Page 1

Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
December, 2007
Americas Headquarters
Cisco Systems, Inc.
170 West Tasman Drive
San Jose, CA 95134-1706
USA
http://www.cisco.com
Tel: 408 526-4000
800 553-NETS (6387)
Fax: 408 527-0883
Text Part Number: OL-1089-11
Page 2

THE SPECIFICATIONS AND INFORMATION REGARDING THE PRODUCTS IN THIS MANUAL ARE SUBJECT TO CHANGE WITHOUT NOTICE. ALL
STATEMENTS, INFORMATION, AND RECOMMENDATIONS IN THIS MANUAL ARE BELIEVED TO BE ACCURATE BUT ARE PRESENTED WITHOUT
WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED. USERS MUST TAKE FULL RESPONSIBILITY FOR THEIR APPLICATION OF ANY PRODUCTS.
THE SOFTWARE LICENSE AND LIMITED WARRANTY FOR THE ACCOMPANYING PRODUCT ARE SET FORTH IN THE INFORMATION PACKET THAT
SHIPPED WITH THE PRODUCT AND ARE INCORPORATED HEREIN BY THIS REFERENCE. IF YOU ARE UNABLE TO LOCATE THE SOFTWARE LICENSE
OR LIMITED WARRANTY, CONTACT YOUR CISCO REPRESENTATIVE FOR A COPY.
The Cisco implementation of TCP header compression is an adaptation of a program developed by the University of California, Berkeley (UCB) as part of UCB’s public
domain version of the UNIX operating system. All rights reserved. Copyright © 1981, Regents of the University of California.
NOTWITHSTANDING ANY OTHER WARRANTY HEREIN, ALL DOCUMENT FILES AND SOFTWARE OF THESE SUPPLIERS ARE PROVIDED “AS IS” WITH
ALL FAULTS. CISCO AND THE ABOVE-NAMED SUPPLIERS DISCLAIM ALL WARRANTIES, EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING, WITHOUT
LIMITATION, THOSE OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT OR ARISING FROM A COURSE OF
DEALING, USAGE, OR TRADE PRACTICE.
IN NO EVENT SHALL CISCO OR ITS SUPPLIERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY INDIRECT, SPECIAL, CONSEQUENTIAL, OR INCIDENTAL DAMAGES, INCLUDING,
WITHOUT LIMITATION, LOST PROFITS OR LOSS OR DAMAGE TO DATA ARISING OUT OF THE USE OR INABILITY TO USE THIS MANUAL, EVEN IF CISCO
OR ITS SUPPLIERS HAVE BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES.
CCDE, CCENT, Cisco Eos, Cisco Lumin, Cisco Nexus, Cisco StadiumVision, the Cisco logo, DCE, and Welcome to the Human Network are trademarks; Changing the Way
We Work, Live, Play, and Learn is a service mark; and Access Registrar, Aironet, AsyncOS, Bringing the Meeting To You, Catalyst, CCDA, CCDP, CCIE, CCIP, CCNA,
CCNP, CCSP, CCVP, Cisco, the Cisco Certified Internetwork Expert logo, Cisco IOS, Cisco Press, Cisco Systems, Cisco Systems Capital, the Cisco Systems logo,
Cisco Unity, Collaboration Without Limitation, EtherFast, EtherSwitch, Event Center, Fast Step, Follow Me Browsing, FormShare, GigaDrive, HomeLink, Internet Quotient,
IOS, iPhone, iQ Expertise, the iQ logo, iQ Net Readiness Scorecard, iQuick Study, IronPort, the IronPort logo, LightStream, Linksys, MediaTone, MeetingPlace, MGX,
Networkers, Networking Academy, Network Registrar, PCNow, PIX, PowerPanels, ProConnect, ScriptShare, SenderBase, SMARTnet, Spectrum Expert, StackWise, The
Fastest Way to Increase Your Internet Quotient, TransPath, WebEx, and the WebEx logo are registered trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. and/or its affiliates in the United
States and certain other countries.
All other trademarks mentioned in this document or Website are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership relationship
between Cisco and any other company. (0805R)
Any Internet Protocol (IP) addresses used in this document are not intended to be actual addresses. Any examples, command display output, and figures included in the
document are shown for illustrative purposes only. Any use of actual IP addresses in illustrative content is unintentional and coincidental.
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
© 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Page 3

CONTENTS
Preface xi
Document Objective xi
Audience xi
Document Organization xii
Document Conventions xii
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Documentation Suite xv
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Documentation Map xvi
Obtaining Documentation, Obtaining Support, and Security Guidelines xvii
Summary History of Document Changes xvii
CHAPTER
1 Billing Interfaces 1-1
Billing Capabilities Overview 1-1
System Interfaces 1-1
Physical Interface 1-1
RADIUS Interface 1-2
Message Interface 1-2
CDB Message Format 1-2
Tag Values 1-3
Formats and Codes 1-4
CDB Record Types 1-4
Call Data Block Descriptions 1-6
Enabling Call Screening 1-7
Configuring Call Detail Record File Output 1-7
Configuring Call Detail Record Message Types 1-8
Enabling Call Screening 1-8
Configuring Call Detail Record File Output 1-8
Call Data Element Descriptions 1-9
Cisco MGC Billing Interfaces 1-19
FTP Interface 1-20
Generic Interface 1-20
OL-1089-11
Redundant Cisco MGC Configuration 1-20
Cisco MGC Clock Synchronization 1-21
Detailed CDB Description 1-21
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
iii
Page 4

Contents
Answered CDB Record (Tag: 1010/Release 5 or Later) 1-21
Deselected Outgoing Circuit CDB Record (Tag: 1020/Release 5 or Later) 1-25
Aborted Attempt CDB Record (Tag: 1030/Release 5 or Later) 1-27
Release CDB Record (Tag: 1040/Release 5 or Later) 1-31
Interrupted CDB Record (Tag: 1050/Release 5 or Later) 1-34
On-Going (Call) CDB Record (Tag: 1060/Release 5 or Later) 1-34
Maintenance CDB Record (Tag: 1070/Release 5 or Later) 1-37
SS7 CIC Audit CDB Record (Tag: 1071/Release 9 or Later) 1-37
External Access CDB (Tag: 1080/Release 7 or Later) 1-39
File Header CDB (Tag: 1090/Release 7 or Later) 1-40
File Footer CDB (Tag: 1100/Release 7 or Later) 1-40
End of the Call CDB (Tag: 1110/Release 7 or Later) 1-41
Slave End-of-Call CDB Record (Tag: 1210/Release 9.6 or Later) 1-46
Slave Long Duration Call CDB Record (Tag: 1260/Release 9.6 or Later) 1-47
CDE Detail Description 1-48
CDEs Encoded in ANSI 1-49
Calling Party Category (Tag: 2000/ANSI) 1-49
User Service Information (Tag: 2001/ANSI) 1-50
Originating Line Information (Tag: 2002/ANSI) 1-51
Calling Number Nature of Address (Tag: 2003/ANSI) 1-52
Charged Number Nature of Address (Tag: 2004/ANSI) 1-53
Dialed Number Nature of Address (Tag: 2005/ANSI) 1-54
LRN Nature of Address (Tag: 2006/ANSI) 1-55
Called Number Nature of Address (Tag: 2007/ANSI) 1-56
Reason Code (Tag: 2008/ANSI) 1-57
Forward Call Indicators Received (Tag: 2009/ANSI) 1-58
Forward Call Indicators Sent (Tag: 2010/ANSI) 1-59
Nature of Connection Indicators Received (Tag: 2011/ANSI) 1-60
Nature of Connection Indicators Sent (Tag: 2012/ANSI) 1-61
Transit Network Selection (Tag: 2013/ANSI) 1-62
Carrier Identification Parameter (Tag: 2014/ANSI) 1-63
Carrier Selection Parameter (Tag: 2015/ANSI) 1-63
Jurisdiction Information Parameter (Tag: 2016/ANSI) 1-64
Redirecting Number Nature of Address (Tag 2017/ANSI) 1-64
Egress Calling Number Nature of Address (Tag 2018/ANSI) 1-65
Egress Redirecting Number Nature of Address (Tag 2019/ANSI) 1-66
Egress Original Called Number Nature of Address (Tag 2020/ANSI) 1-67
CDE Encoded as ITU Recommendation 1-68
Calling Party Category (Tag: 3000/ITU) 1-68
User Service Information (Tag: 3001/ITU) 1-69
iv
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
OL-1089-11
Page 5

Originating Line Information (Tag: 3002/ITU) Retired 1-70
Calling Number Nature of Address (Tag: 3003/ITU) 1-70
Charged Number Nature of Address (Tag: 3004/ITU) Retired 1-71
Dialed Number Nature of Address (Tag: 3005) 1-72
LRN Nature of Address (Tag: 3006/ITU) 1-73
Called Number Nature of Address (Tag: 3007/ITU) 1-74
Reason Code (Tag: 3008/ITU) 1-75
Forward Call Indicators Received (Tag: 3009/ITU) 1-88
Forward Call Indicators Sent (Tag: 3010/ITU) 1-89
Nature of Connection Indicators Received (Tag: 3011/ITU) 1-91
Nature of Connection Indicators Sent (Tag: 3012/ITU) 1-92
Transit Network Selection (Tag: 3013/ITU) 1-93
Redirecting Number Nature of Address (Tag 3017/ITU) 1-94
Egress Calling Number Nature of Address (Tag 3018/ITU) 1-95
Egress Redirecting Number Nature of Address (Tag 3019/ITU) 1-96
Egress Original Called Number Nature of Address (Tag 3020/ITU) 1-97
MGC Generic CDEs 1-98
CDB Version (Tag: 4000) 1-98
CDB Timepoint (Tag: 4001) 1-98
Call Reference ID (Tag: 4002) 1-98
IAM/Setup Timepoint (Tag: 4003) 1-99
ACM/Alert Timepoint (Tag: 4004) 1-99
ANM/Answer Timepoint (Tag: 4005) 1-99
REL/Release Timepoint (Tag: 4006) 1-100
Crash Timepoint (Tag: 4007) 1-100
Originating Trunk Group (Tag: 4008) 1-100
Originating Member (Tag: 4009) 1-101
Calling Number (Tag: 4010) 1-101
Charged Number (Tag: 4011) 1-101
Dialed Number (Tag: 4012) 1-102
LRN Number (Tag: 4013) 1-102
Called Number (Tag: 4014) 1-102
Terminating Trunk Group (Tag: 4015) 1-103
Terminating Member (Tag: 4016) 1-103
Maintenance Trunk Group (Tag: 4017) 1-103
Maintenance Circuit Member (Tag: 4018) 1-104
Glare Encountered (Tag: 4019) 1-104
RLC/RELEASE Complete Timepoint (Tag: 4020) 1-104
First Release Source (Tag: 4028) 1-105
LNP Dip (Tag: 4029) 1-105
Contents
OL-1089-11
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
v
Page 6

Contents
Total Meter Pulses (Tag: 4030) 1-106
Maintenance Type (Tag: 4032) 1-106
Maintenance Reason (Tag: 4033)—Retired 1-107
Ingress Originating Point Code (Tag: 4034) 1-108
Ingress Destination Point Code (Tag: 4035) 1-108
Egress Originating Point Code (Tag: 4036) 1-109
Egress Destination Point Code (Tag: 4037) 1-109
Ingress Media Gateway ID (Tag: 4038) 1-110
Egress Media Gateway ID (Tag: 4039) 1-110
TCAP Transaction ID (Tag: 4040) 1-110
Transaction Start Time (Tag: 4041) 1-111
Transaction End Time (Tag: 4042) 1-111
TCAP Database ID (Tag: 4043) 1-111
Announcement ID (Tag: 4044) 1-112
Route Selection Info (Tag: 4045) Retired 1-112
Ingress Packet Info (Tag: 4046) Restored 1-113
Egress Packet Info (Tag: 4047) Restored 1-114
Directional Flag (Tag: 4048) 1-114
Service Logic ID (Tag: 4049) 1-115
AMA Line Number (Tag: 4050) 1-115
OOriginating Gateway Primary Select (Tag: 4052) Defined for Future Use 1-116
Terminating Gateway Primary Select (Tag: 4053) Defined for Future Use 1-116
Redirecting Number (Tag: 4060) 1-116
Scale Factor (Tag: 4062) 1-117
Test Line Indicator (Tag: 4063) 1-117
Redirection Number (Tag: 4065) 1-118
Ingress SigPath ID (Tag: 4066) 1-118
Ingress Span ID (Tag: 4067) 1-118
Ingress BearChan ID (Tag: 4068) 1-119
Ingress Protocol ID (Tag: 4069) 1-119
Egress SigPath ID (Tag: 4070) 1-120
Egress Span ID (Tag: 4071) 1-120
Egress BearChan ID (Tag: 4072) 1-120
Egress Protocol ID (Tag: 4073) 1-121
Maintenance SigPath ID (Tag: 4074) 1-121
Maintenance Span ID (Tag: 4075) 1-122
Maintenance BearChan ID (Tag: 4076) 1-122
Maintenance Circuits Count (Tag: 4077) 1-122
Charge Band Number (Tag: 4078) 1-123
Furnish Charging Information (Tag: 4079) 1-123
vi
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
OL-1089-11
Page 7

Original Called Number (Tag: 4080) 1-124
T.38 Fax Call (Tag: 4081) 1-124
Charge Unit Number (Tag: 4082) 1-125
Charge Indicator (Tag: 4083) 1-125
Outgoing Calling Party Number (Tag: 4084) 1-126
MCID Request Indicator (Tag: 4085) 1-126
MCID Response Indicator (Tag: 4086) 1-127
Ingress MGCP DLCX Return Code (Tag: 4087) 1-127
Egress MGCP DLCX Return Code (Tag: 4088) 1-127
Network Translated Address Indicator (Tag: 4089) 1-128
Reservation Request Accepted (Tag: 4090) 1-128
Reservation Request Error Count (Tag: 4091) 1-129
ATM Ingress Configured Profile (Tag: 4092) 1-129
ATM Egress Configured Profile (Tag: 4093) 1-130
ATM Negotiated Profile (Tag: 4094) 1-131
Route List Name (Tag: 4095) 1-131
Route Name (Tag: 4096) 1-132
MGCP Script Response String (Tag: 4097) 1-132
Originating Leg DSP Statistics (Tag: 4098) 1-133
Terminating Leg DSP Statistics (Tag: 4099) 1-135
Originating Remote SIP Host (Tag: 4201) 1-136
Originating Local SIP Host (Tag: 4202) 1-136
SIP Call ID (Tag: 4203) 1-136
Source IP Address (Tag: 4204) 1-137
Ingress Media Device Address (Tag: 4205) 1-137
Egress Media Device Address (Tag: 4206) 1-138
Initial Codec (Tag: 4207) 1-138
Final Codec (Tag: 4208) 1-139
Ingress Media Device Port (Tag: 4209) 1-139
Egress Media Device Port (Tag: 4210) 1-139
Originating VPN ID (Tag: 4211) 1-140
Terminating VPN ID (Tag: 4212) 1-140
Meter Pulses Received (Tag: 4213) 1-141
Meter Pulses Sent (Tag: 4214) 1-141
Charge Tariff Info (Tag: 4215) 1-142
Advice of Charge Indicator (Tag: 4216) 1-142
Short Call Indicator (Tag: 4217) 1-143
Charge Limit Exceeded (Tag: 4218) 1-143
Call Recovered Indication (Tag: 4219) 1-144
Partial Calling Line Identity (Tag: 4220) 1-144
Contents
OL-1089-11
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
vii
Page 8

Contents
Service Activation (Tag: 4221) 1-145
PRI AOC Invoke Type (Tag: 4222) 1-145
PRI AOC – S Charge Information (Tag: 4223) 1-146
PRI AOC – D Charge Information (Tag: 4224) 1-146
PRI AOC – E Charge Information (Tag: 4225) 1-147
PRI AOC Invoke Failure (Tag: 4226) 1-147
Route Optimization/Path Replacement Action (Tag: 4227) 1-148
Route Optimization/Path Replacement Call Reference of Associated Call Instance (Tag:
4228) 1-148
Route Optimization/Path Replacement Trunk Group Info (Tag: 4229) 1-149
Route Optimization/Path Replacement Channel Info (Tag: 4230) 1-149
Route Optimization Switchover Timestamp (Tag: 4231) 1-149
Rejecting Location Label (Tag: 4232) 1-150
Rejecting Location Label Direction (Tag: 4233) 1-150
Total Circuit Count (Tag: 4234) 1-151
Total Circuits Unavailable Count (Tag: 4235) 1-151
H323 Destination (Tag 4236) 1-151
Ingress Redirecting Number (Tag 4237) 1-153
Service Usage Data (Tag 4239) 1-153
CNAM DIP (Tag 4240) 1-154
Calling Party Name (Tag 4241) 1-154
Terminating Remote SIP Host (Tag 4242) 1-155
Terminating Local SIP Host (Tag 4243) 1-155
License Rejecting Reason (Tag 4244) 1-155
License Rejecting Direction (Tag 4245) 1-156
SIP Transport (Tag 4246) 1-156
SIP Routing URI Source (Tag 4247) 1-157
SIP Routing URI (Tag 4248) 1-157
Millisecond Granularity CDEs 1-158
IAM Timepoint Received_ms (Tag: 4100) 1-158
IAM Timepoint Sent_ms (Tag: 4101) 1-158
ACM Timepoint Received_ms (Tag: 4102) 1-158
ACM Timepoint Sent_ms (Tag: 4103) 1-159
ANM Timepoint Received_ms (Tag: 4104) 1-159
ANM Timepoint Sent_ms (Tag: 4105) 1-159
First REL Timepoint_ms (Tag: 4106) 1-160
Second REL Timepoint _ms (Tag: 4107) 1-160
RLC Timepoint Received_ms (Tag: 4108) 1-160
RLC Timepoint Sent_ms (Tag: 4109) 1-161
Cisco Reserved CDEs 1-162
viii
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
OL-1089-11
Page 9

Unique Call Correlator ID (Tag: 5000) 1-162
Miscellaneous Fields 1-163
MGC ID (Tag: 6000) 1-163
File Start Time (Tag: 6001) 1-163
File End Time (Tag: 6002) 1-163
Total Number of CDB Records (Tag: 6003) 1-164
MGC Version (Tag: 6004) 1-164
Interim CDB (Tag: 6005) 1-164
Protocol Specific CDEs 1-165
NTT 1-165
TTC Contract Number (Tag: 6100) 1-165
TTC Contract Number NOA (Tag: 6101) 1-165
TTC Charge Info (Tag: 6102) 1-165
TTC Charge Info Type (Tag: 6103) 1-166
TTC Charge Area Info (Tag: 6104) 1-166
Contents
CHAPTER
APPENDIX
I
NDEX
2 MGC Info Field Reference 2-1
MGC Info Subfields 2-1
A CDE Listings by Release A-1
CDE Baseline—Release 9.1(5) and Higher A-1
CDE Changes in Release 9.2(2) A-4
CDE Changes in Release 9.3(1) A-5
CDE Changes in Release 9.3(2) A-5
CDE Changes in Release 9.4(1) A-5
CDE Changes in Release 9.5(2) A-6
CDE Changes in Release 9.6(1) A-7
CDE Changes in Release 9.7 A-8
OL-1089-11
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
ix
Page 10

Contents
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
x
OL-1089-11
Page 11

Preface
This preface includes the following sections:
• Document Objective, page xi
• Audience, page xi
• Document Organization, page xii
• Document Conventions, page xii
• Cisco Media Gateway Controller Documentation Suite, page xv
• Cisco Media Gateway Controller Documentation Map, page xvi
• Obtaining Documentation, Obtaining Support, and Security Guidelines, page xvii
• Summary History of Document Changes, page xvii
Document Objective
This guide provides reference information for the Cisco Media Gateway Controller (MGC) software
Release 9. You should read the system-level documentation supplied with your system before using this
guide. A complete list of these documents is included in the Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software
Release 9 Installation and Configuration Guide that ships with your system.
Note This guide uses the term Media Gateway Controller software or MGC application to mean the
Cisco MGC software that runs in the UNIX environment on a server. The term MGC refers to the
combination of this software and the server. The MGC communicates with the SS7 network to process
and route calls between a traditional time-division multiplexing (TDM) network and a packet data
network. This routing takes place through a variety of media gateways (MGWs), which are separate
devices that perform the conversion between the TDM and data network formats.
Audience
This guide is for network operators and administrators who have experience with telecommunications
networks, protocols, and equipment and who have familiarity with data communications networks,
protocols, and equipment.
OL-1089-11
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
xi
Page 12
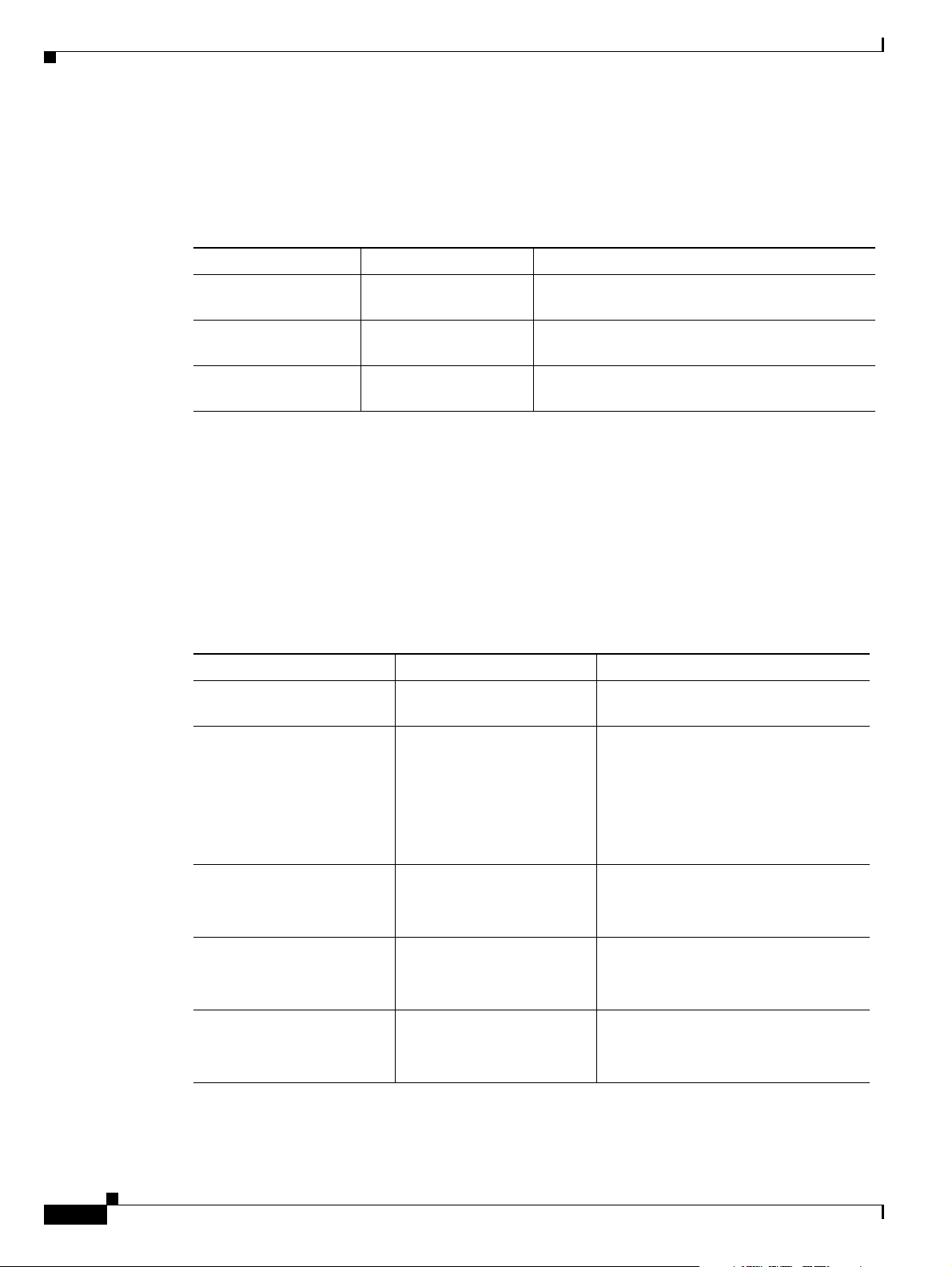
Document Organization
The major sections of this guide are summarized in Tab l e 1.
Table 1 Document Organization
Chapter Title Description
1 Billing Interfaces Describes the Cisco MGC billing interface
2 Info Field Reference Provides additional information about the MGC
Appendix A CDE Listings by
Document Conventions
Release
Preface
capabilities and its call detail records (CDRs).
Info Field (Tag 4031).
Lists the call detail element (CDE) changes made
for each release.
Throughout this guide, $BASEDIR refers to the directory structure in which the Cisco MGC software is
installed. $BASEDIR is a UNIX environment variable that must be set during installation. Refer to the
Cisco MGC Software Release 9 Installation and Configuration Guide for a description of configuring
this environment variable.
Text conventions used in this guide are shown in Tab le 2 .
Table 2 Conventions
Convention Meaning Description/Comments
Boldface Commands and keywords
you enter as shown
Italics Variables for which you
supply values
Square brackets ([ ]) Optional elements command [abc]
Vertical bars ( | ) Separated alternative
elements
Braces ({ }) Required choices command {abc | def}
offset-list
command type interface
You replace the variable with the type
of interface.
In contexts that do not allow italics,
such as online help, arguments are
enclosed in angle brackets (< >).
abc is optional (not required), but you
can choose it.
command [abc | def]
You can choose either abc or def, or
neither, but not both.
xii
Yo u must choose either abc or def, but
not both.
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
OL-1089-11
Page 13
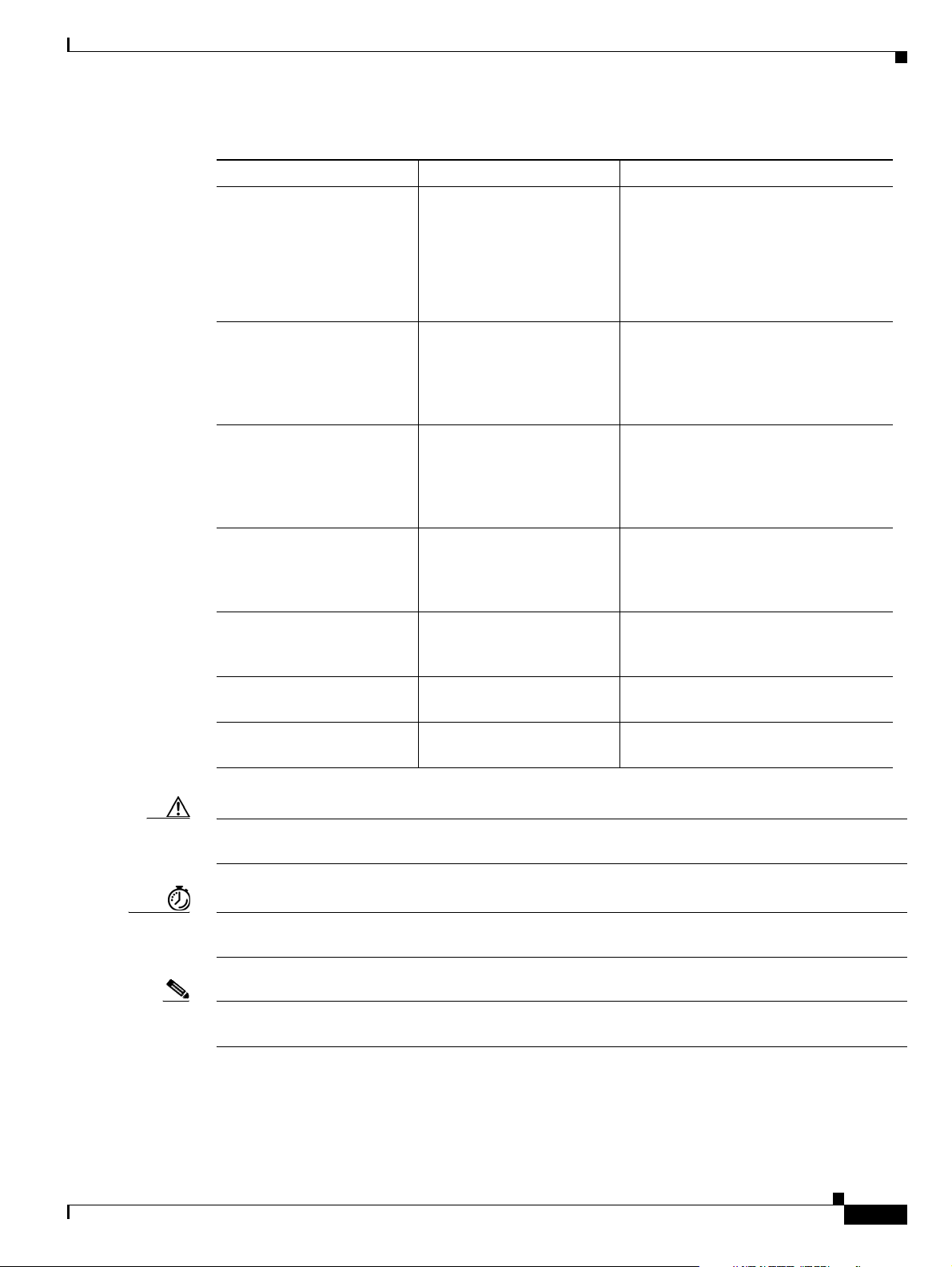
Preface
Table 2 Conventions (continued)
Convention Meaning Description/Comments
Braces and vertical bars
within square brackets
([ { | } ])
Caret character (^) Control key The key combinations ^D and Ctrl-D
A nonquoted set of
characters
System prompts
Screen font Terminal sessions and
Angle brackets (< >) Nonprinting characters such
Exclamation point (!) at the
beginning of a line
A required choice within an
optional element
command [abc {def | ghi}]
You have three options:
Nothing
abc def
abc ghi
are equivalent: Both mean “hold down
the Control key while you press the D
key.” Keys are indicated in capital
letters, but are not case sensitive.
A string For example, when setting an SNMP
community string to public, do not use
quotation marks around the string;
otherwise, the string will include the
quotation marks.
Denotes interactive
sessions, indicates that the
user enters commands at the
prompt
The system prompt indicates the
current command mode. For example,
the prompt
Router (config) #
indicates global configuration mode.
information the system
displays
as passwords
A comment line Comments are sometimes displayed by
the Cisco IOS software.
Caution Means reader be careful. In this situation, you might do something that could result in equipment
damage or loss of data.
Timesaver Means reader may be able to save some time. Taking the action described could achieve a result in less
time than might be achieved otherwise.
Note Means reader take note. Notes contain helpful suggestions or references to material not covered in the
manual.
Conventions used in the Cisco MGC system (such as in MML commands) are shown in Tab l e 3.
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
OL-1089-11
xiii
Page 14
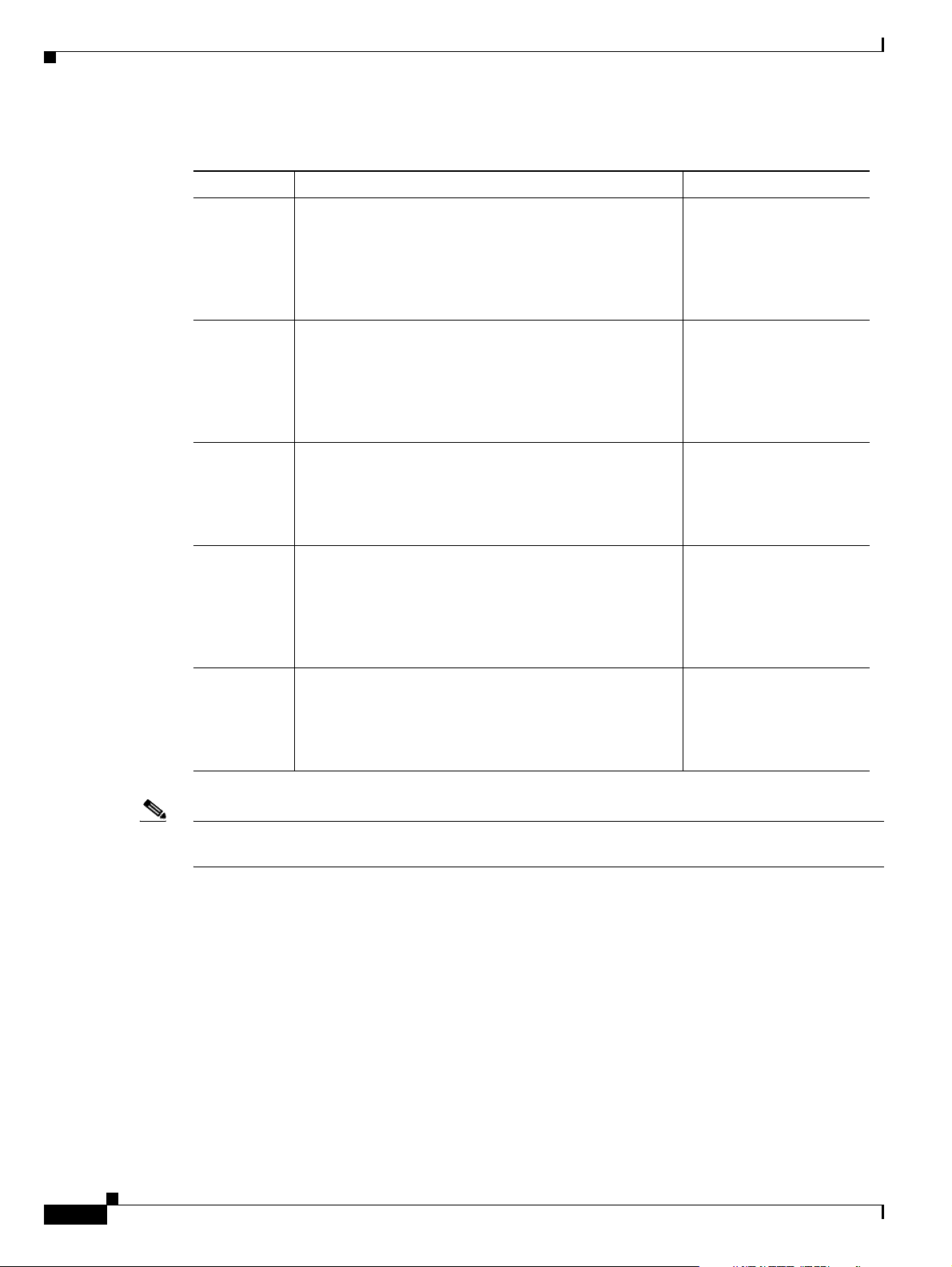
Table 3 Data Type Conventions
Data Type Definition Example
Integer A series of decimal digits from the set of 0 through 9 that
represents a positive integer. An integer can have one or
more leading zero digits (0) added to the left side to align
the columns. Leading zeros are always valid as long as
the number of digits is less than or equal to ten. Values of
this type have a range of 0 through 4294967295.
Signed
integer
This data type has the same basic format as the integer
but can be either positive or negative. When negative, it
is preceded by the sign character (–). As with the integer
data type, this data type can be as many as ten digits in
length, not including the sign character. The value of this
type has a range of –2147483647 through 2147483647.
Hexadecimal A series of 16-based digits from the set of 0 through 9, a
through f, or A through F. The hexadecimal number can
have one or more leading zeros (0) added to the left side.
For all hexadecimal values, the maximum size is
0xffffffff (eight hexadecimal digits).
Text A series of alphanumeric characters from the ASCII
character set, where defined. Tab, space, and double
quote (“ ”) characters cannot be used. Text can be as many
as 255 characters; however, it is recommended that you
limit the text to no more than 32 characters for
readability.
String A series of alphanumeric characters and white-space
characters. A string is surrounded by double quotes (“ ”).
Strings can be as many as 255 characters; however, it is
recommended that you limit the strings to no more than
80 characters for readability.
123
000123
4200000000
123
–000123
–2100000000l
1f3
01f3000
EntityID
LineSES_Threshold999
“This is a descriptive
string.”
Preface
xiv
Note Hexadecimal and integer fields in files can have different widths (number of characters) for column
alignment.
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
OL-1089-11
Page 15
Preface
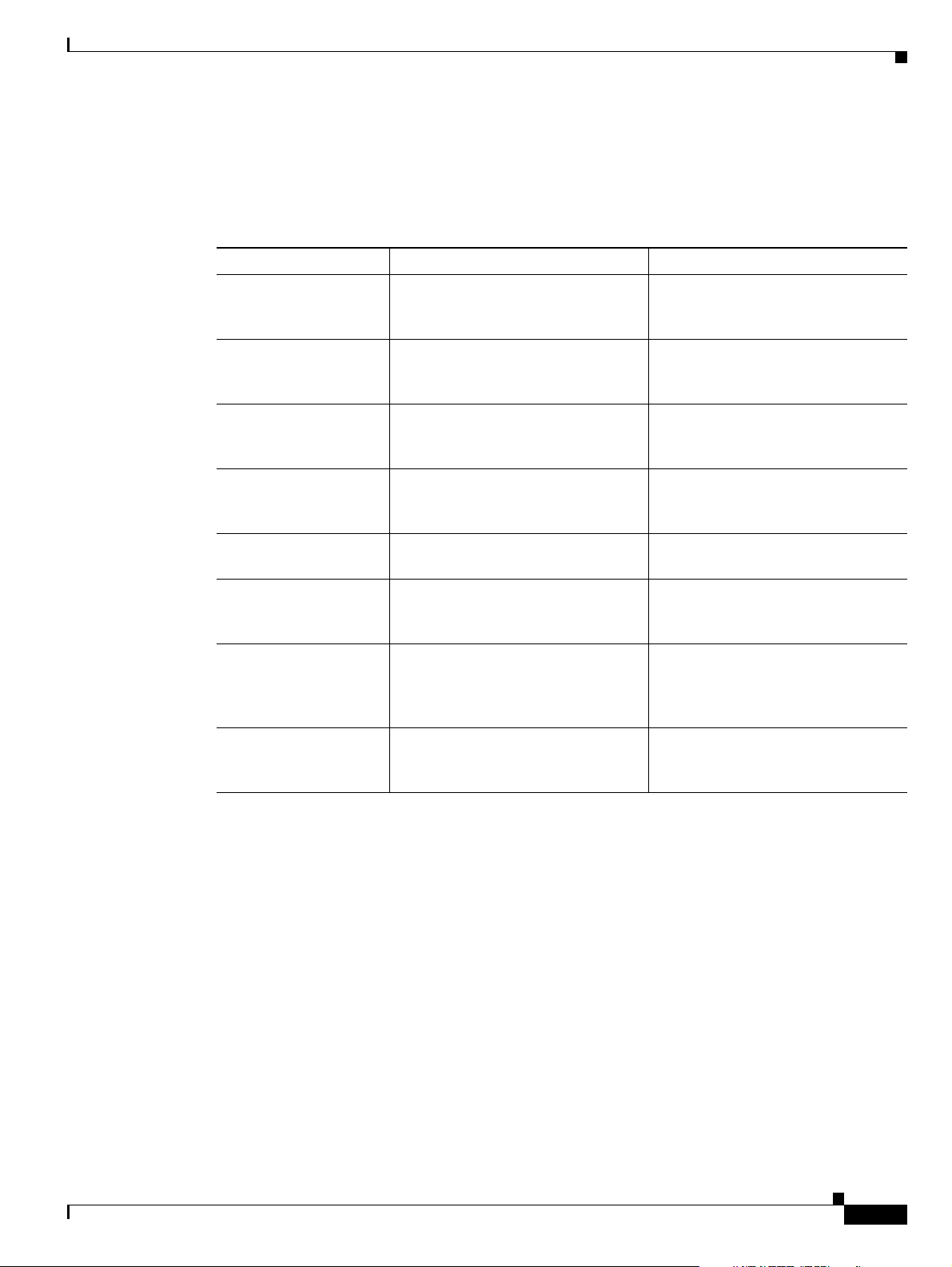
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Documentation Suite
The documents that make up the Cisco MGC documentation set are listed in Tabl e 4.
Table 4 Cisco Media Gateway Controller Documentation Set
Functional Area Document Title Document Description
Hardware Cisco Media Gateway Controller
Hardware Installation Guide
Hardware Regulatory Compliance and Safety
Information for the Cisco Media
Gateway Controller Hardware
Software installation
and configuration
Software installation
and configuration
Software installation
and configuration
Software installation
and configuration
Software installation
and configuration
Software installation
and configuration
Cisco Media Gateway Controller
Software Release 9 Installation and
Configuration Guide
Cisco Media Gateway Controller
Software Release 9 Provisioning
Guide
Cisco Media Gateway Controller
Software Release 9 Dial Plan Guide
Cisco Media Gateway Controller
Software Release 9 Billing Interface
Guide (this book)
Cisco Media Gateway Controller
Software Release 9 Operations,
Maintenance, and Troubleshooting
Guide
Release Notes for Cisco Media
Gateway Controller Software
Release 9
Provides information on how to
install the Cisco SC2200 and
Cisco VSC3000 MGCs
Provides regulatory compliance and
safety information
Provides installation and
configuration information for the
Cisco MGC software Release 9
Provides provisioning information
for the Cisco MGC software
Release 9
Provides dial plan information for the
Cisco MGC software Release 9
Provides reference information for
the Cisco MGC software Release 9
Provides operation, maintenance,
and troubleshooting information for
the Cisco MGC software Release 9
Provides release-specific
information for the Cisco MGC
software Release 9
OL-1089-11
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
xv
Page 16

Cisco Media Gateway Controller Documentation Map
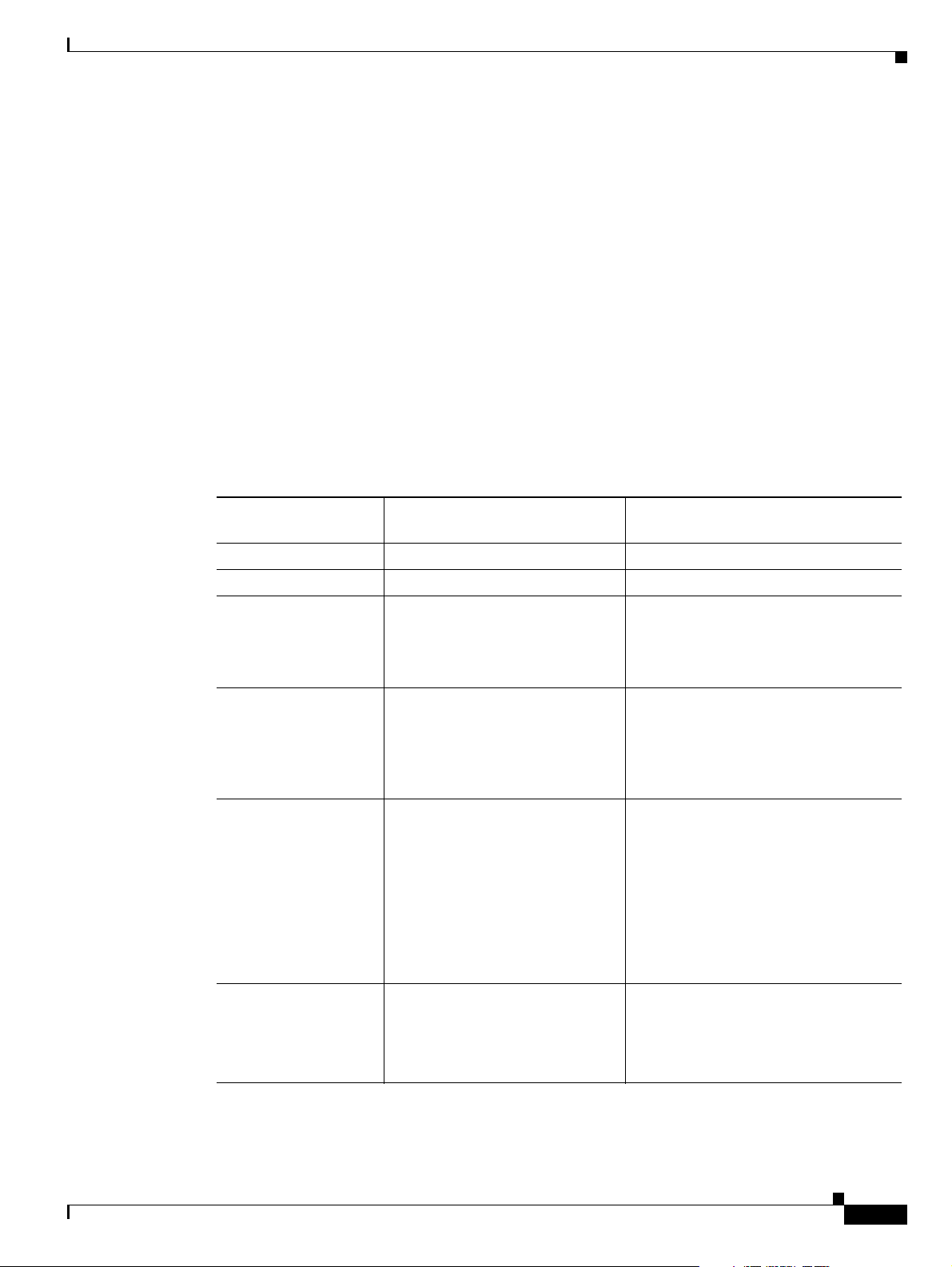
Refer to the map in Figure 1 to navigate through the media gateway controller documentation suite.
Figure 1 Documentation Map
Start
Solution Overview
Preface
Is
MGC host
set up?
No
Regulatory Compliance and Safety
Information for Cisco MGC
Cisco MGC Hardware
Installation Guide
Release Notes for
Cisco MGC Software Release 9
Cisco MGC Software Release 9
Installation and Configuration Guide
Cisco MGC Software Release 9
Provisioning Guide
Cisco MGC Software Release 9
Dial Plan Guide
Ye s
Is
gateway
set up?
No
Regulatory Compliance and Safety
Information for Cisco Media Gateway
Solution Gateway Hardware
Installation Guide
Solution Gateway Software
Installation and Configuration Guide
Solution Gateway
Provisioning Guide
End
Cisco MGC Software Release 9
Billing Interface Guide *
Cisco MGC Software Release 9 MML
Command Reference Guide *
Ye s
xvi
Cisco Voice Services Provisioning
Tool Version 2.x
Cisco MGC Software Release 9 Operations,
Maintenance, and Troubleshooting Guide
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
Cisco MGC Software Release 9
Messages Reference Guide *
Cisco MGC Software Release 9
Management Information Base Guide *
* This guide provides useful information
that is not required during installation.
57051
OL-1089-11
Page 17
Preface
Obtaining Documentation, Obtaining Support, and Security Guidelines
For information on obtaining documentation, obtaining support, providing documentation feedback,
security guidelines, and also recommended aliases and general Cisco documents, see the monthly
What’s New in Cisco Product Documentation, which also lists all new and revised Cisco technical
documentation, at:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/general/whatsnew/whatsnew.html
Summary History of Document Changes
Table 5 describes the document changes made after the initial release of the Cisco Media Gateway
Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide.
Table 5 Summary History of Document Changes
Document Number and Change
Subject
Tag revisioins OL-1089-11, December, 2007
Tag revisions OL-1089-11, October, 2007
Tag revisions OL-1089-11, April 9, 2007
Tag revisions OL-1089-10, March 31, 2006
Tag revisions OL-1089-10, August 5, 2005
Tag revisions OL-1089-09, September 23, 2004
Date Change Summary
• Updated tags in Release 9.6, 9.7
• Added tags 4246, 4247, and 4248
• Modified information for tags 4201
and 4202.
• Added tags 4236, 4238, 4239,
4240, 4242, 4243, 4244, and 4245.
• Modified information for tags 4098
and 4099 for the Support for DSP
Voice Quality Statistics feature.
• Modified information for tags
4078, 4080, and 6000.
• Modified information for tags
4011, 4049, 4050, 4087, 4088,
4215, 4221, and 4223–4225.
• Added tags 2018-2020, 3018-3020,
4227-4233, and 4237.
• Modified definitions for CDBs
1070 and 1071.
• Added CDBs 1210 and 1260
• Added the 1071 CDB.
OL-1089-11
• Added tags 4234 and 4235.
• Removed CDB information from
individual tag tables.
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
xvii
Page 18
Table 5 Summary History of Document Changes
Document Number and Change
Subject
Tag revisions OL-1089-09, May 17, 2004 • Modified the description of the
Tag revisions OL-1089-08, January 9, 2004
Tag revisions OL-1089-08, December 3, 2003
Tag revisions OL-1089-08, August 18, 2003
Date Change Summary
1060 CDB.
• Retired tag 4045.
• Modified information for tags 4044
and 4073.
• Added tags 4083–4097,
4213–4226, and 6005.
• Restored tags 4046 and 4047.
• Modified the description of the
1060 CDB.
• Reordered the tags, placing them in
numeric order.
• Modified the retirement
information for tag 3004.
• Modified release information for
tags 4052 and 4053. They are now
listed as “defined for future use.”
• Added tags 4098 and 4099, which
are part of a Release 9.4(1) patch.
• Added tags 4204–4212.
Preface
Tag revisions OL-1089-07, June 30, 2003
• Retired tag 4033.
• Added data value information for
tags 4030 and 4044.
• Modified the release in which the
3004 tag was retired.
xviii
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
OL-1089-11
Page 19
Preface
Table 5 Summary History of Document Changes
Document Number and Change
Subject
Tag revisions OL-1089-07, June 27, 2003 • Modified CDB information for tag
Tag revisions OL-1089-07, March 14, 2003
Date Change Summary
4081.
• Modified descriptions for the
following tags:
–
2006, 2009, 2010, and 2014
–
2017, 3001, 3002, and 3006
–
3009, 3010, 4048, and 4060
• Modified data values for the
following tags:
–
2011, 2012, 2014, and 2016
–
4013 and 4038—4040
–
4066—4068 and 4070—4072
–
4074—4077, 6000, and 6004
• Modified information and data
values for tags 6100—6104.
• Modified information for tags
2005, 2007, 3007, and 4014.
Tag revisions OL-1089-07, January 20, 2003
Tag revisions OL-1089-07, December 9, 2002
Tag revisions OL-1089-06, October 9, 2002
Tag revisions OL-1089-06, September 19, 2002
Tag revision OL-1089-06, September 5, 2002
Tag revisions OL-1089-06, August 20, 2002
• Added tags 4034–4037, 4068, and
4072 to the 1110 CBD.
• Corrected the octet length
information for tags 3011, 3012,
4032, and 4033.
• Added an appendix that identifies
the CDR changes by release.
• Updated the information for tag
3013.
• Changed the CDB information for
tag 4081.
• Added CDE and CDB information
for tag 4082.
• Expanded data value content of the
3008 tag to include detailed cause
code information.
• Corrected data value information
for tags 4032 and 4033.
• Corrected the data value
information for tag 4048.
• Corrected CDB information for
tags 3001, 4078, 4079, and 4080.
OL-1089-11
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
xix
Page 20
Preface
Table 5 Summary History of Document Changes
Document Number and Change
Subject
Tag revisions OL-1089-06, August 16, 2002 • Added data value information to
Tag revisions OL-1089-06, July 10, 2002
New template OL-1089-06, July 1, 2002
Tag revisions OL-1089-06, July 1, 2002
Date Change Summary
the 3000 series tags from Q.763.
• Identified tags 3002, 3004, 4046,
and 4047 as retired.
• Corrected the CBD information for
tags 4052 and 4053.
• Corrected descriptions for tags
4066–4068, 4070–4072, and
4074–4076.
• Modified the data value
information for the 4100 series tags
to indicate Cisco MGC time.
• Modified the data value
information for ANSI Nature of
Address tags to indicate that the
first value is spare.
• Modified tags to indicate that the
maximum ANSI number is 2
• Updated CDB values for tags 4078,
4079, and 4081.
• Updated CDB values for tags 4077
and 4080.
• Updated this document with the
current user documentation
template.
• Removed Tag 5000 from the
listings for CDBs 1090 and 1100.
14
.
xx
Tag revisions OL-1089-06, May 15, 2002
Revised Table 1-2 OL-1089-05, April 3, 2002
Tag revisions OL-1089-04, March 22, 2002
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
• Replaced Tag 6001 in CDB 1100
with Tag 6002.
• Added MGCP as a valid interface
in Tags 4069 and 4073.
• Added Tags 4078 through 4081.
• Removed references to Tags 4064
and 4065.
• Revised data value and general
information for Tags 4034 through
4037.
OL-1089-11
Page 21
Preface
Table 5 Summary History of Document Changes
Document Number and Change
Subject
Tag revisions OL-1089-03, November 27, 2001 • Revised text for last bullet on
ASCII output OL-1089-02, November 16, 2001
— OL-1089-01, October 18, 2001 Initial release
Date Change Summary
page 1-7 and on page 1-8.
• Removed “(retired in Release
9.0(1))” for Tag 2017 and
Tag 3017.
• Added Tag 4203.
• Removed Tag 4064 and Tag 4065.
• Removed references to ASCII
output on page 1-2 to page 1-4.
• Removed Table 1-1 on page 1-11.
• Removed CdrDmpr.callDetail row
in Table 1-6 on page 1-11.
• Removed Trigger Interface section
on page 1-18.
OL-1089-11
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
xxi
Page 22

Preface
xxii
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
OL-1089-11
Page 23

Billing Interfaces
This chapter describes the Cisco Media Gateway Controller (MGC) billing interface capabilities and its
call detail records (CDRs). This chapter is primarily a reference that contains the following sections:
• Billing Capabilities Overview, page 1-1
• Cisco MGC Billing Interfaces, page 1-19
Billing Capabilities Overview
The generic interface to the CDR dumper interface carries all the billing information in the form of call
detail blocks (CDBs). When the CDR dumper receives the CDB, it writes the record in the CDR file.
CDB generation is based on a point in call (PIC). The MGC predefines several PICs that can trigger the
generation of CDBs. Examples of PICs include Answered, Long Duration, and Released. For example,
the MGC triggers the generation of the Answered CDB when an Answer message (ANM for SS7) is
received.
Each CDB has a type associated with it that distinguishes the PIC.
CDB required events that are triggered are passed to the CDR manager module. When an event is
received, the action the CDR manager module takes is determined by its configuration. The CDR
manager module either handles or ignores the event.
CHAPTER
1
System Interfaces
System interfaces vary according to the configuration. The configuration can be either dual MGC
(hot-standby) or standalone. The physical interface is described in the following section.
Physical Interface
The physical interface between the MGC and the mediation software (for example, Billing and
Measurements Server (BAMS)) relies on guaranteed delivery of the CDB information between both
MGCs. The interface consists of dual Ethernet links. Each link is physically isolated for redundancy.
OL-1089-11
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
1-1
Page 24
Billing Capabilities Overview
RADIUS Interface
Message Interface
Chapter 1 Billing Interfaces
The RADIUS Enhancement for Accounting feature provides RADIUS interface support on the PGW
2200 for CDR data. For more information about the feature, including new CDRs, refer to the RADIUS
Enhancement for Accounting feature guide.
The CDB message interface is a one-way interface to the CDR dumper. The following paragraphs
describe the CDR message format for messages sent to the CDR dumper. The CDR dumper saves the
CDB message into the CDR files without any conversion or data manipulation.
CDBs are written to disk in a binary, tag-length-value (TLV) format. Many mediation systems depend
on input data that is preformatted in an ASCII format. An optional BAMS converts the MGC CDR billing
output files to ASCII.
The accuracy selection for timepoints is configurable on the MGC as seconds or milliseconds. In order
for the ASCII representation of timepoints to be properly displayed, a place holder for each type has been
provided in the ASCII output layout. For each timepoint type, two entries are contained in the output
format, one entry for seconds granularity and another entry for milliseconds granularity.
A downstream mediation or billing system (for example, BAMS) can easily parse these ASCII records.
Each record is prefixed in the ASCII file with a record identifier field, for example a 1110 record would
begin as follows: 1110,1234,5678,2222,...
The ASCII files are named with the same prefix name specified (refer to page 1-20 for a prefix example),
and postfixed with “.csv” rather than “.bin”. Each file resides in the /opt/CiscoMGC/var/bam directory.
Note It is the system operator's responsibility to manage files created by the MGC billing process, including
archiving and deleting files from the system.
CDB Message Format
The format of CDB messages being sent to the CDR dumper is based on tag, length, and value (TLV).
Each field within the CDB message has a tag, length, and value.
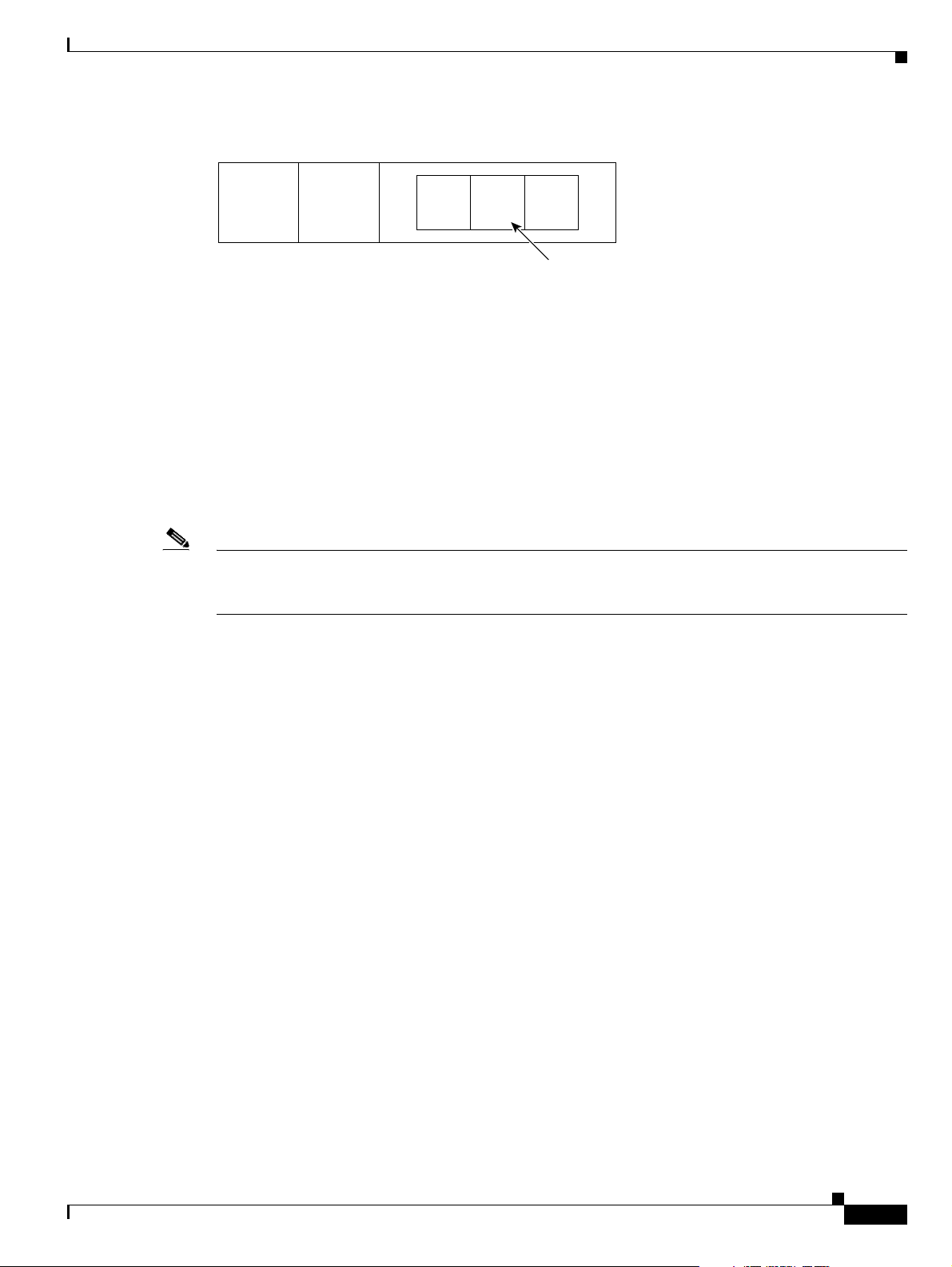
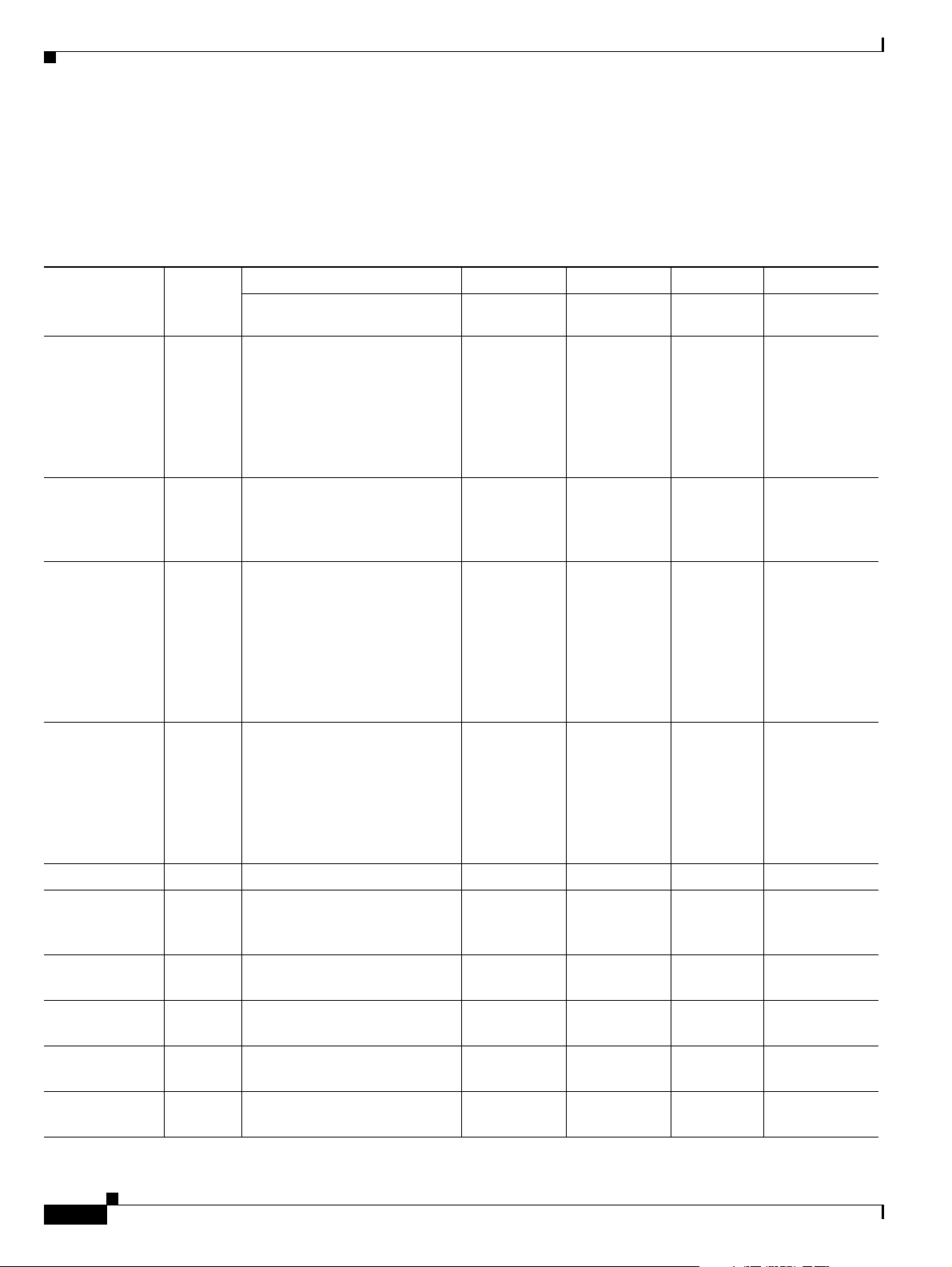
Figure 1-1 shows how the CDB record itself is also in TLV format with the value part composed of
multiple sub-TLVs. For performance reasons the first few fields(tags) of the value portion of the CDB
exists in a fixed order for every message. These fields are the Unique Call ID (tag 5000), CDB Version
(tag 4000), and CDB Timepoint (tag 4001).
Note These three fields are fixed so that the CDR dumper can have direct access to these fields without having
to parse or search through all the CDB message TLV fields.
As shown in Figure 1-1, the first tag in the CDB record identifies the CDB message type. The length
indicates the length of the entire message, excluding 4 bytes (2 bytes for the message tag and 2 bytes for
the length).
1-2
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
OL-1089-11
Page 25
Chapter 1 Billing Interfaces
Figure 1-1 CDB TLV Record Format
Billing Capabilities Overview
Ta g Length
Ta g Length
Value
57859
Sub-TLV messages
The CDB message has both mandatory fields and optional fields. The following fields are mandatory in
each CDB message.
• Unique Call ID
• Ve rs i on
• CDB Timestamp
All other fields in the CDB message are considered optional. The optional fields do not appear in any
sort of predefined order. The TLV format allows the application to be insensitive to the order of the
message data. For example, in a 1010 Answer CDB message, the Call Reference ID tag (4002) could
appear as the first optional field, whereas in another CDB message, such as 1040 Release, the Call
Reference ID tag could appear as the last optional field.
Note The mandatory fields exist in each CDB message, with their associated values and locations. The
optional fields can have no value. Optional fields with no value are not included in the CDB message, to
improve performance.
Tag Values
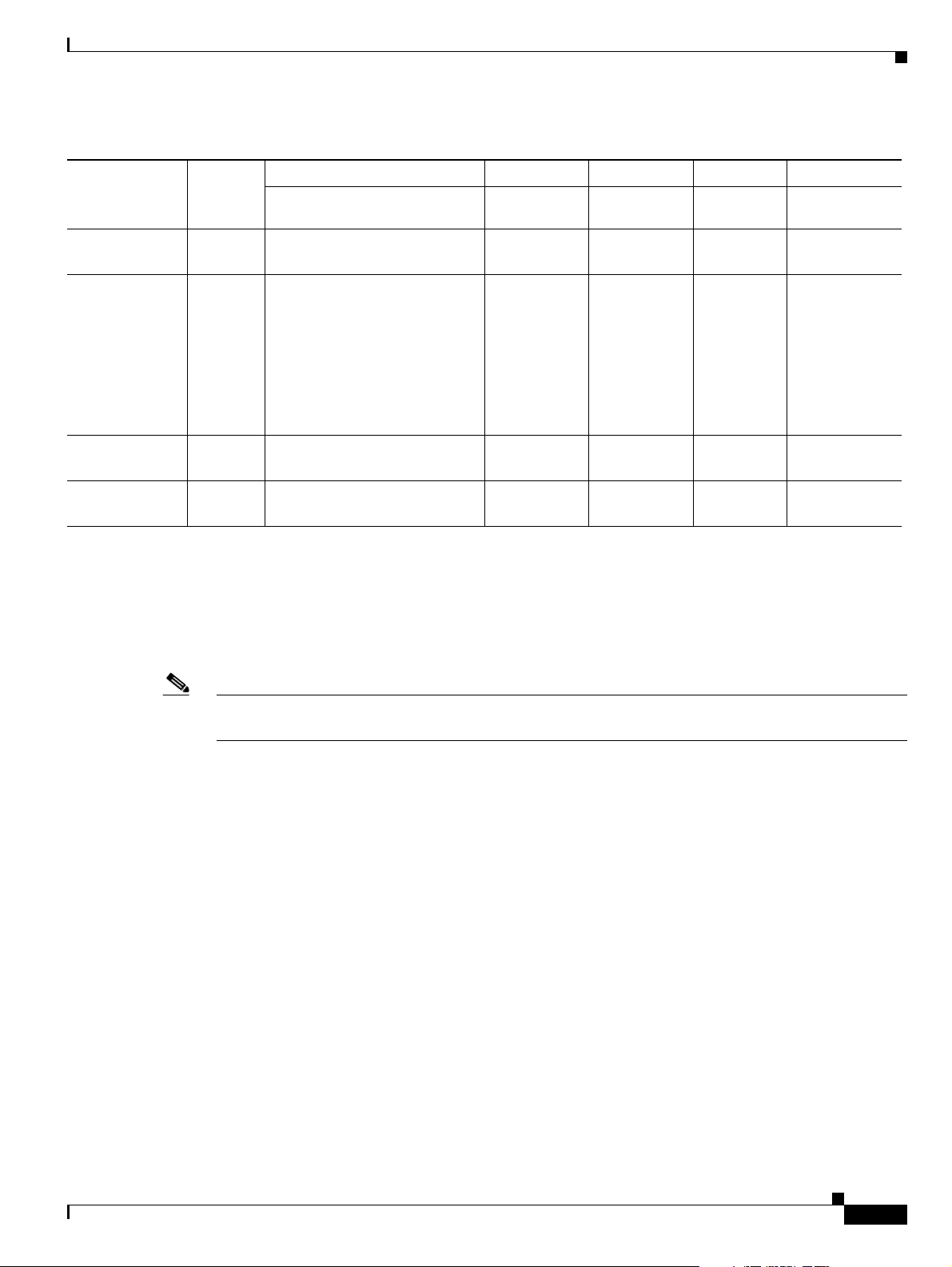
As shown in Figure 1-2, the tags are divided into categories. The first tag category is assigned to the CDB
message ID(s), the second category is assigned to CDB format fields, and the third category is assigned
to miscellaneous usage.
Each category is divided into two or more sections. One section is the MGC range, and another section
is the customer-defined range. Customer-defined ranges (for each category) can be used to further
process the CDB records as required by the customer.
For example, in Figure 1-2, a Cisco MGC message ID range defined by a customer (1900 through 1999)
can be used for generating customer-specific CDB auditing records. The auditing records can be for
beginning and ending the CDR file. The field tag range can also use the customer-defined range for the
field category (5900 through 5999) to define new fields in the CDB auditing records.
OL-1089-11
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
1-3
Page 26

Billing Capabilities Overview
Figure 1-2 CDB Tag Categories
MGC message IDs
Chapter 1 Billing Interfaces
1000
Formats and Codes
Customer defined
MGC ANSI format
MGC ITU format
MGC generic format
Reserved
Customer defined
MGC miscellaneous
Reserved
Customer defined
1900
1999
2999
3999
4999
5900
5999
6999
7900
7999
CDB message ID tag category
CDB fields tag category
Miscellaneous tag category
57860
Note The length indicator value does not include the field tag octets (2 octets) or the length indicator octets
CDB Record Types
The CDB message tag and the length fields are binary encoded using big-endian (BE). The tag field
holds the value to identify the CDB field, and the length field holds the number of octets (length) of the
CDB field.
(2 octets).
The CDB field value is encoded as specified BE, International Alphabet No. 5 (IA5), ANSI T1.113, or
ITU Q.763).
This section describes different types of CDBs and their relation to PIC events. Creation of the CDB is
based on certain PIC events (refer to Tab le 1 - 1 ), and other call events.
1-4
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
OL-1089-11
Page 27
Chapter 1 Billing Interfaces
Billing Capabilities Overview
Ta b le 1- 1 CD B Typ e s
CDB Tag
Point in Call Event Description
Answer call event Call went through and was answered. 1010 Set CDB record
Deselected outgoing
Circuit cannot be used, passed to another. 1020 Deselected outgoing circuit
circuit event
Aborted attempt call event Call did not get to setup status. 1030 Aborted attempt CDB record
Release call event Released call. 1040 Release CDB record
Interrupted call event Call terminating without release message. 1050 Interrupted CDB record
On-going call event Long call. 1060 On-going call CDB record
Maintenance CDB record Circuit maintenance. 1070 Maintenance CDB record
N/A Sent as a result of a Cisco MGC audit or a change in
circuit counts via the sta-aud-cic MML command.
External access CDB Call sent a query to a Service Control Point (SCP) (or
to another external device or database).
File header CDB CDR dumper creates the file header CDB at the
beginning of each CDR file.
File footer CDB CDR dumper creates the file footer CDB at the end of
each CDR file.
End of a call CDB This CDB is generated when the MGC is configured
to have one CDB per call.
It is generated at the end of the call (as in Release
CDB) or when the call did not get to setup status (as
in Aborted attempt CDB).
Note If the Cisco MGC is configured for 1110
output, the 1010, 1030, and 1040 CDBs must
not be configured for inclusion in the output
billing files.
Half call slave release
event CDB
Half call slave ongoing
call event CDB
Refer to the 1110 CDB definition and apply to a
non-controlling slave half call instance.
Refer to th 1060 CDB definition and apply to a
non-controlling slave half call instance.
Value CDB Message/Record
CDB record
1071 SS7 CIC Audit CDB record
1080 External access CDB record
1090 File header CDB record
1100 File footer CDB record
1110 End of a Call CDB
1210 Slave End of a Call CDB
1260 Slave Long Duration Call
CDB
OL-1089-11
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
1-5
Page 28
Chapter 1 Billing Interfaces
Call Data Block Descriptions
Call Data Block Descriptions
The CDB consists of several call data elements (CDEs) that are related to a certain point in call (PIC).
Each CDE has a tag, a length, and a value. Tab le 1 -2 defines the CDE fields in a CDB.
Table 1-2 CDB Call Data Element Fields for Current Release
CDE Tag Numbers
CDB Name CDB Tag
Common
Answered 1010 4000–4005, 4008–4016, 4029,
4034–4043, 4048, 4060, 4063,
4066–4073, 4080, 4081,
4083–4086, 4089, 4090,
4092–4096, 4201–4207,
4209–4212, 4236, 4237,
4240–4243, 5000
Deselected 1020 4000–4003, 4006, 4008, 4009,
4015, 4016, 4019, 4020, 4028,
4034–4037, 4081, 4232, 4233,
5000
Aborted 1030 4000–4004, 4006, 4008–4016,
4019, 4020, 4028, 4029,
4034–4039, 4046–4048,
4060–4062, 4065–4073,
4078–4080, 4082–4096, 4098,
4099, 4201–4212, 4232, 4233,
4236, 4237, 4239, 4240–4245,
4246, 5000
Release 1040 4000–4002, 4006, 4019, 4020,
4028, 4030, 4044, 4046, 4047,
4061, 4062, 4078, 4079,
4082–4091, 4095–4099,
4205–4210, 4213, 4214,
4227–4231, 4239, 4240, 4241,
5000
Interrupted 1050 4000–4002, 4007, 4081, 5000
Ongoing 1060 4000–4005, 4008–4010, 4012,
4014–4016, 4066–4073, 4080,
4081, 4213, 4214, 4237, 5000
Maintenance 1070 4000–4002, 4017, 4018, 4032,
4074–4077, 4081, 5000
SS7 CIC Audit 1071 4000–4002, 4017, 4074, 4081,
5000
External DB 1080 4000–4002, 4040– 4043, 4234,
4235, 5000
File Header
1090 4000–4002 6000, 6001,
CDB
Millisecond
Granularity
4100–4105 2000, 2001,
ANSI
2003–2007,
2009–2020
ITU
3000, 3001,
3003,
3005–3007,
3009–3013,
3017–3020
4100, 4101,
2008–2012 3008–3012 6100–6104
4106, 4108,
4109
4100–4103,
4106–4109,
2000, 2001,
2003–2009,
2011–2020
3000, 3001,
3003,
3005–3009,
3011, 3013,
3017–3020
4106–4109, 2008 3008
4100–4105, 2018–2020 3017–3020
Miscellaneous/
Protocol Specific
6100–6104
6100–6104
6004
1-6
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
OL-1089-11
Page 29
Chapter 1 Billing Interfaces
Table 1-2 CDB Call Data Element Fields for Current Release (continued)
CDE Tag Numbers
CDB Name CDB Tag
File Footer
1100 4000–4002 6000, 6002,
Common
CDB
End of Call 1110 4000–4002, 4008–4012,
4014–4016, 4028, 4034–4037,
4046, 4047, 4060–4063, 4065,
4068, 4072, 4078–4080,
4082–4099, 4201–4212, 4213,
4214, 4227–4231, 4232, 4233,
4236, 4237, 4239, 4240–4245,
4246, 5000
Slave End of
Call
Slave Long
Duration Call
1210 4002, 4003, 4006, 4008, 4009,
4015, 4016, 4227, 4228, 5000
1260 4002, 4003, 4006, 4008, 4009,
4015, 4016, 4227, 4228, 5000
Millisecond
Granularity
4100–4109, 2000–2005,
Call Data Block Descriptions
ANSI
ITU
Miscellaneous/
Protocol Specific
6003, 6004
2007, 2008,
2013, 2015,
2017–2020
3000, 3001,
3003, 3005,
3007, 3008,
3017–3020
Enabling Call Screening
To initialize the database that stores call screening information, modify the SysConnectDataAccess
parameter in the Engine section of the XECfgParm.dat file: For parameter modification, enter
SysConnectDataAccess.
Note Making changes to the XECfgParm.dat file requires the system software to be stopped, the parameter
value changed, and the software restarted. Contact Cisco TAC before stopping the system software.
To enable or disable the A-number and B-number analysis in the call screening database, enter one of
the following values:
• If you do not have the database environment set with all the required data populated, set this value
to false (default).
• If you have the database and want the system to access it, set this value to true.
Configuring Call Detail Record File Output
To configure the CDR file output, modify the following parameters in the Data Dumper and Engine
sections of the XECfgParm.dat file:
Parameter modification: engine.CDRencodingFormat
To specify the CDR file encoding format, enter one of the following values:
• AnsiCDB-North American (default)
OL-1089-11
• ItuCDB-European
Parameter modification: engine.CDRtimeStamp
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
1-7
Page 30
Call Data Block Descriptions
To specify the CDR file timestamp unit, enter one of the following values:
• S-Seconds (default).
• M-Milliseconds; use this parameter if your configuration uses TCAP.
Note If you use 1110 in the engine.CDRmessageTypes parameter (for TCAP), you must specify milliseconds
for the CDRtimeStamp value.
Note The timestamp value is in Coordinated Universal Time (UTC). Previously the term used was Greenwich
Mean Time (GMT).
Configuring Call Detail Record Message Types
Parameter modification: engine.CDRmessageTypes
To specify which CDBs (statistics taken at various points in a call) are recorded during a call, enter one
of the two following sets of values (each number represents a point in a call):
• 1010, 1020, 1030, 1040, 1050, 1060, 1070, 1080—Use this set of values if your CDR files are used
by a measurement server or by another CDR reader.
Chapter 1 Billing Interfaces
• 1060, 1110—Use this set of values if the end-of-call record is desired.
• 1071—Use this set of values for BAMS measurements.
Enabling Call Screening
To initialize the database that stores call screening information, modify the parameters shown in
Table 1-3.
Table 1-3 Call Screening Parameters
Parameter Modification
engine.SysConnectDataAccess To enable or disable the A-number and B-number analysis in
the call screening database, enter one of the following values:
• If you do not have the database environment set with all
• If you have the database and want the system to access it,
Configuring Call Detail Record File Output
the required data populated, set this value to false
(default).
set this value to true.
1-8
To configure the CDR file output, modify the parameters shown in Table 1-4 in the Data Dumper and
Engine sections of the XECfgParm.dat file:
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
OL-1089-11
Page 31

Chapter 1 Billing Interfaces
Table 1-4 Call Detail Record File Output Parameters
Parameter Modification
engine.CDRencodingFormat To specify the call detail record (CDR) file encoding format,
engine.CDRmessageTypes To specify which call detail blocks (CDBs, statistics taken at
engine.CDRtimeStamp To specify the CDR file time-stamp unit, enter one of the
Call Data Element Descriptions
enter one of the following values:
• AnsiCDB—North American (default)
• ItuCDB—European
various points in a call) are recorded during a call, enter one
of the two following sets of values (each number represents a
point in a call):
• 1010, 1020, 1030, 1040, 1050, 1060, 1070, 1080—Use
this set of values if your CDR files are to be read by a
measurement server or other CDR reader.
• 1060, 1110—Use this set of values if the end-of-call
record is desired.
• 1071—Use this set of values for BAMS measurements.
following values:
cdrDmpr.openCDR To indicate whether the standard data dumper writes out CDR
cdrDmpr.seqFile Indicate the location of the file for storing or retrieving the
Call Data Element Descriptions
This section describes the current CDB CDEs. The CDEs are divided into three tables (ANSI, ITU, and
generic format).
The ANSI formatted fields are used for customers requesting ANSI-formatted fields (as is the case for
North American customers) and is based on ANSI T1.113.1995.
• S—Seconds (default).
• M—Milliseconds; use this parameter if your
configuration uses TCAP or BAMS.
Note If you use are using BAMS or 1110 in the
engine.CDRmessageTypes parameter (for TCAP),
you must specify milliseconds (M) for the
CDRtimeStamp value.
files, enter one of the following values:
• true—Standard data dumper opens a CDR file and logs
call detail blocks (CDBs).
• false—Standard data dumper does not open a CDR file
and does not log CDBs.
CDR sequence number (range is 1 to 999999).
Default: ../var/.cdr.seq
OL-1089-11
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
1-9
Page 32

Call Data Element Descriptions
The ITU formatted fields are used for customers requesting ITU-formatted-fields (as is the case for
European customers) and is based on ITU-Q.763.
The generic format provides common CDEs with one encoding scheme. The generic format is used to
handle different protocol variants.
Table 1-5 defines all the fields that can exist in any given CDB along with the associated tag and type
for each one.
Table 1-5 CDE Detail Description for the Current Release
Chapter 1 Billing Interfaces
Field Name
Tag
Value
Answered
(1010)
Deselected
(1020)
Aborted
(1030)
Release
(1040)
Interrupted
(1050)
Ongoing
(1060)
Maintenance
(1070)
External
DB
(1080)
End of
Call
(1110)
ANSI Based Formatted Fields
Calling Party
2000 Y N Y N N N N N Y N
Category
User Service
2001 Y N Y N N N N N Y N
Information
Originating Line
2002 Y N Y N N N N N N N
Information
Calling Number
2003 Y N Y N N N N N Y N
Nature of Address
Charged Number
2004 Y N Y N N N N N Y N
Nature of Address
Dialed Number
2005 Y N Y N N N N N Y N
Nature of Address
LRN Nature of
2006 Y N Y N N N N N N N
Address
Called Number
2007 Y N Y N N N N N Y N
Nature of Address
Reason Code 2008 N Y Y Y N N N N Y N
Forward Call
2009 Y Y Y N N N N N N N
Indicators
Received
Forward Call
2010 Y Y N N N N N N N N
Indicators Sent
Nature of
2011 Y Y Y N N N N N N N
Connection
Indicators
Received
Nature of
2012 Y Y Y N N N N N N N
Connection
Indicators Sent
Transit Network
2013 Y N Y N N N N N Y N
Selection
1071
1210
1260
1-10
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
OL-1089-11
Page 33

Chapter 1 Billing Interfaces
Table 1-5 CDE Detail Description for the Current Release (continued)
Call Data Element Descriptions
Tag
Field Name
Carrier
Value
2014 Y N Y N N N N N N N
Identification
Parameter
Carrier Selection
2015 Y N Y N N N N N Y N
Parameter
Jurisdiction
2016 Y N Y N N N N N N N
Information
Parameter
Redirecting
2017 Y N Y N N N N N Y N
Number NOA
Egress Calling
2018 Y N Y N N Y N N Y N
Number NOA
Egress Redirecting
2019 Y N Y N N Y N N Y N
Number NOA
Egress Original
2020 Y N Y N N Y N N Y N
Called Number
NOA
ITU Based Formatted Fields
Answered
(1010)
Deselected
(1020)
Aborted
(1030)
Release
(1040)
Interrupted
(1050)
Ongoing
(1060)
Maintenance
(1070)
External
DB
(1080)
End of
Call
(1110)
1071
1210
1260
Calling Party
3000 Y N Y N N N N N Y N
Category
User Service
3001 Y N Y N N N N N Y N
Information
Calling Number
3003 Y N Y N N N N N Y N
Nature of Address
Dialed Number
3005 Y N Y N N N N N Y N
Nature of Address
LRN Nature of
3006 Y N Y N N N N N N N
Address
Called Number
3007 Y N Y N N N N N Y N
Nature of Address
Reason Code 3008 N Y Y Y N N N N Y N
Forward Call
3009 Y Y Y N N N N N N N
Indicators
Received
Forward Call
3010 Y Y N N N N N N N N
Indicators Sent
Nature of
3011 Y Y Y N N N N N N N
Connection
Indicators
Received
OL-1089-11
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
1-11
Page 34

Call Data Element Descriptions
Table 1-5 CDE Detail Description for the Current Release (continued)
Chapter 1 Billing Interfaces
Field Name
Nature of
AnsTag
Value
wered
(1010)
3012 Y Y N N N N N N N N
Deselected
(1020)
Aborted
(1030)
Release
(1040)
Interrupted
(1050)
Ongoing
(1060)
Maintenance
(1070)
External
DB
(1080)
End of
Call
(1110)
1071
1210
1260
Connection
Indicators Sent
Transit Network
3013 Y N Y N N N N N N N
Selection
Redirecting
3017 Y N Y N N N N N Y N
Number NOA
Egress Calling
3018 Y N Y N N Y N N Y N
Number NOA
Egress Redirecting
3019 Y N Y N N Y N N Y N
Number NOA
Egress Original
3020 Y N Y N N Y N N Y N
Called Number
NOA
MGC Generic Tags
CDB Version4000YYY YYYYY Y1071
CDB Timepoint 4001 Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y 1071
Call Reference ID 4002 Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y 1210
1260
IAM Timepoint 4003 Y Y Y N N Y N N N
1210
1260
ACM Timepoint4004YNY NNYNN N
ANM Timepoint 4005 Y N N N N Y N N N
REL Timepoint 4006 N Y Y Y N N N N N
Crash Timepoin t 4007 N N N N Y N N N N
Originating Trunk
4008 Y Y Y N N Y N N Y
Group
Originating
4009 Y Y Y N N Y N N Y
Member
Calling Number 4010 Y N Y N N Y N N Y
Charged Number 4011 Y N Y N N N N N Y
Dialed Number 4012 Y N Y N N Y N N Y
LRN Number 4013 Y N Y N N N N N N
Called Number 4014 Y N Y N N Y N N Y
Terminating Trunk
4015 Y Y Y N N Y N N Y
Group
Terminating
4016 Y Y Y N N Y N N Y
Member
N
N
1210
N
1210
1260
1210
1260
N
N
N
N
N
1210
1260
1210
1260
1-12
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
OL-1089-11
Page 35

Chapter 1 Billing Interfaces
Table 1-5 CDE Detail Description for the Current Release (continued)
Call Data Element Descriptions
Field Name
Tag
Value
Answered
(1010)
Deselected
(1020)
Aborted
(1030)
Release
(1040)
Interrupted
(1050)
Ongoing
(1060)
Maintenance
(1070)
External
DB
(1080)
End of
Call
(1110)
1071
1210
1260
Maint Trunk Group 4017 N N N N N N Y N N 1071
Maint Circuit
4018 N N N N N N Y N N N
Member
Glare Encountered 4019 N Y Y Y N N N N N N
RLC Release
4020 N Y Y Y N N N N N N
Timepoint
First Release
4028 N Y Y Y N N N N Y N
Source
LNP Dip 4029 Y N Y N N N N N N N
Total Meter Pulses 4030 N N N Y N N N N N N
Maint Type 4032 N N N N N N Y N N N
Maint Reason
4033 N N N N N N Y N N N
(Retired in Release
9.4(1))
Ingress
Originating Point
Code
Ingress
Destination Point
Code
Egress
Originating Point
Code
Egress
Destination Point
Code
Ingress Media
4034 Y Y Y N N N N N Y (9.3
and
up)
4035 Y Y Y N N N N N Y (9.3
and
up)
4036 Y Y Y N N N N N Y (9.3
and
up)
4037 Y Y Y N N N N N Y (9.3
and
up)
4038 Y Y Y N N N N N N N
N
N
N
N
Gateway ID
Egress Media
4039 Y Y Y N N N N N N N
Gateway ID
TCAP
4040 Y N N N N N N Y N N
Transaction
Identification
Transaction Start
4041 Y N N N N N N Y N N
Time
Transaction End
4042 Y N N N N N N Y N N
Time
TCAP Database
4043 Y N N N N N N Y N N
Identification
OL-1089-11
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
1-13
Page 36

Call Data Element Descriptions
Table 1-5 CDE Detail Description for the Current Release (continued)
Chapter 1 Billing Interfaces
Field Name
Announcement
AnsTag
Value
wered
(1010)
4044 N N N Y N N N N N N
Deselected
(1020)
Aborted
(1030)
Release
(1040)
Interrupted
(1050)
Ongoing
(1060)
Maintenance
(1070)
External
DB
(1080)
End of
Call
(1110)
Identification
Ingress Gateway
4046 N N Y Y N N N N Y N
Packet Info
Egress Gateway
4047 N N Y Y N N N N Y N
Packet Info
Directional Flag 4048 Y N Y N N N N N N N
Service Logic ID 4049 N N N N N N N Y N N
AMA Line
4050 N N N N N N N Y N N
Number
Originating
4052 N N N N N N N N N N
Gateway
Primary Select
Terminating
4053 N N N N N N N N N N
Gateway
Primary Select
Redirecting
4060 Y N Y N N N N N Y N
Number
Tariff Rate 4061 N N Y Y N N N N Y N
Scale Factor 4062 N N Y Y N N N N Y N
Test Line Indicator 4063 Y N Y N N N N N Y N
Redirection
4065 N N Y N N N N N Y N
Number
Ingress SigPath ID 4066 Y N Y N N Y N N N N
Ingress Span ID 4067 Y N Y N N Y N N N N
Ingress BearChan ID4068 Y N Y N N Y N N Y (9.3
and
up)
Ingress Protocol ID4069 Y N Y N N Y N N N N
1071
1210
1260
N
Egress SigPath ID 4070 Y N Y N N Y N N N N
Egress Span ID 4071 Y N Y N N Y N N N N
Egress BearChan ID4072 Y N Y N N Y N N Y (9.3
and
up)
Egress Protocol ID 4073 Y N Y N N Y N N N N
Maintenance
4074 N N N N N N Y N N 1071
SigPath ID
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
1-14
OL-1089-11
N
Page 37

Chapter 1 Billing Interfaces
Table 1-5 CDE Detail Description for the Current Release (continued)
Call Data Element Descriptions
Field Name
Tag
Value
Answered
(1010)
Deselected
(1020)
Aborted
(1030)
Release
(1040)
Interrupted
(1050)
Ongoing
(1060)
Maintenance
(1070)
External
DB
(1080)
End of
Call
(1110)
Maintenance Span ID4075 N N N N N N Y N N N
Maintenance
4076 N N N N N N Y N N N
BearChan ID
Maintenance
4077 N N N N N N Y N N N
Circuits Count
Charge Band
4078 N N Y Y N N N N Y N
Number
Furnish Charging
4079 N N Y Y N N N N Y N
Information
Original Called
4080 Y N Y N N Y N N Y N
Number
T.38 Fax Call 4081 Y Y N N Y Y Y Y N N
Charge Unit
4082 N N Y Y N N N N Y N
Number
Charge Indicator 4083 Y N Y Y N N N N Y N
Outgoing Calling
4084 Y N Y Y N N N N Y N
Party Number
MCID Request
4085 Y N Y Y N N N N Y N
Indicator
MCID Response
4086 Y N Y Y N N N N Y N
Indicator
Ingress MGCP
4087 N N Y Y N N N N Y N
DLCX Return
Code
Egress MGCP
4088 N N Y Y N N N N Y N
DLCX Return
Code
Network
4089 Y N Y Y N N N N Y N
Translated
Address Indicator
Reservation
4090 Y N Y Y N N N N Y N
Request Accepted
Reservation
4091 N N Y Y N N N N Y N
Request Error
Count
ATM Ingress
4092 Y N Y N N N N N Y N
Configured Profile
ATM Egress
4093 Y N Y N N N N N Y N
Configured Profile
1071
1210
1260
OL-1089-11
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
1-15
Page 38

Call Data Element Descriptions
Table 1-5 CDE Detail Description for the Current Release (continued)
Chapter 1 Billing Interfaces
Field Name
ATM Negotiated
AnsTag
Value
wered
(1010)
4094 Y N Y N N N N N Y N
Deselected
(1020)
Aborted
(1030)
Release
(1040)
Interrupted
(1050)
Ongoing
(1060)
Maintenance
(1070)
External
DB
(1080)
End of
Call
(1110)
Profiler
Route List Name 4095 Y N Y Y N N N N Y N
Route Name 4096 Y N Y Y N N N N Y N
MGCP Script
4097 N N N Y N N N N Y N
Response String
Originating Leg
4098 N N Y Y N N N N Y N
DSP statistics (9.4
and up)
Terminating Leg
4099 N N Y Y N N N N Y N
DSP statistics (9.4
and up)
Originating
4201 Y N Y N N N N N Y N
Remote SIP Host
Originating Local
4202 Y N Y N N N N N Y N
SIP Host
SIP Call ID 4203 Y N Y N N N N N Y N
Source IP Address 4204 Y N Y N N N N N Y N
Ingress Media
4205 Y N Y Y N N N N Y N
Device Address
Egress Media
4206 Y N Y Y N N N N Y N
Device Address
Initial Codec 4207 Y N Y Y N N N N Y N
Final Codec 4208 N N Y Y N N N N Y N
Ingress Media
4209 Y N Y Y N N N N Y N
Device Port
Egress Media
4210 Y N Y Y N N N N Y N
Device Port
Originating VPN ID4211 Y N Y N N N N N Y N
1071
1210
1260
Terminating VPN ID4212 Y N Y N N N N N Y N
Meter Pulses
4213 N N N Y N Y N N Y N
Received
Meter Pulses Sent 4214 N N N Y N Y N N Y N
Charge Tariff Info 4215 N N N Y N N N N Y N
Advice of Charge
4216 N N N Y N N N N Y N
Indicator
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
1-16
OL-1089-11
Page 39

Chapter 1 Billing Interfaces
Table 1-5 CDE Detail Description for the Current Release (continued)
Call Data Element Descriptions
Field Name
Short Call
AnsTag
Value
wered
(1010)
4217 N N N Y N N N N Y N
Deselected
(1020)
Aborted
(1030)
Release
(1040)
Interrupted
(1050)
Ongoing
(1060)
Maintenance
(1070)
External
DB
(1080)
End of
Call
(1110)
Indicator
Charge Limit
4218 N N N Y N N N N Y N
Exceeded
Call Recovered
4219 N N N Y N N N N Y N
Indication
Partial Calling
4220 Y N Y N N Y N N Y N
Line Identity
Service Activation 4221 N N N Y N N N N Y N
PRI AOC Invoke
4222 N N Y Y N N N N Y N
Type
PRI AOC – S
4223 N N Y Y N N N N Y N
Charge
Information
PRI AOC – D
4224 N N Y Y N N N N Y N
Charge
Information
PRI AOC – E
4225 N N Y Y N N N N Y N
Charge
Information
PRI AOC Invoke
4226 N N Y Y N N N N Y N
Failure
RO/PR Executed
4227 N N N Y N N N N Y 1210
(added in 9.6)
RO/PR Other Call
4228 N N N Y N N N N Y 1210
Ref (added 9.6)
RO/PR Trunk
4229 N N N Y N N N N Y N
Group Info
(added in 9.6)
RO/PR
4230 N N N Y N N N N Y N
Replacement Chan
ID
(added in 9.6)
RO Switchover
4231 N N N Y N N N N Y N
Timestamp
(added in 9.6)
Rejecting Location
4232 N Y Y N N N N N Y N
Label
(added in 9.6(1))
1071
1210
1260
1260
1260
OL-1089-11
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
1-17
Page 40

Call Data Element Descriptions
Table 1-5 CDE Detail Description for the Current Release (continued)
Chapter 1 Billing Interfaces
Field Name
Rejecting Location
AnsTag
Value
wered
(1010)
4233 N Y Y N N N N N Y N
Deselected
(1020)
Aborted
(1030)
Release
(1040)
Interrupted
(1050)
Ongoing
(1060)
Maintenance
(1070)
External
DB
(1080)
End of
Call
(1110)
Label Direction
(added in 9.6(1))
PRI AOC – E
4234 N N N Y N N N N N 1071
Charge
Information
PRI AOC Invoke
4235 N N N Y N N N N N 1071
Failure
H323 Destination 4236 Y N Y N N N N N Y
Ingress
4237 Y N Y N N Y N N Y N
Redirecting
Number
Service Usage
4239 N N Y Y N N N N Y N
Data
CNAM DIP 4240 Y N Y Y N N N N Y N
Calling Name 4241 Y N Y Y N N N N Y N
Terminating
4242 Y N Y N N N N N Y N
Remote SIP Host
Terminating Local
4243 Y N Y N N N N N Y N
SIP Host
License Rejecting
4244 N N Y N N N N N Y N
Reason
License Rejecting
4245 N N Y N N N N N Y N
Direction
SIP Transport 4246 Y N Y N N N N N Y N
SIP Routing URI
4247 Y N Y N N N N N Y N
Source
SIP Routing URI 4248 Y N Y N N N N N Y N
Millisecond Granularity Timepoint Fields
1071
1210
1260
IAM Timepoint
Received_ms
IAM Timepoint
Sent_ms
ACM Timepoint
Received_ms
ACM Timepoint
Sent_ms
ANM Timepoint
Received_ms
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
1-18
4100 Y Y Y N N Y N N Y N
4101 Y Y Y N N Y N N Y N
4102 Y N Y N N Y N N Y N
4103 Y N Y N N Y N N Y N
4104 Y N N N N Y N N Y N
OL-1089-11
Page 41

Chapter 1 Billing Interfaces
Table 1-5 CDE Detail Description for the Current Release (continued)
Cisco MGC Billing Interfaces
Ans-
Tag
Field Name
ANM Timepoint
Sent_ms
First REL
Timepoint_ms
Second REL
Timepoint_ms
RLC Timepoint
Received_ms
RLC Timepoint
Sent_ms
Cisco Reserved Tags
Unique Call Correlator ID (Release 9
and later)
Miscellaneous Fields This field is used only in the File Header CDB and File Footer CDB. These CDBs are not
MGC ID 6000
File Start Time 6001
File End Time 6002
Total Number of
CDB records
MGC Version 6004
Interim CDB 6005 N N N Y N N N N Y N
Protocol Specific Fields
Value
4105 Y N N N N Y N N Y N
4106 N Y Y Y N N N N Y N
4107 N N Y Y N N N N Y N
4108 N Y Y Y N N N N Y N
4109 N Y Y Y N N N N Y N
5000 Y Y
6003
wered
(1010)
optional and are generated by the CDR dumper for each CDR file.
Deselected
(1020)
Aborted
(1030)
Y
InterRelease
(1040)
Y Y Y Y Y Y 1071
rupted
(1050)
Ongoing
(1060)
Maintenance
(1070)
External
DB
(1080)
End of
Call
(1110)
1071
1210
1260
1210
1260
TTC Contract # 6100 Y Y Y N N N N N N N
TTC Contract #
NOA
TTC Charge Info 6102 Y Y Y N N N N N N N
TTC Charge Info
Type
TTC Charge Area
Info
6101 Y Y Y N N N N N N N
6103 Y Y Y N N N N N N N
6104 Y Y Y N N N N N N N
Cisco MGC Billing Interfaces
There are two billing interfaces provided by the Cisco MGC. They are:
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
OL-1089-11
1-19
Page 42

Redundant Cisco MGC Configuration
• File Transfer Protocol (FTP) interface
• Generic interface
FTP Interface
The FTP interface allows the user to FTP the CDR files from the spool directory. This interface supports
users who own a mediation system or data collocation system. Users can process the CDR files on a
separate system.
The Cisco MGC runs on Solaris UNIX that provides the standard file transfer capability (FTP). The
Cisco MGC can be configured so other systems can download the CDR files from the spool directory.
The FTP download can be restricted by establishing user privileges.
The data collector and mediation systems can use this interface by periodically downloading the files.
The CDR files provide a sequence number and the timestamp of the file creation. The data collection
system or the mediation system can use this information to determine the desired file to download.
The Cisco MGC has several configuration parameters to write the CDR file. The following are the
configuration parameters:
• The prefix in the file name (CDR_YYYYMMDDHHMMSS_SeqNo) where SeqNo is in the format
Chapter 1 Billing Interfaces
(000001 to 999999)
• Spool directory
• Frequent creation of the file
The sequence number provides an audit capability to the data collection system or mediation software.
The sequence number is unique and ranges from 1 to 999999. If the system fails or restarts, it uses the
next sequence number (last sequence number + 1). When the sequence number reaches 999999, it then
restarts at 1.
Generic Interface
The Cisco MGC defines a generic or flexible billing interface. This is an internal interface between the
call processing module and the CDR dumper in Cisco MGC. Users cannot modify this interface.
This interface provides a CDB data stream for the CDR dumper. The generic interface is based on the
flexible CDB record layout. The record layout uses a tag, length, and value (TLV) encoding mechanism.
The detail messages (that is, CDBs) are explained later in this document.
Redundant Cisco MGC Configuration
In a redundant Cisco MGC configuration, the active Cisco MGC creates checkpoint records to
synchronize it with the standby Cisco MGC. The standby Cisco MGC creates call objects with
appropriate states to allow continued call processing after switchover occurs. When the standby Cisco
MGC becomes active, it starts synchronizing with End Offices (circuit audit). Another aspect of the
architecture is that the Cisco 2600s buffer messages while failover occurs.
Billing under a redundant configuration is basically limited to the following: The active Cisco MGC
generates the CDBs and the standby Cisco MGC does not. When failover occurs, the now active
Cisco MGC generates the CDBs.
1-20
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
OL-1089-11
Page 43

Chapter 1 Billing Interfaces
If a call was stable during the failover, then the newly active Cisco MGC eventually generates an end of
a call CDB (Release CDB or possibly an Interrupted CDB) for each call. The CDBs generated by the
previous standby MGC include the same unique Call IDs. The mediation software requires correlating
the CDB records from both systems. For both systems to be properly correlated, both Cisco MGC clocks
must be synchronized with each other.
Cisco MGC Clock Synchronization
The Cisco MGC uses Network Time Protocol (NTP) to synchronize its time to another server or
reference time source, such as a radio or satellite receiver or modem. For example, the NTP provides
client accuracy that is typically within 1 millisecond on LANs and up to a few tenths of a second on
WANs relative to a primary server synchronized to Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) by a Global
Positioning Service (GPS) receiver. To achieve high accuracy and reliability, typical NTP configurations
use multiple redundant servers and diverse network paths. Some configurations include cryptographic
authentication to prevent accidents or malicious protocol attacks.
Note RFC-1305 provides information on the NTP architecture, protocol, and algorithm.
Cisco MGC Clock Synchronization
Detailed CDB Description
This section contains the distinct record layouts for the CDB. Since each type of CDB is for a different
part of a call, the Cisco MGC provides the related CDEs that are needed.
Note The CDE includes only fields that have values. The layout varies based on the Cisco MGC configuration.
For example, if the Cisco MGC is configured with a protocol that does not support a specific CDE, then
the CDB record does not include that particular CDE.
Answered CDB Record (Tag: 1010/Release 5 or Later)
Table 1-6 lists data about the answered message. This CDB is generated when a call went through and
was answered (when the Cisco MGC receives ANM/Answered message).
Table 1-6 Answered CDB Record
Tag
Field Name
ANSI Based Formatted Fields
Calling Party Category 2000
User Service Information 2001
Originating Line Information 2002
Calling Number Nature of Address 2003
Charged Number Nature of Address 2004
Value Comments
When configured for ANSI-based formatted
fields (Release 7 or later option)
OL-1089-11
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
1-21
Page 44

Detailed CDB Description
Chapter 1 Billing Interfaces
Table 1-6 Answered CDB Record (continued)
Tag
Field Name
Dialed Number Nature of Address 2005
LRN Nature of Address 2006
Called Number Nature of Address 2007
Forward Call Indicators Received 2009
Forward Call Indicators Sent 2010
Nature of Connection Indicators
Received
Nature of Connection Indicators Sent 2012
Transit Network Selection 2013
Carrier Identification Parameter 2014
Carrier Selection Parameter 2015
Jurisdiction Information Parameter 2016
Redirecting Number NOA 2017
Egress Calling Number NOA 2018 Added in a Release 9.5(2) patch
Egress Redirecting Number NOA 2019 Added in a Release 9.5(2) patch
Egress Original Called Number NOA 2020 Added in a Release 9.5(2) patch
ITU Based Formatted Fields
Calling Party Category 3000
User Service Information 3001
Originating Line Information 3002
Calling Number Nature of Address 3003
Dialed Number Nature of Address 3005
LRN Nature of Address 3006
Called Number Nature of Address 3007
Forward Call Indicators Received 3009
Forward Call Indicators Sent 3010
Nature of Connection Indicators
Received
Nature of Connection Indicators Sent 3012
Transit Network Selection 3013
Redirecting Number NOA 3017
Egress Calling Number NOA 3018 Added in a Release 9.5(2) patch
Egress Redirecting Number NOA 3019 Added in a Release 9.5(2) patch
Egress Original Called Number NOA 3020 Added in a Release 9.5(2) patch
Value Comments
2011
When configured for ITU-based formatted
fields (Release 7 or later option)
3011
1-22
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
OL-1089-11
Page 45

Chapter 1 Billing Interfaces
Table 1-6 Answered CDB Record (continued)
Field Name
MGC Generic Tags
CDB Versionb 4000
CDB Timepoint 4001
Call Reference ID 4002
IAM Timepoint 4003 When configured for seconds timepoint
ACM Timepoint 4004 When configured for seconds timepoint
ANM Timepoint 4005 When configured for seconds timepoint
Originating Trunk Group 4008
Originating Member 4009
Calling Number 4010
Charged Number 4011
Dialed Number 4012
LRN Number 4013
Called Number 4014
Terminating Trunk Group 4015
Terminating Member 4016
LNP Dip 4029
MGC Info Field 4031 Disabled as of Release 7.3.x, 7.4.x
Ingress Originating Point Code 4034
Ingress Destination Point Code 4035
Egress Originating Point Code 4036
Egress Destination Point Code 4037
Ingress Media Gateway (CU) 4038 Ingress Media Gateway ID
Egress Media Gateway (CU) 4039 Egress Media Gateway ID
TCAP Transaction Identification 4040
Transaction Start Time 4041
Transaction End Time 4042
TCAP Database Identification 4043
Route Selection Info 4045
Directional Flag 4048
Redirecting Number 4060 Number or address from which forwarded
Test Line Indicator 4063
Detailed CDB Description
Tag
Value Comments
(Release 7 or later option)
(Release 7 or later option)
(Release 7 or later option)
OL-1089-11
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
1-23
Page 46

Detailed CDB Description
Chapter 1 Billing Interfaces
Table 1-6 Answered CDB Record (continued)
Tag
Field Name
Ingress SigPath ID 4066
Ingress Span ID 4067
Ingress BearChan ID 4068
Ingress ProtocolId 4069
Egress SigPath ID 4070
Egress Span ID 4071
Egress BearChan ID 4072
Egress ProtocolId 4073
Original Called Number 4080 Release 9.3(1) and later
Charge Indicator 4083 Release 9.5(2) and later
Outgoing Calling Party Number 4084 Release 9.5(2) and later
MCID Request Indicator 4085 Release 9.5(2) and later
MCID Response Indicator 4086 Release 9.5(2) and later
Network Translated Address Indicator 4089 Release 9.5(2) and later
Reservation Request Accepted 4090 Release 9.5(2) and later
Reservation Request Error Count 4091 Release 9.5(2) and later
ATM Ingress Configured Profile 4092 Release 9.5(2) and later
ATM Egress Configured Profile 4093 Release 9.5(2) and later
ATM Negotiated Profile 4094 Release 9.5(2) and later
Route List Name 4095 Release 9.5(2) and later
Route Name 4096 Release 9.5(2) and later
MGCP Script Response String 4097 Release 9.5(2) and later
Originating Remote SIP Host 4201 Release 9 and later (Named as Ingress SIP URL
Originating Local SIP Host 4202 Release 9 and later (Named as Egress SIP URL
SIP Call ID 4203 Release 9 and later
Source IP Address 4204 Release 9.4(1) and later
Ingress Media Device Address 4205 Release 9.4(1) and later
Egress Media Device Address 4206 Release 9.4(1) and later
Initial Codec 4207 Release 9.4(1) and later
Ingress Media Device Port 4209 Release 9.4(1) and later
Egress Media Device Port 4210 Release 9.4(1) and later
Originating VPN ID 4211 Release 9.4(1) and later
Terminating VPN ID 4212 Release 9.4(1) and later
Partial Calling Line Identity 4220 Release 9.5(2) and later
Value Comments
in versions prior to the Release 9.7(3))
in versions prior to the Release 9.7(3))
1-24
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
OL-1089-11
Page 47

Chapter 1 Billing Interfaces
Table 1-6 Answered CDB Record (continued)
Field Name
H323 Destination 4236 Release 9.7 and later
Ingress Redirecting Number 4237 Added in a Release 9.5(2) patch
CNAM DIP 4240 Release 9.7 and later
Calling Name 4241 Release 9.7 and later
Terminating Remote SIP Host 4242 Release 9.7 and later
Terminating Local SIP Host 4243 Release 9.7 and later
SIP Transport 4246 Release 9.7 and later
SIP Routing URI Source 4247 Release 9.7 and later
SIP Routing URI 4248 Release 9.7 and later
Millisecond Granularity Timepoint Fields
IAM Timepoint Received_ms 4100
IAM Timepoint Sent_ms 4101
ACM Timepoint Received_ms 4102
ACM Timepoint Sent_ms 4103
ANM Timepoint Received_ms 4104
ANM Timepoint Sent_ms 4105
Cisco Reserved Tags
Unique Call ID (Release 9 and later) 5000
Detailed CDB Description
Tag
Value Comments
Deselected Outgoing Circuit CDB Record (Tag: 1020/Release 5 or Later)
Table 1-7 lists data about the deselected outgoing circuit. CDB Tag 1020 is generated when a circuit is
attempted to be used and for some reason the circuit can not be used. The call is then passed to another
circuit to complete the call.
Table 1-7 Deselected Outgoing Circuit CDB Record
Tag
Field Name
ANSI Based Formatted Fields
Reason Code 2008
Forward Call Indicators Received 2009
Forward Call Indicators Sent 2010
Nature of Connection Indicators
Received
Nature of Connection Indicators Sent 2012
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
OL-1089-11
Value Comments
When configured for ANSI encoding (Release 7
or later)
2011
1-25
Page 48

Detailed CDB Description
Chapter 1 Billing Interfaces
Table 1-7 Deselected Outgoing Circuit CDB Record (continued)
Tag
Field Name
ITU Based Formatted Fields
Reason Code 3008
Forward Call Indicators Received 3009
Forward Call Indicators Sent 3010
Nature of Connection Indicators
Received
Nature of Connection Indicators Sent 3012
MGC Generic Tags
CDB Version 4000
CDB Timepoint 4001
Call Reference ID 4002
IAM Timepoint 4003 When timepoint in seconds is selected
REL Timepoint 4006 When timepoint in seconds is selected
Originating Trunk Group 4008
Originating Member 4009
Terminating Trunk Group 4015
Terminating Member 4016
Glare Encountered 4019
RLC Timepoint 4020
First Release Source 4028
Ingress Originating Point Code 4034
Ingress Destination Point Code 4035
Egress Originating Point Code 4036
Egress Destination Point Code 4037
Ingress Media Gateway (CU) 4038
Egress Media Gateway (CU) 4039
Rejecting Location Label 4232 Release 9.6(1) and later
Rejecting Location Label Direction 4233 Release 9.6(1) and later
Millisecond Granularity Timepoint Fields
IAM Timepoint Received_ms 4100
IAM Timepoint Sent_ms 4101
First REL Timepoint_ms 4106
RLC Timepoint Received_ms 4108
Value Comments
When configured for ITU encoding (Release 7 or
later)
3011
When configured for milliseconds (Release 7 or
later)
1-26
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
OL-1089-11
Page 49

Chapter 1 Billing Interfaces
Table 1-7 Deselected Outgoing Circuit CDB Record (continued)
Tag
Field Name
Value Comments
RLC Timepoint Sent_ms 4109
Cisco Reserved Tags
Unique Call ID (Release 9 and later) 5000
Aborted Attempt CDB Record (Tag: 1030/Release 5 or Later)
Table 1-8 lists data about the aborted attempt. CDB Tag 1030 is generated for an attempted call that did
not get to Setup status. That is a call that did not get answered.
Table 1-8 Aborted Attempt CDB Record
Tag
Field Name
ANSI Based Formatted Fields
Calling Party Category 2000
User Service Information 2001
Originating Line Information 2002
Calling Number Nature of Address 2003
Charged Number Nature of Address 2004
Dialed Number Nature of Address 2005
LRN Nature of Address 2006
Called Number Nature of Address 2007
Reason Code 2008
Forward Call Indicators Received 2009
Nature of Connection Indicators
Received
Nature of Connection Indicators Sent 2012
Transit Network Selection 2013
Carrier Identification Parameter 2014
Carrier Selection Parameter 2015
Jurisdiction Information Parameter 2016
Redirecting Number NOA 2017
Egress Calling Number NOA 2018 Added in a Release 9.5(2) patch
Egress Redirecting Number NOA 2019 Added in a Release 9.5(2) patch
Egress Original Called Number NOA 2020 Added in a Release 9.5(2) patch
Value Comments
When configured for ANSI based encoding
(Release 7 or later)
2011
Detailed CDB Description
OL-1089-11
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
1-27
Page 50

Detailed CDB Description
Chapter 1 Billing Interfaces
Table 1-8 Aborted Attempt CDB Record (continued)
Tag
Field Name
ITU Based Formatted Fields
Calling Party Category 3000
User Service Information 3001
Originating Line Information 3002
Calling Number Nature of Address 3003
Dialed Number Nature of Address 3005
LRN Nature of Address 3006
Called Number Nature of Address 3007
Reason Code 3008
Forward Call Indicators Received 3009
Nature of Connection Indicators
Received
Transit Network Selection 3013
Redirecting Number NOA 3017
Egress Calling Number NOA 3018 Added in a Release 9.5(2) patch
Egress Redirecting Number NOA 3019 Added in a Release 9.5(2) patch
Egress Original Called Number NOA 3020 Added in a Release 9.5(2) patch
MGC Generic Tags
CDB Version 4000
CDB Timepoint 4001
Call Reference ID 4002
IAM Timepoint 4003 When configured for seconds timepoint
ACM Timepoint 4004 When configured for seconds timepoint
REL Timepoint 4006 When configured for seconds timepoint
Originating Trunk Group 4008
Originating Member 4009
Calling Number 4010
Charged Number 4011
Dialed Number 4012
LRN Number 4013
Called Number 4014
Terminating Trunk Group 4015
Terminating Member 4016
Glare Encountered 4019
Value Comments
When configured for ITU encoding (Release 7 or
later)
3011
1-28
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
OL-1089-11
Page 51

Chapter 1 Billing Interfaces
Table 1-8 Aborted Attempt CDB Record (continued)
Field Name
RLC Timepoint 4020 When timepoint in seconds is selected
First Release Source 4028
LNP Dip 4029
MGC Info Field 4031 Disabled as of Release 7.3.x and 7.4.x
Ingress Originating Point Code 4034
Ingress Destination Point Code 4035
Egress Originating Point Code 4036
Egress Destination Point Code 4037
Ingress Media Gateway (CU) 4038
Egress Media Gateway (CU) 4039
Ingress Gateway Packet Info 4046 Restored as of Release 9.4(1)
Egress Gateway Packet Info 4047 Restored as of Release 9.4(1)
Directional Flag 4048
Redirecting Number 4060
Tariff Rate 4061
Scale Factor 4062
Test Line Indicator 4063
Redirection Number 4065 Release 9.7(3) and later
Ingress SigPath ID 4066
Ingress Span ID 4067
Ingress BearChan ID 4068
Ingress ProtocolId 4069
Egress SigPath ID 4070
Egress Span ID 4071
Egress BearChan ID 4072
Egress ProtocolId 4073
Charge Band Number 4078 Release 9.3(1) and later
Furnish Charging Information 4079 Release 9.3(1) and later
Original Called Number 4080 Release 9.3(1) and later
T.38 Fax Call 4081 Release 9.3(2) and later
Charge Unit Number 4082 Release 9.3(2) and later
Charge Indicator 4083 Release 9.5(2) and later
Outgoing Calling Party Number 4084 Release 9.5(2) and later
MCID Request Indicator 4085 Release 9.5(2) and later
MCID Response Indicator 4086 Release 9.5(2) and later
Detailed CDB Description
Tag
Value Comments
OL-1089-11
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
1-29
Page 52

Detailed CDB Description
Chapter 1 Billing Interfaces
Table 1-8 Aborted Attempt CDB Record (continued)
Tag
Field Name
Ingress MGCP DLCX Return Code 4087 Release 9.5(2) and later
Egress MGCP DLCX Return Code 4088 Release 9.5(2) and later
Network Translated Address
Indicator
Reservation Request Accepted 4090 Release 9.5(2) and later
Reservation Request Error Count 4091 Release 9.5(2) and later
ATM Ingress Configured Profile 4092 Release 9.5(2) and later
ATM Egress Configured Profile 4093 Release 9.5(2) and later
ATM Negotiated Profile 4094 Release 9.5(2) and later
Route List Name 4095 Release 9.5(2) and later
Route Name 4096 Release 9.5(2) and later
Originating Leg DSP Statistics 4098 Release 9.4(1) and later
Terminating Leg DSP Statistics 4099 Release 9.4(1) and later
Originating Remote SIP Host 4201 Release 9 and later (Named as Ingress SIP URL
Originating Local SIP Host 4202 Release 9 and later (Named as Egress SIP URL
SIP Call ID 4203 Release 9 and later
Source IP Address 4204 Release 9.4(1) and later
Ingress Media Device Address 4205 Release 9.4(1) and later
Egress Media Device Address 4206 Release 9.4(1) and later
Initial Codec 4207 Release 9.4(1) and later
Final Codec 4208 Release 9.4(1) and later
Ingress Media Device Port 4209 Release 9.4(1) and later
Egress Media Device Port 4210 Release 9.4(1) and later
Originating VPN ID 4211 Release 9.4(1) and later
Terminating VPN ID 4212 Release 9.4(1) and later
Partial Calling Line Identity 4220 Release 9.5(2) and later
Service Activation 4221 Added in Release 9.5(2), modified in 9.6(1)
PRI AOC Invoke Type 4222 Release 9.5(2) and later
PRI AOC – S Charge Information 4223 Release 9.5(2) and later
PRI AOC – D Charge Information 4224 Release 9.5(2) and later
PRI AOC – E Charge Information 4225 Release 9.5(2) and later
PRI AOC Invoke Failure 4226 Release 9.5(2) and later
Rejecting Location Label 4232 Release 9.6(1) and later
Rejecting Location Label Direction 4233 Release 9.6(1) and later
Value Comments
4089 Release 9.5(2) and later
in versions prior to the Release 9.7(3))
in versions prior to the Release 9.7(3))
1-30
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
OL-1089-11
Page 53

Chapter 1 Billing Interfaces
Table 1-8 Aborted Attempt CDB Record (continued)
Field Name
H323 Destination 4236 Release 9.7 and later
Ingress Redirecting Number 4237 Added in a Release 9.5(2) patch
Service Usage Data 4239 Release 9.7 and later
CNAM DIP 4240 Release 9.7 and later
Calling Name 4241 Release 9.7 and later
Terminating Remote SIP Host 4242 Release 9.7 and later
Terminating Local SIP Host 4243 Release 9.7 and later
License Rejecting Reason 4244 Release 9.7 and later
License Rejecting Direction 4245 Release 9.7 and later
SIP Transport 4246 Release 9.7 and later
SIP Routing URI Source 4247 Release 9.7 and later
SIP Routing URI 4248 Release 9.7 and later
Millisecond Granularity Timepoint Fields
IAM Timepoint Received_ms 4100
IAM Timepoint Sent_ms 4101
ACM Timepoint Received_ms 4102
ACM Timepoint Sent_ms 4103
First REL Timepoint_ms 4106
Second REL Timepoint_ms 4107
RLC Timepoint Received_ms 4108
RLC Timepoint Sent_ms 4109
Cisco Reserved Tags
Unique Call ID (Release 9 and later) 5000
Detailed CDB Description
Tag
Value Comments
When configured for milliseconds granularity
for timepoints fields
Release CDB Record (Tag: 1040/Release 5 or Later)
Table 1-9 lists data about the release CDB. CDB Tag 1040 is generated when the terminating CDB on a
call that went through and was answered and then released.
Table 1-9 Release CDB Record
Tag
Field Name
ANSI Based Formatted Fields
Reason Code 2008
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
OL-1089-11
Value Comments
When configured for ITU encoding (Release 7 or
later)
1-31
Page 54

Detailed CDB Description
Chapter 1 Billing Interfaces
Table 1-9 Release CDB Record (continued)
Tag
Field Name
ITU Based Formatted Fields
Reason Code 3008
MGC Generic Tags
CDB Version 4000
CDB Timepoint 4001
Call Reference ID 4002
REL Timepoint 4006 When configured for seconds granularity
Glare Encountered 4019
RLC Timepoint 4020 When configured for seconds granularity
First Release Source 4028
Total Meter Pulses 4030
Announcement Identification 4044
Ingress Gateway Packet Info 4046 Restored as of Release 9.4(1)
Egress Gateway Packet Info 4047 Restored as of Release 9.4(1)
Tariff Rate 4061
Scale Factor 4062
Charge Band Number 4078 Release 9.3(1) and later
Furnish Charging Information 4079 Release 9.3(1) and later
T.38 Fax Call 4081 Release 9.3(2) and later
Charge Unit Number 4082 Release 9.3(2) and later
Charge Indicator 4083 Release 9.5(2) and later
Outgoing Calling Party Number 4084 Release 9.5(2) and later
MCID Request Indicator 4085 Release 9.5(2) and later
MCID Response Indicator 4086 Release 9.5(2) and later
Ingress MGCP DLCX Return Code 4087 Release 9.5(2) and later
Egress MGCP DLCX Return Code 4088 Release 9.5(2) and later
Network Translated Address
Indicator
Reservation Request Accepted 4090 Release 9.5(2) and later
Reservation Request Error Count 4091 Release 9.5(2) and later
Route List Name 4095 Release 9.5(2) and later
Route Name 4096 Release 9.5(2) and later
MGCP Script Response String 4097 Release 9.5(2) and later
Value Comments
When configured for ITU encoding (Release 7 or
later)
timepoints
timepoints
4089 Release 9.5(2) and later
1-32
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
OL-1089-11
Page 55

Chapter 1 Billing Interfaces
Table 1-9 Release CDB Record (continued)
Field Name
Originating Leg DSP Statistics 4098 Release 9.4(1) and later
Terminating Leg DSP Statistics 4099 Release 9.4(1) and later
Ingress Media Device Address 4205 Release 9.4(1) and later
Egress Media Device Address 4206 Release 9.4(1) and later
Initial Codec 4207 Release 9.4(1) and later
Final Codec 4208 Release 9.4(1) and later
Ingress Media Device Port 4209 Release 9.4(1) and later
Egress Media Device Port 4210 Release 9.4(1) and later
Meter Pulses Received 4213 Release 9.5(2) and later
Meter Pulses Sent 4214 Release 9.5(2) and later
Charge Tariff Info 4215 Release 9.5(2) and later
Advice of Charge Indicator 4216 Release 9.5(2) and later
Short Call Indicator 4217 Release 9.5(2) and later
Charge Limit Exceeded 4218 Release 9.5(2) and later
Call Recovered Indication 4219 Release 9.5(2) and later
Service Activation 4221 Added in Release 9.5(2), modified in 9.6(1)
PRI AOC Invoke Type 4222 Release 9.5(2) and later
PRI AOC – S Charge Information 4223 Release 9.5(2) and later
PRI AOC – D Charge Information 4224 Release 9.5(2) and later
PRI AOC – E Charge Information 4225 Release 9.5(2) and later
PRI AOC Invoke Failure 4226 Release 9.5(2) and later
RO/PR Executed 4227 Release 9.6(1) and later
RO/PR Other Call Ref 4228 Release 9.6(1) and later
RO/PR Replacement Trunk Group 4229 Release 9.6(1) and later
RO/PR Replacement Chan ID 4230 Release 9.6(1) and later
RO/PR Switchover Timestamp 4231 Release 9.6(1) and later
Service Usage Data 4239 Release 9.7 and later
CNAM DIP 4240 Release 9.7 and later
Calling Name 4241 Release 9.7 and later
Millisecond Granularity Timepoint Fields
First REL Timepoint_ms 4106
Second REL Timepoint_ms 4107
RLC Timepoint Received_ms 4108
RLC Timepoint Sent_ms 4109
Detailed CDB Description
Tag
Value Comments
When configured for ITU encoding (Release 7 or
later)
OL-1089-11
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
1-33
Page 56

Detailed CDB Description
Table 1-9 Release CDB Record (continued)
Tag
Field Name
Cisco Reserved Tags
Unique Call ID (Release 9 and later) 5000
Value Comments
Interrupted CDB Record (Tag: 1050/Release 5 or Later)
Table 1-10 lists data about the interrupted CDB. CDB Tag 1050 is created when a call is terminated
without a Release message. This happens for example, in hot standby configuration when dual Cisco
MGCs are used, and when failover occurs and the now active Cisco MGC discovers that a call is no
longer active (the release message probably arrived and was lost during the failover window).
Table 1-10 Interrupt CDB Record
Tag
Field Name
MGC Generic Tags
CDB Version 4000
CDB Timepoint 4001
Call Reference ID 4002
Crash Timepoint 4007
Cisco Reserved Tags
Unique Call ID (Release 9 and later) 5000
Value Comments
Chapter 1 Billing Interfaces
On-Going (Call) CDB Record (Tag: 1060/Release 5 or Later)
The On-going Call CDB (or Long-Call CDB) indicates that a call is still active after the expiration of
the time span defined in the XECfgParm.dat parameter *.LongCallTime. This CDB is generated again
each time the period defined in *.LongCallTime elapses while the call is active. For example, if
*.LongCallTime is set to its default value, 21600000 ms, which is equal to 6 hours, a 1060 CDB is
generated every 6 hours until the call is terminated.
Note When the MGC is configured to create only the 1110 CDB (End-of-Call Summary) and this CDB, all of
the relevant 1060 tags are present and populated. This is because the 1060 CDB may be the first CDB
that is written for a call, if it has been active for the long-call period. In this case, the 1060 CDB contains
the full set of populated tags. However, when the MGC is configured to generate event-based CDBs
(such as 1010, 1020, 1030, 1040, 1050, 1060, 1070, and 1080) the 1060 CDB can contain only a subset
of tags: 5000, 4000–4002, 4213, and 4214. This occurs because the other event-based CDBs contain the
tag information, as they are associated with specific events. Therefore, in this instance the 1060 CDB
does not contain this redunant data, as it would be outside the primary purpose of this CDB.
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
1-34
OL-1089-11
Page 57

Chapter 1 Billing Interfaces
Table 1-11 lists data about the on-going (Call) CDB.
Note In Release 7 and later, the long duration includes more fields than it does in Release 5. The extra fields
are marked Release 7 and later.
Table 1-11 On-going CDB Record
Field Name
ANSI-Specific Tags
Egress Calling Number NOA 2018 Added in a Release 9.5(2) patch. Present only when
Egress Redirecting Number NOA 2019 Added in a Release 9.5(2) patch. Present only when
Egress Original Called Number NOA 2020 Added in a Release 9.5(2) patch. Present only when
ITU-Specific Tags
Egress Calling Number NOA 3018 Added in a Release 9.5(2) patch. Present only when
Egress Redirecting Number NOA 3019 Added in a Release 9.5(2) patch. Present only when
Egress Original Called Number NOA 3020 Added in a Release 9.5(2) patch. Present only when
MGC Generic Tags
CDB Version 4000 Always present and populated in 1060.
CDB Timepoint 4001 Always present and populated in 1060.
Call Reference ID 4002 Always present and populated in 1060.
IAM Timepoint 4003 Optional. Present only when 1110 is configured and if
ACM Timepoint 4004 Optional. Present only when 1110 is configured and if
ANM/Answer Timepoint 4005 Optional. Present only when 1110 is configured and if
Originating Trunk Group 4008 Optional. Present only when 1110 is configured.
Originating Member 4009 Optional. Present only when 1110 is configured.
Detailed CDB Description
Tag
Value Comments
1110 is configured. Not recorded for point-in-call
mode.
1110 is configured. Not recorded for point-in-call
mode.
1110 is configured. Not recorded for point-in-call
mode.
1110 is configured. Not recorded for point-in-call
mode.
1110 is configured. Not recorded for point-in-call
mode.
1110 is configured. Not recorded for point-in-call
mode.
system is configured for seconds timepoint.
system is configured for seconds timepoint.
system is configured for seconds timepoint.
OL-1089-11
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
1-35
Page 58

Detailed CDB Description
Chapter 1 Billing Interfaces
Table 1-11 On-going CDB Record (continued)
Tag
Field Name
Calling Number 4010 Optional. Present only when 1110 is configured.
Dialed Number 4012 Optional. Present only when 1110 is configured.
Called Number 4014 Optional. Present only when 1110 is configured.
Terminating Trunk Group 4015 Optional. Present only when 1110 is configured.
Terminating Member 4016 Optional. Present only when 1110 is configured.
Ingress SigPath ID 4066 Optional. Present only when 1110 is configured.
Ingress Span ID 4067 Optional. Present only when 1110 is configured.
Ingress BearChan ID 4068 Optional. Present only when 1110 is configured.
Ingress ProtocolId 4069 Optional. Present only when 1110 is configured.
Egress SigPath ID 4070 Optional. Present only when 1110 is configured.
Egress Span ID 4071 Optional. Present only when 1110 is configured.
Egress BearChan ID 4072 Optional. Present only when 1110 is configured.
Egress ProtocolId 4073 Optional. Present only when 1110 is configured.
Original Called Number 4080 Release 9.3(1) and later. Optional. Present only when
Meter Pulses Received 4213 Release 9.5(2) and later. Always present and
Meter Pulses Sent 4214 Release 9.5(2) and later. Always present and
Partial Calling Line Identity 4220 Release 9.5(2) and later. Optional. Present only when
Ingress Redirecting Number 4237 Added in a Release 9.5(2) patch. Present only when
Millisecond Granularity Timepoint Fields
IAM Timepoint Received _ms 4100 Optional. Present only when 1110 is configured.
IAM Timepoint Sent_ms 4101 Optional. Present only when 1110 is configured.
ACM Timepoint Received_ms 4102 Optional. Present only when 1110 is configured.
ACM Timepoint Sent_ms 4103 Optional. Present only when 1110 is configured.
ANM Timepoint Received_ms 4104 Optional. Present only when 1110 is configured.
ANM Timepoint Sent_ms 4105 Optional. Present only when 1110 is configured.
Cisco Reserved Tags
Unique Call ID (Release 9 and later) 5000 Always present and populated in 1060.
Value Comments
1110 is configured.
populated in 1060.
populated in 1060.
1110 is configured.
1110 is configured. Not recorded for point-in-call
mode.
1-36
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
OL-1089-11
Page 59

Chapter 1 Billing Interfaces
Maintenance CDB Record (Tag: 1070/Release 5 or Later)
Table 1-12 lists data about the maintenance record CDB type. CDB Tag 1070 is created for maintenance
activity (such as block or unblock) on a circuit.
Table 1-12 Maintenance CDB Record
Tag
Field Name
MGC Generic Tags
CDB Version 4000
CDB Timepoint 4001
Call Reference ID 4002
Maint Trunk Group 4017
Maint Circuit Member 4018
Maint Type 4032
Maint Reason (Retired in Release
9.4(1))
Maintenance SigPath ID 4074
Maintenance Span ID 4075
Maintenance BearChan ID 4076
Maintenance Circuits Count 4077
Cisco Reserved Tags
Unique Call ID (Release 9 and later) 5000
Value
4033
Detailed CDB Description
SS7 CIC Audit CDB Record (Tag: 1071/Release 9 or Later)
Table 1-13 lists data about the SS7 CIC audit record CDB type. This CDB is used to record changes to:
• the number of circuits defined for a trunk group when the MGC is configured in Call Control mode
• the number of circuits defined in a signaling service when the MGC is configured in Signaling mode.
This CDB is modeled after the 1070 CDB but does not contain independent CIC statuses, just total
counts of CICs defined and unavailable. It is triggered by provisioning changes to the number of circuits
in a trunk group (Call Control) or signaling service (Signaling).
Table 1-13 SS7 CIC Audio CDB Record
Tag
Field Name
MGC Generic Tags
CDB Version 4000
CDB Timepoint 4001
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
OL-1089-11
Value Comments
1-37
Page 60

Detailed CDB Description
Note CDB 1071 is configurable in XECfgParm.dat by adding it in engine.CDRmessageType; but if CDB 1110
Table 1-13 SS7 CIC Audio CDB Record (continued)
Tag
Field Name
Maint Trunk Group 4017 Appears when the MGC is
Maintenance SigPath ID 4074 Appears when the MGC is
Total Circuit Count 4234 added in 9.4(1) patch
Total Circuit Unavailable Count 4235 added in 9.4(1) patch
Cisco Reserved Tags
Unique Call ID 5000
is configured, CDB 1071 is suppressed.
Value Comments
configured for call control.
configured for signaling.
Chapter 1 Billing Interfaces
Once configured in XECfgParm.dat, CDB 1071 is generated for the following conditions.
• When the MML command sta-aud-cic is used to generate the current CIC availability information
on each configured ISUP trunk group or signaling service.
• A provisioning change (add or delete) is made in the number of circuits.
• A CIC service state or block state change occurs. A circuit that is unavailable is either blocked, OOS,
or both. A circuit that is blocked and also OOS is not double counted as unavailable circuits. The
following tables show the action taken when there is a service state or block state change.
Table 1-14 Service State Change
Service State Change Blocked Unblocked
OOS Do nothing Increment total unavailable counters
IS Do nothing Decrement total unavailable counters
Table 1-15 Service Block Change
Service Block Change OOS IS
Block Do nothing Increment total unavailable counters
Unblock Do nothing Decrement total unavailable counters
1-38
A blocked state is one or a combination of the following states:
• Manual local block
• Manual remote block
• Auto remote block (hardware failure)
• Auto local block
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
OL-1089-11
Page 61

Chapter 1 Billing Interfaces
• Propagation block (gateway initiated blocking)
CDB Tag 1071 generation rules:
• If CDB Tag 1071 is generated as the result of the sta-aud-cic MML command, it includes the CIC
• CDB Tag 1071 is generated only on the active side.
• To generate the CDB Tag 1071 on a trunk group or signaling service level rather than individual CIC
• The sta-aud-cic MML command is rejected for the following conditions:
• A circuit that has COT failure and has COT retest in progress is not counted as unavailable.
Detailed CDB Description
unavailability information per trunk group for switched configuration, or per signaling service for
nailed up. For other two scenarios, it only generates the information for the trunk groups that are
impacted.
level to minimize CPS impact, an internal 10-second timer is used. 1071 CDB is generated 10
seconds after the initial CIC state change and/or the initial CIC provision change. This delay
prevents the flooding of 1071 CDBs if a large number of CICs have blocks or service state changes
almost simultaneously.
–
The MML command is attempted to be run on the standby side
–
CDB Tag 1071 is not configured in the XECfgParm.dat file
• If the CDB Tag 1071 is configured to be generated for Cisco MGC software Release 9.5(2), that pre
BAMS 3.20 would require a skip-CDE for the CDB Tag 1071 record to be added to BAMS.
External Access CDB (Tag: 1080/Release 7 or Later)
Table 1-16 lists data about the external access CDB type. CDB Tag 1080 is generated whenever a query
is sent to an SCP (or other external device or database).
Table 1-16 External Access CDB Record
Tag
Field Name
MGC Generic Tags
CDB Version 4000
CDB Timepoint 4001 Time written
Universal Call Reference ID 4002
TCAP Transaction Identification 4040 TCAP Transaction ID
Transaction Start Time 4041 Time that TCAP query was sent
Transaction End Time 4042 Time that TCAP response was received
TCAP Database Identification 4043 SCP Selection Number
Service Logic ID 4049 SCP AMASlpID
AMALineNumber 4050 SCP AMALineNumber (Analyze_Route)
Cisco Reserved Tags
Unique Call ID (Release 9 and later) 5000
Value Information Source
OL-1089-11
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
1-39
Page 62

Detailed CDB Description
File Header CDB (Tag: 1090/Release 7 or Later)
The CDR dumper generates the File Header CDB at the beginning of each new CDR file. It is generated
according to the CDB creation guidelines, where the first three fields are mandatory and are located in
their specified positions (refer to Table 1-17).
Note This CDB is not configurable. Users cannot enable or disable the CDB nor can they select which fields
are to be included. This CDB always contains the fields shown in Table 1-17.
Chapter 1 Billing Interfaces
.
Table 1-17 File Header CDB Record
Tag
Field Name
MGC Generic Tags
CDB Version 4000
CDB Timepoint 4001 Time written
Universal Call Reference ID 4002 Always 0 for compatibility with all other CDB
Miscellaneous Fields
File Start Time 6001
Host MGC ID 6000
MGC Software Version 6004
Value Information Source
layouts
File Footer CDB (Tag: 1100/Release 7 or Later)
The CDR dumper generates the File Footer CDB at the end of each new CDR file. It is generated
according to the CDB creation guidelines, where the first three fields are mandatory and are located in
their specified positions (refer to Table 1-18).
1-40
Note This CDB is not configurable. Users cannot enable or disable the File Footer CDB nor can they select
which fields are to be included. This CDB always contains the fields shown in Table 1-18.
Table 1-18 File Footer CDB Record
Tag
Field Name
MGC Generic Tags
CDB Version 4000
CDB Timepoint 4001
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
Value Information Source
OL-1089-11
Page 63

Chapter 1 Billing Interfaces
Table 1-18 File Footer CDB Record (continued)
Tag
Field Name
Call Reference ID 4002 This will always be 0, for compatibility with all
Miscellaneous Fields
File End Time 6002
Total Number of CDB Records 6003
Host ID 6000
MGC Software Version 6004
Value Information Source
other CDB layouts.
End of the Call CDB (Tag: 1110/Release 7 or Later)
When the Cisco MGC software is configured to generate one CDB per call, a CDB is generated that
includes basic billing information. It is generated at the end of the call, as is the Release CDB, or an
attempted call that did not get to Setup status. That is, a call that did not get answered, as in an Aborted
Attempted CDB.
Detailed CDB Description
This End of Call CDB consists of the values listed in Table 1-19.
Table 1-19 End of Call CDB Record
ANSI
Tag
Value Description
2000 Calling Party Category 3000 Calling Party Category
2001 User Service Information 3001 User Service Information
2003 Calling number NOA 3003 Calling Number NOA
2004 Charged number NOA Does not exist for ITU
2005 Dialed number NOA 3005 Dialed Number NOA
2007 Called Number NOA 3007 Called Number NOA
2008 Reason Code 3008 Reason Code
2013 Transit Network Selection
2015 Carrier Selection Parameter
2017 Redirecting Number NOA 3017 Redirecting Number NOA
2018 Egress Calling Number NOA (Release
2019 Egress Redirecting Number NOA
2020 Egress Original Called Number NOA
4000 CDB Version 4000 CDB Version
9.5(2) and later)
(Release 9.5(2) and later)
(Release 9.5(2)) and later)
ITU
Tag
Value Description
3018 Egress Calling Number NOA (Release
3019 Egress Redirecting Number NOA
3020 Egress Original Called Number NOA
9.5(2) and later)
(Release 9.5(2) and later)
(Release 9.5(2) and later)
OL-1089-11
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
1-41
Page 64

Detailed CDB Description
Chapter 1 Billing Interfaces
Table 1-19 End of Call CDB Record (continued)
ANSI
Tag
Value Description
ITU
Tag
Value Description
4001 CDB Timepoint 4001 CDB Timepoint
4002 Call Reference ID 4002 Call Reference ID
4008 Originating Trunk Group 4008 Originating Trunk Group
4009 Originating Member 4009 Originating Member
4010 Calling Number 4010 Calling Number
4011 Charged Number 4011 Charged Number
4012 Dialed Number 4012 Dialed Number
4014 Called Number 4014 Called Number
4015 Terminating Trunk Group 4015 Terminating Trunk Group
4016 Terminating Member 4016 Terminating Member
4028 First Release Source 4028 First Release Source
4031 MGC Info Field (disabled as of
Release 7.3.x and 7.4.x)
4034 Ingress Originating Point Code
(Release 9.3(2) and up)
4035 Ingress Destination Point Code
(Release 9.3(2) and up)
4036 Egress Originating Point Code (Release
9.3(2) and up)
4037 Egress Destination Point Code (Release
9.3(2) and up)
4046 Ingress Gateway Packet Info (Restored
as of Release 9.4(1))
4047 Egress Gateway Packet Info (Restored
as of Release 9.4(1))
4031 MGC Info Field (disabled as of
Release 7.3.x and 7.4.x)
4034 Ingress Originating Point Code
(Release 9.3(2) and up)
4035 Ingress Destination Point Code
(Release 9.3(2) and up)
4036 Egress Originating Point Code (Release
9.3(2) and up)
4037 Egress Destination Point Code (Release
9.3(2) and up)
4046 Ingress Gateway Packet Info (Restored
as of Release 9.4(1))
4047 Egress Gateway Packet Info (Restored
as of Release 9.4(1))
4060 Redirecting Number 4060 Redirecting Number
4061 Tariff Rate 4061 Tariff Rate
4062 Scale Factor 4062 Scale Factor
4063 Test Line Indicator 4063 Test Line Indicator
4065 Redirection Number 4065 Redirection Number (Release 9.7(3)
and later)
4068 Ingress BearChan ID (Release 9.3(2)
and up)
4072 Egress BearChan ID (Release 9.3(2)
and up)
4068 Ingress BearChan ID (Release 9.3(2)
and up)
4072 Egress BearChan ID (Release 9.3(2)
and up)
4078 Charge Band Number 4078 Charge Band Number (
4079 Furnish Charging Information 4079 Furnish Charging Information
1-42
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
OL-1089-11
Page 65

Chapter 1 Billing Interfaces
Table 1-19 End of Call CDB Record (continued)
Detailed CDB Description
ANSI
Tag
Value Description
ITU
Tag
Value Description
4080 Original Called Number 4080 Original Called Number
4082 Charge Unit Number 4082 Charge Unit Number
4083 Charge Indicator (Release 9.5(2) and
up)
4084 Outgoing Calling Party Number
(Release 9.5(2) and up)
4085 MCID Request Indicator (Release
9.5(2) and up)
4086 MCID Response Indicator (Release
9.5(2) and up)
4087 Ingress MGCP DLCX Return Code
(Release 9.5(2) and up)
4088 Egress MGCP DLCX Return Code
(Release 9.5(2) and up)
4089 Network Translated Address Indicator
(Release 9.5(2) and up)
4090 Reservation Request Accepted (Release
9.5(2) and up)
4091 Reservation Request Error Count
(Release 9.5(2) and up)
4092 ATM Ingress Configured Profile
(Release 9.5(2) and up)
4093 ATM Egress Configured Profile
(Release 9.5(2) and up)
4094 ATM Negotiated Profiler (Release
9.5(2) and up)
4095 Route List Name (Release 9.5(2) and
up)
4083 Charge Indicator(Release 9.5(2) and
up)
4084 Outgoing Calling Party Number
(Release 9.5(2) and up)
4085 MCID Request Indicator (Release
9.5(2) and up)
4086 MCID Response Indicator (Release
9.5(2) and up)
4087 Ingress MGCP DLCX Return Code
(Release 9.5(2) and up)
4088 Egress MGCP DLCX Return Code
(Release 9.5(2) and up)
4089 Network Translated Address Indicator
(Release 9.5(2) and up)
4090 Reservation Request Accepted (Release
9.5(2) and up)
4091 Reservation Request Error Count
(Release 9.5(2) and up)
4092 ATM Ingress Configured Profile
(Release 9.5(2) and up)
4093 ATM Egress Configured Profile
(Release 9.5(2) and up)
4094 ATM Negotiated Profile (Release 9.5(2)
and up)
4095 Route List Name (Release 9.5(2) and
up)
4096 Route Name (Release 9.5(2) and up) 4096 Route Name (Release 9.5(2) and up)
4097 MGCP Script Response String (Release
9.5(2) and up)
4098 Originating Leg DSP Statistics (Release
9.4(1) and up)
4099 Terminating Leg DSP Statistics
(Release 9.4(1) and up)
4097 MGCP Script Response String (Release
9.5(2) and up)
4098 Originating Leg DSP Statistics (Release
9.4(1) and up)
4099 Terminating Leg DSP Statistics
(Release 9.4(1) and up)
4100 IAM Timepoint Received_msec 4100 IAM Timepoint Received_msec
4101 IAM Timepoint Sent_msec 4101 IAM Timepoint Sent_msec
4102 ACM Timepoint Received_msec 4102 ACM Timepoint Received_msec
4103 ACM Timepoint Sent_msec 4103 ACM Timepoint Sent_msec
OL-1089-11
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
1-43
Page 66

Detailed CDB Description
Chapter 1 Billing Interfaces
Table 1-19 End of Call CDB Record (continued)
ANSI
Tag
Value Description
ITU
Tag
Value Description
4104 ANM Timepoint Received_msec 4104 ANM Timepoint Received_msec
4105 ANM Timepoint Sent_msec 4105 ANM Timepoint sent_msec
4106 First REL Timepoint_msec 4106 First REL Timepoint_msec
4107 Second REL Timepoint_msec 4107 Second REL Timepoint_msec
4108 RLC Timepoint Received_msec 4108 RLC Timepoint Received_msec
4109 RLC Timepoint Sent_msec 4109 RLC Timepoint Sent_msec
4201 Originating Remote SIP Host (Release
9 and later)
4202 Originating Local SIP Host (Release 9
and later)
4201 Originating Remote SIP Host (Release
9 and later)
4202 Originating Local SIP Host (Release 9
and later)
4203 SIP Call ID (Release 9 and later) 4203 SIP Call ID (Release 9 and later)
4204 Source IP Address (Release 9.4(1) and
later)
4205 Ingress Media Device Address (Release
9.4(1) and later)
4206 Egress Media Device Address (Release
9.4(1) and later)
4204 Source IP Address (Release 9.4(1) and
later)
4205 Ingress Media Device Address (Release
9.4(1) and later)
4206 Egress Media Device Address (Release
9.4(1) and later)
4207 Initial Codec (Release 9.4(1) and later) 4207 Initial Codec (Release 9.4(1) and later)
4208 Final Codec (Release 9.4(1) and later) 4208 Final Codec (Release 9.4(1) and later)
4209 Ingress Media Device Port (Release
9.4(1) and later)
4210 Egress Media Device Port (Release
9.4(1) and later)
4211 Originating VPN ID (Release 9.4(1)
and later)
4212 Terminating VPN ID (Release 9.4(1)
and later)
4213 Meter Pulses Received (Release 9.5(2)
and later)
4214 Meter Pulses Sent (Release 9.5(2) and
later)
4215 Charge Tariff Info (Release 9.5(2) and
later)
4216 Advice of Charge Indicator (Release
9.5(2) and later)
4217 Short Call Indicator (Release 9.5(2) and
later)
4209 Ingress Media Device Port (Release
9.4(1) and later)
4210 Egress Media Device Port (Release
9.4(1) and later)
4211 Originating VPN ID (Release 9.4(1)
and later)
4212 Terminating VPN ID (Release 9.4(1)
and later)
4213 Meter Pulses Received (Release 9.5(2)
and later)
4214 Meter Pulses Sent (Release 9.5(2) and
later)
4215 Charge Tariff Info (Release 9.5(2) and
later)
4216 Advice of Charge Indicator (Release
9.5(2) and later)
4217 Short Call Indicator (Release 9.5(2) and
later)
1-44
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
OL-1089-11
Page 67

Chapter 1 Billing Interfaces
Table 1-19 End of Call CDB Record (continued)
Detailed CDB Description
ANSI
Tag
Value Description
4218 Charge Limit Exceeded (Release 9.5(2)
and later)
4219 Call Recovered Indication (Release
9.5(2) and later)
4220 Partial Calling Line Identity (Release
9.5(2) and later)
4221 Service Activation (Added in Release
9.5(2), modified in Release 9.6(1))
4222 PRI AOC Invoke Type (Release 9.5(2)
and later)
4223 PRI AOC – S Charge Information
(Release 9.5(2) and later)
4224 PRI AOC – D Charge Information
(Release 9.5(2) and later)
4225 PRI AOC – E Charge Information
(Release 9.5(2) and later)
4226 PRI AOC Invoke Failure (Release
9.5(2) and later)
4227 Route Optimization/Path Replacement
Action (Release 9.6(1) and later)
4228 Route Optimization / Path Replacement
Call Reference of Associated Call
Instance (Release 9.6(1) and later)
4229 Route Optimization / Path Replacement
Trunk Group Info (Release 9.6(1) and
later)
4230 Route Optimization / Path Replacement
Channel Info (Release 9.6(1) and later)
4231 Route Optimization Switchover
Timestamp (Release 9.6(1) and later)
4232 Rejecting Location Label (Release
9.6(1) and later)
4233 Rejecting Location Label Direction
(Release 9.6(1) and later)
4236 H323 Destination (Release 9.7 and
later)
4237 Ingress Redirecting Number (Release
9.5(2) and later)
4239 Service Usage Data (Release 9.7 and
later)
ITU
Tag
Value Description
4218 Charge Limit Exceeded (Release 9.5(2)
and later)
4219 Call Recovered Indication (Release
9.5(2) and later)
4220 Partial Calling Line Identity (Release
9.5(2) and later)
4221 Service Activation (Added in Release
9.5(2), modified in Release 9.6(1))
4222 PRI AOC Invoke Type (Release 9.5(2)
and later)
4223 PRI AOC – S Charge Information
(Release 9.5(2) and later)
4224 PRI AOC – D Charge Information
(Release 9.5(2) and later)
4225 PRI AOC – E Charge Information
(Release 9.5(2) and later)
4226 PRI AOC Invoke Failure (Release
9.5(2) and later)
4227 Route Optimization/Path Replacement
Action (Release 9.6(1) and later)
4228 Route Optimization / Path Replacement
Call Reference of Associated Call
Instance (Release 9.6(1) and later)
4229 Route Optimization / Path Replacement
Trunk Group Info (Release 9.6(1) and
later)
4230 Route Optimization / Path Replacement
Channel Info (Release 9.6(1) and later)
4231 Route Optimization Switchover
Timestamp (Release 9.6(1) and later)
4232 Rejecting Location Label (Release
9.6(1) and later)
4233 Rejecting Location Label Direction
(Release 9.6(1) and later)
4236 H323 Destination (Release 9.7 and
later)
4237 Ingress Redirecting Number (Release
9.5(2) and later)
4239 Service Usage Data (Release 9.7 and
later)
OL-1089-11
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
1-45
Page 68

Detailed CDB Description
Chapter 1 Billing Interfaces
Table 1-19 End of Call CDB Record (continued)
ANSI
Tag
Value Description
4240 CNAM DIP (Release 9.7 and later) 4240 CNAM DIP (Release 9.7 and later)
4241 Calling Name (Release 9.7 and later) 4241 Calling Name (Release 9.7 and later)
4242 Terminating Remote SIP Host (Release
4243 Terminating Local SIP Host (Release
4244 License Rejecting Reason (Release 9.7
4245 License Rejecting Direction (Release
4246 SIP Transport 4246 SIP Transport (Release 9.7 and later)
4247 SIP Routing URI Source 4247 SIP Routing URI Source (Release 9.7
4248 SIP Routing URI 4248 SIP Routing URI (Release 9.7 and later)
5000 Unique Call ID (Release 9 and later) 5000 Unique Call ID (Release 9 and later)
6005 Interim CDB (Release 9.5(2) and later) 6005 Interim CDB (Release 9.5(2) and later)
9.7 and later)
9.7 and later)
and later)
9.7 and later)
ITU
Tag
Value Description
4242 Terminating Remote SIP Host (Release
4243 Terminating Local SIP Host (Release
4244 License Rejecting Reason (Release 9.7
4245 License Rejecting Direction (Release
9.7 and later)
9.7 and later)
and later)
9.7 and later)
and later)
Slave End-of-Call CDB Record (Tag: 1210/Release 9.6 or Later)
Table 1-20 lists data about the Slave End-of-Call CDB type. This CDB is defined to be used at the
end-of-call for a non-controlling half-call instance. Only end-of -call summary style CDBs are issued
for slave half-call instances and the appropriate information is check-pointed to ensure the data is
successfully written in the event of a switchover occurring. This CDB is disabled by default on your
Cisco PGW 2200.
Note If you do enable this CDB and your network includes a Cisco BAMS, you must provision the Cisco
BAMS to ignore this CDB.
Table 1-20 Slave End-of-Call CDB Record
Tag
Field Name
MGC Generic Tags
Call Reference ID 4002
IAM Timepoint 4003
REL Timepoint 4006
Originating Trunk Group 4008
Value Comments
1-46
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
OL-1089-11
Page 69

Chapter 1 Billing Interfaces
Detailed CDB Description
Table 1-20 Slave End-of-Call CDB Record (continued)
Tag
Field Name
Value Comments
Originating Member 4009
Terminating Trunk Group 4015
Terminating Member 4016
RO/PR Executed 4227 Added in Release 9.6(1)
RO/PR Other Call Ref 4228 Added in Release 9.6(1)
Cisco Reserved Tags
Unique Call ID (Release 9 and later) 5000
Slave Long Duration Call CDB Record (Tag: 1260/Release 9.6 or Later)
Table 1-21 lists data about the Slave Long Duration Call CDB type. This CDB is used when the call
instance remains active beyond a pre-configured time. The long call duration timer of the slave call is
the same as that of “master” call which is configured in XECfgParm.dat.
Table 1-21 Slave Long Duration Call CDB Record
Tag
Field Name
Value Comments
MGC Generic Tags
Call Reference ID 4002
IAM Timepoint 4003
Originating Trunk Group 4008
Originating Member 4009
Terminating Trunk Group 4015
Terminating Member 4016
RO/PR Executed 4227 Added in Release 9.6(1)
RO/PR Other Call Ref 4228 Added in Release 9.6(1)
Cisco Reserved Tags
Unique Call ID (Release 9 and later) 5000
OL-1089-11
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
1-47
Page 70

Chapter 1 Billing Interfaces
CDE Detail Description
CDE Detail Description
A call data element (CDE) is a field within the CDB that contains basic information about a billing
record. Examples of CDEs are the calling number and the called number.
The CDEs are described in the CDE description form template as shown in Table 1-22. CDE description
forms for each of the CDBs listed near the bottom in Table 1-22 are included in Table 1-23 through
Table 1-213.
Table 1-22 CDE Description Form Template
Name: Name of the call data element Ta g: Its tag value Source: MGC
subsystem that
generates the CDE
value
Description/Purpose: Brief description of the CDE
Format: The format of the CDE value Length: CDE value length
Data Value: Range of CDE values, or valid values
Extended Data Value: This section includes CDE values that are extended (from the ANSI/ITU standard) by the Cisco MGC.
General Information: General information about the CDE and comments.
MGC Release: The Cisco MGC release(s)
supporting this CDE
1-48
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
OL-1089-11
Page 71

Chapter 1 Billing Interfaces
CDE Detail Description
CDEs Encoded in ANSI
Calling Party Category (Tag: 2000/ANSI)
Table 1-23 Calling Party Category Description Form
Name: Calling Party Category Ta g: 2000 Source: MDL
Description/Purpose: Indicates what type of calling party is placing the call.
Format: ANSI T1.113 Length in Octets: 1
Data Value:
The following codes are used in the calling party category (CPC) parameter field:
00000000 Calling party's category unknown (default)
00000001Operator, language French
00000010Operator, language English
00000011Operator, language German
00000100Operator, language Russian
00000101Operator, language Spanish
00000110|
00000111|-> Available to admin. For selecting a particular language.
00001000|
00001001Reserved
00001010Ordinary calling subscriber
00001011Ordinary calling subscriber with priority
00001100Data call
00000001Operator, language French
00001101Test call
00001110Spare
00001111Pay phone
00010000
toCCITT spare
11011111
11100000Emergency service call
11100001High priority emergency service call
11100010National security and emergency
11100011
toANSI spare
11110111
11110000
toNetwork-specific use
11111110
11111111Reserved
Extended Data Value: No extended value.
General Information:
MGC Release: Release 5.0 and later.
OL-1089-11
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
1-49
Page 72

Chapter 1 Billing Interfaces
CDE Detail Description
User Service Information (Tag: 2001/ANSI)
Table 1-24 User Service Information Description Form
Name: User Service Information Tag : 2001 Source: MDL
Description/Purpose: This parameter is used to send the data transmission parameters to the distant exchange. The field
format is the same as the format for the bearer capability information element from ANSI standard T1.607.
Format: ANSI T1.113 Length in Octets: 2 to 13
Data Value: For more detail, please refer to ANSI T1.113.
Extension: octet continues through the next octet, 1 last octet
Coding standard: the setting should be 00 for CCITT standard, 10 for national
Information Transfer Capability. For POTS calling, this field is set at one of the following:
00000 Speech
01000 Unrestricted digital information
01001 Restricted digital information
10000 3.1 kHz audio
10001 Unrestricted digital information with tone and announcements
Transfer Mode (octet 2)
00 Circuit mode
10 Packet mode
7.3 Information Transfer Rate
00000 Packet mode only
10000 64 kb
00011 384 kb
10100 1472 kb
10101 1536 kb
10111 1920 kb
11000 Multi-rate
Structure, Configuration, Establishment, and so on: please refer to T1.113
Extended Data Value: No extended value.
General Information:
1-50
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
OL-1089-11
Page 73

Chapter 1 Billing Interfaces
CDE Detail Description
Originating Line Information (Tag: 2002/ANSI)
Table 1-25 Originating Line Information Description Form
Name: Originating Line Information Ta g: 2002 Source: MDL
Description/Purpose: This information is captured from the originating line information parameter.
Format: ANSI T1.113 Length in Octets: 1
Data Value:
00000000
to Binary equivalent of the digits
01100011
01100100
to Reserved
11111111
Extended Data Value: No extended value.
General Information:
MGC Release: Release 5.0 and later.
OL-1089-11
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
1-51
Page 74

Chapter 1 Billing Interfaces
CDE Detail Description
Calling Number Nature of Address (Tag: 2003/ANSI)
Table 1-26 Calling Number Nature of Address Description Form
Name: Calling Number Nature of Address Ta g: 2003 Source: MDL
Description/Purpose: Indicates to the Cisco MGC how the number was delivered. It indicates the calling party type of
address. In POTS calling, two values are usually used: unique national number and nonunique national number.
Format: ANSI T1.113 Length in Octets: 1
Data Value:
0000000 Spare
0000001 Unique subscriber number
0000010 Spare (national use)
0000011 Unique national number
0000100 Unique international number
0000101
to Spare
1110000
1110001 Nonunique subscriber number
1110010 Spare
1110011 Nonunique national number
111010 0 Nonunique international number
1110101 Spare
1110110 Spare
1110111 Test line
1111000
to Reserved
1111000
1111111 Spare
Extended Data Value: No extended value.
General Information:
MGC Release: Release 5.0 and later.
1-52
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
OL-1089-11
Page 75

Chapter 1 Billing Interfaces
CDE Detail Description
Charged Number Nature of Address (Tag: 2004/ANSI)
Table 1-27 Charged Number Nature of Address Description Form
Name: Charged Number Nature of Address Ta g: 2004 Source: MDL
Description/Purpose: Indicates to the Cisco MGC how the number was delivered.
Format: ANSI T1.113 Length in Octets: 1
Data Value:
0000000 Spare
0000001Unique subscriber number
0000010 Spare (national use)
0000011 Unique national number
0000100 Unique international number
0000101
to Spare
1110000
1110001 Nonunique subscriber number
1110010 Spare
1110011 Nonunique national number
111010 0 Nonunique international number
1110101 Spare
1110110 Spare
1110111 Test line
1111000
to Reserved
1111000
1111111 Spare
Extended Data Value: No extended value.
General Information:
MGC Release: Release 5.0 and later.
OL-1089-11
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
1-53
Page 76

Chapter 1 Billing Interfaces
CDE Detail Description
Dialed Number Nature of Address (Tag: 2005/ANSI)
Table 1-28 Dialed Number Nature of Address Description Form
Name: Dialed Number Nature of Address Tag : 2005 Source: MDL
Description/Purpose: Allows the Call Process to route a call differently based on the Nature of Address (NOA) value
provided in the IAM called number parameter. This tag represents the external (for example, line) value of NOA for the
called part number.
Format: ANSI T1.113 Length in Octets: 1
Data Value:
0000000Spare - If the LEC doesn't know what type of line the calling party is, it will send this value to the Cisco MGC.
The Cisco MGC does not alter this value and does not do anything as far as billing with this field.
0000001Unique subscriber number
0000010 Spare (national use)
0000011 Unique national number
0000100 Unique international number
0000101
to Spare
1110000
1110001Nonunique subscriber number
1110010Spare
1110011Nonunique national number
111010 0Nonunique international number
1110101 Spare
1110110 Spare
1110111 Test line
1111000
to Reserved
1111000
1111111 Spare
Extended Data Value: No extended value.
General Information:
MGC Release: Release 5.0 and later.
1-54
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
OL-1089-11
Page 77

Chapter 1 Billing Interfaces
CDE Detail Description
LRN Nature of Address (Tag: 2006/ANSI)
Table 1-29 LRN Nature of Address Description Form
Name: LRN Nature of Address Tag : 2006 Source: MDL
Description/Purpose: Stores the NOA of LRN from an INAP query.
Format: ANSI T1.113 Length in Octets: 1
Data Value:
0000000Spare
0000001Unique subscriber number
0000010 Spare (national use)
0000011 Unique national number
0000100 Unique international number
0000101
to Spare
1110000
1110001Nonunique subscriber number
1110010Spare
1110011Nonunique national number
111010 0Nonunique international number
1110101 Spare
1110110 Spare
1110111 Test line
1111000
to Reserved
1111000
1111111 Spare
Extended Data Value: No extended value.
General Information:
MGC Release: Release 5.0 and later.
OL-1089-11
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
1-55
Page 78

Chapter 1 Billing Interfaces
CDE Detail Description
Called Number Nature of Address (Tag: 2007/ANSI)
Table 1-30 Called Number Nature of Address Description Form
Name: Called Number Nature of Address Tag: 2007 Source: MDL
Description/Purpose: The tag contains the Nature of Address (NOA) value from the egress protocol message used in the
outbound IAM. The NOA value in this tag is from the ingress protocol message. If no B number NOA is available
(redirected to an unknown number) but an original called number Information Element (IE) is available in the protocol
message, then the NOA from the IE is logged, and this can be modified for number normalization.
Format: ANSI T1.113 Length in Octets: 1
Data Value:
0000000Spare - If the LEC doesn't know what type of line the calling party is, it will send this value to the Cisco MGC.
The Cisco MGC does not alter this value and does not do anything as far as billing with this field.
0000001Unique subscriber number
0000010 Spare (national use)
0000011 Unique national number
0000100 Unique international number
0000101
to Spare
1110000
1110001Nonunique subscriber number
1110010Spare
1110011Nonunique national number
111010 0Nonunique international number
1110101 Spare
1110110 Spare
1110111 Test line
1111000
to Reserved
1111000
1111111 Spare
Extended Data Value: No extended value.
General Information:
MGC Release: Release 5.0 and later.
1-56
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
OL-1089-11
Page 79

Chapter 1 Billing Interfaces
CDE Detail Description
Reason Code (Tag: 2008/ANSI)
Table 1-31 Reason Code Description Form
Name: Reason Code Tag : 2008 Source: MDL
Description/Purpose: Incorporates SS7 release with cause values and any additional reasons that the basic call model
determines.
Format: ANSI T1.113 Length in Octets: 2
Data Value: The value of this field includes the first two octets of the cause indicators. Please refer to the ANSI T1.113
specification. (No diagnostic information included.)
Extended Data Value:
Note Tag 2008 extends ANSI definition by adding COT failure indicators according to ANSI rules, with slight
modification as follows:
Octet 1:
Extension 0
Coding Standard 11
Spare 0
Location 0011
Octet 2:
Extension 1
Cause 1111110
General Information:
MGC Release: Release 5.0 and later.
OL-1089-11
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
1-57
Page 80

Chapter 1 Billing Interfaces
CDE Detail Description
Forward Call Indicators Received (Tag: 2009/ANSI)
Table 1-32 Forward Call Indicators Received Description Form
Name: Forward Call Indicators Received Ta g: 2009 Source: MDL
Description/Purpose: This is for the received Forward Call Indicator parameter in ISUP message. It includes the following
fields: International Call Ind.; End To End Method Ind.; Interworking Ind.; IAM Segmentation Ind.; ISDN User Part Ind.;
ISDN User Part Preference Ind.; ISDN Access Ind.; and SCCP Method Ind.
Format: ANSI T1.113 Length in Octets: 2
Data Value:
National/International call indicator Bit A—For POTS calling, Bit A should be coded as a 0, signifying that this is an
incoming national call. A coding of 1 signifies that the call is an incoming international call.
End-to-end method indicator Bits CB:
00 No end-to-end method available.
01 Pass along method available.
10 SCCP method available.
11 Both Pass along and SCCP methods available.
Interworking indicator Bit D—This field indicates to the Cisco MGC if any interworking has been encountered in the type
of signaling for this call. No pertinent information needs to be acted upon by the Cisco MGC; it should pass the information
to the destination. “0” means no interworking was encountered (SS7 all the way). “1” means interworking was encountered.
IAM Segmentation indicator Bit E—In POTS calling, this segmentation indicator is marked with a 0.
ISDN User Part indicator Bit F, HG, I: This is a more granular field for use by the ISUP. In the United States, the ISUP is
used exclusively. For POTS national numbers, this field is marked 1 for ISUP used all the way. That is, if the Interworking
indicator is set at 0 there was no interworking. If the incoming call has a 0 in this field, there was interworking or the
incoming international call could have used TUP for signaling before reaching the national network. The Cisco MGC
should not have to deal with this bit; it should pass it on to the destination. For more details, please refer to the ANSI T1.113
specification.
Extended Data Value:
General Information:
MGC Release: Release 5.0 and later.
1-58
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
OL-1089-11
Page 81

Chapter 1 Billing Interfaces
CDE Detail Description
Forward Call Indicators Sent (Tag: 2010/ANSI)
Table 1-33 Forward Call Indicators Sent Description Form
Name: Forward Call Indicators Sent Ta g: 2010 Source: MDL
Description/Purpose: This is for the sent Forward Call Indicator parameter in ISUP message. It includes the following
fields: International Call Ind.; End To End Method Ind.; Interworking Ind.; IAM Segmentation Ind.; ISDN User Part
Ind.; ISDN User Part Preference Ind.; ISDN Access Ind.; and SCCP Method Ind.
Format: ANSI T1.113 Length in Octets: 2
Data Value: National/International call indicator Bit A—For POTS calling, Bit A should be coded as a 0, signifying
that this is an incoming national call. A coding of 1 signifies that the call is an incoming international call.
End-to-end method indicator Bits CB
00 No end to end method available.
01 Pass along method available.
10 SCCP method available.
11Both Pass along and SCCP methods available.
Interworking indicator Bit D—This field indicates to the Cisco MGC if any interworking has been encountered in the
type of signaling for this call. No pertinent information needs to be acted upon by the Cisco MGC; it should just pass
the information to the destination. “0” means no interworking encountered (SS7 all the way). “1” means interworking
was encountered.
IAM Segmentation indicator Bit E—In POTS calling, this segmentation indicator is marked with a 0.
ISDN User Part indicator Bit F, HG, I—This is a more granular field for use by the ISUP. In the United States, the ISUP
is used exclusively. For POTS national numbers, this field is marked 1 for ISUP used all the way. That is, if the
Interworking indicator is set at 0, there was no interworking. If the incoming call has a 0 in this field, there was
interworking or the incoming international call could have used TUP for signaling before reaching the national
network. The Cisco MGC should not have to deal with this bit; it passes it on to the destination. For more details, please
refer to the ANSI T1.113 specification.
Extended Data Value:
General Information:
MGC Release: Release 5.0 and later.
OL-1089-11
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
1-59
Page 82

CDE Detail Description
Nature of Connection Indicators Received (Tag: 2011/ANSI)
Table 1-34 Nature of Connection Indicators Received Description Form
Chapter 1 Billing Interfaces
Name: Nature of Connection Indicators
Tag : 2011 Source: MDL
Received
Description/Purpose: Used to record the Nature of Connection received from the IAM. Three possible indicators can be
received: the satellite indicator, the continuity check indicator, and the echo suppressor indicator.
Format: ANSI T1.113 Length in Octets: 1
Data Value:
Assume bit order HGFEDCBA
Satellite Indicator (Bits BA)—This field provides the Cisco MGC with information on how many satellites have been used
on this circuit. If the field is set to 00 and the Cisco MGC sends the circuit out on a circuit going over a satellite, the field
is incremented by one. The same goes for the other incoming settings (for example, 01 goes to 10 and 10 goes to 11). If
the outgoing circuit doesn't go over a satellite, the field is not incremented.
Continuity check indicator (Bits DC)—The Cisco MGC acts upon this field based on what is received. Also depending on
mutual agreements with the LECs, each outgoing trunk group sends Continuity tones to the terminating LECs with a
frequency between 0% to 100% of the time. This is configurable on a per trunk group basis. In addition, the Cisco MGC
interprets the incoming continuity field and passes the appropriate action to the Coding Unit.
Echo suppressor indicator (Bit E)—If this field is filled, the outgoing half echo control is already set on previous circuits,
there is no need for the terminating Cisco MGC to engage the EC. for this call. If the Cisco MGC activates the echo
canceller, this field needs to be set for the outgoing IAM message to subsequent switches.
Bits F-G: spare
Extended Data Value:
General Information:
MGC Release: Release 5.0 and later.
1-60
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
OL-1089-11
Page 83

Chapter 1 Billing Interfaces
Nature of Connection Indicators Sent (Tag: 2012/ANSI)
Table 1-35 Nature of Connection Indicators Sent Description Form
CDE Detail Description
Name: Nature of Connection Indicators
Tag : 2012 Source: MDL
Sent
Description/Purpose: Used to record the Nature of Connection sent. Three possible indicators can be sent: the satellite
indicator, the continuity check indicator, and the echo suppressor indicator.
Format: ANSI T1.113 Length in Octets: 1
Data Value:
Assume bit order HGFEDCBA
Satellite Indicator (Bits BA)—This field provides the Cisco MGC with information on how many satellites have been used
on this circuit. If the field is set to 00 and the Cisco MGC sends the circuit out on a circuit going over a satellite, the field
is incremented by one. The same goes for the other incoming settings (for example, 01 goes to 10 and 10 goes to 11). If
the outgoing circuit doesn't go over a satellite, the field is not incremented.
Continuity check indicator (Bits DC)—The Cisco MGC acts upon this field based on what is received. Also depending on
mutual agreements with the LECs, each outgoing trunk group sends Continuity tones to the terminating LECs with a
frequency between 0% to 100% of the time. This is configurable on a per trunk group basis. In addition, the Cisco MGC
interprets the incoming continuity field and passes the appropriate action to the Coding Unit.
Echo suppressor indicator (Bit E)—If this field is filled, the outgoing half echo control is already set on previous circuits,
there is no need for the terminating Cisco MGC to engage the EC. for this call. If the Cisco MGC activates the echo
canceller, this field needs to be set for the outgoing IAM message to subsequent switches.
Bits F-G: spare
Extended Data Value:
General Information:
MGC Release: Release 5.0 and later.
OL-1089-11
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
1-61
Page 84

Chapter 1 Billing Interfaces
CDE Detail Description
Transit Network Selection (Tag: 2013/ANSI)
Table 1-36 Transit Network Selection Description Form
Name: Transit Network Selection Tag: 2013 Source: MDL
Description/Purpose: Includes Type of Network, Network Identification Plan, Digits, and Circuit Code.
Format: ANSI T1.113 Length in Octets: 4
Data Value:
Network Identification Plan—The Network ID plan field indicates to the Cisco MGC what type of ID the parameter has.
Since POTS calling uses the National Network Plan, there are two values that pertain to the Cisco MGC: 3-digit CIC and
4-digit CAC.
National Network ID:
0000 Unknown
00104 Digit Carrier Identification Code—If this value is used, the layout of the parameter is the second figure.
0011
to Spare
0111
1000
to Reserved for network specific use
1111
Type of Network Identification—This field holds the type of network identification for the transit network parameter.
000 CCITT
010 National Network ID
Spare bit
Digits 1, 2, 3 or Digits 1, 2, 3, 4—These fields hold the Carrier Identification Code of the international transit carrier that
is required.
Circuit Code—The circuit code field indicates to the carrier how the call was dialed. The following values are found in this
field:
0000 Unknown
0001 International call, no operator
0010 International call, operator requested
Extended Data Value:
General Information:
MGC Release: Release 5.0 and later.
1-62
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
OL-1089-11
Page 85

Chapter 1 Billing Interfaces
CDE Detail Description
Carrier Identification Parameter (Tag: 2014/ANSI)
Table 1-37 Carrier Identification Parameter Description Form
Name: Carrier Identification Parameter Ta g: 2014 Source: MDL
Description/Purpose: This is for the Carrier Identification Parameter in ISUP message. It includes the following fields:
Network Identification Plan; Type of Network Identification; Spare; Digit 1; Digit 2; Digit 3; Digit 4 or Null.
Format: ANSI T1.113 Length in Octets: 3 or 4
Data Value:
Network Identification Plan (1st Octet, Bits 4321)—Indicates what type of Carrier Identification the caller is requesting.
The Cisco MGC looks at this field to determine whether the requested CIC is a 3 digit or 4 digit code and how many digits
to expect in the Digits field.
Type of Network Identification(1st Octet, Bits 765)—Gives the identification of the network numbering plan. For POTS
calls from the LECs, the value of this field is 010 (National Network ID).
Spare(1st Octet, Bits 8)—Not applicable
Digit 1-3 or 1-4 (remaining two octets, Bits 8765 are all zeros if only 3 digits present)—Requested CIC
Extended Data Value:
General Information:
MGC Release: Release 5.0 and later.
Carrier Selection Parameter (Tag: 2015/ANSI)
Table 1-38 Carrier Selection Parameter Description Form
Name: Carrier Selection Parameter Ta g: 2015 Source: MDL
Description/Purpose: Indicates to the Cisco MGC how the caller dialed. This parameter can be used to determine how the
call will be routed. The parameter indicates to the Cisco MGC how the Carrier Access Code was dialed. With this
information and the Carrier Identification parameter, the Cisco MGC can route the call in a more granular fashion.
Format: ANSI T1.113 Length in Octets: 1
Data Value:
00000000 No indication
00000001 Selected Carrier Identification Code presubscribed and not input by calling party
00000010 Selected Carrier Identification Code presubscribed and input by calling party
00000011 Selected Carrier Identification Code presubscribed; but no indication of whether input by calling party
00000100 Selected Carrier Identification Code not presubscribed and input by calling party
00000101
to Spare
11111110
11111111 Reserved
Extended Data Value:
General Information:
MGC Release: Release 5.0 and later.
OL-1089-11
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
1-63
Page 86

Chapter 1 Billing Interfaces
CDE Detail Description
Jurisdiction Information Parameter (Tag: 2016/ANSI)
Table 1-39 Jurisdiction Information Parameter Description Form
Name: Jurisdiction Information Parameter Tag: 2016 Source: MDL
Description/Purpose: This parameter provides numerical data indicating the geographic origination of the call.
Format: IA5 Length in Octets: 6
Data Value: Digits from Jurisdiction Information Parameter.
Extended Data Value:
General Information:
MGC Release: Release 5.0 and later.
Redirecting Number Nature of Address (Tag 2017/ANSI)
Table 1-40 Redirecting Number Nature of Address Description Form
Name: Called Number Nature of Address Tag : 2017 Source: MDL
Description/Purpose: NOA of Redirecting Number.
Format: ANSI T1.113 Length in Octet: 1
Data Value:
0000000 Spare
0000001 Unique subscriber number
0000010 Spare (national use)
0000011 Unique national number
0000100 Unique international number
0000101
to Spare
1110000
1110001 Nonunique subscriber number
1110010 Spare
1110011 Nonunique national number
111010 0 Nonunique international number
1110101 Spare
1110110 Spare
1110111 Test line
1111000
to Reserved
1111000
1111111 Spare
Extended Data Value: No extended value.
General Information:
MGC Release: Release 7.4.
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
1-64
OL-1089-11
Page 87

Chapter 1 Billing Interfaces
CDE Detail Description
Egress Calling Number Nature of Address (Tag 2018/ANSI)
Table 1-41 Egress Calling Number Nature of Address Description Form
Name: Egress Calling Number NOA Tag : 2018 Source: MDL
Description/Purpose: This CDE records the calling party NOA sent in the outgoing message by the MGC. This field
indicates the address type of the calling party. In POTS calling, there are usually two values that are used. They are Unique
National Number and Non-unique National Number.
Format: ANSI T1.113 Length in Octet: 1
Data Value:
0000000 Spare
0000001 Unique subscriber number
0000010 Spare (national use)
0000011 Unique national number
0000100 Unique international number
0000101
to Spare
1110000
1110001 Nonunique subscriber number
1110010 Spare
1110011 Nonunique national number
1110100 Nonunique international number
1110101 Spare
1110110 Spare
1110111 Test line
1111000
to Reserved
1111000
1111111 Spare
Extended Data Value: No extended value.
General Information:
Note This CDE is present in the 1060 CDB if the End-of-Call CDB (1110) is configured. For point-in-call mode, the 1060
CDB is usually a short one and does not contain this CDB.
MGC Release: Release 9.5(2) patch xx.
OL-1089-11
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
1-65
Page 88

Chapter 1 Billing Interfaces
CDE Detail Description
Egress Redirecting Number Nature of Address (Tag 2019/ANSI)
Table 1-42 Egress Redirecting Number Nature of Address Description Form
Name: Egress Redirecting Number NOA Tag : 2019 Source: MDL
Description/Purpose: This CDE records the redirecting calling number NOA sent in the outgoing message by the MGC.
Format: ANSI T1.113 Length in Octet: 1
Data Value:
0000000 Spare
0000001 Unique subscriber number
0000010 Spare (national use)
0000011 Unique national number
0000100 Unique international number
0000101
to Spare
1110000
1110001 Nonunique subscriber number
1110010 Spare
1110011 Nonunique national number
1110100 Nonunique international number
1110101 Spare
1110110 Spare
1110111 Test line
1111000
to Reserved
1111000
1111111 Spare
Extended Data Value: No extended value.
General Information:
Note This CDE is present in the 1060 CDB if the End-of-Call CDB (1110) is configured. For point-in-call mode, the 1060
CDB is usually a short one and does not contain this CDB.
MGC Release: Release 9.5(2) patch xx.
1-66
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
OL-1089-11
Page 89

Chapter 1 Billing Interfaces
Egress Original Called Number Nature of Address (Tag 2020/ANSI)
Table 1-43 Egress Calling Number Nature of Address Description Form
CDE Detail Description
Name: Egress Original Called Number
Tag : 2020 Source: MDL
NOA
Description/Purpose: This CDE records the original called party NOA sent in the outgoing message by the MGC.
Format: ANSI T1.113 Length in Octet: 1
Data Value:
0000000 Spare
0000001 Unique subscriber number
0000010 Spare (national use)
0000011 Unique national number
0000100 Unique international number
0000101
to Spare
1110000
1110001 Nonunique subscriber number
1110010 Spare
1110011 Nonunique national number
1110100 Nonunique international number
1110101 Spare
1110110 Spare
1110111 Test line
1111000
to Reserved
1111000
1111111 Spare
Extended Data Value: No extended value.
General Information:
Note This CDE is present in the 1060 CDB if the End-of-Call CDB (1110) is configured. For point-in-call mode, the 1060
CDB is usually a short one and does not contain this CDB.
MGC Release: Release 9.5(2) patch xx.
OL-1089-11
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
1-67
Page 90

Chapter 1 Billing Interfaces
CDE Detail Description
CDE Encoded as ITU Recommendation
Calling Party Category (Tag: 3000/ITU)
Table 1-44 Calling Party Category Description Form
Name: Calling Party Category Ta g: 3000 Source: MDL
Description/Purpose: Indicates what type of calling party is placing the call.
Format: ITU-T Q.763 Length in Octets: 1
Data Value:
00000000 Calling party’s category is unknown (national use).
00000001 Operator, language French
00000010Operator, language English
00000011Operator, language German
00000100Operator, language Russian
00000101Operator, language Spanish
00000110
toAvailable to Administrations for selecting a particular language by mutual agreement
00001000
00001001 Reserved (Refer to Recommendation Q.104) Can be used in national networks to indicate that the calling party
is a national operator
00001010Ordinary calling subscriber
00001011Calling subscriber with priority
00001100Data call (voice band data)
00001101Test call
00001110Spare
00001111Payphone
00010000
toSpare
11011111
11100000
to Reserved for national use
11111110
11111111Spare
Note: The above values are for standard ITU SS7. Variants of ITU SS7 may have different values. Verify the values for
your variant with the appropriate specification, if necessary.
Extended Data Value: No extended value.
General Information:
MGC Release: Release 5.0 and later.
1-68
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
OL-1089-11
Page 91

Chapter 1 Billing Interfaces
CDE Detail Description
User Service Information (Tag: 3001/ITU)
Table 1-45 User Service Information Description Form
Name: User Service Information Tag : 3001 Source: MDL
Description/Purpose: Captures the User Service Information parameter of ITU-T ISUP.
Format: ITU-T Q.763 Length in Octets: 2 to 13
Data Value:
876 5 4 3 2 1
1 Ext. Coding Standard Information Transfer Capability
2 Ext. Transfer Mode Information Transfer Rate
2a Rate multiplier
3 Ext. Layer identity User information Layer 1 protocol
4 Ext. Layer identity User information Layer 2 protocol
5 Ext. Layer identity User information Layer 3 protocol
Notes:
1 Octet 2a is required if octet 2 indicates multirate (64 kbps base rate); otherwise it shall not be present.
2 Octets 3, 4, 5 or any combination of these octets may be omitted. Octet 3 may be extended as described in Table 4-6/Q.931
Note: The above values are for standard ITU SS7. Variants of ITU SS7 may have different values. Verify the values for
your variant with the appropriate specification, if necessary.
For French TUP, the following values apply:
876 5 4 3 2 1
1 Ext. Coding Standard (00) Information Transfer Capability (Mapped from OptaddRoutingInf)
Supported Values:
01 Speech
10 3.1 kHz
11 64 kbps
2 Ext. Transfer Mode (00) Information Transfer Rate (10000)
Extended Data Value: No extended value.
General Information:
MGC Release: Release 7.0 and later.
OL-1089-11
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
1-69
Page 92

Chapter 1 Billing Interfaces
CDE Detail Description
Originating Line Information (Tag: 3002/ITU) Retired
Table 1-46 Originating Line Information Description Form
Name: Originating Line Information Ta g: 3002 Source: MDL
Description/Purpose: Indicates to the Cisco MGC what II digits are being sent from the LEC. This differentiates calls based
on the II digits.
Format: ITU-T Q.763 Length in Octets: 1
Data Value:
Extended Data Value: No extended value.
General Information: For more information on II digits, refer to the Telecordia Local Exchange Routing Guide.
MGC Release: Release 7.0 and later.
Note: This tag was retired in Release 7.4. It is no longer associated with any CDBs.
Calling Number Nature of Address (Tag: 3003/ITU)
Table 1-47 Calling Number Nature of Address Description Form
Name: Calling Number Nature of Address Tag : 3003 Source: MDL
Description/Purpose: Indicates to the Cisco MGC how the number was delivered. This field indicates the address type of
the calling party. In POTS calling, there are usually two values that are used: Unique national number and Nonunique
national number.
Format: ITU-T Q.763 Length in Octets: 1
Data Value:
0000000 Spare
0000001 Subscriber number (national)
0000010 Unknown (national)
0000011 National (significant) number
0000100 International number
0000101
to Spare
1101111
1110000
to Reserved for national use
1111110
1111111 Spare
Note: The above values are for standard ITU SS7. Variants of ITU SS7 may have different values. Verify the values for your
variant with the appropriate specification, if necessary.
Extended Data Value: No extended value.
General Information:
MGC Release: Release 7.0 and later.
1-70
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
OL-1089-11
Page 93

Chapter 1 Billing Interfaces
CDE Detail Description
Charged Number Nature of Address (Tag: 3004/ITU) Retired
Table 1-48 Charged Number Nature of Address Description Form
Name: Charged Number Nature of Address Ta g: 3004 Source: MDL
Description/Purpose: Indicates the address type of the calling party. In POTS calling, the value is typically Unique National
Number or Non-Unique National Number
Format: ITU-T Q.763 Length in Octets: 1
Data Value:
0000000 Spare
0000001 Subscriber number (national)
0000010 Unknown (national)
0000011 National (significant) number
0000100 International number
0000101
to Spare
1101111
1110000
to Reserved for national use
1111110
1111111 Spare
Note: The above values are for standard ITU SS7. Variants of ITU SS7 may have different values. Verify the values for
your variant with the appropriate specification, if necessary.
Extended Data Value: No extended value.
General Information:
MGC Release: Release 7.0 and later. Retired in Release 9.1(2).
OL-1089-11
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
1-71
Page 94

Chapter 1 Billing Interfaces
CDE Detail Description
Dialed Number Nature of Address (Tag: 3005)
Table 1-49 Dialed Number Nature of Address Description Form
Name: Dialed Number Nature of Address Tag : 3005 Source: MDL
Description/Purpose: This value allows the Call Process to route a call differently based on the Nature of Address value
provided in the IAM Called Number parameter.
Format: ANSI T1.113 Length in Octets: 1
Data Value:
0000000 Spare
0000001 Subscriber number (national)
0000010 Unknown (national)
0000011 National (significant) number
0000100 International number
0000101
to Spare
1101111
1110000
to Reserved for national use
1111110
1111111 Spare
Note: The above values are for standard ITU SS7. Variants of ITU SS7 may have different values. Verify the values for
your variant with the appropriate specification, if necessary.
Extended Data Value: No extended value.
General Information:
MGC Release: Release 7.0 and later.
1-72
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
OL-1089-11
Page 95

Chapter 1 Billing Interfaces
CDE Detail Description
LRN Nature of Address (Tag: 3006/ITU)
Table 1-50 LRN Nature of Address Description Form
Name: LRN Nature of Address Tag : 3006 Source: MDL
Description/Purpose: Stores the NOA of LRN from an INAP query.
Format: ITU-T Q.763 Length in Octets: 1
Data Value:
0000000 Spare
0000001 Subscriber number (national)
0000010 Unknown (national)
0000011 National (significant) number
0000100 International number
0000101
to Spare
1101111
1110000
to Reserved for national use
1111110
1111111 Spare
Note: The above values are for standard ITU SS7. Variants of ITU SS7 may have different values. Verify the values for
your variant with the appropriate specification, if necessary.
Extended Data Value: No extended value.
General Information:
MGC Release: Release 7.0 and later.
OL-1089-11
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
1-73
Page 96

Chapter 1 Billing Interfaces
CDE Detail Description
Called Number Nature of Address (Tag: 3007/ITU)
Table 1-51 Called Number Nature of Address Description Form
Name: Called Number Nature of Address Tag : 3007 Source: MDL
Description/Purpose: The tag contains the Nature of Address (NOA) value from the egress protocol message used in the
outbound IAM.The NOA value in this tag is from the ingress protocol message. If no B number NOA is available
(redirected to an unknown number) but an original called number Information Element (IE) is available in the protocol
message, then the NOA from the IE is logged, and this can be modified for number normalization.
Format: ITU-T Q.763 Length in Octets: 1
Data Value:
0000000 Spare
0000001 Subscriber number (national)
0000010 Unknown (national)
0000011 National (significant) number
0000100 International number
0000101
to Spare
1101111
1110000
to Reserved for national use
1111110
1111111 Spare
Note: The above values are for standard ITU SS7. Variants of ITU SS7 may have different values. Verify the values for your
variant with the appropriate specification, if necessary.
Extended Data Value: No extended value.
General Information: The value may be modified during the call because of IN actions (for example, LNP).
MGC Release: Release 7.0 and later.
1-74
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
OL-1089-11
Page 97

Chapter 1 Billing Interfaces
CDE Detail Description
Reason Code (Tag: 3008/ITU)
Table 1-52 Reason Code Description Form
Name: Reason Code Tag : 3008 Source: MDL
Description/Purpose: Incorporates C7 release with cause values and any additional reasons that the basic call model
determines.
Format: based on ITU-T Q.850 Length in Octets: 2
Data Value:
Format:
876 5 4 3 2 1
1 Ext. Coding Standard Spare Location
2 Ext. Cause value
Note: This CDE does not include the Diagnostic and Recommendation octets defined in Q.850. The format of this CDR is
the same for both Q.763 and Q.931 signaling.
Extension:
0 Octet continues through the next octet (for example, octet 1 to 1a)
1 Last octet
Coding Standard
00 ITU-T standardized coding
01 ISO/IEC standard
10 National standard
11 Standard specific to identified location
Note: The coding standards other than ITU-T should only be used when the desired cause value cannot be represented with
the ITU-T standardized codeing.
Location:
0000 User (U)
0001 Private network serving the local user (LPN)
0010 Public network serving the local user (LN)
0011 Transit network (TN)
0100 Public network serving the remote user (RLN)
0101 Private network serving the remote user (RPN)
0111 International network (INTL)
1010 Network beyond interworking point (BI)
1100
to Reserved for National use
1111
All other values are spare.
OL-1089-11
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
1-75
Page 98

Chapter 1 Billing Interfaces
CDE Detail Description
Table 1-52 Reason Code Description Form (continued)
Cause value: (only applicable in the context of Recommendations Q.763 and Q.931)
The cause value is divided into two fields, a class (bits 5 through 7) and a value within the class (bits 1 through 4).
The class indicates the general nature of the event. The valid values are as follows:
000 Normal event
001 Normal event
010 Resource unavailable
011 Service or option not available
100 Service or option not implemented
101 Invalid message (for example, parameter out of range)
110 Protocol error (for example, unknown message)
111 Interworking
The valid class values are listed in Table 1-53.
Extended Data Value:
Note Tag 3008 extends ANSI definition by adding COT failure indicators according to ANSI rules, with slight
modification as follows:
Octet 1:
Extension 0
Coding Standard 11
Spare 0
Location 0011
Octet 2:
Extension 1
Cause 1111110
General Information:
MGC Release: Release 7.0 and later.
The following table lists the Cause information element or parameter definitions for this tag.
Table 1-53 Cause Information Element/Parameter Definitions
Cause
Class/Value/No. Definition
000/0001/1 Unallocated (unassigned) number—indicates
Application
(Note 1)
DSS 1, ISUP Q.931 U, RPN,
that the called party cannot be reached
because, although the called party number is
in a valid format, it is not currently allocated
(assigned)
Reference
(Note 2)
Location
(Note 3) Remarks
LN
RLN, TN,
INTL
No route by
digit analysis
1-76
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
OL-1089-11
Page 99

Chapter 1 Billing Interfaces
Table 1-53 Cause Information Element/Parameter Definitions (continued)
CDE Detail Description
Cause
Class/Value/No. Definition
000/0010/2 No route to specified transit network (national
use)—indicates that the equipment sending
this cause has received a request to route the
call through a particular transit network which
it does not recognize. The equipment sending
this cause does not recognize the transit
network either because the transit network
does not exist or because that particular transit
network, while it does exist, does not serve the
equipment which is sending this cause.
This cause is supported on a
network-dependent basis.
000/0010/3 No route to destination—indicates that the
called party cannot be reached because the
network through which the call has been
routed does not serve the destination desired.
This cause is supported on a networkdependent basis.
000/0100/4 Send special information tone— indicates that
the called party cannot be reached for reasons
that are of a long term nature and that the
special information tone should be returned to
the calling party.
000/0101/5 Misdialled trunk prefix (national
use)—indicates the erroneous inclusion of a
trunk prefix in the called party number.
000/0110/6 Channel unacceptable—indicates that the
channel most recently identified is not
acceptable to the sending entity for use in this
call.
000/0111/7 Call awarded and being delivered in an
established channel—indicates that the user
has been awarded the incoming call, and that
the incoming call is being connected to a
channel already established to that user for
similar calls (for example, packet-mode X.25
virtual calls).
000/1000/8 Preemption—indicates that the call is being
pre-empted.
000/1001/9 Preemption – circuit reserved for
reuse—indicates that the call is being
pre-empted and the circuit is reserved for
reuse by the pre-empting exchange.
Application
(Note 1)
DSS 1,
Reference
(Note 2)
Location
(Note 3) Remarks
Q.931 LN, TN
ISUP(NU)
DSS 1, ISUP Q.931 U, RPN,
LN
ISUP Clause 7/Q.35
ISUP(NU)
DSS 1 Q.931 LN
DSS 1 Q.931 LN
DSS 1, ISUP Q.735.3
MLPP
Q.955.3
ISUP Q.735.3 MLPP
OL-1089-11
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
1-77
Page 100

CDE Detail Description
Table 1-53 Cause Information Element/Parameter Definitions (continued)
Chapter 1 Billing Interfaces
Cause
Class/Value/No. Definition
000/1110/14 QoR:ported number—indicates that an
exchange detected that the called number was
ported out (see Annex C/Q.769.1)
001/0000/16 Normal call clearing—indicates that the call
is being cleared because one of the users
involved in the call has requested that the call
be cleared.
Under normal situations, the source of this
cause is not the network.
001/0001/17 User busy— indicates that the called party is
unable to accept another call because the user
busy condition has been encountered. This
cause value may be generated by the called
user or by the network. In the case of user
determine user busy, it is noted that the user
equipment is compatible with the call.
001/0010/18 No user responding—used when a called
party does not respond to a call establishment
message with either an alerting or connect
indication within the prescribed period of
time allocated.
001/0011/19 No answer from user (user alerted)—used
when the called party has been alerted but
does not respond with a connect indication
within a prescribed period of time.
Note This cause is not necessarily
generated by Q.931 procedures but
may be generated by internalnetwork
timers.
Application
(Note 1)
Reference
(Note 2)
Location
(Note 3) Remarks
ISUP Q.769.1 LN
DSS 1, ISUP Q.931,
U, RPN
2.3/Q.764
DSS 1, ISUP Q.931,
Q.732,
U, RPN,
RLN
Q.733.3
DSS 1, ISUP Q.931,
RLN Call diversion
Q.732
DSS 1, ISUP Q.931 RLN
2.1.4/Q.764,
2.9.8.3/
RLN, TN,
INTL
Q.764
Q.732 RLN Call diversion
Basic call and
call diversion
services
services
Expiry of
waiting ANM
timer (T9)
services
001/0100/20 Subscriber absent—used when a mobile
station has logged off, radio contact is not
obtained with a mobile station or if a personal
telecommunication user is temporarily not
addressable at any user-network interface.
001/0101/21 Call rejected—indicates that the equipment
sending this cause does not wish to accept this
call, although it could have accepted the call
because the equipment sending this cause is
neither busy nor incompatible. This cause
may also be generated by the network,
indicating that the call was cleared due to a
supplementary service constraint..
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
1-78
DSS 1, ISUP Mobile
application
DSS 1, ISUP Q.931 U, RPN
Q.732 RLN Call diversion
services
OL-1089-11
 Loading...
Loading...