show interfaces command to determine if the Ethernet 0 interface is disabled or
misconfigured.
For more information on the show interfaces command, see the CLI appendix in the User Guide
for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine, Release 2.13.
If the Ethernet 0 interface is disabled, enable it. If it is misconfigured, configure it correctly. For
more information, see the interface command description in the CLI appendix in the User
Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine, Release 2.13.
1-6
If the interface is enabled and correctly configured, continue to the next step.
4. Contact your network administrator to verify that there are no conditions on the network that
prevent the system from connecting to the network.
If conditions prevent the system from connecting to the network, have your network
administrator correct them.
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
OL-8376-01
Page 19

Chapter 1 FAQs and Troubleshooting
5. If no conditions are preventing the system from connecting to the network, contact Cisco’s
Symptom Cannot connect to the WLSE using a Web browser.
Possible Cause
–
–
–
–
Recommended Action
1.
2. If you are attempting to connect via HTTP, verify that:
General FAQs and Troubleshooting
Technical Assistance Center.
The system cannot connect to the network.
HTTP or HTTPS is not enabled
If connecting via HTTP, the IP address was not appended with :1741.
The client system is not configured.
Make sure that the system can connect to the network. Attempt to connect the system using a
Web browser.
If you cannot connect, continue.
The IP address is appended with :1741.
HTTP or HTTPs is enabled.
3. Verify that you are using a supported browser and the browser is configured correctly, and
attempt to connect to the WLSE. For more information about browsers, see the Installation and
Configuration Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine or the “Getting Started”
section in the online help.
4. If you still cannot connect through the browser, continue to step 5.
5. At the system console, or through Telnet, verify that the Web Server and tomcat are running by
entering the following:
# services status
If they are running, go to step 8. If they are not running continue to step 6.
6. Stop the system services by entering the following:
# services stop
7. Restart the system services by entering the following:
# services start
8. Try to connect the system using a Web browser.
If you cannot connect, continue to the next step.
9. Reboot the system by entering the reload command.
OL-8376-01
For more information on the reload command, see the CLI appendix in the User Guide for the
CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine, Release 2.13.
10. If you still cannot connect to the system using a Web browser, contact Cisco’s Technical
Assistance Center for assistance.
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
1-7
Page 20
General FAQs and Troubleshooting
Symptom The system time or date is incorrect.
Possible Cause
–
–
Recommended Action Make sure NTP is configured correctly and that the system clock is set
correctly.
For information about maintaining the system time and date, see the User Guide for the CiscoWorks
Wireless LAN Solution Engine, Release 2.13. You can access a PDF version of this guide by clicking
View PDF in the WLSE’s online help.
Symptom The system cannot boot from the hard drive during a reboot.
Possible Cause
–
–
Chapter 1 FAQs and Troubleshooting
NTP is misconfigured.
The system clock is set incorrectly.
The disk has a physical error.
The disk image is corrupted.
Recommended Action If the WLSE cannot boot from the hard drive, the hard drive needs to be
reimaged. Use the Recovery CD to reimage your WLSE. For more information, see the User Guide
for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine, Release 2.13. You can access a PDF version of
this guide by clicking View PDF in the WLSE’s online help.
Symptom Cannot connect to system with Telnet or Telnet interaction is slow.
Possible Cause
–
Telnet is disabled or configured incorrectly.
–
The WLSE cannot recognize host names.
If you are not using name recognition, slow or non-existent telnet interaction is an expected
problem.
Note Telnet is disabled by default. SSH is enabled by default.
Recommended Action
If the problem is not the network, perform the following steps. Connect to the console port if you
cannot Telnet to the WLSE.
1. Check the Telnet settings to be sure Telnet is enabled and configured correctly. For more
information, see the following
1-8
To check the Telnet settings, or to enable or disable Telnet on specific domains or IP addresses,
use the telnetenable CLI command. For more information on this command, see the User Guide
for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine, Release 2.13. You can access a PDF version
of this guide by clicking View PDF in the WLSE’s online help
To enable or disable Telnet on individual ports, use the firewall CLI command. For more
information on this command, see the User Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution
Engine, Release 2.13. You can access a PDF version of this guide by clicking View PDF in the
WLSE’s online help
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
OL-8376-01
Page 21

Chapter 1 FAQs and Troubleshooting
2. If you have specified hosts using the telnetenable CLI command, make sure the host from
3. If you are using a DNS server, perform the following step:
4. Verify that the system can get DNS services from the network by entering the following
5. If the system cannot resolve DNS names to IP addresses, the DNS server it is using is not
General FAQs and Troubleshooting
which you are attempting to Telnet is on the list.
Configure the system to use a functioning DNS server by entering:
# ip name-server
where ip-address is the IP address of the DNS server.
If you are using the import CLI command, proceed to the next step.
command:
# nslookup
where dns-name is the DNS name of a host on the network that is registered in DNS and
hostname and ip-address is the same IP address specified in 2. The command returns the IP
address of the host.
working properly.
Resolve the network DNS problem, then continue.
ip-address
dns-name {hostname | ip-address
}
6. If you are using the import CLI command to resolve host names, verify that the WLSE can
resolve host names by entering the following command:
ping
hostname
where hostname is a host name that has been mapped to an IP address, or imported in a host file,
using the import command.
7. If the system can resolve DNS names to IP addresses but you still cannot connect to the system
using Telnet, or Telnet interaction with the system is extremely slow, contact Cisco’s Technical
Assistance Center.
Symptom Cannot boot from the recovery CD.
Possible Cause The CD may look like it is firmly on the spindle, but it may not be.
Recommended Action Press the CD firmly onto the spindle. Also, see the following symptom,
Symptom Cannot successfully connect to the WLSE by using a console.
Symptom Cannot successfully connect to the WLSE by using a console.
Possible Cause A monitor and/or keyboard are attached to the video port and USB port.
Recommended Action Attach the console terminal or PC to the console/serial port. Use the Hyper
Terminal emulator on the PC.
OL-8376-01
Symptom Pop-up windows are blocked and screens are not refreshed.
Possible Cause A pop-up blocker is running in the browser.
Recommended Action Disable the pop-up blocker while using the WLSE web interface or add the
WLSE to the pop-up allowed list.
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
1-9
Page 22

Deployment Wizard Troubleshooting
Symptom After performing certain operations on the WLSE, such as clicking Apply in the Display Faults
page, then clicking the client browser Refresh button, a pop-up message is generated indicating that the
page cannot be refreshed.
Possible Cause The browser Refresh button was used.
Recommended Action Avoid using the Refresh button on the browser. Instead, use the navigational
tools provided by the WLSE user interface. If either of the following messages display, click
Cancel: on Internet Explorer, “The page cannot be refreshed without resending the information.
Click Retry to send the information again, or click Cancel to return to the page that you are trying
to view;” and on Firefox, “The page you are trying to view contains POSTDATA. If you resend the
data, any action the form carried out (such as search or online purchase) will be repeated. To resend
the data, click OK. Otherwise, click Cancel.
Symptom The Web interface of the WLSE is not available, but you can log in to the CLI.
Possible Cause The SNMP community file may be corrupted.
Recommended Action See the reset device-snmp command in the “Using CLI Commands” chapter
in the User Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine, Release 2.13 on Cisco.com.
This command is intended as a last resort and should be used with caution. Please read the command
description in the User Guide before using this command.
Chapter 1 FAQs and Troubleshooting
Deployment Wizard Troubleshooting
Symptom An error message displays when I try to access the Wizard.
Possible Cause You may not have the appropriate roles and privileges assigned to your login.
Recommended Action Select Admin > User Admin > Manage Roles, and make sure that both the
Wizard > WLSE Wizard and Configure > Auto Update options are checked.
Symptom An error message displays when I try to create an auto-managed configuration in the Deploy
Config screen.
Possible Cause The subnet that you selected is already used in another auto-managed configuration.
Someone may have deleted the configuration template by using the options under the Config tab,
but did not delete the related auto-managed configuration.
Recommended Action Delete the auto-managed configuration from the main Config tab (Configure
> Auto Updated > Auto-Managed Configuration).
1-10
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
OL-8376-01
Page 23

Chapter 1 FAQs and Troubleshooting
Symptom Access points do not get the expected configuration applied from a Wizard template.
Possible Cause An auto-managed configuration template exists that is assigned to meet other
matching criteria.
Recommended Action Check the matching criteria by selecting Configure > Auto Update >
Auto-Managed Configuration > Assign Templates.
Faults FAQs and Troubleshooting
• Faults FAQs, page 1-11
• Faults Troubleshooting, page 1-13
Faults FAQs
• Q.Does acknowledging a fault clear it?
• Q.How can I remove cleared faults? They are taking up a lot of space in my database.
Faults FAQs and Troubleshooting
• Q.Why didn’t the fault color on the device tree change (it remains red) after I Acknowledged a P1
fault on an AP?
• Q.What traps are sent from the WLSE?
• Q.What traps are received by the WLSE?
• Q.Does a MIB or trap definition file exist for the WLSE?
• Q.What information is emailed in a fault notification?
• Q.Why I am not receiving any email fault notifications for low priority faults?
• Q.After I change the refresh rate in the Display Faults screen, why does it revert back to the default
of 300 seconds when I log out, then log back in again?
• Q.Why is a fault that is set to one priority level reported as a different priority level?
• Q.If I have a large number of access points, 1,000 or more, will increasing the polling cycles for
policies that report traps to the WLSE enable faster processing of the faults?
• Q.What happens to faults when radio management features are disabled using the radiomanager
disable CLI command?
• Q.The Fault Summary table is displaying the SSID in hexagonal format (for example,
"\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00"). What causes this?
Q.
Does acknowledging a fault clear it?
A.
No, it only removes it from the Active list. For a description of fault states, see the information on
understanding fault states in the online help.
OL-8376-01
Q.
How can I remove cleared faults? They are taking up a lot of space in my database.
A.
Clearing a fault does not purge the fault itself. To purge the old faults:
a. Select Devices > Discover > Inventory > Polling.
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
1-11
Page 24

Faults FAQs and Troubleshooting
b. Change the Fault History Truncation Interval parameter to reduce the number of days the
Q.
Why didn’t the fault color on the device tree change (it remains red) after I Acknowledged a P1 fault
on an AP?
A.
When you Acknowledge existing fault(s) for a device, the corresponding fault color (red for P1 and
P2 severity faults; orange for P3, P4, and P5 severity faults) for that device in the Reports section of
the WLSE does not change.
Q.
What traps are sent from the WLSE?
A.
Traps are sent based on fault policy and threshold settings on the WLSE. The WLSE only sends out
v2c traps, so make sure your trap listener is configured to accept v2c traps.
Solaris 2.8- based NetView 7.1 receives and displays the SNMP v2c fault notification traps from
WLSE, but Windows-based NetView 7.1 supports only v1 traps and cannot receive and display any
v2c traps from the WLSE.
Q.
What traps are received by the WLSE?
A.
The WLSE is able to receive SNMP traps about two policies from access points rather than having
to poll the access point for the information: RF Port Status and RF Port Admin Status. If the WLSE
is enabled to receive the traps, the poll interval for these policies can be increased, which reduces
the load on the WLSE, and allows faster processing of the faults when they do occur. To enable traps
sent to the WLSE, select Configure > Templates > IOS > Services > SNMP.
Chapter 1 FAQs and Troubleshooting
cleared faults are saved.
Q.
What information is emailed in a fault notification?
A.
For a description see the online help.
Q.
Does a MIB or trap definition file exist for the WLSE?
A.
Yes, from the Cisco.com download site, download MIB
CISCO-DEVICE-EXCEPTION-REPORTING-MIB.my and load it into the trap receiver.
Q.
Why I am not receiving any email fault notifications for low priority faults?
A.
No email notification is sent for lower priority faults if higher priority faults already exists for that
fault.
Q.
After I change the refresh rate in the Display Faults screen, why does it revert back to the default of
300 seconds when I log out, then log back in again?
A.
Changes to the refresh timer are applied only to a particular session. This is done by design.
Q.
Why is a fault that is set to one priority level reported as a different priority level?
A.
When more than one fault is reported against a device, the fault priorities are aggregated, and the
maximum priority of all the active faults for that device is displayed. For example, if the device has
a P1, a P2, and a P3 fault against it, only the P1 is displayed in the Severity column. However, when
you click on the Description for that fault, all three priorities are displayed with an explanation for
each.
Q.
If I have a large number of access points, 1,000 or more, will increasing the polling cycles for
policies that report traps to the WLSE enable faster processing of the faults?
1-12
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
OL-8376-01
Page 25

Chapter 1 FAQs and Troubleshooting
A.
Yes. For more detailed information on which policies can report traps (RF Port Status and RF Port
Admin Status) to the WLSE and how to set it up, see the online help or the User Guide for the
CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine, 2.13.
Q.
What happens to faults when radio management features are disabled using the radiomanager
disable
A.
The following happens:
–
–
Q.
The Fault Summary table is displaying the SSID in hexagonal format (for example,
"\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00"). What causes this?
Faults FAQs and Troubleshooting
CLI command?
No new radio management related faults are generated.
Any radio management related faults that existed before the command was executed must be
cleared manually. After the faults are manually cleared, they are not regenerated even if the fault
condition still exists.
Non radio management faults are generated, then are cleared permanently when the fault
condition is rectified.
Any non radio management faults that existed before the command was executed can be cleared
manually. However, if the fault conditions still exist, the faults are regenerated.
A.
If the SSID contains unprintable characters, the WLSE displays it in hex notation. In this example,
the SSID is set to 9 hex zeros.
The WLSE displays unprintable characters as \xNN, where NN is the hex value of each character,
followed by the length of the SSID in bytes. For example, “\x00” [1] means that the SSID contains
the hex value \x00 and is 1 byte long. In addition, any double quote marks or backslashes that are
part of the SSID octets are displayed using a preceding backslash (for example, \" or \\).
Faults Troubleshooting
This section provides the following troubleshooting information:
• Symptom After adding an AAA server to a WLSE, the fault ‘AAA server is Not available’ is
generated for that AAA server.
• Symptom A polling interval for a fault is increased from one minute to a higher value, yet the fault
reappears after one minute, not in new time set for the polling.
• Symptom The Display Fault view is blank.
• Symptom Email fails to arrive at its destination.
• Symptom No VLAN fault information is displayed for IOS access points.
• Symptom No email notifications are being received for low priority faults.
• Symptom SNMP Unreachable faults are displayed more frequently than the set polling interval.
OL-8376-01
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
1-13
Page 26

Faults FAQs and Troubleshooting
Symptom After adding an AAA server to a WLSE, the fault ‘AAA server is Not available’ is generated
for that AAA server.
Possible Cause There are several reasons for this error messages: the wrong secret (a secret that does
not match what is configured on the AAA server) was entered; the WLSE IP address is not
configured as a NAS on the server, or the server is unreachable.
Recommended Action Enter the correct secret; the one that is configured on the AAA server or
configure the WLSE IP address as NAS on the server.
Symptom A polling interval for a fault is increased from one minute to a higher value, yet the fault
reappears after one minute, not in new time set for the polling.
Possible Cause The new polling time did not register.
Recommended Action Disable fault polling on the relevant policy or threshold, then manually clear
the fault. Change the fault polling interval on the policy or threshold to the new setting, then enable
fault polling on the relevant policy or threshold.
Chapter 1 FAQs and Troubleshooting
Symptom The Display Fault view is blank.
Possible Cause There are no faults to report based on the filtering criteria you entered.
Recommended Action Not applicable.
Symptom Email fails to arrive at its destination.
Possible Cause The SMTP server is not configured properly.
Recommended Action Configure the SMTP server by selecting Admin > Appliance > Configure
Mailroute.
Symptom No VLAN fault information is displayed for IOS access points.
Possible Cause WEP keys have not been configured in each VLAN. When the WEP keys are
configured in the IOS access points, VLAN information is accessible by SNMP.
Recommended Action Configure the WEP keys for the corresponding VLAN.
Symptom No email notifications are being received for low priority faults.
Possible Cause No email notification is sent for lower priority faults if higher priority faults already
exists for that fault
1-14
Recommended Action None.
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
OL-8376-01
Page 27

Chapter 1 FAQs and Troubleshooting
Symptom SNMP Unreachable faults are displayed more frequently than the set polling interval.
Possible Cause When the WLSE polls for any faults, it also checks if the device is SNMP reachable.
If the device is unreachable, it will generate an SNMP Unreachable fault no matter what the SNMP
Reachable poll interval is.
Recommended Action None.
Devices FAQs and Troubleshooting
• Devices FAQs, page 1-15
• Devices Troubleshooting, page 1-17
Devices FAQs
• Q.Can the WLSE auto rename new APs to a unique name - for example incrementally in the form
of ap01, ap02 and so on?
• Q.Why is hostname (device name), sysContact, and sysLocation information not updated in the
WLSE after I change these parameters on the access points?
Devices FAQs and Troubleshooting
• Q.What is an invalid CDP seed?
• Q.Can I discover devices if CDP is disabled?
• Q.What are the extra inventories listed in the Run Now folder?
• Q.What are the results of adding or removing an interface from an access point?
• Q.Can the WLSE discover access points that are connected to non-Cisco switches?
• Q.Can I register an access point as an AAA server to be monitored by the WLSE?
• Q.How does the WLSE handle duplicate IP addresses on APs?
• Q.Will the WLSE discover a router or switch that has no access points connected to it?
Q.
Can the WLSE auto rename new APs to a unique name - for example incrementally in the form of
ap01, ap02 and so on?
A.
Auto assigning incremental names to APs is not possible, but a workaround could be to select
Devices > Discover > Discover > Advanced Options, and use the Name Format field. Click Learn
About Name Format to understand the various options.
Q.
Why is hostname (device name), sysContact, and sysLocation information not updated in the WLSE
after I change these parameters on the access points?
A.
The hostname (device name), sysContact, and sysLocation parameters are updated during discovery,
not during inventory. You should rediscover the devices (without deleting them), after making the
changes on the access points.
OL-8376-01
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
1-15
Page 28

Devices FAQs and Troubleshooting
Q.
What is an invalid CDP seed?
A.
An invalid seed is a device that does not run Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP), such as a PC or
workstation). Such a device does not function as a seed because it does not allow the WLSE to
traverse the network and find other devices. In the discovery run log, invalid seeds are shown as
SNMP unreachable.
Q.
Can I discover devices if CDP is disabled?
A.
If CDP is disabled on network devices, you can still discover access points by entering the IP
addresses of all of them on the WLSE as seed values. However, the WLSE cannot discover switches
directly attached to such access points, and switch-related reports will be empty.
Q.
What are the extra inventories listed in the Run Now folder?
A.
The radio manager automatically runs periodic inventories for relevant functionality.
Q.
What are the results of adding or removing an interface from an access point?
A.
If you physically remove an interface (for example, removing 11b from a dual-interface AP 1200),
the WLSE will automatically detect the change during the next inventory cycle. If you physically
add an interface, you must delete the device and rediscover it. Otherwise, the inventory data might
be invalid.
Chapter 1 FAQs and Troubleshooting
Q.
Can the WLSE discover access points that are connected to non-Cisco switches?
A.
You cannot use CDP to discover the APs, but you can import them from a file or enter them all as
seed devices in the WLSE. Alternatively, if you have configured Wireless Domain Services, the APs
may automatically be discovered if they are within the range of the participating APs.
Q.
Can I register an access point as an AAA server to be monitored by the WLSE?
A.
Yes, you can register an AP 1100 or AP 1210 as an AAA server. However, if you register an AP as
an AAA server, you can no longer use the WLSE to manage that AP as a wireless device.
Q.
How does the WLSE handle duplicate IP addresses on APs?
A.
The WLSE must be able to handle situations in which an AP is assigned an address that is already
assigned to another device that has been discovered by the WLSE. The WLSE handles these
situations by sending appropriate internal events, placing the device that previously had the address
in the Duplicate IP folder and updating the database. Detection of duplicate addresses occurs during
periodic checking for rebooted APs and during discovery.
For information on how you should handle devices in the Duplicate IP folder, see the online help for
the Devices tab or the section called “Handling Duplicate IP Addresses on Access Points” in the
User Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine, Release 2.13 on Cisco.com.
Q.
Will the WLSE discover a router or switch that has no access points connected to it?
A.
The WLSE does not discover a router or switch that has no supported access point or bridge attached
to it.
1-16
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
OL-8376-01
Page 29

Chapter 1 FAQs and Troubleshooting
Devices Troubleshooting
This section contains the following troubleshooting information:
Discovery/Device Management Troubleshooting
• Symptom Devices were discovered but are not displayed in the GUI; for example, in Reports.
• Symptom There is a time discrepancy in the scheduled discovery jobs.
• Symptom The SNMP Query Authorization Exception is recorded in the discovery log.
• Symptom An error message appears in the discovery run log.
• Symptom An IOS access point configured with an iee802dot11 view is not discovered.
• Symptom When importing or exporting devices from an RME server, the message “Failed to
connect to server. WLSE will try to connect as RME 4.0.” appears.
• Symptom After changing the device name format, device names are not updated in the device tree.
• Symptom After creating a customized device name format, truncation of device names in displays
such as device trees makes it difficult or impossible to distinguish one device from another.
• Symptom Instead of a proper device name or IP address, the WLSE is displaying device names as
%dns%, %hostname%, or %description%.
• Symptom After a device is moved from unmanaged to managed, the name format is not applied.
Devices FAQs and Troubleshooting
• Symptom The IP address of a device was changed, but the Device Details display does not reflect
this change.
• Symptom When trying to discover a WLSM, the error message “device is not supported” is listed
in the discovery log.
• Symptom AP 1230 and AP 1231 are not shown in WLSE displays.
Inventory Troubleshooting
• Symptom Frequent client inventories are causing too much network traffic or degrading WLSE
performance.
• Symptom Inventory is taking longer than expected and a message about no logs available appears
in the inventory log.
AAA Server Troubleshooting
• Symptom The name of an AAA server is displayed as %hostname% instead of the name entered
by the user when the AAA server was added.
Symptom Devices were discovered but are not displayed in the GUI; for example, in Reports.
Possible Cause The devices have not been moved to the Managed state.
Recommended Action Select Devices > Discover > Managed Devices. Move the devices from New
or Unmanaged to Managed.
Intermediate switches with no access points directly connected to them are shown to be discovered
in the Devices > Discover > DISCOVERY > Logs but will not show up in Devices > Discover >
Managed Devices > Manage/Unmanage.
OL-8376-01
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
1-17
Page 30
Devices FAQs and Troubleshooting
Symptom There is a time discrepancy in the scheduled discovery jobs.
Possible Cause The local or system time is not set correctly on the WLSE.
Recommended Action
a.
b. Set the local browser time. Select Admin > Appliance > Time/NTP/Name/Webtimeout.
Symptom The SNMP Query Authorization Exception is recorded in the discovery log.
Possible Cause The community string on the access point does not have admin and firmware rights.
Recommended Action In the configuration template or on the access point, assign the missing rights
to the community string. For more information, see the information on setting up devices in the
online help or the User Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine, 2.13.
Chapter 1 FAQs and Troubleshooting
Reset the WLSE system time (UTC) using CLI commands as follows:
Enter services stop to stop services.
Enter the clock command to reset the time.
Enter services start to restart the services.
Symptom An error message appears in the discovery run log.
Table 1-1 Discovery Run Log Messages
Message Possible Cause Recommended Action
No seeds defined.
Although discovery is
initially enabled and runs
every 24 hours, it will not
See the online help or the User Guide for the
CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine,
Release 2.13.
run unless you add seed
devices.
Inventory collection
was not run for
updated devices, run
on-demand inventory
or wait for the next
scheduled inventory
IP conflict for
ip_address
(
hostname
Identifier or
ethernet MAC is
identifier or MAC
address
already exists under
this IP address. If
the original device
was replaced, please
delete it first and
run discovery again.
).
. A device
An automatic inventory does
not run for rediscovered
devices.
A newly discovered device
has the same IP address as a
previously discovered
device. The new device will
not be discovered until the
conflict is resolved. The
identifier shown is for the
previously discovered
device. For access points,
the identifier shown is the
Ethernet MAC address.
Run an on-demand inventory or wait for the
next scheduled inventory. See the online help
or the User Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless
LAN Solution Engine, Release 2.13.
If you want both devices to be managed,
assign a different IP address to the newly
discovered device. If you substituted a new
device for a previous device and want to retain
the IP address, delete the old device. In either
case, run discovery again or wait for the next
scheduled discovery. See the online help or
the User Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless
LAN Solution Engine, Release 2.13.
1-18
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
OL-8376-01
Page 31

Chapter 1 FAQs and Troubleshooting
Table 1-1 Discovery Run Log Messages (continued)
Message Possible Cause Recommended Action
Unable to auto-manage
device: x.x.x.x due
to MAC filter values
or time period for
auto-management has
expired.
Symptom An IOS access point configured with an iee802dot11 view is not discovered.
A new device is being
discovered but could not be
auto-managed because the
MAC filter values exclude
the device or the time period
selected for
auto-management has
expired.
Possible Cause The community string should be configured with an ISO view.
Recommended Action
1. In the Web interface of the AP, select Services > SNMP.
See the online help or the User Guide for the
CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine,
Release 2.13.
Devices FAQs and Troubleshooting
2. Select the Read/Write community string associated with an iee802dot11 view. In the Object
Identifier field, enter “iso.” Select Read-Only or Read-Write and click Apply.
3. On the WLSE, select Devices > Discover > DISCOVER > Advanced Options. Make sure
auto-manage is enabled.
4. Run discovery on the device, using the community string that has the ISO view.
Result: The WLSE discovers the device and places it in the Managed folder.
Symptom When importing or exporting devices from an RME server, the message “Failed to connect to
server. WLSE will try to connect as RME 4.0.” appears.
Possible Cause WLSE tried to connect to the server by using the current mechanism. That method
failed, so the WLSE connected by using the RME 4.0 mechanism.
Recommended Action The import or export has probably succeeded, but you should check the final
job status to make sure (Devices > Discover > DISCOVER > Logs).
Symptom After changing the device name format, device names are not updated in the device tree.
Possible Cause If there are many devices in the device tree, it may take some time to perform the
update and the page may not automatically be refreshed.
Recommended Action Navigate to some other screen and then return to the device tree. The device
tree will be updated correctly to the new name format.
OL-8376-01
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
1-19
Page 32

Devices FAQs and Troubleshooting
Symptom After creating a customized device name format, truncation of device names in displays such
as device trees makes it difficult or impossible to distinguish one device from another.
Possible Cause In device trees, only 30 characters can be displayed.
Recommended Action Reconstruct the device identifier string so that the unique portion of the name
comes first; for example, place the IP address first.
Symptom Instead of a proper device name or IP address, the WLSE is displaying device names as
%dns%, %hostname%, or %description%.
Possible Cause The default device identifier used by the WLSE in its displays is the device’s
hostname. If no hostname is assigned to the device, %hostname% is used instead. For the %dns%
or %description% name, a user has changed the default device identifier but there is no DNS name
or the user has not assigned a description. The default device identifier string is set under Devices >
Discover > DISCOVER > Advanced Options.
Recommended Action If you use the IP address as the default identifier, the device name display will
always be correct. For more information, see the online help or the User Guide for the CiscoWorks
Wireless LAN Solution Engine, Release 2.13 on Cisco.com.
Chapter 1 FAQs and Troubleshooting
Symptom After a device is moved from unmanaged to managed, the name format is not applied.
Possible Cause When devices are moved from unmanaged to managed, the current name format
choice is not applied until the next inventory runs.
Recommended Action Run an inventory on the device. Select Devices > Discover > Inventory > Run
Inventory.
Symptom The IP address of a device was changed, but the Device Details display does not reflect this
change.
Possible Cause The device tree under MANAGED DEVICES shows the state of the system at the
time you select the Managed Devices option. Therefore, if device details change or the device
changes to another state after you display the page, these changes not automatically displayed.
Recommended Action If you refresh the page from the browser or navigate to another page and then
return to Managed Devices, the page will be updated to show changes that have occurred.
Symptom When trying to discover a WLSM, the error message “device is not supported” is listed in the
discovery log.
Possible Cause WLSM does not support CDP and cannot be discovered by using the regular
discovery job mechanism
1-20
Recommended Action None. WLSM will be discovered through WLCCP, as long as WDS is properly
configured. For more information on configuring WDS for the WLSM, see the document
Configuring Devices for Management by the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine on
Cisco.com.
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
OL-8376-01
Page 33

Chapter 1 FAQs and Troubleshooting
Symptom AP 1230 and AP 1231 are not shown in WLSE displays.
Possible Cause These APs have the same sysObjectID as the AP 1210.
Recommended Action Check the AP 1210 system group and other WLSE listings for AP 1210. AP
1230 and AP 1231 will be shown there.
Symptom Frequent client inventories are causing too much network traffic or degrading WLSE
performance.
Possible Cause Running frequent client inventories when managing large numbers of access points
(1,000 or more) generates a great deal of traffic and may degrade WLSE performance.
Recommended Action Increasing the Wireless Client Poll Interval in Devices > Discover > Inventory
> Polling will reduce the polling frequency. If you need more frequent client polling for a subset of
your access points, use the Scheduled Inventory feature instead (Devices > Discover > Inventory >
Run Inventory).
Configuration FAQs and Troubleshooting
Symptom Inventory is taking longer than expected and a message about no logs available appears in the
inventory log.
No logs available. Waiting for resources to start job.
Possible Cause If there are also SNMP timeouts on the network, inventory jobs will take much
longer. Other jobs may be using all of the available resources. Also, the next scheduled inventory
will not run until the current inventory finishes.
Recommended Action None.
Symptom The name of an AAA server is displayed as %hostname% instead of the name entered by the
user when the AAA server was added.
Possible Cause This sometimes occurs after updating the system software to 2.9.1 or 2.11, or 2.13.
Recommended Action Select Devices > Discover > AAA Server and remove the AAA server. Then,
add the server again.
Configuration FAQs and Troubleshooting
• Configuration FAQs, page 1-21
• Configuration Troubleshooting, page 1-25
Configuration FAQs
• Q.Can I override the SSHv2 option for a regular config job?
• Q.Can I use multiple WLSE sessions simultaneously to configure WLSE templates?
OL-8376-01
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
1-21
Page 34

Configuration FAQs and Troubleshooting
• Q.Can I give a configuration job a name that is used for a firmware or radio management job?
• Q.Why do I get the following error message when I upload a configuration template with SCP using
the Overwrite option: Invalid SSH version running on the device?
• Q.What happens when I apply a configuration to a device with an existing configuration?
• Q.If a template is valid for an access point with an 802.11g radio, can I also apply that template to
an access point with an 802.11b radio?
• Q.If a template is valid for a 1310 wireless bridge in bridge mode, can I also apply that template to
a 1310 wireless bridge in access point mode?
• Q.If I create a configuration template that includes WEP key settings how can I verify that they were
set on the access point.
• Q.How long is the configuration job history kept in the WLSE?
• Q.What mechanism do configuration jobs use to initiate a configuration upload?
• Q.What kinds of job logs are available?
• Q.What is startup configuration template?
• Q.If I make changes to the startup template, will those modifications be automatically uploaded to
the access points that already had a startup template applied?
Chapter 1 FAQs and Troubleshooting
• Q.What is auto configuration?
• Q.Can I use Device Specific settings with Startup templates?
• Q.Why is my configuration job for a crypto key taking so long to complete?
Q.
Can I override the SSHv2 option for a regular config job?
A.
By default, if you select SSH as the transport protocol for your config job, the WLSE will use either
SSHv1 or SSHv2 depending on the device version. For the devices with version 12.3(7) JA or earlier,
SSHv1 is used; for version12.3(8)JA or later, SSHv2 is used.
If you want to override the SSHv2 option for devices with version 12.3(8)JA or later, and use SSHv1
instead, you must do the following:
a. Enter the following in your browser window: http://<wlseip>:1741/debug/jobprops.jsp.
b. Select the SSHv1 for the SSH version.
c. Click Save.
Q.
Can I use multiple WLSE sessions simultaneously to configure WLSE templates?
A.
No. You should not open two sessions of the WLSE at the same time to configure the templates.
Q.
Can I give a configuration job a name that is used for a firmware or radio management job?
A.
No. Job names cannot be duplicated.
1-22
Q.
Why do I get the following error message when I upload a configuration template with SCP using
the Overwrite option: Invalid SSH version running on the device?
A.
This message displays when the access point is running a software version that does not support
SCP. SCP is supported starting with version 12.3(4)JA.
Q.
What happens when I apply a configuration to a device with an existing configuration?
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
OL-8376-01
Page 35

Chapter 1 FAQs and Troubleshooting
A.
The two configurations are merged unless you have specified that you want to overwrite the existing
configuration when you ran the job. If you select Apply Template to Running Configuration when
you create the Configuration job, the selected configuration template will replace the startup-config
on the selected device(s).
Q.
If a template is valid for an access point with an 802.11g radio, can I also apply that template to an
access point with an 802.11b radio?
A.
No. You can only apply a template valid for an access point with an 802.11g radio to an access point
with an 802.11g radio.
Q.
If a template is valid for a 1310 wireless bridge in bridge mode, can I also apply that template to a
1310 wireless bridge in access point mode?
A.
No. You can only apply a template valid for a 1310 wireless bride in bridge mode, to a 1310 wireless
bridge in bridge mode.
Q.
If I create a configuration template that includes WEP key settings how can I verify that they were
set on the access point.
(The access point does not show WEP key settings on its web interface)?
A.
For security reasons, the access point does not show or send WEP key information. One of the ways
to verify the update is to look at the WEP Key length. The only way to verify the contents of the
WEP key is to try associating a client that uses that WEP key.
Configuration FAQs and Troubleshooting
Q.
How long is the configuration job history kept in the WLSE?
A.
The default time is 30 days. You can change this by navigating to Devices > Discover > Inventory >
Polling > Job History Truncation Interval. Also, by default, for the recurring jobs, the last 30 runs
are maintained in the database.
Q.
What mechanism do configuration jobs use to initiate a configuration upload?
A.
WLSE configuration jobs use Telnet/SSH or TFTP/SCP:
–
Telnet/SSH is used when merging the selected configuration to the running configuration, or
when copying the running configuration to the startup configuration.
–
SCP/TFTP is sued when the selected configuration template will replace the startup-config on
the selected device(s), or when the device(s) will be rebooted after the copy to startup-config
succeeds.
Q.
What kinds of job logs are available?
A.
There are two kinds of job logs: Job run log and the jobvm log.
• The job run log is where events are logged for a particular job’s run. This log can be used to check
what went wrong with the job and make any required corrections. The job run log can be viewed by
selecting a particular job from the job list, then clicking Job Run Detail. From the window that pops
up, select a particular run for the job, then click Job Run Log.
• The jobvm.log is a global log for all types of jobs. It is used mainly for development troubleshooting.
The jobvm.log can be viewed by selecting Admin > Appliance > View Log File, then clicking
jobvm.log.
OL-8376-01
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
1-23
Page 36

Configuration FAQs and Troubleshooting
Q.
What is startup configuration template?
Startup configuration template is used right after a device (access point) reboots. It requires DHCP
server to be properly set up to allow the access point to pick its startup configuration from WLSE.
For this to work, you must set up the following:
a. Enter the <IP address of the WLSE> in the Boot Server Host Name field (option number 066)
on the DHCP server.
b. Enter <startup file name> in the BootfileName field (option number 067) on the DHCP
server.
For additional information, or for information about configuring a router as a DHCP server, see the
online help.
Q.
What is auto configuration?
A.
Auto configuration is used after the device has been discovered and inventory has been collected for
it. This template can be applied based on criteria you define while saving your auto-configuration
template.
Q.
If I make changes to the startup template, will those modifications be automatically uploaded to the
access points that already had a startup template applied?
Chapter 1 FAQs and Troubleshooting
A.
No. If you make modifications to the startup template, you will have to Reload the access point to
apply the new template.
Q.
Can I use Device Specific settings with Startup templates?
A.
Device Specific settings are applicable only with Config Regular and Config Auto jobs. Because the
commands for Device Specific settings are generated at job runtime based on the device attributes,
a Startup template configuration will not contain Device Specific configurations.
Q.
Why is my configuration job for a crypto key taking so long to complete?
A.
When a crypto key that has more than 512 bytes is configured using custom commands or a template,
the job might take longer to complete than a typical configuration job. The command output is as
follows:
ssl-proxy(config)# crypto key generate rsa general-keys label ssh-key
The name for the keys will be: ssh-key
Choose the size of the key modulus in the range of 360 to 2048 for your
General Purpose Keys. Choosing a key modulus greater than 512 may take a few minutes.
1-24
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
OL-8376-01
Page 37

Chapter 1 FAQs and Troubleshooting
Configuration Troubleshooting
This section provides the following troubleshooting information:
• Symptom When I perform a configuration update to the startup-configuration of a device, the
device becomes unreachable.
• Symptom Configuration jobs fail when the hostname command is used in the Custom Values page.
• Symptom The WLSE will not save a newly-created configuration template.
• Symptom A configuration job fails using a template imported from an IOS access point.
• Symptom The banner command in an IOS custom template fails or is incomplete.
• Symptom An IOS template job failed.
• Symptom Configuration jobs fail because the Telnet/SSH credentials are not valid, even though
credentials have been entered on the WLSE.
• Symptom Access points do not get the expected configuration applied from an auto-managed
configuration template.
• Symptom An SCP job fails with username having 15 privilege.
Configuration FAQs and Troubleshooting
Symptom When I perform a configuration update to the startup-configuration of a device, the device
becomes unreachable.
Possible Cause The template is missing the Integrated Routing and Bridging configurations.
Recommended Action Edit the template and add the following configuration to Custom Value page:
bridge irb
interface FastEthernet0
bridge-group 1
bridge 1 route ip
Symptom Configuration jobs fail when the hostname command is used in the Custom Values page.
Possible Cause If the template is configured to disable Telnet or SSH using the Services >
Telnet/SSH page, and if the hostname command precedes the enabling of Telnet or SSH in the
Custom Values page, the configuration job will fail after applying the hostname command.
Recommended Action Enter the hostname command as the last command in the Custom Values page.
Symptom The WLSE will not save a newly-created configuration template.
Possible Cause The popup blocker on the Web interface has not been disabled.
OL-8376-01
Recommended Action Disable popup-blocking software or add the WLSE to the “allow” list.
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
1-25
Page 38

Configuration FAQs and Troubleshooting
Symptom A configuration job fails using a template imported from an IOS access point.
Possible Cause It has commands such as power local 100 that cause it to fail.
Recommended Action Check the job log to see which commands failed; remove the commands from
the template using the Custom Values screen; then save the template and rerun the configuration job.
Symptom The banner command in an IOS custom template fails or is incomplete.
Possible Cause The banner command fails because it contains 240 or more characters.
Possible Cause A delimiter in the banner string, can cause a partial banner to be applied to the device.
For example,
banner motd c This is to check banner c, the following is displayed when previewed: “banner
motd c This is to c.
(check) that begins with the same character used as the delimiter.
Recommended Action Use less than 240 characters in the banner string, and do not use characters for
delimiters if the characters are also used in the text of the banner.
Chapter 1 FAQs and Troubleshooting
if the following command is typed in the custom template using the letter “c” as the delimiter:
” The banner displays incorrectly because there is a word in the banner
Symptom An IOS template job failed.
Possible Cause The template has the hostname configured instead of the IP address, and the DNS
name resolution is not configured correctly on the access point.
Recommended Action Use the IP address or configure the DNS name correctly on the access point.
Symptom Configuration jobs fail because the Telnet/SSH credentials are not valid, even though
credentials have been entered on the WLSE.
Possible Cause The credentials entered on the WLSE do not exactly match the data entered in
Devices > Discovery > Device Credentials > Telnet/SSH User/Password.
Recommended Action Make sure that the Telnet/SSH credentials data entered on the WLSE show the
correct device login response. Match the device login sequence with the credential fields, as shown
in Symptom Firmware jobs fail because the Telnet/SSH credentials are not valid., page 1-30.
Symptom Access points do not get the expected configuration applied from an auto-managed
configuration template.
Possible Cause An auto-managed configuration template exists that is assigned to meet other
matching criteria.
1-26
Recommended Action Check the matching criteria by selecting Configure > Auto Update >
Auto-Managed Configuration > Assign Templates.
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
OL-8376-01
Page 39

Chapter 1 FAQs and Troubleshooting
Symptom An SCP job fails with username having 15 privilege.
Possible Cause If the device is having the following configuration:
aaa new-model
no aaa authentication login default
no aaa authorization exec default
Logging in with privilege 15 username/password, requires that the enable secret/password be
entered in exec mode.
Recommended Action Configure the authentication to use local or server level authentication.
Firmware FAQs and Troubleshooting
• Firmware FAQs, page 1-27
• Firmware Troubleshooting, page 1-28
Firmware FAQs and Troubleshooting
Firmware FAQs
Q.
A.
Q.
A.
• Q.I have an AP 1232, but under Firmware > Images > Import, there is no AP1232 Device Type to
select. Which one should I choose?
• Q.How can firmware images be imported?
• Q.Are firmware jobs run by using both HTTP and SNMP?
• Q.What kinds of job logs are available?
• Q.How many devices can I have in one firmware job?
• Q.Can I give a firmware job a name that is used for a configuration or radio management job?
I have an AP 1232, but under Firmware > Images > Import, there is no AP1232 Device Type to
select. Which one should I choose?
AP1210.
How can firmware images be imported?
Firmware images can be imported to WLSE from the desktop as well as Cisco.com. While importing
any image from Cisco.com, the WLSE reads the version string and the device type for the image
attributes. For imports from the desktop, you must make sure that the version and the device type
strings are correctly entered in the image attributes.
OL-8376-01
Q.
Are firmware jobs run by using both HTTP and SNMP?
A.
No. Firmware upgrades use SNMP only. Make sure the following setup parameters are in place
before running the upgrade job:
SNMP credentials for the device (with admin and firmware privileges on the AP) must match those
entered on the WLSE SNMP device credentials screen.
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
1-27
Page 40

Firmware FAQs and Troubleshooting
Q.
What kinds of job logs are available?
A.
There are two kinds of job logs: Job run log and the jobvm log.
• The job run log is where events are logged for a particular job’s run. This log can be used to check
what went wrong with the job and make any required corrections. The job run log can be viewed by
selecting a particular job from the job list, then clicking Job Run Detail. From the window that pops
up, select a particular run for the job, then click Job Run Log.
• The jobvm.log is a global log for all types of jobs. It is used mainly for development troubleshooting.
The jobvm.log can be viewed by selecting Admin > Appliance > View Log File, then clicking
jobvm.log.
Q.
How many devices can I have in one firmware job?
A.
There is no limit, although it is recommended that you work with device groups and set up jobs
accordingly (for example, by location or building). The WLSE can run 10 jobs in parallel. While a
job is running, the WLSE allocates resources for updating 20 devices in parallel. At any given time,
20 devices will be upgrading and the remainder will be waiting for resources to become available.
Creating a single job with more than 100 access points is not recommended. If you are updating the
firmware on a large number of access points, you might want to convert a few APs initially to get
familiar with the process. Once you are familiar with the process, you can create a job with 20
devices, then increase the number of devices if no devices are failing. By running a smaller job, you
will also know how much time it takes for the job to complete.
Chapter 1 FAQs and Troubleshooting
Q.
Can I give a firmware job a name that is used for a configuration or radio management job?
A.
No. Job names cannot be duplicated.
Firmware Troubleshooting
This section provides the following troubleshooting information:
• Symptom When uploading an image to an access point from a from a remote TFTP server, the
access point reports an Invalid checksum error or Unknown failure.
• Symptom There is a time discrepancy in a job.
• Symptom Email about job completion fails to arrive at destination.
• Symptom Firmware is not updated on all the devices included in a job.
• Symptom An SNMP job fails.
• Symptom When downloading firmware from Cisco.com, an error message about cryptography
permissions appears.
• Symptom When downloading firmware from Cisco.com, an error message about connectivity
failure appears.
• Symptom Firmware jobs fail because the Telnet/SSH credentials are not valid.
1-28
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
OL-8376-01
Page 41

Chapter 1 FAQs and Troubleshooting
Symptom When uploading an image to an access point from a from a remote TFTP server, the access
point reports an Invalid checksum error or Unknown failure.
Possible Cause The image filename entered in the job does not match the image filename on the
remote TFTP server.
Recommended Action Make sure the filenames on the job and on the server are the same.
Possible Cause The selected image and the selected devices are of different device types. For
example, if an AP1100 image and the BR1300 device type are chosen.
Recommended Action Make sure the selected image and the selected devices are of same type.
Symptom There is a time discrepancy in a job.
Possible Cause The time was not set correctly on the WLSE.
Recommended Action
a.
Firmware FAQs and Troubleshooting
Reset the WLSE time to Universal Coordinated Time (UTC) using CLI commands as follows:
Enter services stop to stop services.
Enter the clock command to reset the time.
Enter services start to restart the services.
b. Set the time in local browser time, select Admin > Appliance > Time/NTP/Name.
For more information on setting the time, see the User Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN
Solution Engine, Release 2.13. You can access a PDF version of this guide by clicking View PDF
in the WLSE’s online help.
Symptom Email about job completion fails to arrive at destination.
Possible Cause The SMTP server is not specified.
Recommended Action Configure the mail route by selecting Admin > Appliance > Configure
Mailroute.
Symptom Firmware is not updated on all the devices included in a job.
Possible Cause There were warnings displayed when the job was saved. Jobs for devices with
warnings do not run; the job runs only for devices that do not have any warnings.
Recommended Action Solve the problems indicated in the warning messages before running the job.
Possible Cause If two firmware jobs were scheduled closely together, the second job contained some
of the same devices as the first job. Those devices could not be updated because the first job was
already running.
OL-8376-01
Recommended Action It is recommended that firmware jobs be run on groups of devices. Each group
should be exclusive; that is, no device should be a member of more than one group.
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
1-29
Page 42

Firmware FAQs and Troubleshooting
For more information on updating firmware, see the User Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN
Solution Engine, 2.13. You can access a PDF version of this guide by clicking View PDF in the
WLSE’s online help.
Symptom An SNMP job fails.
Possible Cause The read community string does not have sufficient permissions.
Recommended Action The access point must have a user with at least SNMP, FIRMWARE, and
ADMIN permissions for read-only access.
Symptom When downloading firmware from Cisco.com, an error message about cryptography
permissions appears.
Possible Cause The first time you attempt to download firmware, the WLSE displays this message:
Error while selecting or displaying image details. Please log into cisco.com and make
sure your username has acknowledged cryptography permissions for downloading IOS
images
Chapter 1 FAQs and Troubleshooting
.
Recommended Action Log into Cisco.com and acknowledge the cryptography permissions. After you
have acknowledged these permissions, you can import IOS images to the WLSE.
Symptom When downloading firmware from Cisco.com, an error message about connectivity failure
appears.
Possible Cause DNS is not configured on the WLSE.
Recommended Action Configure DNS on the WLSE and make sure the WLSE can resolve the
cisco.com domain name. For information about configuring DNS, see the User Guide for the
CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine, Release 2.13 or the Installation and Configuration Guide
for your hardware.
Symptom Firmware jobs fail because the Telnet/SSH credentials are not valid.
Possible Cause The credentials entered on the WLSE do not exactly match the data entered in
Devices > Discovery > Device Credentials > Telnet/SSH User/Password.
Recommended Action Make sure that the Telnet/SSH credentials data entered on the WLSE show the
correct device login response. Match the device login sequence with the credential fields as follows.
1-30
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
OL-8376-01
Page 43

Chapter 1 FAQs and Troubleshooting
Table 1-2 Telnet/SSH Credentials Required
Device Login Sequence Telnet Credential Fields Required
Username:
Password:
prompt>enable
Password:
enable prompt #
Password:
prompt>enable
Password:
enable prompt#
Username:
Password:
enable prompt#
enable prompt#
Username:
prompt>enable
Password:
enable prompt#
Username:
prompt#
Username:
Password:
prompt>enable
Username:
Password:
enable prompt#
Reports FAQs and Troubleshooting
User Name
User Password
Enable Password
User Password
Enable Password
User Name
User Password
(no credentials required)
User Name
Enable Password
User Name
User Name
User Password
Enable User Name
Enable Password
Reports FAQs and Troubleshooting
• Reports FAQs, page 1-31
• Reports Troubleshooting, page 1-32
Reports FAQs
Q.
When does data for the reports get aggregated?
A.
The first weekly/monthly aggregation does not start at the beginning of the week/month. The first
aggregation might happen earlier than the beginning of the week/month. After the first
weekly/monthly aggregation, all subsequent weekly/monthly aggregation occurs every 7 days for
weekly aggregation, or every 30 days for monthly aggregation from the first time the aggregation
occurred.
Q.
Are any of the Current or Trend reports real-time reports?
A.
The reports are not real time. They are based on data that is collected periodically. The frequency
with which the data is collected is user configurable (see Devices > Discover > Inventory > Polling).
The data shown in reports is as current as the time the data was collected from the devices.
Q.
In the Group Performance Report: RF Utilization, how is the value in the As Of column calculated?
OL-8376-01
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
1-31
Page 44

Reports FAQs and Troubleshooting
A.
The As Of column indicates the starting time of the aggregation for the utilization report. Therefore,
the starting time shown might be earlier than the date range selected for the report.
Q.
How long can report data be kept in WLSE?
A.
the trends reports data is kept in the WLSE database for a specific amount of time, which can be
configured (see Devices > Discover > Inventory > Polling).
Q.
The SSID field in the Manage Rogues > Rogue AP List report is being displayed in hexagonal
format (for example, "\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00"). What causes this?
A.
If the SSID contains unprintable characters, the WLSE displays it in hex notation. In this example,
the SSID is set to 9 hex zeros.
The WLSE displays unprintable characters as \xNN, where NN is the hex value of each character,
followed by the length of the SSID in bytes. For example, “\x00” [1] means that the SSID contains
the hex value \x00 and is 1 byte long. In addition, any double quote marks or backslashes that are
part of the SSID octets are displayed using a preceding backslash (for example, \" or \\).
Q.
Why is the device information in the reports under Device Center not displaying properly when I
view them with a Firefox browser?
A.
Firefox does not support line breaks or long text (maximum 50 characters).
Chapter 1 FAQs and Troubleshooting
Reports Troubleshooting
This section provides the following troubleshooting information:
• Symptom The Top N Busiest Clients report and the Client Statistics report display 0 (zero) values.
• Symptom The client association data in the Group Client Association report differs from the data
shown in the Current Client Associations report.
• Symptom The access point data in the Historical Associations report is not accurate.
• Symptom The Summary and/or Detailed report for access points is empty.
• Symptom The group report for a user-defined group contains no data.
• Symptom After running a job, the updated data does not appear in a report.
• Symptom Email fails to arrive at its destination.
• Symptom There is a time discrepancy in the scheduled email jobs.
• Symptom No VLAN information is displayed for IOS access points.
• Symptom There is a discrepancy in the first aggregation intervals after the first time the WLSE
started up or after the WLSE’s software was upgraded.
• Symptom In the Group Client Association Report, the Number of Clients Associated with this
Group displays a 0 (zero).
1-32
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
OL-8376-01
Page 45

Chapter 1 FAQs and Troubleshooting
Symptom The Top N Busiest Clients report and the Client Statistics report display 0 (zero) values.
Possible Cause Wireless client polling frequency is set to 51 minutes by default. The counters could
reset between two polling cycles which would cause zero values when the reports are run.
Recommended Action Increase the polling frequency by selecting Devices > Discover > Inventory >
Polling.
Caution Increasing the polling frequency could have an effect on performance.
Symptom The client association data in the Group Client Association report differs from the data shown
in the Current Client Associations report.
Possible Cause The data for the Group Client Association report is collected using performance
attributes polling and the data shown in the Current Client Association report uses wireless client
polling.
Whichever report has a higher polling frequency will contain the most up to date data. Select
Devices > Discover > Inventory > Polling to view polling frequency.
Reports FAQs and Troubleshooting
Recommended Action None.
Symptom The access point data in the Historical Associations report is not accurate.
Possible Cause The wireless client was associated with an access point managed by the WLSE, but
subsequently associated with an access point that was added to the network, but not yet managed by
the WLSE.
Recommended Action Verify that the associated access points are in the managed devices folder by
selecting Devices > Discover > Managed Devices > Manage/Unmanage.
Symptom The Summary and/or Detailed report for access points is empty.
Possible Cause The SNMP user may not have the correct rights assigned.
Recommended Action
a.
Open a browser window to the access point, and select Setup > Security > User Information.
b. Make sure that the user corresponding to the SNMP community (which is set up in WLSE in
Discovery > Device Credentials) has been granted rights for the following: Ident, firmware,
admin, snmp, and write.
c. If not, click on the user and assign all these rights.
OL-8376-01
Symptom The group report for a user-defined group contains no data.
Possible Cause Reports cannot be displayed for a user-defined group that contains another group.
Recommended Action Display individual reports for the sub-groups or devices within the
user-defined group.
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
1-33
Page 46

Reports FAQs and Troubleshooting
Symptom After running a job, the updated data does not appear in a report.
Possible Cause A full polling cycle has not completed and the new data has not been entered in the
database.
Recommended Action Verify that the polling cycle has completed as follows:
a. Select Admin > Appliance > Status > View Log File.
b. Click jobvm.log.
c. Scroll through the log to find the message: “Finished Inventory” for your particular job.
Symptom Email fails to arrive at its destination.
Possible Cause The SMTP server is not configured properly.
Recommended Action Configure the SMTP server by selecting Admin > Appliance > Configure
Mailroute.
You can also Telnet or SSH to the WLSE and clear the send queue, the user queue, and the mail log
and then send email to yourself. For example:
admin@mywlse: mailcontrl clear
admin@mywlse: mail to
email_address
Chapter 1 FAQs and Troubleshooting
Symptom There is a time discrepancy in the scheduled email jobs.
Possible Cause The time is not set correctly on the WLSE.
Recommended Action
a. Reset the WLSE time to Universal Coordinated Time (UTC) using CLI commands as follows:
Enter services stop to stop services.
Enter the clock command to reset the time.
Enter services start to restart the services.
b. Set the time in local browser time, select Admin > Appliance > Time/NTP/Name.
Symptom No VLAN information is displayed for IOS access points.
Possible Cause WEP keys have not been configured in each VLAN. When the WEP keys are
configured in the IOS access points, VLAN information is accessible by SNMP.
Recommended Action Configure the WEP keys for the corresponding VLAN.
Symptom There is a discrepancy in the first aggregation intervals after the first time the WLSE started
up or after the WLSE’s software was upgraded.
For example, weekly data is displayed within 2 days of initial startup or upgrade, or the aggregation
period began before the initial startup or upgrade.
1-34
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
OL-8376-01
Page 47

Chapter 1 FAQs and Troubleshooting
Possible Cause This is because the very first aggregations are based on day and time that the WLSE’s
system software was installed, and the formula for computing the next aggregation is causing this
discrepancy.
Recommended Action No action is required. Subsequent aggregations will occur at the normal
intervals.
Symptom In the Group Client Association Report, the Number of Clients Associated with this Group
displays a 0 (zero).
Possible Cause The devices in the group have IOS version 12.3(2)JA or earlier, which will provide
a negative value for the number of clients associated.The WLSE ignores negative values and reports
them as 0.
Recommended Action Upgrade the devices to the latest IOS version.
Radio Manager FAQs and Troubleshooting
Radio Manager FAQs and Troubleshooting
• Radio Manager FAQs
• Radio Manager Troubleshooting
Radio Manager FAQs
Configuration
• Q.For each AP to report radio information back to WLSE, does each AP need to be configured as a
WDS AP?
• Q.If so, do I need a separate username and password for each? If not, how many WDS APs would I
need?
• Q.Do I need a separate infrastructure SSID for the APs that are configured as WDS?
• Q.Why does a WLSE radio plan recommend the same channel for adjacent APs?
Radio Monitoring
• Q.Is there a problem if Radio Monitoring is always disabled?
• Q.What is the throughput impact if Radio Monitoring is enabled?
Self Healing
• Q.How do “Hot Standby” and “Self-Healing” work together?
• Q.In a centralized deployment where WLSE is located in a central location and wireless network is
being managed across the WAN, how does Self Healing behave when there is a WAN failure?
• Q.The suggested new settings are confusing—why does Self Healing decrease the transmit power?
OL-8376-01
• Q.After the administrator replaces the failed AP, will WLSE detect it and change the power of that
AP back to its original power?
• Q.I am seeing warning messages in the self healing run log. What do they mean?
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
1-35
Page 48
Radio Manager FAQs and Troubleshooting
Auto Re-Site Survey
• Q.Is there a limit to the number of floors or access points that can be enabled for the auto re-site
survey?
• Q.Will it cause problems if a floor that has no access points yet is added to Auto Re-Site Survey?
Miscellaneous
• Q.Can I give a radio management job a name that is used for a firmware or configuration
management job?
• Q.Can I use a non-Cisco RADIUS server with radio management?
• Q.Why does the Client MAC Spoofing fault reappear after it has been cleared?
Configuration
Q.
For each AP to report radio information back to WLSE, does each AP need to be configured as a
WDS AP?
A.
No, one WDS AP or WDS Router must be configured for each AP subnet. The WDSs should be
configured to know about WLSE.
For example, if you have 3 AP subnets in a building, you must set up 3 APs as WDS APs. Those 3
APs must be configured with the IP of the WLSE, and the non-WDS APs must be configured with
the WLCCP username and password. These configuration settings will allow the APs to send
information to the WDS APs, which the WDS APs will then forward to WLSE.
Chapter 1 FAQs and Troubleshooting
Note You could also set up a WLSM (Wireless LAN Services Module) device to manage your
APs. One WLSM-WDS device can manage multiple AP subnets.
Q.
If so, do I need a separate username and password for each? If not, how many WDS APs would I
need?
A.
No, you do not need a separate username and password for each. Each WDS AP (either 1100 or
1200) supports up to 30 APs.
Q.
Do I need a separate infrastructure SSID for the APs that are configured as WDS?
A.
No, the infrastructure SSID configuration does not need to be altered.
Q.
Why does a WLSE radio plan recommend the same channel for adjacent APs?
A.
In a WLAN (versus a traditional 2G cellular), the co-location of physically adjacent APs on the same
channels is not considered a bad deployment or misconfiguration. For a detailed explanation, see the
section Understanding Frequency and Transmit Power Planning in the online help or the User Guide
for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine, 2.13.
Radio Monitoring
Q.
Is there a problem if Radio Monitoring is always disabled?
A.
If you disable Radio Monitoring, you will not have access to several features, including continuous
detection of rogue APs, self-healing networks, auto re-site surveys, and certain Radio Manager
reports.
1-36
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
OL-8376-01
Page 49

Chapter 1 FAQs and Troubleshooting
Q.
What is the throughput impact if Radio Monitoring is enabled?
A.
Each AP scans all supported non-serving channels every 90 seconds. Each non-serving channel scan
lasts for 20 to 30ms depending on radio type. Because of the short duration, the overall impact to
the throughput should be less than 1% of the total bandwidth.
Self Healing
Q.
How do “Hot Standby” and “Self-Healing” work together?
A.
Hot Standby allows the customer to keep a redundant standby AP set for a primary AP. Then, if the
primary AP goes down, the standby will take over—presumably, with the same or similar
settings—to allow for no loss in coverage.
With Self Healing, the WLSE monitors the wireless network and if it determines a radio is down, it
modifies the power settings of neighboring APs in an attempt to maintain the coverage.
If both Hot Standby and Self Healing are deployed, then Hot Standby takes precedence over Self
Healing. In this case, Self Healing does not modify the neighboring APs unless the standby becomes
the primary AP and that AP goes down as well (a double failure).
Q.
In a centralized deployment where WLSE is located in a central location and wireless network is
being managed across the WAN, how does Self Healing behave when there is a WAN failure?
Radio Manager FAQs and Troubleshooting
A.
The Self Healing feature runs on the WLSE, which means that the downed radio determination is
evaluated on the WLSE. The data for this determination is provided to the WLSE over the wired
network via the WDS and SWAN architecture. The power setting changes are initiated from the
WLSE and deployed over the wired network as well. If there is a prolonged WAN failure between
the WLSE and the wireless network under management, the WLSE cannot provide the Self Healing
feature.
Q.
The suggested new settings are confusing—why does Self Healing decrease the transmit power?
A.
Transmit power is not always increased on neighboring APs. When a radio is detected as down,
WLSE computes the best coverage possible given the available radios and current channel settings.
In response to a downed radio, WLSE only changes power—it does not change the channels. Given
these constraints, the power for some radios is turned down while the power for others is turned up
to ensure the best coverage. While this may not seem intuitive, it is expected.
Q.
After the administrator replaces the failed AP, will WLSE detect it and change the power of that AP
back to its original power?
A.
When the failed AP is up again, the next self-healing event recalculates the power setting for the
surrounding APs based on the latest radio measurement data (if Radio Monitoring is enabled, radio
measurement data is updated every 90 seconds). The new power setting might not be the same as the
original one because WLSE does not save the original power settings.
WLSE assumes you are using it for your initial setup and site planning, and therefore Self Healing
is merely a rerun of the initial calculations minus the downed radio. When WLSE finds that a failed
radio is back up, it reruns the calculations, this time including the radio.
OL-8376-01
If you use WLSE initially, the calculations will yield the same or equivalent results. If you set your
power settings manually, then after the radio is detected as down and then back up, the results of the
calculations could differ from your manual settings.
For example, assume you have a network with four APs {A,B,C,D}.
–
When WLSE is used for initial setup:
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
1-37
Page 50
Radio Manager FAQs and Troubleshooting
You use Assisted Site Survey to generate your power settings and apply the following power
settings (respectively):
{5,10,20,5}
AP C goes down and Self Healing adjusts the power settings:
{5,20,down,20}
AP C comes back up and Self Healing adjusts the power settings:
{10,5,20,5}
In the final state, this is an equivalent coverage—perhaps not the exact settings, but equivalent.
–
When you set the power manually and do not use WLSE to calculate the initial coverage:
You manually set the power setting to:
{10,10,10,10}
AP C goes down and Self Healing adjusts the power settings:
{5,20,down,20}
AP C comes back up and Self Healing adjusts the power settings:
{10,5,20,5}
Chapter 1 FAQs and Troubleshooting
Self Healing uses the WLSE recommended settings when the AP comes back up, not the manual
settings. WLSE is not designed to save check point configurations as part of the management.
Note All Self Healing power settings are temporary, so any reload of the APs will revert to the last
saved configuration on the AP itself.
Q.
I am seeing warning messages in the self healing run log. What do they mean?
A.
These messages are warnings—not errors, faults, or actionable items. There are two types of
warning messages:
Dot11Radio0[MACADDRESS]@IPADDRESS
Does not have any reliable vouchers within range or configuraton
For the given radio there are no other radios that have an acceptable path loss or configuration to
vouch for the monitored radio. To determine if a radio is transmitting, at least one other radio in the
deployment must be able to reliably hear the monitored radio’s beacons. In that case, the monitoring
for the radios in question will rely solely on the WDS/Registration that is maintained over the AP’s
Ethernet connection (that is, not wirelessly).
The determination of a reliable voucher for a monitored radio is made based upon RSSI/Path Loss
and basic rate sets. Keep in mind, however, that the data rates configured on a radio are not
necessarily the same as the basic rate sets (beacon data rates).
The following reports in Reports > Radio Manager can help you here:
–
Configured Radio Parameters Report
1-38
–
Path Loss between Manager APs Report
By looking at the path loss and configured data rates between APs you can see if the radio in
question has any acceptable radios in range.
WARNING: Dot11Radio1[MACADDRESS/BAND]@IPADDRESS
has excessive links to other radios which may make this radio appear stale
(undetectable beacons), total = XX
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
OL-8376-01
Page 51

Chapter 1 FAQs and Troubleshooting
The radio in question is detecting a large amount of neighboring radios. If a radio is detecting too
many other radio beacons (the warning message includes the total detected), it might not have the
bandwidth to process the beacons. This makes the radio in question unreliable for vouching for other
radios.
If the monitored radios do not have enough vouchers or too many radios are detecting excessive links
(due to a very congested air space), self healing will rely only on the WDS registration over the
Ethernet connection. In this case a radio that fails but remains connected to the Ethernet might not
be compensated for. If you are concerned about the likelihood of a downed or tampered radio that
remains network connected, you can:
–
–
If your network is still critically overcrowded, the only means of detection will be over the wired
network. If you are still concerned, you might want to investigate using hot standby APs for your
critical coverage points.
Auto Re-Site Survey
Q.
Is there a limit to the number of floors or access points that can be enabled for the auto re-site
survey?
Radio Manager FAQs and Troubleshooting
Add more APs to the coverage plan, or
Ensure proper coverage with scanning-only APs selectively placed on your critical floors.
A.
Auto Re-Site Survey is only limited by the recommended limits for managed APs.
Q.
Will it cause problems if a floor that has no access points yet is added to Auto Re-Site Survey?
A.
Selecting floors that do not have APs yet should not cause a processing problem. But enabling Auto
Re-Site Survey on an empty floor doesn't make much sense. Instead, you should run Auto Re-Site
Survey to recompute the throughput values after the APs have been placed on the floor and the
coverage and network is stable.
Miscellaneous
Q.
Can I give a radio management job a name that is used for a firmware or configuration management
job?
A.
No. Job names cannot be duplicated.
Q.
Can I use a non-Cisco RADIUS server with radio management?
A.
A RADIUS server that supports LEAP is required for infrastructure authentication. RADIUS servers
other than Cisco ACS have not been extensively tested. Problems have been observed with the Funk
Steel Belt and FreeRADIUS servers.
If you do not want to turn on LEAP in your RADIUS server and you are using AP-based WDS (not
WLSM-based WDS), you can turn on the Local Authentication Server (LAS) software feature on
the WDS AP. Then, you can use LAS for infrastructure authentication via LEAP while using the
external AAA server with non-LEAP authentication for client authentication.
If you use the approach outlined above, you will need to enter the security credential of the WLSE
into the each LAS (WDS AP) and make sure that the same credential is added to all the LAS
(WDS AP).
If you have many subnets with WDS APs, it will be easier to use a centralized AAA server with
LEAP turned on only for SWAN infrastructure authentication. Use AES, PEAP, or a more advanced
security scheme for client authentication.
OL-8376-01
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
1-39
Page 52

Radio Manager FAQs and Troubleshooting
Q.
Why does the Client MAC Spoofing fault reappear after it has been cleared?
A.
The WLSE raises faults for all clients identified by MIB ciscoWdsIdsMacSpoofClient
(1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.457.1.1.3.1.3). It retains the history of all spoofed MAC addresses.
Because the WDS maintains the history of all spoofed MAC addresses, the WLSE raises the MAC
spoofing fault during the poll cycle, even after the fault is cleared on the WLSE. If you have cleared
the MAC spoofing condition in the network, you need to Acknowledge the fault on WLSE.
An entry from the WDS MIB is cleared when on of the following occurs:
–
The WDS AP reaches the maximum number of events to hold for a reporting non-WDS AP. The
maximum number is determined by the following MIBs: ciscoWdsIdsMaxMacAddresses and
ciscoWdsIdsMaxEntriesPerMac.
–
The WDS is unconfigured.
Radio Manager Troubleshooting
This section provides the following troubleshooting information:
• Symptom WDS has been set up on the AP and WLSE, but WDS isn't authenticating with WLSE.
• Symptom My clients are not being authenticated through WDS.
Chapter 1 FAQs and Troubleshooting
• Symptom The Verify RM Capability tool reports the following error: WLSE-WDS Authentication
Test—Failed. FreeRadius 1.5 is being used for authentication.
• Symptom Self Healing is taking a very long time to complete.
Symptom WDS has been set up on the AP and WLSE, but WDS isn't authenticating with WLSE.
The “Not Authenticated” you see in response to the “show wlccp wnm status” command means that the
WDS component has not authenticated the WLSE. There are two possible causes:
Possible Cause The device credentials in the WLSE are not correct. The user name and password
should match the user names and passwords entered on the WDS AP and the AAA server.
Recommended Action To correct the credentials:
1. Select Devices > Discover > Device Credentials > WLCCP Credentials.
2. Change the Radius User Name and Radius Password fields to match the user names and
passwords entered on the WDS AP and the AAA server.
Possible Cause The WDS AP has not been managed in the WLSE.
Recommended Action To manage the WDS AP:
1. Select Devices > Discover > Managed/Unmanaged.
1-40
2. Look in the New folder for your WDS AP.
3. Select it, then select Manage. The process will take 1-2 minutes.
After the WLSE is authenticated by the WDS, the WDS reports its member APs to the WLSE, so
they are “discovered” by the WLSE. After these member APs have been discovered, you will need
to manage them as well.
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
OL-8376-01
Page 53

Chapter 1 FAQs and Troubleshooting
Symptom My clients are not being authenticated through WDS.
Possible Cause You have not created a server group on the WDS for client authentication.
Recommended Action To create a server group on the WDS for client authentication, you can use the
AP CLI, the AP web interface, or the WLSE configuration templates for an AP-WDS, or the WLSM
CLI for a WLSM-WDS. For more information, see the device setup information in the online help
or the User Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine, 2.13.
Symptom The Verify RM Capability tool reports the following error: WLSE-WDS Authentication
Test—Failed. FreeRadius 1.5 is being used for authentication.
Possible Cause If the command show wlccp wnm status on the WDS does not show SECURITY
KEYS SETUP, then the issue is probably a known problem with FreeRADIUS. FreeRADIUS
requires a patch to be fully compliant with Cisco LEAP.
Recommended Action You can download this patch from:
http://lists.freeradius.org/pipermail/freeradius-users/2004-October/037017.html
Sites FAQs and Troubleshooting
Symptom Self Healing is taking a very long time to complete.
Possible Cause Self-Healing compensation is on a per-building basis. If you have too many APs per
building, for example, 200 APs, Self Healing computation can take a long time and, in extreme cases
cases, the WLSE might run out of memory. It is recommended that you do not have more than 200
APs in one building.
Recommended Action If your building has more than 200 APs, create multiple logical buildings so
that no one building has more than 200 APs.
Sites FAQs and Troubleshooting
• Sites FAQs
• Sites Troubleshooting
Sites FAQs
Location Manager
• Q.Is there is a size limitation for the building image that can be imported in Location Manager?
• Q.Why does Location Manager show a coverage map for an AP based on the configured transmit
power setting even when the radios are shut down?
OL-8376-01
• Q.In Location Manager > Rogue > Unknown Radio List, why does the Switch IP Address field say
Unknown?
Assisted Site survey Wizard
• Q.Why don’t I see the building or floor node in the device tree in the Assisted Site Survey Wizard?
• Q.Why don't I see the device that I am looking for in the Assisted Site Survey device tree?
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
1-41
Page 54

Sites FAQs and Troubleshooting
• Q.When I select devices in the Assisted Site Survey Wizard, why are some shown in red?
• Q.When I’m using the Assisted Site Survey Wizard, why is the Next button disabled after I complete
step one?
• Q.In the Assisted Site Survey Wizard, why is Use Old Radio Scan Data disabled?
• Q.In the Assisted Site Survey Wizard, what does None mean in the Last Scan Time field?
• Q.In the Assisted Site Survey Wizard, why is the Next button disabled on the radio scan step?
• Q.Why did my radio scan job fail in the Assisted Site Survey Wizard?
• Q.When I’m using the Assisted Site Survey Wizard, the radio scan progress advances very slowly.
How long does it radio scan normally take?
• Q.Can I skip client walkabout in the Assisted Site Survey Wizard even though the number of data
shown is zero?
• Q.In the client walkabout step in the Assisted Site Survey Wizard, what is the Recall button for?
• Q.What is the difference between the Number of Location Data and Number of New Location Data
fields?
• Q.In the Constraints and Goals step in the Assisted Site Survey Wizard, how do I select multiple
channels in the channel list?
Chapter 1 FAQs and Troubleshooting
• Q.How long should the Constraints and Goals calculation step take in the Assisted Site Survey
Wizard?
• Q.Where can I see the result of the Constraints and Goals calculation in the Assisted Site Survey
Wizard?
• Q.If I don't like result of the Constraints and Goals calculation in the Assisted Site Survey Wizard,
what can I do?
• Q.When I apply the configuration in the Assisted Site Survey Wizard, where do I see the results?
• Q.In the last step of the Assisted Site Survey Wizard, why is the Next button disabled?
AP Radio Scan
• Q.How does AP Radio Scan affect an access point’s performance?
• Q.Is the WDS radio required to be up during an AP radio scan?
• Q.Is it necessary to do an AP radio scan after a firmware upgrade to get faster and better results?
Radio Parameter Generation
Q.When WLSE is trying to calculate new radio parameter generations, why do I get an error about
walkabout locations?
Location Manager
1-42
Q.
Is there is a size limitation for the building image that can be imported in Location Manager?
A.
Although there is no limit on the file size for each image, for the best performance we suggest that
the image file be less than 300KB and less than 1,000x1,000 pixels. For optimal performance, if the
image file was created using a graphic editing application, save the file for use as a “web image” if
possible.
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
OL-8376-01
Page 55

Chapter 1 FAQs and Troubleshooting
Q.
Why does Location Manager show a coverage map for an AP based on the configured transmit
power setting even when the radios are shut down?
A.
If you did not select Display coverage for operational radio interfaces only in Edit >
Preferences, Location Manager displays coverage based on the configured values. Even when a
radio is turned off, it still has a configured transmit power. The coverage display is calculated from
the WLSE RM database (populated by AP radio scan, client walkabout, and RF monitoring) using
a calibrated path loss model. What the display represents is an estimation of the coverage area based
on the RM data.
Q.
In Location Manager > Rogue > Unknown Radio List, why does the Switch IP Address field say
Unknown?
Recommended Action If the switch IP address is Unknown, the IP address of the switch that the
unknown radio is connected to could not be determined. To find the switch port to which the rogue
AP is connected, the Switch Port Location feature uses the rogue AP’s BSSID that it hears over the
air to make a heuristic guess of the rogue’s Ethernet MAC address. This might not be possible,
however, if its Ethernet MAC address and BSSID do not follow the one-off rule, where the MAC
address is the same or one-off of the BSSID. For more information, see the Understanding Switch
Port Location and Suppression section in the online help or the User Guide for the CiscoWorks
Wireless LAN Solution Engine, 2.13.
Sites FAQs and Troubleshooting
Assisted Site Survey Wizard
Q.
Why don’t I see the building or floor node in the device tree in the Assisted Site Survey Wizard?
A.
Expand the building node to see all floors that belong to the building. If you expand the building
node and the floors still do not appear, close the Wizard and make sure the building and floor exist
in the Location Manager navigation tree. If the building or floor does not exist in the Location
Manager navigation tree, you first need to create them and then restart the Assisted Site Survey
Wizard. See the topic Adding Building Information in the online help or the User Guide for the
CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine, 2.13.
Q.
Why don't I see the device that I am looking for in the Assisted Site Survey device tree?
A.
Expand the building and floor nodes to see all devices that belong to a building or floor. If the device
still does not appear, close the Assisted Site Survey Wizard and make sure the device appears in the
Location Manager navigation tree. If the device does not appear in the Location Manager navigation
tree, select Tool s > F i n d D e vi c e to locate it. If you find the device, move it to the desired location.
See the topic Adding Devices to the Floor Map in the online help or the User Guide for the
CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine, 2.13. If the device does not appear in Location Manager,
it might not have been discovered by the system. See the topic Managing Device Discovery in the
online help or the User Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine, 2.13. After adding
the device and specifying its location, restart the Assisted Site Survey Wizard.
Q.
When I select devices in the Assisted Site Survey Wizard, why are some shown in red?
A.
The devices might be red if:
–
The devices are not in the Managed state.
OL-8376-01
–
The devices are not in infrastructure mode.
–
Use the radio management verification tool to check on the status of the devices. Right-click on
the device and select Verify RM Capability. The radio management verification tool displays
problems and information about how to fix the problem. After fixing the devices, you can retry
the wizard.
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
1-43
Page 56

Sites FAQs and Troubleshooting
Q.
When I’m using the Assisted Site Survey Wizard, why is the Next button disabled after I complete
step one?
A.
You have not selected any acceptable devices that are required for the next step. If any of the selected
devices are shown in red, you need to deselect them before you can go to the next step.
Q.
In the Assisted Site Survey Wizard, why is Use Old Radio Scan Data disabled?
A.
You might not have previously run radio scan for the selected devices. You must start a new radio
scan.
Q.
In the Assisted Site Survey Wizard, what does None mean in the Last Scan Time field?
A.
The selected device was not included in a previous radio scan.
Q.
In the Assisted Site Survey Wizard, why is the Next button disabled on the radio scan step?
A.
You need to run radio scan by clicking Start. When the radio scan is complete, you will be able to
click Next.
Q.
Why did my radio scan job fail in the Assisted Site Survey Wizard?
A.
Look at the log window to find out exact failure cause. If radio scan failed:
Chapter 1 FAQs and Troubleshooting
–
Make sure the devices have the correct setup for WDS. Also verify that WDS is authenticated
to WLSE and that WDS has an IP address pointing to WLSE.
–
Make sure the devices have the correct SNMP read/write community strings that match the
WLSE setting.
Q.
When I’m using the Assisted Site Survey Wizard, the radio scan progress advances very slowly. How
long does it radio scan normally take?
A.
Radio scan normally takes about 5 to 10 minutes to complete. If you suspect the program has stalled,
check its status by selecting Radio Manager > AP Radio Scan and viewing the progress of the job.
Q.
Can I skip client walkabout in the Assisted Site Survey Wizard even though the number of data
shown is zero?
A.
Yes, you can skip client walkabout. However, performing a client walkabout will generate better
parameters for your wireless network.
Q.
In the client walkabout step in the Assisted Site Survey Wizard, what is the Recall button for?
A.
You can click Recall to display a list of the last five client MAC addresses that were used for the
previous client walkabout. To retrieve a previously used MAC address, click Recall and select a
MAC address from the list.
Q.
What is the difference between the Number of Location Data and Number of New Location Data
fields?
A.
Number of Location Data is the total number of data found by client walkabout for the current
session plus any previous sessions. Number of New Location Data is the total number of data found
by client walkabout for the current session only. The numbers in these two fields can increase at the
same time during a client walkabout.
1-44
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
OL-8376-01
Page 57

Chapter 1 FAQs and Troubleshooting
Q.
In the Constraints and Goals step in the Assisted Site Survey Wizard, how do I select multiple
channels in the channel list?
A.
For Windows users, control-click on the channels to add them to the selection. The selected channels
are highlighted.
Q.
How long should the Constraints and Goals calculation step take in the Assisted Site Survey Wizard?
A.
It varies depending on the amount of radio scan and client walkabout data. The more data you have,
the longer it will take to calculate.
Q.
Where can I see the result of the Constraints and Goals calculation in the Assisted Site Survey
Wizard?
A.
If the calculation was successful, you can click Next to view the result.
Q.
If I don't like result of the Constraints and Goals calculation in the Assisted Site Survey Wizard,
what can I do?
A.
Go back and specify different constraints and goals, and then recalculate the constraints and goals.
Q.
When I apply the configuration in the Assisted Site Survey Wizard, where do I see the results?
Sites FAQs and Troubleshooting
A.
Check Location Manager to view the configuration changes. You might need to refresh the Location
Manager window by selecting View > Refresh Data. In rare cases, the wizard might have failed to
apply the configuration. In that case, check your SNMP settings, particularly the WRITE
community string, for the devices.
Q.
In the last step of the Assisted Site Survey Wizard, why is the Next button disabled?
A.
This is the last step in Assisted Site Survey Wizard. You can close the Wizard unless you want to
repeat any previous steps.
AP Radio Scan
Q.
How does AP Radio Scan affect an access point’s performance?
A.
With all the APs configured to the same channel and at maximum power, there is some degradation
in throughput. Also, while the APs step through their various power settings, there may be some loss
of coverage. This only lasts for the length of the AP scan (3to 4 minutes).
Q.
Is the WDS radio required to be up during an AP radio scan?
A.
No, but if the WDS radio is not up, the WDS will not be part of the radio scan. If you do include the
WDS radio interface in the scan job, you will see some time-outs from this interface in the logs, but
the scan will work on the other interfaces as expected. If you are not using a WDS to serve clients,
you can turn off the radio to exclude this interface from the scan task.
Q.
Is it necessary to do an AP radio scan after a firmware upgrade to get faster and better results?
OL-8376-01
A.
It is recommended (but not required) that you run AP Radio Scan after any network change. The AP
Radio Scan procedure will identify which radios are capable of detecting other radios. This
information is periodically collected by WLSE via the WDS, but a Radio Scan will retrieve the
information immediately.
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
1-45
Page 58

Sites FAQs and Troubleshooting
Radio Parameter Generation
Q.
When WLSE is trying to calculate new radio parameter generations, why do I get an error about
walkabout locations?
A.
Before WLSE can generate radio parameters, you must have previously collected client walkabout
data or you must have defined the dimensions of your building and floor(s). If you receive an error,
make sure you have entered the correct building and floor dimensions using the Building and Floor
Edit Tool in Location Manager and then try running the parameter generation again.
Sites Troubleshooting
This section contains the following troubleshooting information:
• Symptom Location Manager does not display the location of an AP I know to be a rogue because
the AP is reported to be in an unknown location.
• Symptom After completing the Assisted Site Survey, Location Manager did not update to include
the applied configurations.
• Symptom It takes a very long time to import a building or floor image in to Location Manager.
Chapter 1 FAQs and Troubleshooting
• Symptom AP coverage is not displaying in Location Manager .
• Symptom When selecting View > Radio Band > Show 2.4 GHz, Location Manager does not refresh
to show the 2.4 GHz radios.
• Symptom The Location Manager cannot be launched when using the Mozilla browser.
• Symptom ERROR: Aborting execution of AP Scanning task because there are no applicable Radio
Interfaces that can participate.
• Symptom I've upgraded WLSE but Location Manager seems to be previous version.
• Symptom I've downgraded WLSE to older version, but when I launch Location Manager, it still
seems to be the newer version.
Symptom Location Manager does not display the location of an AP I know to be a rogue because the AP
is reported to be in an unknown location.
Possible Cause The rogue AP was detected by APs whose locations were not specified in Location
Manager, or the locations of the reporting APs were specified after the detection of the rogue AP.
Recommended Action In the Unknown Radio List window, determine which APs reported the
detection. Make sure you have placed the reporting APs on a particular floor in Location Manager.
Turn on Radio Monitoring for the reporting APs and after they detect the same rogue AP, the
possible location of the rogue AP will be available.
1-46
Symptom After completing the Assisted Site Survey, Location Manager did not update to include the
applied configurations.
Possible Cause You did not refresh the Location Manager window.
Recommended Action In the Location Manager window, select View > Refresh Data.
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
OL-8376-01
Page 59

Chapter 1 FAQs and Troubleshooting
Symptom It takes a very long time to import a building or floor image in to Location Manager.
Possible Cause The resolution and pixel size of the image file is very large.
Recommended Action Because the larger an image resolution is, the longer it takes to upload to the
server and the more memory it uses, it is recommended that your building and floor images be less
than 1,000x1,000 pixels.
Symptom AP coverage is not displaying in Location Manager .
Possible Cause You have not imported an image map for the floor and did not enter the floor
dimensions in the Building Tool.
Recommended Action Import an image map for the floor or if you do not want to use an image map,
enter the floor dimensions in the Building Tool. For more information, see the instructions for
adding building information in the online help or the User Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN
Solution Engine, 2.13.
Sites FAQs and Troubleshooting
Symptom When selecting View > Radio Band > Show 2.4 GHz, Location Manager does not refresh to
show the 2.4 GHz radios.
Possible Cause The View > Radio Band menu filters the options (radio channel, transmit power, and
data rate) that you want to display in the Location Manager window; it does not filter the display of
the APs themselves.
Recommended Action Use the View > Radio Band menu to specify which radio band’s view options
to display and which information (radio channel, transmit power, and/or data rate) to display.
Symptom The Location Manager cannot be launched when using the Mozilla browser.
Possible Cause Cookies must be enabled on the browser.
Recommended Action Under Edit > Preferences, select Privacy and Security > Cookies. Enable all
cookies or enable cookies for the originating web site only.
Symptom ERROR: Aborting execution of AP Scanning task because there are no applicable Radio
Interfaces that can participate.
Possible Cause This error message says that the AP radio scan is ending because there are no
interfaces capable of participating in the scan. It is always included with one or more messages that
describe why a given interface was removed from the scan. For example:
OL-8376-01
WARNING: Skipping device 172.xx.xx.xxx because it is not registered with any WDS
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
1-47
Page 60

Sites FAQs and Troubleshooting
There are quite a few reasons why an interface might be removed from the scan. The WLSE
examines each interface separately; after that, if all interfaces have been removed, this error is
displayed.
Recommended Action Use the radio management verification tool to check on the status of the devices
that are displaying errors for AP radio scan. Right-click on each device and select Ve r i f y R M
Capability. The radio management verification tool displays problems and information about how
to fix the problem.
Symptom I've upgraded WLSE but Location Manager seems to be previous version.
Possible Cause You might not have closed the browser before relaunching Location Manager.
Recommended Action Close all browsers and Java Runtime instances, then relaunch Location
Manager. If the symptom persists, check to see if your cache is enabled for the Java Plug-in. If it is,
clear the cache from Java Plug-in Control Panel (for Windows, select Start > Settings > Control
Panel > Java Plug-in), then restart the browser and relaunch Location Manager.
If the problem still exists, clear the Java cache entries as shown in the following steps:
1. Log in to WLSE and select Sites > Location Manager, but do not launch Location Manager.
Chapter 1 FAQs and Troubleshooting
WLSE checks for the Java version and loads the necessary Java plug-in. After the Java plug-in
is loaded, a new icon appears indicating it is loaded.
2. Right-click on the Java icon and select Open Console. The Java console launches. Click on the
console and type the following commands, which are all single-character commands:
g
x
c
Leave the console open.
3. Clear the cache on your browser:
For Internet Explorer, select Tools > Internet Options > General > Settings. Select “Every
visit to the page” and click OK. Click on Delete Files, click OK on the pop-up, then click
OK.This clears all temporary internet files.
For Mozilla Firefox, select Tools > Options > Privacy > Cache, then click Clear.
For Netscape, select Edit > Preferences > Advanced > Cache. Click Clear Cache and select
“Every time I view the page.” Uncheck “Prefetch web pages ...”.
4. Restart your browser.
Symptom I've downgraded WLSE to older version, but when I launch Location Manager, it still seems to
be the newer version.
Recommended Action Close all browsers and Java Runtime instances. Launch the Java Plug-in
Control Panel (for Windows, select Start > Settings > Control Panel > Java Plug-in). Click on
Clear in Cache tab, then click Apply. Relaunch the web browser for WLSE and Location Manager.
1-48
If the problem still exists, clear the Java cache entries as shown in steps 1-4 in the previous
troubleshooting entry above.
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
OL-8376-01
Page 61

Chapter 1 FAQs and Troubleshooting
Intrusion Detection System FAQs and Troubleshooting
Intrusion Detection System FAQs and Troubleshooting
• Intrusion Detection System FAQs
• Intrusion Detection System Troubleshooting
Intrusion Detection System FAQs
Detecting Rogue APs
• Q.How does WLSE detect rogue APs?
• Q.What is the difference between a rogue and a friendly AP?
• Q.How does the WLSE distinguish between a rogue device and an ad-hoc device?
• Q.How often does rogue AP detection occur and can it be customized?
• Q.How long does it typically take for the WLSE to detect a rogue access point after it is connected
to the network?
• Q.Can I disable transmit on an AP and yet allow it to receive signals so that it can participate in
rogue AP detection?
• Q.I want to disable Radio Monitoring and detect rogue APs only when AP Radio Scan jobs are
scheduled. Is this possible?
• Q.What requirements and configuration are needed before a client can participate in rogue AP
detection?
• Q.Can the client be used to help triangulate a rogue AP?
• Q.How can I automatically adjust the channel and power settings on my managed APs to overcome
the coverage problems introduced by rogue APs?
• Q.I understand that WLSE does not accept SNMP traps that indicate an AP detected a rogue. So why
is an AP that is currently designated as the WDS generating rogue AP SNMP traps?
• Q.I configured the Friendly AP-to-Rogue AP no-observation period as 5 minutes, moved a rogue AP
(AP1) to the friendly list, and shut down its radio. After 5 minutes, AP1 was moved to the rogue AP
list. When I moved AP1 back to the friendly list, it was immediately (with in 40 seconds) moved
back to the rogue AP list.
• Q.What should I do when my system is overrun with rogue APs?
• Q.Why is a fault generated regardless of the threshold set for detecting rogue APs with an defined
RSSI value under IDS > Manage Network-Wide IDS Settings?
Interference Detection
Q.Are the Network-Wide > Interference Detection settings of -87dbm for 10% always the same, or are
they the optimal recommended values, or are they calculated depending on the environment? Should they
be left alone, or are there any recommendations?
APs in Scanning-Only Mode
• Q.Why are the APs running in scanning-only mode having problems with sporadic connection loss
and image upgrade failure?
OL-8376-01
• Q.Which WLSE IDS functions require dedicated scanning APs?
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
1-49
Page 62

Intrusion Detection System FAQs and Troubleshooting
Detecting Rogue APs
Q.
How does WLSE detect rogue APs?
A.
Here is a brief summary of the rogue AP detection logic:
a. A rogue AP appears and starts sending out beacons and responding to probe-requests.
b. A nearby managed and RM-enabled AP or client detects the beacon (same channel or
off-channel) or probe response (off-channel). The AP or client sends back a beacon report of
the rogue AP in the next scheduled RM report. The scheduled internal RM reporting interval is
90 seconds, so this step can take up to 90 seconds to complete.
c. The WLSE Radio Manager (RM) receives the beacon report, recognizes that this AP is not in
the system (not a managed AP, and not a previously detected radio), and triggers the rogue AP
switch-port tracing logic. The WLSE RM does not issue a rogue AP fault at this time.
d. The WLSE RM waits for 3 measurement intervals (3x90, or 270 seconds) for other surrounding
APs or clients to report the same radio. This delay allows as many APs as possible to detect the
rogue and helps pinpoint the rogue’s location (which is reported in Step e.) When other APs or
clients detect this radio, the reporting AP and the reported RSSI of the rogue AP are stored or
updated in the WLSE RM database. This period of time also allows the switch port tracing logic
to try to locate the switch port to which this rogue AP might connect. This logic happens in
parallel. Depending on the size of the network, the switch port tracing logic may or may not
finish before the end of this interval (270 seconds).
e. The WLSE RM issues a rogue AP fault. These first steps (b - e) can take from 270 to 360
seconds (3x90 to 4x90) to generate a fault against a particular rogue AP. After the fault has been
generated, the fault notifications follow the standard WLSE fault notification process. (You
must set up the e-mail notification to receive it.) The fault details page is updated so that when
you click on the rogue AP’s location, the system will have enough information (if it is available)
to do a location triangulation based on the RSSI from the different reporting APs.
Chapter 1 FAQs and Troubleshooting
f. The AP or client continues to update the rogue AP’s RSSI, and the Radio Manager continues to
update this information in the WLSE. This allows the WLSE to keep the rogue AP’s location
current and not limited to the position when it was first detected.
Q.
What is the difference between a rogue and a friendly AP?
A.
In WLSE, friendly stations are unknown stations that the administrator has identified as “okay”; all
other are rogues. Unlike a rogue AP, a friendly AP will not trigger a rogue AP fault (that is, a friendly
AP will not be detected as a rogue). To change the category type of a rogue AP to Friendly, select
IDS > Manage Rogues.
Q.
How does the WLSE distinguish between a rogue device and an ad-hoc device?
A.
APs and clients detect beacons in the air and send the beacon information to the WLSE via the WDS.
These beacons are standard 802.11 frames. If the beacon information does not match a managed
radio in the WLSE (by MAC address), the WLSE will identify it as an Unknown Station.
An unknown station is either infrastructure or ad-hoc (IBSS). This determination is made from the
beacon report; the 802.11 frame contains a byte indicating whether or not the beacon is IBSS
(ad-hoc) or not (infrastructure). WLSE relies solely on this flag in the beacon to make this
determination.
1-50
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
OL-8376-01
Page 63

Chapter 1 FAQs and Troubleshooting
WLSE considers hardware, both client and access points, to be trusted sources, and assumes that
vendors are reporting the field correctly. WLSE expects only client machines and peripherals to emit
beacons with the IBSS flag set (it is very unlikely that an access point would emit an IBSS beacon).
In rare cases, however, a malicious station can spoof the field. If this happens, WLSE will report
whatever value the field is set to.
Q.
How often does rogue AP detection occur and can it be customized?
A.
Rogues can be detected within 90 seconds, but are not reported for another 180 seconds. This delay
allows as many APs as possible to detect the rogue, which helps pinpoint the rogue’s location.
Detection frequency cannot be customized, but rogue AP detection and the fault priority that is
assigned can be enabled and disabled for the network.
Q.
How long does it typically take for the WLSE to detect a rogue access point after it is connected to
the network?
A.
To detect a rogue AP, Radio Monitoring must be enabled. Radio monitoring gathers radio reports
every 90 seconds, so if at least one AP can hear the rogue, WLSE will detect the rogue in
approximately 360 to 450 seconds. (It takes 1 to 2 measurement intervals for Radio Monitoring to
report a rogue, and the WLSE waits for 3 measurement intervals for other surrounding APs or clients
to report the same radio.)
Intrusion Detection System FAQs and Troubleshooting
Q.
Can I disable transmit on an AP and yet allow it to receive signals so that it can participate in rogue
AP detection?
A.
The solution you want is called scanning-only AP mode. Scanning-Only AP mode puts a radio
interface in a dedicated mode monitoring the air space surrounding it without carrying any regular
WLAN user traffic. For more information, see the scanning-only AP mode information in the online
help or the User Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine, 2.13.
Q.
I want to disable Radio Monitoring and detect rogue APs only when AP Radio Scan jobs are
scheduled. Is this possible?
A.
Radio Monitoring is the preferred method for detecting rogue APs. AP Radio Scan jobs can detect
rogues, but only during the scan (approximately 3 to 4 minutes); any rogues that show up after the
scan are not detected. In addition, because the scan is so short, it is possible that some rogues will
not be detected because they do not respond with a Probe Request during the active scan. When
Radio Monitoring is enabled, the rogue will eventually be detected by the beacon frame; it is
statistically possible that a beacon will not be seen during an AP scan.
Q.
What requirements and configuration are needed before a client can participate in rogue AP
detection?
A.
Participation is automatic. Cisco and CCX clients gather radio frequency information as instructed
by the APs to which they are associated. APs gather similar information. This data is aggregated at
the WDS device and then analyzed by the WLSE.
Q.
Can the client be used to help triangulate a rogue AP?
OL-8376-01
A.
The client’s data does not get factored into location triangulation; only the AP data is used.
Q.
How can I automatically adjust the channel and power settings on my managed APs to overcome the
coverage problems introduced by rogue APs?
A.
To automatically adjust channel and power settings on managed APs after detecting rogue APs, run
RM Assisted Configuration (or Auto Site Survey from the Location Manager wizard).
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
1-51
Page 64

Intrusion Detection System FAQs and Troubleshooting
Q.
I understand that WLSE does not accept SNMP traps that indicate an AP detected a rogue. So why
is an AP that is currently designated as the WDS generating rogue AP SNMP traps?
A.
The AP is generating the detected rogue trap, not the WDS functionality currently operating within
the AP. This trap is based on authentication tattletale rogue detection, which is currently not reported
to the WLSE.
WLSE uses radio measurements to detect the rogues. The authentication tattletale method uses a
message sent from a participating client that indicates some type of authentication issue with some
other AP. This other AP is considered to be rogue for one of these reasons:
–
The rogue was not running 802.1x.
–
Authentication with the rogue timed out.
–
Bad user password.
–
Authentication challenge failed.
This tattletale method is enabled on the AP itself, detected by the AP, and flagged at the AP via the
trap.
Q.
I configured the Friendly AP-to-Rogue AP no-observation period as 5 minutes, moved a rogue AP
(AP1) to the friendly list, and shut down its radio. After 5 minutes, AP1 was moved to the rogue AP
list. When I moved AP1 back to the friendly list, it was immediately (with in 40 seconds) moved
back to the rogue AP list.
Chapter 1 FAQs and Troubleshooting
A.
When the Friendly-to-Rogue policy evaluates a site, any device that hasn’t been seen in “too long a
time” is reclassified as rogue. This time period starts when WLSE last observed the device, not after
the administrator has set it to Friendly. To keep an unmanaged device as Friendly, set the maximum
unobserved time to a value larger than the amount of time the device is expected to not be observed.
For example, if a friendly AP is turned off after business hours, the maximum unobserved time
should be at least 14 hours (or more for weekends) or the WLSE will reclassify it as rogue.
Q.
What should I do when my system is overrun with rogue APs?
A.
Some networks might experience large numbers of rogues due to the nature of their neighboring
networks or a one-time storm. When the number of unknown (rogue infra-structure or ad-hoc) radios
is high (greater than 5000), your network might experience performance degradation. This can occur
when your network is in a crowded airspace, you have products such as printers that have wireless
functions that create and/or rotate ad-hoc network IDs, that are attacked by the FakeAP program, or
that have APs sending corrupt beacon reports. To handle large numbers of rogues:
–
Use IDS > Manage Network Wide Settings to disable all rogue detection and processing from
either infrastructure or ad-hoc rogues (or both).
–
If your network is in a crowded airspace, examine the report IDS > Manage Rogues. This report
shows you the RSSI value for the detected rogues. Sorting by RSSI might give you a limit of
RSSI values that you could use in IDS > Manage Network Wide Settings as a threshold.
–
Use IDS > Manage Rogues to delete the rogues that are no longer an issue (for example, from
a temporary storm or isolated occurrence) to free up space in the WLSE.
–
For an explanation of the fault, see IDS (Intrusion Detection System) Faults, page 2-14.
1-52
Q.
Why is a fault generated regardless of the threshold set for detecting rogue APs with an defined RSSI
value under IDS > Manage Network-Wide IDS Settings?
For example, the threshold is set for detecting a rouge AP with an RSSI value of greater than
-80dBM, but alerts are being generated for a rogue AP with an RSSI value of -200 dBm.
A.
What happens is as follows:
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
OL-8376-01
Page 65

Chapter 1 FAQs and Troubleshooting
–
–
Interference Detection
Q.
Are the Network-Wide > Interference Detection settings of -87dbm for 10% always the same, or
are they the optimal recommended values, or are they calculated depending on the environment?
Should they be left alone, or are there any recommendations?
A.
This is the default setting. If it is not adequate, you will need to experiment to find the proper setting
for your environment.
APs in Scanning-Only Mode
Q.
Why are the APs running in scanning-only mode having problems with sporadic connection loss and
image upgrade failure?
A.
In a heavy-load environment, APs running in scanning-only mode may face sporadic connection loss
and image upgrade failure. To resolve these problems, use the following configuration commands
to balance CPU time:
scheduler interval <100-xxx>
scheduler allocate <3000-xxx> <1000-xxx>
Intrusion Detection System FAQs and Troubleshooting
First, a rogue is detected which has an RSSI value higher than the configured threshold. For
example, it has an RSSI value of -60dBm and the configured threshold is -80dBm.
Then, the rogue is not seen for a while, and the WLSE marks it for deletion. (Rogue APs that
are not heard from for a long time are candidates for deletion from the WLSE.)
Many newer Cisco platforms use the command scheduler allocate instead of scheduler interval.
The scheduler allocate command takes two parameters: a period in microseconds for the system to
run with interrupts enabled, and a period in microseconds for the system to run with interrupts
masked. Please refer to the IOS documentation for more information about these commands.
Q.
Which WLSE IDS functions require dedicated scanning APs?
A.
Only the Unregistered Client function requires a scanning AP.
Intrusion Detection System Troubleshooting
This section contains the following information for troubleshooting the Intrusion Detection System:
• Q.I configured the Friendly AP-to-Rogue AP no-observation period as 5 minutes, moved a rogue AP
(AP1) to the friendly list, and shut down its radio. After 5 minutes, AP1 was moved to the rogue AP
list. When I moved AP1 back to the friendly list, it was immediately (with in 40 seconds) moved
back to the rogue AP list.
• Q.What should I do when my system is overrun with rogue APs?
• Q.The SSID field in the Manage Rogues > Rogue AP List report is being displayed in hexagonal
format (for example, "\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00"). What causes this?
Q.
I configured the Friendly AP-to-Rogue AP no-observation period as 5 minutes, moved a rogue AP
(AP1) to the friendly list, and shut down its radio. After 5 minutes, AP1 was moved to the rogue AP
list. When I moved AP1 back to the friendly list, it was immediately (with in 40 seconds) moved
back to the rogue AP list.
OL-8376-01
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
1-53
Page 66

Admin FAQs and Troubleshooting
A.
When the Friendly-to-Rogue policy evaluates a site, any device that hasn’t been seen in “too long a
time” is reclassified as rogue. This time period starts when WLSE last observed the device, not after
the administrator has set it to Friendly. To keep an unmanaged device as Friendly, set the maximum
unobserved time to a value larger than the amount of time the device is expected to not be observed.
For example, if a friendly AP is turned off after business hours, the maximum unobserved time
should be at least 14 hours (or more for weekends) or the WLSE will reclassify it as rogue.
Q.
What should I do when my system is overrun with rogue APs?
A.
Some networks might experience large numbers of rogues due to the nature of their neighboring
networks or a one-time storm. When the number of unknown (rogue infrastructure or ad-hoc) radios
is high (greater than 5000), your network might experience performance degradation. This can occur
when your network is in a crowded airspace, you have products such as printers that have wireless
functions that create and/or rotate ad-hoc network IDs, that are attacked by the Fake AP program,
or that have APs sending corrupt beacon reports. To handle large numbers of rogues:
–
–
–
Chapter 1 FAQs and Troubleshooting
Use IDS > Manage Network Wide Settings to disable all rogue detection and processing from
either infrastructure or ad-hoc rogues (or both).
If your network is in a crowded airspace, examine the report IDS > Manage Rogues. This report
shows you the RSSI value for the detected rogues. Sorting by RSSI might give you a limit of
RSSI values that you could use in IDS > Manage Network Wide Settings as a threshold.
Use IDS > Manage Rogues to delete the rogues that are no longer an issue (for example, from
a temporary storm or isolated occurrence) to free up space in the WLSE.
For an explanation of the fault, see IDS (Intrusion Detection System) Faults, page 2-14.
Q.
The SSID field in the Manage Rogues > Rogue AP List report is being displayed in hexagonal
format (for example, "\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00"). What causes this?
A.
If the SSID contains unprintable characters, the WLSE displays it in hex notation. In this example,
the SSID is set to 9 hex zeros.
The WLSE displays unprintable characters as \xNN, where NN is the hex value of each character,
followed by the length of the SSID in bytes. For example, “\x00” [1] means that the SSID contains
the hex value \x00 and is 1 byte long. In addition, any double quote marks or backslashes that are
part of the SSID octets are displayed using a preceding backslash (for example, \" or \\).
Admin FAQs and Troubleshooting
This section contains the following information for understanding and troubleshooting the WLSE
appliance:
• Admin FAQs, page 1-54
• Admin Troubleshooting, page 1-57
• Troubleshooting Tools for the WLSE Appliance, page 1-61
Admin FAQs
1-54
• Q.How can I verify the status of the database?
• Q.What are the rules for WLSE user names and passwords?
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
OL-8376-01
Page 67

Chapter 1 FAQs and Troubleshooting
• Q.Can I restore a backup that I made on a WLSE running beta software to a WLSE running released
software?
• Q.Can I restore a backup from a WLSE 1105 to a WLSE 1130 series?
• Q.Can I upgrade from beta software to released software?
• Q.Are there any special considerations when performing actions on a redundant cluster?
• Q.Why are the WLSEs in my redundant environment exhibiting problems such as duplicate IPs, etc.,
and why am I having trouble accessing them with virtual IP addresses?
• Q.Do I have to get a signed certificate from a certificate authority in order to use WLSE security
features such as SSL (HTTPS)?
• Q.How do I change the password used by WLSE Redundancy?
• Q.How do I change the user ID used by WLSE redundancy?
• Q.What are the different redundancy states?
Q.
How can I verify the status of the database?
A.
You can verify that the WLSE database is running by using the show process CLI command. If the
command output includes the db2sync process, the database is running.
Admin FAQs and Troubleshooting
Q.
What are the rules for WLSE user names and passwords?
A.
User names can be up to 32 characters long. They cannot begin with a number (unless the user is not
using the CLI). You can use the alphanumeric characters (A-Z, a-z, 0-9) and numerous special
characters. For a complete list of the characters allowed, see the Naming Guidelines appendix in the
User Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine, Release 2.13. Passwords are
unlimited in length and you can use all characters except the single quote, double quote, and dollar
sign. Both user names and passwords are case-sensitive.
Q.
Can I restore a backup that I made on a WLSE running beta software to a WLSE running released
software?
A.
No.
Q.
Can I restore a backup from a WLSE 1105 to a WLSE 1130 series?
A.
Ye s.
Q.
Can I upgrade from beta software to released software?
A.
No.
Q.
Are there any special considerations when performing actions on a redundant cluster?
A.
Yes, there are special procedures for backup/restore, upgrading the software, and a few other
operations. See the online help for the redundancy feature or the User Guide for the CiscoWorks
Wireless LAN Solution Engine, Release 2.13 on Cisco.com.
OL-8376-01
Q.
Why are the WLSEs in my redundant environment exhibiting problems such as duplicate IPs, etc.,
and why am I having trouble accessing them with virtual IP addresses?
A.
If DNS is enabled, then it is possible the DNS servers specified for use by the WLSE are not
operational, not reachable due to a network outage, or not configured correctly. If the DNS server is
not set up correctly, proper communication between the Active and Standby WLSEs will not be
maintained, and will result in the status for both WLSEs becoming Active-Lost-Standby.
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
1-55
Page 68

Admin FAQs and Troubleshooting
Check the status by using the CLI command redundancy status, or by selecting Admin > Appliance
> Redundancy > Redundancy Status. On the master DNS server, make sure that the DNS zone file
for the inverse zone (in-addr.arpa) for the netblock contains the necessary PTR records for each
WLSE. Please note that if the time required to get a response from the DNS servers when requesting
a PTR record in the inverse zone exceeds 15 seconds, then this problem may occur.
See also the Installation Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine for instructions
on configuring name resolution, and Redundancy Requirements under Managing the WLSE in the
User Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine or Online Help to make sure you
have set up redundancy correctly.
Q.
Do I have to get a signed certificate from a certificate authority in order to use WLSE security
features such as SSL (HTTPS)?
A.
No, the WLSE will use the self-signed certificate; however, you may see messages from the browser
about the self-signed certificate not being trusted. The self-signed certificate is valid for one year.
After that, you can generate another self-signed certificate.
Q.
If I have set up WLSE redundancy, can I use a one-time password on the WLSE Manage
Redundancy screen?
A.
WLSE does not support one-time passwords in the Manage Redundancy screen (Admin >
Appliance > Redundancy > Manage Redundancy). The user ID and password you enter on this
screen are used by both WLSEs in a redundant environment to authenticate their communication.
The password is encrypted and stored on both WLSEs and is reused as required; therefore, one-time
passwords are not supported.
Chapter 1 FAQs and Troubleshooting
Q.
How do I change the password used by WLSE Redundancy?
A.
If you are using local authentication, you can change the password for the user ID by selecting Admin
> Appliance > User Admin > Manage Users or by using the CLI command
password
new_password
. This command synchronizes the password change of userid to new_password
username
user_id
between both WLSEs in the redundant environment.
If you are using remote AAA authentication, in order to change the password, you must first disable
redundancy (Admin > Appliance > Redundancy > Manage Redundancy), change the password on
the AAA server, and then re-enable redundancy.
Q.
How do I change the user ID used by WLSE redundancy?
To change the user ID used by WLSE redundancy, you must first disable redundancy (Admin >
Appliance > Redundancy > Manage Redundancy), change the user ID and password (Admin >
Appliance > User Admin > Manage Users), and then re-enable redundancy.
Q.
What are the different redundancy states?
A.
Table 1-3 describes the possible redundancy states and what they mean.
Table 1-3 Redundancy States
Redundancy State Description
Not Configured Redundancy is not enabled.
Starting Configured for redundancy and is initializing.
This state can apply to active and standby nodes.
Active Redundancy is enabled. This is the active node at
the current time.
1-56
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
OL-8376-01
Page 69
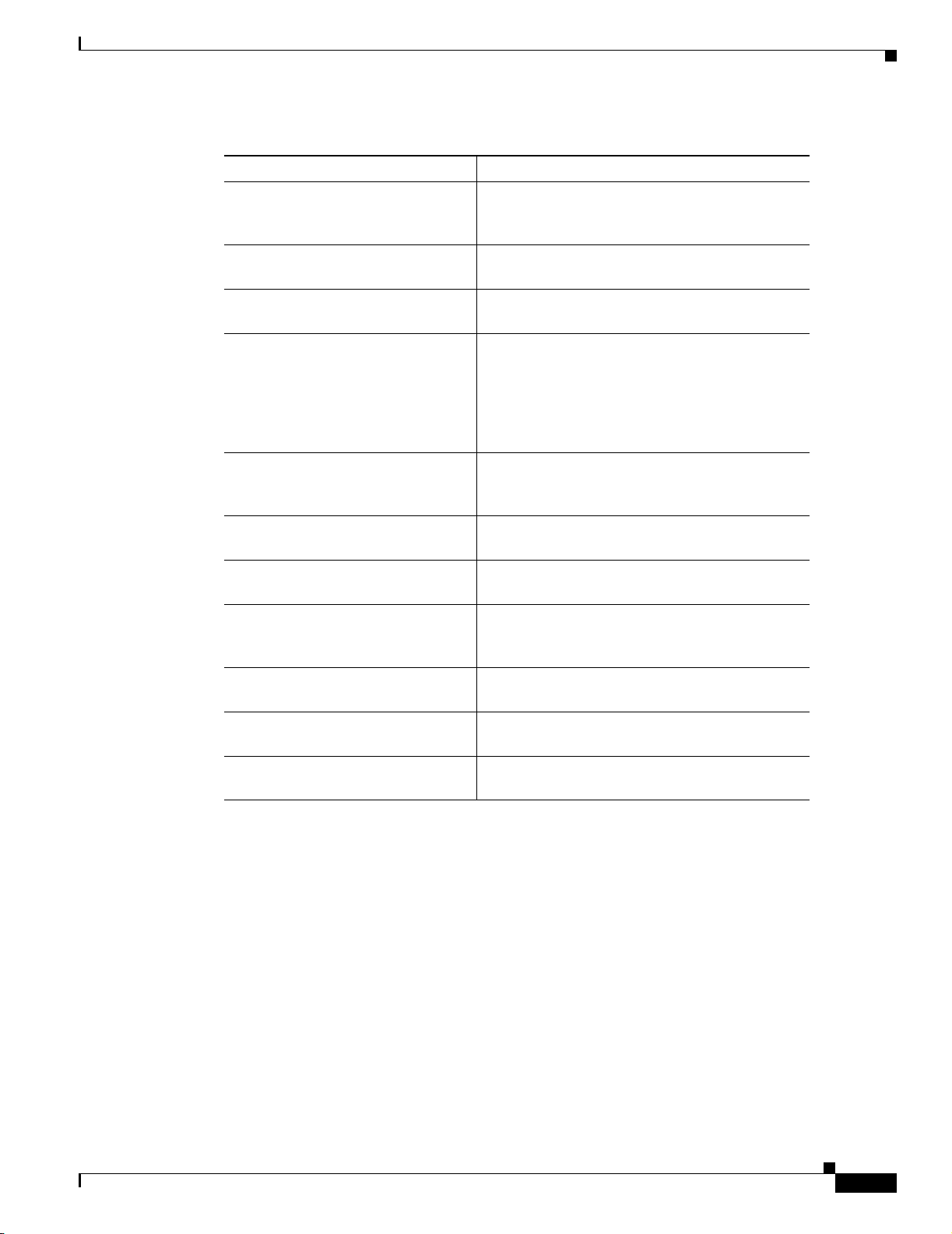
Chapter 1 FAQs and Troubleshooting
Table 1-3 Redundancy States
Redundancy State Description
Active Lost Router Active node is not receiving responses from the
Active Lost Standby Active node is not receiving responses from the
Active Upgrade Active node is waiting for the standby node to
Active Load Standby Standby node requested a full database backup
Active System Check Failure System check process has discovered a problem
Active Password Change Redundancy user ID password is being changed
Active Initialization Appliance is attempting to start the database and
Pre Standby Appliance is configured to be in standby mode
Standby Redundancy is enabled. This is the standby node
Standby Upgrade Standby node is attempting to upgrade WLSE
Standby Password Change Redundancy user ID password is being changed
Admin FAQs and Troubleshooting
standby node or from the default gateway. This
could signify a network issue.
standby node.
complete a WLSE upgrade.
and will not be operational until the backup
database is received from the active node and is
restored on the standby node. The standby node is
in Pre Standby state until the backup database has
been fully restored.
with the active node, but the standby node is not
available.
on the active node.
processes in order to become the active node.
and is attempting to restore data from the active
node, but is not yet in standby mode.
at the current time.
software on the appliance.
on the standby node.
Admin Troubleshooting
This section contains the following information for troubleshooting the appliance:
• Symptom After adding users to an external authentication server and configuring the
authentication module on the WLSE, users cannot log in to the WLSE.
• Symptom Users cannot log in after failure of the alternative authentication source.
• Symptom Some users are not listed under User Admin > Manage Users.
• Symptom When using Internet Explorer 6.0 to install a new image on a WLSE from a repository
located on a Windows XP machine, the progress bar does not appear in the Install Software Updates
window. This problem also occurs when you use Internet Explorer 6.0 and a Windows XP system
as a client to install a new image on a WLSE.
• Symptom Cannot back up the WLSE configuration to a Windows 2000 or Windows XP Server.
OL-8376-01
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
1-57
Page 70

Admin FAQs and Troubleshooting
• Symptom Cannot back up WLSE configuration to a remote server when using the secure file
transfer option.
• Symptom The ACS Failed Login Report link is missing.
• Symptom When using the MS NT Domain authentication module, the user could not log in by
using the domain password.
• Symptom The error message “AAA server not available” is falsely displayed for the following
built-in AAA server types: LEAP server, RADIUS server, PEAP server (applies to WLSE Express
only).
• Symptom In a redundant cluster, faults cannot be created or cleared, and there may be other
symptoms. The daemons.log file contains the following messages, which indicate a virtual machine
crash.
• Symptom Both WLSEs in an HA pair are claiming the same VIP address.
• Symptom The Device Interaction field is empty when I try to test my Telnet/SSH credentials using
the Telnet/SSH Tool under Admin > Appliance > Connectivity Tools.
Symptom After adding users to an external authentication server and configuring the authentication
module on the WLSE, users cannot log in to the WLSE.
Chapter 1 FAQs and Troubleshooting
Possible Cause Users do not have local accounts on the WLSE.
Recommended Action All users must have local accounts on the WLSE. Each user on the external
authentication server must have a local user account matching that username. Set up the local
accounts under Admin > User Admin > Manage Users.
Symptom Users cannot log in after failure of the alternative authentication source.
Possible Cause The WLSE falls back to the Local authentication module.
Recommended Action
–
Users can log in using their local passwords.
–
The system administrator can log in using the admin log in.
–
All users with CLI access can log in using the CLI.
–
If you still cannot log in, follow the procedure on recovering from the loss of all admin
passwords in the User Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine, Release 2.13.
Symptom Some users are not listed under User Admin > Manage Users.
Possible Cause Only the creator of a user can view that user’s name in the list. However, the admin
user and any user with the System Administration role can view all users.
1-58
Recommended Action None.
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
OL-8376-01
Page 71

Chapter 1 FAQs and Troubleshooting
Symptom When using Internet Explorer 6.0 to install a new image on a WLSE from a repository located
on a Windows XP machine, the progress bar does not appear in the Install Software Updates window.
This problem also occurs when you use Internet Explorer 6.0 and a Windows XP system as a client to
install a new image on a WLSE.
Possible Cause The Internet Explorer 6.0 browser on Windows XP does not come with the Java
plug-in installed.
Recommended Action Before using a Windows XP machine as a remote repository to update WLSE
software, review the Readme file that accompanies the software image on Cisco.com.
Symptom Cannot back up the WLSE configuration to a Windows 2000 or Windows XP Server.
Possible Cause The backup directory is not writable.
Recommended Action Set the directory to UNIX mode and make it write-enabled. For more
information, see the backup and restore instructions in the online help or the User Guide for the
CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine, 2.13.
Admin FAQs and Troubleshooting
Symptom Cannot back up WLSE configuration to a remote server when using the secure file transfer
option.
Possible Cause The shared key has changed on the remote server.
Recommended Action If you are sure this is a legitimate change, use the clearbackuphosts CLI
command to clear the key that is stored on the WLSE. Then, rerun the backup.
Symptom The ACS Failed Login Report link is missing.
Possible Cause Someone has deleted the link.
Recommended Action This link requires a special procedure for recreating it. See the online help for
the Links feature or the User Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine, Release 2.13
on Cisco.com.
Symptom When using the MS NT Domain authentication module, the user could not log in by using the
domain password.
Possible Cause The incorrect hostname format may be entered for the primary domain controller
Recommended Action When entering the hostname for the domain controllers, you must use the
WINS name (simple hostname) instead of an IP address or a fully qualified domain name.
OL-8376-01
Symptom If a redundant pair of WLSE Express systems are configured as active AAA RADIUS server
and standby AAA RADIUS server and subsequently configured to be monitored by the WLSE, the “HA
Standby AAA radius server Not Available” fault is generated and then clears shortly afterward.
This fault is generated at synchronization and failover whenever the standby AAA RADIUS server goes
down.
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
1-59
Page 72

Admin FAQs and Troubleshooting
Possible Cause At each instance of synchronization and failover, the standby AAA RADIUS server
goes down, thereby triggering the “HA standby AAA radius server not available” fault during each
instance.
Recommended Action
a.
b. Select the AAA Server settings in the relevant fault profile.
c. Set the consecutive polling cycle count to 2 for the “Radius Server Not Available” fault.
Result: This fault may reoccur, but only rarely.
Symptom The error message “AAA server not available” is falsely displayed for the following built-in
AAA server types: LEAP server, RADIUS server, PEAP server (applies to WLSE Express only).
Possible Cause The IP domain name has not been configured on the WLSE.
Recommended Action Enter the CLI command ip domain-name domain (where domain is your
domain name; for example cisco.com). Then reload the WLSE.
Chapter 1 FAQs and Troubleshooting
Select Faults > Manage Fault Settings.
Symptom In a redundant cluster, faults cannot be created or cleared, and there may be other symptoms.
The daemons.log file contains the following messages, which indicate a virtual machine crash.
Heap at VM Abort:
Heap
def new generation total 13120K, used 10188K [0x44650000, 0x45480000, 0x47f30000)
eden space 11712K, 74% used [0x44650000, 0x44ee32d0, 0x451c0000)
from space 1408K, 100% used [0x45320000, 0x45480000, 0x45480000)
to space 1408K, 0% used [0x451c0000, 0x451c0000, 0x45320000)
tenured generation total 116544K, used 53879K [0x47f30000, 0x4f100000, 0x64650000)
the space 116544K, 46% used [0x47f30000, 0x4b3cdcc8, 0x4b3cde00, 0x4f100000)
compacting perm gen total 16384K, used 5729K [0x64650000, 0x65650000, 0x68650000)
the space 16384K, 34% used [0x64650000, 0x64be84e0, 0x64be8600, 0x65650000)
Local Time = Sat Jul 2 03:21:02 2005
Elapsed Time = 1226
#
# HotSpot Virtual Machine Error : 11
# Error ID : 4F530E43505002EF
# Please report this error at
# http://java.sun.com/cgi-bin/bugreport.cgi
#
# Java VM: Java HotSpot(TM) Server VM (1.4.2_06-b03 mixed mode)
#
# An error report file has been saved as hs_err_pid2874.log.
# Please refer to the file for further information.
#
Using configuration file '/etc/sysconfig/idled.cf'.
received SIGHUP
1-60
Possible Cause A virtual machine crash has occurred after upgrade of a redundant pair from 2.11 to
2.13.
Recommended Action First, confirm that a virtual machine crash has occurred by checking the
daemons.log file (Admin > Appliance > Status > View Log File). Then, perform the following steps:
a. Telnet or SSH into the standby 2.13 system and execute the CLI command services stop.
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
OL-8376-01
Page 73

Chapter 1 FAQs and Troubleshooting
b. Telnet or SSH into the active 2.13 system and execute the CLI command reload. Wait until the
c. Telnet or SSH into the standby 2.13 system and execute the CLI command services start.
Symptom Both WLSEs in an HA pair are claiming the same VIP address.
Possible Cause When two devices (for example, device_A and device_B) claim the same IP address,
it is possible that some other devices (for example, device_C and device_D) might connect to one
of the devices (for example, device_A) while other devices (for example, device_E and device_F)
might connect to the other device, device_B, when specifying the IP address claimed by both
device_A and device_B.
WLSE uses authentication when each WLSE contacts the other WLSEs, and if the authentication
response takes longer than the 15 second timeout, the WLSEs believe the other WLSE appliance is
not functioning properly.
In addition, when the AAA server takes longer than 15 seconds, both WLSEs will be in
Active-Lost-Standby status.
Recommended Action When using external AAA service, make sure the AAA server is able to
respond to the WLSE in less than 10 seconds. If the AAA server cannot respond to the WLSE in less
than 10 seconds, switch the WLSE to use local authentication by selecting Admin > Appliance >
Security > Authentication Modules, and choose Local.
Admin FAQs and Troubleshooting
reload is complete.
Symptom The Device Interaction field is empty when I try to test my Telnet/SSH credentials using the
Telnet/SSH Tool under Admin > Appliance > Connectivity Tools.
Possible Cause Another user using the Telnet/SSH tool page simultaneously can cause the Device
Interaction field to be empty.
Recommended Action Wait a few seconds and try using the Telnet/SSH Tool again.
Troubleshooting Tools for the WLSE Appliance
This section describes some of the tools you can use to troubleshoot the WLSE appliance.
Generating Diagnostics for Technical Assistance
The Diagnostics option of the Admin tab provides tools to aid in troubleshooting. You can use these
tools when you have a problem that might require assistance from the Cisco Technical Assistance Center
(TAC). These tools are:
• WLSE Info—Create an information and status report.
• Self Test—Create a self-test report.
• Processes—View and manage major processes running on the appliance.
Viewing Log Files
OL-8376-01
The Admin > Appliance > Status > View Log option lists available log files and allows you to view
and download them.
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
1-61
Page 74

Chapter 1 FAQs and Troubleshooting
Internal AAA Server (WLSE Express Only) FAQs and Troubleshooting
Consolidating and Saving Log Files
The dumptech CLI command calls the diagnostic-info and tarlog commands, tars their output to an
archive called dumptech.tgz, and sends the output to a named user and location. For information on this
command, see the “Using the CLI” appendix in the User Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN
Solution Engine, Release 2.13 on Cisco.com at
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/rtrmgmt/cwparent/cw_1105/wlse/2_13/u_gd/app_cli
.htm.
Internal AAA Server (WLSE Express Only) FAQs and
Troubleshooting
This section contains the following information for understanding the WLSE Express internal AAA
server.
Internal AAA Server (WLSE Express) FAQs
Q.
Can I use the WLSE Express’ internal AAA server for purposes beside WLSE/WDS authentication?
A.
No. The WLSE AAA server is a RADIUS server that allows client devices to share a common
authentication database, and cannot be used for any other purpose.
Q.
Can you set a maximum number of sessions for one "guest user" per user ID?
A.
No. You cannot set a maximum number of sessions for any user ID or automatically control session
management in any way on the WLSE Express. The only control over AAA sessions you have is
through the AAA session GUI and CLI, which allow you to display the existing sessions, and query
and delete sessions by user ID or session ID.
You can share one "guest user" account between multiple users; there is no built-in session limit.
1-62
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
OL-8376-01
Page 75

CHAPTER
2
Fault Descriptions
This section provides the following information on the faults displayed in Faults > Display Faults. The
following information is provided:
• Fault—The fault as it appears in the Display Faults table.
• Explanation—An explanation as to why the fault occurred.
• Related Setting—The threshold or policy you assigned to devices under Faults > Manage Fault
Settings, IDS > Manage IDS Settings, or IDS > Manage Network-Wide IDS Settings, when
applicable.
• Recommended Action—An action that can be taken to clear the displayed fault.
Fault tables are provided for each device type:
• Access Point /Bridge Faults, page 2-2
• Radio Interface Faults, page 2-8
• IDS (Intrusion Detection System) Faults, page 2-14
• Voice Faults, page 2-24
• WLSE Faults, page 2-24
• AAA Server Faults, page 2-26
• Switch Faults, page 2-31
• Router Fault, page 2-33
• WLSM Faults, page 2-33
OL-8376-01
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
2-1
Page 76

Chapter 2 Fault Descriptions
Access Point /Bridge Faults
Access Point /Bridge Faults
Table 2-1 Access Point Faults
Fault Description Explanation Related Setting Recommended Action
Access point ssid
reclassified from
Friendly to Rogue due
to rule
An access point that was previously
determined to be Friendly has been
reclassified to Rogue:
ssid is the Service Set Identifier of
the unmanaged radio’s BSS.
rule is one of the following:
• Change in RSSI ordering
between observers
The estimated proximity of the
unmanaged radio between two
observers has switched—if the
WLSE thought that observer A
was closer to radio R than
observer B, it now thinks that
observer B is closer to radio R
than observer A.
IDS > Manage
Network-Wide IDS
Settings > Rogue
AP Detection >
Friendly to Rogue
AP Reclassification
or
IDS > Manage
Rogues
Use the fault details page to mark it
friendly if the AP is known, or to
delete it from the WLSE database if it
is an unknown AP.
Access point ssid
reclassified from
Friendly to Rogue due
to rule
(continued)
AP CPU utilization is
Degraded
(utilization %)
• Difference in relative RSSI
between original and current
observers exceeded threshold
While radio R’s strength
changed by factor M between
observer A and observer B, it
changed by factor M+T between
observer B and observer C. That
is, it does not
appear that radio R’s change in
strength is merely due to a
change in its power
configuration.
• Fewer than two observers
• Too long without any
observations
The fault threshold set for the
degraded state has been exceeded.
When this fault has been cleared, the
following message displays: AP CPU
utilization is Ok.
Manage Fault
Settings > Access
Point/Bridge
Thresholds > CPU
Utilization
Verify that the fault threshold is set
correctly.
If the threshold is set correctly, review
your network to determine the action
necessary to clear the fault condition.
2-2
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
OL-8376-01
Page 77

Chapter 2 Fault Descriptions
Access Point /Bridge Faults
Table 2-1 Access Point Faults (continued)
Fault Description Explanation Related Setting Recommended Action
AP CPU utilization is
Overloaded
(utilization %)
AP is not registered
with a WDS
AP memory utilization
is Degraded (utilization
%)
AP memory utilization
is Overloaded
(utilization %)
AP registered with an
Unmanaged WDS:
ipAddressOfTheUnMan
agedWDS
Broadcast Key Rotation
is disabled
Device state is rogue
access point: ssid
The fault threshold set for the
overloaded state has been exceeded.
When this fault has been cleared, the
following message displays: CPU
utilization is Ok.
The managed access point is not
registered with any WDS.
For Radio Manager functionality to
work, all access points must register
with a WDS. If an access point is not
registered, it will be excluded from
all the Radio Manager procedures,
which will provide incorrect results.
The fault threshold set for the
degraded state has been exceeded.
When this fault has been cleared, the
following message displays: AP
memory utilization is Ok.
The fault threshold set for the
overloaded state has been exceeded.
When this fault has been cleared, the
following message displays: AP
memory utilization is Ok.
AP is registered with a WDS but that
WDS is not managed by WLSE.
When this fault is cleared, the
following message displays: AP
registered with a managed WDS.
The broadcast key rotation has been
disabled.
When this fault is cleared, the
following message displays:
Broadcast Key Rotation is enabled.
The WLSE detected a rogue access
point (where ssid is the Service Set
Identifier of the unmanaged radio’s
BSS). This is an access point that is
not being managed and is unknown to
the WLSE.
Manage Fault
Settings > Access
Point/Bridge
Thresholds > CPU
Utilization
Manage Fault
Settings > Access
Point/Bridge >
Registration Error
Manage Fault
Settings > Access
Point/Bridge
Thresholds >
Memory Utilization
Manage Fault
Settings > Access
Point/Bridge
Thresholds >
Memory Utilization
Manage Fault
Settings > Access
Point/Bridge >
Registration Error
Manage Fault
Settings > Access
Point/Bridge
Policies > Key
Rotation per VLAN
IDS > Manage
Network-Wide IDS
Settings > Rogue
AP Detection
or
IDS > Manage
Rogues
Verify that the fault threshold is set
correctly.
If the threshold is set correctly, review
your network to determine the action
necessary to clear the fault condition.
Verify that the WLCCP AP
credentials are configured correctly so
that the AP can register with a WDS in
its subnet.
For more information, see the
managing devices information in the
online help or the User Guide for the
CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution
Engine, Release 2.13.
Verify that the fault threshold is set
correctly.
If the threshold is set correctly, review
your network to determine the action
necessary to clear the fault condition.
Verify that the fault threshold is set
correctly.
If the threshold is set correctly, review
your network to determine the action
necessary to clear the fault condition.
Manage the WDS.
Log in to the access point and enable
the broadcast key rotation interval.
Use the fault details page to mark it
friendly if the AP is known, or to
delete it from the WLSE database if it
is an unknown AP.
These faults do not automatically
clear after the Rogue AP no longer
appears in the network; you must
manually delete or clear the fault.
OL-8376-01
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
2-3
Page 78

Chapter 2 Fault Descriptions
Access Point /Bridge Faults
Table 2-1 Access Point Faults (continued)
Fault Description Explanation Related Setting Recommended Action
Device was not
reachable via SNMP
EAP per SSID for
Cisco-Supplicant is
disabled
EAP per SSID for
Non-Cisco-Supplicant
is disabled
EAP per SSID for
Mixed-Cisco-Supplican
t is disabled
The SNMP Agent could be down.
Using the SNMP threshold setting,
you configure the WLSE to poll the
sysUpTime MIB object periodically.
If at any time the WLSE fails to poll
this MIB object, the WLSE generates
this fault.
Also, if while polling any other MIB
objects for other fault policies or
thresholds associated with the
device, the WLSE observes the
device is SNMP unreachable, it
generates this fault.
And lastly, during rediscovery if a
previously-discovered device is
found to be SNMP unreachable, the
WLSE generate this fault.
When this fault is cleared, the
following message displays: Device
was reachable via SNMP.
The SNMP community string in the
access point has been changed, and
then a discovery job is run.
The Network EAP or the Open
authentication is disabled on this
SSID.
When this fault is cleared, the
following message displays: EAP per
SSID for Cisco Supplicant is
enabled.
The Network EAP or the Open
authentication is disabled on this
SSID.
When this fault is cleared, the
following message displays: EAP per
SSID for Non-Cisco Supplicant is
enabled.
The Network EAP or the Open
authentication is disabled on this
SSID.
When this fault is cleared, the
following message displays: EAP per
SSID for Cisco Supplicant is
enabled.
Manage Fault
Settings > Access
Point/Bridge
Thresholds >
SNMP Reachable
Not applicable. Change the SNMP community string
Manage Fault
Settings > Access
Point/Bridge
Policies > EAP Per
SSID Enforced for
CiscoSupplicant
Manage Fault
Settings > Access
Point/Bridge
Policies > EAP Per
SSID Enforced for
Non-CiscoSupplicant
Manage Fault
Settings > Access
Point/Bridge
Policies > EAP Per
SSID Enforced for
Mixed-CiscoSupplicant
Make sure SNMP is enabled on the
device and that the agent is not down.
Take a MIB walk of the device and
ensure that the sysUpTime returns a
non-zero value, which indicates that
the device is reachable.
on the WLSE to match the new
community string on the access point,
then run discovery again.
Log in to the access point and enable
both Network EAP and Open
authentication on that SSID.
Log in to the access point and enable
both Network EAP and Open
authentication on that SSID.
Log in to the access point and enable
both Network EAP and Open
authentication on that SSID.
2-4
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
OL-8376-01
Page 79

Chapter 2 Fault Descriptions
Access Point /Bridge Faults
Table 2-1 Access Point Faults (continued)
Fault Description Explanation Related Setting Recommended Action
Ethernet bandwidth
utilization is Degraded
(utilization %)
Ethernet bandwidth
utilization is
Overloaded
(utilization %)
Excessive frame counts:
• Action
• Association
The fault threshold set for the
degraded state has been exceeded.
When this fault is cleared, the
following message displays: Ethernet
bandwidth utilization is OK.
The fault threshold set for the
overloaded state has been exceeded.
When this fault is cleared, the
following message displays: Ethernet
bandwidth utilization is OK.
Manage Fault
Settings > Access
Point/Point
Thresholds >
Ethernet Port
Utilization
Manage Fault
Settings > Access
Point/Bridge
Thresholds >
Ethernet Port
Utilization
See IDS (Intrusion Detection System) Faults, page 2-14
Verify that the fault threshold is set
correctly.
If the threshold is set correctly, review
your network to determine the action
necessary to clear the fault condition.
Verify that the fault threshold is set
correctly.
If the threshold is set correctly, review
your network to determine the action
necessary to clear the fault condition.
• Authentication
• Deauthentication
• Disassociation
• Probe
• Reassociation
Firmware version
policy violation
(version number)
The wrong version number for policy
checking has been entered.
When this fault is cleared, the
following message displays:
Firmware version is valid.
The access point is running an
unauthorized firmware version.
When this fault is cleared, the
following message displays:
Firmware version is valid.
Manage Fault
Settings > Access
Point/Bridge
Policies >
Firmware Version
Make sure that the firmware version
that is entered in the policy setting
matches the firmware version on the
access point.
Make sure that you have entered
authorized versions in the policy
setting.
Update the firmware on the access
point to an authorized version.
OL-8376-01
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
2-5
Page 80
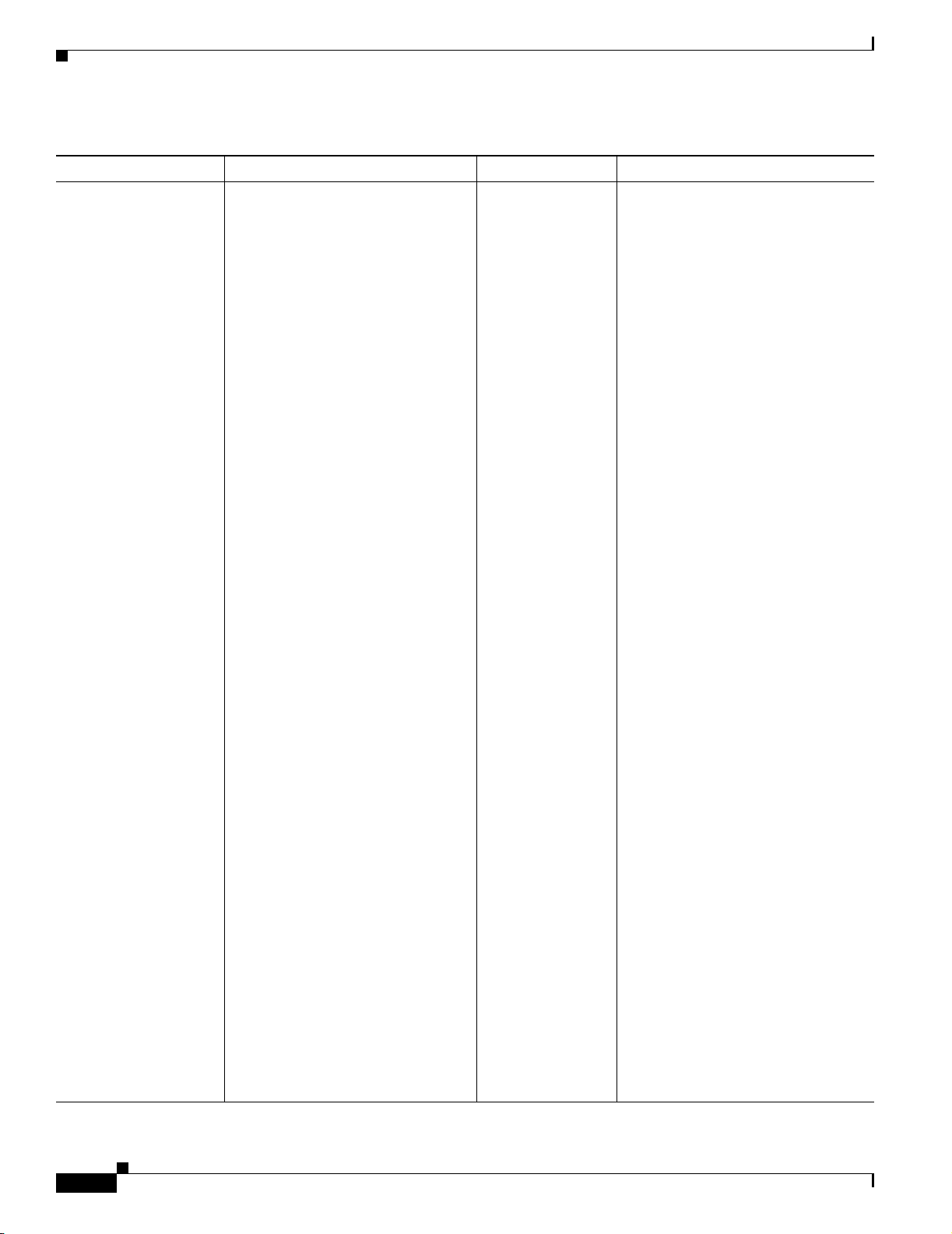
Chapter 2 Fault Descriptions
Access Point /Bridge Faults
Table 2-1 Access Point Faults (continued)
Fault Description Explanation Related Setting Recommended Action
HotStandBy is active The access point that is configured
for hot standby has become active.
The following conditions could cause
the hot standby access point to
become active: the primary access
point is down, the Ethernet port is
down, or the Radio port is down.
When this fault is cleared, the
following message displays:
HotStandBy is disabled.
Manage Fault
Settings > Access
Point/Bridge
Policies >
HotStandby Status
1. Check the primary access point,
the Ethernet port, or the Radio
port to see why the hot standby
access point has been activated.
2. Correct the condition. For
example, if the Radio Port on the
formerly active access point was in a
disabled state, then enable it using the
access point GUI.
3. Launch the GUI for access point
that is currently in Active
Takeover mode.
4. Select Hot Standby, click Disabled ,
then click Apply.
5. Click Enabled, then enter the
Radio MAC address of Monitored
Radio Port, leave the Polling
interval and Timeout for Each
Polling fields blank,.
Inconsistent device
state found: MIB-name
table-name. OID-name
problem-details
One or more configuration values of
the AP/BR are either out-of-range or
are in conflict with another
configuration value. The fault
description and corresponding
swan.log entry provide details about
the suspect value, including the
official public MIB name of the
SNMP OID for which the error was
found.
When a radio is declared to have an
invalid configuration or has failed, it
cannot be manipulated by Radio
Management and is removed from
SWAN RM operations. For example,
if just the 802.11a radio on a WDS is
not configured correctly, only that
radio is excluded from RM
operations; the 802.11b/g radio and
the WDS remains fully
RM-operational. This behavior can
help you isolate the portions of your
network that are affected by
misconfigurations or failures.
6. Click Apply to reconfigure the
access point to Hot Standby
mode.
Not applicable. To resolve an inconsistent
configuration, several possibilities
exist:
• It is possible that the most recent
Inventory failed for the device.
Re-running inventory might clear
the condition.
• If the configuration value being
contested is user-editable, you
can correct the problem using the
WLSE templates, the AP/BR
GUI, or the AP/BR CLI.
• If the configuration value being
contested is not user-editable, this
is probably an IOS error. You will
need to upgrade the affected
AP/BR to the most recent version
of IOS.
For information about the MIB
referenced in the fault description, see
http://www.cisco.com/public/sw-cent
er/netmgmt/cmtk/mibs.shtml.
2-6
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
OL-8376-01
Page 81
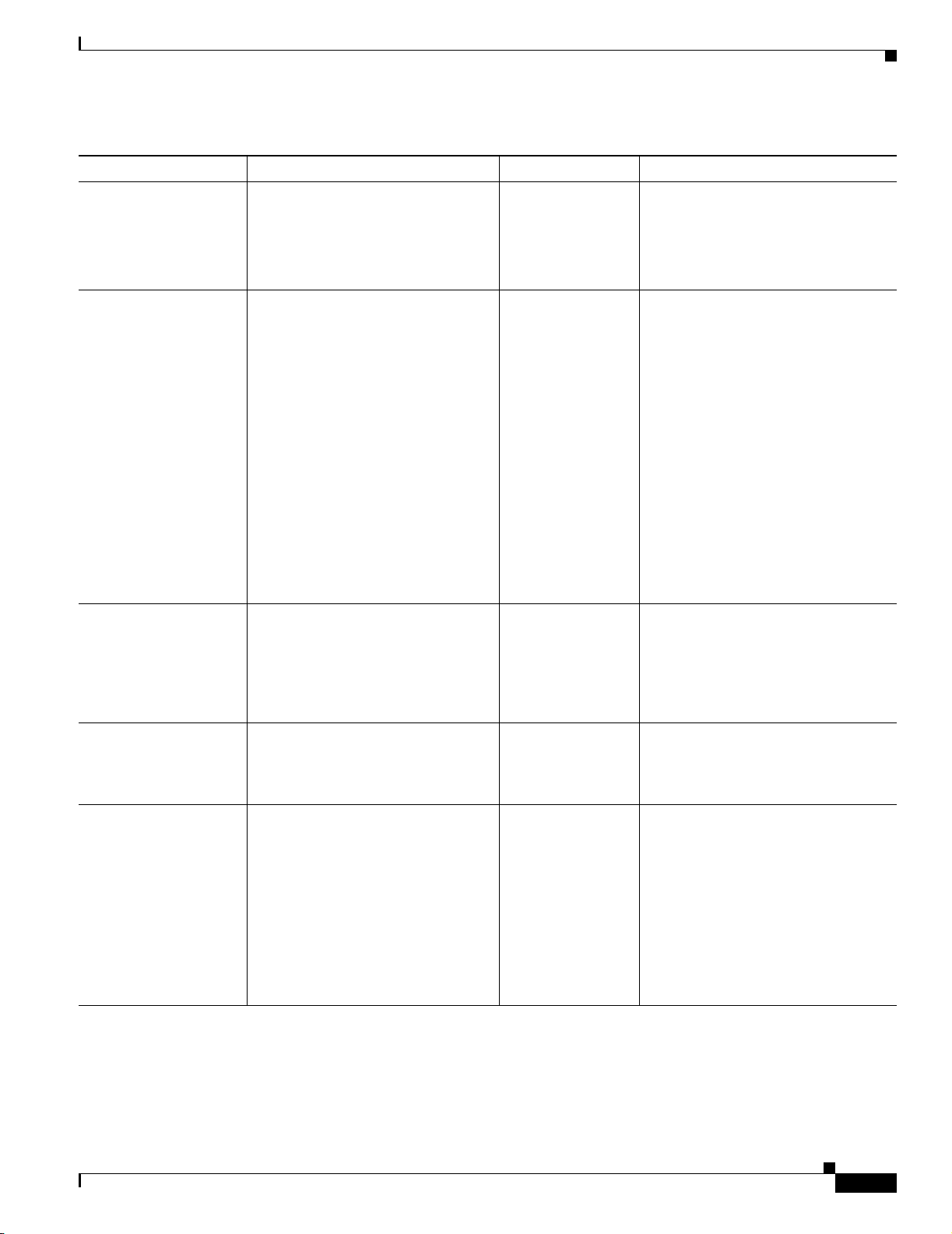
Chapter 2 Fault Descriptions
Access Point /Bridge Faults
Table 2-1 Access Point Faults (continued)
Fault Description Explanation Related Setting Recommended Action
MIC is disabled for the
VLAN number
Radar Detected on
Channel origChannel
MIC is not enabled for the selected
VLAN on the access point.
When the fault is cleared, the
following message displays: MIC is
enabled.
On its current channel, the AP
detected likely contention with a
radar device, so it needs to leave that
channel and find another. The AP
will automatically scan for another
channel, but might be unable to
accept associations for one minute.
This one minute delay is the required
scan time on another Dynamic
Frequency Selection channel that
must elapse before the AP can accept
associations.
Manage Fault
Settings > Access
Point/Bridge
Policies > MIC per
Vlan
Manage Fault
Settings >
Radio-802.11a
Policies > Dynamic
Frequency
Selection (DFS)
Log into the access point and enable
the VLAN. Then, using the WLSE
fault settings, enable the MIC for that
VLAN.
The WLSE will automatically handle
the assignment of another channel for
those APs affected by the Radar
Detection. However, if these faults
become common, you should re-run
Assisted Configuration (RPG) soon
after a DFS event has occurred (or just
manually deselect the DFS channel
from the Assisted Config Wizard).
This will reorganize the site to avoid
the affected channel and make future
conflicts likely.
When this fault is cleared, the
following message displays: No
radar detected on new channel
newChannel
Vlan WEP key length
policy violation
The WEP key length for the selected
VLAN setting has been violated.
When this fault has been cleared, the
following message displays: Vlan
WEP key length is ok.
WDS appears down. The WLSE failed to receive “keep
active” messages from the WDS.
This happens when the WDS is down
or when the network is down.
WDS Registered with
another WLSE
The WDS is registered with a
different WLSE.
(IPaddress)
Manage Fault
Settings > Access
Point/Bridge
Policies > WEP
Encryption per
Vlan
Manage Fault
Settings > WDS >
WLSE-WDS Link
Status
Manage Fault
Settings > WDS >
Authentication
Failures
Make sure the WEP key length
selected in the policy setting matches
the access point settings.
Check the network connectivity, and
the WDS status.
Determine which WLSE is supposed
to manage that WDS from an RM
perspective. Then modify the wnm
configuration on the WDS to point to
the correct WLSE.
For more information, see the
managing devices information in the
online help or the User Guide for the
CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution
Engine, Release 2.13.
OL-8376-01
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
2-7
Page 82

Chapter 2 Fault Descriptions
Radio Interface Faults
Table 2-1 Access Point Faults (continued)
Fault Description Explanation Related Setting Recommended Action
WEP is disabled WEP is not enabled for the VLAN
defined on the access point. (Note
that the VLAN number is displayed
in the Type column under Faults >
Display Faults.)
When the fault is cleared, the
following message displays: WEP is
enabled.
WLSE failed to
authenticate with WDS.
Authentication required to open a
WLCCP channel between the WLSE
and the WDS failed.
Manage Fault
Settings > Access
Point/Bridge
Policies > WEP per
Vlan
Manage Fault
Settings > WDS >
Authentication
Failures
Make sure you have set the policy
correctly for the VLAN.
Verify that the WLSE credentials used
to authenticate with the WDS are
correct.
For more information, see the
managing devices information in the
online help or the User Guide for the
CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution
Engine, Release 2.13.
Radio Interface Faults
Table 2-2 Radio Interface Faults
Fault Description Explanation Related Setting Recommended Action
AP is in a Degraded
state number associated
clients
AP is in an Overloaded
state number associated
clients
The fault threshold set for the
degraded state has been exceeded.
When this fault is cleared, the
following message displays: AP is
in OK state.
The fault threshold set for the
overloaded state has been
exceeded.
When this fault is cleared, the
following message displays: AP is
in OK state.
Manage Fault
Settings >
Radio-802.11x
Thresholds >
Associated Clients
Manage Fault
Settings > Thresholds
> Access Point >
Associated Clients
Verify that the fault threshold is set
correctly.
If the threshold is set correctly,
review your network to determine the
action necessary to clear the fault
condition.
Verify that the fault threshold is set
correctly.
If the threshold is set correctly,
review your network to determine the
action necessary to clear the fault
condition.
2-8
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
OL-8376-01
Page 83

Chapter 2 Fault Descriptions
Radio Interface Faults
Table 2-2 Radio Interface Faults (continued)
Fault Description Explanation Related Setting Recommended Action
Appeared up|down.
Compensated for by
Up/Down radio(s).
Broadcast SSID is
enabled.
Broadcast is enabled for
Radio-x SSID ssid fault.
Client association rate
is Degraded number per
minute
Client association rate
is Overloaded number
per minute
The indicated radio appeared up or
down on this AP, so other radios
were modified to maintain
coverage.
After self healing has been applied
to the other AP, this fault indicates
the radio that had the failure.
The broadcast mode for the SSID
on the interface has been disabled.
When this fault is cleared, the
following message displays:
Broadcast SSID is disabled.
An SSID, which you do not want
broadcast, is being broadcast.
When this fault is cleared, the
following message displays:
Broadcast is disabled for Radio-x
SSID ssid fault.
The fault threshold set for the
degraded state has been exceeded.
When this fault is cleared, the
following message displays: Client
association rate is OK.
The fault threshold set for the
overloaded state has been
exceeded.
Radio Manager > Self
Healing > Finish
Manage Fault
Settings >
Radio-802.11x
Policies > Broadcast
Disabled
Manage Fault
Settings >
Radio-802.11x
Policies > Broadcast
SSID
Manage Fault
Settings >
Radio-802.11x
Thresholds >
Association Rate
Display the Self Healing fault details
page, then select the document with
the eyeglasses. A list of radios with
the old and new power settings is
displayed. These radios can
compensate for the downed or
recovered radio. If self healing is
configured to automatically apply
changes, then these are the values
that were applied. If self healing is
configured for manual application of
the compensation calculations, then
the recommended values are shown
with an option to apply them to the
indicated radios.
Check the radio to determine why it
is down and resolve the problem.
Log in to the access point and disable
the broadcast mode.
Log in to the access point and make
sure that the that the SSID, which is
in WLSE’s “Do not Broadcast SSID”
list is not selected for Broadcast on
the access point.
Verify that the fault threshold is set
correctly.
If the threshold is set correctly,
review your network to determine the
action necessary to clear the fault
condition.
Compensation
determination is in
progress
OL-8376-01
When this fault is cleared, the
following message displays: Client
association rate is OK.
The WLSE determined that a radio
was down or back up. Self Healing
is attempting to compensate for the
failed or recovered radio.
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
Not applicable. There is no action necessary; Self
Healing is attempting to adjust the
power on other neighboring radios
(which can be on other floors) to
maintain coverage.
2-9
Page 84
Chapter 2 Fault Descriptions
Radio Interface Faults
Table 2-2 Radio Interface Faults (continued)
Fault Description Explanation Related Setting Recommended Action
Compensation
calculation did not
complete due to errors
Compensation finished
with errors
Errors forced the cancellation of
Self Healing compensation
calculations.
Self Healing compensation
calculations finished but there
were errors. For example, a power
change cannot be applied to a radio
because:
1) The community strings for the
device are wrong for the AP.
2) AP is down or unreachable
Not applicable. Display the Self Healing fault details
page, then select the document with
the eyeglasses. The error messages
displayed on this page will explain
the problem.
Determine the action necessary to
clear the fault condition.
Not applicable. Determine the action necessary to
clear the fault condition.
For example, if WLSE determines
that five radios are needed to
compensate for a down radio and
only one has bad community strings,
the changes to the other four radios
will take place.
3) Wrong configuration set on the
radio
Compensation did not
complete due to timeout
of timeout (mins)
Self Healing compensation
calculations took longer than 30
minutes.
EAP is disabled The EAP per SSID has been
disabled.
When this fault is cleared, the
following message displays: EAP
is enabled
Infrastructure SSID
policy violation
The infrastructure SSID does not
match the infrastructure SSID set
on the access point.
When this fault is cleared, the
following message displays:
Infrastructure SSID is valid.
Not applicable. Display the Self Healing fault details
page, then select the document with
the eyeglasses. The error messages
displayed on this page will explain
the problem.
Determine the action necessary to
clear the fault condition.
Manage Fault
Settings >
Radio-802.11x
Log in to the access point and enable
the Network EAP and Open
authentication.
Policies >
EAP Enforced for
Cisco Supplicant/
Non-Cisco
Supplicant/
Mixed-Cisco
Supplicant
Manage Fault
Settings >
Radio-802.11x
Policies >
Log in to the access point and make
sure the WLSE’s Infrastructure SSID
matches the access point
infrastructure SSID
Infrastructure SSID
2-10
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
OL-8376-01
Page 85
Chapter 2 Fault Descriptions
Radio Interface Faults
Table 2-2 Radio Interface Faults (continued)
Fault Description Explanation Related Setting Recommended Action
Not Monitored because:
reason, Ignored
Number of CCMP
Replay Discarded is
Overloaded.
Packet Error is in
Degraded state (error
rate %)
To qualify for Self Healing, an AP
must:
• Enable Radio Monitoring on
both Serving and Non-Serving
channels.
• Be configured with a WDS
that is authenticated with the
WLSE (link status must be
okay too).
The fault threshold set for the
overloaded state has been
exceeded.
When the fault is cleared, the
following message displays:
Number of CCMP Replays
Discarded is OK.
The fault threshold set for the
degraded state has been exceeded.
When this fault is cleared, the
following message displays:
Packet Error is in OK state.
The radio interfaces on the devices
may be very under utilized, which
can trigger the degradation
problem.
IDS > Manage IDS
Settings >
IDS-802.11x >
CCMP Replays
Discarded
Manage Fault
Settings >
Radio-802.11x
Thresholds > RF Port
Packet Errors
The faults will clear when the
WDS/WLSE is reauthenicated and
Radio Monitoring is enabled
correctly.
Verify that the fault threshold is set
correctly.
If the threshold is set correctly,
review your network to determine the
action necessary to clear the fault
condition.
Verify that the fault threshold is set
correctly.
If the threshold is set correctly,
review your network to determine the
action necessary to clear the fault
condition.
Remove the alarm from the profile
associated with these devices.
Packet Error is in
Overloaded state (error
rate %)
Port is administratively
set to down
OL-8376-01
For example, if a total of three
packets are sent over the radio, and
two of them are corrupt, the
percentage would be 2/3 = 66%,
and could trigger the alarm.
The fault threshold set for the
overloaded state has been
exceeded.
When this fault is cleared, the
following message displays:
Packet Error is in OK state.
The port has been set to Down by
the administrator.
When this fault is cleared, the
following message displays: Port is
up
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
Manage Fault
Settings >
Radio-802.11x
Thresholds > RF Port
Status
Verify that the fault threshold is set
correctly.
If the threshold is set correctly,
review your network to determine the
action necessary to clear the fault
condition.
There is no action necessary; the port
has been deliberately shut down.
2-11
Page 86
Chapter 2 Fault Descriptions
Radio Interface Faults
Table 2-2 Radio Interface Faults (continued)
Fault Description Explanation Related Setting Recommended Action
Port is down The port is operationally down.
When this fault is cleared, the
following message displays: Port is
up
PSPF is disabled The PSPF port has been disabled.
PSPF (Publicly Secure Packet
Forwarding) is a feature that
prevents client devices associated
to a bridge or access point from
inadvertently sharing files with
other client devices on the wireless
network.
Manage Fault
Settings >
Radio-802.11x
Thresholds > RF Port
AdminStatus
Manage Fault
Settings > Access
Point/Bridge Policies
> PSPF Enabled
Check the device to determine why
the port is down.
If you have added or removed an
interface from an access point, the
WLSE might generate an erroneous
fault. See Q.What are the results of
adding or removing an interface from
an access point?, page 1-16.
The fault RF Port AdminStatus is
enabled by default and must remain
enabled with a default polling time of
5 minutes. Self healing ignores any
radio set as administratively down,
but this can only be detected if fault
polling is enabled.
Log in to the access point and enable
the PSPF setting.
Requires healing:
%reason%.
When the fault is cleared, the
following message displays: The
PSPF is enabled.
The indicated radio appeared up or
down on this AP. Self Healing has
been started.
After compensation results have
been for other radios, this fault
indicates the radio that had the
failure.
Not applicable. There is no action necessary; Self
Healing will attempt to adjust the
power on other radios on the floor to
maintain coverage.
Possible reasons self healing is
required:
• An applicable radio is avoiding
or no longer avoiding radar.
• An AP has unregistered or
re-registered with its WDS
• A radio that had its beacons
heard by other radios has not
been heard by any radio (and
vice-versa)
2-12
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
OL-8376-01
Page 87
Chapter 2 Fault Descriptions
Radio Interface Faults
Table 2-2 Radio Interface Faults (continued)
Fault Description Explanation Related Setting Recommended Action
Retry Count rate is
Degraded number per
minute
Retry Count rate is
Overloaded number per
minute
RF bandwidth
utilization is Degraded
(utilization %)
RF bandwidth
utilization is
Overloaded
(utilization %)
Serving and
non-serving channel
Radio Monitoring must
be enabled
The retry count rate alarm
indicates if the wireless medium is
congested. The alarm will be raised
if the MSDU retransmission rate
per minute is greater than the
specified threshold. For example,
if the overloaded state is set to
greater than 90, a fault will be
raised for an interface that has
more than 90 MSDUs that required
retransmission in a minute.
When the fault is cleared, the
following message displays: Retry
Count rate is OK.
The fault threshold set for the
degraded state has been exceeded.
When the fault is cleared, the
following message displays: RF
bandwidth utilization is OK
The fault threshold set for the
overloaded state has been
exceeded.
When the fault is cleared, the
following message displays: RF
bandwidth utilization is OK
For Self Healing to work, all radios
on the floor must be configured
with Radio Monitoring. The fault
will indicate which radios need to
be configured with both serving
and non serving radio monitoring.
Manage Fault
Settings >
Radio-802.11x
Thresholds > Max
Retry Count
Manage Fault
Settings >
Radio-802.11x
Thresholds > RF Port
Utilization
Not applicable. Enable Radio Monitoring for both
Verify the threshold settings. There
could be too many clients or access
points located near the radio
interface for which fault is raised.
Clear the alarm and increase the
threshold, or reduce the polling time.
Verify that the fault threshold is set
correctly.
If the threshold is set correctly,
review your network to determine the
action necessary to clear the fault
condition.
serving and non-serving channels.
Or, use the Location Manager tool,
Verify RM Capability.
OL-8376-01
When the fault is cleared, the
following message displays:
Qualifies for Self Healing
Monitoring.
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
2-13
Page 88

Chapter 2 Fault Descriptions
IDS (Intrusion Detection System) Faults
Table 2-2 Radio Interface Faults (continued)
Fault Description Explanation Related Setting Recommended Action
WEP Error is in
Degraded state (error
rate %)
WEP Error is in
Overloaded state (error
rate %)
WEP key length policy
violation
The fault threshold set for the
degraded state has been exceeded.
When this fault has been cleared,
the following message displays:
WEP Error is in OK state
The fault threshold set for the
overloaded state has been
exceeded.
When this fault has been cleared,
the following message displays:
WEP Error is in OK state
The WEP key length setting has
been violated.
When this fault has been cleared,
the following message displays:
WEP key length is OK.
Manage Fault
Settings >
Radio-802.11x
Thresholds > RF Port
WEP Errors
Manage Fault
Settings >
Radio-802.11x
Policies > WEP Key
Length
Verify that the fault threshold is set
correctly.
If the threshold is set correctly,
review your network to determine the
action necessary to clear the fault
condition.
Check the WEP key settings on the
interface to make sure they match the
WLSE settings.
IDS (Intrusion Detection System) Faults
Table 2-3 IDS Faults
Fault Description Explanation Related Setting Recommended Action
802.11-B/G Interference
Detected
- or -
802.11-A Interference
Detected
Ad-hoc network creation
detected: ssid
The WLSE detected a non-802.11
interference.
An ad-hoc network was formed
by some wireless clients (where
ssid is the Service Set Identifier
of the UnmanagedRadio’s BSS).
One of your infrastructure APs or
other clients sent this information
to the WLSE via your WDS
setup.
IDS > Manage
Network-Wide IDS
Settings >
Interference
Detection
IDS > Manage
Network-Wide IDS
Settings > Ad-hoc
Network Detection
Look at the fault description to
determine which AP reported the
interference, then take corrective
action by removing the interference
source.
If the information is available, the
WLSE will show the clients that are
participating in the network (and that
it can detect) in the fault details page.
Use the Location Manager to find
these APs and verify that this is not a
security issue.
2-14
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
OL-8376-01
Page 89
Chapter 2 Fault Descriptions
IDS (Intrusion Detection System) Faults
Table 2-3 IDS Faults (continued)
Fault Description Explanation Related Setting Recommended Action
Ad-hoc network ssid
reclassified from Friendly
to Rogue due to rule
An ad-hoc network that was
previously determined to be
Friendly has been reclassified to
Rogue.
ssid is the Service Set Identifier
of the unmanaged radio’s BSS.
rule is one of the following:
• Change in RSSI ordering
between observers
The estimated proximity of
the unmanaged radio
between two observers has
switched—if the WLSE
thought that observer A was
closer to radio R than
observer B, it now thinks that
observer B is closer to radio
R than observer A.
IDS > Manage
Network-Wide IDS
Settings > Ad-hoc
Network Detection >
Friendly to Rogue AP
Reclassification
or
IDS > Manage
Rogues
Use the fault details page to mark it
friendly if the network is known, or
to delete it from the WLSE database
if it is unknown.
• Difference in relative RSSI
between original and current
observers exceeded threshold
While radio R’s strength
changed by factor M between
observer A and observer B, it
changed by factor M+T
between observer B and
observer C. That is, it does
not appear that radio R’s
change in strength is merely
due to a change in its power
configuration.
• Fewer than two observers
• Too long without
observations
OL-8376-01
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
2-15
Page 90

Chapter 2 Fault Descriptions
IDS (Intrusion Detection System) Faults
Table 2-3 IDS Faults (continued)
Fault Description Explanation Related Setting Recommended Action
Bad MIC while MFP
enabled
Bad Sequence Number
while MFP enabled
CCMP
DecryptErrorsClient is
detected
CCMP Replay Client is
detected
Client association rate is
Degraded number per
minute
This fault is raised against the AP
that is observed generating the
violation.
This fault is raised against the AP
that is observed generating the
violation.
The fault threshold has been
exceeded for the number of
decryption errors detected by the
CCMP play mechanism on the
interface.
The fault threshold set has been
exceeded.
When this fault is cleared, the
following message displays:
There is no CCMP Replay
detected
The fault thresholds been
exceeded.
When this fault is cleared, the
following message displays:
Client association rate is OK.
Not applicable. Investigate the possibility that a
rogue AP is conducting a spoofing
attack against the managed network.
Also, make sure that an MFP
configuration error (see MFP
Configuration error (Detect disabled;
should be enabled), page 2-19) is not
the root cause of the MFP Validation
error. It is also possible that
communications problems between
the WDS and its registered APs have
prevented MFP key rotation
messages from reaching either the
detector or generator AP.
Not applicable. See Bad MIC while MFP enabled,
page 2-16).
IDS > Manage IDS
Settings >
CcmpDecryptErrorsC
lient
Verify that the fault threshold is set
correctly.
If the threshold is set correctly,
review your network to determine the
action necessary to clear the fault
condition.
IDS >
Manage IDS Settings
> General Settings >
CcmpReplaysClient
Verify that the fault threshold is set
correctly.
If the threshold is set correctly,
review your network to determine the
action necessary to clear the fault
condition.
IDS >
Manage IDS Settings
> IDS-802.11x >
Authentication Error
Rate
Verify that the fault threshold is set
correctly.
If the threshold is set correctly,
review your network to determine the
action necessary to clear the fault
condition
2-16
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
OL-8376-01
Page 91
Chapter 2 Fault Descriptions
IDS (Intrusion Detection System) Faults
Table 2-3 IDS Faults (continued)
Fault Description Explanation Related Setting Recommended Action
Client authentication error
rate is Degraded number
per minute
Client authentication error
rate is Overloaded number
per minute
Client TKIP
RemoteMICFailure is
detected
EAPOL FLOOD is
detected (Flood count:
floodcount)
Excessive Action Frames
in Channel: channel
[Frames:
framecount,Interval:wind
owsize]
Excessive Action Frames
from STA: station
[Frames:
framecount,Interval:wind
owsize]
The fault threshold set for the
degraded state has been exceeded.
When this fault is cleared, the
following message displays:
Client association error rate is
OK.
The fault threshold set for the
overloaded state has been
exceeded.
When this fault is cleared, the
following message displays:
Client association error rate is
OK.
A wireless client has detected a
MIC failure. The MIB value that
is polled is
cDot11WidsTkipRemoteMicFail
ures.
When this fault is cleared, the
following message displays:
There is no TKIP
RemoteMICFailure detected.
The fault threshold has been
exceeded.
When this fault is cleared, the
following message displays:
There is no EAPOL Flood
detected.
The fault thresholds been
exceeded.
When this fault is cleared, the
following message displays:
Excessive Action Frames not
present in Channel.
The fault thresholds been
exceeded.
When this fault is cleared, the
following message displays:
Excessive Action Frames from
STA: station not present
IDS >
Manage IDS Settings
> IDS-802.11x >
Authentication Error
Rate
IDS >
Manage IDS Settings
> General IDS
Settings >
TkipRemoteMicFailu
reClient
IDS >
Manage IDS Settings
> General IDS
Settings > EAPOL
Detection
IDS > Manage IDS
Settings > General
IDS Settings >
Excessive
Management Frame
Detection
IDS > Manage IDS
Settings > General
IDS Settings >
Excessive
Management Frame
Detection
Verify that the fault threshold is set
correctly.
If the threshold is set correctly,
review your network to determine the
action necessary to clear the fault
condition.
Occasionally MIC failures can occur
during key rotation. To diagnose the
problem, you should:
• Check the IOS version.
• Enable 802.1x logs on the AP.
• Perform an SNMP walk of
cDot11WidsProtectFailClientTa
ble to determine which clients
are reporting the TKIP MIC
failure. If just one client is
reporting the failure, it could be
a client issue
Verify that the fault threshold is set
correctly.
If the threshold is set correctly,
review your network to determine the
action necessary to clear the fault
condition
Verify that the fault threshold is set
correctly.
If the threshold is set correctly,
review your network to determine the
action necessary to clear the fault
condition.
Verify that the fault threshold is set
correctly.
If the threshold is set correctly,
review your network to determine the
action necessary to clear the fault
condition.
OL-8376-01
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
2-17
Page 92

Chapter 2 Fault Descriptions
IDS (Intrusion Detection System) Faults
Table 2-3 IDS Faults (continued)
Fault Description Explanation Related Setting Recommended Action
Excessive Association
Frames in Channel:
channel [Frames:
framecount,Interval:wind
owsize]
Excessive Association
Frames from STA: station
[Frames:
framecount,Interval:wind
owsize]
Excessive Authentication
Frames in Channel:
channel [Frames:
framecount,Interval:wind
owsize]
Excessive Authentication
Frames from STA: station
[Frames:
framecount,Interval:wind
owsize]
Excessive
Deauthentication Frames
in Channel: channel
[Frames:
framecount,Interval:wind
owsize]
Excessive
Deauthentication Frames
from STA: station
[Frames:
framecount,Interval:wind
owsize]
Excessive Disassociation
Frames in Channel:
channel [Frames:
framecount,Interval:wind
owsize]
The fault thresholds been
exceeded.
When this fault is cleared, the
following message displays:
Excessive Association Frames
not present in Channel: channel
The fault thresholds been
exceeded.
When this fault is cleared, the
following message displays:
Excessive Association Frames
from STA: station not present
The fault thresholds been
exceeded.
When this fault is cleared, the
following message displays:
Excessive Authentication Frames
not present in Channel.
The fault thresholds been
exceeded.
When this fault is cleared, the
following message displays:
Excessive Authentication Frames
from STA: station not present
The fault thresholds been
exceeded.
When this fault is cleared, the
following message displays:
Excessive Deauthentication
Frames not present in Channel.
The fault thresholds been
exceeded.
When this fault is cleared, the
following message displays:
Excessive Deauthentication
Frames from STA: station not
present
The fault thresholds been
exceeded.
When this fault is cleared, the
following message displays:
Excessive Disassociation Frames
not present in Channel.
IDS > Manage IDS
Settings > General
IDS Settings >
Excessive
Management Frame
Detection
IDS > Manage IDS
Settings > General
IDS Settings >
Excessive
Management Frame
Detection
IDS > Manage IDS
Settings > General
IDS Settings >
Excessive
Management Frame
Detection
IDS > Manage IDS
Settings > General
IDS Settings >
Excessive
Management Frame
Detection
IDS > Manage IDS
Settings > General
IDS Settings >
Excessive
Management Frame
Detection
IDS > Manage IDS
Settings > General
IDS Settings >
Excessive
Management Frame
Detection
IDS > Manage IDS
Settings > General
IDS Settings >
Excessive
Management Frame
Detection
Verify that the fault threshold is set
correctly.
If the threshold is set correctly,
review your network to determine the
action necessary to clear the fault
condition.
Verify that the fault threshold is set
correctly.
If the threshold is set correctly,
review your network to determine the
action necessary to clear the fault
condition.
Verify that the fault threshold is set
correctly.
If the threshold is set correctly,
review your network to determine the
action necessary to clear the fault
condition.
Verify that the fault threshold is set
correctly.
If the threshold is set correctly,
review your network to determine the
action necessary to clear the fault
condition.
Verify that the fault threshold is set
correctly.
If the threshold is set correctly,
review your network to determine the
action necessary to clear the fault
condition.
Verify that the fault threshold is set
correctly.
If the threshold is set correctly,
review your network to determine the
action necessary to clear the fault
condition.
Verify that the fault threshold is set
correctly.
If the threshold is set correctly,
review your network to determine the
action necessary to clear the fault
condition.
2-18
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
OL-8376-01
Page 93

Chapter 2 Fault Descriptions
IDS (Intrusion Detection System) Faults
Table 2-3 IDS Faults (continued)
Fault Description Explanation Related Setting Recommended Action
Excessive Disassociation
Frames from STA: station
[Frames:
framecount,Interval:wind
owsize]
Excessive Probe Frames
in Channel: channel
[Frames:
framecount,Interval:wind
owsize]
Excessive Probe Frames
from STA: station
[Frames:
framecount,Interval:wind
owsize]
Excessive Reassociation
Frames in Channel:
channel [Frames:
framecount,Interval:wind
owsize]
Excessive Reassociation
Frames from STA: station
[Frames:
framecount,Interval:wind
owsize]
MFP Configuration error
(Detect disabled; should
be enabled)
MFP Timebase Invalid
(bad SNTP)
No MIC while MFP
Enabled
The fault thresholds been
exceeded.
When this fault is cleared, the
following message displays:
Excessive Disassociation Frames
from STA: station not present
The fault thresholds been
exceeded.
When this fault is cleared, the
following message displays:
Excessive Probe Frames not
present in Channel.
The fault thresholds been
exceeded.
When this fault is cleared, the
following message displays:
Excessive Probe Frames from
STA: station not present
The fault thresholds been
exceeded.
When this fault is cleared, the
following message displays:
Excessive Reassociation Frames
not present in Channel.
The fault thresholds been
exceeded.
When this fault is cleared, the
following message displays:
Excessive Reassociation Frames
from STA: station not present
This fault is raised against an AP
that contains an MFP-related
configuration error.
Note No fault is raised against
an AP that does not
support MFP.
This fault is raised against an AP
that has a bad timebase.
This fault is raised against the AP
that is observed generating the
violation.
IDS > Manage IDS
Settings > General
IDS Settings >
Excessive
Management Frame
Detection
IDS > Manage IDS
Settings > General
IDS Settings >
Excessive
Management Frame
Detection
IDS > Manage IDS
Settings > General
IDS Settings >
Excessive
Management Frame
Detection
IDS > Manage IDS
Settings > General
IDS Settings >
Excessive
Management Frame
Detection
IDS > Manage IDS
Settings > General
IDS Settings >
Excessive
Management Frame
Detection
Not applicable. Restart the affected AP.
Configure >
Templates > Services
> SNTP
Not applicable. See Bad MIC while MFP enabled,
Verify that the fault threshold is set
correctly.
If the threshold is set correctly,
review your network to determine the
action necessary to clear the fault
condition.
Verify that the fault threshold is set
correctly.
If the threshold is set correctly,
review your network to determine the
action necessary to clear the fault
condition.
Verify that the fault threshold is set
correctly.
If the threshold is set correctly,
review your network to determine the
action necessary to clear the fault
condition.
Verify that the fault threshold is set
correctly.
If the threshold is set correctly,
review your network to determine the
action necessary to clear the fault
condition.
Verify that the fault threshold is set
correctly.
If the threshold is set correctly,
review your network to determine the
action necessary to clear the fault
condition.
Configure the AP to reference an
SNTP server.
page 2-16).
OL-8376-01
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
2-19
Page 94

Chapter 2 Fault Descriptions
IDS (Intrusion Detection System) Faults
Table 2-3 IDS Faults (continued)
Fault Description Explanation Related Setting Recommended Action
Number of CCMP Replay
Discarded is Degraded.
Number of CCMP Replay
Discarded is Overloaded.
Number of EAPOL Flood
Count is Degraded
Number of EAPOL Flood
Count is Overloaded
The fault threshold set for the
degraded state has been exceeded.
When the fault is cleared, the
following message displays:
Number of CCMP Replays
Discarded is OK.
The fault threshold set for the
overloaded state has been
exceeded.
When the fault is cleared, the
following message displays:
Number of CCMP Replays
Discarded is OK.
The fault threshold set for the
degraded state has been exceeded.
When this fault is cleared, the
following message displays:
EAPOL Flood Count is OK.
The fault threshold set for the
overloaded state has been
exceeded.
IDS >
Manage IDS Settings
> IDS-802.11x
>CCMP Replays
Discarded
IDS >
Manage IDS Settings
> General IDS
Settings > EAPOL
Detection
Verify that the fault threshold is set
correctly.
If the threshold is set correctly,
review your network to determine the
action necessary to clear the fault
condition.
Verify that the fault threshold is set
correctly.
If the threshold is set correctly,
review your network to determine the
action necessary to clear the fault
condition.
Number of TKIP counter
measure is Degraded.
Number of TKIP counter
measure is Overloaded.
When this fault is cleared, the
following message displays:
EAPOL Flood Count is OK.
The fault threshold set for the
degraded state has been exceeded.
When the fault is cleared, the
following message displays:
Number of TKIP Counter
Measure is OK.
The fault threshold set for the
overloaded state has been
exceeded.
When the fault is cleared, the
following message displays:
Number of TKIP Counter
Measure is OK.
IDS >
Manage IDS Settings
> IDS-802.11x
>TKIP Counter
Measure Invoked
Verify that the fault threshold is set
correctly.
If the threshold is set correctly,
review your network to determine the
action necessary to clear the fault
condition.
2-20
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
OL-8376-01
Page 95

Chapter 2 Fault Descriptions
IDS (Intrusion Detection System) Faults
Table 2-3 IDS Faults (continued)
Fault Description Explanation Related Setting Recommended Action
Number of TKIP Local
MIC failures is Degraded.
Number of TKIP Local
MIC failures is
Overloaded.
Number of TKIP Remote
MIC failures is Degraded.
Number of TKIP Remote
MIC failures is
Overloaded.
The fault threshold set for the
degraded state has been exceeded.
When the fault is cleared, the
following message displays:
Number of TKIP Local MIC
failures is OK.
The fault threshold set for the
overloaded state has been
exceeded.
When the fault is cleared, the
following message displays:
Number of TKIP Local MIC
failures is OK.
The fault threshold set for the
degraded state has been exceeded.
When the fault is cleared, the
following message displays:
Number of TKIP Remote MIC
failures is OK.
The fault threshold set for the
overloaded state has been
exceeded.
IDS >
Manage IDS Settings
> IDS-802.11x
>TKIP Local MIC
failures
IDS >
Manage IDS Settings
> IDS-802.11x
>TKIP Remote MIC
failures
Verify that the fault threshold is set
correctly.
If the threshold is set correctly,
review your network to determine the
action necessary to clear the fault
condition.
Verify that the fault threshold is set
correctly.
If the threshold is set correctly,
review your network to determine the
action necessary to clear the fault
condition.
Number of TKIP replay
errors is Degraded.
Number of TKIP replay
errors is Overloaded.
When the fault is cleared, the
following message displays:
Number of TKIP Remote MIC
failures is OK.
The fault threshold set for the
degraded state has been exceeded.
When the fault is cleared, the
following message displays:
Number of TKIP replay errors is
OK.
The fault threshold set for the
overloaded state has been
exceeded.
When the fault is cleared, the
following message displays:
Number of TKIP replay errors is
OK.
IDS >
Manage IDS Settings
> IDS-802.11x
>TKIP Replays
Detected
Verify that the fault threshold is set
correctly.
If the threshold is set correctly,
review your network to determine the
action necessary to clear the fault
condition.
OL-8376-01
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
2-21
Page 96
Chapter 2 Fault Descriptions
IDS (Intrusion Detection System) Faults
Table 2-3 IDS Faults (continued)
Fault Description Explanation Related Setting Recommended Action
Radio Role must be
“roleScanner” to support
Frame Monitoring (was
x).
This fault is raised when a radio is
initially configured for Frame
Monitoring (where x is the integer
value of the SNMP OID
cd11IfStationRole from the
CISCO-DOT11-IF-MIB), but
then someone configures the
radio out of scanning-only mode.
As a side effect, this also disables
Frame Monitoring.
When this fault is cleared, the
following message displays:
Radio Role is “roleScanner” and
supports Frame Monitoring.
TKIP Replay is detected The fault threshold set has been
exceeded.
When this fault is cleared, the
following message displays:
There is no TKIP Replay
detected.
TKIP LocalMICFailure is
detected
The fault threshold set has been
exceeded.
When this fault is cleared, the
following message displays:
There is no TKIP
LocalMICFailure detected.
Unexpected MIC while
MFP Disabled
This fault is raised against the AP
that is observed generating the
violation.
Radio Mgr > Frame
Monitoring
IDS >
Manage IDS Settings
> General IDS
Settings >
TkipReplayClient
IDS >
Manage IDS Settings
> General IDS
Settings >
TkipLocalMicFailure
Client
Not applicable. See Bad MIC while MFP enabled,
Review your network to determine
the action necessary to clear the fault
condition.
Although this situation might simply
be that an administrator no longer
needs to monitor or scan a portion of
their site any longer, it could also be
an intruder who has somehow gained
console access to a Scanning AP and
is attempting to “blind” IDS services
for a portion of a site.
Verify that the fault threshold is set
correctly.
If the threshold is set correctly,
review your network to determine the
action necessary to clear the fault
condition.
Verify that the fault threshold is set
correctly.
If the threshold is set correctly,
review your network to determine the
action necessary to clear the fault
condition.
page 2-16).
2-22
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
OL-8376-01
Page 97
Chapter 2 Fault Descriptions
IDS (Intrusion Detection System) Faults
Table 2-3 IDS Faults (continued)
Fault Description Explanation Related Setting Recommended Action
Unregistered Client(s)
present
One or more unregistered clients
have been detected in the wireless
network, and are unsucessfully
attempting to authenticate with
the APs.
The unregistered client fault is
triggered when an AP in scanning
mode detects a number of probe
requests and association requests
from a station, client, or access
point, which crosses the
configuired threshold in the
configured time.
The registration attempts are not
being made to the scanning AP;
the attempts are being made to
regular APs that the scanning AP
notices.
IDS >
Manage IDS Settings
> General IDS
Settings >
Unregistered Client
Set the priority of the fault to be
generated and the threshold for the
failed authentication attempts by the
client.
Make a physical check near the
scanning AP that reported this fault
to see if there are any rogue clients.
Wireless Client MAC
spoofing detected
The scanning AP counts the
packets per station.
(The fault is generated based on
the configured Client
Registration Request Count
within a 15-minute period. The
default is 100 registrations, but
can be changed to 200, 300, 400
or 500. )
This fault is cleared when no
registration attempts are detected
during the observation interval
(the client leaves the wireless
network or is not seen or reported
by any Scanning APs).
The WLSE has detected a
spoofed MAC address.
Whenever the WDS detects an
authentication taking place for a
known MAC address, it verifies
that the same user ID is being
used. If the user ID does not
match, the authentication is
rejected and a fault is issued.
IDS >
Manage IDS Settings
> General IDS
Settings > Wireless
Client MAC Spoofing
Review your network to determine
the action necessary to clear the fault
condition.
OL-8376-01
When this fault is cleared, the
following message displays: No
Wireless Client MAC Spoofing
Detected.
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
2-23
Page 98
Chapter 2 Fault Descriptions
Voice Faults
Voice Faults
Ta b l e 2 - 4 V o ic e F a ul t s
Fault Description Explanation Related Setting Recommended Action
Voice Bandwidth Exceeded
[Bandwidth In
Use:current%,Threshold:
threshold%]
This is a warning that is
triggered only when the voice
bandwidth in use exceeds the
threshold limit.
The higher the percentage of
bandwidth being used, the less is
available for new phone calls to
be placed or to roam in. The
default configured bandwidth for
voice is 75%. After reaching
100% of the configured
bandwidth in use, no additional
calls can be accepted.
Faults > Manage
Fault Settings, then
Edit the Default
profile. Select
RADIO-802.11a
THRESHOLDS >
Voice Bandwidth.
You can (at the expense of data traffic
clients such as laptops) increase the
amount of bandwidth reserved for
voice traffic. But a better solution
would be to find a solution that would
reduce the voice traffic on the
congested cell.
WLSE Faults
Table 2-5 WLSE Faults
Fault Description Explanation Related Setting Recommended Action
Auto Resite Survey
Performance
Degradations
Data may not have
been successfully
restored from active.
There is at least one floor with a
20% difference in the base and
current performance values on one
or more floors configured for Auto
Re-Site Survey.
The fault will clear when there are
no longer any buildings or any
floors with 20% differences in the
performance values.
The standby WLSE has detected a
failure in the active WLSE and is
becoming active before it
successfully synchronized with the
active WLSE.
Radio Manager >
Auto Re-Site
Survey
Not applicable. Make sure the WLSEs are correctly
Select the document with the eyeglasses in
the detail view of the fault condition. A list
of all buildings and floors that have
performance degradations is displayed.
First, check the details for the floor and if
needed, run Radio Manager Assisted
Configuration. Then select Auto Re-Site
Survey to set the new base values.
configured and functioning properly.
2-24
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
OL-8376-01
Page 99
Chapter 2 Fault Descriptions
Table 2-5 WLSE Faults
Fault Description Explanation Related Setting Recommended Action
Duplicate IP Detection During discovery, an AP with a
duplicate IP is found and placed in
the Duplicate IP folder under
Devices > Managed >
Manage/Unmanage.
This folder contains access points
that are in the pending state.
A device becomes pending and is
placed in this folder when:
• The same IP address is
assigned to more than one
access point.
• An access point’s IP address
changes.
• You replace a managed access
point.
Manage Fault
Settings >
Thresholds >
WLSE >
Duplicate IP
detection
For information on how to move devices
from the Duplicate IP folder, see the topic:
Handling Duplicate IP Addresses on Access
Points in the Managing Devices chapter of
the User Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless
LAN Solution Engine, 2.13. or in the online
help.
WLSE Faults
Fault Engine is
overloaded with
excessive polling.
Lost connectivity with
router.
Lost connectivity with
standby on ip_address.
The IP address shown for a device
in this folder is the last known
address for the device, before the
address change occurred.
The WLSE fault engine is
overloaded due a large number of
fault policy and threshold polling
occurring at one time. This
generally occurs when the WLSE
is configured to monitor large
number of fault policies and
thresholds on large number of
devices.
This fault will clear when the
polling rate drops below the
internally set threshold.
The WLSE is unable to ping the
default router.
The standby WLSE indicated by
the IP address is down.
Not applicable.
• Make sure the WLSE has connectivity
to the network.
• Reduce the amount of fault polling by
disabling certain policies and
thresholds.
Not applicable. Make sure that:
• Connectivity from the WLSE to the
gateway router is okay.
• The gateway router is functioning
properly.
Not applicable. Make sure that:
• The standby WLSE is up and running.
OL-8376-01
• The standby WLSE is network
accessible.
• Redundancy has been correctly setup
on the Active WLSE.
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
2-25
Page 100
Chapter 2 Fault Descriptions
AAA Server Faults
Table 2-5 WLSE Faults
Fault Description Explanation Related Setting Recommended Action
Other node is running
a different version.
Redundancy will be
turned off.
Redundancy active
mode enabled
Redundancy standby
mode.
Redundancy turned
off.
Regained connectivity
with router.
Regained connectivity
with standby on
ip_address
System check failed on
ip_address for reason:
reason.
A mismatch of WLSE software
version has been detected between
the active and the standby WLSEs.
The WLSE sending this message is
now active.
The WLSE sending this message is
now in standby mode.
Redundancy has been disabled. Not applicable. Make sure the WLSEs are correctly
The WLSE that sent this message
is now able to ping the default
router.
The Standby WLSE is up. Not applicable. Confirm that both WLSEs are functioning
The system check failed. Not applicable. Make sure the WLSEs are correctly
Not applicable. Make sure the correct WLSE software has
been installed on both the active and
standby WLSEs.
Not applicable. Confirm that both WLSEs are functioning
respectively as Active and Standby.
Not applicable. Confirm that both WLSEs are functioning
respectively as Active and Standby.
configured and functioning properly.
Not applicable. Confirm that both WLSEs are functioning
respectively as Active and Standby.
respectively as Active and Standby.
configured and functioning properly.
AAA Server Faults
Table 2-6 AAA Server Faults
Fault Description Server Type Explanation Related Setting Recommended Action
Authentication
failed. Please check
EAP-FAST,
EAP-MD5, LEAP,
PEAP, or RADIUS
credentials
All AAA
Servers
Server is reachable but
credentials are incorrect.
When this fault has been
cleared, the following
message displays:
Authentication succeeded
Manage Fault
Settings > AAA >
EAP-FAST/
EAP-MD5 /LEAP/
PEAP/RADIUS>
Response Time
Make sure that the credentials are
set correctly by selecting Devices >
Discover > AAA Server.
2-26
FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide for the CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
OL-8376-01
 Loading...
Loading...