Page 1

CHA PT ER
HTTP Client Requests and Header
Settings
This chapter contains the following sections:
• HTTP Client Requests
• HTTP Header Settings
–
HTTP Refresh Setting
–
MIME Type and Other HTTP Headers
–
Content Expiration Header Setting
• Identifying the Capabilities of IP Phone Clients
–
x-CiscoIPPhoneModelName
–
x-CiscoIPPhoneDisplay
–
x-CiscoIPPhoneSDKVersion
• Accept Header
5
HTTP Client Requests
The following procedure designates how HTTP client requests are handled:
• The Cisco IP Phone HTTP client performs an HTTP GET for a specified
URL.
• The HTPP server processes request and returns an XML object or plain text.
OL-5375-01
Cisco IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
5-61
Page 2

HTTP Header Settings
• The phone processes the supported HTTP headers.
• The phone parses the XML object if ContentType is text/xml.
• The phone presents data and options to the user per the server response.
HTTP Header Settings
The following list provides definitions for HTTP header elements for
Cisco IP Phone services:
• “Refresh” (Time in Seconds, URL)
–
If no time is set or it is zero, the refresh gets set to manual.
–
If no URL is set, the current URL gets used.
See “HTTP Refresh Setting” for details.
• “ContentType” — The ContentType notifies the phone of the MIME type that
was sent. See the “MIME Type and Other HTTP Headers” section.
• “Expires” — Expires sets the Date/Time in GMT when the page is to expire.
Pages that have expired before being loaded do not get added to the URL
stack in the phone. The phone does not cache content. See “Content
Expiration Header Setting” for more information.
Chapter 5 HTTP Client Requests and Header Settings
HTTP Refresh Setting
The HTTP headers that are sent with any page from an HTTP server can include
a Refresh setting. This setting comprises two parameters: a time in seconds and a
URL. These two parameters direct the recipient to wait the time given in the
seconds parameter and then get the data to which the URL points.
The Cisco IP Phone HTTP client properly supports this setting, which gives a
great deal of power to service developers. It means that a new page can replace
any XML object that displays after a fixed time.
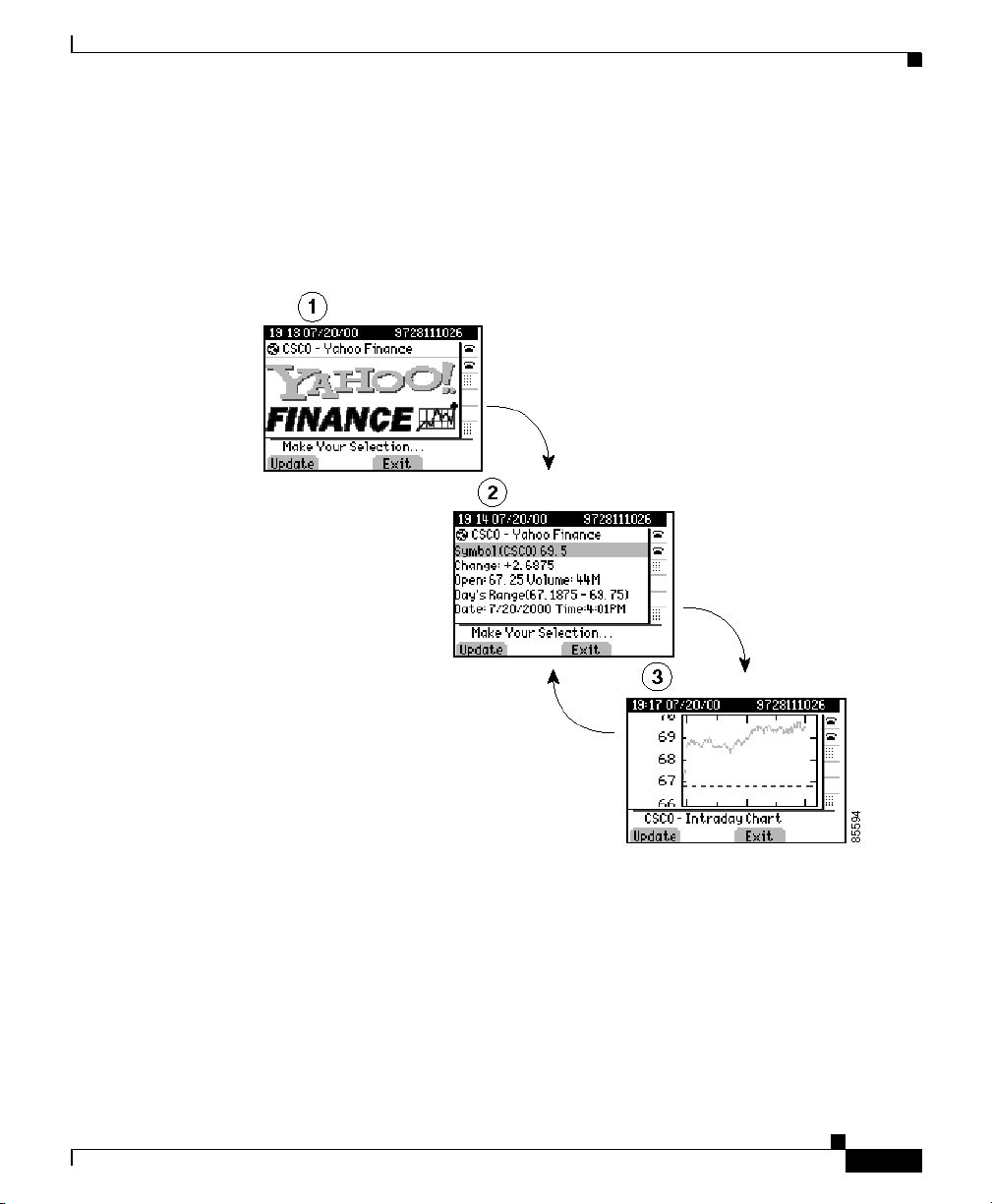
Figure 1 shows a good example of how to use the refresh setting. This sample
page shows the user the current value of Cisco stock.
1. A splash screen that displays the Yahoo logo.
Cisco IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
5-62
OL-5375-01
Page 3
Chapter 5 HTTP Client Requests and Header Settings
2. After a very short time, it displays the numeric Cisco stock parameters.
3. Finally, it shows a graph of Cisco intraday stock performance. The display
then repeatedly cycles between the final two views.
Figure 1 Refresh Display Sample
HTTP Header Settings
OL-5375-01
Refreshing the display can occur without user intervention, because the display
automatically cycles if a timer parameter is specified. On any given screen,
however, the user can force an immediate reload by pressing the Update softkey.
Also, if a timer parameter of 0 was sent in the header, the page never automatically
reloads. In this case, the display will move to the next page only when the Update
softkey is pressed. If no refresh URL is specified, the current page gets reloaded.
Cisco IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
5-63
Page 4

HTTP Header Settings
MIME Type and Other HTTP Headers
Although delivering pages with the proper MIME type and other formatting items
is not difficult, it requires moderately indepth knowledge of your web server. The
following code excerpt, written in JavaScript and used with Microsoft IIS and
ASP, sets these values in a few lines:
<%@ Language=JavaScript %>
<%
Response.AddHeader( "Refresh",
"3; url=http://services.cisco.com/s/q.asp");
Response.ContentType = "text/xml";
//
// Additional page content here
//
%>
Usually, you can set the MIME type for pages in any web server by simply
performing an association to the .xml file extension. Your web server
documentation should explain how to accomplish this. This action allows you to
serve static pages without the need for writing script.
If you want to deliver dynamic content by using the other supported HTTP
headers, you will need to understand how to generate the HTTP headers by using
the desired programming language and have common gateway interface (CGI) or
script access on the target web server.
Chapter 5 HTTP Client Requests and Header Settings
Audio Clips
5-64
You can serve audio clips to the phone from a web server by using the
"audio/basic" MIME type setting. When this MIME type is used, the body of the
response should contain raw audio data in the same format that is used for custom
Cisco IP Phone rings. Refer to the chapter on “Custom Phone Rings” in the
Cisco CallManager System Guide (also available in the online help).
Note The audio file should not be longer than 5 seconds.
Cisco IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
OL-5375-01
Page 5

Chapter 5 HTTP Client Requests and Header Settings
Use the following ASP sample script to set the MIME type and to serve the file
that is specified in the #include command:
<%@ Language=JavaScript%>
<%
Response.ContentType = "audio/basic";
%><!--#include file="filename.raw" --><% Response.End();%>
Using script to generate the MIME header when playing a sound provides an
advantage because you may also include a refresh header to take the phone to a
subsequent URL. Usually, you can set the MIME type for pages in any web server
by simply performing an association to the .xml or .raw file extension. Your web
server documentation should explain how to accomplish this. This action allows
you to serve static pages without the need for writing script.
Content Expiration Header Setting
The expiration header can control which URLs are added to the phone URL
history. This behavior differs slightly from traditional web browsers but is
implemented to perform the same function. Disable the back button functionality
to avoid calling a URL twice.
HTTP Header Settings
OL-5375-01
This functionality allows you to make the content of any page that is sent to the
phone expire. When a user presses the Exit softkey, the user goes back to the last
URL that did not expire when it was loaded. This differs from traditional browsers
by not considering the current freshness of the data but the freshness of the data
when the URL was requested. This requires you to have a page expire when it is
first loaded and to not set a time and date in the future.
The following example shows how to have content on IIS expire by using
Active Server Page (ASP):
<%@ Language=JavaScript %>
<%
Response.ContentType = "text/xml";
Response.Expires = -1;
%>
The "Expires" property specifies the number of minutes to wait for the content to
expire. Setting this value to -1 subtracts 1 minute from the request time and
returns a date and time that have already passed.
Cisco IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
5-65
Page 6

Chapter 5 HTTP Client Requests and Header Settings
Identifying the Capabilities of IP Phone Clients
Identifying the Capabilities of IP Phone Clients
Because XML services are now supported across a wide range of
Cisco IP Phones, web application servers now need to identify the capabilities of
the requesting IP phone to optimize the content returned to the phone. For
example, if the requesting phone is a Cisco IP Phone 7960, which cannot support
color PNG images, the application server must be able to identify this and return
a grayscale CIP image instead.
The IP phone client request to send the relevant information from the IP phone to
the web server application includes three (3) HTTP headers:
• x-CiscoIPPhoneModelName
• x-CiscoIPPhoneDisplay
• x-CiscoIPPhoneSDKVersion
x-CiscoIPPhoneModelName
This Cisco-proprietary header contains the Cisco manufacturing Model Name of
the device, which can typically be found by going to Settings->Model
Information, but varies between different models. Some examples of
manufacturing Model Names are CP-7960, CP-7960G, CP-7940G, CP-7905G,
and CP-7970G.
x-CiscoIPPhoneDisplay
This Cisco-proprietary header contains the display capabilities of the requesting
device with the following four parameters (listed in the order they appear):
• Width (in pixels)
• Height (in pixels)
• Color depth (in bits)
• A single character indicating whether the display is color (''C'') or grayscale
(''G'')
Cisco IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
5-66
OL-5375-01
Page 7

Chapter 5 HTTP Client Requests and Header Settings
These parameters get separated by commas as shown in the following example of
a Cisco IP Phone 7970 header:
x-CiscoIPPhoneDisplay: 298, 168, 12, C
Note The pixel resolutions advertised by the device define the area of the display
accessible by the phone services; not the actual resolution of the display.
x-CiscoIPPhoneSDKVersion
This Cisco-proprietary header contains the version of the IP Phone Services SDK
the requesting phone supports. Knowing the supported SDK version helps in
understanding, among other things, which URIs get supported. Support for
individual URIs (unlike the XML objects) does not get explicitly enumerated in
an HTTP header. The developer therefore must check the
Matrix>>
based on the Phone Model Name and supported SDK version, whether a specific
URI (or specific feature/version of a URI) gets supported.
in the IP Phone Services SDK, so the developer application will know,
Accept Header
<<Supported URIs
Refer to the
support the URIs that are documented in this SDK.
Note Beginning with the IP Phone Services SDK 3.3(3), the SDK version number
matches the minimum Cisco CallManager software that is required to support it.
For example, SDK version 3.3(4) gets supported only on Cisco CallManager
version 3.3(4) or later.
Accept Header
The Accept header represents a standard HTTP header that is used to inform web
servers about the content-handling capabilities of the client.
Cisco IP Phones include proprietary content-types to indicate which XML objects
are supported. These proprietary content-types all begin with x-CiscoIPPhone, to
indicate Cisco IP Phone XML objects, followed by a slash "/", followed by either
a specific XML object or a "*" to indicate all objects.
OL-5375-01
<<Supported URIs Matrix>> to find out which IP phone models
Cisco IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
5-67
Page 8

Accept Header
Chapter 5 HTTP Client Requests and Header Settings
For example, x-CiscoIPPhone/* indicates that all XML objects defined in the
specified version of the SDK are supported, and x-CiscoIPPhone/Menu specifies
that the
As the example illustrates, the name of the XML object can be derived directly
from the content-type by appending the sub-type (the part after the slash) onto
"CiscoIPPhone." The content-type can also include an optional version to indicate
support for a particular SDK version of that object. If a version is not specified,
then the x-CiscoIPPhoneSDKVersion is implied. The syntax of the version
number may vary, but, in general, will be as follows:
Here are some examples of typical content-types:
<CiscoIPPhoneMenu> object gets supported.
<major version>.<minor version>.<maintenance version>
x-CiscoIPPhone/*;version=3.3.3
x-CiscoIPPhone/Text
x-CiscoIPPhone/Menu;version=3.3.4
5-68
Cisco IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
OL-5375-01
 Loading...
Loading...